- 1Department of Neurosurgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming, China
- 2Institute for Ecological Research and Pollution Control of Plateau Lakes, School of Ecology and Environmental Science, Yunnan University, Kunming, China
- 3Hematology and Rheumatology Department, The Pu’er People’s Hospital, Pu’er, China
- 4Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, The First People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province, Kunming, China
- 5Department of Respiratory Medicine, Second Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming, China
- 6Kunming College of Life Science, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
A Corrigendum on
Long non-coding RNA AL139385.1 as a novel prognostic biomarker in lung adenocarcinoma
By Chen X, Guo J, Zhou F, Ren W, Huang X, Pu J, Niu X and Jiang X (2022). Front. Oncol. 12:905871. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.905871
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 10G and Figure 11D as published. The representative picture of BrdU, Wound healing of H1299 cells was presented incorrectly. The error happened due to duplicate in naming the figures which later was not checked again. The corrected Figures 10 and 11 and their captions appear below.
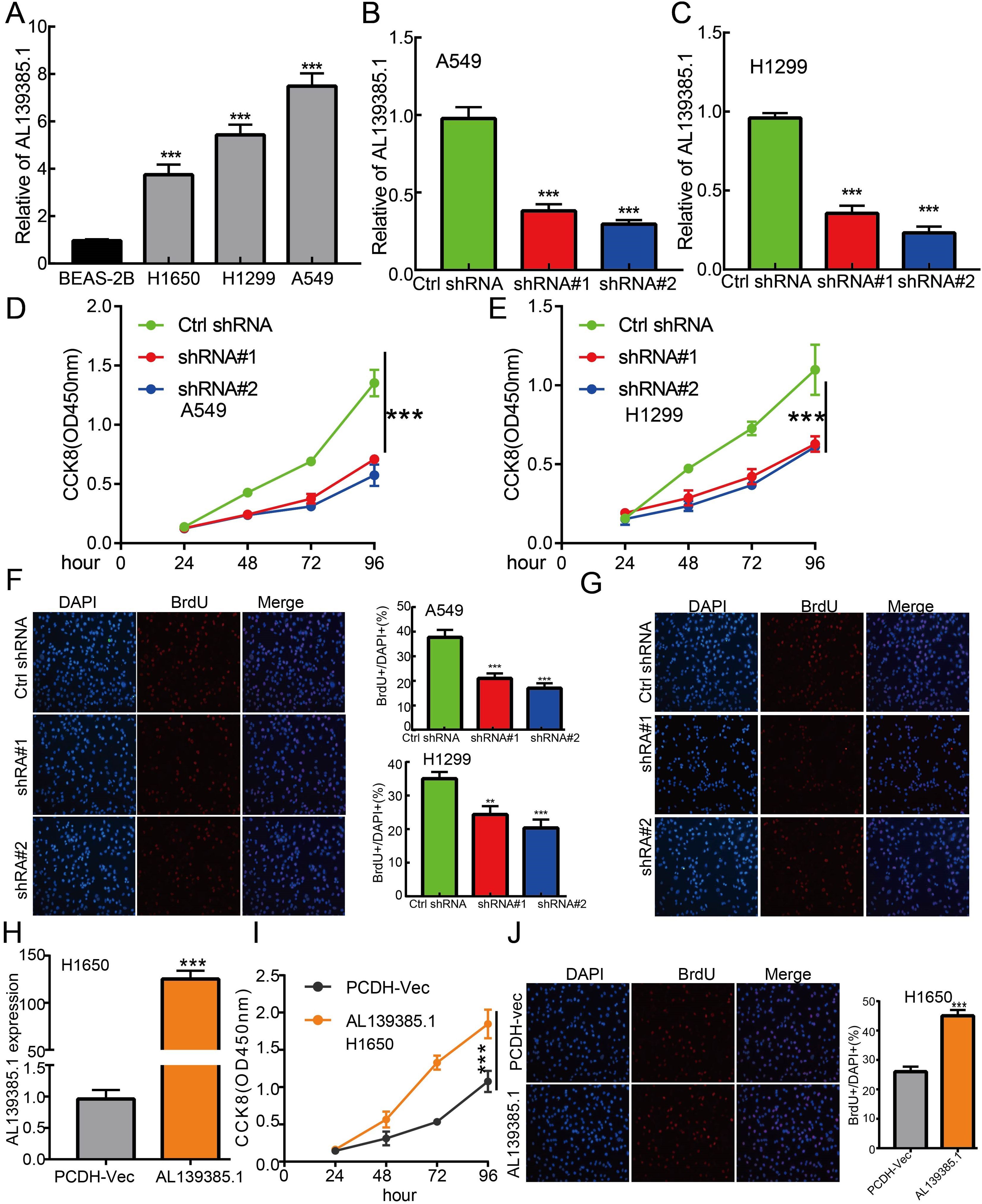
Figure 10. lncRNA-AL139385.1 regulates LUAD cell proliferation in vitro. (A) The relative expression level of AL139385.1 in lung adenocarcinoma cancerous cell lines, including H1299, H1650 and A549 examined by Real-time RT-PCR, compared to normal human bronchial epithelial cell line: BEAS-2B. (B, C) Establishment of AL139385.1 knockdown cell lines in A549 and H1299 verified by Real-time RT-PCR assay (D-G) Knockdown of AL139385.1 significantly inhibits cell proliferation in A549 and H1299 cells, as measured by CCK8 and BrdU incorporation assay. (H) Establishment of AL139385.1 overall cell lines in H1650 verified by Real-time RT-PCR assay (I, J) Overexpression of AL139385.1 significantly promotes cell proliferation in H1650 cells, as measured by CCK8 and BrdU incorporation assay. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. shRNA#1=AL139385.1 shRNA#1, shRNA#2= AL139385.1 shRNA#2. AL139385.1=PCDH-AL139385.1.
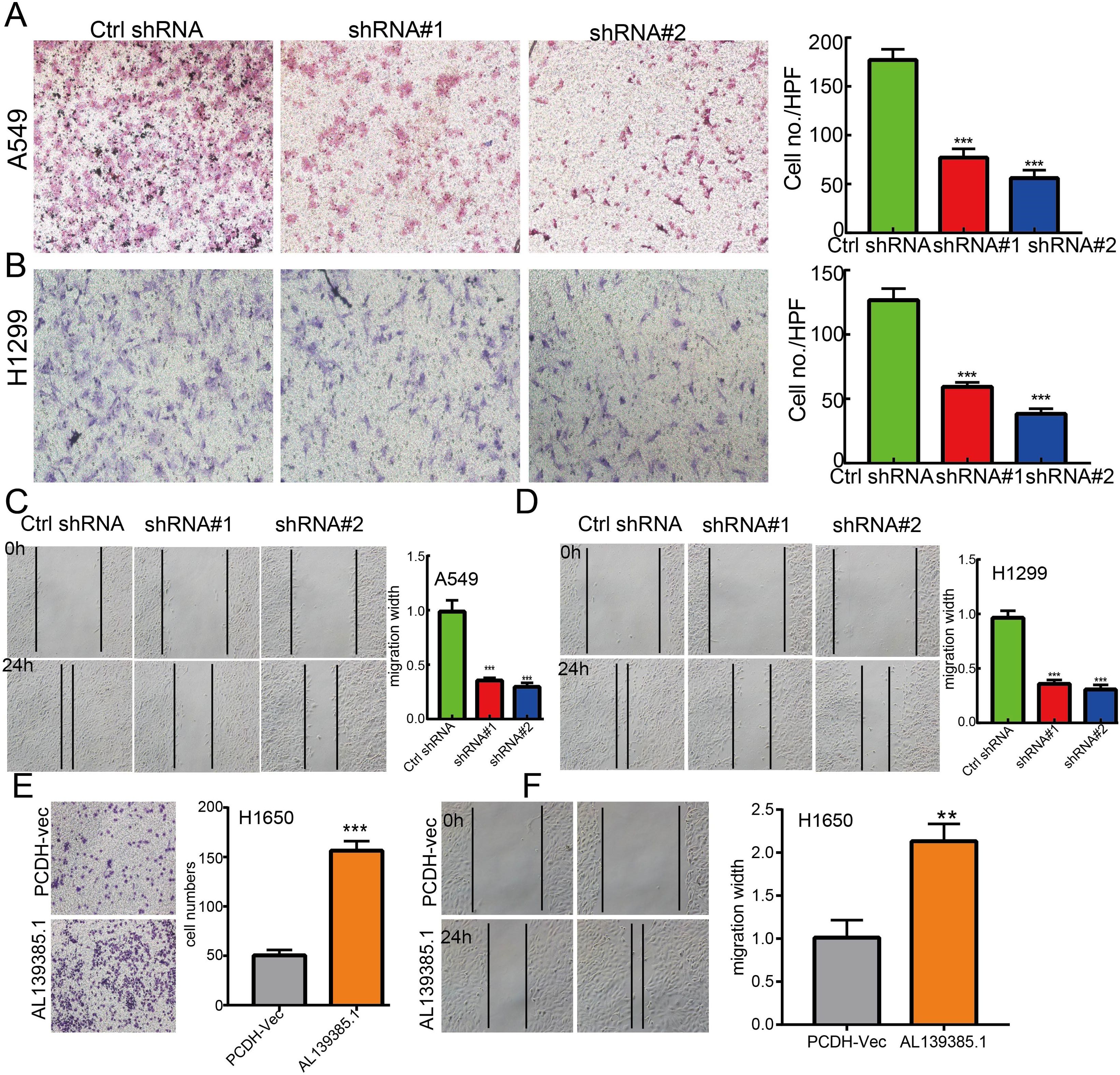
Figure 11. lncRNA-AL139385.1 regulates LUAD cell migration in vitro. (A, B) Knockdown of lncRNA AL139385.1 dramatically inhibits A549 and H1299 cells migration ability examined by transwell assay. (C, D) Knockdown of AL139385.1 dramatically inhibits A549 and H1299 cells migration ability examined by wound healing assay. (E, F) Overexpression of AL139385.1 significantly promotes cell migration in H1650 cells, as measured by transwell and wound healing assay. **P < 0.01,***P < 0.001. shRNA#1=AL139385.1 shRNA#1, shRNA#2= AL139385.1 shRNA#2. AL139385.1=PCDH-AL139385.1.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: AL139385.1, lung adenocarcinoma, prognosis biomarker, DNA methylation, ceRNA, cell proliferation, cell migration
Citation: Chen X, Guo J, Zhou F, Ren W, Huang X, Pu J, Niu X and Jiang X (2024) Corrigendum: Long non-coding RNA AL139385.1 as a novel prognostic biomarker in lung adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 14:1223478. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1223478
Received: 16 May 2023; Accepted: 20 August 2024;
Published: 03 September 2024.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Sharon R. Pine, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, United StatesCopyright © 2024 Chen, Guo, Zhou, Ren, Huang, Pu, Niu and Jiang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiulin Jiang, amlhbmd4aXVsaW5AbWFpbC5raXouYWMuY24=; Xiaoqun Niu, NjczNDA5MjU2QHFxLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xi Chen1†
Xi Chen1† Xiulin Jiang
Xiulin Jiang