- Department of Neurology, Dongzhimen Hospital Affiliated to Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
Objective: The objective of the study is to analyze and explore the characteristics of the video head impulse test (vHIT) for light cupula in the idiopathic horizontal semicircular canal and compare them with those of horizontal semicircular canal cupulolithiasis (HC-cu) in order to investigate the potential mechanism involved.
Methods: Data from 51 cases of idiopathic light cupula and 42 cases of horizontal semicircular canal cupulolithiasis were retrospectively analyzed. The positional nystagmus features, vHIT anomaly rate, gain value, saccades, and other indicators were compared. SPSS 26 and Medcalc 22 were used to analyze the differences and correlations.
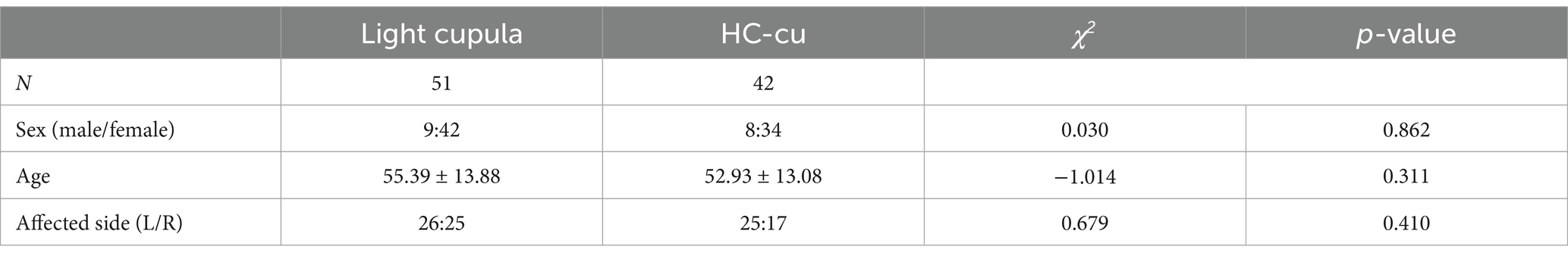
Results: There were no differences in sex, age, the affected side, and positional nystagmus between the light cupula group and HC-cu group (p > 0.05). The overall abnormal rate of the vHIT (56.86% vs. 21.43%), the abnormal rate of the affected side (23.53% vs. 0.00%), and the saccade ratio of the affected side [40.0 (13.0, 76.0) vs. 6.0 (0.0, 15.0)] in the light cupula group were higher than those in the HC-cu group. The HC saccade ratio in the light cupula group was higher on the affected side than on the healthy side [40.0 (13.0, 76.0) vs. 11.0 (0.0, 38.0)], and the differences were statistically significant (p < 0.05). The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis showed that the abnormal vHIT results and saccade ratio of the light cupula group were correlated with the affected side (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: The vHIT results of idiopathic HC light cupula and HC-Cu were different as they are distinct diseases. Light cupula may be associated with some mild lesions in the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) pathway. The lighter cupula theory is the possible mechanism.
1 Introduction
In recent years, the light cupula (1, 2) with no history of alcohol intake has gained attention as an explanation for direction-changing positional nystagmus (DCPN). The main clinical manifestation of this disease is paroxysmal positional vertigo. Physical examination may reveal geotropic DCPN, a zero plane where the nystagmus disappears (3), and pseudo-spontaneous nystagmus (PSN) (4). Light cupula is not rare, accounting for 14.2% of cases of geotropic DCPN (5), and there is no effective treatment available (6, 7). The exploration of its mechanism and treatment methods remains a key focus for clinicians. Currently, the mechanism of this disease is still controversial, but several hypotheses related to the vestibular system have been proposed (8, 9). Existing imaging techniques and anatomical methods offer limited insights into the mechanism of this disease, while vestibular function examination may help enhance our understanding of it. Previous studies have shown that light cupula can occur as a secondary condition to other inner ear-related diseases, such as sudden deafness (10–12) and labyrinthitis (13). These diseases usually have clear vestibular dysfunction. However, light cupula can also occur in isolation, i.e., idiopathically. Is idiopathic light cupula associated with vestibular dysfunction? This is a question of concern, and it may provide clues for exploring the disease’s mechanisms and therapeutic methods. Few studies have addressed this issue. In this study, the video head impulse test (vHIT) was used to evaluate the function of the high-frequency vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) pathway for each semicircular canal (14), and cases of idiopathic horizontal semicircular canal light cupula were analyzed. By comparing idiopathic horizontal semicircular canal light cupula with horizontal semicircular canal cupulolithiasis (HC-cu), this article discusses both the similarities and differences, as well as the related mechanisms. This study aimed to improve clinicians’ understanding of this disease and provide a reference for further exploration into its treatment and prevention. The findings are presented as follows.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Sample sources
This study was a retrospective analysis. It was carried out in the Vertigo Center of Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine. The research participants were selected from the case database of the vestibular function examination room, covering the period from 1 January 2021 to 31 December 2023. The vestibular examination room in our center, established in 2015, includes a complete case database. The database used in this study was sourced from the existing databases. Based on the pre-test results of the abnormal rates of the vHIT in the two groups, with a significance level of 0.05, a test power of 0.8, and a grouping ratio of 1:1, the sample size was calculated. The sampling method involved retrospectively extracting all cases that met the inclusion criteria within a specific time period. We ensured data quality by establishing rigorous data collection standards, training professional staff, conducting double-entry verification, performing comprehensive data cleaning and auditing, and applying multi-method cross-validation.
According to the inclusion/exclusion criteria, the cases were divided into the light cupula group and the HC-cu group. As only a small fraction of typical HC-cu cases had vHIT results and the total number of idiopathic light cupula cases was limited, all eligible cases during the review period were included in this study to increase the sample size.
This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Dongzhimen Hospital (2022DZMEC-251), and a waiver for informed consent was obtained.
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria for the light cupula group were as follows: (a) age ranging from 18 to 80 years. (b) The roll test showing persistent geotropic DCPN with no significant latency and attenuation, and the duration of nystagmus being greater than 1 min. The roll test identifying null plane 2 (NP2) (3), and the Bow and Lean test (BLT) (15) being positive. (c) Brain imaging (MRI/CT) and a nervous system examination excluding central lesions.
The inclusion criteria for the HC-cu group were as follows: (a) age ranging from 18 to 80 years. (b) The diagnostic criteria following the benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) diagnostic criteria for horizontal semicircular canal cupulolithiasis (16), i.e., recurrent vertigo attacks caused by lying down or turning over, with the roll test showing continuous apogeotropic DCPN with a duration of >1 min, which could not be attributed to other diseases.
The exclusion criteria were as follows: (a) coexisting vestibular disorders, such as vestibular migraine, Meniere’s disease, vestibular neuritis, sudden deafness with vertigo, and typical BPPV; (b) a history of alcohol intake within the past 48 h; (c) use of vestibular inhibitors within the past 72 h; and (d) presence of central lesions, posterior circulation ischemia, psychosis, epilepsy, and malignant tumors.
2.3 Examination methods
Positional nystagmus was observed and recorded using video nystagmography (Otometrics ICS Chartr 200) in the state of fixation elimination. The position test, vHIT examination, and repositioning maneuvers for BPPV treatment were all performed on the same day.
The vHIT examination was performed using a video head pulse device (Otometrics ICS Impulse 4.0). At least 15 effective flicks were recorded for each semicircular canal. Both the head and eye movement curves were recorded; and the gain value, gain asymmetry (GA), peak saccade velocity, and corrective saccades (CS) were calculated using the software (17). The ratio of GA was calculated as [1-lower gain/higher gain] × 100%. The ratio of CS was calculated as [the number of head impulses with CS]/[trials number] × 100%. The following conditions are considered abnormal in the vHIT: (a) a horizontal semicircular gain <0.8 and a vertical semicircular gain <0.7 (18), accompanied by CS. (b) a normal gain, with CS occurring in more than 50% of trials, i.e., the ratio of CS is more than 50% (19, 20).
All vHIT procedures in this study were performed by senior neurologists specializing in the field of vertigo and dizziness. Data entry was performed using a double-entry system and checked for accuracy.
2.4 Statistical methods
The means and distributions were compared using SPSS 26.0 software. Count data were expressed as n/% and compared using a chi-squared test. Normal measurement data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation and compared using a t-test. Non-normal data were expressed as M (P25, P75) and compared using the Mann–Whitney U test for two independent samples. Paired samples were compared using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test. The Kruskal–Wallis test was performed to compare between three groups. The Bonferroni correction was used for pairwise comparisons. Correlation analysis was conducted using ROC curves with MedCalc 22 software. A p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 General information
A total of 51 cases were included in the light cupula group and 42 cases in the HC-cu group. There was no significant difference in sex, age, and the affected side between the two groups (p > 0.05), as shown in Table 1.
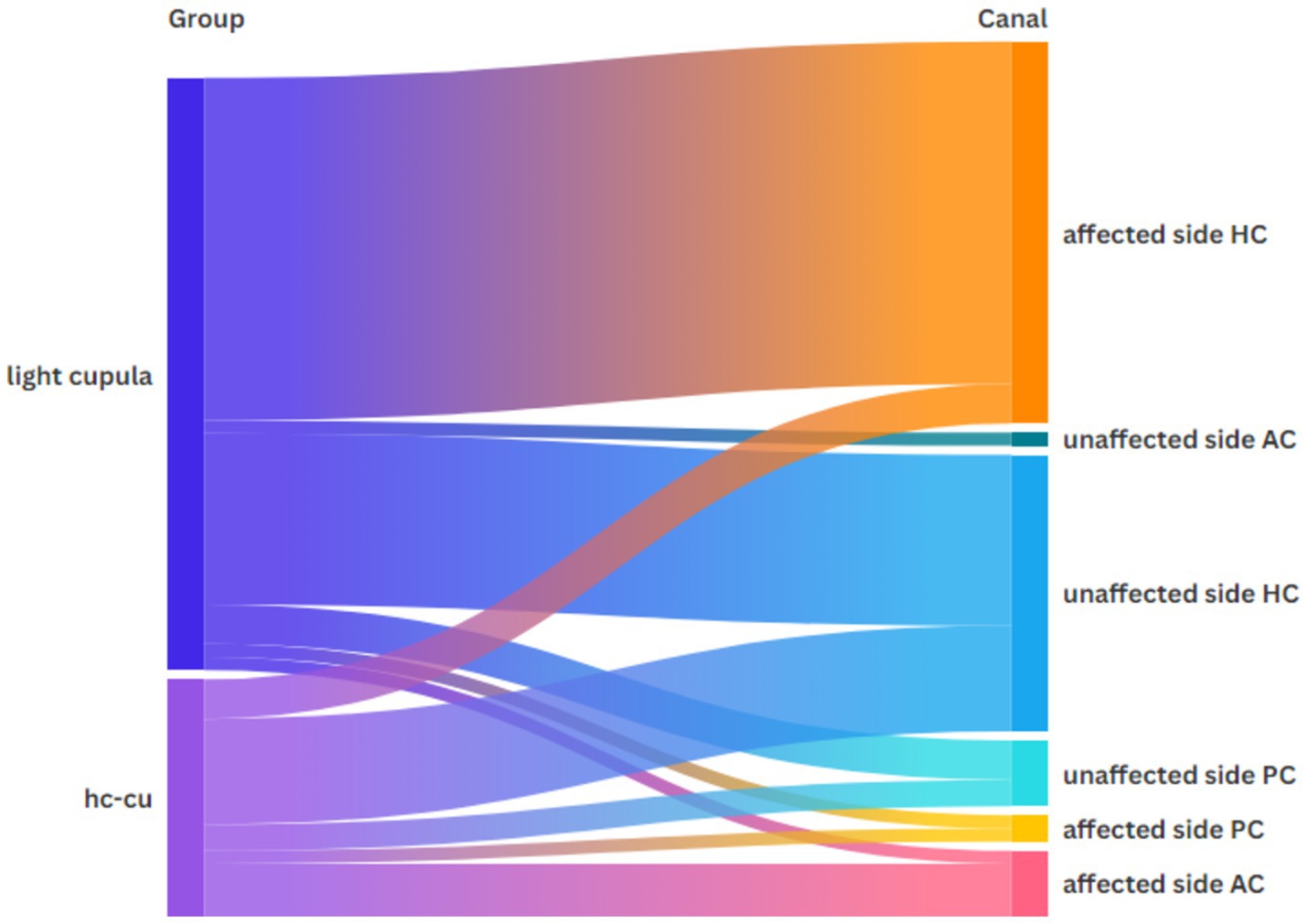
Figure 1 shows the distribution of the vHIT abnormalities across the semicircular canals in both groups. From the figure, we can see that the majority of the abnormalities occurred in the horizontal semicircular canal on the affected side of light cupula.
3.2 Null plane and positional nystagmus
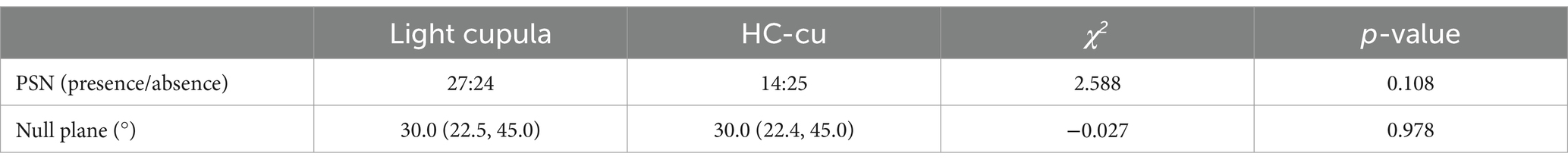
The Bow-and-Lean test was positive in all cases. PSN was observed in 27 cases (52.9%) of the light cupula group and 14 cases (33.3%) of the HC-cu group. The null plane angles of the light cupula and Hc-cu groups were 30.0 (22.5, 45.0)° and 30.0 (22.4, 45.0)°, respectively. There were no statistical differences between the groups (Table 2).
3.3 Comparison of the vHIT results
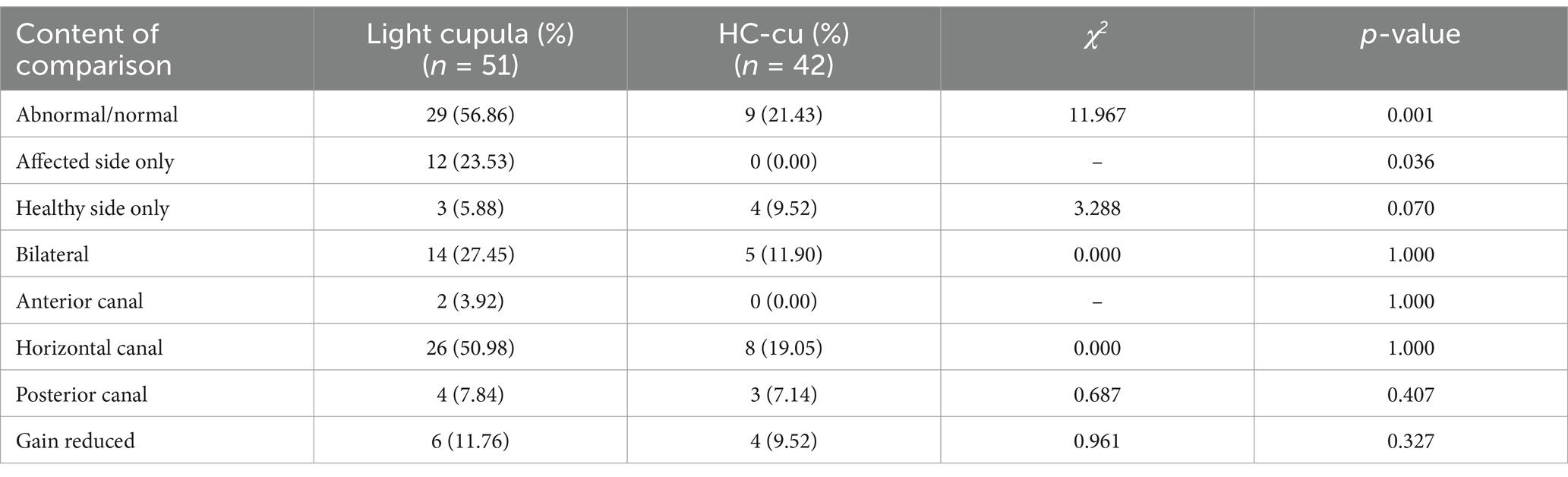
The abnormal rate of the vHIT was 56.7% (29/51) in the light cupula group and 21.3% (9/41) in the HC-cu group, and the difference was statistically significant. Among them, there were 12 cases of abnormal vHIT results on the affected side and normal vHIT results on the healthy side in the light cupula group, while no cases of simple abnormal vHIT results on the affected side were observed in the HC-cu group. The difference was statistically significant. There was no statistically significant difference between the groups in terms of the vHIT abnormalities across different semicircular canals (Table 3).
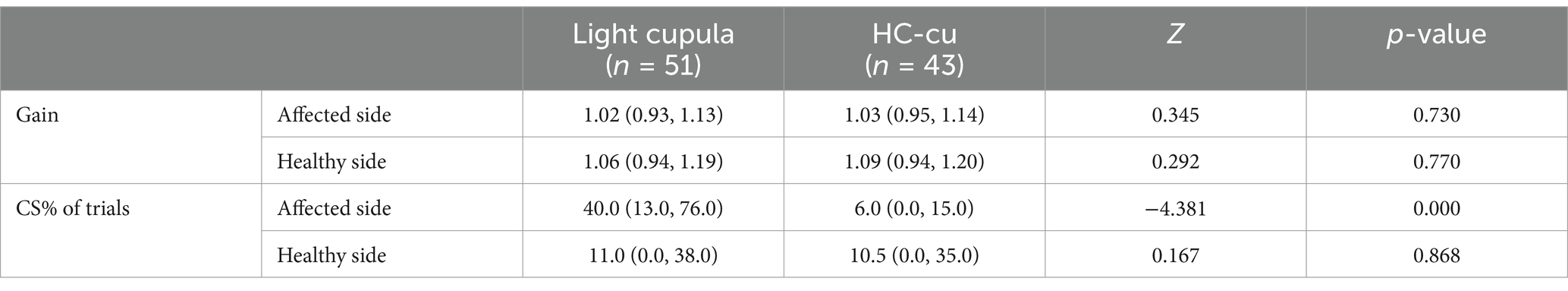
The average gain of the vHIT on the healthy side and the affected side in the two groups was within the normal range, and there was no significant difference between the two groups. The CS% of trials for the HC on the affected side of the light cupula group was higher than that of the HC-cu group, and the difference was statistically significant (see Table 4). The CS% of trials in the light cupula group was higher on the affected side than on the healthy side (the Wilcoxon signed-rank test for the relevant samples, Z = −3.675, p = 0.00).
The ROC curve analysis showed that the vHIT abnormalities in the light cupula group were correlated with the affected side (AUC = 0.608, Z = 2.302, p = 0.021), and the ratio of CS was correlated with the affected side (the best cut-off value was 33, AUC = 0.678, z = 3.304, p = 0.001, sensitivity 54.9%, specificity 74.5%, Figure 2). The vHIT results of the HC-cu group did not show any correlation with the affected side.
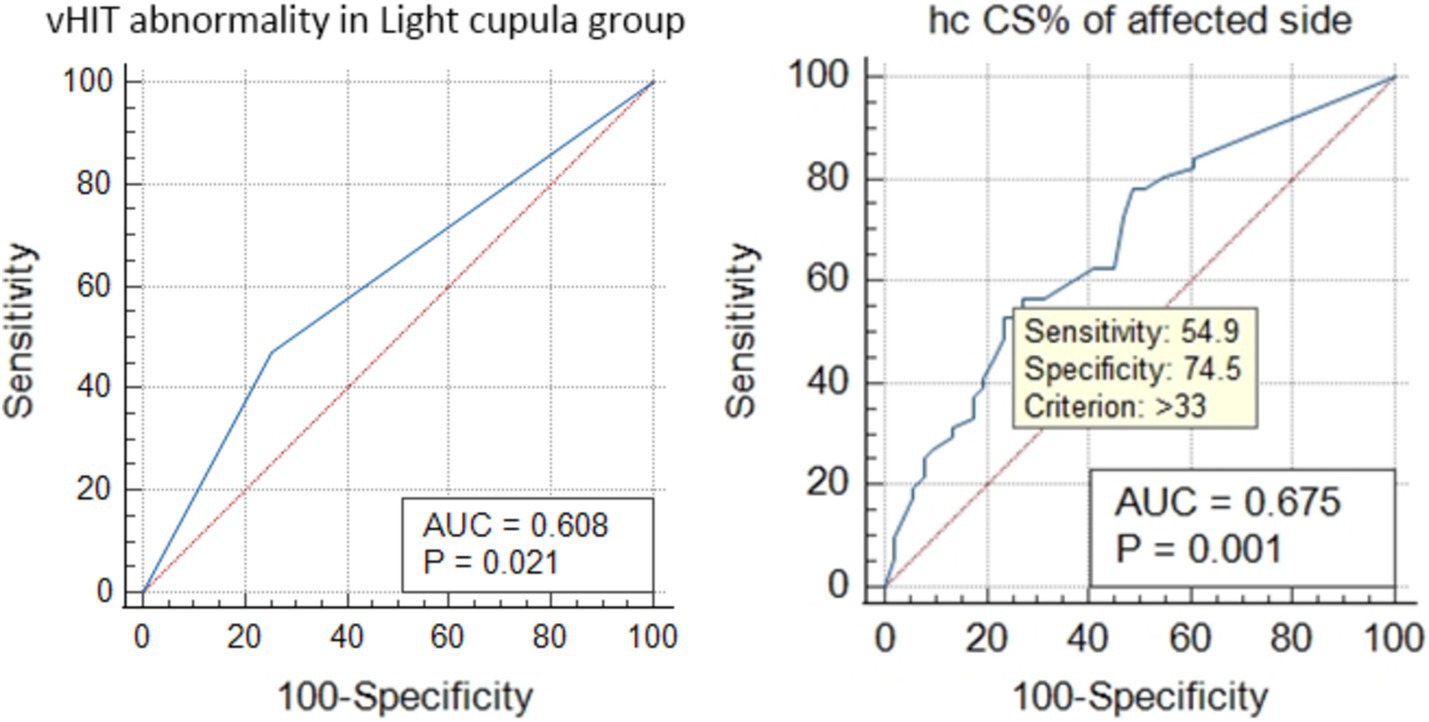
Figure 2. ROC curve analysis of the HC vHIT abnormalities and the correlation of CS% with the affected side in the light cupula group.
4 Discussion
The results showed that the vHIT outcomes in the light cupula group were significantly different from those in the HC-cu group. The abnormal vHIT rate in the light cupula group was higher than in the HC-cu group and showed a correlation with the affected side. In this study, the abnormal rate of the vHIT on the affected side was 23.5% in the light cupula group, while no abnormal results were found in the HC-cu group. This finding was consistent with the results of the caloric test, where 21.4% of the light cupula cases showed canal paresis (CP) on the affected side, while no abnormalities were found in the HC-cu group (21). Although the HC-cu group also showed some vHIT abnormalities, these were not correlated with the affected side, which is consistent with the characteristics of BPPV. Numerous previous studies have shown that while there are some scattered vHIT abnormalities in BPPV, they lack a correlation with the responsible semicircular canal (22–26).
Light cupula and HC-cu are often discussed together. They both exhibit opposite persistent DCPN, a null plane where nystagmus disappears, and similar patterns of nystagmus changes in different head positions (8). In this study, there was no difference in the null plane angle, incidence of PSN, or BLT between the two groups. However, their vHIT results were different, suggesting that they are distinct diseases. This finding aligns with the research by Peng H (27).
Not all cases of light cupula showed abnormal vHIT results; 56.9% showed abnormalities, which constituted the majority. The vHIT abnormalities were mainly concentrated in the HC on the affected side, and it could be considered that the vHIT abnormalities were related to the status of light cupula. The abnormal vHIT results mainly manifested as increased saccades, but the gain value did not show a significant decrease. This condition is commonly seen in the recovery phase of acute unilateral vestibular injury (28). Previous studies have suggested that although the gain value may be normal, significantly increased saccades still indicate the impairment of dynamic visual acuity, which is also a manifestation of VOR pathway damage, albeit to a lesser extent (20, 28). In summary, we consider that light cupula may involve a relatively minor degree of VOR pathway injury.
Could the light cupula state itself cause vHIT abnormalities? In the light cupula state, the crista ampullaris is affected by gravity. However, during the vHIT examination of the HC, the patient’s head is upright, and the plane where the HC is located is perpendicular to the direction of gravity, meaning that the crista ampullaris will hardly be affected by gravity. Previous studies have reported that otolith particles floating in the semicircular canals may cause abnormal vHIT outcomes (29–31); however, cupulolithiasis does not have the same effect. The crista ampullaris of HC-cu is also sensitive to gravity, but their vHIT results showed no abnormalities associated with the affected side. Previous studies on posterior semicircular canal cupulolithiasis (PC-cu) have shown (26) that abnormal vHIT results are not related to PC-cu localization. Therefore, we can assume that the light cupula state itself is not the cause of the abnormal vHIT results.
Therefore, there may be some anomalies in the horizontal VOR pathway in light cupula cases, which could be related to the occurrence of light cupula. Seo T (32) reported a case of persistent light cupula secondary to sudden deafness, which is considered to be associated with the irreversible damage of light cupula. In other words, pathological changes in the crista ampullaris itself can lead to both the development of light cupula and injury to the VOR pathway. We speculate that a similar mechanism may exist in idiopathic light cupula, but with a lesser degree of concomitant VOR injury. Among the existing hypotheses, the lighter cupula theory (32) is the one most closely aligned with the results of this study. Due to certain lesions in the crista ampullaris, its density is reduced and its response to high-frequency VOR is decreased, resulting in the light cupula status and abnormal vHIT results.
Among the existing light cupula mechanism hypotheses, the lighter cupula theory (32) and light debris theory (8, 33–35) can independently affect the semicircular canals. The heavier endolymph theory (10–12) and the density difference between perilymph and endolymph theory (36) must consider the possibility of simultaneous involvement of the vertical semicircular canal. The utricular macula theory (37) does not address the issues related to the semicircular canals.
The light debris theory is the hypothesis most similar to the mechanism of cupulolithiasis. However, in previous studies, light cupula was treated with anti-gravity repositioning maneuvers without any success (7, 38), which raises doubts about the validity of the hypothesis of the light debris theory. It is also inadequate for explaining the abnormal results of the vHIT.
Previous studies have almost exclusively focused on the light cupula phenomenon of the HC. However, it is known that the light cupula phenomenon in alcoholic nystagmus occurs simultaneously in all semicircular canals (39). Cases of light cupula involving all semicircular canals on one side, without alcohol intake, have also been reported (40). Positional nystagmus produced by the vertical semicircular canal may be partially counteracted (5, 40). Moreover, the specific angle of the long axis of the cupula of the vertical semicircular canal still lacks anatomical evidence. Therefore, it is difficult to accurately observe and discuss the light cupula phenomenon of the vertical semicircular canal.
Cases of nystagmus with vertical and rotational components were excluded as much as possible. The vHIT results showed that these cases had the highest abnormal rate in the HC on the affected side, confirming that light cupula can occur in the unilateral HC alone. This situation challenges the three hypotheses of the heavier endolymph theory, the density difference between perilymph and endolymph theory, and the utricular macula theory.
It is important to note that the light cupula phenomenon involving all semicircular canals on the same side at the same time does not conflict with the light cupula phenomenon involving a single semicircular canal, and they may have different mechanisms. Similarly, the heavy cupula of the HC is not the same as HC-cu, which is why we named the control group “HC-cu” rather than “heavy cupula.” The light–heavy cupula transformation in alcoholic nystagmus is well known, and similar transformations in non-alcoholic nystagmus have also been reported (13, 41). The heavy cupula may have other mechanisms similar to those of the light cupula, which are not entirely caused by cupulolithiasis. These cases may have been misidentified for a long time, leading to difficulties in identifying non-reducible HC-cu cases. This confusion could help explain the low success rate of HC-cu reduction (3, 27). Therefore, different ideas and considerations should be taken into account in the future exploration of treatment for this condition.
5 Conclusion
Idiopathic HC light cupula exhibits significantly more vHIT anomalies than HC-Cu and shows an association with the affected side, while HC-Cu does not display this feature, indicating that the two diseases are different.
The abnormal vHIT findings in light cupula of the idiopathic HC are correlated with the affected semicircular canal, which suggests that light cupula may have a causal relationship or homology with certain injuries in the VOR pathway. The lighter cupula theory is the possible mechanism. The pathological changes in the cupula itself may lead to both the occurrence of the light cupula state and the abnormal results of the vHIT.
Light cupula can affect the HC alone or all three semicircular canals on the same side simultaneously. They may have different mechanisms. These differences should also be considered in future therapeutic explorations.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of Dongzhimen Hospital Affiliated to Beijing University of Chinese Medicine. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin due to the retrospective nature of this study.
Author contributions
NS: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CJ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. PX: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Bergenius, J, and Tomanovic, T. Persistent geotropic nystagmus—a different kind of cupular pathology and its localizing signs. Acta Otolaryngol. (2006) 126:698–704. doi: 10.1080/00016480500475609
2. Kim, MB, Hong, SM, Choi, H, Choi, S, Pham, NC, Shin, JE, et al. The light cupula: an emerging new concept for positional Vertigo[J]. J Audiol Otol. (2018) 22:1–5. doi: 10.7874/jao.2017.00234
3. Lee, DH, Kim, TH, Jang, M, and Kim, CH. The light cupula phenomenon: a scoping review[J]. Brain Sci. (2023) 14:15. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14010015
4. Asprella-Libonati, G. Pseudo-spontaneous nystagmus: a new sign to diagnose the affected side in lateral semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. (2008) 28:73–8.
5. Kim, CH, Kim, MB, and Ban, JH. Persistent geotropic direction-changing positional nystagmus with a null plane: the light cupula[J]. Laryngoscope. (2014) 124:E15–9. doi: 10.1002/lary.24048
6. Ban, JH, Kim, MB, and Hong, SM. Immediate and short-term therapeutic results between direction-changing positional nystagmus with short- and long-duration groups. Ear Hear. (2016) 37:243–6. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0000000000000232
7. Kim, CH, and Hong, SM. Is the modified cupulolith repositioning maneuver effective for treatment of persistent geotropic direction changing positional nystagmus? Eur Arch Otorrinolaringol. (2018) 275:1731–6. doi: 10.1007/s00405-018-5006-4
8. Imai, T, Matsuda, K, Takeda, N, Uno, A, Kitahara, T, Horii, A, et al. Light cupula: the pathophysiological basis of persistent geotropic positional nystagmus. BMJ Open. (2015) 5:e006607. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-006607
9. Tang, X, Huang, Q, Chen, L, Liu, P, Feng, T, Ou, Y, et al. Clinical findings in patients with persistent positional nystagmus: the designation of “heavy and light cupula”. Front Neurol. (2019) 10:326. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00326
10. Kim, CH, Choi, JM, Jung, HV, Park, HJ, and Shin, JE. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss with simultaneous positional vertigo showing persistent geotropic direction-changing positional nystagmus. Otol Neurotol. (2014) 35:1626–32. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000000457
11. Kim, CH, Shin, JE, Yang, YS, and Im, D. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss with positional vertigo: initial findings of positional nystagmus and hearing outcomes. Int J Audiol. (2016) 55:541–6. doi: 10.1080/14992027.2016.1194532
12. Kim, YW, Shin, JE, Lee, YS, and Kim, CH. Persistent positional Vertigo in a patient with sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a case report. J Audiol Otol. (2015) 19:104–7. doi: 10.7874/jao.2015.19.2.104
13. Kim, CH, Yang, YS, Im, D, and Shin, JE. Nystagmus in patients with unilateral acute otitis media complicated by serous labyrinthitis. Acta Otolaryngol. (2016) 136:559–63. doi: 10.3109/00016489.2015.1132845
14. Weber, KP, MacDougall, HG, Halmagyi, GM, and Curthoys, IS. Impulsive testing of semicircular-canal function using video-oculography. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (2009) 1164:486–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2008.03730.x
15. Kim, CH, Shin, JE, and Kim, YW. A new method for evaluating lateral semicircular canal cupulopathy. Laryngoscope. (2015) 125:1921–5. doi: 10.1002/lary.25181
16. von Brevern, M, Bertholon, P, Brandt, T, Fife, T, Imai, T, Nuti, D, et al. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: Diagnostic criteria. J Vestib Res. (2015) 25:105–17. doi: 10.3233/VES-150553
17. Rey-Martinez, J, Batuecas-Caletrio, A, Matiño, E, and Perez Fernandez, N. HITCal: a software tool for analysis of video head impulse test responses. Acta Otolaryngol. (2015) 135:886–94. doi: 10.3109/00016489.2015.1035401
18. McGarvie, LA, MacDougall, HG, Halmagyi, GM, Burgess, AM, Weber, KP, and Curthoys, IS. The video head impulse test (vHIT) of Semicircular Canal function - age-dependent normative values of VOR gain in healthy subjects. Front Neurol. (2015) 6:154. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2015.00154
19. McCaslin, DL, Jacobson, GP, Bennett, ML, Gruenwald, JM, and Green, AP. Predictive properties of the video head impulse test: measures of caloric symmetry and self-report dizziness handicap. Ear Hear. (2014) 35:e185–91. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0000000000000047
20. Kabaya, K, Fukushima, A, Katsumi, S, Minakata, T, and Iwasaki, S. Presence of corrective saccades in patients with normal vestibulo-ocular reflex gain in video head impulse test[J]. Front Neurol. (2023) 14:1152052. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1152052
21. Ichijo, H. Caloric testing in patients with heavy or light cupula of the lateral semicircular canal. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. (2016) 1:163–8. doi: 10.1002/lio2.39
22. Jinyu, L, Ling, L, Kun, Z, Fanglei, Y. Analysis of Semicircular Canal function in 190 patients with idiopathic benign paroxysmal positional Vertigo. Chin J Otol. (2021) 19:240–3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2922.2021.02.012
23. Abdulrahim, R, Bhandary, BSK, Rajeshwary, A, Goutham, MK, Bhat, V, and Saldanha, M. The role of video head impulse test (Vhit) in diagnosing benign paroxysmal positional Vertigo (BPPV). Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. (2022) 74:506–10. doi: 10.1007/s12070-020-02351-5
24. Liu, Y, Leng, Y, Zhou, R, Liu, J, Wang, H, Xia, K, et al. Video head impulse test findings in patients with benign paroxysmal positional Vertigo secondary to idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Front Neurol. (2022) 13:877777. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.877777
25. Saltürk, Z, and Yetişer, S. Video head impulse testing in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Acta Otolaryngol. (2020) 140:977–81. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2020.1805123
26. Wenyan, X, Lifeng, Y, Jing, W, and Hui, J. Vestibular function in cases of posterior semicircular canal canalolithiasis and cupulolithiasis. Front Neurol. (2024) 15:1369193. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1369193
27. Peng, H, Wang, L, Song, H, Gao, B, Yang, Y, and Lyu, F. Clinical characteristics of persistent geotropic horizontal direction-changing positional nystagmus: experience in 189 participants[J]. J Vestib Res Equilib Orientat. (2023) 33:203–11. doi: 10.3233/VES-220086
28. Yang, CJ, Cha, EH, Park, JW, Kang, BC, Yoo, MH, Kang, WS, et al. Diagnostic value of gains and corrective saccades in video head impulse test in vestibular neuritis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. (2018) 159:347–53. doi: 10.1177/0194599818768218
29. Elsherif, M, Eldeeb, D, and Eldeeb, M. Clinical significance of video head impulse test in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a meta-analysis. Eur Arch Otorrinolaringol. (2021) 278:4645–51. doi: 10.1007/s00405-021-06832-3
30. Castellucci, A, Malara, P, Martellucci, S, Botti, C, Delmonte, S, Quaglieri, S, et al. Feasibility of using the video-head impulse test to detect the involved canal in benign paroxysmal positional Vertigo presenting with positional downbeat nystagmus. Front Neurol. (2020) 11:578588. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.578588
31. Califano, L, Iannella, R, Mazzone, S, Salafia, F, and Melillo, MG. The video head impulse test in the acute stage of posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo[J]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. (2021) 41:69–76. doi: 10.14639/0392-100X-N1033
32. Seo, T, Saito, K, and Doi, K. Intractable persistent direction-changing geotropic nystagmus improved by lateral semicircular canal plugging[J]. Otolaryngology. (2015) 2015:1–3. doi: 10.1155/2015/192764
33. Ichijo, H. Neutral position of persistent direction-changing positional nystagmus. Eur Arch Otorrinolaringol. (2016) 273:311–6. doi: 10.1007/s00405-014-3487-3
34. Schubert, MC, Dunlap, PM, and Whitney, SL. A case study of high-velocity, persistent geotropic nystagmus: is this BPPV? J Neurol Phys Ther. (2017) 41:182–6. doi: 10.1097/NPT.0000000000000191
35. Ichijo, H. Persistent direction-changing geotropic positional nystagmus. Eur Arch Otorrinolaringol. (2012) 269:747–51. doi: 10.1007/s00405-011-1700-1
36. Kim, CH, and Pham, NC. Density difference between perilymph and endolymph: a new hypothesis for light cupula phenomenon. Med Hypotheses. (2019) 123:55–9. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2018.12.017
37. Hiruma, K, and Numata, T. Positional nystagmus showing neutral points. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. (2004) 66:46–50. doi: 10.1159/000077234
38. Tomanovic, T, and Bergenius, J. Vestibular findings in patients with persistent geotropic positional nystagmus: the ‘light cupula’phenomenon. Acta Otolaryngol. (2014) 134:904–14. doi: 10.3109/00016489.2014.928421
39. Money, KE, Johnson, WH, and Corlett, BM. Role of semicircular canals in positional alcohol nystagmus. Am J Phys. (1965) 208:1065–70. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.208.6.1065
40. Kim, CH, Shin, JE, Shin, DH, Kim, YW, and Ban, JH. “Light cupula” involving all three semicircular canals: a frequently misdiagnosed disorder. Med Hypotheses. (2014) 83:541–4. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2014.09.002
Keywords: light cupula, direction-changing positional nystagmus, video head impulse test, vestibular function test, cupulolithiasis
Citation: Song N, Jingling C, Wenyan X and Xuemei P (2024) Clinical observations from the clinical video head pulse test in patients with idiopathic horizontal semicircular canal light cupula. Front. Neurol. 15:1496430. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1496430
Edited by:
Herman Kingma, Maastricht University, NetherlandsReviewed by:
Jeremy Hornibrook, University of Canterbury, New ZealandTsegaye Alemu, Hawassa University, Ethiopia
Copyright © 2024 Song, Jingling, Wenyan and Xuemei. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Pei Xuemei, NzI0OTkxMjI0QHFxLmNvbQ==
 Niu Song
Niu Song Chang Jingling
Chang Jingling Xu Wenyan
Xu Wenyan Pei Xuemei
Pei Xuemei