- 1Department of Nursing, College of Health Sciences, Woldia University, Woldia, Ethiopia
- 2Department of Adult Health Nursing, College of Health Sciences, Injibara University, Injibara, Ethiopia
- 3Department of Emergency and Critical Care Nursing, School of Nursing, College of Health Sciences, Woldia University, Woldia, Ethiopia
- 4Department of Pharmacology, College of Health Sciences, Debre Markos University, Debre Markos, Ethiopia
- 5Nursing Department, College of Health Sciences, Debre Markos University, Debre Markos, Ethiopia
Introduction: Peripheral neuropathy is a nerve disorder that causes pain, numbness, and tingling in different parts of the body. It is a major and common clinical problem associated with several chemotherapeutic medications frequently used in cancer treatment, with prevalence rates ranging from 19% to 85%. To the best of the authors’ knowledge, there is a lack of data on the magnitude and determinants of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in Ethiopia.
Objective: This study aimed to assess the magnitude and associated factors of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy among adult cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy in northwest Ethiopia oncology centers in 2022.
Method: An institutional-based cross-sectional study was conducted on 406 eligible adult cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy in northwest Ethiopia oncology centers, between May and July 2022.
Results: Out of 406 adult cancer patients included in the study, 54.4% had peripheral neuropathy. The stage of cancer (AOR = 4.36 [95% CI: 1.76; 10.8]), comorbidity (AOR = 2.74 [95% CI: 1.28; 5.83]), drug regimen (AOR = 2.99 [95% CI: 1.36; 6.54]), and cycle of therapy (AOR = 4.00 [CI: 1.67; 9.65]) were significantly associated with the magnitude of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy.
Conclusion: Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy is a common adverse event among Ethiopian cancer patients treated with various chemotherapeutic drugs. Therefore, it is necessary to establish more effective diagnostic methods and incorporate validated assessment tools, such as the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer tools, either alone or in combination with other clinical instruments, into the routine evaluation of all patients receiving chemotherapeutic drug.
Introduction
Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) is a major clinical problem among cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy, leading to symptoms such as pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hands and feet (1). It results from damage to the peripheral nerves, which are responsible for transmitting signals between the periphery and the brain (2, 3). CIPN can also contribute to a decreased quality of life due to complications such as foot ulcers, pain, and muscle weakness (4). CIPN can be acute, lasting for a few months, or chronic, lasting more than 6 months (1, 5).
Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy is a major problem for cancer patients, their care providers, and the healthcare system worldwide (6, 7). Its prevalence varies depending on the type of chemotherapy drugs used (8–11), but it is estimated to affect up to 48% of cancer patients annually (5, 9). In the USA, approximately 68.4% of cancer survivors develop CIPN (12), while in Africa, including Ethiopia, the prevalence of CIPN is not well studied. However, the burden of the disease has increased in recent years, placing significant strain on the healthcare systems due to premature death, high costs, and complications arising from therapies (13, 14).
The average healthcare costs for cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy with PN increased by $8,092 compared to those without PN. On average, each case of CIPN resulted in 12 additional outpatient visits and more days spent in the hospital (15). CIPN is not only a theft of money and time; rather, it is also a theft of equipment and human resources, including medical oncologists, primary care physicians, physician assistants, nurses, neurologists, and pain specialists, who can participate at the same time or in later steps (16). Despite the increased burden of CIPN, there is limited attention given to its assessment, leading to significant underreporting of its prevalence (6, 7). To the best of the authors’ knowledge, there is a lack of data on the magnitude and determinants of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in Ethiopia (17). Consequently, the extent of CIPN remains poorly understood in developing countries, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa, including Ethiopia. The study conducted in East Africa, specifically Kenya, highlights the lack of data regarding the magnitude of CIPN among cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy (17). CIPN may manifest differently in Ethiopia compared to other regions due to several interrelated factors. Genetic diversity, including variations in the CYP450 enzyme in African populations, can influence drug metabolism, potentially altering the risk and severity of CIPN. Additionally, unmeasured levels of nerve-protective nutrients such as vitamins B and E and magnesium in Ethiopia may increase vulnerability to neuropathy. Limited access to healthcare, cost-driven chemotherapeutic regimens (e.g., platinum-based drugs or taxanes), and a lack of supportive therapies can delay the detection and management of CIPN, thereby increasing the risk and severity of its symptoms. Assessing the magnitude and associated factors of CIPN is crucial for early identification, which can help mitigate related health, socioeconomic, and healthcare expenditure issues.
Method
Study design and area
An institutional-based cross-sectional study was conducted between 30 May 30 and 30 July 2022 in northwest Ethiopia oncology centers, which is located in the northwestern part of Ethiopia. Of the 96 government-affiliated and private hospitals in the region, only four had oncology centers with a total of 68 beds during the study period. The total number of cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy during the study period were 920 (18).
Eligibility criteria
All adult cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy during the data collection period were included in the study, while patients with neurological diseases (stroke, Parkinson’s disease, or Alzheimer’s disease), HIV patients on Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy (HAART), TB patients on anti-TB, diabetic patients (19), and those receiving their first cycle of chemotherapy (20) where excluded from the study.
Sampling
The sample size was calculated using the single population proportion formula, with the following assumptions to obtain the maximum sample size: p = 50% (due to the absence of prior studies on this topic in Ethiopia at the time of this thesis), a confidence level of 95%, and margin of error (d) of 5%. After including a 10% allowance for nonresponses, the final sample size was determined to be 423. The sample size was then proportionally allocated based on the population size of each public hospital with oncology centers. Before data collection began, cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy who had neurological diseases, HIV patients on HAART, TB patients on anti-TB, and diabetic patients were excluded from the database. Subsequently, the sampling frame was prepared based on the appointment list for the study period. Finally, the study subjects were selected using a simple random sampling technique, employing a lottery method.
Operational definitions
● CIPN: is defined as peripheral neuropathy that develops after chemotherapy. For patients with pre-existing peripheral neuropathy, PN is considered chemotherapy-induced only if the symptoms worsen, as reported by the patient according to the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) QLQ-PN20 response categories, following the initiation of chemotherapy (21).
● The magnitude of PN is defined as the percentage of patients who reported at least one neuropathy symptom that bothered them, based on the EORTC QLQ-PN20 response categories. Respondents who scored at least one were classified as having peripheral neuropathy, while those who scored below one were classified as not having PN (22).
● We employed the EORTC QLQ-CIPN20 tool, which specifically measures the magnitude of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy through a series of validated questions related to sensory, motor, and autonomic symptoms. While we collected subjective reports from patients regarding their symptoms, we also utilized the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) to ensure a standardized assessment of severity. The tool provides a comprehensive overview of the patient’s experience with CIPN, allowing us to quantify the impact of neurotoxicity on their quality of life.
● Current smoker: an adult who has currently smoked cigarettes sometimes or more than once a week (23).
● Former smoker: an adult who has smoked at least 100 cigarettes in his or her lifetime but who had currently quit smoking (24).
According to IPAQ-SF tool, physical activity is classified as low, moderate, or high.
● High is defined as meeting one of the following two criteria: performing vigorous-intensity activities, such as heavy lifting, aerobics, digging, and plowing, on at least 3 days a week.
● Moderate is defined as meeting one of the following three criteria: engaging 3 or more days of vigorous activity for at least 20 min/day; 5 or more days of moderate-intensity activity or walking for at least 30 min/day; or 5 or more days of any combination of walking.
● Low refers to individuals who do not meet the criteria for either the high or moderate categories and are considered inactive (25).
● Alcohol user: for men, a score of 4 or more is considered positive for alcohol use, and for women, a score of 3 or more is considered positive, according to the AUDIT response (26).
Data collection procedures and tools
Data were collected from the patients’ charts and through an adapted, pretested, structured, interviewer-administered questionnaire. The questionnaire included sociodemographic characteristics, behavioral traits, clinical parameters, and a brief section adapted from the EORTC quality of life tool. It was administered by four nurses with bachelor’s degrees. The questionnaire is a multi-item scale not limited to any specific disease or treatment group. The current version of CIPN20 includes three scales to assess the symptoms and function: sensation (nine items), motor (eight items), and autonomic nerves (three items) (27, 28). The questionnaire was first developed in English and then translated into Amharic by an expert. It was subsequently translated back into English by an independent translator to ensure consistency, and was used to collect the necessary data for CIPN assessment. To ensure the quality of the data, a pretest was conducted with 5% of the total sample size, consisting of cancer patients receiving chemotherapy at Black Lion Hospital (which was not a study area), and those participants were excluded from the actual sample. Necessary adjustments were made to the tool based on the pretest results. The reliability of the tool was checked before data collection, yielding alpha coefficients of 0.93 for the sensory scale, 0.85 for the motor scale, and 0.78 autonomic scale. Each questionnaire and data sheet was checked before data entry. Data were entered daily for nearby sites and weekly for more distant sites, with no major missing data identified.
Statistical analysis
Data were entered into EPI-Data Version 4.6 and then transferred to SPSS version 25.0 for analysis. Bivariable binary logistic regression was performed to identify the independent factors associated with CIPN. The adequacy of the model was tested using Hosmer and Lemeshow’s goodness-of-fit test, with a p-value of 0.209.
Variables with a p-value < 0.25 in the bivariable analysis were entered into a multivariable binary logistic regression model using the backward LR method. A p-value < 0.05 and odds ratio (OR) with a 95% confidence interval (CE) was considered statistically significant in this study. The results were presented using tables, graphs, and narrative descriptions.
Result
Sociodemographic characteristics
A total of 423 adult cancer patients receiving chemotherapy were selected to participate in this study, and 406 adults participated, resulting in a response rate of 96%.
About 252 (62.1%) of respondents were females. Regarding age 145(35.7%) of the participants were within the age range of 35 to 49 years with a minimum of 22 and a maximum of 75 years. The mean age of the participant was 48.56 ± 13.6 years. In terms of educational status about, 158 (38.9%) of the respondents were unable to read and write followed by 107 (26.4%) of respondents learnt secondary school. Only 79 (19.5%) of the respondents learn higher education. According to their place of residence, about 225 respondents (55.4 percent) were urban dwellers (Table 1).
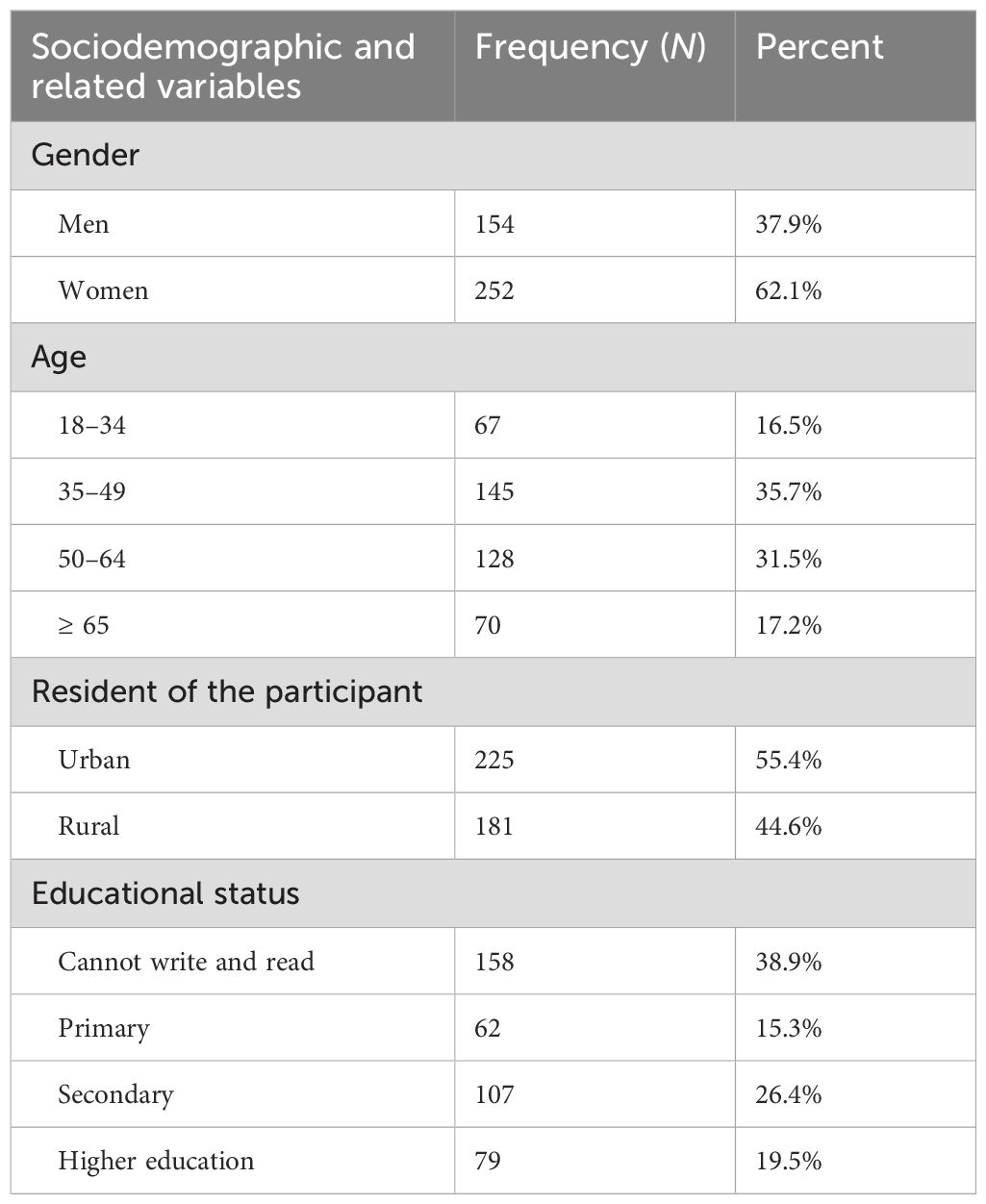
Table 1. Sociodemographic and related clinical characteristics of adult cancer patients receiving chemotherapy in northwest Ethiopia oncology centers, 2022 (N = 406).
Behavioral characteristics of the respondents
Regarding behavioral characteristics, approximately 390 respondents (96.1%) did not smoke cigarettes, 231 respondents (56.9%) engaged in moderate physical exercise, and 361 respondents (88.9%) were nonalcoholic (Table 2).
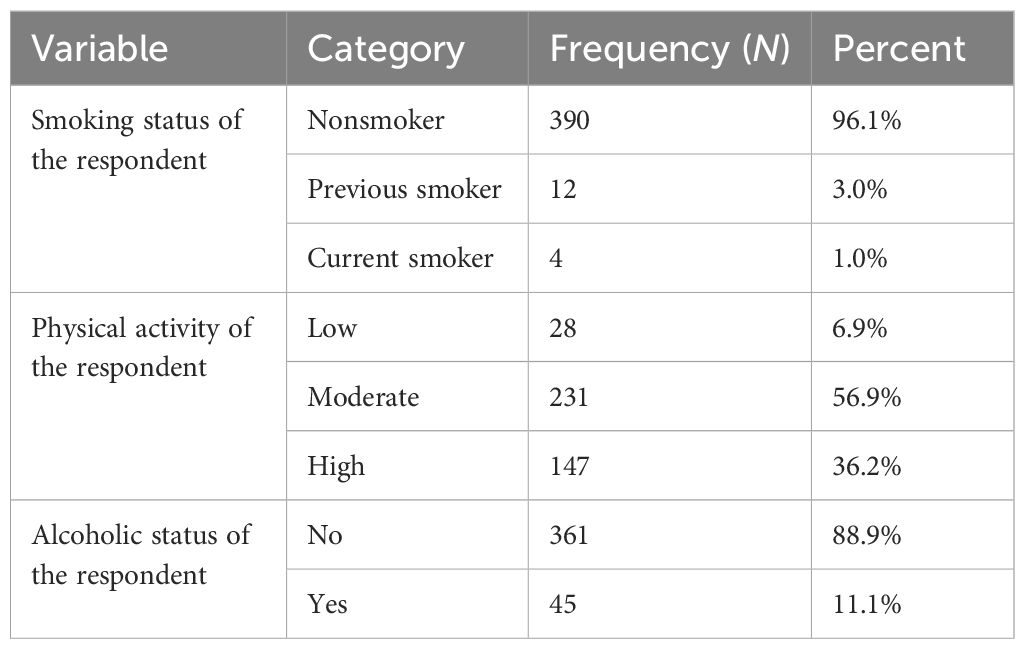
Table 2. Behavioral and clinical characteristics of adult cancer patients receiving chemotherapy in northwest Ethiopia oncology centers, 2022 (N = 406).
Clinical and related characteristics of the respondents
The primary diagnoses in this study group were breast tumors (n = 128; 31.5%), cervical tumors (n = 53; 13.1%), lung tumors (n = 29; 7.1%), non-Hodgkin lymphomas (n = 23; 5.7%), and colon cancers (n = 21; 5.2%). At the time of chemotherapy initiation, 155 patients (38.2%) were in stage 4, while 147 patients (36.2%) were in stage 2 (Table 3; Figure 1).
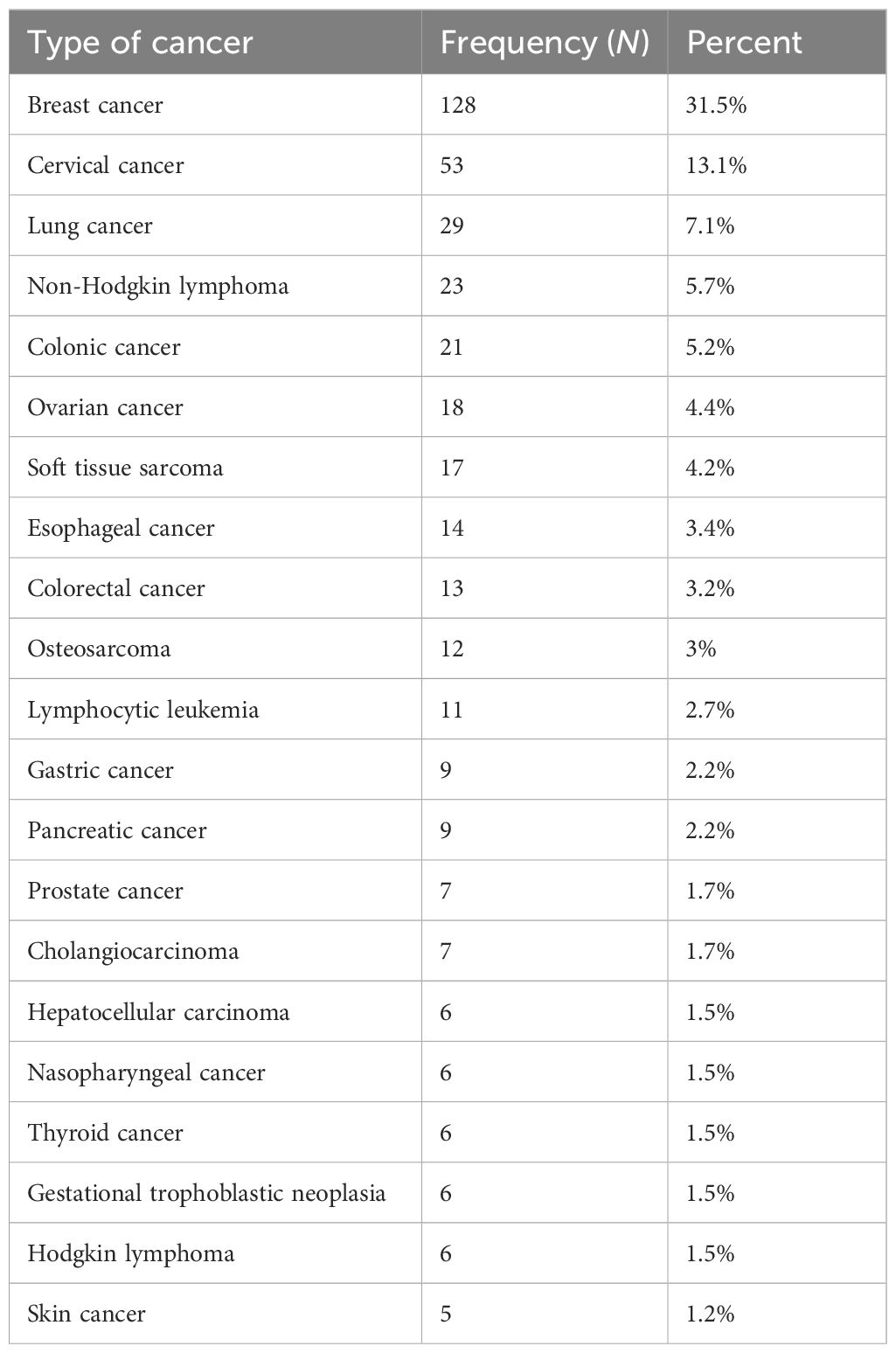
Table 3. Types and magnitude of cancer among patients in northwest Ethiopia oncology centers, 2022 (N = 406).
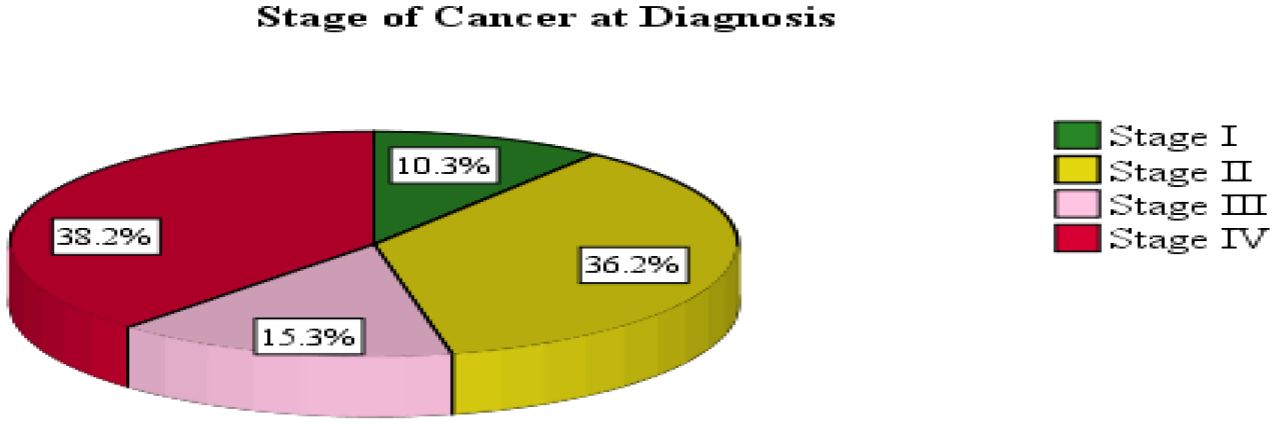
Figure 1. Cancer stage at chemotherapy initiation among adult patients in northwest Ethiopia oncology centers, 2022.
Regarding comorbidity, of the 406 respondents, 61 (15%) had noncommunicable chronic diseases, with hypertension accounting for approximately 46 cases (75.4%). Additionally, 115 respondents (28.3%) were classified as underweight.
Concerning the therapies used to treat the neoplasms included in the study, the taxane regimen (n = 113; 27.8%), consisting of paclitaxel (n = 58; 14.3%) and docetaxel (n = 55; 13.5%), was the most commonly prescribed chemotherapeutic drug. This was followed by alkylating agents with anthracyclines (cyclophosphamide combined with doxorubicine n = 96; 23.6%) and platinum-based regimens, either alone or in combination (n = 80; 19.7%). Among the respondents, 117 (28.8%) were on the second cycle of therapy (Table 4).
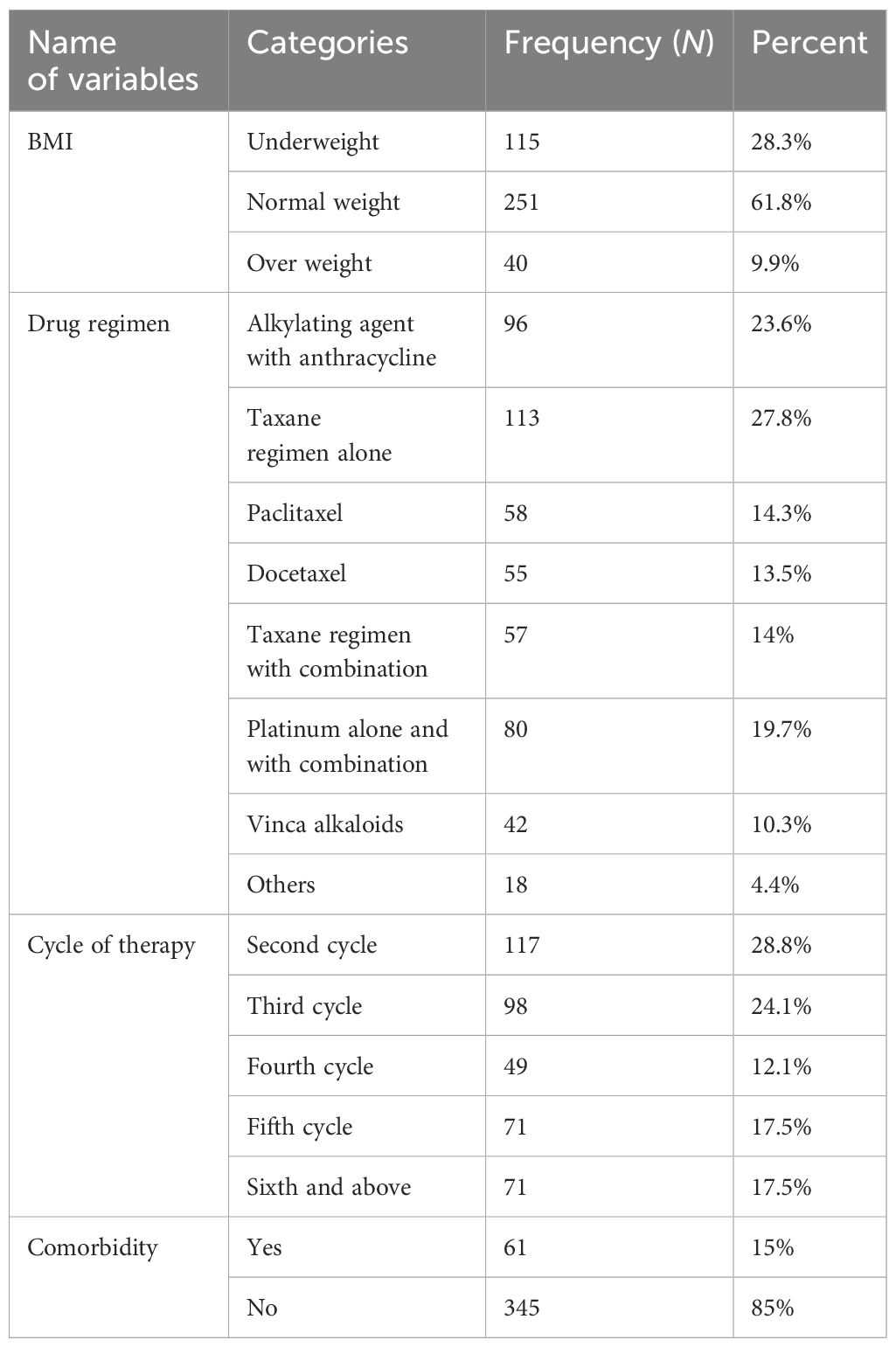
Table 4. Frequency of comorbidities, chemotherapeutic drugs, and therapy cycles among adult cancer patients receiving chemotherapy in northwest Ethiopia oncology centers, 2022 (N = 406).
Magnitude of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy
Among the respondents analyzed, 221 (54.4%) had chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, with a 95% CI of 49.6% to 59.3%. The proportion of sensory PN was higher, affecting 218 (53.7%) of the participants, followed by motor symptoms in 186 (45.8%). Among the sensory manifestations, the most frequently reported symptoms were tingling, burning sensations, and numbness, particularly in the hands and, especially, the legs. Walking difficulties were the most prevalent motor symptoms.
Factors associated with the magnitude of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy
Bivariable and multivariable analysis of CIPN and associated factors
To determine factors associated with the magnitude of CIPN (dependent variable), bivariable logistic regression was performed. Significant variables, including sex, stage of cancer at diagnosis, comorbidity, physical activity, age, body mass index, type of chemotherapeutic drugs, and cycle of therapy, were found to be associated with PN. Variables with a p-value of < 0.25 were included in the multivariable logistic regression model to adjust for possible confounders.
Multivariable logistic regression was then performed using a backward stepwise (likelihood ratio) method to ascertain the effect of the independent variables on CIPN. The results showed that the stage of cancer at diagnosis, comorbidity, type of chemotherapeutic drug, and cycle of therapy were significantly associated with PN (Table 5).
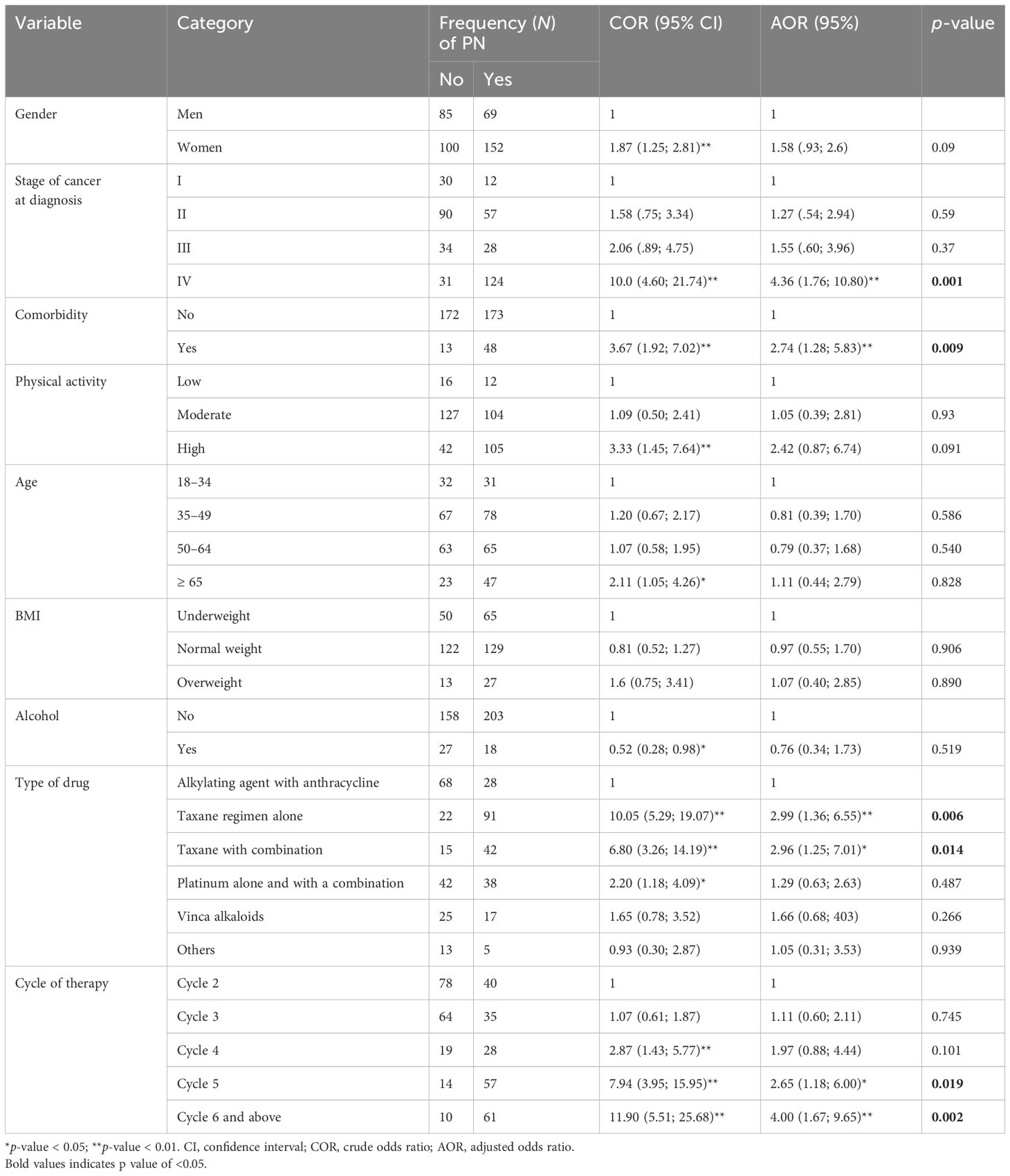
Table 5. Factors associated with the magnitude of CIPN among adult cancer patients receiving chemotherapy in northwest Ethiopia oncology centers, 2022.
Discussion
This study was conducted to assess the magnitude of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy and its associated factors among adult cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy in northwest Ethiopia oncology centers. Accordingly, the overall magnitude in this study was 54.4% (CI: 49.6–59.3). This finding is consistent with the studies conducted in Colombia (49.9%) (29), Minnesota, USA (52.7%) (6), and China (53.4%) (30).
The findings of this study are lower than those of studies conducted in Romania (68.09%) (31) and Kenya (83.6%) (17). The exclusion of participants with diabetic mellitus, HIV, and neurological diseases may be a possible cause of this difference (11). The smallest sample sizes of these two studies (163 and 67, respectively) could also contribute to this disparity. Additionally, differences in the measuring tools used may account for the variation. It is important to use a combination of scales to maximize the “pick up” rates of these tools, incorporating both patient‐reported outcomes and objective CIPN indicators, such as the TNS clinical version (32). This approach is supported by studies conducted by Molassiotis et al. in 2019 and Alberti et al. in 2014 (30, 33). Another consideration, especially for the study conducted in Kenya, is that it focused only on a single chemotherapeutic drug (cisplatin), which may be extremely toxic to peripheral nerves. It may also be related to the lifestyle of the respondents. Additionally, the finding is lower than the meta-analysis conducted by Serenty et al. in 2014, which reported a CIPN occurrence of 68.1% (5). This meta-analysis differentiated the occurrence of CIPN into the first, third, and subsequent sixth months, which are directly related to the cycle of therapy—a known risk factor for the development of CIPN. In contrast, this study did not consider these specific time points, which may explain the discrepancy.
In this study, the magnitude of CIPN is higher than in the French study, where the frequency was 31.3% (34). This difference may be explained by the fact that this study was conducted on cancer patients receiving chemotherapy, while the study in France was carried out after the completion of chemotherapeutic treatment. According to numerous researchers, although CIPN may persist for a long period, its presence decreases once chemotherapeutic treatment is completed (11, 35).
Regarding factors associated with the magnitude of CIPN, the odds of developing chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy were higher among cancer patients in stage IV (AOR = 4.36) compared to those in stage I. This finding is in line with a study conducted by Kamgar et al. in the USA in 2021 (36).
Similarly, the odds of developing CIPN were higher among cancer patients receiving chemotherapy with comorbidities (AOR = 2.74) compared to those without comorbidities. This outcome is consistent with the research done by Miaskowski et al. in the USA in 2017 and 2018 (12, 37). The possible explanation is that conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and renal impairment are associated with pre-existing damage in peripheral nerves. When chemotherapy is administered, these already-compromised nerves become more susceptible to further injury, exacerbating the severity of neuropathy. Additionally, comorbid conditions affecting kidney and liver function can impair the metabolism and clearance of chemotherapeutic drugs, leading to higher concentrations of neurotoxic agents in the bloodstream. This prolonged exposure further increases the risk and severity of CIPN. Furthermore, many chronic diseases are linked to elevated levels of inflammation and oxidative stress. When combined with chemotherapy, this cumulative burden significantly heightens the risk of nerve damage (38).
Regarding the therapeutic regimen, the odds of developing CIPN among cancer patients who received a taxane regimen were about three times more likely than those who received alkylating agent combined with anthracycline, specifically a combination of cyclophosphamide and doxorubicine. This finding is consistent with the studies conducted in Colombia and Romania (29, 31). This may be due to the fact that taxane drugs excessively disrupt normal axonal transport, leading to axonal swelling and subsequent peripheral nerve damage. Taxanes also accumulate in sensory neurons, particularly in the mitochondria, where they impair mitochondrial deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) functions, reduce ATP production, and elevate oxidative stress. These combined effects lead to neuronal injury and degeneration, significantly contributing to the increase in CIPN. Taxanes increase reactive oxygen species (ROS) and trigger inflammation in peripheral nerves, overwhelming antioxidant defenses and damaging cellular components, thereby exacerbating neuropathy symptoms. They also interfere with neurotrophin pathways, particularly nerve growth factor (NGF), which reduces essential nerve support and hinders recovery from injury. Additionally, taxanes directly damage Schwann cells and myelin, impairing nerve conduction and leading to both sensory and motor neuropathy (10). This implies that cancer patients on taxane regimens require special attention and close follow-up.
Furthermore, patients who received taxane-based chemotherapeutic drugs in combination with a platinum-based regimen or other drug categories were 2.96 times more likely to develop CIPN compared to those who received alkylating agent with anthracycline. CIPN developed in 88.9% of patients receiving a carboplatin and docetaxel combination, which is an essential treatment for platinum-resistant ovarian cancer. It developed in 87.5% of patients receiving cisplatin with paclitaxel, commonly used for ovarian cancer, advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), head and neck cancer, and esophageal carcinomas. In 80% of patients receiving carboplatin with paclitaxel, a combination used to treat multiple solid tumors, including ovarian, lung, breast cancer, and cervical cancers, CIPN developed, with minimal regard for scheduling to maximize response. It was seen in 70% of patients receiving cisplatin with docetaxel, a regimen used for certain types of head, neck, and stomach cancers. Lastly, 50% of patients receiving docetaxel with gemcitabine, a regimen used for treating leiomyosarcoma, other soft tissue sarcomas, and carcinomas of unknown origin, developed CIPN, with manageable toxicity (39). This shows that the magnitude of CIPN increases when chemotherapeutic drugs are used in combination (40). This may be due to the fact that, in addition to arresting the progression of cancer by inhibiting DNA synthesis through DNA cross-linkage or interfering with microtubules to block mitosis, leading to cancer cell apoptosis, these drugs also affect normal cells, particularly those of fast-growing tissues. As a result, numerous changes occur in the structure and function of neuronal and glial cells, leading to the activation and recruitment of immune cells. This process results in the release and elevation of proinflammatory cytokines (such as interleukins and chemokines), which cause nociceptor sensitization and hyperexcitability of peripheral neurons. These processes contribute to the development of neuroinflammation (10).
The number of chemotherapy cycles received was a strong risk factor in both in univariable and multivariable analyses in this study. Patients on the sixth cycle of chemotherapy were four times more likely to develop CIPN compared to those on the second cycle. The odds of developing CIPN among respondents on the fifth cycle of chemotherapy (AOR = 2.65) were higher compared to those on the second cycle. This implies that as the number of chemotherapy cycles increases, the risk of developing CIPN also increases, indicating that CIPN is time-dependent (5). The finding is consistent with the study conducted by Mazilu et al. in 2018 in Romania, which states that patients receiving more than four cycles of neurotoxic chemotherapeutic drugs have a higher chance of developing CIPN (31). This may be related to the fact that as the number of therapy cycles increases, the cumulative dose effect of neurotoxic agents also rises, thereby increasing the risk of nerve damage with each cycle. As the body accumulates these agents, the risk and severity of CIPN often escalate with cumulative doses rather than with single-cycle doses. This is primarily due to the limited recovery capacity of nerve cells between cycles. Repeated chemotherapy cycles progressively disrupt the structures of nerve cells, including microtubules, mitochondria, and Schwann cells, leading to axonal degeneration and impaired nerve function, which can manifest as sensory or motor neuropathy. Short intervals between cycles may not provide sufficient time for partial nerve repair, increasing the likelihood of sustained damage, while extended recovery periods may result in less severe CIPN. Furthermore, each chemotherapy cycle introduces additional oxidative stress and inflammatory responses in peripheral nerves, compounding cellular damage and overwhelming antioxidant defenses, which exacerbates neuropathy symptoms with each successive cycle (41).
Although it was not significant in this study, regular physical exercise has numerous benefits, including preventing general health problems and enhancing overall well-being. It can also help in the recovery from chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, particularly for those who experience significant distress from the condition, by improving blood circulation and strengthening nerve tissues through increased oxygen flow (42). A 2017 study in New York City showed that patients who spent more than 5 h/week of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) were 60% less likely to experience increased CIPN (43). In Ethiopia, the lack of significance of physical activity in studies on CIPN may be attributed to the population’s inherently active lifestyle. Many Ethiopians, including those in urban areas, regularly perform physical tasks, often through agricultural work or daily activities essential to meeting basic needs, typically without mechanized assistance. This incidental, widespread physical activity may reduce variability in physical activity levels, making it challenging to detect a distinct impact of physical activity on the risk or severity of CIPN across different groups.
Limitation
Social desirability bias may have influenced responses, particularly regarding behavioral characteristics, despite the specific training provided to data collectors. Methodologically, future studies could benefit from using mixed methods, such as triangulating quantitative findings with qualitative data and employing prospective study designs, to more comprehensively identify risk factors for chemotherapy-associated peripheral neuropathy.
Conclusion
This study is the largest study to date examining the magnitude of CIPN among cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy in the study area, providing valuable baseline data. Approximately half of the study participants experienced CIPN, highlighting that chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy is a common adverse event among Ethiopian cancer patients treated with taxane-based regimen, platinum-based regimen, vinca alkaloids, and other widely used chemotherapeutic drugs, either alone or in combination. The type of drug regimen, therapy cycle, comorbidity, and cancer stage at diagnosis were identified as risk factors in this study. As we expand our understanding of the prevalence and risk factors of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, certain targeted medications—whether preventive or treatment-related—may become more suitable based on the specific chemotherapeutic agents to which a patient is exposed. In general, establishing an effective CIPN monitoring and reporting system and raising awareness among healthcare professionals about the importance of CIPN reporting may aid in reducing and preventing the problem.
Recommendation
The healthcare facilities with oncology center should establish more successful diagnostic methods and incorporate validated scales, such as EORTC assessment tools, either alone or in combination with other clinical tools, in the routine evaluation of all patients receiving chemotherapy in our environment. In addition, healthcare providers should focus not only on the patient’s medical issues during visits but also consider the patient’s overall health. To lessen the burden of CIPN on patient’s life, researchers should concentrate on improving our understanding of the mechanisms underlying the development of CIPN, as well as on preventive and treatment measures using both pharmacological and nonpharmacological therapies.
Data availability statement
The original data supporting the conclusions of this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be addressed to the corresponding author and will be accommodated upon reasonable request, without undue restrictions.
Ethics statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Ethical clearance and approval for the start of the study was obtained from Debre-Markos University College of Health Sciences and institutional research ethical review committee (IRERC) with Ethical Review Board number HSC/R/C/Ser/PG/Co/216/11/14 which was decided on 25/05/2022 G.C.A. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
TH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MA: Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. GA: Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZW: Data curation, Investigation, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AA: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HM: Conceptualization, Investigation, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their deepest gratitude to the study participants, the healthcare facilities, and the data collectors for their commitment and cooperation during the data collection period.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
CIPN, chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy; EORTC, European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer; QLQ, quality of life questionnaire.
References
1. Simon NB, Danso MA, Alberico TA, Basch E, Bennett AV. The prevalence and pattern of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy among women with breast cancer receiving care in a large community oncology practice. Quality Life Res. (2017) 26(10):2763–72. doi: 10.1007/s11136-017-1635-0
2. Hammi C, Yeung B. Neuropathy: National Library of Medicine (2022). Available online at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542220/ (Accessed July 18, 2022).
3. Hershman DL, Lacchetti C, Dworkin RH, Lavoie Smith EM, Bleeker J, Cavaletti G, et al. Prevention and management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in survivors of adult cancers: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline. J Clin Oncol. (2014) 32(18):1941–67. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.54.0914
4. Mols F, Beijers T, Vreugdenhil G, van de Poll-Franse L. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy and its association with quality of life: a systematic review. Supportive Care in Cancer. (2014) 22(8):2261–9. doi: 10.1007/s00520-014-2255-7
5. Seretny M, Currie GL, Sena ES, Ramnarine S, Grant R, MacLeod MR, et al. Incidence, prevalence, and predictors of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain. (2014) 155(12):2461–70. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2014.09.020
6. Shah A, Hoffman EM, Mauermann ML, Loprinzi CL, Windebank AJ, Klein CJ, et al. Incidence and disease burden of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in a population-based cohort. J Neurol, Neurosurg & Psychiat. (2018) 89(6):636–41. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2017-317215
7. Addington J, Freimer M. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: an update on the current understanding. F1000 Research. (2016) 5:. doi: 10.12688/f1000research
8. Balayssac D, Ferrier J, Descoeur J, Ling B, Pezet D, Eschalier A, et al. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathies: from clinical relevance to preclinical evidence. Expert Opinion on Drug Safety. (2011) 10(3):407–17. doi: 10.1517/14740338.2011.543417
9. Kerckhove N, Collin A, Condé S, Chaleteix C, Pezet D, Balayssac D. Long-term effects, pathophysiological mechanisms, and risk factors of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathies: a comprehensive literature review. Front Pharmacol. (2017) 8:86. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00086
10. Zajączkowska R, Kocot-Kępska M, Leppert W, Wrzosek A, Mika J, Wordliczek J. Mechanisms of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:1451. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061451
11. Colvin LA. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN): where are we now? Pain (2019) 160(Suppl 1):S1. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001540
12. Miaskowski C, Paul SM, Mastick J, Abrams G, Topp K, Smoot B, et al. Associations between perceived stress and chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy and otoxicity in adult cancer survivors. J Pain & Sympton Management. (2018) 56(1):88–97. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2018.02.021
13. Memirie ST, Habtemariam MK, Asefa M, Deressa BT, Abayneh G, Tsegaye B, et al. Estimates of cancer incidence in Ethiopia in 2015 using population-based registry data. JCO Global Oncol. (2018) 4:1–11. doi: 10.1200/JGO.17.00175
14. GLOBOCAN U. New Global Cancer Data. Bethesda, Maryland, USA: National Library of Science (2020).
15. Pike CT, Birnbaum HG, Muehlenbein CE, Pohl GM, Natale RB. Healthcare costs and workloss burden of patients with chemotherapy-associated peripheral neuropathy in breast, ovarian, head and neck, and nonsmall cell lung cancer. Chemotherapy Research and Practice. (2012) 2012:. doi: 10.1155/2012/913848
16. Cavaletti G, Alberti P, Argyriou AA, Lustberg M, Staff NP, Tamburin S, et al. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity: a multifaceted, still unsolved issue. J Peripheral Nervous Syst. (2019) 24:S6–S12. doi: 10.1111/jns.v24.S2
17. Ezzi MS, Othieno-Abinya NA, Amayo E, Oyiro P, McLigeyo A, Yatich RB, et al. Prevalence and predictors of cisplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy at the Kenyatta national hospital. JCO Global Oncol. (2019) 5:1–6. doi: 10.1200/JGO.19.00097
18. USAID. HSFR/HFG End of Project Regional Report – Amhara (2018). Available online at: https://www.hfgproject.org/hsfr-hfg-end-of-project-regional-report-amhara/ (Accessed May 13, 2022).
19. Shekarriz R, Ghorbani H, Mousazadeh M, Vahedi K, Salehifar E. The efficacy and safety of silymarin in the treatment of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, a randomized double-blinded clinical trial. (2021). doi: 10.22541/au.162837649.93180154/v1
20. Tofthagen C, McAllister RD, Visovsky CJ. Peripheral neuropathy caused by Paclitaxel and docetaxel: an evaluation and comparison of symptoms. J Advanced Practitioner Oncol. (2013) 4(4):204. doi: 10.6004/jadpro.2013.4.4.2
21. Pereira S, Fontes F, Sonin T, Dias T, Fragoso M, Castro-Lopes JM, et al. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy after neoadjuvant or adjuvant treatment of breast cancer: a prospective cohort study. Supportive Care in Cancer. (2016) 24(4):1571–81. doi: 10.1007/s00520-015-2935-y
22. Beijers AJ, Oerlemans S, Mols F, Eurelings M, Minnema MC, Vreugdenhil A, et al. The magnitude of neurotoxicity in patients with multiple myeloma and the impact of dose modifications: results from the population-based PROFILES registry. Annals of Hematology. (2017) 96(4):653–63. doi: 10.1007/s00277-017-2927-8
23. McNeill A, Brose L, Calder R, Simonavicius E, Robson D. Vaping in England: An evidence update including vaping for smoking cessation, February 2021. (2021), 1–247.
24. Control CfD, Prevention. National Health Interview Survey. General Concepts. Atlanta, Georgia, USA: Center for Disease control and prevention. (2019).
26. Conigrave JH, Lee K, Haber PS, Vnuk J, Doyle MF, KMJAs C, et al. More than three times as many Indigenous Australian clients at risk from drinking could be supported if clinicians used AUDIT-C instead of unstructured assessments. Addiction Science and Clinical Practice. (2022) 17(1):1–11. doi: 10.1186/s13722-022-00306-5
27. Postma TJ, Aaronson N, Heimans J, Muller M, Hildebrand J, Delattre J-Y, et al. The development of an EORTC quality of life questionnaire to assess chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: the QLQ-CIPN20. Euro J Cancer. (2005) 41(8):1135–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2005.02.012
28. Tofthagen CS, McMillan SC, Kip KE. Development and psychometric evaluation of the chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy assessment tool. Cancer Nursing. (2011) 34(4):E10–20. doi: 10.1097/NCC.0b013e31820251de
29. Martinez JW, Sanchez-Naranjo JC, Londono-De Los Rios PA, Isaza-Mejia CA, Sosa-Urrea JD, Martinez-Munoz MA, et al. Prevalence of peripheral neuropathy associated with chemotherapy in four oncology centers of Colombia. (2019) 69(3):94–8. doi: 10.33588/rn.6903.2019035
30. Molassiotis A, Cheng HL, Lopez V, Au JS, Chan A, Bandla A, et al. Are we mis-estimating chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy? Analysis of assessment methodologies from a prospective, multinational, longitudinal cohort study of patients receiving neurotoxic chemotherapy. BMC Cancer. (2019) 19(1):1–19. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5302-4
31. Mazilu L, Stănculeanu D-L, Gheorghe A-D, Voinea F, Suceveanu A-P, Piţuru S, et al. Incidence of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in cancer patients in clinical practice. FARMACIA. (2018) 57(13.21):60.8–12.68. doi: 10.31925/farmacia.2019.3.14
32. McCrary JM, Goldstein D, Boyle F, Cox K, Grimison P, Kiernan MC, et al. Optimal clinical assessment strategies for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN): a systematic review and Delphi survey. Supportive Care in Cancer. (2017) 25(11):3485–93. doi: 10.1007/s00520-017-3772-y
33. Alberti P, Rossi E, Cornblath D, Merkies I, Postma T, Frigeni B, et al. Physician-assessed and patient-reported outcome measures in chemotherapy-induced sensory peripheral neurotoxicity: two sides of the same coin. Annals of Oncol. (2014) 25(1):257–64. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdt409
34. Selvy M, Pereira B, Kerckhove N, Gonneau C, Feydel G, Pétorin C, et al. Long-term prevalence of sensory chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy for 5 years after adjuvant FOLFOX chemotherapy to treat colorectal cancer: a multicenter cross-sectional study. J Clin Med. (2020) 9(8):2400. doi: 10.3390/jcm9082400
35. Flatters SJ, Dougherty PM, Colvin LA. Clinical and preclinical perspectives on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN): a narrative review. Brit J. (2017) 119(4):737–49. doi: 10.1093/bja/aex229
36. Kamgar M, Greenwald MK, Assad H, Hastert TA, McLaughlin EM, Reding KW, et al. Prevalence and predictors of peripheral neuropathy after breast cancer treatment. Cancer Medicine. (2021) 10(19):6666–76. doi: 10.1002/cam4.v10.19
37. Miaskowski C, Mastick J, Paul SM, Topp K, Smoot B, Abrams G, et al. Chemotherapy-induced neuropathy in cancer survivors. Journal of Pain and Symptom management. (2017) 54(2):204–18.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2016.12.342
38. Battaglini E, Goldstein D, Grimison P, McCullough S, Mendoza-Jones P, Park SB. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity in cancer survivors: predictors of long-term patient outcomes. J Natl Compr Cancer Network. (2021) 19:821–8. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2021.7026
39. Pouessel D, Culine S, Becht C, Ychou M, Romieu G, Fabbro M, et al. Gemcitabine and docetaxel as front-line chemotherapy in patients with carcinoma of an unknown primary site. Cancer. (2004) 100(6):1257–61. doi: 10.1002/cncr.v100:6
40. Han Y, Smith MT. Pathobiology of cancer chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN). Front Pharmacol. (2013) 4:156. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2013.00156
41. Mazilu L, Stănculeanu D-L, Gheorghe A-D, Voinea F, Suceveanu A-P, Piţuru S, et al. Incidence of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in cancer patients in clinical practice. Age. (2019) 57:60.8–12.68. doi: 10.31925/farmacia.2019.3.14
42. Dobson JL, McMillan J, Li L. Benefits of exercise intervention in reducing neuropathic pain. Front Cellular Neurosci. (2014) 8:102. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00102
Keywords: cancer, chemotherapy, Ethiopia, peripheral neuropathy, risk factors
Citation: Habtie TE, Abate MD, Abebe GK, Wolie ZT, Alamaw AW and Mitiku HZ (2024) Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy and its determinants among adult cancer patients on chemotherapy in northwest Ethiopia oncology centers, 2022. Front. Oncol. 14:1420518. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1420518
Received: 16 May 2024; Accepted: 07 November 2024;
Published: 10 December 2024.
Edited by:
David Balayssac, Université Clermont Auvergne, FranceReviewed by:
Bikesh Kumar Nirala, Emory University, United StatesYuan Tian, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China
Copyright © 2024 Habtie, Abate, Abebe, Wolie, Alamaw and Mitiku. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tesfaye Engdaw Habtie, dGVzZmF5ZWVuZ2Rhd0BnbWFpbC5jb20=
 Tesfaye Engdaw Habtie
Tesfaye Engdaw Habtie Melsew Dagne Abate
Melsew Dagne Abate Gebremeskel Kibret Abebe
Gebremeskel Kibret Abebe Zenaw Tessema Wolie4
Zenaw Tessema Wolie4 Addis Wondmagegn Alamaw
Addis Wondmagegn Alamaw Haymanot Zeleke Mitiku
Haymanot Zeleke Mitiku