
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
Front. Neurol. , 12 March 2025
Sec. Pediatric Neurology
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2025.1502023
Objective: The aim of this study was to comprehensively evaluate the efficacy of acupuncture combined with language training in the treatment of aphasia in children with cerebral palsy (CP).
Methods: We searched eight electronic databases from their inceptions to July 1, 2024 for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of acupuncture for aphasia in children with CP. The evaluation of methodological quality for RCTs incorporated in this study adhered to the guidelines provided by the Cochrane risk-of-bias tool (ROB2). The Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation Approach (GRADE) was used to evaluate the certainty of evidence of each outcome. The heterogeneity of the included literature was tested using Review Manager 5.4 software, while publication bias was estimated using funnel plots and Egger’s tests by STATA15.1. A trial sequential analysis (TSA) was performed to test the robustness of the conclusiveness of our results.
Results: In this study, we encompassed a total of 56 randomised controlled trials encompassing 4,683 participants. The majority of these trials were characterized by either a high or uncertain risk of bias, predominantly due to the omission of blinding within their experimental setups. Meta-analysis showed that acupuncture combined with language training was significantly better than language training alone in improving the clinical efficiency (RR: 1.25; 95% CI: 1.21, 1.29; p < 0.00001). A subgroup analysis of the different types of acupuncture revealed that acupuncture, electroacupuncture, scalp acupuncture, and auricular point seed-pressing all showed a significant improvement in aphasia in children with CP. Acupuncture combined with language training could significantly improve the adaptive behaviour (MD: 7.46; 95% CI: 3.67, 11.26; p = 0.0001), verbal behaviour (MD: 7.79; 95% CI: 5.66, 9.92; p < 0.00001), fine motor behaviour (MD: 4.66; 95% CI: 1.28, 8.03; p = 0.007), and personal social behaviour (MD: 6.47; 95% CI: 2.38, 10.55; p = 0.002); it was also significantly more effective in improving the language comprehension developmental quotient (SMD: 2.02; 95% CI: 1.54, 2.50; p < 0.00001), the expressive language development quotient (SMD: 2.40; 95% CI: 1.76, 3.03; p < 0.00001), assessment of dysarthria (MD: 0.40; 95% CI: 0.11, 0.69; p = 0.007), and oral motor function (SMD: 2.63; 95% CI: 1.36, 3.90; p < 0.0001).
Conclusion: Acupuncture combined with language training could be an effective treatment for aphasia in children with CP. Due to low or very low certainty of evidence and high heterogeneity, more rigorous RCTs are needed to verify the effect of acupuncture in the management of CP.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/CRD42024501328, identifier CRD42024501328.
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a permanent central nervous system disorder that affects motor control and postural regulation in children. According to statistics, there are approximately 2–3 cases of CP per 1,000 live births worldwide (1). The prevalence rate of CP in China is reported to be 0.246 percent and with this number increasing by 30,000 to 80,000 per year (2). CP mainly manifests as motor dysfunction. In addition, CP may be accompanied by a variety of other comorbidities, of which aphasia is one of the common ones, with an incidence of approximately 80% (3). Aphasia not only affects the patient’s ability to communicate, but may also have a profound impact on their psychological development, social interactions, and overall quality of life. However, in clinical practice, motor dysfunction is often the focus of treatment, thus missing the optimal time for language and speech function treatment and intervention (4).
At present, no targeted medication exists for the treatment of language disorder manifestations in CP cases; language training is one of the main methods to treat language disorders in children with CP, using scientific language training to stimulate the language function of the child’s brain and achieve the role of promoting language development. However, the use of language rehabilitation training is relatively simple, with relatively poor efficacy and limitations in improving the disease prognosis (5).
Acupuncture, as an important part of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), which has been practiced for over two thousand years to modulate body physiology via stimulation at specific body regions (acupoints) (6, 7). It has advantages such as simple operation, non-invasive treatment, and fewer adverse reactions, which can fully exert a therapeutic effect and have a positive effect on shortening the course of treatment (8). Acupuncture stimulates specific areas of the brain cortex, promotes synaptic regeneration, enhances brain compensatory function, helps alleviate brain cell damage, and protects neurons (9, 10). Recent studies have shown that acupuncture can improve the speech expression in children with CP by modulating the nerves (11, 12). However, there is no evidence-based medical evidence to prove whether acupuncture has an ameliorative effect on aphasia in children with CP. Therefore, this paper systematically reviews the research data in recent years, aiming to study the effectiveness of acupuncture in improving aphasia in children with CP more objectively through meta-analysis, with a view to providing evidence for clinical medical research.
Adhering to the PRISMA extension guidelines (13), this research was executed. Our systematic review methodology was registered in advance with PROSPERO under the identifier CRD42024501328, discoverable at https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/.
Our search encompassed a range of pertinent databases, including PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library, Web of Science, along with Chinese databases including the China Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wan-Fang Database, China Science Journal Database (VIP), and SinoMed, spanning from the inception of these databases up to the date of July 1, 2024. The main search terms were “Acupuncture,” “Electroacupuncture,” “Cerebral palsy,” “Aphasia,” “Speech Disorder,” “Dysarthria,” “Language Development Disorder,” and “randomized controlled trial.” The comprehensive search methodology is detailed in the Supplementary File 1.
Eligible for inclusion in our study were RCTs that investigated the acupuncture combined with language training for aphasia among children diagnosed with CP. The term “random” in these trials pertains to the allocation process, which may or may not have incorporated blinding.
The study involved children diagnosed with CP as well as those who fulfilled the criteria for aphasia. The selection of participants was unrestricted by gender or nationality.
In the control arm of the study, participants were exclusively provided with language training. Conversely, the treatment arm included an integrated approach, offering both acupuncture and language training to the patients. Acupuncture therapy included body acupuncture, electroacupuncture, warming acupuncture, catgut implantation at acupoint, auricular pressure beans, and acupoint injection. The study imposed no limitations regarding the precise timing of interventions, selection of acupuncture points, or duration of treatment protocols.
The primary outcomes include clinical effectiveness rate and development quotient (adaptive behaviour, gross motor behaviour, verbal behaviour, fine motor behaviour, and personal social behaviour), while the secondary outcomes include assessment of dysarthria, oral motor function, expressive language development quotient, and language comprehension developmental quotient. According to the evaluation standard of the China Code for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Rehabilitation Medicine from the Department of Medical Administration of the People’s Republic of China: (1) Significant effects: language development delay, language development and understanding ability to improve the two stages, and language expression ability improvement; (2) Effective: language development delay, language development understanding ability to improve a stage, and language expression ability has improved; (3) Invalid: the improvement in language delay was not obvious. Clinical effectiveness rate = (basic cure + significant + effective)/100% of total cases. The development of children was evaluated using the Gesell development scale, which includes the following five aspects: adaptive behaviour, gross motor behaviour, verbal behaviour, fine motor behaviour, and personal social behaviour. The lower the score from this scale, the less ideal the development status is.
The criteria for exclusion were delineated as follows: (1) for repetitive articles, keep only the most recent or comprehensive ones; (2) meta-analyses, retrospective investigations, case reports, animal experiments, non-RCTs, non-English and Chinese papers were excluded; (3) interventions that do not meet the requirements, as well as diseases that do not match those in this study, are excluded; (4) articles that could not be obtained were excluded; (5) articles with non-compliant research subjects were excluded.
The literature was independently evaluated by two researchers against the established inclusion and exclusion criteria, employing the PICOS to guide the selection process.
For the purpose of pinpointing studies compliant with the inclusion criteria, all included studies were uploaded into Endnote 20. Two reviewers, each with specialized training (SZL and YJL), scrutinized each study individually, and removed duplicates studies, and studies that failed to satisfy the inclusion criteria. Data extraction encompassed pertinent details: authorship, year of publication, age, gender, the size of the study sample, the duration of the treatment regimen, the methodology of intervention, and outcome indicators. Upon completion of their individual reviews, the two reviewers performed a cross-verification to confirm the data’s veracity. In instances where discrepancies arose between the reviewers’ assessments or data extractions, a third, neutral assessor (JC) was consulted to reach a consensus.
The evaluation of the methodological quality within the selected RCTs was guided by the Cochrane risk-of-bias tool (ROB2). This assessment was independently carried out by two reviewers (YJL and Y-JL), using Covidence to ensure blinding (14). For any risk domains classified as serious, critical, or lacking information, the reviewers provided detailed justifications. When essential details were not readily available in the reports under review, the reviewers sought and verified information from study protocols, clinical trial registries, and any supplementary documents provided. To resolve any inconsistencies in the assessment, the reviewers engaged in discussions and strived to reach a mutual agreement on the evaluation of each risk domain within the ROB2 tool. In cases where a consensus was not achieved, a third reviewer (JC), was invited to participate in the assessment, ensuring a unified decision was made. ROB2 was conducted at the outcome level.
Furthermore, the certainty of evidence derived from the synthesis of the primary outcomes was appraised using the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) framework (15). For each primary outcome within the network estimate, an evaluation was conducted considering several criteria, including risk of bias, indirectness, inconsistency, imprecision, and publication bias. In accordance with the GRADE framework, the level of evidence was adjusted; it was lowered one tier for issues deemed “serious” and two tiers for those considered “very serious.” Ultimately, an integrated evaluation of the evidence’s certainty was formulated, with each comparison receiving an overall qualitative rating. This rating was based on a four-tiered system of evidence quality: high, moderate, low, and very low.
Data analysis was performed utilizing the Cochrane Collaboration Meta-analysis software (Review Manager 5.4). For dichotomous data, the relative risk (RR) along with its 95% confidence interval (CI) was calculated, whereas for continuous data, the weighted mean difference (WMD) or standard mean difference (SMD) and their corresponding 95% CI were reported. Statistical significance was set at a p-value of less than 0.05. A heterogeneity test was carried out on the included literature. If p ≤ 0.1 and I2 ≥ 50%, it indicated the existence of heterogeneity; the random effect model was used for heterogeneity analysis. Otherwise, a fixed-effects model was used. Given the potential impact of acupuncture type on treatment efficacy, a subgroup analysis was conducted to examine the effectiveness of different acupuncture modalities in treating aphasia in children with CP. Additionally, considering the possible influence of treatment duration, subgroup analyses were performed to compare the efficacy of treatments lasting up to 3 months versus those exceeding this period. A sensitivity analysis was conducted to evaluate the robustness of the findings by sequentially excluding each study and scrutinizing the impact on both the aggregated effectiveness of the remaining studies and the overall efficacy. Furthermore, Egger’s test was applied to determine the presence of publication bias.
To control the risks associated with type I and type II errors, our study implemented a trial sequential analysis (TSA) to assess the clinical efficacy of acupuncture in conjunction with language training for aphasia in children with CP. Utilizing the TSA software, version 0.9.5.10 beta, we adjusted the confidence intervals (CIs) in response to the sparse data and the issue of repeated testing within the cumulative meta-analysis. A conclusive determination is attainable if the cumulative Z-curve surpasses the TSA boundary or intersects with the Required Information Size line, indicating that additional research may not be warranted (16). TSA was performed at an overall 10% risk level of a type I error and with 80% power.
We searched a total of 1,775 articles from eight electronic databases. Following the removal of duplicate studies, 1,092 relevant studies were identified. Upon reviewing the titles and abstracts, we narrowed down the selection to 108 studies that appeared to be pertinent to our investigation. Subsequently, two reviewers, working independently, conducted a thorough examination of the full texts of the studies, who conducted an additional eligibility assessment according to the predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Ultimately, 56 studies were deemed suitable for inclusion in the final meta-analysis, with all trials being published in Chinese. The comprehensive process of literature screening is depicted in Figure 1.
This study encompassed 56 articles, each a randomized controlled trial originating from a single center within China. The English titles, authors and abstracts of all the articles are included in Supplementary File 2. Collectively, these trials enrolled a total of 4,683 patients, with 2,371 allocated to the experimental group and 2,312 to the control group (17–72), and the length of the treatment course ranged from 1 to 9 months. Incomplete baseline feature details were identified in several studies (17, 19, 25, 42, 48, 68), but no significant differences were observed between groups among the characteristics (p > 0.05). Of the 56 studies, 39 used body acupuncture (17–19, 21, 25, 26, 28–30, 33–38, 40–48, 50–52, 55, 58–62, 65–68, 71, 72), 13 used scalp acupuncture (20, 22–24, 27, 32, 39, 49, 53, 54, 56, 69, 70), one used laser acupuncture (31), one used auricular point seed-pressing (59), and three used electroacupuncture (25, 57, 64) [among them, Zou et al. (25) had two experimental groups-one used acupuncture and the other used electroacupuncture]. In addition, only one study (25) that reported on the safety of acupuncture. A summary of the fundamental characteristics of the included studies can be found in Table 1.
We utilised the revised Cochrane risk-of-bias tool (ROB 2.0) to evaluate the risk of bias and the quality of the included studies. Four studies’ outcomes were rated as low risk (19, 30, 41, 61), two studies’ outcomes were rated as high risk (18, 55), and the results of the other studies were rated as having some concerns (Figures 2, 3). All trials mentioned randomisation; Nonetheless, specifics regarding the randomization were reported in merely four RCTs (19, 30, 41, 61), which consequently earned a low risk designation. Notably, among these, two employed a random number table for their randomization process (30, 41), while the other pair adopted a single-blind, randomized controlled methodology (19, 61). In terms of measuring the outcome, there are two studies (18, 55) in which the evaluators were aware of the intervention received by the study participants; as such, the assessment of the outcome had been influenced by this knowledge and these trials were, therefore, rated as high risk. In addition, there are six studies (19, 30, 41, 56, 61, 67) in which the evaluators were unaware of the intervention that the study participants received, these trials were rated as low risk.
The overall certainty of the evidence was rated for meta-analytic outcomes as being moderate to very low. The principal factors that led to the reduction in the evidence rating included concerns related to risk of bias, inconsistency, and imprecision. However, the assessment of indirectness did not undergo demotion, given that this systematic review adhered to stringent parameters for the selection of population, intervention, comparison, and outcome criteria. Evidence of very low certainty indicated that acupuncture combined with language training had no effect on improving either gross or fine motor behaviour. Figure 4 presents a summary of the results, with footnotes explaining the downgrade judgments (decreasing the rating of the certainty of the evidence).
A total of 51 studies (17–42, 45–53, 55–59, 61–66, 68–72) reported the clinical effectiveness rate [among them, Zou et al. (25) had two experimental groups-one used acupuncture and the other used electroacupuncture] and there was no significant heterogeneity between them (p = 0.63, I2 = 0%). Utilizing the fixed-effects model, a significant disparity was observed in the clinical effectiveness rate between the integration of acupuncture with language training and language training alone (RR: 1.25; 95% CI: 1.21, 1.29; p < 0.00001). This finding underscores the potential of acupuncture, when combined with language training, to improve the clinical efficacy of treating aphasia in patients with CP, as shown in Figure 5.
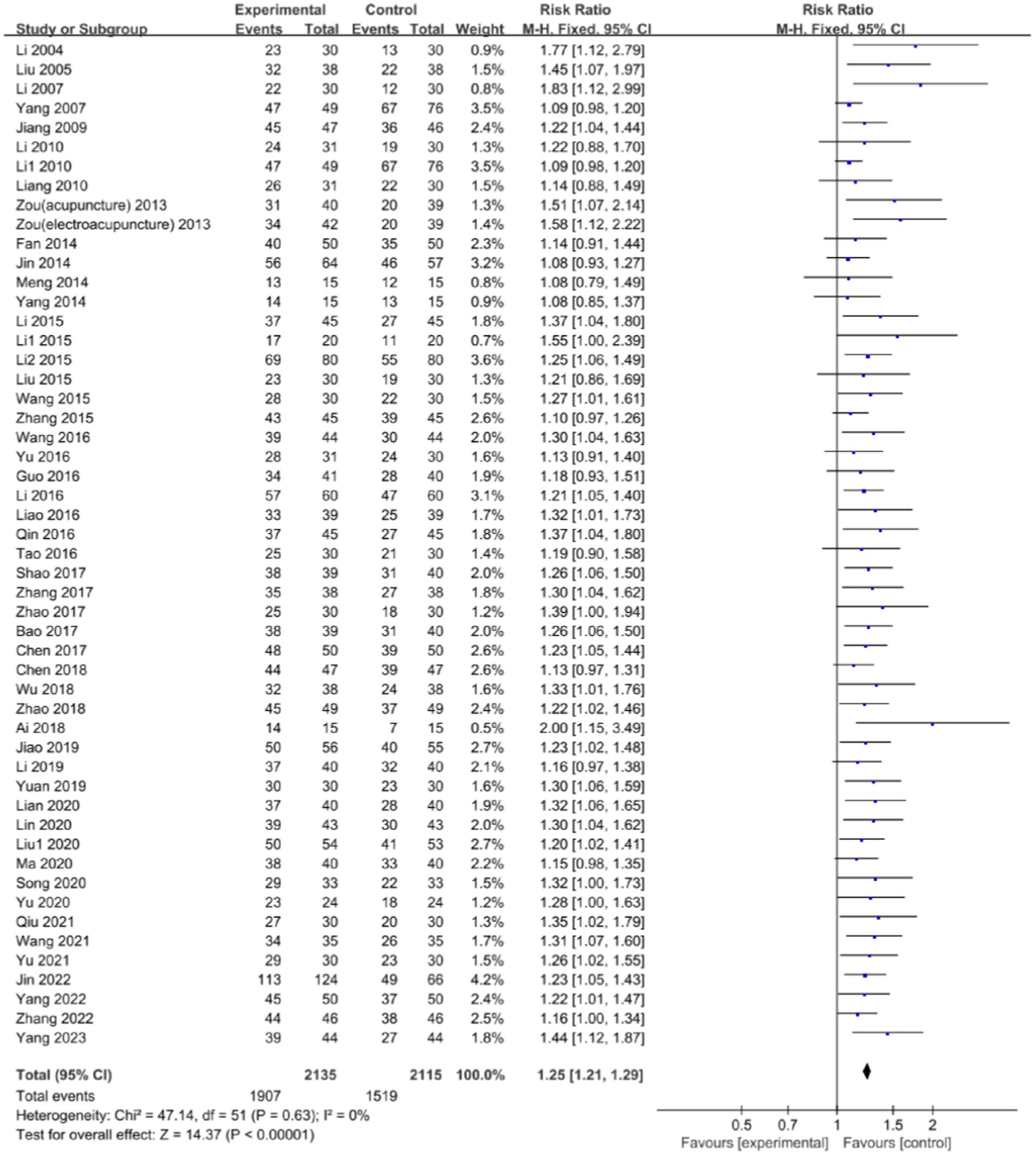
Figure 5. Forest plot of the clinical effectiveness rate comparison between acupuncture and control group.
The GESELL development scale consists of five main dimensions, which are adaptive behaviour, gross motor behaviour, verbal behaviour, fine motor behaviour, and personal social behaviour.
Adaptive behaviour was reported in nine studies (38, 40, 55, 57, 59, 63, 65, 67, 70), and the statistical data revealed that acupuncture combined with language training significantly influenced adaptive behaviour in aphasic children with CP (MD: 7.46; 95% CI: 3.67, 11.26; p = 0.0001; heterogeneity: I2 = 88%; p < 0.00001; Figure 6), which indicated that this treatment method significantly improves adaptive behaviour compared to treatment with language training alone. Three studies (55, 59, 67) reported results showing no significant difference in gross motor behaviour between treatment using acupuncture combined with language training and treatment using language training alone (MD: 4.86; 95% CI: −0.62, 10.34; p = 0.08; heterogeneity: I2 = 88%; p = 0.0002; Figure 6).
Verbal behaviour was reported in 15 studies (18, 25, 31, 40, 44, 52, 55, 57–59, 63, 65, 67, 70, 71) [among them, Zou et al. (25) had two experimental groups]; totally 132 CP children were randomly assigned to the speech training group (Group A, 44 cases), the electroacupuncture combined speech training group (Group B, 44 cases), and the acupuncture combined speech training group (Group C, 44 cases). Patients in Group A received one to one training including game therapy, therapy of communication attitudes, and so on. Those in the other two groups were needled at Baihui (GV20), Sishencong (EX-HN1), the first language zone, the second language zone, and the third language zone. Those in Group B were treated with electric needling and then speech training. Those in Group C were treated with language training, while needling with needle maintaining for 40 min. All patients were treated once daily, 5 times per week, 20 times as one course of treatment, six courses in total, and the results indicated that acupuncture combined with language training produced a notably positive impact on verbal behaviour in aphasic children with CP (MD: 7.79; 95% CI: 5.66, 9.92; p < 0.00001; heterogeneity: I2 = 86%; p < 0.00001; Figure 6), which indicated that this treatment method significantly improves verbal behaviour compared to treatment with language training alone. Statistics from the three studies (55, 59, 67) showed that acupuncture combined with language training exerted a significant influence on the fine motor behaviour in aphasic children with CP (MD: 4.66; 95% CI: 1.28, 8.03; p = 0.007; heterogeneity: I2 = 75%; p = 0.02; Figure 6), which indicated that this method of treatment could significantly improve this type of behaviour compared to treatment with language training alone. Seven studies (40, 55, 59, 63, 65, 67, 70) reported statistical data showing that acupuncture combined with language training significantly impacted the personal social behaviour in the treatment of aphasia in children with CP (MD: 6.47; 95% CI: 2.38, 10.55; p = 0.002; heterogeneity: I2 = 94%; p < 0.00001; Figure 6), which indicated that this method of treatment could significantly improve personal social behaviour in aphasic children with CP compared to treatment using language training alone.
The language comprehension developmental quotient was reported in eight studies (24, 33, 43, 51, 54, 55, 62, 70) and the statistical analysis revealed that the integration of acupuncture with language training yielded a significant impact on this quotient of aphasic children with CP (SMD: 2.02; 95% CI: 1.54, 2.50; p < 0.00001; heterogeneity: I2 = 85%; p < 0.00001; Figure 7A), which indicated that this method of treatment can significantly improve the language comprehension developmental quotient compared to treatment using language training alone.
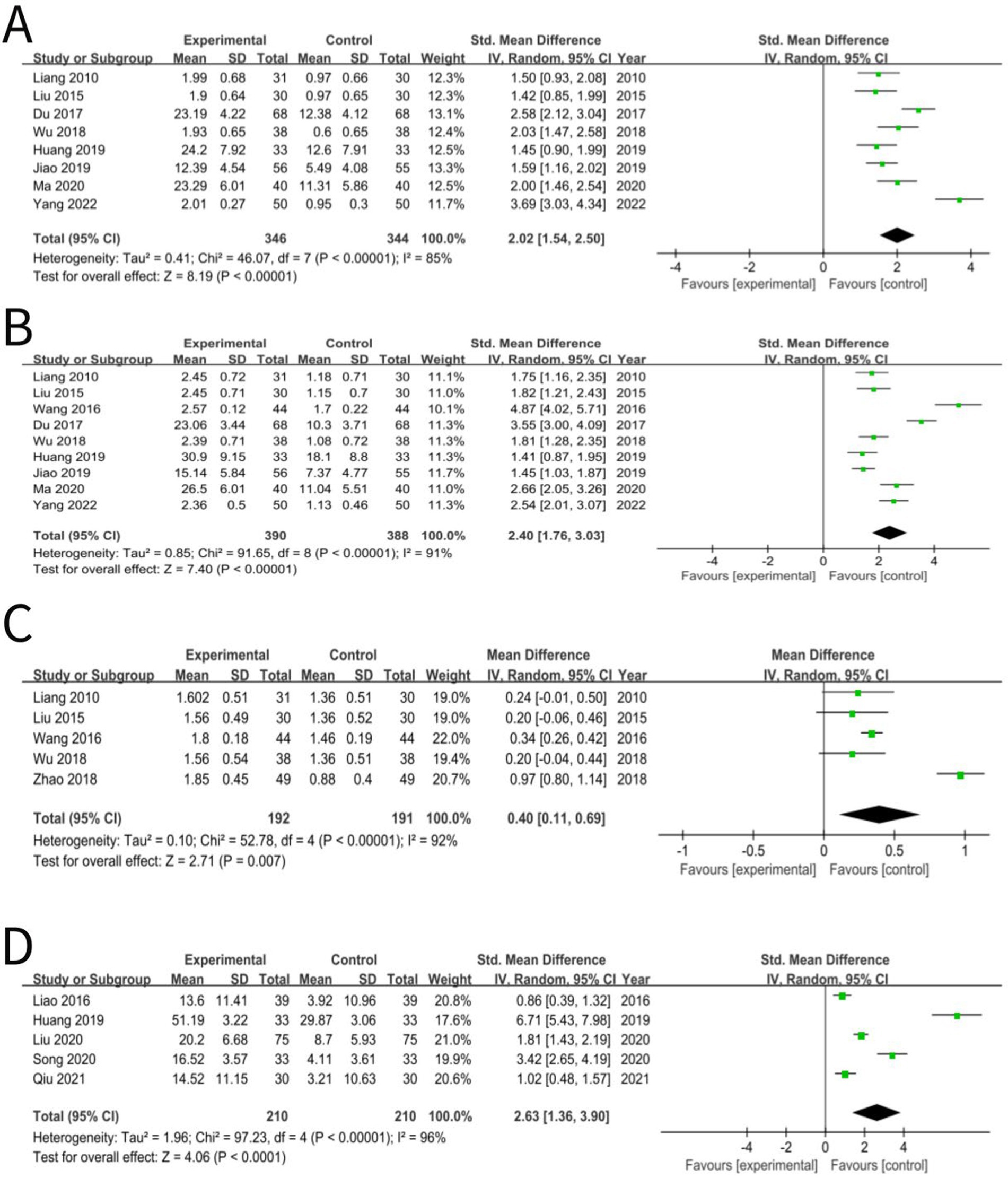
Figure 7. (A) Forest plot of language comprehension developmental quotient comparison between acupuncture and control group. (B) Forest plot of expressive language development quotient comparison between acupuncture and control group. (C) Forest plot of assessment of dysarthria comparison between acupuncture and control group. (D) Forest plot of oral motor function comparison between acupuncture and control group.
Nine studies (24, 33, 36, 43, 51, 54, 55, 62, 70) reported the expressive language development quotient and the analysis of statistical data indicated that the combination of acupuncture and language training significantly influenced this quotient among children with CP (SMD: 2.40; 95% CI: 1.76, 3.03; p < 0.00001; heterogeneity: I2 = 91%; p < 0.00001; Figure 7B), which indicated that this treatment method could improve the expressive language development quotient more so than treatment with language training alone.
An assessment of dysarthria was reported in five studies (24, 33, 36, 51, 52) and the results showed that acupuncture combined with language training exerted a pronounced beneficial effect on dysarthria in aphasic children with CP (MD: 0.40; 95% CI: 0.11, 0.69; p = 0.007; heterogeneity: I2 = 92%; p < 0.00001; Figure 7C), which indicated that this method of treatment could improve dysarthria more so than treatment using language training alone.
Five studies (40, 54, 60, 63, 65) reported oral motor function and the statistical outcomes demonstrated a notable improvement in this characteristic of children with CP who suffered from aphasia, attributed to the concurrent application of acupuncture and language training (SMD: 2.63; 95% CI: 1.36, 3.90; p < 0.0001; heterogeneity: I2 = 96%; p < 0.00001; Figure 7D), which indicated that this treatment method could improve the oral motor function more so than using treatment with language training alone.
Figure 8 shows a subgroup analysis of the effect of different types of acupuncture on the efficacy of aphasia treatment in children with CP. Among them, 35 studies (17–19, 21, 25, 26, 28–30, 33–38, 40–42, 45–48, 50–52, 55, 58, 61–63, 65, 66, 68, 71, 72) used acupuncture as the intervention measure, three studies (25, 57, 64) used electroacupuncture, and 12 studies (20, 22–24, 27, 32, 39, 49, 53, 56, 69, 70) used scalp acupuncture. In addition, the intervention measures of auricular point seed-pressing (59) and laser acupuncture (31) were each discussed in one study. The results showed that acupuncture (RR: 1.27; 95% CI: 1.22, 1.32; p < 0.00001; I2 = 0%), electroacupuncture (RR: 1.36; 95% CI: 1.16, 1.60; p = 0.0001; I2 = 0%), scalp acupuncture (RR = 1.19; 95% CI: 1.13, 1.25; p < 0.00001; I2 = 3%), and auricular point seed-pressing (RR: 1.30; 95% CI: 1.04, 1.62; p = 0.02) significantly improved aphasia in children with CP more so than when compared to treatment without acupuncture. However, the effect of laser acupuncture on the treatment of aphasia in children with CP is limited and there was no significant difference compared with treatment using language training alone (RR: 1.55; 95% CI: 1.00, 2.39; p = 0.05).
Figure 9 shows a subgroup analysis of the effect of different treatment courses on the efficacy of aphasia treatment in children with CP. Among them, 35 studies (17–24, 28–31, 33, 36–39, 41, 46, 47, 49, 51, 52, 55–57, 59, 61–64, 66, 70–72) had a course of treatment of ≤3 months, and 15 studies (25–27, 32, 34, 35, 40, 42, 45, 48, 50, 53, 58, 65, 69) had a course of treatment of >3 months. The results showed significant improvement in aphasia in patients with acupuncture sessions ≤3 months (RR: 1.25; 95% CI: 1.20, 1.30; p < 0.00001; I2 = 0%) and in patients with sessions >3 months (RR: 1.24; 95% CI: 1.17, 1.31; p < 0.00001; I2 = 0%) compared with patients who did not receive acupuncture.
Sensitivity analysis was conducted by excluding each trial individually from the present study; the corresponding results were relatively robust (Figure 10).
Egger’s test was employed to construct a funnel plot aimed at assessing the presence of publication bias, utilizing the metric of clinical effectiveness rate. Figure 11A illustrates that the dispersion of points within the funnel plot exhibited a perceptible asymmetry encircling the axis of symmetry, suggesting publication bias among these studies (p < 0.01; 95% CI: 1.53, 2.46). Using the trim and fill method for correction, after adding 19 articles (p < 0.01; 95% CI: 1.143, 1.207), it was consistent with the pre-correction conclusions, indicating that publication bias had no effect on the conclusion of this study; this is shown in Figure 11B.
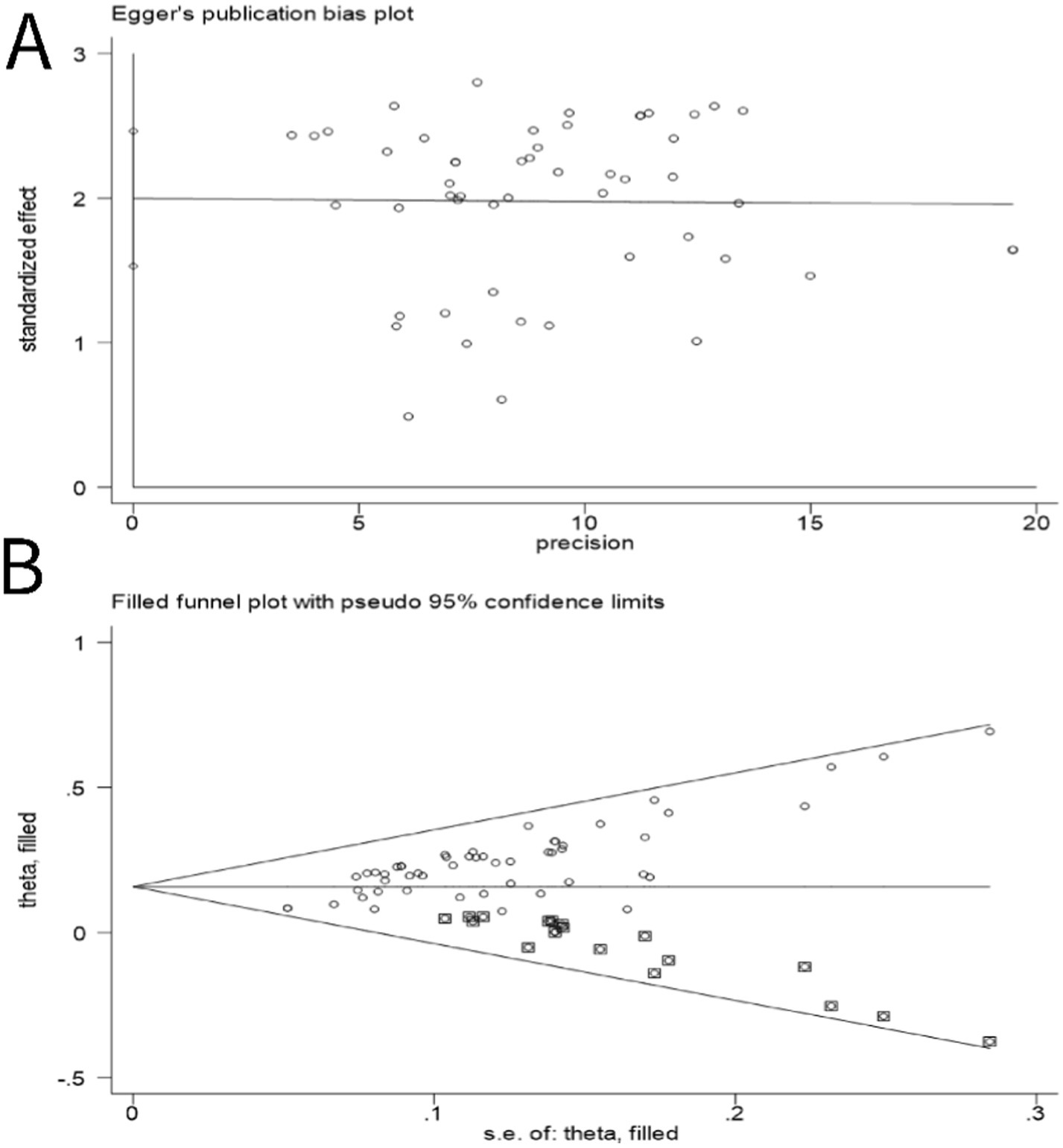
Figure 11. Funnel plots of outcomes: the clinical effectiveness rate. (A) Before correction. (B) After correction.
In all, 51 RCTs (17–42, 45–53, 55–59, 61–66, 68–72) provided data on the overall clinical effectiveness rate, which was subjected to sequential analysis. This analysis was conducted with a type I error of 5% and a statistical power of 80%. The cumulative sample size was designated as the information axis, with the sample size also serving as the required information value (RIS). As depicted in Figure 12, the Z-curve crosses both the conventional and the TSA boundary value, underscoring the meta-analysis’s statistical significance. Additionally, the Z-curve also crosses the RIS boundary value, indicating that the sample size has reached the expected amount and no further RCT validation will be needed in the future.
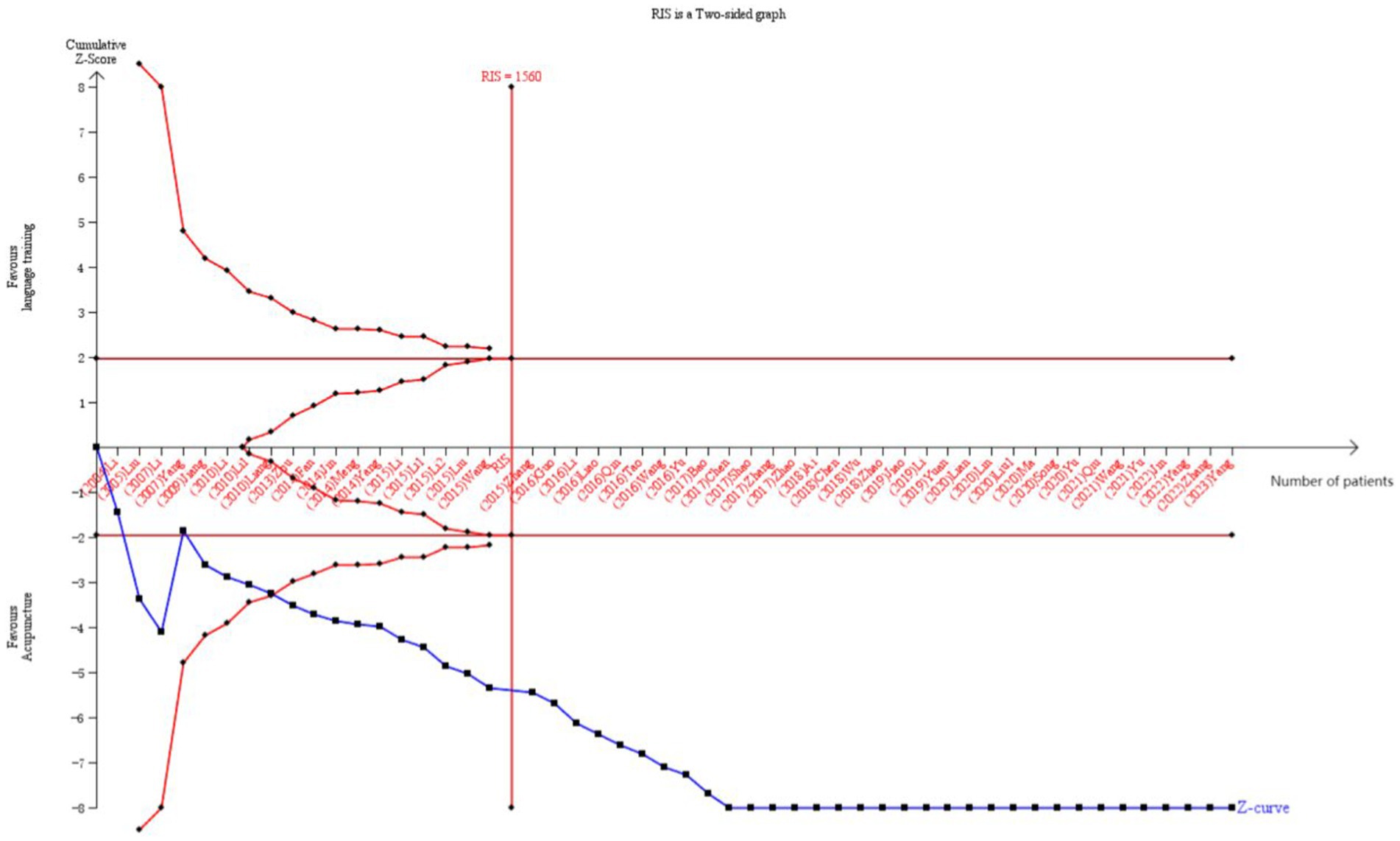
Figure 12. TSA on comparison of acupuncture combined with language training compared to language training alone. The crimson horizontal line represents the conventional statistical boundary of p = 0.05. The blue line indicates the cumulative Z-score of the meta-analysis. The red vertical line indicates the TSA boundary. RIS represents the required size of information.
The results of this meta-analysis show that acupuncture combined with language training has a more favourable clinical efficiency compared with treatment using language training alone. From the GESELL development scale, acupuncture combined with language training was seen to be effective in improving the adaptive, verbal, fine motor, and personal social behaviours of aphasic children with CP, compared to treatment with language training alone. However, there is no significant difference between the effect of acupuncture combined with language training and that of language training alone, in terms of improving gross sports behaviour. In addition, compared with language training alone, acupuncture combined with language training can significantly improve the assessment of dysarthria, oral motor function, the expressive language development quotient, and the language comprehension development quotient.
Through a subgroup analysis of different types of acupuncture, it was found that, compared with language training alone, acupuncture, electroacupuncture, scalp acupuncture, and auricular point seed-pressing combined with language training can effectively improve the clinical efficacy of aphasia treatment in children with CP. However, there is no significant difference between laser acupuncture combined with language training and language training alone. The duration subgroup analysis found that acupuncture combined with language training significantly improved clinical efficiency for a treatment duration of both ≤3 months and >3 months.
Studies have shown that acupuncture in the field of neurorehabilitation can promote the recovery of somatosensory or motor function, repair nerve damage, and promote the repair of speech function (73, 74). Aphasia, a common neurological disorder, is caused by damage to the functional language areas of the brain and its associated language networks (73). Acupuncture can enhance blood circulation at the site of brain lesions and in the language regions of individuals with aphasia, promote the establishment of collateral circulation, activate the language centers, and revive neural conduction pathways (75). Evidence from multiple studies indicates that the integration of various acupuncture modalities with language training can markedly enhance the speech expression and comprehension in children with CP, while also effectively mitigating dysarthria (62, 67, 70). The main types of acupuncture used in the RCTs included in this study were body acupuncture, scalp acupuncture, and electroacupuncture. The main mechanisms of body acupuncture are stimulating the peripheral nerves, improving local blood circulation, accelerating the local activities of the cerebral cortex, strengthening the protection of the cranial nerve, attenuating the negative effects on local nerves caused by the release of lipid peroxidation, and promoting the functional recovery of the cranial nerve (76). Acupuncture can also extend the brain nerve survival cycle and improve the release of the nerve growth factor, by improving the adverse symptoms of CP (77). Modern studies show that scalp acupuncture can effectively activate the cerebral cortex function, inhibit nerve cell apoptosis, promote nerve regeneration and the growth of endogenous neural stem cells, regulate brain cell energy metabolism, and increase the oxygen carrying capacity of brain cells (78–80). In addition, scalp acupuncture has a certain awakening effect on brain cells in the dormant state and can repair the damaged neuronal cells, improving language disorders and intelligence levels (81, 82). Electroacupuncture can stimulate the proliferation and differentiation of endogenous neural stem cells in the hippocampus, preventing their excessive differentiation into astrocytes and helping to accelerate the differentiation of e NSCs into neurons, thus playing a positive role in nerve regeneration (83). It has been found that electroacupuncture can increase the expression of p53 deacetylated Bcl-2, reduce the levels of Bax and Caspase-3, cut off the endogenous apoptotic pathway, and play an anti-apoptotic effect; it can also downregulate CHOP and Caspase-12 mRNA expression to intervene in endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS), thus reducing cell apoptosis and providing positive effects to the brain (84–86). Consequently, advocating for the broader clinical utilization of acupuncture as a therapeutic intervention for aphasia in children with CP is deemed valuable.
In our study, only one study reported adverse events (25), primarily local bleeding, subcutaneous petechiae, and crying. From this, it can be seen that the clinical effect of acupuncture combined with language training in the treatment of aphasic children with CP is remarkable and safe.
Nevertheless, our study has certain limitations. Firstly, the scope of our research is confined to single-center RCTs originating from China, where acupuncture is predominantly utilized, thereby leading to geographical constraints; Secondly, the reliability of our study was limited by the sample size, especially concerning laser acupuncture and auricular point seed-pressing, with only one RCT was included in this study; Thirdly, the specific nature of acupuncture therapy makes it challenging to achieve participant and personnel blinding, predisposing the trials to a heightened risk of bias; Additionally, the literature included in our study is exclusively in Chinese due to the regions and populations where acupuncture is commonly practiced, which may have influenced the overall quality of the studies. Despite these limitations, our meta-analysis offers an exhaustive assessment of the clinical application of acupuncture in conjunction with language training for treating aphasia in children with CP.
Acupuncture demonstrates efficacy when used as an adjunctive treatment for aphasia in children with CP, not only improving the patient’s adaptive, verbal, fine motor, and personal social behaviours, but also the patient’s assessment of dysarthria, oral motor function, expressive language development quotient, and language comprehension development quotient, with significant clinical efficacy. Our findings may provide valuable guidance for the use of acupuncture in clinical applications.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
SZL: Data curation, Investigation, Software, Writing – original draft. YJL: Data curation, Software, Writing – review & editing. JC: Data curation, Software, Writing – review & editing. JWS: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Project administration. LZ: Conceptualization, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Tianjin Science and Technology Plan Project (24ZYJDSY00260). Supported by the Tianjin Graduate Research Innovation Project & TUTCM Graduate Research Innovation Project (No.YJSKC-20231012).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2025.1502023/full#supplementary-material
1. McIntyre, S, Goldsmith, S, Webb, A, Ehlinger, V, Hollung, SJ, McConnell, K, et al. Global prevalence of cerebral palsy: a systematic analysis. Dev Med Child Neurol. (2022) 64:1494–506. doi: 10.1111/dmcn.15346
2. Li, XJ, Qiu, HB, Jiang, ZM, Pang, W, Guo, J, Zhu, LJ, et al. Epidemiological characteristics of cerebral palsy in twelve province in China. Chin J Appl Clin Pediatr. (2018) 33:378–83. doi: 10.3760/CMA.J.ISSN.2095-428X.2018.05.013
3. Mou, Z, Teng, W, Ouyang, H, Chen, Y, Liu, Y, Jiang, C, et al. Quantitative analysis of vowel production in cerebral palsy children with dysarthria. J Clin Neurosci. (2019) 66:77–82. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2019.05.020
4. Valadão, P, Piitulainen, H, Haapala, EA, Parviainen, T, Avela, J, and Finni, T. Exercise intervention protocol in children and young adults with cerebral palsy: the effects of strength, flexibility and gait training on physical performance, neuromuscular mechanisms and cardio metabolic risk factors (EXECP). BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. (2021) 13:17. doi: 10.1186/s13102-021-00242-y
5. Xue, J, and Mo, Y. Application of vocal organ correction combined with language training in the rehabilitation of children with cerebral palsy and language disorder. Transl Pediatr. (2020) 9:645–52. doi: 10.21037/tp-20-223
6. Wang, M, Liu, W, Ge, J, and Liu, S. The immunomodulatory mechanisms for acupuncture practice. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1147718. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1147718
7. Li, F, He, T, Xu, Q, Lin, LT, Li, H, Liu, Y, et al. What is the acupoint? A preliminary review of acupoints. Pain Med. (2015) 16:1905–15. doi: 10.1111/pme.12761
8. Zhu, Y, Yang, Y, and Li, J. Does acupuncture help patients with spasticity? A narrative review. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. (2019) 62:297–301. doi: 10.1016/j.rehab.2018.09.010
9. Zhang, Z, Chen, L, Guo, Y, Li, D, Zhang, J, Liu, L, et al. The neuroprotective and neural circuit mechanisms of acupoint stimulation for cognitive impairment. Chin Med. (2023) 18:8. doi: 10.1186/s13020-023-00707-x
10. Lv, XL, Sun, ZR, Hao, JS, and Hodge, T. Overview of treatment of cerebral palsy with acupuncture in the recent five years. Acta Chin Med Pharmacol. (2017) 45:51–6. doi: 10.19664/j.cnki.1002-2392.2017.01.014
11. Zhang, XY, Fu, JN, and Gao, LJ. Effect of acupuncture therapy for invigorating the kidney and strengthening brain in the adjuvant treatment of children with cerebral palsy and its influence on language development quotient and comprehensive function. Chin Pediatr Integr Tradit West Med. (2021) 13:10–3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3865.2021.01.003
12. Fu, GJ, and Yu, Y. Clinical research on treating language disorder of children with cerebral palsy by acupuncture. Clin J Chin Med. (2019) 11:41–2. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7860.2019.07.015
13. Hutton, B, Salanti, G, Caldwell, DM, Chaimani, A, Schmid, CH, Cameron, C, et al. The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: checklist and explanations. Ann Intern Med. (2015) 162:777–84. doi: 10.7326/M14-2385
14. Sterne, JAC, Savović, J, Page, MJ, Elbers, RG, Blencowe, NS, Boutron, I, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. (2019) 28:l4898. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l4898
15. Salanti, G, Del Giovane, C, Chaimani, A, Caldwell, DM, and Higgins, JP. Evaluating the quality of evidence from a network meta-analysis. PLoS One. (2014) 9:e99682. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099682
16. Wetterslev, J, Jakobsen, JC, and Gluud, C. Trial sequential analysis in systematic reviews with meta-analysis. BMC Med Res Methodol. (2017) 17:39. doi: 10.1186/s12874-017-0315-7
17. Li, HM. Acupuncture plus oral function training promotes recovery of speech disorders in paediatric cerebral palsy. Chin J Tissue Eng Res. (2004) 8:4353. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1673-8225.2004.21.151
18. Liu, ZH, Ma, MM, Pan, PG, Fu, WJ, and Hu, JJ. Treatment of cerebral palsy with aphasia by linguistic training combined with acupuncture. World J Acupunct Moxibust. (2005) 4:31–6.
19. Li, HM. (2007). Acupuncture-based therapy for paediatric cerebral palsy speech disorders. Compilation of papers from the 10th Academic Exchange Conference of Guangdong Province acupuncture and Moxibustion society. Children’s Rehabilitation Centre, Boai Hospital, Zhongshan:3.
20. Yang, YQ. Analysis of the therapeutic effects of scalp acupuncture and speech training on cerebral palsy speech disorders and related factors. Heilongjiang: Jiamusi University (2007).
21. Jiang, ZH. Clinical observation of acupuncture combined with language training in the treatment of language disorders in children with cerebral palsy. Mod Nurse. (2009) 6:26–7.
22. Li, HW, Ma, BX, and Feng, Y. Clinical observation on scalp acupuncture for treatment of speech disorders in paediatric cerebral palsy. Chin Med Mod Distance Educ China. (2010) 8:37–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2779.2010.24.029
23. Li, XJ, Yang, YQ, Pang, W, Zhang, SL, and Chen, BK. The analysis of the effects and related factors of head acupuncture combined with speech therapy in treating the language disorder of cerebral palsy children. Chin Pediatr Integr Tradit West Med. (2010) 2:326–30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3865.2010.04.014
24. Liang, B, Ouyang, BS, and Pu, YP. Observation on the efficacy of scalp acupuncture with needle speech training in the treatment of speech dysfunction in paediatric cerebral palsy. Chin Pediatr Integr Tradit West Med. (2010) 2:21–3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3865.2010.01.008
25. Zou, XY, Yu, ZH, He, YM, Yang, H, and Dong, XL. Effect of acupuncture combined language training on cerebral palsy children with language retardation. Chin J Int Tradit West Med. (2013) 33:924–6. doi: 10.7661/cjim.2013.07.0924
26. Fan, ZL, and Yang, Y. Clinical observation on acupuncture combined with linguistic training in treatment of cerebral palsy children with linguistic barrier. Matern Child Health Care China. (2014) 29:5700–1. doi: 10.7620/zgfybj.j.issn.1001-4411.2014.34.59
27. Jin, YJ, Huang, M, Li, HX, and Wang, HY. Association between therapeutic effect of speech disorders and age on treatment of children with cerebral palsy. Chin J Appl Clin Pediatr. (2014) 29:1874–6. doi: 10.3760/j.issn.2095-428x.2014.24.009
28. Meng, J, and Zhou, YM. Clinical study on treating language disorder in children with cerebral palsy by acupuncture. Clin J Chin Med. (2014) 5:66–7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7860.2014.05.032
29. Yang, HJ. Analysis of acupuncture treatment of language barriers of children with cerebral palsy. China Med Pharm. (2014) 117:106–7.
30. Li, DD, Qin, JF, Xu, X, and Luo, L. (2015). Clinical observation of acupuncture combined with language training on cerebral palsy the language barrier. Proceedings of the 10th Beijing International Rehabilitation Forum. 1666–1669.
31. Li, LY, Dong, SS, and Liu, ZH. Study on laser acupuncture in children with mental retardation and comorbid language disorders. Chin J Acupunct Moxibust. (2015) 3:105–8. doi: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-3240.2015.03.001
32. Li, MJ. Correlation study between efficacy of speech disorder of children with cerebral palsy and treatment age. World Latest Med Inf. (2015) 15:3–4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3141.2015.71.002
33. Liu, Y, and Shi, SH. Clinical observation on 60 cases of speech disorders in paediatric cerebral palsy treated with integrated acupuncture combined with speech training. Inner Mongolia J Tradit Chin Med. (2015) 34:61–2. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0979.2015.10.063
34. Wang, YL, Gao, C, and Song, LX. Clinical observation on the treatment of speech disorders in paediatric cerebral palsy by the acupuncture method of benefit enlightenment. China Pract Med. (2015) 12:278–80. doi: 10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2015.12.194
35. Zhang, Q. Exploring the clinical effects of acupuncture in the treatment of language disorders in children with cerebral palsy. Guide China Med. (2015) 13:224–5. doi: 10.15912/j.cnki.gocm.2015.01.172
36. Wang, YL. Observation on the efficacy of waking up the brain and opening up the orifices acupuncture combined with oral function training in the treatment of cerebral palsy with speech dysfunction. Mod J Integr Tradit Chin West Med. (2016) 25:3962–4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2016.35.031
37. Yu, JJ. Clinical research oil the effects of acupuncture and speech training on language retardation in children with cerebral palsy. Chin Sci J Hear Speech Rehabil. (2016) 14:31–4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4933.2016.01.008
38. Guo, CG, Zhang, HJ, Liu, CL, Yan, H, Hu, JH, and Zhou, PQ. Clinical observation of the combined treatment of needle technique ‘Congnao Tongluo’ and speech training for children with cerebral palsy and intellectual disabilities. Guiding J Tradit Chin Med Pharm. (2016) 22:74–6. doi: 10.13862/j.cnki.cn43-1446/r.2016.18.021
39. Li, SZ, Yang, ZX, Li, XJ, Wang, YQ, and Yuan, HX. Analysis of the clinical efficacy of scalp acupuncture combined with language training in the treatment of language disorders in children with cerebral palsy and its influencing factors. Neural Inj Funct Reconstr. (2016) 11:555–7. doi: 10.16780/j.cnki.sjssgncj.2016.06.031
40. Liao, JS. Exploring the efficacy of acupuncture with language training on children with cerebral palsy with delayed language development. Mod Diagn Treat. (2016) 27:2775–6.
41. Qin, JF, and Li, DD. Clinical observation of acupuncture plus speech training for speech disorders in cerebral palsy. Shanghai J Acupunct Moxibust. (2016) 35:421–2. doi: 10.13460/j.issn.1005-0957.2016.04.0421
42. Tao, F, and Ding, QY. Therapeutic effect of acupuncture on Fengchi, Tianzhu and Wuanjiao combined with language training in the treatment of speech disorders in children with cerebral palsy. Electron J Pract Clin Nurs Sci. (2016) 1:177–7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-2479.2016.07.128
43. Du, X, Chen, J, Jiang, K, Wu, ZF, and Liang, S. The therapeutic effect of acupuncture on cerebral palsy in children with language retardation using the midnight-noon ebb-flow method combined with syndrome differentiation. Acupunct Res. (2017) 42:346–9. doi: doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.2017.04.012
44. Liu, XL, Li, YR, and Song, LJ. Curative effects carrying different treatments for cerebral palsy in children with development language delay. Chin J Appl Clin Pediatr. (2017) 32:867–9. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095428x.2017.11.019
45. Shao, XH. (2017). The clinical research of Jin’s 3-needles combined with speech therapy in treating the language disorder of cerebral palsy children. Proceedings of the Academic Symposium of Cardiovascular Experts Invited by the Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and the Conference on Clinical Experience of Chinese Medicine in Treating Coronary Heart Disease and Angina Pectoris Disease. 49–51.
46. Zhang, YJ. Effect of acupuncture combined with language training on language development delay in children with cerebral palsy. Clin J Chin Med. (2017) 9:90–1. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7860.2017.06.041
47. Zhao, XY. Clinical effect observation of acupuncture combined with language training in the treatment of language disorders in children with cerebral palsy. Clin Res Pract. (2017) 2:117–8. doi: 10.19347/j.cnki.2096-1413.201730057
48. Bao, LL. Analysis of the effects of Jin’s 3-needles combined with speech therapy on treating the language disorder of cerebral palsy children. J Shandong First Med Univ Shandong Acad Med Sci. (2017) 38:744–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7115.2017.07.008
49. Chen, JJ. Analysis of the effect of rehabilitation therapy for language disorders in children with cerebral palsy. Med Forum. (2017) 21:341–3. doi: 10.19435/j.1672-1721.2017.03.061
50. Chen, SY. Analysing the clinical value of acupuncture and language training in the combined treatment of delayed language development in children with cerebral palsy. Health Everyone. (2018) 2:125.
51. Wu, JJ, Zhang, SY, Zhang, XX, and Hu, YJ. A case-control study of group language training combined with acupuncture on children with cerebral palsy language disorder. J Clin Psychosom Dis. (2018) 24:108–10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-187x.2018.06.031
52. Zhao, D, Shang, Q, and Ma, CY. The effect of acupuncture with oral function training on the prognosis of 49 children with cerebral palsy and speech disorders. Guangming J Chin Med. (2018) 33:402–4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8914.2018.03.047
53. Ai, YF, Tao, M, Liu, YT, and Gong, ZK. The effect of acupuncture on the speech nerve centre in children with cerebral palsy. Chin J Trauma Disabil Med. (2018) 26:58–9. doi: 10.13214/j.cnki.cjotadm.2018.08.041
54. Huang, YZ, Li, XJ, Zhou, L, Zhu, Q, and Wang, T. Therapeutic effect of oral muscle training combined with scalp acupuncture on dysarthria in children with spastic cerebral palsy. Chin Pediatr Integr Tradit West Med. (2019) 11:502–5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3865.2019.06.013
55. Jiao, XB. Clinical effect of language rehabilitation combined with acupuncture on language barrier in children with cerebral palsy. J Yan’an Univ. (2019) 17:57–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2639.2019.03.015
56. Li, HZ. The effect of scalp acupuncture combined with verbal cognitive training on the intellectual development level of children with cerebral palsy. China Health Care Nutr. (2019) 29:336.
57. Yuan, S, Ying, YH, and Zhang, M. Study on the treatment of language disorders in preschool children with cerebral palsy. Chin Sci J Hear Speech Rehabil. (2019) 17:379–81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4933.2019.05.015
58. Lian, HJ. Discussion on the effect of acupuncture combined with language training method in the treatment of speech delay due to cerebral palsy. Contemp Med Symp. (2020) 18:32–3.
59. Lin, W, Wang, ML, and Liang, S. Clinical study on the treatment of cerebral palsy with speech disorders by auricular point pressing combined with speech training. World Latest Med Inf. (2020) 20:196–7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3141.2020.32.094
60. Liu, L. The role of acupuncture with language training in children with cerebral palsy with delayed speech development. World Latest Med Inf. (2020) 20:165–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3141.2020.69.096
61. Liu, ML, Mei, SX, Yang, LD, and Mao, PA. Clinical observation on 54 cases of paediatric cerebral palsy combined with speech disorders treated by Tong Guan Li Qiao acupuncture combined with speech training. J Pediatr Tradit Chin Med. (2020) 16:101–4. doi: 10.16840/j.issn1673-4297.2020.06.26
62. Ma, DD. Clinical observation on the treatment of cerebral palsy combined with delayed speech development by acupuncture combined with speech training using the meridian flow injection najia method. Clin Res. (2020) 28:132–4.
63. Song, LJ. Clinical observation of acupuncture combined with language rehabilitation training in the treatment of cerebral palsy with speech delay. China’s Naturopathy. (2020) 28:30–2. doi: 10.19621/j.cnki.11-3555/r.2020.0215
64. Yu, N. Analysis of the efficacy of speech training combined with electroacupuncture therapy on cerebral palsy with speech disorder. Kang Yi. (2020) 12:180. doi: 10.12332/j.issn.2095-6525.2020.12.174
65. Qiu, L. Exploring the clinical efficacy of acupuncture with language training in the treatment of delayed language development in children with cerebral palsy. Heilongjiang J Tradit Chin Med. (2021) 50:37–8.
66. Wang, CX. Clinical efficacy observation of acupuncture combined with language training in treating speech disorders in paediatric cerebral palsy. Healthy Women. (2021) 21:122.
67. Yan, TQ, Wang, S, and Guan, LJ. Effects of acupuncture combined with language training on Frenchay articulation score in children with cerebral palsy combined with dysarthria. Clin J Tradit Chin Med. (2021) 33:957–60. doi: 10.16448/j.cjtcm.2021.053971
68. Yu, N. Observation on the clinical efficacy of Congnao Tongluo acupuncture combined with speech training in treating paediatric cerebral palsy with mental retardation. Clin Nurs Res. (2021) 30:272–3.
69. Jin, YJ, and Huang, M. Comparison of two kinds of cephalic acupuncture therapy for speech disorder in children with cerebral palsy. Med Health. (2022) 3:8–11.
70. Yang, HY, and Liu, CP. Observation on the efficacy of scalp acupuncture with needle speech training in the treatment of speech dysfunction in paediatric cerebral palsy. Zhonghua Yangsheng Baojian. (2022) 40:60–2.
71. Zhang, W, He, X, and Huang, Y. Effect of language rehabilitation training combined with acupuncture in children with cerebral palsy. Henan Med Res. (2022) 31:485–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-437x.2022.03.027
72. Yang, M, and Bai, S. Effects of Xingnao Kaiqiao acupuncture combined with language training on language development delay in children with cerebral palsy. Med J Chin People Health. (2023) 35:69–71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0369.2023.14.021
73. Yang, Y, Cui, YJ, Xu, Y, Yang, YX, Guo, YM, Wang, XY, et al. Research Progress on the advantages of acupuncture and moxibustion rehabilitation techniques in rehabilitation medicine and the key mechanisms of action. J Liaoning Univ Tradit Chin Med. (2023) 25:92–6. doi: 10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2023.11.019
74. Zhang, Y, Tang, YW, Peng, YT, Yan, Z, Zhou, J, and Yue, ZH. Acupuncture, an effective treatment for post-stroke neurologic dysfunction. Brain Res Bull. (2024) 215:111035. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2024.111035
75. Li, J, Jiang, Y, Li, S, and Zhuang, L. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy of acupuncture and moxibustion in rehabilitation treatment for post-stroke aphasia. Am J Transl Res. (2024) 16:5182–90. doi: 10.62347/VYKU6210
76. Danniyaer, H, and Zhou, Y. Progress of clinical research on acupuncture in the treatment of paediatric cerebral palsy. Xinjiang J Tradit Chin Med. (2022) 40:104–6.
77. Liu, ZH, Pan, PG, Qi, YC, Zhao, Y, Chai, TQ, Tang, CZ, et al. Effects of Tongdu Xingshen acupuncture on neuronal cell apoptosis and nerve growth factor protein expression in the brain tissue of young rats with cerebral palsy. Clin J Tradit Chin Med. (2010) 22:36–40. doi: 10.16448/j.cjtcm.2010.01.013
78. Zhang, H, Gao, J, Wang, M, Yu, X, Lv, X, Deng, H, et al. Effects of scalp electroacupuncture on the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway and apoptosis of hippocampal neurons in a rat model of cerebral palsy. Acupunct Med. (2018) 36:96–102. doi: 10.1136/acupmed-2016-011335
79. Zhou, L, Zhang, XY, Zhang, HX, Zou, R, Liu, YN, and Wang, Q. Scalp-acupuncture induced the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cell. Stroke Nerv Dis. (2011) 18:138–41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-0478.2011.03.003
80. Chen, JK, and Liu, ZH. New advances in acupuncture for neural development and repair in the brain. J Changchun Univ Chin. (2012) 28:756. doi: 10.13463/j.cnki.cczyy.2012.04.150
81. Huang, YT, and Liang, HC. Observation on the curative effect of head acupuncture combined with rehabilitation training in children with mental retardation. J External Ther Tradit Chin Med. (2023) 32:1–3.
82. Liu, Q, Hu, W, Lv, LL, Fu, XM, and Chen, LN. Clinical study on scalp acupuncture combined with collective language training for delayed language development in children. New Chin Med. (2024) 56:155–9. doi: 10.13457/j.cnki.jncm.2024.01.030
83. Tan, F, Wang, J, Chen, J, Gu, Y, Zhan, J, Gu, MH, et al. Effect of Electroacupuncture on the expression of hippocampal e NSCs in MCAO model rats. Chin J Int Tradit West Med. (2017) 37:198–203. doi: 10.7661/CJIM.2017.02.0198
84. Wang, B, Zhang, XM, Wu, S, Huang, W, Li, D, Lu, W, et al. Effect on p53 and caspase-3 of hippocampal neuron in the rats with cerebral ischemiareperfusion injury treated with electroacupuncture preconditioning at the acupoints on the basis of biao and ben relationship. Chin Acupunct Moxibust. (2019) 39:957–62. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.2019.09.011
85. Tao, WT, Chen, JJ, and Zheng, Z. Protective effect of electroacupuncture preconditioning at Baihui, Shenshu and Sanyinjiao acupoints on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. J Hubei Univ Chin Med. (2023) 25:15–20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008987x.2023.01.03
Keywords: acupuncture, language training, cerebral palsy, aphasia, meta-analysis, randomised controlled trials
Citation: Liu S, Li Y, Chang J, Shi J and Zhao L (2025) Acupuncture combined with language training for aphasia in children with cerebral palsy: a systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. Front. Neurol. 16:1502023. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1502023
Received: 26 September 2024; Accepted: 24 February 2025;
Published: 12 March 2025.
Edited by:
Sandeep Kumar Singh, Banaras Hindu University, IndiaReviewed by:
Jinhuan Zhang, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Liu, Li, Chang, Shi and Zhao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jiangwei Shi, YWN1c3RvbmVAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Lan Zhao, bGFuemhhbzY5QDE2My5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.