
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Oncol., 30 August 2021
Sec. Molecular and Cellular Oncology
Volume 11 - 2021 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.750277
This article is a correction to:
TFEB Promotes Prostate Cancer Progression via Regulating ABCA2-Dependent Lysosomal Biogenesis
 Xuejin Zhu1,2†
Xuejin Zhu1,2† Yangjia Zhuo3†
Yangjia Zhuo3† Shulin Wu4,5†
Shulin Wu4,5† Yanfei Chen6
Yanfei Chen6 Jianheng Ye3
Jianheng Ye3 Yulin Deng3
Yulin Deng3 Yuanfa Feng2
Yuanfa Feng2 Ren Liu3
Ren Liu3 Shanghua Cai2
Shanghua Cai2 Zhihao Zou2
Zhihao Zou2 Bin Wang6
Bin Wang6 Chin-Lee Wu4,5
Chin-Lee Wu4,5 Guohua Zeng1*
Guohua Zeng1* Weide Zhong1,2,3*
Weide Zhong1,2,3*A Corrigendum on
TFEB Promotes Prostate Cancer Progression via Regulating ABCA2-Dependent Lysosomal Biogenesis
By Zhu X, Zhuo Y, Wu S, Chen Y, Ye J, Deng Y, Feng Y, Liu R, Cai S, Zou Z, Wang B, Wu C-L, Zeng G and Zhong W (2021). Front. Oncol. 11:632524. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.632524
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 6 as published. Figure 6 was misplaced and needs to be corrected. The corrected Figure 6 appears below.
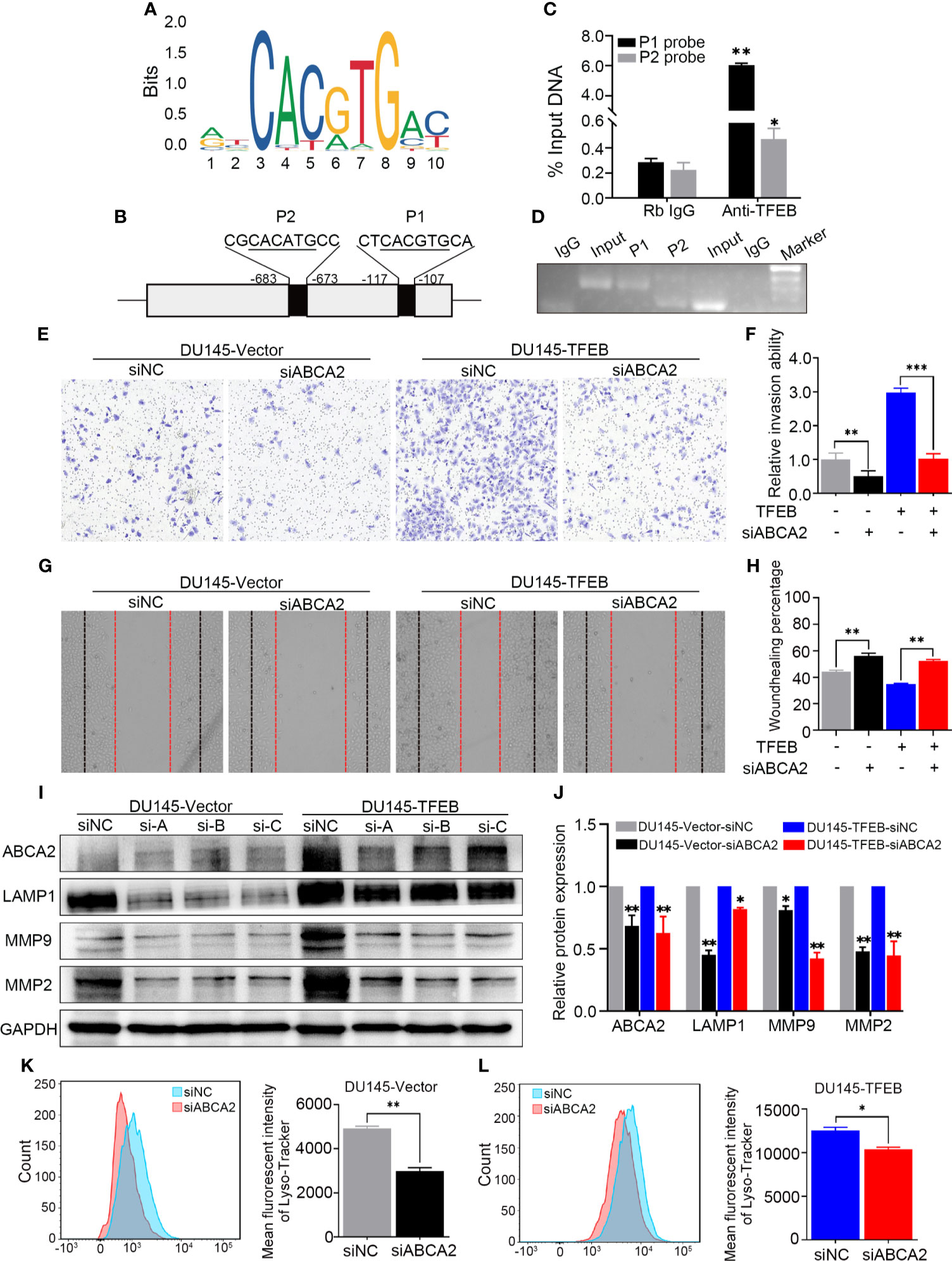
Figure 6 TFEB binding ABCA2 promoter to regulate its expression to involve PCa cell invasion and migration. (A) The binding motif of TFEB were provide from website. (B) The potential binding site of ABCA2 promoter. Mismatch rate is less than 1%. (C) Validation of the DNA fragment pulled down with TFEB chip-level antibody by qRT-PCR. DNA fragment were obtained from CUT&RUN assay and purified by DNA extraction kit. Rb IgG as a negative control. Anti-TFEB as an experimental group. (D) The DNA fragment product from qRT-PCR was validated by nucleic acid electrophoresis. The length of input, P1 and P2 mainly between 60 to 120 bp. (E, F) Transwell assay showed silenced ABCA2 expression inhibited PCa cell invasion. Cancer cells were stained after 24h. (G, H) Woundhealing assay showed silenced ABCA2 expression inhibited PCa cell migration after 48h culture. (I, J) Validation of ABCA2 LAMP1, MMP9, and MMP2 protein expression by western-blot after ABCA2 gene silenced. Quantitative analysis of the western-blot from (I). (K, L) DU145-vector and DU145-TFEB cell line were silenced ABCA2 for 72h and then treated with LysoTracker Red DND-99 (50 nM) for 45 min. Note: Statistical analysis was from three independent experiments and is presented as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared with control group.
In the published article, there was an error in affiliation 1, 2. Instead of “
1Department of Urology, Guangdong Key Laboratory of Clinical Molecular Medicine and Diagnostics, Guangzhou First People’s Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, China
2Department of Urology and Guangdong Key Laboratory of Urology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, China”,
it should be “
1Department of Urology and Guangdong Key Laboratory of Urology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, China
2Department of Urology, Guangdong Key Laboratory of Clinical Molecular Medicine and Diagnostics, Guangzhou First People’s Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, China”.
In the published article, there was an error regarding the affiliations for Weide Zhong. As well as having affiliation(s) 1, 3, they should also have, 2.
The authors apologize for these errors and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: TFEB, ABCA2, prostate cancer, tumor microenvironment, lysosomal biogenesis, biochemical recurrence, metastasis
Citation: Zhu X, Zhuo Y, Wu S, Chen Y, Ye J, Deng Y, Feng Y, Liu R, Cai S, Zou Z, Wang B, Wu C-L, Zeng G and Zhong W (2021) Corrigendum: TFEB Promotes Prostate Cancer Progression via Regulating ABCA2-Dependent Lysosomal Biogenesis. Front. Oncol. 11:750277. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.750277
Received: 30 July 2021; Accepted: 03 August 2021;
Published: 30 August 2021.
Edited and reviewed by:
Kexin Xu, The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, United StatesCopyright © 2021 Zhu, Zhuo, Wu, Chen, Ye, Deng, Feng, Liu, Cai, Zou, Wang, Wu, Zeng and Zhong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Weide Zhong, emhvbmd3ZDIwMDlAbGl2ZS5jbg==; Guohua Zeng, Z3pneXpnaEB2aXAuc2luYS5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.