- 1Tuina Department, First Teaching Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin, China
- 2National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Level Three Laboratory for Tuina Technique Biological Effects, Tianjin, China
Background: The efficacy and acupoint selection of acupuncture in treating chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) remain controversial. This study aims to explore the specific efficacy and acupoint selection of acupuncture in treating CIPN through a meta-analysis and data mining.
Methods: Searching for clinical trials on acupuncture treatment for CIPN in 8 databases, evaluating its efficacy and safety through a meta-analysis, and exploring its acupoint selection through data mining.
Results: The meta-analysis included 21 studies and 2,121 patients, showing that compared with the control group, the acupuncture group could significantly improve neuropathic pain intensity (SMD = −0.66, 95% CI [−1.07, −0.25], p = 0.002), significantly reduce the NCI-CTCAE (MD = −0.29, 95%CI [−0.50, −0.08], p < 0.01), significantly reduce the FACT-NXT score (MD = 2.09, 95% CI [0.73,3.45], p < 0.05), significantly increase the motor conduction velocities (MCV) of median nerve (MD = 2.38, 95% CI [2.10, 2.67], p < 0.001), the sensory conduction velocities (SCV) of the median nerve (MD = 0.56, 95 %CI [−1.45, 2.57], p = 0.58), the SCV of the tibial nerve (MD = 1.78, 95% CI [0.50, 3.05], p < 0.01), and the SCV of sural nerves (MD = 4.60, 95% CI [0.17, 9.02], p < 0.05), as well as improving the quality of life score (MD =7.35, 95% CI [1.53, 13.18], p = 0.01). Data mining showed that the core acupoints for acupuncture treatment of CIPN were LI4, ST36, LI11, LR3, and SP6.
Conclusion: Acupuncture can improve the neuropathic pain intensity, the intensity of the CIPN, MCV of the median nerve, SCV of the tibial nerve and peroneal nerve, quality of life, and has good safety in CIPN patients. LI4 (Hegu), ST36 (Zusanli), LI11 (Quchi), LR3 (Taichong), and SP6 (Sanyinjiao) are the core acupuncture points for treating CIPN, and this protocol has the potential to become a supplementary treatment for CIPN.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero, identifier CRD42024551137.
1 Introduction
Cancer remains the leading cause of death worldwide, with approximately 16.5 million cancer survivors in the United States in 2016 and a projected number of nearly 26.1 million by 2040 (1). Despite the remarkable clinical results of chemotherapy in cancer treatment, numerous patients who undergo chemotherapy experience chronic pain that severely affects their quality of life. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) is a common complication after treatment with various commonly used anticancer drugs (2), such as platinum drugs, taxanes, vincristine drugs, and proteasome inhibitors can induce CIPN, which is one of the most complex symptoms in the clinical treatment of cancer patients (3). A meta-analysis of 31 studies, 4,179 cancer patients, found that the incidence was 68.1 and 60%, respectively, at 1 and 3 months after the start of chemotherapy, and the incidence remained at 30.0% after 6 months (4). Patients experience a range of symptoms and signs, including paresthesia, such as tingling, pain, numbness, or burning. Motor dysfunction: muscle weakness or impaired coordination that may cause difficulty walking or a reduced ability to hold objects. Autonomic dysfunction: May cause abnormal sweating, fluctuating blood pressure, digestive problems, or difficulty urinating (5, 6). These symptoms affect the patients’ sensory function, motor abilities, quality of sleep, psychological status and other aspects, and seriously reduce the quality of life for patients (7, 8). There are very limited available and effective clinical treatment strategies for CIPN. And to relieve the symptoms, occasionally the drug dose has to be reduced or temporarily stopped, which undoubtedly constitutes a great limitation to the treatment of cancer (9).
Acupuncture, as a kind of traditional Chinese medicine therapy, can stimulate the body surface acupoints, give play to the proximal treatment, remote treatment, bidirectional regulation, special functions of acupoints, and adjust the functions of qi, blood and, zang-fu organs through the whole-body meridian conduction, to achieve the purpose of preventing and treating diseases. Acupuncture treatment may alleviate the neurotoxicity of CIPN by down-regulating the level of Na + channels, promoting the secretion of neurotransmitters such as glutamate, inhibiting oxidative stress, and promoting the release of anti-inflammatory cytokines.
However, the efficacy and point selection of acupuncture in the treatment of CIPN remain controversial (10), due to the lack of large-scale the clinical trials, and conflicting results have been reported in relevant randomized controlled trials. Recently, several high-level clinical studies were published. At present, randomized controlled trials of acupuncture intervention timing, course of treatment, intervention type, and treatment frequency are different, resulting in poor quality of evidence on the use of acupuncture for clinical treatment of patients with CIPN. As a new method of objective analysis based on statistical principles, meta-analysis has received more and more attention and application (11–14). This method can comprehensively and objectively analyze the results of multiple independent studies with the same research purpose and obtain comprehensive conclusions. Therefore, this study will systematically evaluate the intervention effect of acupuncture on CIPN. This review differs from previous reviews in that it considers a wider range of outcome measures and analyses the effects of acupuncture intervention variables. At the time, explore the core acupoints of acupuncture on CIPN by using data mining technology, in order to provide reliable data for clinical applications.
2 Materials and methods
The present study was conducted by the 2020 Statement on Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA 2020). This systematic review and meta-analysis has been registered with the PROSPERO Registry (CRD42022370952).
2.1 Meta-analysis methods
2.1.1 Literature search
The two researchers independently searched Pubmed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Embase, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang Database, Weipu (VIP) Database, Sinomed (CBM), self-built repositories - published articles in January 2024. In addition, references to clinical trial registries and websites, as well as relevant reviews and systematic reviews, were searched for all eligible studies. The search strategy is presented in the Supplementary material 1.
2.1.2 Inclusion criteria
(1) The study type was a randomized controlled clinical trial. (2) Participants were cancer patients with or without CPNI, regardless of cancer type or stage. (3) The intervention group was acupuncture/electroacupuncture or acupuncture/electroacupuncture combined with conventional rehabilitation/western medicine therapy. (4) The control group was treated with sham acupuncture or conventional rehabilitation or other Western medicine. (5) Primary outcome measures include any related measures of CIPN.
2.1.3 Exclusion criteria
(1) Studies comparing different types of acupuncture. (2) Studies with a total sample size of less than 10. (3) Conference abstracts, non-randomized controlled trials, reviews, systematic reviews, qualitative studies, protocols, case reports, etc.
2.1.4 Literature selection and data extraction
Two researchers (LLM and HYX) independently conducted literature screening and data extraction. Using Endnote 20.1 software, they removed duplicate articles. Following that, they screened out studies that did not meet the criteria by reading the titles and abstracts. Finally, they read the full texts of the remaining articles, determined the final selection based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria, and then extracted data from randomized controlled trials. First author, publication year, study subjects, study design (randomized, blind), intervention measures, intervention period, evaluation measures, outcomes, and adverse events were included. Subgroups were split if there were three - or multi-arm studies. If data is missing, the author will be contacted via email for further information. Any disagreement is reviewed by a third reviewer (TT) and resolved through discussion by all reviewers.
2.1.5 Risk of bias assessment
The risk of bias in the included studies was assessed by two investigators (LLM and ACF) using the Cochrane Manual of Systematic Review 5.1.0 RCT Bias Risk Assessment tool, encompassing seven aspects: random sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding of patients and investigators, blinding of outcome evaluators, incomplete outcome data reporting, selective reporting, and other sources of bias. In cases where there was disagreement between the two evaluators, a third evaluator (LHN) was involved to resolve any discrepancies.
2.1.6 Statistical analysis
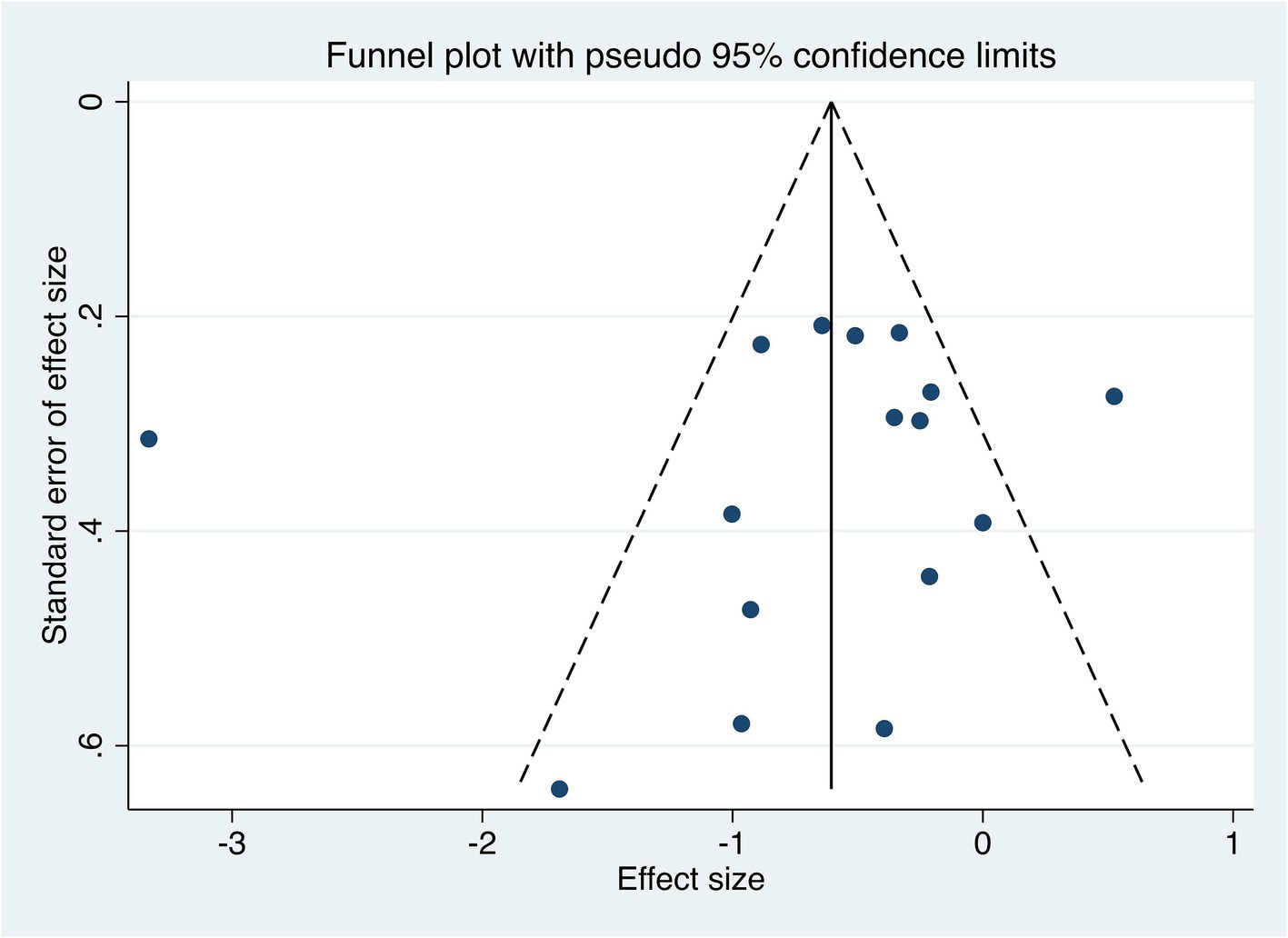
The meta-analysis was performed using Revman 5.3 software. Means and standard deviations of pretreatment and posttreatment results were collected for each group. Multiple levels of data are combined as continuous variables. Continuity variables were expressed in weighted mean difference (MD) or standardized mean difference (SMD), and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated. Referring to the study by Chen HT, for studies with two or more interventions/controls, participants were divided into different subgroups for assessment to prevent sample size overlap (15). The heterogeneity among the included studies was analyzed by χ2 test (α = 0.05), and the heterogeneity was quantitatively determined by I2. When I2 = 0%, no heterogeneity was considered, and the fixed effect model was used to combine the data. When I2 was less than 50%, the heterogeneity was not considered significant, and the random effects model was conservatively used to combine the data. When I2 ≥ 50%, the heterogeneity is considered significant, and the random effects model is used to combine the data. Sources of heterogeneity were analyzed as far as possible, and obvious clinical heterogeneity was treated by sensitivity analysis or descriptive analysis (11, 12, 16). If more than 10 studies were included, the Begg’s tests and funnel plot were analyzed using Stata 17 software. If the funnel plot is symmetrical and p > 0.05, then the possibility of publication bias is relatively low.
2.2 Data mining methods
2.2.1 Literature search
The literature retrieval strategy is the same as meta-analysis.
2.2.2 Inclusion criteria
(1) Randomized controlled trials or case–control studies. (2) The included subjects were patients with CIPN. (3) The experimental group was treated with acupuncture, and the acupoint records were complete. (4)The efficacy of acupuncture was definite.
2.2.3 Exclusion criteria
(1) Duplicate publications. (2) Literature on non-acupuncture therapy. (3)The full study was not available.
2.2.4 Standardization of acupoint names
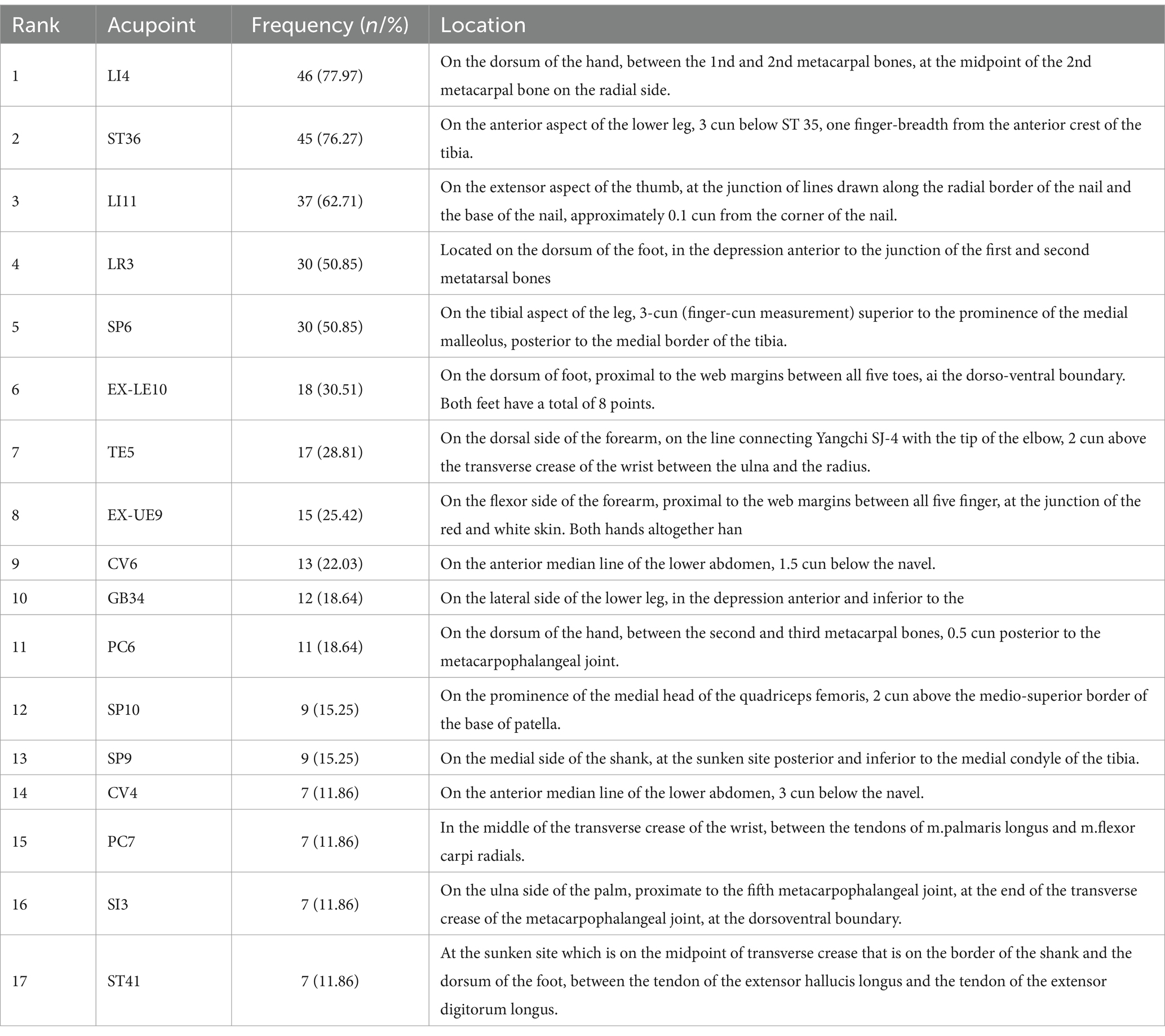
The name of acupoints was standardized according to the name and Location of acupoints. For example, “Zusanli” is standardized as “ST36” and “Bafeng” is standardized as “EX-LE10.”
2.2.5 Data analysis
The Excel 2021 software was used to calculate the frequency of acupoints. R4.3.1 software was used to analyze association rules. Association rules analysis using arules software package, Apriori algorithm, set minimum support of 0.3, minimum confidence of 0.6, lift >1, and use arules Viz software package for visualization.
3 Results
3.1 Literature screening
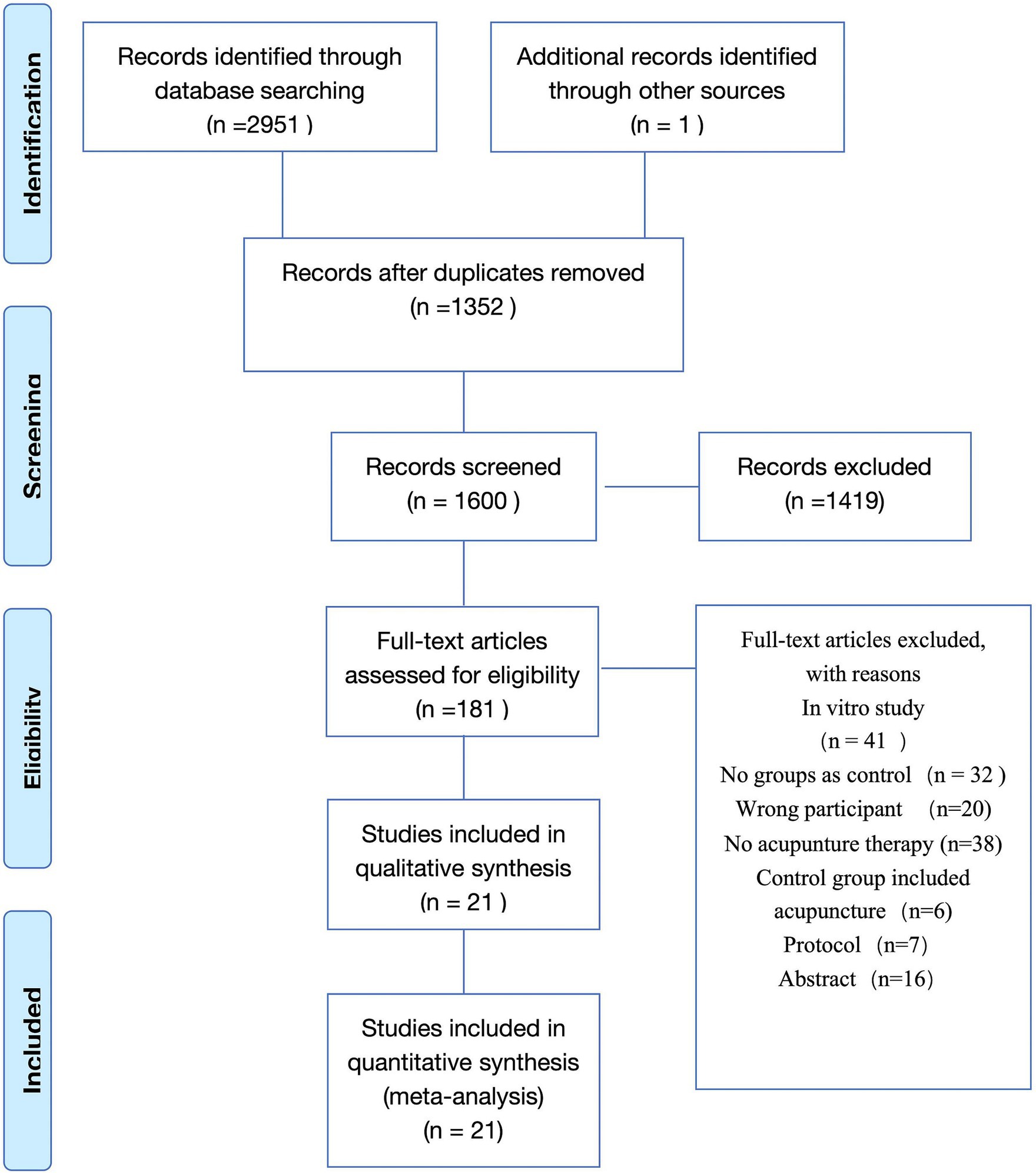
The article screening flow chart is in Figure 1. A total of 2,952 literature were searched, among which 1,352 duplicate literature were excluded, 1,419 irrelevant literature were excluded by title and abstract, 160 literature were excluded by full-text review, and 21 studies (10, 17–36) were finally included (Figure 1).
3.2 Basic characteristics of included studies
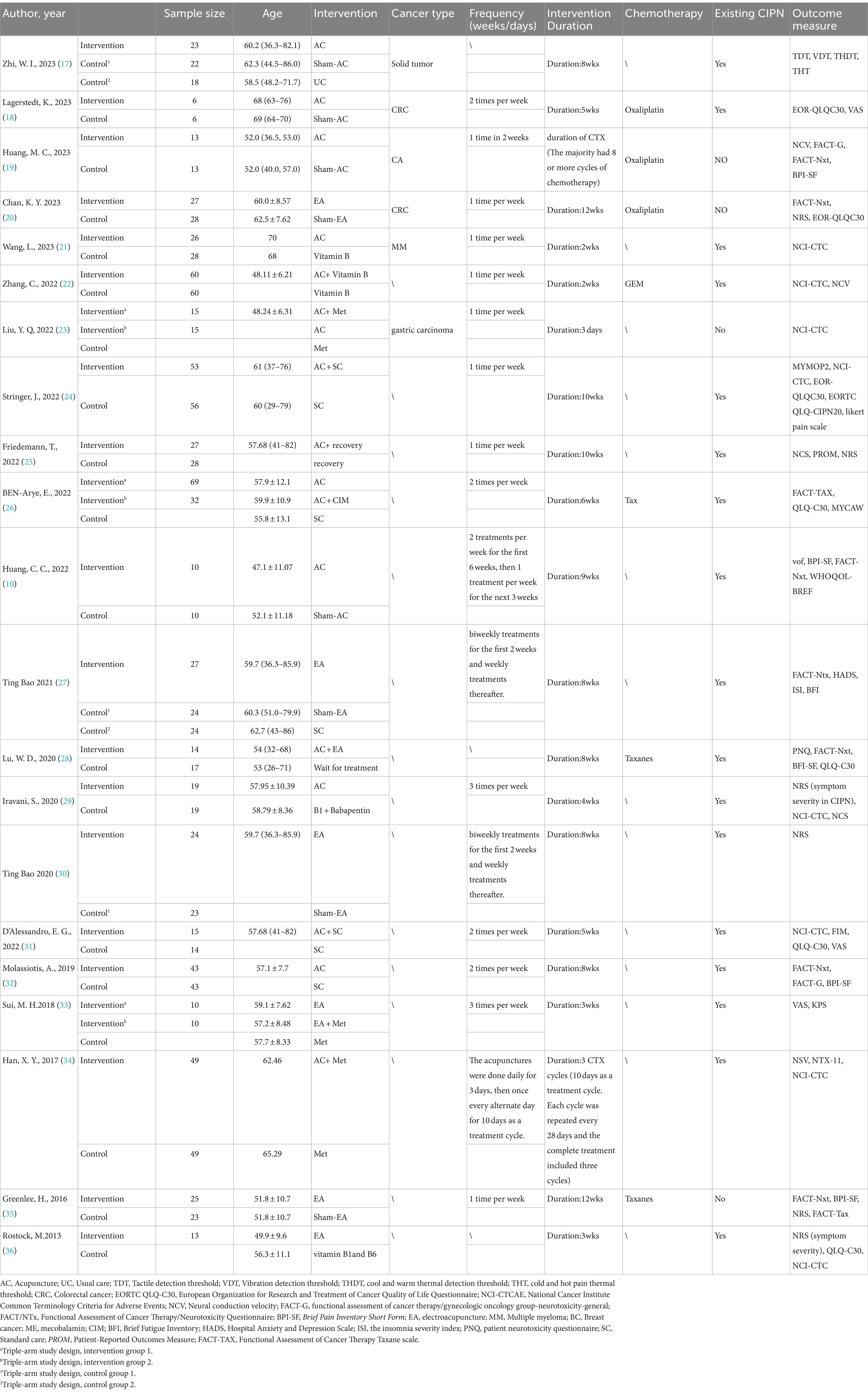
A total of 21 clinical studies were included, of which 3 were published in Chinese and 18 in English. The studies were published between 2013 and 2023, with 17 (80.95%) published in the last five years. Of the included studies, 10 studies were conducted in China, 5 studies in the United States, 1 study in collaboration with institutions in China and Iran, 1 in Brazil, 1 in Sweden, and 1 in Germany. A total of 2,121 subjects were included, including 1,048 in the experimental group and 1,073 in the control group. Baseline information such as sex, age, cancer type, and chemotherapy regimen were comparable between the experimental and control groups. The basic characteristics of the included studies are shown in Table 1.
3.3 Risk of bias assessment
The risk of random method bias was not clear in 1 study, and 11 studies describing envelopes and other ways to assign hiding were rated as low risk. Due to the special nature of acupuncture, 14 studies did not implement blind interventions for patients and participants rated as high risk. The risk of other bias was low. The details are shown in Figure 2.
3.4 Meta-analysis results
3.4.1 Pain intensity
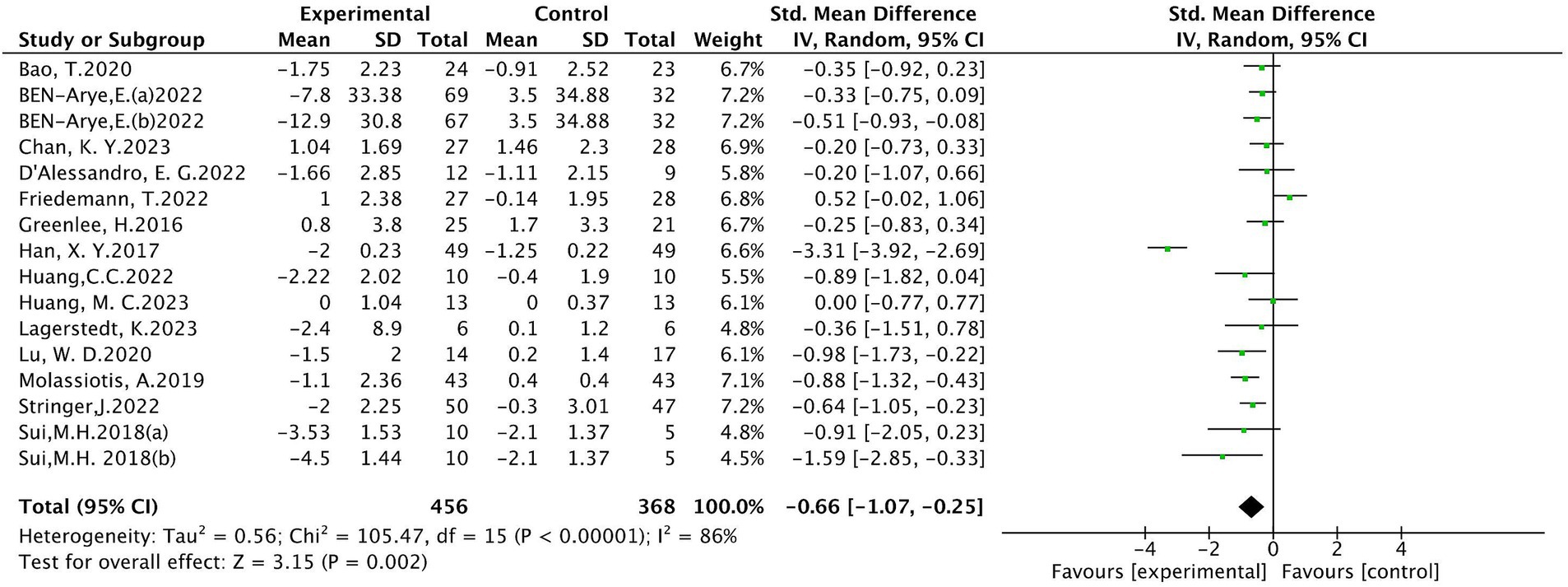
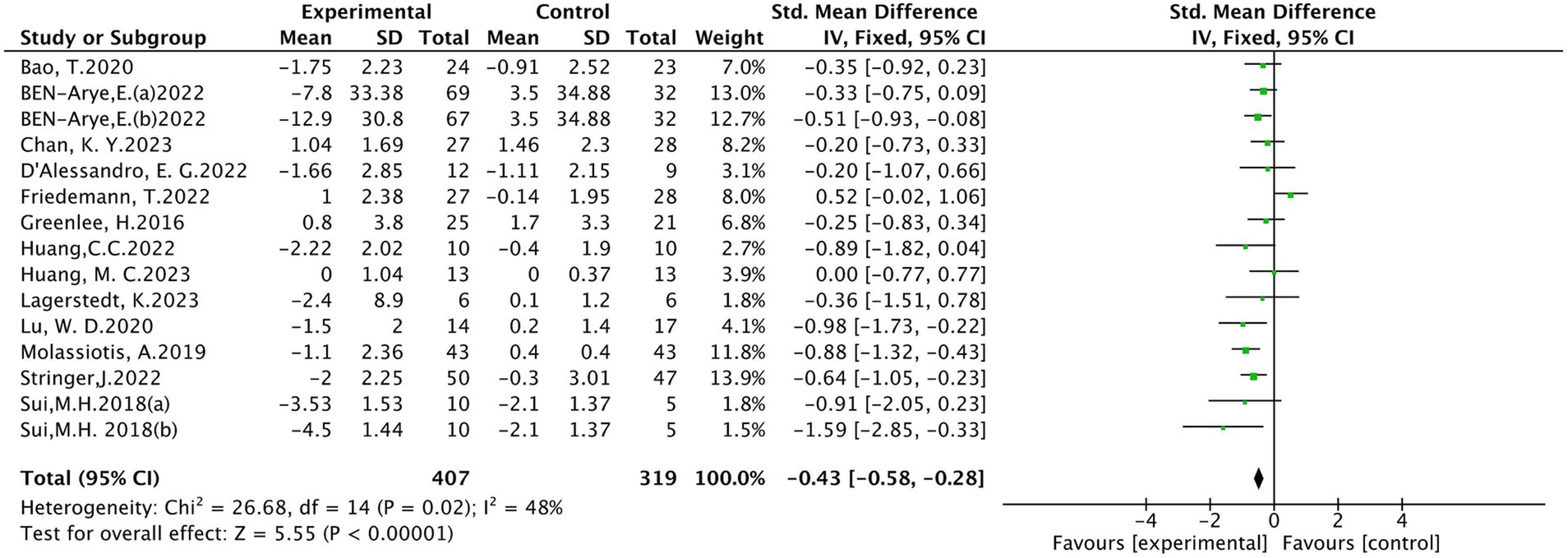
Sixteen (10, 18–20, 24–26, 28, 30–35) studies evaluated peripheral neuropathic pain intensity involving a total of 824 patients. Of these, 4 studies (18, 31, 33, 34) were evaluated using the visual analogue scale (VAS), 5 studies (10, 24, 28, 32, 35) using BPI-SF, and 4 studies (19, 20, 25, 30) using the Numeric Rating Scale (NRS), 1 study (26) using EORTC QLQ-30-Pain scale, The results of heterogeneity analysis show p < 0.001 and I2 = 86%, indicating a high heterogeneity, so a random effects model was used for the analysis. The meta-analysis results showed that compared with the control group, the pain intensity in the acupuncture group decreased more (SMD = −0.66, 95% CI [−1.07, −0.25], p = 0.002), illustrated in Figure 3. Sensitivity analysis showed that after removal of a study (34), I2 decreased to 48% (SMD = −0.43, 95% CI [−0.58, −0.28], p < 0.001) (see Figure 4). The intervention period of this study was greatly larger than that of other studies (3 chemotherapy cycles), suggesting that this study may be the source of high heterogeneity, and the length of acupuncture intervention affects the difference in acupuncture treatment results.
3.4.2 NCI-CTCAE
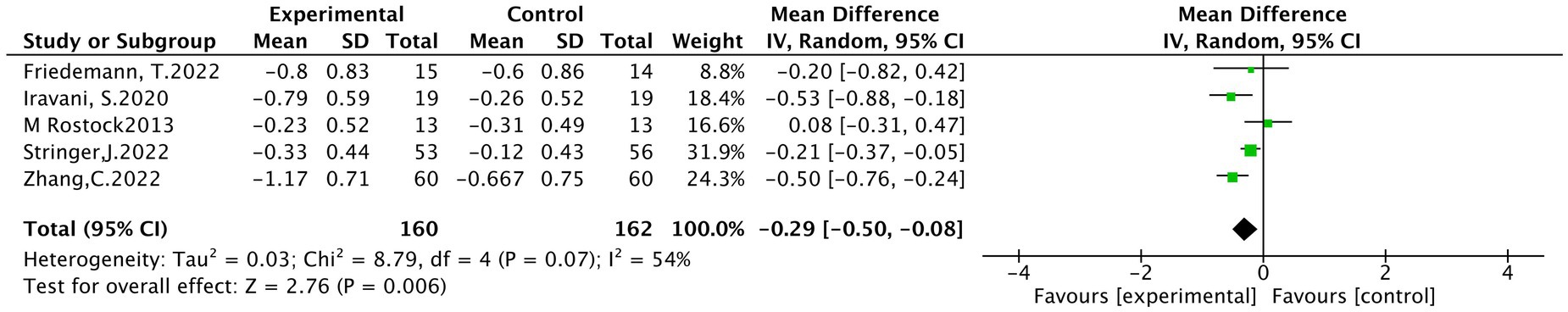
It into five studies (22, 24, 25, 29, 36), involving 322 patients, 160 in the treatment group and 162 people in the control group. A random effects model was used for analysis. Meta-analysis showed a statistically significant difference in the grade of peripheral neurotoxicity between the treatment and control groups (MD = −0.29, 95% CI [−0.50, −0.08], p < 0.001), as shown in Figure 5.
3.4.3 FACT-NXT
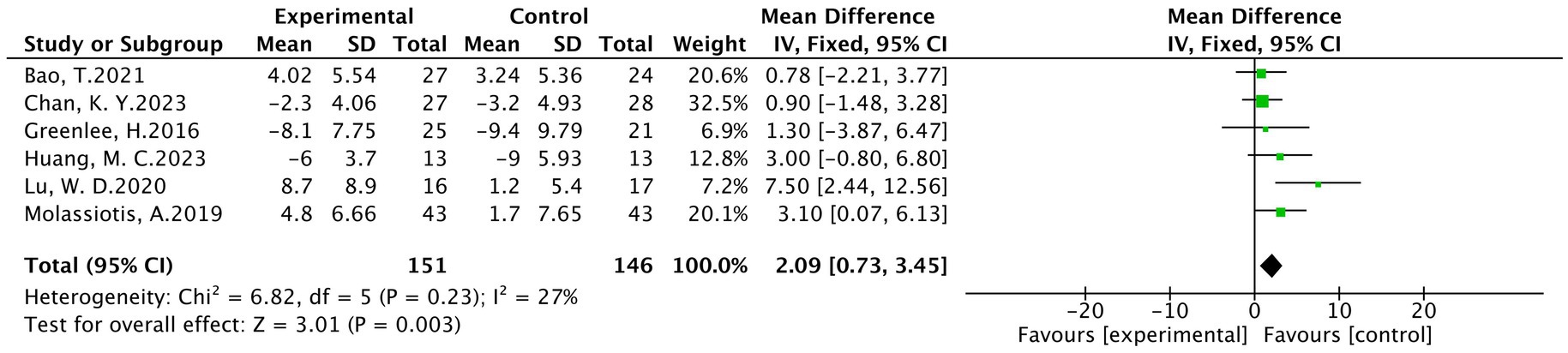
A total of six studies (19, 20, 27, 28, 32, 35) were included, involving 297 patients, of which 151 were in the treatment group and 146 were in the control group. The results of heterogeneity analysis show p = 0.23 and I2 = 27%. Therefore, a fixed effects model was used for analysis. Meta-analysis showed statistically significant between the treatment and control groups (MD = 2.09, 95% CI [0.73,3.45], p < 0.05), as detailed in Figure 6.
3.4.4 Neural conduction velocity
(1) Motor conduction velocities (MCV) of median nerves
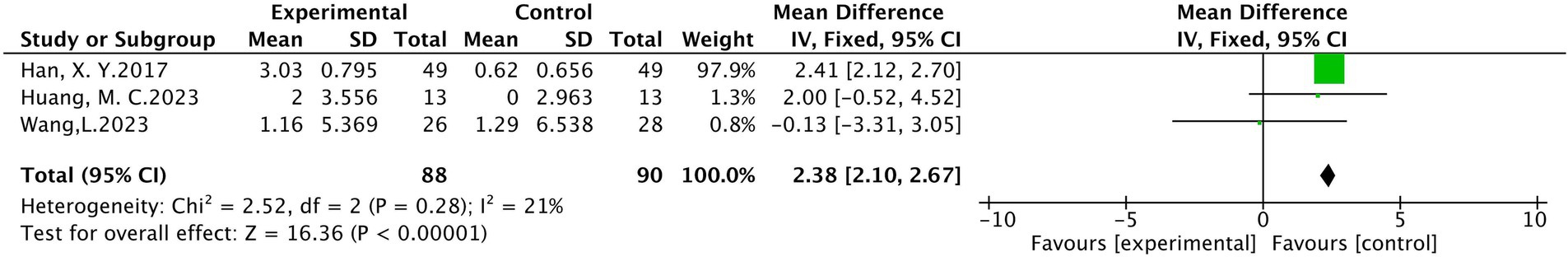
In total, three studies were included, involving 178 patients (19, 21, 34), with 88 patients in the treatment group and 90 in the control group. The results of heterogeneity analysis show p = 0.28 and I2 = 21%, indicating homogeneity among the statistical variables. A fixed effects model analysis showed that there was a statistically significant difference in the motor conduction velocity of the median nerve between the treatment group and the control group (MD = 2.38, 95% CI [2.10, 2.67], p < 0.001), illustrated in Figure 7.
(2) Sensory conduction velocities (SCV) of the median nerve
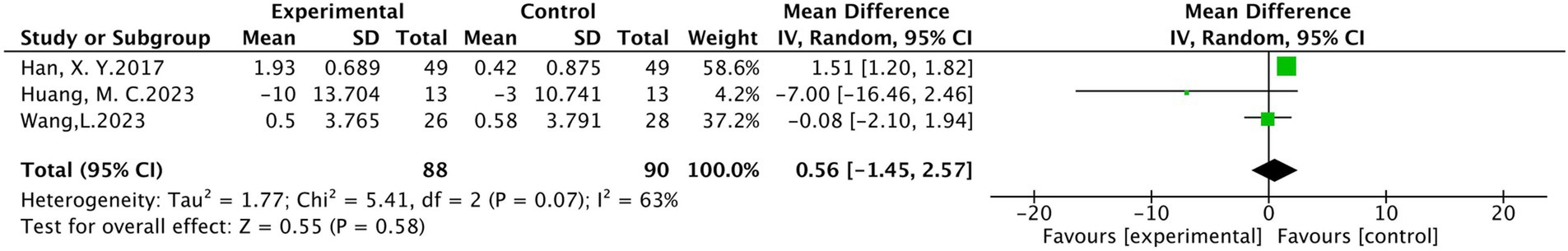
There were three studies included in the analysis, involving a total of 178 patients (19, 21, 34), of which 88 were in the treatment group and 90 were in the control group. The results of heterogeneity analysis show p = 0.07 and I2 = 63%, indicating a high heterogeneity. The random effects model analysis showed no statistically significant difference between the treatment group and the control group in median nerve conduction velocity (MD = 0.56, 95 %CI [−1.45, 2.57], p = 0.58), as detailed in Figure 8.
(3) SCV of the tibial nerve
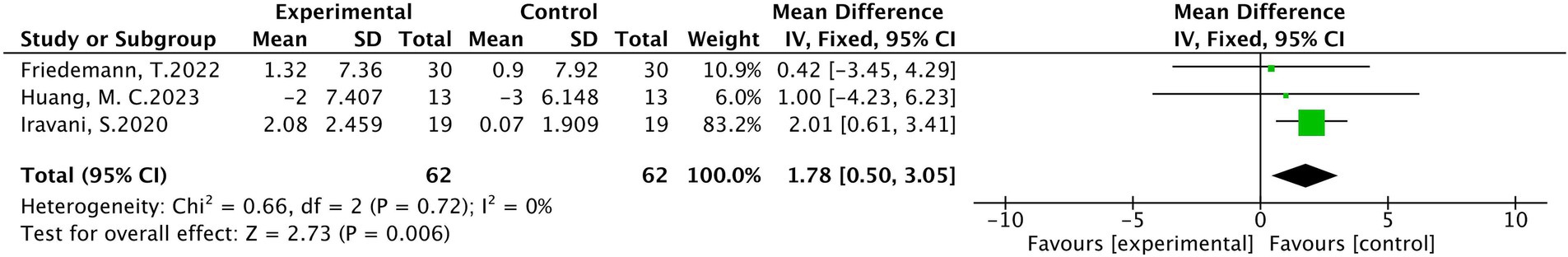
In a total of three studies involving 124 patients (19, 25, 29), with 62 patients in the treatment group and 62 in the control group. The results of heterogeneity analysis show p = 0.72 and I2 = 0%, indicating homogeneity among various statistics. A fixed effects model analysis showed that there was a statistically significant difference in the median nerve motor conduction velocity between the treatment group and the control group (MD = 1.78, 95% CI [0.50, 3.05], p < 0.01), These findings are presented in Figure 9.
(4) SCV of the sural nerver
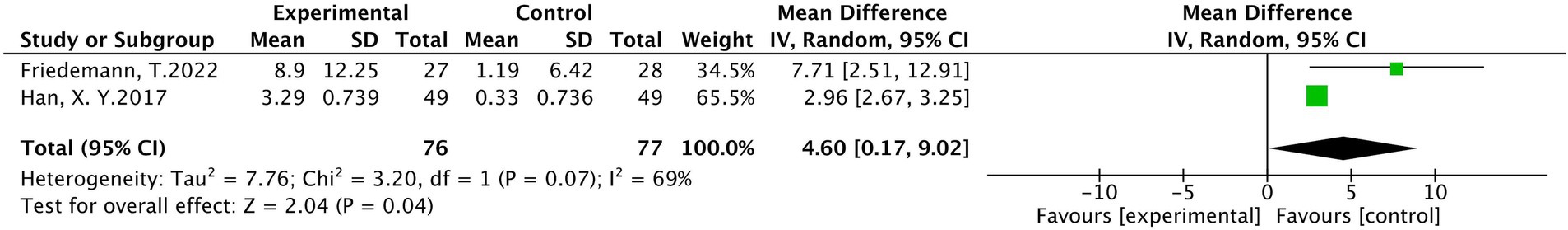
A total of 2 studies were included (25, 34) involving 153 patients, with 76 in the treatment group and 77 in the control group. The results of heterogeneity analysis show p = 0.07 and I2 = 69%, indicating a high heterogeneity. The random effects model analysis showed that there was a statistically significant difference in the median nerve motor conduction velocity between the treatment group and the control group (MD = 4.60, 95% CI [0.17, 9.02], p < 0.05), as shown in Figure 10.
3.4.5 Quality of life score (QOL)
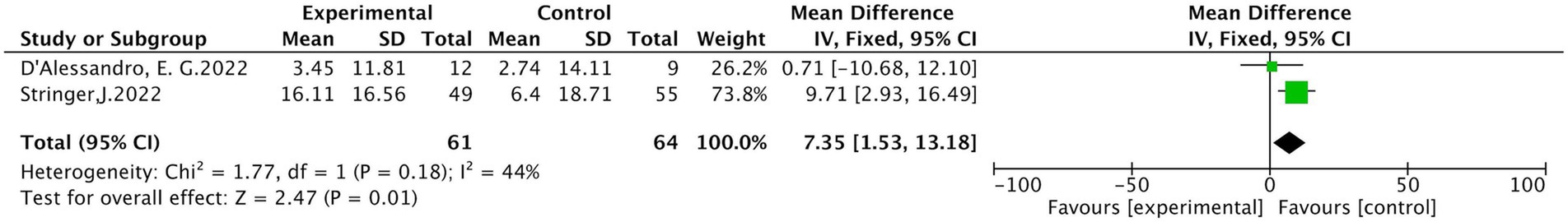
Two studies (24, 31) reported the total score of the EORTC QLQ-30. The results of heterogeneity analysis show p = 0.18 and I2 = 44%, indicating moderate heterogeneity. The fixed effects model analysis showed a statistically significant difference in scores between the treatment and control groups (MD =7.35, 95% CI [1.53, 13.18], p = 0.01), detailed in Figure 11.
3.4.6 Other indicators not combined
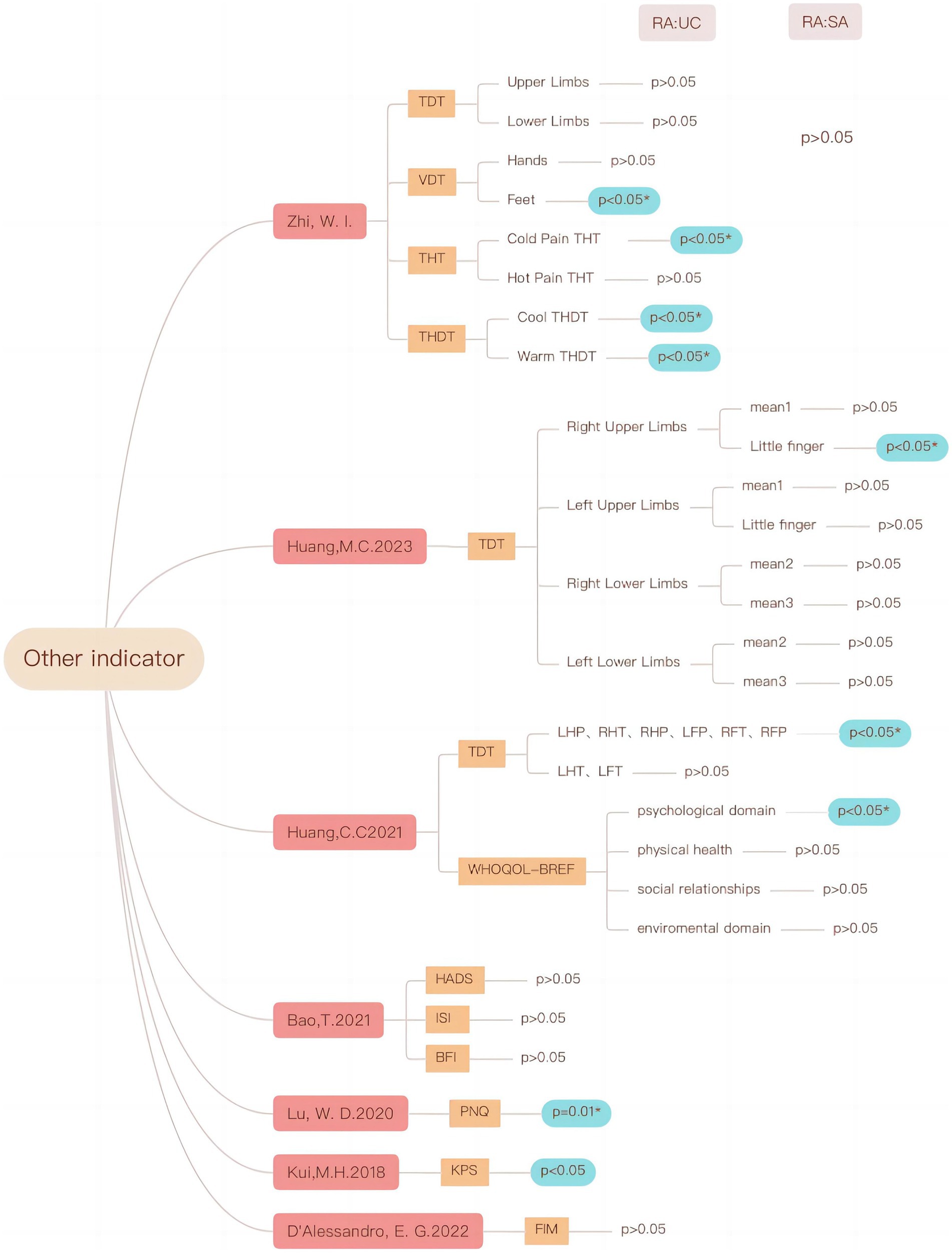
Due to the variety of CIPN indicators, there are both subjective and objective indicators, and individual indicators are reported less frequently or difficult to combine, for example, the results of different vibration sensing detection locations are very different. Therefore additional indicators are summarized. The results showed that acupuncture in patients with CIPN may be at the threshold of vibration sensation, cool and warm thermal detection threshold (THDT), cold and hot pain thermal threshold, the quality of life, and so on (see Figure 12).
3.4.7 Subgroup analysis
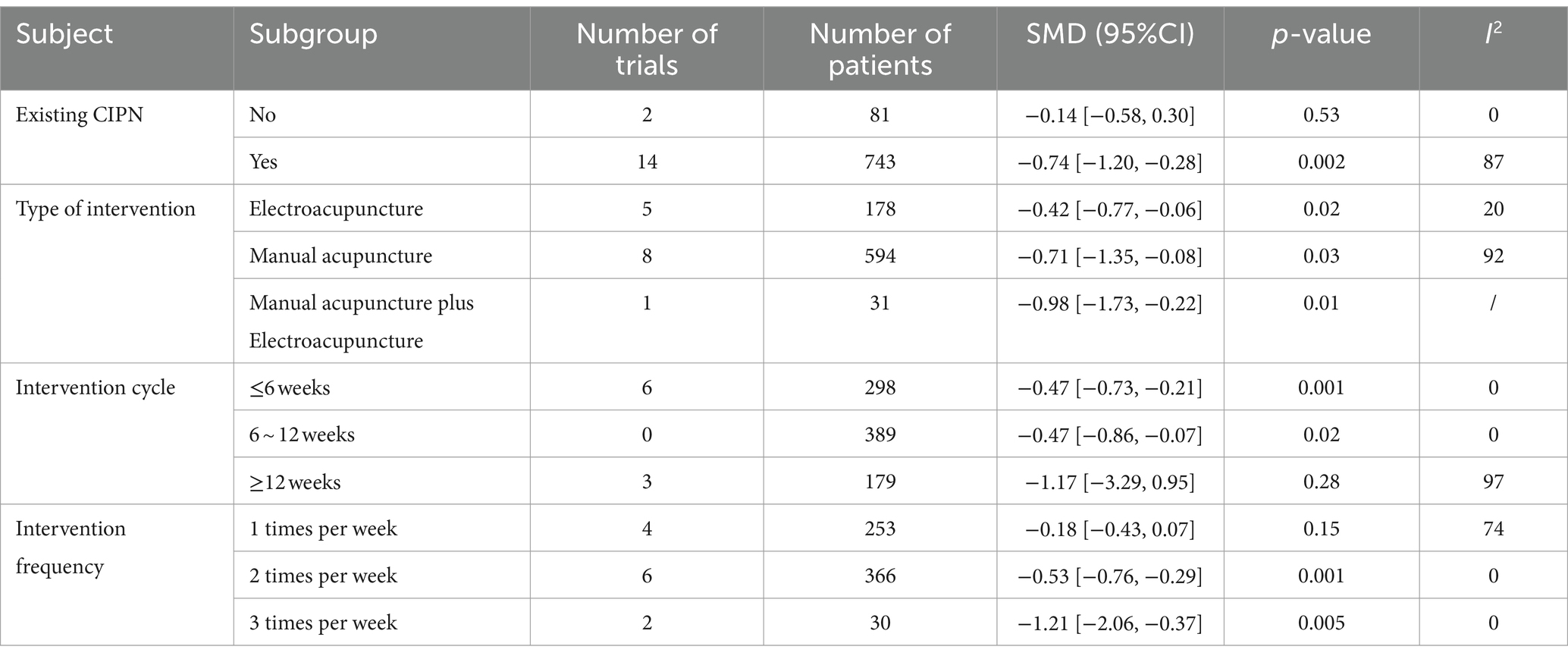
In subgroup analysis, the pain intensity was used as the outcome, and the influence of acupuncture intervention time, type of intervention, treatment duration, and weekly intervention frequency were discussed. The results showed that prophylactic acupuncture intervention did not effectively reduce pain intensity before CIPN (SMD = −0.11, 95%CI −1.46 to 0.24, p = 0.53). Acupuncture after the onset of CIPN can effectively reduce pain intensity (SMD = −0.80, 95% CI −1.34 to −0.26, p < 0.05). Subgroup analysis according to intervention type showed that electropuncture (SMD = −0.42, 95%CI −0.77 to −0.06, p = 0.02), hand acupuncture (SMD = −0.71, 95%CI −1.35 to −0.08, p = 0.03) and electropuncture combined plus hand acupuncture (SMD = −0.98, 95%CI −1.73 to −0.22, p = 0.01) were superior to control group in improving pain intensity. Judging from the course of treatment, within 6 weeks of acupuncture (SMD = −0.64, 95%CI −1.22 to −0.05, p < 0.05), within 6 to 12 weeks of acupuncture (SMD = −0.38, 95% CI 0.64 to −0.13, p < 0.01) can effectively reduce pain intensity. However, there was no significant difference in pain intensity in patients with an intervention period greater than 12 weeks (p = 0.31). From the analysis of weekly intervention frequency, acupuncture twice (SMD = −0.53, 95% CI −0.76 to −0.29, p < 0.001) or three times a week (SMD = −1.21, 95% CI −2.06 to −0.37, p < 0.01) can effectively reduce the pain intensity. However, acupuncture once a week does not show statistically significant compared with the control group (SMD = −0.18, 95% CI −0.43 to 0.07, p = 0.15) (see Table 2).
3.4.8 Safety endpoint
Five studies (20, 23–25, 29) have reported adverse reactions associated with acupuncture, which mainly included blood clotting, pain, and needle stagnation, among others. They returned to normal after treatment, and no serious adverse reactions were reported.
3.4.9 Publication bias
There are 16 studies on pain intensity as an indicator of therapeutic effect. Thus the funnel plot analysis with pain intensity as an example shows that the funnel plot for comparison of pain intensity between the two groups is roughly symmetrical and the Egger’s test p > 0.05, indicating that there is no significant risk of publication bias. These findings are presented in Figure 13.
3.5 Data mining results
3.5.1 Literature screening
A total of 2,952 studies were searched. According to inclusion and exclusion criteria, 59 clinical studies were included. A total of 77 acupoints were involved, with a total frequency of 826.
3.5.2 Frequency analysis
Frequency analysis was performed on the acupoints, resulting in 17 common acupoints with frequencies greater than 5, namely Hegu (LI4), Zusanli (ST36), Quchi (LI11), Taichong (LR3), Sanyinjiao (SP6), Bafeng (EX-LE10), Waiguan (TE5), Baxie (EX-UE9), Qihai (CV6), Yanglingquan (GB34), Neiguan (PC6), Xuehai (SP10), Yinlingquan (SP9), Guanyuan (CV4), Daling (PC7), Houxi (SI3), Jiexi (ST41), as shown in Table 3.
3.5.3 Association rules analysis
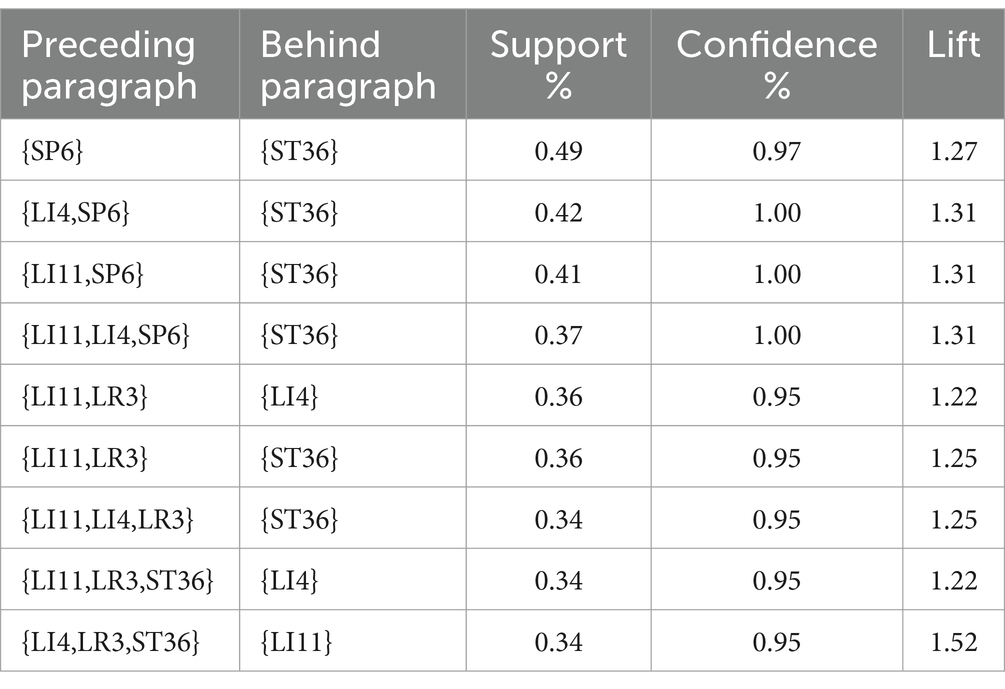
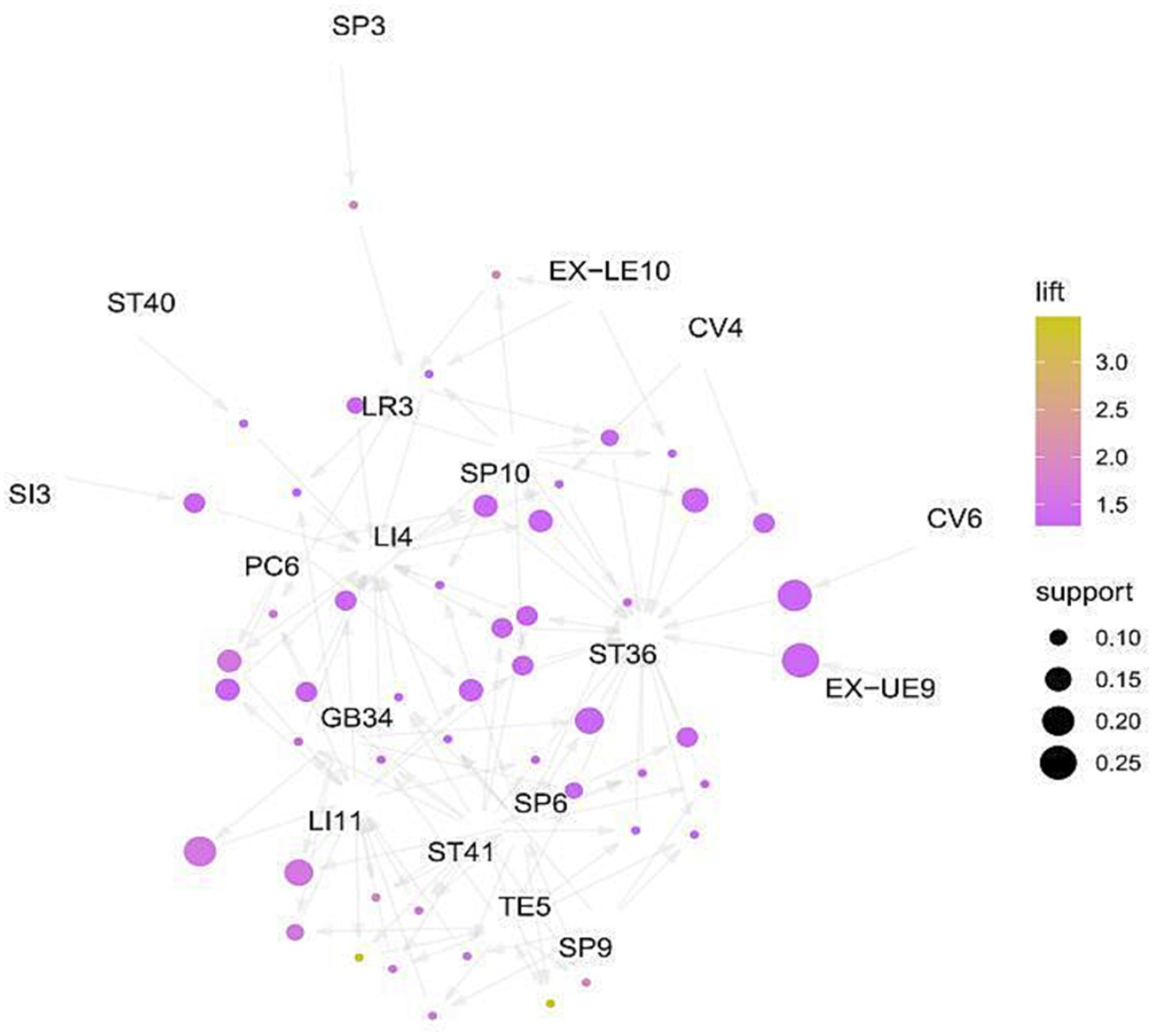
The high-frequency acupoints were introduced into R4.3.1 software, and the Apriori algorithm was used to analyze the association rules. In Rstudio, the model is constructed using the Apriori algorithm with the minimum support level set to 0.3 and the minimum confidence level set to 0.7 for association analysis, 725 rules are obtained, among which the top 5 associations of support are {SP6}= > {ST36}, {LI4, SP6}= > {ST36}, {LI11, SP6}= > {ST36}, {LI11, LI4, SP6}= > {ST36}, {LI11, LI4, SP6} = > {ST36}, as shown in Table 4. The network graph is shown in Figure 14, where the size and color depth of the nodes represent the degree of support and enhancement, respectively, and the arrows indicate the correlation between the leading and trailing terms. The results show that ST36, LI4, LI11, SP6, and LR3 are the core acupoints for the treatment of this disease.
4 Discussion
CIPN commonly occurs in the early stage of chemotherapy, and the typical clinical manifestations are symmetrical burning sensation, tingling sensation, anesthesia, numbness, and other symptoms in the “glove-sock” distribution (37–39). In addition, neurogenic pain is also one of the common manifestations of CIPN, which is more likely to cause physical and mental impact on patients than physical pain, and usually requires analgesic and antidepressant treatment (40). CIPN symptoms can be relieved after discontinuing the drug and can last for months or even years.
This study included 21 RCTs to evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of acupuncture in the treatment of CIPN. The results of the meta-analysis showed that acupuncture was superior to conventional treatment in improving pain intensity, the intensity of the CIPN, MCV of the median nerves, SCV of the bilateral median, SCV of tibial nerve, SCV of sural nerves, quality of life score, physical functioning scale, and other outcome indicators. It is suggested that acupuncture is a safe, effective, simple and feasible non-drug therapy, which can be recommended for patients with CIPN.
Different acupuncture intervention variables may be important factors affecting the therapeutic effect. To conduct a rigorous examination of the efficacy of acupuncture, we embarked on a subgroup analysis based on acupuncture intervention variables. This endeavor aimed to empirically ascertain whether variations in acupuncture intervention variables have a significant impact on the robustness and consistency of the observed outcomes (16). In the results of the subgroup meta-analysis, there was no significant difference in pain intensity reduction between preventive acupuncture and the control group. Considering the small number of included studies, this may be the reason for the insignificant difference. Meanwhile, Greenlee, H. reported that a slightly higher proportion of patients in the sham acupuncture group believed that they had received real acupuncture treatment (35). Studies have shown that when people have a high expectation of a response to acupuncture treatment, this expectation may enhance treatment outcomes for patients who receive sham acupuncture. However, this expectation does not necessarily lead to the same results for patients who receive acupuncture. In terms of treatment duration, acupuncture was more effective in improving pain intensity at 0–6 weeks and 6–12 weeks, while there was no statistically significant difference above 12 weeks. The possible explanation is that the effector substance gradually diminishes as the course of treatment is prolonged, and the pain relief effect is not sustainable. The results of a meta-analysis of the frequency of acupuncture interventions showed that acupuncture therapy performed two to three times per week showed a more positive effect on pain relief. However, the number of included studies is limited, and the credibility of this result needs to be further verified in more multicenter, large-sample studies. In addition, it is important to note that the current research field lacks studies on interventions more than three times per week, which prevents us from directly inferring a clear relationship between intervention frequency and intervention effectiveness. Therefore, because current evidence only recommends acupuncture therapy two to three times per week, participants are not encouraged to improve CIPN neuropathic pain by increasing the frequency of intervention.
For safety assessment, 16 cases of hematoma, 1 case of needle stagnation, and 16 cases of pain were reported in the included studies. Subcutaneous hematoma and pain are related to acupuncture manipulation and can be relieved by themselves. Stagnation of the needle mainly refers to the phenomenon in which, after acupuncture or needle retention, the doctor feels that the needle is astringent, difficult to twist, lift, and insert, and comes out of the needle with severe pain to the patient. Most of these are due to mental strain on the patient or errors in needle handling by the doctor, which causes the muscle to twist the needle handle too much in a single direction. If the patient is overstrained, causing excessive contraction of the local muscles, the needle may be slightly extended, either in the vicinity of the acupuncture point to press or stretch the needle handle or in the vicinity of the additional needle to disperse the qi and blood and relieve the muscle tension. If the sticking of the needle is caused by the wrong needling manipulation or the single direction twist, the needle can be twisted back in the opposite direction, and the needle can be eliminated by scraping and plucking the needle handle to make the entangled tendon playback.
Acupuncture as a long-established means of TCM treatment, has been widely used in all kinds of diseases across the globe (41). Acupuncture therapy modulates the whole body through multiple systems and multiple targets (42). Previous studies have not only confirmed the remarkable effect of acupuncture in relieving neuropathic pain, but also further explored the molecular mechanisms behind it (43–45). Voltage-gated ion channels such as Na + and Ca + play a pivotal role in maintaining many key physiological processes in organisms, including excitability regulation of neurons, information transmission between synapses, muscle contraction, and hormone secretion, which are closely related to the occurrence and development of CIPN (46). Ren conducted electroacupuncture intervention on the PC6, SJ5S, SP6, and ST36 points in neuropathic rats, and the results showed that the expression level of Na + channels in the brain of successfully modeled rats increased, and electroacupuncture intervention could significantly reduce the level of Na + channels in the brain of rats (47). In terms of neurotransmitters, high extracellular glutamate concentrations may trigger excitotoxicity and lead to neuron death. Carla found that intraperitoneal injection of the mGluR5 antagonist MPEP could reverse the SNCV induced by bortezomib treatment in rats by lowering the concentration of Glu in the cerebrospinal fluid of rats. TRPV1 (Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1) is a non-selective cation channel that is mainly expressed at the end of sensory neurons, particularly in neurons that are involved in the perception of pain and heat (48). TRPV1 can be activated by a variety of physical and chemical stimuli, the most well-known of which are high temperatures and capsaicin (the active ingredient in chili peppers). In recent years, more and more research has shown that TRPV1 is closely related to CIPN. Electrical acupuncture can inhibit the TLR4 (Toll-like receptor 4) signal transduction in DRG (dorsal root ganglion) neurons and simultaneously upregulate the expression of TRPV1 (transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 subfamily member 1). These effects further result in the inhibition of activation of spinal glial cells, thereby alleviating the symptoms of CIPN (49). Xiao-Chen Li′s research indicates that acupuncture can inhibit the activation of M1 microglia and pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1 and iNOS in the spinal cord of mice with CIPN induced by cisplatin through the suppression of spinal cord neuron miR-124 (50). GRK2, a G protein-coupled receptor kinase in the spinal cord, is involved in neuropathic pain and sensory abnormalities induced by cisplatin, and preventive electroacupuncture can increase GRK2 expression, thereby inhibiting the activation of microglia (51).
The data mining results show that LI4, ST36, LI11, LR3, and SP6 are the high-frequency acupoints for treating CIPN. (SP6 + ZST36), (LI4, SP6+ ST36), (LI11, SP6+ ST36), (LI11, LI4, SP6+ ST36), (LI11, LI4, SP6+ ST36) are the most commonly used combinations for this disease. According to traditional Chinese medicine theory, Hegu (LI4) is the yuan-source point of the hand Yangming meridian, which can treat finger numbness and paralysis of the upper limbs by promoting blood circulation and relieving pain. Zusanli (ST36) is the acupoint of the stomach meridian, which is the most important health acupoint in the human body and could promote the recovery QI of the spleen and stomach, promote the recovery and circulation of blood and Qi. There is the tibial nerve passing below it, so acupuncturing it can effectively improve the state of hypoxia and ischemia of the tibial nerve, stimulate the excitability of the nerve, and play a local acupoint treatment role. Quchi (LI11) is the he-sea point of the hand Yangming Meridian, which has the function of clearing heat dispersing wind, and regulating the circulation of Qi and blood. Quchi meridian deep layer is the radial nerve, which can also regulate the function of important nerves. SanYinjiao (SP6) is the rendezvous point of the Liver, Spleen, and Kidney meridians, which can improve the physiological state of the internal organs. The superficial layer below it is the branch of the saphenous nerve, and the deep layer has the tibial nerve, the posterior tibial artery, and the vein, which can regulate the function of the tibial nerve (52). Tai Chong (LR3) is a shu-stream acupoint and jing-river acupoint of the foot JueYin Liver Meridian, “liver controlling conveyance and dispersion, liver storing blood.” It is responsible for pain caused by the disrupted Qi flow, so Tai Chong has the function of regulating the flow of Qi. It is located on the sole of the foot, which has a local treatment effect.
4.1 Comparison of similar studies
At present, there are five meta-analyses on acupuncture treatment for CIPN (53–56). Consistent with previous systematic reviews and meta-analyses, acupuncture was associated with a significant reduction in pain intensity in patients with chemotherapy-associated peripheral neuropathy. However, this meta-analysis shows that acupuncture can significantly improve motor conduction velocities of nerve and sensory conduction velocities of nerve, which is different from previous evaluation results. This study evaluated the impact of acupuncture on the QOL of patients with CIPN. The assessment of QOL is an appropriate endeavor, constituting a multidimensional concept that comprehensively measures an individual’s satisfaction with their life (57). At the same time, a variety of intervention variables were used for acupuncture therapy in these meta-analyses, including but not limited to intervention duration, type of intervention, weekly intervention frequency, and total intervention duration. This inconsistency of intervention variables directly leads to significant differences in intervention effects among various studies, which further leads to the lack of uniformity and comparability in the formulation of clinical protocols, which has aroused widespread concern and deep concern among clinicians. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct a meta-analysis on the effects of acupuncture intervention with different intervention variables on CIPN, in order to provide evidence-based evidence for effective improvement of CIPN. In addition, this study follows the current guidelines for systematic review reports. It employs a comprehensive search strategy to retrieve the latest and high-quality randomized controlled trial evidence from multiple databases. The present study provides an updated synthesis of the current evidence of acupuncture in the treatment of CIPN.
4.2 Limitations and future research
The number of researches included in this paper is limited, and some studies have a high risk of bias, including unclear allocation hiding, inadequate blind method setting, and lack of Intention to treat analysis. Chemotherapy regimen, cancer type, cancer stage, and acupuncture treatment regimen may be the source of heterogeneity. In addition, the tools used to evaluate CNPI are not uniform and are mostly subjective scales. The study included only studies published in English and Chinese, which could be biased. In addition, in the process of diagnosing peripheral neuropathy, electromyography, and nerve conduction velocity testing are used as key tools for differentiating different types of nerve fibers. In particular, nerve conduction studies (NCS) have shown their unique applicability in detecting large fiber neuropathy. However, the detection results often show normal status in the face of CIPN (58). Considering the complexity of the underlying mechanisms of CIPN and the significant inconsistency between subjective symptoms and neurophysiological tests, there has been no established and widely accepted diagnostic method for CIPN so far.
5 Conclusion
Acupuncture can improve neuropathic pain, the intensity of the CIPN, nerve conduction velocity, quality of life, and other indicators in patients with CIPN, and has good safety. In addition, we observed that acupuncture intervention had a positive effect after the occurrence of CIPN symptoms, and all types of acupuncture intervention had a positive effect on the pain of patients with CIPN. At the same time, treatment intervention within 12 weeks could improve the pain intensity of patients with CIPN. ST36, LI4, LI11, SP6, and LR3 are core acupuncture points for CIPN treatment and are expected to be complementary therapies for CIPN.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
LL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Validation. YH: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. CA: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. NJ: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. CX: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. XW: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. HL: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. TT: Conceptualization, Project administration, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was financially supported by the National Science Foundation of China (No. 82274674) and Tianjin Famous Traditional Chinese Medicine Inheritance Studio Construction Project (No.tjmzy2405).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2024.1442841/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Mezzanotte, JN, Grimm, M, Shinde, NV, Nolan, T, Worthen-Chaudhari, L, Williams, NO, et al. Updates in the treatment of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Curr Treat Options in Oncol. (2022) 23:29–42. doi: 10.1007/s11864-021-00926-0
2. Klafke, N, Bossert, J, Kröger, B, Neuberger, P, Heyder, U, Layer, M, et al. Prevention and treatment of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) with non-pharmacological interventions: clinical recommendations from a systematic scoping review and an expert consensus process. Med. Sci. (2023) 11. doi: 10.3390/medsci11010015
3. Maihöfner, C, Diel, I, Tesch, H, Quandel, T, and Baron, R. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN): current therapies and topical treatment option with high-concentration capsaicin. Support Care Cancer. (2021) 29:4223–38. doi: 10.1007/s00520-021-06042-x
4. Seretny, M, Currie, GL, Sena, ES, Ramnarine, S, Grant, R, MacLeod, MR, et al. Incidence, prevalence, and predictors of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain. (2014) 155:2461–70. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2014.09.020
5. Wang, M, Cheng, HL, Lopez, V, Sundar, R, Yorke, J, and Molassiotis, A. Redefining chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy through symptom cluster analysis and patient-reported outcome data over time. BMC Cancer. (2019) 19:1151. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6352-3
6. Loprinzi, CL, Lacchetti, C, Bleeker, J, Cavaletti, G, Chauhan, C, Hertz, DL, et al. Prevention and Management of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in survivors of adult cancers: ASCO guideline update. J Clin Oncol. (2020) 38:3325–48. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.01399
7. Li, X, Zhi, L, Han, KY, Li, SQ, Ahmad, K, Seluzicki, C, et al. Impact of baseline expectancy on outcome prediction of real and sham acupuncture for persistent chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy pain in solid tumor survivors: a secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial. Integr Cancer Ther. (2023) 22:15347354221149992. doi: 10.1177/15347354221149992
8. Pike, CT, Birnbaum, HG, Muehlenbein, CE, Pohl, GM, and Natale, RB. Healthcare costs and workloss burden of patients with chemotherapy-associated peripheral neuropathy in breast, ovarian, head and neck, and nonsmall cell lung cancer. Chemother Res Pract. (2012) 2012:913848. doi: 10.1155/2012/913848
9. Flatters, SJL, Dougherty, PM, and Colvin, LA. Clinical and preclinical perspectives on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN): a narrative review. Br J Anaesth. (2017) 119:737–49. doi: 10.1093/bja/aex229
10. Huang, CC, Ho, TJ, Ho, HY, Chen, PY, Tu, CH, Huang, YC, et al. Acupuncture relieved chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in patients with breast cancer: a pilot randomized sham-controlled trial. J Clin Med. (2021) 10:694. doi: 10.3390/jcm10163694
11. Zhang, J, Zhou, X, Jiang, H, Zhu, W, Chi, H, Jiang, L, et al. Acupuncture for insomnia symptoms in hypertensive patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Neurol. (2024) 15:1329132. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1329132
12. Pu, T, Liu, Y, Wang, J, Zhang, J, Zhang, J, Ran, Z, et al. Acupuncture and other traditional Chinese medicine therapies in the treatment of children’s tic syndrome: a network meta-analysis. Front Neurosci. (2023) 17:1156308. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1156308
13. Zhou, X, Zhang, J, Jiang, L, Zhang, S, Gu, Y, Tang, J, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of acupuncture point stimulation for stomach cancer pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Neurol. (2024) 15:1334657. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1334657
14. Zhao, J, Dong, L, Lin, Z, Sui, X, Wang, Y, Li, L, et al. Effects of selenium supplementation on polycystic ovarian syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis on randomized clinical trials. BMC Endocr Disord. (2023) 23:33. doi: 10.1186/s12902-023-01286-6
15. Chen, HT, Hung, KC, Huang, YT, Wu, JY, Hsing, CH, Lin, CM, et al. Efficacy of electroacupuncture in improving postoperative ileus in patients receiving colorectal surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg. (2024) 110:1113–25. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000000848
16. Xiong, J, Zhou, X, Luo, X, Gong, X, Jiang, L, Luo, Q, et al. Acupuncture therapy on myofascial pain syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Neurol. (2024) 15:1374542. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1374542
17. Zhi, WI, Baser, RE, Talukder, D, Mei, YZ, Harte, SE, and Bao, T. Mechanistic and thermal characterization of acupuncture for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy as measured by quantitative sensory testing. Breast Cancer Res Treat. (2023) 197:535–45. doi: 10.1007/s10549-022-06846-3
18. Lagerstedt, K, and Efverman, A. A randomized sham-controlled mixed methods pilot study of the feasibility of acupuncture for chemotherapy-induced neuropathy: lessons learned from patient experiences in integrative cancer care. Integr Cancer Ther. (2023) 22:15347354231178877. doi: 10.1177/15347354231178877
19. Huang, MC, Chang, SC, Liao, WL, Ke, TW, Lee, AL, Wang, HM, et al. Acupuncture may help to prevent chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a randomized, sham-controlled, single-blind study. Oncologist. (2023) 28:e436–47. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyad065
20. Chan, K, Lui, L, Lam, Y, Yu, K, Lau, K, Lai, M, et al. Efficacy and safety of electroacupuncture for oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy in colorectal cancer patients: a single-blinded, randomized, sham-controlled trial. Acupunct Med. (2023) 41:268–83. doi: 10.1177/09645284221125421
21. Wang, L, Xu, XD, Yao, LJ, Huang, YT, Zou, Q, Wu, B, et al. Intervention effect of acupuncture and moxibustion in treatment of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in patients with multiple myeloma. J Clin Med Prac. (2022) 26:28–30. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20212712
22. Zhang, C, Li, S, and Mi, S. Clinical observation of acupuncture treatment of peripheral nerve damage after capecitabine chemotherapy. Pharm Week. (2022) 2022:1–10. doi: 10.1155/2022/5432223
23. Liu, YQ, Ni, ZX, Yao, XL, Yue, XQ, Yu, CQ, and Sun, S. Clinical observation of wrist-ankle acupuncture in the prevention of acute peripheral neurotoxicity caused by chemotherapy in elderly female patients with gastric cancer. Geriatr Heal Care. (2022) 28:1054–7. Available at: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=WnCf0VAm38rnI9H6gX2tfRIM4cBid9Vk1DU6rsyiPVSxS0oHZ3ijWf-xtvfpwRAwsH8syoMQLHAdlEdxOGNVxpJS0XtFaevBEzYzulgT1_anUtt0ND6A0TDSlAcmdKcwP6eutwrkliUrKiT2cam_B5vHIrG_jDG4ocectIZOm88JjMorHJtZGtQFd7AKgnByfwSPqdhg3PY=&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS
24. Stringer, J, Ryder, WD, Mackereth, PA, Misra, V, and Wardley, AM. A randomised, pragmatic clinical trial of acupuncture plus standard care versus standard care alone FOr chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy (ACUFOCIN). Eur J Oncol Nurs. (2022) 60:102171. doi: 10.1016/j.ejon.2022.102171
25. Friedemann, T, Kark, E, Cao, N, Klaßen, M, Meyer-Hamme, G, Greten, JH, et al. Acupuncture improves chemotherapy-induced neuropathy explored by neurophysiological and clinical outcomes - the randomized, controlled, cross-over ACUCIN trial. Phytomedicine. (2022) 104:154294. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154294
26. Ben-Arye, E, Hausner, D, Samuels, N, Gamus, D, Lavie, O, Tadmor, T, et al. Impact of acupuncture and integrative therapies on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a multicentered, randomized controlled trial. Cancer. (2022) 128:3641–52. doi: 10.1002/cncr.34422
27. Bao, T, Baser, R, Chen, C, Weitzman, M, Zhang, YL, Seluzicki, C, et al. Health-related quality of life in cancer survivors with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a randomized clinical trial. Oncologist. (2021) 26:e2070–8. doi: 10.1002/onco.13933
28. Lu, W, Giobbie-Hurder, A, Freedman, RA, Shin, IH, Lin, NU, Partridge, AH, et al. Acupuncture for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in breast cancer survivors: a randomized controlled pilot trial. Oncologist. (2020) 25:310–8. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0489
29. Iravani, S, Kazemi Motlagh, AH, Emami Razavi, SZ, Shahi, F, Wang, J, Hou, L, et al. Effectiveness of acupuncture treatment on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a pilot, randomized, assessor-blinded, Controlled Trial Pain. Res Manag. (2020) 2020:2504674. doi: 10.1155/2020/2504674
30. Bao, T, Patil, S, Chen, C, Zhi, IW, Li, QS, Piulson, L, et al. Effect of acupuncture vs sham procedure on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy symptoms: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. (2020) 3:e200681. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.0681
31. D’Alessandro, EG, Nebuloni Nagy, DR, de Brito, CMM, Almeida, EPM, Battistella, LR, and Cecatto, RB. Acupuncture for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a randomised controlled pilot study. BMJ Support Palliat Care. (2022) 12:64–72. doi: 10.1136/bmjspcare-2018-001542
32. Molassiotis, A, Suen, LKP, Cheng, HL, Mok, TSK, Lee, SCY, Lee, P, et al. A randomized assessor-blinded wait-list-controlled trial to assess the effectiveness of acupuncture in the management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Integr Cancer Ther. (2019) 18:1534735419836501. doi: 10.1177/1534735419836501
33. Sui, MH, Xu, N, Xiang, Y, Shu, GJ, Jin, DM, and Yan, TB. The influence of electrical acupuncture on the chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain and quality of life.Chin J Integr med. Cerebrovasc Dis. (2018) 16:1331–3. doi: 10.12102/j.issn.1672-1349.2018.10.06
34. Han, X, Wang, L, Shi, H, Zheng, G, He, J, Wu, W, et al. Acupuncture combined with methylcobalamin for the treatment of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in patients with multiple myeloma. BMC Cancer. (2017) 17:40. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-3037-z
35. Greenlee, H, Crew, KD, Capodice, J, Awad, D, Buono, D, Shi, Z, et al. Randomized sham-controlled pilot trial of weekly electro-acupuncture for the prevention of taxane-induced peripheral neuropathy in women with early stage breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. (2016) 156:453–64. doi: 10.1007/s10549-016-3759-2
36. Rostock, M, Jaroslawski, K, Guethlin, C, Ludtke, R, Schröder, S, and Bartsch, HH. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in cancer patients: a four-arm randomized trial on the effectiveness of electroacupuncture. Evid Based Complement Altern Med. (2013) 2013:349653. doi: 10.1155/2013/349653
37. Bonomo, R, and Cavaletti, G. Clinical and biochemical markers in CIPN: a reappraisal. Rev Neurol (Paris). (2021) 177:890–907. doi: 10.1016/j.neurol.2020.11.001
38. Tay, N, Laakso, E-L, Schweitzer, D, Endersby, R, Vetter, I, and Starobova, H. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in children and adolescent cancer patients. Front Mol Biosci. (2022) 9:1015746. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1015746
39. Castelli, V, Palumbo, P, d’Angelo, M, Moorthy, NK, Antonosante, A, Catanesi, M, et al. Probiotic DSF counteracts chemotherapy induced neuropathic pain. Oncotarget. (2018) 9:27998–8008. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25524
40. Mahfouz, FM, Li, T, Timmins, HC, Horvath, LG, Harrison, M, Grimison, P, et al. Impact of pain on symptom burden in chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw. (2024) 22:108–16. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2023.7083
41. Fan, AY, Zheng, L, and Yang, G. Evidence that dry needling is the intent to bypass regulation to practice acupuncture in the United States. J Altern Complement Med. (2016) 22:591–3. doi: 10.1089/acm.2016.0066
42. Li, X, Wang, L, Ying, X, Zheng, Y, Tan, Q, Yu, X, et al. Electroacupuncture pre-treatment alleviates sepsis-induced cardiac inflammation and dysfunction by inhibiting the calpain-2/STAT3 pathway. Front Physiol. (2022) 13:961909. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.961909
43. Zhou, K, Wu, Q, Yue, J, Yu, X, Ying, X, Chen, X, et al. Electroacupuncture suppresses spinal nerve ligation-induced neuropathic pain via regulation of synaptic plasticity through upregulation of basic fibroblast growth factor expression. Acupunct Med. (2022) 40:379–88. doi: 10.1177/09645284211066499
44. Wu, Q, Zheng, Y, Yu, J, Ying, X, Gu, X, Tan, Q, et al. Electroacupuncture alleviates neuropathic pain caused by SNL by promoting M2 microglia polarization through PD-L1. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 123:110764. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110764
45. Tu, W, Yue, J, Li, X, Wu, Q, Yang, G, Li, S, et al. Electroacupuncture alleviates neuropathic pain through regulating miR-206-3p targeting BDNF after CCI. Neural Plast. (2022) 2022:1489841. doi: 10.1155/2022/1489841
46. Kacem, H, Cimini, A, d’Angelo, M, and Castelli, V. Molecular and cellular involvement in CIPN. Biomedicines. (2024) 12:751. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12040751
47. Ren, L, Wang, YK, Fang, YN, Zhang, AW, and Li, XL. Effect of electroacupuncture therapy on the expression of na(v)1.1 and na(v)1.6 in rat after acute cerebral ischemia. Neurol Res. (2010) 32:1110–6. doi: 10.1179/016164110X12700393823453
48. Ghelardini, C, Menicacci, C, Cerretani, D, and Bianchi, E. Spinal administration of mGluR5 antagonist prevents the onset of bortezomib induced neuropathic pain in rat. Neuropharmacology. (2014) 86:294–300. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.08.004
49. Li, Y, Yin, C, Li, X, Liu, B, Wang, J, Zheng, X, et al. Electroacupuncture alleviates paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathic pain in rats via suppressing TLR4 Signaling and TRPV1 upregulation in sensory neurons. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:917. doi: 10.3390/ijms20235917
50. Li, XC, Chen, H, Chen, Y, Chu, YX, Mi, WL, Wang, YQ, et al. Spinal neuronal miR-124 inhibits microglial activation and contributes to preventive effect of electroacupuncture on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in mice. J Immunol. (2024) 212:410–20. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2300539
51. Ma, X, Chen, Y, Li, XC, Mi, WL, Chu, YX, Wang, YQ, et al. Spinal neuronal GRK2 contributes to preventive effect by electroacupuncture on cisplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy in mice. Anesth Analg. (2022) 134:204–15. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000005768
52. Zhang, HJ, and Zhang, SS. On the nerves and meridians associated with each level of “Sanyinjiao” point. Anat Res. (2016) 38:487–488+507. Available at: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=WnCf0VAm38pcXOCwfl99aBQCxWJE630cTPP2fZWHHNQB__F9jNKJvjhLx1_EI3EVZeTveM8WjUs4Zkzjy4DhrSL1i-tKBreRRhJYdZNPVHEtyh9SZ9EaN-qGvnDlWH_N43-V6u0XPdf2IX5RpwhlLnVeQALtCcRJQb20YZV1RmPIMuToJsn3dMiBPbNyA_cV&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS
53. Hwang, MS, Lee, HY, Choi, TY, Lee, JH, Ko, YS, Jo, DC, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy of acupuncture and electroacupuncture against chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Medicine (Baltimore). (2020) 99:e19837. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019837
54. Jin, Y, Wang, Y, Zhang, J, Xiao, X, and Zhang, Q. Efficacy and safety of acupuncture against chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2020) 2020:8875433. doi: 10.1155/2020/8875433
55. Pei, LX, Yi, Y, Guo, J, Chen, L, Zhou, JY, Wu, XL, et al. The effectiveness and safety of acupuncture/electroacupuncture for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acupunct Med. (2023) 41:73–85. doi: 10.1177/09645284221076512
56. Xu, Z, Wang, X, Wu, Y, Wang, C, and Fang, X. The effectiveness and safety of acupuncture for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Neurol. (2022) 13:963358. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.963358
57. Chien, T-J, Liu, C-Y, Fang, C-J, and Kuo, C-Y. The efficacy of acupuncture in chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: systematic review and meta-analysis. Integr Cancer Ther. (2019) 18:1534735419886662. doi: 10.1177/1534735419886662
Keywords: acupuncture, systematic review, chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, data mining, complementary and alternative therapies
Citation: Li L, Huang Y, An C, Jing N, Xu C, Wang X, Li H and Tan T (2024) Acupuncture in the treatment of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a meta-analysis and data mining. Front. Neurol. 15:1442841. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1442841
Edited by:
Hao Chi, Southwest Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Kan Li, Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey, United StatesXuancheng Zhou, Southwest Medical University, China
Hongshuo Shi, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China
Copyright © 2024 Li, Huang, An, Jing, Xu, Wang, Li and Tan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tao Tan, MTMwNzIyNDA5NzdAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Limeng Li
Limeng Li Yingxue Huang1,2
Yingxue Huang1,2 Xiaoyu Wang
Xiaoyu Wang Huanan Li
Huanan Li