
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
BRIEF RESEARCH REPORT article
Front. Neurol., 27 January 2025
Sec. Epilepsy
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2025.1524799
This article is part of the Research TopicPharmaco-Resistance in Epileptic ConditionsView all 5 articles
 Hui Jin Shin1
Hui Jin Shin1 Seonae Ryu1
Seonae Ryu1 NaRae Lee2
NaRae Lee2 Eunjoo Lee2
Eunjoo Lee2 Ara Ko1
Ara Ko1 Hoon-Chul Kang1
Hoon-Chul Kang1 Joon Soo Lee1
Joon Soo Lee1 Se Hee Kim1*
Se Hee Kim1* Heung Dong Kim1,3*
Heung Dong Kim1,3*Objective: To assess the anti-seizure efficacy and safety of a C10-enriched medium-chain triglyceride (MCT) ketogenic diet (KD) compared with the classic KD in pediatric patients with refractory epilepsy.
Methods: This 16-week, open-label, randomized, controlled, crossover pilot study was conducted at Severance Children’s Hospital, Seoul, South Korea, between August 2022 and September 2023. Fifteen pediatric patients with refractory epilepsy were enrolled and received classic KD and C10-enriched KD for 8 weeks each. The study compared seizure reduction rate, tolerability, and safety of the two diets.
Results: Fifteen patients were enrolled. Patients were divided into 2 groups depending on the type of KD initiated. Ten patients completed the trial. Initial treatment with the C10-enriched KD resulted in seizure reduction in all five patients, with two becoming seizure-free. Initial treatment with classic KD was effective in two out of five patients. Upon crossover, those initially on C10-enriched KD maintained their seizure reduction, while patients initially on the classic KD showed additional seizure reduction when switched to C10-enriched KD. Adverse effects included transient hypoglycemia, metabolic acidosis, hypercalciuria, and gastrointestinal symptoms, all of which were manageable.
Discussion: The C10-enriched KD demonstrated comparable efficacy and tolerability to the classic KD, offering a promising option for patients with refractory epilepsy who do not respond adequately to the classic KD alone. This study, the first to directly compare a C10-enriched KD with a classic KD, highlights the potential synergistic effects of decanoic acid.
The addition of medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) to the ketogenic diet has gained significant scientific attention due to their unique metabolic properties and potential for greater anticonvulsant efficacy compared with traditional long-chain triglycerides (LCTs). Particularly, decanoic acid (C10), which is one of the main components of MCT oil, is recognized for its capacity to optimize mitochondrial functionality, modulate astrocyte activity, increase neuronal GABA production through augmented glutamine supply, and inhibit mTORC1 activity, contributing to improved neurological function (1–3). Decanoic acid also functions as a direct anticonvulsant by attenuating excitatory postsynaptic currents, inhibiting AMPA receptor activity, and promoting GABA synthesis in astrocytes (4, 5).
Previous studies have shown that MCT ketogenic diet (KD) has comparable therapeutic efficacy to the classic KD (6–10). The ratio of MCT incorporated into the KD ranges from 30 to 60% of total energy requirement. Higher ratios of MCT have usually resulted in lower patient compliance with the KD, usually due to poor appetite or gastrointestinal side effects. To overcome these side effects, recently, attempts have been made to improve the compliance of the KD while maintain the therapeutic efficacy. Griffen et al. (11) introduced KetoCal, a novel MCT-enriched liquid nutritional feed, which consisted of a 2.5:1 fat-to-non-fat ratio, with MCT at 25.6% (C10 at 9.8%) of total fat and approximately 19.5% (C10 at 8.2%) of total energy requirement. Beyond just increasing the ratio of MCT, Schoeler et al. (12) introduced K. Vita, a thickened liquid, enriched with decanoic acid (72.1% of total fat, 15–24% of total energy requirement). However, both of these previous studies have not directly compared the therapeutic efficacy of the MCT or C10-enriched KD with the classic KD.
Our group previously demonstrated the therapeutic effects of a liquid ketogenic formula (Classic Ketonia) containing C10 at 0.4% of total fat (13). In this study, we introduce a new liquid ketogenic formula (C10-enriched Ketonia) with a significantly higher concentration of decanoic acid (33.3% of total fat, 28.7% of total energy requirement).
We conducted a pilot study, using an open-label, randomized, controlled, crossover design to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy and safety of a C10-enriched KD, incorporating C10-enriched Ketonia, developed by Namyang Dairy Products. Notably, this study provides a direct comparison between the C10-enriched KD and the classic KD, a comparison not previously undertaken. Our findings highlight the therapeutic potential of a C10-enriched ketogenic diet, supporting the need for further investigation in larger and more diverse epilepsy cohorts.
An open-label, randomized, controlled, crossover design pilot study was conducted between August 2022 and September 2023 at Severance Children’s Hospital, Seoul, South Korea. Patients were enrolled to receive either the classic KD for 8 weeks followed by the C10-enriched KD for another 8 weeks, or vice versa, totaling 16 weeks. Prior to study commencement, we obtained complete approval from the Institutional Review Board of Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine (4–2022-0758). Written consent was provided by patients and guardians.
Patients underwent initial screening for eligibility. Clinical information and other test results including epilepsy diagnoses, seizure semiology, previous electroencephalogram (EEG) and brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) were obtained. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) age between 3 months and 20 years, (2) diagnosed with refractory epilepsy, having persistent seizures even after administration of two or more ASMs, (3) history of seizures within 2 weeks before the study, (4) baseline seizure frequency of more than 2 times per month Patients with a broad spectrum of seizure frequency was included to reflect the clinical heterogeneity of refractory epilepsy. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) admitted for medical issues other than epilepsy, (2) pregnancy or planning to become pregnant, (3) history of milk allergy or lactose intolerance, (4) contraindications to KD such as diagnosed metabolic diseases, (5) diagnosis of a progressive neurological disorder. Patients with a prior history of KD were eligible for inclusion if their last KD intervention occurred at least 1 year before study enrollment.
Prior to randomization into treatment groups, patients completed a 2-week observation period to confirm eligibility for study inclusion. Following random allocation, patients commenced either the classic KD or the C10-enriched KD for 8 weeks. Thereafter, they switched to the other regimen for another 8 weeks, resulting in a trial duration of 16 weeks. For both diet regimens, if the patient could not tolerate the baseline KD with a 3:1 ratio of fat to non-fat, the ratio was adjusted to the modified Atkins diet (MAD) within 1 week (Supplementary Figure S1). Patients visited the clinic for physical examination, clinical evaluation, and biochemical tests via blood and urine samples at 4, 8, and 16 weeks of follow-up.
Ketogenic diet regimens adhered to a revised version of the Johns Hopkins Protocol, as modified by Severance Hospital (14–16). Baseline KD regimens included the classic ketogenic diet (KD) with a 3:1 fat-to-nonfat ratio (protein and carbohydrate) and the modified Atkins diet (MAD) with a 1.7:1 ratio. These regimens were supplemented with permitted foods consistent with KD, including beef, cheese, vegetable oils, and almonds. Classic Ketonia was added to classic KD, while C10-enriched Ketonia, distinguished by its high decanoic acid content, was included in the C10-enriched KD. The classic KD was administered using Classic Ketonia, while the C10-enriched KD utilized C10-enriched Ketonia, (Supplementary Table S1).
Energy targets for each patient on all KDs were calculated based on age, height, and body weight. Initial calorie prescription was 75% of the basal energy expenditure for age. Without an initial fasting period, on the first day of each new KD, patients received meals amounting to one-third of the planned daily energy requirement; on the second day, it was two-thirds of the daily energy requirement; and from the third day onwards, patients received their full energy requirements.
Both Classic and C10-enriched Ketonia were liquid ketogenic formulations produced by Namyang Dairy Products (Seoul, South Korea), with patients consuming one 180 mL pack three times daily. Classic Ketonia, previously introduced at our center, contains refined olive oil (extra olive oil, mixed d-tocopherol concentrate), soybean oil, whey protein concentrate, sodium caseinate, and PE-30A (an emulsion stabilizer) (13). The Classic Ketonia formulation provided 0.05 g/100 mL of decanoic acid. In contrast, the C10-enriched Ketonia was identical in composition except for an increased decanoic acid content of 4.0 g/100 mL (Supplementary Table S2). Overall, the classic KD included MCT at 4.2% of total fat and decanoic acid at 0.4% of total fat, while the C10-enriched KD consisted of MCT at 83.3% of total fat and decanoic acid at 33.3% of total fat (Table 1). Each patient also received sugar-free L-carnitine, elemental calcium, vitamin D2, multivitamins, and mineral supplements to prevent potential micronutrient deficiencies.
Between August 2022 and September 2023, fifteen patients were enrolled, with six patients initially assigned to the classic KD group and nine to the C10-enriched KD group. Five patients withdrew early from the trial and were subsequently excluded from the analysis. Four patients discontinued the study due to challenges in adhering to the KD protocol. One patient experienced a mild anaphylactic reaction, including brief urticaria, tachypnea, and tachycardia, following the initiation of the C10-enriched ketogenic diet on day one. These symptoms were likely related to an undisclosed sensitivity to milk and soy-based products, prompting the patient to withdraw from the study as a precaution (Figure 1).
The mean age at the start of the study was 8.9 years. Etiology of epilepsy varied among patients, including seven patients (7/15, 47%) with unknown etiology, three (20%) with structural and infection etiologies, and two (13%) with genetic etiologies. Eight patients (8/15, 53%) were diagnosed with non-lesional focal epilepsy, and six (6/15, 40%) with developmental and epileptic encephalopathy. Majority of patients (12/15, 80%) exhibited generalized seizures. Eleven (11/15, 73%) patients demonstrated focal epileptiform discharges on EEG. Four patients had abnormal brain MRI findings such as perisylvian polymicrogyria and cortical dysplasia. The enrolled patients were administered with an average number of five ASM at baseline. Four out of 15 patients (27%) had a prior history of KD, with three patients on classic KD and one patient on MAD. Previously, these patients discontinued KD due to either poor compliance or ineffectiveness of KD (Table 2).
Ten out of fifteen patients (67%) completed the 16-week trial. One patient (P4) switched from the classic KD regimen of a 3:1 ratio to the MAD during the first week due to repeated hypoglycemic events. Initial treatment with the C10-enriched KD resulted in seizure reduction in all five patients, with two (P6, P8) achieving complete seizure freedom, whereas the classic KD was effective in only two out of five patients (40%). Upon crossover, patients who started on the C10-enriched KD maintained their seizure reduction, while those switching from the classic KD to the C10-enriched KD experienced additional benefits, with 60% (three out of five) showing further seizure reduction (Figure 1). Notably, two of the three patients who did not respond well to the classic KD responded favorably to the C10-enriched KD, including one with a marked reduction in focal seizures. Only one patient (P4) who initially benefited from the classic KD did not maintain similar improvements on the C10-enriched KD, primarily due to lower adherence toward the trial’s end (Table 3). These findings indicate that the C10-enriched KD may provide an added benefit in seizure control, particularly for patients with limited response to the classic KD (Figure 2).
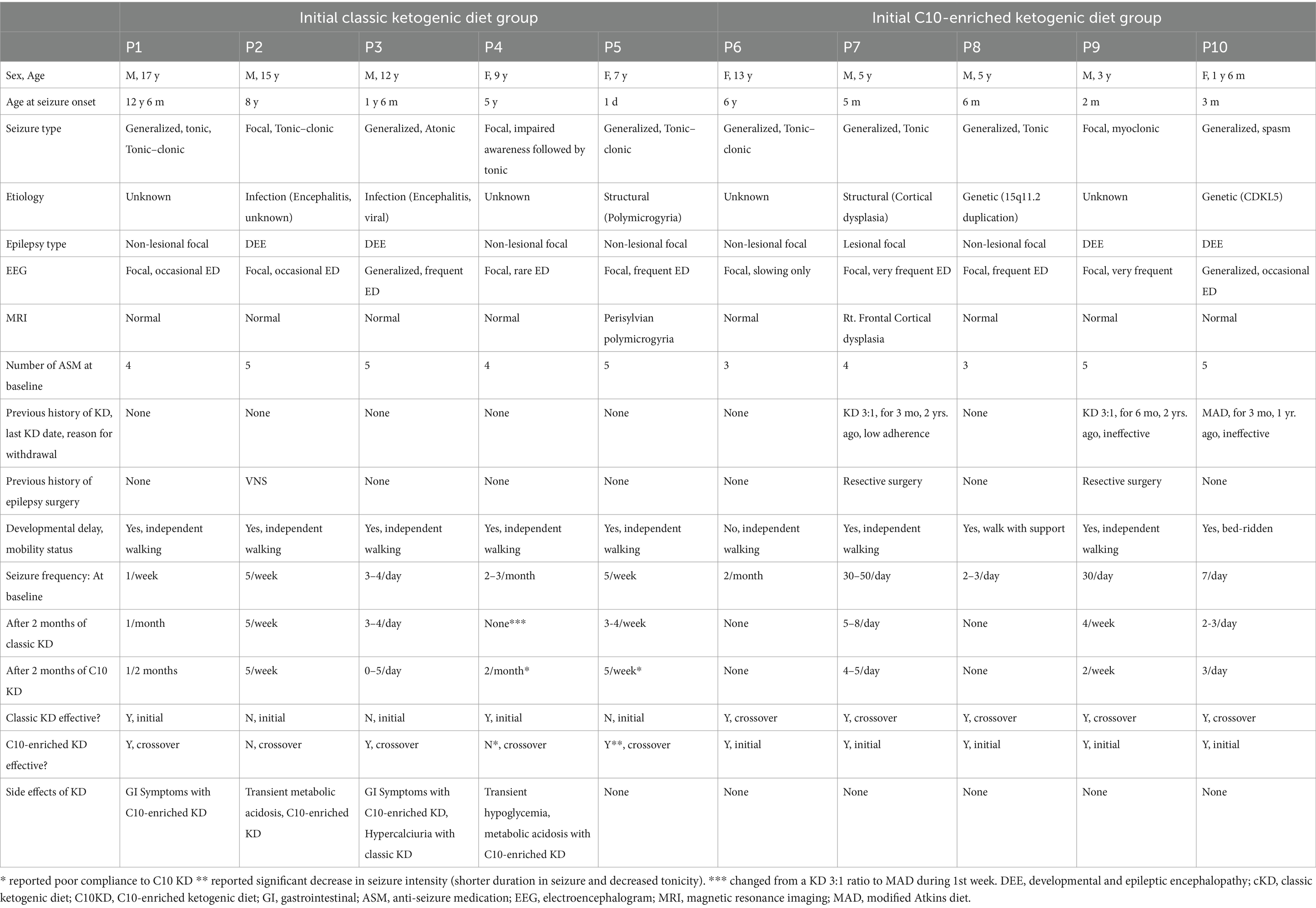
Table 3. Clinical characteristics and seizure outcomes for each patient who completed the 16-week study on the ketogenic diet.
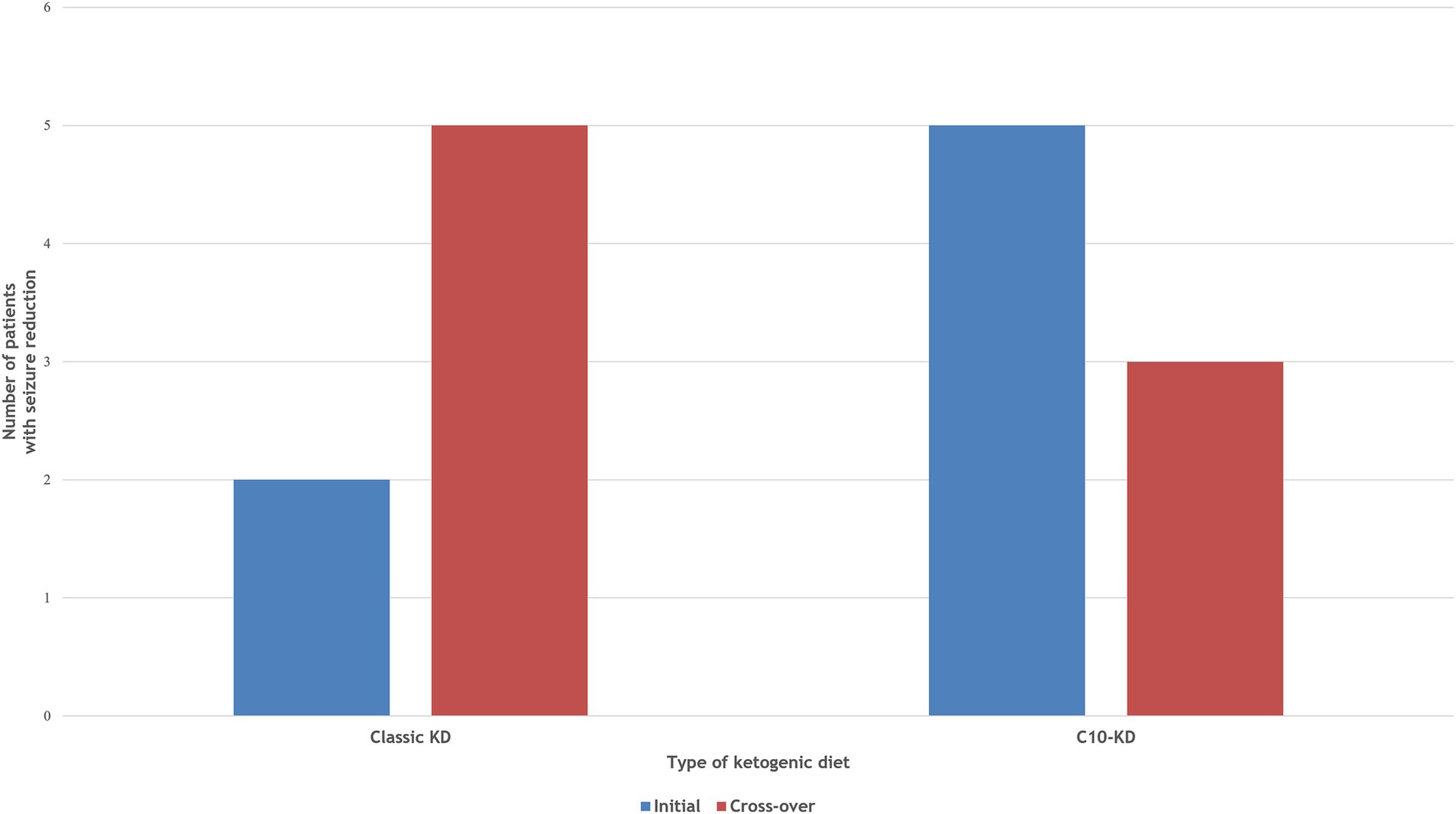
Figure 2. Comparison of therapeutic efficacy between Classic KD vs C10-enriched KD. Two patients achieved ≥50% seizure reduction on the initial classic KD, increasing to three after cross-over to C10-KD. All patients responded to the initial C10-KD, maintaining seizure reduction after cross-over to classic KD.
The average age of patients who responded well to KD (P1, P6–10) was 7.6 years, younger than the 10.9 years observed in non-responders (P2–P5). No significant changes were observed in anthropometric parameters such as body weight, height, or body mass index among patients during the trial (Supplementary Table S3). Additionally, no significant changes were observed in biochemical laboratory tests conducted throughout the study.
Adverse effects of the C10-enriched KD included transient hypoglycemia and metabolic acidosis in two patients (P2, P4), transient hypercalciuria in one patient (P3), and transient gastrointestinal symptoms in two patients (P1, P3). For hypoglycemia, intravenous dextrose injection was administered when glucose levels were < 40 in asymptomatic patients and < 50 in symptomatic patients until resolution, typically within the first 3–5 days of the diet. For metabolic acidosis, patients were administered intravenous and oral sodium bicarbonate until resolution, typically within the first 2 weeks into the diet. Patient P3 recovered from hypercalciuria without further intervention. Transient gastrointestinal symptoms were resolved within the first to second week of the diet with or without oral gastrointestinal medication such as domperidone maleate or magnesium hydroxide (Table 3).
The effect of decanoic acid within KD treatment for epilepsy remains inadequately explored in human studies. Our 16-week prospective pilot study focused exclusively on a pediatric cohort with refractory epilepsy of various etiologies, comparing the efficacy and tolerability of a C10-enriched KD to that of a classic KD. We administered C10-enriched Ketonia, which contained MCTs (83.3% of total fat) and C10 (33.3% of total fat), in conjunction with KD to explore potential synergistic effects. Our findings suggest that the efficacy and tolerability of the C10-enriched KD are comparable to those of the classic KD. The majority of enrolled patients showed a ≥ 50% reduction in seizures when treated with C10-enriched KD. The banana-flavored C10-enriched Ketonia was also well-accepted by the pediatric patients. Adverse effects were primarily mild gastrointestinal disturbances, similar to those in other KD studies.
Griffen et al. (11) conducted a two-month study introducing KetoCal, an MCT-enriched liquid feed, to patients with refractory epilepsy on a KD. KetoCal had a 2.5:1 fat-to-non-fat ratio, with MCTs constituting 25.6% of total fat and C10 at 9.8%. The study included both children and adults, with a control period where patients were on KD only, followed by an intervention period where KetoCal was introduced. Both children and adults using KetoCal exhibited improved KD adherence without gastrointestinal side effects, maintaining therapeutic efficacy comparable to the control group. Although not particularly enriched in decanoic acid, KetoCal showed potential in reducing seizures (17).
Schoeler et al. (12) conducted a 12-week study introducing K. Vita, a decanoic acid-enriched medical food, to children with Dravet syndrome or early-onset genetic epilepsy and adults with refractory epilepsy. K. Vita contained 98.5% MCTs, with C10 constituting 72.1% of total fat. Participants followed a diet excluding high-refined sugar foods and beverages. In their trial, six of 16 children (38%) and eight of 16 adults (50%) achieved a ≥ 50% reduction in seizures or paroxysmal events. K. Vita was generally well-accepted by patients. Gastrointestinal disturbances were the primary adverse effects which decreased over time (12).
Unlike the two previously mentioned studies, our pilot study directly compared the therapeutic outcomes of a standard KD with a C10-enriched KD. Our findings indicate that the C10-enriched KD provides comparable efficacy in seizure reduction, suggesting it as a promising alternative for pediatric patients with refractory epilepsy who do not achieve adequate seizure control with the classic KD alone. These results align with the observations of Schoeler et al. (12, 20) and Griffen et al. (11), underscoring the potential synergistic benefits when both dietary approaches are integrated.
While both decanoic and octanoic acid levels increase during an MCT KD, decanoic acid exhibits notable efficacy in seizure management, likely due to its brain-sparing properties via beta-oxidation (12, 18–20). Decanoic acid undergoes limited beta-oxidation in the liver, leading to its accumulation in the bloodstream and subsequent transport to the brain. Once in the brain, decanoic acid acts as a direct anticonvulsant by inhibiting excitatory postsynaptic currents and AMPA receptors and increase in GABA synthesis in astrocytes. (21–24) Meanwhile, octanoic acid undergoes more extensive beta-oxidation in the liver, resulting in lower brain levels compared to decanoic acid.
Chang et al. (25) conducted both in vitro and in vivo studies to compare the effects of various medium-chain fatty acids on seizure control. In their in vitro pentylenetetrazol model, octanoic acid had no significant effect on seizure control while decanoic acid exhibited a marked reduction in epileptiform discharges. Additionally, in vivo studies using a drug-resistant status epilepticus model demonstrated that decanoic acid was more potent in controlling seizures compared to valproic acid and showed less sedation and enhanced neuroprotection (25). Tan et al. (26) also showed that that chronic feeding of tridecanoin (a triglyceride form of decanoic acid), but not trioctanoin (a triglyceride form of octanoic acid), was reproducibly anticonvulsant in mouse seizure models. Decanoic acid increased mitochondrial function and antioxidant capacity, leading to better seizure control compared to octanoic acid (26).
Decanoic acid also acts as an agonist of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ), promoting mitochondrial biogenesis and enhancing mitochondrial complex I activity (1, 2). This improvement in mitochondrial function is shown to synergistically enhance the seizure-reducing effects of the KD in mouse models (27). Additionally, Warren et al. (3) demonstrated that decanoic acid decreases mTORC1 activity under low insulin and glucose conditions, similar to those induced by KD, thereby reducing neuronal excitability. These findings support our study, suggesting that decanoic acid may enhance the efficacy of the ketogenic diet in reducing seizure activity among patients (3, 28).
In our study, younger patients tended to be more responsive to KD than older patients. Heales et al. (29) also demonstrated that younger patients exhibit higher rates of glycolysis and beta-oxidation, alongside increased concentrations of C10, than older patients (29). Although we cannot deduce such conclusions from out study, it may be noteworthy to further investigate the effect of age in the therapeutic efficacy of decanoic acid-enriched KD across different age groups.
Limitations of this study include the following: (1) the number of patients was limited, (2) plasma levels of MCTs such as C10 and C8 were not measured to correlate with therapeutic efficacy, (3) an absence of further investigation on the cognitive/behavioral impact of the KD. To address these limitations, it is essential to conduct a more extensive clinical trial, incorporating meticulous monitoring of laboratory parameters and clinical developmental scales.
Our study demonstrated that a C10-enriched KD is comparable to the classic KD in treating refractory epilepsy. Decanoic acid shows promise for incorporation into KD regimens, offering comparable efficacy and tolerability. This approach could potentially ease the strict dietary restrictions associated with traditional KDs while maintaining therapeutic benefits for patients with refractory epilepsy. Further research is warranted to explore strategies to improve adherence to KDs and enhance their clinical outcomes.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
The studies involving humans were approved by Institutional Review Board of Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine (4-2022-0758). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin. Written informed consent was obtained from the minor(s)’ legal guardian/next of kin for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
HS: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology. SR: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. NL: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. EL: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. AK: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. H-CK: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. JL: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. SK: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. HK: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization.
The authors declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. SK and HK have received grants from Namyang Dairy Products Co. The funder was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article, or the decision to submit it for publication; SK has received a grant from Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI, RS-2023-00266971).
The authors would like to thank Namyang Dairy Products Co., Ltd for their support of this study and Editage (www.editage.co.kr) for the English language editing.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2025.1524799/full#supplementary-material
1. Hughes, SD, Kanabus, M, Anderson, G, Hargreaves, IP, Rutherford, T, O'Donnell, M, et al. The ketogenic diet component Decanoic acid increases mitochondrial citrate synthase and complex I activity in neuronal cells. J Neurochem. (2014) 129:426–33. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12646
2. Dabke, P, and Das, AM. Mechanism of action of ketogenic diet treatment: impact of Decanoic acid and Beta-Hydroxybutyrate on Sirtuins and energy metabolism in hippocampal murine neurons. Nutrients. (2020) 12:379. doi: 10.3390/nu12082379
3. Warren, EC, Dooves, S, Lugarà, E, Damstra-Oddy, J, Schaf, J, Heine, VM, et al. Decanoic acid inhibits Mtorc1 activity independent of glucose and insulin signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2020) 117:23617–25. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2008980117
4. Augustin, K, Williams, S, Cunningham, M, Devlin, AM, Friedrich, M, Jayasekera, A, et al. Perampanel and Decanoic acid show synergistic action against Ampa receptors and seizures. Epilepsia. (2018) 59:e172–8. doi: 10.1111/epi.14578
5. Wlaź, P, Socała, K, Nieoczym, D, Żarnowski, T, Żarnowska, I, Czuczwar, SJ, et al. Acute anticonvulsant effects of Capric acid in seizure tests in mice. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. (2015) 57:110–6. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2014.10.013
6. Neal, EG, Chaffe, H, Schwartz, RH, Lawson, MS, Edwards, N, Fitzsimmons, G, et al. A randomized trial of classical and medium-chain triglyceride ketogenic diets in the treatment of childhood epilepsy. Epilepsia. (2009) 50:1109–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2008.01870.x
7. Lowe, H, Keller, AE, Tanzini, E, Aimola, S, Liu, YMC, Zak, M, et al. Ketonuria and seizure control in the medium chain triglyceride and classic ketogenic diets. Can J Neurol Sci. (2022) 49:433–6. doi: 10.1017/cjn.2021.122
8. Chomtho, K, Suteerojntrakool, O, and Chomtho, S. Effectiveness of medium chain triglyceride ketogenic diet in Thai children with intractable epilepsy. J Med Assoc Thail. (2016) 99:159–65.
9. Li, H, Wang, Y, Guo, J, Zhang, P, Xu, Z, Peng, K, et al. Efficacy and safety of modified medium-chain triglyceride ketogenic diet in patients with drug-resistant epilepsy. Acta Epileptol. (2024) 6:9. doi: 10.1186/s42494-024-00150-x
10. Rita Yu, EJL, Lee, JS, Kang, H-C, and Kim, HD. A mixed-lipid diet (medium-chain and long-chain triglycerides) for better tolerability and efficiency in pediatric epilepsy patients. Annals of child. Neurology. (2022) 30:164–72. doi: 10.26815/acn.2022.00094
11. Griffen, C, Schoeler, NE, Browne, R, Cameron, T, Kirkpatrick, M, Thowfeek, S, et al. Tolerance, adherence, and acceptability of a ketogenic 2.5:1 ratio, nutritionally complete, medium chain triglyceride-containing liquid feed in children and adults with drug-resistant epilepsy following a ketogenic diet. Epilepsia Open. (2024) 9:727–38. doi: 10.1002/epi4.12910
12. Schoeler, NE, Orford, M, Vivekananda, U, Simpson, Z, Van de Bor, B, Smith, H, et al. Vita: a feasibility study of a blend of medium chain triglycerides to manage drug-resistant epilepsy. Brain Commun. (2021) 3:fcab160. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcab160
13. Lee, YJ, Kang, H-C, Kim, DW, Lee, JS, Eun, B-L, Eun, SH, et al. Usefulness of liquid ketogenic Milk for intractable childhood epilepsy. e-SPEN, Eur J Clin Nutr Metab. (2010) 5:e203–7. doi: 10.1016/j.eclnm.2010.08.001
14. Freeman, JM, Kelly, MT, and Freeman, JB. The epilepsy diet treatment: An introduction to the ketogenic diet. New York, NY: Elsevier (1996).
15. Chul Kang, H, Joo Kim, Y, Wook Kim, D, and Dong, KH. Efficacy and safety of the ketogenic diet for intractable childhood epilepsy: Korean multicentric experience. Epilepsia. (2005) 46:272–9. doi: 10.1111/j.0013-9580.2005.48504.x
16. Kim, JT, Kang, HC, Song, JE, Lee, MJ, Lee, YJ, Lee, EJ, et al. Catch-up growth after long-term implementation and weaning from ketogenic diet in pediatric epileptic patients. Clin Nutr. (2013) 32:98–103. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2012.05.019
17. Ye, F, Li, X-J, Jiang, W-L, Sun, H-B, and Liu, J. Efficacy of and patient compliance with a ketogenic diet in adults with intractable epilepsy: a meta-analysis. J Clin Neurol. (2015) 11:26–31. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2015.11.1.26
18. Haidukewych, D, Forsythe, WI, and Sills, M. Monitoring Octanoic and Decanoic acids in plasma from children with intractable epilepsy treated with medium-chain triglyceride diet. Clin Chem. (1982) 28:642–5. doi: 10.1093/clinchem/28.4.642
19. Sills, MA, Forsythe, WI, and Haidukewych, D. Role of Octanoic and Decanoic acids in the control of seizures. Arch Dis Child. (1986) 61:1173–7. doi: 10.1136/adc.61.12.1173
20. Schoeler, NE, Marston, L, Lyons, L, Halsall, S, Jain, R, Titre-Johnson, S, et al. Classic ketogenic diet versus further Antiseizure medicine in infants with drug-resistant epilepsy (Kiwe): a Uk, multicentre, open-label. Randomised Clin Trial Lancet Neurol. (2023) 22:1113–24. doi: 10.1016/s1474-4422(23)00370-8
21. Khabbush, A, Orford, M, Tsai, YC, Rutherford, T, O'Donnell, M, Eaton, S, et al. Neuronal Decanoic acid oxidation is markedly lower than that of Octanoic acid: a mechanistic insight into the medium-chain triglyceride ketogenic diet. Epilepsia. (2017) 58:1423–9. doi: 10.1111/epi.13833
22. Chang, P, Augustin, K, Boddum, K, Williams, S, Sun, M, Terschak, JA, et al. Seizure control by Decanoic acid through direct Ampa receptor inhibition. Brain. (2016) 139:431–43. doi: 10.1093/brain/awv325
23. Lee, N, Sa, M, Hong, YR, Lee, CJ, and Koo, J. Fatty acid increases camp-dependent lactate and Mao-B-dependent Gaba production in mouse astrocytes by activating a G (Αs) protein-coupled receptor. Exp Neurobiol. (2018) 27:365–76. doi: 10.5607/en.2018.27.5.365
24. Andersen, JV, Westi, EW, Jakobsen, E, Urruticoechea, N, Borges, K, and Aldana, BI. Astrocyte metabolism of the medium-chain fatty acids Octanoic acid and Decanoic acid promotes Gaba synthesis in neurons via elevated glutamine supply. Mol Brain. (2021) 14:132. doi: 10.1186/s13041-021-00842-2
25. Chang, P, Terbach, N, Plant, N, Chen, PE, Walker, MC, and Williams, RS. Seizure control by ketogenic diet-associated medium chain fatty acids. Neuropharmacology. (2013) 69:105–14. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.11.004
26. Tan, KN, Carrasco-Pozo, C, McDonald, TS, Puchowicz, M, and Borges, K. Tridecanoin is anticonvulsant, antioxidant, and improves mitochondrial function. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. (2017) 37:2035–48. doi: 10.1177/0271678x16659498
27. Simeone, TA, Matthews, SA, and Simeone, KA. Synergistic protection against acute Flurothyl-induced seizures by adjuvant treatment of the ketogenic diet with the type 2 diabetes drug pioglitazone. Epilepsia. (2017) 58:1440–50. doi: 10.1111/epi.13809
28. Liu, H, Huang, J, Liu, H, Li, F, Peng, Q, and Liu, C. Effects of ketogenic diet containing medium-chain fatty acids on serum inflammatory factor and Mtor signaling pathway in rats. Chem Biol Technol Agric. (2020) 7:27. doi: 10.1186/s40538-020-00194-4
Keywords: Decanoic acid, ketogenic diet, epilepsy, refractory, seizure
Citation: Shin HJ, Ryu S, Lee N, Lee E, Ko A, Kang H-C, Lee JS, Kim SH and Kim HD (2025) Decanoic acid-enriched ketogenic diet in refractory epilepsy. Front. Neurol. 16:1524799. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1524799
Received: 08 November 2024; Accepted: 10 January 2025;
Published: 27 January 2025.
Edited by:
Joyce Wu, Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago, United StatesReviewed by:
Cameron S. Metcalf, The University of Utah, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Shin, Ryu, Lee, Lee, Ko, Kang, Lee, Kim and Kim. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Heung Dong Kim, aGRraW1tZEB5dWhzLmFj; Se Hee Kim, c2VoZWVraW1AeXVocy5hYw==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.