- 1Department of Obstetrics, Affiliated Maternity and Child Health Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei, China
- 2Department of Neurocritical Care Unit, The First Affiliated Hospital of USTC, Division of Life Sciences and Medicine, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China
Objectives: Research on neurobehavioral abnormalities in neonates of mothers with subclinical hypothyroidism (SCH) is limited. The link between umbilical cord blood brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels and neurobehavioral outcomes in neonates has not been explored. This study investigates the correlation between alterations in umbilical cord blood BDNF levels and early neurobehavioral abnormalities in neonates born to pregnant women with SCH.
Methods: This study recruited 72 pregnant women with SCH and 76 healthy controls (HC). The study collected general information for all subjects, including body mass index, parity, thyroid function assessed during early to late pregnancy, and neonatal birth weight. Neonatal behavioral and neural abilities were evaluated using the Neonatal Behavioral Neurological Assessment (NBNA). BDNF levels in umbilical cord blood were measured using the Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay method.
Results: The results indicated that neonates with SCH during pregnancy had lower total NBNA scores, behavioral ability, passive muscle tone, active muscle tone, primitive reflexes, general assessment, and lower levels of cord blood BDNF compared to healthy controls. The cord blood BDNF of newborns with SCH during pregnancy was positively correlated with total NBNA score, behavioral ability, active muscle tone, and general assessment. Moreover, multiple linear regression analysis demonstrated an association between cord blood BDNF levels in pregnant patients with SCH and multiple measures of newborn health, including total NBNA score, behavioral ability, active muscle tone, and general assessment.
Conclusion: Infants born to pregnant women with SCH exhibit reduced behavioral and neural abilities linked to BDNF levels in umbilical cord blood.
Introduction
Subclinical hypothyroidism (SCH) during pregnancy is a type of pregnancy-related thyroid dysfunction characterized by a high serum level of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) above the pregnancy-specific reference range, while the level of serum-free thyroxine (FT4) remains within the pregnancy-specific reference range (1). Studies have indicated that subclinical hypothyroidism during pregnancy is associated with a higher risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes, such as spontaneous abortion, preterm delivery, neonatal asphyxia, and neonatal death (2, 3).
Although SCH during pregnancy has received increasing attention from clinicians regarding its impact on pregnancy outcomes, there is still no consistent conclusion on whether SCH during pregnancy affects the offspring’s neurodevelopment. Williams demonstrated in a study of cognitive behavior in children aged around 5 years that for every 1 mL increase in maternal serum TSH levels during pregnancy, the score on the general cognitive index decreased by 3.2 points (4). Liu found that the offspring of mothers with SCH performed worse on the Morris water maze test than normal controls (5). However, some studies have discovered no association between maternal SCH and the mental deficits seen in the offspring (6). The conflicting results of previous studies may be attributed to variations in the TSH cutoff values used between studies. In addition, previous research on cognitive function in the offspring of SCH during pregnancy has focused on childhood, even as they approach adulthood. Giulia Bramati demonstrated that environmental enrichment increases complex spatial learning abilities and leads to long-lasting morphological changes in the hippocampus (7). Exercise has also been found to promote synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus and improve cognitive functions such as learning memory (8). Therefore, it is essential to minimize the adverse interference of the acquired environment on the neonate and to emphasize the influence of the intrauterine environment on the cognitive level of the offspring. This study evaluated the behavioral and neurological abilities of newborns with gestational SCH within 3 days of birth to minimize the influence of the acquired environment on the experimental results.
The Neonatal Behavioral Neurological Assessment (NBNA) is a widely used behavioral neurological assessment tool in neonatal medicine designed to assess neonatal behavioral neurology’s developmental level and functional status (9). Although the validity of the NBNA scale has been extensively demonstrated, scale testing requires extensive training, its results are highly subjective, and assessment is time-consuming and labor-intensive. Therefore, there is a great need for clinicians to have a more accessible and objective indicator of the behavioral and neurological abilities of newborns. Hematologic indicators are easily accessible, and monitoring instruments are well-established, convenient, and practical, making them highly promising as objective indicators for assessing the neurobehavioral abilities of neonates.
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is currently the most comprehensively researched neurotrophic factor, which is primarily expressed in the central nervous system and is involved in many brain functions, including neuronal survival, axonal growth, cell migration, regulation of excitatory-inhibitory balance, and glutamate-dependent dendritic growth, synapse formation, stabilization, and plasticity (10, 11). BDNF plays a crucial role in hippocampal neurogenesis, experience-dependent neural plasticity, neuronal formation, and survival (12, 13). While markers such as S100B and NSE are commonly used to assess glial injury and neuronal damage, their primary roles are associated with pathological conditions, such as hypoxic–ischemic encephalopathy or traumatic brain injury (14). In contrast, BDNF is a key neurotrophic factor involved in normal neurodevelopment and has been specifically linked to cognitive and behavioral outcomes. Given the exploratory nature of this study, BDNF was prioritized as a biomarker for its direct relevance to the neurodevelopmental processes under investigation. Numerous animal experiments and clinical trials have demonstrated that BDNF may be essential to cognitive processes. For example, research has indicated that thyroid hormones may induce morphological changes in the hippocampus by upregulating BDNF (15). Furthermore, the previous research conducted by our research group has revealed that the levels of BDNF in patients with insomnia are significantly reduced, which is notably associated with cognitive function (16).
During fetal development, changes in thyroid function may affect the expression of BDNF in the hippocampus of offspring, leading to structural and functional dysplasia of the central nervous system. Abdelhaffez observed a decrease in BDNF levels in the offspring of rats with Methimazole induced pregnancy-induced hypothyroidism. BDNF showed a negative correlation with TSH levels and a positive correlation with FT4 levels (17). Shafiee found that the reduction of BDNF in the hippocampus is associated with impaired spatial learning and working memory of offspring born to mothers with pregnancy-induced hypothyroidism (18). Although many studies have found a close relationship between thyroid function and BDNF, previous research has mainly focused on patients with pregnancy-induced hypothyroidism. There is limited research on the impact of SCH on BDNF during pregnancy, and the experimental findings are inconclusive. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct more research to explore the relationship between pregnancy-induced hypothyroidism and BDNF, and the neurodevelopment of offspring, especially in clinical research.
In this study, we hypothesize that newborns of pregnant women with SCH exhibit a decrease in BDNF levels in umbilical cord blood compared to normal controls and that this decrease is linked to the early behavioral and neurological abilities of the newborn. This study is the first to explore the relationship between early neurobehavioral abilities and cord blood BDNF levels in pregnant women with SCH, to provide clinical evidence for diagnosing and treating cognitive impairments related to SCH.
Materials and methods
Subjects
The study recruited expectant mothers from the Affiliated Maternity and child health Hospital of Anhui Medical University. All participants in the study satisfied the diagnostic criteria for gestational SCH outlined by the Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Thyroid Diseases in Pregnancy and Postpartum (2nd edition), published by the Chinese Medical Association Obstetrics and Gynecology Branch (1). Subjects with hyperthyroidism, thyroid tumors, or other thyroid disorders were excluded from the study. Healthy pregnant women from the same hospital were recruited during the same period as the control group. The study comprised 81 cases of gestational SCH, of which 5 gestational SCH patients refused to sign the informed consent form and 4 patients declined to undergo neurobehavioral assessments. The study group comprised 72 patients, while the control group had 76 participants. The Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital Ethics Committee affiliated with Anhui Medical University approved this experiment (No. YYLL2019-2019xlj17-02-01). All participants provided informed consent.
Baseline data collection
Basic information on pregnant women, such as age, height, weight, health condition, parity, adverse obstetric history, previous pregnancy details, and medical history, were obtained through face-to-face interviews.
Thyroid function and cord blood BDNF
Chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay was used to determine thyroid peroxidase antibodies (TPOAB), TSH, and FT4 levels in the blood. The level of BDNF in cord blood was assessed using Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay.
NBNA scale
The NBNA scale was used to assess the neurobehavioral capabilities of newborns (9). This assessment tool consists of five clusters: behavioral capacity (6 items), passive muscle tone (4 items), active muscle tone (4 items), primitive reflexes (3 items), and general assessment (3 items). Each item is assessed using a scale of 0 to 2, with a total possible score of 40. A score greater than 37 indicates an excellent developmental profile, whereas a score below 35 indicates abnormal neurobehavioral development. Scoring was conducted by experienced pediatricians who were blinded to maternal clinical data and group assignments.
Statistical analysis
The statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 22.0. The results were presented as X ± S for normally distributed continuous variables, and independent sample t-tests were performed for intergroup comparison. Non-normally distributed variables were analyzed using median (interquartile range) [M (Q1, Q3)], and the Mann–Whitney-U test was used for intergroup comparison. Spearman’s rank correlation was used to analyze the correlation between BDNF and maternal thyroid function levels during pregnancy and neonatal behavioral neurology. Additionally, multiple linear regression analysis was conducted to investigate the relationship between BDNF, TSH, and cognitive function. A p-value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
General information and clinical data
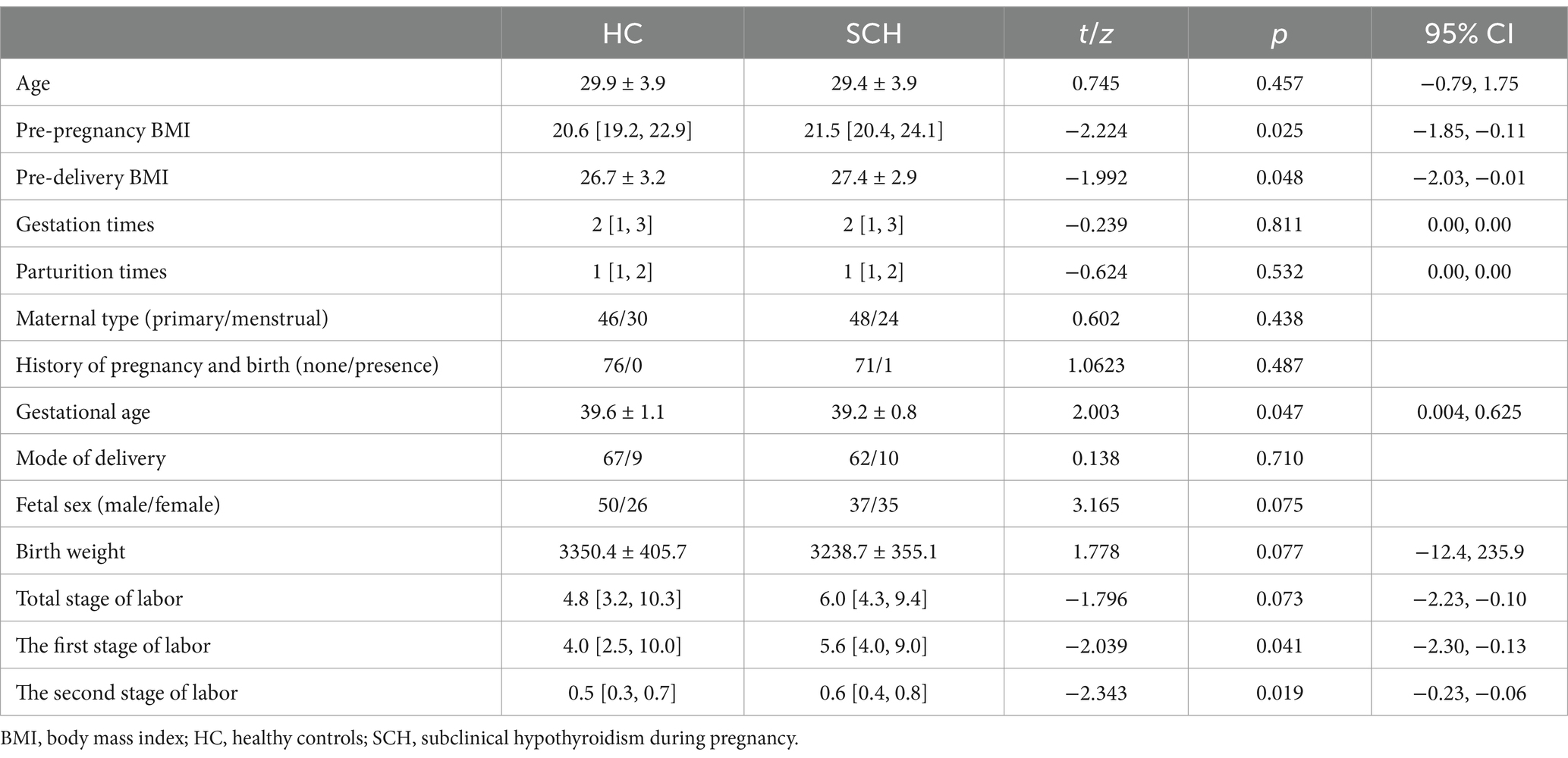
No significant differences in age, parturition times, total stage of labor, birth weight, fetal sex, and mode of delivery were observed between the pregnant women with subclinical hypothyroidism (SCH) and the healthy control group (p > 0.05). The gestational age of the SCH group was lower than that of the healthy control group (t = 2.003, p < 0.05). The pre-pregnancy BMI (Z = −2.224, p < 0.05) and pre-delivery BMI (t = −1.992, p < 0.05) were higher in the SCH group than in the healthy control group. The first stage of labor (Z = −2.039, p < 0.05) and the second stage of labor (Z = −2.343, p < 0.05) were longer in the SCH group than in the healthy control group (Table 1).
Comparison of thyroid function during early, middle, and late pregnancy in two groups of participants
The pregnant women with SCH exhibited significant differences in thyroid function in early, middle, and late pregnancy compared to the healthy control group. The TSH level during the early and middle pregnancy of the SCH group was higher than that of the healthy control group (p < 0.001). During late pregnancy, the TPOAb level (Z = −2.878, p < 0.01) and TSH level (Z = −5.925, p < 0.001) of the SCH group were higher than those of the healthy control group. No significant differences were observed in the other thyroid function levels (Table 2).
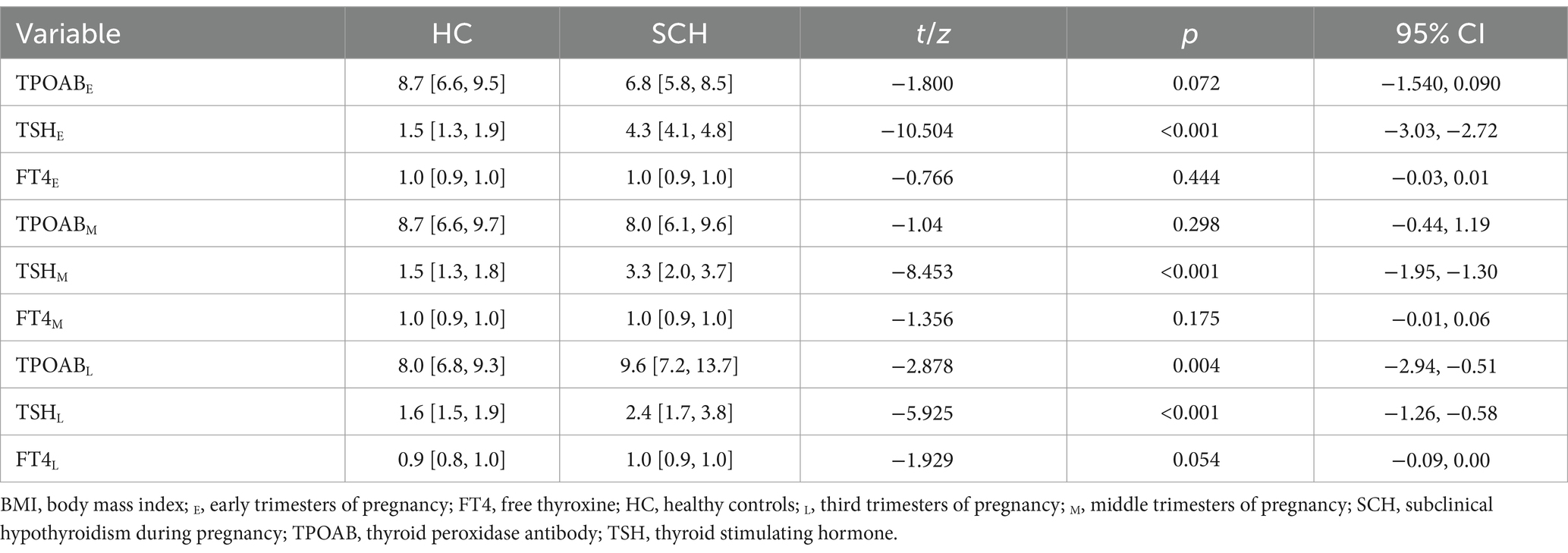
Table 2. Comparison of thyroid function in the early, middle, and third trimesters of pregnancy between the two groups.
Comparison of neonatal behavioral neurologic assessment scores and umbilical cord blood BDNF levels between two groups of subjects
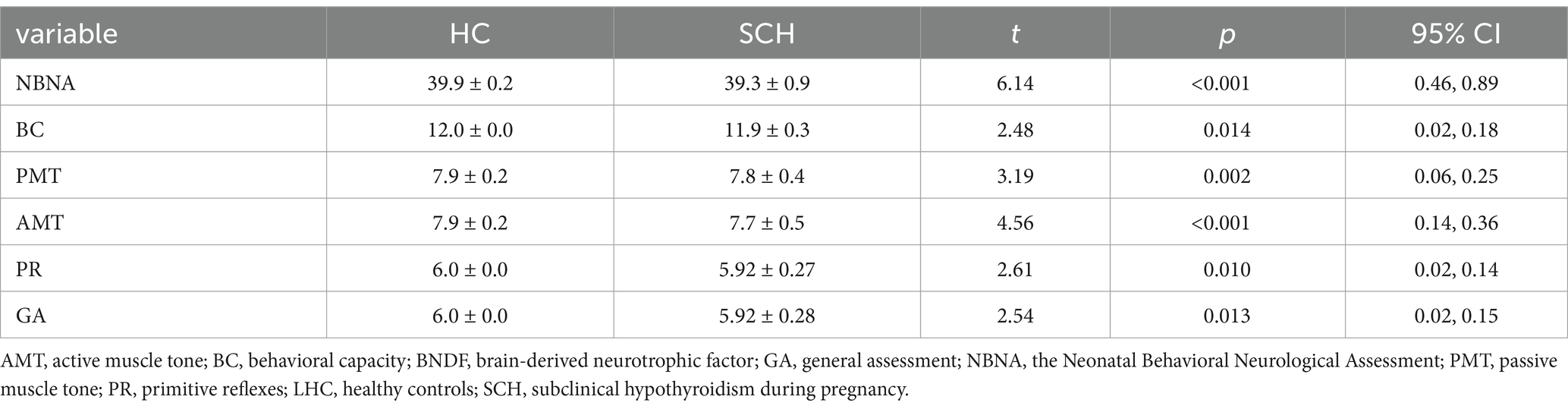
Newborns of the SCH group during pregnancy demonstrate lower total scores (t = 6.14, p < 0.001) on NBNA evaluation, as well as lower scores in behavior capacity (t = 2.48, p < 0.05), passive muscle tension (t = 3.19, p < 0.01), active muscle tension (t = 4.56, p < 0.001), primitive reflexes (t = 2.61, p < 0.05), and general assessment (t = 2.61, p < 0.05) as compared to the healthy control group. Furthermore, newborns in the SCH group had significantly lower levels of BDNF in their umbilical cord blood (t = 13.212, p < 0.001) (Table 3 and Figure 1).
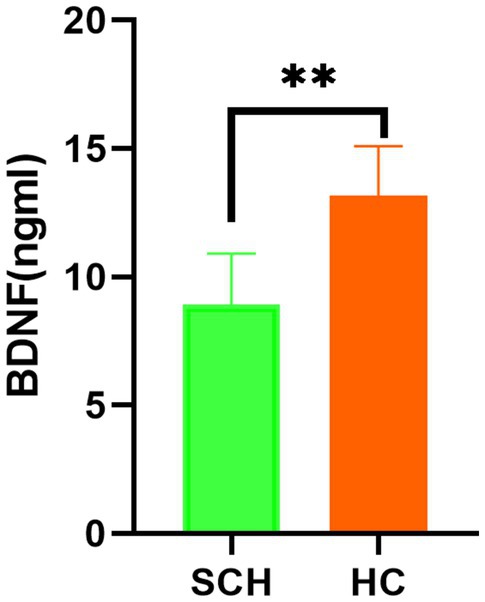
Figure 1. Comparison of the level of BDNF in the two groups. BNDF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; HC, healthy controls; SCH, subclinical hypothyroidism during pregnancy. ** p < 0.01.
The correlation between the umbilical cord blood BDNF levels of newborns of pregnant women with SCH during different pregnancy stages (early, middle, and late) and thyroid function and cognitive function
The level of BDNF in the umbilical cord blood of newborns with SCH during pregnancy is negatively correlated with TSH levels in early pregnancy (r = −0.35, p < 0.01). However, no significant correlation is observed between BDNF levels and TPOAb and FT4 levels in early pregnancy, as well as thyroid function in middle and late pregnancy. In SCH patients during pregnancy, the level of BDNF in newborn umbilical cord blood is positively correlated with the NBNA total score within 3 days of birth (r = 0.56, p < 0.001), as well as behavior capacity (r = 0.45, p < 0.001), active muscle tension (r = 0.52, p < 0.001), and general assessment (r = 0.35, p < 0.01) of newborns. However, there is no significant correlation between BDNF level and passive muscle tension or primitive reflexes of newborns (Figure 2).
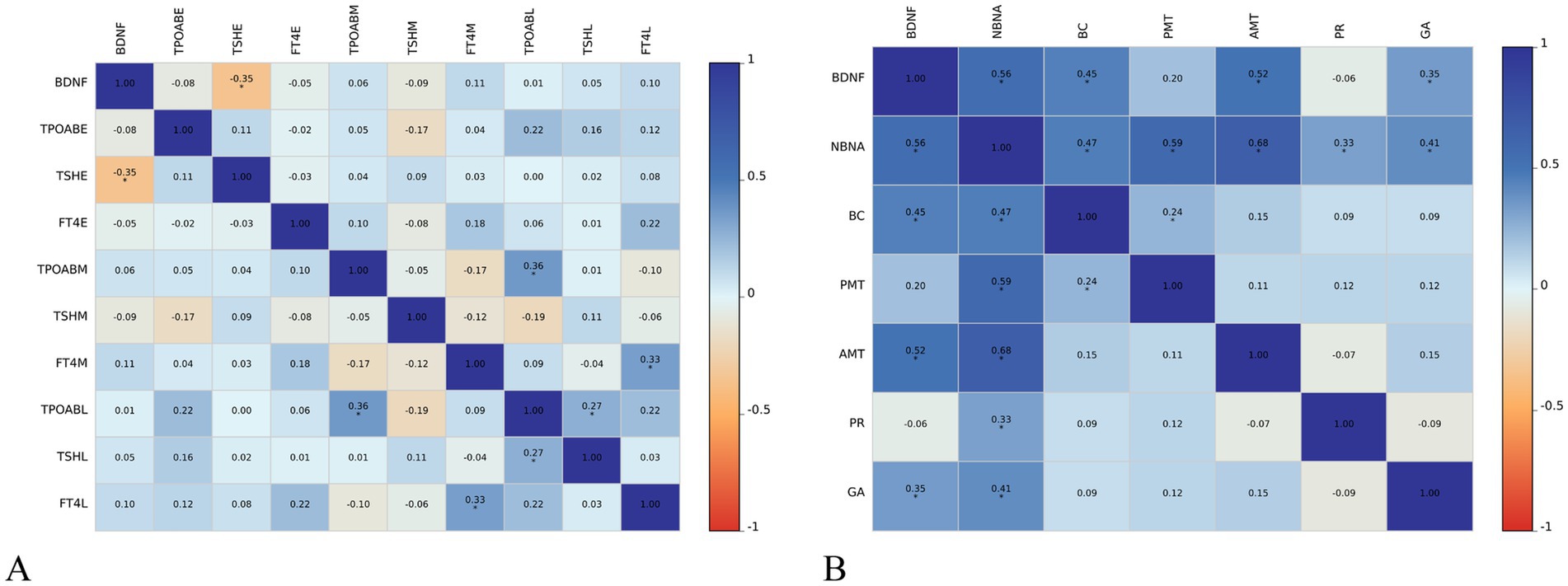
Figure 2. Relationship between cord blood BDNF level and thyroid function (A) and neonatal neurobehavioral abilities (B) in pregnancy in subclinical hypothyroidism group AMT, active muscle tone; BC, behavioral capacity; E, early trimesters of pregnancy; FT4, free thyroxine; GA, general assessment; L, third trimesters of pregnancy; M, middle trimesters of pregnancy; NBNA, the Neonatal Behavioral Neurological Assessment; PMT, passive muscle tone; PR, primitive reflexes; TPOAB, thyroid peroxidase antibody; TSH, thyroid stimulating hormone; HC, healthy controls; SCH, subclinical hypothyroidism during pregnancy. The color scale depicts the r range from −1 to 1.
Subsequent multiple linear regression analysis (control age and birth weight) revealed that the BDNF level in pregnant women with SCH was positively associated with NBNA total score (β = 0.49, t = 4.26, p < 0.001), behavioral capacity (β = 0.32, t = 2.71, p < 0.01), active muscle tension (β = 0.54, t = 4.36, p < 0.001), and general assessment (β = 0.34, t = 2.54, p < 0.01). Conversely, TSH level showed a negative association with behavioral capacity (β = −0.35, t = −3.10, p < 0.01) in pregnant women with SCH (Table 4).
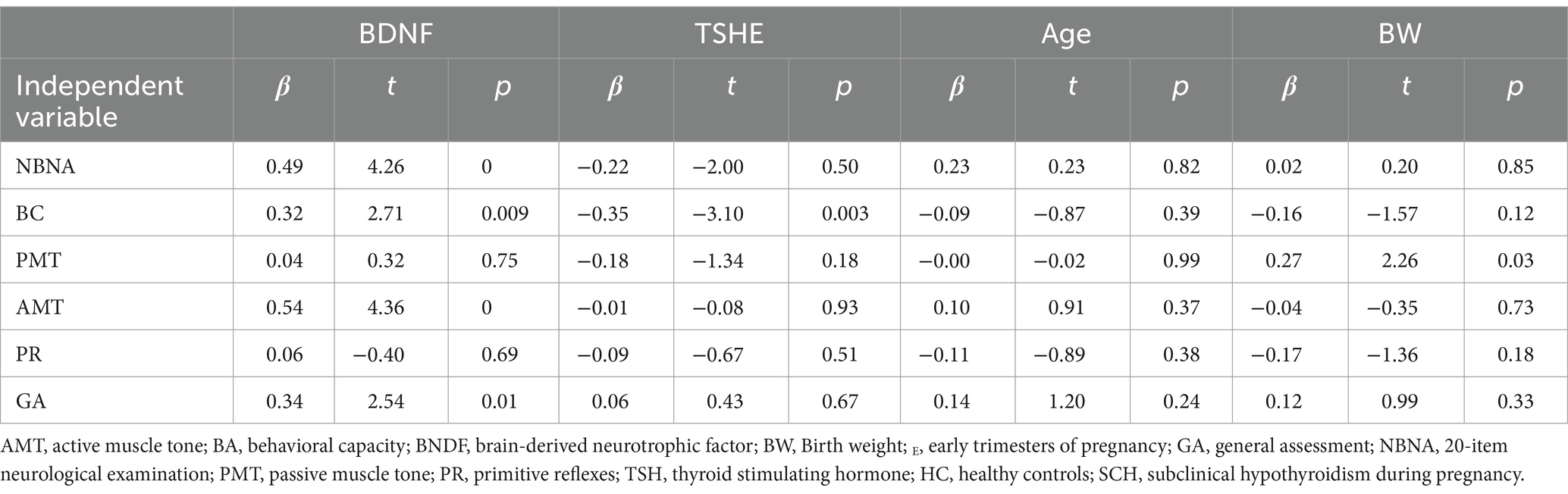
Table 4. Impact of BDNF and thyroid function in the multiple linear regression analyses in subclinical hypothyroidism group.
Discussion
Brain development from the fetal period to early life is crucial for various neurological and psychological domains throughout an individual’s life (19). This is the first study to investigate the relationship between the behavior and neural capacity of newborns in pregnant women with SCH and the level of BDNF in umbilical cord blood. Our study reveals that newborns’ early behavior and neural capacity in pregnant women with SCH were reduced and strongly correlated with the level of BDNF in umbilical cord blood.
The impact of SCH on pregnancy outcomes is relatively well established. However, the effect of SCH on the cognitive development of offspring remains inconclusive. A previous cohort study in the Netherlands involving 3,659 children and their mothers failed to establish a correlation between maternal TSH levels during early pregnancy and the cognitive development of offspring at 18 and 30 months (20). Similarly, a population-based cohort study in Spain, with 1,761 children and their mothers, failed to demonstrate any link between maternal serum TSH levels during pregnancy and neurodevelopment in children (21). We assessed newborns’ behavioral and neurological abilities in the SCH and normal control groups using the NBNA scoring method. Our results demonstrated that newborns in the SCH group had significantly lower total NBNA scores compared to those in the normal control group, and this difference was also observed in each section score. The inconsistent conclusions regarding the relationship between SCH during pregnancy and offspring neurodevelopment may be caused by varying cutoff values of TSH used in different studies, which could result in differences in the subjects included and lead to inconsistent results. Second, the age ranges of the study subjects differed substantially. Both the Dutch and Spanish studies focused on cognitive outcomes at 18 months or later, while our study assessed newborns within 3 days of birth. This early evaluation minimizes the influence of postnatal factors, such as education, social environment, or diet, which are known to affect cognitive development (22–24). Studies involving children and adult offspring often face confounding variables, possibly leading to biased outcomes. Our study evaluated the early behavioral and neurological abilities of newborns within 3 days after birth using the NBNA scale, which minimized interference from other factors, such as stress, and facilitated a more precise reflection of intrauterine effects on neonates. Future research should focus on standardizing SCH diagnostic criteria and incorporating longitudinal designs to better capture the long-term effects of maternal thyroid function on offspring neurodevelopment.
BDNF is a crucial protein molecule for neuronal growth, development, plasticity, and maintenance of the nervous system function (25). The binding of BDNF to the TrkB receptor triggers the activation of multiple signaling pathways, which regulate cellular biological processes, including cell proliferation, synaptic formation, and cell survival (26). Studies have shown that BDNF is essential in neural development, memory formation, learning, and neurological diseases (27). Abnormal regulation of BDNF levels is associated with various neurological disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease, anxiety, depression, and Alzheimer’s disease (28–30).
We observed a positive correlation between the levels of BDNF in newborn serum and their neurodevelopmental behavioral abilities, particularly with NBNA total score, passive muscle tone, and general assessment in the SCH group during pregnancy. Subsequent multivariate linear regression also revealed that BDNF levels in pregnant women with SCH were significantly associated with NBNA total score, active muscle tone, and general evaluation of behavioral abilities. Our research results suggest that BDNF may be involved in the pathological process of abnormal neurodevelopment in the offspring of mothers with SCH during pregnancy. Insufficient induction of high expression of BDNF in pregnant women with SCH may limit the behavioral neurodevelopment of fetuses during gestation, resulting in lower NBNA scores in newborns. BDNF, as a biological indicator, is more objective for evaluating newborn behavioral neurodevelopmental abilities than scales. However, these findings are preliminary, and the sensitivity, specificity, and predictive value of BDNF as a clinical diagnostic marker need further validation. Given the limitations of correlation analysis in establishing causality, future longitudinal and prospective studies should focus on pregnant women with SCH to better elucidate the relationships between maternal thyroid function, BDNF levels, and neonatal neurobehavioral outcomes. As far as we know, some researchers have developed drugs to elevate peripheral BDNF levels. Exploring the potential use of such drugs to enhance the neurodevelopmental behavioral abilities of the offspring of mothers with SCH is an exciting direction for further investigation (31).
Limitations
This study has several limitations. Firstly, due to difficulty in follow-up, we could not evaluate newborns at 14 and 28 days after birth. Therefore, NBNA scoring was only conducted immediately after delivery, limiting our ability to assess whether the observed neurobehavioral outcomes persist or evolve over time. Secondly, although some studies have found a correlation between BDNF levels in the brain and peripheral blood, it remains uncertain whether alterations in peripheral blood BDNF levels directly correspond to modifications in central nervous system BDNF levels. Thirdly, this study was conducted with a limited sample size in a single center, which may not fully represent broader populations with diverse socio-economic, ethnic, or geographic backgrounds. Potential confounding factors, such as maternal diet, stress, and socioeconomic status, were also not accounted for in this study due to data unavailability. Finally, while BDNF screening shows potential as an early biomarker for neurodevelopmental risks, its clinical application faces ethical and practical challenges, including cost, accessibility, and the need for further validation in diverse populations. Future studies should incorporate multi-center designs, more diverse populations, and longitudinal approaches to address these limitations and enhance the generalizability and applicability of the findings.
Conclusion
The umbilical cord blood brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels in pregnant women with subclinical hypothyroidism (SCH) are positively correlated with newborns’ behavioral and neurological abilities.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital Ethics Committee affiliated with Anhui Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s), and minor(s)’ legal guardian/next of kin, for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
HX: Data curation, Resources, Writing – original draft. Y-ND: Data curation, Writing – original draft. SY: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. Y-WG: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Funding was provided by key program of Anhui Provincial Maternal and Child Health Hospital (zd2021-2-5).
Acknowledgments
The authors a grateful to the patients for their participation in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Shan, Z, and Weiping, T. Guideline on diagnosis and management of thyroid diseases during pregnancy and postpartum (2nd edition): an essential introduction. Chin J Endocrinol Metab. (2019) 35:632–5. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6699.2019.08.002
2. Dincgez, B, Ercan, I, Sahin, I, and Erturk, NK. The risk of developing gestational diabetes mellitus in maternal subclinical hypothyroidism: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Gynecol Obstet. (2024) 309:765–74. doi: 10.1007/s00404-023-07137-y
3. Liu, X, Zhang, C, Lin, Z, Zhu, K, He, R, Jiang, Z, et al. Association of maternal mild hypothyroidism in the first and third trimesters with obstetric and perinatal outcomes: a prospective cohort study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (2024) 30:47. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2024.08.047
4. Williams, GR. Neurodevelopmental and neurophysiological actions of thyroid hormone. J Neuroendocrinol. (2008) 20:784–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2008.01733.x
5. Liu, D, Teng, W, Shan, Z, Yu, X, Gao, Y, Wang, S, et al. The effect of maternal subclinical hypothyroidism during pregnancy on brain development in rat offspring. Thyroid. (2010) 20:909–15. doi: 10.1089/thy.2009.0036
6. Williams, FL, Watson, J, Ogston, SA, Visser, T, Hume, R, and Willatts, P. Maternal and umbilical cord levels of T4, FT4, TSH, TPOAb, and TgAb in term infants and neurodevelopmental outcome at 5.5 years. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2013) 98:829–38. doi: 10.1210/jc.2012-3572
7. Bramati, G, Stauffer, P, Nigri, M, Wolfer, DP, and Amrein, I. Environmental enrichment improves hippocampus-dependent spatial learning in female C57BL/6 mice in novel IntelliCage sweet reward-based behavioral tests. Front Behav Neurosci. (2023) 17:1256744. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2023.1256744
8. Vaynman, S, Ying, Z, and Gomez-Pinilla, F. Hippocampal BDNF mediates the efficacy of exerciseon synaptic plasticity and cognition. Eur J Neurosci. (2004) 20:2580–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2004.03720.x
9. Bao, X. Neonatal behavioral ability and its testing methods. J Pract Diagn Ther. (2003) 17:625–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3474.2003.06.001
10. Notaras, M, and van den Buuse, M. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF): novel insights into regulation and genetic variation. Neuroscientist. (2019) 25:434–54. doi: 10.1177/1073858418810142
11. Ferraguti, G, Terracina, S, Micangeli, G, Lucarelli, M, Tarani, L, Ceccanti, M, et al. NGF and BDNF in pediatrics syndromes. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. (2023) 145:105015. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2022.105015
12. Lima Giacobbo, B, Doorduin, J, Klein, HC, Dierckx, RAJO, Bromberg, E, and de Vries, EFJ. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in brain disorders: focus on Neuroinflammation. Mol Neurobiol. (2019) 56:3295–312. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1283-6
13. Przybylska, I, Marusiak, J, Toczyłowska, B, Stępień, A, Brodacki, B, Langfort, J, et al. Association between the Val66Met (rs6265) polymorphism of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene, BDNF protein level in the blood and the risk of developing early-onset Parkinson's disease. Acta Neurobiol Exp. (2024) 84:296–308. doi: 10.55782/ane-2024-2476
14. Gang, S, Janko, J, Lamprecht, E, Riedl, D, Konzett, K, and Simma, B. Significant correlation between serum biomarkers and outcome in neonatal hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. Acta Paediatr. (2024) 113:2543–9. doi: 10.1111/apa.17368
15. Toll, A, Blanco-Hinojo, L, Berge, D, Manzano, A, el Abidi, K, Perez-Solà, V, et al. Relationship between thyroid-stimulating hormone, BDNF levels, and hippocampal volume in antipsychotic-naïve first-episode psychosis patients. Front Psych. (2023) 14:1301714. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1301714
16. Zhang, P, Li, YX, Zhang, ZZ, Yang, Y, Rao, JX, Xia, L, et al. Astroglial mechanisms underlying chronic insomnia disorder: a clinical study. Nat Sci Sleep. (2020) 12:693–704. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S263528
17. Abedelhaffez, AS, and Hassan, A. Brain derived neurotrophic factor and oxidative stress index in pups with developmental hypothyroidism: neuroprotective effects of selenium. Acta Physiol Hung. (2013) 100:197–210. doi: 10.1556/APhysiol.100.2013.2.7
18. Shafiee, SM, Vafaei, AA, and Rashidy-Pour, A. Effects of maternal hypothyroidism during pregnancy on learning, memory and hippocampal BDNF in rat pups: beneficial effects of exercise. Neuroscience. (2016) 329:151–61. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.04.048
19. Georgieff, MK. Early life nutrition and brain development: breakthroughs, challenges and new horizons. Proc Nutr Soc. (2023) 82:104–12. doi: 10.1017/S0029665122002774
20. Henrichs, J, Bongers-Schokking, JJ, Schenk, JJ, Ghassabian, A, Schmidt, HG, Visser, TJ, et al. Maternal thyroid function during early pregnancy and cognitive functioning in early childhood: the generation R study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2010) 95:4227–34. doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-0415
21. Julvez, J, Alvarez-Pedrerol, M, Rebagliato, M, Murcia, M, Forns, J, Garcia-Esteban, R, et al. Thyroxine levels during pregnancy in healthy women and early child neurodevelopment. Epidemiology. (2013) 24:150–7. doi: 10.1097/EDE.0b013e318276ccd3
22. Liu, F, Xu, J, Guo, L, Qin, W, Liang, M, Schumann, G, et al. Environmental neuroscience linking exposome to brain structure and function underlying cognition and behavior. Mol Psychiatry. (2023) 28:17–27. doi: 10.1038/s41380-022-01669-6
23. Key, MN, and Szabo-Reed, AN. Impact of diet and exercise interventions on cognition and brain health in older adults: a narrative review. Nutrients. (2023) 15:2495. doi: 10.3390/nu15112495
24. Li, W, Luo, Z, Jiang, J, Li, K, and Wu, C. The effects of exercise intervention on cognition and motor function in stroke survivors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurol Sci. (2023) 44:1891–903. doi: 10.1007/s10072-023-06636-9
25. Song, M, Martinowich, K, and Lee, FS. BDNF at the synapse: why location matters. Mol Psychiatry. (2017) 22:1370–5. doi: 10.1038/mp.2017.144
26. Sun, YX, Su, YA, Wang, Q, Zheng, JY, Zhang, CC, Wang, T, et al. The causal involvement of the BDNF-TrkB pathway in dentate gyrus in early-life stress-induced cognitive deficits in male mice. Transl Psychiatry. (2023) 13:173. doi: 10.1038/s41398-023-02476-5
27. Zhang, S, Fu, W, Jia, X, Bade, R, Liu, X, Xie, Y, et al. Hypoxic preconditioning modulates BDNF and its signaling through DNA methylation to promote learning and memory in mice. ACS Chem Neurosci. (2023) 14:2320–32. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.3c00069
28. Numakawa, T, and Kajihara, R. Neurotrophins and other growth factors in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Life. (2023) 13:647. doi: 10.3390/life13030647
29. Singh, S, Fereshetyan, K, Shorter, S, Paliokha, R, Dremencov, E, Yenkoyan, K, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in perinatal depression: side show or pivotal factor? Drug Discov Today. (2023) 28:103467. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2022.103467
30. Wang, CS, Kavalali, ET, and Monteggia, LM. BDNF signaling in context: from synaptic regulation to psychiatric disorders. Cell. (2022) 185:62–76. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.003
31. Abiero, A, Botanas, CJ, Custodio, RJ, Sayson, LV, Kim, M, Lee, HJ, et al. 4-MeO-PCP and 3-MeO-PCMo, new dissociative drugs, produce rewarding and reinforcing effects through activation of mesolimbic dopamine pathway and alteration of accumbal CREB, deltaFosB, and BDNF levels. Psychopharmacology. (2020) 237:757–72. doi: 10.1007/s00213-019-05412-y
Keywords: subclinical hypothyroidism during pregnancy, neurobehavioral capabilities, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, neonatal behavioral neurological assessment, newborns
Citation: Xu H, Du Y-N, Yang S and Guo Y-W (2025) Relationship between BDNF content in cord blood and early neurobehavior in newborns with subclinical hypothyroidism during pregnancy: a preliminary study. Front. Neurol. 15:1465715. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1465715
Edited by:
Anna Maria Lavezzi, University of Milan, ItalyReviewed by:
Riffat Mehboob, National Institutes of Health (NIH), United StatesRafał Staszkiewicz, 5th Military Clinical Hospital in Krakow, Poland
Copyright © 2025 Xu, Du, Yang and Guo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yu-Wen Guo, Z3VveXV3ZW4wMDFAc29odS5jb20=; Shuai Yang, eWFuZ3NodWFpZHJAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Hui Xu1
Hui Xu1 Shuai Yang
Shuai Yang