- 1Department of Neurology, The Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
- 2The Key Laboratory of Neurology, Hebei Medical University, Ministry of Education, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
- 3Neurological Laboratory of Hebei Province, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
- 4Department of Emergency, The Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
Introduction: Geranylgeranyltransferase Subunit Beta (RABGGTB) was expressed at higher levels in patients with Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) compared with healthy controls. This study aims to observe the expression of RABGGTB in different cells from patients with ALS and different diseases.
Methods: In this case–control study, we collected peripheral blood from patients with ALS and healthy controls, and compared the expression of RABGGTB in natural killer cells (NK), T cells and B cells between patients with ALS and healthy controls by flow cytometry. And compared the expression of RABGGTB in monocytes and monocyte-derived macrophages from patients with ALS, Parkinson’s disease (PD), acute cerebrovascular disease (ACVD), and healthy controls by flow cytometry and immunofluorescence. Then flow cytometry was used to detect the expression of RABGGTB in monocytes from SOD1G93A mice and WT mice.
Results: The expression of RABGGTB was not significantly changed in NK cells, cytotoxic T cells (CTL), helper T cells (Th), regulatory T cells (Treg), and B cells from patients with ALS compared to healthy controls. And the expression of RABGGTB in monocytes and monocyte-derived macrophages was higher in the ALS group than in the PD, ACVD and control group. The expression of RABGGTB was significantly higher in monocytes of SOD1G93A mice compared to WT mice.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that RABGGTB expression was increased in monocytes and monocyte-derived macrophages from patients with ALS, not in NK, CTL, Th, Treg, and B cells. Future studies are needed to find the clinical implication of RABGGTB in ALS.
1 Introduction
ALS is a chronic, progressive and fatal neurodegenerative disease in which the motor neurons in the anterior horn cells of the spinal cord, the brainstem, and the cerebral cortex undergo degenerative changes. About 10% of ALS cases are inherited, although the majority of cases are sporadic (1). The clinical and pathological features of sporadic and familial ALS are similar. About 20% of familial cases are associated with mutations in the Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) gene in an autosomal dominant pattern (2). Currently, there is no known cure and few effective treatments for ALS because the exact mechanism of ALS remains elusive and the multifactorial nature of ALS includes genetic susceptibility (3), environmental exposures (4), and clinical heterogeneity (5).
Inflammation is associated with ALS. Microglia and astrocytes are key regulators of inflammatory responses (6–8), and peripheral inflammation plays an important role in ALS (9–11). Accumulating evidence suggests that inflammation including the CNS and the peripheral immune system, contributes to the progression of ALS in both humans and in mouse models (12–15). First, microglia and astroglia activation have been reported as prominent features in the spinal cord and motor cortex of ALS patients and transgenic rodent models, and microglia and astroglia have been used as therapeutic targets for ALS (16–20). Furthermore, the central and peripheral nervous systems of ALS patients and animal models have been reported to be infiltrated by macrophages, natural killer cells and T lymphocytes, and modulation these cells have been reported to improve motor function or prolong survival in ALS (10, 11, 21–24).
In recent years, several studies have focused on the role of RABGGTB in diseases. In our previous studies, we found that the expression of RabGGTase is lower in the spinal cord motoneurons in SOD1G93A mice compared with WT mice, and autophagy defects could be ameliorated by modulating RABGGTB in neurons (25), Rab geranylgeranyltransferase subunit alpha (RABGGTA) and Rab geranylgeranyltransferase subunit beta (RABGGTB) composed RabGGTase (26) that mediated the prenylation modification of Rab7, which was inhibited in the ALS model (27). In our previous studies, we have found that the expression of RABGGTB was higher in peripheral mononuclear-macrophages of ALS patients compared with healthy controls, and the expression of RABGGTB was significantly correlated with disease progression in ALS patients (28). The RABGGTB was significantly downregulated in the peripheral blood from patients with multiple sclerosis compared with healthy subjects (29), whereas high RABGGTB expression has been reported in tumor-associated disease (30).
In the present study, we first reported that the expression of RABGGTB was not significantly changed in natural killer cells (NK), cytotoxic T cells (CTL), helper T cells (Th), regulatory T cells (Treg), and B cells from patients with ALS compared to healthy controls. And the expression of RABGGTB in monocytes and monocyte-derived macrophages was higher in the ALS group than in the PD, ACVD, and control group.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Subjects
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University (2022-R196). Between January 2021 and August 2023, we collected medical histories and physical examination records from patients diagnosed with ALS, PD, and ACVD at the Department of Neurology. Patients included met the appropriate diagnostic criteria for ALS (31), PD (32), and ACVD (33). The patients with ALS included in the study are sporadic and depending on the site of onset, are divided into those with bulbar-onset ALS and those with limb-onset ALS. Meanwhile, the information of the corresponding healthy controls was collected from the physical examination department, including gender, age, past history, family history, and so on. All the participants with ALS, PD, and ACVD were excluded from acute or chronic inflammatory diseases, for instance, acute pneumonia, and rheumatoid arthritis. And all the participants signed informed consent forms.
2.2 Serum sample
Venous blood was collected from the cubital region of patients with ALS, PD, ACVD, and healthy controls in the morning after an overnight fast.
2.3 Flow cytometry
Erythrocyte lysis was performed by mixing 2 mL of erythrocyte lysis buffer Erythrocyte Lysis Buffer (Lysing Buffer 10X Concentrate, BD, 555899) with 1 mL of whole blood and incubating for 10 min at RT. The leukocytes were centrifuged at 500 × g for 5 min at 4°C and washed twice with PBS. The leukocytes were resuspended in 2 mL PBS and stained with antibodies specific for cell surface antigens (CD3-PE-cy7, 25-0037-42; CD4-Percp-cy5.5, 45-0049-42; CD8-eFluor450, 48-0088-42; CD56-PE, 12-0567-42; CD25-APC, 17–0257-42; CD127-PE, 12-1,278-42; CD19-APC, 17-0199-42; CD14-APC, 17-0149-42; CD16-Percp-cy5.5,46–0168-42; PE anti-mouse Ly6C, 1:100, BD, 128007; and CD45 BB515, 1:100, BD, 564590) for 30 min on ice in the dark. After washing with PBS, stained cells were fixed and permeabilized by adding 500 μL of fixation/permeabilization solution (Cytofix/CytopermTM Plus Fixation/Permeabilization Kit, BD, 554714) and incubated for 20 min at RT in the dark. The thoroughly resuspended fixed/permeabilized cells were incubated with anti-RABGGTB (1,500, GeneTeX, GTX105874) at 4°C for 30 min in the dark. The cells were then incubated again with FITC-conjugated goat anti-rabbit 1gG (H + L) (1,100, PROTEINTECH, SA00003-2) at 4°C for 30 min in the dark. After the cells were washed twice with 1 × BD Perm/WashTM buffer and resuspended in staining buffer, flow cytometry analysis was performed.
2.4 Isolation of PBMCs from blood samples
Human peripheral blood lymphocyte separation liquid (LTS1077) was added in a high-efficiency centrifuge tube (Tianjin Haoyang Biological Products Science & Technology Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China; 601,002), and centrifuged at 200× g for 2 min at room temperature. The peripheral blood samples were then added and centrifuged for an additional 30 min at 800× g. The intermediate mononuclear cell layer was carefully aspirated into a new centrifuge tube and centrifuged at 300× g for 13 min. The precipitate is mononuclear cells after aspiration of the supernatant.
2.5 In vitro culture of macrophages
The peripheral blood mononuclear cells were maintained in RPMI-1640 medium (Gibco, C11875500BT) supplemented with 10% FBS and 1% penicillin–streptomycin (P/S). Macrophage colony stimulating factor (M-CSF, PeproTech, 300-25-10) was added to the culture medium for 7 days to induce differentiation of monocytes into macrophages. The culture medium was changed every 3 days. On day 7, the cell culture medium was collected and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS (34).
2.6 Immunofluorescence and confocal microscopy analysis
Cells were washed three times with PBS, and fixed with containing 0.3% Triton-X-100 for 15 min and blocked with 10% sheep serum for 1 h at room temperature. Then primary antibodies against CD68 (1,500, Abcam, ab31630), F4/80 (1,200, Abcam, ab6640), and RABGGTB (1,500, GeneTeX, GTX105874) were used overnight at 4°C. After washed three times, cells were incubated with the appropriate secondary antibody: Donkey anti-rat IgG (H + L) highly cross-adsorbed secondary antibody, Alexa Fluor™ 488 (1,1,000, Invitrogen, A21208), Alexa Fluor 594-conjugated goat anti-mouse secondary antibody (1,1,000, Thermo Fisher, #A-11032), and Alexa Fluor 647-labeled goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody (1,1,000, Invitrogen, A21245) for 1 h at room temperature. Cells were observed using a fluorescence confocal microscope (LSM900, ZEISS, Germany). Microscope parameters were set at the beginning of each imaging session and remained constant throughout the imaging session.
2.7 Animals and treatments
SOD1G93A mice (B6SJL-Tg [SOD1G93A]1Gur/J) were originally obtained from Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME, United States). DNA was extracted from the tails of hemizygous mice and genotyped by PCR. Mice were housed under constant temperature (22–24°C), constant humidity (40–60%) and 12 h light/dark cycle and fed with sterilised water and aseptic granular food. Mice were deeply anesthetized by pentobarbital sodium and blood was collected from the heart of mice. All studies were conducted in accordance with the Guidelines for the Management of Laboratory Animals formulated by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China, and the Animal Ethics Committee of the Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University also approved the experimental procedures (Approval no. 2023-R248). Throughout the experiment, we did our best to reduce the suffering of all animals.
2.8 Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses and graphing were performed using GraphPad Prism 9 (GraphPad software). All data were presented as mean ± SD, and performed with skewness and kurtosis tests for normal distribution check. For data with normal distribution, unpaired t-test was used for differences analysis between patients with ALS and healthy controls, and paired t-test were used between SOD1G93A mice and WT mice. For abnormal distributed data, Mann–Whitney U-test was used for the differences analysis. p ≤ 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Expression of RABGGTB in different cells from patients with ALS and healthy control
In our previous studies, we have found that the expression of RABGGTB was higher in peripheral mononuclear-macrophages of ALS patients compared with healthy controls (28), so we want to compare the RABGGTB levels in other cells from patients with ALS and healthy controls. So, we collected 43 patients diagnosed with ALS at the Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University between January 2021 and August 2023. The healthy control group consisted of 20 male and seven female with a mean age of 57 ± 6 years, and ALS group included a total of 32 male and 11 female with a mean age of 58 ± 7 years. The distributions of age and gender did not differ significantly (Table 1).
T Cells were divided into three subpopulations based on the level of CD3 CD4 CD8 CD25 and CD127 surface expression: Treg cell (CD4 + CD25 + CD127-), Th cell (CD3 + CD4 + CD8-), and CTL cell (CD3 + CD4-CD8+). Flow cytometry was used to detect RABGGTB levels in natural killer cells (NK), cytotoxic T cells (CTL), helper T cells (Th), regulatory T cells (Treg), and B cells from patients with ALS compared with healthy controls (Figures 1A–D). Comparing the expression levels of RABGGTB between the groups, we discovered that RABGGTB was not significantly changed in peripheral natural killer cells (NK), cytotoxic T cells (CTL), helper T cells (Th), regulatory T cells (Treg), and B cells of patients with ALS (Figure 1E).
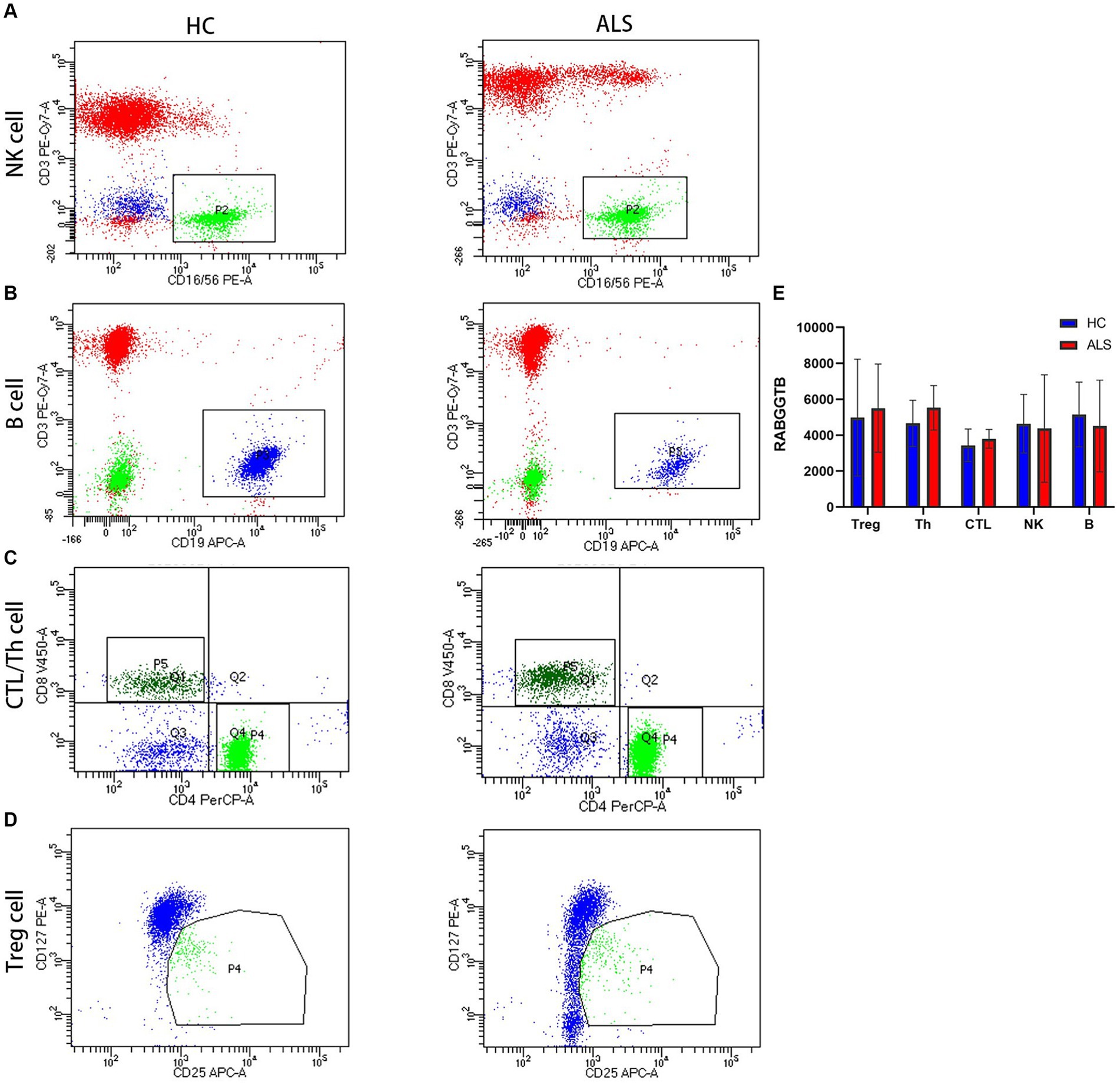
Figure 1. Evaluation of the RABGGTB level in different cells from patients with ALS and healthy controls. (A) RABGGTB levels in NK cells from patients with ALS and healthy controls by BD flow cytometry. (B) RABGGTB levels in B cells from patients with ALS and healthy controls by BD flow cytometry. (C) RABGGTB levels in CTL and Th cells from patients with ALS and healthy controls by BD flow cytometry. (D) RABGGTB levels in Treg cells from patients with ALS and healthy controls by BD flow cytometry. (E) Quantitative analysis of the RABGGTB level in different cells. The statistical significance was determined using an unpaired t-test. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001. HC, healthy control; ALS, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; RABGGTB, Rab geranylgeranyltransferase subunit beta.
3.2 Expression of RABGGTB in the monocytes from patients and healthy control
Combining the above results, we hypothesized whether the increased expression of RABGGTB in monocytes from patients with ALS is specific. Therefore, we included two neurological diseases, including patients with PD and ACVD, as controls. The data of 90 patients diagnosed with ALS, 35 patients diagnosed with PD, 20 patients diagnosed with ACVD at the Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University between January 2021 and August 2023, were collected. The healthy control group consisted of 34 male and 16 female with a mean age of 56 ± 8 years, and ALS group included a total of 62 male and 28 female with a mean age of 59 ± 9 years, and PD group consisted of 23 male and 12 female with a mean age of 57 ± 8 years, and ACVD group included a total of 13 male and seven female with a mean age of 55 ± 8 years. The distributions of age and gender did not differ significantly (Table 2).
BD flow cytometry was used to detect the RABGGTB levels in the monocytes from ALS patients, PD patients, ACVD patients, and healthy controls (Figures 2A–D). We compared the expression of RABGGTB in monocytes between the four groups, and we discovered that RABGGTB was significant highly upregulated in monocytes of patients with ALS (Figure 2E).
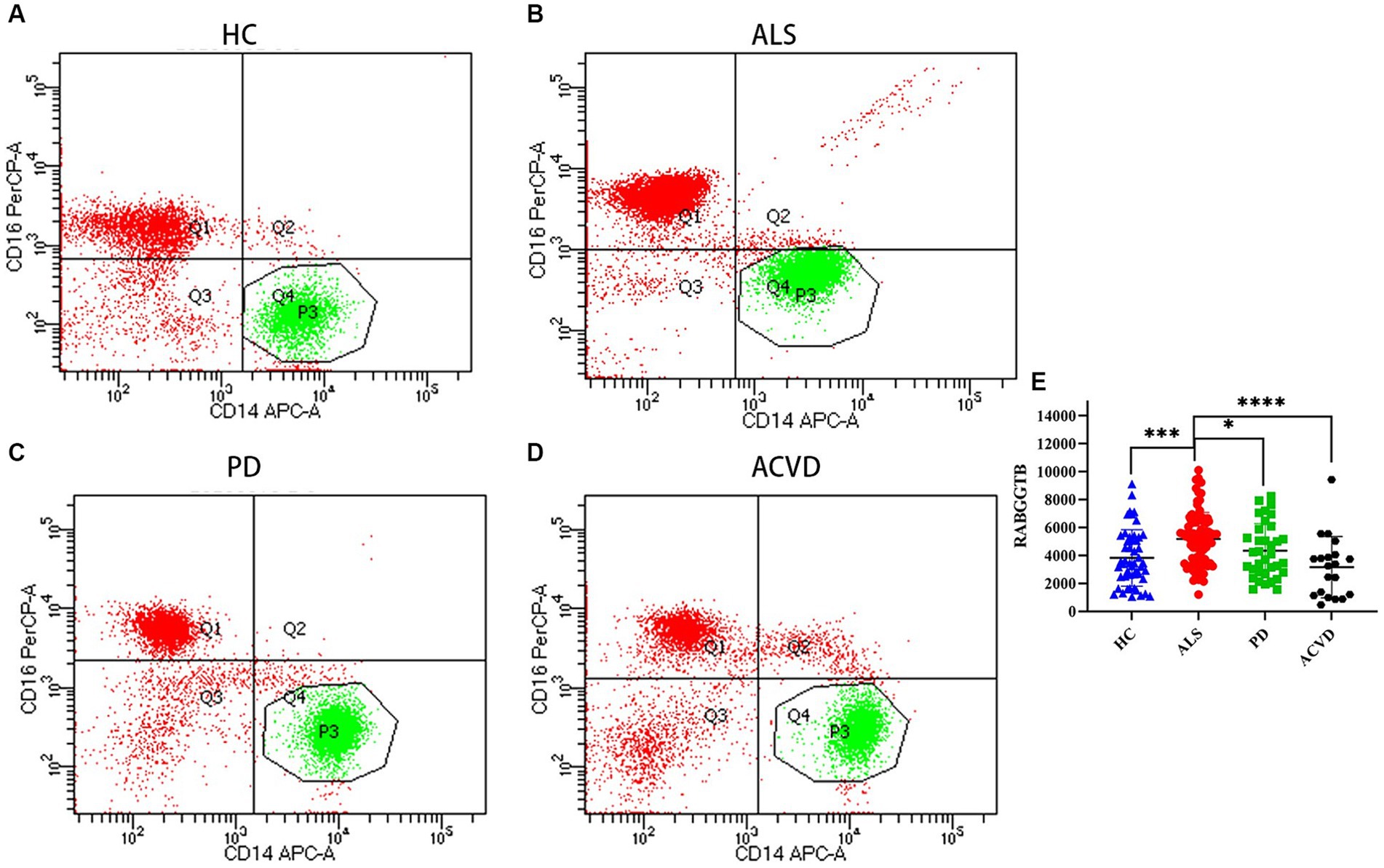
Figure 2. Evaluation of the RABGGTB level in classical monocytes from patients with ALS, PD, ACVD, and healthy controls. (A) RABGGTB levels in monocytes from healthy controls by BD flow cytometry. (B) RABGGTB levels in monocytes from ALS patients by BD flow cytometry. (C) RABGGTB levels in monocytes from PD patients by BD flow cytometry. (D) RABGGTB levels in monocytes from ACVD patients by BD flow cytometry. (E) Quantitative analysis of the RABGGTB level in monocytes. The statistical significance was determined using an unpaired t-test. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001. HC, healthy control; ALS, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; PD, Parkinson’s disease; ACVD, acute cerebrovascular disease; RABGGTB, Rab geranylgeranyltransferase subunit beta.
3.3 Expression of RABGGTB in the monocyte-derived macrophages from patients and healthy control
In order to further validate this result, the monocytes extracted from peripheral blood were differentiated into macrophages after stimulated by M-CSF. The cells presented typical macrophages morphology, with macrophage markers CD68 and F4/80 expressed on the cell surface (Figure 3A). We discovered that the expression of RABGGTB in monocyte-derived macrophages was significantly higher in ALS group than that in the other three groups (Figure 3B).
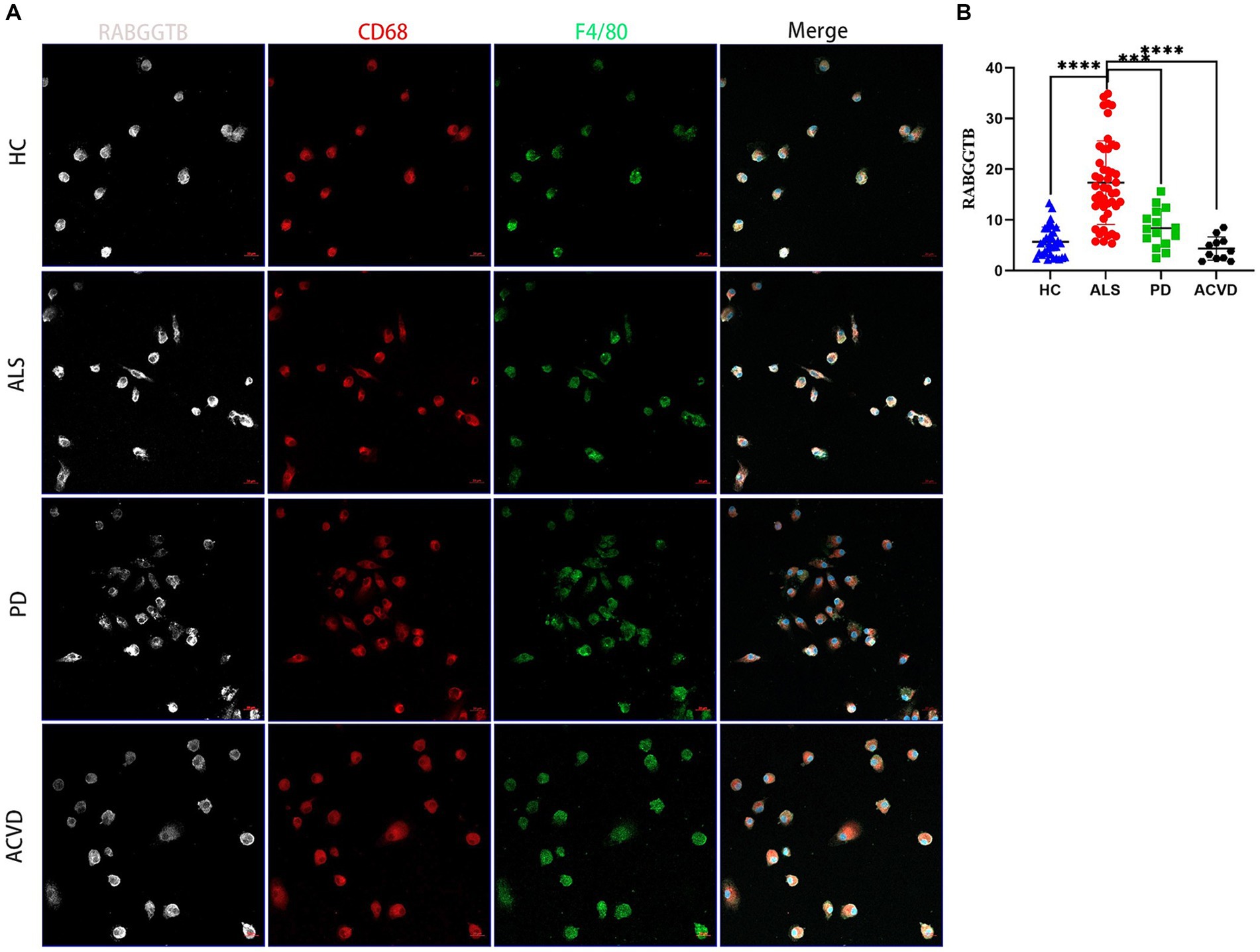
Figure 3. Evaluation of the RABGGTB level in monocytes-derived macrophages from patients with ALS, PD, ACV and healthy controls. (A) Immunofluorescence labeling for RABGGTB (gray/white), CD68 (red), and F4/80 (green) in monocyte-derived macrophages from patients and healthy controls. DAPI was used to stain nuclei (blue). Scale bars = 20 μm. (B) Quantitative analysis of RABGGTB levels in monocyte-derived macrophages from patients and healthy controls. The statistical significance was determined using an unpaired t-test. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001. HC, healthy control; ALS, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; PD, Parkinson’s disease; ACVD, acute cerebrovascular disease; RABGGTB, Rab geranylgeranyltransferase subunit beta.
3.4 The expression of RABGGTB increased in the monocytes of SOD1G93A
The above findings suggest that the expression of RABGGTB in monocytes and macrophages was significantly higher in the ALS group than in the other groups, but the data collected come from sporadic ALS, and these data are not representative of familial ALS (fALS), such as those with mutations in the Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase (SOD1) gene. In order to detect the expression of RABGGTB in monocytes with mutations in the SOD1 gene, we used flow cytometry to detect the expression of RABGGTB in monocytes of SOD1G93A mice, comparing the expression levels of RABGGTB in monocytes of WT mice (Figures 4A,B), we discovered that the expression of RABGGTB was significantly upregulated in monocytes of SOD1G93A mice (Figure 4C).
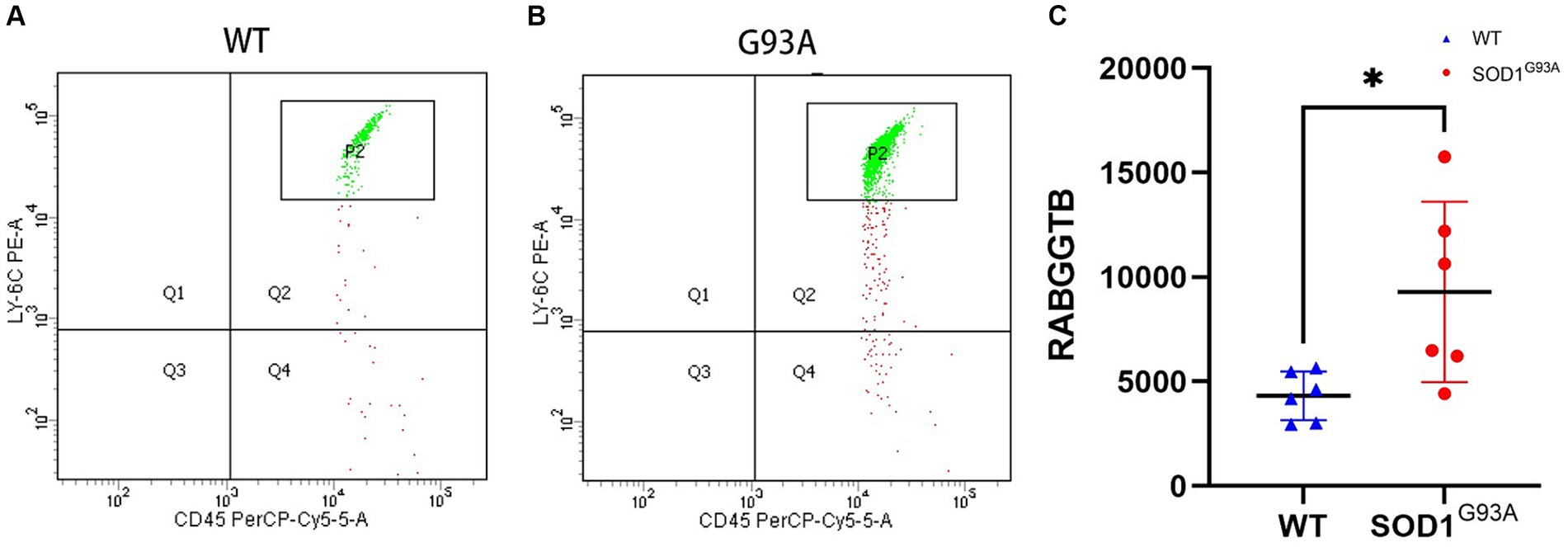
Figure 4. Evaluation of the RABGGTB level in monocytes of SOD1G93A and WT mice. (A). RABGGTB levels in LY6C-positive and CD45-positive monocytes of WT mice by BD flow cytometry. (B). RABGGTB levels in LY6C-positive and CD45-positive monocytes of SOD1G93A mice by BD flow cytometry. (C). Quantitative analysis of the RABGGTB level in monocytes. The statistical significance was determined using an unpaired t-test. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001. RABGGTB, Rab geranylgeranyltransferase subunit beta.
4 Discussion
Inflammation plays a key role in the development and progression of ALS, and chronic inflammation can contribute to progressive neuron loss (35–37). The study of inflammation and ALS has been going on for decades, but few anti-inflammatory treatments have reached the clinic (37). Previous research has shown that different inflammatory cells play different roles in ALS, and our previous studies found that the expression of RABGGTB was higher in peripheral mononuclear-macrophages from ALS patients (28), in this study, we discovered that the expression levels of RABGGTB was not significantly changed in peripheral NK, CTL, Th, Treg, and B cells between patients with ALS and healthy controls. And the expression of RABGGTB in peripheral monocyte and monocyte-derived macrophages was significantly higher in the ALS group than in the PD group, ACVD group and the control group. These findings suggested that it might be specific that the high expression of RABGGTB in peripheral monocyte and monocyte-derived macrophages from patients with ALS.
The expression of RABGGTB was significantly high in peripheral monocyte and monocyte-derived macrophages from patients with ALS, but the data collected come from sporadic ALS, and these data are not representative of familial ALS (fALS), such as those with mutations in the Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase (SOD1) gene, so we detect the expression of RABGGTB in monocytes of SOD1G93A mice and found that the expression of RABGGTB was significantly upregulated in monocytes of SOD1G93A mice. These findings show that the expression of RABGGTB is increased in peripheral blood mononuclear macrophages from ALS patients and SOD1G93A mice.
Taken together, these results suggest that perhaps the high expression of RABGGTB in ALS may have a specificity, but further experiments are necessary for verification. Of course, these results raise the question why the RABGGTB expression is increased in monocytes from patients with ALS. Our speculation is that the main reason may be that the inflammatory states of ALS are different from the other diseases. A second reason is the different nature and pathogenesis of the diseases. However, the mechanisms involved in this are not clear, and we will be investigating these mechanisms in future studies. Inflammation plays an important role in ALS and there has been a lot of research on anti-inflammatory drugs in ALS, such as celecoxib and minocycline (38–40). However, few anti-inflammatory drugs in ALS have reached the clinic. Our results may suggest that some indicators or functions of inflammatory cells in ALS are different from the other diseases, and this may be one of the reasons why anti-inflammatory drugs have been not reached the clinic in ALS.
Although our results are interesting, there are some limitations in the study. The main limitation is that it may be a coincidence that we only observed high expression of RABGGTB in ALS. Furthermore, there may be a selection bias among the other diseases as controls. The Second limitation is that the number of patients included was limited. ALS is an adult-onset, rare, severe neurodegenerative disease with a median survival of 3–5 years. Cases are therefore difficult to recruit, resulting in relatively small sample sizes. The third limitation is that patients with ALS have not been genetically tested for the presence of SOD1 mutations. Therefore, we used the SOD1G93A mice as a proxy for SOD1 mutation and observed that the expression of RABGGTB is increased in SOD1 mutant mice, but these data are not fully representative of humans. The four limitation is that we did not carry out a mechanistic study of the effect. However, this research is ongoing and we will be investigating the mechanisms in a future study, and future studies are needed to find the clinical implication of RABGGTB in ALS.
In conclusion, our data demonstrate that it might be specific that the high expression of RABGGTB in peripheral monocyte and monocyte-derived macrophages from patients with ALS, further emphasizing the contribution of monocyte s to physiological processes. These findings provide additional evidence for peripheral immune cells to participate in ALS, and provide a new insight for peripheral immunotherapy in ALS, and then we will further verify in the follow-up study.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of the Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University (2022-R196). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
JY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Writing – original draft. MT: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. LZ: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft. CX: Investigation, Resources, Software, Writing – original draft. JH: Data curation, Software, Writing – original draft. QL: Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. HD: Conceptualization, Investigation, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. RL: Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Writing – review & editing. YL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (H2021206310), the Key Project of Technical Health Research and Achievement Transformation of Hebei Provincial Department of Health (zh2018004), and Training Project for Professional Leaders of Hebei Provincial Department of Finance and the Health Commission of Hebei Province (20240205).
Acknowledgments
We thank Hua kang Liu for information in patients with ALS, PD, and ACVD.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Turner, MR, Hardiman, O, Benatar, M, Brooks, BR, Chio, A, de Carvalho, M, et al. Controversies and priorities in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. (2013) 12:310–22. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70036-X
2. Rosen, DR, Siddiquet, T, Pattersont, D, Figlewicz, DA, Sapp, P, Hentatit, A, et al. Mutations in cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene are associated with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nature. (1993) 362:59–62. doi: 10.1038/362059a0
3. Renton, AE, Chiò, A, and Traynor, BJ. State of play in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis genetics. Nat Neurosci. (2013) 17:17–23. doi: 10.1038/nn.3584
4. Goutman, SA, Savelieff, MG, Jang, DG, Hur, J, and Feldman, EL. The amyotrophic lateral sclerosis exposome: recent advances and future directions. Nat Rev Neurol. (2023) 19:617–34. doi: 10.1038/s41582-023-00867-2
5. Goyal, NA, Berry, JD, Windebank, A, Maragakis, NJ, van den Berg, LH, Genge, A, et al. Addressing heterogeneity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis clinical trials. Muscle Nerve. (2020) 62:156–66. doi: 10.1002/mus.26801
6. Kwon, HS, and Koh, S-H. Neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative disorders: the roles of microglia and astrocytes. Transl Neurodegener. (2020) 9:42. doi: 10.1186/s40035-020-00221-2
7. Xu, L, He, D, and Bai, Y. Microglia-mediated inflammation and neurodegenerative disease. Mol Neurobiol. (2015) 53:6709–15. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9593-4
8. Subhramanyam, CS, Wang, C, Hu, Q, and Dheen, ST. Microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Semin Cell Dev Biol. (2019) 94:112–20. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2019.05.004
9. La Vitola, P, Balducci, C, Baroni, M, Artioli, L, Santamaria, G, Castiglioni, M, et al. Peripheral inflammation exacerbates α-synuclein toxicity and neuropathology in Parkinson's models. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. (2020) 47:43–60. doi: 10.1111/nan.12644
10. Garofalo, S, Cocozza, G, Porzia, A, Inghilleri, M, Raspa, M, Scavizzi, F, et al. Natural killer cells modulate motor neuron-immune cell cross talk in models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:1773. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15644-8
11. Chiot, A, Zaïdi, S, Iltis, C, Ribon, M, Berriat, F, Schiaffino, L, et al. Modifying macrophages at the periphery has the capacity to change microglial reactivity and to extend ALS survival. Nat Neurosci. (2020) 23:1339–51. doi: 10.1038/s41593-020-00718-z
12. Beers, DR, and Appel, SH. Immune dysregulation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: mechanisms and emerging therapies. Lancet Neurol. (2019) 18:211–20. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30394-6
13. Lu, CH, Allen, K, Oei, F, Leoni, E, Kuhle, J, Tree, T, et al. Systemic inflammatory response and neuromuscular involvement in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. (2016) 3:e244. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000244
14. McCombe, PA, Lee, JD, Woodruff, TM, and Henderson, RD. The peripheral immune system and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Front Neurol. (2020) 11:279. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00279
15. Alexianu, ME, Kozovska, M, and Appel, SH. Immune reactivity in a mouse model of familial ALS correlates with disease progression. Neurology. (2001) 57:1282–9. doi: 10.1212/WNL.57.7.1282
16. Lall, D, and Baloh, RH. Microglia and C9orf72 in neuroinflammation and ALS and frontotemporal dementia. J Clin Invest. (2017) 127:3250–8. doi: 10.1172/JCI90607
17. Dols-Icardo, O, Montal, V, Sirisi, S, Lopez-Pernas, G, Cervera-Carles, L, Querol-Vilaseca, M, et al. Motor cortex transcriptome reveals microglial key events in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. (2020) 7:1–11. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000829
18. Migliarini, S, Scaricamazza, S, Valle, C, Ferri, A, Pasqualetti, M, and Ferraro, E. Microglia morphological changes in the motor cortex of hSOD1(G93A) transgenic ALS mice. Brain Sci. (2021) 11:1–9. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11060807
19. Yamanaka, K, and Komine, O. The multi-dimensional roles of astrocytes in ALS. Neurosci Res. (2018) 126:31–8. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2017.09.011
20. Izrael, M, Slutsky, SG, and Revel, M. Rising stars: astrocytes as a therapeutic target for ALS disease. Front Neurosci. (2020) 14:824. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00824
21. Zhao, W, Beers, DR, Liao, B, Henkel, JS, and Appel, SH. Regulatory T lymphocytes from ALS mice suppress microglia and effector T lymphocytes through different cytokine-mediated mechanisms. Neurobiol Dis. (2012) 48:418–28. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2012.07.008
22. Beers, DR, Zhao, W, Wang, J, Zhang, X, Wen, S, Neal, D, et al. ALS patients' regulatory T lymphocytes are dysfunctional, and correlate with disease progression rate and severity. JCI Insight. (2017) 2:e89530. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.89530
23. Murdock, BJ, Famie, JP, Piecuch, CE, Raue, KD, Mendelson, FE, Pieroni, CH, et al. NK cells associate with ALS in a sex- and age-dependent manner. JCI Insight. (2021) 6:1–15. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.147129
24. Shiraishi, W, Yamasaki, R, Hashimoto, Y, Ko, S, Kobayakawa, Y, Isobe, N, et al. Clearance of peripheral nerve misfolded mutant protein by infiltrated macrophages correlates with motor neuron disease progression. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:16438. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-96064-6
25. Gao, T, Huo, J, Xin, C, Yang, J, Liu, Q, Dong, H, et al. Protective effects of intrathecal injection of AAV9-RabGGTB-GFP(+) in SOD1(G93A) mice. Front Aging Neurosci. (2023) 15:1092607. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1092607
26. Shirakawa, R, Goto-Ito, S, Goto, K, Wakayama, S, Kubo, H, Sakata, N, et al. A SNARE geranylgeranyltransferase essential for the organization of the Golgi apparatus. EMBO J. (2020) 39:e104120. doi: 10.15252/embj.2019104120
27. Bai, L, Wang, Y, Huo, J, Li, S, Wen, Y, Liu, Q, et al. Simvastatin accelerated motoneurons death in SOD1(G93A) mice through inhibiting Rab7-mediated maturation of late autophagic vacuoles. Cell Death Dis. (2021) 12:392. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03669-w
28. Yang, J, Xin, C, Huo, J, Li, X, Dong, H, Liu, Q, et al. Rab Geranylgeranyltransferase subunit Beta as a potential Indicator to assess the progression of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain Sci. (2023) 13:1531. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13111531
29. Taheri, M, Ghafouri-Fard, S, Sayad, A, Arsang-Jang, S, Mazdeh, M, Toghi, M, et al. Assessment of protein Prenylation pathway in multiple sclerosis patients. J Mol Neurosci. (2018) 64:581–90. doi: 10.1007/s12031-018-1052-z
30. Deraeve, C, Guo, Z, Bon, RS, Blankenfeldt, W, DiLucrezia, R, Wolf, A, et al. Psoromic acid is a selective and covalent Rab-prenylation inhibitor targeting autoinhibited RabGGTase. J Am Chem Soc. (2012) 134:7384–91. doi: 10.1021/ja211305j
31. Brooks, BR, Miller, RG, Swash, M, and Munsat, TL. El Escorial revisited: revised criteria for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord. (2000) 1:293–9. doi: 10.1080/146608200300079536
32. Li, J, Jin, M, Wang, L, Qin, B, and Wang, K. MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease in China. J Neurol. (2016) 264:476–81. doi: 10.1007/s00415-016-8370-2
34. Quek, H, Cuni-Lopez, C, Stewart, R, Colletti, T, Notaro, A, Nguyen, TH, et al. ALS monocyte-derived microglia-like cells reveal cytoplasmic TDP-43 accumulation, DNA damage, and cell-specific impairment of phagocytosis associated with disease progression. J Neuroinflammation. (2022) 19:58. doi: 10.1186/s12974-022-02421-1
35. Schain, M, and Kreisl, WC. Neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative disorders-a review. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. (2017) 17:25. doi: 10.1007/s11910-017-0733-2
36. Liu, Z, Cheng, X, Zhong, S, Zhang, X, Liu, C, Liu, F, et al. Peripheral and central nervous system immune response crosstalk in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Front Neurosci. (2020) 14:575. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00575
37. Anderson, FL, Biggs, KE, Rankin, BE, and Havrda, MC. NLRP3 inflammasome in neurodegenerative disease. Transl Res. (2023) 252:21–33. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2022.08.006
38. Keller, AF, Gravel, M, and Kriz, J. Treatment with minocycline after disease onset alters astrocyte reactivity and increases microgliosis in SOD1 mutant mice. Exp Neurol. (2011) 228:69–79. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2010.12.010
39. Gordon, PH, Moore, DH, Miller, RG, Florence, JM, Verheijde, JL, Doorish, C, et al. Efficacy of minocycline in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a phase III randomised trial. Lancet Neurol. (2007) 6:1045–53. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(07)70270-3
Keywords: RABGGTB, mononuclear cells-macrophages, ALS, PD, ACVD
Citation: Yang J, Tian M, Zhang L, Xin C, Huo J, Liu Q, Dong H, Li R and Liu Y (2024) Assessment of Rab geranylgeranyltransferase subunit beta in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 15:1447461. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1447461
Edited by:
Jens Schmidt, Immanuel Klinik Rüdersdorf, GermanyReviewed by:
Mariam Kekenadze, University College London, United KingdomMuhammad Zahid Iqbal, Lahore University of Biological and Applied Sciences, Pakistan
Copyright © 2024 Yang, Tian, Zhang, Xin, Huo, Liu, Dong, Li and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rui Li, bGlydWlAaGIyaC5jb20=; Yaling Liu, bGl1eWFsaW5nQGhiMmguY29t
 Jing Yang
Jing Yang Mei Tian1,2,3
Mei Tian1,2,3 Qi Liu
Qi Liu Hui Dong
Hui Dong Yaling Liu
Yaling Liu