
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Neurosci., 20 March 2025
Sec. Neurogenesis
Volume 19 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2025.1536055
Cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury (CIRI) is a complex pathophysiological process faced by brain tissues after ischemic stroke treatment, which involves mechanisms of inflammatory response, oxidative stress and apoptosis, and severely affects treatment outcome. Lipocalin-2 (LCN2), an acute-phase protein, is significantly up-regulated after CIRI and promotes neural repair by enhancing astrocyte phagocytosis, but its over-activation may also trigger secondary inflammation and demyelination injury. LCN2 also plays a key role in neuroinflammation regulation by regulating the polarization state of astrocytes and the release of inflammatory factors, and may affect the integrity of the blood–brain barrier and a variety of pathologic injury processes. In view of the important role of LCN2 in CIRI, this article reviews the mechanism of LCN2, aiming to provide new ideas and methods for the treatment of ischemic stroke.
Cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury (CIRI) is a phenomenon in which brain tissue undergoes further damage due to a series of complex biochemical and molecular biological changes when blood supply is restored after ischemia, a process that involves complex pathophysiological mechanisms including inflammatory response, oxidative stress, and apoptosis (Tuo et al., 2022). This injury not only exacerbates neuronal cell death, but also may trigger more extensive brain tissue dysfunction. Currently, despite the success of thrombolysis and thrombectomy in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke, reperfusion injury is still an important factor affecting the treatment outcome (Zhang et al., 2022). Therefore, in-depth study of the molecular mechanisms of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury and searching for effective therapeutic targets are of great significance for improving the therapeutic outcome of ischemic stroke.
Lipocalin-2 (LCN2), a member of the lipid carrier protein family, functions as an acute-phase protein after brain injury, and LCN2, an important marker of reactive astrocytes, is significantly up-regulated after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury, which promotes neurological repair by enhancing phagocytosis of astrocytes and removing damaged tissue debris (Jung and Ryu, 2023). However, excessive phagocytic activation may also lead to secondary inflammatory responses and demyelination injury, suggesting a delicate balance between LCN2’s role in regulating inflammatory responses and cytoprotection (Zhao et al., 2023). Second, LCN2 plays a key role in the regulation of neuroinflammation by affecting the polarization state of astrocytes and regulating the type of inflammatory factors they release, a process that not only affects the extent of local brain tissue damage, but may also further modulate the systemic inflammatory response by affecting the integrity of the blood–brain barrier, as well as participating in a variety of pathological damage processes such as oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis (Zhang et al., 2022; Tan et al., 2024). Given that the pathophysiological mechanism of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury involves a number of aspects mentioned above, we hypothesize that LCN2 may play an important role in this process. This article comprehensively reviews the mechanism of LCN2 in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury, not only aims to provide new ideas and methods for the treatment of ischemic stroke, but also hopes to explore the possibilities of LCN2 as a potential therapeutic target by systematically sorting out the results of the existing research, so as to lay a solid theoretical foundation for the subsequent preclinical studies and clinical trials. Further, by clarifying the specific pathway of LCN2 in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury, we can help to develop more targeted therapeutic drugs with fewer side effects and optimize the clinical therapeutic regimen to improve the quality of patients’ survival and prognosis. Meanwhile, a deeper understanding of the mechanism of LCN2 can also enrich the theoretical system of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury and provide new perspectives and directions for basic research in this field.
Oxidative stress is one of the core mechanisms of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Under ischemia, brain cells are unable to carry out normal aerobic metabolism, leading to disorders in energy metabolism (Qin et al., 2022). When the blood supply is restored, a large influx of oxygen triggers an abnormal oxidative phosphorylation process, generating a large number of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and free radicals, such as superoxide anion and hydroxyl radicals, etc. (Chen et al., 2020). These highly reactive molecules undergo oxidative reactions with biomolecules, such as cell membranes, proteins, and nucleic acids, leading to severe damage to the structure and function of the cells. Serious damage to cell structure and function (Granger and Kvietys, 2015; Sies, 2015). Oxidative stress not only directly destroys cellular components, but also activates a series of downstream signaling pathways that further exacerbate cell damage and death (Zhu et al., 2022).
Inflammatory response is a key factor leading to neurological impairment after cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. During ischemia, damaged cells release inflammatory factors such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), which attracts immune cells to gather in the ischemic area (Li et al., 2023). Upon reperfusion, microglia and astrocytes further activate and release large amounts of inflammatory mediators, leading to an increased local inflammatory response (Mao et al., 2023). The inflammatory response not only directly damages brain tissue, but also creates a vicious cycle by destroying the blood–brain barrier, allowing harmful substances and inflammatory cells in the blood to enter brain tissue (Levard et al., 2021). In addition, the inflammatory response activates the complement system, exacerbating microvascular injury and thrombosis, further worsening ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Calcium ion overload is another important mechanism of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Under ischemia, cell membrane permeability increases and calcium ion channels open, leading to a large inward flow of extracellular calcium ions. When reperfusion occurs, due to the impairment of the intracellular calcium ion clearance mechanism, calcium ions further accumulate, forming calcium overload (Zhang et al., 2019). Calcium overload not only directly destroys the cytoskeleton and membrane structure, but also activates a series of calcium-dependent enzymes, such as phospholipases and proteases, which promote the degradation of membrane phospholipids and the breakdown of cellular structural proteins (Cataldi, 2013). Under calcium overload, calmodulin (CaM) binds to calcium ions in complexes increasing the release of vasoconstrictor factors, causing vasospastic constriction affecting blood flow and exacerbating ischemic–hypoxic injury after CIRI (Ludhiadch et al., 2022). Accumulation of intracellular calcium ions in mitochondria leads to damage to the mitochondrial membrane, inhibiting ATP synthesis, which in turn leads to impaired energy synthesis, and these changes ultimately lead to apoptosis and necrosis, which exacerbate the damage to brain tissue (Rahi and Kaundal, 2024; Bodalia et al., 2013).
Apoptosis is an important form of cell death in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. During ischemia/reperfusion, the above factors work together to activate apoptotic signaling pathways, which induce orderly cell death by regulating the expression of apoptosis-related genes and the activation of apoptosis proteins (Momenabadi et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2020). The B-cell lymphoma (Bcl) family plays an important role in apoptosis, which includes the anti-apoptotic gene Bcl-2 and the pro-apoptotic gene Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax) (Yang et al., 2022). Apoptosis involving the Bcl family usually works through cystatinases (Caspases) mediating protein cleavage, and when CIRI occurs, Caspase-3 is activated, inducing apoptosis in neuronal cells, resulting in further damage to neuronal cells (Niizuma et al., 2010). In addition, the cellular contents released by apoptotic cells may further activate the inflammatory response, forming a vicious cycle and exacerbating brain tissue damage and dysfunction (Chen et al., 2011).
In summary, oxidative stress, inflammatory response, calcium ion overload and apoptosis are the main mechanisms of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. These mechanisms are interrelated and interact with each other, and together they lead to severe injury and dysfunction of brain tissue. Therefore, therapeutic strategies targeting these mechanisms are important for reducing cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury and promoting neurological function recovery.
LCN2 is a small-molecule protein whose structure consists mainly of β-folding to form a barrel-like structure known as the β-folding barrel, and one end of this β-folding barrel is closed by a short N-terminal 310-helix, while the other end is open for ligand binding (Jaberi et al., 2021). The β-folding barrel of LCN2 consists of multiple antiparallel β-folds that are interconnected by interchain hydrogen bonds to form a stable structure (Chandrasekaran et al., 2024). Hydrophobic aromatic and aliphatic amino acid residues are arranged in the interior of the barrel structure to form a hydrophobic nucleus, which provides a site for the binding of lipophilic ligands that have specific chemical and physical properties to bind to specific ligands (e.g., iron ions, small molecule metabolites, etc.) (Schröder et al., 2023). Upon binding a ligand, the structure of LCN2 may undergo minor changes to adapt to the shape and charge of the ligand (Li et al., 2020). The structure of LCN2 may also contain specific functional regions that may be involved in interactions with other proteins or cellular receptors to regulate cell signaling or cell–cell interactions (Krizanac et al., 2024).
LCN2 is expressed in a variety of cell types, such as neutrophils, endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, cardiomyocytes, and macrophages (Tarín et al., 2016). LCN2 is widely present in human tissues, but its expression is low, and is only elevated when epithelial cells are stimulated by infection, inflammation, and ischemia, and is involved in inflammation, lipid metabolism, iron transport, and renal tubular repair (Rehwald et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2019). Recent studies show that LCN2 is an autocrine promoter of chemokine inducers and reactive astrocytosis (Jang et al., 2013). Astrocytes can undergo functional polarization under pathological conditions and exhibit either classically activated or alternatively activated phenotypes, and LCN2 may regulate the polarization state of astrocytes by affecting their signal transduction pathways (Ni et al., 2015) (Figure 1). Specifically, LCN2 may promote the conversion of astrocytes to a classically activated phenotype, release pro-inflammatory factors, and exacerbate the inflammatory response; however, under certain conditions, LCN2 may also induce the conversion of astrocytes to an alternatively activated phenotype, release anti-inflammatory factors, and promote tissue repair (Wang et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2024).
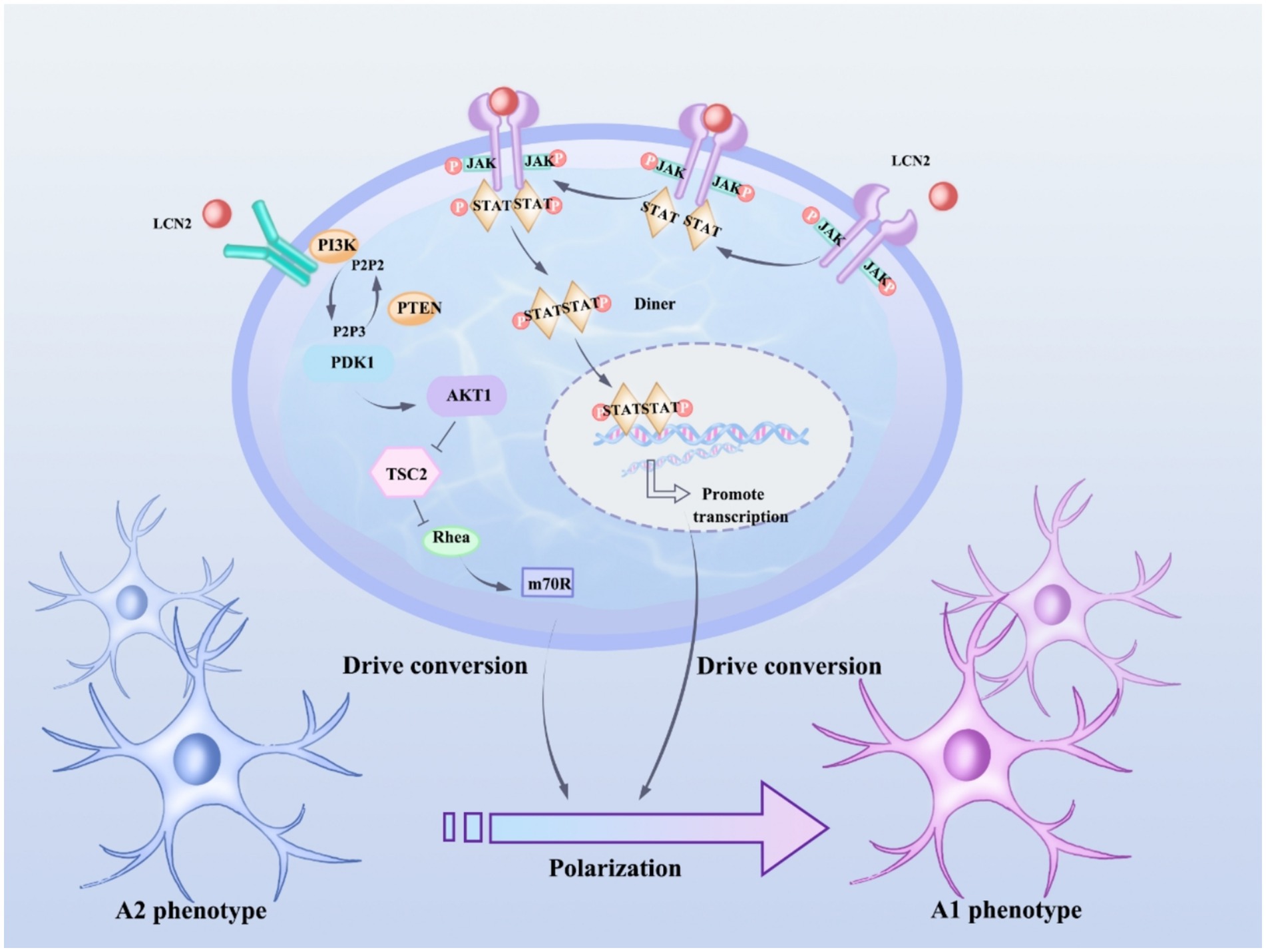
Figure 1. LCN2 affects astrocyte polarization status by regulating JAK/STAT and PI3K/Akt pathways. JAK activation phosphorylates STAT proteins, and phosphorylated STAT3 forms a dimer and translocates to the nucleus, where the STAT3 dimer binds to the promoter regions of genes associated with astrocyte polarization and promotes gene transcription, thus promoting the shift from an anti-inflammatory phenotype (type A2) to a pro-inflammatory phenotype (type A1) in astrocytes. After activation of PI3K, phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3) is produced, which in turn activates Akt, which regulates a variety of downstream targets, including tuberous sclerosis complex 2 (TSC2) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), which play important roles in cell metabolism and the synthesis of polarization-associated proteins, and thus drives the transformation of astrocytes from A2 to A1 phenotypes.
Under pathological conditions such as cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury, astrocytes are activated and express LCN2. LCN2 activates downstream phagocytic signaling pathways by binding to receptors that mediate phagocytosis, such as LRP1, which enhances phagocytosis by astrocytes, a process that may play an important role in removing debris from damaged tissues and facilitating tissue repair, but may also lead to excessive inflammatory responses and secondary damage (Jha et al., 2015) (Figure 2). LCN2, an important inflammatory mediator in the central nervous system, induces the activation of astrocytes and microglia, releases pro-inflammatory factors, and participates in the regulation of neuroinflammation (Jung et al., 2023). In a variety of neurodegenerative lesions, aberrant expression of LCN2 may be associated with degeneration of dopaminergic neurons and decline in cognitive function, and LCN2 may exacerbate neuronal damage and death through mechanisms that promote oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction (Bi et al., 2013). In a variety of CNS injuries (e.g., cerebral ischemia, cerebral hemorrhage, traumatic brain injury, etc.), reactive astrocytes characteristically express LCN2, which can therefore be used as a marker of reactive astrocytes for assessing the extent and prognosis of CNS injury (Liu et al., 2022). In addition, the expression level of LCN2 may serve as a diagnostic indicator for certain neurological disorders and as a monitor of treatment efficacy (Suk, 2016).
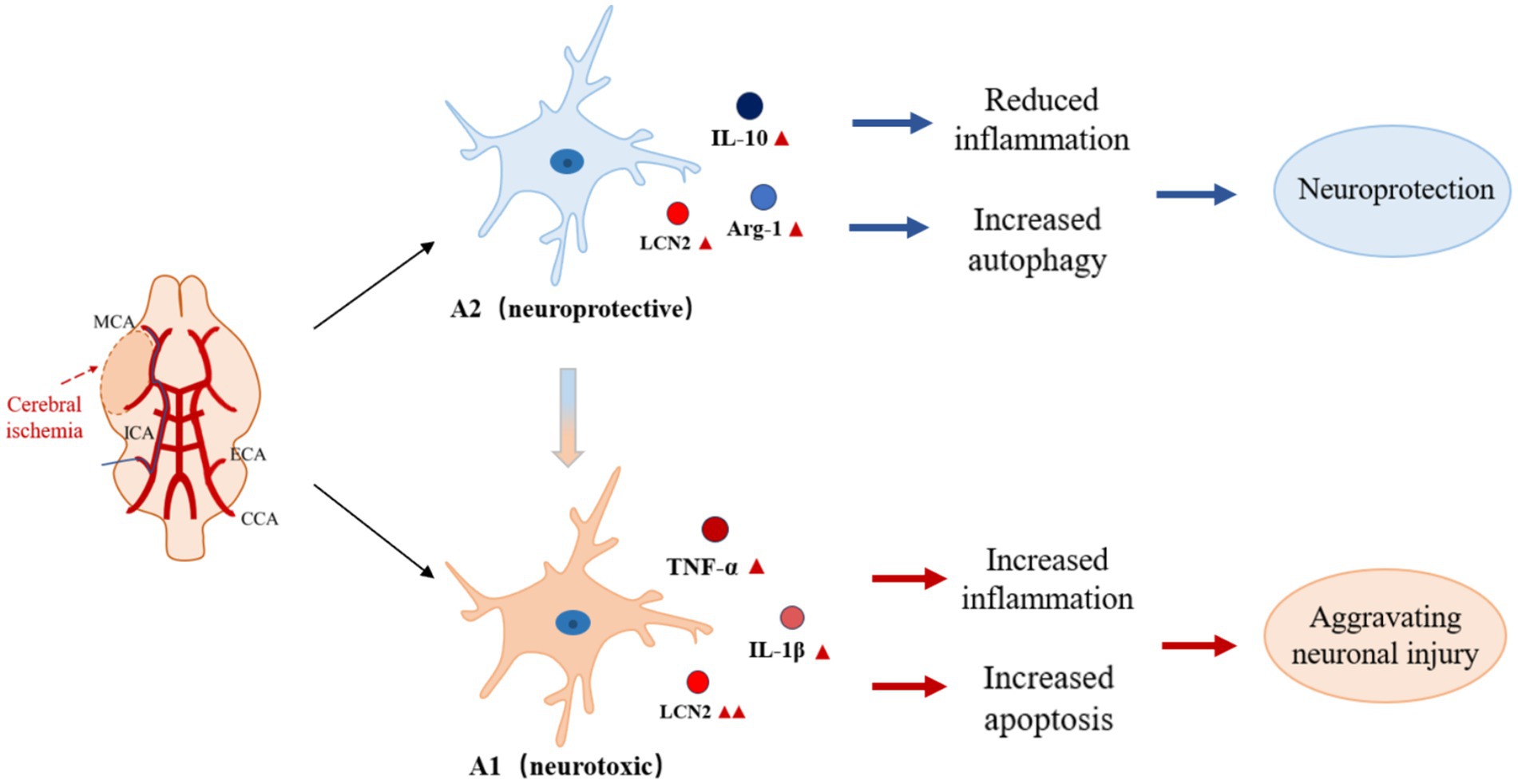
Figure 2. Role of LCN2 in CIRI by regulating astrocyte activation state. Under pathological conditions such as cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury, astrocytes are activated and express LCN2. LCN2 enhances phagocytosis in astrocytes by activating downstream phagocytosis signaling pathways through binding to receptors mediating phagocytosis, a process that may play an important role in removing debris from damaged tissues and promoting tissue repair. However, over-activation of LCN2 may lead to inflammatory responses and secondary injury. As an important inflammatory mediator in the central nervous system, LCN2 can promote the shift of astrocytes from anti-inflammatory to pro-inflammatory phenotype, participate in the regulation of neuroinflammation, and exacerbate neuronal damage and death by promoting oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and other mechanisms.
In summary, LCN2 associated with astrocytes has multiple functions and plays an important role in the physiological and pathological processes of the central nervous system. Further studies on the functions and mechanisms of LCN2 can help to reveal the pathogenesis of neurological diseases and provide new targets and strategies for their treatment.
One study revealed the important role of LCN2 in regulating the activation state of astrocytes, and they found that LCN2 treatment significantly promoted astrocytes’ expression of cytokines closely related to the classical activation pathway, such as IL-1β, TNF-α, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and CXCL10 (Wang et al., 2015; Adler et al., 2023). In contrast, LCN2 treatment did not induce the expression of alternative activation-associated cytokines such as Arg1, IL-10, MRC1, YM1, and Fizz1 (Zhao et al., 2019). This finding further emphasizes the specific role of LCN2 in regulating the activation state of astrocytes. In addition, studies have identified a critical role for LCN2 in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)/interferon gamma (IFN-γ)-induced classical activation of astrocytes, and provide strong evidence to support this idea (Kim et al., 2017). Their study shows that LCN2 is not only an important regulator of astrocyte classical activation after ischemic stroke, but also likely a key determinant of its activation status.
The neurotoxic and neuroprotective effects exhibited by LCN2 in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury depend largely on the timing and conditions of injury. It has been shown that iNOS expression is significantly impaired in astrocytes knocked down for LCN2, which highlights the critical role of LCN2 in promoting the classical activation of the astrocyte pathway, suggesting that it may be one of the key factors exacerbating cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury under certain conditions (Zhao et al., 2019). Ranjbar Taklimie et al. (2019) cultured astrocytes from the cerebral cortex of mice under hypoxic conditions and observed that the level of LCN2 gradually increased with the duration of hypoxia, especially reaching a peak at 24 and 72 h, and that LCN2 was able to promote a shift from an anti-inflammatory phenotype to a pro-inflammatory phenotype of astrocytes, which further exacerbated cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. In addition, Wang et al. (2015) conducted an in-depth study using a rat middle cerebral artery infarction model and found that after the onset of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury, the expression of LCN2 was gradually elevated mainly in astrocytes and endothelial cells, and that this elevation reached a peak 24 h after cerebral infarction in rats. This suggests that changes in LCN2 expression are closely related to the development of injury at specific time nodes after the onset of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury, and that LCN2 exhibits more neurotoxic effects at this critical time.
In terms of injury conditions, numerous findings have shown that LCN2 can exert neurotoxic effects after the onset of IS. The underlying mechanism may be that LCN2 up-regulates glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) produced during astrocyte activation through the Ras homolog-Rho-associated helical coiled-coil protein kinase signaling pathway, which leads to morphological changes of astrocytes in response to inflammatory stimuli, and then causes neurological damage (Mao et al., 2016; Jin et al., 2014). This suggests that under the specific conditions of ischemic injury, LCN2 triggers neurotoxicity through specific signaling pathways. However, it has also been shown that in the early stage of brain injury, LCN2 can promote neural repair by enhancing phagocytosis of astrocytes and removing damaged tissue fragments, reflecting a neuroprotective effect. This suggests that the function of LCN2 changes under different injury timing and conditions, and that its neurotoxic and neuroprotective effects are not absolute, but are dynamically regulated by a variety of factors. The in-depth study of these relationships is of great significance to the understanding of the pathological mechanisms of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury and the search for precise therapeutic strategies for LCN2.
After cerebral ischemia-reperfusion, LCN2 expression is up-regulated. On the one hand, LCN2 may inhibit the gene transcription of antioxidant enzymes, such as SOD, GPx, etc., by binding to specific transcription factors in the promoter region of antioxidant enzyme genes, or accelerate protein degradation of antioxidant enzymes through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, which reduces the cell’s scavenging ability of free radicals; on the other hand, in the metabolism of ferric ions, LCN2 can combine with iron ions to form a complex, which affects the intracellular transport and storage of iron ions (Wang et al., 2022; Yamada et al., 2016). For example, LCN2 may promote the expression of transferrin receptor 1 (TfR1), which increases cellular uptake of iron ions, resulting in elevated intracellular free iron ion concentrations (Wang et al., 2024). In the Fenton reaction, iron ions act as catalysts to promote the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to produce highly reactive hydroxyl radicals; the Haber-Weiss reaction also accelerates the generation of free radicals due to the involvement of iron ions, further exacerbating the oxidative stress (Fei et al., 2024). In addition, LCN2, as a lipid transporter protein, can bind to phospholipid molecules in the cell membrane, altering the lipid bilayer structure of the cell membrane, making the unsaturated fatty acids of the membrane phospholipids more susceptible to attack by free radicals, forming lipid peroxidation products, destabilizing cell membranes, and increasing the sensitivity of cells to oxidative stress (Ferreira et al., 2018; Ferreira et al., 2018). In summary, LCN2 plays an important regulatory role in the oxidative stress process in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury, and it exacerbates the generation of free radicals and cellular damage by regulating the activity of antioxidant enzymes, influencing iron metabolism, and altering the lipid composition of cell membranes.
Compared with other common biomarkers in ischemic stroke, such as neuron-specific enolase (NSE) and S100 calcium-binding protein B (S100B), LCN2 has unique diagnostic and therapeutic potential. NSE is mainly found in neurons and neuroendocrine cells (Persson et al., 1987). After ischemic stroke, neuronal damage leads to the release of NSE into the blood, and its serum level may rise within hours after the onset of the disease, which is valuable for early diagnosis, but its specificity is relatively limited (Isgrò et al., 2015). S100B is mainly secreted by astrocytes and enters the blood circulation when the blood–brain barrier is damaged after brain injury. Changes in its level can reflect the degree of brain injury, but it is also affected by a variety of factors, such as peripheral tissue damage (Lamers et al., 2003). LCN2, as an important marker of reactive astrocytes, was significantly upregulated after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury, which not only reflects the activation status of astrocytes, but also participates in a number of pathological processes such as inflammatory response, oxidative stress, and neuronal apoptosis (Wan et al., 2022). This study reviews the recent research progress of LCN2 in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury, revealing that LCN2 is involved in the functional regulation of astrocytes through multiple mechanisms, which in turn affects the injury and repair process of brain tissue. This finding provides potential molecular targets for the development of novel therapeutic strategies against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Although a large number of studies have supported the pathological role of LCN2 in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury, some studies have suggested a different viewpoint. Some studies suggest that LCN2 may have neuroprotective effects under certain conditions. In the early stage of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury, low levels of LCN2 may help to maintain neuronal survival and function by activating specific intracellular signaling pathways, promoting the conversion of astrocytes to A2 type, and releasing neuroprotective factors such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) (Xiao et al., 2025). It has also been found that LCN2 may be involved in the body’s self-repair mechanism, and that the up-regulation of LCN2 expression during a certain period of time after injury can promote the removal of necrotic tissues and apoptotic cells by phagocytes and accelerate the repair process of the injured area (Liu et al., 2018).
From the perspective of therapeutic significance and potential clinical application, it is crucial to deeply investigate the mechanism of LCN2. Clarifying the interactions between LCN2 and other inflammatory factors can help to understand the inflammatory network and develop therapeutic tools to comprehensively regulate inflammation; and realizing the precise regulation of LCN2 levels can intervene in the damage process from the source. In addition, the development of new drugs targeting LCN2 is promising, which can inhibit its overexpression in the neurotoxic stage and promote its function in the neuroprotective stage. Meanwhile, the development of new diagnostic markers based on LCN2 can provide a more accurate assessment of disease conditions and prognosis, and provide strong support for clinical treatment decisions.
Although this study reviewed the multiple mechanisms of LCN2 in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury, there are still some limitations, and further in-depth studies are needed to investigate the interaction mechanism between LCN2 and other inflammatory factors, its specific mode of action in different pathological stages, and how to achieve the best therapeutic effect by precisely regulating the level of LCN2, etc. In the future, more studies are needed to reveal the role of LCN2 in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury comprehensively and objectively, providing a more accurate theoretical basis for clinical treatment.
L-yC: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. YY: Visualization, Writing – review & editing, Supervision. HH: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. X-yZ: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. X-mZ: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Natural Science Research Program of Hubei Provincial Department of Education (Grant No. D20202006), the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (Grant No. 2023AFD170), and the Wuhan Municipal Bureau of Science and Technology’s Aurora Project (Grant No. 2022020801020507).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Adler, O., Zait, Y., Cohen, N., Blazquez, R., Doron, H., Monteran, L., et al. (2023). Reciprocal interactions between innate immune cells and astrocytes facilitate neuroinflammation and brain metastasis via lipocalin-2. Nat. Cancer 4, 401–418. doi: 10.1038/s43018-023-00519-w
Bi, F., Huang, C., Tong, J., Qiu, G., Huang, B., Wu, Q., et al. (2013). Reactive astrocytes secrete lcn2 to promote neuron death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 110, 4069–4074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1218497110
Bodalia, A., Li, H., and Jackson, M. F. (2013). Loss of endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ homeostasis: contribution to neuronal cell death during cerebral ischemia. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 34, 49–59. doi: 10.1038/aps.2012.139
Cataldi, M. (2013). The changing landscape of voltage-gated calcium channels in neurovascular disorders and in neurodegenerative diseases. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 11, 276–297. doi: 10.2174/1570159X11311030004
Chandrasekaran, P., Weiskirchen, S., and Weiskirchen, R. (2024). Structure, functions, and implications of selected Lipocalins in human disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25:4290. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084290
Chen, S., Chen, H., Du, Q., and Shen, J. (2020). Targeting myeloperoxidase (MPO) mediated oxidative stress and inflammation for reducing brain ischemia injury: potential application of natural compounds. Front. Physiol. 11:433. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00433
Chen, S. D., Yang, D. I., Lin, T. K., Shaw, F. Z., Liou, C. W., and Chuang, Y. C. (2011). Roles of oxidative stress, apoptosis, PGC-1α and mitochondrial biogenesis in cerebral ischemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 12, 7199–7215. doi: 10.3390/ijms12107199
Fei, X., Dou, Y., Yang, Y., Zheng, B., Luo, P., Dai, S., et al. (2024). Lipocalin-2 inhibition alleviates neural injury by microglia ferroptosis suppression after experimental intracerebral hemorrhage in mice via enhancing ferritin light chain expression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. basis Dis. 1870:167435. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2024.167435
Ferreira, A. C., Santos, T., Sampaio-Marques, B., Novais, A., Mesquita, S. D., Ludovico, P., et al. (2018). Lipocalin-2 regulates adult neurogenesis and contextual discriminative behaviours. Mol. Psychiatry 23, 1031–1039. doi: 10.1038/mp.2017.95
Ferreira, A. C., Sousa, N., Bessa, J. M., Sousa, J. C., and Marques, F. (2018). Metabolism and adult neurogenesis: towards an understanding of the role of lipocalin-2 and iron-related oxidative stress. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 95, 73–84. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.09.014
Granger, D. N., and Kvietys, P. R. (2015). Reperfusion injury and reactive oxygen species: the evolution of a concept. Redox Biol. 6, 524–551. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.08.020
Isgrò, M. A., Bottoni, P., and Scatena, R. (2015). Neuron-specific enolase as a biomarker: biochemical and clinical aspects. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 867, 125–143. doi: 10.1007/978-94-017-7215-0_9
Jaberi, S. A., Cohen, A., D'souza, C., Abdulrazzaq, Y. M., Ojha, S., Bastaki, S., et al. (2021). Lipocalin-2: structure, function, distribution and role in metabolic disorders. Biomed. Pharmacother. 142:112002. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112002
Jang, E., Kim, J. H., Lee, S., Kim, J. H., Seo, J. W., Jin, M., et al. (2013). Phenotypic polarization of activated astrocytes: the critical role of lipocalin-2 in the classical inflammatory activation of astrocytes. J. Immunol. 191, 5204–5219. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301637
Jha, M. K., Lee, S., Park, D. H., Kook, H., Park, K. G., Lee, I. K., et al. (2015). Diverse functional roles of lipocalin-2 in the central nervous system. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 49, 135–156. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.12.006
Jin, M., Kim, J. H., Jang, E., Lee, Y. M., Soo Han, H., Woo, D. K., et al. (2014). Lipocalin-2 deficiency attenuates neuroinflammation and brain injury after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 34, 1306–1314. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2014.83
Jung, B. K., Park, Y., Yoon, B., Bae, J. S., Han, S. W., Heo, J. E., et al. (2023). Reduced secretion of LCN2 (lipocalin 2) from reactive astrocytes through autophagic and proteasomal regulation alleviates inflammatory stress and neuronal damage. Autophagy 19, 2296–2317. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2023.2180202
Jung, B. K., and Ryu, K. Y. (2023). Lipocalin-2: a therapeutic target to overcome neurodegenerative diseases by regulating reactive astrogliosis. Exp. Mol. Med. 55, 2138–2146. doi: 10.1038/s12276-023-01098-7
Kim, J. H., Ko, P. W., Lee, H. W., Jeong, J. Y., Lee, M. G., Kim, J. H., et al. (2017). Astrocyte-derived lipocalin-2 mediates hippocampal damage and cognitive deficits in experimental models of vascular dementia. Glia 65, 1471–1490. doi: 10.1002/glia.23174
Krizanac, M., Mass Sanchez, P. B., Weiskirchen, R., and Schröder, S. K. (2024). Overview of the expression patterns and roles of Lipocalin 2 in the reproductive system. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 15:1365602. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1365602
Lamers, K. J., Vos, P., Verbeek, M. M., Rosmalen, F., van Geel, W. J. A., van Engelen, B. G. M., et al. (2003). Protein S-100B, neuron-specific enolase (NSE), myelin basic protein (MBP) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and blood of neurological patients. Brain Res. Bull. 61, 261–264. doi: 10.1016/s0361-9230(03)00089-3
Levard, D., Buendia, I., Lanquetin, A., Glavan, M., Vivien, D., and Rubio, M. (2021). Filling the gaps on stroke research: focus on inflammation and immunity. Brain Behav. Immun. 91, 649–667. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.09.025
Li, D., Yan Sun, W., Fu, B., Xu, A., and Wang, Y. (2020). Lipocalin-2-the myth of its expression and function. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 127, 142–151. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.13332
Li, W., Yang, X., Ding, M., Shi, W., Huang, Y., An, Q., et al. (2023). Zinc accumulation aggravates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by promoting inflammation. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 17:1065873. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1065873
Liu, M., Chen, J., Zhang, S., and Ren, C. (2018). Downregulation of lipocalin-2 and Bim expression after remote limb preconditioning in the ischemic rat brain. Brain Res. 1679, 1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2017.11.003
Liu, C., Guo, Y., Deng, S., Zhou, S., Wu, S., Chen, T., et al. (2024). Hemorrhagic stroke-induced subtype of inflammatory reactive astrocytes disrupts blood-brain barrier. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 44, 1102–1116. doi: 10.1177/0271678X241235008
Liu, R., Wang, J., Chen, Y., Collier, J. M., Capuk, O., Jin, S., et al. (2022). NOX activation in reactive astrocytes regulates astrocytic LCN2 expression and neurodegeneration. Cell Death Dis. 13:371. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04831-8
Ludhiadch, A., Sharma, R., Muriki, A., and Munshi, A. (2022). Role of calcium homeostasis in ischemic stroke: a review. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 21, 52–61. doi: 10.2174/1871527320666210212141232
Mao, L., Wu, D. H., Hu, G. H., and Fan, J. H. (2023). TLR4 enhances cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via regulating NLRP3 Inflammasome and autophagy. Mediat. Inflamm. 2023:9335166. doi: 10.1155/2023/9335166
Mao, S., Xi, G., Keep, R. F., and Hua, Y. (2016). Role of Lipocalin-2 in thrombin-induced brain injury. Stroke 47, 1078–1084. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.012153
Momenabadi, S., Vafaei, A. A., Zahedi Khorasani, M., and Vakili, A. (2022). Pre-ischemic oxytocin treatment alleviated neuronal injury via suppressing NF-κB, MMP-9, and apoptosis regulator proteins in a mice model of stroke. Cell J. 24, 337–345. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2022.7884
Ni, W., Zheng, M., Xi, G., Keep, R. F., and Hua, Y. (2015). Role of lipocalin-2 in brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 35, 1454–1461. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2015.52
Niizuma, K., Yoshioka, H., Chen, H., Kim, G. S., Jung, J. E., Katsu, M., et al. (2010). Mitochondrial and apoptotic neuronal death signaling pathways in cerebral ischemia. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1802, 92–99. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2009.09.002
Persson, L., Hårdemark, H. G., Gustafsson, J., Rundström, G., Mendel-Hartvig, I., Esscher, T., et al. (1987). S-100 protein and neuron-specific enolase in cerebrospinal fluid and serum: markers of cell damage in human central nervous system. Stroke 18, 911–918. doi: 10.1161/01.str.18.5.911
Qin, C., Yang, S., Chu, Y. H., Zhang, H., Pang, X. W., Chen, L., et al. (2022). Signaling pathways involved in ischemic stroke: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 7:215. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01064-1
Rahi, V., and Kaundal, R. K. (2024). Exploring the intricacies of calcium dysregulation in ischemic stroke: insights into neuronal cell death and therapeutic strategies. Life Sci. 347:122651. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.122651
Ranjbar Taklimie, F., Gasterich, N., Scheld, M., Weiskirchen, R., Beyer, C., Clarner, T., et al. (2019). Hypoxia induces astrocyte-derived Lipocalin-2 in ischemic stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20:1271. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061271
Rehwald, C., Schnetz, M., Urbschat, A., Mertens, C., Meier, J. K., Bauer, R., et al. (2020). The iron load of lipocalin-2 (LCN-2) defines its pro-tumour function in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 122, 421–433. doi: 10.1038/s41416-019-0655-7
Schröder, S. K., Gasterich, N., Weiskirchen, S., and Weiskirchen, R. (2023). Lipocalin 2 receptors: facts, fictions, and myths. Front. Immunol. 14:1229885. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1229885
Sies, H. (2015). Oxidative stress: a concept in redox biology and medicine. Redox Biol. 4, 180–183. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.01.002
Suk, K. (2016). Lipocalin-2 as a therapeutic target for brain injury: An astrocentric perspective. Prog. Neurobiol. 144, 158–172. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2016.08.001
Tan, Q., Zhang, C., Rao, X., Wan, W., Lin, W., Huang, S., et al. (2024). The interaction of lipocalin-2 and astrocytes in neuroinflammation: mechanisms and therapeutic application. Front. Immunol. 15:1358719. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1358719
Tarín, C., Fernandez-Garcia, C. E., Burillo, E., Pastor-Vargas, C., Llamas-Granda, P., Castejón, B., et al. (2016). Lipocalin-2 deficiency or blockade protects against aortic abdominal aneurysm development in mice. Cardiovasc. Res. 111, 262–273. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvw112
Tuo, Q. Z., Zhang, S. T., and Lei, P. (2022). Mechanisms of neuronal cell death in ischemic stroke and their therapeutic implications. Med. Res. Rev. 42, 259–305. doi: 10.1002/med.21817
Wan, T., Zhu, W., Zhao, Y., Zhang, X., Ye, R., Zuo, M., et al. (2022). Astrocytic phagocytosis contributes to demyelination after focal cortical ischemia in mice. Nat. Commun. 13:1134. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28777-9
Wang, X., Feng, L., Xin, M., Hao, Y., Wang, X., Shang, P., et al. (2020). Mechanisms underlying astrocytic connexin-43 autophagy degradation during cerebral ischemia injury and the effect on neuroinflammation and cell apoptosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 127:110125. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110125
Wang, X., Li, X., Zuo, X., Liang, Z., Ding, T., Li, K., et al. (2021). Photobiomodulation inhibits the activation of neurotoxic microglia and astrocytes by inhibiting Lcn2/JAK2-STAT3 crosstalk after spinal cord injury in male rats. J. Neuroinflammation 18:256. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02312-x
Wang, H., Wang, Z., Gao, Y., Wang, J., Yuan, Y., Zhang, C., et al. (2024). STZ-induced diabetes exacerbates neurons ferroptosis after ischemic stroke by upregulating LCN2 in neutrophils. Exp. Neurol. 377:114797. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2024.114797
Wang, G., Weng, Y. C., Han, X., Whaley, J. D., McCrae, K. R., and Chou, W. H. (2015). Lipocalin-2 released in response to cerebral ischaemia mediates reperfusion injury in mice. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 19, 1637–1645. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12538
Wang, X., Zhang, C., Zou, N., Chen, Q., Wang, C., Zhou, X., et al. (2022). Lipocalin-2 silencing suppresses inflammation and oxidative stress of acute respiratory distress syndrome by ferroptosis via inhibition of MAPK/ERK pathway in neonatal mice. Bioengineered 13, 508–520. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2009970
Xiao, R., Pan, J., Yang, M., Liu, H., Zhang, A., Guo, X., et al. (2025). Regulating astrocyte phenotype by Lcn2 inhibition toward ischemic stroke therapy. Biomaterials 317:123102. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2025.123102
Yamada, Y., Miyamoto, T., Kashima, H., Kobara, H., Asaka, R., Ando, H., et al. (2016). Lipocalin 2 attenuates iron-related oxidative stress and prolongs the survival of ovarian clear cell carcinoma cells by up-regulating the CD44 variant. Free Radic. Res. 50, 414–425. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2015.1134795
Yang, Y. D., Li, Z. X., Hu, X. M., Wan, H., Zhang, Q., Xiao, R., et al. (2022). Insight into crosstalk between Mitophagy and apoptosis/necroptosis: mechanisms and clinical applications in ischemic stroke. Curr. Med. Sci. 42, 237–248. doi: 10.1007/s11596-022-2579-3
Zhang, Q., Jia, M., Wang, Y., Wang, Q., and Wu, J. (2022). Cell death mechanisms in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Neurochem. Res. 47, 3525–3542. doi: 10.1007/s11064-022-03697-8
Zhang, J., Liu, J., Li, D., Zhang, C., and Liu, M. (2019). Calcium antagonists for acute ischemic stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 15, 255–259. doi: 10.1002/14651858
Zhang, Y., Liu, J., Yao, M., Song, W., Zheng, Y., Xu, L., et al. (2019). Sailuotong capsule prevents the cerebral Ischaemia-induced Neuroinflammation and impairment of recognition memory through inhibition of LCN2 expression. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019:8416105. doi: 10.1155/2019/8416105
Zhang, J., Wang, Z., Zhang, H., Li, S., Li, J., Liu, H., et al. (2022). The role of lipocalin 2 in brain injury and recovery after ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 15:930526. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.930526
Zhao, R. Y., Wei, P. J., Sun, X., Zhang, D. H., He, Q. Y., Liu, J., et al. (2023). Role of lipocalin 2 in stroke. Neurobiol. Dis. 179:106044. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2023.106044
Zhao, N., Xu, X., Jiang, Y., Gao, J., Wang, F., Xu, X., et al. (2019). Lipocalin-2 may produce damaging effect after cerebral ischemia by inducing astrocytes classical activation. J. Neuroinflammation 16:168. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1556-7
Zhou, Z., Zhang, P., Ya, D., Liu, J., Xu, Y., Zhang, Y., et al. (2024). Withaferin a protects against epilepsy by promoting LCN2-mediated astrocyte polarization to stopping neuronal ferroptosis. Phytomedicine 132:155892. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155892
Keywords: cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury, lipocalin-2, inflammatory response, astrocyte, apoptosis
Citation: Cai L-y, Yuan Y, Huang H, Zhang J, Zou X-y and Zhang X-m (2025) Mechanism of LCN2 in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Front. Neurosci. 19:1536055. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1536055
Received: 28 November 2024; Accepted: 10 March 2025;
Published: 20 March 2025.
Edited by:
Rajiv Dixit, St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, United StatesReviewed by:
Alokkumar Jha, Weill Cornell Medical Center, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Cai, Yuan, Huang, Zhang, Zou and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiao-ming Zhang, emhhbmd4bXpqQGFsaXl1bi5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.