- 1Department of Radiology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
- 2The Second Clinical College, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
Objective: This study aimed to develop and validate a multivariate logistic regression model for predicting intracranial aneurysm (IA) rupture by integrating clinical data, aneurysm morphology, and parent artery characteristics using high-resolution vessel wall imaging (HR-VWI).
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on 298 patients with 386 aneurysms. Patients were randomly divided into training (n = 308) and validation (n = 78) sets. Key predictors, including aneurysm size, shape, aneurysm wall and parent artery wall enhancement, were identified through univariate analysis and then used to build the prediction model using multivariate logistic regression. The model was visualized as a nomogram and compared to PHASES and ELAPSS scores.
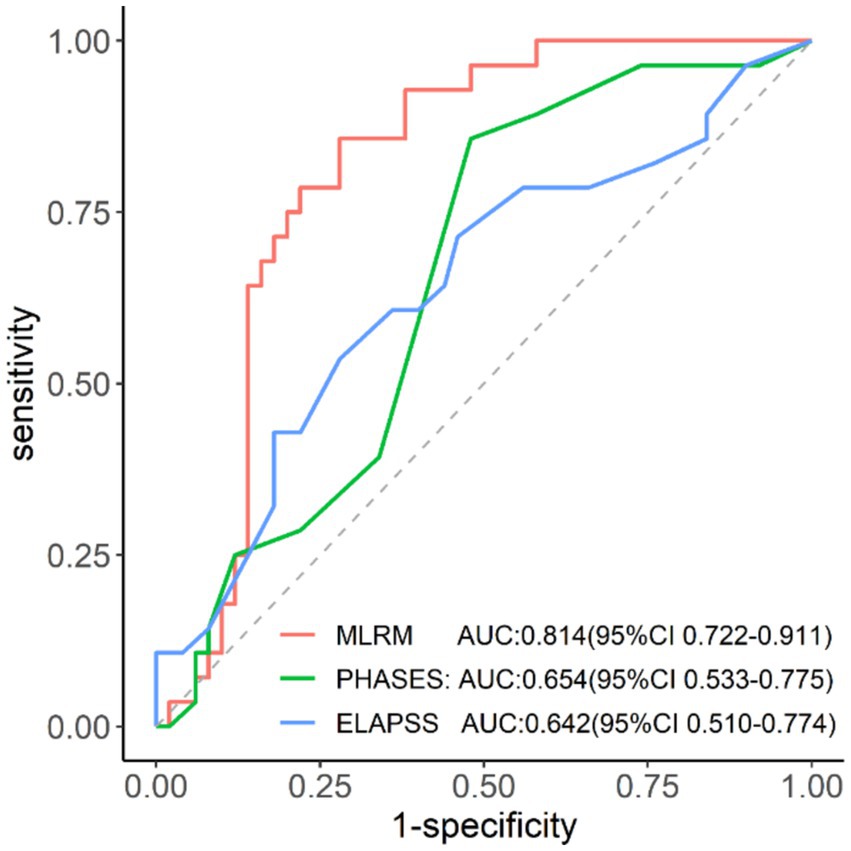
Results: The logistic regression model demonstrated superior predictive performance with an area under the curve of 0.814, which was significantly higher than PHASES and ELAPSS scores (p < 0.05). The model revealed strong calibration and good agreement between predicted and observed rupture probabilities.
Conclusion: The multivariate model based on HR-VWI, which incorporates aneurysm and parent artery features, provides a more accurate prediction of IA rupture risk than conventional scoring systems, offering a valuable tool for clinical decision-making.
1 Introduction
Intracranial aneurysms (IAs) are common vascular conditions that can lead to subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), a severe form of stroke with a fatality rate approaching 50% (1, 2). Accurate evaluation of rupture risk is crucial for clinical decision-making. Traditional models, such as PHASES and ELAPSS scores, only rely on clinical and morphological data, resulting in moderate predictive accuracy (3–6).
High-resolution vessel wall imaging (HR-VWI) surpasses conventional vascular imaging by providing detailed insight into aneurysm architecture and wall enhancement (AWE) (7). Studies suggest that AWE, which reflects inflammatory activity after contrast administration, strongly correlates with aneurysm rupture risk, thus improving the accuracy of IA risk predictions (8). This technique is more effective for assessing the likelihood of IA rupture. Current research using HR-VWI for IA rupture risk primarily focuses on qualitative and quantitative assessments of AWE (9, 10), often neglecting the role of the parent artery. However, emerging evidence indicates that vessel wall enhancement near the aneurysm neck is associated with aneurysm development and progression (11). Despite this, few studies have incorporated parent artery analysis in HR-VWI-based rupture risk assessments, underutilizing its predictive potential.
This study aimed to improve IA rupture risk prediction by integrating clinical profiles, aneurysm and parent artery morphometrics, and HR-VWI-derived features. We developed a predictive model using multivariate logistic regression, visualized it as a nomogram, and compared its performance against PHASES and ELAPSS scoring systems.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study subjects
This study was approved by our institutional review committee (Ethics Committee: Ke Lun Review No. 194) and obtained written informed consent from all participants. We conducted a retrospective analysis of patients diagnosed with IAs through head computed tomography angiography at our hospital between October 2019 and October 2023. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) ruptured or unruptured saccular aneurysms with SAH attributable to aneurysm rupture; (2) high-quality three-dimensional (3D) HR-VWI data indicating the aneurysm and adjacent 3 mm of the parent artery. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) incomplete HR-VWI images; (2) dissection or fusiform aneurysms; (3) post-treatment aneurysms; (4) multiple aneurysms with unclear rupture source; (5) poor HR-VWI image quality or aneurysms too small to assess wall features.
2.2 Data collection
2.2.1 Patient information
We collected data on age, gender, ethnicity, and previous medical history (including hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, coronary heart disease, smoking, and history of SAH). We also recorded the history of the present illness and the date of imaging, as obtained from the hospital’s electronic medical records for both inpatients and outpatients. For incomplete records, supplementary information was gathered through telephone follow-up.
2.2.2 Risk scoring
The PHASES score (12) was used to assess aneurysm rupture risk based on ethnicity, hypertension, age, aneurysm size, history of SAH, and location. The ELAPSS score (13) was applied to evaluate the growth risk of IA, considering the history of SAH, aneurysm location, age, ethnicity, aneurysm size, and shape.
2.3 Imaging examination
2.3.1 Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) protocol
MRI scans were conducted using an Ingenia CX 3.0 T scanner with a 32-channel head coil. The protocol began with 3D time-of-flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) for IA localization, followed by axial 3D T1-weighted volume isotropic turbo spin echo acquisition (VISTA) sequences for targeted imaging of the parent artery. A contrast agent, gadopentetate dimeglumine (0.1 mmol/kg, Gd-DOTA, Jiangsu, China), was manually injected into the antecubital vein. HR-VWI was repeated 5 min after the contrast injection to acquire contrast-enhanced HR-VWI (CE-HR-VWI). Scan parameters included a field of view (FOV) 200 × 200 mm2, slice thickness 0.50 mm, slices 80, TR/TE 800/22 ms, flip angle 90°, and voxel size 0.6 × 0.6 × 0.6 mm3. Images were processed using the Philips IntelliSpace Portal V12 workstation.
2.4 Imaging assessment
2.4.1 Morphological features of IAs and parent arteries
We evaluated the location, configuration (whether at bifurcations or sidewalls), and shape (including regularity and the presence of daughter sacs) of aneurysms using three-dimensional reconstructed images from TOF-MRA. Using two-dimensional measurement tools on HR-VWI images, we obtained the size of aneurysms, including neck width (NW), maximum height (MH), maximum width (MW), and parent artery diameter (PAD) (Figure 1) (14). From these measurements, we calculated the aneurysm’s aspect ratio (AR), size ratio (SR), and neck-to-parent ratio (NPR).
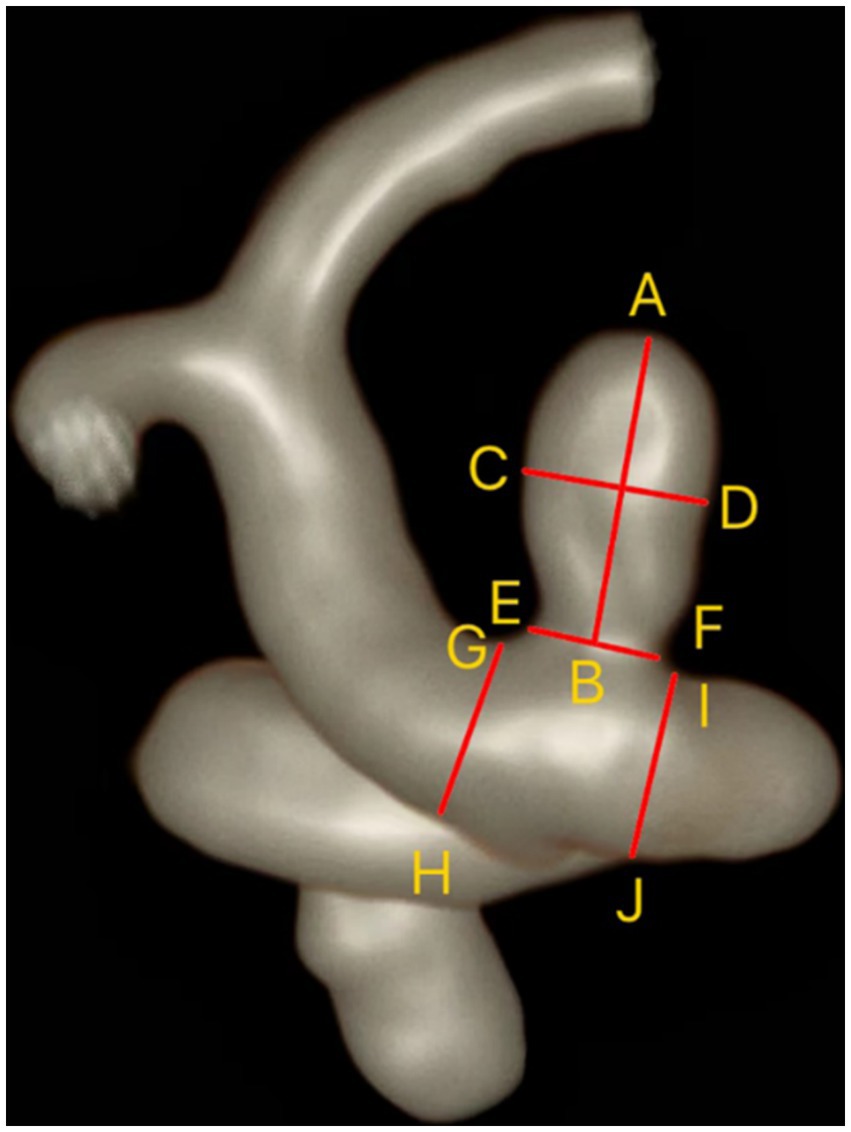
Figure 1. Measurement of IAs and parent artery. Maximum height (MH) = AB; Maximum width (MW) = CD; Neck width (NW) = EF; Parent artery diameter (PAD) = (GH + IJ)/2.
2.4.2 Characteristics of aneurysm and parent artery walls on HR-VWI
Two neuroradiologists with over 10 years of diagnostic experience independently performed a blinded analysis of the HR-VWI and CE-HR-VWI images. The two neuroradiologists were unaware of the clinical data but were aware of the location of the aneurysm. When there was a disagreement, a third neuroradiologist with over 20 years of diagnostic experience would intervene to negotiate a resolution.
2.4.2.1 Qualitative analysis
A qualitative analysis was conducted to evaluate AWE severity, which was categorized into three grades: Grade 0 (no enhancement, similar signal intensity on both images), Grade 1 (focal, localized non-circular enhancement), and Grade 2 (ring enhancement, with enhancement throughout the entire aneurysm wall) (15) (Figure 2).
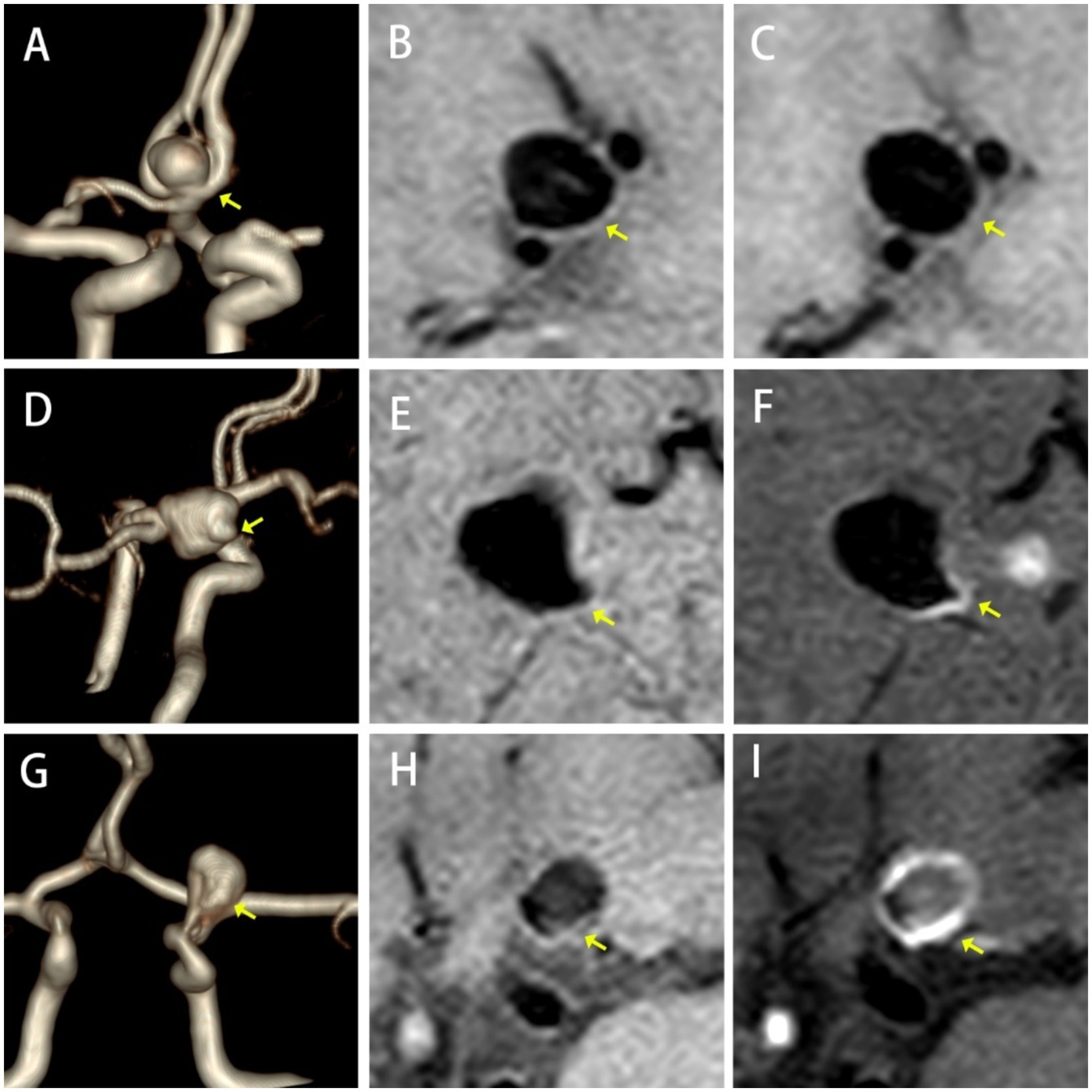
Figure 2. Types of AWE. No Enhancement, (A) TOF-MRA, (B) HR-VWI, and (C) CE-HR-VWI; Focal Enhancement, (D) 3D-TOF-MRA, (E) HR-VWI, and (F) CE-HR-VWI; Ring Enhancement, (G) 3D-TOF-MRA, (H) HR-VWI, and (I) CE-HR-VWI.
2.4.2.2 Quantitative analysis
Two neuroradiologists conducted quantitative measurements evaluating the following parameters from the optimal viewing angle (sagittal, frontal plane, and horizontal plane). All measurements were made at an image magnification of 500%.
The thickest part of the aneurysm wall and the parent artery wall were measured three times at the direct boundary, and the average value was calculated as aneurysm wall thickness (AWT) and parent artery wall thickness (PAWT) (Figures 3A,C).
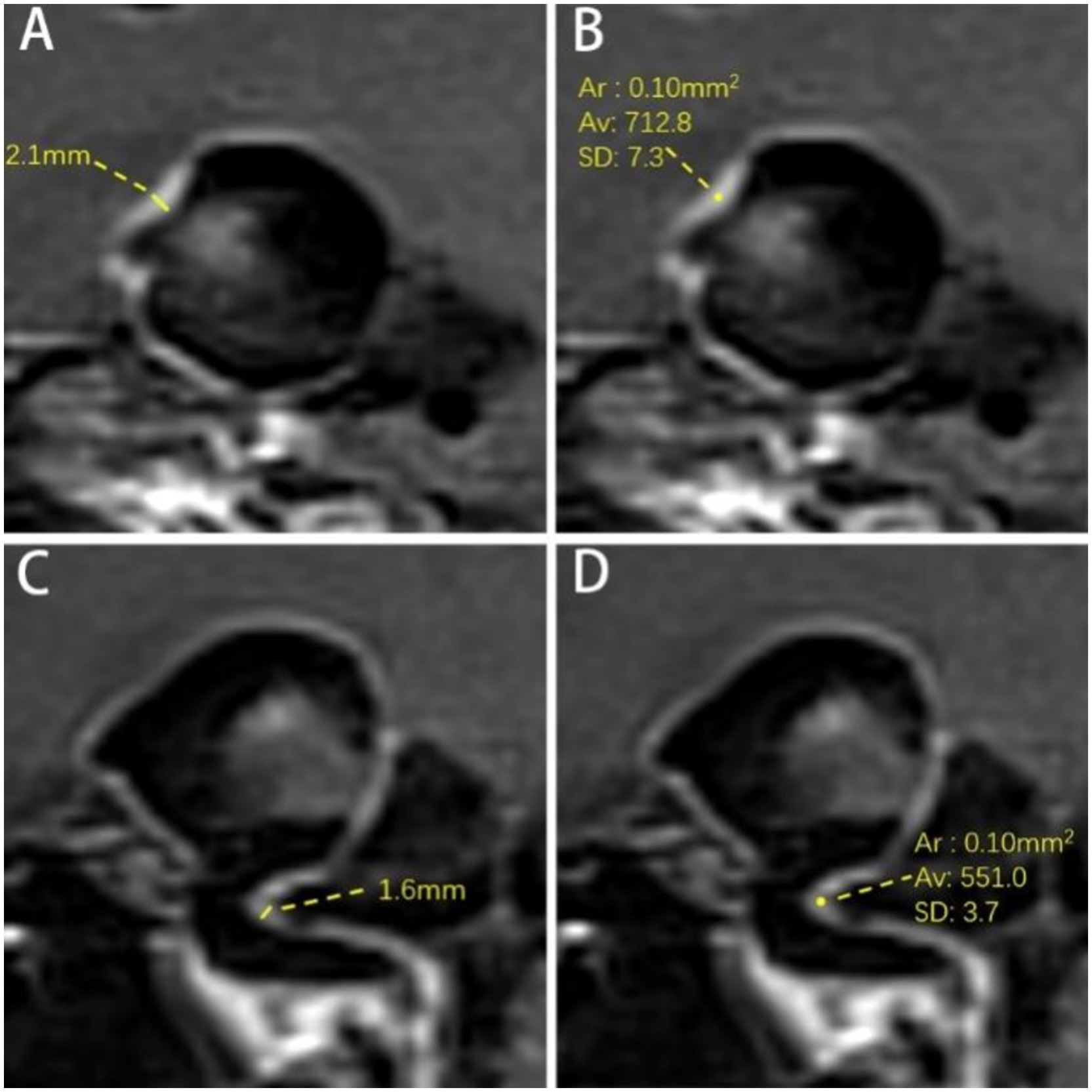
Figure 3. Measurement of aneurysm wall and parent artery. (A) Measurement of AWT. The AWT is 2.1 mm. (B) Measurement SI of AWE. The signal intensity of the aneurysm wall is 712.8. (C) Parent artery wall thickness (PAWT). The PAWT is 1.6 mm. (D) Parent artery wall signal intensity. The signal intensity of the parent artery wall is 551.0. Ar = Average Range; Av = Average Signal Intensity of ROI; SD = Standard Deviation.
AWE was evaluated using the Wall Enhancement Index (WEI) and the contrast ratio between the aneurysm wall and the pituitary stalk (CRstalk) (Equations 1, 2) (16, 17). Parent artery wall enhancement (PAWE) was evaluated using the parent artery wall enhancement index (PWEI) and the contrast ratio between the parent artery wall and the pituitary stalk (PCRstalk) (Equations 3, 4).
The post-contrast SI of the aneurysm wall (SIAW(post)) and parent artery (SIPA(post)) was measured separately three times on post-contrast images on the layer of their respective maximum diameters, and the highest value was recorded as the enhanced SI (Figures 3B,C). Furthermore, the measurement range for parent artery was within 3 mm of the aneurysm neck. The region of interest (ROI) was 0.1 mm2. The pre-contrast SI of the aneurysm wall (SIAW(pre)) and parent artery (SIPA(pre)) was measured using the same method at the corresponding site. The SI of the right frontal white matter (SIRFWM) was measured as a reference on both pre- and post-contrast images. The ROI was 20 mm2. Additionally, the pituitary stalk SI (SIPS(post)) was measured three times on the upper, middle, and lower parts of the pituitary stalk on CE-HR-VWI images and the highest value among them was recorded. The ROI was 0.1 mm2 (18).
2.5 Statistical methods
Statistical analysis was performed using R software (version 4.2.3). Kappa statistics evaluated inter-rater agreement on AWE (κ > 0.75, indicating good concordance). Intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC) was used to assess the reliability for WEI, PWEI, CRstalk, PCRstalk, AWT, and PAWT (ICC > 0.75, indicating good reliability). The Shapiro–Wilk test was applied to assess the distributions of variables. T-tests, F-tests, and Chi-square tests were used to differentiate ruptured and unruptured IAs. Multivariate logistic regression including univariate predictors (p < 0.2) attained aneurysm rupture with 95% confidence interval [CI] and then selected predictors (p < 0.05) for model construction. Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to benchmark model accuracy, and the PHASES and ELAPSS normalized scores (0–1) were compared with the logistic regression model. The DeLong test (p < 0.05) was applied to determine statistical significance (19).
3 Results
3.1 Univariate and multivariate analyses of IA rupture prediction factors
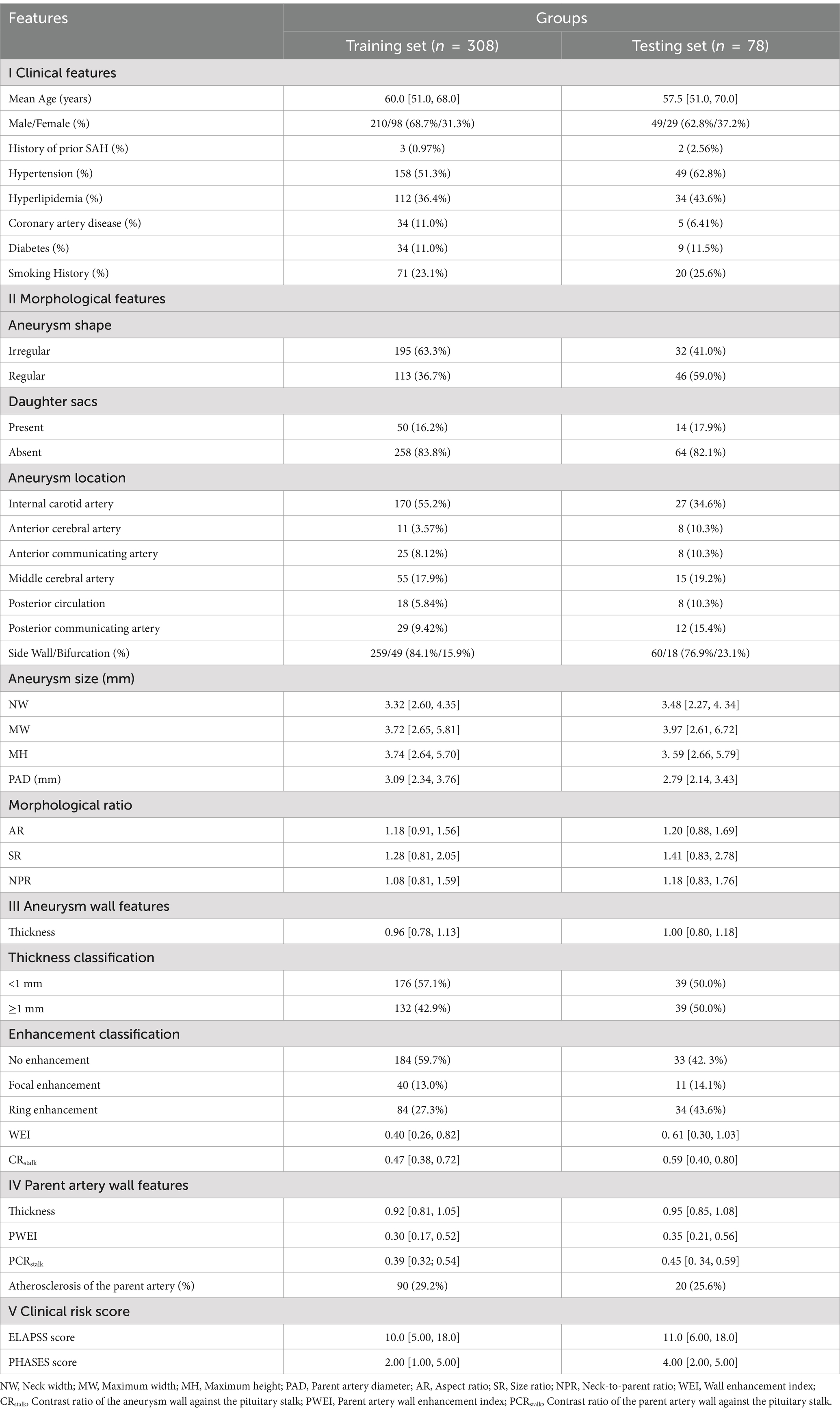
A total of 386 IAs from 298 patients were randomly divided into training (80%) and validation (20%) sets to analyze predictors of IA rupture and for model development and validation (Table 1; Figure 4). In both sets, IAs were classified into two groups: ruptured IAs were classified as the ruptured group, and unruptured IAs were classified as the unruptured group.
Inter-rater reliability for AWE classification was high (κ = 0.871; 95% CI: 0.751–0.991). The consistency between the two evaluators in measuring morphological features and assessing enhancement SI assessments was also strong (ICC = 0.933; 95% CI: 0.886–0.961).
3.1.1 Collection of prediction factors
In this study, 25 potential predictors were evaluated, covering clinical traits, morphological attributes of the aneurysm and its parent artery, and characteristics of both the aneurysm and parent artery walls. Specifically, clinical factors included age, gender, a history of hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, coronary artery disease, smoking, and prior SAH. Morphological parameters included aneurysm location, configuration (bifurcation or sidewall), morphology (regularity, presence of daughter sacs), size (NW, MH, and MW), and indices such as PAD, AR, SR, and NPR. Wall features were assessed using WEI, CRstalk, and AWT for the aneurysm wall, and PWEI, PCRstalk, and PAWT for the parent artery wall.
3.1.2 Results of univariate analysis and multivariate logistic analysis
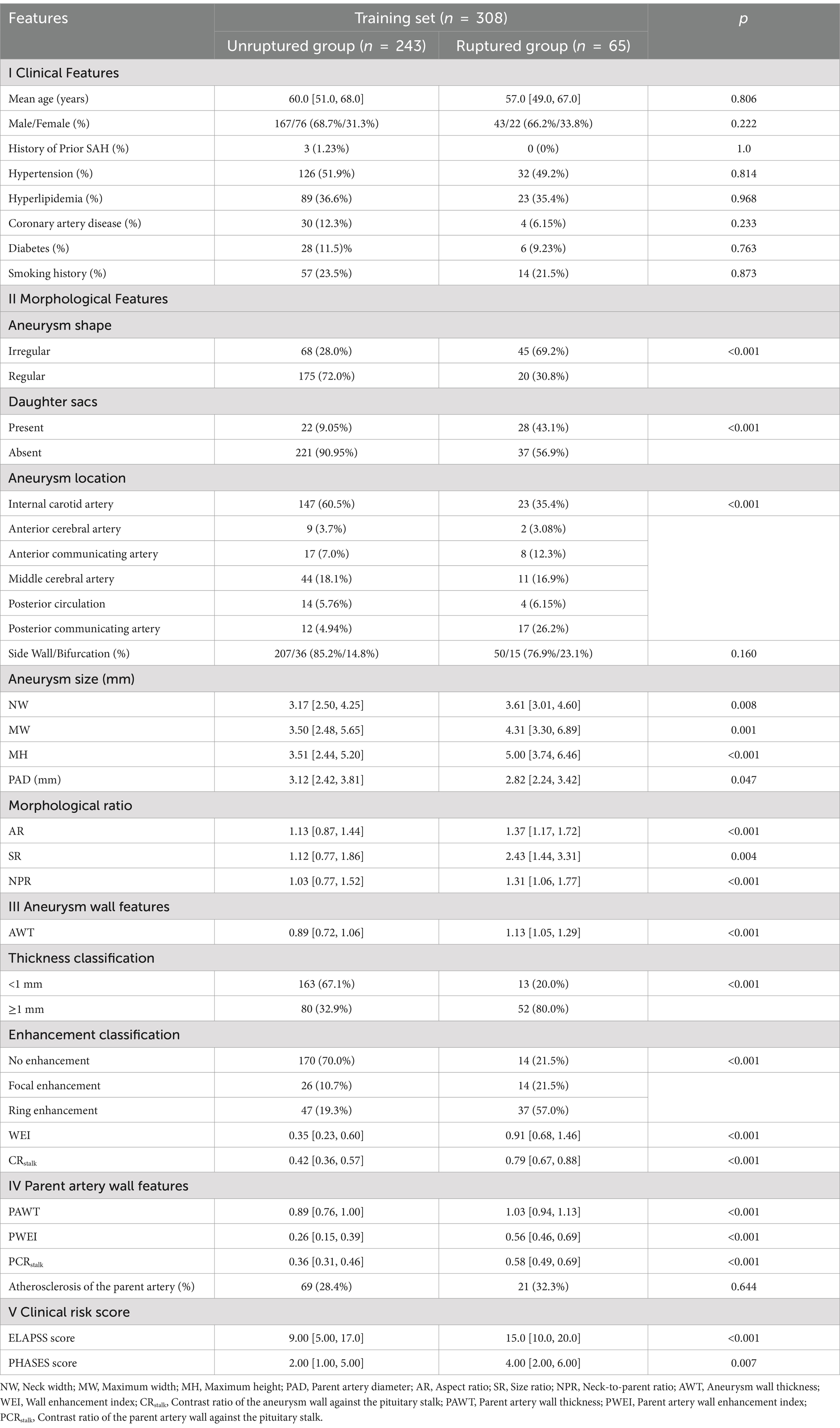
Univariate analysis identified 18 factors associated with aneurysm rupture, including (1) morphological characteristics: aneurysm location, shape (regularity, presence of daughter sacs), NW, MH, MW, PAD, AR, SR, NPR; (2) aneurysm wall characteristics: wall enhancement classification, parent artery thickness classification, WEI, CRstalk and AWT; (3) parent artery wall characteristics: PWEI, PCRstalk and PAWT (p < 0.05) (Table 2).
Multivariate analysis identified the following independent risk factors for IA rupture: irregular aneurysm shape (p = 0.004, odds ratio [OR] = 5.55, 95% CI: 1.72–17.89), MW of the aneurysm (p = 0.03, OR = 0.62, 95% CI: 0.40–0.96), CRstalk (p = 0.01, OR = 107.21, 95% CI: 3.00–3828.00) and PCRstalk (p = 0.007, OR = 189.0, 95% CI: 4.30–8309.76).
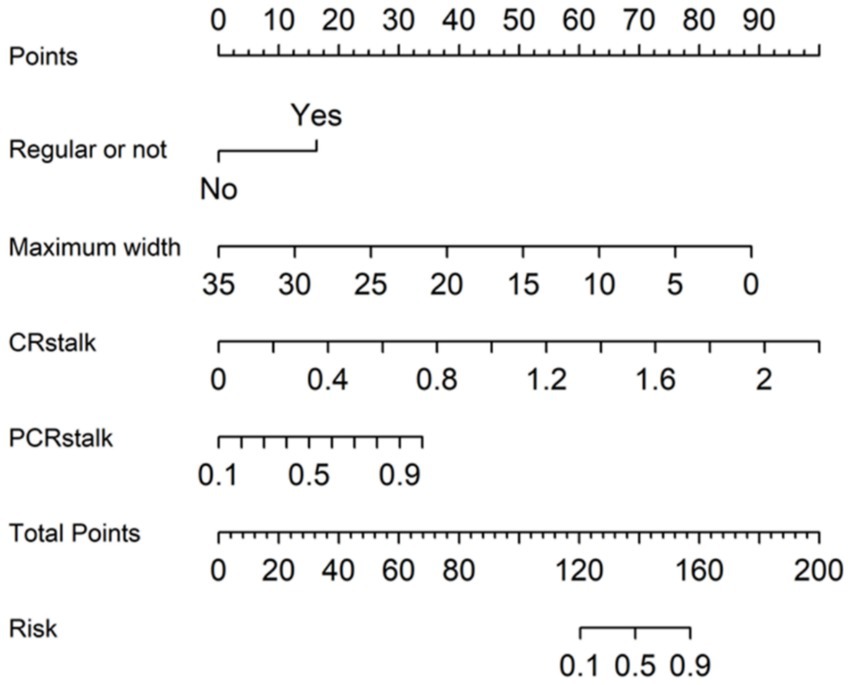
3.2 Construction and visualization of the multivariate logistic regression model
A multivariate logistic regression model (MLRM) was developed, incorporating four independent risk factors for IA rupture into a numerical assessment of rupture probability. The Equation is as follows:
Equation 5 shows MLRM of IAs rupture risk.
In this Equation, p(An) represents the estimated rupture probability of the aneurysm rupture. This predictive model has been converted into a visual nomogram (Figure 5).
3.3 Validation of the MLRM and comparison with ELAPSS and PHASES scores
The MLR nomogram model demonstrated strong predictive performance in the validation set, with an area under the ROC curve of 0.814 (95% CI: 0.722–0.911) (Figure 6), the highest among the three predictive models (Table 3). The DeLong test indicated a significant difference in predictive efficacy, with the MLR model outperforming the ELAPSS Score (p = 0.037) and the PHASES Score (p = 0.040).
The calibration curve (Figure 7) aligned closely with the diagonal line, suggesting good agreement between predicted and observed probabilities of IA rupture.
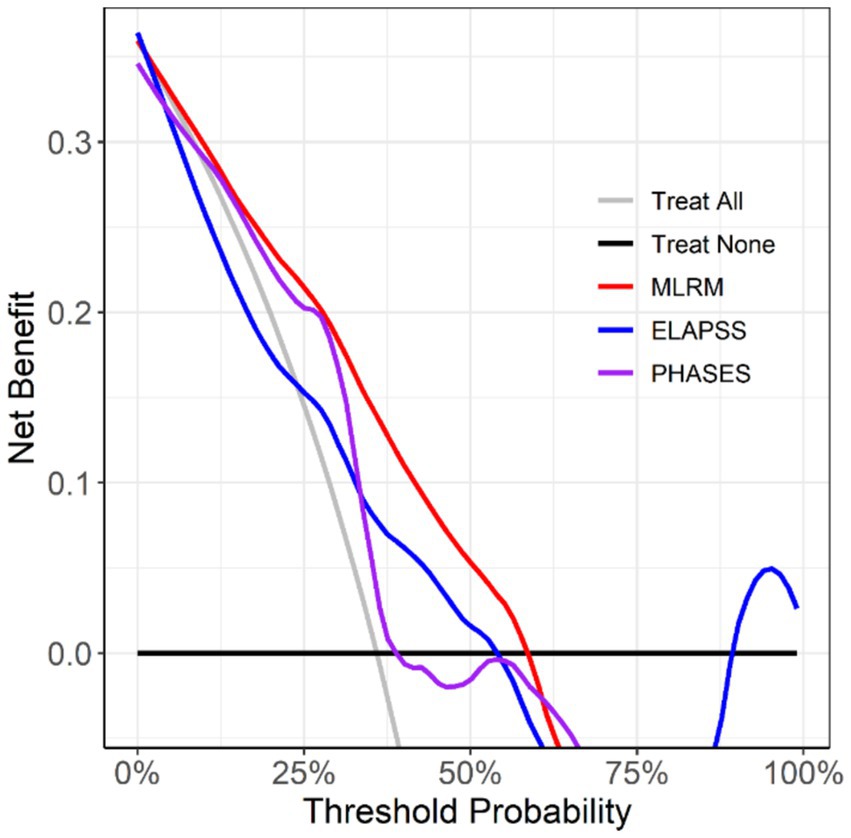
Decision curve analysis (Figure 8) revealed that the MLR model, which incorporates aneurysm morphology, aneurysm wall characteristics, and parent artery wall features, provided more significant clinical benefit in decision-making than the other models.
4 Discussion
The PHASES and ELAPSS scores are widely used for assessing the risk of IA rupture, focusing on a limited set of clinical and morphological factors. HR-VWI is recognized as a superior diagnostic tool for intracranial vascular pathologies, including aneurysm diagnosis (20, 21). As research into IA imaging progresses, evidence suggests that the pathological changes in the aneurysm wall and parent artery, identified by HR-VWI, are associated with IA rupture. This study expanded upon traditional clinical and morphological characteristics by incorporating aneurysm and parent artery features from HR-VWI. We identified irregular aneurysm shape, MW, CRstalk, and PCRstalk as independent predictors of IA rupture through univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses. Based on these four variables, an MLRM was developed.
In this study, we assessed aneurysm size in three dimensions—NW, MW, and MH—and identified MW as an independent risk factor for IA rupture. While previous research has used various morphological factors to differentiate IA statuses, aneurysm size remains a key factor in guiding treatment decisions (22). Akio et al. (23) found that aneurysms larger than 7 mm are at higher risk of SAH, with an annual rupture rate of 0.95% for larger aneurysms. Our findings confirm that aneurysm size is linked to rupture risk, with the MW significantly larger in the ruptured group compared to unruptured groups. This is likely due to the increased pressure on the aneurysm wall as it enlarges. However, some studies have found that about one-third of patients with aneurysmal SAH have IAs smaller than 5 mm (24). In our study, the median MW in the ruptured group was 4.31 [3.30, 6.89], indicating that the risk of rupture for smaller aneurysms should not be overlooked.
Consistent with previous research, this study identified irregular aneurysm shape as a significant predictor of IA rupture. A study of 713 IAs demonstrated that irregular shape is associated with rupture, independent of size, location, and clinical characteristics (25). Another study focusing on mirror IAs at the middle cerebral artery bifurcation indicates that size and shape were the only predictive factors for rupture (26). Additionally, irregular aneurysm shape is an independent risk factor for rebleeding in patients with SAH (27). Irregularity in IAs often manifests as lobulated or multilobed structures with uneven surfaces or small protrusions linked to hemodynamic factors (28). The swirling blood flow within the aneurysm sac can cause uneven wall stress, resulting in local protrusions. As stress on these protrusions increases, the aneurysm wall thins due to continuous tension, making these weak points more susceptible to rupture under sudden pressure changes.
Inflammation plays a key factor in the formation, progression, and rupture of IAs, and AWE is a reliable indicator of the inflammatory state within the aneurysm wall. Samaniego EA et al. (29) highlighted that HR-VWI enhancement is crucial for assessing IA rupture risk, especially the absence of wall enhancement, indicating low rupture risk. HR-VWI is increasingly seen as an inflammatory biomarker. Previous studies, such as the review by Lehman VT et al. (30), compared HR-VWI images of different types of aneurysms with conventional MRI images. They concluded that HR-VWI characterizes aneurysm walls in greater in-vivo detail than was previously possible and may complement other forms of luminal imaging. Based on its excellent imaging features for aneurysms and parent arteries, we chose to extract morphological parameters and measure enhancement on HR-VWI images for model construction. Our study conducted qualitative and quantitative analyses of AWE in ruptured intracranial aneurysms (RIAs) and unruptured intracranial aneurysms (UIAs), confirming previous findings (16). The qualitative analysis demonstrated that 78.4% of RIAs exhibited focal or ring-like enhancement compared to 30.0% of UIAs (p < 0.05), suggesting that AWE helps identify ruptured and unstable IAs. However, since focal and ring-like AWE can also occur in UIAs, and qualitative distinction is challenging, quantitative analysis is more helpful in assessing rupture risk. This study used two quantitative measurement methods for AWE assessment: one using the right frontal lobe SI as a reference for WEI and another using pituitary enhancement SI as a reference for CRstalk. Results found that WEI and CRstalk were significantly higher in the ruptured group, with CRstalk identified as an independent risk factor for IA rupture. Compared to WEI, CRstalk measurement is more straightforward, reproducible, and offers higher sensitivity and specificity, making it more suitable for quantitative analysis (16). Furthermore, building on the correlation between parent artery wall enhancement within 3 mm of the aneurysm neck and AWE (11), this study included PAWE in the analyses. It was found that both PWEI and PCRstalk were significantly higher in the ruptured group, with PCRstalk identified as an independent risk factor for IA rupture.
An MLRM incorporating the four identified variables—irregular aneurysm shape, MW, CRstalk, and PCRstalk—achieved an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.814. This model demonstrated superior performance with 91.7% sensitivity, 70.4% specificity, and 76.5% accuracy, notably outperforming the PHASES (AUC = 0.654) and ELAPSS (AUC = 0.642) scores. The visual nomogram derived from this model exhibited strong discrimination and calibration, offering a comprehensive tool for predicting IA rupture and guiding personalized risk management and treatment. Compared to models based on CTA and DSA that utilized multivariable logistic regression and reported AUCs of 0.80 and 0.771 (31–33), respectively, our HR-VWI-based model achieved an AUC of 0.814, indicating enhanced performance in leveraging HR-VWI for aneurysm assessment. However, machine learning and deep learning models from these studies, which integrate clinical, morphological, and radiomic features, reported even higher AUCs, such as 0.878 and 0.929. These discrepancies underscore distinct methodological approaches: while our study emphasizes HR-VWI-specific features, these prior studies highlight the importance of multi-modality integration to enhance predictive accuracy. To advance this field, integrating HR-VWI-based radiomic data into machine learning and deep learning frameworks can leverage the strengths of high-resolution imaging and multi-feature analysis. This integration may offer deeper insights into aneurysm characteristics and enhance clinical applicability. Future research should explore the complementary value of different imaging modalities and analytical techniques to develop more robust and clinically relevant models.
There are areas for improvement in this study. First, long-term follow-up of patients was not conducted, and the dynamic observation of their aneurysm development had a certain impact on the reliability of the results. Second, the dataset used for model training was derived from a single center, which may introduce selection bias. Third, the limited data volume is insufficient to support artificial intelligence modeling. Future research should explore intelligent prediction methods for assessing aneurysm risk using multicenter, big data approaches.
5 Conclusion
This study identified MW, aneurysm shape (irregularity), CRstalk, and PCRstalk as independent risk factors for IA rupture. A visual nomogram based on HR-VWI was developed and outperformed the conventional PHASES and ELAPSS scores. This model provides a valuable tool for non-invasive, non-radiative, comprehensive, and precise assessment of IA rupture risk.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of the Second Hospital of Chongqing Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants' legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
ZW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CY: Data curation, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. WY: Data curation, Supervision, Writing – original draft. SJ: Data curation, Writing – original draft. YJ: Writing – review & editing, Methodology. TC: Writing – review & editing, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81971608), Chongqing medical scientific research project (Joint project of Chongqing Health Commission and Science and Technology Bureau) (2024MSXM044), funding from the Qihang Kuanren Undergraduate Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program at the Second Clinical College of Chongqing Medical University, and Chongqing Natural Science Foundation (Chongqing Science and Technology Development Foundation) Project (2024NSCQ-KJFZZDX0036).
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to the Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University for providing the research facilities and access to the essential datasets used in this study. We also appreciate the support and funding provided by the Qihang Kuanren Undergraduate Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program, which contributed significantly to this research.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Thompson, BG, Jr, BRD, Amin-Hanjani, S, Broderick, JP, Cockroft, KM, Connolly, ES Jr, et al. Guidelines for the Management of Patients with Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. (2015) 46:2368–400. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000070
2. Morris, Z, Whiteley, WN, Jr, LWT, Weber, F, Lee, YC, Tsushima, Y, et al. Incidental findings on brain magnetic resonance imaging: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. (2009) 339:b3016. doi: 10.1136/bmj.b3016
3. Tominari, S, Morita, A, Ishibashi, T, Yamazaki, T, Takao, H, Murayama, Y, et al. Prediction model for 3-year rupture risk of unruptured cerebral aneurysms in Japanese patients. Ann Neurol. (2015) 77:1050–9. doi: 10.1002/ana.24400
4. Sturiale, CL, Stumpo, V, Ricciardi, L, Trevisi, G, Valente, I, D’Arrigo, S, et al. Retrospective application of risk scores to ruptured intracranial aneurysms: would they have predicted the risk of bleeding? Neurosurg Rev. (2021) 44:1655–63. doi: 10.1007/s10143-020-01352-w
5. Molenberg, R, Aalbers, MW, Mazuri, A, Luijckx, GJ, Metzemaekers, JD, Groen, RJ, et al. The Unruptured intracranial aneurysm treatment score as a predictor of aneurysm growth or rupture. Eur J Neurol. (2021) 28:837–43. doi: 10.1111/ene.14636
6. Juvela, S. Treatment scoring of Unruptured intracranial aneurysms. Stroke. (2019) 50:2344–50. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.025599
7. Molenberg, R, Aalbers, MW, Appelman, APA, Uyttenboogaart, M, and van Dijk, JMC. Intracranial aneurysm wall enhancement as an indicator of instability: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Neurol. (2021) 28:3837–48. doi: 10.1111/ene.15046
8. Zhong, W, Su, W, Li, T, Tan, X, Chen, C, Wang, Q, et al. Aneurysm Wall enhancement in Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: a histopathological evaluation. J Am Heart Assoc. (2021) 10:e018633. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.018633
9. Fu, Q, Wang, Y, Zhang, Y, Zhang, Y, Guo, X, Xu, H, et al. Qualitative and Quantitative Wall enhancement on magnetic resonance imaging is associated with symptoms of Unruptured intracranial aneurysms. Stroke. (2021) 52:213–22. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.029685
10. Xu, G, Luo, N, and Deng, Y. Qualitative and quantitative wall enhancement associated with unstable intracranial aneurysms: a meta-analysis. Acta Radiol. (2023) 64:1974–84. doi: 10.1177/02841851221141238
11. Samaniego, EA, Roa, JA, Zhang, H, Koscik, TR, Ortega-Gutierrez, S, Bathla, G, et al. Increased contrast enhancement of the parent vessel of unruptured intracranial aneurysms in 7T MR imaging. J Neurointerv Surg. (2020) 12:1018–22. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2020-015915
12. Greving, JP, Wermer, MJ, Jr, BRD, Morita, A, Juvela, S, Yonekura, M, et al. Development of the PHASES score for prediction of risk of rupture of intracranial aneurysms: a pooled analysis of six prospective cohort studies. Lancet Neurol. (2014) 13:59–66. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70263-1
13. Backes, D, Rinkel, GJE, Greving, JP, Velthuis, BK, Murayama, Y, Takao, H, et al. ELAPSS score for prediction of risk of growth of unruptured intracranial aneurysms. Neurology. (2017) 88:1600–6. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003865
14. Pagano, P, Cortese, J, Soize, S, Caroff, J, Manceau, PF, Moret, J, et al. Aneurysm Treatment with Woven EndoBridge-17: Angiographic and Clinical Results at 12 Months from a Retrospective, 2-Center Series. Am J Neuroradiol. (2023) 44:467–73. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A7830
15. Wang, GX, Wen, L, Lei, S, Ran, Q, Yin, JB, Gong, ZL, et al. Wall enhancement ratio and partial wall enhancement on MRI associated with the rupture of intracranial aneurysms. J Neuro Interven Surg. (2018) 10:566–70. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2017-013308
16. Roa, JA, Zanaty, M, Osorno-Cruz, C, Ishii, D, Bathla, G, Ortega-Gutierrez, S, et al. Objective quantification of contrast enhancement of unruptured intracranial aneurysms: a high-resolution vessel wall imaging validation study. J Neurosurg. (2020) 134:862–9. doi: 10.3171/2019.12.JNS192746
17. Sabotin, RP, Varon, A, Roa, JA, Raghuram, A, Ishii, D, Nino, M, et al. Insights into the pathogenesis of cerebral fusiform aneurysms: high-resolution MRI and computational analysis. J Neurointerven Surg. (2021) 13:1180–6. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2020-017243
18. Peng, F, Fu, M, Xia, J, Niu, H, Liu, L, Feng, X, et al. Quantification of aneurysm wall enhancement in intracranial fusiform aneurysms and related predictors based on high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging: a validation study. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. (2022) 15:17562864221105342. doi: 10.1177/17562864221105342
19. DeLong, ER, DeLong, DM, and Clarke-Pearson, DL. Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics. (1988) 44:837–45. doi: 10.2307/2531595
20. Zhu, X, Shan, Y, Guo, R, Zheng, T, Zhang, X, Liu, Z, et al. Three-dimensional high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of cervical artery dissection. Front Aging Neurosci. (2022) 14:7–8. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.785661
21. Han, M, Rim, NJ, Lee, JS, Kim, SY, and Choi, JW. Feasibility of high-resolution MR imaging for the diagnosis of intracranial vertebrobasilar artery dissection. Eur Radiol. (2014) 24:3017–24. doi: 10.1007/s00330-014-3296-5
22. Xu, WD, Wang, H, Wu, Q, Wen, LL, You, ZQ, Yuan, B, et al. Morphology parameters for rupture in middle cerebral artery mirror aneurysms. J Neurointerv Surg. (2020) 12:858–61. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2019-015620
23. UCAS Japan Investigators. The natural course of unruptured cerebral aneurysms in a Japanese cohort. N Engl J Med. (2012) 366:2474–82. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1113260
24. Roessler, K, Cejna, M, and Zachenhofer, I. Aneurysmatic subarachnoidal haemorrhage: incidence and location of small ruptured cerebral aneurysms - a retrospective population-based study. Wien Klin Wochenschr. (2011) 123:444–9. doi: 10.1007/s00508-011-1598-z
25. Bjorkman, J, Frosen, J, Tahtinen, O, Backes, D, Huttunen, T, Harju, J, et al. Irregular shape identifies ruptured intracranial aneurysm in subarachnoid hemorrhage patients with multiple aneurysms. Stroke. (2017) 48:1986–9. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.017147
26. Maslehaty, H, Capone, C, Frantsev, R, Fischer, I, Jabbarli, R, Cornelius, JF, et al. Predictive anatomical factors for rupture in middle cerebral artery mirror bifurcation aneurysms. J Neurosurg. (2018) 128:1799–807. doi: 10.3171/2017.2.JNS162705
27. Koopman, I, Greving, JP, van der Schaaf, IC, van der Zwan, A, Rinkel, GJ, and Vergouwen, MD. Aneurysm characteristics and risk of rebleeding after subarachnoid haemorrhage. Eur Stroke J. (2019) 4:153–9. doi: 10.1177/2396987318803502
28. Futami, K, Uno, T, Misaki, K, Tamai, S, Nambu, I, Uchiyama, N, et al. Identification of Vortex cores in cerebral aneurysms on 4D flow MRI[J]. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. (2019) 40:2111–6. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A6322
29. Samaniego, EA, Roa, JA, and Hasan, D. Vessel wall imaging in intracranial aneurysms. J Neurointerven Surg. (2019) 11:1105–12. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2019-014938
30. Lehman, VT, Brinjikji, W, Mossa-Basha, M, Lanzino, G, Rabinstein, AA, Kallmes, DF, et al. Conventional and high-resolution vessel wall MRI of intracranial aneurysms: current concepts and new horizons. J Neurosurg. (2018) 128:969–81. doi: 10.3171/2016.12.JNS162262
31. Turhon, M, Li, M, Kang, H, Huang, J, Zhang, F, Zhang, Y, et al. Development and validation of a deep learning model for prediction of intracranial aneurysm rupture risk based on multi-omics factor. Eur Radiol. (2023) 33:6759–70. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-09672-3
32. Shi, Z, Chen, GZ, Mao, L, Li, XL, Zhou, CS, Xia, S, et al. Machine learning–based prediction of small intracranial aneurysm rupture status using CTA-derived hemodynamics: a multicenter study. Am J Neuroradiol. (2021) 42:648–54. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A7034
33. Chen, Y, Xing, H, Lin, B, Zhou, J, Ding, S, and Wan, J. Morphological risk model assessing anterior communicating artery aneurysm rupture: development and validation. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. (2020) 197:106158. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.106158
Glossary
AR - Aspect ratio
AUC - Area under curve
AWE - Aneurysm wall enhancement
AWT - Aneurysm wall thickness
CE-HR-VWI - Contrast-enhanced high-resolution vessel wall imaging
CI - Confidence interval
CRstalk - Contrast ratio of the aneurysm wall against the pituitary stalk
DCA - Decision curve analysis
FOV - Field of view
HR-VWI - High-resolution vessel wall imaging
IAs - Intracranial aneurysms
ICC - Intraclass correlation coeffcient
MH - Maximum height
MLRM - Multivariate logistic regression model
MW - Maximum width
NPR - Neck-to-parent ratio
NW - Neck width
PAD - Parent artery diameter
PCRstalk - Contrast ratio of the parent artery wall against the pituitary stalk
PAWT - Parent artery wall thickness
PWEI - Parent artery wall enhancement index
ROC - Receiver operating characteristic
ROI - Region of interest
SAH - Subarachnoid hemorrhage
SI - Signal intensitySR - Size ratio
TOF - Time-of-flight
VISTA - Volume isotropic turbo spin echo acquisition
WEI - Wall enhancement index
Keywords: intracranial aneurysm, parent artery, HR-VWI, PHASES score, ELAPSS score
Citation: Wang Z, Yan C, Yuan W, Jiang S, Jiang Y and Chen T (2025) Enhancing intracranial aneurysm rupture risk prediction with a novel multivariable logistic regression model incorporating high-resolution vessel wall imaging. Front. Neurol. 15:1507082. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1507082
Edited by:
Vishal K. Chavda, Sardar Hospital, IndiaReviewed by:
Majed Katati, University of Granada, SpainMaimaitili Aisha, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Yan, Yuan, Jiang, Jiang and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yongxiang Jiang, ZG9jdG9yamlhbmcyMDAzQDE2My5jb20=; Ting Chen, Y3QyMDIwMDIwMkBob3NwaXRhbC5jcW11LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Zihang Wang
Zihang Wang Chang Yan
Chang Yan Wenqing Yuan
Wenqing Yuan Shuangyan Jiang
Shuangyan Jiang Yongxiang Jiang
Yongxiang Jiang Ting Chen
Ting Chen