- Department of Acupuncture and Tuina, Changchun University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Changchun, China
Objective: Although fMRI has been widely used in the field of acupuncture. However, the literature analysis in this field still has significant differences. This study summarizes the current status of functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) in the field of acupuncture and moxibustion and predicts its future trends through Web of Science bibliometric analysis.
Methods: This study uses “fMRI” and “acupuncture” as keywords to search for literature related to functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) in acupuncture research in the Web of Science Core Collection database from January 1, 2004, to April 30, 2024. Visualization analyses were conducted using Citespace (version 6.3 R1) and VOSviewer (version 1.6.20). Citespace was employed to analyze annual publications, countries, institutions, keywords, and co-cited references. VOSviewer was used to analyze authors and co-cited authors, as well as journals and co-cited journals.
Results: From 2004 to 2024, a total of 967 publications were retrieved, of which 557 were included after screening. Despite annual fluctuations, the overall trend shows an increase. China and the Chinese Academy of Sciences are the countries and institutions with the highest number of publications, with Tian, J being the author with the most publications, and Kong, J having the highest Co-citation frequency. The article by Dhond, RP, published in 2008, has the highest Co-citation frequency among the co-cited literature. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine is the journal with the most publications, while Neuroimage is the co-cited journal with the highest citation frequency. Keyword co-occurrence and burst reveal the main research hotspots, including the diversity of intervention methods, cortical activation, mechanisms related to pain-associated diseases, and brain-related diseases. Keyword burst detection reflects emerging trends, including meta-analysis and systematic reviews, the relationship between ischemic stroke and women, and the connection between mild cognitive impairment and prevention.
Conclusion: This study employs bibliometric methods to explore the current status, research hotspots, and frontier issues regarding the application of functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) technology in the field of acupuncture, providing new perspectives and directions for acupuncture fMRI research.
1 Introduction
As a green and effective therapeutic method, acupuncture has a history of over 3,000 years in China and is widely applied in the treatment of neurological, endocrine, and respiratory systems (Wen et al., 2021). Despite its study since the 18th century and significant progress in clinical practice as well as in the understanding of acupoints and meridians, the clinical efficacy and physiological and biological mechanisms of acupuncture remain incompletely elucidated (Zhuang et al., 2013). Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), a leading non-invasive neuroimaging technique, offers excellent spatial and temporal resolution. Since the 1990s, fMRI has been applied in acupuncture research, including studies on the characterization of needling stimulation and brain responses before and after acupuncture (Napadow et al., 2008). Currently, fMRI is frequently used to evaluate the clinical effects of acupuncture interventions or to investigate its mechanisms of influence on the central nervous system (Yan et al., 2022).
This study employs Citespace and VOSviewer for visualization analysis. Citespace is used to analyze annual publications, countries, institutions, keywords, and co-cited references, while VOSviewer is applied to examine authors and co-cited authors, journals, and co-cited journals. The aim is to explore the application of fMRI in the field of acupuncture and conduct an in-depth analysis of its current research status and trends, thereby providing guidance and a foundation for further studies on the application of fMRI in acupuncture.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Data source and retrieval strategy
The literature utilized in this study was sourced from the SCI-EXPANDED database within the Web of Science Core Collection, which is accessible at Changchun University of Traditional Chinese Medicine Library. The retrieval period spanned from January 1, 2004, to April 30, 2024. The retrieval process was concluded on May 26, 2024. The database search strategy encompassed the utilization of keywords “acupuncture” and “fMRI.”
2.2 Criteria for inclusion and exclusion of literature
Inclusion criteria: article or review article. The language is English, without any restrictions on the country of publication.
Exclusion criteria: editorial material, meeting abstract, proceeding paper, letter, correction, retracted publication, early access, book chapters, and literature unrelated to the topic.
2.3 Data collection and analysis
The data should be converted to “txt” format, named “download_*.txt,” and subsequently imported into Citespace (version 6.3 R1) and VOSviewer (version 1.6.20) for conducting data analysis on selected literature. The analysis includes information such as annual publications, journals, countries, institutions, authors, keywords, authors and their Co-citations, journal and their Co-citations, and references Co-citations. In CiteSpace, the parameter settings are as follows: (1) The time range is set from 2004 to 2024 with a yearly interval; (2) Only one node type is selected at a time; (3) The g-index selection k-value is set to 25; (4) The Top-N option is set to 50. In the Citespace network knowledge map, nodes represent the informational units of the analyzed items, with node size indicating the frequency of occurrence. The color and width of the “annual rings” within nodes reflect the timing and quantity of occurrences for the analyzed items, while a purple outer ring signifies high betweenness centrality within the overall network. The thickness of the connecting lines illustrates the strength of the relationships between different analyzed items.
3 Results
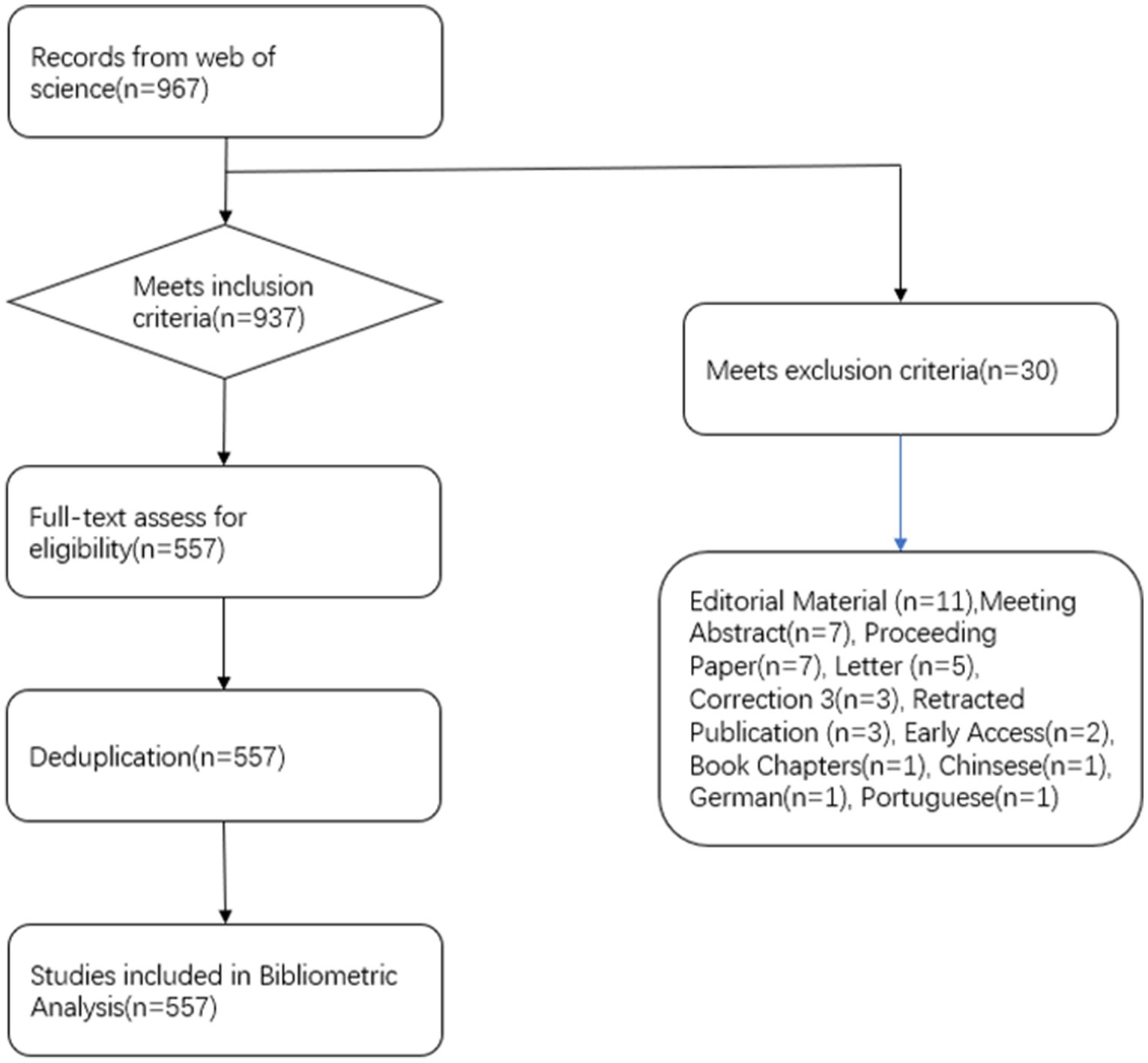
3.1 Document screening situation
We acquired a total of 967 sources, consisting of 838 articles, 103 review articles, 11 editorial materials, seven meeting abstracts, seven proceeding papers, five letters, and three corrections. Additionally, there were also three retracted publications and two early-access manuscripts. Furthermore, we identified one book chapter in our search. In terms of language, there are 964 articles written in English, one in Chinese, one in German, and one in Portuguese. After applying inclusion criteria, we selected a total of 937 articles and excluded an additional 380 articles that were deemed irrelevant to the topic. Therefore, a total of 557 records were included for further visualization and analysis in this study. Quantitative methods were employed to analyze the current status and trends of functional magnetic resonance imaging technology in acupuncture, following the process depicted in Figure 1. The task of conducting database searches and screening literature was assigned to two researchers, Zhongke Wang, and Lu Chen, while the responsibility of handling potential disputes or disagreements were undertaken by senior researcher Fuchun Wang.
3.2 Analysis of annual publications
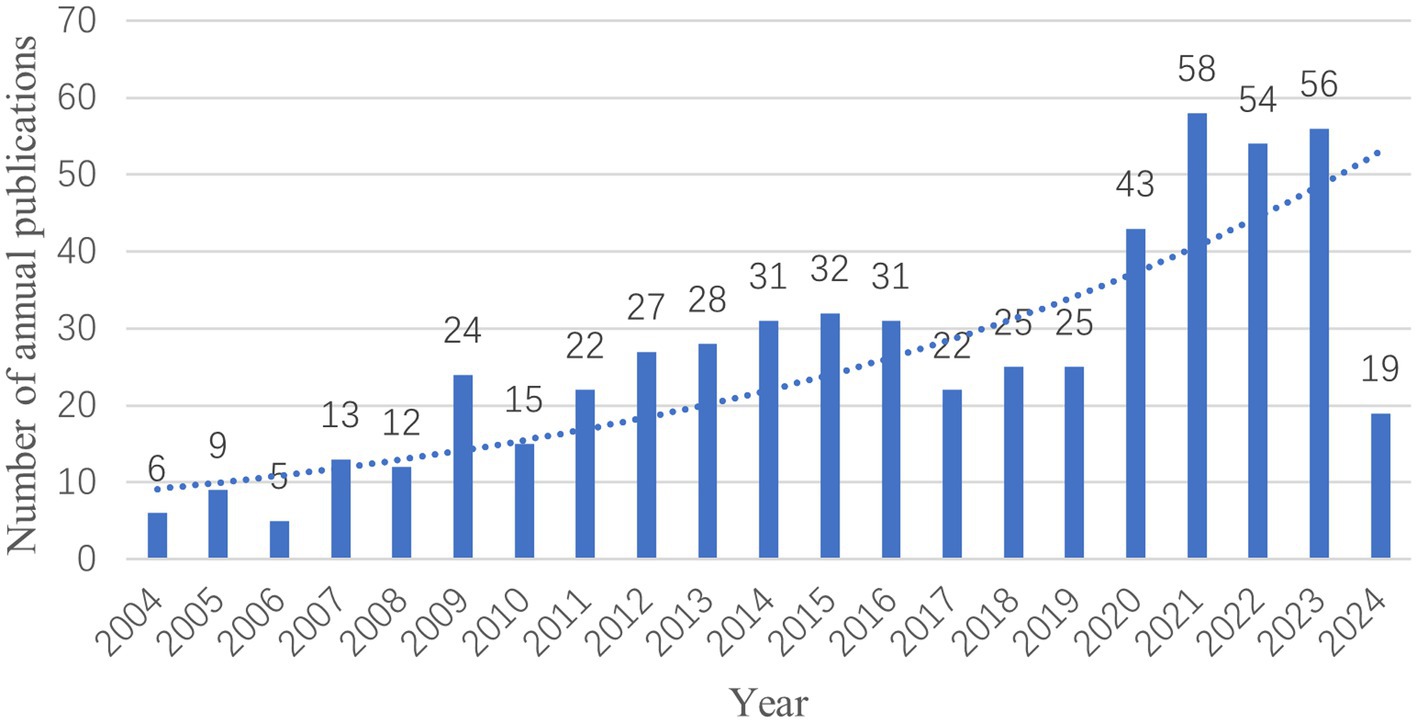
The number of publications per year is shown in Figure 2, which can be divided into three stages. The first stage, from 2004 to 2010, saw slight fluctuations in the number of publications but exhibited a continuous growth trend, with a peak of 24 articles in 2009. However, the number of publications decreased to 15 articles in 2010. The second stage, from 2010 to 2017, was characterized by a steady increase in publication volume, although the rate of increase was relatively slow, with a decline to 22 articles in 2017. The third stage, from 2017 to 2024, witnessed a gradual increase in publications, particularly between 2019 and 2021, where the growth rate was notably higher, peaking in 2021. Based on data available up to April 2024, it is expected that the number of publications will continue to remain relatively high in the future.
3.3 Analysis of national cooperative networks
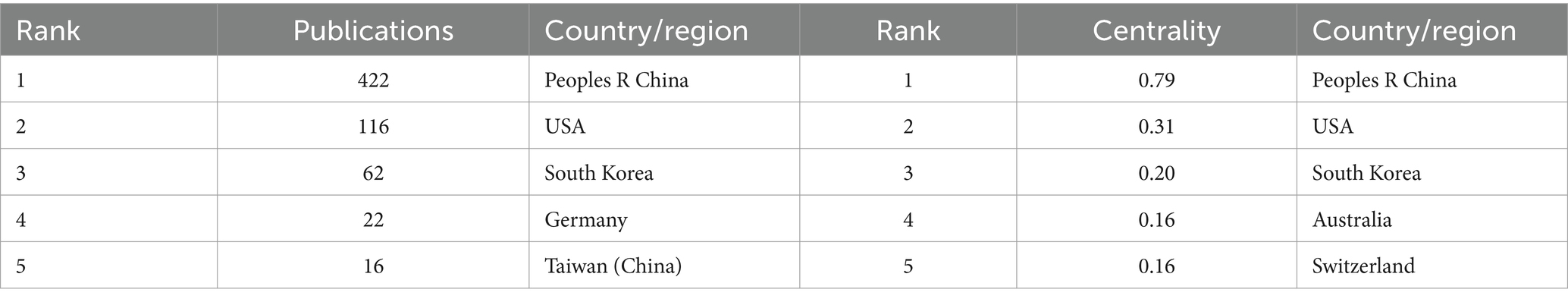
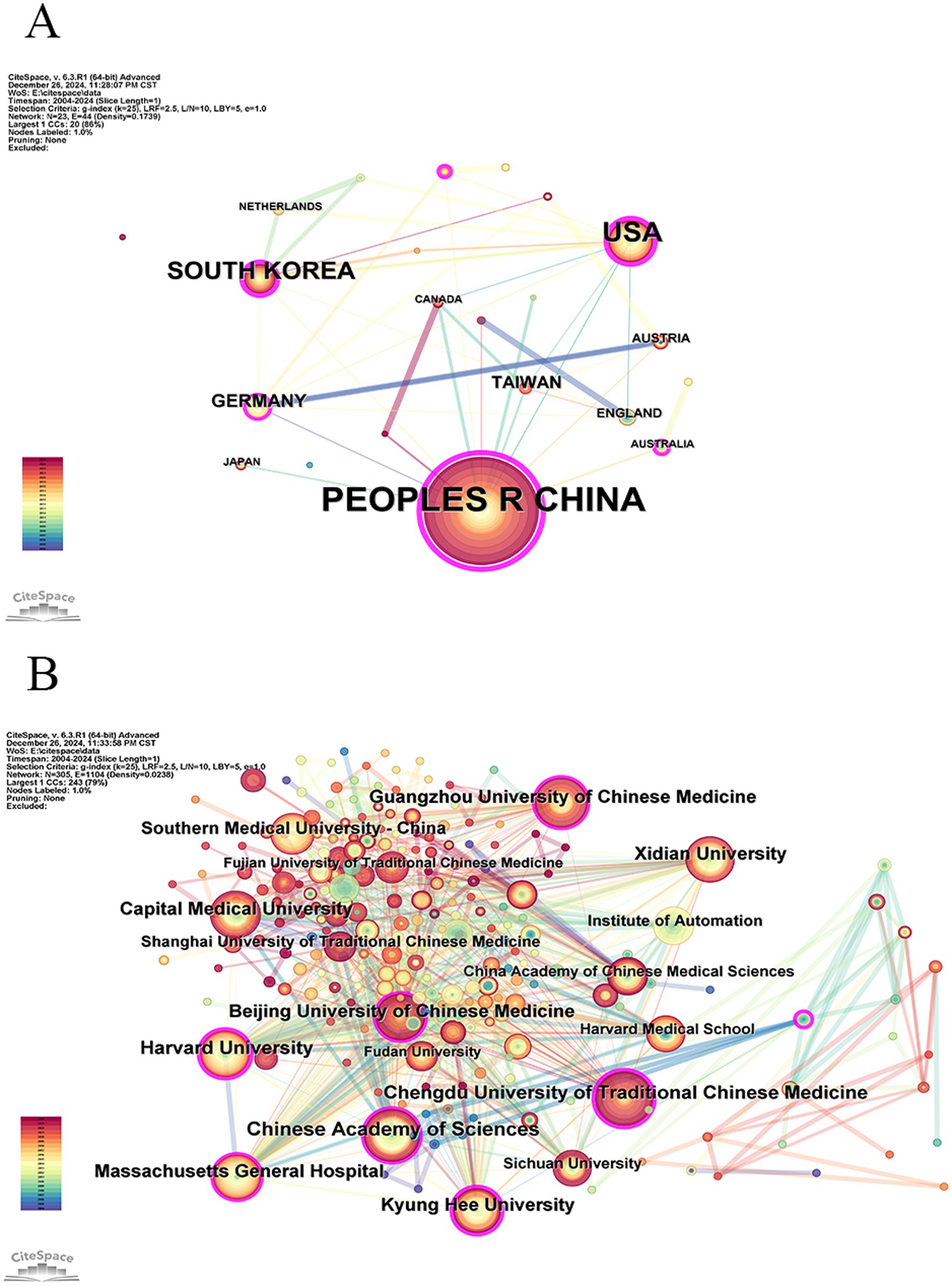
The “Country” node should be selected for conducting a visual analysis of the countries mentioned in the literature using a knowledge graph. The study yielded a total of 23 nodes and 44 links, spanning across 23 countries or regions. The top five countries in terms of national publications are Peoples R China (422 articles), USA (116 articles), South Korea (62 articles), Germany (22 articles), and Taiwan (China) (16 articles). According to the centrality ranking, the top five countries are Peoples R China (0.79), USA (0.31), the Republic of Korea (0.2), Australia (0.16), and Switzerland (0.16, Table 1). The rankings of Peoples R China, USA, and South Korea consistently occupy the top three positions based on considerations of publication frequency and centrality. As shown in Figure 3A, the formation of China, USA, and South Korea as three cores signifies the presence of strong internal connections among these countries. The density value of 0.1739 suggests a relatively moderate level of inter-country cooperation.
3.4 Network analysis of institutional collaboration
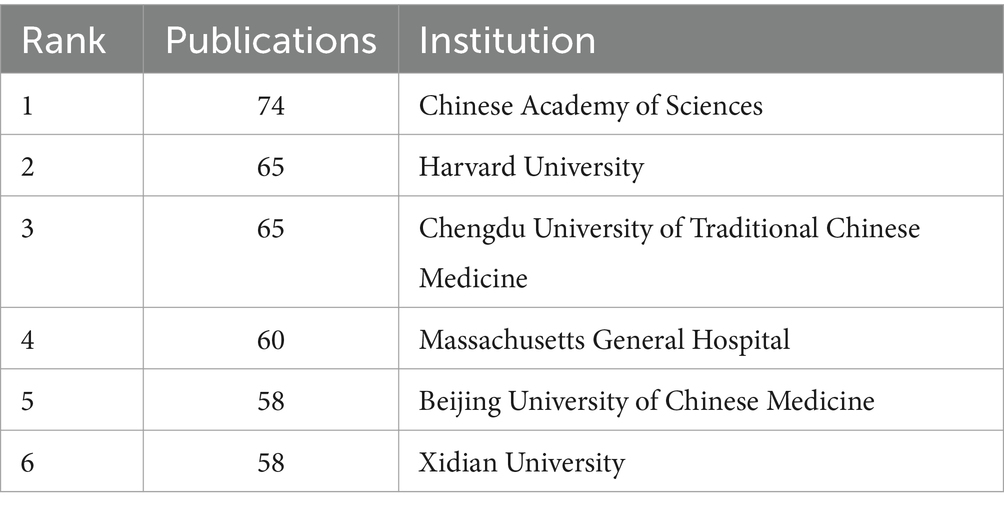
The “Institution” node should be selected to visualize and analyze the knowledge graph of institutions mentioned in the literature. The network consists of 305 nodes and 1,104 links, encompassing a total of 305 distinct institutions. Table 2 lists the top five institutions in terms of publication and centrality. Chinese Academy of Sciences takes the lead with the highest research output (74 articles), followed by Harvard University (65 articles) and Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (65 articles), which are tied for second place. Massachusetts General Hospital ranks fourth (60 articles), while Beijing University of Chinese Medicine and Xidian University share fifth place with 58 articles each. In terms of centrality, the institutions are ranked as follows: Kyung Hee University (0.35), Harvard University (0.23), Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (0.21), University of California System (0.2), and Massachusetts General Hospital (0.19, Table 3). The nodes of the Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, and other institutions are prominently large in Figure 3B, indicating their central position and strong connections within their respective organizations. However, the density value is 0.0238, indicating a lack of cohesive collaboration among various institutions. Moreover, China boasts a substantial number of institutions engaged in fMRI research applied to acupuncture.
3.5 Analysis of the authors and co-cited authors
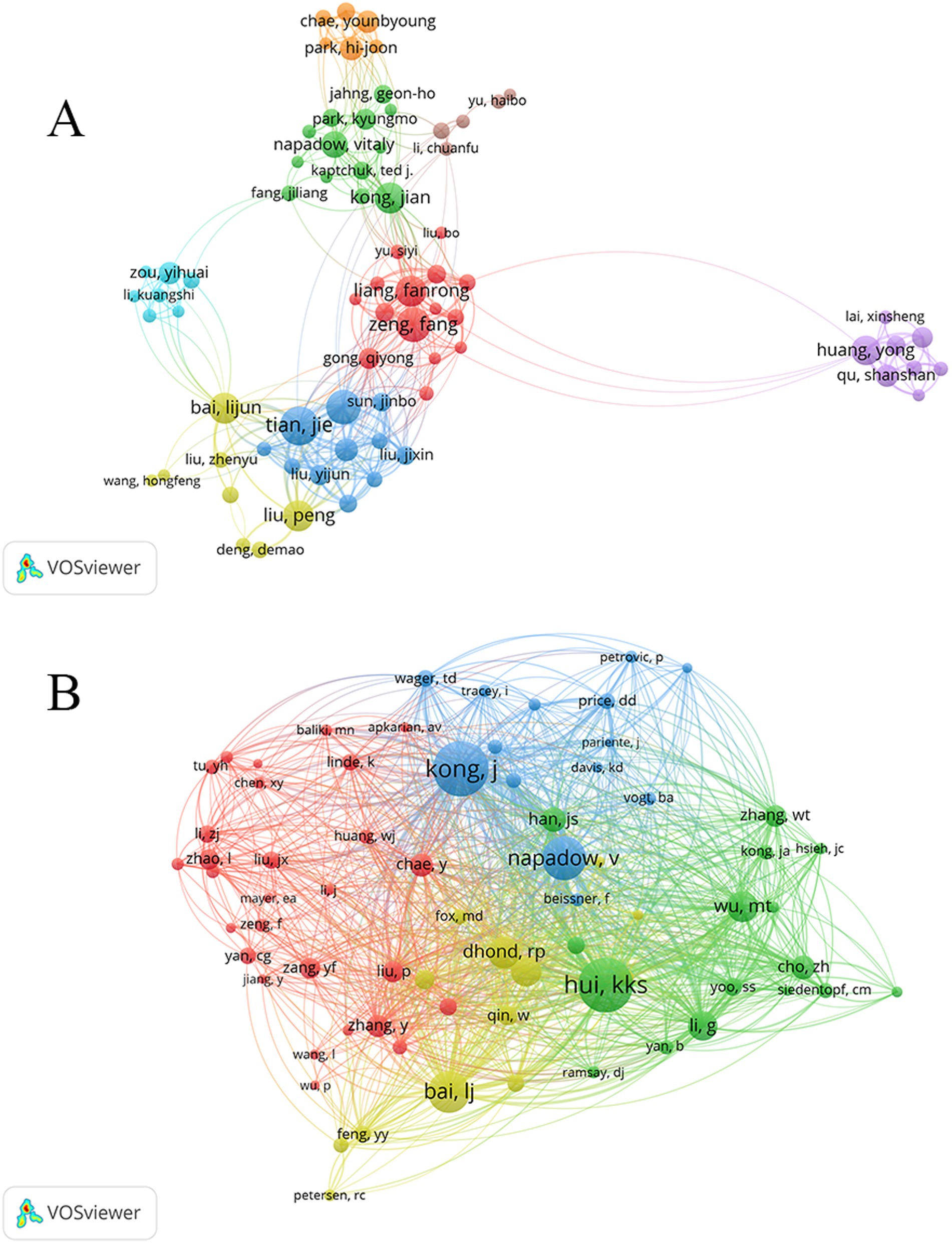
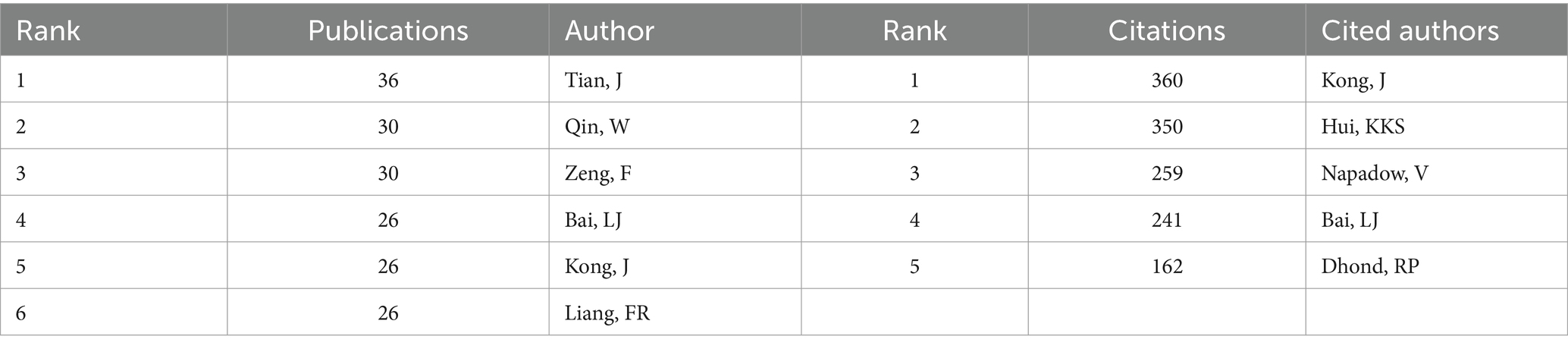
The author collaboration network was generated using VOSviewer, which includes 2,706 authors who published 557 articles. In Figure 4A, authors with more than 7 publications are displayed. Each node represents an author, with the size of the node positively correlated with the number of publications. The connections between nodes represent collaborative relationships, with thicker lines indicating stronger cooperation. In the context of fMRI research related to acupuncture, the top 10 authors are shown in Table 4. Tian, J ranks first (n = 36), followed by Qin, W; Zeng, F; Bai, LJ; Kong, J; and Liang, FR. Among them, Kong, J and Liang, FR are tied for fifth place (n = 26). Analysis of the author collaboration network using VOSviewer reveals the formation of 8 clusters, with each cluster consisting of multiple authors engaged in long-term collaboration.
The total number of co-cited authors is 10,734, among whom 12 authors have received more than 100 citations. Figure 4B illustrates the authors with citation frequencies exceeding 30, while Table 4 showcases the top five most frequently cited authors. Among them, Kong, J has received the highest number of citations with a count of 360. Following closely are Hui, KKS with 350 citations, Napadow, V with 259 citations, Bai, LJ with 241 citations, and Dhond, RP with 162 citations.
3.6 Analysis of journals and co-cited journals
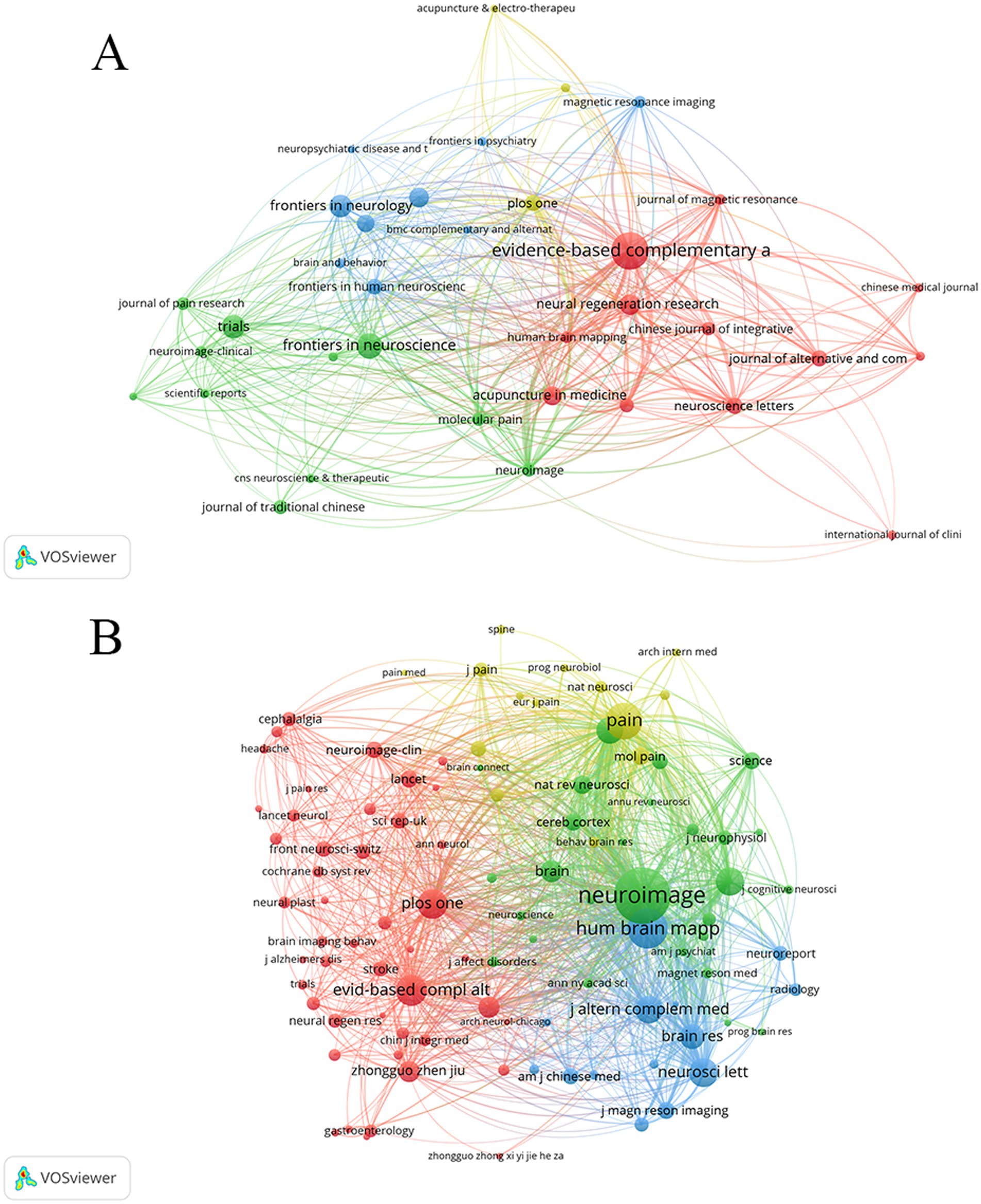
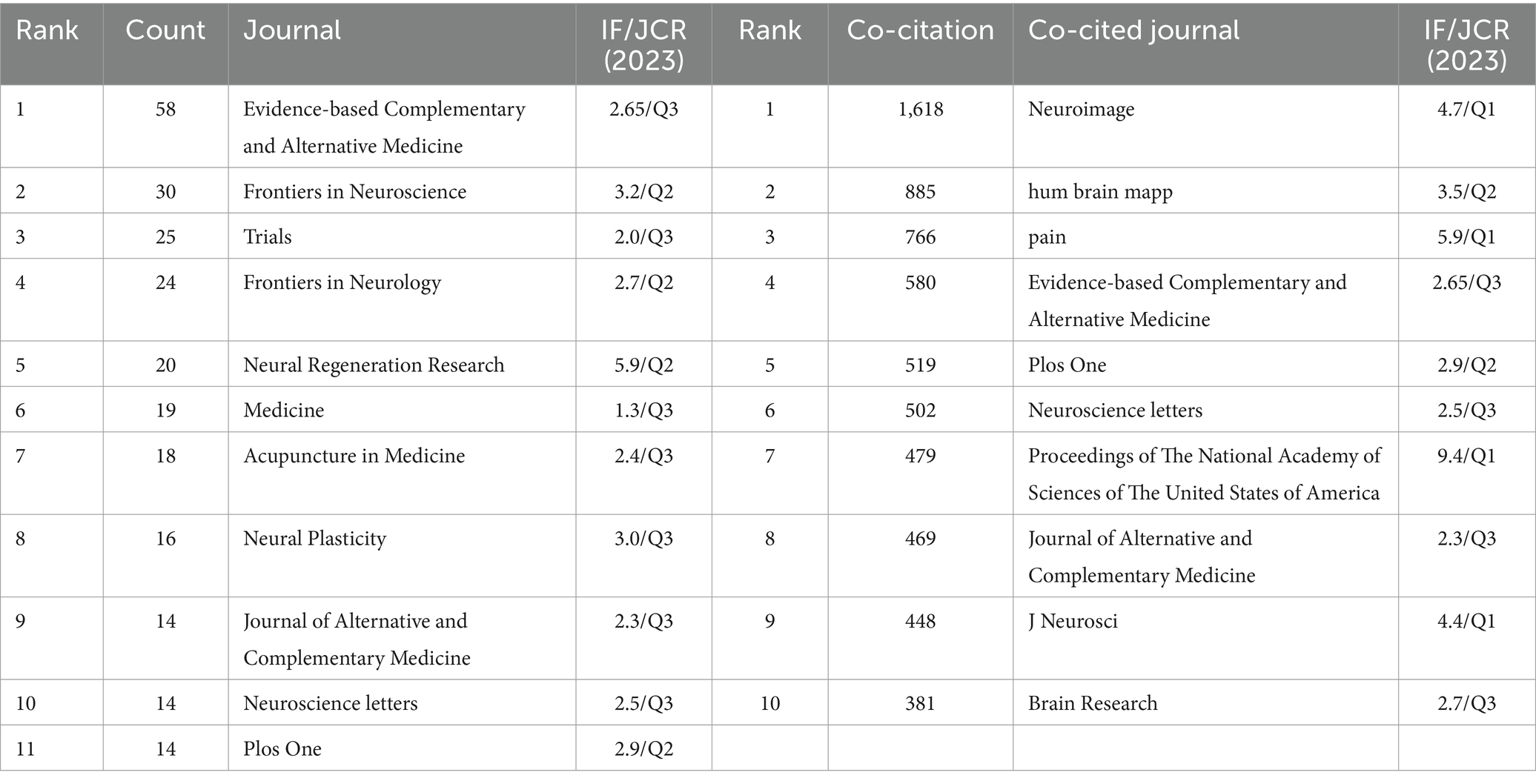
Journal and journal Co-citation analysis was conducted using VOSviewer. Publications on the application of fMRI in the field of acupuncture were published in over 138 journals, with Figure 5A displaying the journals that appeared more than four times. Table 5 presents the top 10 most popular academic journals in the field, with Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine having the highest number of publications (n = 58), followed by Frontiers in Neuroscience (n = 30), Trials (n = 25), Frontiers in Neurology (n = 24), and Neural Regeneration Research (n = 20). Furthermore, Neuroscience Letters and Plos One are tied for tenth place. According to Journal Citation Reports 2023, Neural Regeneration Research has achieved a high impact factor (IF =5.9). Unfortunately, the majority of journals have an impact factor below five, and JCR categories are primarily concentrated within Q3.
The total number of cited journals is 3,278, out of which 6 journals have citation counts exceeding 500. Figure 5B shows that journals are cited more than 40 times. As shown in Table 5, the top 10 academic journals are Neuroimage (Co-citation = 1,618), followed by Hum Brain Mapp (Co-citation = 885), Pain (Co-citation = 766), Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine (Co-citation = 580), Plos One (Co-citation = 519) and Neuroscience letters (Co-citation = 502). Additionally, Proceedings of The National Academy of Sciences of The United States of America has the highest impact factor (IF = 9.4), followed by pain (IF = 5.9) and Neuroimage (IF = 4.7), while the remaining journals have impact factors below 5.
3.7 Analysis of co-cited references
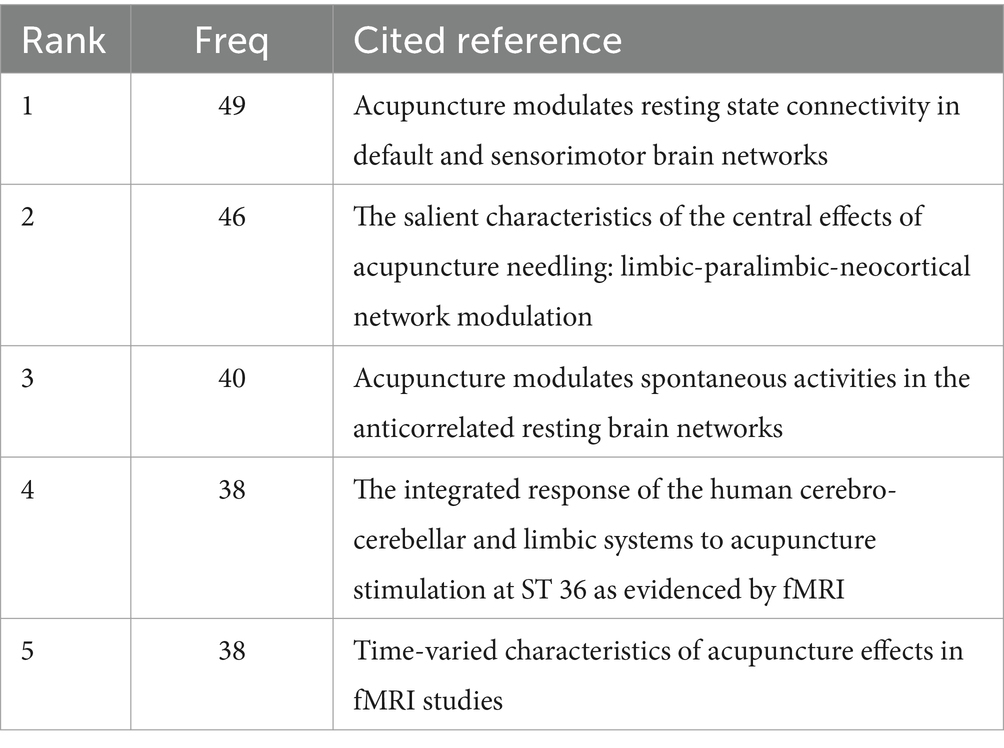
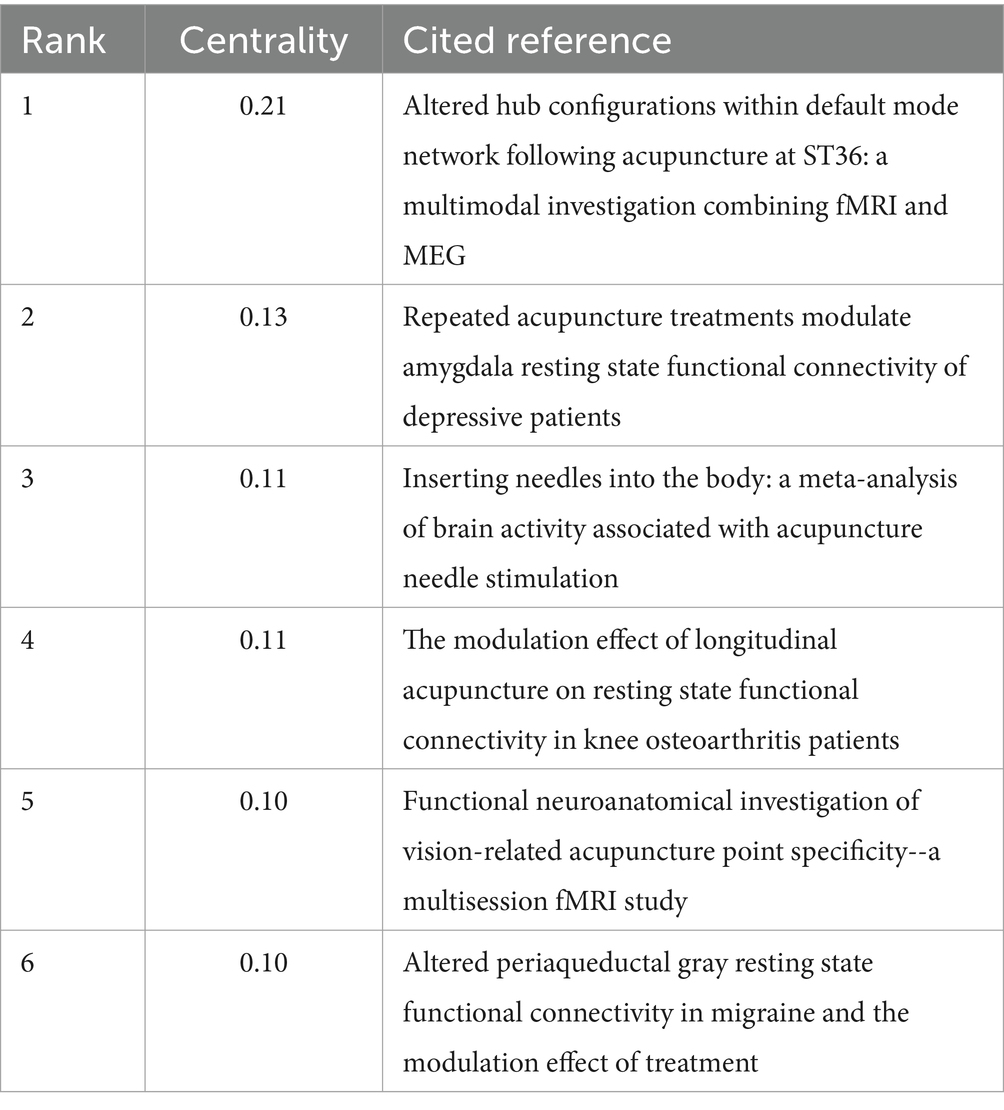
A Co-citation analysis of references was conducted using the “Reference” feature, as shown in Figure 6A. The analysis revealed a network consisting of 825 nodes and 3,014 links, with a network density of 0.0089, indicating relatively weak connections between these 825 cited references. According to Table 6, the top five most frequently cited references include Dhond RP, 2008; Fang JL, 2009; Bai LJ, 2009; Hui KKS, 2005; and Bai LJ, 2009, which are considered representative. In terms of the centrality ranking of cited references, the top five are You YB, 2013 (0.21); Wang XY, 2016 (0.13); Chae Y, 2013 (0.11); Chen XY, 2015 (0.11); Kong J, 2009 (0.1); and Li ZJ, 2016 (0.1), as shown in Table 7. Notably, Kong J, 2009, and Li ZJ, 2016 (0.1) are tied for fifth place. It is worth mentioning that despite these two references being published later, Kong J and Li ZJ are highly representative of the application of fMRI in the field of acupuncture.
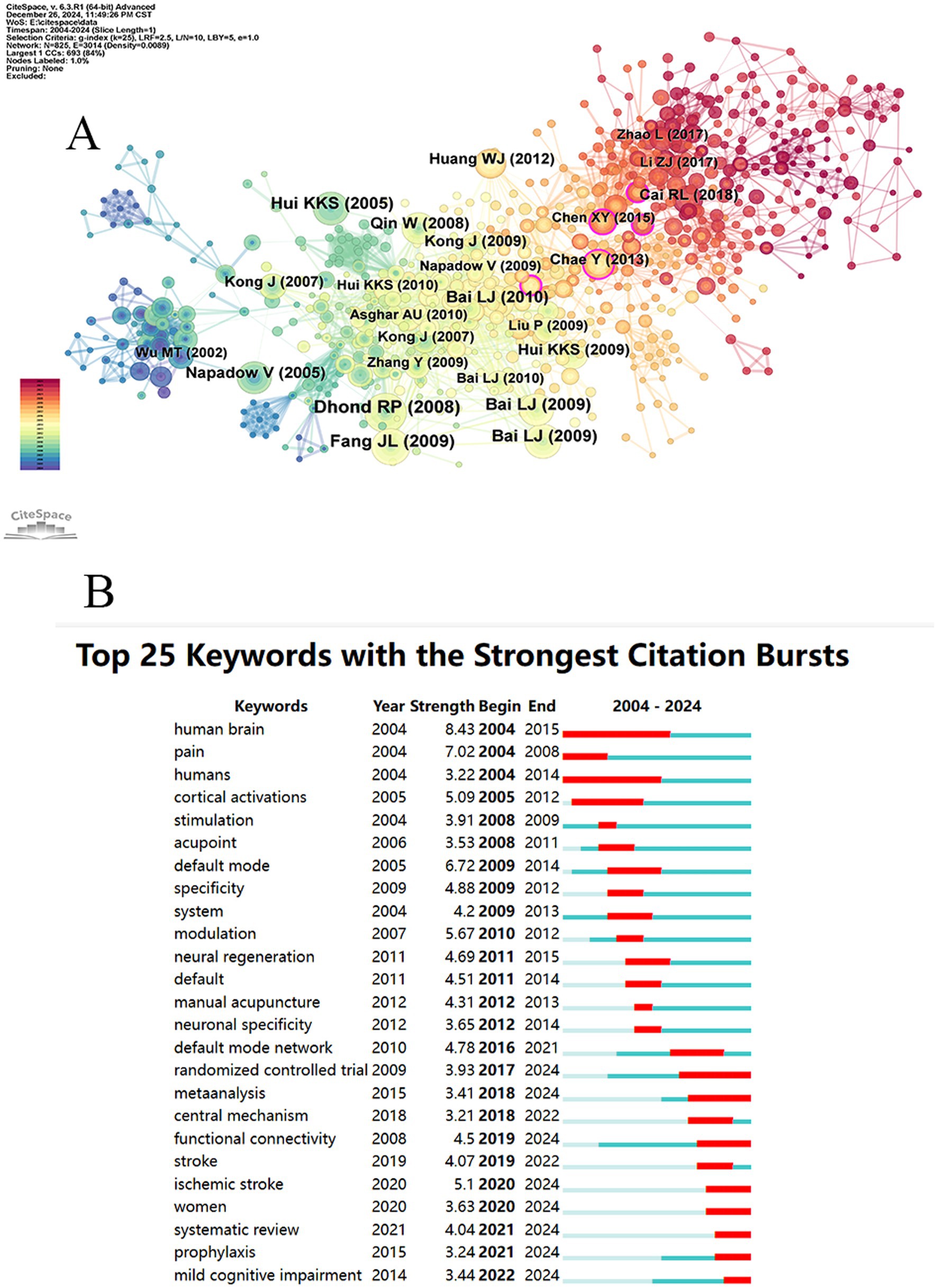
Figure 6. Map of co-cited references (A) and Top 25 keywords with the strongest citation bursts (B).
3.8 Co-occurrence analysis of keywords
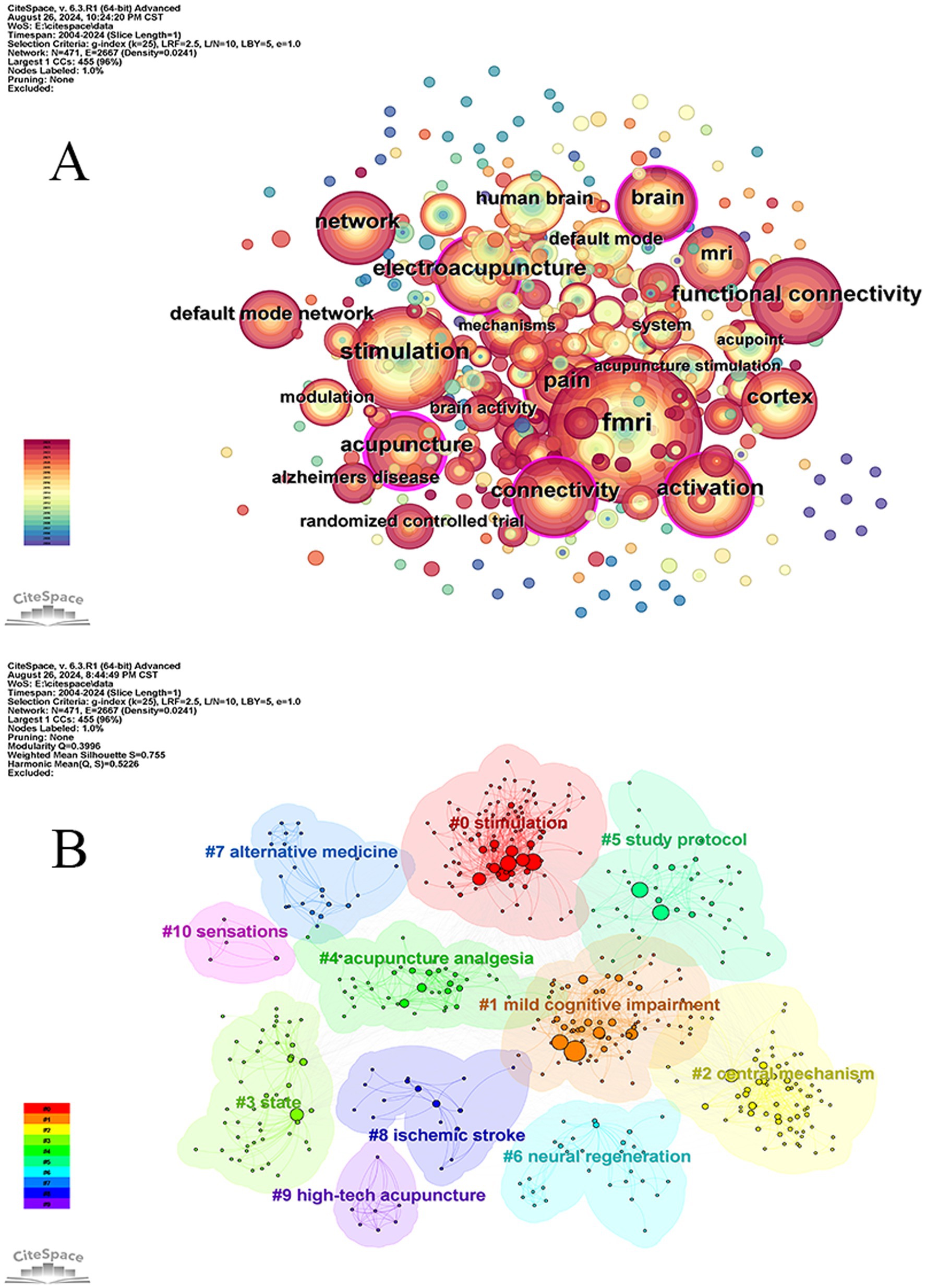
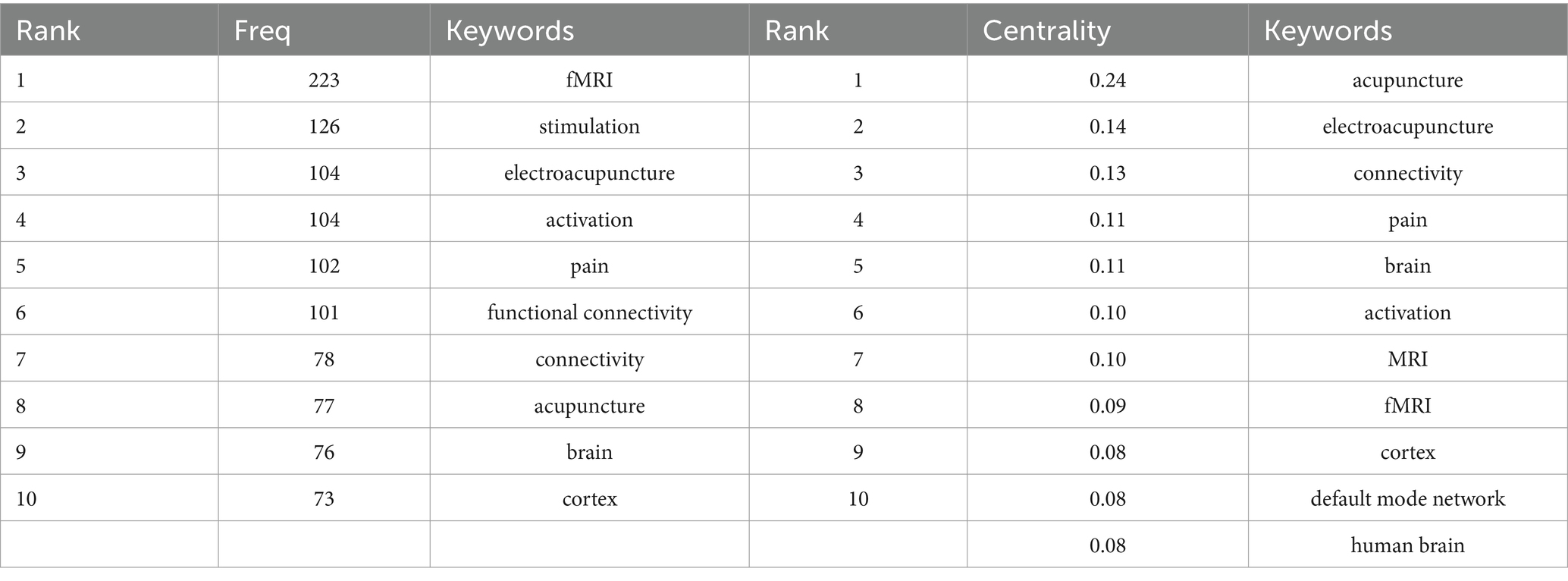
The visualization analysis graph of the keyword co-occurrence network in this study consisted of 471 nodes and 2,667 links, resulting in a network density of 0.0241 (Figure 7A). The top 10 keywords, listed in descending order, include fMRI (223), stimulation (126), electroacupuncture (104), activation (104), pain (102), functional connectivity (101), connectivity (78), acupuncture (77), brain (76) and cortex (Zhang et al., 2021) as shown in Table 8. The frequency analysis indicates that fMRI is currently a research hotspot, with acupuncture having the highest centrality (0.24). A centrality value >0.1 suggests that this node has the highest attention and influence within the research field, representing a key area of focus in the domain.
3.9 Analysis of keyword clustering
The keywords about acupuncture research utilizing fMRI were examined through the implementation of the “K” clustering-LLR algorithm. Figure 7B results demonstrated that the modularity Q value surpassed the threshold of 0.3, reaching 0.3996, thereby indicating a distinct and substantial clustering structure. Additionally, the mean silhouette value for clustering was determined to be 0.755, implying that this particular clustering method is both rational and dependable. Based on different cluster labels, a total of 11 clusters were obtained: #0 stimulation, #1 mild cognitive impairment, #2 central mechanism, #3 state, #4 acupuncture analgesia, #5 research design, #6 neural regeneration, #7 alternative medicine, #8 ischemic stroke and #9 high-tech acupuncture as well as #10 sensation. The labels #0, #7, and #9 primarily pertain to intervention methods, indicating a diverse range of approaches for interventions and highlighting the need for further research in the field of alternative medicine on this specific topic. The primary focus of Labels #1 and #8 lies in brain-related diseases, while Labels #2, #3, #4, #6, and #10 are associated with research mechanisms. This suggests that scholars have begun to direct their attention toward the action mechanisms of acupuncture.
3.10 Analysis of keywords with the strongest citation bursts
Through burst analysis of the selected literature keywords, 25 burst terms were identified (Figure 6B). Early research primarily focused on foundational concepts such as “human brain,” “pain,” “humans,” “stimulation,” and “cortical activation,” with studies on the human brain being the earliest and most sustained. Mid-term research emphasized mechanism exploration, with keywords like “default mode,” “specificity,” “modulation,” and “neural regeneration” emerging. Later, the focus shifted to randomized controlled trials (RCT) to explore disease mechanisms and summarize the applications of fMRI in the field of acupuncture. During this phase, keywords such as “randomized controlled trial,” “meta-analysis,” “functional connectivity,” “ischemic stroke,” “women,” “systematic review,” “prophylaxis,” and “mild cognitive impairment” emerged, which remain significant today. These keywords are expected to become key areas of research focus and trends in the future.
4 Discussion
4.1 General information
This study employed Citespace and VOSviewer software to conduct a visual analysis of fMRI research in the field of acupuncture, encompassing a total of 557 articles. Through analyses of annual publications, collaboration networks, and Co-citation patterns, the latest advancements in fMRI research within the field of acupuncture were unveiled.
The distribution of annual publications shows that research on fMRI in acupuncture can be divided into three phases. The period from 2004 to 2010 is considered the initiation phase, with a relatively low number of publications and limited research in the field. During this phase, studies mainly focused on the mechanisms of acupuncture stimulation and pain. From 2010 to 2017, there was a steady upward trend in publications. Research during this phase mainly concentrated on neuroregeneration, neural specificity, and the default network. Since 2017, there has been a notable increase in the number of publications, with broader attention given to this area of research. Studies in this later phase have focused on randomized controlled trials, meta-analysis, systematic reviews, ischemic stroke in women, and the prevention of mild cognitive impairment. As the search strategy was conducted with a cutoff date of April 30, 2024, the publication volume for 2024 is lower. However, with 19 publications already published, it is expected that the publication volume for 2024 will at least match or even exceed that of 2023.
The Peoples R China has the highest number of publications, significantly outpacing the USA and other countries and regions, and holds the highest centrality, indicating a deep engagement with research in this field. This is likely related to China’s role as the birthplace of acupuncture. The USA and South Korea rank second and third in terms of publication volume, and notably, they also rank second and third in centrality, reflecting their broader research activities and the publication of influential articles. Germany and Taiwan (China) are ranked fourth and fifth in terms of publication volume. Compared to these four countries, Australia and Switzerland have published fewer studies on fMRI in acupuncture, but both countries show similar performance in centrality. Furthermore, there is limited exchange between countries, highlighting the need to strengthen international collaboration.
According to the collaborative network of institutions, it is evident that China holds four out of the top five positions in terms of publication volume. Similarly, when considering centrality, four out of the top five institutions are from China. These institutions primarily comprise research institutes or universities as their core teams. Kyung Hee University ranks fifth in terms of publication volume, yet it possesses a high centrality score of 0.18 > 0.1, indicating its significant research output and considerable influence in this field. Although Harvard University’s publication volume did not rank among the top five, its centrality score of 0.16 > 0.1 suggests that despite a relatively lower number of publications, their exceptional quality remains evident.
The collaborative network analysis results conducted by the author, Tian, J has emerged as the most prolific researcher, demonstrating an impressive publication count of 36. Closely following are Qin, W, Zeng, F, Bai, LJ, Kong, J and Liang FR. After analyzing the results of co-cited authors, it is found that Kong, J has the highest number of citations, followed by Hui, KKS, Napadow, V, Bai, LJ, and Dhond, RP.
Tian, J and Qin, W have mostly focused on acupoint specificity. They focused on changes in the brain area after needling acupuncture points. Zeng, F and Liang, FR have mostly focused on the central mechanisms of acupuncture for the treatment of diseases. Bai, LJ’s study focused on acupoint specificity, followed by more research on brain area changes after acupuncture treatment of disease. Much of Kong, J’s research has focused on the central mechanisms and brain region changes in the acupuncture treatment of disease. Hui, KKS research focused on brain networks and cortical plasticity. Napadow, V. and Dhond, RP’s research focused on brain networks and neuroplasticity.
The analysis of journal and co-cited journals reveals that Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine has the highest number of publications. The journal also ranks 4th in terms of citation count, indicating its significant contribution and dissemination of fMRI research in the field of acupuncture. Among the top 10 journals in terms of publication frequency, Neural Regeneration Research (IF = 5.9), Frontiers in Neuroscience (IF = 3.2), and Neural Plasticity (IF = 3.0) exhibit the highest impact factors. The majority of impact factors are below 5, and the JCR classification is mainly Q3, implying that fMRI research in acupuncture needs to be published in high-quality articles to enhance its influence. The journal with the highest number of citations is Neuroimage, which primarily falls into the Q1 and Q2 categories, indicating a superior level of quality and providing a solid foundation for fMRI research in acupuncture.
The analysis of journal and co-cited journals reveals that the most frequently published journal is Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. Furthermore, this journal ranks fourth in terms of citation count, indicating that it has provided substantial support for research on fMRI in the field of acupuncture and has a certain level of dissemination impact. Among the top 10 journals by publication volume, the journals with the highest impact factors are Neural Regeneration Research (IF = 5.9), Frontiers in Neuroscience (IF = 3.2), and Neural Plasticity (IF = 3.0). Most of the journals have impact factors below 5, and the majority are categorized in the Q3 quartile according to JCR, suggesting that research on fMRI in acupuncture needs to be published in higher-quality journals to enhance its influence. The most frequently cited journal is Neuroimage, and the journals that are most frequently cited are primarily in the Q1 and Q2 quartiles, demonstrating their high quality and providing a solid foundation for research on fMRI in the field of acupuncture.
Co-citation analysis of references reveals that these cited studies are all clinical trials. The sample sizes of the included studies range from 10 to 36 participants, which, despite being relatively small, may be attributed to the high cost associated with fMRI. The most frequently cited reference is the 2008 article by Dhond et al. (2008), which demonstrated that acupuncture can enhance the spatial extent of resting-state brain networks, including brain regions related to pain modulation, memory processing, and emotional regulation. The second most cited reference is the article by Fang et al. (2009), which, through fMRI detection of real and sham acupuncture points, demonstrated that acupuncture leads to widespread deactivation of the limbic-paralimbic-neocortical system. The third and fourth most cited references are two articles by Bai LJ published in 2009. The third article Bai et al. (2009) demonstrated through fMRI findings that acupuncture can enhance the bipartite division of the anti-correlated resting-state networks and regulate the spontaneous activity of the intrinsic sensory-autonomic networks. The fourth article Bai et al. (2009) confirmed that brain activity patterns during rest are related to the type of stimulation. Significant stimulation-related activity was still present during the “rest” phase, particularly in the cerebellum and limbic brain regions. The fifth article Hui et al. (2005) used fMRI to explore how acupuncture at the Zusanli (ST36) point can modulate the neural activity of cortical and subcortical structures, including the cerebellum, diencephalon, and brainstem, at multiple levels. The highest centrality is held by the article by You et al. (2013), which used fMRI and MEG analysis to explore the specific biological mechanisms underlying acupuncture across spatial and temporal domains. This study found that modulation of the posterior cingulate cortex (PCC) within the theta (4–8 Hz), alpha (8–13 Hz), and gamma (30–48 Hz) frequency bands regulates the Default Mode Network (DMN) hub. The second most central reference is the article by Yeo et al. (2012), which used fMRI to show that acupuncture at GB34 (Yanglingquan) can increase neural responses in regions such as the substantia nigra, caudate nucleus, thalamus, and putamen, which are affected by Parkinson’s disease, confirming that acupuncture at GB34 may effectively improve symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. The third article is by Chen et al. (2015), which used fMRI to discover that acupuncture at GB34 can increase motor-cognitive connectivity while simultaneously reducing contralateral motor cortex compensation, thus promoting the rehabilitation of hemiplegia and spasticity. The articles by Chen et al. (2015), Li et al. (2010), and Wang et al. (2016) are tied for fourth. Chen et al. (2015) used fMRI to show that acupuncture can treat pain caused by knee osteoarthritis by enhancing functional connectivity between the right frontoparietal network (fFPN), the executive control network (ECN), and the descending pain modulation pathways. Li et al. (2010), conducted a multi-voxel pattern analysis (MVPA) based on fMRI data to explore the specificity of acupuncture at Guangming (GB37) and a nearby non-acupoint (NAP) on visual-related brain activation patterns. The study found that multiple brain regions could distinguish the central nervous response patterns caused by acupuncture at these two points, with the most significant areas being the occipital cortex, the limbic-cerebellar system, and subregions of the somatosensory cortex. Wang et al. (2016) conducted experiments that showed acupuncture can enhance resting-state functional connectivity between the left amygdala and the anterior cingulate cortex, as well as between the right amygdala and the left parahippocampal gyrus, thus helping to counter depression.
4.2 Research hotspots
By conducting keyword co-occurrence analysis and keyword clustering, the main research hotspots can be summarized as follows: different acupuncture techniques, acupoint specificity, and mechanisms of acupuncture in the treatment of diseases.
4.2.1 Different acupuncture techniques
Common intervention methods include electroacupuncture, acupuncture, and high-tech acupuncture, which encompasses techniques such as balance acupuncture, auricular acupuncture, and wrist-ankle acupuncture. Electroacupuncture is the most frequently used method. FMRI studies have shown that electroacupuncture induces a broader range of activation changes (Kong et al., 2007). Vitaly Napadow et al. (2005) suggested that all acupuncture stimuli result in a signal reduction in the amygdala, anterior hippocampus, the cortices of the subgenual and retrosplenial, and ventromedial prefrontal cortex, while signals increase in the anterior insula. However, compared to manual acupuncture, electroacupuncture at low frequencies induces a larger area of fMRI signal increase, with significant signals only observed in the anterior mid-cingulate cortex. Acupuncture is a widely used intervention. Wang et al. (2020) utilized fMRI to study the efficacy of multi-point acupuncture for treating primary insomnia and its effects on brain activity. High-tech acupuncture mainly refers to laser acupuncture, which is considered a safe and reliable option (Beissner et al., 2011). Existing studies have used fMRI to observe the impact of laser acupuncture on brain activity when stimulating acupuncture points (Lv et al., 2016; Chang et al., 2023).
4.2.2 Acupoint specificity
Stimulation of acupoints activates the brain Acupoints reflect the specificity of acupoints. Jung et al. (2015) found that both real acupuncture and fake acupuncture could activate the insula, anterior cingulate cortex, secondary somatic sensory cortex parietal cortex, and inactivate the medial prefrontal cortex, posterior cingulate cortex, inferior parietal cortex, and parahippocampal brain (Cao et al., 2019). Compared with shame acupuncture, real acupuncture showed greater brain activation in the posterior insula, posterior gill cover, and the tail of the anterior cingulate cortex. The study conducted by Ma et al. (2020) demonstrated the inhibitory effect of acupuncture on the marginal zone in rats with dysmenorrhea. Furthermore, acupuncture can modulate thalamocortical networks by enhancing connectivity between the mediodorsal thalamus (MD) and angular gyrus/posterior cingulate cortex/parahippocampal gyrus (PHG), as well as between motor thalamus subregions (Mthal) and medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC)/PCC/lateral temporal lobe cortical regions, while simultaneously reducing connectivity between MD and precuneus (PCU)/ middle cingulate cortex (MCC) (Kong et al., 2023). The findings of a review article suggest that acupuncture exerts an influence not only on the primary motor cortex and premotor cortex, but also leads to structural changes in language-related brain regions, including the inferior frontal gyrus, temporal lobe, occipital lobe, and parietal lobe (Zhang et al., 2021).
4.2.3 Mechanisms of acupuncture in the treatment of diseases
Functional connectivity can be used to study the mechanisms of acupuncture-induced analgesia. Pain is a widespread and complex symptom, and many patients heavily rely on analgesics. However, analgesics often present issues such as safety concerns and the potential for addiction (Qiao et al., 2020). In contrast, acupuncture is well-tolerated and generates fewer adverse effects. Acupuncture can alleviate pain by stimulating specific acupuncture points on the body (Chen et al., 2020; Robinson et al., 2022), which has made it increasingly popular. Neuroimaging techniques are essential for exploring the central mechanisms of acupuncture analgesia, with fMRI being able to reveal multifunctional brain networks associated with pain perception (Damascelli et al., 2022). Additionally, functional connectivity analysis has been used to explore the relationships between brain regions, helping to better understand analgesic mechanisms (Lee et al., 2019). In a study by Xiang et al. (2021), it was noted that ankle acupuncture alleviated chronic low back pain symptoms by modulating the cerebellum and right insula. Yang et al. (2022) used fMRI to explore the mechanisms of moxibustion in alleviating pain in patients with primary dysmenorrhea and found that moxibustion significantly increased the resting-state functional connectivity (rs-FC) of the left inferior frontal gyrus (IFG), bilateral anterior cingulate cortex (ACC)/middle cingulate cortex (MCC), left posterior cingulate cortex (PCC)/precuneus (PCU), and left parahippocampal gyrus (PHG). Wang et al. (2021) used fMRI to investigate the immediate analgesic effects of acupuncture on patients with primary dysmenorrhea, discovering that acupuncture significantly reduced the resting-state functional connectivity between the rostral anterior cingulate cortex (rACC) and left precentral gyrus. Wei et al. (2022) used fMRI to analyze changes in functional connectivity in patients with migraine without aura. The results showed that electroacupuncture at the rate of shuaigu (GB80) could modulate the functional connectivity between the right insular subregion and the parietal lobe, specifically the right dorsal anterior insula and the right postcentral gyrus, as well as between the right posterior insula and the left precuneus, thereby improving symptoms in patients with migraine without aura.
Neural regeneration is an important central mechanism for studying brain-related diseases. The regeneration of the nervous system necessitates the repair or replacement of impaired nerve cells resulting from injury or disease (Steward et al., 2013). Ischemic stroke is a sudden neurological deficit resulting from the cessation of blood flow to a specific region of the brain (Haupt et al., 2023). While acupuncture can stimulate neurogenesis, activate axonal regeneration and sprouting, improve synaptic structure and function, and enhance neural plasticity (Qin et al., 2022), especially when using appropriate electroacupuncture parameters for treatment, it can play a role in neuroprotection and promoting nerve regeneration (Chang et al., 2018). The loss of neurons and synapses is a primary pathological feature of cognitive impairment. Stimulating acupoints can restore brain functional activity and connectivity, promote neuroregeneration, and regulate synaptic plasticity to facilitate the formation of normal neural circuits (Zhang et al., 2023). FMRI can assess spontaneous neuronal activity through measures such as ALFF (Amplitude of Low-Frequency Fluctuations) and ReHo (Regional Homogeneity) (Zang et al., 2023). Changes in ReHo values can serve as one of the neurobiological markers reflecting disease (Zhang et al., 2018). Research by Li et al. (2022) demonstrated that electroacupuncture at Zusanli (ST36) and Quchi (LI11) significantly increased ReHo values in the ipsilateral posterior hippocampus, contralateral anterior hippocampus, contralateral subhippocampus, contralateral dorsolateral thalamus, ipsilateral somatosensory cortex, and ipsilateral substantia gelatinosa area, thereby promoting the activation of neurons in brain regions associated with cognition and behavior, reducing neuronal death. According to a comprehensive summary by Yin et al. (2023), acupuncture for cognitive disorders, through stimulation of 10 key brain areas such as the cingulate cortex, middle frontal gyrus, and hippocampus, can effectively promote neuroplasticity and facilitate repair. Zhang et al. (2024) utilized fMRI to investigate the underlying mechanism of acupuncture treatment for mild cognitive impairment (MCI). The findings revealed that following acupuncture intervention, MCI patients exhibited contrasting alterations in ReHo values within the hippocampus/parahippocampal and insular regions compared to baseline, while a notable increase in ReHo values was observed within the middle frontal gyrus region. These results suggest that acupuncture has the potential to modulate brain activity, particularly within the default mode network and salience network, thereby facilitating cognitive enhancement in individuals with MCI.
4.3 Research trend analysis
The emergence of keywords to a certain extent reflects the prevailing research trends. The graph reveals that keywords such as randomized controlled trial, meta-analysis, functional connectivity, ischemic stroke, women, systematic review, prophylaxis, mild cognitive impairment, and others have consistently maintained their popularity in current research directions.
4.3.1 Randomized controlled trials and functional connectivity
From the perspective of evidence-based medicine, well-designed randomized controlled trials (RCT) provide the essential information and guidance required for clinical practice decisions and are considered the gold standard, sitting at the top of the evidence pyramid. RCT is the most rigorous and reliable research method to determine whether there is a causal relationship between interventions and outcomes (Li et al., 2018; Bhide et al., 2018). Although fMRI has made significant progress in studying the safety and efficacy of acupuncture for treating diseases, the central mechanisms remain unclear and require further investigation. RCT is the best approach for this purpose. Functional connectivity can be used to explore the connectivity and interactions between brain regions within brain networks during specific stimuli (Xie et al., 2014; Liu et al., 2015). Therefore, using RCTs to explore brain functional connectivity can help reveal the underlying central mechanisms. Several RCT has shown (Liu et al., 2022; Li et al., 2022) that acupuncture treatment can enhance functional connectivity between specific regions when treating conditions such as anxiety and migraines, and that different doses of laser acupuncture lead to changes in functional connectivity between the regions of interest (ROI) and other brain areas (Chang et al., 2023). Additionally, an ongoing RCT is exploring the effectiveness and safety of acupuncture in treating post-stroke depression, particularly focusing on its impact on the functional connectivity of the cognitive control network (CCN) (Luo et al., 2022).
4.3.2 Meta-analysis and systematic review
Meta-analysis is a method that synthesizes, combines, and analyzes data from multiple studies to estimate a single effect and answer research questions (Arya et al., 2020), while systematic reviews are considered the gold standard for evidence synthesis (Paul and Leibovici, 2014). The literature included in this article related to meta-analysis and systematic reviews predominantly focuses on using fMRI to systematically summarize the mechanisms of acupuncture in treating brain disorders. Research by Zang et al. (2023) showed that fMRI revealed significant effects of acupuncture on the default mode network in patients with primary insomnia, particularly in the frontal and precuneus regions. A study by Zhang et al. (2021) demonstrated that after acupuncture treatment for depression, fMRI showed an increase in the N-acetylaspartate/creatine (NAA/Cr) ratio, increased ALFF in the right precuneus, decreased ALFF in the inferior frontal gyrus (IFG), and enhanced functional connectivity in the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC).
4.3.3 Ischemic stroke and women
Ischemic stroke is one of the most common and severe manifestations of cerebrovascular disease (Feske, 2021). Clinically, it presents as focal neurological deficits such as hemiplegia, aphasia, dysphagia, visual impairment, and cognitive impairments (Li et al., 2022). The incidence of stroke ranks second among the leading causes of death worldwide, accounting for 11.6% of all mortalities, and it also stands as the third most prevalent cause of disability globally, affecting 5.7% of the population (GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators, 2021). Compared with males, females with ischemic stroke exhibit accelerated physiological aging, especially among younger populations where the incidence of ischemic stroke is higher in females than in males (Gallego-Fabrega et al., 2022; Ekker and de Leeuw, 2020). Additionally, females have a higher lifetime risk of developing ischemic stroke compared to males (Bruce et al., 2020). Acupuncture can promote neuroplasticity by modulating the functional reorganization of the entire brain after ischemia and by altering neural structure and function (Qin et al., 2022; Chavez et al., 2017) and has been used in the treatment of stroke and post-stroke rehabilitation (Lu et al., 2016). The main analysis methods utilized in fMRI are ReHo and ALFF, which have been extensively employed in investigating brain function and neural plasticity following ischemic stroke (Li et al., 2022; Lv et al., 2021). The findings of an fMRI-based study (Wang et al., 2023) demonstrate that acupuncture has the potential to enhance motor function following ischemic stroke. The results of animal experiments have demonstrated that electrical acupuncture stimulation applied to the GV20 and DU24 acupoints can significantly enhance the levels of N-acetyl aspartate (NAA) and choline (Cho) in both the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex, thereby effectively improving learning and memory abilities in rats with ischemic stroke (He et al., 2018).
4.3.4 Mild cognitive impairment and prophylaxis
MCI is a disease in which individuals exhibit cognitive impairments with minimal impact on daily activities. The prevalence of MCI in the age group of 60–64 years is 6.7%, whereas it increases to 8.4% in the age group of 65–69 years, exhibiting an ascending trend with advancing age (Petersen et al., 2018). MCI can be regarded as the primary cognitive manifestation of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), but it may also occur in other diseases such as Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, and human immunodeficiency virus (Sanford, 2017). Therefore, effectively treating MCI can prevent the onset and progression of AD and other related diseases. The practice of acupuncture is widely recognized as an effective medical system that not only provides treatment for various diseases but also offers preventive measures for maintaining optimal health (Mallory et al., 2016). Task-based fMRI can enable the assessment of pre-and post-acupuncture treatment changes in brain activity (Yan et al., 2022), while resting-state fMRI measures spontaneous neuronal activity through the recording of blood oxygen level-dependent BOLD signals (Zhao et al., 2023). Thus, fMRI can be applied to investigate the development of acupuncture for the prevention of MCI. Xu et al. (2022) using fMRI during acupuncture treatment for MCI patients, observed a significant voxel-wise centrality increase in bilateral medial frontal cortex (MFC) and bilateral MCC after acupuncture stimulation, along with decreased voxel-wise centrality in left precuneus region. This effectively enhanced patients’ cognitive function and mitigated the progression of MCI. When Lai et al. (2022) explored the efficacy and mechanism of moxibustion treatment for patients with MCI using fMRI, they observed a significant increase ALFF values in the left precuneus, left thalamus, and right temporal pole after moxibustion therapy. Additionally, there was a significant decrease observed in the ALFF values within the bilateral lingual gyrus. This improvement in cognitive function prevented further deterioration of MCI patients.
4.4 Analysis of FMRI in the field of acupuncture
From the above analysis, it can be observed that while the number of annual publications on fMRI in the field of acupuncture fluctuates, there is an overall upward trend. The countries and institutions with the highest publication volumes are primarily from China, the USA, and South Korea, with fewer studies emerging from other countries. Unfortunately, based on the journals in which the articles are published, research on fMRI in acupuncture appears primarily in a few high-quality journals, with most journals having a lower impact factor. Our study reveals that the current research hotspots mainly focus on different acupuncture techniques, the specificity of acupoints, and the mechanisms of acupuncture in treating diseases. Furthermore, we have predicted future research trends. The results indicate that studying fMRI in acupuncture from the perspective of evidence-based medicine is a growing trend, as it can provide high-quality evidence. Additionally, there is a clear need for more meta-analyses and systematic reviews to summarize the application of fMRI in the acupuncture field. Moreover, our findings also suggest that fMRI research in acupuncture includes studies on the reasons why women have a higher incidence of ischemic stroke compared to men, as well as its role in preventing mild cognitive impairment.
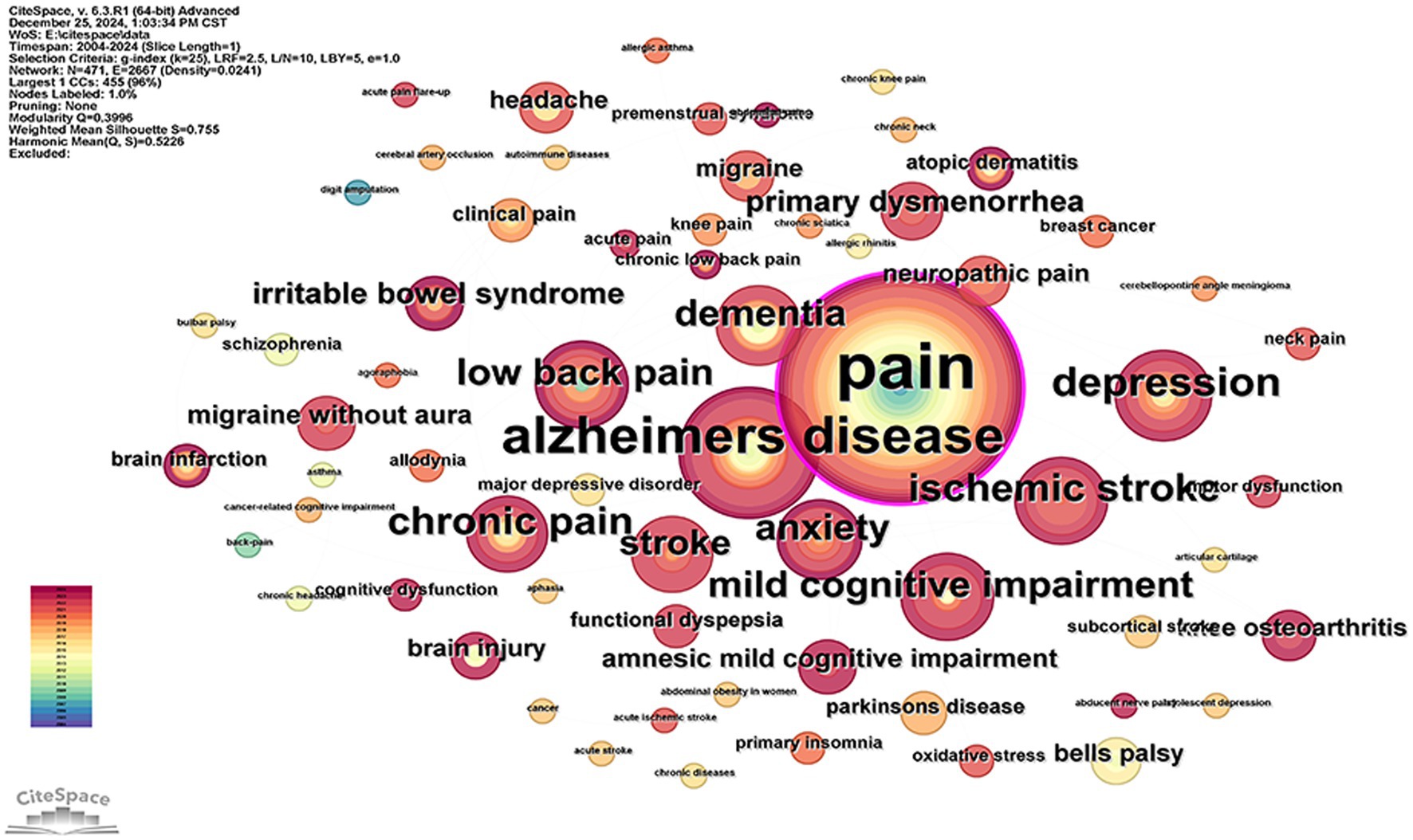
FMRI has been used in the field of acupuncture for a wide range of disorders, focusing on motor system disorders, neurological disorders, and mental disorders (Figure 8). Disorders of the locomotor system include chronic pain, low back pain, neck pain, knee pain, carpal tunnel syndrome, motor dysfunction, and more! Neurological disorders include headache, migraine, abducent nerve palsy, bulbar palsy, bells palsy, dementia, aphasia, mild cognitive impairment, cancer-related cognitive dysfunction, cerebral arterial occlusion, and stroke. Mental disorders include primary insomnia, anxiety, depression, and schizophrenia. All of these illustrate the variety and wide range of applications of using fMRI to study acupuncture for the treatment of diseases.
5 Advantages and limitations
Zhang et al. (2021) have summarized the history and research hotspots of acupuncture in the field of MRI. The similarities between his study and the present study are that the country with the highest number of annual publications is China and the author with the highest number of publications is Tian, J. The journal with the most publications is Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. The highest co-cited journal frequency was Neuroimage. The keywords are similar in that they all have fMRI, Pain Acupuncture, etc. The difference is that his findings show that the trends lie in Connectivity, fMRI, Modulation, and DMN. The results of this study show trends include the randomized controlled trial, meta-analysis, functional connectivity, ischemic stroke, women, systematic review, prophylaxis, and mild cognitive impairment.
This study employs bibliometric methods to visualize the application of fMRI in the field of acupuncture from 2004 to 2024, summarizing the current research status and predicting future trends. However, it is important to note that there are certain limitations in this study. First, we relied solely on the WOS database as the data source, which may have excluded some relevant literature. Second, all the studies included were published in English, without considering literature in other languages. Third, during the exclusion process, some types of literature that belonged to two categories were not fully excluded, which may have affected the thoroughness of the analysis.
6 Conclusion
This study aims to explore the application of fMRI in the field of acupuncture from 2004 to 2024. It provides an overview of current research status and offers predictions for future trends. The current research suggests that fMRI has a broad range of applications in the field of acupuncture and exhibits significant potential for further development. Despite the limitations of this work, the results may help researchers studying fMRI and acupuncture. We predicted future research trends. We believe that studying the application of FMRI in the field of acupuncture from the perspective of evidence-based medicine is the future trend and that high-quality evidence can be obtained from the perspective of evidence-based medicine. More Meta-analyses and systematic evaluations are also needed to conclude the application of fMRI in the field of acupuncture. In addition, we believe that the application of fMRI in the field of acupuncture also includes the reasons why women get ischaemic stroke higher than men, and the prevention of mild cognitive impairment.
Author contributions
ZW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LC: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. TJ: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. QZ: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Methodology, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. FW: Methodology, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number: 82374600) and the seventh batch of the Jilin Province Youth Science and Technology Talent Lifting Project (Grant number: QT202319).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
WOS, Web of Science; fMRI, functional magnetic resonance imaging; PCC, posterior cingulate cortex; DMN, default mode network; fFPN, frontoparietal network; ECN, executive control network; MVPA, multivoxel pattern analysis; NAP, non-acupoint; MD, mediodorsal thalamus; PHG, parahippocampal gyrus; Mthal, motor thalamus subregions; mPFC, medial prefrontal cortex; PCU, precuneus; MCC, middle cingulate cortex; rs-FC, resting-state functional connectivity; IFG, inferior frontal gyrus; rACC, rostral anterior cingulate cortex; ALFF, amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations; ReHo, regional homogeneity; MCI, mild cognitive impairment; CCN, cognitive control network; NAA/Cr, N-acetyl aspartate/creatine ratio; ACC, anterior cingulate cortex; NAA, N-acetyl aspartate; Cho, choline; AD, Alzheimer's disease; MFC, medial frontal cortex.
References
Arya, S., Schwartz, T. A., and Ghaferi, A. A. (2020). Practical guide to meta-analysis. JAMA Surg. 155, 430–431. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2019.4523
Bai, L., Qin, W., Tian, J., Dong, M., Pan, X., Chen, P., et al. (2009). Acupuncture modulates spontaneous activities in the anticorrelated resting brain networks. Brain Res. 1279, 37–49. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.04.056
Bai, L., Qin, W., Tian, J., Liu, P., Li, L., Chen, P., et al. (2009). Time-varied characteristics of acupuncture effects in fMRI studies. Hum. Brain Mapp. 30, 3445–3460. doi: 10.1002/hbm.20769
Beissner, F., Nöth, U., and Schockert, T. (2011). The problem of metal needles in acupuncture-fMRI studies. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2011:808203. doi: 10.1155/2011/808203
Bhide, A., Shah, P. S., and Acharya, G. (2018). A simplified guide to randomized controlled trials. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 97, 380–387. doi: 10.1111/aogs.13309
Bruce, S. S., Merkler, A. E., Bassi, M., Chen, M. L., Salehi Omran, S., Navi, B. B., et al. (2020). Differences in diagnostic evaluation in women and men after acute ischemic stroke. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 9:e015625. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.015625
Cao, J., Tu, Y., Orr, S. P., Lang, C., Park, J., Vangel, M., et al. (2019). Analgesic effects evoked by real and imagined acupuncture: a neuroimaging study. Cereb. Cortex 29, 3220–3231. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhy190
Chang, Y. C., Chen, C. M., Lay, I. S., Lee, Y. C., and Tu, C. H. (2023). The effects of laser acupuncture dosage at PC6 (Neiguan) on brain reactivity: a pilot resting-state fMRI study. Front. Neurosci. 17:1264217. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1264217
Chang, Q. Y., Lin, Y. W., and Hsieh, C. L. (2018). Acupuncture and neuroregeneration in ischemic stroke. Neural Regen. Res. 13, 573–583. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.230272
Chavez, L. M., Huang, S. S., MacDonald, I., Lin, J. G., Lee, Y. C., and Chen, Y. H. (2017). Mechanisms of acupuncture therapy in ischemic stroke rehabilitation: a literature review of basic studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18:2270. doi: 10.3390/ijms18112270
Chen, X., Spaeth, R. B., Freeman, S. G., Scarborough, D. M., Hashmi, J. A., Wey, H. Y., et al. (2015). The modulation effect of longitudinal acupuncture on resting state functional connectivity in knee osteoarthritis patients. Mol. Pain 11:67. doi: 10.1186/s12990-015-0071-9
Chen, T., Zhang, W. W., Chu, Y. X., and Wang, Y. Q. (2020). Acupuncture for pain management: molecular mechanisms of action. Am. J. Chin. Med. 48, 793–811. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X20500408
Chen, X., Zhang, H., and Zou, Y. (2015). A functional magnetic resonance imaging study on the effect of acupuncture at GB34 (Yanglingquan) on motor-related network in hemiplegic patients. Brain Res. 1601, 64–72. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2015.01.011
Damascelli, M., Woodward, T. S., Sanford, N., Zahid, H. B., Lim, R., Scott, A., et al. (2022). Multiple functional brain networks related to pain perception revealed by fMRI. Neuroinformatics 20, 155–172. doi: 10.1007/s12021-021-09527-6
Dhond, R. P., Yeh, C., Park, K., Kettner, N., and Napadow, V. (2008). Acupuncture modulates resting state connectivity in default and sensorimotor brain networks. Pain 136, 407–418. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2008.01.011
Ekker, M. S., and de Leeuw, F. E. (2020). Higher incidence of ischemic stroke in young women than in young men: mind the gap. Stroke 51, 3195–3196. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.032062
Fang, J., Jin, Z., Wang, Y., Li, K., Kong, J., Nixon, E. E., et al. (2009). The salient characteristics of the central effects of acupuncture needling: limbic-paralimbic-neocortical network modulation. Hum. Brain Mapp. 30, 1196–1206. doi: 10.1002/hbm.20583
Gallego-Fabrega, C., Muiño, E., Cullell, N., Cárcel-Márquez, J., Lazcano, U., Soriano-Tárraga, C., et al. (2022). Biological age acceleration is lower in women with ischemic stroke compared to men. Stroke 53, 2320–2330. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.037419
GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators (2021). Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 20, 795–820. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00252-0
Haupt, M., Gerner, S. T., Bähr, M., and Doeppner, T. R. (2023). Neuroprotective strategies for ischemic stroke-future perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24:4334. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054334
He, J., Zhao, C., Liu, W., Huang, J., Liang, S., Chen, L., et al. (2018). Neurochemical changes in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex associated with electroacupuncture for learning and memory impairment. Int. J. Mol. Med. 41, 709–716. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3287
Hui, K. K., Liu, J., Marina, O., Napadow, V., Haselgrove, C., Kwong, K. K., et al. (2005). The integrated response of the human cerebro-cerebellar and limbic systems to acupuncture stimulation at ST 36 as evidenced by fMRI. NeuroImage 27, 479–496. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.04.037
Jung, W. M., Lee, I. S., Wallraven, C., Ryu, Y. H., Park, H. J., and Chae, Y. (2015). Cortical activation patterns of bodily attention triggered by acupuncture stimulation. Sci. Rep. 5:12455. doi: 10.1038/srep12455
Kong, J., Gollub, R. L., Webb, J. M., Kong, J. T., Vangel, M. G., and Kwong, K. (2007). Test-retest study of fMRI signal change evoked by electroacupuncture stimulation. NeuroImage 34, 1171–1181. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.10.019
Kong, Q., Sacca, V., Walker, K., Hodges, S., and Kong, J. (2023). Thalamocortical mechanisms underlying real and imagined acupuncture. Biomedicines. 11:1830. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11071830
Lai, Z., Zhang, Q., Liang, L., Wei, Y., Duan, G., Mai, W., et al. (2022). Efficacy and mechanism of Moxibustion treatment on mild cognitive impairment patients: an fMRI study using ALFF. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 15:852882. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.852882
Lee, J., Eun, S., Kim, J., Lee, J. H., and Park, K. (2019). Differential influence of acupuncture somatosensory and cognitive/affective components on functional brain connectivity and pain reduction during low Back pain state. Front. Neurosci. 13:1062. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.01062
Li, G., Bhatt, M., Wang, M., Mbuagbaw, L., Samaan, Z., and Thabane, L. (2018). Enhancing primary reports of randomized controlled trials: three most common challenges and suggested solutions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 115, 2595–2599. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1708286114
Li, L., Qin, W., Bai, L., and Tian, J. (2010). Exploring vision-related acupuncture point specificity with multivoxel pattern analysis. Magn. Reson. Imaging 28, 380–387. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2009.11.009
Li, C., Wang, Y., Li, B., and Su, S. (2022). Effects of acupuncture at Neiguan in neural activity of related brain regions: a resting-state fMRI study in anxiety. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 18, 1375–1384. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S368227
Li, S. S., Xing, X. X., Hua, X. Y., Zhang, Y. W., Wu, J. J., Shan, C. L., et al. (2022). Alteration of brain functional networks induced by electroacupuncture stimulation in rats with ischemia-reperfusion: an independent component analysis. Front. Neurosci. 16:958804. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.958804
Li, L., Zhu, W., Lin, G., Chen, C., Tang, D., Lin, S., et al. (2022). Effects of acupuncture in ischemic stroke rehabilitation: a randomized controlled trial. Front. Neurol. 13:897078. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.897078
Liu, L., Lyu, T. L., Fu, M. Y., Wang, L. P., Chen, Y., Hong, J. H., et al. (2022). Changes in brain connectivity linked to multisensory processing of pain modulation in migraine with acupuncture treatment. Neuroimage Clin. 36:103168. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2022.103168
Liu, X., Yan, Z., Wang, T., Yang, X., Feng, F., Fan, L., et al. (2015). Connectivity pattern differences bilaterally in the cerebellum posterior lobe in healthy subjects after normal sleep and sleep deprivation: a resting-state functional MRI study. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 11, 1279–1289. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S84204
Lu, L., Zhang, X. G., Zhong, L. L., Chen, Z. X., Li, Y., Zheng, G. Q., et al. (2016). Acupuncture for neurogenesis in experimental ischemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 6:19521. doi: 10.1038/srep19521
Luo, M., Duan, Z., Song, X., Liu, C., Li, R., Su, K., et al. (2022). Effects of optimized acupuncture and Moxibustion treatment on depressive symptoms and executive functions in patients with post-stroke depression: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Front. Neurol. 13:833696. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.833696
Lv, J., Shi, C., Deng, Y., Lou, W., Hu, J., Shi, L., et al. (2016). The brain effects of laser acupuncture at thirteen ghost acupoints in healthy individuals: a resting-state functional MRI investigation. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 54, 48–54. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2016.08.003
Lv, Q., Xu, G., Pan, Y., Liu, T., Liu, X., Miao, L., et al. (2021). Effect of acupuncture on neuroplasticity of stroke patients with motor dysfunction: a Meta-analysis of fMRI studies. Neural Plast. 2021:8841720. doi: 10.1155/2021/8841720
Ma, Z. Z., Lu, Y. C., Wu, J. J., Xing, X. X., Hua, X. Y., and Xu, J. G. (2020). Acupuncture induces reduction in limbic-cortical feedback of a neuralgia rat model: a dynamic causal modeling study. Neural Plast. 2020:5052840. doi: 10.1155/2020/5052840
Mallory, M. J., Do, A., Bublitz, S. E., Veleber, S. J., Bauer, B. A., and Bhagra, A. (2016). Puncturing the myths of acupuncture. J. Integr. Med. 14, 311–314. doi: 10.1016/S2095-4964(16)60269-8
Napadow, V., Ahn, A., Longhurst, J., Lao, L., Stener-Victorin, E., Harris, R., et al. (2008). The status and future of acupuncture mechanism research. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 14, 861–869. doi: 10.1089/acm.2008.SAR-3
Napadow, V., Makris, N., Liu, J., Kettner, N. W., Kwong, K. K., and Hui, K. K. (2005). Effects of electroacupuncture versus manual acupuncture on the human brain as measured by fMRI. Hum. Brain Mapp. 24, 193–205. doi: 10.1002/hbm.20081
Paul, M., and Leibovici, L. (2014). Systematic review or meta-analysis? Their place in the evidence hierarchy. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 20, 97–100. doi: 10.1111/1469-0691.12489
Petersen, R. C., Lopez, O., Armstrong, M. J., Getchius, T. S. D., Ganguli, M., Gloss, D., et al. (2018). Practice guideline update summary: mild cognitive impairment: report of the guideline development, dissemination, and implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of neurology. Neurology 90, 126–135. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000004826
Qiao, L., Guo, M., Qian, J., Xu, B., Gu, C., and Yang, Y. (2020). Research advances on acupuncture analgesia. Am. J. Chin. Med. 48, 245–258. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X20500135
Qin, S., Zhang, Z., Zhao, Y., Liu, J., Qiu, J., Gong, Y., et al. (2022). The impact of acupuncture on neuroplasticity after ischemic stroke: a literature review and perspectives. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 16:817732. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.817732
Robinson, C. L., Berger, A., Sottosanti, E., Li, M., Kaneb, A., Keefe, J., et al. (2022). Acupuncture as part of multimodal analgesia for chronic pain. Orthop. Rev. 14:38321. doi: 10.52965/001c.38321
Sanford, A. M. (2017). Mild cognitive impairment. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 33, 325–337. doi: 10.1016/j.cger.2017.02.005
Steward, M. M., Sridhar, A., and Meyer, J. S. (2013). Neural regeneration. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 367, 163–191. doi: 10.1007/82_2012_302
Wang, Y. K., Li, T., Ha, L. J., Lv, Z. W., Wang, F. C., Wang, Z. H., et al. (2020). Effectiveness and cerebral responses of multi-points acupuncture for primary insomnia: a preliminary randomized clinical trial and fMRI study. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 20:254. doi: 10.1186/s12906-020-02969-6
Wang, Y., Lu, M., Liu, R., Wang, L., Wang, Y., Xu, L., et al. (2023). Acupuncture alters Brain's dynamic functional network connectivity in stroke patients with motor dysfunction: a randomised controlled neuroimaging trial. Neural Plast. 2023:8510213. doi: 10.1155/2023/8510213
Wang, X., Wang, Z., Liu, J., Chen, J., Liu, X., Nie, G., et al. (2016). Repeated acupuncture treatments modulate amygdala resting state functional connectivity of depressive patients. Neuroimage Clin. 12, 746–752. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2016.07.011
Wang, Y., Xu, J., Zhang, Q., Zhang, Q., Yang, Y., Wei, W., et al. (2021). Immediate analgesic effect of acupuncture in patients with primary dysmenorrhea: a fMRI study. Front. Neurosci. 15:647667. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.647667
Wei, X. Y., Luo, S. L., Chen, H., Liu, S. S., Gong, Z. G., and Zhan, S. H. (2022). Functional connectivity changes during migraine treatment with electroacupuncture at Shuaigu (GB8). J. Integr. Med. 20, 237–243. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2022.01.009
Wen, J., Chen, X., Yang, Y., Liu, J., Li, E., Liu, J., et al. (2021). Acupuncture medical therapy and its underlying mechanisms: a systematic review. Am. J. Chin. Med. 49, 1–23. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X21500014
Xiang, A., Chen, M., Qin, C., Rong, J., Wang, C., Shen, X., et al. (2021). Frequency-specific blood oxygen level dependent oscillations associated with pain relief from ankle acupuncture in patients with chronic low Back pain. Front. Neurosci. 15:786490. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.786490
Xie, Z., Cui, F., Zou, Y., and Bai, L. (2014). Acupuncture enhances effective connectivity between cerebellum and primary sensorimotor cortex in patients with stable recovery stroke. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2014:603909. doi: 10.1155/2014/603909
Xu, K., Wei, Y., Liu, C., Zhao, L., Geng, B., Mai, W., et al. (2022). Effect of Moxibustion treatment on degree centrality in patients with mild cognitive impairment: a resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 16:889426. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2022.889426
Yan, Y., Sheng, R. Y., Wang, Y., and Zhang, C. H. (2022). Acupuncture mechanism studies employing task-based fMRI: a scoping review protocol. Syst. Rev. 11:128. doi: 10.1186/s13643-022-02007-1
Yang, H., Li, X., Guo, X. L., Zhou, J., Shen, Z. F., Liu, L. Y., et al. (2022). Moxibustion for primary dysmenorrhea: a resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging study exploring the alteration of functional connectivity strength and functional connectivity. Front. Neurosci. 16:969064. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.969064
Yeo, S., Lim, S., Choe, I. H., Choi, Y. G., Chung, K. C., Jahng, G. H., et al. (2012). Acupuncture stimulation on GB34 activates neural responses associated with Parkinson's disease. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 18, 781–790. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2012.00363.x
Yin, Z., Wang, Z., Li, Y., Zhou, J., Chen, Z., Xia, M., et al. (2023). Neuroimaging studies of acupuncture on Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review. BMC Compl. Med. Ther. 23:63. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-03888-y
You, Y., Bai, L., Dai, R., Cheng, H., Liu, Z., Wei, W., et al. (2013). Altered hub configurations within default mode network following acupuncture at ST36: a multimodal investigation combining fMRI and MEG. PLoS One 8:e64509. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064509
Zang, S., Chen, Y., Chen, H., Shi, H., and Zhou, L. (2023). Effects of acupuncture on the brain in primary insomnia: a coordinate-based meta-analysis of fMRI studies. Front. Neurol. 14:1180393. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1180393
Zhang, Z., Chen, L., Guo, Y., Li, D., Zhang, J., Liu, L., et al. (2023). The neuroprotective and neural circuit mechanisms of acupoint stimulation for cognitive impairment. Chin. Med. 18:8. doi: 10.1186/s13020-023-00707-x
Zhang, Q., Liang, L., Lai, Z., Wei, Y., Duan, G., Lai, Y., et al. (2024). Altered regional homogeneity following moxibustion in mild cognitive impairment. Brain Imaging Behav. 18, 343–351. doi: 10.1007/s11682-023-00830-1
Zhang, J., Lu, C., Wu, X., Nie, D., and Yu, H. (2021). Neuroplasticity of acupuncture for stroke: an evidence-based review of MRI. Neural Plast. 2021:2662585. doi: 10.1155/2021/2662585
Zhang, S., Wang, X., Yan, C. Q., Hu, S. Q., Huo, J. W., Wang, Z. Y., et al. (2018). Different mechanisms of contralateral-or ipsilateral-acupuncture to modulate the brain activity in patients with unilateral chronic shoulder pain: a pilot fMRI study. J. Pain Res. 11, 505–514. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S152550
Zhang, J., Wu, X., Nie, D., Zhuo, Y., Li, J., Hu, Q., et al. (2021). Magnetic resonance imaging studies on acupuncture therapy in depression: a systematic review. Front. Psych. 12:670739. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.670739
Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., Hu, L., Huang, X., Liu, Y., Li, J., et al. (2021). Global trends and performances of magnetic resonance imaging studies on acupuncture: a bibliometric analysis. Front. Neurosci. 14:620555. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.620555
Zhao, J., Guo, L. X., Li, H. R., Gou, X. Y., Liu, X. B., Zhang, Y., et al. (2023). The effects of acupuncture therapy in migraine: an activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis. Front. Neurosci. 16:1097450. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1097450
Keywords: acupuncture, fMRI, bibliometric analysis, Citespace, VOSviewer
Citation: Wang Z, Chen L, Jiang T, Zhang Q, Zhao J and Wang F (2025) Research status and trends of functional magnetic resonance imaging technology in the field of acupuncture: a bibliometric analysis over the past two decades. Front. Neurosci. 19:1489049. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1489049
Edited by:
Lijun Bai, Xi’an Jiaotong University, ChinaReviewed by:
Jiliang Fang, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, ChinaShangjie Chen, Shenzhen Baoan People’s Hospital, China
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Chen, Jiang, Zhang, Zhao and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jinying Zhao, emhhb2ppbnlpbmcyN0AxMjYuY29t; Fuchun Wang, ZnVjaGVud2FuZzQyMEAxMjYuY29t
 Zhongke Wang
Zhongke Wang Lu Chen
Lu Chen Tianyu Jiang
Tianyu Jiang Qi Zhang
Qi Zhang Jinying Zhao*
Jinying Zhao* Fuchun Wang
Fuchun Wang