- 1Department of Dermatology, Tangshan Fengnan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tangshan, China
- 2Department of Dermatology, First Teaching Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin, China
- 3National Clinical Research Center for Chinese Medicine Acupuncture and Moxibustion, Tianjin, China
Objectives: This meta-analysis investigated the relationship between herpes zoster and the risk of dementia or Parkinson’s disease by analyzing published clinical studies.
Methods: We systematically searched PubMed, Cochrane, Embase, and Web of Science Core Collection databases on April 25, 2024. Hazard ratios (HR) were used for statistical analyses. Random-effects models were applied, and heterogeneity was assessed using the I2 statistic.
Results: Herpes zoster was associated with a non-significant trend toward increased dementia risk (HR = 1.11, 95% CI 0.99–1.24, p = 0.07) but significantly increased Parkinson’s disease risk (HR = 1.15, 95% CI 1.03–1.30, p = 0.02). Subgroup analyses revealed that herpes zoster significantly elevated the risk of the prospective study subgroup (HR = 1.08, 95% CI 1.02–1.13, p = 0.004) and vascular dementia subgroup (HR = 1.17, 95% CI 1.00–1.37, p = 0.05). Significant heterogeneity was observed for both outcomes (dementia: I2 = 98%, p < 0.00001; Parkinson’s disease: I2 = 94%, p < 0.00001).
Conclusion: Herpes zoster raises the risk of Parkinson’s disease and vascular dementia, with a potential causal link to dementia. Early vaccination against herpes zoster is recommended over post-infection antiviral treatment to mitigate risks.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/ and our registration number is CRD42024555620.
Introduction
With the global population increasing and aging, neurodegenerative diseases, particularly Parkinson’s disease (PD) and dementia, have become significant causes of disability worldwide, posing a substantial public health burden. PD is a neurodegenerative movement disorder strongly associated with aging, with a lifetime prevalence of 1–5%, and its risk increases significantly with age. In addition to motor symptoms such as bradykinesia and resting tremor, Parkinson’s also leads to non-motor symptoms like depression, sleep disturbances, and cognitive deficits, all of which severely impact patients’ quality of life. Similarly, dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia, and dementia with Lewy bodies, is an irreversible, progressive brain disorder primarily characterized by persistent cognitive impairment, significantly disrupting daily life. According to the 2015 World Alzheimer’s Disease Report, the global population of people living with dementia reached 46.8 million and is projected to double every 20 years (1–5).
Aging, genetic predisposition, educational level, and socioeconomic status are widely recognized as potential risk factors for dementia and PD (6). Emerging evidence suggests a significant correlation between neuroviral infections, accelerated brain aging, and heightened susceptibility to neurodegenerative diseases (7, 8). A variety of viruses can trigger neuroinfections, including Herpesviridae family members [e.g., Epstein–Barr virus (EBV), herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1), varicella zoster virus (VZV)], hepatitis C virus (HCV), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and human endogenous retroviruses (HERVs) (9–14). Among these, more than 95% of individuals over the age of 50 globally have been exposed to VZV and the risk for this group is significant (15), necessitating further investigation into its association with dementia and PD.
A number of prospective or retrospective clinical studies have examined the relationship between herpes zoster and dementia or PD, yet the findings have been inconsistent. For instance, Cheng et al. (16) and Lai et al. (17) found an increased risk of PD in patients with herpes zoster, while Tunnicliffe et al. (18) reached the opposite conclusion. Similarly, studies investigating the relationship between herpes patients and dementia (19–21) have also yielded contradictory results. To better understand the relationship between herpes zoster and dementia or PD, we collected, analyzed, and summarized data from a wide range of studies across four commonly used databases.
Materials and methods
Literature search
This study followed the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) (Supplementary Table S1) checklist published in 2020 (22) and was registered in the PROSPERO (CRD42024555620) system. We conducted a systematic literature search in four databases: PubMed, Cochrane, Embase, and Web of Science Core Collection, with a cut-off date of April 25, 2024. The search was performed in English using the keywords “herpes zoster,” “Parkinson’s disease,” and “dementia” (Supplementary Table S2). At least two clinicians manually reviewed all relevant literature multiple times to ensure relevance, eliminate disagreements, and meet the requirements.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The following PICOS principles guided the inclusion criteria:
Participants: Patients with herpes zoster and a control population without herpes zoster;
Intervention: Herpes zoster;
Comparison: Control population without herpes zoster;
Outcome: Prevalence of dementia and PD (calculated as hazard ratio);
Study design: Cohort or case–control studies.
Studies were excluded if they (1) investigated infectious diseases caused by herpes viruses other than herpes zoster, (2) did not provide accessible data on the prevalence of dementia or PD, (3) were non-original papers (e.g., conference abstracts, letters, editorials, or replies), (4) were reviews, case reports, or similar, or (5) were not published in English.
Data extraction
Yanfeng Zhang and Weiping Liu independently conducted the literature search, content screening, data extraction, and risk of bias assessment. Disagreements were resolved through consultation with a more experienced third author, Yang Xu, and consensus decision-making. Studies meeting the inclusion criteria and reporting data were included in the analyses, and outcome data related to study characteristics were extracted. Notably, despite being a conference abstract, Chen et al. (23) provided the required data for analysis and was included to collect a larger number of studies.
Quality assessment
The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) was used to independently assess the included case–control and cohort studies. Studies scoring 7–9 were considered high quality (24). As with data extraction, disagreements were resolved through discussion.
Statistical analysis
Meta-analyses were performed using Review Manager version 5.4.1 (Cochrane Collaboration, Oxford, UK), with HR as the uniform assessment measure. We calculated 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) for all outcome metrics and estimated heterogeneity between studies using the inconsistency index (I2) (25). Significant heterogeneity was defined as p < 0.05 or I2 > 50%. All data were analyzed using a random effects model. For analyses with ≥10 studies, funnel plots were created using Review Manager 5.4.1, and potential publication bias was evaluated using Egger’s regression tests with Stata version 15.0 (Stata Corp, College Station, Texas, United States). p-values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
Study characteristics and results of the screening process
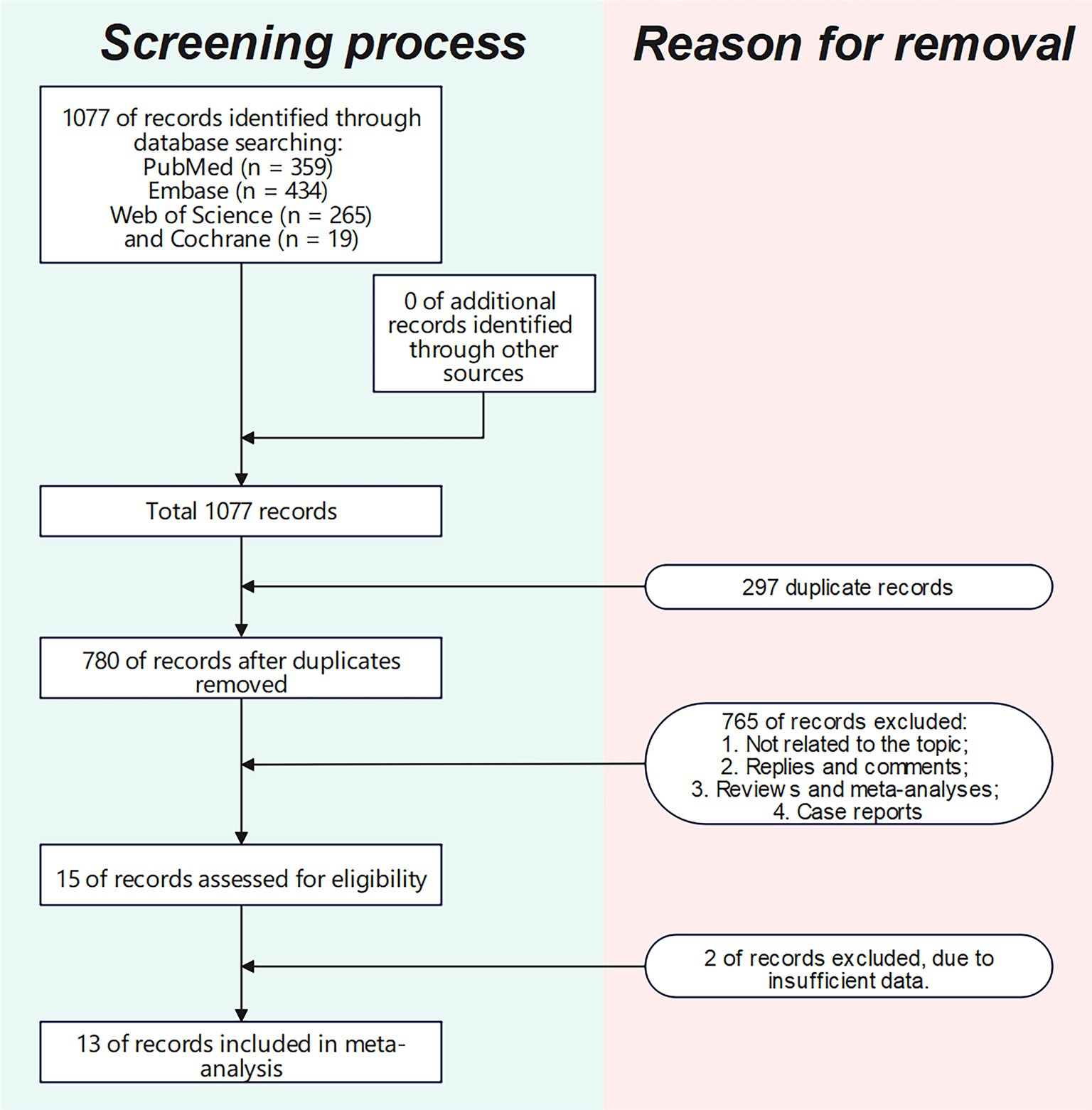
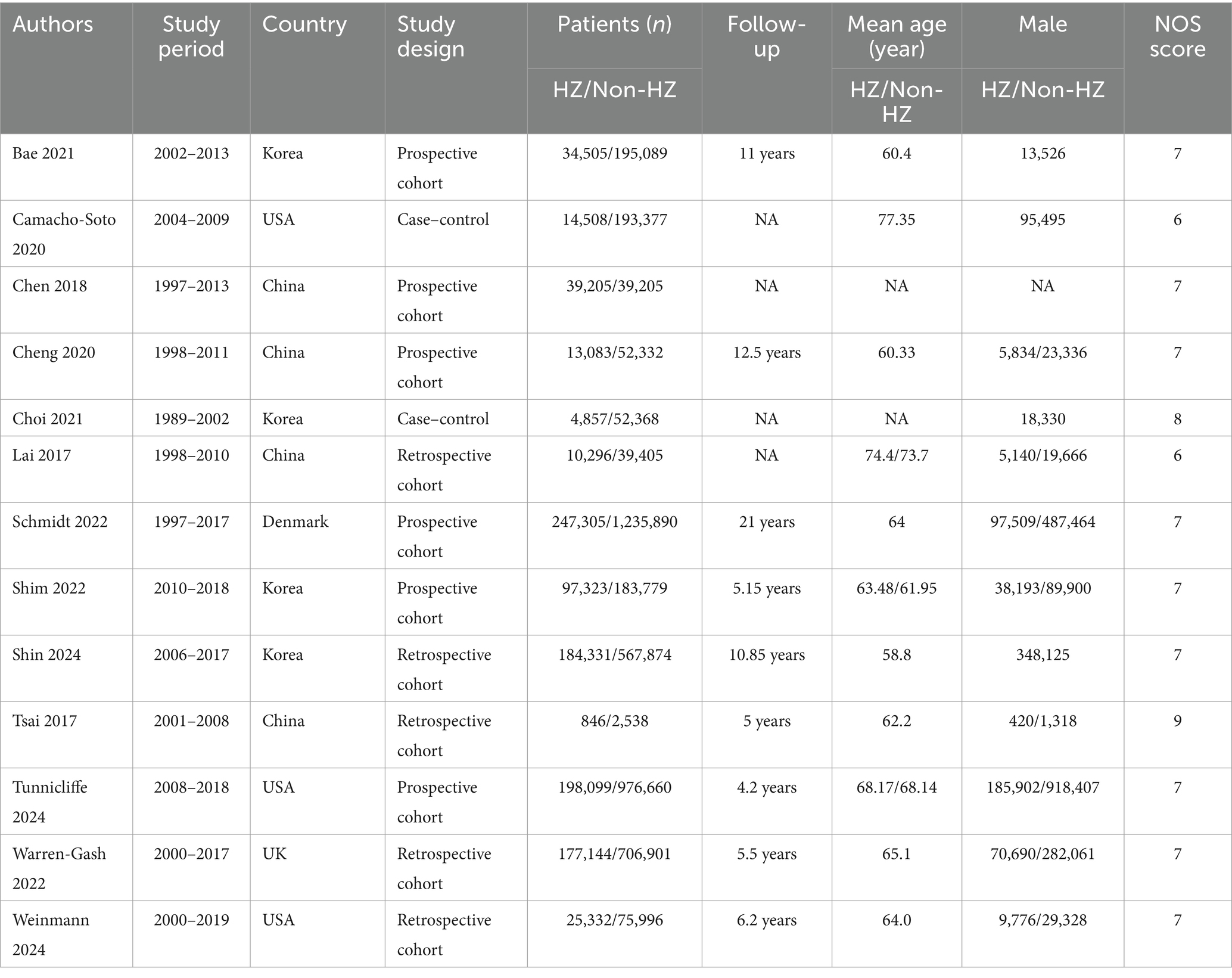
The literature screening methodology and process are displayed in Figure 1. We searched 1,077 publications: 359 from PubMed, 434 from Embase, 19 from Cochrane, and 265 from Web of Science Core Collection. After excluding publications not meeting the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 13 studies (16–21, 23, 26–31) were included for analysis. The basic characteristics of each study are presented in Table 1.
Assessment of study quality
The quality scores of the included studies are shown in Supplementary Table S3. One study (30) scored 9, one (20) scored 8, nine (16, 18, 19, 21, 23, 27–29, 31) scored 7, and two (17, 26) scored 6.
Outcomes of meta-analysis
Results of overall analysis
Herpes zoster did not significantly affect dementia (HR = 1.11, 95% CI 0.99–1.24, p = 0.07; Figure 2A) but significantly affected PD (HR = 1.15, 95% CI 1.03–1.30, p = 0.02; Figure 2B). Heterogeneity was present for both outcomes (dementia: I2 = 98%, p < 0.00001; PD: I2 = 94%, p < 0.00001).
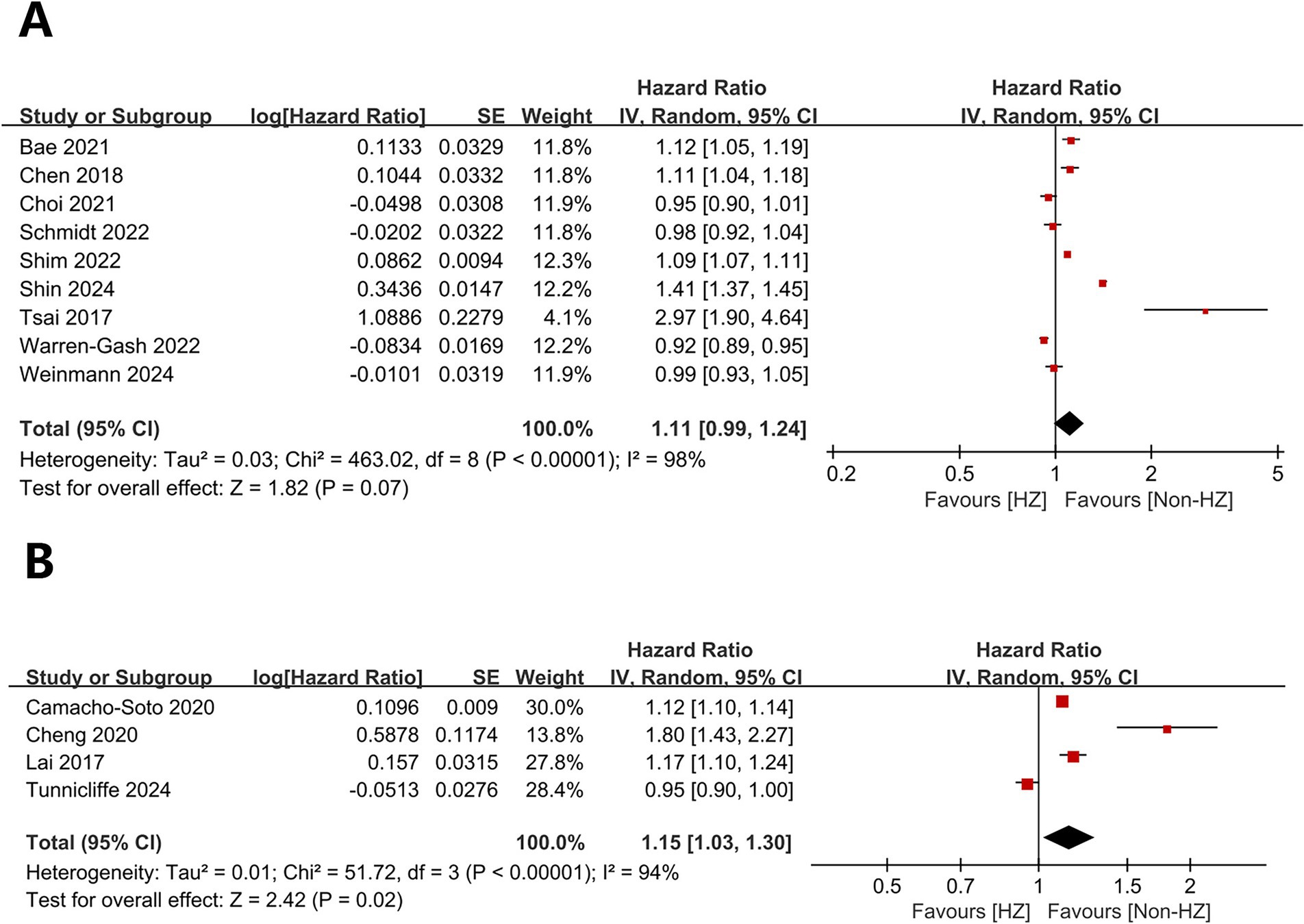
Figure 2. Forest plot of overall analysis results. (A) Forest plots for overall dementia-related analyses; (B) Forest plots for overall analyses related to Parkinson’s disease.
Results of subgroup analyses
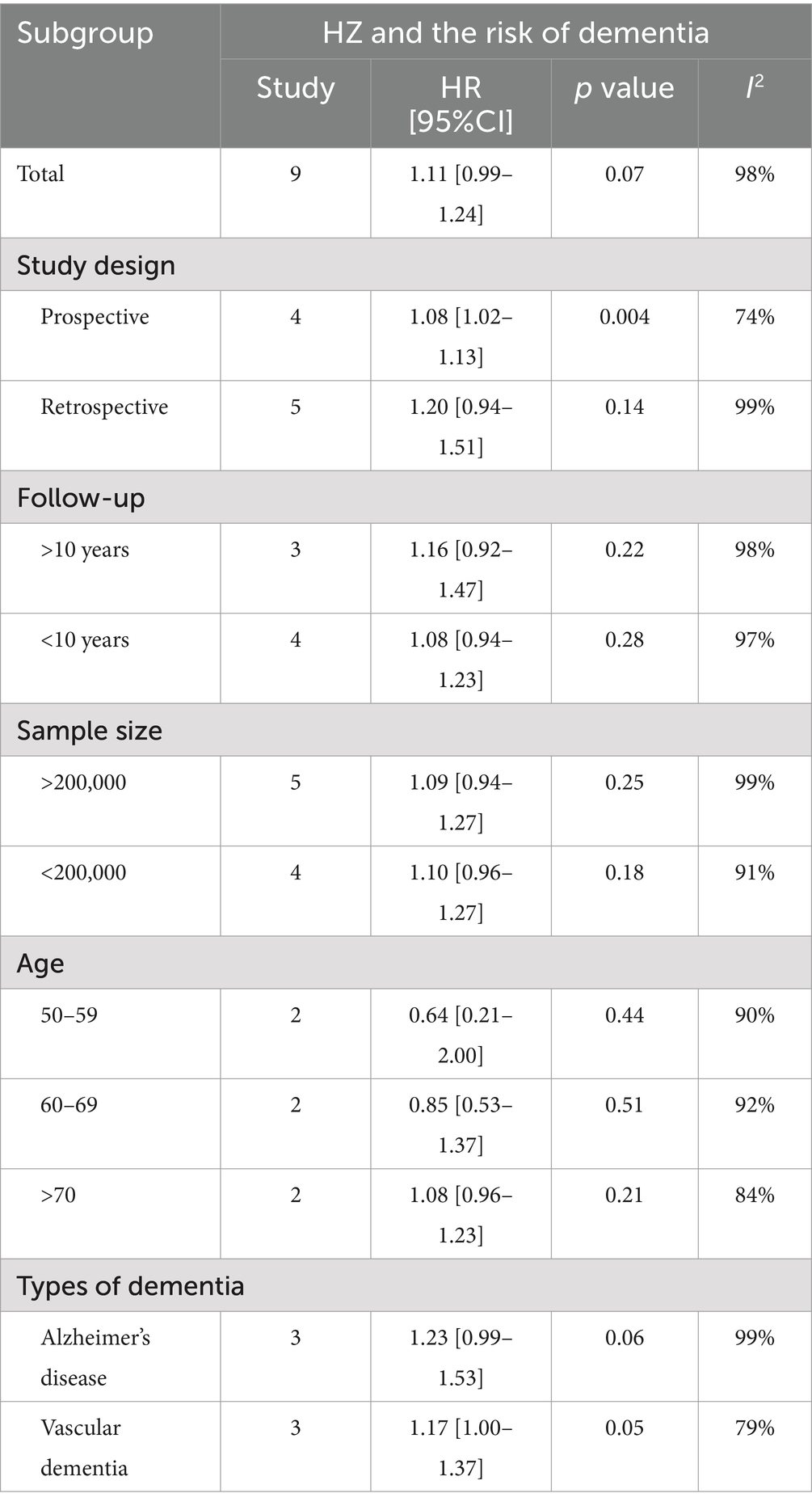
Subgroup analyses were conducted for the risk of herpes zoster and dementia but not for herpes zoster and PD due to limited data. Subgroup analyses demonstrated no significant relationships (p > 0.05) except for prospective studies (p = 0.004) in the study type subgroup. Notably, the p-value for vascular dementia in the dementia type subgroup was 0.05, suggesting a potential association between the variables. Heterogeneity was present in all subgroups (I2 > 50%) (Table 2).
Sensitivity analysis
A one-way sensitivity analysis demonstrated the instability of both overall analyses. In the analyses of herpes zoster and dementia, the overall results were destabilized if studies by Choi et al. (20), Schmidt et al. (27), or Warren-Gash et al. (19) were individually excluded. Similarly, when evaluating herpes zoster and PD, the results became unstable with the removal of Camacho-Soto et al. (26), Cheng et al. (16), or Lai et al. (17) (Figure 3).
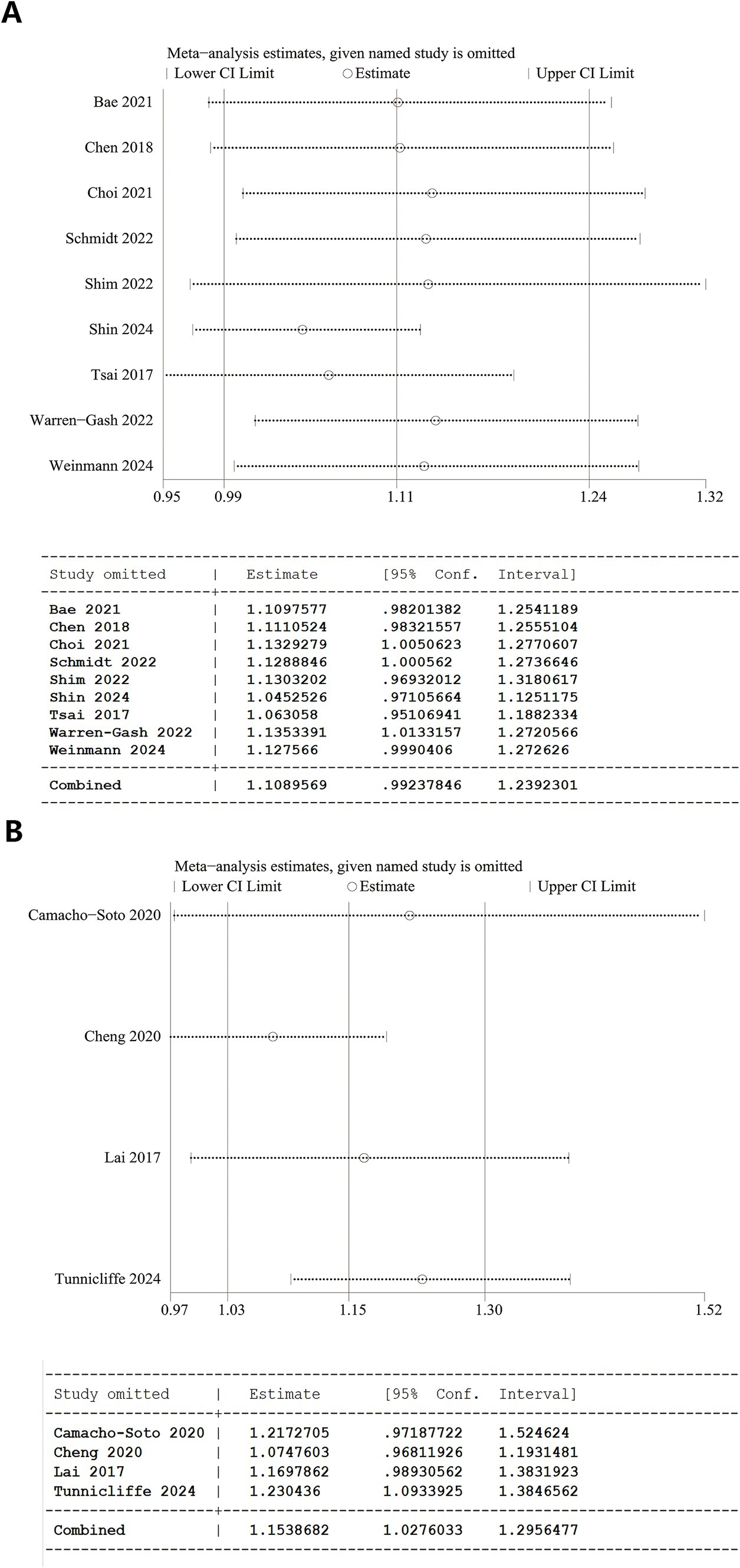
Figure 3. Sensitivity analysis results. (A) Overall analysis of herpes zoster and dementia and 95% CI calculations from Stata software. (B) Overall analysis of herpes zoster and Parkinson’s disease and 95% CI calculations from Stata software.
Discussion
The potential link between nervous system infections and neurodegeneration has gained widespread attention since Bowery et al.’s pioneering study in 1992, which demonstrated tetanus toxin-induced neurodegeneration in rats (32, 33). A variety of viruses that can cause infections in the nervous system [e.g., herpesvirus family (EBV, HSV, VZV, etc.), HCV, HIV, RSV, etc.] may cause protein aggregation, abnormalities in energy balance, and inflammation and lead to neurodegenerative pathologies. In recent years, viral stimulation of microglia activation in neurodegeneration has become a hot topic again in the context of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Given that over 95% of individuals aged 50 and older globally have been exposed to varicella-zoster virus, a large portion of the population is at risk for herpes zoster (15). Its potential association with dementia and PD is therefore a relevant topic. Due to the many unresolved physiological mechanisms and the ongoing controversy in current clinical study conclusions, we collected and reviewed as much relevant literature as possible to better understand the association between herpes zoster and these two neurodegenerative diseases.
Regarding dementia, our comprehensive analysis results showed that although a positive trend was observed between herpes zoster and dementia, this association lacked statistical significance. Dementia encompasses various types, such as Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia, dementia with Lewy bodies, frontotemporal dementia, Huntington’s disease, and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, each with distinct pathogenic mechanisms and marker factors. Herpes zoster may influence only certain types of dementia. To further investigate the potential link, we thoroughly reviewed the data from the included studies and performed subgroup analyses based on five factors: study type, follow-up duration, sample size, subject age, and dementia classification.
The subgroup analysis revealed that factors such as follow-up duration, sample size, and participant age did not significantly affect the results. However, prospective studies demonstrated a clear positive association between herpes zoster and the risk of dementia, while retrospective studies showed no such significance. Notably, in the sensitivity analysis, excluding a larger number of retrospective studies led to a trend indicating an increased risk of dementia linked to herpes zoster.
This suggests a potential causal relationship between the two. More rigorous methods are needed to determine causality, considering confounding factors. Recent advances in evidence-based medicine have enabled Mendelian randomization to offer a more robust approach to causal inference. A recent Mendelian randomization study on the causal relationship between herpes zoster and dementia supports this conclusion, consistent with findings from a subgroup of prospective studies (34).
In a subgroup analysis of dementia types, herpes zoster was found to significantly increase the risk of vascular dementia, while the effect on Alzheimer’s disease, although showing an upward trend, did not reach statistical significance. This observation may warrant a mechanistic explanation. Although the mechanisms by which viruses cause neurodegenerative diseases remain poorly understood, based on available studies, the significant increase in the risk of vascular dementia may result from primary varicella-zoster virus infection, which initially causes chickenpox and subsequently remains latent. Under conditions such as aging or immunosuppression, the virus may reactivate and trigger herpes zoster. During this process, VZV may invade the central nervous system, causing vasculopathy and impairing cerebral blood flow, which can result in cerebral infarction and vascular dementia (35–40). In Alzheimer’s disease, neuroinflammation caused by the abnormal accumulation of amyloid β (Aβ) peptide and tau protein is the main pathogenesis. Systemic inflammation, triggered by viral infections and microglial activation, exacerbates Aβ and tau protein accumulation, thereby promoting Alzheimer’s disease progression (41, 42) Moreover, Aβ is not only a key pathological protein in Alzheimer’s disease but also a potential cellular receptor for VZV (43). The presence of Aβ may interfere with VZV replication, partially protecting the host against viral infection. This mechanism could lead to a gradual accumulation of Aβ during Alzheimer’s disease progression and a reduction in VZV’s effects (44–47) potentially explaining the nonsignificant association with herpes zoster despite a trend of increased Alzheimer’s disease risk.
Our analysis revealed a significant increase in the risk of developing PD following herpes zoster infection. However, due to the limited data in existing studies, a more detailed subgroup analysis could not be performed. PD is a complex neurodegenerative disorder presenting both motor and non-motor symptoms. The hallmark pathological features include the loss of dopaminergic neurons (48) and abnormal α-synuclein aggregation (49). The reduction of dopaminergic neurons primarily contributes to motor symptoms such as resting tremor, muscle rigidity, and bradykinesia, whereas non-motor symptoms, including cognitive impairment, autonomic dysfunction, and neurobehavioral abnormalities, are linked to α-synuclein aggregation (50). There is currently insufficient research to directly clarify the relationship between VZV and the dopamine system. Consequently, we concentrate on the non-motor symptoms of PD, particularly Parkinson’s dementia. While no definitive study has yet identified the exact mechanism through which VZV contributes to Parkinson’s dementia, we hypothesize that herpes zoster might increase the risk through the following mechanisms: abnormal aggregation of α-synuclein is a key pathological process in PD (51, 52). VZV may influence α-synuclein expression, a protein crucial to PD pathogenesis, by inducing vasculopathy, which impairs α-synuclein clearance and results in its abnormal accumulation in the brain, thereby promoting PD development (53, 54). Cross-reactivity between α-synuclein and herpesvirus peptides has been observed in PD patients (55). Abnormal α-synuclein aggregation is not limited to PD but is also linked to other α-synucleinopathies, including dementia with Lewy bodies, multiple system atrophy, the Lewy body variant of Alzheimer’s disease, and pure autonomic failure. Cognitive impairment in these conditions often accompanies cerebrovascular-like diseases (56), and VZV infection can induce vasculopathy. Thus, a theoretical association between VZV infection and other α-synucleinopathies may exist, though this hypothesis remains infrequently explored and requires further investigation.
Two key aspects of VZV infection and neurodegenerative diseases warrant attention. First, HERV-DNA transposable elements that constitute about 8% of the human genome—play a crucial role (14). Studies suggest a synergistic effect of HERVs and VZV in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis, potentially accelerating disease progression (57). The role of HERVs in conjunction with VZV in major neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and PD, remains inadequately explored, with numerous aspects still uncharted. The mitochondrial dysfunction hypothesis provides new insights into neurodegenerative disease mechanisms. Recent theories suggest that viruses might expedite microglial aging and facilitate neurodegenerative disease progression by activating microglia and inducing mitochondrial dysfunction. Moreover, VZV infection has been shown to alter mitochondrial morphology, causing fragmentation and swelling. These mitochondrial abnormalities may result in cellular damage or death during infection, thereby contributing to the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases (58).
Given the risks associated with herpes zoster, neurodegenerative diseases, and the significant impact of postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) on patients’ quality of life, appropriate coping strategies are crucial. Antiviral drugs are commonly used to treat herpes zoster. Among these, acyclovir (including its derivatives such as valaciclovir and famciclovir) is often the preferred choice. Evidence from clinical practice suggests that early antiviral therapy may lead to better outcomes. This is supported by some studies (59). It is important to note that the use of antiviral drugs is limited by various factors, including financial capacity, medical conditions, and individual health status, leading to differences in treatment outcomes. Among the 13 papers analyzed, four focused on antiviral therapy. Two studies did not find significant antiviral treatment effects after accounting for factors such as BMI, comorbidities, and unhealthy habits, while the other two suggested a potential protective effect. These findings highlight the ongoing controversy surrounding the role of antiviral therapy in reducing the risk of herpes zoster in patients with two neurodegenerative diseases.
We consider timely vaccination, especially in the absence of disease, to be the most optimal strategy at present. Various herpes zoster vaccines, including Mosquirix, Shingrix, and Nuvaxovid, are available on the market. Notably, Shingrix, the most effective vaccine, shows efficacy ranging from 96.6 to 97.9% across all age groups, with an overall efficacy of 97.2% (60). Furthermore, recently developed vaccines based on multi-nanoparticle (NP) platforms have achieved superior protective efficacy (61).
In reviewing our study, we must face up to its limitations, which are critical to fully understand and accurately assess the potential impact of the relationship between herpes zoster and dementia and PD. Firstly, despite our best efforts to include a large number of studies and to strictly control for inter-data variability factors, the high heterogeneity of the data remains a problem that cannot be ignored. This heterogeneity stems mainly from sample size limitations, which prevented certain in-depth subgroup analyses from being conducted or, if they were conducted, made it difficult to produce results with low heterogeneity. Therefore, we are cautious about the findings obtained and recognize that they may need to be further validated in larger, more refined studies in the future. Secondly, as our study primarily focused on older individuals, the applicability to younger age groups should be interpreted with caution. Further, some known risk factors for dementia or Parkinson’s, such as genetic factors, alcohol abuse, smoking, exposure to pesticides, or use of well water, were not comprehensively documented in the data from all studies in our study. This lack of information may have led to some bias in our findings, which do not fully and accurately reflect the impact of these potential factors on disease risk. Finally, our study did not break down the location of the appearance of herpes zoster. It has been shown that the association between VZV infection in the oral cavity and eyes and the risk of dementia is much stronger (29). Also, the different locations of herpes zoster may affect the diagnostic accuracy of physicians and the motivation of patients, which in turn may have an impact on the prevention and control of the disease. This factor was not fully considered in our study and may also be a reason for the biased results.
Conclusion
In conclusion, based on a comprehensive review of 13 relevant studies, we investigated the association between herpes zoster and dementia or PD. The findings indicate that herpes zoster significantly raises the risk of PD and vascular dementia. Additionally, a causal relationship exists between herpes zoster infection and dementia. Early vaccination against herpes zoster is recommended to mitigate risks, rather than antiviral treatment post-infection.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
YZ: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. WL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. YX: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Scientific Research Project of Hebei Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine [Fund No. 2022555]. Wang Jun National Famous Elderly Chinese Medicine Experts Inheritance Workshop [Chinese Medicine Teaching Letter (2022) No. 75].
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2024.1471736/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Coelho, M, and Ferreira, JJ. Late-stage Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurol. (2012) 8:435–42. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2012.126
2. Fernandez, HH, Galvez-Jimenez, N, and Fernandez, HH. Nonmotor complications of Parkinson disease. Cleve Clin J Med. (2012) 79:S14–8. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.79.s2a.03
3. Noyce, AJ, Bestwick, JP, Silveira-Moriyama, L, Hawkes, CH, Giovannoni, G, Lees, AJ, et al. Meta-analysis of early nonmotor features and risk factors for Parkinson disease. Ann Neurol. (2012) 72:893–901. doi: 10.1002/ana.23687
4. Matthews, KA, Xu, W, Gaglioti, AH, Holt, JB, Croft, JB, Mack, D, et al. Racial and ethnic estimates of Alzheimer's disease and related dementias in the United States (2015–2060) in adults aged ≥65 years. Alzheimers Dement. (2019) 15:17–24. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2018.06.3063
5. Prince, M, Wimo, A, Guerchet, M, Ali, GC, Wu, Y-T, Prina, M, et al. World Alzheimer report 2015: The global impact of dementia. London: Alzheimer’s Disease International (2015).
6. Weiss, J, Puterman, E, Prather, AA, Ware, EB, and Rehkopf, DH. A data-driven prospective study of dementia among older adults in the United States. PLoS One. (2020) 15:e0239994. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0239994
7. Osorio, C, Sfera, A, Anton, JJ, Thomas, KG, Andronescu, CV, Li, E, et al. Virus-induced membrane fusion in neurodegenerative disorders. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2022) 12:845580. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.845580
8. Leblanc, P, and Vorberg, IM. Viruses in neurodegenerative diseases: more than just suspects in crimes. PLoS Pathog. (2022) 18:e1010670. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010670
9. Soldan, SS, and Lieberman, PM. Epstein-Barr virus and multiple sclerosis. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2023) 21:51–64. doi: 10.1038/s41579-022-00770-5
10. Amirsardari, Z, Rahmani, F, and Rezaei, N. Cognitive impairments in HCV infection: from pathogenesis to neuroimaging. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. (2019) 41:987–1000. doi: 10.1080/13803395.2019.1652728
11. Murray, J, Meloni, G, Cortes, EP, KimSilva, A, Jacobs, M, Ramkissoon, A, et al. Frontal lobe microglia, neurodegenerative protein accumulation, and cognitive function in people with HIV. Acta Neuropathol Commun. (2022) 10:69. doi: 10.1186/s40478-022-01375-y
12. Jia, X, Gao, Z, and Hu, H. Microglia in depression: current perspectives. Sci China Life Sci. (2021) 64:911–25. doi: 10.1007/s11427-020-1815-6
13. Hu, M, Bogoyevitch, MA, and Jans, DA. Subversion of host cell mitochondria by RSV to favor virus production is dependent on inhibition of mitochondrial complex I and ROS generation. Cells. (2019) 8:1417. doi: 10.3390/cells8111417
14. Adler, GL, Le, K, Fu, Y, and Kim, WS. Human endogenous retroviruses in neurodegenerative diseases. Genes. (2024) 15:745. doi: 10.3390/genes15060745
15. Johnson, RW, Alvarez-Pasquin, MJ, Bijl, M, Franco, E, Gaillat, J, Clara, JG, et al. Herpes zoster epidemiology, management, and disease and economic burden in Europe: a multidisciplinary perspective. Ther Adv Vaccines. (2015) 3:109–20. doi: 10.1177/2051013615599151
16. Cheng, CM, Bai, YM, Tsai, CF, Tsai, SJ, Wu, YH, Pan, TL, et al. Risk of Parkinson's disease among patients with herpes zoster: a nationwide longitudinal study. CNS Spectr. (2020) 25:797–802. doi: 10.1017/S1092852919001664
17. Lai, SW, Lin, CH, Lin, HF, Lin, CL, Lin, CC, and Liao, KF. Herpes zoster correlates with increased risk of Parkinson's disease in older people: a population-based cohort study in Taiwan. Medicine. (2017) 96:e6075. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006075
18. Tunnicliffe, L, Weil, RS, Breuer, J, Rodriguez-Barradas, MC, Smeeth, L, Rentsch, CT, et al. Herpes zoster and risk of incident Parkinson's disease in US veterans: a matched cohort study. Mov Disord. (2024) 39:438–44. doi: 10.1002/mds.29701
19. Warren-Gash, C, Williamson, E, Shiekh, SI, Borjas-Howard, J, Pearce, N, Breuer, JM, et al. No evidence that herpes zoster is associated with increased risk of dementia diagnosis. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. (2022) 9:363–74. doi: 10.1002/acn3.51525
20. Choi, HG, Park, BJ, Lim, JS, Sim, SY, Jung, YJ, and Lee, SW. Herpes zoster does not increase the risk of neurodegenerative dementia: a case-control study. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Dement. (2021) 36:15333175211006504. doi: 10.1177/15333175211006504
21. Bae, S, Yun, SC, Kim, MC, Yoon, W, Lim, JS, Lee, SO, et al. Association of herpes zoster with dementia and effect of antiviral therapy on dementia: a population-based cohort study. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. (2021) 271:987–97. doi: 10.1007/s00406-020-01157-4
22. Page, MJ, McKenzie, JE, Bossuyt, PM, Boutron, I, Hoffmann, TC, Mulrow, CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
23. Chen, VC, Wu, SI, Huang, KY, Yang, YH, Kuo, TY, Liang, HY, et al. Herpes zoster and dementia: a Nationwide population-based cohort study. J Clin Psychiatry. (2018) 79:16m11312. doi: 10.4088/JCP.16m11312
24. Wells, G, Shea, B, O’Connell, D, Peterson, J, Welch, V, Losos, M, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. (2000). Available at: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (Accessed October 30, 2020).
25. Higgins, JP, and Thompson, SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a Meta-analysis. Stat Med. (2002) 21:1539–58. doi: 10.1002/sim.1186
26. Camacho-Soto, A, Faust, I, Racette, BA, Clifford, DB, Checkoway, H, and Searles Nielsen, S. Herpesvirus infections and risk of Parkinson’s disease. Neurodegener Dis. (2020) 20:97–103. doi: 10.1159/000512874
27. Schmidt, SAJ, Veres, K, Sørensen, HT, Obel, N, and Henderson, VW. Incident herpes zoster and risk of dementia: a population-based Danish cohort study. Neurology. (2022) 99:e660–8. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000200709
28. Shim, Y, Park, M, and Kim, J. Increased incidence of dementia following herpesvirus infection in the Korean population. Medicine. (2022) 101:e31116. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000031116
29. Shin, E, Chi, SA, Chung, TY, Kim, HJ, Kim, K, and Lim, DH. The associations of herpes simplex virus and varicella zoster virus infection with dementia: a nationwide retrospective cohort study. Alz Res Therapy. (2024) 16:57. doi: 10.1186/s13195-024-01418-7
30. Tsai, M-C, Cheng, WL, Sheu, JJ, Huang, CC, Shia, BC, Kao, LT, et al. Increased risk of dementia following herpes zoster ophthalmicus. PLoS One. (2017) 12:e0188490. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188490
31. Weinmann, S, Rawlings, A, Koppolu, P, Rosales, AG, Prado, YK, and Schmidt, MA. Herpes zoster diagnosis and treatment in relation to incident dementia: a population-based retrospective matched cohort study. PLoS One. (2024) 19:e0296957. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0296957
32. Bowery, NG, Bagetta, G, Nisticó, G, Britton, P, and Whitton, P. Intrahippocampal tetanus toxin produces generalized convulsions and neurodegeneration in rats: antagonism by NMDA receptor blockers. Epilepsy Res Suppl. (1992) 9:249–56.
33. Mattson, MP. Infectious agents and age-related neurodegenerative disorders. Ageing Res Rev. (2004) 3:105–20. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2003.08.005
34. Huang, SY, Yang, YX, Kuo, K, Li, HQ, Shen, XN, Chen, SD, et al. Herpesvirus infections and Alzheimer's disease: a Mendelian randomization study. Alzheimers Res Ther. (2021) 13:158. doi: 10.1186/s13195-021-00905-5
35. Kling, MA, Trojanowski, JQ, Wolk, DA, Lee, VM, and Arnold, SE. Vascular disease and dementias: paradigm shifts to drive research in new directions. Alzheimers Dement. (2013) 9:76–92. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2012.02.007
36. Gilden, D, Cohrs, RJ, Mahalingam, R, and Nagel, MA. Varicella zoster virus vasculopathies: diverse clinical manifestations, laboratory features, pathogenesis, and treatment. Lancet Neurol. (2009) 8:731–40. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70134-6
37. Steain, M, Sutherland, JP, Rodriguez, M, Cunningham, AL, Slobedman, B, and Abendroth, A. Analysis of T cell responses during active varicella-zoster virus reactivation in human ganglia. J Virol. (2014) 88:2704–16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03445-13
38. Skripuletz, T, Pars, K, Schulte, A, Schwenkenbecher, P, Yildiz, Ö, Ganzenmueller, T, et al. Varicella zoster virus infections in neurological patients: a clinical study. BMC Infect Dis. (2018) 18:238. doi: 10.1186/s12879-018-3137-2
39. Nagel, MA, and Bubak, AN. Varicella zoster virus vasculopathy. J Infect Dis. (2018) 218:S107–12. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiy425
40. Silver, B, Nagel, MA, Mahalingam, R, Cohrs, R, Schmid, DS, and Gilden, D. Varicella zoster virus vasculopathy: a treatable form of rapidly progressive multi-infarct dementia after 2 years’ duration. J Neurol Sci. (2012) 323:245–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2012.07.059
41. Wozniak, MA, Itzhaki, RF, Shipley, SJ, and Dobson, CB. Herpes simplex virus infection causes cellular beta-amyloid accumulation and secretase upregulation. Neurosci Lett. (2007) 429:95–100. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2007.09.077
42. De Chiara, G, Marcocci, ME, Civitelli, L, Argnani, R, Piacentini, R, Ripoli, C, et al. APP processing induced by herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) yields several APP fragments in human and rat neuronal cells. PLoS One. (2010) 5:e13989. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013989
43. Li, Q, Ali, MA, and Cohen, JI. Insulin degrading enzyme is a cellular receptor mediating varicella-zoster virus infection and cell-to-cell spread. Cell. (2006) 127:305–16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.08.046
44. Bernstein, HG, Keilhoff, G, Dobrowolny, H, and Steiner, J. Binding varicella zoster virus: an underestimated facet of insulindegrading enzyme s implication for Alzheimer s disease pathology? Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. (2019) 270:495–6. doi: 10.1007/s00406-019-00995-1
45. Bourgade, K, Garneau, H, Giroux, G, Le Page, AY, Bocti, C, Dupuis, G, et al. beta-amyloid peptides display protective activity against the human Alzheimer’s disease-associated herpes simplex virus-1. Biogerontology. (2015) 16:85–98. doi: 10.1007/s10522-014-9538-8
46. Eimer, WA, Vijaya Kumar, DK, Navalpur Shanmugam, NK, Rodriguez, AS, Mitchell, T, Washicosky, KJ, et al. Alzheimer’s disease-associated betaamyloid is rapidly seeded by herpesviridae to protect against brain infection. Neuron. (2018) 99:56–63.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.06.030
47. Cribbs, DH, Azizeh, BY, Cotman, CW, and LaFerla, FM. Fibril formation and neurotoxicity by a herpes simplex virus glycoprotein B fragment with homology to the Alzheimer’s a beta peptide. Biochemistry. (2000) 39:5988–94. doi: 10.1021/bi000029f
48. Erkkinen, MG, Kim, M-O, and Geschwind, MD. Clinical neurology and epidemiology of the major neurodegenerative diseases. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. (2018) 10:a033118. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a033118
49. Simon, DK, Tanner, CM, and Brundin, P. Parkinson disease epidemiology, pathology, genetics, and pathophysiology. Clin Geriatr Med. (2020) 36:1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.cger.2019.08.002
51. Spillantini, MG, Schmidt, ML, Lee, VM, Trojanowski, JQ, Jakes, R, Goedert, M, et al. α-Synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature. (1997) 388:839–40. doi: 10.1038/42166
52. Reeve, AK, Ludtmann, MH, Angelova, PR, Simcox, EM, Horrocks, MH, Klenerman, D, et al. Aggregated α-synuclein and complex I deficiency: exploration of their relationship in differentiated neurons. Cell Death Dis. (2015) 6:e1820. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.166
53. Ryman, SG, Vakhtin, AA, Mayer, AR, van der Horn, HJ, Shaff, NA, Nitschke, SR, et al. Abnormal cerebrovascular activity, perfusion, and Glymphatic clearance in Lewy body diseases. Mov Disord. (2024) 39:1258–68. doi: 10.1002/mds.29867
54. Alster, P, Madetko, N, Koziorowski, D, and Friedman, A. Microglial activation and inflammation as a factor in the pathogenesis of progressive Supranuclear palsy (PSP). Front Neurosci. (2020) 14:893. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00893
55. Caggiu, E, Paulus, K, Arru, G, Piredda, R, Sechi, GP, and Sechi, LA. Humoral cross reactivity between α-synuclein and herpes simplex-1 epitope in Parkinson's disease, a triggering role in the disease? J Neuroimmunol. (2016) 291:110–4. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2016.01.007
56. Zhang, Q, Duan, Q, Gao, Y, He, P, Huang, R, Huang, H, et al. Cerebral microvascular injury induced by Lag3-dependent α-Synuclein fibril endocytosis exacerbates cognitive impairment in a mouse model of α-Synucleinopathies. Adv Sci (Weinh). (2023) 10:e2301903. doi: 10.1002/advs.202301903
57. Brudek, T, Lühdorf, P, Christensen, T, Hansen, HJ, and Møller-Larsen, A. Activation of endogenous retrovirus reverse transcriptase in multiple sclerosis patient lymphocytes by inactivated HSV-1, HHV-6 and VZV. J Neuroimmunol. (2007) 187:147–55. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2007.04.003
58. Jiang, T, Zhu, K, Kang, G, Wu, G, Wang, L, and Tan, Y. Infectious viruses and neurodegenerative diseases: the mitochondrial defect hypothesis. Rev Med Virol. (2024) 34:e2565. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2565
59. Zandi, PP, Anthony, JC, Khachaturian, AS, Stone, SV, Gustafson, D, Tschanz, JT, et al. Reduced risk of Alzheimer disease in users of antioxidant vitamin supplements. Arch Neurol. (2004) 61:82–8. doi: 10.1001/archneur.61.1.82
60. Lal, H, Cunningham, AL, Godeaux, O, Chlibek, R, Diez-Domingo, J, Hwang, SJ, et al. Efficacy of an adjuvanted herpes zoster subunit vaccine in older adults. N Engl J Med. (2015) 372:2087–96. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1501184
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease, dementia, meta-analysis, herpes zoster, systematic review, vascular dementia
Citation: Zhang Y, Liu W and Xu Y (2024) Association between herpes zoster and Parkinson’s disease and dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Neurol. 15:1471736. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1471736
Edited by:
Sanjay G. Manohar, University of Oxford, United KingdomReviewed by:
Piotr Alster, Medical University of Warsaw, PolandQingwei Lu, First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China
Copyright © 2024 Zhang, Liu and Xu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yang Xu, MjI4MjgzMTk5MEBxcS5jb20=
†These authors share first authorship
 Yanfeng Zhang
Yanfeng Zhang Weiping Liu
Weiping Liu Yang Xu
Yang Xu