- 1School of Physical Education and Sports Science, South China Normal University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
- 2School of Health and Kinesiology, Georgia Southern University, Statesboro, CA, United States
- 3Physical Education Department, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
Background: This study aims to evaluate the optimal rehabilitation regimen for lower limb dysfunction in stroke patients by analyzing the effects of proprioceptive training (PT) in combination with different rehabilitation interventions.
Methods: Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published up to April 23, 2024, were searched from PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, CNKI, Wanfang, VIP, and SinoMed. The quality of the included studies was assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool (ROB 2.0). Network meta-analysis was performed via R studio and STATA 15.0.
Results: A total of 64 RCTs involving 4,084 stroke patients with lower limb dysfunction were included. For balance ability in stroke patients, PT in combination with motor relearning programme (PT + MRP) demonstrated the optimal rehabilitation effect [surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) 77.94%]. For lower limb motor function, PT in combination with closed kinematic chain exercises (PT + CKCE) was most effective (SUCRA 88.39%). For walking ability, PT in combination with visual feedback training (PT + VFT) was superior (SUCRA 96.61%). Cluster analysis indicated that PT + CKCE and PT + RT1 were the optimal rehabilitation regimens for lower limb dysfunction in stroke patients.
Conclusion: PT+MRP was the optimal rehabilitation regimen for improving balance ability in stroke patients; PT+CKCE was the best for enhancing lower limb motor function; and PT+VFT was most effective for improving walking ability. Overall, PT+CKCE and PT+RT1 represented the optimal rehabilitation regimens for lower limb dysfunction in stroke patients, while PT+RT1 is most effective within 5 days of stroke onset.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/#recordDetailsCRD42024548889, PROSPERO CRD42024548889.
1 Introduction
Among adults worldwide, stroke ranks third in terms of disability and is the second most common cause of death (1). The high incidence, disability rate, recurrence rate, and mortality associated with stroke have increasingly become a concerning global social issue. Among stroke survivors, lower limb hemiplegia is a common post-stroke sequela, which is clinically manifested by stiffness, contracture, and pain in the affected limb (2). This sequela often leads to decreased muscle strength, restricted joint mobility, balance disorders, abnormal gait, and other lower limb dysfunctions in patients during daily work and life (3), causing significant physical and psychological distress. Given the substantial harm that stroke causes to society and individuals, the rehabilitation of lower limb dysfunction following stroke is crucial.
Current research indicates that rehabilitation measures such as acupuncture, electrical stimulation, core stability training, and proprioceptive training (PT) are commonly used for lower limb rehabilitation in stroke patients in clinical practice (4–7) PT has been reported to have particularly outstanding therapeutic effects (8). Proprioception is the sense of the movement and position of the body and limbs in space (9). PT is an exercise method for improving the body's proprioceptive functions, such as muscle sensation, postural balance, and joint stability (8). It is a complex neuromuscular process involving the internal awareness of body posture and movement (10). Studies have shown that at least 30% of stroke patients experience proprioceptive deficits, which are negatively correlated with limb function, motor ability, and independence in daily life (11). This explains why PT achieves superior efficacy in treating post-stroke lower limb dysfunction compared to other rehabilitation interventions. Various clinical studies have also confirmed that PT can enhance lower limb proprioception in stroke patients and promote the recovery of lower limb function. For example, Chae et al. (7) found that stroke patients who received PT as a therapeutic measure exhibited better recovery in balance and walking function compared to those who underwent conventional rehabilitation. Similarly, a study by Mao et al. (12) demonstrated that PT was superior to conventional rehabilitation therapy in restoring lower limb motor function in stroke patients. Over the past two decades, using PT to treat lower limb dysfunction in stroke patients has matured and achieved favorable outcomes in clinical practice.
To further mitigate the impact of lower limb dysfunction in stroke patients, clinicians have combined PT with other commonly used rehabilitation interventions for stroke-induced lower limb dysfunction, aiming to achieve better therapeutic results. For instance, Shim et al. (13) found that combining PT with electrical stimulation therapy was more effective in the rehabilitation of balance and gait abilities in stroke patients than PT alone. Additionally, the study by Kim and Kim (14) showed that combining thermotherapy with PT significantly outperformed traditional rehabilitation therapies in improving balance and gait abilities in stroke patients. These combination therapies, involving PT and other rehabilitation interventions, are generally more efficacious in the rehabilitation of lower limb dysfunction caused by stroke compared to either PT or conventional rehabilitation alone. However, there are currently no studies comparing the efficacy of PT in combination with other rehabilitation interventions.
Unlike standard meta-analyses that compare two therapies directly, network meta-analysis (NMA) can integrate direct, indirect, and mixed comparisons of data, allowing for the ranking of several therapies according to their efficacy (15). This study employed NMA to compare the efficacy of PT, conventional rehabilitation therapy, and PT in combination with other rehabilitation interventions in the recovery of lower limb function after stroke, so as to identify the optimal rehabilitation regimen and provide guidance for clinical practice.
2 Methods
This NMA was conducted as per the guidelines outlined in the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) 2020 statement and the procedures detailed in the Cochrane Handbook (16). The protocol for this systematic review has been registered on the PROSPERO under registration ID CRD42024548889.
2.1 Search strategy
Eight electronic databases were searched thoroughly, including CNKI, VIP, Wanfang, SinoMed, PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science. In addition to the conventional English databases including PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science, we included four Chinese databases: CNKI, VIP, Wanfang, and SinoMed, to enhance the comprehensiveness of our literature search. The time period for the search was set as of April 23, 2024. To meet the requirements of each database, various search strategies were used. The comprehensive search techniques are given in Supplementary Table S1. This search strategy has certain limitations, such as excluding literature in languages other than Chinese and English and not excluding older studies.
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) Participants: Stroke patients with lower limb dysfunction at any stage and time of onset, regardless of gender, race, or nationality. (2) Interventions: PT alone or PT in combination with other rehabilitation interventions. (3) Control group: PT alone or conventional rehabilitation therapy. (4) Outcome measures: The outcome measures included the Berg Balance Scale (BBS), Fugl-Meyer Assessment-lower extremity (FMA-LE), and Timed Up-and-Go Test (TUGT). The BBS scale is used to assess the balance ability of stroke patients, with higher scores indicating better balance; the FMA-LE scale is used to evaluate lower limb motor function in stroke patients, with higher scores indicating better motor function; the TUGT is used to measure the walking ability of stroke patients, with shorter test times indicating better walking ability. (5) Study design: Only peer-reviewed randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with available and detailed data were included.
The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) Reviews, meta-analyses, conference papers, replies, letters, guidelines, case reports, and animal experiments. (2) Studies with inaccessible full text. (3) Other reasons, including articles with inaccessible original data, incomplete data, or erroneous data.
2.3 Literature screening and data extraction
Studies were imported into EndNote X9 for literature screening. Two independent reviewers removed duplicates, and reviewed titles and abstracts. Based on inclusion and exclusion criteria, irrelevant studies were excluded. Then, the full texts of the remaining studies were checked to eliminate ineligible studies. In cases of disagreement, the two reviewers discussed or consulted with a third researcher. The primary data extracted from the studies included basic information on the articles (author, year of publication, country), patient information (age, sample size, disease course), intervention (interventions in the experimental and control groups), and outcome measures.
2.4 Quality assessment
The quality of the included studies was assessed by two researchers using the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool (ROB 2.0). The studies were categorized into “low risk,” “moderate risk,” or “high risk.” Any discrepancies in the assessment results were resolved through discussion with a third researcher.
The researchers evaluated the risk of bias in the studies based on the following five aspects: (1) bias arising from the randomization process, (2) bias due to deviations from intended interventions, (3) bias due to missing outcome data, (4) bias in outcome measurement, and (5) bias in selective reporting of outcomes.
2.5 Data analysis
Bayesian NMA was conducted by using the software, R Studio. Data preprocessing was performed using the “gemtc” package in Stata 15, which also plotted the network of relationships among the interventions. Data from the final included RCTs were analyzed using the “gemtc” and “coda” packages in R Studio 4.2.1. Using 50,000 sampling iterations and 20,000 burn-in iterations, a consistency model was built. The data were considered consistent if there was a difference of < 5 between the deviance information criterion (DIC) obtained from the iteration results and the DIC of the inconsistency model, suggesting that there was no substantial difference between the NMA results and the direct comparisons. The efficacy of various interventions was ranked using the surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA). To investigate the optimal intervention, a two-dimensional hierarchical clustering analysis was used, and publication bias for each outcome measure was evaluated.
3 Results
3.1 Search results
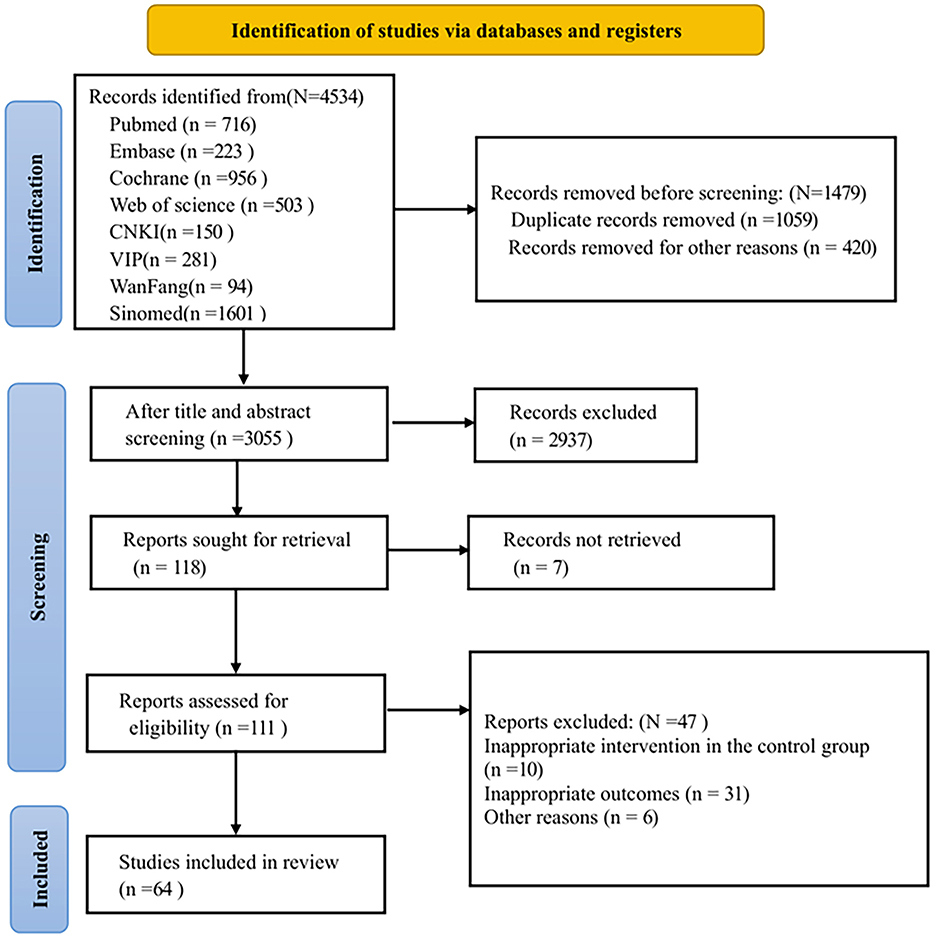
Initially, 4,534 records were searched based on the search strategy. After removing 1,059 duplicates, 420 records were excluded as reviews, animal experiments, non-RCTs, or conference papers, leaving 3,055 records. After screening titles and abstracts, 2,937 records were excluded. One hundred and eighteen articles were left for full-text review. Among these, the full texts of seven articles were not available; 10 articles had inappropriate control group interventions; 31 articles had inappropriate outcome measures, and six articles were excluded for other reasons. Ultimately, 64 RCTs (3, 7, 12–14, 17–75) were included in this study, all of which were published. Figure 1 shows the flow chart for the literature screening process in the study.
3.2 Characteristics of included studies
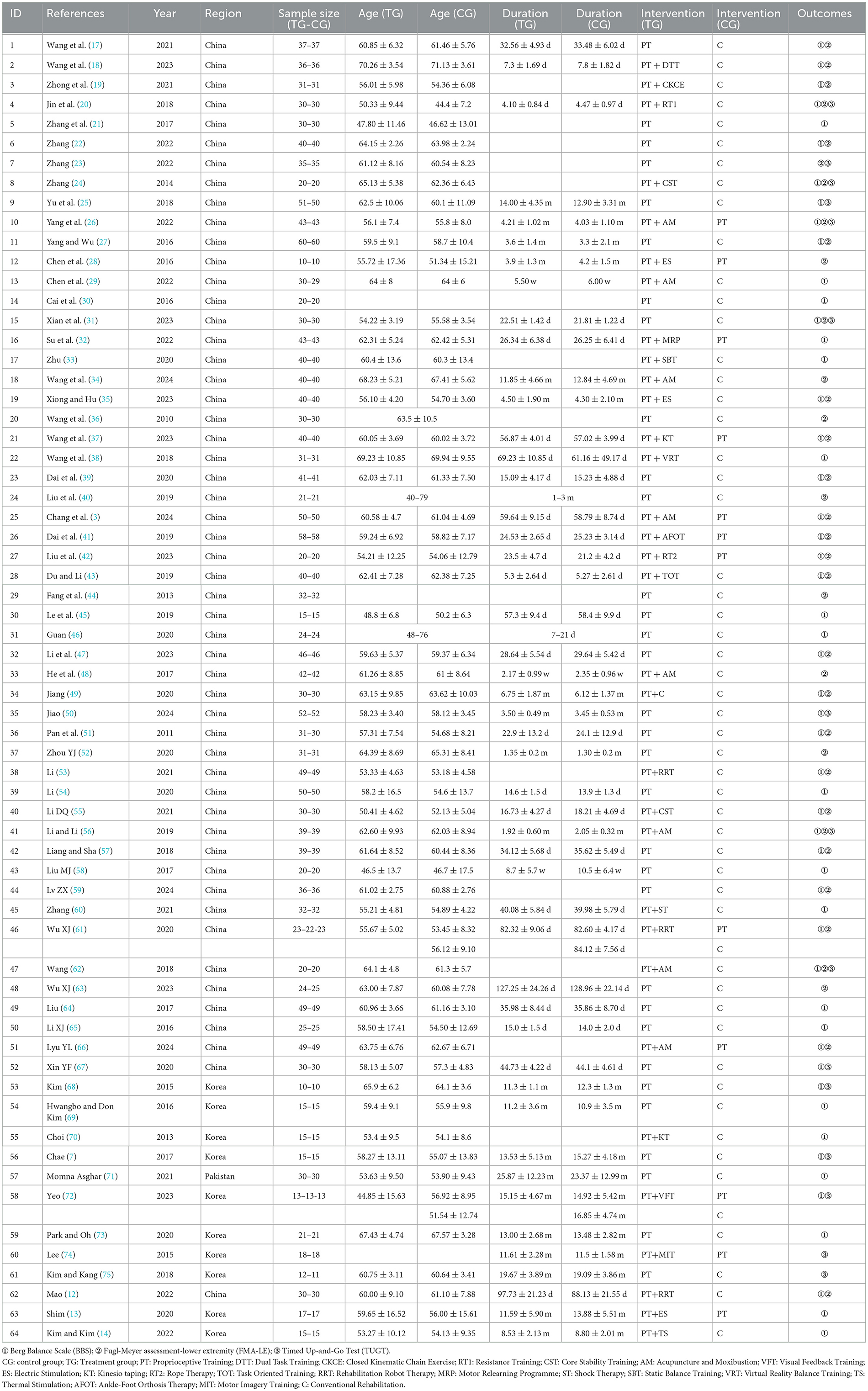
All 64 included studies were RCTs, involving a total of 4,084 stroke patients and 20 interventions. In the experimental groups, in addition to PT, there were 18 combined rehabilitation interventions. These 18 combined interventions were as follows: PT + dual-task training (PT + DTT), PT + closed kinematic chain exercises (PT + CKCE), PT + resistance training (PT + RT1), PT + core stability training (PT + CST), PT + acupuncture and moxibustion (PT + AM), PT + visual feedback training (PT + VFT), PT + electrical stimulation (PT + ES), PT + kinesio taping (PT + KT), PT + rope therapy (PT + RT2), PT + task-oriented training (PT + TOT), PT + robotic rehabilitation therapy (PT + RRT), PT + motor relearning programme (PT + MRP), PT + shock therapy (PT + ST), PT + static balance training (PT + SBT), PT + virtual reality training (PT + VRT), PT + thermal stimulation (PT + TS), PT + motor imagery training (PT + MIT), and PT + ankle-foot orthosis treatment (PT + AFOT). The basic characteristics of the included studies are detailed in Table 1.
3.3 Quality evaluation of included studies
Forty-one studies (3, 12, 17–19, 22–24, 26, 28, 31–37, 39, 40, 42, 43, 45, 47–50, 53, 55, 56, 58–61, 63–68, 71, 73) had a low risk of bias; 22 studies (7, 13, 14, 20, 21, 25, 27, 29, 30, 38, 41, 46, 51, 52, 54, 57, 62, 69, 70, 72, 74, 75) had a moderate risk of bias; and one study (44) had a high risk of bias. In terms of the randomization, 22 studies had a moderate risk of bias and 42 studies had a low risk of bias. In terms of whether the intervention measures deviated from the expected, one study had a moderate risk of bias and 63 studies had a low risk of bias. For missing result data, one study had a moderate risk of bias and 63 studies had a low risk of bias. In terms of outcome measurement, 64 studies had a low risk of bias. In terms of selective reporting, 64 studies had a low risk of bias. In summary, the moderate risk of bias in the randomization domain was the main source of bias in the included studies. The risk of bias of the included studies is depicted in Figure 2.
3.4 Network meta-analysis
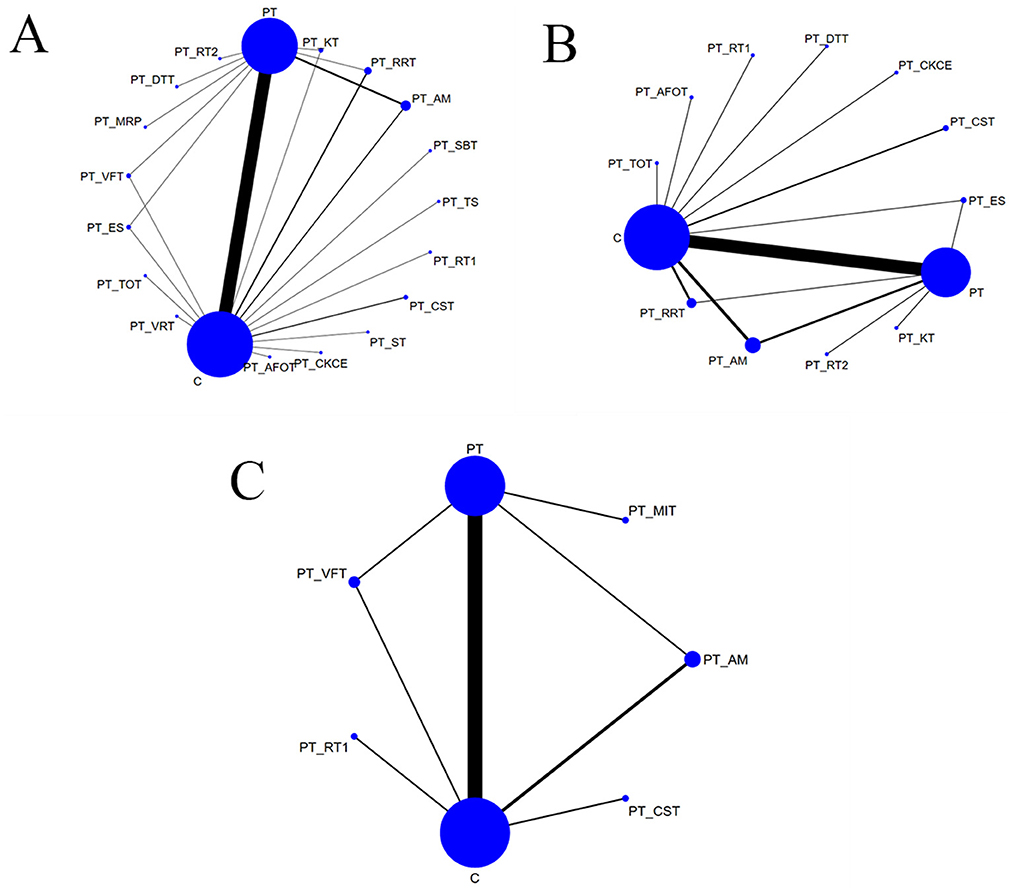
The network diagrams corresponding to the three outcome measures are shown in Figure 3. The size of each node was directly proportional to the sample size involved in each intervention, and the thickness of the lines between nodes represented the number of studies comparing the interventions connected by the lines. Larger nodes indicate a greater sample size, while thicker lines represent a higher number of studies.
3.4.1 Berg Balance Scale
A total of 53 studies (3, 7, 12–14, 17–22, 24–27, 29–33, 35, 37–39, 41–43, 45–47, 49–51, 53–62, 64–73) reported BBS scores, involving 19 rehabilitation interventions: C (conventional rehabilitation), PT (proprioceptive training), PT + DTT (dual-task training), PT + RT1 (resistance training), PT + CST (core stability training), PT + AM (acupuncture and moxibustion), PT + MRP (motor relearning programme), PT + SBT (static balance training), PT + ES (electrical stimulation), PT + KT (kinesio taping), PT + VRT (virtual reality training), PT + RT2 (rope therapy), PT + TOT (task-oriented training), PT + RRT (robotic rehabilitation therapy), PT + ST (shock therapy), PT + VFT (visual feedback training), PT + TS (thermal stimulation), and PT + AFOT (ankle-foot orthosis treatment), PT + CKCE (closed kinematic chain exercises). Direct comparisons were conducted between PT + VFT, PT + AM, PT + KT, PT + RRT, PT + ES and PT as well as C. Additionally, PT was directly compared with PT + MRP, PT + DTT, PT + RT2, and C, while C was directly compared with PT + TOT, PT + VRT, PT + SBT, PT + TS, PT + RT1, PT + CST, PT + ST, PT + CKCE, PT + AFOT, and PT. The results are provided in Figure 3A.
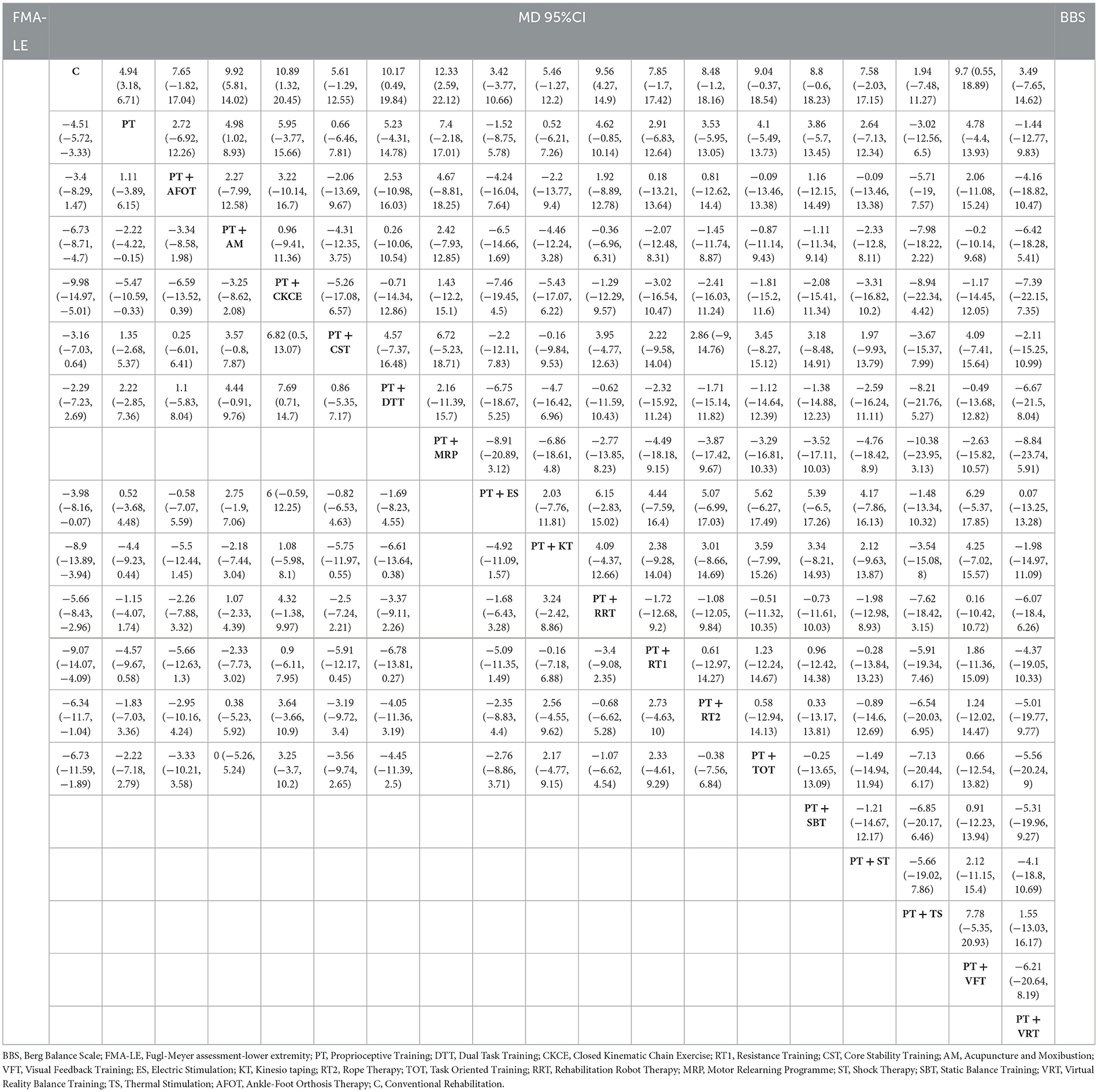
The league table for BBS is shown in the upper right part of Table 2. The data in the league table were derived from pairwise comparisons between various interventions. In terms of improving BBS scores, the following interventions were found to be more effective than the control (C): PT (MD = 4.94, 95% CI: 3.18–6.71), PT + AM (MD = 9.92, 95% CI: 5.81–14.02), PT + CKCE (MD = 10.89, 95% CI: 1.32–20.45), PT + DTT (MD = 10.17, 95% CI: 0.49–19.84), PT + MRP (MD = 12.33, 95% CI: 2.59–22.12), PT + RRT (MD = 9.56, 95% CI: 4.27–14.9), and PT + VFT (MD = 9.7, 95% CI: 0.55–18.89). Additionally, PT + AM (MD = 4.98, 95% CI: 1.02–8.93) was more effective than PT alone, with all differences being statistically significant (P < 0.05).
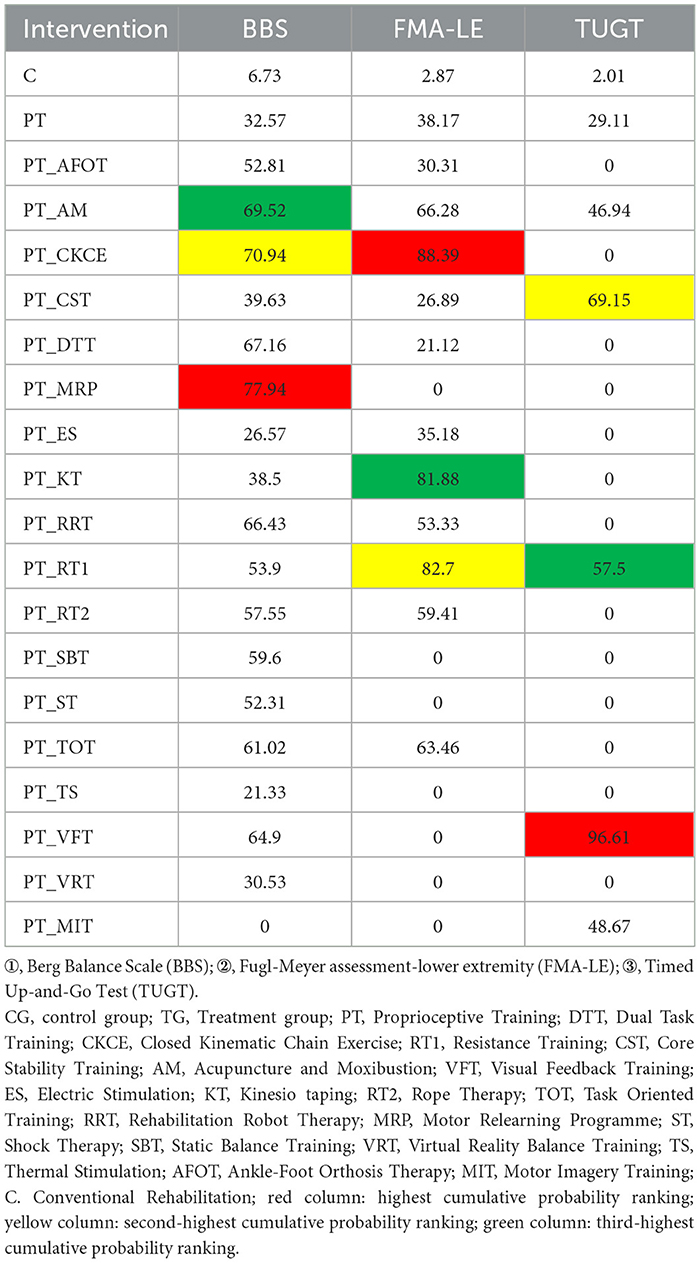
The cumulative probability ranking for BBS is shown in Table 4. After comparing all interventions, the cumulative probability ranking was calculated to determine the effectiveness of each intervention, thereby identifying the optimal intervention. According to the SUCRA ranking, the top three optimal interventions were PT+MRP (77.94%), PT + CKCE (70.94%), and PT + AM (69.52%). The cumulative probability curve for BBS is shown in Figure 4A. PT + MRP was identified as the optimal treatment regimen for improving lower limb balance in stroke patients.
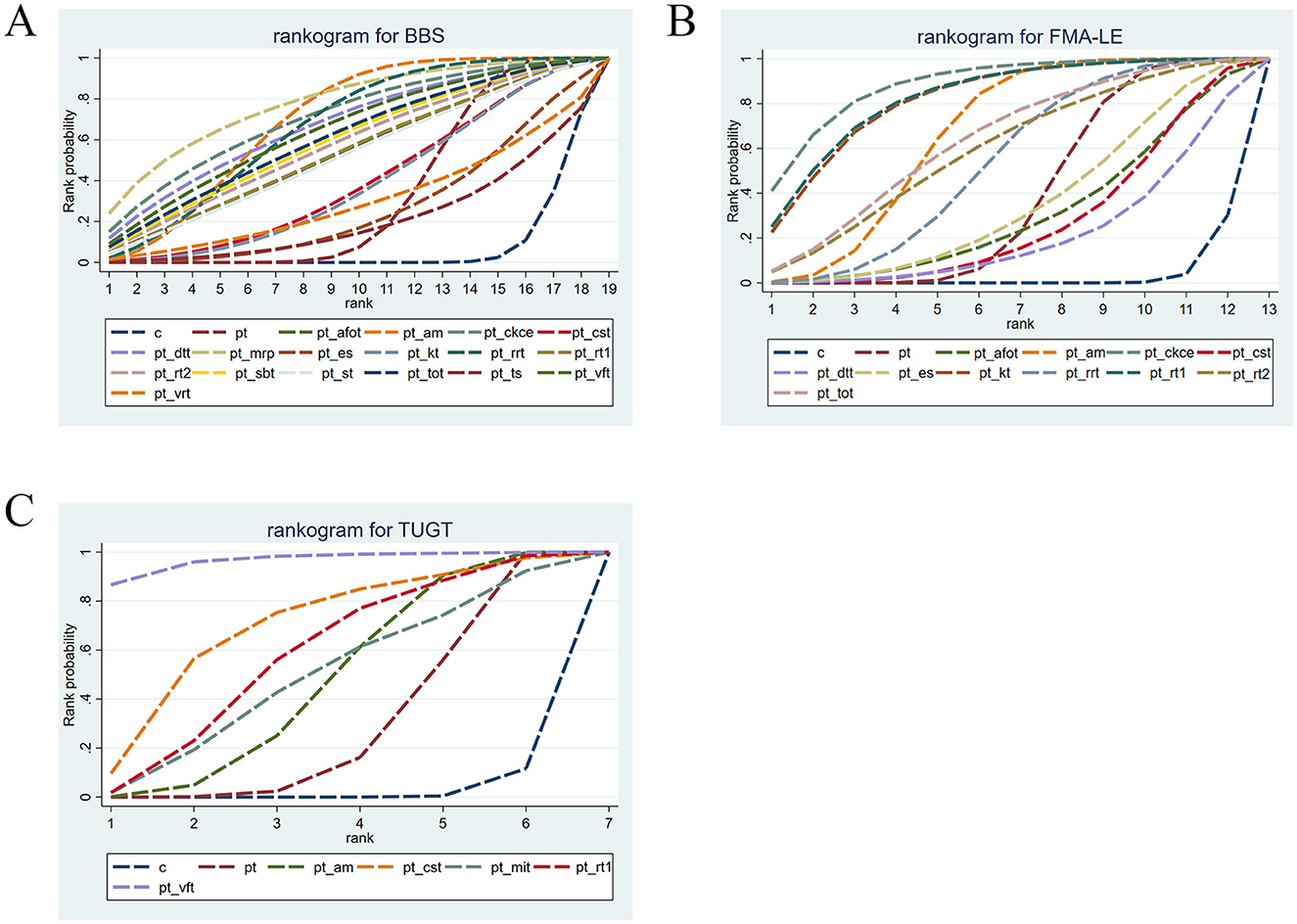
Figure 4. (A) Cumulative probability ranking of BBS; (B) cumulative probability ranking of FMA-LE; (C) cumulative probability ranking of TUGT.
3.4.2 Fugl-Meyer Assessment for Lower Extremity
A total of 37 studies (3, 12, 17–20, 22–24, 26–28, 31, 34–37, 39–44, 47–49, 51–53, 55–57, 59, 61–63, 66) reported FMA-LE scores, involving 13 rehabilitation interventions: C (conventional rehabilitation), PT (proprioceptive training), PT + DTT (dual-task training), PT + CKCE (closed kinematic chain exercises), PT + RT1 (resistance training), PT + CST (core stability training), PT + AM (acupuncture and moxibustion), PT + ES (electrical stimulation), PT + KT (kinesio taping), PT + RT2 (rope therapy), PT + TOT(task-oriented training), PT + RRT (robotic rehabilitation therapy), and PT + AFOT (ankle-foot orthosis treatment). Direct comparisons were made between PT + ES, PT + AM, PT + RRT, and PT as well as C. PT was also directly compared with PT + RT2, PT + KT, and C, while C was directly compared with PT + CKCE, PT + CST, PT + DTT, PT + RT1, PT + AFOT, PT + TOT, and PT. The results are shown in Figure 3B.
The league table for FMA-LE is shown in the lower left part of Table 2. In terms of improving FMA-LE scores, the following interventions were found to be more effective than the control (C): PT (MD = 4.51, 95% CI: 3.33–5.72), PT + AM (MD = 6.73, 95% CI: 4.7–8.71), PT + CKCE (MD = 9.98, 95% CI: 5.01–14.97), PT + ES (MD = 3.98, 95% CI: 0.07–8.16), PT + KT (MD = 8.9, 95% CI: 3.94–13.89), PT + RRT (MD = 5.66, 95% CI: 2.96–8.43), PT + RT1 (MD = 9.07, 95% CI: 4.09–14.07), PT + RT2 (MD = 6.34, 95% CI: 1.04–11.7), and PT + TOT (MD = 6.73, 95% CI: 1.89–11.59). Additionally, PT + AM (MD = 2.22, 95% CI: 0.15–4.22) and PT + CKCE (MD = 5.47, 95% CI: 0.33–10.59) were more effective than PT alone, while PT + CKCE was more effective than PT + CST (MD = −6.82, 95% CI: −13.07 to −0.5) and PT + DTT (MD = −7.69, 95% CI: −14.7 to −0.71), with all differences being statistically significant (P < 0.05).
The cumulative probability ranking for FMA-LE is shown in Table 4. According to the SUCRA ranking, the top three optimal interventions were PT + CKCE (88.39%), PT + RT1 (82.7%), and PT + KT (81.88%). The cumulative probability curve for FMA-LE is shown in Figure 4B. PT + CKCE was identified as the optimal treatment regimen for improving lower limb motor function in stroke patients.
3.4.3 Timed Up and Go Test
A total of 15 studies (7, 20, 23–26, 31, 50, 56, 62, 67, 68, 72, 74, 75) reported TUGT times, involving seven rehabilitation interventions: C (conventional rehabilitation), PT (proprioceptive training), PT + RT1 (resistance training), PT + CST (core stability training), PT + AM (acupuncture and moxibustion), PT + VFT (visual feedback training), and PT + MIT (motor imagery training). Direct comparisons were made between PT + VFT, PT + AM and PT as well as C. Additionally, PT was directly compared with PT + MIT, while C was directly compared with PT + CST and PT + RT1. The results are shown in Figure 3C.
The league table for TUGT is shown in Table 3. In terms of reducing TUGT time, the following interventions were found to be more effective than the control (C): PT (MD = −3.07, 95% CI: −4.32 to −1.78), PT + AM (MD = −4.29, 95% CI: −7 to −1.75), PT + CST (MD = −7.73, 95% CI: −15.45 to 0), PT + RT1 (MD = −5.63, 95% CI: −10.47 to −0.55), and PT + VFT (MD = −15.54, 95% CI: −25.1 to −5.86). However, PT alone (MD = −12.47, 95% CI: −22.07 to −2.8) and PT + AM (MD = −11.22, 95% CI: −21.12 to −1.17) were less effective than PT + VFT, with all differences being statistically significant (P < 0.05).
The cumulative probability ranking for TUGT is shown in Table 4. Based on the SUCRA ranking for reducing TUGT time, the top three optimal interventions were PT + VFT (96.61%), PT + CST (69.15%), and PT + RT1 (57.5%). The cumulative probability curve for TUGT is shown in Figure 4C. PT + VFT was identified as one of the optimal treatments for improving walking ability in stroke patients.
3.5 Cluster analysis
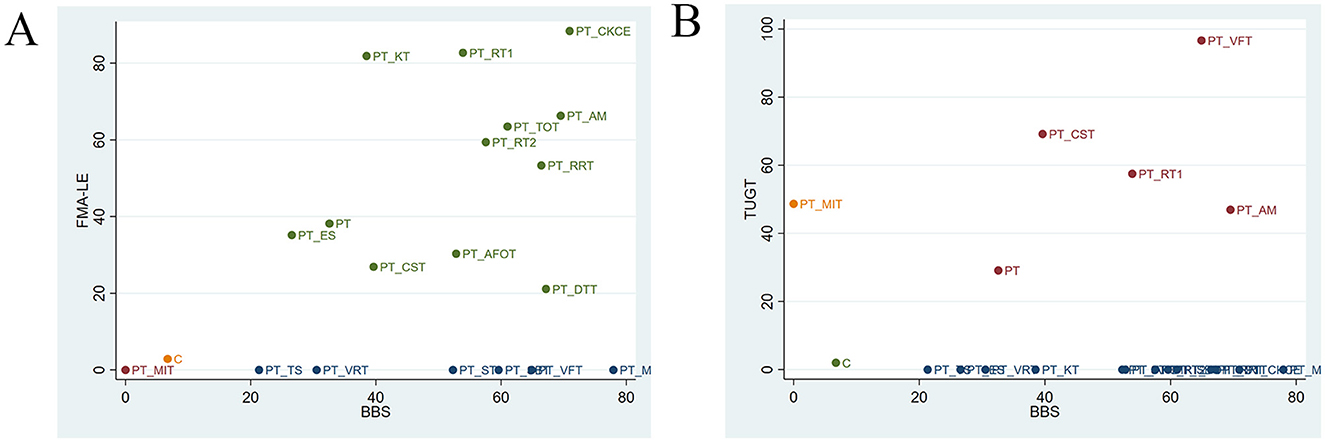
The cluster analysis is shown in Figure 5. The most effective interventions for improving balance and lower limb motor function in stroke patients were identified to be PT + CKCE (70.94%/88.39%), PT + RT1 (53.9%/82.7%), and PT + AM (69.52%/66.28%), as shown in Figure 5A; PT + VFT (64.9%/96.61%) and PT + RT1 (53.9%/57.5%) were identified to be particularly effective in enhancing balance and walking function in stroke patients, as shown in Figure 5B. PT + CKCE exhibited the best therapeutic effect on balance and lower limb motor function in stroke patients; PT + RT1 demonstrated good efficacy in improving balance, lower limb motor function, and walking ability; PT + VFT, while being the best option for improving balance and walking ability in stroke patients, is less effective in enhancing balance compared to PT + RRT, PT + CKCE, PT + AM, PT + MRP, and PT + DTT. Therefore, the choice of PT + VFT should be made cautiously based on the patient's specific condition. Overall, PT + CKCE and PT + RT1 were identified as the two most effective rehabilitation interventions for treating lower limb dysfunction in stroke patients.
3.6 Publication bias
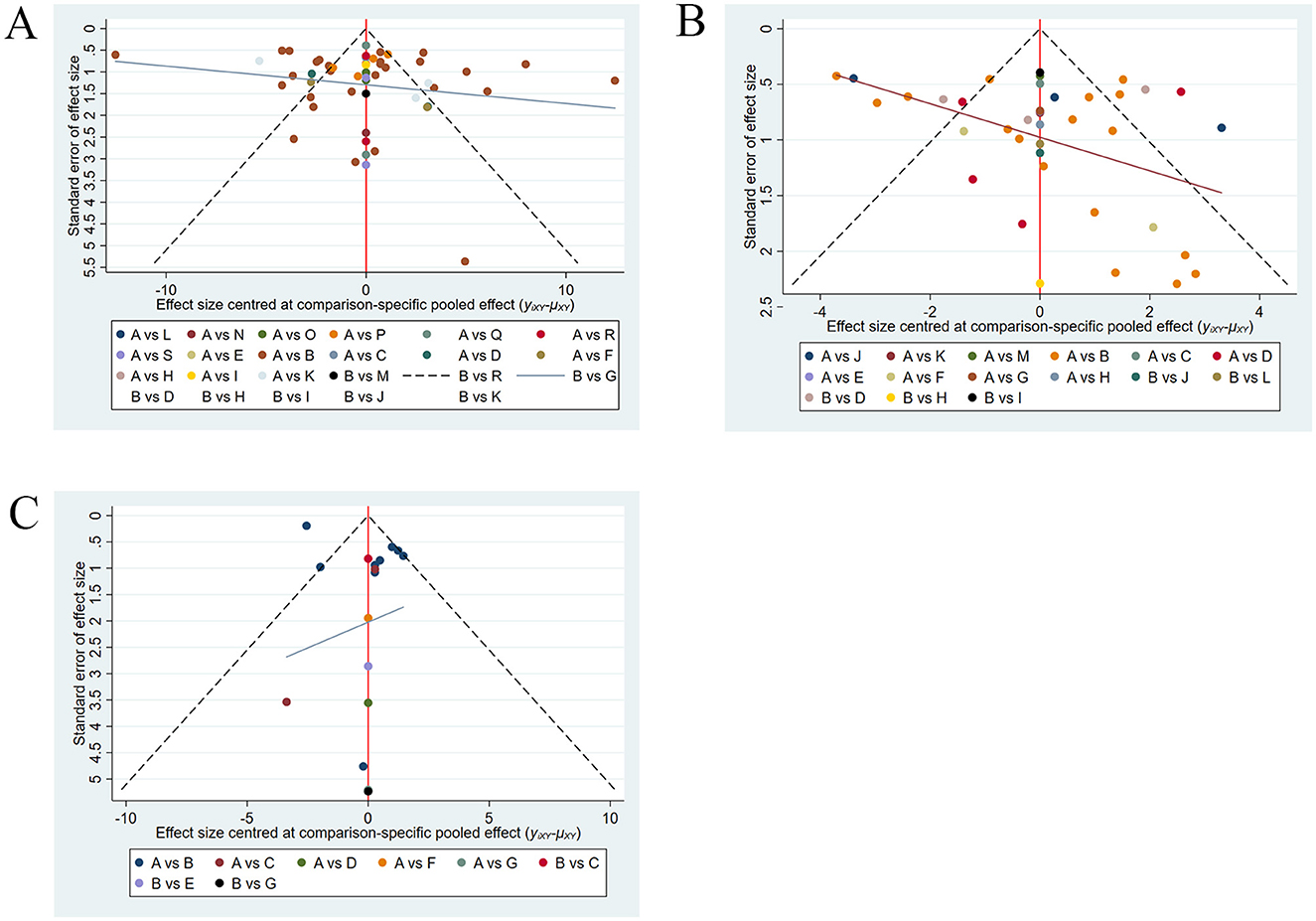
As shown in Figure 6, publication bias was assessed for BBS, FMA-LE, and TUGT. The funnel plots for FMA-LE and TUGT were generally symmetrical, with only a few points falling outside the funnel and a relatively large angle between the reference line and the X-axis, suggesting minimal publication bias for these two outcome measures. The funnel plot for BBS was overall symmetrical, with some points falling outside the funnel and a relatively small angle between the reference line and the X-axis, suggesting possible publication bias for BBS.
4 Discussion
This NMA included 64 RCTs involving 4,084 stroke patients with lower limb dysfunction. Study findings indicated that the optimal intervention for improving BBS scores in stroke patients was PT + motor relearning programme; for FMA-LE scores, PT + closed kinematic chain exercises was the most effective; and for TUGT scores, PT + visual feedback training was the optimal intervention. Overall, PT + closed kinematic chain exercises and PT + resistance training were identified as the two most effective rehabilitation interventions for treating lower limb dysfunction in stroke patients.
BBS score is reflective of the balance ability of stroke patients. The optimal rehabilitation intervention for restoring lower limb balance function in stroke patients was identified to be PT + motor relearning programme. Proprioception helps the body perceive spatial positions, and PT improves neuromuscular control, enhancing postural stability and balance ability (76). In recent years, motor relearning programme has gained significant attention from clinical rehabilitation therapists. This method, proposed by Australian physiotherapists, is a movement therapy based on the neuroplasticity of the central nervous system. It underscores the importance of early rehabilitation in patients with functional impairments, encouraging active patient participation and repetitive training. Under the guidance of professional therapists, it aims to restore the lost lower limb function in stroke patients as early as possible (77). The rehabilitative effect of motor relearning programme on balance function in stroke patients is grounded in the theoretical basis of balance function reorganization following central nervous system injury. This method views the restoration of balance function as a task-oriented process, emphasizing active patient participation and the integration of balance tasks into real-life environments. It focuses on functionality and practicality, re-educating and retraining patients to continuously correct faulty movements and address deficiencies, thereby facilitating the early recovery of balance function (78). Implementing motor relearning programme based on PT is more conducive to promoting the reshaping of the central nervous system in patients with lower limb dysfunction, thereby more efficiently enhancing the recovery of their balance abilities.
FMA-LE score is reflective of the lower limb motor function of stroke patients. The optimal rehabilitation intervention for restoring lower limb motor function in stroke patients was identified to be PT + closed kinematic chain exercises. The recovery of lower limb motor function in stroke patients requires both the enhancement of lower limb muscle strength and the strengthening of proprioceptive input. Therefore, it is evident that PT is an effective method to improve proprioception in the affected limb and promote the recovery of lower limb motor function (12). Closed kinematic chain exercises is a commonly used rehabilitation training method characterized by specific movements with the distal part of the body fixed (79). This method has been proven to enhance lower limb motor function in stroke patients with hemiplegia (80). On one hand, closed kinematic chain exercises involves coordinated linear movements of the three major joints, aligning with the principle of neural development from the hip to the foot. The closed-chain model drives repetitive flexion and extension of the joints, requiring the recruitment of more motor neuron signals for simultaneous contraction of agonist and antagonist muscles. This approach is beneficial for improving muscle strength in the affected limb and enhancing coordination between muscles. On the other hand, post-stroke motor dysfunction is associated with reduced proprioceptive input. Closed kinematic chain exercises, through repetitive training of the three major joints, stimulates joint and position sense, creating conditions for the recovery of lower limb proprioception, and enhances neuromuscular control of the lower limb (81, 82). Closed kinematic chain exercises can effectively improve muscle strength in the affected limb of stroke patients, and when combined with PT for the restoration of proprioception, it can lead to better neuromuscular control of the lower limb. This mechanism is likely the reason why PT+ closed kinematic chain exercises is more effective in improving lower limb motor function in stroke patients.
TUGT score is reflective of the walking ability of stroke patients. The optimal rehabilitation intervention for restoring walking ability in stroke patients was identified to be PT+ visual feedback training. Research has shown that PT is an effective method for enhancing walking ability in stroke patients. The key to improving gait through PT lies in enhancing control of the trunk, pelvis, and lower limbs. During the stance phase, therapists apply compression to the patient's pelvis, and during the swing phase, they utilize traction reflexes on the pelvis. This approach promotes coordinated muscle movement between the lower limbs and trunk, thereby improving the patient's walking ability (42). A study by Yeo et al. (72) suggested that the combination of visual feedback training and PT improves postural stability, thereby enhancing gait kinematic variables. Research has pointed out that the prerequisite for maintaining postural stability is the normal functioning of sensory systems such as proprioception, the visual system, and the vestibular organs. A deficiency in any of these systems can lead to varying degrees of postural instability, subsequently reducing walking ability (83). Visual feedback training utilizes light to provide feedback on body movements, which can be used to compensate for the reduced position and joint sense caused by lower limb dysfunction in stroke patients. PT+ visual feedback training can enhance the input of visual and proprioceptive information during walking, thereby improving postural stability and walking ability in stroke patients.
We reviewed studies on interventions PT + closed kinematic chain exercises and PT + resistance training. The studies on PT + closed kinematic chain exercises did not report the stroke onset stage, whereas the studies on PT + resistance training reported an onset stage of 4.1 days. Therefore, we recommend using PT + resistance training for treating lower limb dysfunction in stroke patients within 5 days of onset.
However, our study has certain limitations. Due to the limited number of studies included for some rehabilitation interventions, The included literature is all from the Asian region, the age of stroke patients in the included studies ranged from 45 to 70 years, and the lack of direct comparisons between different intervention regimens, the results may be subject to some bias. The results of this study are limited to the data analysis of the included literature and may not accurately reflect the true efficacy of clinical treatments. Caution is advised when referencing these findings for recommending treatment regimens. Further validation through high-quality, large-sample, multicenter RCTs with long-term follow-up is needed. We look forward to future research focusing more on older stroke patients using PT combination regimens for the treatment of lower limb dysfunction.
5 Conclusion
In conclusion, PT + MRP was the optimal rehabilitation regimen for improving balance ability in stroke patients; PT + CKCE was the best for enhancing lower limb motor function; and PT + VFT was most effective for improving walking ability. Overall, PT + CKCE and PT + RT1 represented the most effective interventions for lower limb functional rehabilitation in stroke patients, while PT + RT1 is most effective within 5 days of stroke onset.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
KZ: Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LL: Conceptualization, Resources, Writing – original draft. YZ: Supervision, Writing – original draft. XG: Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. GZ: Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. LG: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The research was funded by the Guangzhou Sports Science and Technology Collaborative Innovation Center (No. 2023B04J0466).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2024.1503585/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Feigin VL, Brainin M, Norrving B, Martins S, Sacco RL, Hacke W, et al. World Stroke Organization (WSO): Global Stroke Fact Sheet 2022. Int J Stroke. (2022) 17:18–29. doi: 10.1177/17474930211065917
2. Shen J, Fu JM, Li Y, Wu H, Li h, Sun Y. Observation on the influence of “Supplementing Yang and Tongluo” electroacupuncture combined with hand rehabilitation robot on patients with hemiplegia after ischemic stroke. Chin Arch Trad Chi. 1–8.
3. Chang SF, Yang BY Di XL. Clinical study on scalp-body acupuncture and contralateral meridian needling method combined with proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation technique for hemiplegia after stroke. New Chin Med. (2024) 56:125–31. doi: 10.13457/j.cnki.jncm.2024.03.025
4. Liu CH, Hsieh YT, Tseng HP, Lin HC, Lin CL, Wu TY, et al. Acupuncture for a first episode of acute ischaemic stroke: an observer-blinded randomised controlled pilot study. Acupunct Med. (2016) 34:349–55. doi: 10.1136/acupmed-2015-010825
5. Pereira S, Mehta S, McIntyre A, Lobo L, Teasell RW. Functional electrical stimulation for improving gait in persons with chronic stroke. Top Stroke Rehabil. (2012) 19:491–8. doi: 10.1310/tsr1906-491
6. Haruyama K, Kawakami M, Otsuka T. Effect of core stability training on trunk function, standing balance, and mobility in stroke patients. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. (2017) 31:240–9. doi: 10.1177/1545968316675431
7. Chae SH, Kim YL, Lee SM. Effects of phase proprioceptive training on balance in patients with chronic stroke. J Phys Ther Sci. (2017) 29:839–44. doi: 10.1589/jpts.29.839
8. Apriliyasari RW, Van Truong P, Tsai PS. Effects of proprioceptive training for people with stroke: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Rehabil. (2022) 36:431–48. doi: 10.1177/02692155211057656
9. Marasco PD, de Nooij JC. Proprioception: a new era set in motion by emerging genetic and bionic strategies? Annu Rev Physiol. (2023) 85:1–24. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-040122-081302
10. Lesinski M, Hortobágyi T, Muehlbauer T, Gollhofer A, Granacher U. Effects of balance training on balance performance in healthy older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. (2015) 45:1721–38. doi: 10.1007/s40279-015-0375-y
11. Rand D. Proprioception deficits in chronic stroke-upper extremity function and daily living. PLoS ONE. (2018) 13:e0195043. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195043
12. Mao Y, Gao Z, Yang H, Song C. Influence of proprioceptive training based on ankle-foot robot on improving lower limbs function in patients after a stroke. Front Neurorobot. (2022) 16:969671. doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2022.969671
13. Shim J, Hwang S, Ki K, Woo Y. Effects of EMG-triggered FES during trunk pattern in PNF on balance and gait performance in persons with stroke. Restor Neurol Neurosci. (2020) 38:141–50. doi: 10.3233/RNN-190944
14. Kim KH, Kim DH. Effects of ankle joint proprioceptive training and thermal approach on stroke patients' trunk, balance stability and gait parameter. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. (2022) 35:1237–46. doi: 10.3233/BMR-210141
15. Cipriani A, Higgins JP, Geddes JR, Salanti G. Conceptual and technical challenges in network meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. (2013) 159:130–7. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-159-2-201307160-00008
16. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
17. Kai W, Xun Z, Luwen Z. The effect of proprioceptive training on limb function and balance ability in patients with hemiplegia after stroke. Reflexol Rehabil Med. (2021) 2:102–4, 37.
18. Wang X, Hu S, Huang CF, Lei L, Peng J, Jiang D, et al. Effects of dual task training combined with proprioceptive training on cognitive function and motor function in elderly patients with hemiplegia after stroke. Chin J Gerontol. (2023) 43:2428–31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2023.10.035
19. Zhong XB, Wang HQ, Liang JY, Lai XB Li JC, Liu MC, et al. Effect of PNF lower extremity training mode combined with closed-chain exercise training of affected lower extremity on walking function of stroke patients with hemiplegia. Reflexol Rehabil Med. (2021) 2:119–22.
20. Jin YL, Fang CB, Xue N, Yin CP, Zhang Y. Effects of PNF technique combined with the healthy limb step resistance training in standing position on walking func-tion of stroke patients with hemiplegia. Chin J Rehabil. (2018) 33:11–4. doi: 10.3870/zgkf.2018.01.003
21. Zhang XH, Liu HZ, Sun D, Zhang C, Bi X. Effect of intensive proprioceptive training on ankle joint dysfunction. Chin J Geriatr Care. (2017) 15:30–1. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4860.2017.01.013
22. Zhang P. Effect analysis of proprioceptive promoting training and balance function training on walking ability of stroke patients. Zhonghua Yangsheng Baojian. (2022) 40:52–4, 30.
23. Zhang JJ. Effect of proprioceptive neuromuscular promotion in early stage of acute ischemic stroke. J Henan Med Coll Staff Work. (2022) 34:412–5.
24. Zhng B, Ding D, Lyu L. Effect of proprioceptive training and core stability training on lower limbs motor function and balance in patients with hemi-plegia after stroke. Chin. J. Rehabil. Theory Pract. (2014) 20:1109–12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9771.2014.12.003
25. Yu H, Lu J, Wang YC. Influence of proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation neck motor pattern on trunk control and balance function in patients with chronic stroke. Chin J Cardiovasc Rehabil Med. (2018) 27:390–3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0074.2018.04.06
26. Yang X, Yi XQ, Lu L, Ma T. Observation on therapeutic effect of Xingnaokaiqiao acupuncture combined with proprioceptive training on hemiplegia after cerebral infarction. Mod J Integr Trad Chin West Med. (2022) 31:3468–71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2022.24.022
27. Yang JL, Wu QL. Study of proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation on the fall of Ischemic stroke patients. J ShanDong First Med Univ. (2016) 37:615–7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7115.2016.06.006
28. Chen J, Li S, Yan CL. Clinical observation of surface electromyography biofeedback combined with proprioceptive neuromuscular promotion technique in the treatment of foot drop in stroke patients. Chin J Rehabil Med. (2016) 31:899–902. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1242.2016.08.014
29. Chen W, Liu JZ Li JX, Cai MT, Zhou LC, Hu F, et al. Clinical study on acupuncture plus PNF for post-stroke balance dysfunction. Shang J Acupunct Moxibust. (2022) 41:323–9. doi: 10.13460/j.issn.1005-0957.2022.04.0323
30. Cai ZZ, Zuo YF, Yang JY, Zhu Y. A clinical study on the effect of PNF trunk training mode on trunk control and balance ability in stroke patients. Med Inf. (2016) 29:290–1.
31. Xian ZX, Chen HZ, Liu L. Effects of PNF technique sitting trunk training on balance function and activities of daily living in patients with early stroke. Trad Chin Med Rehabil. (2023) 14:12–4, 8. doi: 10.19797/j.issn.1008-1879.2023.04.004
32. Su ZX, Ding YQ, Wang YL. Effect of exercise relearning therapy and onoception training on exercise function and daily activity of patients after stroke. Chin J Geriatr Care. (2022) 20:124–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2671.2022.02.035
33. Zhu HG. Observation on the effect of static balance combined with proprioceptive rehabilitation exercise for hemiplegic patients with stroke. Cont Med. (2020) 27:15–7. doi: 10.12083/SYSJ.231012
34. Wang XY, Tang XQ Li L, Luo Y, Chen HM, Wang T, et al. Effect of acupuncture combined with proprioception training on functional recovery and electromyography in elderly patients with hemiplegia after stroke. Chine J Pract Nerv Dis. (2024) 27:468–72.
35. Xiong Y, Hu DF. Effects of PNF technique combined with medium frequency electric stimulation in treatment of patients with ankle joint dysfunction after stroke. Med J Chin Peoples Health. (2023) 35:98–100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0369.2023.18.030
36. Wang J, Yang CS, Dong XC. Application of proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation in the rehabilitation of patients with lower extremity hemiparalysis. J Xinxiang Med Univ. (2010) 27:598–600.
37. Wang CL, Zhuang QR, Peng RZ, Qang HM. Clinical study on the effect of intramural adhesive combined with pro-prioceptive strengthening training on stroke patients with gait abnormality. China For Med Treat. (2023) 42:5–8. doi: 10.16662/j.cnki.1674-0742.2023.26.005
38. Wang F, He W, Cai YJ, Sheng L. PNF combined with virtual reality training on balance function after stroke. Trad Chin Med Rehabil. (2018) 9:20–2.
39. Dai M, Zhang T, Zhang JP, Sun GM. Application of proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation therapy in the adjuvant treatment of patients with hemiplegia after stroke. Chin J Convalesc Med. (2020) 29:1161–2. doi: 10.13517/j.cnki.ccm.2020.11.016
40. Liu XL, Yuan HX, Dai YY, Zhao Q, Huang SF, Shi GF. Effect of proprioception training on lower extremity motor function and life quality in patients with hemiplegia due to ischemic stroke. J Qiannan Med Coll National. (2019) 32:47–50.
41. Dai LL, Zhang Q, Rao GF. Effect of ankle-foot orthosis assisted proprioceptive training on motor function and surface electromyography stroke patients with hemiplegia. Chin J Rehabil. (2019) 34:287–90. doi: 10.3870/zgkf.2019.06.002
42. Liu z, Long YW, Liang TJ, Huang FC, Mo MY, Ning YY, et al. Effectiveness of rope therapy combined with PNF technique on walking ability of stroke pa-tients. J Guangxi Med Univ. (2023) 40:2078–83. doi: 10.16190/j.cnki.45-1211/r.2023.12.022
43. Du ZF Li R. Effect of PNF combined with task oriented training on the recovery of limb function in patients with cerebral vascular diseases in lag phase. Clin Res Pract. (2019) 4:169–70. doi: 10.19347/j.cnki.2096-1413.201934071
44. Fang XY, Wang N, Zhao JH, Li ZQ, Huang YP. Effect analysis of proprioceptive intensive training on hemiplegic function in convalescent stroke patients. Mod Diagn Treat. (2013) 2308–9.
45. Le L, Li Z, Guo GH, Liang YZ, Wang GS Li XL, et al. Effect of PNF on trunk control in patients with stroke and analysis of surface electromyography of trunk flexor and extensor muscles. Chin J Rehabil. (2019) 34:627–30. doi: 10.3870/zgkf.2019.12.003
46. Guan Q. Clinical effect of proprioceptive training and nursing of knee joint on anti-fall ability and improvement of negative emotion in patients with hemiplegia. Chin J Trauma Disabil Med. (2020) 28:69–70. doi: 10.13214/j.cnki.cjotadm.2020.22.046
47. Li J, Zhang DW, Fan X, Liu YF, Guo Y. Effect of proprioceptive intensive training on gait and balance ability of patients with hemiplegia at early stage of stroke. J Clin Res. (2023) 40:937–40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7171.2023.06.039
48. He YY, Xie XL Yi Q. Effect of acupuncture combined with pnf technique treating sequela of apoplexy hemiplegia. J Clin Acupunct Moxibust. (2017) 33:19–22.
49. Jiang XK. Effect of proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation technique on lower extremity function and balance function in stroke patients. World Latest Med Inf. (2020) 20:52–3. doi: 10.19613/j.cnki.1671-3141.2020.5.031
50. Jiao HP. Application effect of proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation therapy in convalescent stroke patients. Pract Clin J Integr Trad Chin West Med. (2024) 24:26–8, 35. doi: 10.13638/j.issn.1671-4040.2024.03.007
51. Pan HP, Feng H, Li YJ, Jin HZ. Effects of load-controlled proprioceptive training on lower extremity motor and balance function of stroke patients. Chin J Rehabil Med. (2011) 26:1025–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1242.2011.11.008
52. Zhou YJ, Chen F, Liu QY Li XH, Lan XF. Effect of proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation techniques on motor function and daily living ability in patients with lower limb hemiplegia after stroke. Nurs Pract Res. (2020) 17:68–70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9676.2020.16.025
53. Li JX. The effect of plantar-driven lower limb rehabilitation robot combined with PNF on the lower limb function of stroke patients with hemiplegia. Reflexol Rehabil Med. (2021) 2:150–3.
54. Li C. Influence of proprioceptive rehabilitation nursing of knee joint on balance function and mental state in patients with hemiplegia after stroke. Chin J Trauma Disabil Med. (2020) 28:69–70. doi: 10.13214/j.cnki.cjotadm.2020.17.046
55. Li DQ, Li JH, Jia D, Zhang WQ. Rehabilitation effect of transverse muscle control training combined with PNF pelvic pattern training on trunk ability of hemiplegic patients with cerebral hemorrhage. China Med Pharm. (2021) 11:24–7, 31.
56. Li ZY Li J. Clinical study of proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation regulating control of pelvic in improving walking and balance function in stroke patients with hemiplegia. Tianjin J Trad Chin Med. (2019) 36:685–90. doi: 10.11656/j.issn.1672-1519.2019.07.16
57. Liang ZM, Sha W. Application of proprioception training in rehabilitation of stroke-induced lower extremity motor dysfunction. Nurs Pract Res. (2018) 15:151–3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9676.2018.04.064
58. Liu MJ, Ma GM, Feng CR, Zhang XF. Observation of the effect of neck proprioceptive promoting technique on balance function after stroke. World Latest Med Inf. (2017) 17:47. doi: 10.19613/j.cnki.1671-3141.2017.93.030
59. Lyu ZQ, Zhao YY, Zhang SL. Application effects of proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation technique-based rehabilitation training in patients with stroke in recovery period. Med J Chin Peoples Health. (2024) 36:70–3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0369.2024.02.022
60. Zhang SJ. Effect of PNF extension technique combined with impact therapy on patients with spastic hemiplegia. Med J Chin Peoples Health. (2021) 33:46–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0369.2021.12.019
61. Wu XJ, Zhu YL, Ding XQ, Peng GW, Shen XH, Rong JF. The therapeutic effect of lower limb robot combined with PNF technique on lower limb function in stroke patients. Chin J Rehabil Med. (2020) 35:938–43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1242.2020.08.010
62. Wang WS. Effect of proprioceptive training combined with head acupuncture therapy on lower limb movement and balance function in stroke patients with hemiplegia. Chin J Rural Med Pharm. (2018) 25:43–4. doi: 10.19542/j.cnki.1006-5180.001902
63. Wu XJ, Peng GW, Shen XH, Deng MK, Ding XQ, Hu GW, et al. Effect of proprioceptive training combined with head acupuncture therapy on lower limb movement and balance function in stroke patients with hemiplegia. Chin J Rehabil Med. (2023) 38:1677–82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1242.2023.12.007
64. Liu YY. The influence of ankle-foot proprioceptive training on balance function and walking ability in stroke patients. Diet Health. (2017) 4:272–3.
65. Li XJ, Han XL, Tian XF, Wang CH. Influence of proprioceptive intervention of knee joint on balance function and mental state in patients with hemiplegia after stroke. Chin J Phys Med Rehabil. (2016) 38:845–7. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-1424.2016.11.012
66. Lyu YL, Wang CL, Wang FT, Chang LG. Therapeutic effect of acupuncture and moxibustion combined with proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation for patients with limb dysfunction after stroke. Int Med Health Guid News. (2024) 30:398–403. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-1245.2024.03.010
67. Xin YF, Zhang XG, Zhao ZW, Sun SQ, Ma M, Sun WD, et al. Effects of proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation therapy on activities of daily living, balance function and walking ability in stroke patients. Chin J Phys Med Rehabil. (2020) 42:1071–4. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-1424.2020.12.004
68. Kim K, Lee DK, Jung SI. Effect of coordination movement using the PNF pattern underwater on the balance and gait of stroke patients. J Phys Ther Sci. (2015) 27:3699–701. doi: 10.1589/jpts.27.3699
69. Hwangbo PN, Don Kim K. Effects of proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation neck pattern exercise on the ability to control the trunk and maintain balance in chronic stroke patients. J Phys Ther Sci. (2016) 28:850–3. doi: 10.1589/jpts.28.850
70. Choi YK, Nam CW, Lee JH, Park YH. The effects of taping prior to PNF treatment on lower extremity proprioception of hemiplegic patients. J Phys Ther Sci. (2013) 25:1119–22. doi: 10.1589/jpts.25.1119
71. Momna Asghar AF, Soleman W, Muhammad H, Ullah K, Ashfaq Ahmad KS. Effectiveness of proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation on balance in chronic stroke patients. Rawal Med J. (2021) 46:212–5.
72. Yeo SS, Koo DK, Ko SY, Park SY. Effect of balance training in sitting position using visual feedback on balance and gait ability in chronic stroke patients. J Clin Med. (2023) 12:4383. doi: 10.3390/jcm12134383
73. Park SJ, Oh S. Effect of diagonal pattern training on trunk function, balance, and gait in stroke patients. Appl Sci. (2020) 10:4635. doi: 10.3390/app10134635
74. Lee H, Kim H, Ahn M, You Y. Effects of proprioception training with exercise imagery on balance ability of stroke patients. J Phys Ther Sci. (2015) 27:1–4. doi: 10.1589/jpts.27.1
75. Kim BR, Kang TW. The effects of proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation lower-leg taping and treadmill training on mobility in patients with stroke. Int J Rehabil Res. (2018) 41:343–8. doi: 10.1097/MRR.0000000000000309
76. Yilmaz O, Soylu Y, Erkmen N, Kaplan T, Batalik L. Effects of proprioceptive training on sports performance: a systematic review. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. (2024) 16:149. doi: 10.1186/s13102-024-00936-z
77. Song LH, Niu BZ, Cao Y. Effect of acupuncture combined with motor relearning rehabilitation therapy on neurological function recovery after stroke. Chin Arch Trad Chin Med. (2024) 42:78–81. doi: 10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2024.01.016
78. Gao PC, Yang L, Tang F, Liu WG. Clinical effect of “Jin's three-needle” therapy and motor relearning regimen on the upper limb motor function in patients with ischemic stroke. Acupunct Res. (2021) 46:235–9. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.200424
79. Dai YL, Wang LK, Wang YJ, Wang Z, Wang LT. Effects of galvanic vestibular stimulation combined with closed-chain functional training on lower limb movement and balance functions in stroke patients. Chin J Rehabil. (2024) 39:259–63. doi: 10.3870/zgkf.2024.05.001
80. Shao JW, Zhang C, Sun D, Zhai SY, Mu JK. Isokinetic chain closing training and isokinetic chain opening training for patients with poststroke dyskinesia influence of muscle strength, balance function and walking ability of lower limbs. Clin J Med Off. (2022) 50:267–9, 73. doi: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2022.03.12
81. Duan HY Li ZL, Lyu FX, Liu N, Yan ZH. Effect evaluation of isokinetic muscle strength training with different flexor and extensor muscle strength ratios in treatment of hyperextension of knee after stroke. J Jilin Univ. (2021) 47:1538–43. doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210626
82. Radwan NL, Mahmoud WS, Mohamed RA, Ibrahim MM. Effect of adding plyometric training to physical education sessions on specific biomechanical parameters in primary school girls. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. (2021) 21:237–46.
Keywords: stroke, proprioceptive training, lower limb function, network meta-analysis, closed kinematic chain exercise
Citation: Zheng K, Li L, Zhou Y, Gong X, Zheng G and Guo L (2024) Optimal proprioceptive training combined with rehabilitation regimen for lower limb dysfunction in stroke patients: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Front. Neurol. 15:1503585. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1503585
Received: 29 September 2024; Accepted: 02 December 2024;
Published: 20 December 2024.
Edited by:
Fan Gao, University of Kentucky, United StatesReviewed by:
Kai Guo, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), ChinaAgnieszka Wareńczak-Pawlicka, Poznan University of Medical Sciences, Poland
Copyright © 2024 Zheng, Li, Zhou, Gong, Zheng and Guo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Liang Guo, bGlhbmdndW9AbS5zY251LmVkdS5jbg==
 Kaiqi Zheng
Kaiqi Zheng Li Li
Li Li Yahui Zhou3
Yahui Zhou3 Gangbin Zheng
Gangbin Zheng Liang Guo
Liang Guo