
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
Front. Neurosci., 31 March 2025
Sec. Brain Imaging Methods
Volume 19 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2025.1556639
Background: Resting-state fMRI (rs-fMRI) has revealed a range of neural activity patterns in patients with postherpetic neuralgia (PHN). However, inconsistencies in study design have led to conflicting findings in previous research studies. This meta-analysis used the anisotropic effect size-signed differential mapping (AES-SDM) approach to evaluate rs-fMRI studies on PHN and to provide more robust insights into the brain networks involved in processing PHN pain.
Materials and methods: A systematic search of PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and the Cochrane Database was performed for rs-fMRI studies comparing PHN patients with healthy controls, up until 1 November 2024. The AES-SDM approach was then employed to meta-analyze the abnormal brain activity patterns observed in PHN patients.
Results: A total of eight articles were included in the analysis comprising 148 patients with PHN and 179 healthy controls. The meta-analysis found that patients with PHN exhibited increased activity in the right middle temporal gyrus (MTG.R), right precuneus (PCUN.R), and right superior frontal gyrus, orbital part (ORBsup.R). In contrast, a reduction in functional activity was observed in the left superior frontal gyrus, medial (SFGmed.L), left calcarine fissure/surrounding cortex (CAL.L), right precentral gyrus (PreCG.R), and right inferior temporal gyrus (ITG.R). Sensitivity analysis revealed that all of these regions exhibited high reproducibility, and no significant publication bias was identified.
Conclusion: This meta-analysis reveals altered specific brain activity in PHN patients, providing a foundation for targeted treatments that address both sensory and affective aspects of chronic pain.
Systematic review registration: PROSPERO, registration no. CRD42024614718; https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/CRD42024614718.
Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is a chronic neuropathic pain syndrome described as pain that lasts at least 90 days after the appearance of an acute herpes zoster rash (Johnson and Rice, 2014). The pain associated with PHN is often neuropathic, with patients reporting sensations such as burning, stabbing, or electrical shocks (Hadley et al., 2016). This condition is a significant cause of morbidity, with substantial impacts on quality of life, sleep, and emotional wellbeing (Mallick-Searle et al., 2016). The prevalence of PHN has steadily risen over the years, significantly exacerbating the societal medical burden (Thompson et al., 2021). Despite its high prevalence, the central nervous system mechanisms underlying PHN remain incompletely understood.
With the transition from gate control theory (Melzack and Wall, 1965) to “pain matrix” theory (Melzack, 1990), our understanding of pain has evolved from a simple sensory input to recognizing it as an output from a wide range of neural networks in the brain. Research on PHN also extends from herpes zoster infection, which exposes afflicted neurons to abnormal firing and inflammation, to central changes in the structure and function of the brain. Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), which uses fluctuations in blood oxygenation-level-dependent signals to examine changes in cerebral function, has emerged as an important tool for studying the brain’s role in pain processing (Biswal et al., 2010). According to a systematic review, PHN was found to be associated with brain functional abnormalities in the “pain matrix,” which includes the thalamus, insula, amygdala, parahippocampus, precentral gyrus, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, and other areas such as the precuneus, lentiform, and brain stem (Tang et al., 2021). However, because of the limitations in imaging methods, scanning methods, sampling size, data analysis, and other methods, the results are heterogeneous, making it difficult to draw reliable and complete conclusions. Therefore, meta-analyses are necessary to analyze the previous findings.
Anisotropic effect size-signed differential mapping (AES-SDM) is an effective technique for delineating brain areas by coordinate-based meta-analysis of neuroimaging data (Radua and Mataix-Cols, 2009; Radua et al., 2012; Radua et al., 2014). In comparison to activation likelihood estimation (ALE), the AES-SDM method has higher sensitivity to small-effect regions, better ability to manage anisotropic voxel space, incorporates both positive and negative activation effects, and enhances the statistical management of heterogeneity across studies (Radua et al., 2012). This meta-analysis aimed to combine the findings of fMRI studies that examined the brain activity of patients with PHN using the AES-SDM. We aimed to identify consistent brain activation patterns associated with PHN and explore the possibility of alterations in pain processing circuitry by combining data from various analytical approaches, such as amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (ALFF), fractional amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (fALFF), regional homogeneity (ReHo), and functional connectivity density (FCD), among others. This analysis may help understand the neural mechanisms underlying PHN and inform the development of targeted therapeutic interventions for this complex condition.
From inception to 1 November 2024, a systematic literature search was conducted across PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane Database, in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines (Page et al., 2021), and the results were registered with the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews at the University of York (PROSPERO, registration no. CRD42024614718). The search terms of PubMed were as follows: (“Neuralgia, Postherpetic” OR “postherpetic neuralgia” OR “PHN”) AND (“neuroimaging” OR “magnetic resonance imaging” OR “MRI” OR “amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation” OR “ALFF” OR “fractional amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation” OR “fALFF” OR “regional homogeneity” OR “ReHo” OR “independent component analysis” OR “functional connectivity”). The remaining three databases’ search methodologies were adjusted to fit with the aforementioned methodology. Moreover, review articles and the reference lists of the selected articles were examined for additional acceptable publications.
The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) studies in which patients were selected based on PHN diagnostic criteria; (2) studies that used fMRI as the imaging technique; (3) studies that used whole-brain analysis to compare differences between PHN patients and healthy controls; (4) studies with results reported in standard stereotactic coordinate space (Talairach or the Montreal Neurological Institute, MNI); and (5) original article published in a peer-reviewed journal.
The exclusion criteria were as follows:(1) reviews, protocols, conference articles, letters, animal studies, or case reports; (2) patients who received any intervention or stimulation during or before the neuroimaging scan; and (3) studies that were conducted using seed-based functional connectivity analysis.
Two investigators independently analyzed the identified articles and subsequently examined the entire texts to determine compliance with the inclusion and exclusion criteria. The third author addressed and resolved any disagreements or uncertainties that arose between the two investigators. The following study information was gathered: (1) publication indexes; (2) demographic and clinical characteristics (sample size, sex, and mean age of PHN patients and healthy controls); (3) disease-associated variables (disease duration and VAS score); (4) neuroimaging method (scanning device and analytic approach); and (5) functional brain activity differences between PHN patients and healthy controls (peak coordinates of different regions in Talairach or MNI space, cluster size, and statistical threshold).
A 12-point checklist based on previous meta-analyses of fMRI studies was used to evaluate the quality of the included studies (Wang et al., 2024). The Quality Assessment Checklist included the demographical and clinical characteristics of the subjects, methods for image acquisition and analysis, and quality of results and conclusions. All included studies must meet the quality evaluation threshold, with a total score greater than 6.0.
The coordinate-based meta-analysis study was carried out using the AES-SDM (version 6.23, https://www.sdmproject.com/software). First, the peak coordinates and effect sizes (T-values) for the clusters of difference between PHN and healthy controls were gathered from each collection of data. The variance maps and effect sizes of the brain function differences were then reconstructed using an anisotropic Gaussian kernel with a full width at half maximum of the Gaussian kernel set to 20 mm (Radua et al., 2014). Thresholds (p < 0.005 with peak Z > 1 and a cluster extent >10 voxels) that optimize sensitivity and specificity are shown on the standardized template in MNI coordinates (Radua et al., 2010; Radua et al., 2012). The mean map was eventually produced by a voxel-wise calculation of the random effects mean of the study maps, which was weighted by the sample size, the variance of each study, and between-study heterogeneity. The Egger’s test was used to evaluate potential publication bias, with a threshold of p < 0.05 indicating statistical significance.
A jackknife sensitivity analysis was performed to evaluate the robustness of the findings by iteratively excluding one dataset at a time during the investigation (Radua and Mataix-Cols, 2009). If a brain region consistently shows significance across most or all study combinations, it can be concluded that this finding is highly reproducible.
Meta-regression analysis was also performed to explore potential correlations between mean age, VAS score, and disease duration in PHN patients. Consistent with previous meta-analyses, the potential influence of the aforementioned indicators is assessed through simple linear regression, weighted by the square root of the sample size, and limited to predicting feasible SDM values (i.e., from −1 to 1) within the observed range of the variable (Saarinen et al., 2020). To minimize false associations, the probability cutoff was restricted to p < 0.005. These procedures were only carried out in the regions recognized in the primary impact.
A total of 454 articles were retrieved using our search strategy, with 8 meeting the inclusion criteria for the meta-analysis. The flowchart shows the entire process (Figure 1). The reference lists of selected articles did not contain any relevant studies that met the criteria. The study used the following resting-state analysis methods: ALFF, fALFF, ReHo, and FCD. Three articles (Cao et al., 2017a; Cao et al., 2017b; Dai et al., 2020) employed two different analytical methods; as a result, the meta-analysis included 8 papers containing 11 studies (Xian et al., 2015; Cao et al., 2017a; Cao et al., 2017b; Hong et al., 2018; Gu et al., 2019; Dai et al., 2020; Huang et al., 2020; Jiang et al., 2024). This analysis involved148 PHN patients (78 male subjects and 70 female subjects) and 179 healthy controls (92 male subjects and 87 female subjects). Comprehensive information about the included research is shown in Table 1.
The AES-SDM meta-analysis results comparing PHN patients with healthy controls indicated a total of seven clusters, which are shown in Table 2 and Figure 2. Increased brain activity in PHN was mainly observed in the right middle temporal gyrus (MTG.R), right precuneus (PCUN.R), and right superior frontal gyrus, orbital part (ORBsup.R). In contrast, decreased brain activity in PHN was predominantly found in the left superior frontal gyrus, medial (SFGmed.L), left calcarine fissure/surrounding cortex (CAL.L), right precentral gyrus (PreCG.R), and right inferior temporal gyrus (ITG.R).
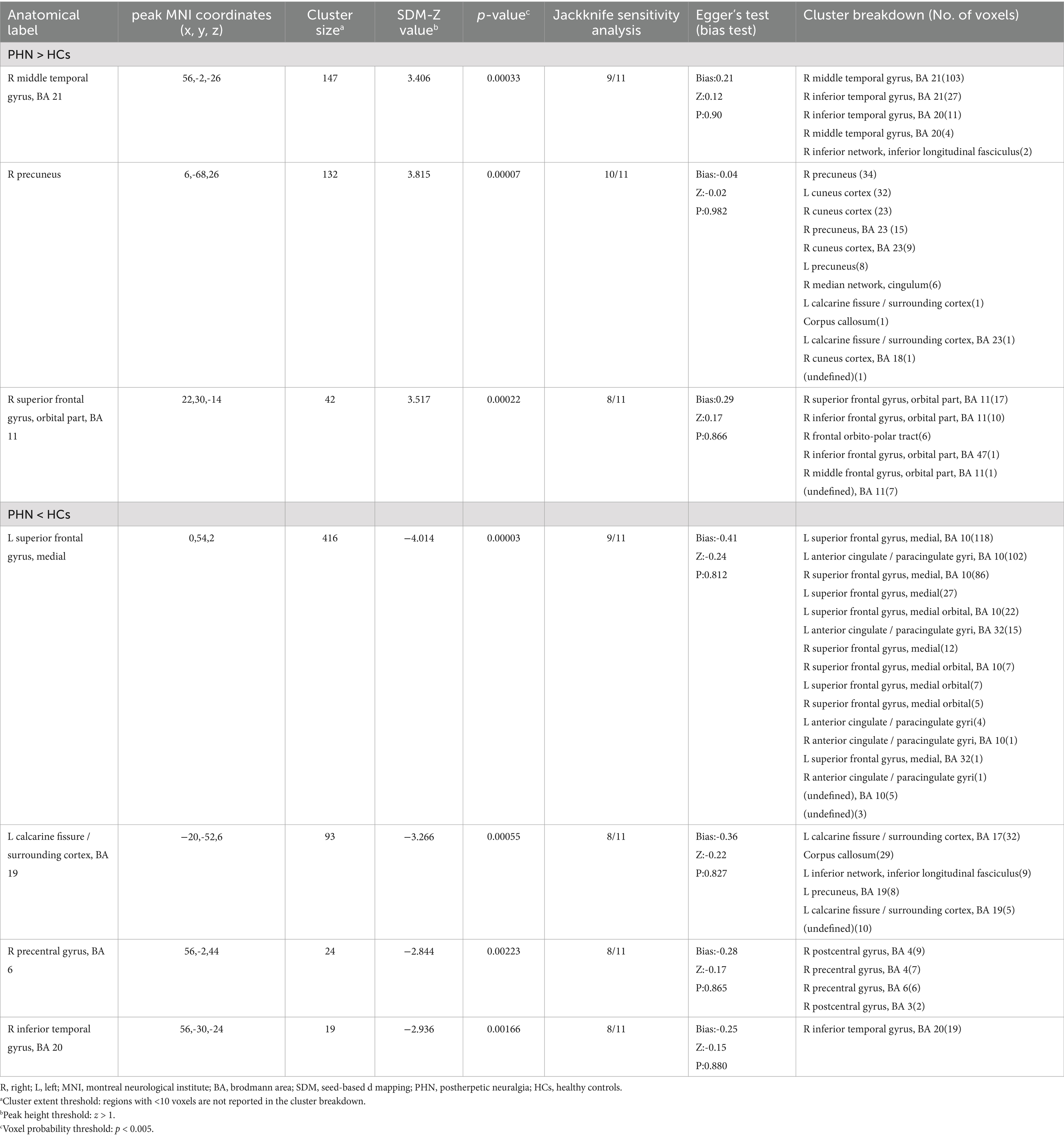
Table 2. Clusters of voxels with abnormal brain activity in PHN patients compared to healthy controls.
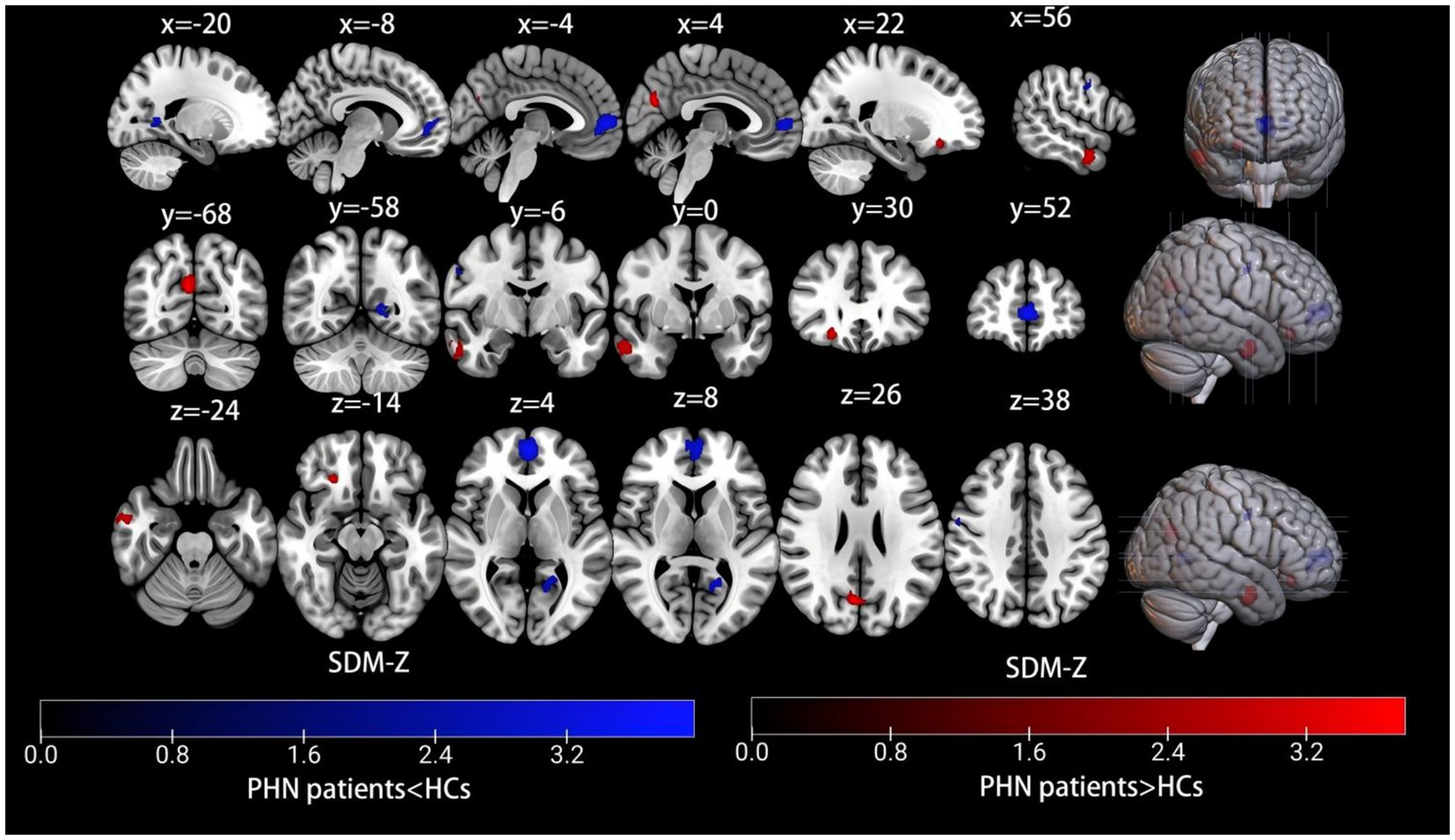
Figure 2. Meta-analysis comparing brain functional alterations between PHN patients and healthy controls. Red and blue clusters represent increased and decreased brain activity, respectively. The color bar indicates the maximum and minimum SDM-Z values. HCs, healthy controls; PHN, postherpetic neuralgia, SDM, seed-based mapping.
The results of Egger’s test for the MTG.R (Bias 0.21, Z 0.12, P 0.90), PCUN.R (Bias −0.04, Z -0.02, P 0.982), ORBsup.R (Bias 0.29, Z 0.17, P 0.866), SFGmed.L (Bias −0.41, Z -0.24, P 0.812), CAL.L (Bias −0.36, Z -0.22, P 0.827), PreCG.R (Bias −0.28, Z -0.17, P 0.865), and ITG.R (Bias −0.25, Z -0.15, P 0.880) confirmed no significant heterogeneity among the studies (Table 2). A whole-brain analysis of the sensitivity of the jackknife revealed high reproducibility in all brain regions. The results for the PCUN.R were replicated in 10 out of 11 iterations, while the MTG.R and SFGmed.L were replicated in 9 out of 11 iterations. The ORBsup.R, CAL.L, SFGmed.L, and ITG.R were replicated in 8 out of 11 iterations (Table 3).
A meta-regression analysis was conducted to investigate the potential relationship between mean age, VAS score, and disease duration in patients with PHN. The findings indicated that the left precuneus (PCUN.L) exhibited a positive correlation with mean age and disease duration. Additionally, the left inferior network and inferior longitudinal fasciculus was positively correlated with the VAS score (Table 4).
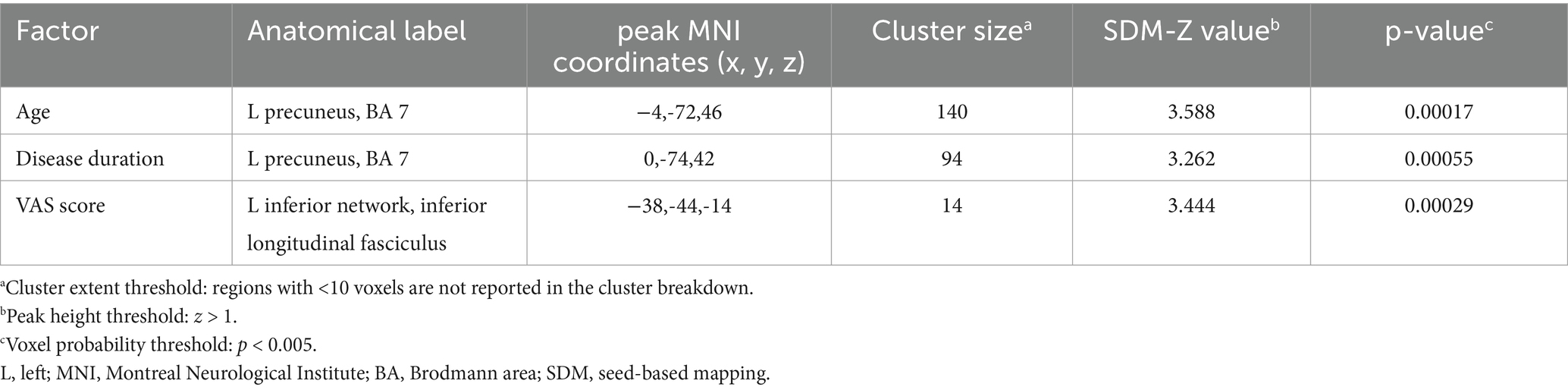
Table 4. Correlation between alterations in brain activity and age, disease duration, and VAS score in PHN revealed by meta-regression analysis.
This was the initial rs-fMRI meta-analysis using AES-SDM to investigate changes in brain activity in PHN patients. The analysis revealed increased brain activity in the MTG.R, PCUN.R, and ORBsup.R, while decreased brain activity was found in the SFGmed.L, CAL.L, PreCG.R, and ITG.R. The sensitivity of the jackknife analysis revealed high reproducibility in all brain regions. Furthermore, meta-regression analysis indicated that the PCUN.L exhibited a positive correlation with mean age and disease duration, whereas the left inferior network and inferior longitudinal fasciculus had a positive correlation with the VAS score.
Pain is a multidimensional experience that includes sensory-discriminative, affective-motivational, and cognitive-evaluative components (Mercer Lindsay et al., 2021). Neuroimaging and neurophysiological studies on humans have shown that noxious stimuli consistently activate a network of brain areas; these brain areas, or a subset or superset of them, have been termed the “pain matrix” and are used as a brain signature for a pattern of activity associated with pain (Legrain et al., 2011). In contrast to acute pain, neuroimaging studies on chronic pain involve subgroup comparisons between chronic pain patients and healthy volunteers. Recent evidence has refuted the “pain matrix” hypothesis by challenging the notion that there is no uniform set of brain regions that can be equated with the presence of pain, particularly for different clinical chronic pain conditions that show unique patterns of brain activity (Apkarian et al., 2011). This meta-analysis reveals distinct brain activity patterns in PHN, differentiating it from other chronic pain disorders such as cervical spondylosis (Zhang and Ding, 2024) and knee osteoarthritis (Cheng et al., 2024).
The regions that showed the most significant decline in brain activity were the SFGmed, CAL, PreCG, and ITG, with more pronounced decrease observed in the SFGmed. This suggests that the abnormal activity patterns in the SFGmed may be a crucial central pathological feature of PHN. Functional deactivation in PHN pain patients is consistent with findings from other chronic pain patients. The review indicates that activation of the SFGmed occurs during the perception of acute pain stimuli, while chronic pain patients typically show functional deactivation in this region (Seminowicz and Moayedi, 2017). The SFGmed is a major node of the default mode network (DMN) that is anatomically connected to the descending pain modulatory system (Menon, 2023). This region is important for processing both the affective and cognitive components of pain sensations (Bushnell et al., 2013). The PCUN is also a part of the DMN and, as found in our meta-analysis, has shown significantly increased functional activity. Additionally, it was positively correlated with both mean age and disease duration. Due to a lack of localized lesions in this deeply seated region and a limited understanding of its architecture, the precuneus’ role in complex cognitive activities has remained relatively unclear (Dadario and Sughrue, 2023). A recent MRS study also found higher levels of GABA+/tCr in the PCUN of PHN patients (Wu et al., 2022a). Alterations in the SFGmed and PCUN within the DMN suggest that this network may exhibit a condition of sustained hyperexcitability in PHN. Previous studies (Wu et al., 2020; Wu et al., 2022b; Wu et al., 2025) have found that the abnormal functional connectivity of the DMN in PHN patients includes decreased internal connectivity, abnormal cross-network connectivity, and impaired dynamic connectivity. These changes may contribute to the persistence of pain, emotional disturbances, and cognitive dysfunction.
Changes in brain function activity were found in both the MTG and ITG, with the MTG showing the most significant activation in brain function activity. Previously, the MTG and ITG were not considered to play a role in pain processing, which includes language and semantic memory processing, visual perception, and multimodal sensory integration (Onitsuka et al., 2004). However, some recent studies have found structural and functional alterations in the temporal cortex of patients with various chronic pain disorders (Niddam et al., 2017; Chehadi et al., 2018; Henssen et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2023). The functions of the MTG and ITG in chronic pain may be related to higher cognitive functions, such as memory and emotion processing (Houde et al., 2020). Chronic pain frequently impacts the mood, behavior, and overall quality of life in PHN patients. The MTG and ITG may serve as potential targets for mood therapy.
The ORBsup is an important part of the reward system (Farr et al., 2016) and has been shown to have increased functional activity in our study. Fundamentally, pain is an unpleasant experience, and alleviating aversive states, including pain, can produce rewarding effects (Navratilova and Porreca, 2014). The activation of the ORBsup could indicate an adaptive change designed to counteract the negative effects of pain. Recent studies (Becker et al., 2017) have found the brain circuit that suppresses pain when a reward is present, and the inhibitory effect of reward on pain is mediated by the orbitofrontal cortex, which has a positive correlation with pain. The PreCG is known as the primary motor area (Banker and Tadi, 2023). It has been shown to have reduced functional activity in PHN. If the pain caused by PHN is severe, the brain may change its motor plan to avoid moving the painful area. This can result in movement inhibition and a reduced range of motion, which can eventually lead to muscle atrophy or joint dysfunction (Butera et al., 2016). The CAL, located in the occipital lobe of the brain, is involved in visuospatial attention, which refers to the ability to focus on visual stimuli and orient attention to specific locations in the visual field (Wandell et al., 2009). Chronic pain patients frequently have a heightened focus on the painful area of the body, which can lead to increased attentional processing of the affected region. This enhanced attentional bias toward the pain site may result in increased pain perception (Cheng et al., 2024).
Some limitations in this study need to be taken into account. First, to fully describe the changes in brain activity in PHN, this meta-analysis combines different methods of analysis, such as ALFF, fALFF, ReHo, and FCD, which may increase the heterogeneity of the study but may also provide complementary results. Eventually, different analytical methods produced similar results, and we proved the robustness of our findings using the jackknife sensitivity analysis. Second, although this meta-analysis included as many PHN rs-fMRI studies with different analysis methods as possible, the number of rs-fMRI studies was still limited, and the total sample size of the studies was small. Third, only articles published in English that used a global brain analysis were included in the study. The majority of the studies were conducted in China, and the studies published in other languages, as well as unpublished information, were excluded, as these factors may potentially introduce bias into the results. Finally, this meta-analysis only included cross-sectional studies; future longitudinal studies can help us understand the central neural system mechanisms underlying the transition from acute to chronic pain.
This meta-analysis reveals altered specific brain activity in PHN patients. Alterations in SFGmed and PCUN within the DMN indicate that this network may exhibit a condition of sustained hyperexcitability in PHN. Moreover, aberrant activity in MTG, ITG, ORBsup, PreCG, and CAL affects emotion regulation, memory processing, reward circuitry, and motor control. The observed changes in the DMN may reflect the interplay between chronic pain and self-referential processing, while disturbances in emotional and reward-related regions may contribute to the affective and motivational components of chronic pain. Alterations in motor control regions may indicate compensatory or maladaptive mechanisms related to the physical manifestation of pain. These findings provide a basis for targeted treatments that address both the sensory and affective aspects of chronic pain.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
GW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. YL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. DG: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. SL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. JY: Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was mainly supported by the Key Laboratory of Functional Molecular Imaging of Tumour and Interventional Diagnosis and Treatment of Shaoxing City (No. 2020ZDSYSO1, Shaoxing People’s Hospital, Shaoxing, Zhejiang, China), Shaoxing Medicine and Health Science and Technology Project (2022SY06, 2022KY026), and Zhejiang Medicine and Health Science and Technology Project (2023KY1251).
The authors thank everyone who participated in this study, with special thanks to Xiaopan Huang for her help.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Apkarian, A. V., Hashmi, J. A., and Baliki, M. N. (2011). Pain and the brain: specificity and plasticity of the brain in clinical chronic pain. Pain 152, S49–S64. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2010.11.010
Banker, L., and Tadi, P. (2023). “Neuroanatomy, precentral gyrus,” in StatPearls. (Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing).
Becker, S., Gandhi, W., Pomares, F., Wager, T. D., and Schweinhardt, P. (2017). Orbitofrontal cortex mediates pain inhibition by monetary reward. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 12, 651–661. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsw173
Biswal, B. B., Mennes, M., Zuo, X.-N., Gohel, S., Kelly, C., Smith, S. M., et al. (2010). Toward discovery science of human brain function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 107, 4734–4739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0911855107
Bushnell, M. C., Ceko, M., and Low, L. A. (2013). Cognitive and emotional control of pain and its disruption in chronic pain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 14, 502–511. doi: 10.1038/nrn3516
Butera, K. A., Fox, E. J., and George, S. Z. (2016). Toward a transformed understanding: from pain and movement to pain with movement. Phys. Ther. 96, 1503–1507. doi: 10.2522/ptj.20160211
Cao, S., Li, Y., Deng, W., Qin, B., Zhang, Y., Xie, P., et al. (2017a). Local brain activity differences between herpes zoster and Postherpetic neuralgia patients: a resting-state functional MRI study. Pain Physician 20, E687–e699.
Cao, S., Song, G., Zhang, Y., Xie, P., Tu, Y., Li, Y., et al. (2017b). Abnormal local brain activity beyond the pain matrix in Postherpetic neuralgia patients: a resting-state functional MRI study. Pain Physician 2, E303–e314. doi: 10.36076/ppj.2017.E314
Chehadi, O., Rusu, A., Konietzny, K., Schulz, E., Köster, O., Schmidt-Wilcke, T., et al. (2018). Brain structural alterations associated with dysfunctional cognitive control of pain in patients with low back pain. Eur. J. Pain 22, 745–755. doi: 10.1002/ejp.1159
Cheng, S., Dong, X., Lai, P., Chen, X., Zhou, J., Li, Z., et al. (2024). A multimodal Meta-analysis of structural and functional alterations in the brain of knee osteoarthritis. Pain Physician 27, E557–E566
Dadario, N. B., and Sughrue, M. E. (2023). The functional role of the precuneus. Brain 146, 3598–3607. doi: 10.1093/brain/awad181
Dai, H., Jiang, C., Wu, G., Huang, R., Jin, X., Zhang, Z., et al. (2020). A combined DTI and resting state functional MRI study in patients with postherpetic neuralgia. Jpn. J. Radiol. 38, 440–450. doi: 10.1007/s11604-020-00926-4
Farr, O. M., Chiang-shan, R. L., and Mantzoros, C. S. (2016). Central nervous system regulation of eating: insights from human brain imaging. Metabolism 65, 699–713. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2016.02.002
Gu, L., Hong, S., Jiang, J., Liu, J., Cao, X., Huang, Q., et al. (2019). Bidirectional alterations in ALFF across slow-5 and slow-4 frequencies in the brains of postherpetic neuralgia patients. J. Pain Res. 12, 39–47. doi: 10.2147/jpr.S179077
Hadley, G. R., Gayle, J. A., Ripoll, J., Jones, M. R., Argoff, C. E., Kaye, R. J., et al. (2016). Post-herpetic neuralgia: a review. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 20, 1–5. doi: 10.1007/s11916-016-0548-x
Henssen, D., Dijk, J., Knepflé, R., Sieffers, M., Winter, A., and Vissers, K. (2019). Alterations in grey matter density and functional connectivity in trigeminal neuropathic pain and trigeminal neuralgia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. NeuroImage 24:102039. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2019.102039
Hong, S., Gu, L., Zhou, F., Liu, J., Huang, M., Jiang, J., et al. (2018). Altered functional connectivity density in patients with herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia. J. Pain Res. 11, 881–888. doi: 10.2147/jpr.S154314
Houde, F., Martel, M., Coulombe-Lévêque, A., Harvey, M.-P., Auclair, V., Mathieu, D., et al. (2020). Perturbing the activity of the superior temporal gyrus during pain encoding prevents the exaggeration of pain memories: a virtual lesion study using single-pulse transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 169:107174. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2020.107174
Huang, J., Li, Y., Xie, H., Yang, S., Jiang, C., Sun, W., et al. (2020). Abnormal intrinsic brain activity and neuroimaging-based fMRI classification in patients with herpes zoster and Postherpetic neuralgia. Front. Neurol. 11:532110. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.532110
Jiang, J., Hou, X., Gu, L., Liu, X., Lv, H., Xiong, J., et al. (2024). Disrupted balance of short- and long-range functional connectivity density in patients with herpes zoster or Postherpetic neuralgia: a resting-state fMRI study. J. Pain Res. 17, 2753–2765. doi: 10.2147/jpr.S472349
Johnson, R. W., and Rice, A. S. (2014). Postherpetic neuralgia. N. Engl. J. Med. 371, 1526–1533. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp1403062
Legrain, V., Iannetti, G. D., Plaghki, L., and Mouraux, A. (2011). The pain matrix reloaded: a salience detection system for the body. Prog. Neurobiol. 93, 111–124. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2010.10.005
Liu, N., Li, Y., Hong, Y., Huo, J., Chang, T., Wang, H., et al. (2023). Altered brain activities in mesocorticolimbic pathway in primary dysmenorrhea patients of long-term menstrual pain. Front. Neurosci. 17:1098573. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1098573
Mallick-Searle, T., Snodgrass, B., and Brant, J. M. (2016). Postherpetic neuralgia: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and pain management pharmacology. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 9, 447–454. doi: 10.2147/jmdh.S106340
Melzack, R. (1990). Phantom limbs and the concept of a neuromatrix. Trends Neurosci. 13, 88–92. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90179-E
Melzack, R., and Wall, P. D. (1965). Pain mechanisms: a new theory: a gate control system modulates sensory input from the skin before it evokes pain perception and response. Science 150, 971–979. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3699.971
Menon, V. (2023). 20 years of the default mode network: a review and synthesis. Neuron 111, 2469–2487. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2023.04.023
Mercer Lindsay, N., Chen, C., Gilam, G., Mackey, S., and Scherrer, G. (2021). Brain circuits for pain and its treatment. Sci. Transl. Med. 13:eabj7360. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abj7360
Navratilova, E., and Porreca, F. (2014). Reward and motivation in pain and pain relief. Nat. Neurosci. 17, 1304–1312. doi: 10.1038/nn.3811
Niddam, D., Lee, S. H., Su, Y. T., and Chan, R. C. (2017). Brain structural changes in patients with chronic myofascial pain. Eur. J. Pain 21, 148–158. doi: 10.1002/ejp.911
Onitsuka, T., Shenton, M. E., Salisbury, D. F., Dickey, C. C., Kasai, K., Toner, S. K., et al. (2004). Middle and inferior temporal gyrus gray matter volume abnormalities in chronic schizophrenia: an MRI study. Am. J. Psychiatry 161, 1603–1611. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.161.9.1603
Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., et al. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
Radua, J., and Mataix-Cols, D. (2009). Voxel-wise meta-analysis of grey matter changes in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Br. J. Psychiatry 195, 393–402. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.108.055046
Radua, J., Mataix-Cols, D., Phillips, M. L., El-Hage, W., Kronhaus, D. M., Cardoner, N., et al. (2012). A new meta-analytic method for neuroimaging studies that combines reported peak coordinates and statistical parametric maps. Eur. Psychiatry 27, 605–611. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2011.04.001
Radua, J., Rubia, K., Canales-Rodríguez, E. J., Pomarol-Clotet, E., Fusar-Poli, P., and Mataix-Cols, D. (2014). Anisotropic kernels for coordinate-based meta-analyses of neuroimaging studies. Front. Psych. 5:13. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2014.00013
Radua, J., van den Heuvel, O. A., Surguladze, S., and Mataix-Cols, D. (2010). Meta-analytical comparison of voxel-based morphometry studies in obsessive-compulsive disorder vs other anxiety disorders. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 67, 701–711. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2010.70
Saarinen, A. I. L., Huhtaniska, S., Pudas, J., Björnholm, L., Jukuri, T., Tohka, J., et al. (2020). Structural and functional alterations in the brain gray matter among first-degree relatives of schizophrenia patients: a multimodal meta-analysis of fMRI and VBM studies. Schizophr. Res. 216, 14–23. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2019.12.023
Seminowicz, D. A., and Moayedi, M. (2017). The dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in acute and chronic pain. J. Pain 18, 1027–1035. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2017.03.008
Tang, Y., Wang, M., Zheng, T., Xiao, Y., Wang, S., Han, F., et al. (2021). Structural and functional brain abnormalities in postherpetic neuralgia: a systematic review of neuroimaging studies. Brain Res. 1752:147219. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2020.147219
Thompson, R. R., Kong, C. L., Porco, T. C., Kim, E., Ebert, C. D., and Acharya, N. R. (2021). Herpes zoster and Postherpetic neuralgia: changing incidence rates from 1994 to 2018 in the United States. Clin. Infect. Dis. 73, e3210–e3217. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa1185
Wandell, B. A., Dumoulin, S. O., and Brewer, A. A. (2009). Visual cortex in humans. Encycl. Neurosci. 10, 251–257. doi: 10.1016/B978-008045046-9.00241-2
Wang, L., Han, K., Huang, Q., Hu, W., Mo, J., Wang, J., et al. (2024). Systemic lupus erythematosus-related brain abnormalities in the default mode network and the limbic system: a resting-state fMRI meta-analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 355, 190–199. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2024.03.121
Wu, Y., Wang, C., Qian, W., Wang, L., Yu, L., Zhang, M., et al. (2025). Default mode network-basal ganglia network connectivity predicts the transition to postherpetic neuralgia. IBRO Neurosci. Rep. 18, 135–141. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2025.01.009
Wu, Y., Wang, C., Qian, W., Yu, L., Xing, X., Wang, L., et al. (2020). Disrupted default mode network dynamics in recuperative patients of herpes zoster pain. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 26, 1278–1287. doi: 10.1111/cns.13433
Wu, Y., Wang, C., Yu, L., Qian, W., Xing, X., Zhang, M., et al. (2022b). Abnormal within- and cross-networks functional connectivity in different outcomes of herpes zoster patients. Brain Imaging Behav. 16, 366–378. doi: 10.1007/s11682-021-00510-y
Wu, X., Yuan, J., Yang, Y., Han, S., Dai, H., Wang, L., et al. (2022a). Elevated GABA level in the precuneus and its association with pain intensity in patients with postherpetic neuralgia: an initial proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Eur. J. Radiol. 157:110568. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2022.110568
Xian, L., Fu-Yong, C., Wei, T., Ying, L., Han, Z., Yong-Jie, L., et al. (2015). Dynamic observation of baseline brain activities in patients with Postherpetic neuralgia revealed by resting-state functional MRI. Prog. Biochem. Biophys. 42, 947–954.
Keywords: postherpetic neuralgia, chronic pain, meta-analysis, AES-SDM, rs-fMRI
Citation: Wu G, Luo Y, Guo D, Lv S and Yang J (2025) A meta-analysis of resting-state fMRI in postherpetic neuralgia using AES-SDM. Front. Neurosci. 19:1556639. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1556639
Received: 07 January 2025; Accepted: 12 March 2025;
Published: 31 March 2025.
Edited by:
Xiaofei Hu, Army Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Mohammed Abu El-Hamd, Sohag University, EgyptCopyright © 2025 Wu, Luo, Guo, Lv and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jianfeng Yang, eWFuZ2pmQHVzeC5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.