- 1Department of Radiology, The First Hospital of Huhhot, Huhhot, China
- 2Department of Radiotherapy, Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Huhhot, China
Objective: To systematically review the literature on radiomics for predicting intracranial aneurysm rupture and conduct a meta-analysis to obtain evidence confirming the value of radiomics in this prediction.
Methods: A systematic literature search was conducted in PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, and The Cochrane Library databases up to March 2024. The QUADAS-2 tool was used to assess study quality. Stata 15.0 and Review Manager 5.4.1 were used for statistical analysis. Outcomes included combined sensitivity (Sen), specificity (Spe), positive likelihood ratio (+LR), negative likelihood ratio (−LR), diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), and their 95% confidence intervals (CI), as well as pre-test and post-test probabilities. The SROC curve was plotted, and the area under the curve (AUC) was calculated. Publication bias and small-study effects were assessed using the Deeks’ funnel plot.
Results: The 9 included studies reported 4,284 patients, with 1,411 patients with intracranial aneurysm rupture (prevalence 32.9%). The overall performance of radiomics for predicting intracranial aneurysm rupture showed a combined Sen of 0.78 (95% CI: 0.74–0.82), Spe of 0.74 (95% CI: 0.70–0.78), +LR of 3.0 (95% CI: 2.7–3.4), −LR of 0.29 (95% CI: 0.25–0.35), DOR of 10 (95% CI: 9–12), and AUC of 0.83 (95% CI: 0.79–0.86). Significant heterogeneity was observed in both Sen (I2 = 90.93, 95% CI: 89.00–92.87%) and Spe (I2 = 94.28, 95% CI: 93.21–95.34%).
Conclusion: Radiomics can improve the diagnostic efficacy of intracranial aneurysm rupture. More large-sample, prospective, multicenter clinical studies are needed to further evaluate its predictive value.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/.
1 Introduction
Intracranial aneurysm is a tumor-like protrusion formed when the lumen of an intracranial artery gradually expands and bulges due to localized damage to the arterial wall caused by congenital developmental abnormalities or acquired injuries, under the influence of hemodynamic load or other factors (Etminan and Rinkel, 2016). With the development of imaging technology, the detection rate of unruptured intracranial aneurysms is increasing annually (Greving et al., 2014). However, the treatment decision for unruptured intracranial aneurysms remains controversial. Many intracranial aneurysms are asymptomatic and do not rupture for an extended period (Korja et al., 2014). Currently, preventive treatment for unruptured intracranial aneurysms includes endovascular treatment and neurosurgical interventional treatment, both associated with the inevitable risk of treatment-related complications (Naggara et al., 2010; Zhu et al., 2020). Conversely, once an intracranial aneurysm ruptures, it leads to subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), a severe subtype of stroke often accompanied by high mortality and disability rates (Vlak et al., 2011). Therefore, early screening of patients with intracranial aneurysms at high risk of rupture and providing them with timely preventive treatment are crucial for improving patient prognosis.
Previous studies have demonstrated that the risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture is associated with its morphological characteristics (Lindgren et al., 2016). Researchers have measured and defined these characteristics, such as neck width, aneurysm angle, and height, on computed tomographic angiography (CTA) or digital subtraction angiography (DSA) images of intracranial aneurysms (Zhang et al., 2019; Chen et al., 2020). Radiomics, a new computer-assisted technology, extracts quantitative features (e.g., shape, intensity, and texture) from biomedical images in an objective, reproducible, and high-throughput manner (Zhou et al., 2018; Hua et al., 2020; Tomaszewski and Gillies, 2021). The principle is that pathophysiological changes of certain diseases are manifested in digital medical images, and radiomics can extract this information through quantitative analysis and subsequent biological information mining (Gillies et al., 2016). Recently, the application of radiomics in cerebrovascular diseases has increased (Chen et al., 2021; Zhu et al., 2021; Zhu et al., 2021). Some studies have demonstrated an association between radiomics characteristics of aneurysms and the risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture (Liu et al., 2019; Ou et al., 2021). However, these studies did not analyze the stability of the imaging features, which can be affected by differences in scanning parameters or image segmentation methods (Mackin et al., 2015; Choe et al., 2019). Furthermore, most previous studies on imaging features of intracranial aneurysms have not been validated by external datasets, leaving the reproducibility and generalizability of their results uncertain (Zhu et al., 2021; Luo et al., 2023; Turhon et al., 2023).
Recently, the rapid development of computer science, particularly the progress of artificial intelligence, has led to algorithms such as machine learning and deep learning playing an increasingly important role in medical data processing (Chen et al., 2021). Algorithms, including support vector machines, random forests, and artificial neural networks, have been successfully applied to disease diagnosis, metastasis prediction, and treatment prognosis evaluation (Orru et al., 2012; Beig et al., 2019; Khorrami et al., 2019). Appropriate algorithms can maximize the mining of data information and assist in disease diagnosis. To date, many radiomic models have been used to predict ruptured intracranial aneurysms. However, no relevant meta-analysis has been reported, and its sensitivity and specificity remain undetermined. Therefore, this study systematically searched Pubmed, Embase, Cochrane and Web of Science to obtain all literatures on radiomics in predicting intracranial aneurysm rupture, and conducted a meta-analysis for the first time to obtain the latest and most comprehensive evidence-based confirmation of the value of radiomics in predicting intracranial aneurysm rupture.
2 Methods
2.1 Protocol and registration
This systematic review and meta-analysis, prospectively registered in PROSPERO (CRD42024453092), was performed following the PRISMA 2020 statement (Page et al., 2021).
2.2 Search strategy
A systematic literature search was conducted in PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, and The Cochrane Library databases using medical subject headings and free words, including “radiomics,” “aneurysm,” “rupture,” and “intracranial.” The search strategies for PubMed were as follows: ((“Intracranial Aneurysm”[Mesh]) OR (((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((((Aneurysms, Intracranial) OR (Intracranial Aneurysms)) OR (Aneurysm, Intracranial)) OR (Aneurysm, Anterior Communicating Artery)) OR (Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysm)) OR (Aneurysm, Basilar Artery)) OR (Aneurysms, Basilar Artery)) OR (Artery Aneurysm, Basilar)) OR (Artery Aneurysms, Basilar)) OR (Basilar Artery Aneurysms)) OR (Basilar Artery Aneurysm)) OR (Aneurysm, Middle Cerebral Artery)) OR (Middle Cerebral Artery Aneurysm)) OR (Aneurysm, Posterior Cerebral Artery)) OR (Posterior Cerebral Artery Aneurysm)) OR (Berry Aneurysm)) OR (Aneurysm, Berry)) OR (Aneurysms, Berry)) OR (Berry Aneurysms)) OR (Brain Aneurysm)) OR (Aneurysm, Brain)) OR (Aneurysms, Brain)) OR (Brain Aneurysms)) OR (Cerebral Aneurysm)) OR (Aneurysms, Cerebral)) OR (Cerebral Aneurysms)) OR (Aneurysm, Cerebral)) OR (Giant Intracranial Aneurysm)) OR (Aneurysm, Giant Intracranial)) OR (Aneurysms, Giant Intracranial)) OR (Giant Intracranial Aneurysms)) OR (Intracranial Aneurysm, Giant)) OR (Intracranial Aneurysms, Giant)) OR (Aneurysm, Anterior Cerebral Artery)) OR (Anterior Cerebral Artery Aneurysm)) OR (Aneurysm, Posterior Communicating Artery)) OR (Posterior Communicating Artery Aneurysm))) AND (((radiomic*) OR (Histogram*)) OR (Texture*)). The search time was up to March, 2024. Furthermore, we manually screened the bibliography lists of all included studies. Two authors retrieved and assessed eligible articles independently. Any differences in literature retrieval were resolved by discussion. All retrieved literature was manually reviewed and verified through EndNote X9.
2.3 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
This study included prospective and retrospective studies investigating the predictive value of radiomics for intracranial aneurysm rupture. Inclusion criteria:
P: patients with suspected or confirmed ruptured intracranial aneurysms.
I: radiomics as the evaluated experiment, regardless of model and method.
C: gold standard, including CTA, MRA, or DSA.
O: sensitivity (Sen), specificity (Spe), positive likelihood ratio (+LR), negative likelihood ratio (−LR), diagnostic odds ratio (DOR), pre-test probability, post-test probability, summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) area under the curve (AUC).
S: prospective and retrospective studies focusing on the predictive value of radiomics for intracranial aneurysm rupture.
Exclusion criteria: (Etminan and Rinkel, 2016) duplicate publications; (Greving et al., 2014) irrelevant articles; (Korja et al., 2014) reviews, meta-analyses, conferences, letters, comments; (Naggara et al., 2010) animal models, studies with low sample size; (Zhu et al., 2020) articles with no or incomplete data; (Vlak et al., 2011) non-English articles.
2.4 Data extraction
Two independent reviewers extracted data from eligible studies, including first author, publication year, study design, subjects’ age, gender, radiomics models, gold standard, sample size of case and control groups, true positives (TP), false positives (FP), true negatives (TN), false negatives (FN), Sen, Spe, +LR, −LR, DOR, pre-test probability, post-test probability, and AUC value. Disagreements between the two reviewers were resolved by consulting a third party. Corresponding authors were contacted for full data if research data was insufficient. All data were summarized in a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet.
2.5 Quality assessment
The quality assessment of the included literature was conducted using the QUADAS-2 tool, following the guidelines in the Cochrane Handbook for systematic reviews of diagnostic trials. The final evaluation findings were presented using the Review Manager 5.4.1 software (Qu et al., 2018). Two reviewers independently assessed the literature quality, with disagreements resolved through discussion or adjudication by a third reviewer when necessary. The QUADAS-2 tool assesses literature quality from two aspects: risk of bias and clinical applicability. The risk of bias comprises four aspects: patient selection, index test, reference standard, and flow and timing. The clinical applicability questions consist of three aspects: patient selection, index test, and reference standard. Each evaluation domain in the risk of bias contains signaling questions with “yes/no/unclear” answer options. If all signaling questions in a domain are answered “yes,” the risk of bias in that aspect is considered low. If one answer is “no,” there is a possibility of bias. Clinical applicability has no signaling questions, only an overall assessment with “high risk/low risk/unclear” answer options. The “unclear” option can only be selected when the literature provides incomplete information during the assessment process. In addition, the Radiomics Quality Score (RQS) was used to assess the characteristics and quality of each included radiomics study. This scoring scale has 36 potential scores based on 16 criteria, with 36 indicating the highest quality (Spadarella et al., 2023).
2.6 Data analysis
Stata 15.0 and Review Manager 5.4.1 software were used for statistical analysis. A bivariate mixed-effects regression model was employed after the random-effects model to combine Sen, Spe, +LR, −LR, DOR, and their 95% confidence intervals (95% CI), as well as pre-test and post-test probabilities. The SROC curve was plotted, and the AUC was calculated. The χ2 test, with a test level of α = 0.05, was used to analyze the statistical heterogeneity among studies, and the I2 value quantitatively determined the heterogeneity. An I2 ≤ 50% indicated low heterogeneity, while a higher value suggested high heterogeneity. The Deeks’ funnel plot assessed publication bias and assumed small-study effects, with p < 0.05 indicating publication bias in the included literature. When publication bias is present, the trim-and-fill method is used to assess the effect of the bias on the combined statistics (Zhang and Zhong, 2008).
3 Results
3.1 Literature screening process and results
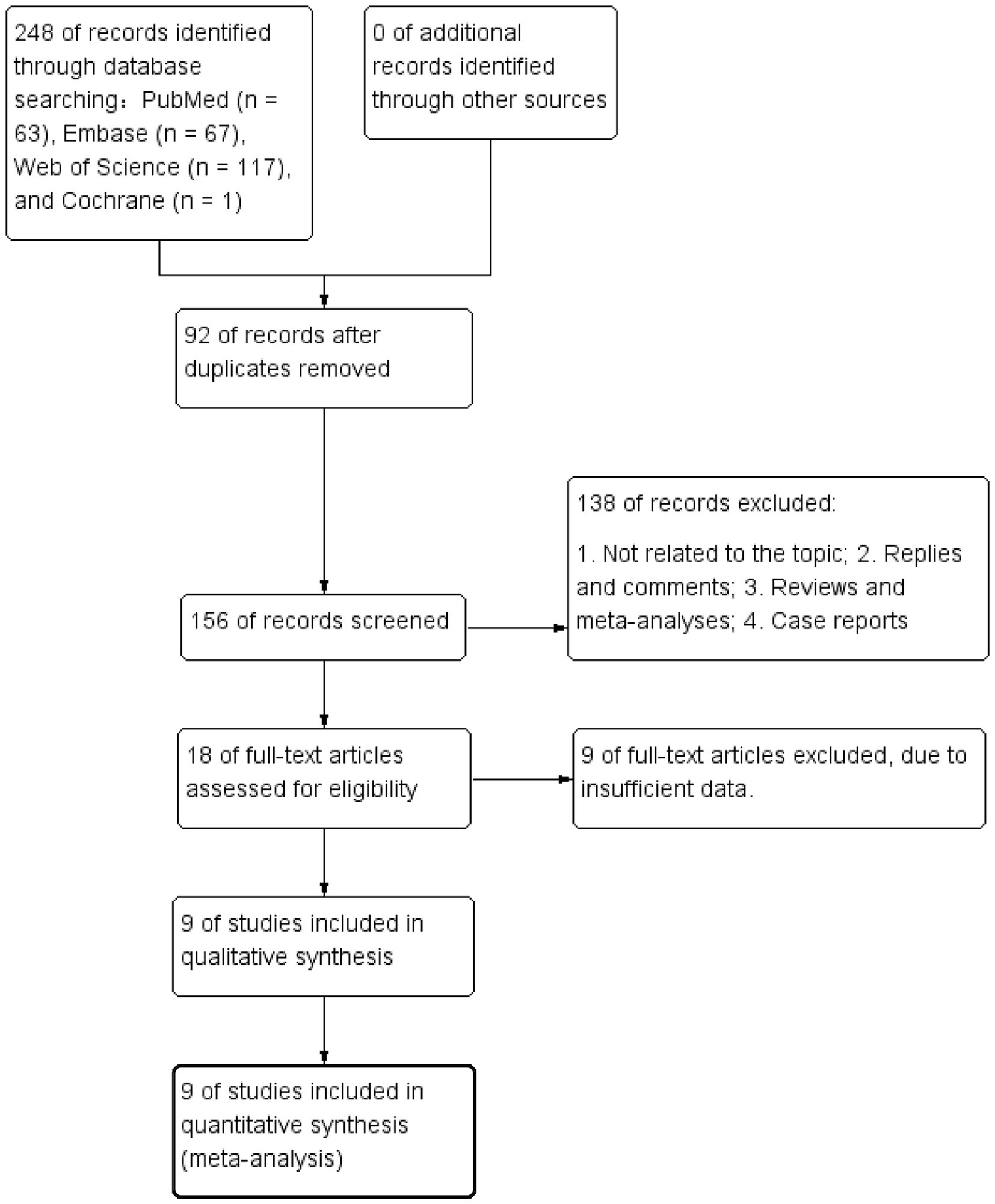
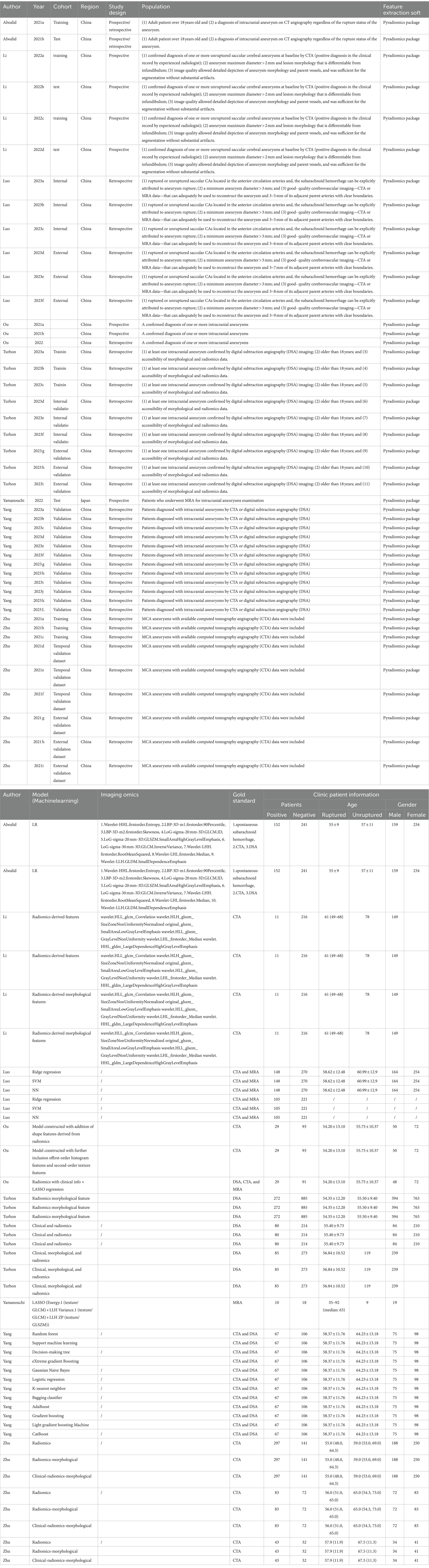
A total of 248 articles were obtained using the literature search strategy. After removing duplicates using EndNote X9, 156 articles remained. Following the exclusion of 138 articles based on titles and abstracts, 18 articles underwent initial screening. Among these, 9 articles were further excluded after full-text review due to incomplete information and not meeting the requirements, resulting in a final inclusion of 9 articles (Ou et al., 2021; Alwalid et al., 2021; Zhu et al., 2021; Li et al., 2022; Ou et al., 2022; Yamanouchi et al., 2022; Luo et al., 2023; Turhon et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2023). Figure 1 illustrates the literature screening process flowchart, and Table 1 presents the fundamental characteristics of the included studies. For studies with multiple models or cohorts, separate extraction was performed, distinguished by adding the letters “a, b, c, or d” after the study names.
3.2 Quality assessment of included studies
The QUADAS-2 tool was used to assess the risk of bias and the RQS was used to assess the quality of each included study. Figure 2 presents the methodological quality evaluation results for the included studies. Overall, the included studies showed high quality, with most exhibiting low or unclear risk of bias. Detailed RQS of each study was presented in Supplementary Table S1.
3.3 Meta-analysis results
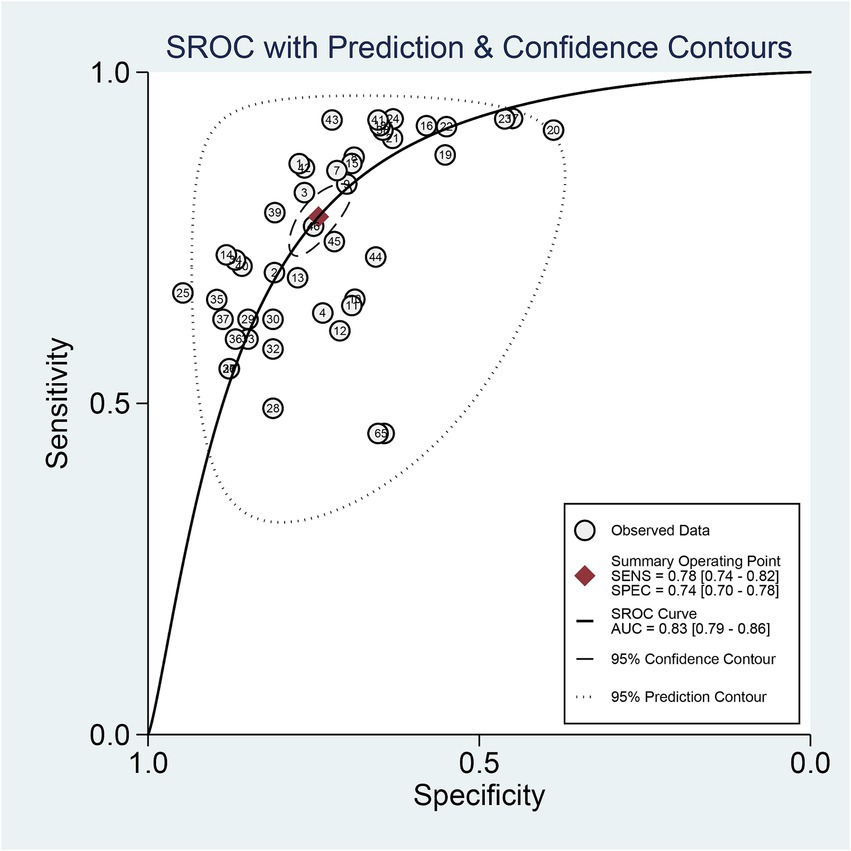
The 9 included studies reported 4,284 patients, with 1,411 patients having intracranial aneurysm rupture, resulting in a prevalence of 32.9%. The overall performance of radiomics for predicting intracranial aneurysm rupture showed a combined Sen of 0.78 (95% CI: 0.74–0.82), Spe of 0.74 (95% CI: 0.70–0.78), +LR of 3.0 (95% CI: 2.7–3.4), −LR of 0.29 (95% CI: 0.25–0.35), and DOR of 10 (95% CI: 9–12) (Figure 3). The overall forest plot revealed significant heterogeneity in both sensitivity and specificity, with I2 = 90.93% (95% CI: 89.00–92.87%) for Sen and I2 = 94.28% (95% CI: 93.21–95.34%) for Spe (Figure 3). Figure 4 presented the SROC with prediction and confidence contours, yielding an AUC value of 0.83 (95% CI: 0.79–0.86).
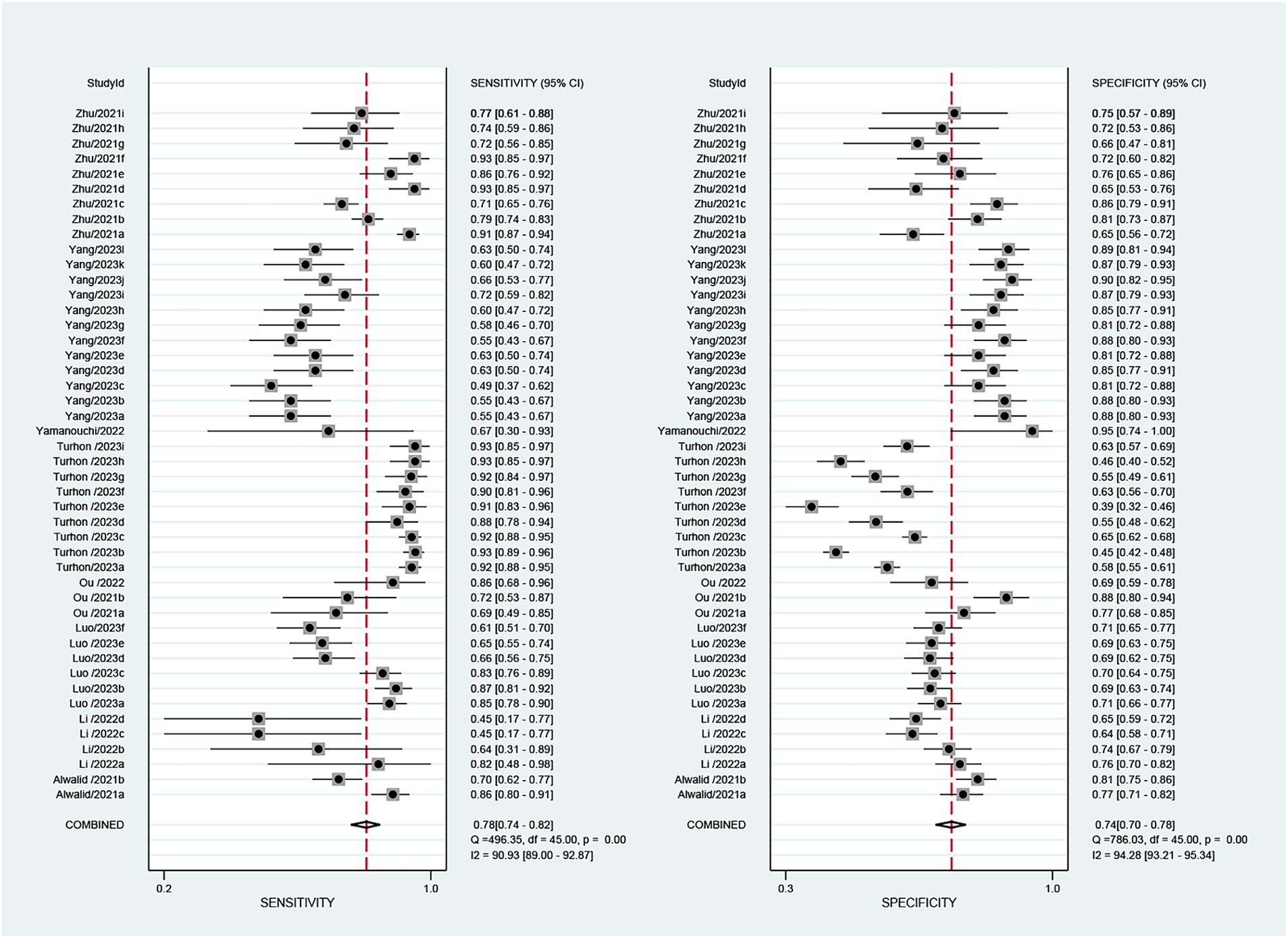
Figure 3. The forest map of the combined sensitivity, specificity of the predictive value of radiomics for intracranial aneurysm rupture.
3.4 Publication bias
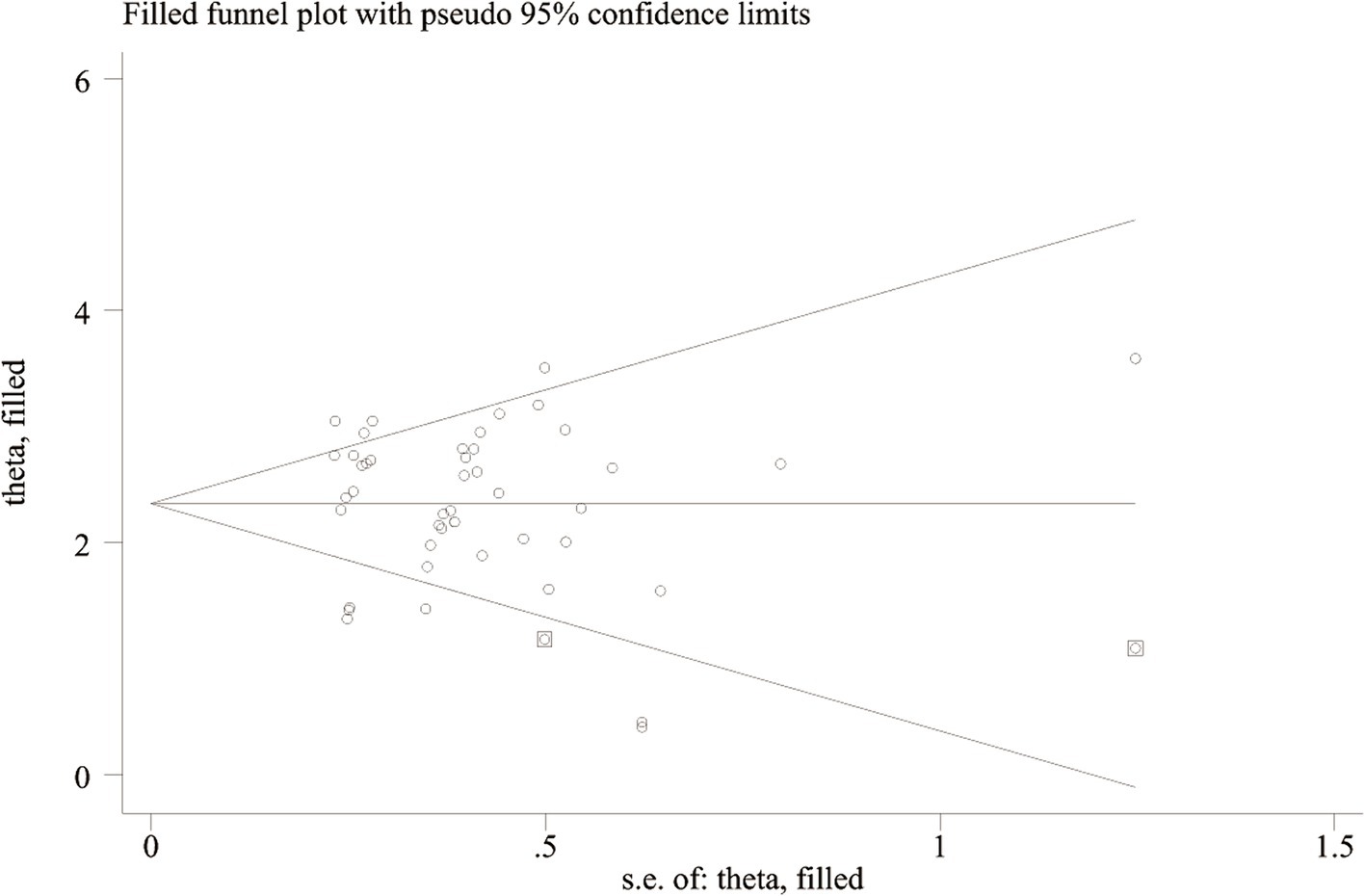
Deeks’ test was employed to assess publication bias in the included studies, yielding a p value of 0.03. As the p value was less than 0.05, it suggested that this meta-analysis was affected by significant publication bias (Figure 5). After the number of missing published papers was filled by the “trim-and-fill method,” the results showed that the values of the corresponding variables did not change significantly before and after filling, suggesting that publication bias did not affect the overall effect size of the merger (Figure 6).
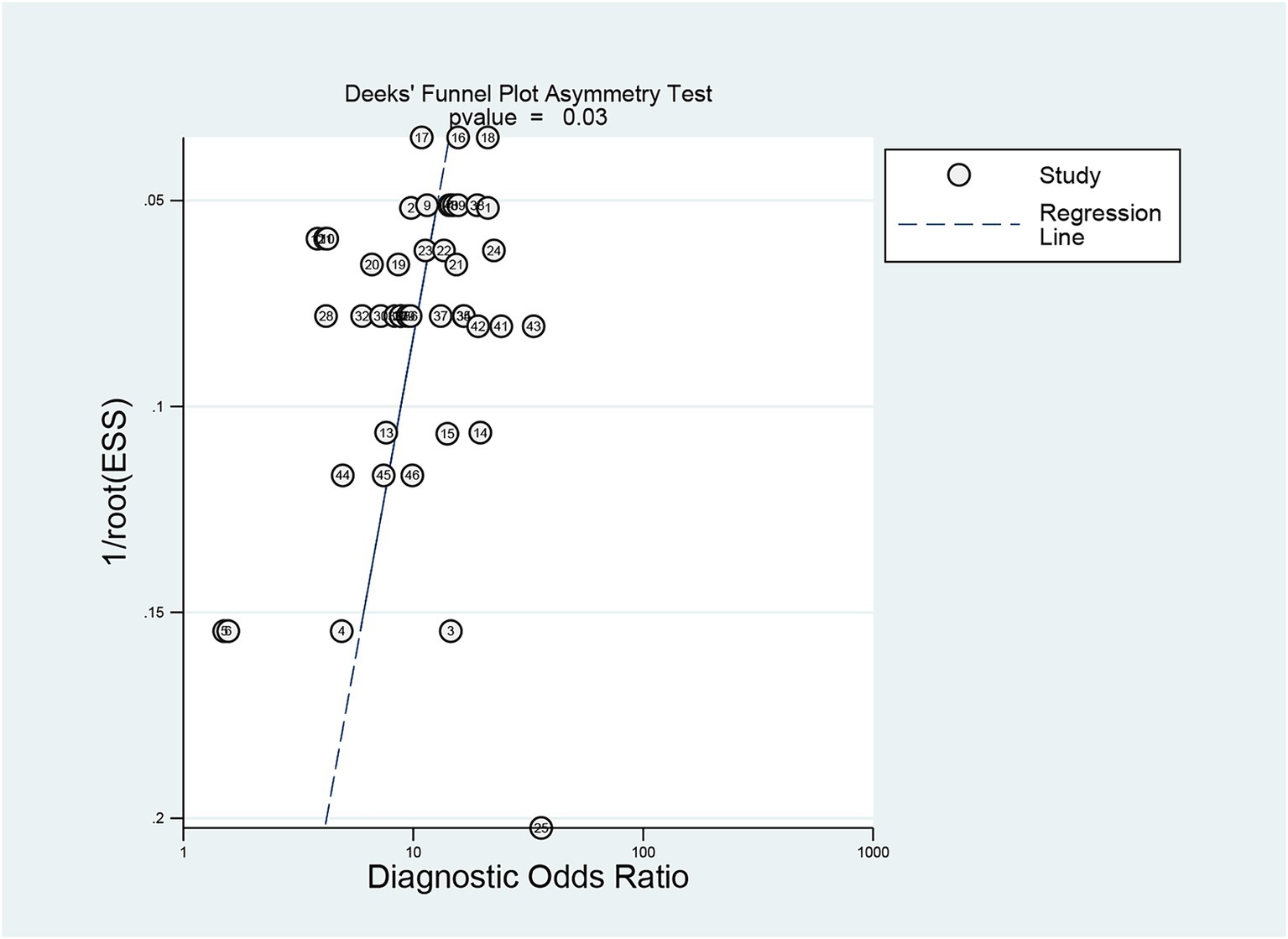
Figure 5. Detection of publication bias in predicting intracranial aneurysm rupture using radiomics.
3.5 Post-test probability
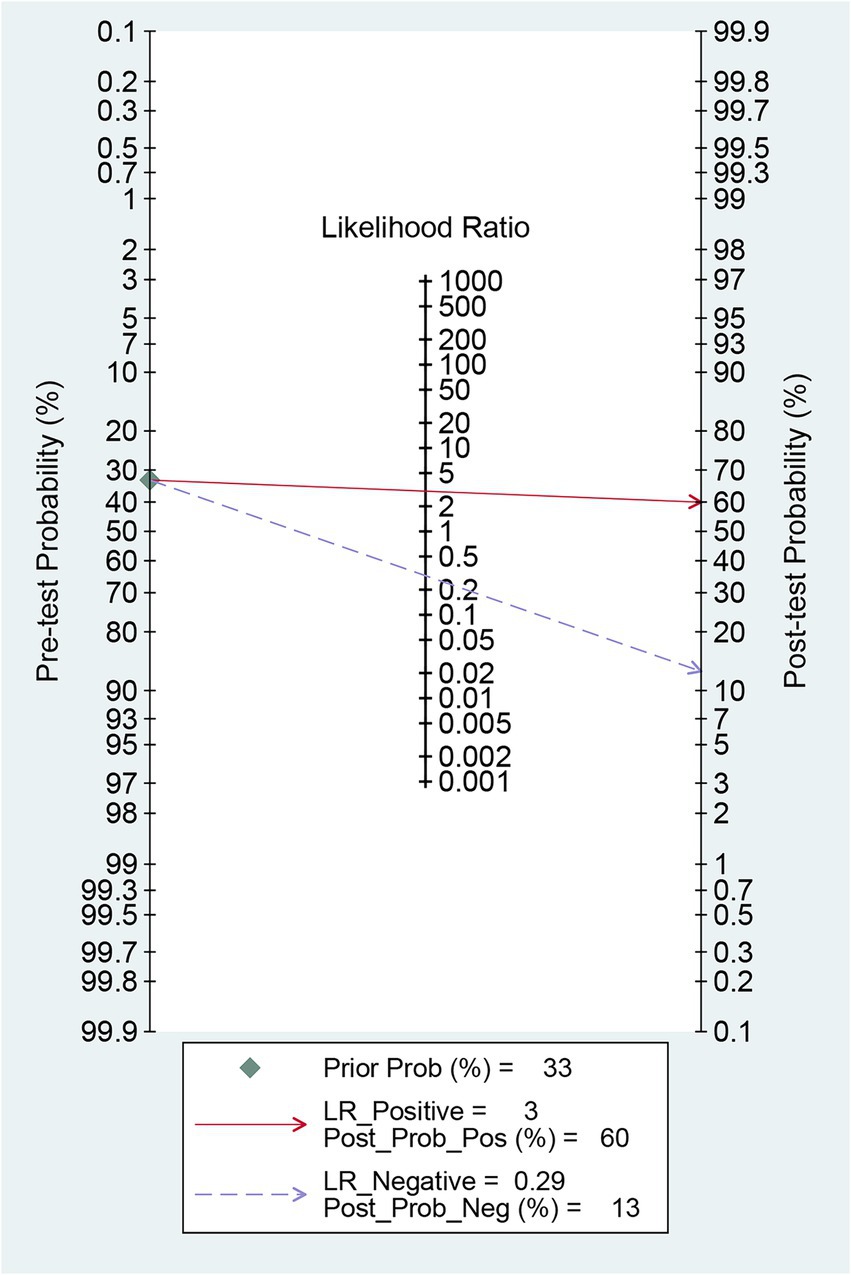
Before the application of radiomics, the pre-test probability of intracranial aneurysm rupture was 33%. The post-test probability of diagnosing ruptured intracranial aneurysms with positive radiomics results was 60%, while negative radiomics results yielded a post-test probability of 13%. When radiomics was positive, the prevalence of ruptured intracranial aneurysms was 60%, and when radiomics was negative, the prevalence was 13% (Figure 7).
4 Discussion
Radiomics and traditional morphological features of intracranial aneurysms are both derived from CTA images but differ in their biological significance and analysis methods. Radiomics features describe the shape and texture characteristics of intracranial aneurysms from a microscopic perspective (Collins et al., 2015; Xu et al., 2019), while traditional morphological features reflect the macroscopic observation. Radiomics features are three-dimensional, high-throughput biomarkers, but lack biological interpretability. Despite being based on two-dimensional image measurements and containing relatively little information, traditional morphological features remain an important tool for evaluating intracranial aneurysm stability in clinical practice due to their operability and intuitiveness. Numerous studies support the complementary role of combining radiomics and traditional morphological features.
This study combined existing clinical data on the use of radiomics to predict intracranial aneurysm rupture through a systematic review and meta-analysis, obtaining the combined diagnostic efficacy to comprehensively evaluate the predictive value of radiomics. The results suggest that radiomics can be used as an additional tool in assessing the rupture risk of intracranial aneurysms in clinical practice, with a combined Sen of 0.78, Spe of 0.74, +LR of 3.0, −LR of 0.29, and DOR of 10. However, considering the significant publication bias in the study conclusions, further research is needed to confirm the predictive value of radiomics for intracranial aneurysm rupture.
Machine learning, a subfield of artificial intelligence, can identify and process complex relationships between multiple variables in large data sets through computer algorithms, applying them to predict unknown data. Yang et al. (2023) demonstrated that 12 machine learning models established using radiomics features could predict the risk of intracranial aneurysm rupture in 576 cases (AUC: 0.713–0.889), with varying predictive performance among algorithms. The ensemble learning algorithm, particularly the adaptive enhancement model, exhibited the best predictive performance, with an AUC of 0.889 (95% CI: 0.842–0.936) in the training set. When the validation set underwent 3-fold cross-validation, repeated 5 times, the AUC of the adaptive enhancement model ranged from 0.842 to 0.918. Turhon et al. (2023) analyzed clinical data and DSA images of 1740 patients with intracranial aneurysms, confirming the importance of radiomics in assessing aneurysm rupture risk. The deep learning model, constructed by combining clinical, morphological, and imaging features, significantly outperformed the machine learning model (AUC: 0.878, 95% CI: 0.840–0.916) and the traditional Logistic regression model (AUC: 0.849, 95% CI: 0.808–0.890) in predicting aneurysm rupture (AUC: 0.929, 95% CI: 0.893–0.965; all p < 0.01). The deep learning model’s performance was also verified in internal and external data.
Ou et al. (2022) proposed a self-supervised and pre-trained deep learning model to predict the rupture risk of unruptured intracranial aneurysms in a follow-up of 2 years or more. The morphologically aware deep embedding method outperformed the deep learning model trained from scratch and the traditional morphological and imaging genomics models in predicting aneurysm rupture. The study also developed a computer-assisted risk assessment system based on the model. Preliminary tests by 5 neurosurgeons showed that the system could improve their ability to predict intracranial aneurysm rupture and assist in making clinical decisions based on case reasoning. This study overcame the influence of morphological changes before and after aneurysm rupture, enabling the training of deep neural networks with limited data, and has the potential to become an auxiliary tool for clinical intracranial aneurysm rupture risk assessment. Feng et al. (2023) first applied a three-dimensional convolutional neural network for automatic detection, segmentation, and morphological measurement of intracranial aneurysms on CTA. Morphological and radiomic features related to aneurysm rupture were input into machine learning models (support vector machines, random forests, and multilayer perceptrons) for training, resulting in a well-performing model on the training and test sets (AUC: 0.85–0.90). This method can automatically analyze CTA images of intracranial aneurysms and evaluate their rupture status within 1 min, improving clinical work efficiency. Radiomics demonstrates great application potential in assessing intracranial aneurysm stability, and combining machine learning, particularly deep learning, with radiomics is expected to enhance the ability to predict intracranial aneurysm stability.
This study has several limitations. First, most of the included studies are retrospective, which may have potential uncontrollable bias risks. Second, the majority of studies are from Asia, and further research is needed to confirm whether the predictive value of radiomics for intracranial aneurysm rupture can be extended to other regions or countries. Additionally, the numerous and scattered types of radiomics models involved in this study contribute to the significant overall heterogeneity. However, due to data limitations, subgroup analysis based on the model to explore potential sources of heterogeneity could not be performed. The lack of biological interpretability of radiomics is also one of the limitations of this paper, and in order to address the challenge of biological interpretability, future research can focus on combining radiomics with genomic or molecular data to improve the interpretability and clinical relevance of models. Lastly, some studies included in this meta-analysis contained images from external validation populations, obtained by different scanning parameters and machines, which may affect the results and heterogeneity of model validation. In the future, more research is needed to explore the radiomics of different types of aneurysms and to develop models that combine clinical data with radiomics while testing these models in real-world clinical scenarios.
5 Conclusion
Although the results of this study suggest that radiomics can be used as an auxiliary tool to improve the diagnostic efficacy of ruptured intracranial aneurysms to some extent, the quality of the evidence is limited by significant heterogeneity, potential publication bias, small sample size, and retrospective study design. In the future, more large-scale, prospective, multicenter clinical studies are needed to further evaluate the value of radiomics in predicting intracranial aneurysm rupture.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
HW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HX: Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft. JF: Formal analysis, Investigation, Resources, Writing – original draft. JL: Investigation, Software, Supervision, Writing – original draft. LL: Formal analysis, Investigation, Software, Writing – original draft. ZK: Investigation, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. HZ: Data curation, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnins.2024.1474780/full#supplementary-material
References
Alwalid, O., Long, X., Xie, M., Yang, J., Cen, C., Liu, H., et al. (2021). CT angiography-based Radiomics for classification of intracranial aneurysm rupture. Front. Neurol. 12:864. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.619864
Beig, N., Khorrami, M., Alilou, M., Prasanna, P., Braman, N., Orooji, M., et al. (2019). Perinodular and intranodular radiomic features on lung CT images distinguish adenocarcinomas from granulomas. Radiology 290, 783–792. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2018180910
Chen, Y., Lin, B., Zhou, J., Chen, L., Yang, Y., and Zhao, B. (2020). Morphological predictors of middle cerebral artery bifurcation aneurysm rupture. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 192:105708. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.105708
Chen, Q., Xia, T., Zhang, M., Xia, N., Liu, J., and Yang, Y. (2021). Radiomics in stroke neuroimaging: techniques, applications, and challenges. Aging Dis. 12, 143–154. doi: 10.14336/AD.2020.0421
Choe, J., Lee, S. M., Do, K.-H., Lee, G., Lee, J.-G., Lee, S. M., et al. (2019). Deep learning–based image conversion of CT reconstruction kernels improves radiomics reproducibility for pulmonary nodules or masses. Radiology 292, 365–373. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2019181960
Collins, G. S., Reitsma, J. B., Altman, D. G., and Moons, K. G. M. (2015). Transparent reporting of a multivariable prediction model for individual prognosis or diagnosis (TRIPOD): the TRIPOD statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 162, 55–63. doi: 10.7326/M14-0697
Etminan, N., and Rinkel, G. J. (2016). Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: development, rupture and preventive management. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 12, 699–713. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2016.150
Feng, J., Zeng, R., Geng, Y., Chen, Q., Zheng, Q., Yu, F., et al. (2023). Automatic differentiation of ruptured and unruptured intracranial aneurysms on computed tomography angiography based on deep learning and radiomics. Insights Imaging 14:423. doi: 10.1186/s13244-023-01423-8
Gillies, R. J., Kinahan, P. E., and Hricak, H. (2016). Radiomics: images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology 278, 563–577. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2015151169
Greving, J. P., Wermer, M. J. H., Brown, R. D., Morita, A., Juvela, S., Yonekura, M., et al. (2014). Development of the PHASES score for prediction of risk of rupture of intracranial aneurysms: a pooled analysis of six prospective cohort studies. Lancet Neurol. 13, 59–66. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70263-1
Hua, W., Xiao, T., Jiang, X., Liu, Z., Wang, M., Zheng, H., et al. (2020). Lymph-vascular space invasion prediction in cervical cancer: exploring radiomics and deep learning multilevel features of tumor and peritumor tissue on multiparametric MRI. Biomed. Sig Proc. Control 58:101869. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2020.101869
Khorrami, M., Jain, P., Bera, K., Alilou, M., Thawani, R., Patil, P., et al. (2019). Predicting pathologic response to neoadjuvant chemoradiation in resectable stage III non-small cell lung cancer patients using computed tomography radiomic features. Lung Cancer 135, 1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.06.020
Korja, M., Lehto, H., and Juvela, S. (2014). Lifelong rupture risk of intracranial aneurysms depends on risk factors: a prospective Finnish cohort study. Stroke 45, 1958–1963. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.114.005318
Li, R., Zhou, P., Chen, X., Mossa-Basha, M., Zhu, C., and Wang, Y. (2022). Construction and evaluation of multiple Radiomics models for identifying the instability of intracranial aneurysms based on CTA. Front. Neurol. 13:876238. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.876238
Lindgren, A. E., Koivisto, T., Björkman, J., von und zu Fraunberg, M., Helin, K., Jääskeläinen, J. E., et al. (2016). Irregular shape of intracranial aneurysm indicates rupture risk irrespective of size in a population-based cohort. Stroke 47, 1219–1226. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.012404
Liu, Q., Jiang, P., Jiang, Y., Ge, H., Li, S., Jin, H., et al. (2019). Prediction of aneurysm stability using a machine learning model based on PyRadiomics-derived morphological features. Stroke 50, 2314–2321. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.025777
Luo, X., Wang, J., Liang, X., Yan, L., Chen, X., He, J., et al. (2023). Prediction of cerebral aneurysm rupture using a point cloud neural network. J. Neurointervent Surg. 15, 380–386. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2022-018655
Mackin, D., Fave, X., Zhang, L., Fried, D., Yang, J., Taylor, B., et al. (2015). Measuring computed tomography scanner variability of radiomics features. Investig. Radiol. 50, 757–765. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000180
Naggara, O. N., White, P. M., Guilbert, F., Roy, D., Weill, A., and Raymond, J. (2010). Endovascular treatment of intracranial unruptured aneurysms: systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature on safety and efficacy. Radiology 256, 887–897. doi: 10.1148/radiol.10091982
Orru, G., Pettersson-Yeo, W., Marquand, A. F., Sartori, G., and Mechelli, A. (2012). Using support vector machine to identify imaging biomarkers of neurological and psychiatric disease: a critical review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 36, 1140–1152. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2012.01.004
Ou, C., Chong, W., Duan, C.-Z., Zhang, X., Morgan, M., and Qian, Y. (2021). A preliminary investigation of radiomics differences between ruptured and unruptured intracranial aneurysms. Eur. Radiol. 31, 2716–2725. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07325-3
Ou, C., Li, C., Qian, Y., Duan, C.-Z., Si, W., Zhang, X., et al. (2022). Morphology-aware multi-source fusion–based intracranial aneurysms rupture prediction. Eur. Radiol. 32, 5633–5641. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-08608-7
Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., et al. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
Qu, Y. J., Yang, Z. R., Sun, F., and Zhan, S. Y. (2018). Risk on bias assessment: (6) A Revised Tool for the Quality Assessment on Diagnostic Accuracy Studies (QUADAS-2). Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 4, 524–531. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2018.04.028
Spadarella, G., Stanzione, A., Akinci D'Antonoli, T., Andreychenko, A., Fanni, S. C., Ugga, L., et al. (2023). Systematic review of the radiomics quality score applications: an EuSoMII Radiomics auditing group initiative. Eur. Radiol. 33, 1884–1894. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-09187-3
Tomaszewski, M. R., and Gillies, R. J. (2021). The biological meaning of radiomic features. Radiology 298, 505–516. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2021202553
Turhon, M., Li, M., Kang, H., Huang, J., Zhang, F., Zhang, Y., et al. (2023). Development and validation of a deep learning model for prediction of intracranial aneurysm rupture risk based on multi-omics factor. Eur. Radiol. 33, 6759–6770. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-09672-3
Vlak, M. H. M., Algra, A., Brandenburg, R., and Rinkel, G. J. E. (2011). Prevalence of unruptured intracranial aneurysms, with emphasis on sex, age, comorbidity, country, and time period: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 10, 626–636. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70109-0
Xu, X., Zhang, H.-L., Liu, Q.-P., Sun, S.-W., Zhang, J., Zhu, F.-P., et al. (2019). Radiomic analysis of contrast-enhanced CT predicts microvascular invasion and outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 70, 1133–1144. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.02.023
Yamanouchi, M., Arimura, H., Kodama, T., and Urakami, A. (2022). Prediction of intracranial aneurysm rupture risk using non-invasive Radiomics analysis based on follow-up magnetic resonance angiography images: a preliminary study. Appl. Sci. 12:615. doi: 10.3390/app12178615
Yang, B., Li, W., Wu, X., Zhong, W., Wang, J., Zhou, Y., et al. (2023). Comparison of ruptured intracranial aneurysms identification using different machine learning algorithms and Radiomics. Diagnostics 13:627. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13162627
Zhang, J., Can, A., Mukundan, S. Jr., Steigner, M., Castro, V. M., Dligach, D., et al. (2019). Morphological variables associated with ruptured middle cerebral artery aneurysms. Neurosurgery 85, 75–83. doi: 10.1093/neuros/nyy213
Zhang, T. S., and Zhong, W. Z. (2008). Meta-DiSc software in meta-analysis of diagnostic test[J]. J. Evid. Based Med. 8, 97–108.
Zhou, Y., Xu, J., Liu, Q., Li, C., Liu, Z., Wang, M., et al. (2018). A radiomics approach with CNN for shear-wave elastography breast tumor classification. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 65, 1935–1942. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2018.2844188
Zhu, D.-Q., Chen, Q., Xiang, Y.-L., Zhan, C.-Y., Zhang, M.-Y., Chen, C., et al. (2021). Predicting intraventricular hemorrhage growth with a machine learning-based, radiomics-clinical model. Aging 13, 12833–12848. doi: 10.18632/aging.202954
Zhu, D., Chen, Y., Zheng, K., Chen, C., Li, Q., Zhou, J., et al. (2021). Classifying ruptured middle cerebral artery aneurysms with a machine learning based, radiomics-morphological model: A multicentral study. Front. Neurosci. 15:721268. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.721268
Zhu, W., Li, W., Tian, Z., Zhang, Y., Wang, K., Zhang, Y., et al. (2020). Stability assessment of intracranial aneurysms using machine learning based on clinical and morphological features. Transl. Stroke Res. 11, 1287–1295. doi: 10.1007/s12975-020-00811-2
Keywords: radiomics, intracranial aneurysm rupture, meta-analysis, systematic review, diagnosis
Citation: Wang H, Xu H, Fan J, Liu J, Li L, Kong Z and Zhao H (2024) Predictive value of radiomics for intracranial aneurysm rupture: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Neurosci. 18:1474780. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1474780
Edited by:
Mario Sansone, University of Naples Federico II, ItalyReviewed by:
Roberta Fusco, IGEA (Italy), ItalyMarika Valentino, National Research Council (CNR), Italy
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Xu, Fan, Liu, Li, Kong and Zhao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hui Zhao, emhhb2h1aTEyMDVAb3V0bG9vay5jb20=
 Haoda Wang1
Haoda Wang1 Hui Zhao
Hui Zhao