
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Neurosci., 31 October 2024
Sec. Neurodegeneration
Volume 18 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2024.1499458
This article is part of the Research TopicMyeloid Cells as Active Players in Human Neurodegenerative DiseasesView all 4 articles
 Eleftheria Kodosaki1,2*
Eleftheria Kodosaki1,2* Rosie Bell1,2
Rosie Bell1,2 Aitana Sogorb-Esteve2,3
Aitana Sogorb-Esteve2,3 Katharine Wiltshire3
Katharine Wiltshire3 Henrik Zetterberg1,2,4,5,6,7
Henrik Zetterberg1,2,4,5,6,7 Amanda Heslegrave1,2*
Amanda Heslegrave1,2*The role of myeloid cells (granulocytes and monocytes) in neurodegeneration and neurodegenerative disorders (NDD) is indisputable. Here we discuss the roles of myeloid cells in neurodegenerative diseases, and the recent advances in biofluid and imaging myeloid biomarker research with a focus on methods that can be used in the clinic. For this review, evidence from three neurodegenerative diseases will be included, Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD), and multiple sclerosis (MS). We discuss the potential for these biomarkers to be used in humans with suspected NDD as prognostic, diagnostic, or monitoring tools, identify knowledge gaps in literature, and propose potential approaches to further elucidate the role of myeloid cells in neurodegeneration and better utilize myeloid biomarkers in the understanding and treatment of NDD.
Myeloid cells are classically defined as granulocyte (e.g., neutrophils, mast cells) and monocyte/dendritic (monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells)-lineage cells originally derived from the bone marrow (De Kleer et al., 2014). However, myeloid stem cells also develop into erythrocytes and platelets (Svoboda and Bartunek, 2015). An interesting exception is the main myeloid cell type in the brain, the microglia that arise from primitive yolk sac macrophages that engraft the developing neuroectoderm destined to become the central nervous system (CNS) parenchyma during embryogenesis (Mendes and Majewska, 2021; Bennett et al., 2018). However, other CNS-resident macrophages have been identified with different origins and characteristics (Prinz et al., 2011; Dermitzakis et al., 2023), and also other myeloid cells [i.e., dendritic cells, granulocytes, such as resident neutrophils and mast cells (Silver et al., 1996), and monocytes (once these infiltrate)]. Although not in the CNS, other peripheral myeloid cells have also been shown to be involved in NDD, including granulocytes, platelets, and erythrocytes, as well as peripheral tissue macrophages (Gopinath et al., 2020). As the brain is surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and communicates with the periphery via the blood–brain barrier (BBB), biomarker analysis focusing on CSF and blood to detect biomarkers from myeloid cells that indicate their status, such as activation or senescence, are extremely useful in studying these cells with respect to their contributions and behavior in NDD. These biomarkers are usually investigated using immunoassays or mass spectrometry methods, to detect quantities and the different forms of proteins. In addition, in the CSF and blood the cells themselves can be used as biomarkers either in their behavior (e.g., how they respond to stimuli), surface expression markers, epigenetic markers, or disease-related myeloid specific genetic polymorphisms. Imaging biomarkers for myeloid cells have also been explored. This review will briefly focus on the myeloid cells and biomarkers in AD, PD, and MS, as they are major NDD of different etiology with both shared and distinct progression mechanisms.
As the brain’s resident immune cells, microglia play a variety of roles in the development and manifestation of NDD. They are found throughout the brain and exhibit both heterogeneity and plasticity, suggesting that they are a versatile cell type responding to different exposures (Benusa et al., 2020; Augusto-Oliveira et al., 2022). They not only reside in the brain tissue; evidence also shows their presence in the CSF (Esaulova et al., 2020), suggesting that the ability to travel through the CNS. The other resident CNS macrophages are restricted to specific locations (e.g., border-associated macrophages) and have roles correlating to these areas; however, they also exhibit heterogeneity in both their characteristics and functions (Dermitzakis et al., 2023; Sun and Jiang, 2024; Mildenberger et al., 2022). CNS macrophages are involved brain homeostasis and are the cells that are often the first line of response to conditions such as injury or infection. That response includes the secretion of molecules ranging from proteins to inflammatory mediators and vesicles (Kremlev et al., 2004; Lee et al., 2002; Paolicelli et al., 2019; Gibbons and Dragunow, 2006), alteration of membrane receptor expression levels and variability to control damage by phagocytosis and communication with other cells to elicit protective tissue responses (Fu et al., 2014); these roles are often dysregulated in NDD and aging with consequences such as accumulation of misfolded proteins which can lead to neurotoxicity and neurodegeneration (Gabandé-Rodríguez et al., 2020; Nizami et al., 2019). Both overactivation and exhaustion of myeloid cells in the CNS have been suggested to contribute to NDD.
Non-microglia CNS resident macrophages are often found in the meninges, perivascular spaces, and choroid plexus (Mildenberger et al., 2022). They take part in microglial-like functions, such as immune surveillance and maintenance of homeostasis, but they also have further roles in regulating CNS entry via modulation of the BBB of, e.g., circulating peripheral cells and molecules (Dermitzakis et al., 2023; Giladi et al., 2020), they are also involved in the glymphatic system, the dysfunction of which has been linked to accumulation of NDD-related proteins such as amyloid-β and tau in the brain (Da Mesquita and Rua, 2024).
Non-resident CNS macrophages may also enter the brain from the periphery as monocytes migrating across the blood–brain barrier under certain conditions such as disease. In the brain tissue they may subsequently differentiate into microglia-like cells, often expressing microglia cell-based markers, and affect NDD processes (Silvin et al., 2023). However, these cells do not become permanent residents of the CNS (De Vlaminck et al., 2022), and have been shown to have different functions to resident immune cells with some studies indicating anti-inflammatory and regulatory functions (De Vlaminck et al., 2022; Greenhalgh et al., 2018; Shechter et al., 2009), while damaging actions in the CNS have also been shown (DePaula-Silva, 2024; Fiala et al., 2002). Peripheral macrophages and monocytes [with their ability to engulf amyloid (Hallé et al., 2015)] and peripheral nervous system macrophages [with the latter overlapping in activation and homeostatic gene expression with microglia (Wang et al., 2020)], have been implicated to be involved in neurodegenerative processes in the CNS (Wakabayashi et al., 2010; Yang et al., 2020), either via their interactions with the BBB, disease-specific factors, inflammatory processes, or via crosstalk with other CNS cells (Yu et al., 2022).
Dendritic cells (DCs) are mainly regulatory antigen-presenting cells of the peripheral immune system, primarily known for their role in initiating and regulating immune responses. Recent studies, mainly in mice have suggested the existence of cells with DC characteristics in the CNS, especially where border-associated macrophages reside (D’Agostino et al., 2012). They are optimally positioned to interact with and activate T cells, which can make them accidental culprits for targeting of other CNS cells by T cells, which may contribute to neurodegeneration or neuroinflammatory injury in diseases such as MS (D’Agostino et al., 2012). They are also able to produce cytokines and recruit more immune cells (including more DCs) to the CNS and therefore exacerbate neuroinflammation and BBB disruption, although neuroprotective roles have also been attributed to them (Gallizioli et al., 2020; Ludewig et al., 2016; Pashenkov et al., 2003).
One of the main type of granulocytes under investigation are neutrophils, which under normal conditions are found in the CNS in very low numbers in the meninges, pia membrane, and the CSF (Kanashiro et al., 2020). They can infiltrate the CNS via a compromised BBB. There they contribute to neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration with the generation of inflammatory molecules in AD (Jacobs et al., 2024), MS where a primed phenotype has been found (Naegele et al., 2012), and PD where their infiltration differs between brain areas and correlates with neuronal damage (Ji et al., 2008). Clinically, dramatically increased CSF neutrophil count is pathognomonic for bacterial meningitis, which induces prominent recruitment of neutrophils to the CNS within minutes of the infection (Fuchs et al., 2019). Other types of granulocytes are under-investigated in NDD. Eosinophils, cells involved in the development of allergic reactions and infection, contribute to the overall inflammatory environment that is often found in NDD periphery and have been shown to have neurotoxic effects upon entry in the CNS with disease-specific findings (Weaver et al., 1988; Inoue et al., 1996). Similar to eosinophils, basophils are involved in the recruitment of cells that potentially could be responsible for certain symptoms that arise during NDD (Miyake et al., 2022). Lastly, mast cells have also been shown to increase neuroinflammation in neurodegeneration when they release neuroinflammatory mediators, and have been observed in the CNS under physiological and pathological conditions (Silver et al., 1996; Duraisamy et al., 2019).
Erythrocytes are not involved per se in the development of NDD, but alterations in their function have been shown during the course of NDD, so there could be a link with disease progression. As they are responsible for oxygen delivery and have a significant role in oxidative stress, issues arising with their function may lead to problems with the energy required for brain metabolic processes; indeed issues with energy and metabolism have been found throughout the spectrum of NDD (Kosenko et al., 2020; Park and Choi, 2020; Johansson et al., 2020) and a case has been made for their role in iron accumulation which has also been related to NDD processes (Prohaska et al., 2012). Haemolysis of erythrocytes in the brain parenchyma after micro- or macrobleeds or upon traumatic brain injury may be causally related to the development of tau pathology in diseases like superficial CNS siderosis (Kondziella and Zetterberg, 2008) and chronic traumatic encephalopathy (Juan et al., 2022).
Platelets may play a role in the development and progression of NDD, with the prime example being AD. Blood platelets produce amyloid beta (Aβ) peptides, using the same machinery as neurons and oligodendrocytes [the main Aβ producers in the brain (Rajani et al., 2024; Sasmita et al., 2024; Plant et al., 2003; Hampel et al., 2021)], and the precursor protein of Aβ, amyloid precursor protein (APP), was soon after cloning (Kang et al., 1987; Goldgaber et al., 1987) identified as the previously described coagulation factor protease nexin-II (Nostrand et al., 1989; Oltersdorf et al., 1989). However, whether blood platelets contribute to Aβ plaque formation in the brain remains unknown (Humpel, 2017). Nevertheless, they have been found to contribute to the vascular pathology of AD (Zhang et al., 2013). In MS, there is evidence for platelet-leukocyte interactions, which contribute to the pathophysiology of the disease (Dziedzic and Bijak, 2019), and potentially may be relevant in PD as well (Beura et al., 2022). For both erythrocytes and platelets, changes in their function or morphology may be considered as biomarkers in NDD, discussed further below.
The term biomarker is defined by the National Institutes of Health Biomarkers Definitions Working Group as “a characteristic that is objectively measured and evaluated as an indicator of normal biological processes, pathogenic processes, or pharmacologic responses to a therapeutic intervention” (Biomarkers Definitions Working Group et al., 2001). Myeloid-related molecules such as proteins (and variations thereof) found in blood and CSF are quantified by immunoassays or mass spectrometry, indicate disease-or disease processes and are therefore considered myeloid biomarkers. Other biomarkers are myeloid cell characteristics (activation/function, number) measured by imaging, and variations of the different myeloid cells found in biofluids and tissues.
A rather gray area is the field of genomic/genetic biomarkers, as genotypes are not biomarkers per se due to them not reflecting biological or pathological processes; however, they can be associated with biomarkers. Epigenetic changes, on the other hand can be considered biomarkers, and so can the results of these changes. In this section, we will first discuss findings of typical biomarkers of NDD found in biofluids that can be measured with, e.g., immunoassays. We will then move to those less commonly thought of as biomarkers (including the gray area genetics-related myeloid biomarkers), and lastly, we will discuss findings from imaging myeloid cell biomarkers studies.
Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2), is expressed in microglia and indicates activation, but also in other CNS and non-CNS macrophages, monocytes, dendritic cells, and granulocytes (Jay et al., 2017), is one of the most studied myeloid NDD biomarkers. A major reason for this focus is the identification of a loss of function mutation in the TREM2 gene as a genetic etiology of AD (Guerreiro et al., 2013; Jonsson et al., 2013). Its soluble form (sTREM2) can be measured in both CSF and blood, and elevated levels have been associated with AD in a variety of CSF (Piccio et al., 2016; Heslegrave et al., 2016) and plasma (Hu et al., 2014; Zhao et al., 2022) studies, hinting that the function of TREM2 is protective rather than detrimental for AD (Brown and St George-Hyslop, 2022; Nabizadeh et al., 2024). Nevertheless, the plasma findings regarding sTREM2 have not been confirmed (Ashton et al., 2019), and some data suggest that plasma sTREM2 concentration is likely linked to cerebrovascular dysfunction rather than AD (Tsai et al., 2021). In other NDD such as PD there are also some findings for sTREM2, where it was found to potentially indicate indirectly toward neuronal injury (Wilson et al., 2020) whereas elsewhere higher CSF sTREM2 predicted a more rapid cognitive decline (Qin et al., 2022). In MS and other neuroinflammatory conditions, CSF sTREM2 concentration is increased (Piccio et al., 2008; Öhrfelt et al., 2016), and reduced after treatment (Öhrfelt et al., 2016). Another genetically linked biomarker is the presence of a specific isoform of Apolipoprotein E (APOE). The protein has three isoforms: E2, E3, E4 and most people express apoE E3. The protein is involved in lipid metabolism, been shown to affect the function of myeloid cells (Bonacina et al., 2018) [including via interacting with patient sex as a factor and affecting the interactions of microglia with plaques in mice (Stephen et al., 2019)] and is a ligand for TREM2 (Atagi et al., 2015). The AD genetic risk variant, ApoE ɛ4 is considered an important genetically linked biomarker for AD pathophysiology as it correlates with enhanced amyloid plaque formation (Drzezga et al., 2009), and in humans it has been found associated with an increased immune response (Gale et al., 2014). ApoE ε4 has been linked with differential biomarker profiles depending on the AD-related amyloid presence (Reinvang et al., 2013), whereas the APOE isoforms quantified in biofluids showed association with AD (Minta et al., 2020).
Amyloid, although due to its involvement in plaque formation is primarily considered a CNS biomarker as it is secreted by neurons, astrocytes, microglia [via extracellular vesicles (EVs)], and oligodendrocytes (Hampel et al., 2021; Trotta et al., 2018; Skaper et al., 2009). It is also secreted in the periphery primarily by platelets (Chen et al., 1995); unlike tau [which has also been found in microglia-derived EVs (Trotta et al., 2018) and has a distinct brain-derived form (Gonzalez-Ortiz et al., 2023)] so far there is no specific way to distinguish between brain and blood derived amyloid. Interestingly, though, various methods of amyloid detection do show some inconsistencies in the correlations between their measurements (Pannee et al., 2021). This could be attributed to assay-specific conditions and characteristics, or antibodies raised against epitopes which are not necessarily reflecting changes to the sequence of the proteins, but perhaps to structure. For example, the coagulation system has also been found to exhibit changes in its levels of certain biomarkers in NDD (Begic et al., 2020; Park et al., 2021; Festoff et al., 2016; Sharma et al., 2021; Bartl et al., 2023; Ziliotto et al., 2018; Koudriavtseva et al., 2023), and members of the coagulation system have been known to act as chaperones for amyloid and have been shown to interfere with its ability to aggregate (Geraghty et al., 2021) while others have been found to contribute toward neurodegeneration and amyloid aggregation (Ahn et al., 2017). Other chaperone proteins, such as Heat shock proteins (HSP)70/90 have also been found to be involved in NDD via their potential interactions with amyloid, and have been found to change with disease progression (Son et al., 2015). So, differences in amyloid between studies could be attributed -in part- to its differential interaction with chaperones and other proteins. Also expressed by platelets in the periphery, the chemokine platelet factor 4 (PF4) (Jian et al., 2017) has exhibited differences in blood levels in AD when compared to controls (Yang et al., 2023), and similarly for MS (Cananzi et al., 1987) and PD (Shen et al., 2020). Surprisingly though, PF4 was also found (in mice at least) to exhibit cognition enhancing effects (Schroer et al., 2023), and correlation with younger age in both mice and humans (Schroer et al., 2023), however the latter was not confirmed in another human study while cognition was not investigated in this study (Duchez et al., 2024).
Chitinase-3-like protein 1 (Ch3l1/YKL-40), an injury response protein that regulates tissue remodeling and is involved in inflammatory processes, is secreted by microglia as well as astrocytes in the CNS, and most of the peripheral myeloid cells (Llorens et al., 2017; Baldacci et al., 2017). It can be detected in both the blood and the CSF, and elevated levels have been observed in a variety of neurodegenerative and neuroinflammatory disorders (Llorens et al., 2017; Villar-Piqué et al., 2019). The structurally-similar chitotriosidase has also been studied and has been found to be a biomarker for microglial reactivity in the CNS (Olsson et al., 2012) and altered in NDD (Rosén et al., 2014; Møllgaard et al., 2016). Other markers include Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1), which is detected both in CSF and blood and increased levels have been found in a variety of NDD where they are often related to disease progression, and CNS myeloid cell infiltration (Singh et al., 2021); this protein is secreted by myeloid cells, but also other CNS and BBB cells and attracts myeloid cells from the periphery to the CNS aiding in the movement of cells within the CNS (Yao and Tsirka, 2014). Interestingly, some biomarkers have altered relationships when it comes to their levels vs. controls depending on the disease, perhaps reflecting disease-specific neurodegenerative mechanisms; for example CX3CL1 is increased in the CSF and blood of people with both MS (Kastenbauer et al., 2003) and AD (Bivona et al., 2022) vs. controls, but decreased in PD (Hatcher-Martin et al., 2020), whereas it seems unaffected in non-AD dementia (Bivona et al., 2022), although in all the above mentioned conditions neurodegeneration is apparent. Similarly, sCD163 has been found increased in PD (Nissen et al., 2021) in CSF in women indicating a sex-specific disease activity present in blood. The same was also not true in CSF for the transition of patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) to AD for men but it is true for women (Gross et al., 2019). In MS a CSF/serum ratio (Stilund et al., 2015; Stilund et al., 2014) was linked to disease progression and was found increased vs. controls.
Other myeloid-related markers (that are mostly considered inflammatory/immune system activation markers) such as cytokines (Guerreiro et al., 2007; Kodosaki et al., 2024; Qu et al., 2023) and chemokines (including the aforementioned CX3CL1) have also attracted attention as potential biomarkers that can be secreted by the entire repertoire or majority of myeloid cells. In addition, polymorphisms in immune-related molecules such as cytokines have been found to play either protective or detrimental roles in the development of AD (Su et al., 2016) most of which can be attributed to their effects on cytokine production.
Complement system proteins and related proteins including lectin pathway proteins [such as galectin-3 (Boza-Serrano et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2015) and mannan-binding lectin (MBL) (Lanzrein et al., 1998)], as well as the more investigated classical and alternative pathways have exhibited differential expression in PD, AD, and MS (Kodosaki et al., 2024; Dufek et al., 2009; Naskar et al., 2022; Khosousi et al., 2023; Krance et al., 2021). Members of the complement system have also exhibited amyloid chaperone activity as well (Geraghty et al., 2021). Interestingly, a group of granulocyte specific activation markers have also been found as discriminatory between MS and related neurological disorders (Leppert et al., 2023). Similarly, neutrophil-related activation markers myeloperoxidase and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin were found increased in the peripheral blood of AD relative to controls (Wu et al., 2020) but most of these markers are also expressed in other myeloid and non-myeloid cells. Most markers mentioned here are not selective for one cell type or function; however, grouping biomarkers according to their function and cell type origin may offer advantages compared to focusing on single markers. Lastly, an under-investigated, but promising area of fluid biomarker research includes studying EVs depending on their cellular origin and content. There have been studies showing that certain microglial EVs may contribute to CNS processes such as neurogenesis via miRNA (Fan et al., 2022), and other studies have shown that the contents of EVs that relate to myeloid activity exhibit changes in AD (McKeever et al., 2018), MS (Palacio et al., 2023), and PD (Marchetti et al., 2020), however this is a developing field.
Another interesting area of research is using the cells themselves as biomarkers by employing techniques to evaluate cellular characteristics, for example flow cytometry for membrane markers, or microscopy for phenotypic changes, while epigenetic changes may also reveal novel biomarkers. Erythrocytes and platelets have both been shown to have alterations in functions, activation, and membrane characteristics in neurodegenerative disorders (Behari and Shrivastava, 2013; Bosman, 2018) with disease specific alterations found in platelets in AD (Davies et al., 1996), MS (Sheremata et al., 2008), and PD (Beura et al., 2022; Benecke et al., 1993; Factor et al., 1994). Dendritic cells have been shown by one study to be decreased in AD compared to controls, and associated with disease progression (Ciaramella et al., 2016). In this study, specific subsets of DC, namely myeloid DC were found depleted in the blood of AD patients however that was not observed when the patients were under AD treatment with acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (Ciaramella et al., 2016); elsewhere both subpopulations of DCs were found increased in both cognitively normal and patients with MCI who were amyloid positive (Grayson et al., 2023). In addition, monocyte-derived DC from AD patients exhibited more pro-inflammatory/reactive behavior via secretion of more inflammatory biomarkers following inflammatory stimuli exposure compared to controls (Ciaramella et al., 2010). For monocytes, differential expression of the surface markers CD14 and CD16 is correlated with the expression of other surface markers that can functionally categorize these cells (Savinetti et al., 2021); different categories are more prominent in the blood of patients with PD (Grozdanov et al., 2014), MS (Chuluundorj et al., 2014), and AD (Saresella et al., 2014), with the findings in AD also indicating a reduced amyloid uptake from these cells (Chen et al., 2020) which was not the case for PD patient derived cells in the same study. Similarly, in a relatively small study, patient derived monocytes showed differential activation and surface markers at baseline and upon inflammatory receptor [Toll-like receptor (TLR)-2 and TLR-4] activation, with inflammatory response peaking in the MCI stage compared to both controls, pre-MCI, and AD cells, and decreased phagocytic ability when moving from HC to the other categories (pre-MCI, MCI, AD) (Munawara et al., 2021). Overall, functional and numerical alterations in peripheral myeloid cells (including different populations such as granulocytes and monocyte-lineage cells) have been demonstrated during the course of NDD (Thome et al., 2018; Lunnon et al., 2012). Although both microglia and macrophages have been detected in CSF (Esaulova et al., 2020) and could potentially be isolated and characterized, so far no studies exist utilizing their presence in CSF in order to study the subset of microglia and macrophages in NDD. It has been demonstrated that the initiation and termination of the neuroinflammatory response of these cells often relies on epigenetic changes (Kaminska et al., 2016), and that the cause of their dysregulation is also often caused by epigenetic factors (Martins-Ferreira et al., 2021). Interestingly focusing on the epigenetics of these cells may provide clues about the state of both their plasticity and reveal various NDD specific microglial and peripheral leukocyte phenotypes (Cheray and Joseph, 2018; Wang et al., 2021; Masliah et al., 2013).
Imaging has also been employed in the detection of myeloid biomarkers. Most widely known is the use of imaging for the detection of microglia- and macrophage-related neuroinflammation in the brain, by detecting the translocator protein (TSPO) with the help of radioligands (such as [11C]PK11195, [18F]DPA-714) and positron emission tomography (PET) (Zhou et al., 2021). A systematic review showed that there are increases in specific brain regions in a variety of inflammatory brain disorders, as well as in NDD (De Picker et al., 2023). A limitation is that other CNS-resident cells, such as astrocytes, can also express TSPO, and that microglia overactivation cannot easily be distinguished from gliosis in the scans. There are studies indicating that TSPO imaging indeed may reveal microglial activation but it is hard to determine whether this is protective or detrimental (Beckers et al., 2018). Others argue that while this type of imaging may be useful in rodents in detecting microglial activation/reactivity or gliosis, in humans the sensitivity is suboptimal for this (Nutma et al., 2023). Other methods, such as Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with for example susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) (Stüber et al., 2016) or quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) (Kaunzner et al., 2019), are used to detect iron deposition in CNS myeloid cells which is associated with NDD (Andersen et al., 2014). Additionally, Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) (Jiemy et al., 2018) has also shown promise as a method to measure activation of myeloid cells in the brain.
The summary of the current findings for the above are demonstrated in Figure 1.
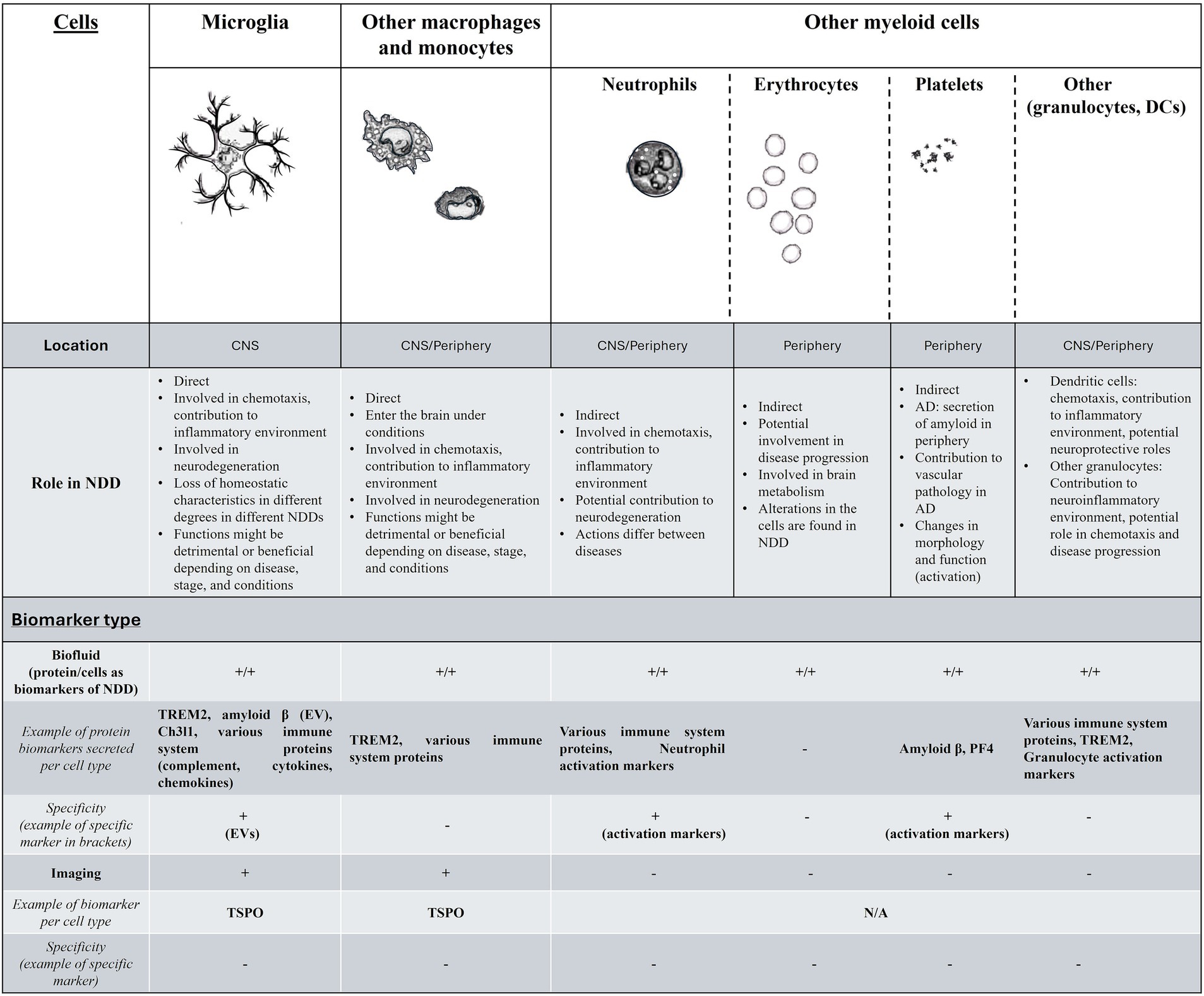
Figure 1. A summary of the findings for myeloid cells and biomarkers in neurodegenerative disorders. In the first part of this figure/table we include the myeloid cells that have been relevant to NDD, their location, and function in NDDs. For the second part (Biomarker type) while biofluid markers exist and are easy to research for monitoring the function of all myeloid cells, these are not cell specific (with the exception of markers such as neutrophil- or platelet-specific activation markers or EVs), while other biomarkers ranging from genetics and epigenetics-related, or cell behavior and morphology are more widely accessible, but under-investigated. The existence of biofluid biomarker per cell type is indicated with + for either proteins secreted that have been found to have potential as biomarkers in NDD (with examples) or for cell-specific changes that have been observed that can also act as biomarkers (behavior, function, morphology etc.). Myeloid cell related imaging biomarkers for NDD are currently limited to macrophage and microglia-specific, without the ability to distinguish between the two. More details are found in the text. DC, dendritic cells; NDD, neurodegenerative disorders; EV, extracellular vesicles.
Developing markers that are more specific to a cell type or even a tissue (CNS vs. periphery derived biomarkers) would improve the precision of diagnostics and research. For myeloid cells, due to their ubiquity throughout the body, isolating and focusing on CNS findings is rather challenging. Although there are clearly encouraging results from CSF biomarkers, and both blood and imaging studies also show promising findings there is a need for improvement in sensitivity, specificity, and functional correlation, while taking into account that NDD processes change during the disease. For example, the detection of activated microglia, may signify the early stages of NDD, or could be due to other non-NDD etiology. Further, in the development of AD microglia get over-activated and hyper-reactive (which may be referred as primed), and eventually become exhausted and present a senescent phenotype; currently there are no validated markers to distinguish between microglial states. Moreover, hyperactivation and senescence in microglia is also found in normal aging (Niraula et al., 2017), as well as non-microglial cells (Munawara et al., 2021; Sharma, 2021), which makes investigating this function using biomarkers rather complex, although there is potential of pharmaceutically targeting senescent cells (Chaib et al., 2022). Current research focusing on EVs from different CNS myeloid cells for example is promising, and so is the discovery of tissue-specific isoforms; both tissue and even cell-specific isoforms of proteins have been discussed as potential therapeutic targets elsewhere (Kjer-Hansen et al., 2024), and while there is progress in CNS-disease linked myeloid biomarker isoforms [e.g., the brain-specific complement system clusterin protein with both cell-type specific and subcellular isoforms (Herring et al., 2019), the brain-specific TREM2 isoform (Shaw et al., 2022), and brain region specific APP isoforms in mice (Löffler and Huber, 1992)] this field needs further studies.
Moreover, standardization of biomarker measurements is needed in both the components of the methods (e.g., method characteristics, such as antibodies, buffers, and technologies) and the characteristics of samples and the individuals they originate from. For example, a lot of protein levels and cell functions are subjects to circadian changes (Fonken et al., 2015; Fagiani et al., 2022), so studies without standardized collection protocols when it comes to when these samples were collected (either time of the day or time after waking up) will introduce unnecessary “noise” in the data. Perhaps more accurate record keeping for all factors that have been identified including time since waking up, and whether the sample donor has a normal sleep/awake routine could be used to address this and these factors could be used as covariates. Similarly differences in disease activity or disease type for diseases such as MS (Graber and Dhib-Jalbut, 2011) may lead to different results depending on the disease stage, so an overall MS group heterogeneity will be present that will make interpretation of any results difficult. Confounding factors such as pre-analytical conditions when it comes to studies from multi center sample collections should also be considered, ranging from consumables used for sample collection, to sample pre-processing storage temperatures and time, to post-processing storage conditions, as they have all been shown to affect a variety of analytes in different ways (Walter et al., 2020; Ruiz-Godoy et al., 2019). Lastly, investigating usual confounding factors in the context of the disease in focus and how that interaction may affect biomarkers differently (i.e., different disease biomarker signatures in males and females) should be taken into account. Especially in diseases where the immune system is involved it has been repeatedly shown that male and female immune systems are not the same, and that is reflected for example on the differential manifestation of neuroimmune (including ND) diseases in males and females (Alvarez-Sanchez and Dunn, 2023; Ferretti et al., 2018; Gillies et al., 2014). Moreover, even if we look at cell-specific functions of immune cells such as microglia there are differences in function and physiology (Yanguas-Casás, 2020; Kodama and Gan, 2019). A variety of reasons may be responsible for these changes, including the fact that the X chromosome contains a large amount of immune system related genes (Bianchi et al., 2012), and the differential exposure to factors such as hormones during development (Calvo and Einstein, 2023), but as NDDs manifest in different ways between sexes, we cannot expect for the markers of the disease or even treatment to be measured in the population as a whole. Although using statistics to account for sex as a confounding factor is an approach that is generally considered as appropriate, a suggestion for future studies would be a sex-specific characterization of the disease in question (including markers of development, diagnosis, and response to treatment) in addition to results in the population as a whole. Additionally, statistical methods of clustering patients in groups based on biomarkers depending on their function (e.g., neutrophil function, overall myeloid function etc.) may offer new ways of stratification of -already heterogenous- NDD and a divide and conquer approach may be more beneficial in both research and treatment.
The NDD myeloid biomarkers do tell us that there is often enhanced inflammation in NDD, but focusing on single-cell or single-process groups may tell a different story; for example, microglia have been found to be senescent in AD (Saez-Atienzar and Masliah, 2020; Hu et al., 2021) but also found to be primed (Bivona et al., 2023). This priming is an overall NDD phenomenon too (Perry and Holmes, 2014); both phenotypes are inflammatory but aid in the inflammation in different ways. When considering the regional and temporal heterogeneity of microglia (Tan et al., 2020) and other cell types, alongside factors such as genetics, epigenetics, and patient-specific variables, it becomes clear that simplistic approaches—such as targeting a single biomarker to treat neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs) as a whole—are often ineffective and potentially hazardous. A pertinent example is the recent development and approval of disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) for Alzheimer’s disease (AD), specifically anti-amyloid drugs (Mintun et al., 2021). While some individuals experience delayed progression in certain aspects of the disease and a reduction in a myeloid cell-related biomarker (amyloid plaques), these treatments have been associated with severe side effects, such as amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA) (Roytman et al., 2023), which remain unpredictable in their manifestation and potentially lethal. These adverse effects stem from both vascular and immune system dysfunctions, with evidence—at least from mouse models (Taylor et al., 2023)—indicating involvement of myeloid cells. Therefore, caution is essential when prioritizing a single biomarker, as it may interact with and influence the broader biological system in unforeseen ways.
Similarly, ignoring resilience to the development of symptoms, or delay of pathology development regardless of the presence of the factors that otherwise indicate disease progression, misses opportunities to learn more about mechanisms which may lead to treatments. An unorthodox way to show this is by mentioning a recent study that indicated that the mechanisms that aid in developing neuroinflammation in MS, may inhibit the development of amyloidogenesis in AD (Brier et al., 2024), although tau may be telling a different story in the same disease (Zeydan et al., 2020). This could indicate that the mechanisms responsible for the development of MS are inhibitory toward amyloid pathology, or the drugs used in MS (as some participants of both studies were on MS DMT) had that effect, both of which could be investigated by using myeloid biomarkers. Conversely, conditions such as depression (Schneider et al., 2011), traumatic brain injury (Brett et al., 2022), and viral infections (Levine et al., 2023) have been shown to be associated with the future development of NDD so studying the relationship between these conditions and NDD development may lead to early stage NDD markers. Looking at both resilience factors and risk factors and how these interact, may lead to further stratification of NDD to more functional categories than only phenotype, which will potentially make a difference in how we think of and treat these diseases.
Focusing on cell-based studies, in this category characteristics are altered both under normal conditions, and upon activation of the cells in vitro, depending on the study. This indicates that the immune system dysfunction present in NDD (or pre-NDD) may -in cases- only appear upon activation of the immune system. Similarly, with the differences in disease activity discussed in the context of MS, differences in immune response may be subject to immune system triggering and activation.
It is apparent that when considering myeloid cells and biomarkers and their relationship with NDD, we need to not only think and study beyond microglia, but often beyond the CNS. Instead of having a disease focus in biomarker research, we need to understand what the variations within and between diseases mean, and how they translate to function and dysfunction, as the brain’s immune privilege disappears when the nature of the disease is (neuro)immune.
EK: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RB: Writing – review & editing. AS-E: Writing – review & editing. KW: Writing – review & editing. HZ: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. AH: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
HZ is a Wallenberg Scholar and a Distinguished Professor at the Swedish Research Council supported by grants from the Swedish Research Council (#2023-00356; #2022-01018 and #2019-02397), the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 101053962, Swedish State Support for Clinical Research (#ALFGBG-71320), the Alzheimer Drug Discovery Foundation (ADDF), USA (#201809-2016862), the AD Strategic Fund and the Alzheimer’s Association (#ADSF-21-831376-C, #ADSF-21-831381-C, #ADSF-21-831377-C, and #ADSF-24-1284328-C), the European Partnership on Metrology, co-financed from the European Union’s Horizon Europe Research and Innovation Programme and by the Participating States (NEuroBioStand, #22HLT07), the Bluefield Project, Cure Alzheimer’s Fund, the Olav Thon Foundation, the Erling-Persson Family Foundation, Familjen Rönströms Stiftelse, Stiftelsen för Gamla Tjänarinnor, Hjärnfonden, Sweden (#FO2022-0270), the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement No 860197 (MIRIADE), the European Union Joint Programme – Neurodegenerative Disease Research (JPND2021-00694), the National Institute for Health and Care Research University College London Hospitals Biomedical Research Centre, and the UK Dementia Research Institute at UCL (UKDRI-1003).
HZ has served at scientific advisory boards and/or as a consultant for Abbvie, Acumen, Alector, Alzinova, ALZPath, Amylyx, Annexon, Apellis, Artery Therapeutics, AZTherapies, Cognito Therapeutics, CogRx, Denali, Eisai, LabCorp, Merry Life, Nervgen, Novo Nordisk, Optoceutics, Passage Bio, Pinteon Therapeutics, Prothena, Red Abbey Labs, reMYND, Roche, Samumed, Siemens Healthineers, Triplet Therapeutics, and Wave, has given lectures sponsored by Alzecure, Biogen, Cellectricon, Fujirebio, Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Roche, and WebMD, and is a co-founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program (outside submitted work).
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
AD, Alzheimer’s disease; Αβ, Amyloid beta; APP, Amyloid precursor protein; ARIA, Amyloid-related imaging abnormalities; APOE, Apolipoprotein E; BBB, Blood brain barrier; CNS, Central nervous system; CSF, Cerebrospinal fluid; Ch3l1, Chitinase-3-lik3 protein 1; DC, Dendritic cells; DMTs, Disease modifying therapies; EVs, Extracellular vesicles; HSP, Heat shock proteins; MRI, Magnetic resonance imaging; MBL, Mannan-binding lectin; MCI, Mild cognitive impairment; MCP-1, Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; MS, Multiple sclerosis; NDD, Neurodegenerative disorders; PD, Parkinson’s disease; PF4, Platelet factor 4; PET, Positron emission tomography; QSM, Quantitative susceptibility mapping; SPECT, Single-photon emission computed tomography; s/TREM2, Soluble/triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2; SWI, Susceptibility-weighted imaging; TLR, Toll-like receptor; TSPO, Translocator protein.
Ahn, H. J., Chen, Z.-L., Zamolodchikov, D., Norris, E. H., and Strickland, S. (2017). Interactions of β-amyloid peptide with fibrinogen and coagulation factor XII may contribute to Alzheimer's disease. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 24, 427–431. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000368
Alvarez-Sanchez, N., and Dunn, S. E. (2023). Potential biological contributers to the sex difference in multiple sclerosis progression. Front. Immunol. 14:1175874. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1175874
Andersen, H. H., Johnsen, K. B., and Moos, T. (2014). Iron deposits in the chronically inflamed central nervous system and contributes to neurodegeneration. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 71, 1607–1622. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1509-8
Ashton, N. J., Suárez-Calvet, M., Heslegrave, A., Hye, A., Razquin, C., Pastor, P., et al. (2019). Plasma levels of soluble TREM2 and neurofilament light chain in TREM2 rare variant carriers. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 11, 1–7. doi: 10.1186/s13195-019-0545-5
Atagi, Y., Liu, C.-C., Painter, M. M., Chen, X.-F., Verbeeck, C., Zheng, H., et al. (2015). Apolipoprotein E is a ligand for triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2). J. Biol. Chem. 290, 26043–26050. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.679043
Augusto-Oliveira, M., Arrifano, G. P., Delage, C. I., Tremblay, M. È., Crespo-Lopez, M. E., and Verkhratsky, A. (2022). Plasticity of microglia. Biol. Rev. 97, 217–250. doi: 10.1111/brv.12797
Baldacci, F., Lista, S., Cavedo, E., Bonuccelli, U., and Hampel, H. (2017). Diagnostic function of the neuroinflammatory biomarker YKL-40 in Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases. Expert Rev. Proteomics 14, 285–299. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2017.1304217
Bartl, M., Dakna, M., Schade, S., Otte, B., Wicke, T., Lang, E., et al. (2023). Blood markers of inflammation, neurodegeneration, and cardiovascular risk in early Parkinson's disease. Mov. Disord. 38, 68–81. doi: 10.1002/mds.29257
Beckers, L., Ory, D., Geric, I., Declercq, L., Koole, M., Kassiou, M., et al. (2018). Increased expression of translocator protein (TSPO) marks pro-inflammatory microglia but does not predict neurodegeneration. Mol. Imaging Biol. 20, 94–102. doi: 10.1007/s11307-017-1099-1
Begic, E., Hadzidedic, S., Obradovic, S., Begic, Z., and Causevic, M. (2020). Increased levels of coagulation factor XI in plasma are related to Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. J. Alzheimers Dis. 77, 375–386. doi: 10.3233/JAD-200358
Behari, M., and Shrivastava, M. (2013). Role of platelets in neurodegenerative diseases: a universal pathophysiology. Int. J. Neurosci. 123, 287–299. doi: 10.3109/00207454.2012.751534
Benecke, R., Strümper, P., and Weiss, H. (1993). Electron transfer complexes I and IV of platelets are abnormal in Parkinson's disease but normal in Parkinson-plus syndromes. Brain 116, 1451–1463. doi: 10.1093/brain/116.6.1451
Bennett, F. C., Bennett, M. L., Yaqoob, F., Mulinyawe, S. B., Grant, G. A., Gephart, M. H., et al. (2018). A combination of ontogeny and CNS environment establishes microglial identity. Neuron 98, 1170–1183.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.05.014
Benusa, S. D., George, N. M., and Dupree, J. L. (2020). Microglial heterogeneity: distinct cell types or differential functional adaptation? Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflam. 2020, 248–263. doi: 10.20517/2347-8659.2020.03
Beura, S. K., Panigrahi, A. R., Yadav, P., and Singh, S. K. (2022). Role of platelet in Parkinson’s disease: insights into pathophysiology & theranostic solutions. Ageing Res. Rev. 80:101681. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2022.101681
Bianchi, I., Lleo, A., Gershwin, M. E., and Invernizzi, P. (2012). The X chromosome and immune associated genes. J. Autoimmun. 38, J187–J192. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2011.11.012
Biomarkers Definitions Working GroupAtkinson, A. J. Jr., Colburn, W. A., DeGruttola, V. G., DeMets, D. L., Downing, G. J., et al. (2001). Biomarkers and surrogate endpoints: preferred definitions and conceptual framework. Clin. Pharmacol. Therapeut. 69, 89–95. doi: 10.1067/mcp.2001.113989
Bivona, G., Iemmolo, M., Agnello, L., Lo Sasso, B., Gambino, C. M., Giglio, R. V., et al. (2023). Microglial activation and priming in Alzheimer’s disease: state of the art and future perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24:884. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010884
Bivona, G., Iemmolo, M., Piccoli, T., Agnello, L., Lo Sasso, B., Ciaccio, M., et al. (2022). High cerebrospinal fluid CX3CL1 levels in Alzheimer’s disease patients but not in non-Alzheimer’s disease dementia. J. Clin. Med. 11:5498. doi: 10.3390/jcm11195498
Bonacina, F., Coe, D., Wang, G., Longhi, M. P., Baragetti, A., Moregola, A., et al. (2018). Myeloid apolipoprotein E controls dendritic cell antigen presentation and T cell activation. Nat. Commun. 9:3083. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05322-1
Bosman, G. J. (2018). Disturbed red blood cell structure and function: an exploration of the role of red blood cells in neurodegeneration. Front. Med. 5:198. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2018.00198
Boza-Serrano, A., Vrillon, A., Minta, K., Paulus, A., Camprubí-Ferrer, L., Garcia, M., et al. (2022). Galectin-3 is elevated in CSF and is associated with Aβ deposits and tau aggregates in brain tissue in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 144, 843–859. doi: 10.1007/s00401-022-02469-6
Brett, B. L., Gardner, R. C., Godbout, J., Dams-O’Connor, K., and Keene, C. D. (2022). Traumatic brain injury and risk of neurodegenerative disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 91, 498–507. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2021.05.025
Brier, M. R., Schindler, S. E., Salter, A., Perantie, D., Shelley, N., Judge, B., et al. (2024). Unexpected low rate of amyloid-β pathology in multiple sclerosis patients. Ann. Neurol. 96, 453–459. doi: 10.1002/ana.27027
Brown, G. C., and St George-Hyslop, P. (2022). Does soluble TREM2 protect against Alzheimer's disease? Front. Aging Neurosci. 13:834697. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.834697
Calvo, N., and Einstein, G. (2023). Steroid hormones: risk and resilience in women’s Alzheimer disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 15:1159435. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1159435
Cananzi, A., Ferro-Milone, F., Grigoletto, F., Toldo, M., Meneghini, F., Bortolon, F., et al. (1987). Relevance of platelet factor four (PF4) plasma levels in multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol. Scand. 76, 79–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1987.tb03550.x
Chaib, S., Tchkonia, T., and Kirkland, J. L. (2022). Cellular senescence and senolytics: the path to the clinic. Nat. Med. 28, 1556–1568. doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-01923-y
Chen, M., Inestrosa, N. C., Ross, G. S., and Fernandez, H. L. (1995). Platelets are the primary source of amyloid β-peptide in human blood. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 213, 96–103. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.2103
Chen, S.-H., Tian, D.-Y., Shen, Y.-Y., Cheng, Y., Fan, D.-Y., Sun, H.-L., et al. (2020). Amyloid-beta uptake by blood monocytes is reduced with ageing and Alzheimer’s disease. Transl. Psychiatry 10:423. doi: 10.1038/s41398-020-01113-9
Cheray, M., and Joseph, B. (2018). Epigenetics control microglia plasticity. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 12:243. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00243
Chuluundorj, D., Harding, S. A., Abernethy, D., and La Flamme, A. C. (2014). Expansion and preferential activation of the CD14+ CD16+ monocyte subset during multiple sclerosis. Immunol. Cell Biol. 92, 509–517. doi: 10.1038/icb.2014.15
Ciaramella, A., Bizzoni, F., Salani, F., Vanni, D., Spalletta, G., Sanarico, N., et al. (2010). Increased pro-inflammatory response by dendritic cells from patients with Alzheimer's disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 19, 559–572. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2010-1257
Ciaramella, A., Salani, F., Bizzoni, F., Orfei, M. D., Caltagirone, C., Spalletta, G., et al. (2016). Myeloid dendritic cells are decreased in peripheral blood of Alzheimer’s disease patients in association with disease progression and severity of depressive symptoms. J. Neuroinflammation 13, 1–11. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0483-0
D’Agostino, P. M., Gottfried-Blackmore, A., Anandasabapathy, N., and Bulloch, K. (2012). Brain dendritic cells: biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 124, 599–614. doi: 10.1007/s00401-012-1018-0
Da Mesquita, S., and Rua, R. (2024). Brain border-associated macrophages: common denominators in infection, aging, and Alzheimer’s disease? Trends Immunol. 45, 346–357. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2024.03.007
Davies, T. A., Long, H. J., Rathbun, W. H., Sgro, K. R., Tibbles, H., Smith, S. J., et al. (1996). Platelets from patients with Alzheimer's disease or other dementias exhibit disease-specific and apolipoprotein E correlatable defects. Amyloid 3, 13–19. doi: 10.3109/13506129609014350
De Kleer, I., Willems, F., Lambrecht, B., and Goriely, S. (2014). Ontogeny of myeloid cells. Front. Immunol. 5:423. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00423
De Picker, L. J., Morrens, M., Branchi, I., Haarman, B. C., Terada, T., Kang, M. S., et al. (2023). TSPO PET brain inflammation imaging: a transdiagnostic systematic review and meta-analysis of 156 case-control studies. Brain Behav. Immun. 113, 415–431. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2023.07.023
De Vlaminck, K., Van Hove, H., Kancheva, D., Scheyltjens, I., Antunes, A. R. P., Bastos, J., et al. (2022). Differential plasticity and fate of brain-resident and recruited macrophages during the onset and resolution of neuroinflammation. Immunity 55, 2085–2102.e9. e9. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.09.005
DePaula-Silva, A. B. (2024). The contribution of microglia and brain-infiltrating macrophages to the pathogenesis of neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases during TMEV infection of the central nervous system. Viruses 16:119. doi: 10.3390/v16010119
Dermitzakis, I., Theotokis, P., Evangelidis, P., Delilampou, E., Evangelidis, N., Chatzisavvidou, A., et al. (2023). CNS border-associated macrophages: ontogeny and potential implication in disease. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 45, 4285–4300. doi: 10.3390/cimb45050272
Drzezga, A., Grimmer, T., Henriksen, G., Muhlau, M., Perneczky, R., Miederer, I., et al. (2009). Effect of APOE genotype on amyloid plaque load and gray matter volume in Alzheimer disease. Neurology 72, 1487–1494. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181a2e8d0
Duchez, A. C., Heestermans, M., Arthaud, C.-A., Eyraud, M.-A., Portier, M., Prier, A., et al. (2024). In platelet single donor apheresis, platelet factor 4 levels correlated with donor’s age and decreased during storage. Sci. Rep. 14:6231. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56826-4
Dufek, M., Hamanová, M., Lokaj, J., Goldemund, D., Rektorová, I., Michálková, Z., et al. (2009). Serum inflammatory biomarkers in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 15, 318–320. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2008.05.014
Duraisamy, K., Premkumar, K., Selvakumar, G. P., Thangavel, R., Ahmed, M. E., Zaheer, S. A., et al. (2019). Mast cells augment Neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. FASEB J. 33:791.5. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2019.33.1_supplement.791.5
Dziedzic, A., and Bijak, M. (2019). Interactions between platelets and leukocytes in pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 28, 277–285. doi: 10.17219/acem/83588
Esaulova, E., Cantoni, C., Shchukina, I., Zaitsev, K., Bucelli, R. C., Wu, G. F., et al. (2020). Single-cell RNA-seq analysis of human CSF microglia and myeloid cells in neuroinflammation. Neurology 7:e732. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000732
Factor, S. A., Ortof, E., Dentinger, M. P., Mankes, R., and Barron, K. D. (1994). Platelet morphology in Parkinson's disease: an electron microscopic study. J. Neurol. Sci. 122, 84–89. doi: 10.1016/0022-510X(94)90056-6
Fagiani, F., Di Marino, D., Romagnoli, A., Travelli, C., Voltan, D., Di Cesare, M. L., et al. (2022). Molecular regulations of circadian rhythm and implications for physiology and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 7:41. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-00899-y
Fan, C., Li, Y., Lan, T., Wang, W., Long, Y., and Yu, S. Y. (2022). Microglia secrete miR-146a-5p-containing exosomes to regulate neurogenesis in depression. Mol. Ther. 30, 1300–1314. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.11.006
Ferretti, M. T., Iulita, M. F., Cavedo, E., Chiesa, P. A., Schumacher Dimech, A., Santuccione Chadha, A., et al. (2018). Sex differences in Alzheimer disease—the gateway to precision medicine. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 14, 457–469. doi: 10.1038/s41582-018-0032-9
Festoff, B. W., Sajja, R. K., van Dreden, P., and Cucullo, L. (2016). HMGB1 and thrombin mediate the blood-brain barrier dysfunction acting as biomarkers of neuroinflammation and progression to neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroinflammation 13, 1–12. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0670-z
Fiala, M., Liu, Q., Sayre, J., Pop, V., Brahmandam, V., Graves, M., et al. (2002). Cyclooxygenase-2-positive macrophages infiltrate the Alzheimer’s disease brain and damage the blood–brain barrier. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 32, 360–371. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2362.2002.00994.x
Fonken, L. K., Frank, M. G., Kitt, M. M., Barrientos, R. M., Watkins, L. R., and Maier, S. F. (2015). Microglia inflammatory responses are controlled by an intrinsic circadian clock. Brain Behav. Immun. 45, 171–179. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2014.11.009
Fu, R., Shen, Q., Xu, P., Luo, J. J., and Tang, Y. (2014). Phagocytosis of microglia in the central nervous system diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 49, 1422–1434. doi: 10.1007/s12035-013-8620-6
Fuchs, T., Puellmann, K., Dreyfus, D. H., Piehler, A. P., Reuter, B., Schwarzbach, C., et al. (2019). Immediate neutrophil-variable-T cell receptor host response in bacterial meningitis. Front. Neurol. 10:307. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00307
Gabandé-Rodríguez, E., Keane, L., and Capasso, M. (2020). Microglial phagocytosis in aging and Alzheimer's disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 98, 284–298. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24419
Gale, S. C., Gao, L., Mikacenic, C., Coyle, S. M., Rafaels, N., Dudenkov, T. M., et al. (2014). APOε4 is associated with enhanced in vivo innate immune responses in human subjects. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 134, 127–134.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.01.032
Gallizioli, M., Miró-Mur, F., Otxoa-de-Amezaga, A., Cugota, R., Salas-Perdomo, A., Justicia, C., et al. (2020). Dendritic cells and microglia have non-redundant functions in the inflamed brain with protective effects of type 1 cDCs. Cell Rep. 33:108291. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108291
Geraghty, N. J., Satapathy, S., Kelly, M., Cheng, F., Lee, A., and Wilson, M. R. (2021). Expanding the family of extracellular chaperones: identification of human plasma proteins with chaperone activity. Protein Sci. 30, 2272–2286. doi: 10.1002/pro.4189
Gibbons, H. M., and Dragunow, M. (2006). Microglia induce neural cell death via a proximity-dependent mechanism involving nitric oxide. Brain Res. 1084, 1–15. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.02.032
Giladi, A., Wagner, L. K., Li, H., Dörr, D., Medaglia, C., Paul, F., et al. (2020). Cxcl10+ monocytes define a pathogenic subset in the central nervous system during autoimmune neuroinflammation. Nat. Immunol. 21, 525–534. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-0661-1
Gillies, G. E., Pienaar, I. S., Vohra, S., and Qamhawi, Z. (2014). Sex differences in Parkinson’s disease. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 35, 370–384. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2014.02.002
Goldgaber, D., Lerman, M. I., McBride, O. W., Saffiotti, U., and Gajdusek, D. C. (1987). Characterization and chromosomal localization of a cDNA encoding brain amyloid of Alzheimer's disease. Science 235, 877–880. doi: 10.1126/science.3810169
Gonzalez-Ortiz, F., Turton, M., Kac, P. R., Smirnov, D., Premi, E., Ghidoni, R., et al. (2023). Brain-derived tau: a novel blood-based biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease-type neurodegeneration. Brain 146, 1152–1165. doi: 10.1093/brain/awac407
Gopinath, A., Collins, A., Khoshbouei, H., and Streit, W. J. (2020). Microglia and other myeloid cells in central nervous system health and disease. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 375, 154–160. doi: 10.1124/jpet.120.265058
Graber, J. J., and Dhib-Jalbut, S. (2011). Biomarkers of disease activity in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 305, 1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2011.03.026
Grayson, J. M., Short, S. M., Lee, C. J., Park, N., Marsac, C., Sette, A., et al. (2023). T cell exhaustion is associated with cognitive status and amyloid accumulation in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 13:15779. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-42708-8
Greenhalgh, A. D., Zarruk, J. G., Healy, L. M., Baskar Jesudasan, S. J., Jhelum, P., Salmon, C. K., et al. (2018). Peripherally derived macrophages modulate microglial function to reduce inflammation after CNS injury. PLoS Biol. 16:e2005264. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2005264
Gross, A. L., Walker, K. A., Moghekar, A. R., Pettigrew, C., Soldan, A., Albert, M. S., et al. (2019). Plasma markers of inflammation linked to clinical progression and decline during preclinical AD. Front. Aging Neurosci. 11:229. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2019.00229
Grozdanov, V., Bliederhaeuser, C., Ruf, W. P., Roth, V., Fundel-Clemens, K., Zondler, L., et al. (2014). Inflammatory dysregulation of blood monocytes in Parkinson’s disease patients. Acta Neuropathol. 128, 651–663. doi: 10.1007/s00401-014-1345-4
Guerreiro, R. J., Santana, I., Brás, J. M., Santiago, B., Paiva, A., and Oliveira, C. (2007). Peripheral inflammatory cytokines as biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neurodegener. Dis. 4, 406–412. doi: 10.1159/000107700
Guerreiro, R., Wojtas, A., Bras, J., Carrasquillo, M., Rogaeva, E., Majounie, E., et al. (2013). TREM2 variants in Alzheimer's disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 368, 117–127. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1211851
Hallé, M., Tribout-Jover, P., Lanteigne, A.-M., Boulais, J., St-Jean, J. R., Jodoin, R., et al. (2015). Methods to monitor monocytes-mediated amyloid-beta uptake and phagocytosis in the context of adjuvanted immunotherapies. J. Immunol. Methods 424, 64–79. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2015.05.002
Hampel, H., Hardy, J., Blennow, K., Chen, C., Perry, G., Kim, S. H., et al. (2021). The amyloid-β pathway in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Psychiatry 26, 5481–5503. doi: 10.1038/s41380-021-01249-0
Hatcher-Martin, J., McKay, J., Sommerfeld, B., Howell, J., Goldstein, F., Hu, W., et al. (2020). Cerebrospinal fluid Aβ42 and fractalkine are associated with Parkinson’s disease with freezing of gait. medRxiv. doi: 10.1101/2020.12.16.20248342
Herring, S. K., Moon, H.-J., Rawal, P., Chhibber, A., and Zhao, L. (2019). Brain clusterin protein isoforms and mitochondrial localization. eLife 8:e48255. doi: 10.7554/eLife.48255
Heslegrave, A., Heywood, W., Paterson, R., Magdalinou, N., Svensson, J., Johansson, P., et al. (2016). Increased cerebrospinal fluid soluble TREM2 concentration in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 11, 1–7. doi: 10.1186/s13024-016-0071-x
Hu, Y., Fryatt, G. L., Ghorbani, M., Obst, J., Menassa, D. A., Martin-Estebane, M., et al. (2021). Replicative senescence dictates the emergence of disease-associated microglia and contributes to Aβ pathology. Cell Rep. 35:109228. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109228
Hu, N., Tan, M.-S., Yu, J.-T., Sun, L., Tan, L., Wang, Y.-L., et al. (2014). Increased expression of TREM2 in peripheral blood of Alzheimer's disease patients. J. Alzheimers Dis. 38, 497–501. doi: 10.3233/JAD-130854
Humpel, C. (2017). Platelets: their potential contribution to the generation of beta-amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 14, 290–298. doi: 10.2174/1567202614666170705150535
Inoue, M., Yagishita, S., Itoh, Y., Koyano, S., Amano, N., and Matsushita, M. (1996). Eosinophilic bodies in the cerebral cortex of Alzheimer’s disease cases. Acta Neuropathol. 92, 555–561. doi: 10.1007/s004010050561
Jacobs, T., Jacobson, S. R., Fortea, J., Berger, J. S., Vedvyas, A., Marsh, K., et al. (2024). The neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio associates with markers of Alzheimer’s disease pathology in cognitively unimpaired elderly people. Immun. Ageing 21:32. doi: 10.1186/s12979-024-00435-2
Jay, T. R., von Saucken, V. E., and Landreth, G. E. (2017). TREM2 in neurodegenerative diseases. Mol. Neurodegener. 12, 1–33. doi: 10.1186/s13024-017-0197-5
Ji, K. A., Eu, M. Y., Kang, S. H., Gwag, B. J., Jou, I., and Joe, E. H. (2008). Differential neutrophil infiltration contributes to regional differences in brain inflammation in the substantia nigra pars compacta and cortex. Glia 56, 1039–1047. doi: 10.1002/glia.20677
Jian, J., Pang, Y., Yan, H. H., Min, Y., Achyut, B. R., Hollander, M. C., et al. (2017). Platelet factor 4 is produced by subsets of myeloid cells in premetastatic lung and inhibits tumor metastasis. Oncotarget 8, 27725–27739. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9486
Jiemy, W. F., Heeringa, P., Kamps, J. A., van der Laken, C. J., Slart, R. H., and Brouwer, E. (2018). Positron emission tomography (PET) and single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) imaging of macrophages in large vessel vasculitis: current status and future prospects. Autoimmun. Rev. 17, 715–726. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2018.02.006
Johansson, E., Westermarck, T., Ek, P., Latvus, A., and Atroshi, F. (2020). “Comparison of erythrocytes for individual indications of metabolism changes in Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases” in Personalized medicine, in relation to redox state, diet and lifestyle (London, UK: IntechOpen). Available at: https://www.intechopen.com/about-intechopen
Jonsson, T., Stefansson, H., Steinberg, S., Jonsdottir, I., Jonsson, P. V., Snaedal, J., et al. (2013). Variant of TREM2 associated with the risk of Alzheimer's disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 368, 107–116. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1211103
Juan, S. M., Daglas, M., and Adlard, P. A. (2022). Tau pathology, metal dyshomeostasis and repetitive mild traumatic brain injury: an unexplored link paving the way for neurodegeneration. J. Neurotrauma 39, 902–922. doi: 10.1089/neu.2021.0241
Kaminska, B., Mota, M., and Pizzi, M. (2016). Signal transduction and epigenetic mechanisms in the control of microglia activation during neuroinflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 1862, 339–351. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.10.026
Kanashiro, A., Hiroki, C. H., da Fonseca, D. M., Birbrair, A., Ferreira, R. G., Bassi, G. S., et al. (2020). The role of neutrophils in neuro-immune modulation. Pharmacol. Res. 151:104580. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104580
Kang, J., Lemaire, H.-G., Unterbeck, A., Salbaum, J. M., Masters, C. L., Grzeschik, K.-H., et al. (1987). The precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature 325, 733–736. doi: 10.1038/325733a0
Kastenbauer, S., Koedel, U., Wick, M., Kieseier, B. C., Hartung, H.-P., and Pfister, H.-W. (2003). CSF and serum levels of soluble fractalkine (CX3CL1) in inflammatory diseases of the nervous system. J. Neuroimmunol. 137, 210–217. doi: 10.1016/S0165-5728(03)00085-7
Kaunzner, U. W., Kang, Y., Zhang, S., Morris, E., Yao, Y., Pandya, S., et al. (2019). Quantitative susceptibility mapping identifies inflammation in a subset of chronic multiple sclerosis lesions. Brain 142, 133–145. doi: 10.1093/brain/awy296
Khosousi, S., Hye, A., Velayudhan, L., Bloth, B., Tsitsi, P., Markaki, I., et al. (2023). Complement system changes in blood in Parkinson's disease and progressive Supranuclear palsy/Corticobasal syndrome. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 108:105313. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2023.105313
Kjer-Hansen, P., Phan, T. G., and Weatheritt, R. J. (2024). Protein isoform-centric therapeutics: expanding targets and increasing specificity. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 23, 759–779. doi: 10.1038/s41573-024-01025-z
Kodama, L., and Gan, L. (2019). Do microglial sex differences contribute to sex differences in neurodegenerative diseases? Trends Mol. Med. 25, 741–749. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2019.05.001
Kodosaki, E., Watkins, W. J., Loveless, S., Kreft, K. L., Richards, A., Anderson, V., et al. (2024). Combination protein biomarkers predict multiple sclerosis diagnosis and outcomes. J. Neuroinflammation 21:52. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03036-4
Kondziella, D., and Zetterberg, H. (2008). Hyperphosphorylation of tau protein in superficial CNS siderosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 273, 130–132. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2008.06.009
Kosenko, E., Tikhonova, L., Alilova, G., Urios, A., and Montoliu, C. (2020). The erythrocytic hypothesis of brain energy crisis in sporadic Alzheimer disease: possible consequences and supporting evidence. J. Clin. Med. 9:206. doi: 10.3390/jcm9010206
Koudriavtseva, T., Lorenzano, S., Cellerino, M., Truglio, M., Fiorelli, M., Lapucci, C., et al. (2023). Tissue factor as a potential coagulative/vascular marker in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 14:1226616. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1226616
Krance, S. H., Wu, C.-Y., Zou, Y., Mao, H., Toufighi, S., He, X., et al. (2021). The complement cascade in Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol. Psychiatry 26, 5532–5541. doi: 10.1038/s41380-019-0536-8
Kremlev, S. G., Roberts, R. L., and Palmer, C. (2004). Differential expression of chemokines and chemokine receptors during microglial activation and inhibition. J. Neuroimmunol. 149, 1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2003.11.012
Lanzrein, A.-S., Jobst, K. A., Thiel, S., Jensenius, J. C., Sim, R. B., Perry, V. H., et al. (1998). Mannan-binding lectin in human serum, cerebrospinal fluid and brain tissue and its role in Alzheimer's disease. Neuroreport 9, 1491–1495. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199805110-00045
Lee, Y. B., Nagai, A., and Kim, S. U. (2002). Cytokines, chemokines, and cytokine receptors in human microglia. J. Neurosci. Res. 69, 94–103. doi: 10.1002/jnr.10253
Leppert, D., Watanabe, M., Schaedelin, S., Piehl, F., Furlan, R., Gastaldi, M., et al. (2023). Granulocyte activation markers in cerebrospinal fluid differentiate acute neuromyelitis spectrum disorder from multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 94, 726–737. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2022-330796
Levine, K. S., Leonard, H. L., Blauwendraat, C., Iwaki, H., Johnson, N., Bandres-Ciga, S., et al. (2023). Virus exposure and neurodegenerative disease risk across national biobanks. Neuron 111, 1086–1093.e2. e2. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.12.029
Llorens, F., Thüne, K., Tahir, W., Kanata, E., Diaz-Lucena, D., Xanthopoulos, K., et al. (2017). YKL-40 in the brain and cerebrospinal fluid of neurodegenerative dementias. Mol. Neurodegener. 12, 1–21. doi: 10.1186/s13024-017-0226-4
Löffler, J., and Huber, G. (1992). β-Amyloid precursor protein isoforms in various rat brain regions and during brain development. J. Neurochem. 59, 1316–1324. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb08443.x
Ludewig, P., Gallizioli, M., Urra, X., Behr, S., Brait, V. H., Gelderblom, M., et al. (2016). Dendritic cells in brain diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 1862, 352–367. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.11.003
Lunnon, K., Ibrahim, Z., Proitsi, P., Lourdusamy, A., Newhouse, S., Sattlecker, M., et al. (2012). Mitochondrial dysfunction and immune activation are detectable in early Alzheimer's disease blood. J. Alzheimers Dis. 30, 685–710. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2012-111592
Marchetti, B., Leggio, L., L’Episcopo, F., Vivarelli, S., Tirolo, C., Paternò, G., et al. (2020). Glia-derived extracellular vesicles in Parkinson’s disease. J. Clin. Med. 9:1941. doi: 10.3390/jcm9061941
Martins-Ferreira, R., Leal, B., Costa, P. P., and Ballestar, E. (2021). Microglial innate memory and epigenetic reprogramming in neurological disorders. Prog. Neurobiol. 200:101971. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2020.101971
Masliah, E., Dumaop, W., Galasko, D., and Desplats, P. (2013). Distinctive patterns of DNA methylation associated with Parkinson disease: identification of concordant epigenetic changes in brain and peripheral blood leukocytes. Epigenetics 8, 1030–1038. doi: 10.4161/epi.25865
McKeever, P. M., Schneider, R., Taghdiri, F., Weichert, A., Multani, N., Brown, R. A., et al. (2018). MicroRNA expression levels are altered in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with young-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 55, 8826–8841. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1032-x
Mendes, M. S., and Majewska, A. K. (2021). An overview of microglia ontogeny and maturation in the homeostatic and pathological brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 53, 3525–3547. doi: 10.1111/ejn.15225
Mildenberger, W., Stifter, S. A., and Greter, M. (2022). Diversity and function of brain-associated macrophages. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 76:102181. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2022.102181
Minta, K., Brinkmalm, G., Janelidze, S., Sjödin, S., Portelius, E., Stomrud, E., et al. (2020). Quantification of total apolipoprotein E and its isoforms in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with neurodegenerative diseases. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 12, 1–11. doi: 10.1186/s13195-020-00585-7
Mintun, M. A., Lo, A. C., Duggan Evans, C., Wessels, A. M., Ardayfio, P. A., Andersen, S. W., et al. (2021). Donanemab in early Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 384, 1691–1704. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2100708
Miyake, K., Ito, J., and Karasuyama, H. (2022). Role of basophils in a broad spectrum of disorders. Front. Immunol. 13:902494. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.902494
Møllgaard, M., Degn, M., Sellebjerg, F., Frederiksen, J., and Modvig, S. (2016). Cerebrospinal fluid chitinase-3-like 2 and chitotriosidase are potential prognostic biomarkers in early multiple sclerosis. Eur. J. Neurol. 23, 898–905. doi: 10.1111/ene.12960
Munawara, U., Catanzaro, M., Xu, W., Tan, C., Hirokawa, K., Bosco, N., et al. (2021). Hyperactivation of monocytes and macrophages in MCI patients contributes to the progression of Alzheimer's disease. Immun. Ageing 18:29. doi: 10.1186/s12979-021-00236-x
Nabizadeh, F., Seyedmirzaei, H., and Karami, S. (2024). Neuroimaging biomarkers and CSF sTREM2 levels in Alzheimer’s disease: a longitudinal study. Sci. Rep. 14:15318. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66211-w
Naegele, M., Tillack, K., Reinhardt, S., Schippling, S., Martin, R., and Sospedra, M. (2012). Neutrophils in multiple sclerosis are characterized by a primed phenotype. J. Neuroimmunol. 242, 60–71. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2011.11.009
Naskar, A., Stezin, A., Dharmappa, A., Hegde, S., Philip, M., Kamble, N., et al. (2022). Fibrinogen and complement Factor H are promising CSF protein biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease with cognitive impairment─ a proteomics–ELISA-based study. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 13, 1030–1045. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.2c00019
Niraula, A., Sheridan, J. F., and Godbout, J. P. (2017). Microglia priming with aging and stress. Neuropsychopharmacology 42, 318–333. doi: 10.1038/npp.2016.185
Nissen, S. K., Ferreira, S. A., Nielsen, M. C., Schulte, C., Shrivastava, K., Hennig, D., et al. (2021). Soluble CD163 changes indicate monocyte association with cognitive deficits in Parkinson's disease. Mov. Disord. 36, 963–976. doi: 10.1002/mds.28424
Nizami, S., Hall-Roberts, H., Warrier, S., Cowley, S. A., and Di Daniel, E. (2019). Microglial inflammation and phagocytosis in Alzheimer's disease: potential therapeutic targets. Br. J. Pharmacol. 176, 3515–3532. doi: 10.1111/bph.14618
Nostrand, W. E. V., Wagner, S. L., Suzuki, M., Choi, B. H., Farrow, J. S., Geddes, J. W., et al. (1989). Protease nexin-II, a potent anti-chymotrypsin, shows identity to amyloid β-protein precursor. Nature 341, 546–549. doi: 10.1038/341546a0
Nutma, E., Fancy, N., Weinert, M., Tsartsalis, S., Marzin, M. C., Muirhead, R. C., et al. (2023). Translocator protein is a marker of activated microglia in rodent models but not human neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Commun. 14:5247. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40937-z
Öhrfelt, A., Axelsson, M., Malmeström, C., Novakova, L., Heslegrave, A., Blennow, K., et al. (2016). Soluble TREM-2 in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with multiple sclerosis treated with natalizumab or mitoxantrone. Mult. Scler. J. 22, 1587–1595. doi: 10.1177/1352458515624558
Olsson, B., Malmeström, C., Basun, H., Annas, P., Höglund, K., Lannfelt, L., et al. (2012). Extreme stability of chitotriosidase in cerebrospinal fluid makes it a suitable marker for microglial activation in clinical trials. J. Alzheimers Dis. 32, 273–276. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2012-120931
Oltersdorf, T., Fritz, L. C., Schenk, D. B., Lieberburg, I., Johnson-Wood, K. L., Beattie, E. C., et al. (1989). The secreted form of the Alzheimer's amyloid precursor protein with the Kunitz domain is protease nexin-II. Nature 341, 144–147. doi: 10.1038/341144a0
Palacio, P. L., Pleet, M. L., Reátegui, E., and Magaña, S. M. (2023). Emerging role of extracellular vesicles in multiple sclerosis: from cellular surrogates to pathogenic mediators and beyond. J. Neuroimmunol. 377:578064. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2023.578064
Pannee, J., Shaw, L. M., Korecka, M., Waligorska, T., Teunissen, C. E., Stoops, E., et al. (2021). The global Alzheimer's Association round robin study on plasma amyloid β methods. Alzheimer's Dement. 13:e12242. doi: 10.1002/dad2.12242
Paolicelli, R. C., Bergamini, G., and Rajendran, L. (2019). Cell-to-cell communication by extracellular vesicles: focus on microglia. Neuroscience 405, 148–157. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.04.003
Park, S. J., and Choi, J. W. (2020). Brain energy metabolism and multiple sclerosis: progress and prospects. Arch. Pharm. Res. 43, 1017–1030. doi: 10.1007/s12272-020-01278-3
Park, J. E., Lim, D. S., Cho, Y. H., Choi, K. Y., Lee, J. J., Kim, B. C., et al. (2021). Plasma contact factors as novel biomarkers for diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease. Biomark. Res. 9, 1–8. doi: 10.1186/s40364-020-00258-5
Pashenkov, M., Teleshova, N., and Link, H. (2003). Inflammation in the central nervous system: the role for dendritic cells. Brain Pathol. 13, 23–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2003.tb00003.x
Perry, V. H., and Holmes, C. (2014). Microglial priming in neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 10, 217–224. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2014.38
Piccio, L., Buonsanti, C., Cella, M., Tassi, I., Schmidt, R. E., Fenoglio, C., et al. (2008). Identification of soluble TREM-2 in the cerebrospinal fluid and its association with multiple sclerosis and CNS inflammation. Brain 131, 3081–3091. doi: 10.1093/brain/awn217
Piccio, L., Deming, Y., Del-Águila, J. L., Ghezzi, L., Holtzman, D. M., Fagan, A. M., et al. (2016). Cerebrospinal fluid soluble TREM2 is higher in Alzheimer disease and associated with mutation status. Acta Neuropathol. 131, 925–933. doi: 10.1007/s00401-016-1533-5
Plant, L. D., Boyle, J. P., Smith, I. F., Peers, C., and Pearson, H. A. (2003). The production of amyloid β peptide is a critical requirement for the viability of central neurons. J. Neurosci. 23, 5531–5535. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-13-05531.2003
Prinz, M., Priller, J., Sisodia, S. S., and Ransohoff, R. M. (2011). Heterogeneity of CNS myeloid cells and their roles in neurodegeneration. Nat. Neurosci. 14, 1227–1235. doi: 10.1038/nn.2923
Prohaska, R., Sibon, O. C., Rudnicki, D. D., Danek, A., Hayflick, S. J., Verhaag, E. M., et al. (2012). Brain, blood, and iron: perspectives on the roles of erythrocytes and iron in neurodegeneration. Neurobiol. Dis. 46, 607–624. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2012.03.006
Qin, Q., Wan, H., Wang, D., Li, J., Qu, Y., Zhao, J., et al. (2022). The association of CSF sTREM2 with cognitive decline and its dynamic change in Parkinson's disease: analysis of the PPMI cohort. Front. Aging Neurosci. 14:892493. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.892493
Qu, Y., Li, J., Qin, Q., Wang, D., Zhao, J., An, K., et al. (2023). A systematic review and meta-analysis of inflammatory biomarkers in Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Parkinson's Dis. 9:18. doi: 10.1038/s41531-023-00449-5
Rajani, R. M., Ellingford, R., Hellmuth, M., Harris, S. S., Taso, O. S., Graykowski, D., et al. (2024). Selective suppression of oligodendrocyte-derived amyloid beta rescues neuronal dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS Biol. 22:e3002727. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002727
Reinvang, I., Espeseth, T., and Westlye, L. T. (2013). APOE-related biomarker profiles in non-pathological aging and early phases of Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 37, 1322–1335. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2013.05.006
Rosén, C., Andersson, C.-H., Andreasson, U., Molinuevo, J. L., Bjerke, M., Rami, L., et al. (2014). Increased levels of chitotriosidase and YKL-40 in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with Alzheimer's disease. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. Extra 4, 297–304. doi: 10.1159/000362164
Roytman, M., Mashriqi, F., Al-Tawil, K., Schulz, P. E., Zaharchuk, G., Benzinger, T. L., et al. (2023). Amyloid-related imaging abnormalities: an update. Am. J. Roentgenol. 220, 562–574. doi: 10.2214/AJR.22.28461
Ruiz-Godoy, L., Enríquez-Cárcamo, V., Suárez-Roa, L., Lopez-Castro, M. L., Santamaría, A., Orozco-Morales, M., et al. (2019). Identification of specific pre-analytical quality control markers in plasma and serum samples. Anal. Methods 11, 2259–2271. doi: 10.1039/C9AY00131J
Saez-Atienzar, S., and Masliah, E. (2020). Cellular senescence and Alzheimer disease: the egg and the chicken scenario. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 21, 433–444. doi: 10.1038/s41583-020-0325-z
Saresella, M., Marventano, I., Calabrese, E., Piancone, F., Rainone, V., Gatti, A., et al. (2014). A complex proinflammatory role for peripheral monocytes in Alzheimer's disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 38, 403–413. doi: 10.3233/JAD-131160
Sasmita, A. O., Depp, C., Nazarenko, T., Sun, T., Siems, S. B., Ong, E. C., et al. (2024). Oligodendrocytes produce amyloid-β and contribute to plaque formation alongside neurons in Alzheimer’s disease model mice. Nat. Neurosci. 27, 1668–1674. doi: 10.1038/s41593-024-01730-3
Savinetti, I., Papagna, A., and Foti, M. (2021). Human monocytes plasticity in neurodegeneration. Biomedicines 9:717. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9070717
Schneider, B., Prvulovic, D., Oertel-Knöchel, V., Knöchel, C., Reinke, B., Grexa, M., et al. (2011). Biomarkers for major depression and its delineation from neurodegenerative disorders. Prog. Neurobiol. 95, 703–717. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2011.08.001
Schroer, A. B., Ventura, P. B., Sucharov, J., Misra, R., Chui, M. K., Bieri, G., et al. (2023). Platelet factors attenuate inflammation and rescue cognition in ageing. Nature 620, 1071–1079. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06436-3
Sharma, R. (2021). Perspectives on the dynamic implications of cellular senescence and immunosenescence on macrophage aging biology. Biogerontology 22, 571–587. doi: 10.1007/s10522-021-09936-9
Sharma, A., Müller, J., Schuetze, K., Rolfes, V., Bissinger, R., Rosero, N., et al. (2021). Comprehensive profiling of blood coagulation and fibrinolysis marker reveals elevated plasmin-antiplasmin complexes in Parkinson’s disease. Biology 10:716. doi: 10.3390/biology10080716
Shaw, B. C., Snider, H. C., Turner, A. K., Zajac, D. J., Simpson, J. F., and Estus, S. (2022). An alternatively spliced TREM2 isoform lacking the ligand binding domain is expressed in human brain. J. Alzheimers Dis. 87, 1647–1657. doi: 10.3233/JAD-215602
Shechter, R., London, A., Varol, C., Raposo, C., Cusimano, M., Yovel, G., et al. (2009). Infiltrating blood-derived macrophages are vital cells playing an anti-inflammatory role in recovery from spinal cord injury in mice. PLoS Med. 6:e1000113. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000113
Shen, J., Chen, X.-C., Li, W.-J., Han, Q., Chen, C., Lu, J.-M., et al. (2020). Identification of Parkinson’s disease-related pathways and potential risk factors. J. Int. Med. Res. 48:0300060520957197. doi: 10.1177/0300060520957197
Sheremata, W. A., Jy, W., Horstman, L. L., Ahn, Y. S., Alexander, J. S., and Minagar, A. (2008). Evidence of platelet activation in multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroinflammation 5, 1–6. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-5-27
Silver, R., Silverman, A.-J., Vitković, L., and Lederhendler, I. I. (1996). Mast cells in the brain: evidence and functional significance. Trends Neurosci. 19, 25–31. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(96)81863-7
Silvin, A., Qian, J., and Ginhoux, F. (2023). Brain macrophage development, diversity and dysregulation in health and disease. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 20, 1277–1289. doi: 10.1038/s41423-023-01053-6
Singh, S., Anshita, D., and Ravichandiran, V. (2021). MCP-1: function, regulation, and involvement in disease. Int. Immunopharmacol. 101:107598. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107598
Skaper, S. D., Evans, N. A., Soden, P. E., Rosin, C., Facci, L., and Richardson, J. C. (2009). Oligodendrocytes are a novel source of amyloid peptide generation. Neurochem. Res. 34, 2243–2250. doi: 10.1007/s11064-009-0022-9
Son, S. J., Lee, K. S., Chung, J. H., Chang, K. J., Roh, H. W., Kim, S. H., et al. (2015). Increased plasma levels of heat shock protein 70 associated with subsequent clinical conversion to mild cognitive impairment in cognitively healthy elderly. PLoS One 10:e0119180. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119180
Stephen, T., Cacciottolo, M., Balu, D., Morgan, T., LaDu, M., Finch, C., et al. (2019). APOE genotype and sex affect microglial interactions with plaques in Alzheimer’s disease mice. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 7, 1–11. doi: 10.1186/s40478-019-0729-z
Stilund, M., Gjelstrup, M. C., Petersen, T., Møller, H. J., Rasmussen, P. V., and Christensen, T. (2015). Biomarkers of inflammation and axonal degeneration/damage in patients with newly diagnosed multiple sclerosis: contributions of the soluble CD163 CSF/serum ratio to a biomarker panel. PLoS One 10:e0119681. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119681
Stilund, M., Reuschlein, A.-K., Christensen, T., Møller, H. J., Rasmussen, P. V., and Petersen, T. (2014). Soluble CD163 as a marker of macrophage activity in newly diagnosed patients with multiple sclerosis. PLoS One 9:e98588. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098588
Stüber, C., Pitt, D., and Wang, Y. (2016). Iron in multiple sclerosis and its noninvasive imaging with quantitative susceptibility mapping. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 17:100. doi: 10.3390/ijms17010100
Su, F., Bai, F., and Zhang, Z. (2016). Inflammatory cytokines and Alzheimer’s disease: a review from the perspective of genetic polymorphisms. Neurosci. Bull. 32, 469–480. doi: 10.1007/s12264-016-0055-4
Sun, R., and Jiang, H. (2024). Border-associated macrophages in the central nervous system. J. Neuroinflammation 21:67. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03059-x
Svoboda, O., and Bartunek, P. (2015). Origins of the vertebrate erythro/megakaryocytic system. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015:632171, 1–10. doi: 10.1155/2015/632171
Tan, Y.-L., Yuan, Y., and Tian, L. (2020). Microglial regional heterogeneity and its role in the brain. Mol. Psychiatry 25, 351–367. doi: 10.1038/s41380-019-0609-8
Taylor, X., Clark, I. M., Fitzgerald, G. J., Oluoch, H., Hole, J. T., DeMattos, R. B., et al. (2023). Amyloid-β (Aβ) immunotherapy induced microhemorrhages are associated with activated perivascular macrophages and peripheral monocyte recruitment in Alzheimer’s disease mice. Mol. Neurodegener. 18:59. doi: 10.1186/s13024-023-00649-w
Thome, A. D., Faridar, A., Beers, D. R., Thonhoff, J. R., Zhao, W., Wen, S., et al. (2018). Functional alterations of myeloid cells during the course of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 13, 1–11. doi: 10.1186/s13024-018-0293-1
Trotta, T., Panaro, M. A., Cianciulli, A., Mori, G., Di Benedetto, A., and Porro, C. (2018). Microglia-derived extracellular vesicles in Alzheimer’s disease: a double-edged sword. Biochem. Pharmacol. 148, 184–192. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.12.020
Tsai, H.-H., Chen, Y.-F., Yen, R.-F., Lo, Y.-L., Yang, K.-C., Jeng, J.-S., et al. (2021). Plasma soluble TREM2 is associated with white matter lesions independent of amyloid and tau. Brain 144, 3371–3380. doi: 10.1093/brain/awab332
Villar-Piqué, A., Schmitz, M., Hermann, P., Goebel, S., Bunck, T., Varges, D., et al. (2019). Plasma YKL-40 in the spectrum of neurodegenerative dementia. J. Neuroinflammation 16, 1–5. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1531-3
Wakabayashi, K., Mori, F., Tanji, K., Orimo, S., and Takahashi, H. (2010). Involvement of the peripheral nervous system in synucleinopathies, tauopathies and other neurodegenerative proteinopathies of the brain. Acta Neuropathol. 120, 1–12. doi: 10.1007/s00401-010-0706-x
Walter, M., Wiltfang, J., and Vogelgsang, J. (2020). Pre-analytical sampling and storage conditions of amyloid-β peptides in venous and capillary blood. J. Alzheimers Dis. 78, 529–535. doi: 10.3233/JAD-200777
Wang, P. L., Yim, A. K., Kim, K.-W., Avey, D., Czepielewski, R. S., Colonna, M., et al. (2020). Peripheral nerve resident macrophages share tissue-specific programming and features of activated microglia. Nat. Commun. 11:2552. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16355-w
Wang, L., Yu, C.-C., Liu, X.-Y., Deng, X.-N., Tian, Q., and Du, Y.-J. (2021). Epigenetic modulation of microglia function and phenotypes in neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Plast. 2021, 1–13. doi: 10.1155/2021/9912686
Wang, X., Zhang, S., Lin, F., Chu, W., and Yue, S. (2015). Elevated galectin-3 levels in the serum of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Am. J. Alzheimers Dis. Other Dement. 30, 729–732. doi: 10.1177/1533317513495107
Weaver, D., Heffernan, L., Purdy, R., and Ing, V. (1988). Eosinophil-induced neurotoxicity: axonal neuropathy, cerebral infarction, and dementia. Neurology 38:144. doi: 10.1212/WNL.38.1.144
Wilson, E. N., Swarovski, M. S., Linortner, P., Shahid, M., Zuckerman, A. J., Wang, Q., et al. (2020). Soluble TREM2 is elevated in Parkinson’s disease subgroups with increased CSF tau. Brain 143, 932–943. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa021
Wu, C.-Y., Bawa, K. K., Ouk, M., Leung, N., Yu, D., Lanctot, K. L., et al. (2020). Neutrophil activation in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment: a systematic review and meta-analysis of protein markers in blood and cerebrospinal fluid. Ageing Res. Rev. 62:101130. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2020.101130
Yang, L., He, L., Bu, Z., Xuan, C., Yu, C., and Wu, J. (2023). Serum protein-based profiles for the diagnostic model of Alzheimer’s disease. Am. J. Alzheimers Dis. Other Dement. 38:15333175231220166. doi: 10.1177/15333175231220166
Yang, Q., Wang, G., and Zhang, F. (2020). Role of peripheral immune cells-mediated inflammation on the process of neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Immunol. 11:582825. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.582825
Yanguas-Casás, N. (2020). Physiological sex differences in microglia and their relevance in neurological disorders. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflam. 7, 13–22. doi: 10.20517/2347-8659.2019.31
Yao, Y., and Tsirka, S. E. (2014). Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and the blood–brain barrier. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 71, 683–697. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1459-1
Yu, W., He, J., Cai, X., Yu, Z., Zou, Z., and Fan, D. (2022). Neuroimmune crosstalk between the peripheral and the central immune system in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Front. Aging Neurosci. 14:890958. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.890958
Zeydan, B., Lowe, V. J., Reichard, R. R., Przybelski, S. A., Lesnick, T. G., Schwarz, C. G., et al. (2020). Imaging biomarkers of Alzheimer disease in multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 87, 556–567. doi: 10.1002/ana.25684
Zhang, W., Huang, W., and Jing, F. (2013). Contribution of blood platelets to vascular pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Blood Med. 4, 141–147. doi: 10.2147/JBM.S45071
Zhao, A., Jiao, Y., Ye, G., Kang, W., Tan, L., Li, Y., et al. (2022). Soluble TREM2 levels associate with conversion from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s disease. J. Clin. Invest. 132:e158708. doi: 10.1172/JCI158708
Zhou, R., Ji, B., Kong, Y., Qin, L., Ren, W., Guan, Y., et al. (2021). PET imaging of neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Immunol. 12:739130. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.739130
Keywords: myeloid biomarkers, neuroinflammation, neurodegeneration, myeloid cells, microglia, biomarker utility, biomarker standardization
Citation: Kodosaki E, Bell R, Sogorb-Esteve A, Wiltshire K, Zetterberg H and Heslegrave A (2024) More than microglia: myeloid cells and biomarkers in neurodegeneration. Front. Neurosci. 18:1499458. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1499458
Received: 20 September 2024; Accepted: 16 October 2024;
Published: 31 October 2024.
Edited by:
Miguel Moutinho, Indiana University Bloomington, United StatesReviewed by:
Noela Rodriguez Losada, University of Malaga, SpainCopyright © 2024 Kodosaki, Bell, Sogorb-Esteve, Wiltshire, Zetterberg and Heslegrave. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Eleftheria Kodosaki, ci5rb2Rvc2FraUB1Y2wuYWMudWs=; Amanda Heslegrave, YS5oZXNsZWdyYXZlQHVjbC5hYy51aw==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.