
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Neurosci. , 25 November 2024
Sec. Brain Imaging Methods
Volume 18 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2024.1495435
Background: Stroke is a neurological condition characterized by high rates of disability and mortality. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is widely used to examine the mechanisms of acupuncture in stroke treatment.
Purpose: This review provides neuroimaging evidence for the efficacy of acupuncture in treating stroke using MRI.
Method: We conducted a comprehensive search of databases, including PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wan Fang Data, Chinese BioMedical Literature Database (CBM), and Chonqing VIP (CQVIP), from inception to April 2024. Relevant neuroimaging studies on acupuncture for stroke were included, and the research findings were presented through charts and textual analyses.
Results: A total of 158 studies were included, and the overall methodological quality of the included studies was moderate to high. The results were divided into three categories: basic characteristics, clinical characteristics, and quality assessment of the included literature.
Conclusion: We elucidated the neural mechanisms underlying the effects of acupuncture on stroke; however, the evidence remains preliminary. There is a need for large-scale, well-designed, multimodal neuroimaging trials. This review represents the first active use of an evidence map to systematically review and illustrate the current state of neuroimaging research on the acupuncture treatment of stroke, thereby providing a valuable reference for future research.
Globally, stroke has consistently been the leading cause of mortality and disability among individuals aged 50 and older (GBD Diseases and Injuries Collaborators, 2019), respectively, often resulting in varying degrees of neurological deficits (Benjamin et al., 2019). By 2050, over 200 million patients with stroke are expected to survive (Brainin et al., 2020), imposing a substantial financial burden on the healthcare system (Feigin et al., 2016; Katan and Luft, 2018). According to the Screening and Intervention Project for Individuals at High Risk of Stroke, the number of patients with stroke aged 40 and above in China has reached 12.42 million (Report on Stroke Prevention and Treatment in China Writing Group, 2023). Numerous scholars demonstrate the efficacy of acupuncture for stroke in high-impact academic journals (Zhang J. et al., 2023; Zhang J. S. et al., 2023; Zhang Y. et al., 2023). Clinical guidelines, including the Brazilian Practice Guidelines for Stroke Rehabilitation and Chinese Stroke Association Guidelines for Clinical management of Cerebrovascular Diseases, have integrated evidence-based recommendations for acupuncture in stroke management (Zhang et al., 2020; Minelli et al., 2022).
Abnormal variations in brain structure and function have been found in patients with stroke patients (Wang et al., 2019), suggesting its critical role in nerve function outcome and recovery. Consequently, assessing these post-stroke abnormalities and investigating the neural mechanisms of dysfunction is crucial for advancing treatment strategies and improving prognosis. In addition, exploring the mechanism of action of acupuncture can lay a solid theoretical foundation for the prevention and treatment of stroke by acupuncture, which is conducive to promoting the clinical application of acupuncture and has important clinical significance. The rapid development of neuroimaging, particularly magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), enables precise, non-invasive, and multimodal fusion to explore the pathophysiological mechanisms related to neuropsychiatric diseases. MRI technology has been widely used to identify functional and structural changes in the brain of patients with stroke and investigate acupuncture’s mechanism in treating stroke (Zhang J. et al., 2023; Zhang J. S. et al., 2023; Zhang Y. et al., 2023). We systematically reviewed MRI research on stroke treatments in recent years and used evidence mapping to provide clinical researchers with neuroimaging insight into acupuncture and stroke, offering new directions for future research.
The electronic databases used for the systematic search from databases inception to 12 April 2024, included PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR), Cochrane Controlled Trials Register (CENTRAL), China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Chinese BioMedical Literature Database (CBM), Chonqing VIP (CQVIP), and Wanfang. Detailed search strategies are provided in Supplementary file S1.
The inclusion criteria were: (1) Study types: This review included clinical studies on acupuncture for stroke, limited to journal articles. (2) Participants: Study participants were diagnosed with stroke based on various diagnostic criteria. The study subjects underwent two MRI scans before or after acupuncture or one MRI scan during acupuncture. (3) Intervention types: The experimental group received acupuncture therapy alone or in combination with other conventional therapies. (4) Type of control: The control group evaluated the effects of acupuncture, with participants receiving sham acupuncture (SA), placebo acupuncture, no treatment, drugs, Chinese medicine, rehabilitation therapy, or other therapies. (5) Types of outcome: At least one MRI technique was used, resulting in MRI outcome measures. The exclusion criteria were: (1) Animal experiments, reviews, case studies, experience reports, or protocols; (2) Duplicate studies or data; (3) Studies where contacting the author via email did not resolve missing data or yield the necessary information.
Two authors (Chao Ke and Wenying Shi) independently screened and examined the features of all articles identified using the PICOS (population, interventions, comparators, outcomes, study design) selection criteria, and extracted the data for further evaluation. Subsequently, a cross-check was performed, and any disagreements were resolved through arbitration by a third author (Wei Zhang). Data extraction included the following: general study information (title, author, country, journal, journal level, year of publication, registration, and funding source); patient demographics (lesion location, first-episode, functional disorder category, stroke type, and disease stage); trial design (study type, total sample size, trial design, control design, and neuroimaging design); and outcome evaluation (MRI type and outcomes).
The results were presented in a preferred reporting item for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) flow diagram using a combination of textual descriptions and charts, and visual representations were created using Microsoft Excel 2003, Original, and chiPlot website (https://www.chiplot.online/) for data analysis and synthesis. The presentation also included bubble plots, a fold line diagram, three-line table.
A total of 2,841 literature items were retrieved using the search strategy. Initially, 1,948 articles remained after duplicates were removed. Subsequently, 1,722 records were excluded after reviewing the titles and abstracts. Three articles failed to obtain the full text. Finally, 158 studies were included in this meta-analysis. Details of the literature screening process are displayed in the PRISMA flowchart (Figure 1).
MRI studies on acupuncture for stroke began in 2,000, with 158 studies published between 2000 and April 2024. Results showed an increasing trend in research in recent years, peaking in 2023. The annual distribution of the literature is shown (Figure 2). A total of 158 studies were published across 96 distinct journals. Approximately 25.31% of the selected papers were published in the Science Citation Index Journal (SCI), 59.49% in core journals such as the Chinese Core Journal Criterion of Peking University (CSCD) and the China Core Periodicals of Science and Technology (CSTPCD), and the remaining 15.19% in other journals. Most studies received project funding (130/158, 82.28%), such as the Natural Science Foundation of China and 973 projects; very few studies reported registration status (13/158, 8.23%). Most studies were authored by Chinese authors, with only Germany and Boston contributing a single study each (Table 1).
The sample sizes of the 158 studies ranged from 5 to 200. Most studies (108, 68.35%) had sample sizes between 1 and 50. Of the studies, 46.2% reported that the patients recruited had a first-episode stroke. Concurrently, patients primarily had ischaemic stroke (134/158, 84.81%) and post-stroke motor impairment (80/158, 50.63%). Participants were mostly in the acute period and recovery period (112/158, 70.89%). The lesions were primarily distributed in the basal ganglia, corona radiata, and internal capsule. The results are presented in Table 2.
We reviewed the MRI trial design for acupuncture in stroke studies, focusing on four commonly used methods: two-group pre–post control, single-group single-session, two-group single-session, and single-group pre-post control designs (Figure 3). Regarding MRI intervention design, most studies (85/158, 53.8%) used a resting-state mode, while the remaining (73/158, 46.2%) used a task-state mode. Among the task-state modes, 27 studies used the classical BLOCK design paradigm, 14 used the NRER paradigm, 9 used the MIX-BLOCK paradigm, 5 used the Pre-Post paradigm, and 3 used the Single-BLOCK paradigm (Figure 4).
Consequently, we created a bubble map illustrating the trial design and MRI intervention design (Figure 5). The most commonly used study protocol was the two pre-group control studies-resting-state mode observation. The control design was divided into two main purposes: mechanisms of acupuncture therapy and efficacy of acupuncture. The three most common control designs were: verum acupuncture combined with other therapies versus other therapies, verum acupuncture versus healthy control, and verum acupuncture versus SA. The outcomes are presented in Table 3.
Our results suggest that MRI of cerebral blood oxygen metabolism (104/158, 65.82%), diffusion MRI (30/158, 18.18%), magnetic resonance spectrum (16/158, 10.13%), perfusion MRI (7/158, 4.43%), and structural MRI (5/158, 3.16%) have been extensively used in acupuncture for stroke treatment. Researchers are increasingly preferring data collection using advanced MRI techniques. The detailed results are presented in Table 4. We conducted a comprehensive summary of the annual frequency chart for each type of MRI and post-stroke dysfunction (Figures 6, 7). The three most frequently used MRI modalities are blood-oxygen-level-dependent (BOLD)-functional MRI (BOLD fMRI), diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), and magnetic resonance spectroscopy/Proton-MRS (MRS/1H-MRS) (Figure 6). BOLD-fMRI has been in use since 2003, DTI since 2012, and MRS/1H-MRS since 2013. The three disorders under investigation were post-stroke motor, speech, and cognitive impairments (Figure 7). We further summarized the annual frequency maps of most BOLD fMRI indicators (Figure 8). The frequencies of brain activation areas, functional connectivity (FC), and regional homogeneity (Reho) have increased annually (Figure 8a). Since 2003, various indicators representing local brain activity, such as the activation of brain regions, Reho, amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (ALFF)/fractional amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (fALFF)/percent amplitude of fluctuation (PerAF) and lateralization index (LI) have emerged. Since 2013, the frequency of interval-brain connectivity patterns, such as FC, voxel-mirrored homotopic connectivity (VMHC), independent component analysis (ICA), and Granger causality (GC), has increased. Furthermore, since 2020, graph theory metrics, including degree centrality (DC), differential degree centrality (DDC), and other indicators representing whole-brain connectivity patterns, have been introduced (Figures 8b,c).
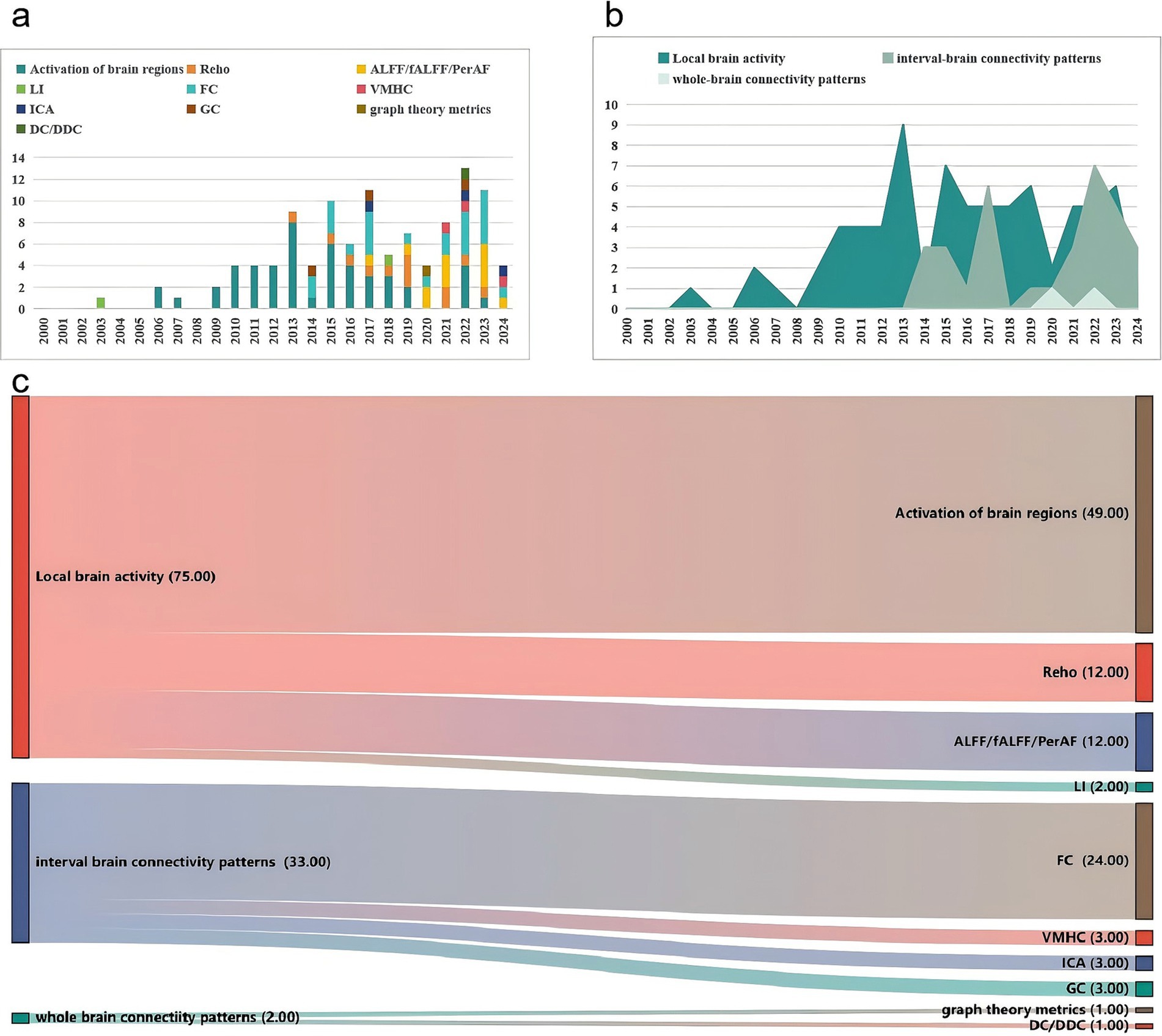
Figure 8. Frequency analysis chart of the efficacy of evaluation indices of BOLD-fMRI. (a) Annual frequency analysis chart of the efficacy of evaluation indices of BOLD-fMRI. (b) Mulberry fruit diagram of the frequency of evaluation indices of BOLD-fMRI (According to the three categories). (c) Mulberry fruit diagram of the frequency of evaluation indices of BOLD-fMRI.
Ischemic stroke accounts for approximately 87% of all stroke cases in the United States (Feigin et al., 2013) and 80% of all stroke cases in China (Barthels and Das, 2020). The review of the evidence in previous literature suggests that the primary subtype of stroke is ischemic stroke, aligning with epidemiological trends (GBD Parkinson’s Disease Collaborators, 2016). Additionally, MRI studies of acupuncture for stroke address multiple post-stroke dysfunctions, such as motor, speech, cognitive, swallowing, and sensory impairments, with a significant emphasis on motor impairments. Our results similarly support this conclusion. Post-stroke motor impairment is a common complication, with over 70% of stroke survivors experiencing motor dysfunctions (Wang et al., 2017). These studies make the functional abnormalities and reorganization between brain regions or networks observable.
Several commonly used experimental design methods are described as follows: (1) Single-group, single-session design: A group of patients with stroke participated in the study and received a single intervention and single-signal acquisition to observe immediate brain activity. (2) Single-group pre-post control design: A group of patients with stroke participated in the study and received a period of intervention, with signal acquisition conducted before and after the intervention to observe brain activity over time. (3) Two-group single-session design: Two groups of patients with stroke participated in the study, each receiving different interventions and undergoing single-signal acquisition after randomization, allowing the observation of immediate brain activity. (4) Two-group pre-post control design: Two groups of patients with stroke participated in the study, with different interventions administered after randomization. Signal-acquisition was performed before and after the intervention to observe brain activity over time. Healthy controls could/could not be included in this study.
Additionally, two other studies focused on natural recovery state design (Zhao et al., 2017; Stinear et al., 2020). These studies compared brain activity in patients with stroke under natural recovery conditions and observed brain activity changes over time. During this period, no acupuncture intervention was performed, although the acupuncture BLOCK intervention was used to stimulate brain activity at each visiting viewpoint. Five studies employed two-group cross-over control designs (Chang et al., 2003; Zhang et al., 2014; Chen et al., 2015; Liao et al., 2016; Chen C. et al., 2024; Chen T. et al., 2024), which involved two groups of single-session designs with another intervention after the washout period to create two groups of cross-control studies. Consequently, immediate brain activity was observed. This design was mostly used in the group design of acupuncture and SA acupuncture controls. Two studies used a single-group, multi-control design (Si et al., 2013; Chen et al., 2014), where a group of patients with stroke received several different interventions in sequence, separated by a washout period. In the two-group crossover control and single-group multi-control designs, each patient received two different interventions, reducing the sample size and eliminating individual differences.
Resting-state (rs)-fMRI and task-state fMRI are the two primary paradigms for fMRI studies.
1. Resting-state mode: This mode refers to the spontaneous regulation activity of neurones in the specific area of the brain observed using MRI when subjects are awake and at rest, without specific brain activity. This state exhibits a significant degree of stability. Rs-MRI is used to investigate changes in fMRI signals before and after acupuncture treatment. This approach is suitable for single-group pre-post control and two-group pre-post control designs to explore how acupuncture treatment affects brain activity over time.
2. Task-state mode: Acupuncture is used as a passive input stimulus to investigate alterations in brain activation during and after needle stimulation. This model investigates both the immediate and sustained effects of acupuncture, necessitating a series of predetermined acupuncture or non-acupuncture task stimuli to induce changes in the brain regions. ① Classical BLOCK paradigm: Each experimental session alternates between resting-state and stimulation blocks, including acupuncture (Huang et al., 2013) and non-acupuncture task BLOCKs (like finger movement, language test) (Xu et al., 2022). Acupuncture BLOCK applies to single-group single-session design, two-group single-session design, two-group crossover control design, single-group multi-control design, and natural recovery state design. It explores altered brain activity as an immediate effect of acupuncture treatment. Conversely, non-acupuncture task BLOCK applies to the single-group pre-post control design and two-group pre-post control design, exploring altered brain activity during the task after a period of acupuncture treatment. ② NRER paradigm: Initially, an acupuncture needle is inserted at the acupoint, rested for 1 min, manipulated for 1 min, and subsequently left inserted for another 8 min. This approach is applicable to the Single-group single-session design and two groups single-session design to investigate sustained effects after instant acupuncture administration (Xiao et al., 2020). Therefore, we employed the BLOCK design to avoid the cumulative and confounding effects of acupuncture. ③ MIX-BLOCK paradigm: A series of non-acupuncture tasks are combined with acupuncture, often stimulating specific brain activities through body movements during acupuncture. For example, researchers have explored the differences in brain activity in patients with stroke during fist-grasping tasks with non-acupuncture, acupuncture, and SA (Lu et al., 2023). It is mostly applicable to a single-group, single-session design, making brain activity more complex when receiving a single stimulus and potentially confusing the exact acupuncture effect. ④ Pre-post paradigm: The MRI signal scan was not performed during the acupuncture intervention; however, before and after the acupuncture intervention, the subject was required to remain still or perform a task, with signal changes attributed to the acupuncture event. It is mostly applicable to single-group, single-session and two-group single-session designs. Several studies have conducted swallowing BLOCK scans before and after acupuncture, revealing increased brain function activation areas post-acupuncture compared with pre-acupuncture. These findings suggest that acupuncture at the tongue root can enhance the involvement of additional brain regions during swallowing (Schockert et al., 2010; Liu et al., 2019). ⑤ Single-Block paradigm: The resting state and acupuncture stimulation events are only repeated once, which avoids the signal baseline elevation caused by cumulative acupuncture effects in the BLOCK design, reducing the accumulation of acupuncture effect to some extent.
Our results showed that the most frequently observed patterns were the resting-state, classical BLOCK, non-repeated event-related (NRER), and MIX-BLOCK paradigms. Each research paradigm has different objectives and purposes.
Our findings indicate that the control design of acupuncture in stroke MRI studies primarily addresses two major research objectives: the mechanism of acupuncture and its efficacy. The investigation of mechanisms includes comparisons such as VA / VA combined with other therapies, VA versus HC, VA versus SA, self-control before and after, and VA 1 versus VA 2. The purpose of SA is to prove that the positive effects of acupuncture treatment are due to the placebo effect. Of the included studies, 18 used the following three types of SA: (1) acupuncture treatment at non-acupoints, with two studies emphasizing that non-meridian points should be avoided De-qi (Zhang J. et al., 2023; Zhang J. S. et al., 2023; Zhang Y. et al., 2023; Chen C. et al., 2024; Chen T. et al., 2024); (2) mild stimulation such as superficial acupuncture (Chen et al., 2014; Wang et al., 2023); and (3) tactile stimulation (Chen et al., 2015), use of non-penetrating and flexible needles (Huang et al., 2013), and application of no-current electric stimulators (Schaechter et al., 2007). SA plays a critical role in understanding and analysing the effects of acupuncture; however, the overall quality of reporting is suboptimal. SA reports are recommended based on the guidelines outlined in the fake needle report list (Jiang et al., 2017). The purpose of the healthy population is to demonstrate the functional specificity of acupuncture, suggesting that acupuncture exerts a significant effect under pathological conditions. The therapeutic efficacy of acupuncture is attained by restoring the internal environmental balance. Imaging studies conducted in healthy subjects may reflect pre-intervention brain homeostasis in patients, thereby providing a more comprehensive understanding of the mechanisms underlying the efficacy of acupuncture.
Several potential factors were considered regarding efficacy, including needle timing, needle retention time, Deqi and non-Deqi, and different acupoints. A study investigating the differential activation responses of the brains of patients with stroke in the morning and afternoon revealed a stronger activation effect in the morning than in the afternoon (Ma et al., 2023). Another study categorized participants into groups based on needle retention times of 1, 2, and 3 min, utilizing a consistent acupoint prescription across groups. These findings indicate that varying the retention time of acupuncture treatment results in distinct neural effects in patients with stroke, with the volume of the activated voxel cluster showing a positive correlation with the duration of acupuncture (Gao et al., 2015). Several studies have demonstrated that the Deqi group exhibits significant activation in relevant brain regions compared with the non-Deqi group (Zhou et al., 2023). Additionally, researchers have compared the effects of cardiac and pericardial meridian acupoints on disease and brain mechanisms, with results showing a better effect of pericardial meridian acupoints than that of cardiac meridian acupoints (Li et al., 2015). Furthermore, the central effect of the Baihui acupoint is more potent than that of Yanglingquan in ameliorating memory impairment post-stroke, potentially due to the enhanced functional connectivity of the hippocampus and the brain network between the frontal and parietal lobes (Zhang et al., 2019). These studies provide neuroimaging evidence supporting the underlying mechanisms in acupuncture.
MRI is an emerging neuroimaging method for exploring the central mechanism of acupuncture in patients with stroke. Our review indicates that multimodal MRI technologies are increasingly attracting research attention.
In neuroimaging, fMRI is widely used to explore brain function, behavior, perception, and emotions. Our findings indicate that these trends are significantly expanding both transversely and longitudinally. Researchers’ observation index has broadened from initially focusing on local neural activity within specific brain regions to including the effects on different regions within the ipsilateral and contralateral hemispheres, extending to the overall brain network. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy imaging (MRS/1H-MRS) is primarily employed to quantify the concentration of specific metabolites in the brain or other tissues and is frequently used to investigate the metabolic state and pathological lesions of the brain. Different lesion areas can be selected for detection based on stroke complications. Additionally, dynamic, non-invasive monitoring of critical brain metabolites can be conducted, thereby providing robust evidence supporting molecular imaging in the acupuncture treatment of stroke. Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging (DWI/DTI) is predominantly used to delineate the structural architecture and white matter pathways within the brain and investigate acupuncture as a treatment modality for motor dysfunction following stroke. This imaging technique enables quantitative analysis of nerve fiber damage and motor dysfunction, which is crucial for understanding acupunctures’ efficacy in motor function rehabilitation. DTI is often combined with fMRI to explore the interrelationships between the brain structure and function. Magnetic resonance perfusion imaging, including arterial spin labelling (ASL) and perfusion-weighted imaging (PWI), offers a rapid assessment of haemodynamic alterations in the brain tissue. ASL perfusion imaging is a common technique for measuring cerebral blood flow (CBF). In patients with stroke, variations in infarct location correspond to differences in cerebral blood flow signals. Alterations in local cerebral blood flow within specific brain regions may constitute a critical neural mechanism underlying functional impairment. Additionally, acupuncture may facilitate neural repair by augmenting the local cerebral blood flow. Structural magnetic resonance imaging (sMRI) provides high-resolution images of the brain and other anatomical structures, facilitating the detailed observation of anatomical features. This modality is extensively utilized for diagnostic purposes, disease monitoring, and investigating structural changes in the brain.
Thus, fMRI focuses on brain activity and function, MRS/1H-MRS on chemical and metabolic states, DWI/DTI on white matter structure and function, sMRI on anatomical structures, and ASL/PWI on cerebral blood flow. Collectively, these neuroimaging techniques provide robust scientific and quantitative evidence supporting the efficacy of acupuncture in stroke treatment by addressing various dimensions, such as functional activity, metabolic processes, structural integrity, and cerebral perfusion. This multifaceted approach highlights the comprehensive therapeutic potential of acupuncture for stroke rehabilitation.
This review presents the first systematic review using evidence map to illustrate the current state of neuroimaging research on the acupuncture treatment of stroke. It provides a significant reference for future scholarly research, offering imaging evidence that elucidates the brain network mechanism of acupuncture interventions in stroke. However, the current study has certain limitations, including a predominance of single-center studies with small sample sizes and a lack of long-term follow-up. Future research should consider the implementation of multicenter, large-sample, clinical randomized controlled studies to further investigate the clinical efficacy of acupuncture and the potential brain network mechanisms that could enhance stroke recovery.
CK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. WS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZZ: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. ZX: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. MS: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. JY: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. SS: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. WZ: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by Program of National Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine Inheritance and Innovation Center: Predominant diseases (ischemic stroke), National Natural Science Foundation of China (82374596); Hunan province key areas of research and development plan (No.2023SK2049). We thank the Home for Researchers editorial team (www.home-forresearchers.com) and editage team (https://www.editage.cn/) for the language editing service.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnins.2024.1495435/full#supplementary-material
Barthels, D., and Das, H. (2020). Current advances in ischemic stroke research and therapies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. basis Dis. 1866:165260. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.09.012
Benjamin, E. J., Muntner, P., Alonso, A., Bittencourt, M. S., Callaway, C. W., Carson, A. P., et al. (2019). Heart disease and stroke Statistics-2019 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 139, e56–e528. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000659
Brainin, M., Feigin, V. L., Norrving, B., Martins, S. C. O., Hankey, G. J., Hachinski, V., et al. (2020). Global prevention of stroke and dementia: the WSO declaration. Lancet Neurol. 19, 487–488. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30141-1
Chang, S. X., Kong, X. Q., Li, G., Liu, D. X., and Xiong, Y. (2003). fMRI to monitor the recovery of cortical activity in stroke with acupoints electroacupuncture stimulation. Chin. Imaging J. Integr. Trad. West. Med. 1:34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0512.2003.01.006
Chen, T., Chen, T., Zhang, Y., Wu, K., and Zou, Y. (2024). Bilateral effect of acupuncture on cerebrum and cerebellum in ischaemic stroke patients with hemiparesis: a randomised clinical and neuroimaging trial. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 9, 306–317. doi: 10.1136/svn-2023-002785
Chen, C., Li, K. S., and Yu, X. (2024). Immediate effects of acupuncture at Yanglingquan on functional connectivity of brain network in patients with stroke and hemiplegia. Chin. J. Inf. Trad. Chin. Med. 31, 149–154. doi: 10.19879/j.cnki.1005-5304.202304529
Chen, J., Wang, J., Huang, Y., Lai, X., Tang, C., Yang, J., et al. (2014). Modulatory effect of acupuncture at Waiguan (TE5) on the functional connectivity of the central nervous system of patients with ischemic stroke in the left basal ganglia. PLoS One 9:e96777. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096777
Chen, X., Zhang, H., and Zou, Y. (2015). A functional magnetic resonance imaging study on the effect of acupuncture at GB34 (Yanglingquan) on motor-related network in hemiplegic patients. Brain Res. 1601, 64–72. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2015.01.011
Feigin, V. L., Mensah, G. A., Norrving, B., Murray, C. J. L., and Roth, G. A. (2013). Stroke panel experts group. (2015). Atlas of the global burden of stroke (1990–2013): the GBD 2013 study. Neuroepidemiology 45, 230–236. doi: 10.1159/000441106
Feigin, V. L., Roth, G. A., Naghavi, M., Parmar, P., Krishnamurthi, R., Chugh, S., et al. (2016). Global burden of stroke and risk factors in 188 countries, during 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2013. Lancet Neurol. 15, 913–924. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(16)30073-4
Gao, Y., Lin, Z., Tao, J., Yang, S., Chen, R., Jiang, C., et al. (2015). Evidence of timing effects on acupuncture: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Exp. Ther. Med. 9, 59–64. doi: 10.3892/etm.2014.2056
GBD Diseases and Injuries Collaborators (2019). Diseases and injuries collaborators. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. (2020). Lancet 396, 1204–1222. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30925-9
GBD Parkinson’s Disease Collaborators (2016). Global, regional, and national burden of Parkinson’s disease, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 17, 939–953. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30295-3
Huang, Y., Chen, J. Q., Lai, X. S., Tang, C. Z., Yang, J. J., Chen, H., et al. (2013). Lateralisation of cerebral response to active acupuncture in patients with unilateral ischaemic stroke: an fMRI study. Acupunct. Med. 31, 290–296. doi: 10.1136/acupmed-2012-010299
Jiang, Z., Zhuo, L. P., Liao, S. Q., and Huang, S. E. (2017). Clinical observation of different acupoint stimulation methods to improve hand dysfunction in patients with ischemic stroke. J. Rehabil. Med. 27, 7–12. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1329.2017.04007
Katan, M., and Luft, A. (2018). Global burden of stroke. Semin. Neurol. 38, 208–211. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1649503
Li, M. K., Li, Y. J., Zhang, G. F., Chen, J. Q., Zhang, J. P., Qi, J., et al. (2015). Acupuncture for ischemic stroke: cerebellar activation may be a central mechanism following Deqi. Neural Regen. Res. 10, 1997–2003. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.172318
Liao, Y. T., Liu, F. B., and Lin, Q. (2016). The study of Qiuxu point induced brain activation effect of Bechterev flexion reflex in patients with cerebral apoplexy. China Med. Pharm. 6:15.
Liu, C. R., Zhang, X. F., and Mo, H. F. (2019). MRl effects of treatment for dysphagia after pseudobulbar palsy by needling the root of tongue. Guiding J. Trad. Chin. Med. Pharmacol. 25, 112–115.
Lu, M., Du, Z., Zhao, J., Jiang, L., Liu, R., Zhang, M., et al. (2023). Neuroimaging mechanisms of acupuncture on functional reorganization for post-stroke motor improvement: a machine learning-based functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Front. Neurosci. 17:1143239. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1143239
Ma, P., Liu, X., Liu, Z., Guo, Y., Zhou, K., Bian, Z., et al. (2023). The SHARE: SHam acupuncture REporting guidelines and a checklist in clinical trials. J. Evid. Based Med. 16, 428–431. doi: 10.1111/jebm.12560
Minelli, C., Luvizutto, G. J., Cacho, R. O., Neves, L. O., Magalhães, S. C. S. A., Pedatella, M. T. A., et al. (2022). Brazilian practice guidelines for stroke rehabilitation: part II. Arq. Neuro Psiquiatr. 80, 741–758. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-1757692
Report on Stroke Prevention and Treatment in China Writing Group (2023). Brief report on stroke prevention and treatment in China, 2021. Chin. J. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 20, 783–793. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5921.2023.11.00
Schaechter, J. D., Connell, B. D., Stason, W. B., Kaptchuk, T. J., Krebs, D. E., Macklin, E. A., et al. (2007). Correlated change in upper limb function and motor cortex activation after verum and sham acupuncture in patients with chronic stroke. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 13, 527–532. doi: 10.1089/acm.2007.6316
Schockert, T., Schnitker, R., Boroojerdi, B., Smith, I. Q., Yamamoto, T., Vietzke, K., et al. (2010). Cortical activation by Yamamoto new scalp acupuncture in the treatment of patients with a stroke: a sham-controlled study using functional MRI. Acupunct. Med. 28, 212–214. doi: 10.1136/aim.2010.002683
Si, W. J., Zhang, H., Wang, P., Tan, Z. J., and Cui, F. Y. (2013). Observation on the immediate effects of acupuncture at Yanglingquan(GB 34) on passive movement in cerebral infarction patients. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu 33, 131–136
Stinear, C. M., Lang, C. E., Zeiler, S., and Byblow, W. D. (2020). Advances and challenges in stroke rehabilitation. Lancet Neurol. 19, 348–360. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30415-6
Wang, W., Jiang, B., Sun, H., Ru, X., Sun, D., Wang, L., et al. (2017). Prevalence, incidence, and mortality of stroke in China: results from a nationwide population-based survey of 480687 adults. Circulation 135, 759–771. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.025250
Wang, Y., Lu, M., Liu, R., Wang, L., Wang, Y., Xu, L., et al. (2023). Acupuncture alters Brain’s dynamic functional network connectivity in stroke patients with motor dysfunction: a randomised controlled neuroimaging trial. Neural Plast. 2023:8510213. doi: 10.1155/2023/8510213
Wang, X., Seguin, C., Zalesky, A., Wong, W. W., Chu, W. C. W., and Tong, R. K. Y. (2019). Synchronization lag in post stroke: relation to motor function and structural connectivity. Netw. Neurosci. 3, 1121–1140. doi: 10.1162/netn_a_00105
Xiao, H., He, J., and Kuangshi, L. (2020). Acupuncture modulates disrupted whole-brain network after ischemic stroke: Evidence based on graph theory analysis. Neural Plast. 2020:8838498. doi: 10.1155/2020/8838498
Xu, M., Gao, Y., Zhang, H., Zhang, B., Lyu, T., Tan, Z., et al. (2022). Modulations of static and dynamic functional connectivity among brain networks by electroacupuncture in post-stroke aphasia. Front. Neurol. 13:956931. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.956931
Zhang, Y., Chen, M., Liu, C., He, B., Dang, H., Li, J., et al. (2023). Global trends and research hotspots of stroke and magnetic resonance imaging: a bibliometric analysis. Medicine 102:e36545. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036545
Zhang, J., Ji, C., Zhai, X., Ren, S., and Tong, H. (2023). Global trends and hotspots in research on acupuncture for stroke: a bibliometric and visualization analysis. Eur. J. Med. Res. 28:359. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01253-w
Zhang, W., Liao, L., and Li, P. (2019). Based on MR ASL to investigate the effects on ROI-CBF of patients with cerebral infarction during recovery period by acupuncturing pericardium meridian and heart meridian acupoints. World Chin. Med. 14, 536–541. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2019.03.005
Zhang, H., Si, W. J., Tan, Z. J., Yuan, Y. E., and Zou, Y. H. (2014). Effect of acupuncture at Yanglingquan on white matter structures of stroke patients. Chin. J. Rehabil. Theor. Pract. 20, 955–959. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9771.2014.10.17
Zhang, J. S., Zhang, L., and Zhu, L. (2023). Mechanism of electroacupuncture at Baihui(GV20) and Yintang(ex-HN3)in treating depression based on magnetic resonance imaging. World Chin. Med. 18, 2953–2958. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2023.20.017
Zhang, T., Zhao, J., Li, X., Bai, Y., Wang, B., Qu, Y., et al. (2020). Chinese Stroke Association guidelines for clinical management of cerebrovascular disorders: executive summary and 2019 update of clinical management of stroke rehabilitation. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 5, 250–259. doi: 10.1136/svn-2019-000321
Zhao, Y., Wang, W., and Zhou, L. J. (2017). Mechanism of motor recovery in hemiplegic patients with ischemic stroke: a study of acupuncture-induced blood oxygenation level dependent functional magnetic resonance imaging and diffusion tensor imaging. Int. J. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 025, 904–909. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4165.2017.10.006
Keywords: stroke, neuroimaging, acupuncture, magnetic resonance imaging, evidence map
Citation: Ke C, Shi W, Zhou Z, Xie Z, Sun M, Yu J, Shan S and Zhang W (2024) Overview of evidence-based research on acupuncture for stroke treatment using magnetic resonance imaging technology. Front. Neurosci. 18:1495435. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1495435
Received: 12 September 2024; Accepted: 28 October 2024;
Published: 25 November 2024.
Edited by:
Masako Kinoshita, National Hospital Organization Utano National Hospital, JapanReviewed by:
Jiliang Fang, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Ke, Shi, Zhou, Xie, Sun, Yu, Shan and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wei Zhang, endfNjk5OTZAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.