
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Oncol., 03 October 2024
Sec. Gastrointestinal Cancers: Hepato Pancreatic Biliary Cancers
Volume 14 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2024.1427332
This article is part of the Research TopicHepatocellular Carcinoma: Novel Treatment Strategies - Volume IIIView all 19 articles
 Eleni Gkika1,2,3,4*
Eleni Gkika1,2,3,4* Gianluca Radicioni1,2
Gianluca Radicioni1,2 Alexandra Eichhorst1,2
Alexandra Eichhorst1,2 Simon Kirste1,2
Simon Kirste1,2 Tanja Sprave1,2,3
Tanja Sprave1,2,3 Nils Henrik Nicolay1,2,3,5
Nils Henrik Nicolay1,2,3,5 Stefan Fichtner-Feigl3,6
Stefan Fichtner-Feigl3,6 Robert Thimme3,7
Robert Thimme3,7 Rolf Wiehle1,2
Rolf Wiehle1,2 Thomas B. Brunner8
Thomas B. Brunner8 Anca-Ligia Grosu1,2,3
Anca-Ligia Grosu1,2,3Introduction: To evaluate the outcomes after stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for locally advanced primary liver cancer.
Materials and methods: Patients with locally advanced liver cancer unsuitable for other loco-regional treatments were treated with SBRT with 50–60 Gy in 3–12 fractions in two consecutive prospective trials.
Results: A total of 83 patients were included, of whom 14 were excluded, leaving 69 evaluable patients with 74 treated lesions. A total of 50 patients had hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and 11 patients had cholangiocarcinoma (CCC). Approximately 76% had a Child-Pugh (CP) score of A, while 54% had an albumin–bilirubin (ALBI) score of 1. With a median follow-up of 29 months, the median overall survival (OS) was 11 months, and the progression-free survival (PFS) was 18 months. The ALBI score was an important predictor of overall survival (HR 2.094, p = 0.001), which remained significant also in the multivariate analysis. Patients with an ALBI grade of ≥1 had an OS of 4 months versus 23 months in patients with an ALBI grade of 1 (p ≤ 0.001). The local control at 1 and 2 years was 91%. Thirteen patients developed grade ≥ 3 toxicities, of whom nine patients experienced liver toxicities. Patients with a higher ALBI score had a high risk for developing hepatic failure (OR 6.136, p = 0.006).
Discussion: SBRT is a very effective treatment with low toxicity and should be considered as a local treatment option in patients with HCC and CCC. Patients with a higher ALBI grade are at risk for developing toxicities after SBRT and have a significantly lower survival rate.
Liver cancer has a very poor prognosis. Approximately 90% of the cases globally are diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which is the most common primary liver tumor, while other primary tumors including cholangiocarcinoma (CCC) are rare. The only curative treatment options are either surgery or transplantation and, in some cases, radiofrequency ablation (RFA). However, fewer than 30% of patients are eligible for these treatments (1, 2). Other local treatment options include trans-arterial chemoembolization (TACE) especially for HCC, selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT), high-dose-rate (HDR) brachytherapy, or stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT). The immune microenvironment plays a significant role in the development and progression of HCC, while inflamed and non-inflamed classes of HCC and genomic signatures have been associated with response to immune checkpoint inhibitors (3). In the past years, there has been increasing evidence of the role of circular RNAs in the modulation of proliferation and metastases of cancer cells, while epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) enhances metastasis and invasion of tumor cells and can trigger resistance to therapy (4). Additionally, the tumor microenvironment remolds, and the acceleration of immunotherapy and vaccines can be provided by peptide nanoparticles (4, 5).
Due to the technological advances of the past decades, SBRT has been proven to be a very efficacious local treatment with high rates of local control ranging from 75% to 100% and can be used safely with low rates of toxicity in both HCC and CCC. SBRT leads to similar local control rates compared to RFA or TACE (6–9). Thus, according to the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines, SBRT is not only an alternative for HCC patients ineligible for other local treatments but also a treatment option a priori equal to other local treatments, such as ablation or arterially directed therapies. Nevertheless, due to the lack of randomized trials, SBRT is not yet included in the current Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) classification. However, in patients with CCC, data concerning the role of SBRT are scarce, and radiotherapy is restricted to patients who are not eligible for other treatments (6).
While liver function plays a significant role in patient stratification, the Child-Pugh (CP) classification incorporates serum albumin, bilirubin, and international normalized ratio (INR) and also the presence of hepatic encephalopathy and ascites for the evaluation, which are highly subjective and thus not easily reproducible, therefore leading to a significant detection bias with the result of under- or overestimation of liver function (10). Thus, the albumin–bilirubin (ALBI) grade was introduced as a more objective method to evaluate liver function (11) but has not been evaluated longitudinally in patients with primary liver cancer treated with SBRT within prospective trials. Since SBRT can lead to radiation-induced liver disease, a validated baseline assessment of liver function is critical for the accurate evaluation of candidates for SBRT.
In this study, we evaluated the role of SBRT in patients with locally advanced HCC or CCC treated within two consecutive prospective trials conducted in our institution (LAPIS trial and Heracles trial) with a focus on liver function.
Study protocols and patient consent forms were approved by the institutional ethics committee (EK 374/15 and 38/16). Both trials were registered at the German Clinical Trials Register (Lapis trial, DRKS 00008566; Heracles trial, DRKS00011266). Patients unsuitable for any other local or systemic treatments or who progressed under local or systemic treatments were eligible for both trials after a multidisciplinary tumor board discussion. Inclusion and exclusion criteria are provided in the Supplementary Material.
Treatment planning and delivery have been also described in detail elsewhere (7, 12, 13). Patients were immobilized using a customized vacuum cushion, patient positioning boards, knee cushions, and abdominal compression and received a 4D and multiphase CT (arterial phase and/or delayed phase and venous phase). The gross tumor volume (GTV) was defined as the primary tumor and the tumor vascular thrombus if present. Image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT) was mandatory for every fraction. At-risk adopted dose prescription was applied considering the constraints for the organs at risk (OARs), aiming at a biologically effective dose (BED) of up to approximately 100 Gy depending on the proximity of the organs at risk. Dose prescription was chosen so that 95% of the planning target volume (PTV) received at least the nominal fraction dose and that 99% of the PTV received a minimum of 90% of the nominal dose [according to the International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements (ICRU) 83, 91]. The dose maximum within the PTV was 110%–120% of the prescribed dose. Patients with smaller tumors not abutting any OARs received 3 × 18.75 Gy to the D50% such that 95% of the PTV received a minimum of 45 Gy (3 × 15 Gy, 80% of the nominal dose) and a dose maximum between 110% and 120% (14). For tumors abutting/overlapping with organs at risk, fractionations such as 5 × 10 Gy or 8 × 7.5 Gy were chosen in order to achieve the constraints for the organs at risk, while ultra-central tumors received mostly 66 Gy in 12 fractions of 5.5 Gy. For lesions where dose constraints for the OARs according to Timmerman (15) could not be achieved, a simultaneous integrated protection (SIP) dose prescription was used as described elsewhere (16, 17) in order to avoid dose reduction for the entire PTV.
For analysis, the prescribed dose matrices were converted to BEDs and equieffective doses for 2-Gy fractions (EQD2), using the linear quadratic model (LQ) as previously described (18). BEDs in Gy (10) for tumors or Gy (3) for normal lungs were calculated and converted to equivalent doses in 2-Gy fractions [=normalized total dose (NTD)] and to estimated log cell kill (18). For liver toxicity, we assumed an α/β value of 2 Gy, as also performed in previous analyses (19).
The Child-Pugh score and the albumin–bilirubin grade were assessed as previously described (11, 20, 21) at baseline (prior to treatment) and at every subsequent follow-up. Clinical outcome was assessed at 6 weeks after SBRT and then every 3 months. The response was evaluated according to the international criteria proposed in the modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (mRECIST) Guideline version 1.1 (22). Toxicity was scored according to the National Cancer Institute (NCI) Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v4.0 for adverse events. Response assessment, toxicity evaluation, and blood tests (complete blood counts and biochemical analysis including liver function) were repeated every 3 months.
Overall survival (OS) was calculated as the time from the start of treatment until death from any cause, with censoring at the date last seen alive. Progression-free survival (PFS) was calculated as the time from the start of treatment until the last documented response assessment. OS and PFS were estimated using the Kaplan–Meier method. Continuous variables are presented as median with the corresponding range (minimum and maximum) and categorical variables as absolute and relative frequencies unless stated otherwise. The Cox proportional hazards regression model was used for further analyses of possible prognostic factors for OS and PFS and the logistic regression for the development of toxicities. The small number of patients did not allow complex multivariate modeling with variable selection using forward selection. Therefore, variables considered in a multivariate model were selected according to relevant univariate impact on OS or PFS. A forward variable selection approach was then applied. Local control (LC) was defined as the time from the start of SBRT until the progression of the treated lesion. Patients without progression were censored at the earlier of the last response assessment. Analyses for LC were conducted at the lesion level.
Death was considered a competing event. Analyses were performed using the SPSS software (IBM, SPSS, v27).
Between 06/2016 and 06/2017, 83 patients were included in both prospective trials. A total of 20 patients were planned for SBRT in the Heracles trial, of whom two patients were excluded due to disease progression, resulting in 18 evaluable patients. In the LAPIS trial, 63 patients were included, of whom 12 were excluded either due to disease progression or alternative treatments, resulting in a total of 69 evaluable patients with 74 SBRT-treated liver lesions. Patients had HCC in 84% of the cases and CCC in 16%. Most patients had an underlying liver disease (58%) and were pre-treated (49%). Nine patients (13%) had metastatic disease, and 16% had a portal vein tumor thrombus. Patient and treatment characteristics are shown in Table 1.
The median follow-up was 29 months. The OS rates at 1 and 2 years were 49% and 38%, respectively, with a median OS of 11 months (Figure 1A). Patients with a higher CP score (HR 1.247, 95% CI 1.030–1.509, p = 0.02) and ALBI grade (HR 2.094, 95% CI 1.344–3.262, p = 0.001), larger tumors (HR 1.011, 95% CI 1.002–1.020, p = 0.02), and presence of portal vein thrombosis (PVT) (HR 2.137, 95% CI 1.094–4.173, p = 0.02) had a worse OS. Only the ALBI score remained significant in multivariate analysis (Tables 2A, B). Patients with an ALBI score of 1 (54%) had a median OS of 23 months (95% CI 3.148–42.852), while patients (46%) with an ALBI grade of ≥2 had a median OS of 4 months (95% CI 2.419–5.581, p < 0.001 log rank, Figure 1B). However, patients with a CP score of A had a median OS of 11 months versus 8 months for patients with a CP score of ≥B (p = 0.32 log rank, Figure 1C).
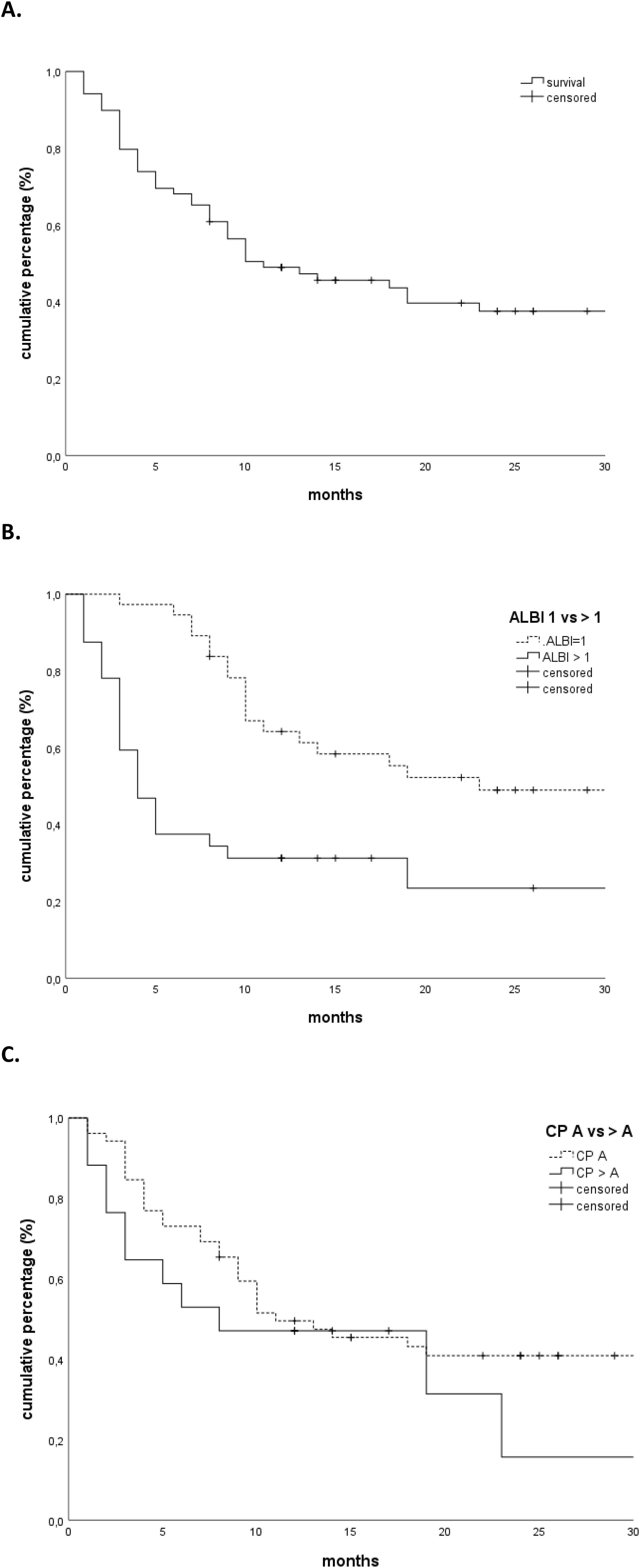
Figure 1. (A) Overall survival. (B) Overall survival stratified according to the ALBI grade (1 vs. >1). (C) Overall survival stratified according to Child-Pugh score (A vs. >A). ALBI, albumin–bilirubin.
Four (6%) patients developed a local progression, of whom two had a regional progression in the liver at the same time. A total of 24 (35%) patients developed a regional regression, of whom five had distant metastases at the same time. In total, 16 patients (23%) developed distant metastases. The median PFS was 18 months. The PFS rates at 1 and 2 years were 53% and 38%, respectively. Patients with a PVT had a worse PFS (HR 2.659, 95% CI 1.271–5.549, p = 0.009, Table 3). The LC at 1 and 2 years was 91%. None of the clinical or treatment parameters correlated with the incidence of local tumor progression.
Thirteen patients developed grade ≥ 3 toxicities. Nine patients developed a hepatic failure, one patient developed a fistula, and three patients with pre-existing stents developed cholangitis. None of the patient characteristics for the dosimetric parameters correlated significantly with the development of grade 3 hepatic failure except for the Child-Pugh score (OR 1.539, 95% CI 0.998–2.373, p = 0.05) and the ALBI grade (OR 6.136, 95% CI 1.664–22.626, p = 0.006) (Table 4).
Over the past decades, there have been significant advances in the treatment of primary liver tumors. Although SBRT seems to lead to high rates of local control, overall survival prospective data are scarce. Furthermore, most prospective studies on SBRT include highly selected patients with a CP score of A or B7 and rarely report results using the ALBI score.
We show that patients with an ALBI score of 1 had a significantly better median overall survival (23 months, 95% CI 3.148–42.852) than patients with an ALBI grade of ≥2 (4 months, 95% CI 2.419–5.581, p < 0.001 log rank). However, the difference between the median overall survival in patients with a CP score of A (median OS of 11 months) compared to patients with a CP score of ≥B (median OS 8 months) was only moderate and not statistically significant (p = 0.32, log rank). Interestingly, none of the dosimetric parameters such as the mean liver dose or the dose or the low-dose region of the liver dose volume histogram curves (e.g., 800 cc or 700 cc) correlated with the incidence of toxicity. Our findings suggest that the ALBI score should be considered for treatment decisions in SBRT of HCC using a cut-off of 1, rather than the more subjective CP score that has been used previously. The ALBI score is a simple, evidence-based, objective, and discriminatory method of assessing liver function in HCC. It has been extensively tested in an international setting, unlike the CP score, which includes more subjective variables such as ascites and encephalopathy (11) and should be routinely calculated prior to treatment. These results should be validated in larger prospective trials, emphasizing patient stratification for SBRT depending on liver function.
In a recent meta-analysis (23) that reported long-term outcomes of SBRT for HCC and included 17 mostly retrospective studies, acute hepatic toxicity ≥ grade 3 ranged from 0% to 30%, but late toxicity was rare. The incidence of severe hepatic toxicity varied according to the criteria applied. Most studies included only patients with a CP score of A and/or up to B7. Importantly, the selection was based on the CP score and not on the most recent ALBI score. In addition, most studies were of retrospective design, thus limiting the evaluation of liver toxicity at follow-up and explaining the big range of reported acute hepatic toxicity ≥ grade 3. Indeed, it is a challenge to interpret liver toxicity in patients with HCC; thus, retrospective data without regular clinical evaluation and blood tests including liver parameters should be used with caution.
Previous smaller studies reported outcomes in patients with a CP score of B or C, showing a big difference in the median overall survival between patients treated with SBRT with a CP B7 score (median OS 10 months) versus patients with a CP score ≥ 8 (24). Andolino et al. (25) demonstrated that there is a relationship between the pretreatment CP score and the development of any type of toxicity (p = 0.035) as well as an increase of more than one grade in hematologic or hepatic dysfunction (p = 0.008). In a study by Lee et al. [17], 17% of patients had an increase in CP score of more than 2 points at 6 months. This suggests that patients with a CP score of A of B7 can be safely offered SBRT for HCC (26). Nevertheless, an ALBI grade of 1 does not correspond to a Child-Pugh score of A. In patients with a CP score of A, Murray et al. (27) showed in a retrospective study that the baseline ALBI score was superior compared to the CP score in predicting OS and toxicity. Indeed, they showed that patients with ALBI scores of 1 and 2 had a median OS of 19.8 and 8.5 months, respectively (p = 0.008), while CP-A5 and CP-A6 patients had median survivals of 17.5 and 10.4 months, respectively (p = 0.061), which is similar to our results. In the study by Jackson et al., ALBI-centric models performed similarly to indocyanine green retention (ICG)-centric models on multivariate analyses predicting toxicity (28).
Our study has several limitations such as the small sample size, potential selection bias, and the heterogeneous patient population regarding the baseline liver function and the dose per fraction. Another limitation of the study may be the inclusion of patients with different primary liver tumor histologies, as HCC tends to develop on the basis of an inflamed cirrhotic liver contrary to CCC and thus has the tendency to have higher CP or ALBI scores. We tried to address this point in the univariate analysis showing no statistical differences between the two histologies, although there were only a small number of patients with CCC, making the results not easy to interpret especially concerning patients with CCC. Nevertheless, this heterogeneity provided additional information concerning the sensitivity of the liver to radiotherapy. Additionally, this analysis was based on two consecutive prospective studies, providing important aspects concerning liver function and toxicity.
In conclusion, our results suggest that patient selection with adequate liver function based on the ALBI score may minimize SBRT-related liver toxicity. Our findings indicate that the ALBI score should be considered for treatment decision in SBRT of HCC using a cut-off of 1, rather than the more subjective CP score. These results should be validated in larger prospective trials, emphasizing patient stratification for SBRT depending on liver function. Patients with adequate liver function had significantly longer overall survival, while neither tumor characteristics nor dosimetric parameters correlated with the development of toxicity of SBRT.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee University of Freiburg. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
EG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. GR: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AE: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SK: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. TS: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. NN: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SF: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RT: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RW: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. TB: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AG: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2024.1427332/full#supplementary-material
1. Bruix J, Sherman M, American Association for the Study of Liver D. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology. (2011) 53:1020–2. doi: 10.1002/hep.24199
2. Bruix J, Reig M, Sherman M. Evidence-based diagnosis, staging, and treatment of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. (2016) 150:835–53. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.12.041
3. Llovet JM, Castet F, Heikenwalder M, Maini MK, Mazzaferro V, Pinato DJ, et al. Immunotherapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2022) 19:151–72. doi: 10.1038/s41571-021-00573-2
4. Ashrafizadeh M, Dai J, Torabian P, Nabavi N, Aref AR, Aljabali AAA, et al. Circular RNAs in EMT-driven metastasis regulation: modulation of cancer cell plasticity, tumorigenesis and therapy resistance. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2024) 81:214. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05236-w
5. Dai J, Ashrafizadeh M, Aref AR, Sethi G, Ertas YN. Peptide-functionalized, -assembled and -loaded nanoparticles in cancer therapy. Drug Discovery Today. (2024) 29:103981. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2024.103981
6. Gkika E, Hawkins MA, Grosu AL, Brunner TB. The evolving role of radiation therapy in the treatment of biliary tract cancer. Front Oncol. (2020) 10:604387. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.604387
7. Brunner TB, Bettinger D, Schultheiss M, Maruschke L, Sturm L, Bartl N, et al. Efficacy of stereotactic body radiotherapy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma not suitable for transarterial chemoembolization (HERACLES: HEpatocellular carcinoma stereotactic RAdiotherapy CLinical efficacy study). Front Oncol. (2021) 11:653141. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.653141
8. Méndez Romero A, van der Holt B, Willemssen F, De Man RA, Heijmen BJM, Habraken S, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization with drug-eluting beads versus stereotactic body radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: outcomes from a multicenter, randomized, phase 2 trial (the TRENDY trial). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2023) 117:45–52. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2023.03.064
9. Lee J, Shin I-S, Yoon WS, Koom WS, Rim CH. Comparisons between radiofrequency ablation and stereotactic body radiotherapy for liver Malignancies: Meta-analyses and a systematic review. Radiother Oncol. (2020) 145:63–70. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2019.12.004
10. Gkika E, Bettinger D, Krafft L, Schultheiss M, Neeff HP, Maruschke L, et al. The role of albumin-bilirubin grade and inflammation-based index in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy. Strahlenther Onkol. (2018) 194:403–13. doi: 10.1007/s00066-017-1256-0
11. Johnson PJ, Berhane S, Kagebayashi C, Satomura S, Teng M, Reeves HL, et al. Assessment of liver function in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a new evidence-based approach-the ALBI grade. J Clin Oncol. (2015) 33:550–8. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.57.9151
12. Gkika E, Schultheiss M, Bettinger D, Maruschke L, Neeff HP, Schulenburg M, et al. Excellent local control and tolerance profile after stereotactic body radiotherapy of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiat Oncol. (2017) 12:116. doi: 10.1186/s13014-017-0851-7
13. Gkika E, Firat E, Adebahr S, Graf E, Popp I, Radicioni G, et al. Systemic immune modulation by stereotactic radiotherapy in early-stage lung cancer. NPJ Precis Oncol. (2023) 7:24. doi: 10.1038/s41698-023-00358-z
14. Guckenberger M, Andratschke N, Alheit H, Holy R, Moustakis C, Nestle U, et al. Definition of stereotactic body radiotherapy: principles and practice for the treatment of stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Strahlentherapie und Onkol: Organ der Deutschen Rontgengesellschaft … [et al]. (2014) 190:26–33. doi: 10.1007/s00066-013-0450-y
15. Timmerman RD. An overview of hypofractionation and introduction to this issue of seminars in radiation oncology. Semin Radiat Oncol. (2008) 18:215–22. doi: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2008.04.001
16. Brunner TB, Nestle U, Adebahr S, Gkika E, Wiehle R, Baltas D, et al. Simultaneous integrated protection: A new concept for high-precision radiation therapy. Strahlenther Onkol. (2016) 192:886–94. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.06.2147
17. Gkika E, Adebahr S, Kirste S, Schimek-Jasch T, Wiehle R, Claus R, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) in recurrent or oligometastatic pancreatic cancer : A toxicity review of simultaneous integrated protection (SIP) versus conventional SBRT. Stereotaktische Strahlentherapie (SBRT) beim wiederkehrenden oder oligometastatischen Pankreaskarzinom : Bewertung der Toxizität bei simultan integrierter Protektion (SIP) versus konventioneller SBRT. Strahlentherapie und Onkologie : Organ der Deutschen Rontgengesellschaft ... [et al]. (2017) 193:433–43. doi: 110.1007/s00066-017-1099-8
18. Fowler JF, Tome WA, Fenwick JD, Mehta MP. A challenge to traditional radiation oncology. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2004) 60:1241–56. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.07.691
19. Prayongrat A, Kobashi K, Ito YM, Katoh N, Tamura M, Dekura Y, et al. The normal tissue complication probability model-based approach considering uncertainties for the selective use of radiation modality in primary liver cancer patients. Radiother Oncol. (2019) 135:100–6. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2019.03.003
20. Pugh R, Murray-Lyon I, Dawson J, Pietroni M, Williams R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. (1973) 60:646–9. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800600817
21. Child CG, Turcotte JG. Surgery and portal hypertension. Major problems in clinical surgery. (1964) 1:1–85.
22. Lencioni R, Llovet JM. Modified RECIST (mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. (2010) 30:52–60. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1247132
23. Bae SH, Chun S-J, Chung J-H, Kim E, Kang J-K, Jang WI, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: meta-analysis and international stereotactic radiosurgery society practice guidelines. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2023) 118:337–51. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2023.08.015
24. Culleton S, Jiang H, Haddad CR, Kim J, Brierley J, Brade A, et al. Outcomes following definitive stereotactic body radiotherapy for patients with Child-Pugh B or C hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiother Oncol. (2014) 111:412–7. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2014.05.002
25. Andolino DL, Johnson CS, Maluccio M, Kwo P, Tector AJ, Zook J, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2011) 81:e447–53. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.04.011
26. Apisarnthanarax S, Barry A, Cao M, Czito B, Dematteo R, Drinane M, et al. External beam radiation therapy for primary liver cancers: an ASTRO clinical practice guideline. Pract Radiat Oncol. (2022) 12:28–51. doi: 10.1016/j.prro.2021.09.004
27. Murray LJ, Sykes J, Brierley J, Kim JJ, Wong RKS, Ringash J, et al. Baseline albumin-bilirubin (ALBI) score in western patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2018) 101:900–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.04.011
Keywords: HCC, CCC, SBRT, hepatocellular carcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma, radiotherapy
Citation: Gkika E, Radicioni G, Eichhorst A, Kirste S, Sprave T, Nicolay NH, Fichtner-Feigl S, Thimme R, Wiehle R, Brunner TB and Grosu A-L (2024) The role of ALBI score in patients treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy for locally advanced primary liver tumors: a pooled analysis of two prospective studies. Front. Oncol. 14:1427332. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1427332
Received: 03 May 2024; Accepted: 10 September 2024;
Published: 03 October 2024.
Edited by:
Sharon R. Pine, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, United StatesReviewed by:
Brett Diamond, Tufts Medical Center, United StatesCopyright © 2024 Gkika, Radicioni, Eichhorst, Kirste, Sprave, Nicolay, Fichtner-Feigl, Thimme, Wiehle, Brunner and Grosu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Eleni Gkika, ZWxlbmkuZ2tpa2FAdWtib25uLmRl
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.