- 1Department of Neurological Surgery, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA, United States
- 2Sagol Center for Hyperbaric Medicine and Research, Shamir (Assaf Harofeh) Medical Center, Be'er Ya'akov, Israel
- 3Foundation for the Study of Inflammatory Disease, Bethesda, MD, United States
- 4Aviv Clinic, The Villages, FL, United States
- 5The Villages Health, The Villages, FL, United States
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) has recently emerged as a promising neuromodulatory modality for treating several neurological and psychological disorders. Various studies indicate that HBOT can promote brain recovery and neuroplasticity through the modulation of key cellular and molecular mechanisms. HBOT affects multiple primary pathways and cellular functions including mitochondrial biogenesis and function (increased Bcl-2, reduced Bax, and enhanced ATP production), neurogenesis (upregulation of Wnt-3 and VEGF/ERK signaling), synaptogenesis (elevated GAP43 and synaptophysin expression), and anti-inflammatory responses (reduced TNF-α and IL-6). These mechanisms contribute to significant clinical benefits, such as enhanced cognitive function, improved recovery from traumatic brain injury and post-concussion syndrome, and symptom reduction in conditions like post-traumatic stress disorder and fibromyalgia. By influencing these molecular targets, HBOT offers a novel approach to neuromodulation that warrants further exploration. This review discusses the representative mechanisms of action of HBOT and highlights its therapeutic neuromodulatory effects and potential clinical applications across various neurological and psychiatric conditions.
1 Introduction
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is a medical treatment that involves breathing pure oxygen at higher than atmospheric pressure (1). HBOT has a rich history that dates back to the early 20th century when it was initially used to treat decompression sickness in divers. Its applications have since expanded due to its unique mechanism of action, which involves breathing pure oxygen at pressures higher than atmospheric levels (1). This enhanced oxygen delivery promotes healing processes and has been applied in both clinical and preclinical settings. More recently, researchers have investigated the potential of HBOT to treat neurological and psychiatric disorders such as traumatic brain injury (TBI), post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), post-concussion syndrome (PCS), major depressive disorder (MDD), and post-stroke depression, among other (1–6). Preclinical murine models have also been extensively used to study the effects of HBOT, providing valuable insights into its biological mechanisms (1–3, 5, 6). The mechanism of HBOT is based on its ability to significantly increase the oxygen concentration in the blood and tissues (1–6). By breathing 100% oxygen under elevated atmospheric pressure, HBOT facilitates the dissolution of oxygen in the plasma, leading to enhanced tissue oxygenation even in areas with compromised blood flow (1–6). This hyperoxia triggers various physiological responses, including the upregulation of oxygen-sensitive genes and the activation of cellular repair processes (1–6).
The existing evidence supports the potential therapeutic effects of HBOT for individuals suffering from neurological and some psychiatric disorders. This is attributed to HBOT’s ability to alter brain activity and improve function for individuals with these conditions. A prospective, randomized controlled trial of veterans with treatment-resistant PTSD evaluated the effect of HBOT compared to a control group (3). After undergoing HBOT, the clinician-administered PTSD scale-V scores showed a notable improvement in the HBOT group, while no changes were observed in the control group. Furthermore, significant enhancements were observed in the brief symptom inventory and BECK depression inventory scores, indicating the efficacy of HBOT in ameliorating the symptoms of PTSD and depression. Additionally, functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) revealed notable improvements in brain activity in regions including the left dorsolateral prefrontal, middle temporal gyri, both thalami, left hippocampus, and left insula following the HBOT treatment. These brain areas are crucial for various cognitive functions such as executive function, memory, and emotional regulation. Improvements in these regions suggest that HBOT may enhance cognitive processing, emotional stability, and overall mental health. Several retrospective studies also investigated HBOT for other mental disorders including autism and sleep disorders and showed various improvement effects with HBOT on various parameters (7–9).
It is now recognized that increasing oxygenation of blood and plasma to supraphysiological levels by breathing 100% oxygen under hyperbaric pressure results in improvement in neurological function by activating oxygen and pressure sensitive genes—such as p21 and Bax (10). The intermittent increase of oxygen concentration induces many of the mediators and cellular mechanisms needed for regeneration during hypoxia, but does so without the hazardous effects of hypoxia; this phenomenon is termed the hyperoxic-hypoxic paradox (10). This article reviews the various cellular pathways associated with neurogenesis, angiogenesis, and synaptogenesis which are critical elements of neuroplasticity and hence, neuromodulation.
2 Neuroplastic capacity of hyperbaric oxygen therapy
Neuroplasticity refers to the capability of the nervous system to reorganize and adapt to a changing environment – a fundamental process underpinning learning, memory and recovery from brain damage (11, 12). HBOT can potentially harness this property to improve outcomes in various neurological conditions via multiple cellular mechanisms (11, 13, 14). The capacity of HBOT to modulate neuroplasticity has been demonstrated in clinical settings (13, 14). For instance, a randomized, prospective trial of using 40 daily sessions of HBOT over 2 months in post-stroke patients showed a significant improvement in the neurological functions and life quality of all patients in both treated and cross control groups after undergoing HBOT therapy (15). Conversely, no improvement was observed during the control period for patients in a crossover group. Furthermore, single-photon emission computerized tomography (SPECT) imaging showed a strong correlation with respective Brodmann area maps of the cerebral cortex associated with the clinical improvements.
Additionally, in a controlled crossover study on persistent post-concussion syndrome (PPCS) following mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI), HBOT demonstrated a significant neuroplastic potential (16). Sixty-three civilian subjects underwent either 40 daily sessions of HBOT or a no-treatment control period, with the control group later receiving HBOT. Pre- and post-treatment evaluations, including symptoms, neuropsychological, and psychological testing, indicated significant improvements in neurobehavioral symptoms, memory index, depression, anxiety, sleep, and quality of life in the HBOT group. These enhancements, indicative of enhanced neuroplasticity, persisted even 2 months post-treatment, underscoring the role of HBOT in promoting brain recovery and function enhancement in individuals with mTBI/PPCS.
Another randomized, double-blind trial explored HBOT’s ability to enhance neuroplasticity in children aged 8–15 years suffering from PCS following mild to moderate TBI (9). The 25 participants were given either 60 daily HBOT sessions or sham treatments. Post-HBOT, there were notable improvements in cognitive functions, memory, and executive functions, suggesting increased neuroplasticity. Further, brain MRI detected significant microstructural changes in areas such as the insula, supramarginal, and inferior frontal gyri, reflecting neuroplastic changes induced by HBOT. The study thus highlights HBOT’s potential in promoting neuroplasticity, improving cognitive and behavioral functions, and enhancing the quality of life in pediatric PPCS patients, even years post-injury.
The long-term effects of HBOT were examined in a study of 22 veterans with treatment-resistant PTSD, further evaluating its role in neuroplasticity (17). PTSD symptoms, particularly in cognition and mood, exhibited sustained improvements approximately 704 days post-HBOT, highlighting the therapy’s potential for inducing durable neuroplastic changes. The study also noted secondary benefits including enhanced social function and reduced medication use, reinforcing the long-lasting impact of HBOT-induced neuroplasticity. While the literature offers promising evidence of HBOT’s neuroplastic effects, a deeper understanding of these mechanisms could lead to developing more effective treatment strategies using HBOT in neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders.
3 Proposed mechanisms of HBOT neuromodulation
Most neuromodulatory techniques use various energy sources to primarily suppress or stimulate specific neural pathways. These sources include magnetism (as in transcranial magnetic stimulation), electricity (as in transcranial direct and alternating current stimulation), photons (as in photo biomodulation), and ultrasound. Through hyperoxygenation of tissues, HBOT increases mitochondrial biogenesis and thus addresses the metabolic mismatch in the function of damaged cells, synapses, and conduction pathways (18, 19). This strategy fosters the direct revitalization and repair of neural circuits, enhancing their sensitivity to inherent stimulatory and inhibitory signals (19). Essentially, HBOT’s primary mechanism of action is to restore neural function by promoting intrinsic recovery and enhancement of neural circuits, rather than through external magnetic, electrical, photonic or ultrasonic stimulation of neural pathways (13, 19–21). This process is integral to neuroplasticity, a central aspect of HBOT’s neuromodulatory effect. The key proposed mechanisms necessitating further examination are further discussed (Table 1; Figure 1).
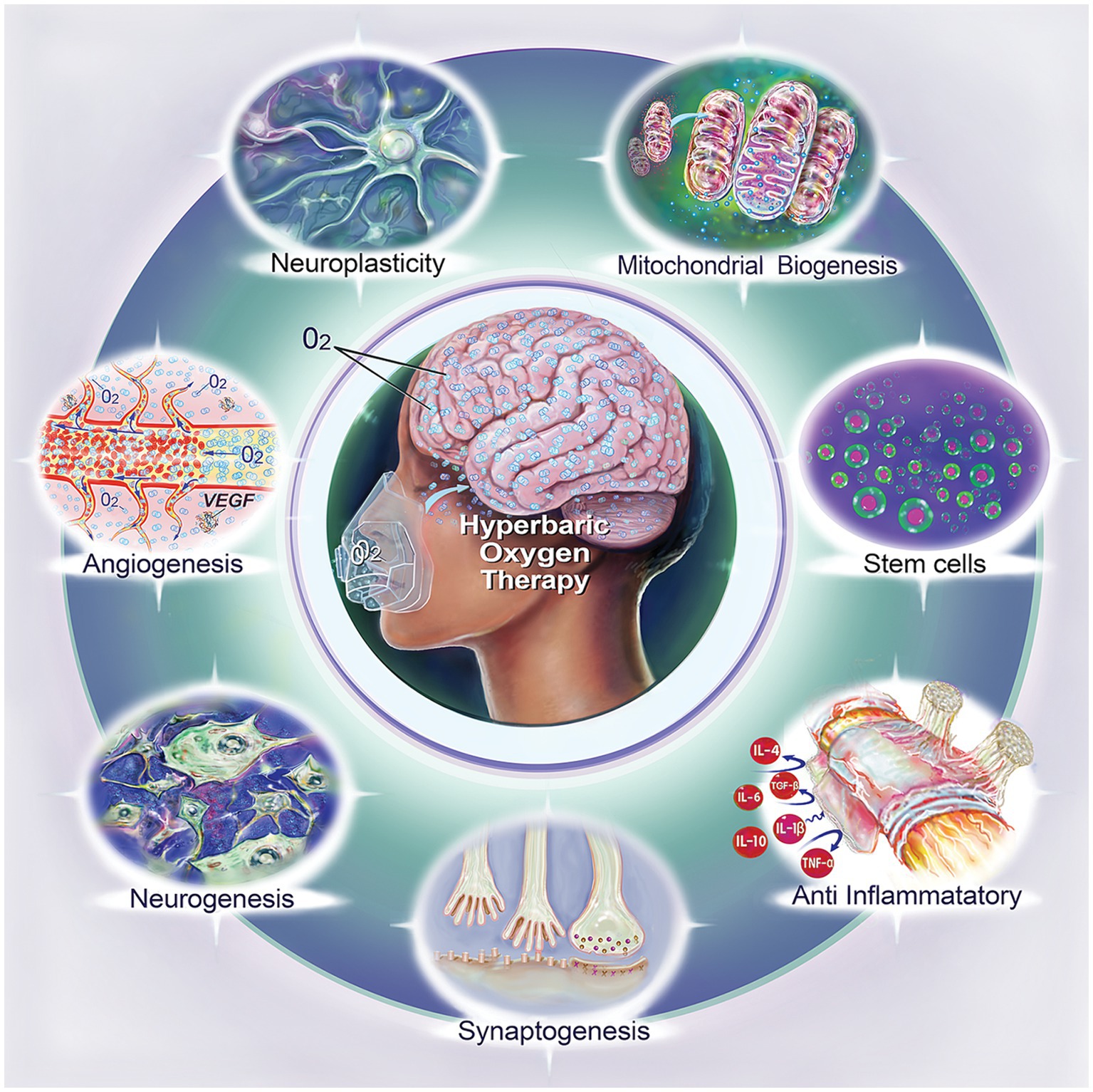
Figure 1. Biological effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT). This illustration summarizes the diverse biological impacts of HBOT, including neuroplasticity, mitochondrial biogenesis, stem cell enhancement, anti-inflammatory effect, synaptogenesis, neurogenesis, and angiogenesis.
3.1 Mitochondrial function enhancement and neuroprotection
Over the past two decades, researchers have studied the effect of HBOT on mitochondrial function and neural cells in murine models using varied protocols (22, 23). While some studies showed shorter HBOT treatment to be associated with decreased mitochondrial function, several other studies noted increased energy production and improved complex IV activity with prolonged HBOT treatment of 4 weeks duration (23, 24). Additionally, investigators have shown that 10–14 days of HBOT increases ATP production and reduces mitochondria-mediated apoptosis signaling (12, 23, 25, 26). In one particular study on mice, 14 days of HBOT has increased Bcl-2 and decreased Bax after 2 weeks (12). This suggests that HBOT may enhance intracellular oxygen bio-availability and Bcl-2 expression, preserve mitochondrial integrity and mitigate the activation of the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway.
In a study using Sprague–Dawley rats with induced cortical lesions, HBOT-treated subjects demonstrated improved neuronal counts and denser axonal networks in the perilesional area, compared to non-treated rats (12). In their study, HBOT was found to effectively reverse the loss of mitochondrial transmembrane potential in mitochondria isolated from injured brain tissue. A significant reduction in caspases 3 and 9 activation, but not caspase 8, pointed to a selective effect on the intrinsic apoptosis pathway. Therefore, HBOT’s neuroprotective effect could be attributed to preserved mitochondrial integrity, inhibition of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore and reduction of the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway.
Additionally, recent research has revealed that HBOT facilitates the transfer of mitochondria from astrocytes to neuronal cells, suggesting a mechanism for enhancing neural cells, dendritic formation, and their function during stress (27, 28). In a murine study, they utilized a 90-min HBOT treatment at 2.5 absolute atmospheres before inducing injury with either tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) or lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to simulate inflammation-related secondary cell death, common in stroke and TBI (27). Post-incubation with TNF-alpha or LPS, cell viability was assessed. Results showed a significant increase in cell viability and mitochondrial transfer in the HBOT-preconditioned injury groups compared to the injury-only groups (44 ± 5.2 vs. 68 ± 4.48, n = 20, p < 0.05). They concluded that HBOT preconditioning likely aids in transferring resilient mitochondria from astrocytes to inflammation-susceptible neuronal cells, thereby reducing cell death. These findings highlight HBOT’s ability to augment specific neural functions to enhance neural resilience in the presence of physical stress. Complementary studies suggest that HBOT preconditioning is an innovative approach to foster neuroplasticity and mitigate neuronal cell death (27, 28). These studies found that by transferring resilient mitochondria from astrocytes to neurons, HBOT preconditioning improved cell viability and resilience to inflammation-induced injury, which is the hallmark of stroke and traumatic brain injury (27, 28). The increase in mitochondrial robustness is a cornerstone in facilitating neuroplasticity, an important process for neuronal recovery and regeneration. While the HBOT neuromodulatory effect may be partially explained by the interplay between neurons and glial cells through mitochondrial transfer, further research is needed to further our understanding of this mechanism (Table 1).
3.2 Neurogenesis and angiogenesis
HBOT’s neuromodulatory role encompasses both neurogenesis and angiogenesis with potential benefits for cognitive function. A capacity for stimulating stem cell proliferation, as noted in the upregulation of key markers like BrdU, doublecortin, nestin, and Wnt-3 has been demonstrated (19, 29, 30). This reflects an augmentation of neuronal cell proliferation in strategic neurogenic regions such as the hippocampal dentate gyrus and the subventricular zone. Notably, these regions play significant roles in spatial learning and memory (30).
HBOT’s potential for TBI recovery is proven based on its ability to promote stem cell proliferation and migration to injury sites (19, 30). In addition, HBOT increases the levels of key vascular and neuronal growth signaling molecules, such as VEGF, VEGFR-2, Raf-1, MEK1/2, and phospho-ERK 1/2 protein, suggesting that it may bolster neurogenesis and angiogenesis through VEGF/ERK signaling (29, 31, 32). Similarly, in a vascular dementia rat model, HBOT also facilitated neurogenesis and enhanced blood supply in the piriform cortex (33). It showed a capacity to mobilize bone marrow stem cells toward ischemic regions, and to promote the release of trophic factors that can foster brain and neuronal recovery, thereby augmenting neurogenesis.
Interestingly, in patients with delayed encephalopathy after acute carbon monoxide poisoning, HBOT has been shown to mobilize stem cells in the peripheral blood, leading to cognitive improvement (34). Similarly, HBOT has increased cerebral blood flow and cognitive performance in elderly patients with significant memory loss (35). Concurrently, a surge in the number of cells displaying BrdU and NeuN - indicators of neuronal proliferation and maturity - was witnessed in an experimental rat study, implicating HBOT in fostering neurogenesis (36). This connection between cognitive enhancement and cerebral angiogenesis underlines the potential of HBOT in improving brain perfusion and activity (Table 1).
3.3 Synaptic and axonal formation
Another mechanism of enhancement is in synaptic and axonal formation, a closely linked mechanism to neurogenesis. Growth-associated protein 43 (GAP43) is a crucial membrane-bound protein involved in neurite outgrowth, and synaptophysin (SYP) is an integral membrane protein located within the synaptic vesicles. GAP43 and SYP gene expressions have been used as markers for studying brain and spinal injuries due to their critical roles in neuroplasticity, neurogenesis, synapse reformation, and axonal regeneration (37, 38). In a study by Brkic et al. (37) the authors investigated whether HBOT could enhance the recovery of motor functions in rats after suction ablation of the right sensorimotor cortex, using the expression profile of GAP43 and SYP genes as plasticity markers. The authors found a significant upregulation in GAP43 and SYP genes in the injured cortex of rats following HBOT, compared to a control group. They also observed that HBOT significantly increased SYP protein labeling of long axons in the non-injured cortex and subcortical white matter of control and sham-operated rat brain sections. SYP immunoreactivity was clustered on neuronal cell bodies, apical dendrites, and along axons. These findings suggest that HBOT can induce synapse formation independently of neural injury (Table 1).
3.4 p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway
Furthermore, there is compelling evidence indicating that HBOT influences the p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway, a serine/threonine protein kinase that plays a crucial role in cellular responses to various stress stimuli and a pivotal player in synaptic plasticity and the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders (39, 40). The activation of N-methyl-d-aspartate ionotropic glutamate receptors or group I metabotropic glutamate receptors can trigger signaling pathways that lead to a prompt and sustained decline in excitatory postsynaptic potentials (39, 40). HBOT has a modulatory effect on the MAPK cascade, specifically p38 MAPK, which suggests that it may have the potential to induce neuromodulation and neuroplasticity (39–41). Moreover, several investigations have explored the electrophysiological characteristics and molecular mechanisms underlying long-term potentiation and depression induced by HBOT in the hippocampus, a region of the brain involved in learning and memory (40–42). These studies have revealed promising findings that suggest that HBOT may influence the MAPK cascade, leading to modulatory effects on synaptic plasticity and possibly the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders (Table 1).
3.5 Telomere elongation and anti-inflammation
Recent research highlights the interplay between telomere shortening and inflammation in the manifestation of depression, offering a perspective for HBOT’s neuromodulatory role (43). Telomere shortening, an indicator of cellular aging, is accelerated in chronic inflammatory states and is commonly associated with depressive disorders (44–46). This relationship highlights a potential avenue for HBOT’s therapeutic effects, considering its established anti-inflammatory properties and telomere elongation. A study, by Hachmo et al. (47) involving 35 healthy adults underwent 60 daily HBOT exposures was conducted to examine the effects on telomere length and cellular senescence. Post-HBOT evaluations showed significant telomere elongation in various immune cells. These findings suggest that HBOT might not only counteract key aspects of the aging process at a cellular level but also enhance overall physiological rejuvenation in an aging population. A self-conducted case study, by the senior author, involving 60 daily HBOT therapy sessions over three months demonstrated significant neurocognitive improvements and intriguing biological changes (48). The study revealed a twofold increase in telomere length, suggesting potential anti-aging effects at the cellular level.
Additionally, there is substantial evidence linking telomere shortening and psychiatric disorders, particularly depression, further indicating HBOT’s potential neuromodulatory impact (49–51). Telomere attrition has been consistently associated with increased risk for psychiatric disorders, including depression (49, 51). Studies have revealed that decreased telomerase levels, resulting in shortened telomeres, are linked to increased oxidative stress in depression models (49–51). Furthermore, chronic low-grade inflammation, often observed in depressive states, has been negatively correlated with telomere length, contributing to accelerated cellular aging (49, 52). The connection between systemic inflammation and shortened leukocyte telomere length (LTL) is particularly compelling (44, 45). Increase in inflammatory cytokines such as CRP, TNF-α, and IL-6 have been shown to negatively impact the psychopathology of depression, anxiety, and LTL (44, 45). This link between inflammation, depression, and telomere shortening has been substantiated in numerous studies that have demonstrated a significant association between depression and shorter LTL (44, 46). Several clinical studies have indicated that less stress is associated with increased telomerase activity and telomere elongation, suggesting the potential association on another level (53, 54).
Given these insights, HBOT’s capability to induce telomere elongation and reduce inflammation presents it as a potentially effective neuromodulatory and therapeutic modality to enhance neuroplasticity (Table 1).
3.6 Brain-derived neurotrophic factor
Recent research has elucidated the impact of HBOT on the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and its implications for neuroplasticity and brain function (55–58). BDNF is a critical factor involved in neuronal survival, growth, and synaptic plasticity and is pivotal in cognitive processes, including learning and memory (55–59). Studies have shown that HBOT can promote the release of BDNF and enhance its signaling pathways, thereby influencing neuroplasticity and neural circuit function (56, 59). A study by Hsu et al. (59) showed that HBOT treatment in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease resulted in increased BDNF levels, which correlated with the improvement of motor function and protection of dopaminergic neurons. Similarly, in a study in a rat model of spinal cord injury, HBOT was found to reduce apoptosis and dendritic/synaptic degeneration through the BDNF/TrkB signaling pathways, leading to neuroprotection (56). These findings suggest that HBOT can stimulate BDNF production in different regions of the central nervous system. Furthermore, it was demonstrated that HBOT increased the proliferation of human mesenchymal stem cells and enhanced BDNF release (55).
In addition, a recent study investigated neuronal cells migration in transient brain ischemic rats after HBOT and found that HBOT increased BDNF expression and promoted cell migration toward the penumbra area (58). This has important implications for the treatment of patients with strokes. Collectively, all of these studies highlight the potential of HBOT to influence BDNF levels and signaling pathways, thereby promoting neuroplasticity, neuroprotection, and tissue repair in various neurological conditions.
By enhancing BDNF release and modulating its downstream effects, HBOT holds promise as a therapeutic approach for improving brain function and facilitating recovery. Further research is needed to fully characterize the specific mechanisms by which HBOT exerts its effects on BDNF and to explore its potential applications in clinical settings. Nonetheless, the findings underscore the significance of BDNF as a key player in the neuroplastic and neuromodulatory activities of HBOT, offering valuable insights into its therapeutic potential (Table 1).
4 Clinical applications
Given the promising research demonstrating its neuromodulatory effect, HBOT has gained attention in treating neurological and psychiatric disorders. A recent meta-analysis evaluated the effect of HBOT in patients with acute TBI and found significantly improved cognitive function and decreased mortality rates compared to those who did not undergo HBOT (60). These results were augmented by multiple clinical trials that showed a significant effect of HBOT in the brain cognitive function outcomes in chronic TBI and stroke patients (9, 16, 61).
In addition, several studies specifically investigated the efficacy of HBOT in patients with fibromyalgia, the prototype of central sensitization syndrome (62, 63). A systematic review and meta-analysis demonstrated that HBOT had a positive effect in improving pain, tender points, fatigue, multidimensional function, patient global assessment, and sleep disturbance in fibromyalgia patients (62). Another randomized controlled trial compared HBOT to pharmacological intervention in fibromyalgia patients with a history of TBI and found that HBOT significantly reduced pain intensity compared to medications (63). In a longitudinal follow-up of a randomized controlled trial of patients with COVID-19, HBOT demonstrated sustained improvements in cognitive, psychiatric, fatigue, sleep, and pain symptoms 1 year after treatment, confirming the enduring benefits of HBOT across multiple quality of life domains (64). In the broader applications of HBOT, a study specifically investigated the effect of HBOT in patients with fibromyalgia who had a history of childhood sexual abuse (CSA) (13). The study conducted a prospective randomized clinical trial, where participants (N = 30) were randomly assigned to treatment group (60 HBOT daily sessions) and a control/crossover group (psychotherapy), and found that HBOT induced significant clinical improvement in fibromyalgia symptoms, quality of life, PTSD symptoms, and psychological distress in patients with CSA-related fibromyalgia. Moreover, brain imaging techniques revealed increased brain activity and improved brain microstructure (measured by diffusion tensor imaging) in specific regions following HBOT treatment. These findings suggest that HBOT holds promise as a potential therapeutic intervention for fibromyalgia.
Furthermore, other researchers have attempted to uncover the effect of HBOT on psychiatric disorders. A systematic review and meta-analysis of 27 clinical trials with various HBOT treatment protocols involving 2,250 patients found that HBOT exhibited a statistically significant response, surpassing the control group, in managing post-stroke depression (2). This was evidenced to have superior response rates compared to conventional monotherapy with antidepressants. Several researchers have also assessed the effect of HBOT in PTSD and TBI and in patients with PPCS and have reported promising results (14, 65–68). These insights reaffirm HBOT as a potential therapeutic adjunct in the domain of selective psychiatric disorders.
Despite the extensive efforts to clarify the neuromodulatory impact of HBOT and the underlying biological mechanisms, there remains extensive aspects that are unclear and numerous questions that are unanswered.
5 Conclusion
HBOT offers significant neuromodulatory potential by affecting key cellular and molecular mechanisms. The most representative molecules and pathways influenced by HBOT include mitochondrial biogenesis and function (enhanced ATP production, increased Bcl-2 expression, and reduced Bax expression), neurogenesis (upregulation of Wnt-3 and VEGF/ERK signaling), synaptogenesis (elevated GAP43 and synaptophysin expression), and anti-inflammatory pathways (reduced TNF-α and IL-6). These molecular changes collectively contribute to enhanced neuroplasticity, improved cognitive function, and better clinical outcomes in conditions such as TBI, PTSD, fibromyalgia, and post-stroke depression. Clinically, these effects translate into improved recovery, cognitive performance, and quality of life in patients with persistent neurological and psychiatric disorders. However, further research is required to refine dosing protocols and explore additional pathways that might contribute to HBOT’s therapeutic benefits. Such work is critical for optimizing the clinical application of HBOT across a range of neurological conditions.
Author contributions
OB-A: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HA-A-S: Writing – review & editing. SE: Validation, Writing – review & editing. AH: Writing – review & editing. RB: Writing – review & editing. ME: Writing – review & editing. ES: Validation, Writing – review & editing. JCM: Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was supported in part by the following: The Alba Tull, Dennis Heindl, Lewis Topper, Nelson Peltz, and Neuroscience Research Foundations.
Conflict of interest
JCM consultant to Pittsburgh Steelers, WWE, Aviv Clinics, NFL Head and Spine Committee. RB was employed by the Foundation for the Study of Inflammatory Disease. AH and ME works for AVIV Scientific LTD. SE is a shareholder and co-founder of AVIV Scientific LTD.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Ortega, MA, Fraile-Martinez, O, García-Montero, C, Callejón-Peláez, E, Sáez, MA, Álvarez-Mon, MA, et al. A general overview on the hyperbaric oxygen therapy: applications, mechanisms and translational opportunities. Medicina. (2021) 57:864. doi: 10.3390/MEDICINA57090864
2. Liang, XX, Guo, HY, Ming, DX, Lan, HX, and Xia, CX. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for post-stroke depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. (2020) 195:105910. doi: 10.1016/J.CLINEURO.2020.105910
3. Doenyas-Barak, K, Catalogna, M, Kutz, I, Levi, G, Hadanny, A, Tal, S, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy improves symptoms, brain’s microstructure and functionality in veterans with treatment resistant post-traumatic stress disorder: a prospective, randomized, controlled trial. PLoS One. (2022) 17:e0264161. doi: 10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0264161
4. Bennett, MH, Trytko, B, and Jonker, B. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for the adjunctive treatment of traumatic brain injury. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2012) 12:CD004609. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004609.PUB3
5. Mi, K, Guo, Q, Xu, BY, Wang, M, and Bi, H. Efficacy of hyperbaric oxygen combined with escitalopram in depression and its effect on cognitive function. Pak J Med Sci. (2021) 37:1054. doi: 10.12669/PJMS.37.4.3993
6. CADTH. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for adults with mental illness: a review of the clinical effectiveness. (2014) Available online at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK253746/ (Accessed October 28, 2023).
7. Xu, JJ, Yang, ST, Sha, Y, Ge, YY, and Wang, JM. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment for Parkinson’s disease with severe depression and anxiety: a case report. Medicine. (2018) 97:e0029. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010029
8. Xiong, T, Chen, H, Luo, R, and Mu, D. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for people with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2016) 2016:1–10. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010922.PUB2
9. Long, Y, Tan, J, Nie, Y, Lu, Y, Mei, X, and Tu, C. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is safe and effective for the treatment of sleep disorders in children with cerebral palsy. Neurol Res. (2017) 39:239–47. doi: 10.1080/01616412.2016.1275454
10. Hadanny, A, and Efrati, S. The Hyperoxic-hypoxic paradox. Biomol Ther. (2020) 10:958. doi: 10.3390/biom10060958
11. Schellart, NAM, Reits, D, Van Der Kleij, AJ, and Stalpers, LJA. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment improved neurophysiologic performance in brain tumor patients after neurosurgery and radiotherapy: a preliminary report. Cancer. (2011) 117:3434–44. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25874
12. Pan, X, Chen, C, Huang, J, Wei, H, and Fan, Q. Neuroprotective effect of combined therapy with hyperbaric oxygen and madopar on 6-hydroxydopamine-induced Parkinson’s disease in rats. Neurosci Lett. (2015) 600:220–5. doi: 10.1016/J.NEULET.2015.06.030
13. Hadanny, A, Bechor, Y, Catalogna, M, Daphna-Tekoah, S, Sigal, T, Cohenpour, M, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy can induce neuroplasticity and significant clinical improvement in patients suffering from fibromyalgia with a history of childhood sexual abuse-randomized controlled trial. Front Psychol. (2018) 9:2495. doi: 10.3389/FPSYG.2018.02495/BIBTEX
14. Eve, DJ, Steele, MR, Sanberg, PR, and Borlongan, CV. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy as a potential treatment for post-traumatic stress disorder associated with traumatic brain injury. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. (2016) 12:2689–705. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S110126
15. Efrati, S, Fishlev, G, Bechor, Y, Volkov, O, Bergan, J, Kliakhandler, K, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen induces late neuroplasticity in post stroke patients--randomized, prospective trial. PLoS One. (2013) 8:e53716. doi: 10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0053716
16. Harch, P, Andrews, S, Rowe, C, Lischka, J, Townsend, M, Yu, Q, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for mild traumatic brain injury persistent postconcussion syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Med Gas Res. (2020) 10:8–20. doi: 10.4103/2045-9912.279978
17. Doenyas-Barak, K, Kutz, I, Levi, G, Lang, E, Beberashvili, I, and Efrati, S. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for veterans with treatment-resistant PTSD: a longitudinal follow-up study. Mil Med. (2022) 188:e2227–33. doi: 10.1093/MILMED/USAC360
18. DeGeorge, B, and Gampper, TJ. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Biomed Technol Dev. (2013) 14:673–88. doi: 10.1201/b15085-33
19. Gottfried, I, Schottlender, N, and Ashery, U. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment—from mechanisms to cognitive improvement. Biomol Ther. (2021) 11:1520. doi: 10.3390/biom11101520
20. Zhao, B, Pan, Y, Wang, Z, Xu, H, and Song, X. Hyperbaric oxygen pretreatment improves cognition and reduces hippocampal damage via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in a rat model. Yonsei Med J. (2017) 58:131. doi: 10.3349/YMJ.2017.58.1.131
21. Hadanny, A, Catalogna, M, Yaniv, S, Stolar, O, Rothstein, L, Shabi, A, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in children with post-concussion syndrome improves cognitive and behavioral function: a randomized controlled trial. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:15233. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-19395-y
22. Schottlender, N, Gottfried, I, and Ashery, U. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment: effects on mitochondrial function and oxidative stress. Biomol Ther. (2021) 11:1827. doi: 10.3390/BIOM11121827
23. Dave, KR, Prado, R, Busto, R, Raval, AP, Bradley, WG, Torbati, D, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy protects against mitochondrial dysfunction and delays onset of motor neuron disease in wobbler mice. Neuroscience. (2003) 120:113–20. doi: 10.1016/S0306-4522(03)00244-6
24. Kurt, B, Kurt, Y, Karsliogˇlu, Y, Topal, T, Erdamar, H, Korkmaz, A, et al. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen on energy production and xanthine oxidase levels in striated muscle tissue of healthy rats. J Clin Neurosci. (2008) 15:445–50. doi: 10.1016/J.JOCN.2007.01.010
25. Zhou, Z, Daugherty, WP, Sun, D, Levasseur, JE, Altememi, N, Hamm, RJ, et al. Protection of mitochondrial function and improvement in cognitive recovery in rats treated with hyperbaric oxygen following lateral fluid-percussion injury. J Neurosurg. (2007) 106:687–94. doi: 10.3171/JNS.2007.106.4.687
26. Tian, XQ, Da Zhang, L, Wang, JM, Dai, JG, Shen, SS, Yang, L, et al. The protective effect of hyperbaric oxygen and Ginkgo biloba extract on Aβ25-35-induced oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis in rats. Behav Brain Res. (2013) 242:1–8. doi: 10.1016/J.BBR.2012.12.026
27. Lippert, T, and Borlongan, CV. Prophylactic treatment of hyperbaric oxygen treatment mitigates inflammatory response via mitochondria transfer. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2019) 25:815–23. doi: 10.1111/CNS.13124
28. Gonzales-Portillo, B, Lippert, T, Nguyen, H, Lee, J-Y, and Borlongan, C. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy: a new look on treating stroke and traumatic brain injury. Brain Circ. (2019) 5:101. doi: 10.4103/BC.BC_31_19
29. Wang, XL, Yang, YJ, Xie, M, Yu, XH, Liu, CT, and Wang, X. Proliferation of neural stem cells correlates with Wnt-3 protein in hypoxic-ischemic neonate rats after hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Neuroreport. (2007) 18:1753–6. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0B013E3282F0EC09
30. Liu, S, Shen, GY, Deng, SK, Bin, WX, Qf, W, and As, G. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy improves cognitive functioning after brain injury. Neural Regen Res. (2013) 8:3334–43. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1673-5374.2013.35.008
31. Yang, Y, Wei, H, Zhou, X, Zhang, F, and Wang, C. Hyperbaric oxygen promotes neural stem cell proliferation by activating vascular endothelial growth factor/extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling after traumatic brain injury. Neuroreport. (2017) 28:1232–8. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000000901
32. Wei, L, Wang, J, Cao, Y, Ren, Q, Zhao, L, Li, X, et al. Hyperbaric oxygenation promotes neural stem cell proliferation and protects the learning and memory ability in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. (2015) 8:1752
33. Lee, YS, Chio, CC, Chang, CP, Wang, LC, Chiang, PM, Niu, KC, et al. Long course hyperbaric oxygen stimulates neurogenesis and attenuates inflammation after ischemic stroke. Mediat Inflamm. (2013) 2013:512978. doi: 10.1155/2013/512978
34. Zhang, L, Sun, Q, Xin, Q, Qin, J, Zhang, L, Wu, D, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy mobilized circulating stem cells and improved delayed encephalopathy after acute carbon monoxide poisoning with up-regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Am J Emerg Med. (2021) 42:95–100. doi: 10.1016/J.AJEM.2021.01.021
35. Shapira, R, Gdalyahu, A, Gottfried, I, Sasson, E, Hadanny, A, Efrati, S, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy alleviates vascular dysfunction and amyloid burden in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model and in elderly patients. Aging. (2021) 13:20935–61. doi: 10.18632/AGING.203485
36. Lin, KC, Niu, KC, Tsai, KJ, Kuo, JR, Wang, LC, Chio, CC, et al. Attenuating inflammation but stimulating both angiogenesis and neurogenesis using hyperbaric oxygen in rats with traumatic brain injury. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. (2012) 72:650–9. doi: 10.1097/TA.0B013E31823C575F
37. Brkic, P, Stojiljkovic, M, Jovanovic, T, Dacic, S, Lavrnja, I, Savic, D, et al. Hyperbaric oxygenation improves locomotor ability by enhancing neuroplastic responses after cortical ablation in rats. Brain Inj. (2012) 26:1273–84. doi: 10.3109/02699052.2012.667593
38. Jing, C, and Yan-hui, C. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen on synaptic ultrastructure and synaptophysin expression in hippocampus of neonatal rats with hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Chin J Pediatr. (2010) 48:199–203. doi: 10.3760/CMA.J.ISSN.0578-1310.2010.03.010
39. Shepherd, JD, and Huganir, RL. The cell biology of synaptic plasticity: AMPA receptor trafficking. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. (2007) 23:613–43. doi: 10.1146/ANNUREV.CELLBIO.23.090506.123516
40. Collingridge, GL, Isaac, JTR, and Yu, TW. Receptor trafficking and synaptic plasticity. Nat Rev Neurosci. (2004) 5:952–62. doi: 10.1038/NRN1556
41. Collingridge, GL, Peineau, S, Howland, JG, and Wang, YT. Long-term depression in the CNS. Nat Rev Neurosci. (2010) 11:459–73. doi: 10.1038/NRN2867
42. Gladding, CM, Fitzjohn, SM, and Molnár, E. Metabotropic glutamate receptor-mediated Long-term depression: molecular mechanisms. Pharmacol Rev. (2009) 61:395–412. doi: 10.1124/PR.109.001735
43. Bazaz, MR, Balasubramanian, R, Monroy-Jaramillo, N, and Dandekar, MP. Linking the triad of telomere length, inflammation, and gut Dysbiosis in the manifestation of depression. ACS Chem Neurosci. (2021) 12:3516–26. doi: 10.1021/ACSCHEMNEURO.1C00457
44. Lindqvist, D, Epel, ES, Mellon, SH, Penninx, BW, Révész, D, Verhoeven, JE, et al. Psychiatric disorders and leukocyte telomere length: underlying mechanisms linking mental illness with cellular aging. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. (2015) 55:333–64. doi: 10.1016/J.NEUBIOREV.2015.05.007
45. Jurk, D, Wilson, C, Passos, JF, Oakley, F, Correia-Melo, C, Greaves, L, et al. Chronic inflammation induces telomere dysfunction and accelerates ageing in mice. Nat Commun. (2014) 5:4172. doi: 10.1038/NCOMMS5172
46. Darrow, SM, Verhoeven, JE, Révész, D, Lindqvist, D, Penninx, BWJH, Delucchi, KL, et al. The association between psychiatric disorders and telomere length: a meta-analysis involving 14,827 persons. Psychosom Med. (2016) 78:776–87. doi: 10.1097/PSY.0000000000000356
47. Hachmo, Y, Hadanny, A, Abu Hamed, R, Daniel-Kotovsky, M, Catalogna, M, Fishlev, G, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy increases telomere length and decreases immunosenescence in isolated blood cells: a prospective trial. Aging. (2020) 12:22445. doi: 10.18632/AGING.202188
48. Maroon, JC. The effect of hyperbaric oxygen therapy on cognition, performance, proteomics, and telomere length-the difference between zero and one: a case report. Front Neurol. (2022) 13:949536. doi: 10.3389/FNEUR.2022.949536
49. Zhou, QG, Wu, HY, Zhou, H, Liu, MY, Lee, HW, Liu, X, et al. Reactivation of Tert in the medial prefrontal cortex and hippocampus rescues aggression and depression of Tert(−/−) mice. Transl Psychiatry. (2016) 6:e836. doi: 10.1038/TP.2016.106
50. Yu, M, Jia, H, Zhou, C, Yang, Y, Zhao, Y, Yang, M, et al. Variations in gut microbiota and fecal metabolic phenotype associated with depression by 16S rRNA gene sequencing and LC/MS-based metabolomics. J Pharm Biomed Anal. (2017) 138:231–9. doi: 10.1016/J.JPBA.2017.02.008
51. Bin, WY, Martinsson, L, Jj, L, Forsell, Y, Schalling, M, Backlund, L, et al. hTERT genetic variation in depression. J Affect Disord. (2016) 189:62–9. doi: 10.1016/J.JAD.2015.09.025
52. Amsellem, V, Gary-Bobo, G, Marcos, E, Maitre, B, Chaar, V, Validire, P, et al. Telomere dysfunction causes sustained inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2011) 184:1358–66. doi: 10.1164/RCCM.201105-0802OC
53. Ornish, D, Lin, J, Daubenmier, J, Weidner, G, Epel, E, Kemp, C, et al. Increased telomerase activity and comprehensive lifestyle changes: a pilot study. Lancet Oncol. (2008) 9:1048–57. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70234-1
54. Ornish, D, Lin, J, Chan, JM, Epel, E, Kemp, C, Weidner, G, et al. Effect of comprehensive lifestyle changes on telomerase activity and telomere length in men with biopsy-proven low-risk prostate cancer: 5-year follow-up of a descriptive pilot study. Lancet Oncol. (2013) 14:1112–20. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70366-8
55. Schulze, J, Kaiser, O, Paasche, G, Lamm, H, Pich, A, Hoffmann, A, et al. Effect of hyperbaric oxygen on BDNF-release and neuroprotection: investigations with human mesenchymal stem cells and genetically modified NIH3T3 fibroblasts as putative cell therapeutics. PLoS One. (2017) 12:e0178182. doi: 10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0178182
56. Ying, X, Tu, W, Li, S, Wu, Q, Chen, X, Zhou, Y, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy reduces apoptosis and dendritic/synaptic degeneration via the BDNF/TrkB signaling pathways in SCI rats. Life Sci. (2019) 229:187–99. doi: 10.1016/J.LFS.2019.05.029
57. Chiang, MK, Lin, TC, Lin, KH, Chang, YC, Hsieh-Li, HM, and Lai, DM. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy attenuated the motor coordination and cognitive impairment of Polyglutamine spinocerebellar Ataxia SCA17 mice. Cerebellum. (2023) 23:401–17. doi: 10.1007/S12311-023-01548-Y
58. Wang, RY, Yang, YR, and Chang, HC. The SDF1-CXCR4 Axis is involved in the hyperbaric oxygen therapy-mediated neuronal cells migration in transient brain ischemic rats. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:1780. doi: 10.3390/IJMS23031780
59. Te Hsu, H, Yang, YL, Chang, WH, Fang, WY, Huang, SH, Chou, SH, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy improves Parkinson’s disease by promoting mitochondrial biogenesis via the SIRT-1/PGC-1α pathway. Biomol Ther. (2022) 12:661. doi: 10.3390/BIOM12050661
60. Wang, F, Wang, Y, Sun, T, and Yu, H. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for the treatment of traumatic brain injury: a meta-analysis. Neurol Sci. (2016) 37:693–701. doi: 10.1007/s10072-015-2460-2
61. Boussi-Gross, R, Golan, H, Fishlev, G, Bechor, Y, Volkov, O, Bergan, J, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy can improve post concussion syndrome years after mild traumatic brain injury - randomized prospective trial. PLoS One. (2013) 8:e79995. doi: 10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0079995
62. Chen, X, You, J, Ma, H, Zhou, M, and Huang, C. Efficacy and safety of hyperbaric oxygen therapy for fibromyalgia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. (2023) 13:e062322. doi: 10.1136/BMJOPEN-2022-062322
63. Ablin, JN, Lang, E, Catalogna, M, Aloush, V, Hadanny, A, Doenyas-Barak, K, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy compared to pharmacological intervention in fibromyalgia patients following traumatic brain injury: a randomized, controlled trial. PLoS One. (2023) 18:e0282406. doi: 10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0282406
64. Hadanny, A, Zilberman-Itskovich, S, Catalogna, M, Elman-Shina, K, Lang, E, Finci, S, et al. Long term outcomes of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in post COVID condition: longitudinal follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:3604. doi: 10.1038/S41598-024-53091-3
65. Mozayeni, B, Duncan, W, Zant, E, Love, T, Beckman, R, and Stoller, K. The national brain injury rescue and rehabilitation study - a multicenter observational study of hyperbaric oxygen for mild traumatic brain injury with post-concussive symptoms. Med Gas Res. (2019) 9:1–12. doi: 10.4103/2045-9912.254636
66. Biggs, AT, Littlejohn, LF, and Dainer, HM. Alternative uses of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in military medicine: current positions and future directions. Mil Med. (2022) 187:E40–6. doi: 10.1093/milmed/usab022
67. Bennett, MH. Evidence brief: hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) for traumatic brain injury and/or post-traumatic stress disorder. Diving Hyperb Med. (2018) 48:115. doi: 10.28920/dhm48.2.115
Keywords: hyperbaric oxygen therapy, neuromodulation, mental illness, neurological disorders, post-concussion syndrome, post-traumatic stress disorder, traumatic brain injury
Citation: Bin-Alamer O, Abou-Al-Shaar H, Efrati S, Hadanny A, Beckman RL, Elamir M, Sussman E and Maroon JC (2024) Hyperbaric oxygen therapy as a neuromodulatory technique: a review of the recent evidence. Front. Neurol. 15:1450134. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1450134
Edited by:
Pengxu Wei, Chinese Association of Rehabilitative Medicine, ChinaReviewed by:
Susana Bulnes Sesma, University of the Basque Country, SpainIoana-Miruna Balmus, Alexandru Ioan Cuza University, Romania
Copyright © 2024 Bin-Alamer, Abou-Al-Shaar, Efrati, Hadanny, Beckman, Elamir, Sussman and Maroon. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Othman Bin-Alamer, T2FiaW5hbGFtZXJAZ21haWwuY29t
 Othman Bin-Alamer
Othman Bin-Alamer Hussam Abou-Al-Shaar1
Hussam Abou-Al-Shaar1 Mohammed Elamir
Mohammed Elamir Joseph C. Maroon
Joseph C. Maroon