
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Neurosci., 05 March 2025
Sec. Gut-Brain Axis
Volume 19 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2025.1506566
Background: The gut–brain axis (GBA) represents a complex, bidirectional communication network that connects the central nervous system (CNS) and the gastrointestinal system. Our study aimed to explore the correlation between the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases from a bibliometric perspective, focusing on research since 2014.
Methods: A comprehensive search was carried out on the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC) to locate studies on the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases, with a focus on publications from 1 January 2014 to 29 March 2024. We visualized and analyzed the data using VOSviewer, CiteSpace, and Charticulator.
Results: We gathered 429 scholarly articles on the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating disorders published in the past 10 years. Research concerning the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases has demonstrated a consistent increase in frequency over time. The USA has the highest number of publications, while Canada has the highest average number of citations, reaching as high as 3,429, which is greater than that of the USA. Moreover, the journal with the highest number of publications was Frontiers in Immunology, with 33 publications and 1,494 citations. The majority of the scholars focused on “multiple sclerosis” and “gut microbiota,” which are the primary keywords in the field of the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases.
Conclusion: This study conducted a comprehensive analysis of existing research investigating the correlation between the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases. Using advanced bibliometric tools such as VOSviewer and CiteSpace, this study analyzed the intricate relationship between the intestinal microbiota and the pathogenesis of demyelinating conditions. In addition, the study used literature statistical analysis to identify research hotspots and future directions in the field.
A significant part of human physiology is the gut microbiota, which consists of a dynamic and intricate community of bacteria, fungi, viruses, and the metabolites they produce. It is responsible for regulating a wide range of vital processes necessary for maintaining homeostasis in the host, including metabolic, endocrine, nutritional, immune, and neurological functions (Cabrera-Mulero et al., 2019). Alterations in the gut microbiota can affect bodily homeostasis; conversely, shifts in body homeostasis can influence the gut microbiota (Wijesekara et al., 2024; Clemente et al., 2012). In other words, the relationship between the gut microbiota and human body function is bidirectional, functioning as a two-way communication system between the host and microbiome (Wang et al., 2023). Despite the anatomical separation between the gut and brain, the connection between the gut and brain through the nervous and immune systems provides multiple potential pathways for communication (Cryan et al., 2019). Over the past 20 years, the field of biomedicine has undergone a shift with the recognition that the gut microbiota and the microbiome play crucial roles in modulating the central nervous system (CNS). This recognition has opened new avenues for understanding the intricate relationships between gut microorganisms and brain function, marking the beginning of a new era in biomedical research (Cryan et al., 2020). In recent years, interest in the role and significance of bidirectional communication mediated by the gut–brain axis (GBA) in the etiology of diverse central nervous disorders has increased (Chidambaram et al., 2022; Wang and Kasper, 2014). This area of study, often characterized by intricate interactions between the brain and the gastrointestinal system, is rapidly emerging as one of the most promising and dynamic fields of research (Seguella et al., 2019; Heiss and Olofsson, 2019). A previous study revealed that the GBA contributes to normal CNS function and pathology (Cryan et al., 2019; Socała et al., 2021). For the past few years, a growing body of evidence has implicated dysregulation of the GBA in the pathophysiology of several neurological disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease (Dissanayaka et al., 2024), autism spectrum disorder (Kang et al., 2019), multiple sclerosis (MS) (Parodi and Kerlero de Rosbo, 2021), Parkinson’s disease, and stroke (Zhao et al., 2021; Bogiatzi et al., 2018). Some studies have demonstrated that fundamental neural processes, including development, myelination, neurogenesis, and microglial activation, are critically influenced by the composition of the microbiota (Gao et al., 2019; Luczynski et al., 2016). These findings further underscore the significant impact of microbial communities on the structural and functional maturation of the nervous system.
The myelin sheath encases the majority of nerve fibers in the central and peripheral nervous systems, and its primary objective is to increase nerve conduction and preserve the energy expended during the propagation of action potentials (Bernardo and Visentin, 2023). Demyelinating diseases are a group of disorders characterized by changes in myelin. MS is a chronic autoimmune inflammatory disorder of the CNS. This condition is characterized by the development of inflammatory lesions within the CNS, resulting in the degradation of myelin sheaths and subsequent damage to demyelinated axons (Thirion et al., 2023). The development of various pathological conditions is increasingly linked to the composition of the microbiota and the GBA. A previous study suggested that the GBA may be important in the onset and progression of MS (Preiningerova et al., 2022). Active lesions in MS exhibit inflammatory alterations, indicative of concurrent assault by autoreactive T and B lymphocytes in the white matter of the brain. The initiation of this autoimmune response has often been linked to environmental influences, with microbial infection standing out as a primary factor (Berer et al., 2011). In addition, Banati et al. reported that antibodies against gastrointestinal antigens may reflect alterations in the microbiota and immune responses in the gut. They found that patients with MS and neuromyelitis optica (NMO) had higher levels of antibodies against gastrointestinal antigens compared to healthy controls, indicating a close relationship between the intestinal microbiota and the immune response in patients with demyelinating diseases (Cheng et al., 2022). Studies have shown that alterations in the gut microbiota or its metabolites can modulate inflammation and demyelination, especially the intermittent fasting-induced enrichment of lactobacilli (Berer et al., 2011; Lee et al., 2011), which can reduce inflammatory immune responses (Umbrello and Esposito, 2016).
To date, significant controversy surrounds the extent and exact mechanisms through which the altered GBA may influence demyelination (Ghezzi et al., 2021). To address this knowledge gap, we conducted a bibliometric analysis using tools such as VOSviewer and CiteSpace to examine research trends and emerging frontiers in the fields of the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases. This analysis focused on authors, key publications, journals, institutions, countries, and the research network of publications. Through this approach, we aimed to identify pivotal themes that characterize the intersection of these two critical areas of study. We identified Helen Tremlett as the most influential author, known for her work on the etiology, risk factors, and epidemiology of MS and gut microbiome research in demyelinating diseases. Moreover, we also found that the relationship between the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases has garnered increasing attention by analyzing the annual publication volume of related literature. In general, the relationships and underlying processes linking the intestinal microbiota to demyelinating diseases remain prominent research topics.
Web of Science (WOS) is one of the most commonly used academic database sources (Wu et al., 2021). Data for the present study were retrieved from the Web of Science Core Collection (WOSCC) database starting 1 January 2014. To minimize bias stemming from daily updates in the database, we conducted the literature search on WOSCC in a single day on 29 March 2024. We visualized the comprehensive data using VOSviewer, CiteSpace, and Charticulator.
We used TS = ((“gut microbiota” OR “intestinal microbiota” OR “fecal microbiota” OR “gastrointestinal microbiota” OR “gut microbiome” OR “intestinal microbiome” OR “fecal microbiome” OR “gastrointestinal microbiome” OR “intestinal bacteria” OR “gut bacteria” OR “fecal bacteria” OR “gastrointestinal bacteria” OR “intestinal flora” OR “gut flora” OR “fecal flora” OR “gastrointestinal flora” OR “gut microflora” OR “intestinal microflora” OR “fecal microflora” OR “gastrointestinal microflora”) AND (“demyelinating” OR “demyelinating diseases” OR “demyelinating syndrome” OR “inflammatory demyelination” OR “multiple sclerosis”). The publication period was 1 January 2014, and original articles and reviews were the types of documents that were considered. A total of 949 publications were included, with 379 original articles and 448 reviews, all in English. The article selection process was conducted independently by Chen and Wu, with any disagreements resolved by a third researcher. We excluded studies that were not related to intestinal microbiota or demyelinating diseases. Figure 1 provides visual representations of the search strategy.
The software programs CiteSpace (version 6.1. R3) and VOSviewer (version 1.6.18) are crucial for performing data analysis and visualization and identifying hotspots and trends within scientific publications. In this study, we exported the records retrieved from WOS in plain text format. This file, which was given the name download_XX.txt, contained both complete records and references. Afterward, VOSviewer and CiteSpace were used for bibliometric and visual analysis of the imported data. Comprehensive analyses across a wide range of dimensions, including countries, journals, authors, research fronts, and emerging trends, were expertly performed using VOSviewer and CiteSpace. They were used to analyze the number of annual outputs, growth trends, and frequently used keywords, as well as to identify strong citation burst keywords over time. We used Charticulator to draw a chord diagram illustrating the relationships between countries.
A total of 429 articles were included in this analysis, authored by 2,397 individuals representing 821 institutions across 47 countries. The articles were published in 193 journals, citing 23,774 sources from 3,498 journals. Since 2014, 422 articles related to the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases have been published, indicating an increasing trend with occasional oscillations (Figure 2). Overall, since 2014, the number of published articles on the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases has shown an increasing trend. These findings suggest that, with advancements and progress in medicine, an increasing number of researchers are focusing on exploring the relationship between the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases.
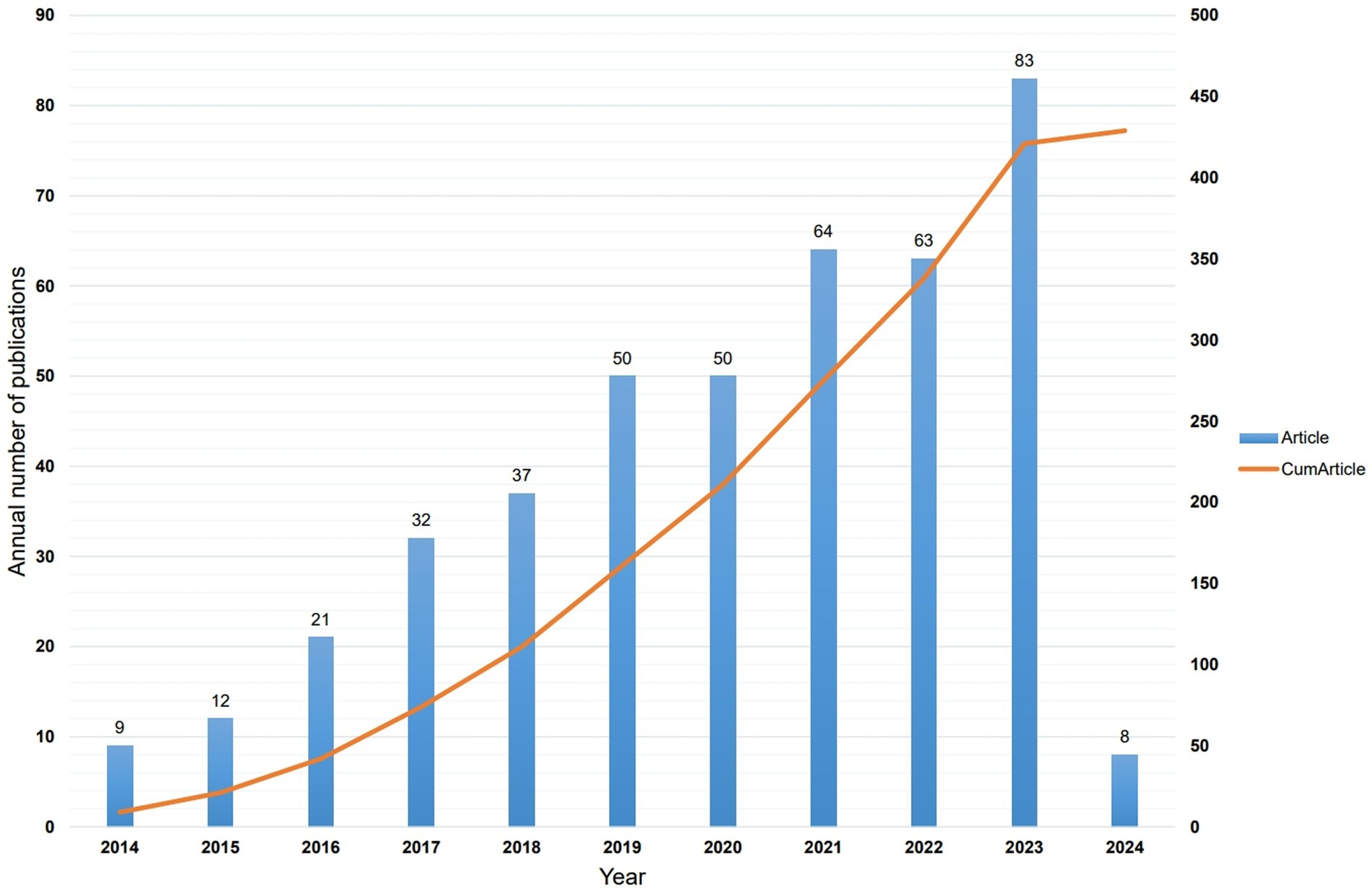
Figure 2. Distribution of publication on intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases since 2014.
The bibliometric principle known as Prices’ Law states that a core author in a given field must have produced a certain minimum number of articles: m = 0.749× (nmax is the number of articles written by the most prolific authors in the field). In this study, m = 0.749× ≈ 2.80. Thus, authors who have published three or more articles are considered core contributors to the field of the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases. Since 2014, a total of 2,397 authors have contributed to the field of the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases, and 111 authors are considered core authors, having published more than three articles (Figure 3).
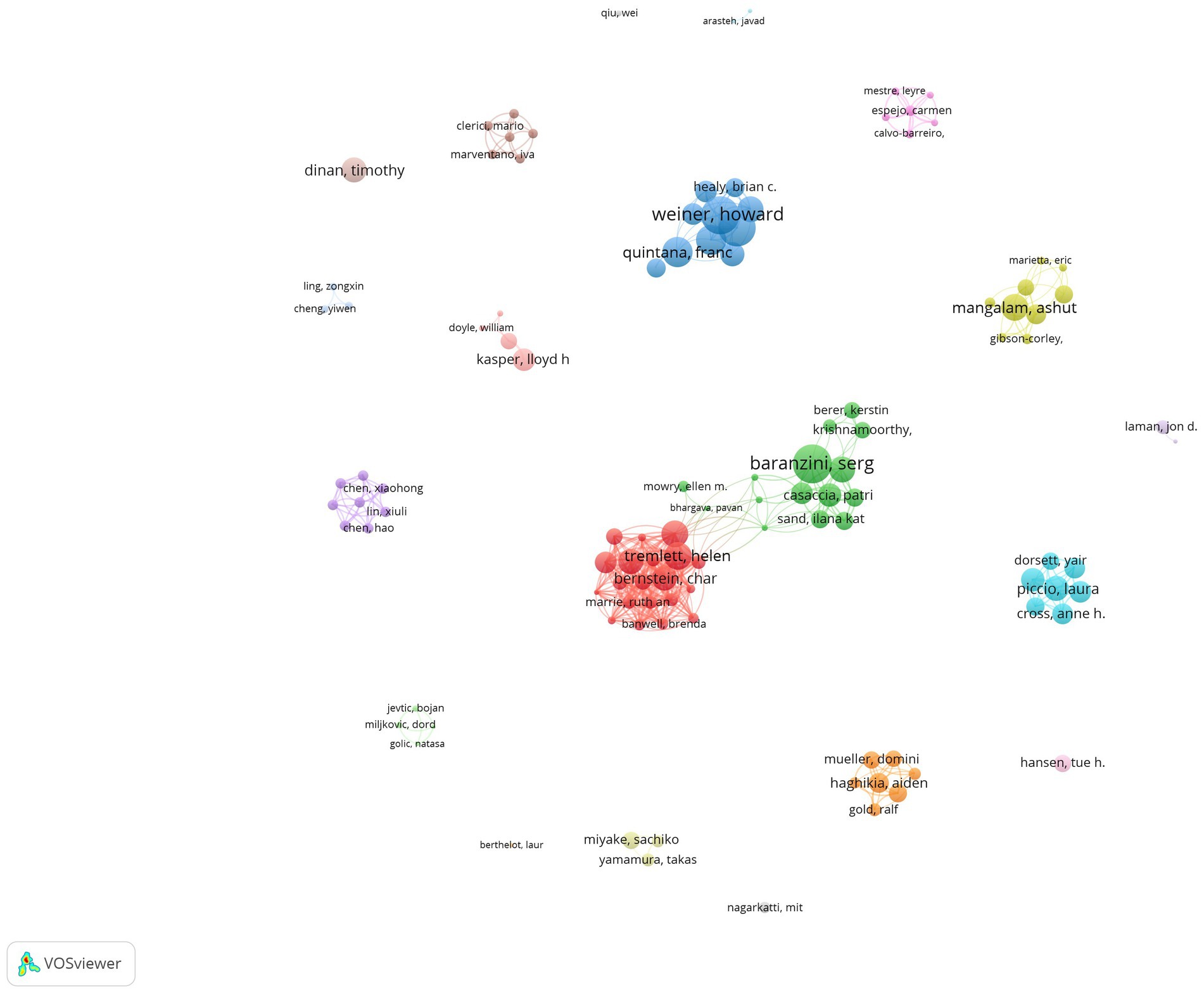
Figure 3. Network visualization of core authors. The larger the node, the greater the number of published articles. The node connection lines represent the strength of the relationship between authors.
The authors who have published more than 11 articles in this field are listed in Table 1, which displays the highly productive authors. The three authors with the most publications were found to be Helen Tremlett (14, 3.2%), Emmanuelle Waubant (13, 3.0%), and Lloyd H. Kasper (13, 3.0%). The most productive author was Helen Tremlett, having published 14 articles in this field. Her research has focused on the etiology, risk factors, and epidemiology of MS and gut microbiome research in demyelinating diseases. However, Lloyd H. Kasper was found to be the most influential author, having published 13 articles with the highest number of citations, with an average of 86.69 citations.
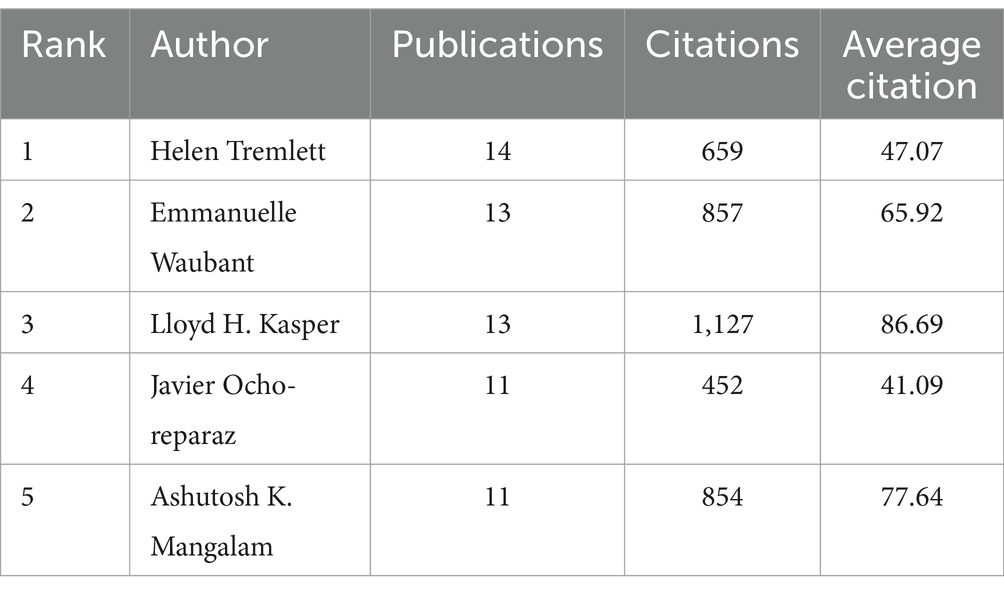
Table 1. Top five productive authors in the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating disease research field since 2014.
Since 2014, 47 countries have published articles in the field of the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases. Figure 4 shows the cooperative relationships between countries via VOSviewer and Microsoft Charticulator, and Table 2 presents the top five countries with the highest number of articles published, along with their respective publication and citation counts. To further analyze the high-productivity countries, we found that the United States has published the most articles (158, 36.8%), followed by the People’s Republic of China (54, 12.6%) and Italy (49, 11.4%). Notably, Canada has only 38 publications, but the number of citations is as high as 3,429, which is greater than that of the USA, the People’s Republic of China, and Italy and is closely related to Helen Tremlett. Helen Tremlett has contributed to the study of demyelinating diseases with numerous publications in high-impact journals. Furthermore, Microsoft Charticulator revealed that the most frequent collaboration has been between the United States and Canada (Figure 4).
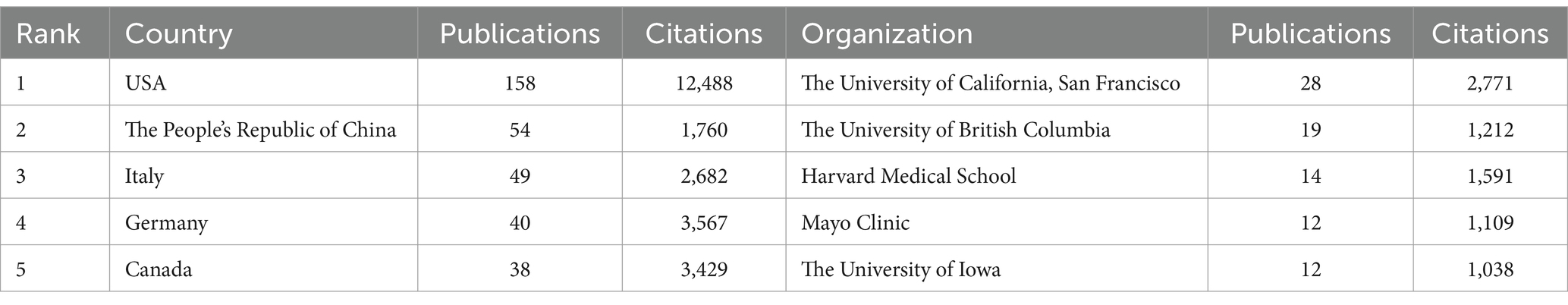
Table 2. Top five countries and organizations for publications in the field of the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases.
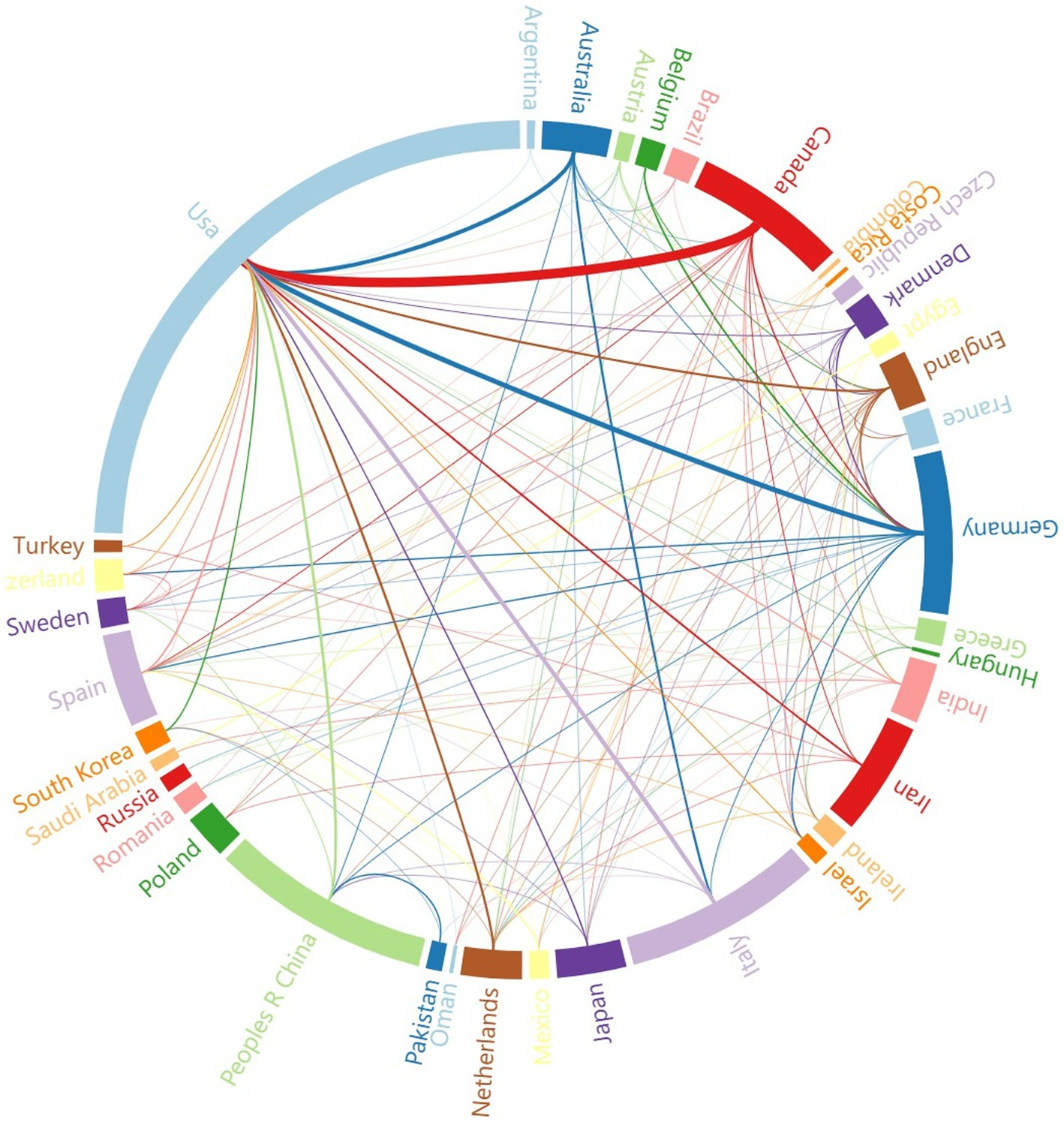
Figure 4. The cooperative relationship between countries. The thickness of the line represents the strength of the collaboration between countries.
An examination of institutional collaboration was carried out using VOSviewer, which ultimately led to the creation of a network map of institutional collaboration (Figure 5). The minimum publication threshold was set at 3, and 101 institutions met this criteria. As depicted in Figure 5, these institutions demonstrated close collaboration. The most significant research institution was found to be the University of California, San Francisco, which has the highest number of publications and citations. The University of British Columbia ranked second with 19 publications and 1,212 total citations. Among the top five organizations, four were from the USA and one was from Canada (Table 2). Moreover, among the top three authors in terms of publications, Helen Tremlett is affiliated with the University of British Columbia, followed by Emmanuelle Waubant and Lloyd H. Kasper, both of whom are from the USA, with Emmanuelle Waubant from the University of California, San Francisco. This observation is consistent with our previous research on authorship, further substantiating the reliability of our study.
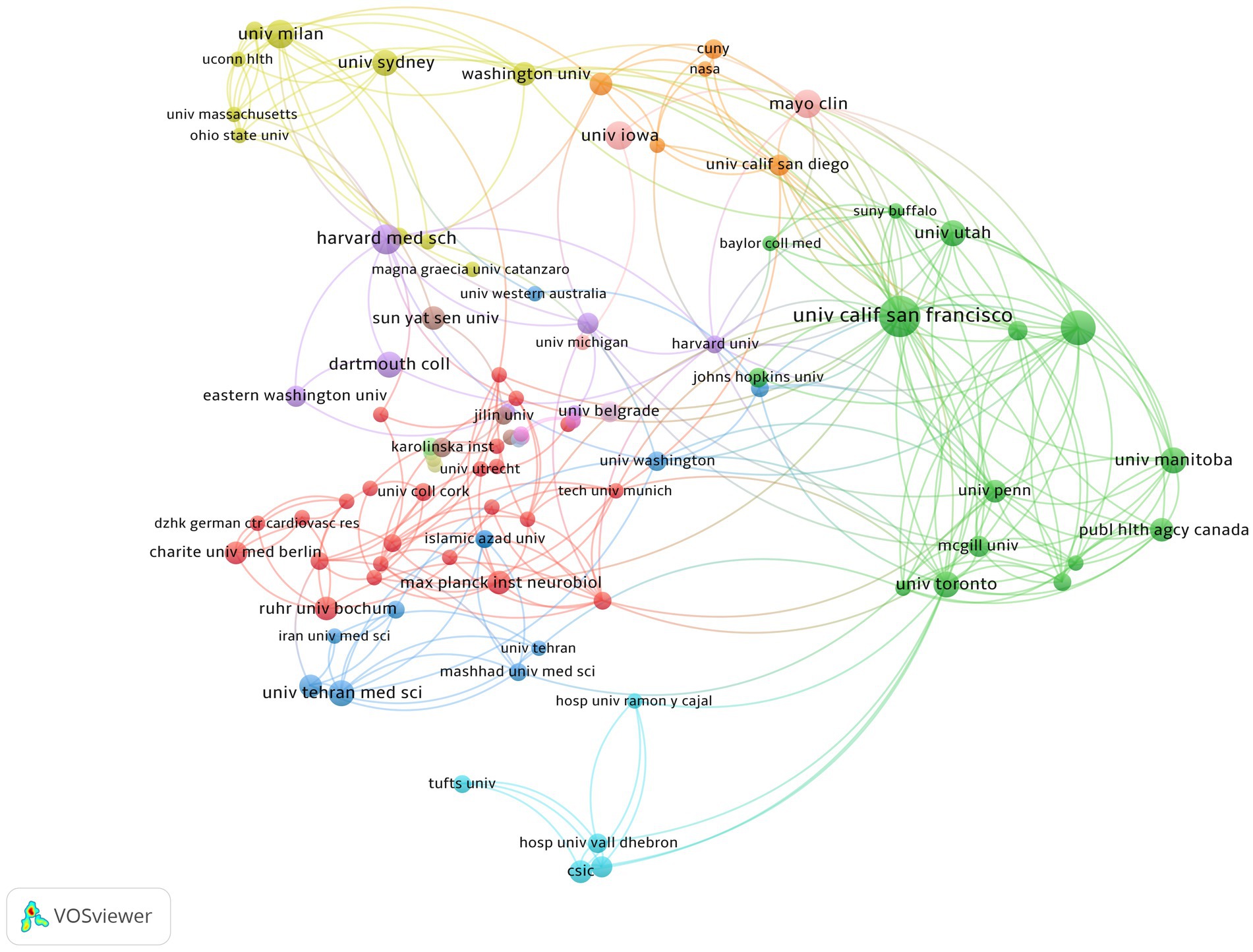
Figure 5. Cooperation map of intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases. The larger the node, the greater the publications, and the node connection lines represent the strength of the relationship between organizations.
A total of 429 articles related to the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases have been published across 193 journals. Figure 6 shows that after 2019, the number of articles published in the majority of the journals reached its highest point. The field of the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases has developed rapidly in the past 5 years, which is consistent with the findings shown in Figure 2. Table 3 lists the journals with the most publications in the top 10. Frontiers in Immunology was found to be the journal with the highest number of publications, with 33 articles, accounting for 7.7%. The International Journal of Molecular Sciences came in second with 21 articles, accounting for 4.9%, followed by Scientific Reports and the Multiple Sclerosis Journal with 14 articles, accounting for 3.3%. The journal with the most average citations was Scientific Reports, which published just 14 articles.
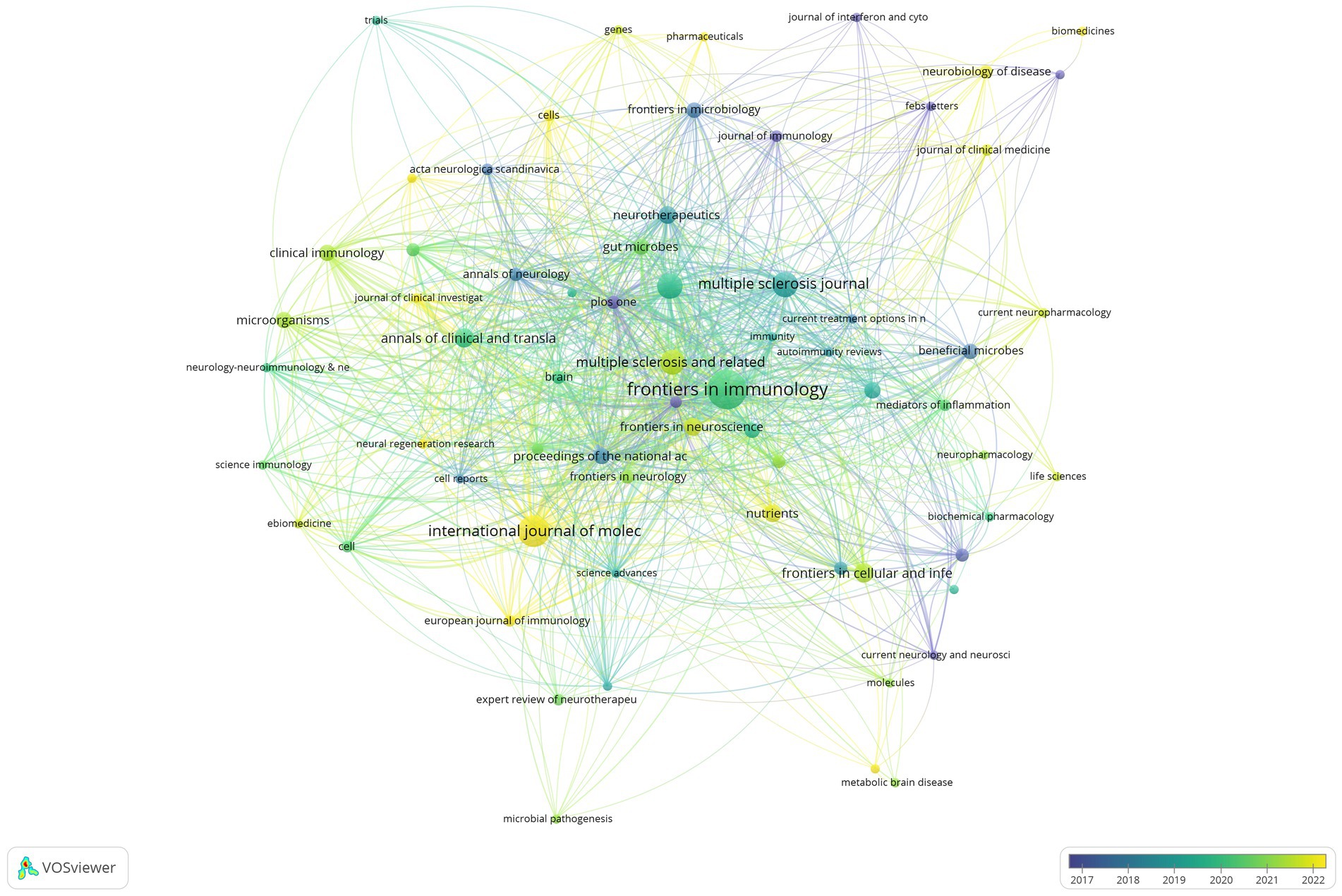
Figure 6. Visualization of the journal network. The larger the node is, the greater the volume of published articles and the node connection lines represent the strength of the relationship between journals. The darker the color, the earlier the article was published, and the lighter the color, the later the article was published.
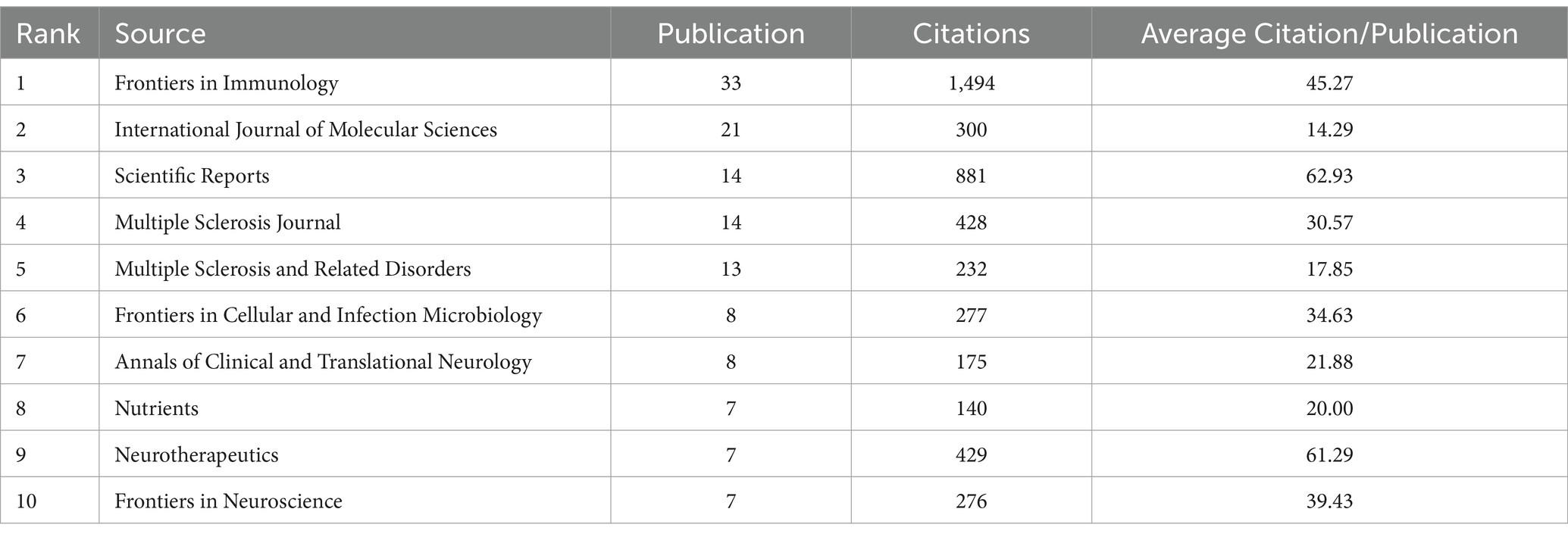
Table 3. Top 10 journals: the number of publications in intestinal microbiota and demyelinating disease research.
Keyword frequency reveals the focus and hot spots of a research field. Thus our analysis was conducted on 1,785 keywords in the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating disease research field using VOSviewer software (Figure 7A). We analyzed the frequency of co-occurring keywords related to the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases. The larger the node
the higher the frequency of keyword co-occurrence. The common top 10 keywords are listed in Table 4. The top three keywords were multiple sclerosis (frequency: 283), gut microbiota (frequency: 166), and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (frequency: 94).
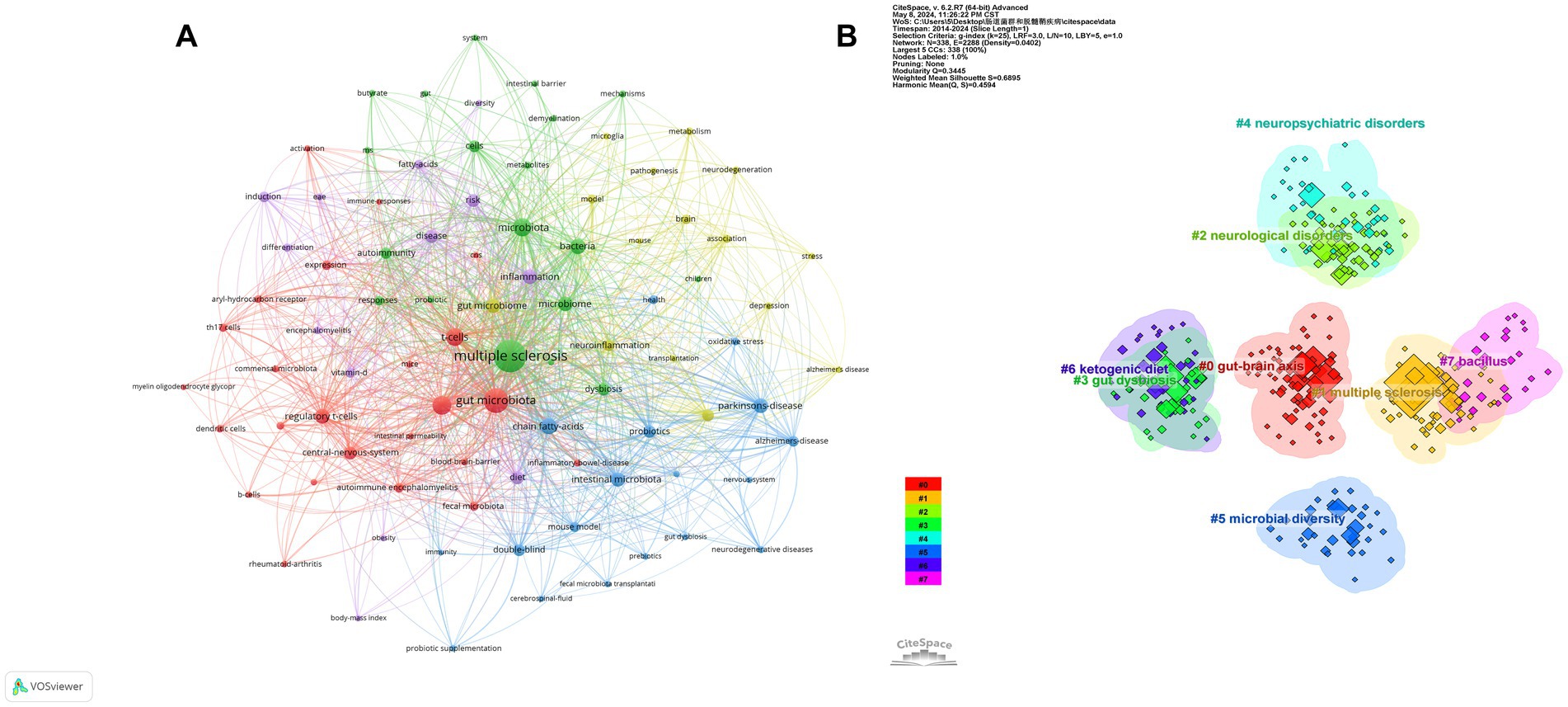
Figure 7. (A) The network map and cluster of keywords in intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases. The larger the node, the greater the frequency of keywords that appear. The node connection lines represent the strength of the relationship between keywords. (B) Visualization of the keywords cluster analysis. Each cluster is depicted with a unique color.
The keywords related to the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases were grouped into eight clusters using CiteSpace. These clusters were as follows: #0 for the gut–brain axis, #1 for multiple sclerosis, #2 for neurological disorders, #3 for gut dysbiosis, #4 for neuropsychiatric disorders, #5 for microbial diversity, #6 for the ketogenic diet, and #7 for bacillus (Figure 7B). A cluster’s average silhouette (S-value) is used as an indicator to evaluate clustering. According to earlier research, a silhouette coefficient (S) exceeding 0.5 is deemed acceptable, whereas an S-value greater than 0.7 signifies strong clustering evidence (Wang et al., 2022). In our study, each of the obtained clusters had an S-value greater than 0.5, suggesting that our results are reasonable (Table 4).
Finally, we identified 15 keywords with the strongest citation bursts since 2014 for the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases using CiteSpace (Figure 8). The keyword with the strongest citation burst was found to be regulatory T cells, which are a type of T-cell in the immune system. The primary function of regulatory T cells is to regulate the immune response and prevent autoimmune diseases and excessive immune responses (Ferreira et al., 2019).
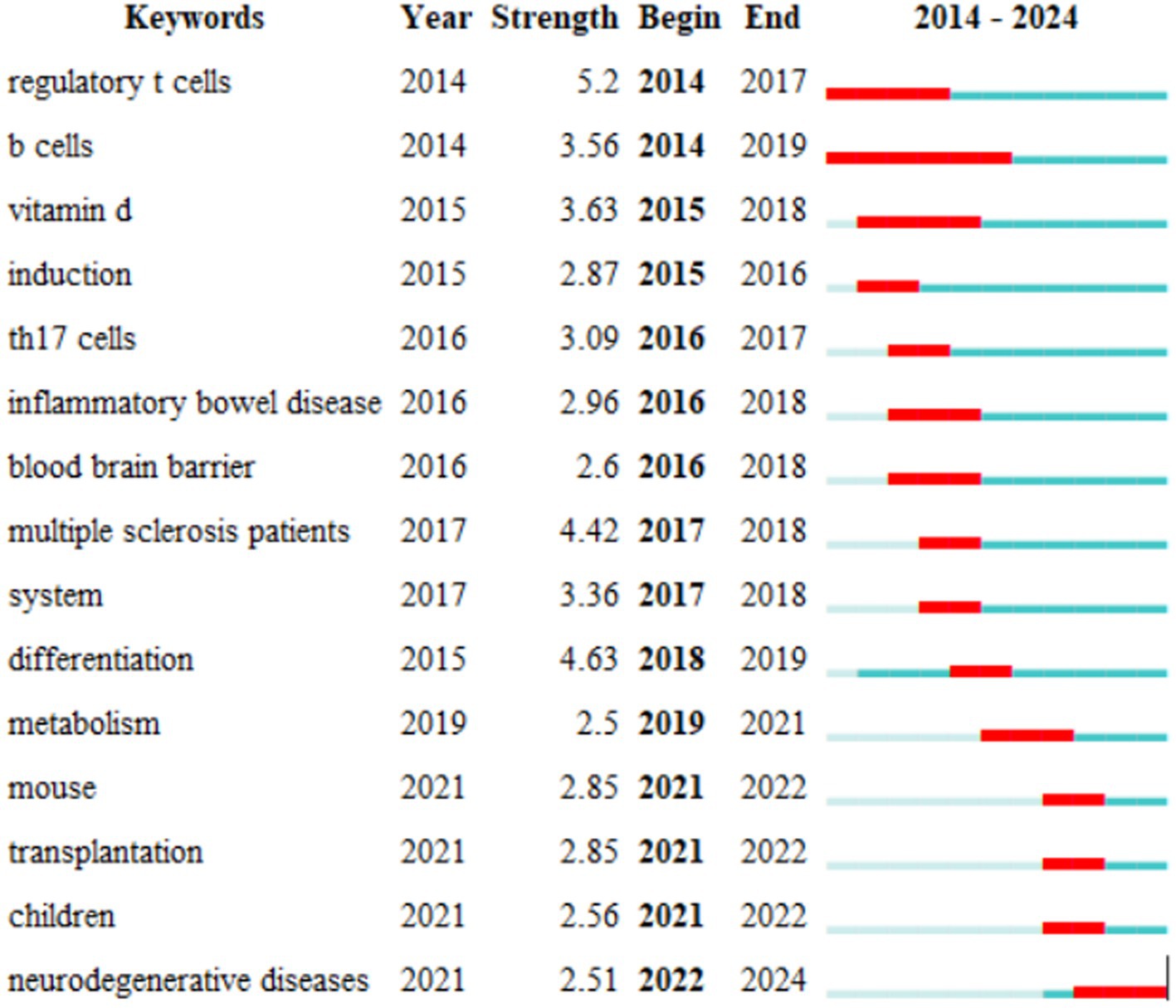
Figure 8. The top 15 keywords with the strongest citation bursts. The blue line represents the time interval, while the red line represents the period when the keyword bursts were found.
The analysis included a total of 23,774 cited publications sourced from 3,498 journals. First, we examined the five most frequently cited publications related to the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases (Table 5). The observations in Table 5 indicate that all highly cited publication types were found to be “Articles.” These publications focused on studying and analyzing the changes in and mechanisms of the gut microbiome in patients with autoimmune demyelination, including autoimmune encephalomyelitis, multiple sclerosis, and myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein IgG-associated disorders. However, the publication with the highest impact factor was “Commensal microbiota and myelin autoantigens cooperate to trigger autoimmune demyelination,” which was published in “Nature.” Moreover, among the top five most cited publications, three articles were published in JCR1 (JCR: Journal Citation Reports is a widely recognized tool used to evaluate the impact and influence of academic journals). Journals are often categorized into different quartiles based on their citation metrics. JCR1 refers to the top 25% of journals in a specific subject category, indicating the highest impact and most cited journals. One article is published in JCR2, which refers to the next 25% of journals, ranking between the 26th and 50th percentiles, and represents high-quality and influential journals, and One article is published in JCR3, which refers to the next 25% of journals, ranking between the 51st and 75th percentiles, and is still considered to have significant value and impact within its respective fields. The journal co-citation was observed to comprise three distinct clusters, which correspond to the three colors depicted in Figure 9. Most of the journals in the green cluster are comprehensive journals that explore the correlation between immunity and the gut microbiota. The journals in the blue cluster are dedicated to publishing articles on neurological and neuroimmune diseases. The journals in the red cluster focus on the overall study of the gut microbiota, with an emphasis on investigating the pathogenic mechanisms of the GBA in demyelinating diseases. The three journals with the highest citation frequencies were found to be Nature, PLOS One, and Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America.
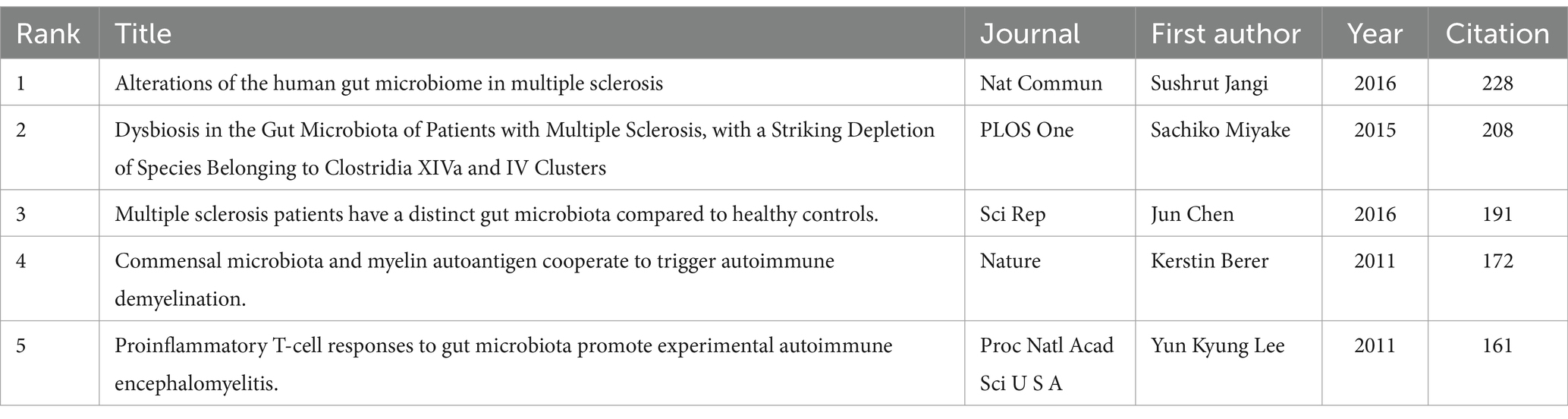
Table 5. Top five most cited publications in the research field of the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases.
The intestines represent the most extensive microecosystem in the human body. Under optimal conditions, the balance of the gut microbiota is extremely delicate. Disruptions caused by internal or external factors can upset this equilibrium and potentially result in illness (Sochocka et al., 2019). Research has shown that the gut microbiota plays a crucial role in the regulation of brain activity, which interacts with the metabolic, peripheral immune, and central nervous systems via the GBA (Chen et al., 2021; Hamamah et al., 2022; Ullah et al., 2023). Changes in the gut microbiota have been shown to influence neurological diseases such as MS (Tremlett et al., 2017). MS, a chronic demyelinating disease with an autoimmune etiology, is a multifaceted interplay involving a variety of genetic and environmental elements and is characterized by demyelination and varying levels of damage to axons (Garg and Smith, 2015). Research has revealed that the gut microbiota, through intricate mechanisms, plays a role in the development and maturation of the central nervous system (CNS), including the process of myelination (Pröbstel et al., 2020). Therefore, we used bibliometric analysis to study the relationship between the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases.
Bibliometric analyses have been conducted across various professional fields, including cardiovascular disease, infectious diseases, neurology, and oncology. However, a bibliometric analysis focusing on the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases remains uncommon. Our research analyzed 429 publications from the WoSCC database on the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases using VOSviewer, CiteSpace, and Charticulator. Research on the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases has shown a steadily increasing trend. However, from 2014 to 2016, studies in this field received limited attention from researchers, with an average annual publication output of only 14 articles. From 2017 to the study’s deadline, there was a notable surge in the number of publications, averaging 54.1 articles per year. This trend suggests that the field of the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases is currently undergoing rapid growth and garnering increasing attention from the academic community.
The USA, the People’s Republic of China, and Italy are the leading countries in research on the relationships between the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases (n = 261, 60.8%). Among the three countries, the USA ranks first, and approximately 80% of the top five organizations are located in the USA. The USA has made the most substantial contribution to the literature in the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases field, emphasizing the significant research contributions made by the USA in this field. In addition, our findings indicate that the USA has the most extensive collaborations with other countries, which is conducive to the long-term development of research on the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases. Therefore, we recommend that organizations worldwide engage in broad, cross-institutional, and even cross-national collaborations to further advance the understanding of the correlation between the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases. Among the top five organizations in terms of the number of publications, three are tied for fourth place and six are tied for fifth place. Half of these organizations are based in the USA, including the University of California, San Francisco, Harvard Medical School, Mayo Clinic, University of Iowa, Dartmouth College, and University of Utah. The USA has received a high level of attention and importance in the field of the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases. Based on these data, to advance the field, increased collaboration between more countries and institutions in the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating disease research is necessary.
From the perspective of the author, when evaluating prolific authors, it is essential to consider both the number of publications and the number of citations they have received. In terms of the number of publications, Helen Tremlett from the University of British Columbia, Canada, has the highest number of publications, followed by Emmanuelle Waubant, Lloyd H. Kasper, Javier Ocho-reparaz, and Ashutosh K. Mangalam. Her research has focused on the etiology, risk factors, and epidemiology of MS, as well as gut microbiome research in demyelinating diseases. She and her colleagues published an article in the Lancet Neurol and conducted the first systematic exploration of risk factors for multiple sclerosis, laying the foundation for subsequent investigations into the disease’s underlying mechanisms and potential interventions (McKay and Tremlett, 2015). Furthermore, Helen Tremlett and her colleagues identified the gut microbiome commonly linked to pediatric patients with multiple sclerosis and established a sizable biobank of stool samples from children with MS, published in JAMA Neurology (Tremlett and Waubant, 2018). Her significant contribution to the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating disease field suggests that she has been actively involved in advancing the knowledge and understanding of this field. Regarding publication citations, Lloyd H. Kasper from Dartmouth College has the highest number of publication citations, with an average of 86.69 citations. Following him are Ashutosh K. Mangalam, Emmanuelle Waubant, Helen Tremlett, and Javier Ocho-reparaz. A high number of citations usually indicates that these publications have a significant influence on the academic community and are widely acknowledged and referenced. The finding reflects the contributions and reputation of Lloyd H. Kasper’s team or academic institution within the field of the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases. It has had a substantial impact on the academic community as his work has been widely recognized and referenced by other researchers.
Regarding the number of publications, the top five most active journals are Frontiers in Immunology (n = 33), International Journal of Molecular Sciences (n = 21), Scientific Reports (n = 12), Multiple Sclerosis Journal (n = 14), and Multiple Sclerosis and Related Disorders (n = 13). As the journal with the highest number of publications and total citations in this field, Frontiers in Immunology (IF: 7.3 JCR2) holds a leading position in research on the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases. Nevertheless, Scientific Reports (IF: 4.2 JCR2) has the highest average citations/publications. This inconsistency highlights the profound influence and quality of the publications in Frontiers in Immunology.
Most cited publications are works that have been referenced by other researchers. They play a crucial role in academic research by providing a foundation for new studies, acknowledging the contributions of previous studies, and helping to build a comprehensive understanding of a particular field. In our research, we found that the top five most cited publications are committed to studying and analyzing the changes in and mechanism of the gut microbiome in patients with autoimmune demyelination, including autoimmune encephalomyelitis, multiple sclerosis, and myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein IgG-associated disorders. The publication with the greatest impact factor was found to be “Commensal microbiota and myelin autoantigens cooperate to trigger autoimmune demyelination,” which was published in “Nature.” The study presented the first description of the sequential roles of intact gut microbiota and myelin autoantigens in the onset of a sophisticated, spontaneous demyelinating autoimmune condition. Furthermore, the authors suggested that dietary risk factors may play a role, potentially contributing to the noticeable rise in the incidence of multiple sclerosis in Asian countries, such as Japan, a phenomenon often attributed to the adoption of a “Westernized” lifestyle (Berer et al., 2011).
Keywords represent the words of the core and are highly refined in an article. In bibliometrics frequently used keywords help pinpoint the main areas of focus and emerging trends within a specific research domain. Based on the cluster analysis and keyword co-occurrence map produced using CiteSpace and VOSviewer it was found that the majority of scholars focused on “multiple sclerosis (n = 284)” and “gut microbiota (n = 166)” in the field of the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases which led to the identification of keywords. In demyelinating diseases of the nervous system the relationships between MS and the gut microbiota have been extensively studied (Correale et al., 2022; Altieri et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2022). Currently the primary research focus is on the GBA MS neurological disorders microbial diversity the ketogenic diet and bacillus
The GBA acts as a bidirectional link between the gut microbiome and the immune system, potentially enhancing our understanding of the pathophysiology of inflammatory demyelinating diseases (Camara-Lemarroy et al., 2018). The communication between the vagus nerve and enteric nervous system is an important connection between the CNS and the gut. One of the pathways through which the brain communicates with the intestinal microbiota involves direct interaction via the vagus nerve with the spinal cord (Shokufeh Ghasemian et al., 2022). Gut microbiota establishes a direct neural link between the brain and gastrointestinal microbiota via the vagus nerve and the activation of the enteric nervous system afferent neurons (Neil, 2017). In addition, they can transmit microbial signals either through the diffusion of compounds or with the help of other cells (Bonaz et al., 2018), highlighting the complicated interplay and pathophysiology between the gut and CNS. Another crucial link between the CNS and the gut is through the bloodstream. The gut microbiome can generate a wide array of microbial components, metabolites, and neurotransmitters, which are released into the bloodstream and directly influence the CNS to regulate the host’s neural function and immune response (Lai et al., 2021). In other words, communication between the brain and the gastrointestinal tract is bidirectional and intricate.
MS is an autoimmune disease of the CNS characterized by demyelination, axonal damage, and degeneration, and increasing evidence indicates that the GBA may play a vital role in neurological disorders such as MS (iMSMS Consortium, 2022; Parodi et al., 2021). A previous study revealed that changes in the composition of the intestinal microbiota, leading to an impaired immune system, could initiate the development of MS or exacerbate its symptoms (Fan and Zhang, 2019). Diet and dietary elements significantly influence the composition of the gut microbiota and are key factors in altering the bacterial flora. A ketogenic diet can alter the composition of the gut microbiota (Beam et al., 2021; Olson et al., 2018). MS causes damage to the myelin sheaths that protect neurons, thereby disrupting the normal transmission of nerve impulses. Research indicates that a ketogenic diet may contribute to the potential reconstruction and repair of the myelin sheaths (Dyńka et al., 2022). Objective evidence suggests that the use of a ketogenic diet in the treatment of MS is recognized. It can influence the progression and prevention of the disease while also being safe and feasible to implement (Lin et al., 2022).
Moreover, Berer et al. demonstrated that gut commensal bacteria could initiate a relapsing–remitting autoimmune disease characterized by demyelination and driven by myelin-specific CD4+ T cells in transgenic mice (Berer et al., 2011). In addition, among peripheral immune cells, intestinal Th17 cells have been reported to play a crucial role in the immunopathology of MS (Steinman, 2001). Research has revealed that Th17 cells are prevalent in the peripheral blood, cerebrospinal fluid, and brain lesions of individuals with MS, with elevated levels and increased levels of inflammatory mediators observed during disease recurrence (Moser et al., 2020). These findings indicate that reducing pathogenic Th17 cells may help prevent the recurrence of autoimmunity in individuals with MS (Sie et al., 2014; Issazadeh-Navikas et al., 2012). Similarly, alterations in the gut microbiota or its metabolites can also modulate inflammation and demyelination in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (Lee et al., 2011). Evidence indicates that changes in the composition and diversity of the microbiome may affect the progression of MS (Zangeneh et al., 2021). In the treatment of relapsing–remitting MS, monoclonal B-cell-depleting antibodies have shown significant efficacy in controlling inflammation (Laurent et al., 2023). Researchers analyzed oral swab samples using 16S rDNA sequencing followed by bioinformatic analyses. The study revealed that patients with MS displayed lower alpha diversity in their oral microbiota patterns, while an increase in alpha diversity was observed in the gut microbiota of these patients following B-cell depletion (Troci et al., 2022). The relationship between changes in the intestinal microbiota and MS has not been thoroughly studied and necessitates further investigation.
CD4+ T cells (Th17 cells), which produce IL-17, are implicated in the development of various autoimmune and inflammatory diseases and are known to play a significant role in the intestinal mucosa (Schnell et al., 2023). Research has confirmed that human Th17 lymphocytes contribute to the disruption of the blood–brain barrier and that antigen-specific Th17 cells migrate through the choroid plexus into the subarachnoid space and then become reactivated (Kebir et al., 2007). A significant influx of activated Th17 cells and other inflammatory cells into the white matter of the CNS leads to tissue damage, including demyelination, ultimately causing neurological deficits (Zepp et al., 2011). During acute episodes of MS, particularly in patients with relapsing–remitting MS, there is a notable increase in the frequency of Th17 cells in both the peripheral blood and cerebrospinal fluid (Matusevicius et al., 1999). Moreover, successful therapeutic interventions in patients with MS have been linked to a decrease in Th17 cells in the peripheral blood (Mehling et al., 2010; Durelli et al., 2009). Chris et al. confirmed that the concentration of IL-17 in patients with MS is directly proportional to the number of active lesions observed through magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (Hedegaard et al., 2008).
Furthermore, a connection has been established between Th17 cells and the pathogenesis of neuromyelitis optica (NMO), along with its spectrum of disorders known as NMOSD. In patients with NMO who test positive for AQP4-IgG, a defining characteristic is astrocyte damage that results in secondary demyelination (Dos Passos et al., 2016). In conclusion, Th17 cells might be important in driving the pathology of demyelinating diseases.
Our study provides the first comprehensive systematic bibliometric analysis of the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases, offering extensive insights and directions for both clinical practitioners and academic researchers in this domain. The application of bibliometric techniques, coupled with visual methods, enables scientists to gain a clear and direct understanding of focal areas, progression, and emerging trends within research on the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating conditions. However, our study also has limitations. Our analysis was limited to articles that appeared on WoSCC during a designated period and were written in English, which might have led to the exclusion of findings from alternative databases. Nevertheless, using visual methods to discern the prevailing conditions, focal points, and directional shifts within an academic domain continues to be beneficial.
Using VOSviewer, CiteSpace, and Charticulator, we conducted a bibliometric analysis of articles related to the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases. Following the identification of significant articles, authors, journals, institutions, and countries, we conducted an additional analysis of the research network. Owing to the increasing annual publication volume of related literature, the relationship between the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases has attracted growing attention. Regarding the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases, Helen Tremlett stands out as the most prolific author, having published 30 articles that have garnered 659 citations. The USA, the People’s Republic of China, and Italy are the leading countries where the relationships between the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases have been studied. Furthermore, while there is currently limited collaboration among various countries, strengthening partnerships and communication between different nations and organizations is crucial. The publications of Helen Tremlett and Lloyd H. Kasper have shaped the current understanding of the role of the gut microbiota in demyelinating diseases. Furthermore, this comprehensive analysis underscores the importance of continued research into the role of the gut microbiome in disease, particularly in the context of demyelinating diseases such as multiple sclerosis. The relationships and underlying processes linking the gut microbiota to demyelinating diseases remain key research topics. The insights gained from this analysis will help guide future research directions, potentially leading to breakthroughs in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of these complex conditions.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
LC: Conceptualization, Software, Writing – original draft. L-LW: Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft. C-YY: Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. Z-CX: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. HH: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81760247, 82171450, and 32160190), the Graduate Workstation of Neurology, Zunyi Medical College (No. GZZ2017004), the Collaborative Innovation Center of the Chinese Ministry of Education (2020-39) and the Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Foundation (No. (2019) 1350).
We would like to thank Yi Zhou for his invaluable academic advice.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Altieri, C., Speranza, B., Corbo, M. R., Sinigaglia, M., and Bevilacqua, A. (2023). Gut-microbiota, and multiple sclerosis: background, evidence, and perspectives. Nutrients 15:15. doi: 10.3390/nu15040942
Beam, A., Clinger, E., and Hao, L. (2021). Effect of diet and dietary components on the composition of the gut microbiota. Nutrients 13:13. doi: 10.3390/nu13082795
Berer, K., Mues, M., Koutrolos, M., Rasbi, Z. A., Boziki, M., Johner, C., et al. (2011). Commensal microbiota and myelin autoantigen cooperate to trigger autoimmune demyelination. Nature 479, 538–541. doi: 10.1038/nature10554
Bernardo, A., and Visentin, S. (2023). Demyelinating diseases: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24:24. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054596
Bogiatzi, C., Gloor, G., Allen-Vercoe, E., Reid, G., Wong, R. G., Urquhart, B. L., et al. (2018). Metabolic products of the intestinal microbiome and extremes of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 273, 91–97. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2018.04.015
Bonaz, B., Bazin, T., and Pellissier, S. (2018). The Vagus nerve at the Interface of the microbiota-gut-brain Axis. Front. Neurosci. 12:49. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00049
Cabrera-Mulero, A., Tinahones, A., Bandera, B., Moreno-Indias, I., Macías-González, M., and Tinahones, F. J. (2019). Keto microbiota: a powerful contributor to host disease recovery. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 20, 415–425. doi: 10.1007/s11154-019-09518-8
Camara-Lemarroy, C. R., Metz, L. M., and Yong, V. W. (2018). Focus on the gut-brain axis: multiple sclerosis, the intestinal barrier and the microbiome. World J. Gastroenterol. 24, 4217–4223. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i37.4217
Chen, Y., Xu, J., and Chen, Y. (2021). Regulation of neurotransmitters by the gut microbiota and effects on cognition in neurological disorders. Nutrients 13:13. doi: 10.3390/nu13062099
Cheng, X., Zhou, L., Li, Z., Shen, S., Zhao, Y., Liu, C., et al. (2022). Gut microbiome and bile acid metabolism induced the activation of CXCR5+ CD4+ T follicular helper cells to participate in Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum disorder recurrence. Front. Immunol. 13:827865. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.827865
Chidambaram, S. B., Rathipriya, A. G., Mahalakshmi, A. M., Sharma, S., Hediyal, T. A., Ray, B., et al. (2022). The influence of gut Dysbiosis in the pathogenesis and Management of Ischemic Stroke. Cells 11:1239. doi: 10.3390/cells11071239
Clemente, J. C., Ursell, L. K., Parfrey, L. W., and Knight, R. (2012). The impact of the gut microbiota on human health: an integrative view. Cell 148, 1258–1270. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.01.035
Correale, J., Hohlfeld, R., and Baranzini, S. E. (2022). The role of the gut microbiota in multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 18, 544–558. doi: 10.1038/s41582-022-00697-8
Cryan, J. F., O'Riordan, K. J., Cowan, C. S. M., Sandhu, K. V., Bastiaanssen, T. F. S., Boehme, M., et al. (2019). The microbiota-gut-brain Axis. Physiol. Rev. 99, 1877–2013. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00018.2018
Cryan, J., O'Riordan, K., Sandhu, K., Peterson, V., and Dinan, T. (2020). The gut microbiome in neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol. 19, 179–194. doi: 10.1016/s1474-4422(19)30356-4
Dissanayaka, D. M. S., Jayasena, V., Rainey-Smith, S. R., Martins, R. N., and Fernando, W. M. A. D. B. (2024). The role of diet and gut microbiota in Alzheimer's disease. Nutrients 16:412. doi: 10.3390/nu16030412
Dos Passos, G. R., Sato, D. K., Becker, J., and Fujihara, K. (2016). Th17 cells pathways in multiple sclerosis and Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum disorders: pathophysiological and therapeutic implications. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016:5314541. doi: 10.1155/2016/5314541
Durelli, L., Conti, L., Clerico, M., Boselli, D., Contessa, G., Ripellino, P., et al. (2009). T-helper 17 cells expand in multiple sclerosis and are inhibited by interferon-beta. Ann. Neurol. 65, 499–509. doi: 10.1002/ana.21652
Dyńka, D., Kowalcze, K., and Paziewska, A. (2022). The role of ketogenic diet in the treatment of neurological diseases. Nutrients 14:14. doi: 10.3390/nu14235003
Fan, Y., and Zhang, J. (2019). Dietary modulation of intestinal microbiota: future opportunities in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosis. Front. Microbiol. 10:740. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00740
Ferreira, L. M. R., Muller, Y. D., Bluestone, J. A., and Tang, Q. (2019). Next-generation regulatory T cell therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 18, 749–769. doi: 10.1038/s41573-019-0041-4
Gao, W., Salzwedel, A. P., Carlson, A. L., Xia, K., Azcarate-Peril, M. A., Styner, M. A., et al. (2019). Gut microbiome and brain functional connectivity in infants-a preliminary study focusing on the amygdala. Psychopharmacology 236, 1641–1651. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-5161-8
Garg, N., and Smith, T. W. (2015). An update on immunopathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of multiple sclerosis. Brain Behav. 5:e00362. doi: 10.1002/brb3.362
Ghezzi, L., Cantoni, C., Pinget, G. V., Zhou, Y., and Piccio, L. (2021). Targeting the gut to treat multiple sclerosis. J. Clin. Invest. 131:131. doi: 10.1172/JCI143774
Hamamah, S., Aghazarian, A., Nazaryan, A., Hajnal, A., and Covasa, M. (2022). Role of microbiota-gut-brain Axis in regulating dopaminergic signaling. Biomedicines 10:436. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10020436
Hedegaard, C. J., Krakauer, M., Bendtzen, K., Lund, H., Sellebjerg, F., and Nielsen, C. H. (2008). T helper cell type 1 (Th1), Th2 and Th17 responses to myelin basic protein and disease activity in multiple sclerosis. Immunology 125, 161–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.02837.x
Heiss, C. N., and Olofsson, L. E. (2019). The role of the gut microbiota in development, function and disorders of the central nervous system and the enteric nervous system. J. Neuroendocrinol. 31:e12684. doi: 10.1111/jne.12684
iMSMS Consortium (2022). Gut microbiome of multiple sclerosis patients and paired household healthy controls reveal associations with disease risk and course. Cell 185, 3467–3486.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.08.021
Issazadeh-Navikas, S., Teimer, R., and Bockermann, R. (2012). Influence of dietary components on regulatory T cells. Mol. Med. 18:311. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2011.00311
Kang, D.-W., Adams, J. B., Coleman, D. M., Pollard, E. L., Maldonado, J., McDonough-Means, S., et al. (2019). Long-term benefit of microbiota transfer therapy on autism symptoms and gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 9:5821. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42183-0
Kebir, H., Kreymborg, K., Ifergan, I., Dodelet-Devillers, A., Cayrol, R., Bernard, M., et al. (2007). Human TH17 lymphocytes promote blood-brain barrier disruption and central nervous system inflammation. Nat. Med. 13, 1173–1175. doi: 10.1038/nm1651
Lai, Y., Liu, C.-W., Yang, Y., Hsiao, Y.-C., Ru, H., and Lu, K. (2021). High-coverage metabolomics uncovers microbiota-driven biochemical landscape of interorgan transport and gut-brain communication in mice. Nat. Commun. 12:6000. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26209-8
Laurent, S. A., Strauli, N. B., Eggers, E. L., Wu, H., Michel, B., Demuth, S., et al. (2023). Effect of Ocrelizumab on B- and T-cell receptor repertoire diversity in patients with relapsing multiple sclerosis from the randomized phase III OPERA trial. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflam. 10:10. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000200118
Lee, Y. K., Menezes, J. S., Umesaki, Y., and Mazmanian, S. K. (2011). Proinflammatory T-cell responses to gut microbiota promote experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108, 4615–4622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1000082107
Lin, W.-S., Lin, S.-J., Liao, P.-Y., Suresh, D., Hsu, T.-R., and Wang, P.-Y. (2022). Role of ketogenic diets in multiple sclerosis and related animal models: an updated review. Adv. Nutr. 13, 2002–2014. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmac065
Luczynski, P., McVey Neufeld, K.-A., Oriach, C. S., Clarke, G., Dinan, T. G., and Cryan, J. F. (2016). Growing up in a bubble: using germ-free animals to assess the influence of the gut microbiota on brain and behavior. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 19:pyw020. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyw020
Matusevicius, D., Kivisäkk, P., He, B., Kostulas, N., Ozenci, V., Fredrikson, S., et al. (1999). Interleukin-17 mRNA expression in blood and CSF mononuclear cells is augmented in multiple sclerosis. Multiple Sclerosis 5, 101–104. doi: 10.1177/135245859900500206
McKay, K. A., and Tremlett, H. (2015). The systematic search for risk factors in multiple sclerosis. The lancet. Neurology 14, 237–238. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(15)70015-3
Mehling, M., Lindberg, R., Raulf, F., Kuhle, J., Hess, C., Kappos, L., et al. (2010). Th17 central memory T cells are reduced by FTY720 in patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurology 75, 403–410. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181ebdd64
Moser, T., Akgün, K., Proschmann, U., Sellner, J., and Ziemssen, T. (2020). The role of TH17 cells in multiple sclerosis: therapeutic implications. Autoimmun. Rev. 19:102647. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102647
Neil, J. V. (2017). Animal communication: when I'm calling you, will you answer too? Curr. Biol. 27, R713–R715. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2017.05.064
Olson, C. A., Vuong, H. E., Yano, J. M., Liang, Q. Y., Nusbaum, D. J., and Hsiao, E. Y. (2018). The gut microbiota mediates the anti-seizure effects of the ketogenic diet. Cell 173, 1728–1741.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.04.027
Parodi, B., and Kerlero de Rosbo, N. (2021). The gut-brain Axis in multiple sclerosis. Is its dysfunction a pathological trigger or a consequence of the disease? Front. Immunol. 12:718220. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.718220
Preiningerova, J. L., Jiraskova Zakostelska, Z., Srinivasan, A., Ticha, V., Kovarova, I., Kleinova, P., et al. (2022). Multiple sclerosis and microbiome. Biomol. Ther. 12:12. doi: 10.3390/biom12030433
Pröbstel, A.-K., Zhou, X., Baumann, R., Wischnewski, S., Kutza, M., Rojas, O. L., et al. (2020). Gut microbiota-specific IgA+ B cells traffic to the CNS in active multiple sclerosis. Sci. Immunol. 5:5. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abc7191
Schnell, A., Littman, D. R., and Kuchroo, V. K. (2023). TH17 cell heterogeneity and its role in tissue inflammation. Nat. Immunol. 24, 19–29. doi: 10.1038/s41590-022-01387-9
Seguella, L., Capuano, R., Sarnelli, G., and Esposito, G. (2019). Play in advance against neurodegeneration: exploring enteric glial cells in gut-brain axis during neurodegenerative diseases. Expert. Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 12, 555–564. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2019.1612744
Shokufeh Ghasemian, S., Hanieh Shakeri, M., Reza, J.-E., and Saman, S. (2022). A comprehensive review on the role of the gut microbiome in human neurological disorders. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 35:e0033820. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00338-20
Sie, C., Korn, T., and Mitsdoerffer, M. (2014). Th17 cells in central nervous system autoimmunity. Exp. Neurol. 262, 18–27. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.03.009
Socała, K., Doboszewska, U., Szopa, A., Serefko, A., Włodarczyk, M., Zielińska, A., et al. (2021). The role of microbiota-gut-brain axis in neuropsychiatric and neurological disorders. Pharmacol. Res. 172:105840. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105840
Sochocka, M., Donskow-Łysoniewska, K., Diniz, B. S., Kurpas, D., Brzozowska, E., and Leszek, J. (2019). The gut microbiome alterations and inflammation-driven pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease-a critical review. Mol. Neurobiol. 56, 1841–1851. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1188-4
Steinman, L. (2001). Multiple sclerosis: a two-stage disease. Nat. Immunol. 2, 762–764. doi: 10.1038/ni0901-762
Thirion, F., Sellebjerg, F., Fan, Y., Lyu, L., Hansen, T. H., Pons, N., et al. (2023). The gut microbiota in multiple sclerosis varies with disease activity. Genome Med. 15:1. doi: 10.1186/s13073-022-01148-1
Tremlett, H., Bauer, K. C., Appel-Cresswell, S., Finlay, B. B., and Waubant, E. (2017). The gut microbiome in human neurological disease: a review. Ann. Neurol. 81, 369–382. doi: 10.1002/ana.24901
Tremlett, H., and Waubant, E. (2018). Gut microbiome and pediatric multiple sclerosis. Multiple Sclerosis 24, 64–68. doi: 10.1177/1352458517737369
Troci, A., Zimmermann, O., Esser, D., Krampitz, P., May, S., Franke, A., et al. (2022). B-cell-depletion reverses dysbiosis of the microbiome in multiple sclerosis patients. Sci. Rep. 12:3728. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-07336-8
Ullah, H., Arbab, S., Tian, Y., Liu, C. Q., Chen, Y., Qijie, L., et al. (2023). The gut microbiota-brain axis in neurological disorder. Front. Neurosci. 17:1225875. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1225875
Umbrello, G., and Esposito, S. (2016). Microbiota and neurologic diseases: potential effects of probiotics. J. Transl. Med. 14:298. doi: 10.1186/s12967-016-1058-7
Wang, Y., Huo, X., Li, W., Xiao, L., Li, M., Wang, C., et al. (2022). Knowledge atlas of the co-occurrence of epilepsy and autism: a bibliometric analysis and visualization using VOSviewer and CiteSpace. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 18, 2107–2119. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S378372
Wang, Y., and Kasper, L. H. (2014). The role of microbiome in central nervous system disorders. Brain Behav. Immun. 38, 1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2013.12.015
Wang, X., Liang, Z., Wang, S., Ma, D., Zhu, M., and Feng, J. (2022). Role of gut microbiota in multiple sclerosis and potential therapeutic implications. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 20, 1413–1426. doi: 10.2174/1570159X19666210629145351
Wang, Y., Zhuo, Z., and Wang, H. (2023). Epilepsy, gut microbiota, and circadian rhythm. Front. Neurol. 14:1157358. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1157358
Wijesekara, T., Abeyrathne, E. D. N. S., and Ahn, D. U. (2024). Effect of bioactive peptides on gut microbiota and their relations to human health. Food Secur. 13:1853. doi: 10.3390/foods13121853
Wu, H., Li, Y., Tong, L., Wang, Y., and Sun, Z. (2021). Worldwide research tendency and hotspots on hip fracture: a 20-year bibliometric analysis. Arch. Osteoporos. 16:73. doi: 10.1007/s11657-021-00929-2
Zangeneh, Z., Abdi-Ali, A., Khamooshian, K., Alvandi, A., and Abiri, R. (2021). Bacterial variation in the oral microbiota in multiple sclerosis patients. PLoS One 16:e0260384. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0260384
Zepp, J., Wu, L., and Li, X. (2011). IL-17 receptor signaling and T helper 17-mediated autoimmune demyelinating disease. Trends Immunol. 32, 232–239. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2011.02.007
Zhao, Z., Ning, J., Bao, X. Q., Shang, M., Ma, J., Li, G., et al. (2021). Fecal microbiota transplantation protects rotenone-induced Parkinson's disease mice via suppressing inflammation mediated by the lipopolysaccharide-TLR4 signaling pathway through the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Microbiome 9:226. doi: 10.1186/s40168-021-01107-9
Keywords: intestinal microbiota, multiple sclerosis, demyelinating diseases, bibliometrics, visualization analysis
Citation: Chen L, Wu L-L, Yu C-Y, Xu Z-C and Huang H (2025) Bibliometric analysis of the intestinal microbiota and demyelinating diseases, particularly multiple sclerosis, since 2014. Front. Neurosci. 19:1506566. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1506566
Received: 10 October 2024; Accepted: 19 February 2025;
Published: 05 March 2025.
Edited by:
Domizia Vecchio, University of Eastern Piedmont, ItalyReviewed by:
Giuseppe Cappellano, Scuola di Medicina, Università degli Studi del Piemonte Orientale, ItalyCopyright © 2025 Chen, Wu, Yu, Xu and Huang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hao Huang, aGFvaHVhbmczMjVAMTYzLmNvbQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.