- 1Department of Gastric Surgery, Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
- 2Department of Hematology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Quanzhou, China
- 3Department of Oncology, Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
- 4Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Beijing Hospital, Beijing, China
A Corrigendum on
EXOSC5 as a Novel Prognostic Marker Promotes Proliferation of Colorectal Cancer via Activating the ERK and AKT Pathways
by Pan, H., Pan, J., Song, S., Ji, L., Lv, H., and Yang, Z. (2019). Front. Oncol. 9:643. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00643
In the original article, there were mistakes in Figure 2 as published. In Figure 2D and F, an unintentional error occurred upon using Adobe Illustrator to organize the images, and incorrect images of the colony formation assay for sh-1 and sh-2 in HT29 and SW480 cells were imported by mistake. In Figure 2G, a draft image of tumorigenesis that should have been discarded was imported by mistake. The corrected Figure 2 appears below.
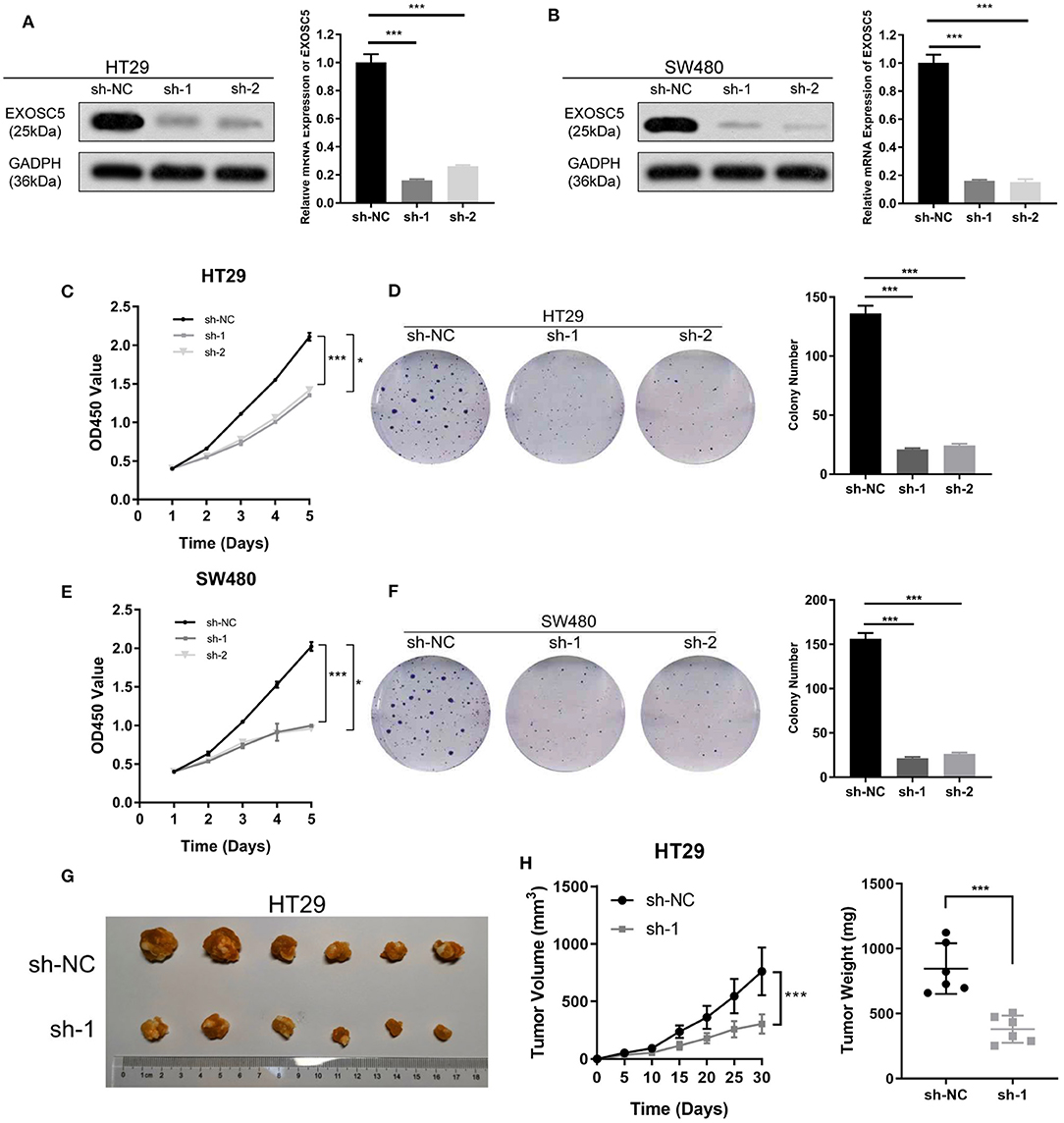
Figure 2. Knockdown of EXOSC5 suppressed the proliferation and tumorigenesis of human CRC cells in vivo and in vitro. (A,B) The efficiency of EXOSC5 knockdown in HT29 and SW480 cells were determined by Western blot, GAPDH was used as a loading control. (C–F) Knockdown of EXOSC5 repressed cell proliferation by CCK-8 assays and colony formation assays. (G) Tumorigenesis assay by subcutaneous injection of HT29/sh-NC and HT29/sh-EXOSC5 cells in nude mice (n = 6/group). (H) Tumor volumes were measured by growth curve every 5 days, and weights were measured on the terminal days. The results are presented as the mean ± SD. (*P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001).
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Keywords: EXOSC5, proliferation, colorectal cancer, Akt signaling pathway, ERK signaling pathway, prognosis
Citation: Pan H, Pan J, Song S, Ji L, Lv H and Yang Z (2021) Corrigendum: EXOSC5 as a Novel Prognostic Marker Promotes Proliferation of Colorectal Cancer via Activating the ERK and AKT Pathways. Front. Oncol. 11:670041. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.670041
Received: 20 February 2021; Accepted: 22 February 2021;
Published: 09 April 2021.
Edited and reviewed by: Marco Demaria, University Medical Center Groningen, Netherlands
Copyright © 2021 Pan, Pan, Song, Ji, Lv and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hongda Pan, cGFuaG9uZ2RhQGZveG1haWwuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Hongda Pan
Hongda Pan Jingxin Pan2†
Jingxin Pan2†