- 1Department of Neurosurgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou, China
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong Second Medical University, Weifang, Shandong, China
Background: Human interleukin-33 (IL-33), a member of the IL-1 family, has been identified as a therapeutic target due to its role as a proinflammatory mediator in various diseases. This study aims to evaluate the prognostic value of serum IL-33 levels in patients admitted with their first-ever acute ischemic stroke.
Methods: This single-center, prospective, observational study included 216 patients with acute ischemic stroke. Serum IL-33 levels were measured at hospital admission to assess their predictive value for functional outcomes and mortality within 3 months. IL-33 levels were dichotomized at the median into two groups: the reduced group (IL-33 ≤ median) and the normal group (IL-33 > median).
Results: The median age of the 216 patients was 66 years (interquartile range [IQR], 56–75), with 132 (61.6%) being women. IL-33 serum levels were inversely correlated with stroke severity, as measured by the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score and lesion size. Patients in the reduced IL-33 group had a higher rate of unfavorable outcomes (55.6% vs. 18.5%; absolute difference, 29.2% [95% confidence interval (CI), 24.5% to 34.4%]; odds ratio (OR), 3.19 [95% CI, 1.72 to 5.91]) and mortality (24.1% vs. 3.7%; absolute difference, 15.8% [95% CI, 13.1% to 18.3%]; OR, 4.12 [95% CI, 1.38 to 12.31]) compared to the normal group. Furthermore, IL-33 levels enhanced the prognostic accuracy of the NIHSS for predicting functional outcomes (combined area under the curve [AUC], 0.84; 95% CI, 0.79–0.84; P < 0.001) and mortality (combined AUC, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.83–0.94; P < 0.001).
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that lower IL-33 levels are associated with increased stroke severity and poorer prognosis. These findings suggest that IL-33 may serve as a valuable biomarker for predicting poor outcomes following acute ischemic stroke.
Introduction
Stroke remains a leading cause of mortality and long-term physical and cognitive disability in China, with over 2 million new cases each year (1, 2). According to the National Epidemiological Survey of Stroke in China (NESS-China), there were approximately 11 million prevalent stroke cases, 2.4 million new strokes, and 1.1 million stroke-related deaths in 2013 (3). These statistics underscore the urgent need for enhanced stroke prevention and management strategies in China (4).
Interleukin-33 (IL-33), a member of the IL-1 family, functions as an endogenous alarmin released by damaged or necrotic barrier cells, such as endothelial and epithelial cells, during homeostasis and inflammation (5). IL-33 is a therapeutic target due to its role as a proinflammatory mediator in various diseases (6), including allergic airway inflammation (7), anaphylaxis (8), and autoimmune diseases (9). Additionally, IL-33 has been shown to reduce atherosclerosis in animal models (10) and protect against cardiac dysfunction in mechanically overloaded hearts (11). Li et al. (12) demonstrated that IL-33 protects mice from abdominal aortic aneurysm formation by enhancing ST2-dependent regulatory T-cell expansion and their immunosuppressive activities, suggesting that IL-33 signaling possesses both proinflammatory and cardioprotective properties (13). Nuclear IL-33 functions as a stored alarmin that is released when barriers are breached (14).
In the context of central nervous system diseases, IL-33/ST2 signaling plays a dual role, impacting conditions such as neurodegenerative diseases (15), cerebrovascular diseases (16), traumatic CNS injury (17), and chronic pain (18). Previous studies have demonstrated that elevated serum IL-33 concentrations are associated with inflammation, disease severity, and prognosis in conditions such as traumatic brain injury (19) and aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (20). Liu et al. found that serum IL-33 levels increase with infarct size, suggesting IL-33's role in the pathogenesis and progression of acute cerebral infarction (21). Despite these observations, the mechanisms underlying IL-33 release remain poorly understood. Chen et al. further identified low serum IL-33 as an independent predictive biomarker for hemorrhagic transformation and adverse outcomes in acute ischemic stroke (22).
These findings underscore the importance of exploring the relationship between IL-33 levels and clinical severity or prognosis in stroke patients. To address this, we assessed the prognostic value of serum IL-33 at the time of hospital admission in a cohort of 216 patients experiencing their first-ever acute ischemic stroke (AIS).
Materials and methods
Study design and setting
This prospective observational cohort study was conducted at the Affiliated hospital of Shandong Second Medical University. Between December 2018 and February 2020, we included consecutive patients who were admitted with their first-ever acute ischemic stroke. We obtained written informed consent from either the patient or a relative. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (1964) and adhered to the consolidated standards for reporting observational trials (23). Approval was obtained from the Ethics Committee of the Affiliated hospital of Shandong Second Medical University.
Patients and clinical variables
Patients admitted with acute ischemic stroke within 48 h of symptom onset, as defined by World Health Organization criteria (24), were included in the analysis. Within the first 24 h after admission, we collected data on age, sex, BMI, blood pressure, body temperature, and traditional risk factors including smoking and drinking habits, history of hypertension, diabetes, hypercholesterolemia, coronary heart disease, atrial fibrillation, and family history of cardiovascular events. We also documented pre-stroke medications—oral anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, antihypertensives, and statins—and acute treatments like IV thrombolysis and mechanical thrombectomy. Stroke severity was evaluated using the NIH Stroke Scale (25), and etiology was classified according to TOAST criteria (26), identifying the primary causes as large-artery arteriosclerosis, cardioembolism, small-artery occlusion, or other undetermined etiologies.
Within the first 24 h after admission, cranial computed tomography (CT) and/or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) were performed on all patients to rule out intracranial hemorrhage and confirm the diagnosis of ischemic stroke. MRI with diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) was available for some patients. Lesion sizes were quantified using a semi-quantitative method (27) and categorized into three groups to reflect typical stroke patterns: small lesions (< 10 mL), medium lesions (10–100 mL), and large lesions (>100 mL) (28).
Laboratory analysis
Fasting blood samples were collected and processed within the first 24 h after admission. Blood was centrifuged at 4°C for 15 min at 1,000 x g. Serum was then separated and stored at−80°C. Serum IL-33 levels were measured using a Human IL-33 ELISA Kit (No. ab119547; ABCAM, LTD, Shanghai, China), with a detection sensitivity of 0.2 pg/ml and a range of 7.8 to 500 pg/ml. The intra-assay and inter-assay coefficients of variation were 4.0–4.7% and 6.0–6.9%, respectively, with a sample recovery rate of 67% to 79%. Additional biomarkers, including C-reactive protein (CRP), glucose (GLU), and homocysteine (HCY), were also measured using an enzyme cycling method with the BS800M analyzer (MINDRAY, Shenzhen, China). Values below the detection limit were recorded as the lower limit of detection.
Follow-up and outcomes
Three months after admission, all discharged survivors underwent a structured telephone interview as part of the follow-up. The primary endpoint was a favorable functional outcome, defined as a score of 0 to 2 on the modified Rankin Scale (mRS) (29). The secondary endpoint was mortality from any cause within the 3-month follow-up period. Outcome assessments were conducted by two trained medical students, who were blinded to the patients' IL-33 levels, via telephone interviews with either the patient or, if necessary, the closest relative.
Statistical analysis
Data were summarized as counts (percentage) for categorical variables and medians (interquartile ranges [IQRs]) for continuous variables. Continuous variables were compared between groups using the Mann–Whitney U test for two-group comparisons or the Kruskal–Wallis one-way analysis for multigroup comparisons. Categorical variables were compared using the Chi-square test.
The association between IL-33 levels and stroke severity was assessed using Spearman's rank correlation with NIHSS scores and lesion size. NIHSS scores were categorized into minor stroke (NIHSS ≤ 5), moderate (NIHSS 6–10), and high clinical severity (NIHSS > 10) for further analysis.
Statistical analyses were conducted to evaluate the predictive ability of IL-33 for functional outcomes and mortality at 3 months. Logistic regression models were used to examine the relationship between IL-33 levels—categorized by median values as reduced (≤ median) or normal (> median)—and the two endpoints, with results reported as odds ratios (ORs) along with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Both unadjusted and multivariate models, accounting for significant predictors, were applied.
The predictive models' discrimination was assessed using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis, with results reported as the area under the curve (AUC). The improvement in score performance by adding IL-33 to NIHSS was evaluated using nested logistic regression models. We employed a reclassification model to further assess the added benefit of IL-33 levels compared to the NIHSS score alone in risk prediction. For net reclassification improvement, only changes in estimated prediction probabilities that resulted in a shift from one risk category to another were considered.
For mortality prediction, Kaplan–Meier survival curves stratified by median IL-33 levels were calculated. All statistical tests were two-tailed with a significance level of P < 0.05. Analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism (version 5.0), R version 2.8.1 with the ROCR package (version 1.0–2), and Stata 9.2.
Data available
Please contact the corresponding author for the data request.
Results
Patients
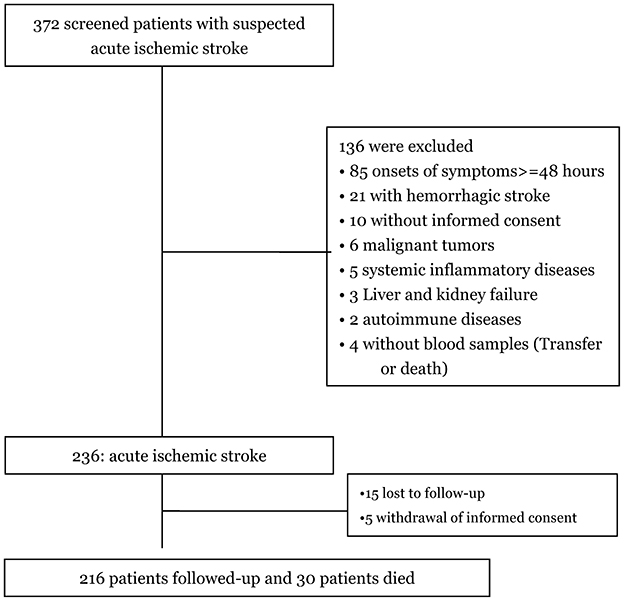
Among the 372 patients initially screened for suspected first-ever acute ischemic stroke, 236 were confirmed with the diagnosis, and 216 completed follow-up and were included in the final analysis (Figure 1). The baseline characteristics of these 216 patients—including age (P = 0.12), gender (P = 0.93), BMI (P = 0.44), and NIHSS scores (P = 0.35)—were similar to those of the overall cohort of ischemic stroke patients.
Baseline characteristics of the study population
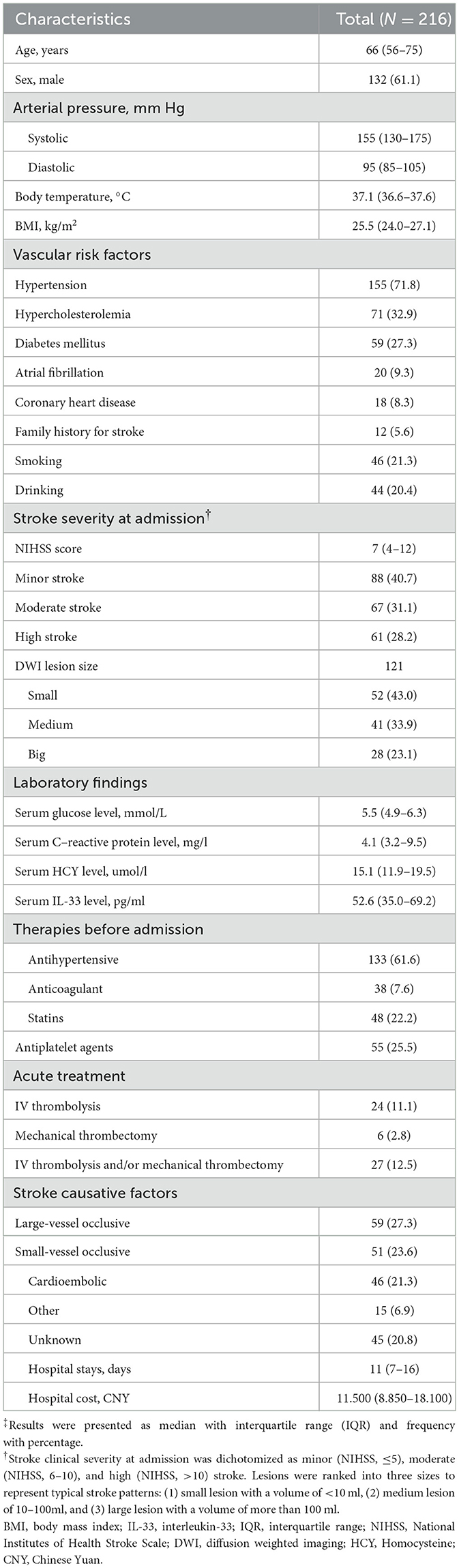
The included patients had a median age of 66 years (IQR, 56–75), with 132 (61.6%) being women. The median systolic and diastolic blood pressures were 155 mmHg (IQR, 130–175) and 95 mmHg (IQR, 85–105), respectively. Among them, 155 (71.8%) were diagnosed with hypertension, 59 (27.3%) with diabetes mellitus, 20 (9.3%) had atrial fibrillation, 12 (5.6%) reported a family history of stroke, and 46 (21.3%) were smokers. Upon admission, the median NIHSS score was 7 (IQR, 4–12), and 24 patients (11.1%) received IV thrombolysis. The median serum IL-33 level was 52.6 pg/ml (IQR, 35.0–69.2). These baseline characteristics are summarized in Table 1.
IL-33 and stroke characteristics
IL-33 serum levels were found to decrease with increasing stroke severity as defined by NIHSS scores and lesion size. There was a significant negative correlation between NIHSS scores and IL-33 levels (r = −0.257, P < 0.001). At admission, 88 patients (40.7%) had minor strokes (NIHSS ≤ 5), 67 (31.1%) had moderate strokes (NIHSS 6–10), and 61 (28.2%) had severe strokes (NIHSS > 10). Interestingly, the median IL-33 level was highest in patients with minor strokes (56.1 pg/ml [IQR, 40.0–71.9]) and moderate strokes (57.8 pg/ml [IQR, 40.7–69.3]), and lowest in severe strokes (45.2 pg/ml [IQR, 29.5–57.2]), with significant differences noted (p < 0.01, Figure 2A). Among the 121 patients with available MRI data, IL-33 levels inversely correlated with lesion size (Figure 2B). Median IL-33 levels were 60.6 pg/ml (IQR, 51.5–74.9) for small lesions, 50.2 pg/ml (IQR, 38.4–68.0) for medium lesions, and 34.0 pg/ml (IQR, 18.2–48.5) for large lesions (P < 0.05). Additionally, patients with large artery ischemic strokes exhibited significantly higher median IL-33 levels (47.4 pg/ml [IQR, 30.5–55.1]) compared to those with other ischemic stroke subtypes (54.2 pg/ml [IQR, 37.2–71.3]; P = 0.013).
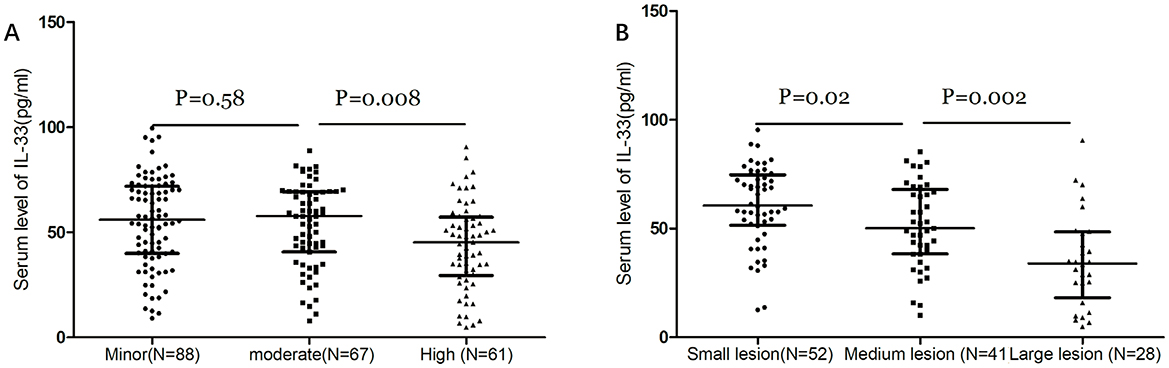
Figure 2. Dot plots of the serum level of IL-33 according to the stroke severity. (A) Dot plots of serum levels of IL-33 according to the severity of stroke as defined by the NIHSS score. Stroke patients were divided into 3 groups by NIHSS score according to the following standards: minor stroke (NIHSS ≤ 5), moderate (NIHSS, 6–10) and high clinical severity (NIHSS > 10). (B) Dot plots of serum levels of IL-33 according to the severity of stroke as defined by lesion size. Stroke patients with diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) data were divided into 3 groups by lesions: small lesions with a volume of <10 ml; medium lesions of 10–100 ml; and large lesions with a volume of more than 100 ml. Mann–Whitney U Test; All data are medians and interquartile ranges (IQR), with dot plots representing all values.
IL-33 and stroke prognosis
A total of 80 patients (37.0%) experienced an unfavorable functional outcome, defined as a modified Rankin Scale (mRS) score of 3–6, and 30 patients died within 90 days, resulting in a mortality rate of 13.9%.
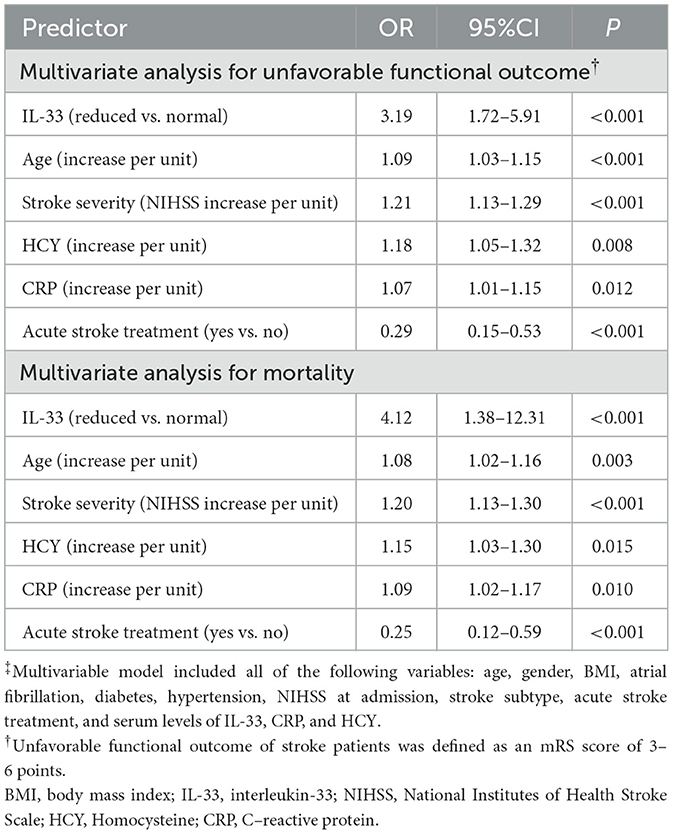
As depicted in Figure 3A, median IL-33 levels were significantly higher in patients with favorable outcomes compared to those with unfavorable outcomes (60.0 pg/ml [IQR, 45.8–71.9] vs. 37.6 pg/ml [IQR, 26.6–48.9]; P < 0.001). In the multivariate logistic regression analysis, lower IL-33 levels were associated with a higher rate of unfavorable outcomes (reduced vs. normal: 55.6% vs. 18.5%; absolute difference, 29.2% [95% CI, 24.5% to 34.4%]; OR, 3.19 [95% CI, 1.72 to 5.91]) (Table 2). Among the subgroup of 121 patients who underwent MRI evaluations, reduced IL-33 remained an independent predictor of poor outcome (OR, 3.57 [95% CI, 1.82–6.63]; P < 0.001), after adjusting for lesion size (OR, 1.75 [95% CI, 1.25–2.32]; P = 0.003) and NIHSS score (OR, 1.15 [95% CI, 1.05–1.24]; P < 0.001).
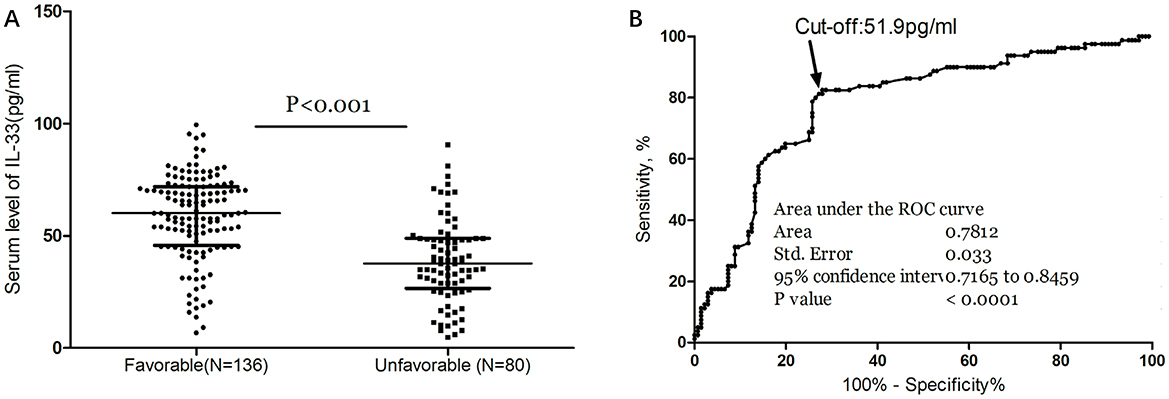
Figure 3. Serum IL-33 and stroke functional outcome. (A) IL-33 levels in stroke patients with favorable and unfavorable functional outcome; Mann–Whitney U Test; All data are medians and interquartile ranges (IQR), with dot plots representing all values. (B) Receiver operator characteristic curve demonstrating sensitivity as a function of 1-specificity for predicting the functional outcome within 3 months based on serum level of IL-33.
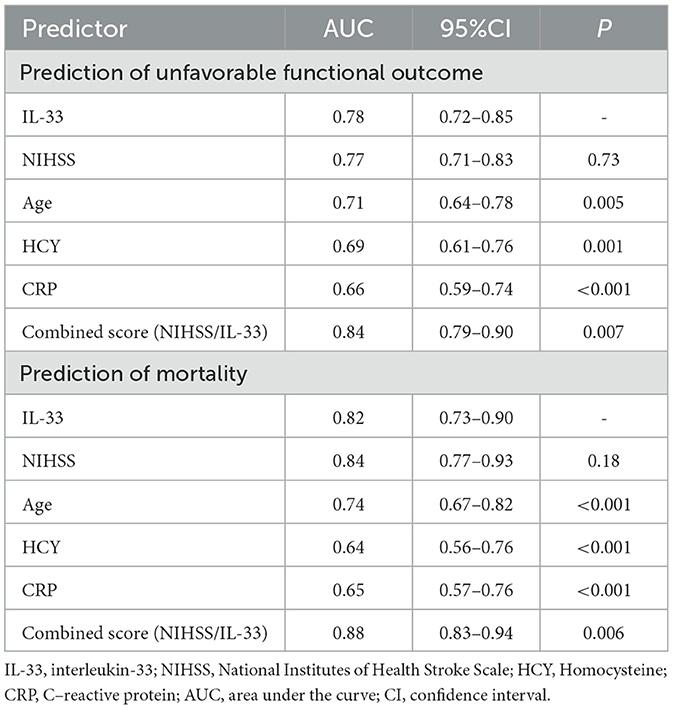
The ROC curve identified an optimal cut-off of IL-33 serum level at 51.9 pg/ml for predicting unfavorable outcomes, with a sensitivity of 82.5% and a specificity of 72.1% (Figure 3B). This threshold yielded an AUC of 0.78 (95% CI, 0.72–0.85), demonstrating significantly greater discriminatory ability compared to age, sex, homocysteine (HCY), and C-reactive protein (CRP), and comparable to the NIHSS score (Table 3). Combining IL-33 with the NIHSS score improved the AUC to 0.84 (95% CI, 0.79–0.90; P < 0.001), with this enhancement confirmed through internal 5-fold cross-validation yielding an average AUC of 0.77 (standard error, 0.034) for NIHSS alone and 0.84 (0.025) for the combined model—a difference of 0.07 (0.008).
Moreover, median IL-33 levels were significantly higher in survivors compared to non-survivors (56.4 [IQR, 42.2–69.9] vs. 25.7 [IQR, 15.6–38.9] pg/ml; P < 0.001; Figure 4A). In multivariate logistic regression analysis, lower IL-33 levels were associated with a higher mortality rate (reduced vs. normal: 24.1% vs. 3.7%; absolute difference, 15.8% [95% CI, 13.1%−18.3%]; OR, 4.12 [95% CI, 1.38–12.31]) (Table 2). Among the 121 patients who underwent MRI evaluations, reduced IL-33 levels independently predicted mortality, with an OR of 4.63 (95% CI, 1.18–13.15; P = 0.002) after adjusting for lesion size (OR, 1.88 [95% CI, 1.35–2.76]; P < 0.001) and NIHSS score (OR, 1.19 [95% CI, 1.03–1.34]; P < 0.001).
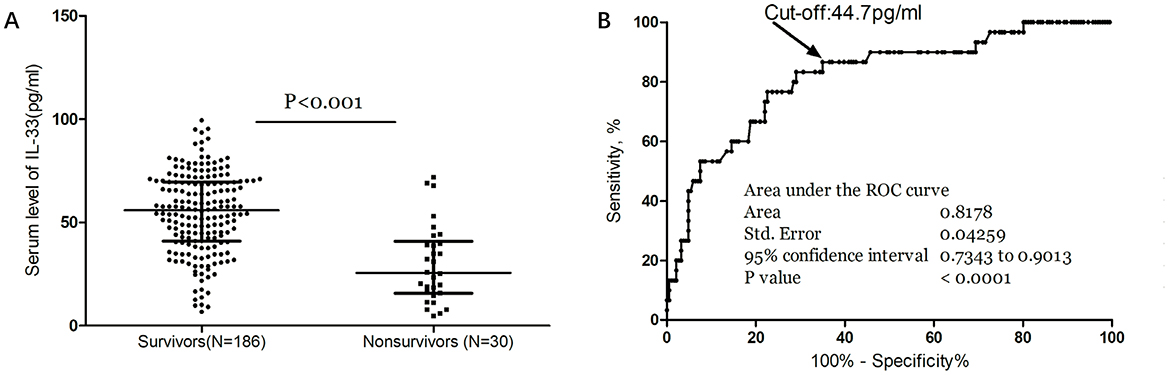
Figure 4. Serum IL-33 and stroke mortality. (A) IL-33 levels in survivors and nonsurvivors of stroke; Mann–Whitney U Test; All data are medians and interquartile ranges (IQR), with dot plots representing all values. (B) Receiver operator characteristic curve demonstrating sensitivity as a function of 1-specificity for predicting the mortality within 3 months based on serum level of IL-33.
The ROC curve analysis determined that the optimal cut-off value for IL-33 serum level in predicting mortality was 44.7 pg/ml, achieving a sensitivity of 83.3% and a specificity of 71.0% (Figure 4B). This resulted in an AUC of 0.82 (95% CI, 0.73–0.90), indicating that IL-33 has significantly greater discriminatory ability compared to age, sex, homocysteine (HCY), and C-reactive protein (CRP), and comparable to the NIHSS score (Table 3). Furthermore, combining IL-33 with the NIHSS score improved the AUC to 0.88 (95% CI, 0.83–0.94; P < 0.001), with this enhancement supported by an internal 5-fold cross-validation showing an average AUC of 0.84 (standard error, 0.041) for the NIHSS alone and 0.88 (0.035) for the combined model, a difference of 0.04 (0.006). Kaplan–Meier survival curves, stratified by the median IL-33 level (reduced vs. normal), illustrated that patients in the reduced group (≤ 52.6 pg/ml) had a significantly higher risk of death (P < 0.001) (Figure 5).
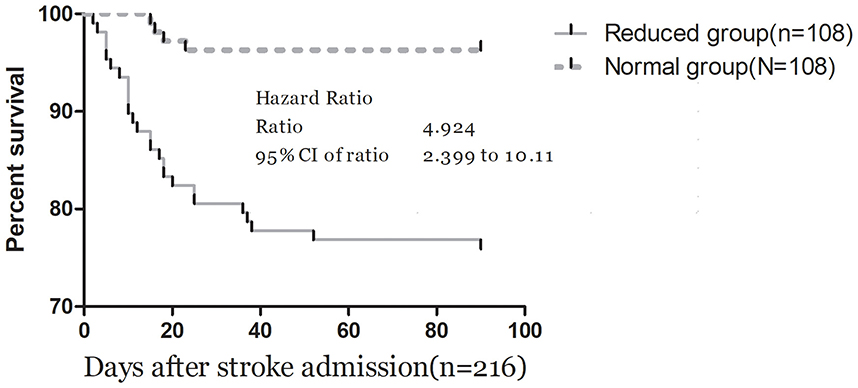
Figure 5. Kaplan–Meier survival based on IL-33 median. Time to death was analyzed by Kaplan–Meier curves based on IL-33 median. Patients in the reduced group (≤52.6 pg/ml) had an increased risk of death compared with patients in the normal group (P < 0.001).
The association between IL-33 and stroke prognosis was analyzed in a subgroup excluding patients who received acute reperfusion therapy. Among the 75 patients (39.7%) who experienced an unfavorable functional outcome, 29 died within 90 days, resulting in a mortality rate of 15.3%. In multivariate logistic regression analysis, lower IL-33 levels (reduced vs. normal) were linked to a higher rate of unfavorable outcomes (OR, 3.24; 95% CI, 1.66–5.99) and mortality (OR, 4.18; 95% CI, 1.25–12.42).
Discussion
In this prospective observational study, we found that low serum IL-33 levels are independently associated with greater clinical severity at admission and poorer prognosis at follow-up. IL-33 serves as an independent prognostic marker for both functional outcomes and mortality in patients with ischemic stroke, providing significant additional predictive value beyond the NIHSS clinical score. Furthermore, the prognostic accuracy of IL-33 in stroke patients surpasses that of other commonly measured laboratory parameters and clinical measures.
In previous research, Li et al. (30) identified IL-33 as an independent predictor of functional outcomes in ischemic stroke, with an adjusted OR of 0.932 (95% CI, 0.882–0.986), highlighting its role as a protective prognostic factor. Additional studies support the significance of low IL-33 levels in predicting long-term outcomes in patients with first-ever acute ischemic stroke, with one such study noting a closely related adjusted hazard ratio of 0.979 (95% CI, 0.961–0.997, P = 0.025) for recurrent ischemic stroke (31). Moreover, a concentration of IL-33 ≤ 71.85 ng/L was independently predictive of post-stroke depression, as shown by a multivariate logistic regression analysis (95% CI, 1.129–7.515, P = 0.027) (32). Another study reported that low IL-33 levels, alongside increased sST2 levels, predict mortality risk in critically ill patients (33). Consistent with these findings, our research also demonstrated that lower serum IL-33 levels are associated with larger infarction volumes and greater stroke severity in AIS patients, corroborating evidence from earlier studies (30). Compared to previous studies (30–32), this research provides new insights into the prognostic value of low serum IL-33 levels in acute ischemic stroke (AIS) by demonstrating that lower IL-33 levels are associated with increased stroke severity, worse functional outcomes, and higher mortality rates. Unlike earlier studies (30–32), this research adds a combined analysis with NIHSS scores to improve the prognostic accuracy of IL-33, showing its enhanced predictive power for unfavorable outcomes and mortality. It also uniquely evaluates the serum IL-33 levels as a biomarker in a cohort of Chinese patients, contributing to the regional understanding of stroke prognosis.
These studies, together with our findings, support the hypothesis that IL-33 might has a protective role in cerebral stroke. However, further clinical research is necessary to determine whether IL-33 supplementation could improve stroke prognosis. Notably, one study demonstrated that IL-33 promotes a Th2 response while suppressing a Th17 response following middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO), indicating a protective mechanism (34). Another study observed that IL-33 administration not only increased levels of interleukin-4 in the brain and periphery but also conferred protection in a mouse model of cerebral stroke (35). Beyond neuroprotection, IL-33 has been identified as potentially therapeutic in other conditions. Veeraveedu et al. (36) highlighted its cardioprotective role in stressed myocardium, suggesting its utility in treating nonischemic heart failure. Additionally, IL-33 has been shown to prevent cardiomyocyte apoptosis, improve cardiac function and survival post-myocardial infarction via ST2 signaling (13), and reduce mortality in experimental sepsis by enhancing neutrophil influx to infection sites (37). Furthermore, Martínez-Martínez et al. (38) found that IL-33 could attenuate metabolic disorders associated with aldosterone excess and inhibit aldosterone-induced adipocyte differentiation and inflammation. Another study indicated IL-33's protective role in mitigating adipose tissue inflammation during obesity (39).
Limitations
Several limitations of this study warrant consideration. First, its observational nature precludes determination of causality, and residual confounding factors such as poorer health status may influence the findings. Second, IL-33 levels were measured only once upon admission, which may not accurately reflect chronic levels. Third, although IL-33/ST2 signaling plays a dual role in various central nervous system (18) and cardiovascular diseases (40, 41), this study did not measure ST2 levels, which limits our ability to fully assess the role of IL-33/ST2 signaling in stroke prognosis. Fourth, although one study identified a significant association between the IL-33 gene polymorphism rs4742170 and ischemic stroke development (42), this study did not examine genetic variations. Fifth, since this study focuses primarily on stroke patients, I did not analyze IL-33 concentrations in a healthy population. However, previous research has shown that serum IL-33 levels are significantly higher (P < 0.001) in patients with AIS [57.68 ng/L (IQR, 44.95–76.73)] compared to healthy controls [47.48 ng/L (IQR, 38.67–53.78)] (30). Lastly, the study cohort consisted solely of Chinese patients recruited from a single hospital, which may introduce selection bias. Validation with an independent cohort would enhance the generalizability and validity of the results.
Conclusion
In conclusion, our findings suggest that low IL-33 levels are linked to greater stroke severity and poorer outcomes, reinforcing the potential of IL-33 as a biomarker for predicting adverse prognosis following acute ischemic stroke. Further research is needed to determine whether IL-33 supplementation could benefit patients with low serum levels, thereby potentially improving stroke outcomes.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Affiliated Hospital of Shandong Second Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants' legal guardians/next of kin.
Author contributions
WL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Validation, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition. DL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft. XL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Software. YZ: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Visualization. ZW: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was subsidized by grants from the Shandong Province Medical and Health Science and Technology Development Program (202204040712). The funding organizations had no role in the study's design and concept; the collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; or the preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
All authors have contributed significantly and agreed with the content of the manuscript. We are grateful to all the people who participated in our study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
NESS-China, National Epidemiological Survey of Stroke in China; IL-33, interleukin-33; ST2, Suppression of Tumorigenicity 2; CNS, central nervous system; AIS, acute ischemic stroke; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; BMI, body mass index; TIA, transient ischemic attack; NIHSS, National Institute of Health Stroke Scale (); TOAST, Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment; DWI, diffusion-weighted imaging; mRS, modified Rankin Scale; CRP, C-reactive protein; HCY, homocysteine; GLU, glucose; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; CV, coefficients of variation; OR, odds ratios; ROC, receiver operating characteristic curves; AUC, area under the curve; IQR, interquartile ranges; MCAO, middle cerebral artery occlusion.
References
1. Tu WJ, Zhao Z, Yin P, Cao L, Zeng J, Chen H, et al. Estimated burden of stroke in China in 2020. JAMA network open. (2023) 6:e231455–e231455. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.1455
2. Wu S, Wu B, Liu M, Chen Z, Wang W, Anderson CS, et al. Stroke in China: advances and challenges in epidemiology, prevention, and management. Lancet Neurol. (2019) 18:394–405. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30500-3
3. Wang W, Jiang B, Sun H, Ru X, Sun D, Wang L, et al. Prevalence, incidence, and mortality of stroke in China: results from a nationwide population-based survey of 480 687 adults. Circulation. (2017) 135:759–71. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.025250
4. Tu WJ, Wang LD. China stroke surveillance report 2021. Military Med Res. (2023) 10:33. doi: 10.1186/s40779-023-00463-x
5. Shen JX, Liu J, Zhang GJ. Interleukin-33 in malignancies: friends or foes? Front Immunol. (2018) 9:3051. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.03051
6. Dinarello CA. An IL-1 family member requires caspase-1 processing and signals through the ST2 receptor. Immunity. (2005) 23:461–2. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2005.10.004
7. Watanabe Y, Tajiki-Nishino R, Tajima H, Fukuyama T. Role of estrogen receptors α and β in the development of allergic airway inflammation in mice: a possible involvement of interleukin 33 and eosinophils. Toxicology. (2019) 411:93–100. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2018.11.002
8. Pushparaj PN, Tay HK, H'ng SC, Pitman N, Xu D, McKenzie A, et al. The cytokine interleukin-33 mediates anaphylactic shock. Proc Nat Acad Sci. (2009) 106:9773–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0901206106
9. Pei C, Barbour M, Fairlie-Clarke KJ, Allan D, Mu R, Jiang HR. Emerging role of interleukin-33 in autoimmune diseases. Immunology. (2014) 141:9–17. doi: 10.1111/imm.12174
10. Miller AM, Xu D, Asquith DL, Denby L, Li Y, Sattar N, et al. IL-33 reduces the development of atherosclerosis. J Exp Med. (2008) 205:339–46. doi: 10.1084/jem.20071868
11. Sanada S, Hakuno D, Higgins LJ, Schreiter ER, McKenzie AN, Lee RT. IL-33 and ST2 comprise a critical biomechanically induced and cardioprotective signaling system. J Clin Invest. (2007) 117:1538–49. doi: 10.1172/JCI30634
12. Li J, Xia N, Wen S, Li D, Lu Y, Gu M, et al. IL (Interleukin)-33 suppresses abdominal aortic aneurysm by enhancing regulatory T-cell expansion and activity. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2019) 39:446–58. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.312023
13. Seki K, Sanada S, Kudinova AY, Steinhauser ML, Handa V, Gannon J, et al. Interleukin-33 prevents apoptosis and improves survival after experimental myocardial infarction through ST2 signaling. Circulation: Heart Failure. (2009) 2:684–91. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.109.873240
14. Martin NT, Martin MU. Interleukin 33 is a guardian of barriers and a local alarmin. Nat Immunol. (2016) 17:122. doi: 10.1038/ni.3370
15. Augustine J, Pavlou S, Ali I, Harkin K, Ozaki E, Campbell M, et al. IL-33 deficiency causes persistent inflammation and severe neurodegeneration in retinal detachment. J Neuroinflammation. (2019) 16:1–15. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1625-y
16. Miller AM, Liew FY. The IL-33/ST2 pathway—a new therapeutic target in cardiovascular disease. Pharmacol Therapeut. (2011) 131:179–86. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2011.02.005
17. Wicher G, Wallenquist U, Lei Y, Enoksson M, Li X, Fuchs B, et al. Interleukin-33 promotes recruitment of microglia/macrophages in response to traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. (2017) 34:3173–82. doi: 10.1089/neu.2016.4900
18. Du LX, Wang YQ, Hua GQ Mi WL. IL-33/ST2 pathway as a rational therapeutic target for CNS diseases. Neuroscience. (2018) 369:222–30. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.11.028
19. Zhang ZY, Li J, Ye Q, Dong Y, Bao GM, Shen YK, et al. Usefulness of serum interleukin-33 as a prognostic marker of severe traumatic brain injury. Clinica Chimica Acta. (2019) 497:6–12. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.07.008
20. Gong J, Zhu Y, Yu J, Jin J, Chen M, Liu W, et al. Increased serum interleukin-33 concentrations predict worse prognosis of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Clinica Chimica Acta. (2018) 486:214–8. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2018.08.011
21. Liu J, Xing Y, Gao Y, Zhou C. Changes in serum interleukin-33 levels in patients with acute cerebral infarction. J Clini Neurosci. (2014) 21:298–300. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2013.04.036
22. Chen Z, Hu Q, Huo Y, Zhang R, Fu Q, Qin X. Serum interleukin-33 is a novel predictive biomarker of hemorrhage transformation and outcome in acute ischemic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. (2020) 30:105506. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2020.105506
23. von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, Pocock SJ, Gotzsche PC, Vandenbroucke JP. The strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. Lancet. (2007) 370:1453–7. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61602-X
24. Hatano S. Experience from a multicentre stroke register: a preliminary report. Bull World Health Organ. (1976) 54:541–53.
25. Brott T, Marler JR, Olinger CP, Marler JR, Barsan WG, Biller J, et al. Measurements of acute cerebral infarction: lesion size by computed tomography. Stroke. (1989) 20:871–5. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.20.7.871
26. Adams HP Jr, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, et al. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke. (1993) 24:35–41. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.24.1.35
27. Szabo K, Kern R, Gass A, Hirsch J, Hennerici M. Acute stroke patterns in patients with internal carotid artery disease: a diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging study. Stroke. (2001) 32:1323–9. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.32.6.1323
28. Katan M, Fluri F, Morgenthaler NG, Schuetz P, Zweifel C, Bingisser R, et al. Copeptin: a novel, independent prognostic marker in patients with ischemic stroke. Ann Neurol. (2009) 66:799–808. doi: 10.1002/ana.21783
29. Tu WJ, Qiu HC, Zhang Y, Cao JL, Wang H, Zhao JZ, et al. Lower serum retinoic acid level for prediction of higher risk of mortality in ischemic stroke. Neurology. (2019) 92:e1678–87. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000007261
30. Li Q, Lin Y, Huang W, Zhou Y, Chen X, Wang B, et al. Serum IL-33 is a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in acute ischemic stroke. Aging Dis. (2016) 7:614–22. doi: 10.14336/AD.2016.0207
31. Li XM, Wang XY, Feng XW, Shao MM, Liu WF, Ma QQ, et al. Serum interleukin-33 as a novel marker for long-term prognosis and recurrence in acute ischemic stroke patients. Brain Behav. (2019) 9:e01369. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1369
32. Chen Z, Zhang R, Wu Y, Fu Q, Qin X. Serum interleukin-33 is a predictor of depression in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Curr Neurovasc Res. 17:719–24. doi: 10.2174/1567202617999210101223635
33. Krychtiuk KA, Stojkovic S, Lenz M, Brekalo M, Huber K, Wojta J, et al. Predictive value of low interleukin-33 in critically ill patients. Cytokine. (2018) 103:109–13. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2017.09.017
34. Luo YI, Zhou Y, Xiao W, Liang Z, Dai J, Weng X, et al. Interleukin-33 ameliorates ischemic brain injury in experimental stroke through promoting Th2 response and suppressing Th17 response. Brain Res. (2015) 1597:86–94. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.12.005
35. Korhonen P, Kanninen KM, Lehtonen Š, Lemarchant S, Puttonen KA, Oksanen M, et al. Immunomodulation by interleukin-33 is protective in stroke through modulation of inflammation. Brain Behav Immun. (2015) 49:322–36. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2015.06.013
36. Veeraveedu PT, Sanada S, Okuda K, Fu HY, Matsuzaki T, Araki R, et al. Ablation of IL-33 gene exacerbate myocardial remodeling in mice with heart failure induced by mechanical stress. Biochem Pharmacol. (2017) 138:73–80. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.04.022
37. Alves-Filho JC, Sônego F, Souto FO, Freitas A, Verri WA, Auxiliadora-Martins M, et al. Interleukin-33 attenuates sepsis by enhancing neutrophil influx to the site of infection. Nat Med. (2010) 16:708–12. doi: 10.1038/nm.2156
38. Martínez-Martínez E, Cachofeiro V, Rousseau E, Álvarez V, Calvier L, Fernández-Celis A, et al. Interleukin-33/ST2 system attenuates aldosterone-induced adipogenesis and inflammation. Mol Cell Endocrinol. (2015) 411:20–7. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2015.04.007
39. Miller AM, Asquith DL, Hueber AJ, Anderson LA, Holmes WM, McKenzie AN, et al. Interleukin-33 induces protective effects in adipose tissue inflammation during obesity in mice. Circ Res. (2010) 107:650–8. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.218867
40. Thanikachalam PV, Ramamurthy S, Mallapu P, Varma SR, Narayanan J, Abourehab M, et al. Modulation of IL-33/ST2 signaling as a potential new therapeutic target for cardiovascular diseases. Cytok Growth Factor Rev. (2023) 71:94–104. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2023.06.003
41. Guo S, Qian C, Li W, Zeng Z, Cai J, Luo Y. Modulation of neuroinflammation: advances in roles and mechanisms of the IL-33/ST2 axis involved in ischemic stroke. Neuroimmunomodulation. (2023) 30:226–36. doi: 10.1159/000533984
Keywords: ischemic stroke, prognosis, biomarker, IL-33, Chinese
Citation: Liu W, Luo D, Liu X, Zhang Y and Wang Z (2024) Predictive value of low serum interleukin-33 levels in acute ischemic stroke outcomes. Front. Neurol. 15:1503443. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1503443
Received: 29 September 2024; Accepted: 28 October 2024;
Published: 22 November 2024.
Edited by:
Wen-Jun Tu, Capital Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Shumei Man, Cleveland Clinic, United StatesHuatuo Huang, Affiliated Hospital of Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities, China
Copyright © 2024 Liu, Luo, Liu, Zhang and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhong Wang, d2FuZ3pob25nNjY2NjE4QDEyNi5jb20=
 Wei Liu1,2
Wei Liu1,2 Zhong Wang
Zhong Wang