- 1Department of Acupuncture, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanchang, China
- 2Graduate School, Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanchang, China
- 3Department of Asset Management, Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanchang, China
- 4Department of Gastroenterology, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanchang, China
- 5Medical Department, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanchang, China
Background: Recent studies have shown that migraine significantly increases the incidence of anxiety and is positively correlated with the severity and frequency of migraine. The relationship between migraine and anxiety has attracted extensive attention. This study focused on the association between migraine and anxiety, aiming to predict potential future research trends.
Methods: A bibliometric analysis was conducted using publications from the Core Collection of Web of Science. We utilized CiteSpace.5.8.R3 and VOSviewer 1.6.17 to evaluate the value of articles over the past 10 years.
Results: The number of publications has increased significantly over the past 10 years. The cooperative network analysis shows that the United States is the most collaborative country. Additionally, Harvard University is the institution and Richard B. Lipton the individual with the highest number of studies on migraine. The analysis of keyword outbreaks indicates that the strong citation burst words are closely related to sex differences, activation, allodynia, and preventive treatment, which represent emerging new research areas and potential hotspots for future research.
Conclusion: An overall upward trend in the research of migraine and anxiety was observed. Sex differences, functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), activation, allodynia, and preventive treatment are predicted to be hotspots in the future.
1 Introduction
Migraine is a common neurological disorder that has remained one of the major health issues affecting the quality of life and daily functioning of patients (1). Severe headaches that afflict both men and women and recur at different frequencies are the representative features of migraine (2). According to comprehensive assessment of research studies, the anticipated worldwide lifetime prevalence of migraine was 17.5% for both genders, 21.0% for women, and 11.6% for men (3). According to the Global Burden of Disease 2019 report, migraine ranks top among the health issues affecting women under 50 years of age and the second overall in terms of causes of disability (4).
Clinical studies have found that long-term migraine patients are prone to mental and emotional problems such as anxiety, depression, and insomnia, and these patients have poor prognosis and are prone to recurrence (5, 6). The incidence of anxiety and depression in migraine patients is 2–10 times higher than that of the general population, greatly affecting their quality of life (7). Migraine and emotional disorders, such as anxiety and depression, coexist (8). Compared to individuals with depression or anxiety alone or without both, individuals with serious depressive and anxiety disorders together are more likely to experience migraines (9).
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Data collection and retrieval strategies
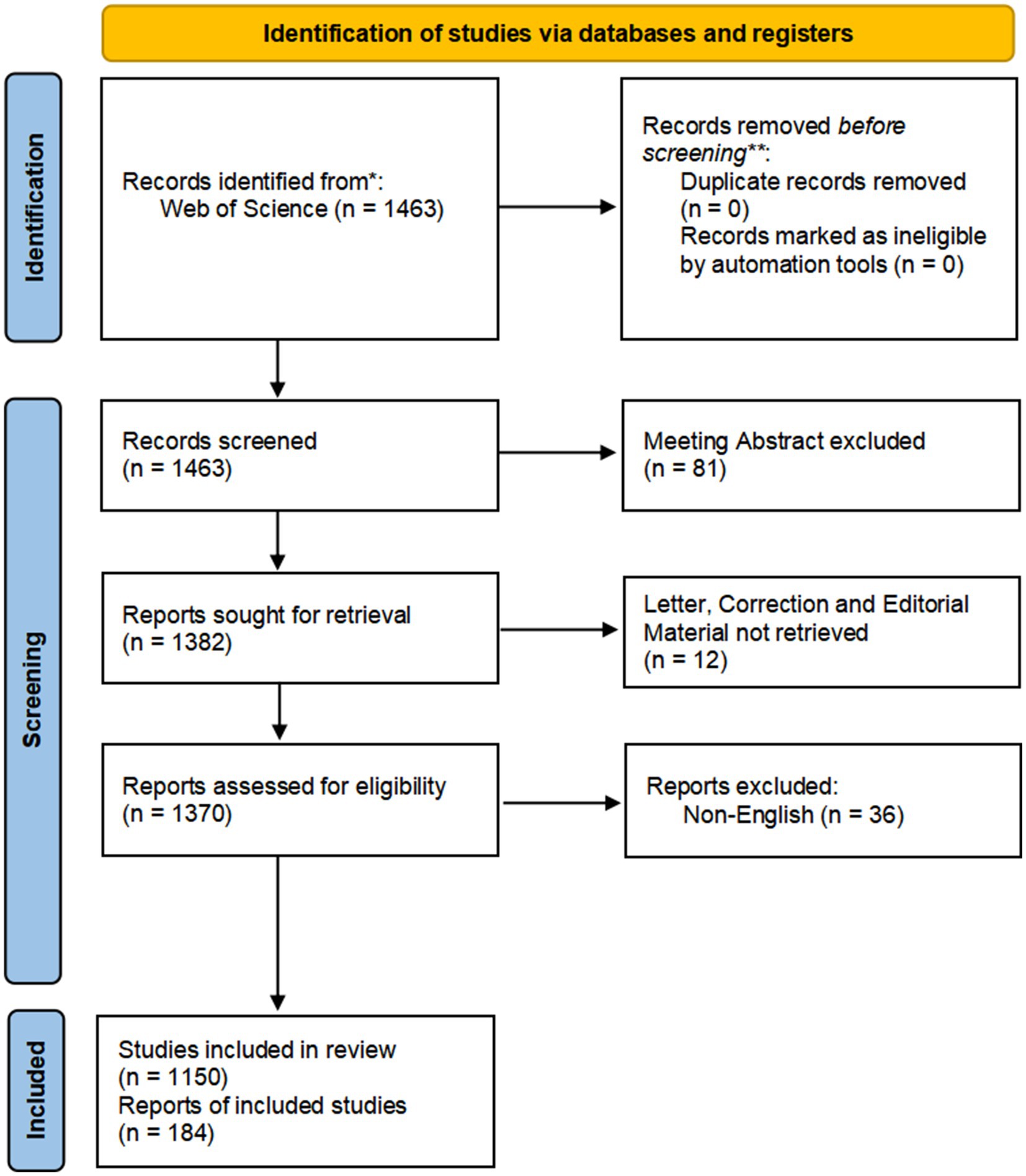
We selected the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC) from Clarivate Analytics as the retrieval database for this study. The WoSCC is a highly authoritative citation index database that is widely used in scientific research and bibliometric studies. We used a combination of subject words and free words for line search. The subject words included migraine and anxiety. The free words mainly included migraine and anxiety. We set the search language as “English.” The search document type was set to “Article or Review.” We set the publication date condition of the retrieved literature as “2012 to 2021.” The retrieval process was carried out independently by two researchers on 5 May 2022. The detailed results of this retrieval are shown in Figure 1.
2.2 Data analysis
The software packages used for data analysis in this study are Microsoft Office Excel 2021, CiteSpace.5.8.R3, and Vosviewer1.6.17. Microsoft Office Excel 2021 was used for the statistics of literature years and the production of related tables. CiteSpace.5.8.R3 was used to analyze the number of published countries, institutions, and authors in the data, to examine their collaboration relationships, and to generate the keyword occurrence map and keyword burst map. Vosviewer1.6.17 was used to analyze highly cited and co-cited references in the data. This study utilizes WoSCC to analyze the publication output, subject category, publication year, author, and other functions. Then, the selected documents were imported into CiteSpace, and the time span was 2012–2021. The node was selected based on the type of analysis to be performed. The specific parameter settings in CiteSpace were as follows: Time slicing: January 2012–December 2021; Term source: Title, Abstract, Author Keywords, and Keyword Plus; Node type: Author, Institution, Country, and Keyword; Link strength: Cosine; and Selection Criteria: Top N = 50. In the generated map, the color of the circular nodes represents the time when the article was published. The thickness of the node is positively related to the frequency. The thickness of the line describes the strength between the projects, and the color of the line describes the year when the two projects first collaborated. The nodes in the map represent elements such as author, country/region, or institution. The link lines between the nodes indicate the collaboration relationship. The larger the circle, the greater the number of articles that were published. The wider the line, the stronger the relationship. The outermost purple ring represents the centrality. The centrality value represents the cooperation intensity, and the higher the value, the stronger the cooperation. VOSviewer software was used to statistically analyze highly cited and co-cited documents. First, the results obtained were imported through WOS into software. Then, the number of terms to be selected was set to 10. Finally, the results were imported to Excel for sorting.
Bibliometrics is a research investigation assessment methodology that has been used extensively. By using both quantitative and qualitative scientific analytical approaches, researchers can investigate detailed information on trends in the growth of related subjects (10). It is utilized to analyze many aspects of publications in a certain topic, including data and contributions about countries, organizations, authors, journals, keywords, and references (11). Numerous studies have demonstrated the potential association and pathophysiological mechanisms between migraine and anxiety (12–15). However, no specific investigation has yet been conducted on the knowledge mapping of migraine and anxiety. Thus, this research was aimed at comprehensively analyzing the knowledge base and emerging trends on migraine and anxiety.
3 Results
3.1 Literature screening results
According to the literature search strategy, a total of 1,463 articles were retrieved. Titles, abstracts, and even the full texts of articles were used to filter out articles that are closely related to our subject. Only 1,334 publications were selected for the review. Detailed retrieval results are shown in Figure 1.
3.2 Analysis of publication trends
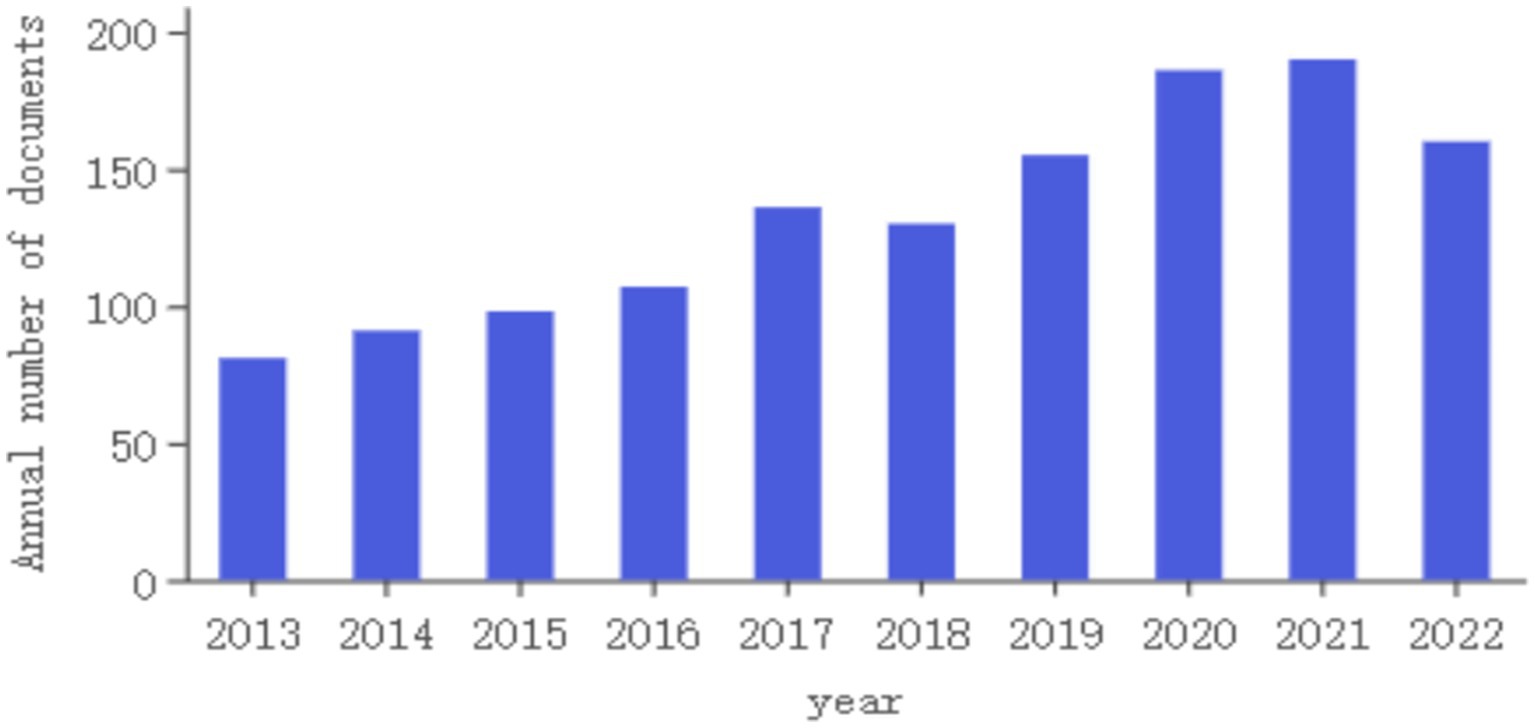
As shown in Figure 2, the number of articles published in 2013 was at least 81, and the number of articles published in 2021 was at most 190. From 2013 to 2022, the annual publications on migraine and anxiety have consistently increased, indicating that this field has become more popular and attracted increasing attention.
3.3 Analysis of the contribution of major countries
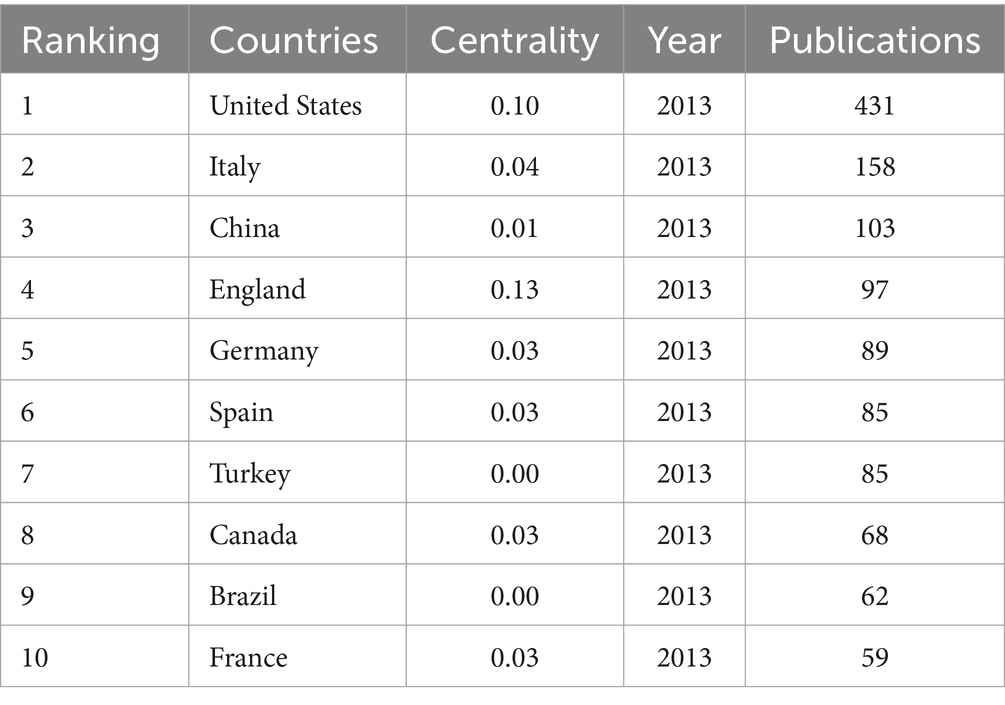
A total of 109 countries participated in research on migraine and anxiety from 2013 to 2022. Table 1 lists the top 10 countries that have conducted research on migraine and anxiety over the past 10 years. The United States had the highest number of publications (431), followed by Italy (158), and China (103). Italy, Britain, Germany, France, Spain, and Turkey are all European countries, while China is the only Asian country represented in this research. Both the United States and Canada are located in North America, while Brazil is located in South America. In terms of centrality, England ranked first among 10 countries (0.13), showing its global influence in the study of migraine and anxiety.
3.4 Analysis of major institutions
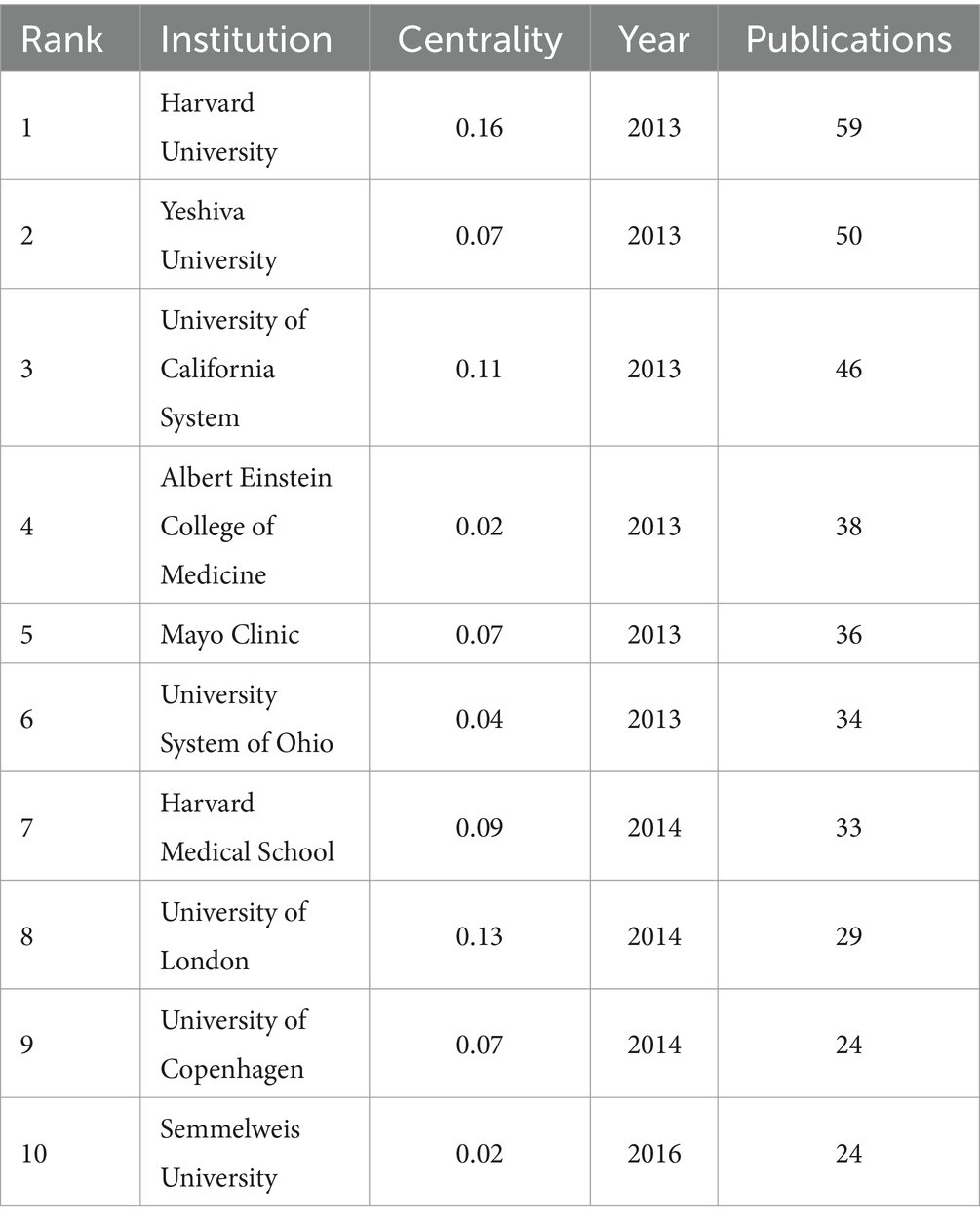
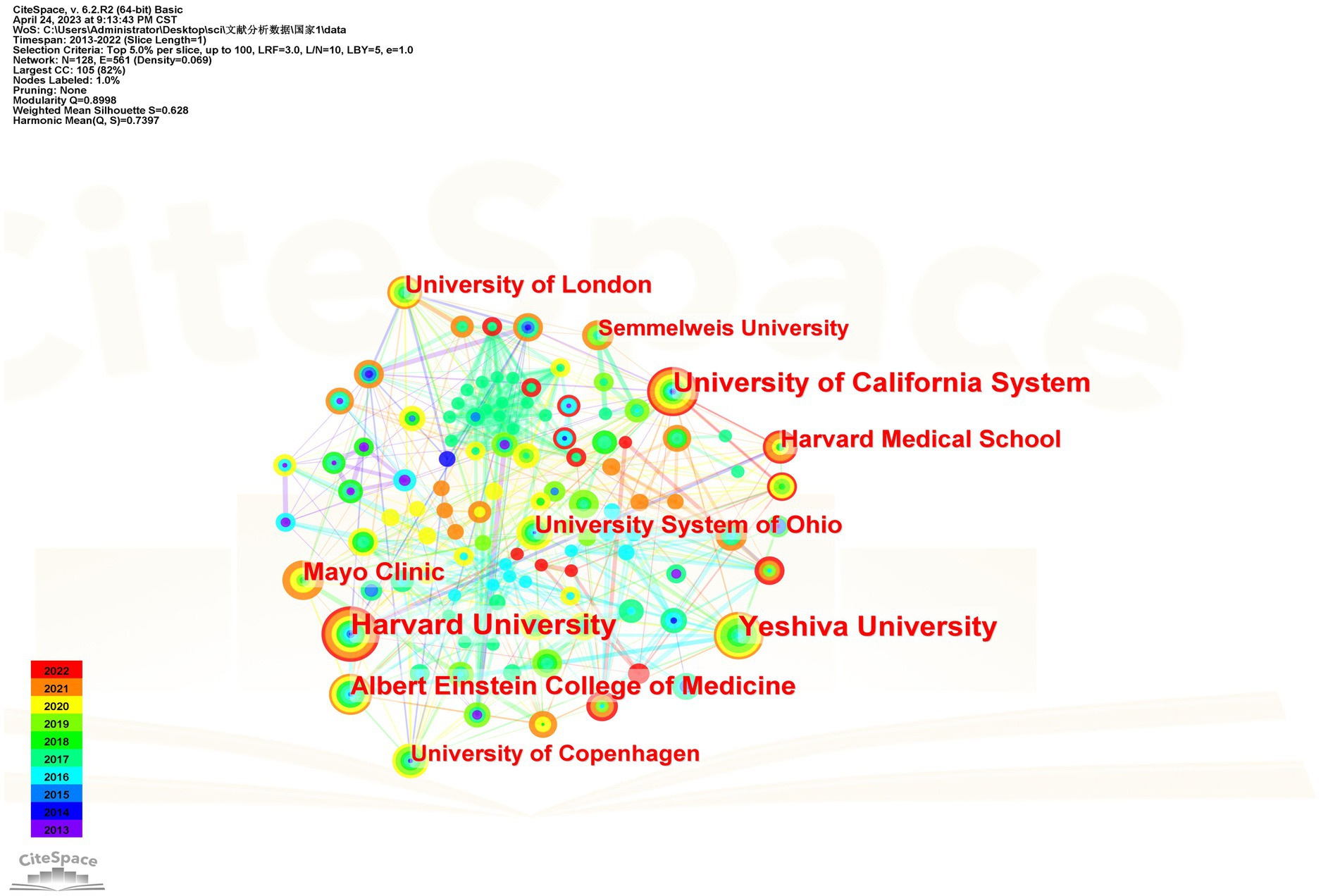
From 2013 to 2022, a total of 320 institutions participated in migraine and anxiety research. Table 2 shows the top 10 institutions. Of these, institutions with a publication volume greater than 35 articles include Harvard University (n = 59), Yeshiva University (n = 50), University of California System (n = 46), Albert Einstein College of Medicine (n = 38), and Mayo Clinic (n = 36). Figure 3 shows the collaborative network between major publishing institutions in this topic. The greater the centrality, the stronger the representativeness.
3.5 Analysis of the main authors
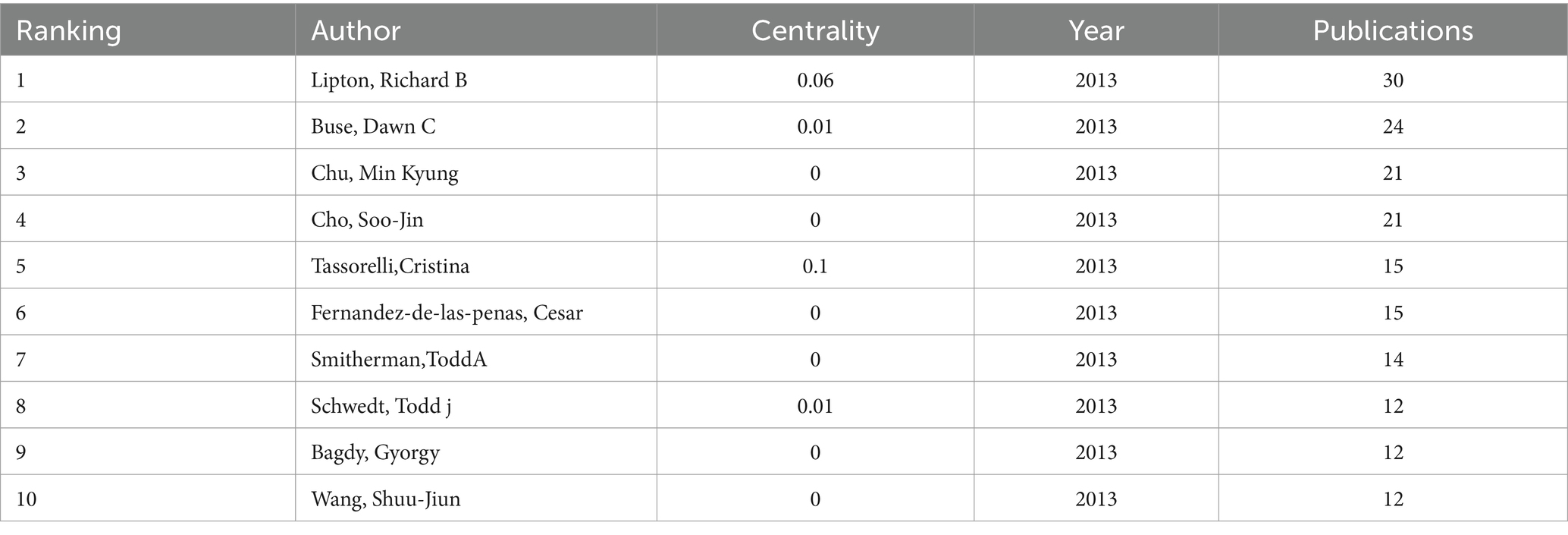
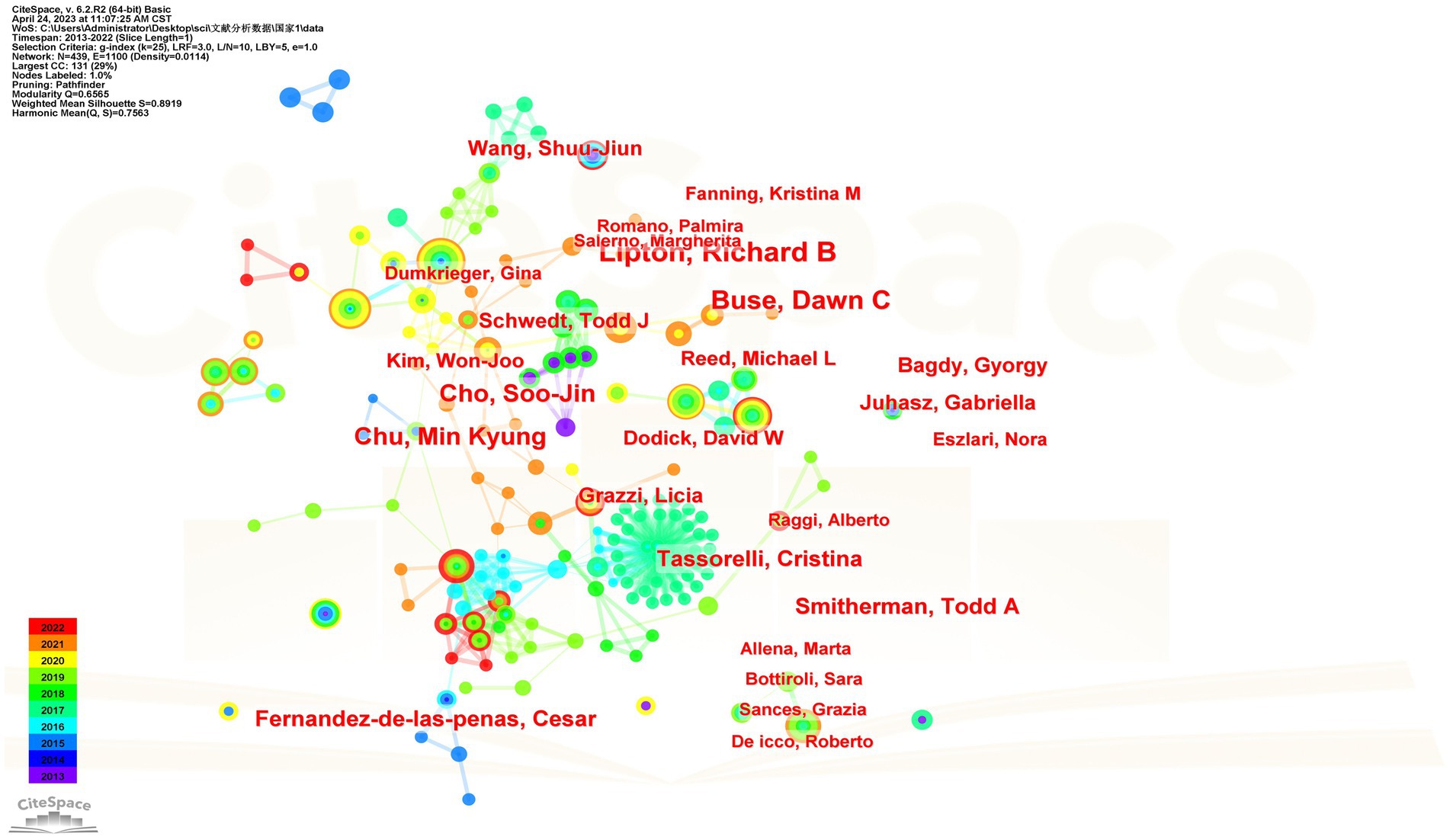
Over the past 10 years, a total of 433 authors participated in the study of migraine and anxiety. Table 3 shows the top 10 authors. Richard B. Lipton (n = 30), Buse Dawn C (n = 24), Chu Min Kyung (n = 21), and Cho Soo-Jin (n = 21) each published over 20 articles. Figure 4 depicts the network of relationships between the main authors in this field. Among them, Richard B. Lipton and Chu Min Kyung have collaborated. Bochnia Kuster, Joao Guilherme, and Tan. Bin Cheng worked together. Additionally, Cho, Soo Jin, and Chu Min Kyung also collaborated with one another.
3.6 Keyword analysis
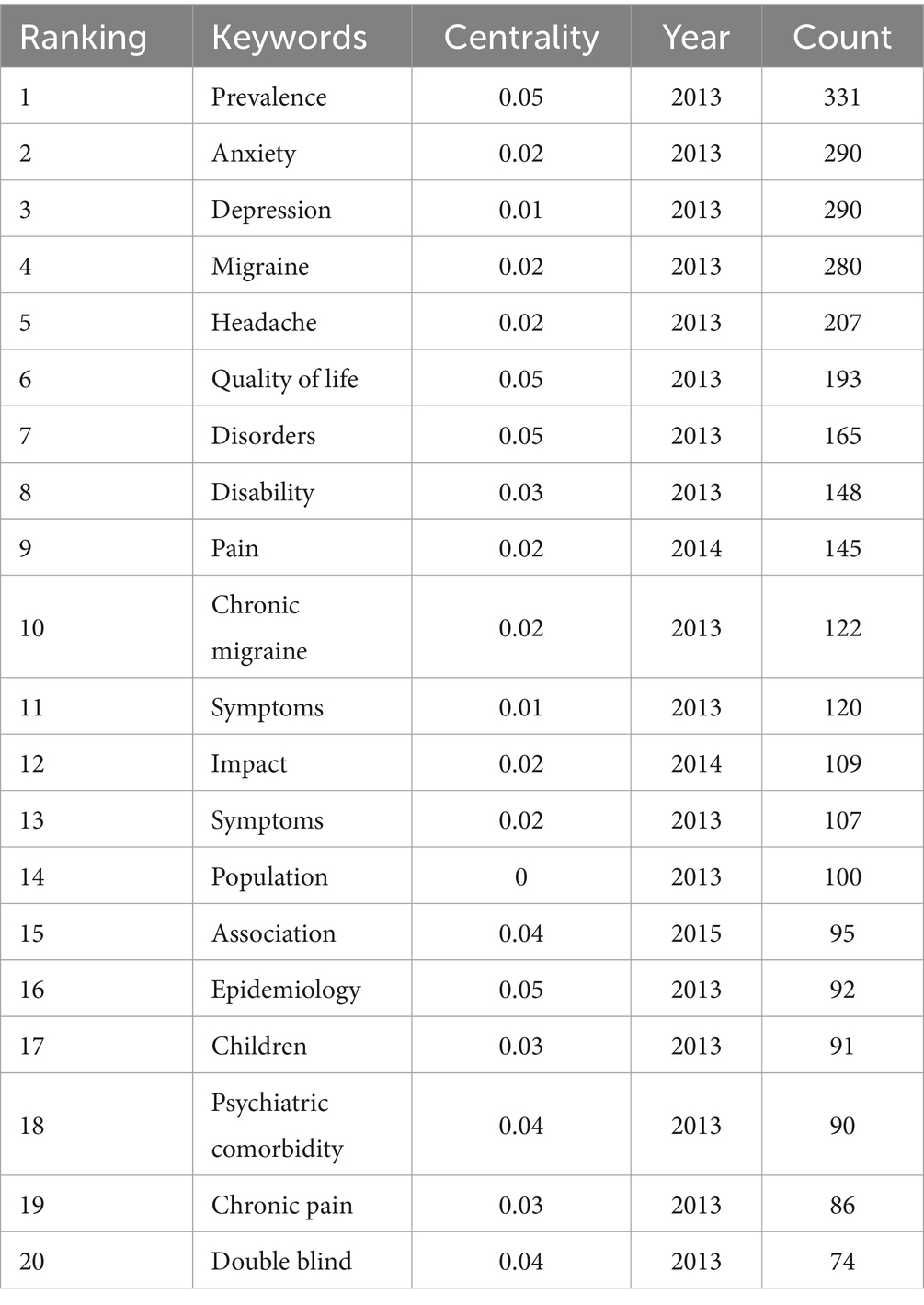
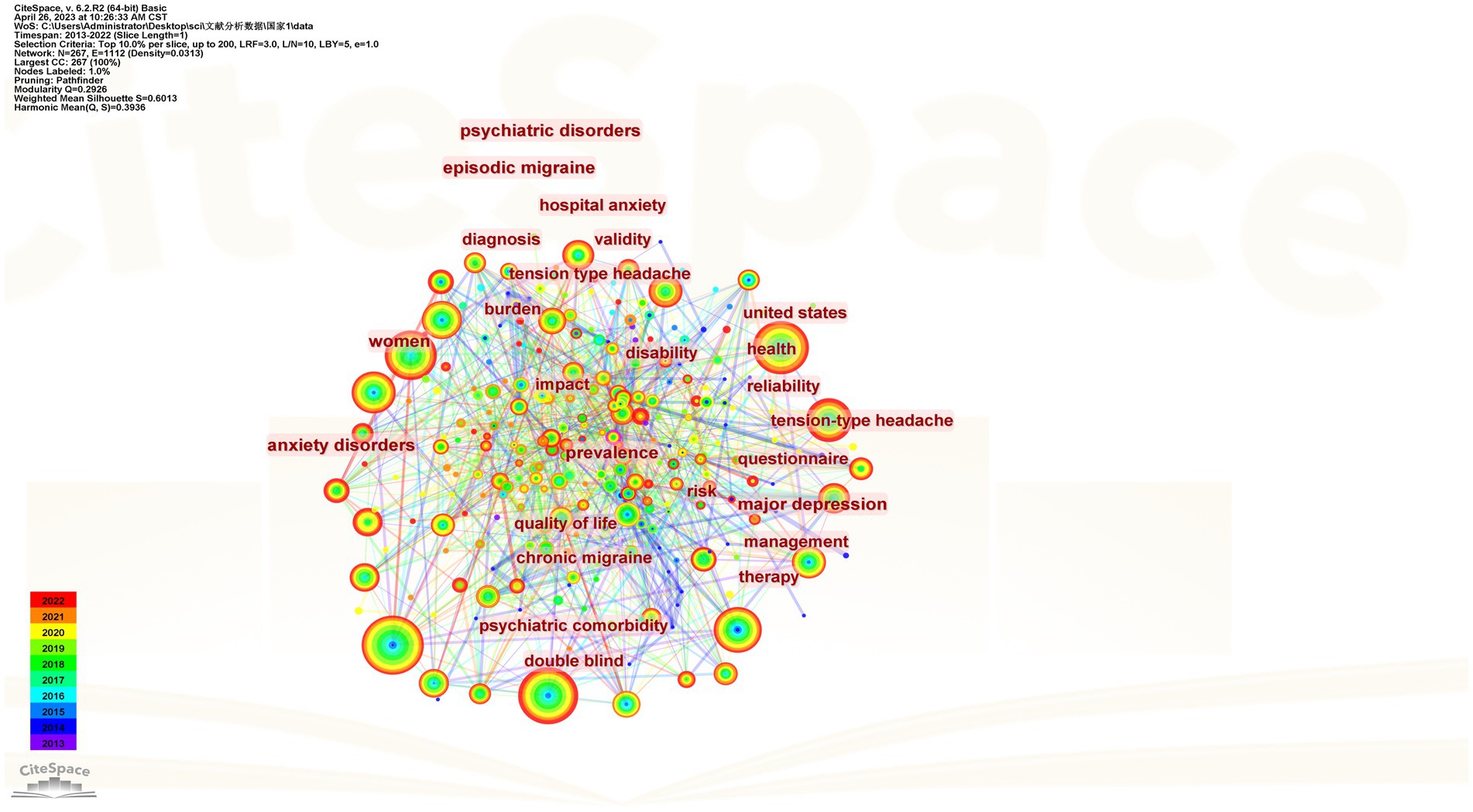
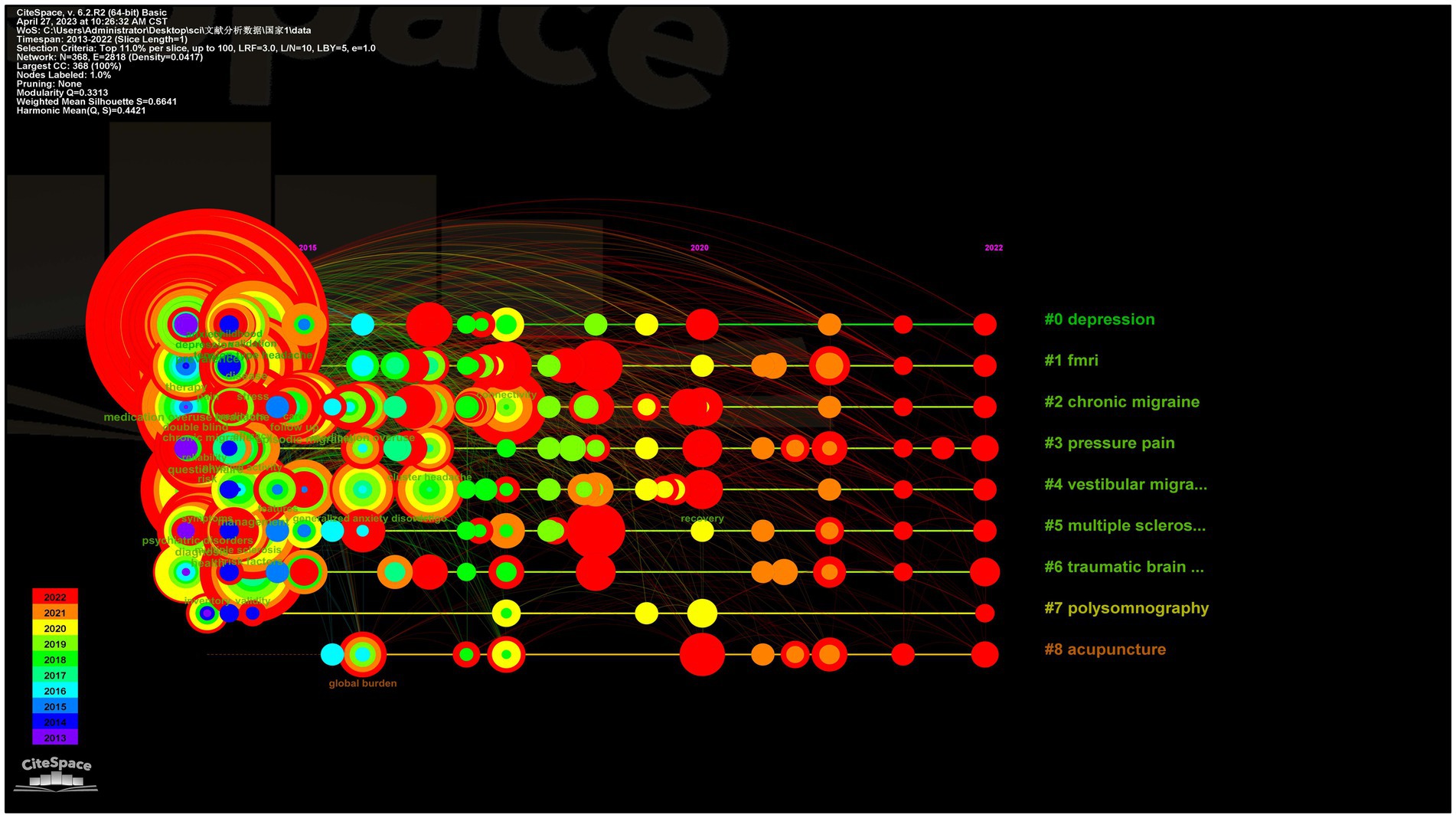
From 2013 to 2022, 460 keywords were found in 1,334 articles on migraine and anxiety. Table 4 lists the top 20 terms sorted by frequency in this field in Table 4. The terms “anxiety,” “depression,” “migraine,” and “headache” are four diseases with a frequency greater than 200. Figure 5 displays the co-occurrence network of keywords with a frequency surpassing 25 in studies related to migraine and anxiety. The node size represents the frequency of the keywords, and the connection between nodes represents two keywords appearing simultaneously in the same article. “Prevalence,” “anxiety,” “depression,” “migraine,” “headache,” and “quality of life” were high-frequency keywords, indicating that these terms were closely related research topics. As shown in Figure 6, 25 items with the highest prevalence are listed. Since 2019, sex difference, expression, activation, and allodynia have emerged as significant keywords in this field. Figure 7 illustrates the correlation between keyword clustering and time. The nine major keyword groups related to migraine and anxiety research are “#0 depression,” “#1 fmri,” “#2 chronic migraine,” “#3 pressure pain,” “#4 vestibular migraine,” “#5 multiple sclerosis,” “#6 traumatic brain injury,” “#7 polysomnography,” and “#8 acupuncture.”
3.7 Analysis of high-yielding journals
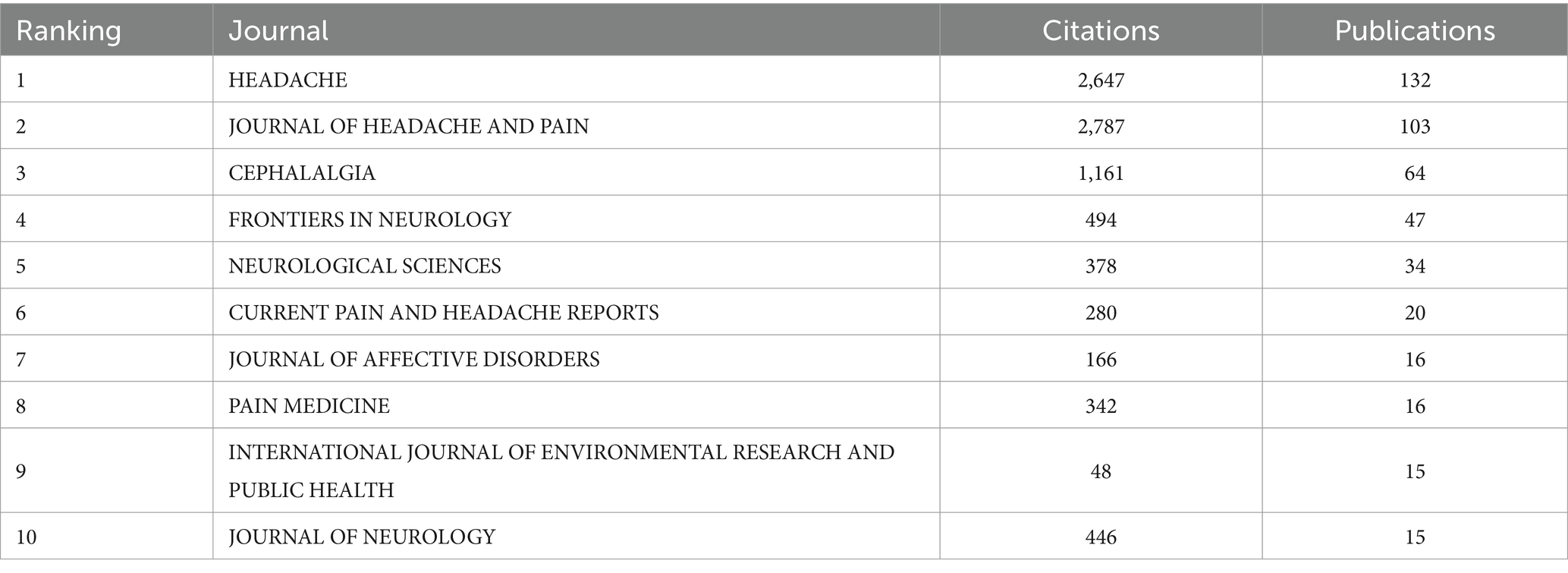
Table 5 lists the top 10 journals published on this topic. Headache (n = 123), Journal of Headache and Pain (n = 103), Cephaalgia (n = 64), Frontiers in Neurology (n = 47), and Neurological Sciences (n = 34) are journals that have published more than 30 articles. In addition, Headache (n = 2,647), Journal of Headache and Pain (n = 2,787), and Cephaalgia (n = 1,161) all have citations greater than 1,000 times.
3.8 Analysis of highly cited articles
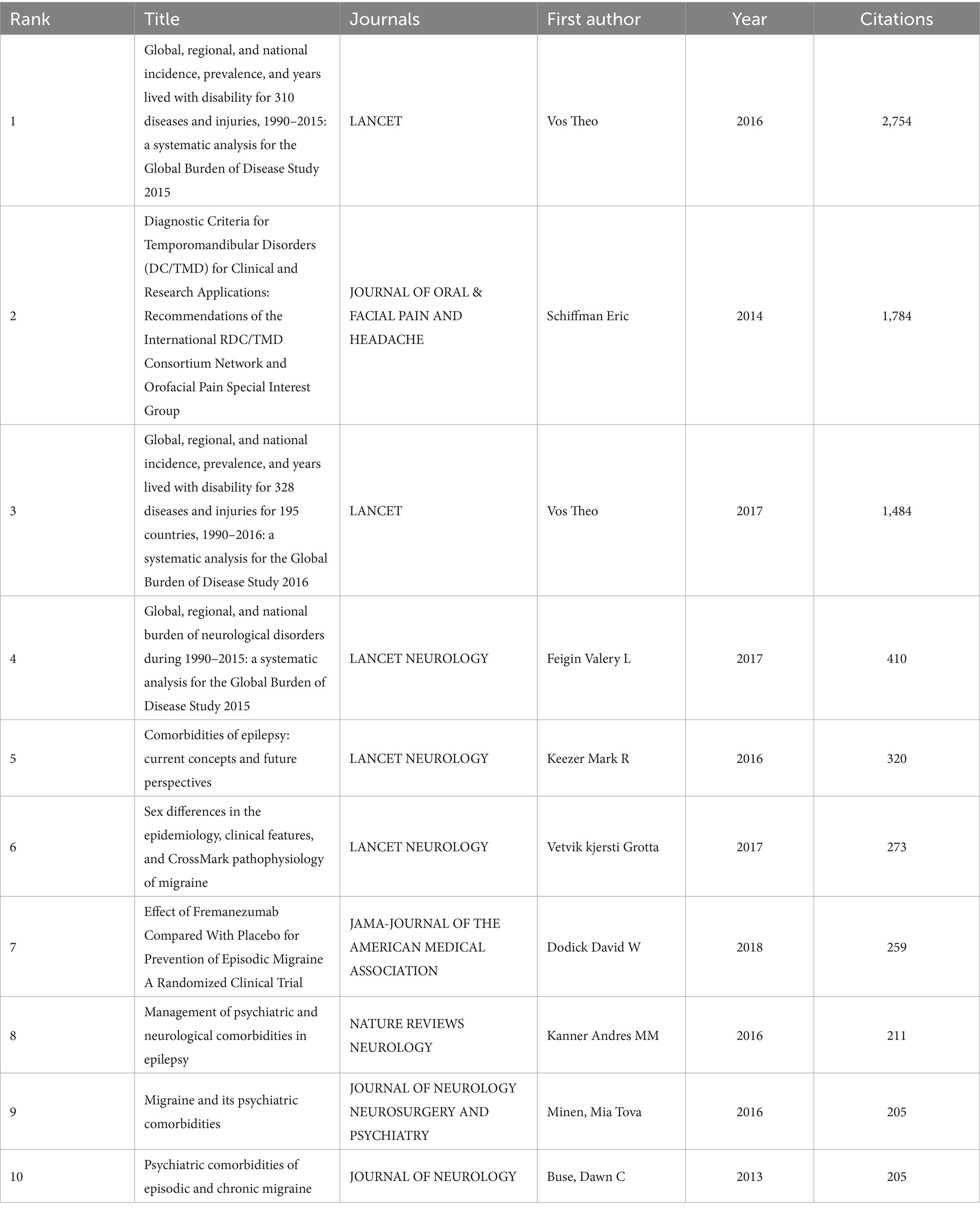
During the period of 2013 to 2022, a total of 1,334 articles were published on migraine and anxiety. Among them, three studies have been cited over 500 times. Table 6 shows the top 10 articles with the highest number of citations in this field. Three of them have been cited in over 1,000 publications.
4 Discussion
4.1 General information
In this study, we used CiteSpace 58.R3 and VOSviewer 1.6.17 to evaluate the value of articles over the past 10 years. Since 2013, a significant number of academic achievements showed a growing frequency of migraine and anxiety research, with 109 countries, 320 institutions, 433 authors, and 1,334 journals publishing articles. Over the past 10 years, the United States had published the highest number of research articles on migraine and anxiety among all countries, while the country with the highest centralization was the United Kingdom. We found that Richard B. Lipton was the notable contributor with a high scholarly influence on the field. However, it is obvious that many researchers lack cooperation and communication with other scholars. Harvard University, Yeshiva University, University of California System, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, and Mayo Clinic were considered central institutions in the field with high publications. Additionally, we also noticed that institutions are closely interconnected and engage in extensive collaboration. “Prevalence,” “anxiety,” “depression,” “migraine,” “headache,” and “quality of life” were closely related to the topic of research. The keyword timeline graph suggests that research on functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) is an significant topic in this field. Finally, research on acupuncture has emerged as a significant area in this field after 2015 and continues to be prominent.
4.2 Frontier and hotspots
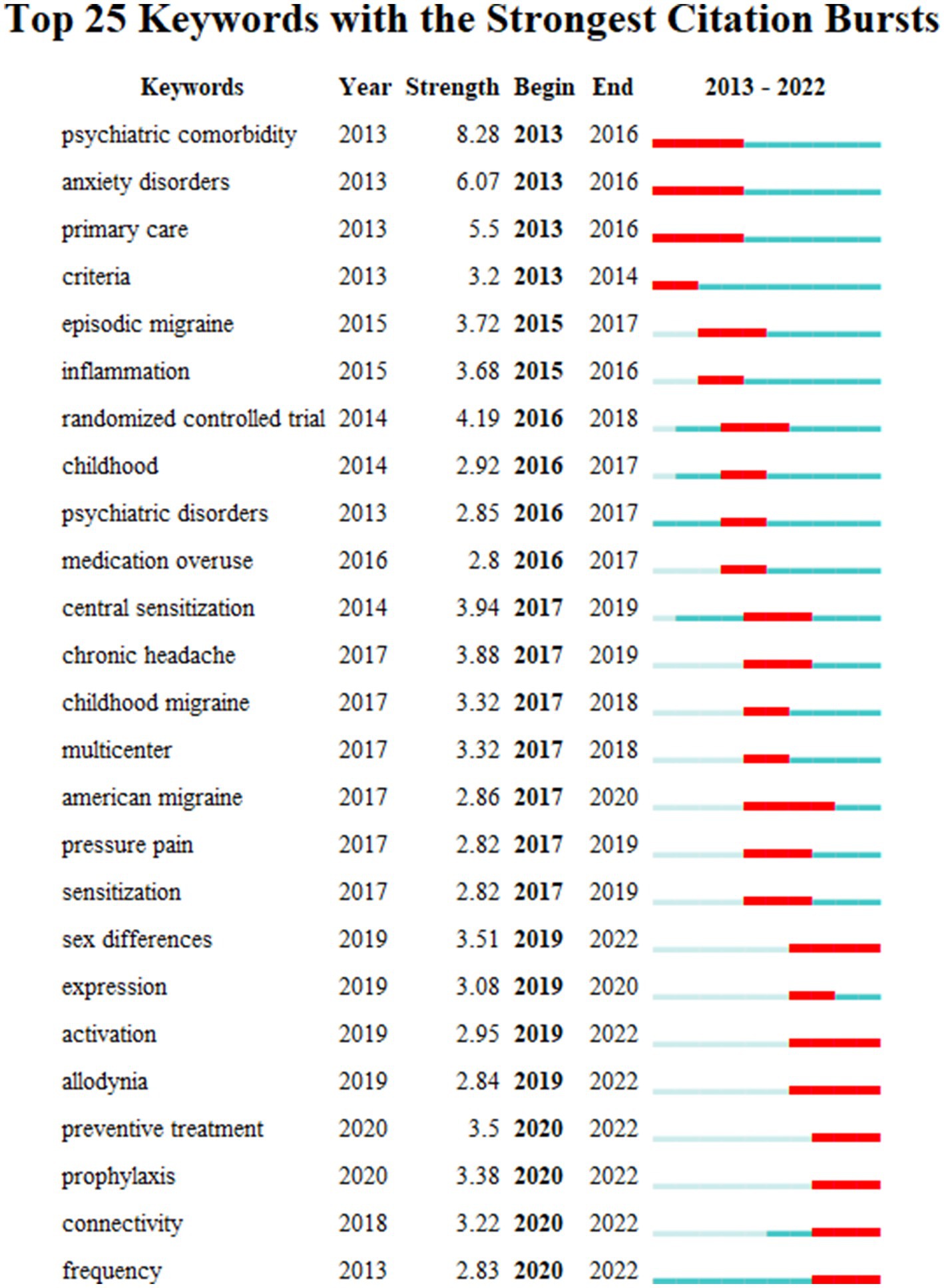
Keywords with red lines extending into the latest year may indicate future research frontiers. Figure 6 shows the top 25 keywords with the strongest citation bursts. Sex differences, activation, allodynia, preventive treatment, prophylaxis, connectivity, and frequency were the keywords presenting us with the main areas of current migraine and anxiety research.
4.2.1 Sex differences
It was reported that there existed a significant interaction between anxiety and depression in relation to the development of migraines, influenced by age and gender (16). From the study of women’s health across the nation, it was found that migraine was associated with an increased prevalence of anxiety in midlife women (17). One cross-sectional study concluded that anxiety significantly predicts the occurrence of migraines (18), and the female gender was a significant predictor of anxiety, with women being 7.2 times more likely to experience anxiety compared to men. The majority of people with migraines were women, which may be related to estrogen levels (19). The occurrence of migraine can be influenced by menarche, menstruation, pregnancy, menopause, usage of hormonal contraceptives, and hormone replacement therapy. These changes are caused by fluctuations in estrogen levels, which have an impact on the cerebral vasculature or cellular excitability (19). In addition, the drop of estrogen levels may be a trigger for migraine in women and the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in the hippocampus caused by estrogen deficiency has been demonstrated in animal studies to contribute to anxiety-like behavior in female rodents (16). The above results showed that hormone levels might be a potential mechanism of the sex differences in migraine and anxiety. However, these findings require confirmation in prospective studies.
4.2.2 Preventive treatment
It is possible for anxiety and/or depression to precipitate migraine episodes, and those who have frequent occurrences and those with chronic migraine are more likely to experience psychological distress (20). Previously, it has been proposed that migraine and psychological comorbidities may have a common pathophysiology with unique pathophysiological pathways that overlap or interact (20). In patients with migraine, preventive (prophylactic) treatment includes the use of prescription drugs such as beta-blockers, antidepressants, antiepileptics, calcium-channel blockers, and anti-CGRP mAbs (21, 22). The purpose of preventive treatment is to reduce the frequency, length, or intensity of episodes. The choice of medicine, response to preventative medication, behavioral migraine therapy, and compliance with migraine treatment programs can all be affected by co-occurring depression and/or anxiety (23). Amitriptyline and nortriptyline are tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) that have been proven to be effective in treating episodic migraines (24). TCAs have been shown to prevent migraines by inhibiting serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake as well as antagonizing the 5-HT2 receptor. To prevent episodic migraines, greater dosages of TCAs may be necessary to treat the underlying depression in patients with comorbid depression (25). Monoclonal antibody treatments targeting calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) are used widely as preventive migraine pharmacotherapies. It has been identified as a neuropeptide that plays a critical role in the pathophysiology of migraines, both centrally and peripherally (26). The innovative preventative medicines for migraine that target the CGRP system have an impact on anxiety, depressed symptoms, and exhaustion in addition to improving the intensity of the disease (9). Patients with comorbid depression and migraine may benefit from fremanezumab as it can lower disability and lessen the frequency of migraine and headache days (27). Compared to fremanezumab, galcanezumab and erenumab appear to be more successful in treating concurrent depression and anxiety symptoms in migraine patients. To completely comprehend the effect of CGRP antagonists on mental health conditions linked to migraines, it is helpful to analyze the results of validated questionnaires such as PHQ-9, HDRS, BDI-II, HARS, and GAD-7 (28). However, because of their novelty, the effectiveness of CGRP antagonists in treating comorbid psychiatric patients is limited (29). In addition, in order to avoid diminished quality of life and lower the burden of migraines, preventative medication should be initiated early in the course of the disease. In Europe, there is a critical need for access to migraine preventive treatment that is both effective and comfortable (30).
4.2.3 Allodynia
The location of central sensitization (CS) in migraine is generally considered to be the spinal trigeminal nucleus, which receives convergent input from the dura and the face (31). Migraine-associated allodynia, which is defined as a nociceptive reaction to ordinary harmless stimuli, involves the activation of the trigeminal system and development of central sensitization (32). A cross-sectional study showed that reduced pressure pain threshold, an inhibitory prognostic profile, and impaired somatosensory function were observed in the migraine group. These patients had a high level of central sensitization, mild anxiety symptoms, and pain catastrophizing as part of their psychosocial profile (33). It was proposed that headache chronification is caused by shared neural pathways between anxiety and depression (34). A major risk factor leading to the trigeminal nerve system’s hyperexcitability is long-term, unregulated stress and anxiety (35). One study found that chronic exposure to secondary environmental stress caused persistent alterations in the expression of proteins related to the development of peripheral and central sensitization in the trigeminal nerve (36), including elevated levels of CGRP and GFAP as well as the active forms of the MAP kinases ERK, p38, and JNK. These modifications all contribute to and sustain the trigeminal nerve system’s hyperexcited condition (36). Moreover, in patients with migraine, excessive occupation of the NMDA receptor due to elevated glutamatergic system activity may intensify and reinforce pain transmission, as well as cause allodynia and central sensitization (37).
4.2.4 fMRI
The fMRI technique has the advantages of high spatial resolution, no radiation, and non-invasiveness, which enable researchers to measure structural and functional brain changes non-invasively in patients with migraine or anxiety/depression (38, 39). One of the hot topics in study was the functional connectivity of brain regions. The top 10 brain regions where depressed patients exhibited significant differences from healthy controls were the Amygdala_L, Insula_R, Frontal_Inf_Oper_R, Cingulum_Post_L, Putamen_L, Thalamus_R, Angular_L, Precuneus_R, Frontal_Sup_R, and Occipital_Inf_L, according to a bibliometrics study and meta-analysis (40). Brain regions shown to have altered functional connectivity (FC) in patients with migraine include those that participate in sensory-discriminative processing of pain (e.g., the somatosensory cortex and posterior insula regions), affective processing (e.g., the anterior insula and amygdala), cognitive processing (e.g., the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus), and pain modulation (e.g., the periaqueductal gray) (41). Clinical studies have shown that the degree of anxiety for patients with chronic pain is closely related to the activation of specific brain regions and connectivity of resting brain networks (42). During migraine attacks, DMN has increased functional connectivity in pain-related brain regions such as the thalamus, insula, and left posterior central gyrus (43). A previous fMRI study investigated the abnormal activity of the left medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) in people with migraine and depression comorbidities (44). The intrinsic activity of the left mPFC was activated in patients with depression, and the activity of the left mPFC was also increased in patients with migraine (44). As the anterior node of the DMN, the mPFC had high activation at rest but had increased activity during cognitive and emotional processing. Moreover, ESN, PPN, and VN were involved in the neuropathological mechanisms of co-occurrence of migraine and depression (45).
4.3 Limitations
First, in the process of literature retrieval, the newly published literature and some keywords may not have been retrieved and included in the statistical analysis, and the results may be affected by incomplete literature collection. Second, this study only retrieved data from WoSCC, ignoring other databases, so some articles may have been missed. Finally, solely English publications were incorporated, which potentially introduced the impact of non-English scholarly contributions.
5 Conclusion
In this study, we utilized CiteSpace.5.8.R3 and VOSviewer 1.6.17 to evaluate the value of articles over the past 10 years. Since 2013, there has been an overall upward trend in the number of publications on migraine and anxiety research, with 109 countries, 320 institutions, 433 authors, and 1,334 journals publishing articles. However, international cooperation is expected in the future. Sex differences, activation, allodynia, and preventive treatment will be emerging research areas and potential hotspots for future research. In conclusion, this article provides the recent research status and research hotspots and frontiers in this field, delivering a perspective on the progressive direction of migraine and anxiety research, which may be valuable for further study of this field in the future.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
BH: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. WC: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CP: Writing – original draft, Data curation. YW: Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis. XS: Writing – review & editing, Data curation. QZ: Writing – review & editing, Data curation. LY: Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis. JW: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by Jiangxi Provincial Science and Technology Department (20212BAG70037), Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation Youth Fund (20202BAL216065), and Jiangxi Provincial Education Department Science Program (GJJ201259).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Amiri, P, Kazeminasab, S, Nejadghaderi, SA, Mohammadinasab, R, Pourfathi, H, Araj-Khodaei, M, et al. Migraine: a review on its history, global epidemiology, risk factors, and comorbidities. Front Neurol. (2022) 12:800605. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.800605
2. Serrano, D, Lipton, RB, Scher, AI, Reed, ML, Stewart, WF, Adams, AM, et al. Fluctuations in episodic and chronic migraine status over the course of 1 year: implications for diagnosis, treatment and clinical trial design. J Headache Pain. (2017) 18:101. doi: 10.1186/s10194-017-0787-1
3. Stovner, LJ, Hagen, K, Linde, M, and Steiner, TJ. The global prevalence of headache: an update, with analysis of the influences of methodological factors on prevalence estimates. J Headache Pain. (2022) 23:34. doi: 10.1186/s10194-022-01402-2
4. Steiner, TJ, Stovner, LJ, Jensen, R, Uluduz, D, and Katsarava, Z. Migraine remains second among the world’s causes of disability, and first among young women: findings from GBD2019. J Headache Pain. (2020) 21:137. doi: 10.1186/s10194-020-01208-0
5. Liu, TH, Wang, Z, Xie, F, Liu, YQ, and Lin, Q. Contributions of aversive environmental stress to migraine chronification: research update of migraine pathophysiology. World J Clin Cases. (2021) 9:2136–45. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i9.2136
6. Pradeep, R, Nemichandra, SC, Harsha, S, and Radhika, K. Migraine disability, quality of life, and its predictors. Ann Neurosci. (2020) 27:18–23. doi: 10.1177/0972753120929563
7. Ashina, S, Serrano, D, Lipton, RB, Maizels, M, Manack, AN, Turkel, CC, et al. Depression and risk of transformation of episodic to chronic migraine. J Headache Pain. (2012) 13:615–24. doi: 10.1007/s10194-012-0479-9
8. Yalinay Dikmen, P, Yavuz, BG, and Aydinlar, EI. The relationships between migraine, depression, anxiety, stress, and sleep disturbances. Acta Neurol Belg. (2015) 115:117–22. doi: 10.1007/s13760-014-0312-0
9. Della, A, de, C, Becattini, L, Curto, L, Ferrari, E, Siciliano, G, et al. Beyond pain relief: unveiling the multifaceted impact of anti-CGRP/R mAbs on comorbid symptoms in resistant migraine patients. Biomedicines. (2024) 12:677. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12030677
10. Zhu, X, Zhou, Z, and Pan, X. Research reviews and prospects of gut microbiota in liver cirrhosis: a bibliometric analysis (2001-2023). Front Microbiol. (2024) 15:1342356. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1342356
11. Ke, L, Lu, C, Shen, R, Lu, T, Ma, B, and Hua, Y. Knowledge mapping of drug-induced liver injury: a Scientometric investigation (2010-2019). Front Pharmacol. (2020) 11:842. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00842
12. Karimi, L, Wijeratne, T, Crewther, SG, Evans, AE, Ebaid, D, and Khalil, H. The migraine-anxiety comorbidity among migraineurs: a systematic review. Front Neurol. (2021) 11:613372. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.613372
13. Buse, DC, Reed, ML, Fanning, KM, Bostic, R, Dodick, DW, Schwedt, TJ, et al. Comorbid and co-occurring conditions in migraine and associated risk of increasing headache pain intensity and headache frequency: results of the migraine in America symptoms and treatment (MAST) study. J Headache Pain. (2020) 21:23. doi: 10.1186/s10194-020-1084-y
14. Breslau, N, Merikangas, K, and Bowden, CL. Comorbidity of migraine and major affective disorders. Neurology. (1994) 44:S17–22.
15. Dresler, T, Caratozzolo, S, Guldolf, K, Huhn, J-I, Loiacono, C, Niiberg-Pikksööt, T, et al. Understanding the nature of psychiatric comorbidity in migraine: a systematic review focused on interactions and treatment implications. J Headache Pain. (2019) 20:51. doi: 10.1186/s10194-019-0988-x
16. Luo, J. Association between migraine and anxiety symptoms: results from the study of women's health across the nation. J Affect Disord. (2021) 295:1229–33. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2021.09.036
17. Duan, S, Ren, Z, Xia, H, Wang, Z, Zheng, T, Li, G, et al. Associations between anxiety, depression with migraine, and migraine-related burdens. Front Neurol. (2023) 14:1090878. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1090878
18. Qarah, M, Alshammari, N, Alsharif, R, Albalawi, M, Fida, M, Alshehri, K, et al. Prevalence of anxiety and depression and their association with migraine among PHC center visitors in Madina, Saudi Arabia. Cureus. (2024) 16:e55404. doi: 10.7759/cureus.55404
19. Sacco, S, Ricci, S, Degan, D, and Carolei, A. Migraine in women: the role of hormones and their impact on vascular diseases. J Headache Pain. (2012) 13:177–89. doi: 10.1007/s10194-012-0424-y
20. Vikelis, M, Dermitzakis, EV, Xiromerisiou, G, Rallis, D, Soldatos, P, Litsardopoulos, P, et al. Effects of Fremanezumab on psychiatric comorbidities in difficult-to-treat patients with chronic migraine: post hoc analysis of a prospective, multicenter, real-world Greek registry. J Clin Med. (2023) 12:4526. doi: 10.3390/jcm12134526
21. Meyers, JL, Davis, KL, Lenz, RA, Sakai, F, and Xue, F. Treatment patterns and characteristics of patients with migraine in Japan: a retrospective analysis of health insurance claims data. Cephalalgia. (2019) 39:1518–34. doi: 10.1177/0333102419851855
22. Takizawa, T, Kitano, T, Iijima, M, Togo, K, and Yonemoto, N. Treatment patterns and characteristics of patients with migraine: results from a retrospective database study in Japan. J Headache Pain. (2024) 25:19. doi: 10.1186/s10194-024-01722-5
23. Lipton, RB, Seng, EK, Chu, MK, Reed, ML, Fanning, KM, Adams, AM, et al. The effect of psychiatric comorbidities on headache-related disability in migraine: results from the chronic migraine epidemiology and outcomes (CaMEO) study. Headache. (2020) 60:1683–96. doi: 10.1111/head.13914
24. George, A, and Minen, MT. Episodic migraine and psychiatric comorbidity: a narrative review of the literature. Curr Pain Headache Rep. (2023) 27:461–9. doi: 10.1007/s11916-023-01123-4
25. Parikh, SK, and Silberstein, SD. Preventive treatment for episodic migraine. Neurol Clin. (2019) 37:753–70. doi: 10.1016/j.ncl.2019.07.004
26. Deen, M, Correnti, E, Kamm, K, Kelderman, T, Papetti, L, Rubio-Beltrán, E, et al. Blocking CGRP in migraine patients - a review of pros and cons. J Headache Pain. (2017) 18:96. doi: 10.1186/s10194-017-0807-1
27. Lipton, RB, Cohen, JM, Galic, M, Seminerio, MJ, Yeung, PP, Aycardi, E, et al. Effects of fremanezumab in patients with chronic migraine and comorbid depression: subgroup analysis of the randomized HALO CM study. Headache. (2021) 61:662–72. doi: 10.1111/head.14097
28. Omaer, A, Albilali, A, Bamogaddam, R, Almutairi, F, Alsaif, R, Almohammadi, O, et al. Improvement of comorbid anxiety and depression in patients with migraine treated with injectable preventive calcitonin gene-related peptide antagonists: review of clinical evidence. Saudi Pharm J. (2024) 32:101989. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2024.101989
29. McCracken, HT, Thaxter, LY, and Smitherman, TA. Psychiatric comorbidities of migraine. Handb Clin Neurol. (2024) 199:505–16. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-823357-3.00013-6
30. Buse, DC, Pozo-Rosich, P, Dupont-Benjamin, L, Balkaran, BL, Lee, L, Jauregui, A, et al. Impact of headache frequency and preventive medication failure on quality of life, functioning, and costs among individuals with migraine across several European countries: need for effective preventive treatment. J Headache Pain. (2023) 24:115. doi: 10.1186/s10194-023-01655-5
31. Burstein, R, Yarnitsky, D, Goor-Aryeh, I, Ransil, BJ, and Bajwa, ZH. An association between migraine and cutaneous allodynia. Ann Neurol. (2000) 47:614–24. doi: 10.1002/1531-8249(200005)47:5<614::AID-ANA9>3.0.CO;2-N
32. Burstein, R, Cutrer, MF, and Yarnitsky, D. The development of cutaneous allodynia during a migraine attack clinical evidence for the sequential recruitment of spinal and supraspinal nociceptive neurons in migraine. Brain. (2000) 123:1703–9. doi: 10.1093/brain/123.8.1703
33. Barone, M, Imaz, F, De la Torre, CG, Venosta, M, Dri, J, and Intelangelo, L. Somatosensory and psychosocial profile of migraine patients: a cross-sectional study. Musculoskelet Sci Pract. (2024) 70:102924. doi: 10.1016/j.msksp.2024.102924
34. Hamelsky, SW, and Lipton, RB. Psychiatric comorbidity of migraine. Headache. (2006) 46:1327–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2006.00576.x
35. Borsook, D, Maleki, N, Becerra, L, and McEwen, B. Understanding migraine through the lens of maladaptive stress responses: a model disease of allostatic load. Neuron. (2012) 73:219–34. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.01.001
36. Hawkins, JL, Moore, NJ, Miley, D, and Durham, PL. Secondary traumatic stress increases expression of proteins implicated in peripheral and central sensitization of trigeminal neurons. Brain Res. (2018) 1687:162–72. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.03.003
37. Burstein, R, Noseda, R, and Borsook, D. Migraine: multiple processes, complex pathophysiology. J Neurosci. (2015) 35:6619–29. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0373-15.2015
38. Zhang, Y, Wang, Z, du, J, Liu, J, Xu, T, Wang, X, et al. Regulatory effects of acupuncture on emotional disorders in patients with menstrual migraine without Aura: a resting-state fMRI study. Front Neurosci. (2021) 15:726505. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.726505
39. Wei, HL, Yu, YS, Wang, MY, Zhou, GP, Li, J, Zhang, H, et al. Exploring potential neuroimaging biomarkers for the response to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in episodic migraine. J Headache Pain. (2024) 25:104. doi: 10.1186/s10194-024-01812-4
40. Wang, X, Nie, X, Zhang, F, Wei, Y, Zeng, W, Zhang, Y, et al. Functional magnetic resonance imaging of depression: a bibliometrics and meta-analysis. Ann General Psychiatry. (2024) 23:39. doi: 10.1186/s12991-024-00525-x
41. Messina, R, Gollion, C, Christensen, RH, and Amin, FM. Functional MRI in migraine. Curr Opin Neurol. (2022) 35:328–35. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0000000000001060
42. Gustin, SM, Peck, CC, Wilcox, SL, Nash, PG, Murray, GM, and Henderson, LA. Different pain, different brain: thalamic anatomy in neuropathic and non-neuropathic chronic pain syndromes. J Neurosci. (2011) 31:5956–64. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5980-10.2011
43. Edes, AE, Kozak, LR, Magyar, M, Zsombok, T, Kokonyei, G, Bagdy, G, et al. Spontaneous migraine attack causes alterations in default mode network connectivity: a resting-state fMRI case report. BMC Res Notes. (2017) 10:165. doi: 10.1186/s13104-017-2484-1
44. Ma, M, Zhang, J, Chen, N, Guo, J, Zhang, Y, and He, L. Exploration of intrinsic brain activity in migraine with and without comorbid depression. J Headache Pain. (2018) 19:48. doi: 10.1186/s10194-018-0876-9
Keywords: migraine, anxiety, global research trends, bibliometric analysis, visualization
Citation: Huang B, Chen W, Peng C, Wang Y, Shen X, Zhang Q, Yang L and Wu J (2025) Global trends in migraine and anxiety over the past 10 years: a bibliometric analysis. Front. Neurol. 15:1448990. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1448990
Edited by:
Claudia Altamura, Fondazione Policlinico Campus Bio-Medico, ItalyReviewed by:
Marta Waliszewska-Prosół, Wroclaw Medical University, PolandAndrea Burgalassi, Careggi University Hospital, Italy
Copyright © 2025 Huang, Chen, Peng, Wang, Shen, Zhang, Yang and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jun Wu, MTIxODg3MDJAcXEuY29t
†These authors share first authorship
 Biao Huang
Biao Huang Weining Chen2†
Weining Chen2† Yu Wang
Yu Wang