- 1Department of Oncology, Hangzhou TCM Hospital Affiliated to Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Zhejiang, China
- 2Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, The First People’s Hospital of Tongxiang, Zhejiang, China
Objectives: Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is defined as a highly aggressive type of breast cancer which lacks specific biomarkers and drug targets. Damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP)-induced immunogenic cell death (ICD) may influence the outcome of immunotherapy for TNBC patients. This study aims to develop a DAMPs gene signature to classify TNBC patients and to further predict their prognosis and immunotherapy outcome.
Methods: We identified the DAMPs-associated subtypes of 330 TNBCs using K-means analysis. Differences in immune status, genomic alterations, and predicted immunotherapy outcome were compared among each subtype.
Results: A total of 330 TNBCs were divided into three subtypes according to DAMPs gene expression: the nuclear DAMPs subtype, featuring the upregulation of nuclear DAMPs; the inflammatory DAMPs subtype, characterized by the gene set enrichment of the adaptive immune system and cytokine signaling in the immune system; and the DAMPs-suppressed subtype, having the lowest level of ICD-associated DAMPs. Among them, the inflammatory subtype patients had the most favorable survival, while the DAMPs-suppressed subtype was associated with the worst prognosis. The DAMPs subtyping system was successfully validated in the TCGA cohort. Furthermore, we systemically revealed the genomic alterations among the three DAMPs subtypes. The inflammatory DAMPs subtype was predicted to have the highest response rate to immunotherapy, suggesting that the constructed DAMPs clustering had potential for immunotherapy efficacy prediction.
Conclusion: We established a novel ICD-associated DAMPs subtyping system in TNBC, and DAMPs expression might be a valuable biomarker for immunotherapy strategies. Our work could be helpful to the development of new immunomodulators and may contribute to the development of precision immunotherapy for TNBC.
Introduction
Female breast cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer and the second leading cause of cancer death worldwide in 2020 (1). Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is a highly aggressive subtype of breast cancer that lacks estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR) and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER-2) expression (2). Due to its high invasiveness, strong metastatic ability and early recurrence, TNBC causes a larger number of breast cancer-related deaths than other types (3). Nevertheless, recent approvals for immunotherapy have offered potential long-term survival outcomes for metastatic TNBC (mTNBC) patients, regardless of different histological subtypes (4).
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), the most successful immunotherapeutic agents for TNBC, can significantly improve patients’ progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) if they respond (5). The response rates to ICIs in TNBC are associated with tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) expression and nonsynonymous mutations (6). In addition, preclinical models (7) and clinical trials (8) confirm that the induction of immunogenic cell death (ICD) sensitizes TNBC to ICIs treatments, which suggests that ICD biomarkers may be candidate prognostic factors for immunotherapy.
The major immunogenic characteristic of ICD is defined by the emission of a series of immunostimulatory damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), such as cell surface-exposed calreticulin (CALR), extracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) (9). Previous studies have demonstrated that TNBC cell-derived HMGB1 elicited by chemo/radiotherapy augmented the antitumor immunity induced by activated CD8+ T cells (10, 11), which revealed the importance of DAMPs in treating TNBC with immunotherapy.
Various innate immune receptors are involved in DAMPs-mediated ICD, such as pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs), G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), and triggering receptors expressed on myeloid cells (TREMs) (12), and their interaction with DAMPs is necessary for ICD and anticancer immunity. Moreover, the expression patterns of toll-like receptors (TLRs), the most widely studied PRRs, are diverse between TNBC and other types of breast cancer and are associated with different cancer incidence and progression (13). Targeting DAMPs-sensing receptors may provide new insights for the treatment of TNBC, since they have the potential to ignite positive immune responses in the tumor-immune-microenvironment (TIME) (14).
Sensitization to ICIs by ICD-associated DAMPs strongly relies on the immunoreactive TIME, in which TILs and tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) play an important role in the prognostic prediction of TNBC (15). In this regard, assessing the distinct TIME helps to understand the immune signature of different TNBC subtypes, optimize immunotherapy and improve the outcome of TNBC patients (16). Although a large number of immune-related biomarkers and prognostic models have been developed to describe and quantify the TIME of TNBC (17, 18), few have considered ICD-associated DAMPs and sensing receptors as actionable targets.
In the present study, we comprehensively analyzed the DAMPs gene signature to explore the effect of ICD-associated DAMPs and sensing receptors on the TIME and survival of TNBC patients. Moreover, we constructed a DAMPs-based risk score model to evaluate the prognostic value of DAMPs and correlated sensing receptors in TNBC (the whole process of data analysis is depicted in Figure 1). Our work may provide a novel clue for exploring the underlying molecular mechanisms of different responses to immunotherapy in TNBC patients, which sheds a novel light on the immunotherapy strategy of TNBC.
Figure 1 Flow chart of the data analysis process. The DAMPs-associated subtypes were established based on 330 TNBCs from the FUSCC cohort and validated in the TCGA cohort. DAMPs, damage-associated molecular patterns; FUSCC, Fudan University Cancer Center; TCGA, The Cancer Genome Atlas.
Materials and Methods
Data Collection
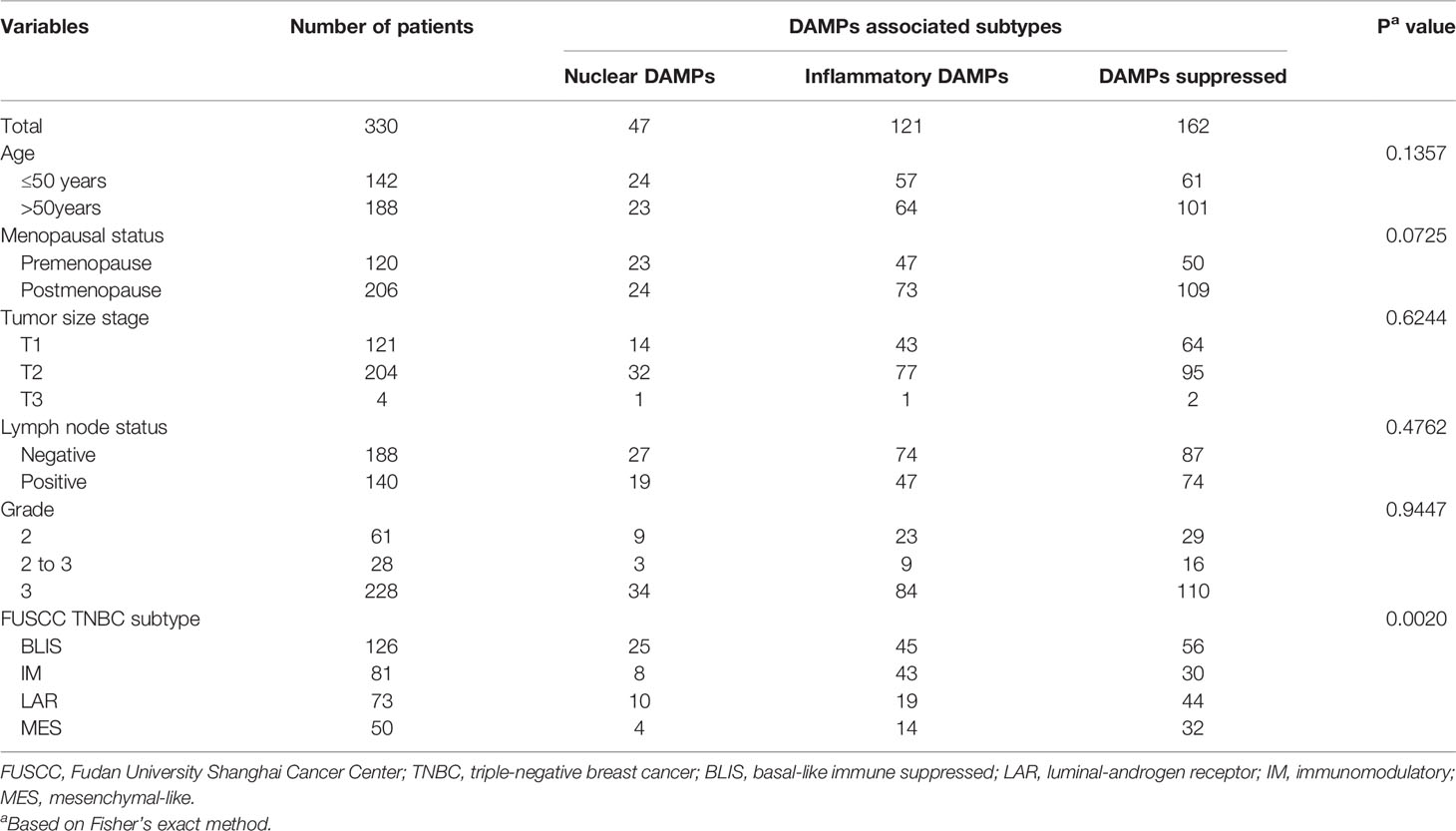
Our study included cohorts of breast cancer patients from Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center (FUSCC, a total of 465 TNBC patients, 100% female, average age = 53 ± 11 years; 360 patients with RNA-seq data, 401 patients with CNA data and 279 patients with WES data) (19) and TCGA (a total of 1,096 patients, including 161 TNBC patients, 100% female, average age = 55 ± 12 years) (20–22). To exclude the influence of pathological heterogeneity, we included 330 TNBC samples of invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) in the FUSCC cohort. The microarray data and sequence data of the FUSCC cohort have been deposited in the NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO: GSE118527) and Sequence Read Archive (SRA: SRP157974). Expression and clinical data of TCGA cohorts were downloaded from the website (http://www.cbioportal.org/). TNBC sample selection of FUSCC and TCGA was based on the immunohistochemistry (IHC) results, which lack expression of ER, PR, and HER2 in IDC. The demographic data and clinical features are listed in Table 1.
Identification of DAMPs Subgroups by K-means Analysis
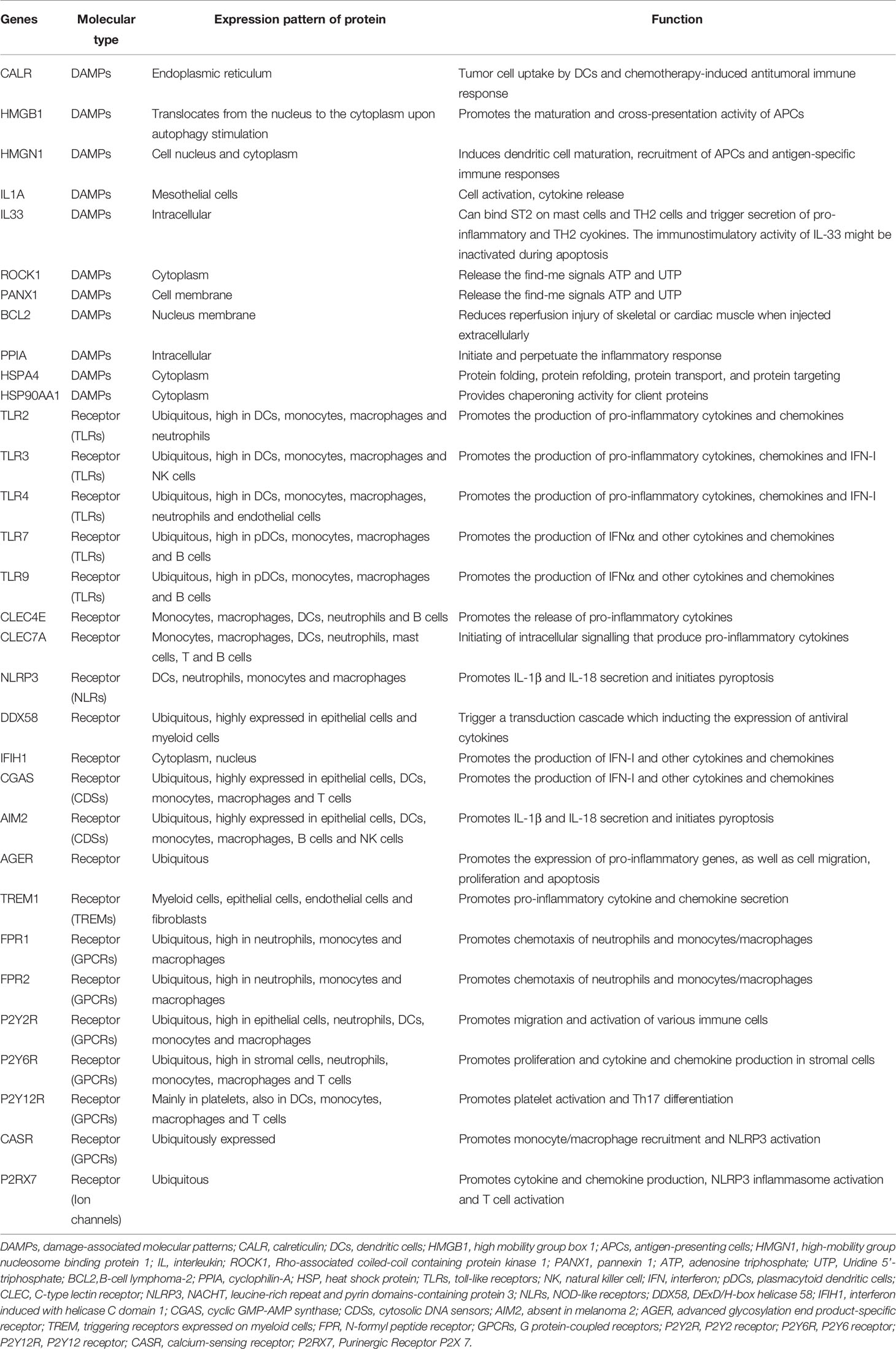
First, 32 DAMPs-related genes were collected according to previous research, and their information is shown in Table 2 (9, 12, 23, 34). 28 DAMPs-related genes were found to be expressed in the FUSCC cohort. Consensus clustering was analyzed by the R package “ConsensusClusterPlus” based on the DAMPs-related gene expression matrix. Consist with previous FUSCC TNBC research, k-means clustering (the “kmeans” function in R) was utilized to determine stable DAMPs-associated TNBC subtypes (19, 24).
PAM50 Subtype and Lehmann TNBC Subtype
The PAM50 subtype of FUSCC TNBC was analyzed by the PAM50 predictor (the “genefu” package in R). To identify Lehmann TNBC molecular subtypes, only TNBC samples that were determined by mixed Gaussian distribution were subtyped as individual datasets using the TNBC type online subtyping tool (http://cbc.mc.vanderbilt.edu/tnbc/) (25).
Functional Analyses
Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) among the three subtypes were identified by the threshold value of |log2FC|≥1 and false discovery rate (FDR) ≤0.05. Gene Ontology (GO) analysis and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis were performed and visualized in Metascape (26). Furthermore, gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) was utilized among DAMPs-associated TNBC subtypes to compare the differences (27).
Genomic Analysis
Copy number alterations (CNA) were analyzed using GISTIC2.0 from the FUSCC TNBC cohort (28). We compared the differences in amplification or deletion events at the arm level among DAMPs-associated TNBC subtypes. The waterfall plot of CNV data was visualized by the “ComplexHeatmap” package in R. The tumor mutation burden (TMB) was calculated by the number of mutations per patient (29).
Immune Analyses
CIBERSORT immune infiltrating analysis was performed to calculate the abundance of 22 immune infiltrating cells (30). We calculated the stromal score and immune score through the Estimation of Stromal and Immune cells in Malignant Tumor tissues using Expression data (ESTIMATE) algorithm (31).
Calculation of the Immunophenscore
The immunophenoscore (IPS) was calculated by the algorithm as previously reported (32). Briefly, IPS was calculated on a 0-10 scale based on the expression of the representative genes or gene sets of the immunophenogram. Samplewise z scores are positively weighted according to stimulatory factors (cell types) and negatively weighted according to inhibitory factors (cell types) and averaged. Z scores ≥3 were designated IPS10, and z scores ≤0 were designated IPS0.
Statistical Analyses
Statistical analyses were conducted by R (version 3.5.2) and GraphPad Prism (version 8.0). Survival analysis was performed through the Kaplan–Meier algorithm by the R package “survival”. Two-sided Student’s t test or two-sided Wilcoxon-rank sum test were used for comparison of two groups. For comparison of more than three groups, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) or Kruskal-Wallis test were performed. A P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Identification of Three DAMPs-Associated Subtypes
To exclude the influence of pathological heterogeneity, we included TNBC samples of IDC (n=330) from the FUSCC cohort. We classified them into three DAMPs-associated subtypes based on the expression of DAMPs-related genes by a consensus clustering approach, identifying the optimal clustering stability at K=3 (Figures 2A-D). Of the 330 TNBC patients included in the study, 47 patients were clustered in the nuclear DAMPs subtype, 121 in the inflammatory DAMPs subtype and 162 in the DAMPs-suppressed subtype. The heatmap shows the normalized enrichment scores of DAMPs-related genes in the three subtypes (Figure 2E), with significant differences in expression between the three distinct clusters. Nuclear-associated DAMPs, such as HMGB1 and high-mobility group nucleosome binding protein 1 (HMGN1), were highly expressed in the nuclear DAMPs subtype. The inflammatory DAMPs subtype was characterized by high expression of CALR. In the DAMPs-suppressed subtype, DAMPs genes were expressed at low levels, but DAMPs receptors were highly expressed (Figure 2E). Stacked bar plots show the distribution of FUSCC TNBC subtypes and Lehmann TNBC subtypes among the DAMPs-associated subtypes (Figure 2F), demonstrating that the immunomodulatory (IM) subtypes of four FUSCC TNBC subtypes (luminal androgen receptor/IM/basal-like immune-suppressed/mesenchymal-like) account for the highest proportion of the inflammatory DAMPs subtype. These results suggest that DAMPs-related genes classify TNBC patients into three distinguishable subtypes with significantly different gene expression patterns, as well as different predominant clinical subtypes.
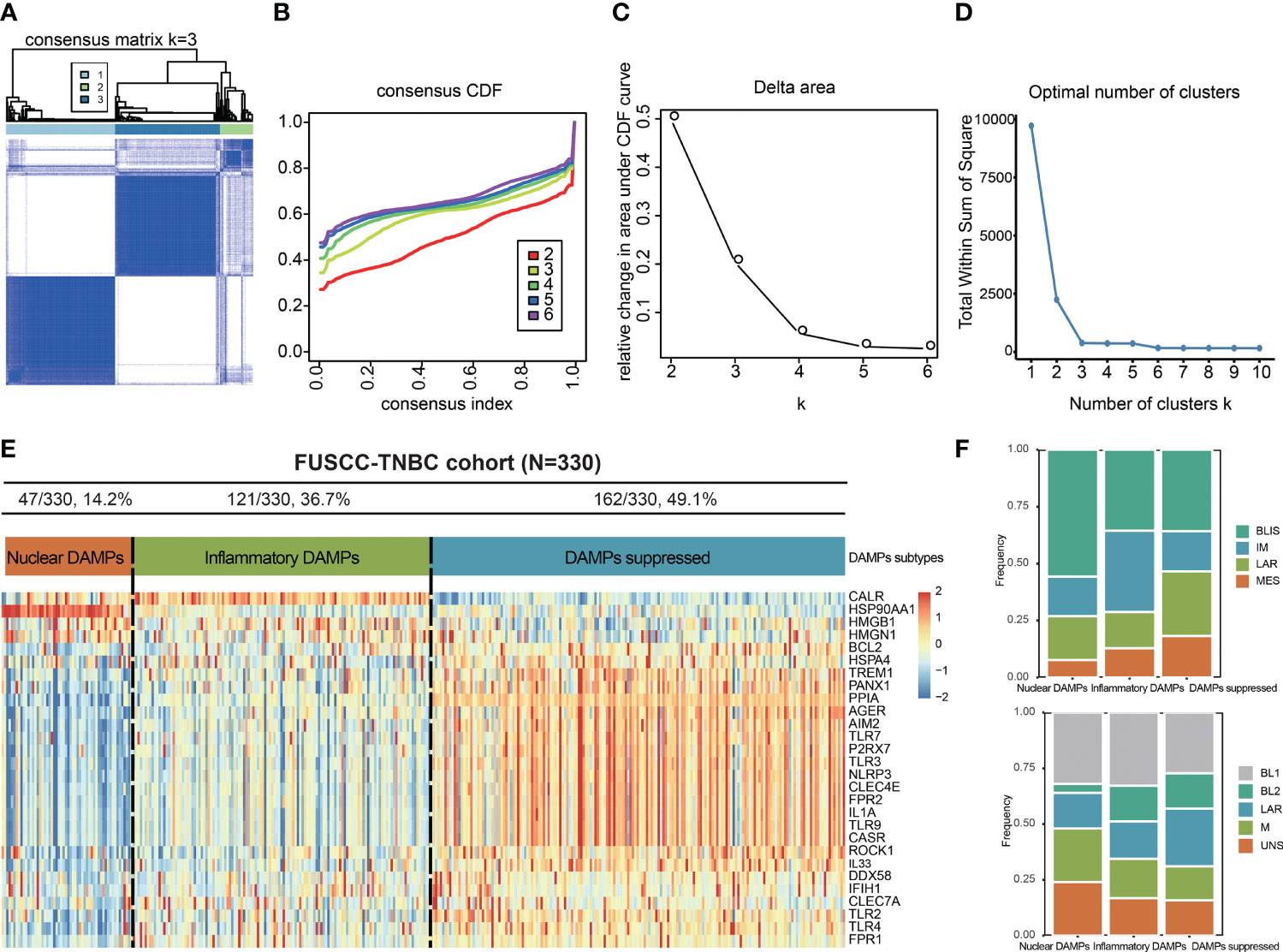
Figure 2 Identification of DAMPs-associated subtypes by K-means analysis. (A-C) K = 3 was identified as the optimal value for consensus clustering. (D) K = 3 was identified as the optimal value for cluster sums of squares. (E) DAMPs-associated subtyping of TNBC samples (n = 330) in the FUSCC cohort. Heatmap shows normalized enrichment scores of the three DAMPs-associated subtypes. (F) Bar plots showing the distribution of FUSCC TNBC subtypes and Lehmann TNBC subtypes among the DAMPs-associated subtypes.
Differentially Expressed Gene Analysis and Functional Analyses
We next identified DEGs among the three subtypes and performed functional analysis to explore their potential signaling mechanisms. A total of 1,406 DEGs were detected, of which 166 were in the nuclear DAMPs subtype, 893 were in the inflammatory DAMPs subtype and 347 were in the DAMPs-suppressed subtype. For the nuclear DAMPs subtype, KEGG enrichment analysis revealed that the DEGs were mainly enriched in heat shock protein (HSP)-related signaling pathways, including protein folding, the HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHRs), the presence of ligands and neutrophil degranulation (Figure 3A). Likewise, GO enrichment analysis also showed that the DEGs were enriched in HSP-related signaling pathways (Figure 3D), indicating that HSPs play an important role in the presentation of tumor antigens. Consistently, GSEA showed that the nuclear DAMPs subtype proliferates vigorously. (Figure 3G). For the inflammatory DAMPs subtype, KEGG enrichment analysis revealed that the DEGs were significantly enriched in immune-related signaling pathways, including the adaptive immune system, cytokine signaling in the immune system, neutrophil degranulation, the immune response-regulating signaling pathway, signaling by the B cell receptor (BCR), and the T cell receptor (TCR) signaling pathway (Figure 3B). Similarly, GO enrichment analysis also identified that the DEGs were enriched in immune-related signaling pathways (Figure 3E). GSEA revealed that the interferon gamma (INF-γ) response, inflammatory response, and interferon alpha (INF-ɑ) response differentiation were highly expressed in the inflammatory DAMPs subtype (Figure 3H). For the DAMPs-suppressed subtype, KEGG enrichment analysis revealed that the DEGs were notably upregulated in cell stress-related pathways, including cellular responses to stress and negative regulation of phosphorylation (Figure 3C). GO analysis also presented a similar result (Figure 3F). GSEA showed a significant upregulation in oxidative phosphorylation, fatty acid metabolism and adipogenesis (Figure 3I).
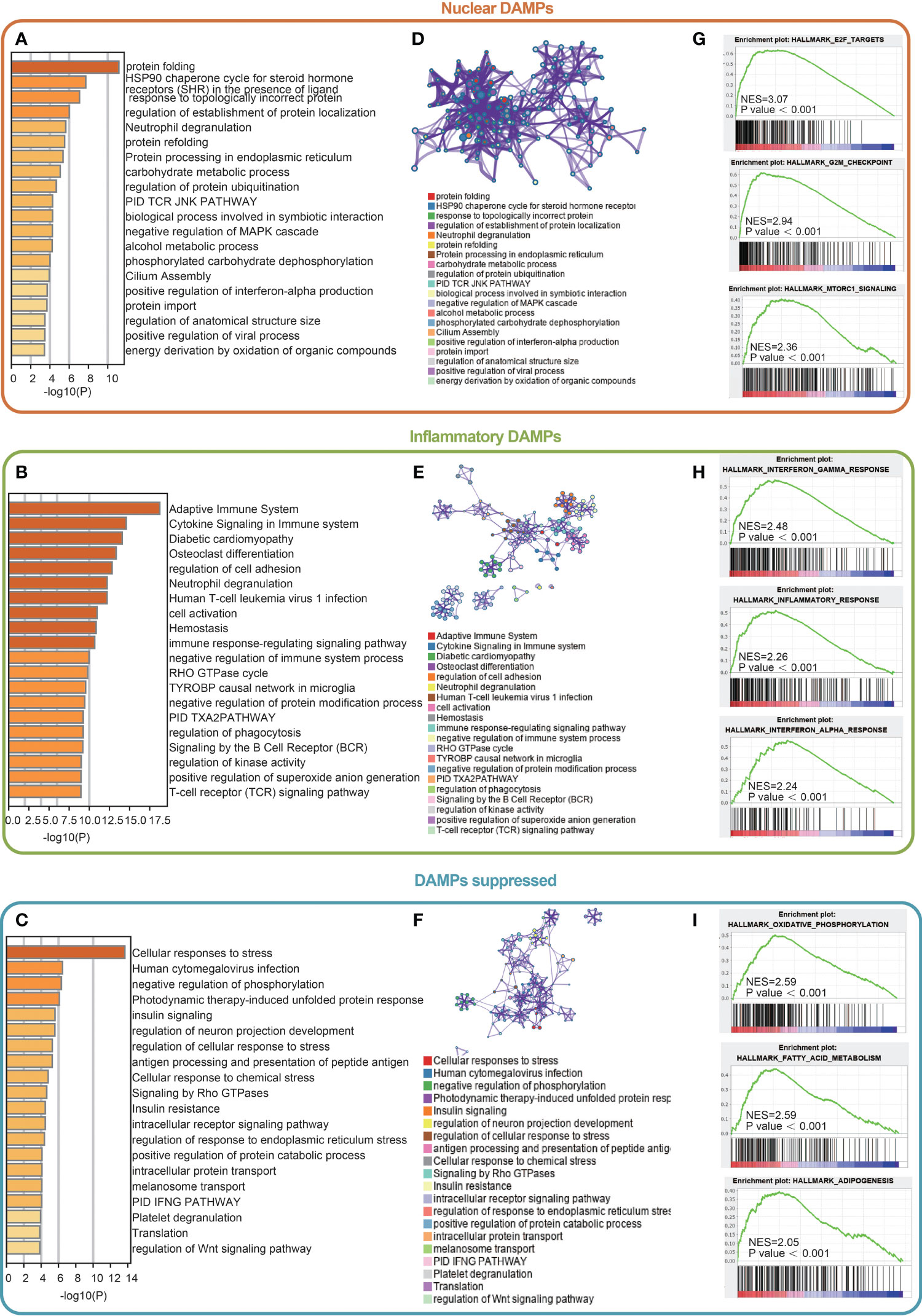
Figure 3 Differentially expressed gene (DEG) analysis and functional analyses. (A-C) Bar diagram showing the signaling pathways enriched by Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis. (D-F) Circle plot and network visualizing the biological processes enriched by gene ontology (GO) analysis. (G-I) Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) results showing the activated signaling pathways in the DAMPs-associated subtypes.
Comparison of Genomic Alterations of DAMPs-Associated Subtypes in the FUSCC-TNBC Cohort
We used oncoplot to identify genomic alterations among the three DAMPs-associated subtypes in the FUSCC-TNBC cohort, and the results showed that PI3K/AKT pathway mutations were least frequently observed in nuclear DAMPs subtypes and most commonly observed in DAMPs-suppressed subtypes (P=0.0037; Figures 4A, B), which may be related to the fact that DAMPs-suppressed subtypes contain more luminal/androgen receptor (LAR) subtypes. Interestingly, split ends (SPEN) mutations were only observed in the inflammatory DAMPs subtype. The TMB of the nuclear DAMPs subtype was higher than that of the remaining two subtypes (Figure 4C). Although the frequency of CNV in the nuclear DAMPs subtype was also higher than that in the other two subtypes, it failed to achieve statistical significance (Figures 4D–F).
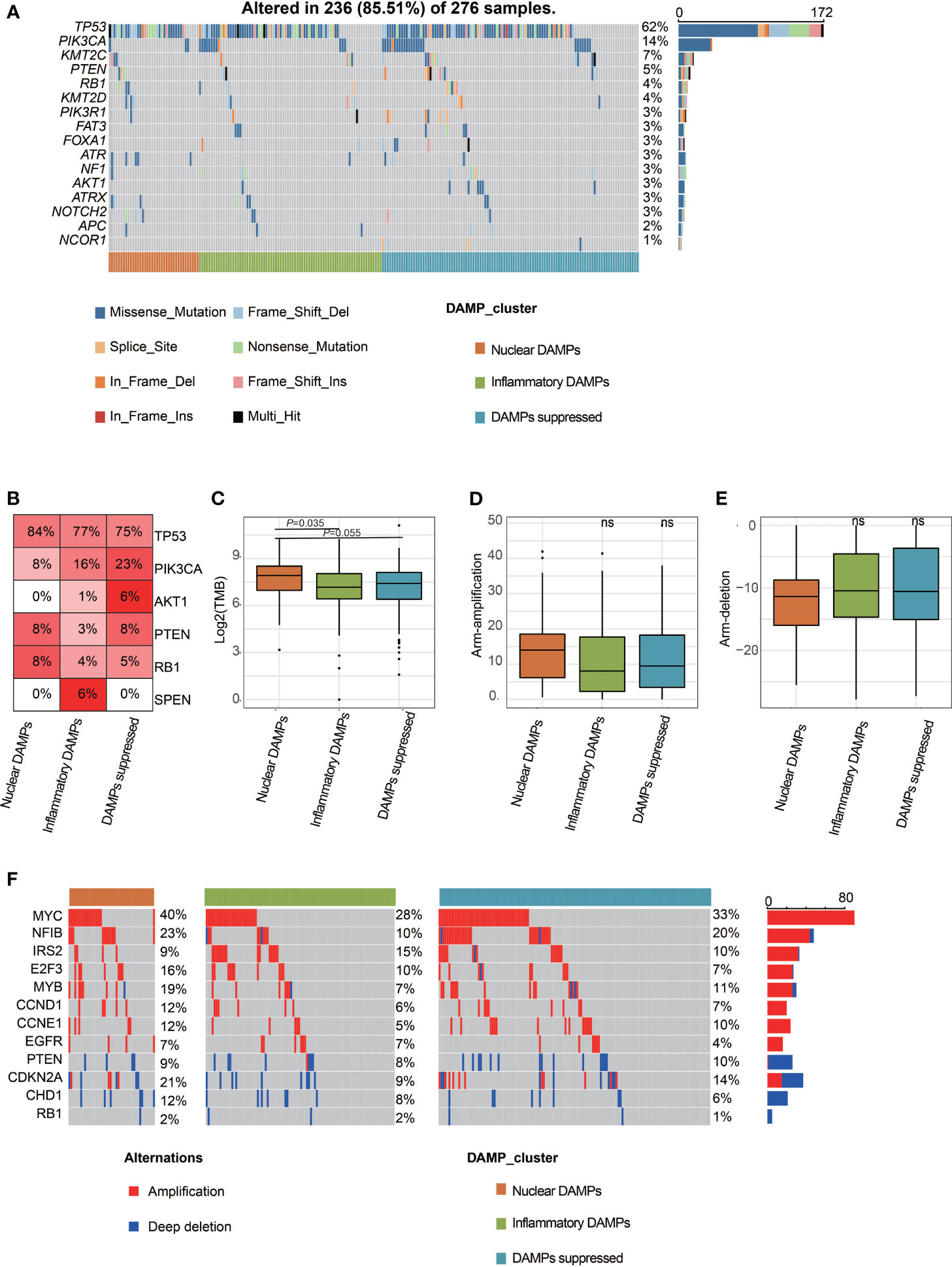
Figure 4 Comparison of genomic alterations of DAMPs-associated subtypes in the FUSCC-TNBC cohort. (A) Differential somatic mutation analysis among the three subgroups. (B) Somatic mutation percentage of mostly mutated genes. (C) Tumor mutant burden difference among the three subtypes in the FUSCC cohort. (D) Arm-level copy number amplification in DAMPs-associated subtypes. (E) Arm-level copy number deletion in DAMPs-associated subtypes. (F) Distinct CNA profile among the three subgroups. ns, not significant.
Patients in the Three Molecular Subtypes Exhibited Different Immune Statuses
Immune analyses were conducted to explore the immune differences between the three subtypes. The CIBERSORT algorithm revealed that CD8+ T cells in the inflammatory DAMPs subtype increased significantly, while M2-like macrophages increased significantly in the DAMPs-suppressed subtype (Figure 5A). Kaplan–Meier survival analysis revealed that patients in the inflammatory DAMPs subtype had the best disease-free survival (DFS) and distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS), while patients in the DAMPs-suppressed subtype tended to have the worst outcome. (DFS: P=0.047, DMFS: P=0.057; Figure 5B). Furthermore, the ESTIMATE algorithm revealed that patients in the inflammatory DAMPs subtype had significantly higher stromal scores, immune scores and ESTIMATE scores than the others, with no significant difference found in sTILs (Figures 5C–F). Interestingly, however, the prognosis of the nuclear DAMPs subtype is better than that of the DAMPs-suppressed subtype, despite having the lowest immune score. In addition, the expression of CD8A (P=0.0035) and PD-1 (P=0.0022) in the inflammatory DAMPs subtype was significantly higher than that in the other two subtypes, while no statistical significance was detected regarding the expression of PD-L1 (P= 0.0622) and CTLA4 (P=0.0685; Figure 5G), which suggested that PD-L1 and CTLA4 may not be the best markers of PD-1 efficacy in TNBC.
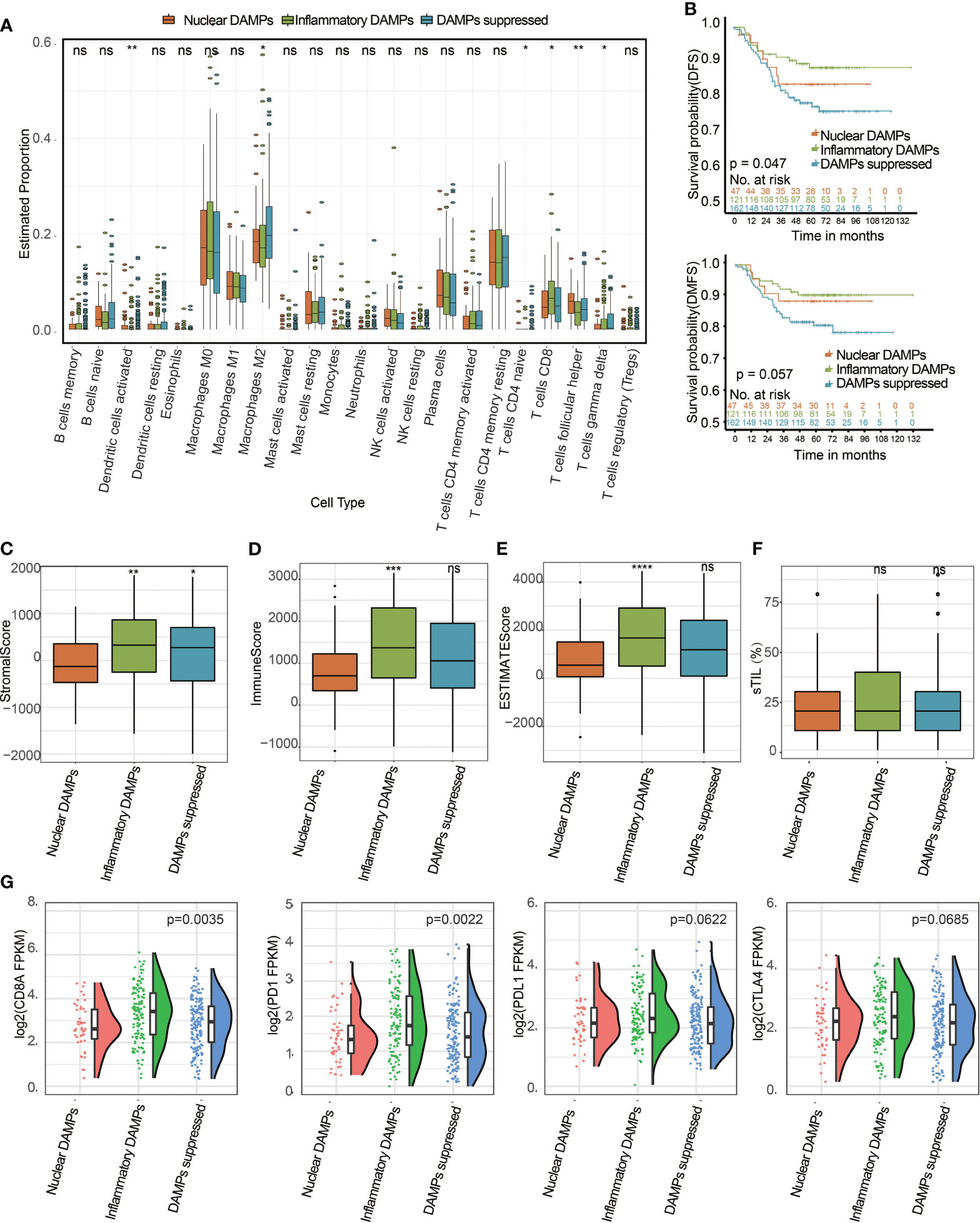
Figure 5 Identification of DAMPs-associated subtypes among the FUSCC-TNBC cohort and comparison of their differences in tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte immune biomarker expression levels. (A) The differential estimated proportion of 22 CIBERSORT immune cell types in DAMPs-associated subtypes. The central line represents the median value. The bottom and top of the boxes are the 25th and 75th percentiles (interquartile range). The whiskers encompass 1.5 times the interquartile range. (B) Kaplan-Meier curves of disease-free survival (DFS) and distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS) among the three subtypes in the FUSCC cohort. (C) Stromal score in DAMPs-associated subtypes. (D) Immune score in DAMPs-associated subtypes. (E) ESTIMATE score difference among the three subtypes in the FUSCC cohort. (F) The sTIL difference among DAMPs-associated subtypes. (G) Expression differences in CD8A, PD-1, PD-L1 and CTLA4 among the three subtypes. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; ns, not significant.
Successful Validation of the Immunophenotypes in the TCGA Cohort
To further validate whether the immune differences we found among the different subtypes of the FUSCC cohort could be generalized, we selected TNBC patients from the TCGA public database and divided them into 3 DAMPs-associated subtypes. According to the CIBERSORT algorithm as above, we found that CD8+ T cells in the inflammatory DAMPs subtype increased significantly and M2-like macrophages in the DAMPs-suppressed subtype increased significantly, which is similar to the results of the FUSCC cohort (Figure 6A). Survival analysis also revealed that patients in the inflammatory DAMPs subtype enjoyed the best OS and DFS, while patients in the DAMPs-suppressed subtype had the worst (DFS: P=0.010, OS: P=0.09; Figure 6B). Additionally, patients in the inflammatory DAMPs subtype had higher immune scores than others (Figure 6D), while no significant difference was found in stromal scores and ESTIMATE scores (Figures 6C, E). In addition, the expression of CD8A (P=0.0312) and PD-1 (P=0.0023; Figure 6F) in the inflammatory DAMPs subtype from the TCGA cohort was notably higher than that in the other two subtypes. The expression of PD-L1 and CTLA4 was similar to the trend in the FUSCC cohort, which again indicated that PD-L1 and CTLA4 may not be the best markers of PD-1 efficacy in TNBC.
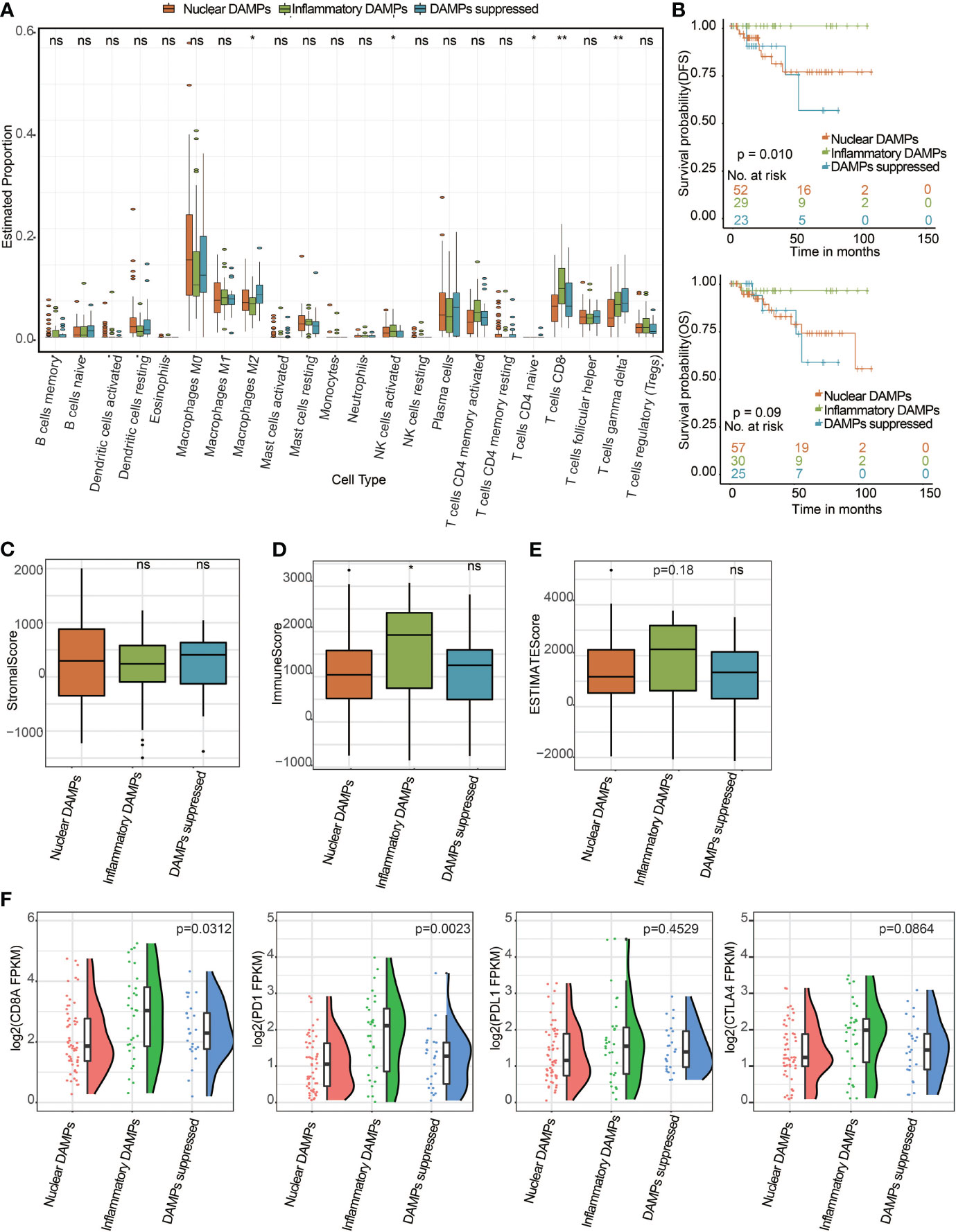
Figure 6 Successful validation of DAMPs-associated subtypes in the TCGA cohort. (A) The differential estimated proportion of 22 CIBERSORT immune cell types in DAMPs-associated subtypes. The central line represents the median value. The bottom and top of the boxes are the 25th and 75th percentiles (interquartile range). The whiskers encompass 1.5 times the interquartile range. (B) Kaplan-Meier curves of overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) among the three subtypes in the TCGA-TNBC cohort. Arm-level copy number amplification in DAMPs-associated subtypes. (C) Stromal score in DAMPs-associated subtypes. (D) Immune score in DAMPs-associated subtypes. (E) ESTIMATE score difference among the three subtypes in the TCGA cohort. (F) Expression differences in CD8A, PD-1, PD-L1 and CTLA4 among the three subtypes. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ns, not significant.
DAMPs-Associated Subtypes Can Predict Immunotherapy Outcome
We next explored the predictive ability of immunotherapy outcome across different DAMPs-associated subtypes. First, the expression of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) and immunomodulatory molecules for DAMPs-associated subtypes is shown via the heatmap (Figure 7A), which revealed that MHC molecules and immunostimulatory and immunoinhibitory molecules are differentially expressed in different subtypes, with the highest expression in the inflammatory DAMPs subtype, both in FUSCC and in TCGA. In addition, the IPS algorithm was performed to evaluate the IPS and the response rate of the three subtypes from FUSCC. The results revealed that the inflammatory DAMPs subtype had the highest response rate (57%; Figures 7B, C). Similarly, we used TNBC patients from TCGA as the validation cohort to test the stability of the above findings, and the results showed that the inflammatory DAMPs subtype also had the highest response rate (55%; Figures 7D, E). These results suggested that the constructed DAMPs-associated clusters had potential for the prediction of PD-1 treatment efficacy in TNBC.

Figure 7 DAMPs-associated clusters can predict immunotherapy outcome. (A) Expression of MHC and immunomodulatory molecules for DAMPs-associated subtypes. Expression values are represented by z scores calculated across all tumors and color coded according to the legend. (B) Waterfall plot illustrating the Immunophenoscores (IPS) according to the DAMPs-associated subtypes in the FUSCC cohort. (C) Proportion of patients: Responder and Nonresponder: 40%/60% in the nuclear DAMPs subtype, 57%/43% in the inflammatory DAMPs subtype and 44%/56% in the DAMPs-suppressed subtype. (D) Waterfall plot illustrating the IPS according to DAMPs-associated subtypes in the TCGA-TNBC cohort. (E) Proportion of patients: Responder and Non−responder: 42%/58% in the nuclear DAMPs subtype, 55%/45% in the inflammatory DAMPs subtype and 28%/72% in the DAMPs-suppressed subtype.
Discussion
TNBC is a highly invasive subtype of breast cancer and is an extremely difficult challenge for treatment due to its relatively low response to conventional therapeutics. Despite the booming development of immunotherapy and promising results of ICIs to treat TNBC, it still leads to high mortality in women worldwide (33). Therefore, the current major challenges are how to improve the response of TNBC patients to ICIs treatment and recognize ICIs nonresponders and responders before treatment. Since the emission of ICD-associated DAMPs and their interactions with innate immune receptors play an important role in the activation of anticancer immunity (34), DAMPs and sensing receptors are potential predictors of the response to ICIs treatments in TNBC. In the present study, we identified three molecular subtypes (nuclear/inflammatory/suppressed) based on the gene expression of DAMPs and sensing receptors, which exhibited significantly different DAMPs landscapes. Functional analyses of DEGs revealed that upregulation of immune (INF-γ) and HSP (HSP90) relative genes was implicated with a better prognosis. Further immune analyses indicated that patients with a better prognosis were in a relatively high immune status (CD8Ahigh, PD-1high) and possessed a higher immune score and ESTIMATE score. Moreover, we established a novel prognostic risk model based on DAMPs and sensing receptors, which predicted the immunotherapy outcome of TNBC patients in FUSCC and TCGA. Our results may meet the need of precision immunotherapy designing for TNBC.
It is becoming increasingly clear that DAMPs show robust adjuvanticity during ICD procedures (35), thus enhancing the antitumor immune effect of ICIs therapy (36). Therefore, we propose here to identify ICD-activating or ICD-suppressive DAMPs subtypes or hallmarks to explore the potential role of a combined DAMPs and immune status classifier for TNBC. In our study, 330 TNBC patients were divided into three DAMPs subtypes. Among them, nuclear-associated HMGB1 and HMGN1 were highly expressed in the nuclear DAMPs subtype, while CALR was highly expressed in the inflammatory DAMPs subtype. HMGB1 and HMGN1 are important nuclear DAMPs, and their translocation to the cytoplasm can activate proinflammatory signaling by binding to PRRs, resulting in TIL influx in breast cancer (37). As an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) marker, when exposed on the tumor cell surface during ICD, CALR promotes the uptake of tumor-specific antigen (TSA), and its mutation compromises immunosurveillance (38). In animal models, the decreased expression of CALR and increased expression of PD-L1 on TNBC cells are associated with fewer CD8+ cytotoxic T cells and more regulatory T cells (39).
Recently, another study of FUSCC TNBC subtypes showed that the basal-like immune-suppressed (BLIS) subtype exhibits high genomic instability, and PI3K signaling pathway mutations are observed in the LAR subtype, while immune cell signaling and TILs are elevated in the IM subtype (19). In our classification, the IM subtype is the major inflammatory DAMPs subtype, while the BLIS subtype has the highest frequency of nuclear DAMPs, and the DAMPs-suppressed subtype contains more LAR subtypes. Interestingly, mutations of SPEN, an estrogen receptor (ERα) corepressor, were found in the inflammatory DAMPs subtype. A previous study showed that high SPEN expression is associated with early metastasis in patients with ERα-negative breast cancer (40), while its relationship with DAMPs is still unclear. In addition, a high level of TMB is a characteristic of nuclear DAMPs, which are potential biomarkers of genomic instability and ICIs response (41). Similarly, we found that PI3K/AKT pathway mutations were mostly observed in the DAMPs-suppressed subtype, and it has been reported that dysfunction of the PI3K/AKT pathway is associated with suppressed DAMPs release (42).
The tumor microenvironment (TME), TILs and TAMs play a crucial role in tumor progression, ICIs response and patient outcomes in TNBC (43). In our study, the CIBERSORT and ESTIMATE algorithms revealed that TNBC patients in the three molecular subtypes exhibited different immune statuses. The CIBERSORT algorithm indicated that the inflammatory DAMPs subtype had the largest proportion of CD8+ T cells compared with the other two subtypes and was associated with the best predicted outcome. However, we found that M2-like macrophages in the DAMPs-suppressed subtype increased significantly. M2-like macrophages have been recently reported to lead to resistance to ICIs therapy (44) and are associated with unfavorable prognosis in TNBC patients (45). The ESTIMATE algorithm showed that patients with this subtype had significantly higher stromal scores, immune scores and ESTIMATE scores than the remaining two subtypes. Moreover, the significantly higher expression of CD8A and PD-1 in the inflammatory DAMPs subtype may be related to its better DFS and DMFS. These observations are in line with previous reports that TNBC patients with elevated CD8A (46) and PD-1 (47) expression can potentially benefit from ICIs. Additionally, these results were successfully validated with the TCGA public database.
Furthermore, functional analyses were conducted to explore the underlying biological mechanisms. Based on the identified DEGs, GO analysis and KEGG analysis synergistically suggested that DEGs in the inflammatory DAMPs subtype were significantly enriched in the adaptive immune system and cytokine signaling in the immune system. GSEA further elucidated that INF-γ response expression in the inflammatory DAMPs subtype was higher than that in the other two subtypes. INF-γ is exclusively involved in both innate and adaptive immune responses against tumor cells (48). For the nuclear DAMPs subtype, KEGG and GO enrichment analyses both revealed that the DEGs were mainly enriched in HSP-related signaling pathways, such as the HSP90 chaperone cycle. Several studies have demonstrated that the cell surface exposure of HSP90 followed by chemotherapy is correlated with dendritic cell (DC) maturation, resulting in the enhancement of the anticancer immune response (49, 50). For the DAMPs-suppressed subtype, KEGG and GO enrichment analyses indicated that the DEGs were largely upregulated in cell stress-related pathways, and GSEA further showed a significant upregulation in adipogenesis. Since TNBC patients with high adipogenesis have low CD8+ T cell and high M2 macrophage infiltration (51), this finding explains why the DAMPs-suppressed subtype has a worse outcome.
As mentioned above, although high TIL, PD-1 or PD-L1 expression indicates that patients are more likely to respond to immunotherapy, these biomarkers fit only a minority of the responders. Therefore, the development of prognostic models that enable the stratification of patients into responders and nonresponders to immunotherapy is urgently needed. In our work, the expression of MHC molecules (class I, class II, and nonclassical), immunostimulators and immunoinhibitors were analyzed, and an immunophenoscores algorithm was performed to predict the immunotherapy outcome. The results revealed that the inflammatory DAMPs subtype had the highest expression of MHC and immunomodulators, along with the highest response rate, which was further validated in the TCGA cohort. MHC molecules, especially human leukocyte antigen class I (HLA-I) alleles, play a critical role in anticancer immunity by recognizing tumor-specific antigens, and their heterozygosity influences patient survival after ICIs treatments (52). Several immunomodulators are involved in immune destruction and tumor escape. Evidence shows that higher expression of immunostimulators is associated with a higher vulnerability to ICIs in breast cancer (53). These results suggested that there is a possible relationship between DAMPs-associated hallmarks and MHC molecules and immunomodulators, which shows good potential for predicting ICIs treatment efficacy.
Consistent with our results, as mediators of tumor immunogenicity, ICD-associated DAMPs and the sensing receptor landscape were correlated with the TIME. This landscape deserves serious attention in determining the immunotherapy approach for TNBC patients. It is also worth noting that ICD-associated DAMPs and sensing receptors have been mentioned more frequently in recent studies regarding the TIME, which contributes to a better understanding of TNBC subtype classification (54). However, limitations and drawbacks exist in our researches. Since ATP is not a gene like CALR or HMGB1, we cannot analyze ATP directly through the transcriptome. We also included ATP receptor molecules in the DAMPs-related gene list. However, these molecules had no significant effect on clustering of DAMPs-associated subtypes. Further studies are warranted to validate the clinical significance of DAMPs-associated molecules and the mechanisms involved in TNBC immunomodulation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, in the present study, three molecular subtypes were identified based on K-means analysis in TNBC. Immune analysis and functional analyses revealed that the expression of ICD-associated DAMPs and sensing receptors may determine tumor immunogenicity, thereby resulting in good prognosis. Our work could shed a novel light on the development of new immunomodulators that target ICD-associated DAMPs and sensing receptors and may facilitate the development of precision immunotherapy for TNBC.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics Statement
Ethical review and approval were not required for the study on human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author Contributions
MX was responsible for data analysis and writing of the draft of the manuscript. J-HL, Y-ZZ and JJ researched the data. Y-ZS and J-YS evaluated the images and contributed to the discussion. S-YL reviewed/edited the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
The study was supported by the construction fund of medical key disciplines of Hangzhou (OO20200385), Zhejiang Lin Shengyou famous traditional Chinese medicine expert inheritance studio project (GZS202002), and the science and technology planning projects of Zhejiang Province (2018C03025).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin (2021) 71(3):209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
2. Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI, Hanna WM, Kahn HK, Sawka CA, et al. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Clinical Features and Patterns of Recurrence. Clin Cancer Res (2007) 13(15 Pt 1):4429–34. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432
3. Schneider BP, Winer EP, Foulkes WD, Garber J, Perou CM, Richardson A, et al. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Risk Factors to Potential Targets. Clin Cancer Res (2008) 14(24):8010–8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432
4. Azim HA, Ghosn M, Oualla K, Kassem L. Personalized Treatment in Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: The Outlook in 2020. Breast J (2020) 26(1):69–80. doi: 10.1111/tbj.13713
5. Heimes AS, Schmidt M. Atezolizumab for the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs (2019) 28(1):1–5. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2019.1552255
6. Keenan TE, Tolaney SM. Role of Immunotherapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw (2020) 18(4):479–89. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2020.7554
7. Pilones KA, Hensler M, Daviaud C, Kraynak J, Fucikova J, Galluzzi L, et al. Converging Focal Radiation and Immunotherapy in a Preclinical Model of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Contribution of VISTA Blockade. Oncoimmunology (2020) 9(1):1830524. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2020.1830524
8. Voorwerk L, Slagter M, Horlings HM, Sikorska K, van de Vijver KK, de Maaker M, et al. Immune Induction Strategies in Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer to Enhance the Sensitivity to PD-1 Blockade: The TONIC Trial. Nat Med (2019) 25(6):920–8. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0432-4
9. Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Warren S, Adjemian S, Agostinis P, Martinez AB, et al. Consensus Guidelines for the Definition, Detection and Interpretation of Immunogenic Cell Death. J Immunother Cancer (2020) 8(1):e000337. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2019-000337
10. Qiu X, Qu Y, Guo B, Zheng H, Meng F, Zhong Z. Micellar Paclitaxel Boosts ICD and Chemo-Immunotherapy of Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J Control Release (2021) 341:498–510. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.12.002
11. Krombach J, Hennel R, Brix N, Orth M, Schoetz U, Ernst A, et al. Priming Anti-Tumor Immunity by Radiotherapy: Dying Tumor Cell-Derived Damps Trigger Endothelial Cell Activation and Recruitment of Myeloid Cells. Oncoimmunology (2018) 8(1):e1523097. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2018.1523097
12. Gong T, Liu L, Jiang W, Zhou R. Damps-Sensing Receptors in Sterile Inflammation and Inflammatory Diseases. Nat Rev Immunol (2020) 20(2):95–112. doi: 10.1038/s41577-019-0215-7
13. Shi S, Xu C, Fang X, Zhang Y, Li H, Wen W, et al. Expression Profile of Toll−Like Receptors in Human Breast Cancer. Mol Med Rep (2020) 21(2):786–94. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10853
14. Roychowdhury A, Jondhale M, Saldanha E, Ghosh D, Kumar Panda C, Chandrani P, et al. Landscape of Toll-Like Receptors Expression in Tumor Microenvironment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC): Distinct Roles of TLR4 and TLR8. Gene (2021) 792:145728. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2021.145728
15. Gruosso T, Gigoux M, Manem VSK, Bertos N, Zuo D, Perlitch I, et al. Spatially Distinct Tumor Immune Microenvironments Stratify Triple-Negative Breast Cancers. J Clin Invest (2019) 129(4):1785–800. doi: 10.1172/JCI96313
16. Singh S, Zhang XHF, Rosen JM. TIME is a Great Healer-Targeting Myeloid Cells in the Tumor Immune Microenvironment to Improve Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Outcomes. Cells (2020) 10(1):11. doi: 10.3390/cells10010011
17. Zhang J, Tian Q, Zhang M, Wang H, Wu L, Yang J. Immune-Related Biomarkers in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer (2021) 28(4):792–805. doi: 10.1007/s12282-021-01247-8
18. Zhang J, Wang L, Xu X, Li X, Guan W, Meng T, et al. Transcriptome-Based Network Analysis Unveils Eight Immune-Related Genes as Molecular Signatures in the Immunomodulatory Subtype of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Front Oncol (2020) 10:1787. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01787
19. Jiang YZ, Ma D, Suo C, Shi J, Xue M, Hu X, et al. Genomic and Transcriptomic Landscape of Triple-Negative Breast Cancers: Subtypes and Treatment Strategies. Cancer Cell (2019) 35(3):428–440.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.02.001
20. Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE, Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, et al. The Cbio Cancer Genomics Portal: An Open Platform for Exploring Multidimensional Cancer Genomics Data. Cancer Discovery (2012) 2(5):401–4. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0095
21. Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G, Gross B, Sumer SO, et al. Integrative Analysis of Complex Cancer Genomics and Clinical Profiles Using the Cbioportal. Sci Signal (2013) 6(269):pl1. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2004088
22. Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive Molecular Portraits of Human Breast Tumours. Nature (2012) 490(7418):61–70. doi: 10.1038/nature11412
23. Hernandez C, Huebener P, Schwabe RF. Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns in Cancer: A Double-Edged Sword. Oncogene (2016) 35(46):5931–41. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.104
24. Yu J, Wu X, Lv M, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Li J, et al. A Model for Predicting Prognosis in Patients With Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Based on Joint Representation Learning. Oncol Lett (2020) 20(6):387. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12250
25. Lehmann BD, Jovanović B, Chen X, Estrada MV, Johnson KN, Shyr Y, et al. Refinement of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Molecular Subtypes: Implications for Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Selection. PloS One (2016) 11(6):e0157368. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157368
26. Zhou Y, Zhou B, Pache L, Chang M, Khodabakhshi AH, Tanaseichuk O, et al. Metascape Provides a Biologist-Oriented Resource for the Analysis of Systems-Level Datasets. Nat Commun (2019) 10(1):1523. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09234-6
27. Wu F, Zhao Z, Chai RC, Liu YQ, Li GZ, Jiang HY, et al. Prognostic Power of a Lipid Metabolism Gene Panel for Diffuse Gliomas. J Cell Mol Med (2019) 23(11):7741–8. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14647
28. Mermel CH, Schumacher SE, Hill B, Meyerson ML, Beroukhim R, Getz G. GISTIC2.0 Facilitates Sensitive and Confident Localization of the Targets of Focal Somatic Copy-Number Alteration in Human Cancers. Genome Biol (2011) 12(4):R41. doi: 10.1186/gb-2011-12-4-r41
29. Gu Z, Eils R, Schlesner M. Complex Heatmaps Reveal Patterns and Correlations in Multidimensional Genomic Data. Bioinformatics (2016) 32(18):2847–9. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw313
30. Newman AM, Liu CL, Green MR, Gentles AJ, Feng W, Xu Y, et al. Robust Enumeration of Cell Subsets From Tissue Expression Profiles. Nat Methods (2015) 12(5):453–7. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3337
31. Yoshihara K, Shahmoradgoli M, Martínez E, Vegesna R, Kim H, Torres-Garcia W, et al. Inferring Tumor Purity and Stromal and Immune Cell Admixture From Expression Data. Nat Commun (2013) 4:2612. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3612
32. Charoentong P, Finotello F, Angelova M, Mayer C, Efremova M, Rieder D, et al. Pan-Cancer Immunogenomic Analyses Reveal Genotype-Immunophenotype Relationships and Predictors of Response to Checkpoint Blockade. Cell Rep (2017) 18(1):248–62. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.12.019
33. Thomas R, Al-Khadairi G, Decock J. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Treatment: Promising Future Prospects. Front Oncol (2021) 10:600573:600573. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.600573
34. Krysko DV, Garg AD, Kaczmarek A, Krysko O, Agostinis P, Vandenabeele P. Immunogenic Cell Death and Damps in Cancer Therapy. Nat Rev Cancer (2012) 12(12):860–75. doi: 10.1038/nrc3380
35. Lamberti MJ, Nigro A, Casolaro V, Rumie Vittar NB, Dal Col J. Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns Modulation by Microrna: Relevance on Immunogenic Cell Death and Cancer Treatment Outcome. Cancers (Basel) (2021) 13(11):2566. doi: 10.3390/cancers13112566
36. Hossain DMS, Javaid S, Cai M, Zhang C, Sawant A, Hinton M, et al. Dinaciclib Induces Immunogenic Cell Death and Enhances Anti-PD1-Mediated Tumor Suppression. J Clin Invest (2018) 128(2):644–54. doi: 10.1172/JCI94586
37. Lee HJ, Kim JY, Song IH, Park IA, Yu JH, Ahn JH, et al. High Mobility Group B1 and N1 (HMGB1 and HMGN1) are Associated With Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in HER2-Positive Breast Cancers. Virchows Arch (2015) 467(6):701–9. doi: 10.1007/s00428-015-1861-1
38. Fucikova J, Spisek R, Kroemer G, Galluzzi L. Calreticulin and Cancer. Cell Res (2021) 31(1):5–16. doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-0383-9
39. Sami E, Paul BT, Koziol JA, ElShamy WM. The Immunosuppressive Microenvironment in BRCA1-IRIS-Overexpressing TNBC Tumors is Induced by Bidirectional Interaction With Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Cancer Res (2020) 80(5):1102–17. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-2374
40. Légaré S, Chabot C, Basik M. SPEN, a New Player in Primary Cilia Formation and Cell Migration in Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res (2017) 19(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s13058-017-0897-3
41. Wang C, Liang H, Lin C, Li F, Xie G, Qiao S, et al. Molecular Subtyping and Prognostic Assessment Based on Tumor Mutation Burden in Patients With Lung Adenocarcinomas. Int J Mol Sci (2019) 20(17):4251. doi: 10.3390/ijms20174251
42. Black GE, Sokol KK, Moe DM, Simmons JD, Muscat D, Pastukh V, et al. Impact of a Novel Phosphoinositol-3 Kinase Inhibitor in Preventing Mitochondrial DNA Damage and Damage-Associated Molecular Pattern Accumulation: Results From the Biochronicity Project. J Trauma Acute Care Surg (2017) 83(4):683–9. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000001593
43. Kuroda H, Jamiyan T, Yamaguchi R, Kakumoto A, Abe A, Harada O, et al. Tumor Microenvironment in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: The Correlation of Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes. Clin Transl Oncol (2021) 23(12):2513–25. doi: 10.1007/s12094-021-02652-3
44. Chen X, Gao A, Zhang F, Yang Z, Wang S, Fang Y, et al. ILT4 Inhibition Prevents TAM- and Dysfunctional T Cell-Mediated Immunosuppression and Enhances the Efficacy of Anti-PD-L1 Therapy in NSCLC With EGFR Activation. Theranostics (2021) 11(7):3392–416. doi: 10.7150/thno.52435
45. Bao X, Shi R, Zhao T, Wang Y, Anastasov N, Rosemann M, et al. Integrated Analysis of Single-Cell RNA-Seq and Bulk RNA-Seq Unravels Tumor Heterogeneity Plus M2-Like Tumor-Associated Macrophage Infiltration and Aggressiveness in TNBC. Cancer Immunol Immunother (2021) 70(1):189–202. doi: 10.1007/s00262-020-02669-7
46. Katsuta E, Yan L, Opyrchal M, Kalinski P, Takabe K. Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Infiltration and Chemokine Predict Long-Term Patient Survival Independently of Tumor Mutational Burden in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Ther Adv Med Oncol (2021) 13:17588359211006680. doi: 10.1177/17588359211006680
47. Denkert C, von Minckwitz G, Brase JC, Sinn BV, Gade S, Kronenwett R, et al. Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy With or Without Carboplatin in Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Positive and Triple-Negative Primary Breast Cancers. J Clin Oncol (2015) 33(9):983–91. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.58.1967
48. Al-Rashidi HE, Refaat S, Ahmed E, Hussein DT, Eltantawy FM, Hamed S. Involvement of INF-γ Functional Single Nucleotide Polymorphism +874 T/a (Rs2430561) in Breast Cancer Risk. Saudi J Biol Sci (2021) 28(11):6289–96. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.06.083
49. Zunino B, Rubio-Patiño C, Villa E, Meynet O, Proics E, Cornille A, et al. Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy Leads to an Anticancer Immune Response via Exposure of Cell Surface Heat Shock Protein 90. Oncogene (2016) 35(2):261–8. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.82
50. Cirone M, Di Renzo L, Lotti LV, Conte V, Trivedi P, Santarelli R, et al. Primary Effusion Lymphoma Cell Death Induced by Bortezomib and AG 490 Activates Dendritic Cells Through CD91. PloS One (2012) 7(3):e31732. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031732
51. Oshi M, Tokumaru Y, Angarita FA, Lee L, Yan L, Matsuyama R, et al. Adipogenesis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer is Associated With Unfavorable Tumor Immune Microenvironment and With Worse Survival. Sci Rep (2021) 11(1):12541. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-91897-7
52. Chowell D, Morris LGT, Grigg CM, Weber JK, Samstein RM, Makarov V, et al. Patient HLA Class I Genotype Influences Cancer Response to Checkpoint Blockade Immunotherapy. Science (2018) 359(6375):582–7. doi: 10.1126/science.aao4572
53. Bertucci F, Boudin L, Finetti P, Van Berckelaer C, Van Dam P, Dirix L, et al. Immune Landscape of Inflammatory Breast Cancer Suggests Vulnerability to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Oncoimmunology (2021) 10(1):1929724. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2021.1929724
Keywords: triple-negative breast cancer, damage-associated molecular patterns, subtype, immunogenic cell death, immune microenvironment, immunotherapy
Citation: Xu M, Lu J-h, Zhong Y-z, Jiang J, Shen Y-z, Su J-y and Lin S-y (2022) Immunogenic Cell Death-Relevant Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns and Sensing Receptors in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Molecular Subtypes and Implications for Immunotherapy. Front. Oncol. 12:870914. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.870914
Received: 07 February 2022; Accepted: 08 March 2022;
Published: 04 April 2022.
Edited by:
Zhijie Jason Liu, The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, United StatesReviewed by:
Kejing Zhang, Central South University, ChinaGen-Hong Di, Fudan University, China
Yujie Wang, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China
Copyright © 2022 Xu, Lu, Zhong, Jiang, Shen, Su and Lin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sheng-you Lin, bGluc3kwNjI4QDE2My5jb20=
 Ming Xu1,2
Ming Xu1,2 Jing Jiang
Jing Jiang Jing-yang Su
Jing-yang Su Sheng-you Lin
Sheng-you Lin