
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Oncol., 07 November 2024
Sec. Radiation Oncology
Volume 14 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2024.1406759
Background: To explore new modulatory intervention targets for radiation-induced lung injury, bioinformatics analysis technology was used to search for the core driving genes in the pathogenesis of radiation pneumonitis, and the results were verified by a radiation-induced murine lung injury model to find possible new targets for the treatment of radiation lung injury.
Method: Gene Expression Omnibus Database was used to identify differentially expressed genes in radiation pneumonitis. DAVID database was used for gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genome (KEGG) enrichment analysis. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis was used to analyze abnormal expressions. Protein–protein interaction networks were constructed using STRING and Cytoscape. Discovery Studio 4.5 software was used to find the preferred inhibitor of the specific gene. A radiation-induced lung injury model was induced in female C57BL/6N mice. The specific inhibitors were administered by intraperitoneal injection 24 h before and for 7 consecutive days after radiation. Lungs were harvested for further analysis 14 days and 10 weeks post-irradiation.
Results: We screened Syk as one of the most important driver genes of radiation pneumonitis by bioinformatics analysis and screened the preferred Syk inhibitor fostamatinib from the drug database. Syk was highly expressed in irradiated lung tissue, and fostamatinib inhibited the level of Syk expression. Syk inhibitor significantly alleviated the radiation-induced lung injury and downregulated the increased expression of p38 MAPK, p53, IL-1β, and IL-6 in lung tissue at 2 weeks after radiation. The levels of TGF-β, COL1A1, and α-SMA and degree of pulmonary fibrosis at 10 weeks after radiation were also decreased by Syk inhibitor.
Conclusion: Syk inhibitor may have a potential to be used as a targeted drug to mitigate radiation pneumonitis and inhibit radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis.
Radiotherapy is an important treatment method for intrathoracic malignant tumor. Patients receiving radiotherapy on the chest are at a risk for radiation-induced lung injury (RILI) (1, 2). The lungs are moderately sensitive to radiation, and the lung tissue adjacent to the tumor may be damaged by radiation therapy. Alveolar type II cells are one of the most radiation-sensitive cells in lung tissue and are the earliest cells to undergo morphological changes after lung radiation. Radiation-associated pulmonary fibrosis may develop within 6 months, with increased interstitial myofibroblasts and collagen, intravascular fibrosis, and then a decrease in lung volume, and the patient then develops irreversible respiratory failure (3).
The development of radiation pneumonitis and pulmonary fibrosis seriously affects the quality-of-life of patients, and its poor prognosis imposes a burden on families and society. To date, there are no effective treatments for radiation pneumonitis and pulmonary fibrosis. Glucocorticoids can only alleviate the disease in the acute phase of radiation pneumonitis but cannot prevent the progression of pulmonary fibrosis (4). Therefore, it is of great clinical significance and value to study the pathogenesis of radiation pneumonitis, find effective drugs to treat radiation pneumonitis, and reduce the risk of radiation pulmonary fibrosis.
Bioinformatic methods, especially in combination with microarray technology, provide new avenues to study the molecular pathogenesis of various diseases through data mining at the molecular level (5, 6).
Spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) is a cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase which contains two SRC homology 2 (SH2) domains and a kinase domain (BOX 1), and it plays an essential role in signal transduction initiated by the classic immunoreceptors, including B-cell receptors (BCRs), Fc receptors, and the activated natural killer receptors (7). Syk is highly expressed in hematopoietic cells (8), including B cells, immature T cells, mast cells, neutrophils, platelets, macrophages, monocytes, and non-immune osteoclasts (9). As most of these cells are involved in the instigation and establishment of tissue pathology in autoimmune allergic and autoinflammatory diseases, patients who are suffering from RA, SLE, ITP, AHA, and allergic rhinitis stand a good chance to benefit from Syk inhibition (7). Several recent studies have found that Syk had other functions beyond immune regulation. Syk has been shown to promote pulmonary angiogenesis by activating downstream ERK1/2 and Akt signaling pathways in a rat hepatopulmonary syndrome (HPS) model (10) and to promote platelet-derived-growth factor-BB-induced proliferation of rat pulmonary vascular smooth muscle cells (11, 12). Syk inhibition could prevent toxin-induced liver fibrosis, associated hepatocellular damage and intra-hepatic inflammation, and hepatocarcinogenesis (12, 13). However, the involvement of Syk in the regulation of p38 and p53 in radiation pneumonitis and radiation pulmonary fibrosis has not been investigated. In the present study, we evaluated the effects of Syk inhibitor on radiation-related lung injury in a mouse model.
The mRNA micro-array datasets used in biological information analysis are GSE85359 and GSE41789. These data were based on the Agilent GPL1261 platform ([mouse430_2] Affymetrix mouse genome 430 2.0 array), and a total of 50 radiation pneumonitis samples and 22 normal control samples were included. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in radiation pneumonitis were identified using Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. DAVID database was used for gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genome (KEGG) enrichment analysis, and then Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) was used to analyze abnormal expressions. Protein–protein interaction (PPI) networks were constructed using STRING (String: http://string.embl.de/) and Cytoscape. Syk inhibitors were analyzed using Discovery Studio 4.5 software.
C57BL/6N mice (female, 6–8 weeks) purchased from Charles River Laboratories (China, Beijing) were raised in specific pathogen-free (SPF) barrier environment in the Laboratory Animal Center of Jilin University with suitable temperature, humidity, and light control. Animal experiments were carried out in accordance with the ethical approval issued by the Animal Ethics Committee at the First Bethune Hospital of Jilin University (IACUC approval number 2022-0034).
Syk inhibitor fostamatinib was purchased from Invitrogen™ (Carlsbad, CA, USA), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), phospho-p38 (p-p38), p53, α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), collagen type 1-alpha1 (COL1A1), transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, and Syk antibodies were purchased from ZEN BioScience (Chengdu, Sichuan, China), and the p-Syk antibody was from the β-tubulin antibody purchased from Abcam (Cambridge, MA, USA). Hydroxyproline content assay kit was purchased from Solarbio (cat# BC0255). All other reagents were obtained from Sigma Chemical Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA).
The female C57BL/6N mice were anesthetized by an intraperitoneal injection of pentobarbital (60 mg/kg). A total of 30 were fixed and placed in the supine position for radiation. The mouse head and the abdomen were shielded by using lead plates. Thoracic radiation was performed with a single dose of 18 Gy in an X-ray irradiator (Faxitron, USA). The mice were randomly allocated into group R (n = 10) and group R+S (intraperitoneal injection of 20 mg/kg·day fostamatinib, n = 10; fostamatinib was dissolved in 0.5% DMSO). The other 10 untreated mice served as controls (group C). The mice in groups C and R received an equal volume of 0.5% DMSO simultaneously. All mice received intraperitoneal injection 1 day before radiation and after 7 days. Five mice in each group were randomly selected and sacrificed 2 weeks after radiation. The remaining mice were sacrificed at 10 weeks after radiation by cervical dislocation.
The mice were sacrificed, and both lungs were harvested. Part of the lungs were snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen for western blot analysis. Some lungs were fixed in 10% neutral-buffered formalin at 4°C for 12 h, processed, embedded in paraffin wax, sliced into 5-μm sections, and observed by using a light microscope after hematoxylin/eosin (HE) and Masson’s trichrome staining. The number of inflammatory cells per high-power field, width of blood vessels, and width of interalveolar septa were quantitatively determined from five random fields in high magnification. Smith scale was applied to evaluate the degree of lung injury at 2 weeks after radiation, according to the presence of pneumonedema, inflammation, hemorrhage, atelectasis, and hyaline membrane formation. Each of these features was scored as follows: no damage (0), mild (1), moderate (2), and severe (3) (14, 15). Each mouse was observed at five high-power fields, and then the average was taken. Ashcroft score was used to assess the grade of lung fibrosis at 10 weeks after radiation (16, 17).
The immunohistochemistry of Syk was performed as described previously (18). The slides were treated overnight with primary antibody SYK (1:50) at 4°C and incubated with secondary antibody (1:500) (HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG).
Total cellular protein was extracted as previously described. Equal amounts of proteins were mixed with an equal volume of reducing SDS sample buffer and boiled at 95°C for 5 min. Protein samples were resolved by 10% SDS-PAGE and electroblotted on nitrocellulose membranes (BioRad, Hercules, CA, USA). After electroblotting, nonspecific binding was blocked with 5% bovine serum albumin (BSA). The membrane was incubated overnight with primary antibodies at 4°C and incubated with horseradish-peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies for 1 h at room temperature. Primary antibodies against the following proteins were used at 1:1,000 dilutions unless otherwise indicated: p-SYK, IL-1β, IL-6, TGF-β1 p-p38, p53, α-SMA, COL1A1, and GAPDH antibodies (1:5,000 or 1:10,000). During the western blot experiments, some blots were cut prior to hybridization with antibodies. Immunoreactive bands were visualized using enhanced chemiluminescence (Amersham, Arlington, IL, USA) as previously described. Western blot was repeated at least five times.
All experiments were conducted at least three times. Data depicted in graphs represent the mean ± SE for each group. Brown–Forsythe and Bartlett tests were employed to assess the homogeneity of variances. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted for comparison among multiple groups, and Tukey multiple comparison test was used to evaluate the significance between groups. In all analyses, P-values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
The Venn diagram in Figure 1A shows the DEGs between radioactive pneumonitis and normal lung tissue, and the heatmap of core genes is shown in Figure 1B. We constructed a PPI network and then performed molecular complex detection (MCODE) to screen out PPI network modules with MCODE score >10 and number of nodes >11. The core driver genes of radiation pneumonitis were screened and are listed in Table 1. Among these genes, Syk was highly expressed, with a node degree of 48 in radiation pneumonitis. By analyzing the PPI network of all DEGs and using MCODE to screen out the three most important modules (as shown in Figure 1C), we annotated the functions of these module genes and their abundances (as shown in Supplementary Table S1), including leukocyte chemotaxis, cell cycle, integral component of membrane, mitotic cytokinesis, ATP binding, and P53 signaling pathway.
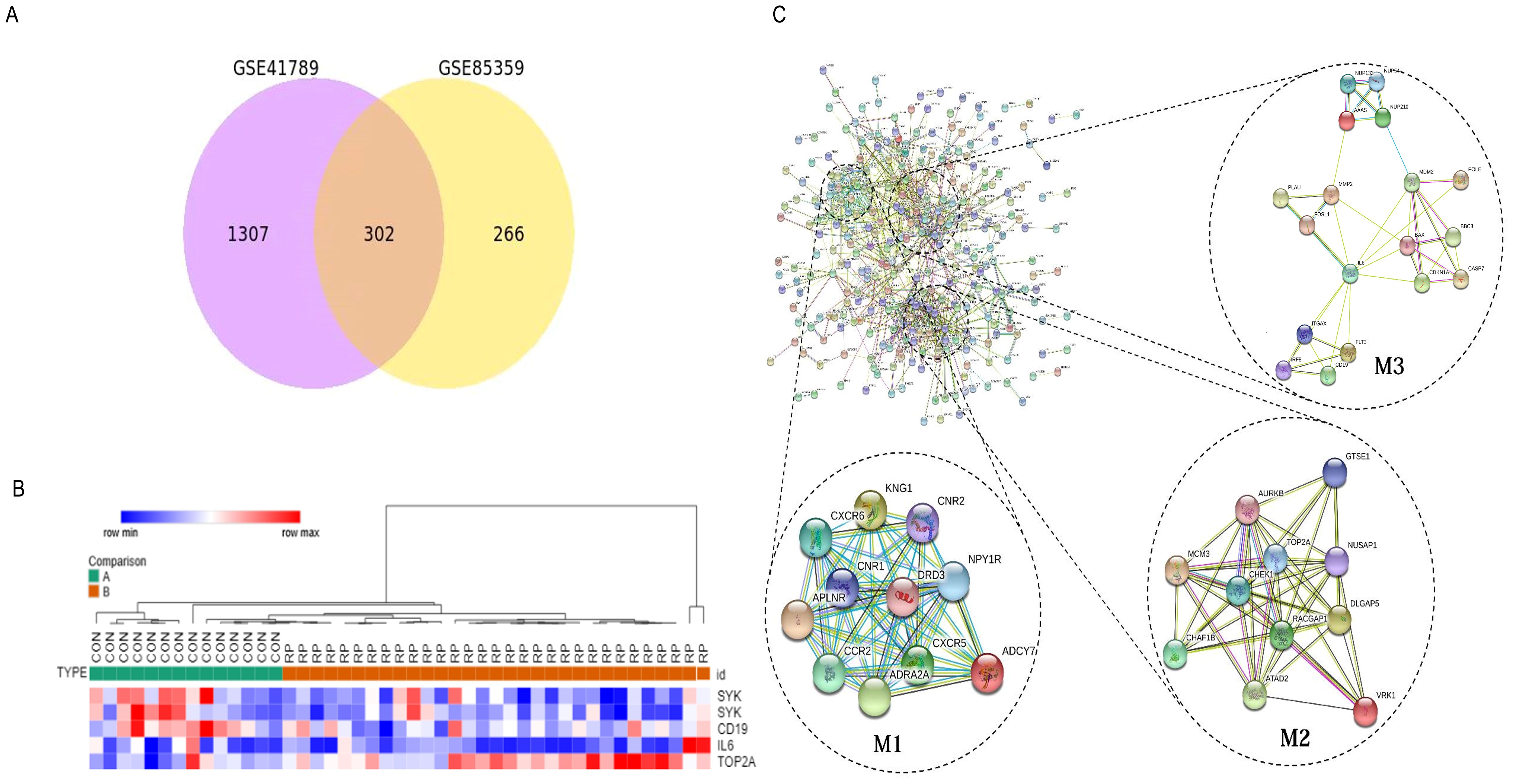
Figure 1. Identify the core driving genes of radioactive pneumonitis from differentially expressed genes (DEGs). (A) Venn diagram of differentially expressed genes in the three groups. (B) Heatmap of the core genes of radioactive pneumonitis. (C) Protein network interaction diagram of DEGs, mainly three modules.
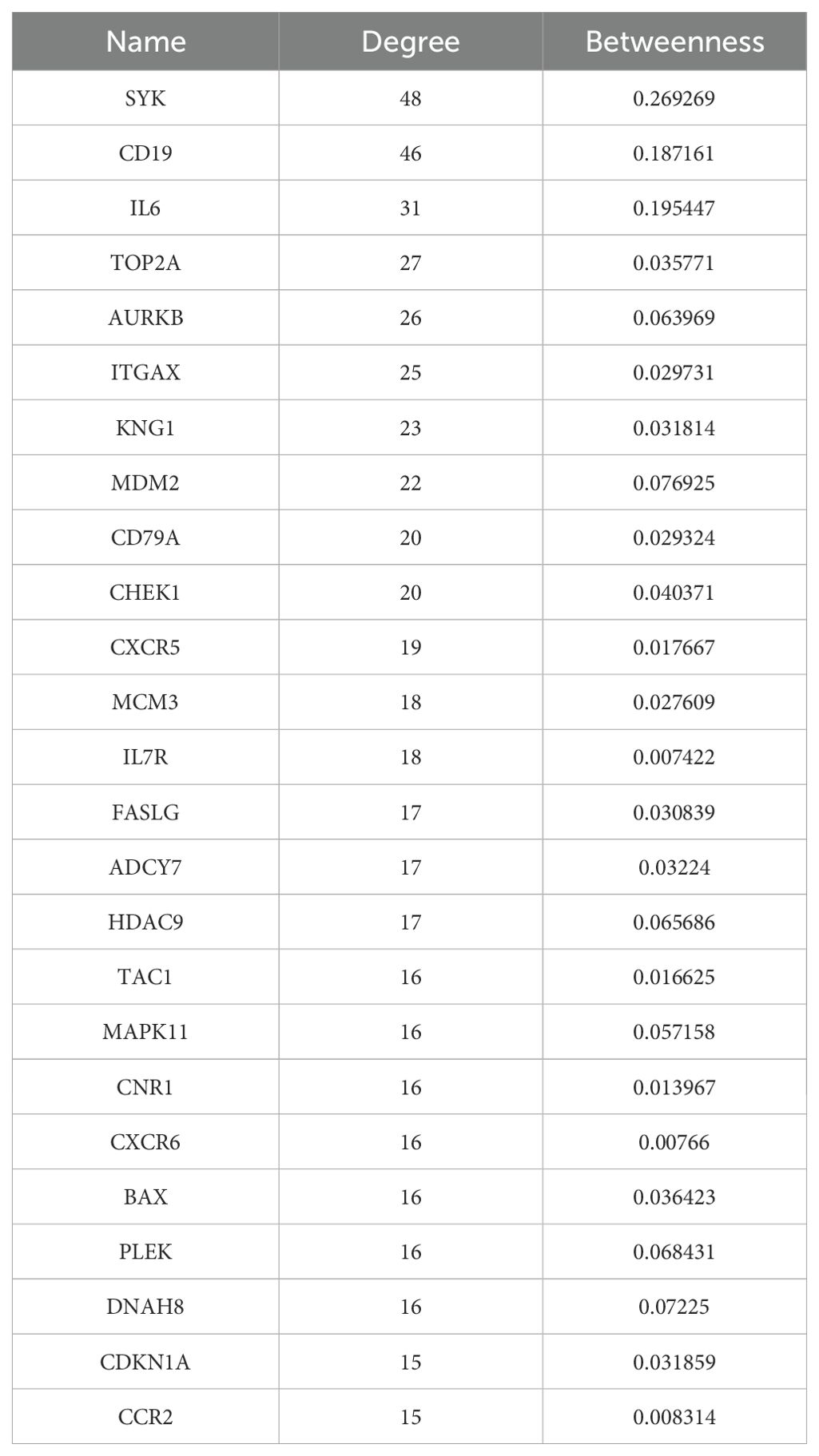
Table 1. Key nodes in the protein–protein interaction network with degrees >15 of radiation pneumonitis.
The GO analysis showed that the DEGs between radioactive pneumonitis and normal lung tissue were enriched in B-cell receptor signaling pathway, transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway, integrin-mediated signaling pathway, positive regulation of cytokinesis, and mobile behavior. The KEGG analysis revealed enrichment of DEGs in chemokine signaling pathway, cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, P53 signaling pathway, primary immune deficiency, and hematogenesis cell lines (Supplementary Figure S1, Supplementary Table S2). The GSEA of DEGs showed that there was a significant abnormal regulation of mechanical ventilation pathways in radiation pneumonitis (Supplementary Figure S2).
We conducted drug molecular docking analysis targeting the inhibition of Syk gene in the drug database. The criteria of drug screening include the following: (1) it has the ability to specifically kill the cells with abnormal expression of Syk and has already entered in clinical trials, (2) minor toxicity and side effects to the human body, and (3) good solubility and high absorption. The top 20 drug molecules scored out of 7,049 drugs that specifically act on the SYK transcriptional protein were selected and are presented in Supplementary Table S3, among which ZINC43131420 (fostamatinib) had the most favorable pharmacokinetic profile and less hepatotoxicity according to ADMET analysis (Table 2). Fostamatinib binds to SYK transcriptional protein primarily through hydrogen bonding and van der Waals forces (Figure 2A). The intermolecular potential energy curves revealed the potential energy changes between the drug and target protein molecules (Supplementary Figure S3). The interaction energy curve and RMSD curve (Figures 2B, C) indicated that fostamatinib is very stable and not prone to be allosteric. The toxicity analysis results are shown in Figure 2D. Fostamatinib has no potential of mutagenic and developmental toxicity, which could be an ideal drug.
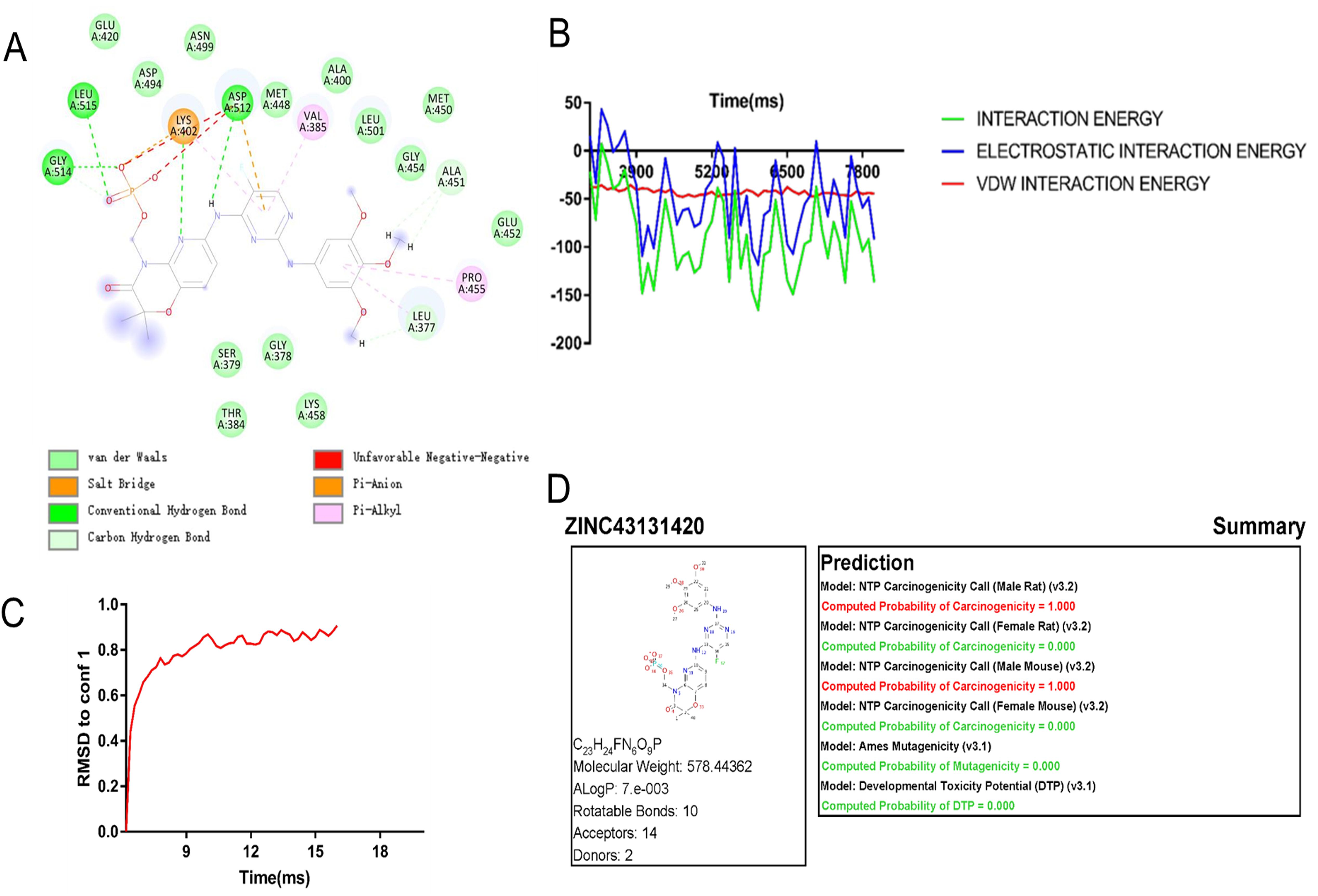
Figure 2. Drug molecule action mechanism analysis and toxicity analysis of fostamatinib. (A) Fostamatinib binds to SYK transcription protein through hydrogen bond and van der Waals force. (B) Interaction energy curves between drug molecule and SYK transcription protein. (C) RMSD curve of ZINC43131420 (fostamatinib). (D) Toxicology report of fostamatinib.
We observed the pathological changes in the lung tissue of mice at 2 weeks after radiation. Compared with group C, the alveolar walls were significantly widened, the capillaries were dilated and congested (yellow arrows), and there were inflammatory cell infiltration around bronchioles and pulmonary interstitial inflammation (black arrows) in group R (Figures 3A–D). The application of Syk inhibitor significantly reduced pulmonary interstitial inflammation, slightly widened alveolar walls, and reduced telangiectasia and inflammatory cell exudation (Figures 3A–D). Lung injury score confirmed that there was a statistical decrease in group R+S compared with group R (Figure 3E). Therefore, it can be inferred that Syk inhibitors have a protective effect on radiation pneumonitis.
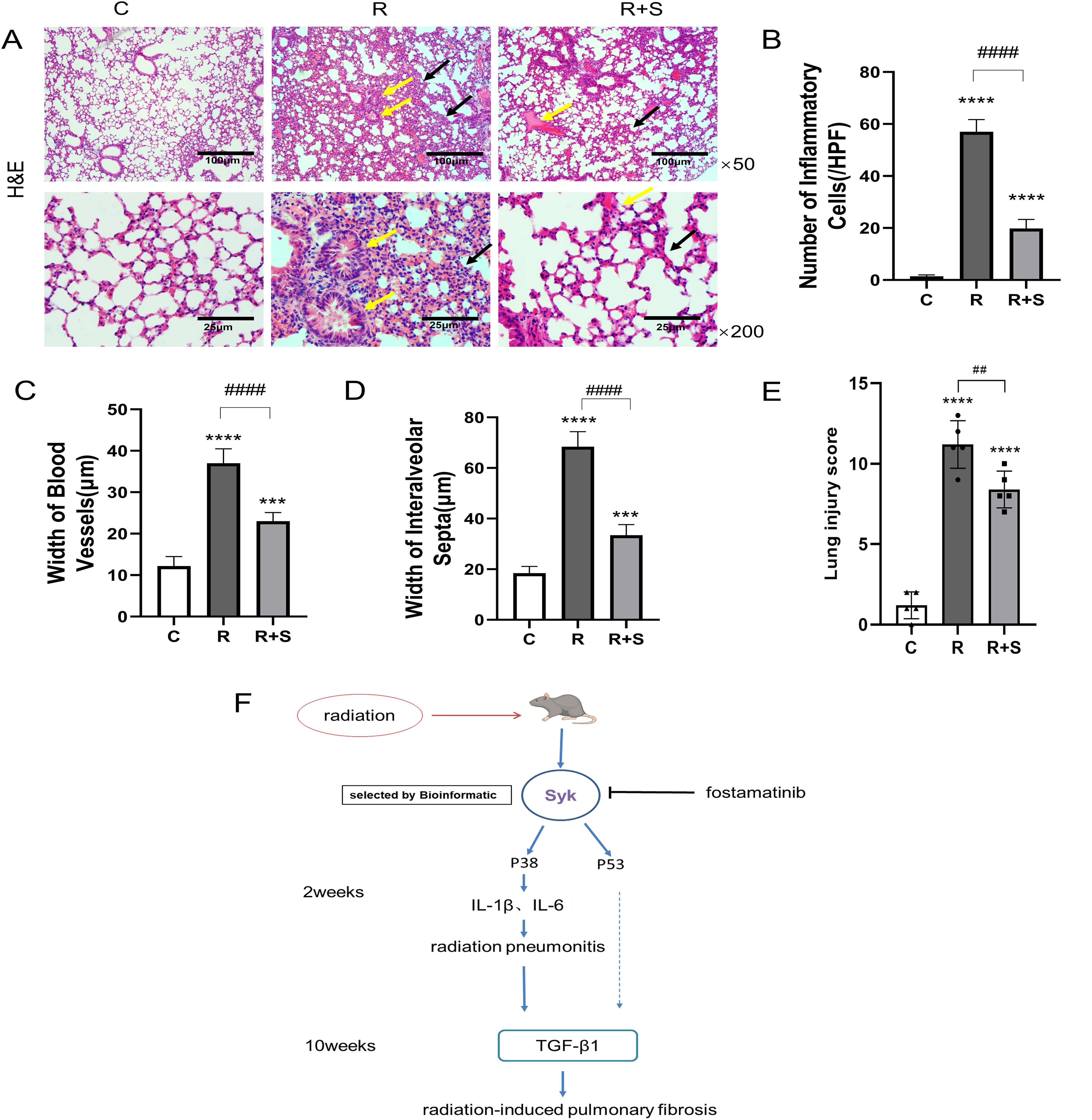
Figure 3. Pathological changes of the lung at 2 weeks after radiation. (A) Photomicrographs show the H&E staining of lung tissues of mice in different groups at ×50 and ×200 magnification. Scale bar, 100 μm for ×50 and 25 μm for ×200. (B–D) The number of inflammatory cells per high-power field of vision, width of blood vessels, and width of interalveolar septa were determined from five random fields in high magnification in lung tissue (n = 5 for each group). (E) H&E staining area from five random fields in high magnification was analyzed, and Smith scale was used to evaluate the degree of lung injury (n = 5 for each group). (F) Diagram of the hypothetical mechanism by which Syk and its inhibition regulate radiation-related lung injury. ***P < 0.0005, ****P < 0.00005 vs. C group, ##P < 0.005, ####P < 0.00005. HPF, high-power field.
Consistent with the results of the bioinformatics analysis, we found that the protein level and phosphorylation of Syk were highly expressed in the lung tissue of irradiated mice and significantly decreased in mice administered with the Syk inhibitor (Figures 4A–C).
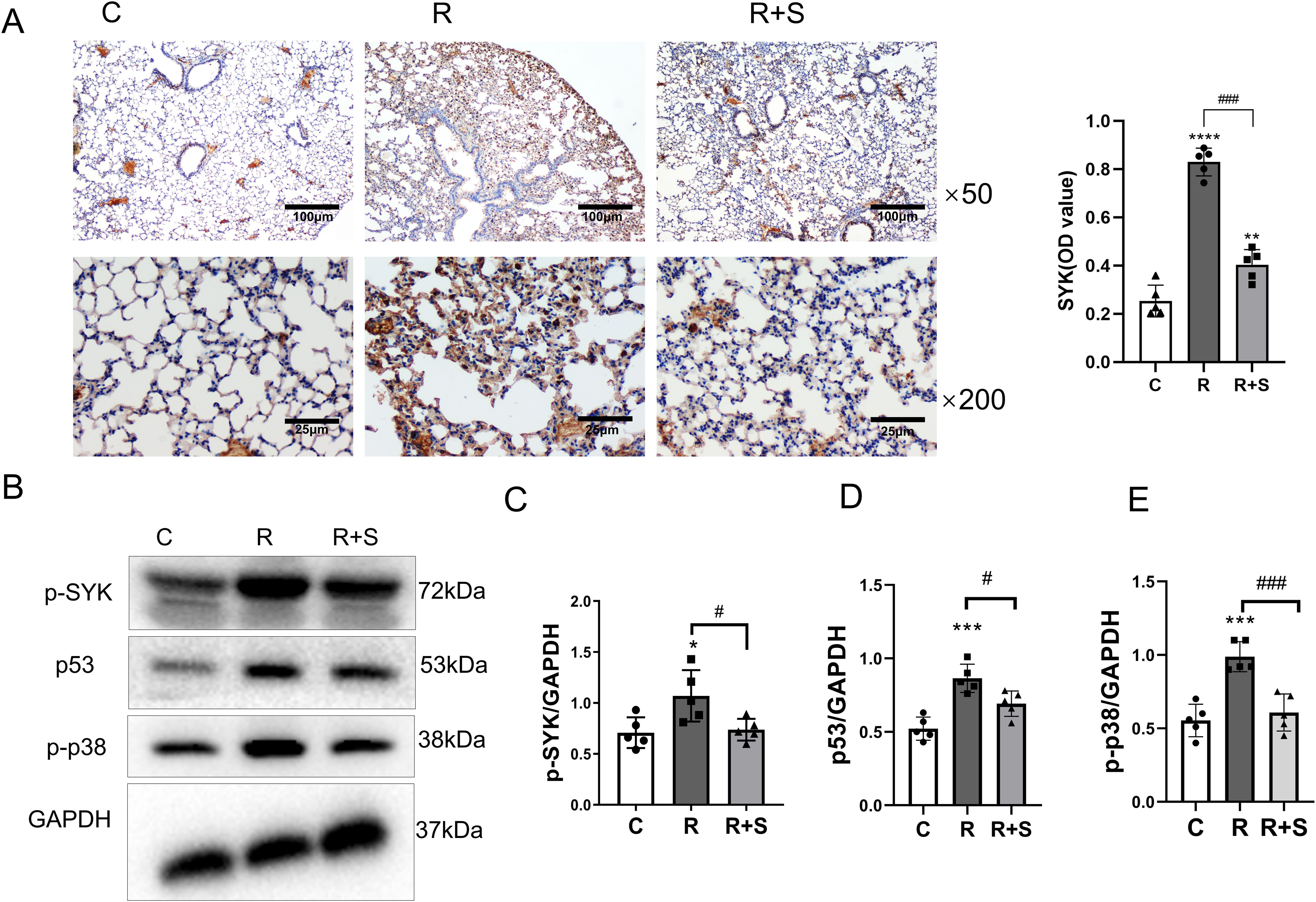
Figure 4. Relative expression of Syk, p-p38, and p53 in lung tissue at 2 weeks after radiation. (A) Immunohistochemical staining for Syk in lung sections from different groups at ×50 and ×200 magnification. Scale bar, 100 μm for ×50 and 25 μm for ×200. (B) The protein levels of p-Syk, p53, and p-p38 in lung tissues from the indicated mouse groups were detected by using Western blot. Typical images are shown. (C–E) Relative protein expression levels of p-Syk, p53, and p-p38 in lung tissue from different parts of the same gel were compared among different groups. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.0005, ****P < 0.00005 vs. C group; #P < 0.05; ###P < 0.0005.
Western blot analysis demonstrated that the expression of p-p38 and p53 in lung tissue increased at 2 weeks after radiation compared with that observed in the control group, which was also consistent with the findings in the bioinformatics analysis. p-p38 and p53 were downstream sites of the Syk signaling pathway, and their expressions decreased in the lung tissue of the group administered with the Syk inhibitor (Figures 4D, E).
IL-1β and IL-6 are the major cytokines in radiation pneumonitis (19, 20). To determine whether inflammation was suppressed by Syk inhibitor, the expression of IL-1β and IL-6 at 2 weeks after radiation was evaluated by Western blot analysis. The levels of IL-6 and IL-1β expressions in lung tissue were significantly increased in irradiated lung tissue and were downregulated in the Syk-inhibitor-administered group, as shown in Figures 5A–C.
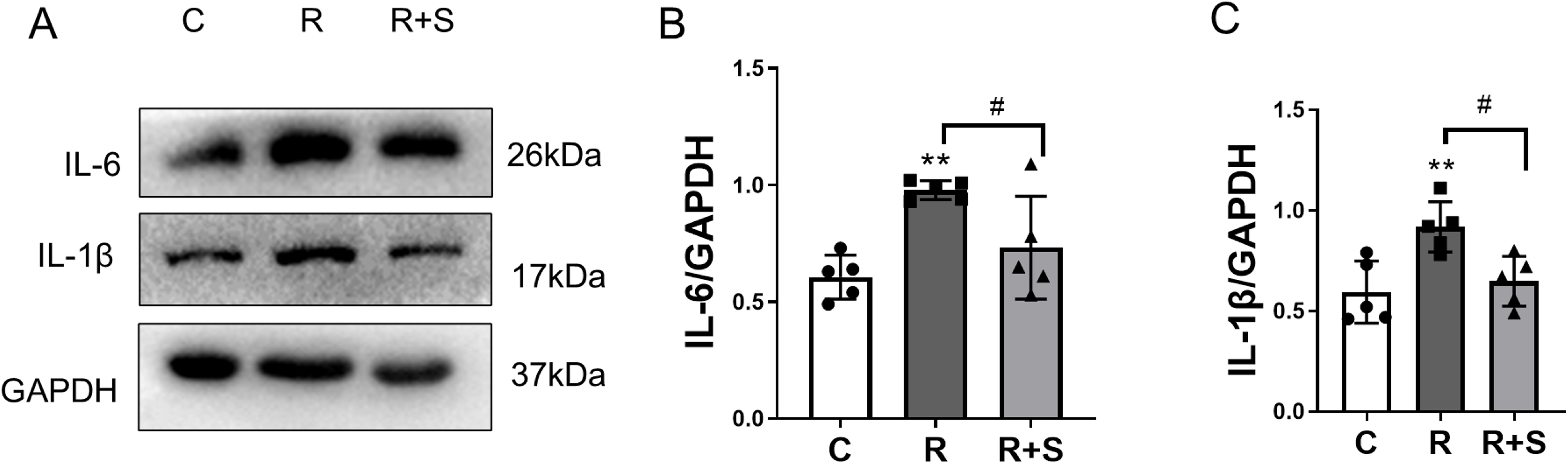
Figure 5. Relative expression of IL-1β and IL-6 in lung tissue at 2 weeks after radiation. (A) The protein levels of IL-6 and IL-1β in lung tissues from the indicated mouse groups were detected by using Western blot. Typical images are shown. (B, C) The relative protein expression levels of IL-1β and IL-6 from different parts of the same gel in lung tissue were compared among the different groups. Each bar represents the mean ± S.E. **P < 0.005 vs. C group; #P < 0.05.
The experimental results discussed above indicated that Syk inhibitors can alleviate radiation pneumonitis. We further investigated whether pulmonary fibrosis was influenced by Syk inhibition. Mice were sacrificed at 10 weeks after radiation. H&E and Masson’s trichrome staining showed that, in group R, the alveolar walls were widened, the capillaries were moderately dilated and congested (green arrows), there was some lymphocyte and monocyte infiltration (Figures 6A–D), and mild to moderate fibrous and collagen hyperplasia was observed, with alveolar collapse and poor aeration (black arrows). Compared with group R, the degree of lung interstitial inflammation and fibrous and collagen hyperplasia (black arrows) was significantly reduced in the Syk-inhibitor-administered group (Figures 6A–D). The Ashcroft score and collagen volume fraction (CVF) confirmed changes in pulmonary fibrosis in these three groups (Figures 6E, F). The content of hydroxyproline in the lung tissue of group R was significantly higher (yellow arrows) than that of the control group, suggesting collagen hyperplasia, which was significantly reduced by Syk inhibitor (Figure 6G).
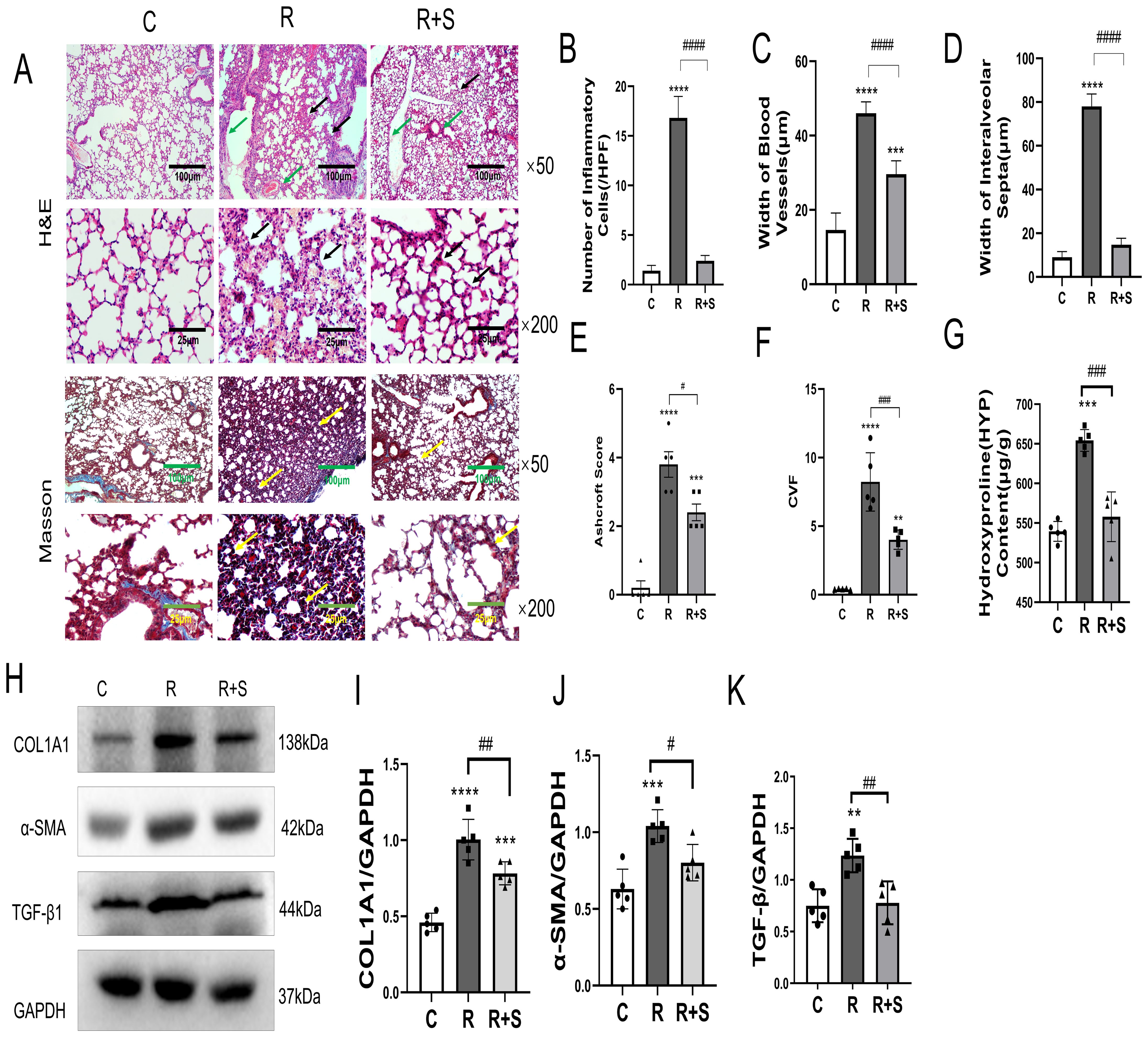
Figure 6. Pathological changes and relative expression of hydroxyproline content, COL1A1, α-SMA, and TGF-β in the lung at 10 weeks after irradiation. (A) Photomicrographs at ×50 and ×200 magnification shows H&E staining and Masson’s trichrome staining of the lung tissue of mice in the different groups. Scale bar, 100 μm for ×50 and 25 μm for ×200. (B–D) The number of inflammatory cells per high-power field of vision, width of blood vessels, and width of interalveolar septa were determined from five random fields in high magnification in lung tissue. (E) Ashcroft score was used to evaluate the degree of lung fibrosis. (F) Collagen volume fraction (CVF) in Masson staining in different groups. (G) Hydroxyproline content in lung tissues in the different groups. (H) The protein levels of COL1A1, α-SMA, and TGF-β in lung tissues from the indicated mouse groups were detected by using Western blot. Typical images are shown. (I–K) The relative protein levels of COL1A1, α-SMA, and TGF-β in lung tissues were compared between different groups. **P < 0.005; ***P < 0.0005, ****P < 0.00005 vs. C group; #P < 0.05; ##P < 0.005; ###P < 0.0005. HPF, high-power field.
TGF-β is an important cytokine that promotes the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis by inducing the production of collagen and the loss of lung elasticity (21). α-SMA and COL1A1 are usually used as biomarkers to evaluate the degree of pulmonary fibrosis (22, 23). We demonstrated that the expressions of TGF-β1, SMA, and COL1A1 in the lung tissue were significantly increased in group R and were inhibited by Syk inhibitor in group R+S (Figures 6H–K). The results showed that Syk inhibitor could attenuate the development of pulmonary fibrosis.
At present, it is believed that the occurrence of radiation pneumonitis is closely related to the damage of alveolar type II cells and vascular endothelial cells. Damage of alveolar type II cells affects alveolar tension, leading to lung compliance decrease, alveolar collapse, and atelectasis. The damage of vascular endothelial cells leads to increased vascular permeability and microthrombus formation. In previous studies, Syk has been shown to promote pathological pulmonary angiogenesis and the proliferation of pulmonary vascular smooth muscle cells (9–11). However, the role of Syk in radiation pneumonitis has not been characterized. By comparing radiation pneumonitis with normal lung tissue using bioinformation technology, spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) was identified as one of the most important driving genes of radiation pneumonitis, and the safest and most effective Syk inhibitor, fostamatinib, was selected as the inhibitor. Rube, CE and colleagues reported that the expression of the pulmonary inflammatory cytokine TGF-β significantly increased 12 h after irradiation and then returned to normal within a week, which is the so-called latent period. The most significant increase in cytokine occurred 2–4 weeks after irradiation (24). Consequently, administering fostamatinib before and for 7 days after exposure may potentially reverse or inhibit the evolution of radiation pneumonitis. Our study preliminarily demonstrated the important role of Syk in the pathogenesis of radiation pneumonitis. Inhibition of Syk could significantly reduce the degree of radiation pneumonitis and pulmonary fibrosis, and its effect was mediated in part by downregulating the activation of p-p38 and p53 (Figure 3F).
The DEGs between radiation pneumonitis and normal lung tissues were obtained by bioinformatics analysis, and the core driver genes were screened, among which Syk had the highest interaction and node degree. Mathew, B. et al. reported Syk as one of the most important regulatory nodes in activated radiation-induced lung injury network through a topological analysis of gene product interaction networks (18), which is consistent with our result. Furthermore, the results of GO and KEGG enrichment analysis revealed that DEGs were mainly enriched in B cell receptor signaling pathway, B cell receptor complex, chemokine signaling pathway, primary immunodeficiency, cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, etc. It indicated that the occurrence of radiation pneumonitis was directly related to the abnormal immune response. Syk is an immune receptor-associated protein tyrosine kinase with the highest expression in hematopoietic cells and is involved in the development and proliferation of B cells (8). It has a good specific activation effect on classical immune receptors such as B-cell receptors and active Fc receptors (FcRs) (7), and it is one of the important therapeutic targets for autoimmune diseases. B-cell receptor activation stimulates downstream cascade that involves Syk activation and, subsequently, B-cell activation (25). Syk is also expressed in many other types of cells, such as fibroblasts, epithelial cells, and vascular endothelial cells (26). Several studies have shown Syk as an important therapeutic target for inflammatory diseases (27, 28)—for instance, Syk was found to be activated at high levels in asthma patients and mouse models, and Syk inhibitor showed potent synergistic anti-inflammatory effects (29). In another study, the expression of total and phosphorylation levels of Syk was increased in patients with IgA nephropathy, and Syk inhibitor attenuated IgA-induced inflammation in tubular cells (30). In a recent study, the Syk inhibitor fostamatinib prevented skin and lung fibrosis and inflammation in bleomycin-induced systemic scleroderma mice, and the anti-fibrotic effects of fostamatinib were associated with decreased Syk phosphorylation and TGF-β expression (31). For the first time, we discovered and demonstrated Syk as a therapeutic target in radiation pneumonitis and pulmonary fibrosis.
The results of GO and KEGG enrichment analyses showed that DEGs were enriched in the p53 signaling pathway, ligase activity, and positive regulation of cytokinesis, indicating that radiation pneumonitis was associated with abnormal cell division. p53 is involved in cell cycle regulation and plays an important role in cell growth and inhibiting tumor proliferation. When cell DNA is damaged, the p53 gene exhibits the role of an oncogene to promote abnormal cell proliferation, resulting in a malignant phenotype of all cells (32). Furthermore, a recent study determined that senescence, rather than loss, of alveolar type II cells promoted progressive fibrosis and showed that interventions targeting p53 activation could block pulmonary fibrosis (33). The connection between SYK and p53 has been studied earlier. Inhibiting SYK in vitro downregulated the expression of p53 in pro-B-ALL (SEM cells) (34), HCT116, and HT1080 cell lines (25), which highlights the effect of SYK inhibition on p53 expression and activity. Our animal experiments showed that p53 expression was elevated in radiation pneumonitis, which was consistent with the bioinformatics results, whereas inhibition of Syk downregulated p53 expression.
p38, a member of the mitogen-activated kinase (MAPK) family, plays an essential role in inflammation and host defense in immunity by regulating the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, such as IL-6 and IL-1β (35, 36). In B cells stimulated by oxidative stress, Syk was required for p38 activation and the regulation of cell cycle progression (37). Syk inhibitor could improve glomerulosclerosis of lupus nephritis and inhibit the increase of TGF-β1 mRNA levels and p38MAPK signaling pathways in the kidney (38). Inhibition of Syk in vitro could attenuate the epidermal growth factor-induced activation of p38 MAPK in A431, CAL27, and SAS cells (39). In our experiment, the increase of p-p38 expression in radiation pneumonitis was downregulated in Syk-inhibitor-treated mice.
IL-1β, produced by a variety of pulmonary cells in response to a microbial challenge, drives the inflammation cascade, localizes neutrophils, and promotes the production of inflammatory modulators, such as IL-6 production (40, 41). IL-6 is a pleiotropic cytokine that is commonly produced at local tissue sites and released into circulation in almost all situations of homeostatic perturbation, typically including endotoxemia, endotoxic lung, trauma, and acute infections (42, 43). In our studies, Syk inhibitor treatment could downregulate the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-6 (44). Syk inhibitor may treat radiation pneumonitis by reducing the expression of pro-inflammatory factors through the p38 pathway.
Inflammatory cells and macrophages at the injury site after ionizing radiation induce the synthesis and release of cytokines, promote the differentiation of fibroblasts into myoblast fibroblasts, stimulate the formation of collagen and fibronectin, and accelerate the deposition of extracellular matrix, which inhibits matrix degradation, leading to the formation of pulmonary fibrosis (45–47). Myofibroblasts are the main cells that result in the abnormal deposition of extracellular matrix and play an important role in the formation of pulmonary fibrosis. TGF-β plays an essential role in the development of pulmonary fibrosis (48). The p38MAPK signaling pathway contributes to TGF-β-induced fibroblast differentiation (49). α-SMA mainly exists in the cytoplasm of myofibroblasts and is the main marker molecule of myofibroblasts. COL1A1 is the main component of collagen. In our study, α-SMA and COL1A1 were measured to assess the degree of pulmonary fibrosis. Our results showed that the elevated levels of TGF-β, α-SMA, and COL1A1 in irradiated lung tissue were significantly reduced with Syk inhibitor administration, and the degree of fibrosis was also reduced by histopathological examination.
Syk inhibitor alleviated the pneumonitis and fibrosis caused by radiation through decreasing the expression of p38 MAPK and p53 and downregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β and IL-6 and pro-fibrotic cytokine TGF-β. Syk inhibitor may have the potential to be a targeted drug in the intervention of radiation-induced lung injury.
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The name of the repository and accession number can be found below: https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.20113898.v1.
Ethical approval was not required for the study involving humans in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent to participate in this study was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements. The animal study was approved by Animal Ethics Committee at the First Bethune Hospital of Jilin University. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
GZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition. NS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis. XL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This search was supported by Jilin Provincial Department of Health Fund (no. 2023JC062) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province (no. 20200201541JC).
The authors would like to express their gratitude to EditSprings (https://www.editsprings.cn) for the expert linguistic services provided.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2024.1406759/full#supplementary-material
AHA, anti-histone antibody; Akt, threonine kinase; BCRs, B-cell receptors; BSA, bovine serum albumin; Col1a1, collagen type 1-alpha1; CVF, collagen volume fraction; ERK1/2, extracellular signal regulated kinases 1/2; HE, hematoxylin/eosin; HPS, hepatopulmonary syndrome; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; IL-6, interleukin-6; ITP, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinases; mRNA, messenger ribonucleic acid; p-p38, phospho-p38; p-Syk, phosphorylation spleen tyrosine kinase; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; RILI, radiation-induced lung injury; SDS, sodium dodecyl sulfate; SDS-PAGE, sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; SH2, SRC homology 2; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus; SPF, specific pathogen-free; Syk, spleen tyrosine kinase; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; α-SMA, alpha smooth muscle actin.
1. Arroyo-Hernández M, Maldonado F, Lozano-Ruiz F, Muñoz-Montaño W, Nuñez-Baez M, Arrieta O. Radiation-induced lung injury: current evidence. BMC Pulmonary Med. (2021) 21:9. doi: 10.1186/s12890-020-01376-4
2. Bledsoe TJ, Nath SK, Decker RH. Radiation pneumonitis. Clinics Chest Med. (2017) 38:201–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ccm.2016.12.004
3. Simone CB. Thoracic radiation normal tissue injury. Semin Radiat Oncol. (2017) 27:370–7. doi: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2017.04.009
4. Abratt RP, Morgan GW, Silvestri G, Willcox P. Pulmonary complications of radiation therapy. Clinics Chest Med. (2004) 25:167–77. doi: 10.1016/S0272-5231(03)00126-6
5. Zhong S, Wu B, Han Y, Cao Y, Yang L, Luo SX, et al. Identification of driver genes and key pathways of pediatric brain tumors and comparison of molecular pathogenesis based on pathologic types. World Neurosurg. (2017) 107:990–1000. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2017.07.094
6. Zhong S, Yan Q, Ge J, Dou G, Xu H, Zhao G. Identification of driver genes and key pathways of ependymoma. Turkish Neurosurg. (2024) 34(2):184–95. doi: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.21876-17.5
7. Pamuk ON, Tsokos GC. Spleen tyrosine kinase inhibition in the treatment of autoimmune, allergic and autoinflammatory diseases. Arthritis Res Ther. (2010) 12:222. doi: 10.1186/ar3198
8. Mócsai A, Ruland J, Tybulewicz VLJ. The SYK tyrosine kinase: a crucial player in diverse biological functions. Nat Rev Immunol. (2010) 10:387–402. doi: 10.1038/nri2765
9. Tohyama Y, Yamamura H. Protein tyrosine kinase, syk: A key player in phagocytic cells. J Biochem. (2009) 145:267–73. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvp001
10. Gao WZ, Yang YH, Dan L, Zhu XW. Splenic tyrosine kinase promotes pulmonary angiogenesis in rats with hepatopulmonary syndrome. Sheng Li Xue Bao. (2020) 72:785–92.
11. Gao Z, Cao L, Luo Q, Wang X, Yu L, Wang T, et al. Spleen tyrosine kinase modulates the proliferation and phenotypes of vascular smooth muscle cells induced by platelet-derived growth factor. DNA Cell Biol. (2011) 30:149–55. doi: 10.1089/dna.2010.1146
12. Qu C, Zheng D, Li S, Liu Y, Lidofsky A, Holmes JA, et al. Tyrosine kinase SYK is a potential therapeutic target for liver fibrosis. Hepatology. (2018) 68:1125–39. doi: 10.1002/hep.29881
13. Torres-Hernandez A, Wang W, Nikiforov Y, Tejada K, Torres L, Kalabin A, et al. Targeting SYK signaling in myeloid cells protects against liver fibrosis and hepatocarcinogenesis. Oncogene. (2019) 38:4512–26. doi: 10.1038/s41388-019-0734-5
14. Hirano Y, Aziz M, Yang W-L, Wang Z, Zhou M, Ochani M, et al. Neutralization of osteopontin attenuates neutrophil migration in sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Crit Care. (2015) 19:53. doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-0782-3
15. Aziz M, Ode Y, Zhou M, Ochani M, Holodick NE, Rothstein TL, et al. B-1a cells protect mice from sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Mol Med. (2018) 24:26. doi: 10.1186/s10020-018-0029-2
16. Ashcroft T, Simpson JM, Timbrell V. Simple method of estimating severity of pulmonary fibrosis on a numerical scale. J Clin Pathol. (1988) 41:467–70. doi: 10.1136/jcp.41.4.467
17. Colunga Biancatelli RML, Solopov P, Dimitropoulou C, Catravas JD. Age-dependent chronic lung injury and pulmonary fibrosis following single exposure to hydrochloric acid. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22(16):8833. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168833
18. Mathew B, Huang Y, Jacobson JR, Berdyshev E, Gerhold LM, Wang T, et al. Simvastatin attenuates radiation-induced murine lung injury and dysregulated lung gene expression. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2011) 44:415–22. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2010-0122OC
19. Rübe CE, Rodemann HP, Rübe C. Die Bedeutung von Zytokinen für die radiogene Lungenreaktion. Strahlenther Und Onkol. (2004) 180:541–9. doi: 10.1007/s00066-004-1279-1
20. Arpin D, Perol D, Blay J-Y, Falchero L, Claude L, Vuillermoz-Blas S, et al. Early variations of circulating interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 levels during thoracic radiotherapy are predictive for radiation pneumonitis. J Clin Oncol. (2005) 23:8748–56. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.01.7145
21. Wei P, Xie Y, Abel PW, Huang Y, Ma Q, Li L, et al. Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1-induced miR-133a inhibits myofibroblast differentiation and pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Death Dis. (2019) 10:670. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1873-x
22. Wang Y, Li S, Zhao J, Li Q, Xu C, Wu H, et al. Snail-mediated partial epithelial mesenchymal transition augments the differentiation of local lung myofibroblast. Chemosphere. (2021) 267:128870. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128870
23. Yao L, Conforti F, Hill C, Bell J, Drawater L, Li J, et al. Paracrine signalling during ZEB1-mediated epithelial–mesenchymal transition augments local myofibroblast differentiation in lung fibrosis. Cell Death Differentiation. (2019) 26(5):943–57. doi: 10.1038/s41418-018-0175-7
24. Rube CE, Uthe D, Schmid KW, Richter KD, Wessel J, Schuck A, et al. Dose-dependent induction of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) in the lung tissue of fibrosis-prone mice after thoracic irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2000) 47:1033–42. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(00)00482-x
25. Althubiti M. Spleen tyrosine kinase inhibition modulates p53 activity. J Cell Death. (2017) 10:1179066017731564. doi: 10.1177/1179066017731564
26. Yanagi S, Inatome R, Takano T, Yamamura H. Syk expression and novel function in a wide variety of tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2001) 288:495–8. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.5788
27. Geahlen RL. Getting Syk: spleen tyrosine kinase as a therapeutic target. Trends Pharmacol Sci. (2014) 35:414–22. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2014.05.007
28. Kaur M, Singh M, Silakari O. Inhibitors of switch kinase ‘spleen tyrosine kinase’ in inflammation and immune-mediated disorders: A review. Eur J Med Chem. (2013) 67:434–46. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2013.04.070
29. Liu Q, Hua L, Bao C, Kong L, Hu J, Liu C, et al. Inhibition of spleen tyrosine kinase restores glucocorticoid sensitivity to improve steroid-resistant asthma. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:885053. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.885053
30. Yiu WH, Chan KW, Chan LYY, Leung JCK, Lai KN, Tang SCW. Spleen tyrosine kinase inhibition ameliorates tubular inflammation in igA nephropathy. Front Physiol. (2021) 12:650888. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.650888
31. Wang M, Zhang Z, Liu J, Song M, Zhang T, Chen Y, et al. Gefitinib and fostamatinib target EGFR and SYK to attenuate silicosis: a multi-omics study with drug exploration. Signal Transduction Targeted Ther. (2022) 7:157. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-00959-3
32. Zhu G, Pan C, Bei J-X, Li B, Liang C, Xu Y, et al. Mutant p53 in cancer progression and targeted therapies. Front Oncol. (2020) 10:595187. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.595187
33. Yao C, Guan X, Carraro G, Parimon T, Liu X, Huang G, et al. Senescence of alveolar type 2 cells drives progressive pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2021) 203:707–17. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202004-1274OC
34. Sender S, Sekora A, Villa Perez S, Chabanovska O, Becker A, Ngezahayo A, et al. Precursor B-ALL cell lines differentially respond to SYK inhibition by entospletinib. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22(2):592. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020592
35. Kumar S, Boehm J, Lee JC. p38 MAP kinases: key signalling molecules as therapeutic targets for inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. (2003) 2:717–26. doi: 10.1038/nrd1177
36. Yong H-Y, Koh M-S, Moon A. The p38 MAPK inhibitors for the treatment of inflammatory diseases and cancer. Expert Opin Investigational Drugs. (2009) 18:1893–905. doi: 10.1517/13543780903321490
37. He J, Takano T, Ding J, Gao S, Noda C, Sada K, et al. Syk is required for p38 activation and G2/M arrest in B cells exposed to oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signaling. (2002) 4:509–15. doi: 10.1089/15230860260196317
38. Kitai M, Fukuda N, Ueno T, Endo M, Maruyama T, Abe M, et al. Effects of a spleen tyrosine kinase inhibitor on progression of the lupus nephritis in mice. J Pharmacol Sci. (2017) 134:29–36. doi: 10.1016/j.jphs.2017.02.015
39. Huang D-Y, Chen W-Y, Chen C-L, Wu N-L, Lin W-W. Synergistic anti-tumour effect of syk inhibitor and olaparib in squamous cell carcinoma: roles of syk in EGFR signalling and PARP1 activation. Cancers. (2020) 12(2):489. doi: 10.3390/cancers12020489
40. Tregoning JS, Pizzutto SJ, Upham JW, Yerkovich ST, Chang AB. High pulmonary levels of IL-6 and IL-1β in children with chronic suppurative lung disease are associated with low systemic IFN-γ Production in response to non-typeable haemophilus influenzae. PloS One. (2015) 10:e0129517. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129517
41. Edwards MR, Mukaida N, Johnson M, Johnston SL. IL-1β induces IL-8 in bronchial cells via NF-κB and NF-IL6 transcription factors and can be suppressed by glucocorticoids. Pulmonary Pharmacol Ther. (2005) 18:337–45. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2004.12.015
42. Keyel PA. How is inflammation initiated? Individual influences of IL-1, IL-18 and HMGB1. Cytokine. (2014) 69:136–45. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2014.03.007
43. Tanaka T, Narazaki M, Kishimoto T. Interleukin (IL-6) immunotherapy. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Biol. (2018) 10(8):a028456. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a028456
44. Yahyapour R, Amini P, Rezapoor S, Rezaeyan A, Farhood B, Cheki M, et al. Targeting of inflammation for radiation protection and mitigation. Curr Mol Pharmacol. (2018) 11:203–10. doi: 10.2174/1874467210666171108165641
45. Falanga V, Zhou L, Yufit T. Low oxygen tension stimulates collagen synthesis and COL1A1 transcription through the action of TGF-β1. J Cell Physiol. (2002) 191:42–50. doi: 10.1002/jcp.v191:1
46. Yarnold J, Vozenin Brotons M-C. Pathogenetic mechanisms in radiation fibrosis. Radiother Oncol. (2010) 97:149–61. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2010.09.002
47. Hanania AN, Mainwaring W, Ghebre YT, Hanania NA, Ludwig M. Radiation-induced lung injury. Chest. (2019) 156:150–62. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.03.033
48. Györfi AH, Matei A-E, Distler JHW. Targeting TGF-β signaling for the treatment of fibrosis. Matrix Biol. (2018) 68-69:8–27. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2017.12.016.
Keywords: bioinformatics, radiation pneumonitis, Syk, p38 MAPK, p53
Citation: Zhang G, Sun N and Li X (2024) Spleen tyrosine kinase inhibition mitigates radiation-induced lung injury through anti-inflammatory effects and downregulation of p38 MAPK and p53. Front. Oncol. 14:1406759. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1406759
Received: 25 March 2024; Accepted: 11 October 2024;
Published: 07 November 2024.
Edited by:
Jie-Young Song, Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, Republic of KoreaReviewed by:
Zissis C. Chroneos, The Pennsylvania State University, United StatesCopyright © 2024 Zhang, Sun and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaohua Li, bGl4aWFvaHVhQGpsdS5lZHUuY24=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.