- 1Department of Public Health, Yanet-Liyana College of Health Sciences, Hawassa, Ethiopia
- 2School of Public Health, College of Medicine and Health Sciences, Hawassa University, Hawassa, Ethiopia
- 3Department of Pharmacy, School of Medicine, Komar University of Science and Technology, Sulaymaniyah, Iraq
Introduction: Traumatic brain injuries are a major public health concern that contributes to youth morbidity and mortality in developing nations, including Ethiopia. Despite of this, little is known about head injury in the study area. The goal of the study was to identify the incidence, risk factors and outcomes for traumatic head injury among trauma patients who visited at the Yanet Trauma and Surgery Specialized Centre.
Methods: This was a 5 year an institutional-based retrospective cohort study conducted among 1,029 patients who experienced trauma and admitted at the Yanet Trauma and Surgical Specialized Centre. The research was carried out between September 01/2023 to October 15/2023. The study units were selected by using simple random sampling techniques through computer-generated random numbers. The data were collected via a checklist designed on the Kobo toolbox with a smart smartphone. The collected data were exported to a statistical package for Social Science version 27. Then, descriptive statistical analysis was conducted to determine the mean, standard deviation, and median. Bivariate and multivariate logistic regression was subsequently conducted to determine the associations between head injury and the independent variables.
Result: A total of 1,029 injured patients were followed for 2,302 person-days. Over all, incidence density rate of 14.03/100 person-days (323, 31.4%) [95% CI: 29.5–34%]. The third year of follow-up showed the greatest incidence compared to other years. The most common type of head injury observed during following up were brain contusion (38.1%), followed by epidural hematoma (33.1%), skull fracture (15.8%), and intracerebral hematoma (13.0%). In multivariate logistic model, rural residence [AOR = 1.6; 95% CI: 1.18–2.16], mechanism of injury namely road traffic accident [AOR = 5.5; 95% CI: 2.27–13.34], assault [AOR = 3.4; 95% CI: 1.35–8.37] and comorbidity of chronic disease [AOR = 2.2; 95% CI: 1.13–4.18] were the risk factors significantly associated with head injury.
Discussions: The incidence density rate of 14.03/100 person-days. As the result, more has to be done by health professionals, traffic police officers and local government raise awareness and enforce the implementation of driving rules and regulations.
1 Introduction
Head injury, often known as traumatic brain injury (TBI), refers to damage to the brain caused by rapid trauma. The extent of the injury might vary, depending on which parts of the brain are damaged (1). Worldwide, the occurrence of TBI is estimated to range from 27 to 69 million cases per year, with an average of 801 incidents per 100,000 patients annually, according to the WHO (2–4). In low-and middle-income countries (LMICs), the burden of injury is high, particularly among where more than 90% of deaths are due to injuries (8).
The WHO states that traumatic head injury is a major public health concern (5) due to its frequent occurrence as a cause of death and disability among young individuals, and its substantial impact on health care system (6). Approximately, 5.3 million individuals in the United States and 7.7 million individuals in the European Union are estimated to have impairments resulting from traumatic brain injury (7, 8). Head injuries are the main cause of disability and death worldwide and have become one of the largest public health challenges, including in Ethiopia (9, 10). The present research reveals that it is the leading cause of death, especially in low-to middle-income countries (11).
According to epidemiological research, about 57 million individuals globally are experiencing the neurological effects of severe head traumas (11, 12). Nevertheless, a significant number of calculations relied on data from industrialized nations, which lacked sufficient representation of low-and middle-income countries, especially in the African area, such as Ethiopia. Besides, untreated intracranial injuries, such as epidural and subdural hemorrhages or skull fractures, may lead to mortality or persistent impairment (13, 14). Therefore, Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) poses a substantial worldwide risk to public health, affecting about 69 million people annually on a global scale (3, 15). Moreover, a significant percentage of traumatic brain injuries were recorded in low-income countries (3). Furthermore, road traffic accidents (RTAs), fall-down accidents, and interpersonal violence (assaults) were the major risk factors for head injury (16, 17). Therefore, the World Assembly considered RTAs to be one of the agenda for Sustainable Development Goals (18).
Moreover, the Yanet Trauma and Surgery Specialized Center is the largest trauma center in Hawassa, serving more than 4 regions in Ethiopia (patients from the Oromia, Southern, Sidama, and Somalia regions). However, no studies have investigated the incidence, risk factors, and outcomes of traumatic head injury among trauma patients in the study area.
Therefore, this study aimed to determine incidence, risk factors and outcomes for traumatic head injury among trauma patients who visited at the Yanet Trauma and Surgery Specialized Centre.
2 Methods and materials
2.1 Study design
An institution-based retrospective cohort study was conducted.
2.2 Study area and period
This study was conducted at Yanet Trauma and Surgery Specialized Center, Hawassa, Ethiopia. The Yanet Trauma and Surgery Specialized Center (YTSSC) is a tertiary health institution designed to provide services to two specialized centers under one roof, namely, the Yanet Trauma Specialized Center and the Yanet Surgery Specialized Center. It is a private health institution under the Liyana Health Care PLC; it was inaugurated and started functioning on January 12, 2019. Tertiary care is provided in both diagnostic and therapeutic services. As it is the only specialized trauma and surgery center in the Sidama region, its service is also focused especially on trauma. It offers diagnosis and treatment services for an average patient flow of 13,473 patients, which includes 2026 trauma patients and 11,447 non-trauma patients per year since 2014. The study was conducted from September 01/2023 to October 15/2023.
2.3 Population
2.3.1 Source population
The source population included all trauma patients who visited the YTSSC from July 2019 to July 2023.”
2.3.2 Study population
All randomly selected trauma patients charts at the YTSSC from July 2019 to July 2023.
2.4 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
2.4.1 Inclusion criteria
All trauma patient cards registered at the Yanet Trauma and Surgery Specialized Centre from July 2019 to July 2023 were eligible for the study.
2.4.2 Exclusion criteria
Patient records with incomplete information were excluded from the study.
2.5 Sample size determination
2.5.1 Sample size for the first objective
In this study, we considered a single and double population proportion formula. Using a 95% confidence interval, 3% margin of error, and 40.5% incidence of head injury from a previous study (19), the calculated sample size was 1,029.
2.5.2 Sample size for the second objective
The double population formula was used for sample size determination in the second objective. Epi-info version 7.0 with a confidence level of 95% and a power of 80%, and the ratio of the unexposed group to the exposed group was considered to be one. As shown in below assessing the exposure of gender or being male gender requires the highest sample size. Therefore, the final sample size required for conducting this study was 1,029 (19, 20).
2.6 Sampling technique and procedure
This study was conducted at Yanet Trauma and Surgery Specialty Center, Sidama region, Hawassa, Ethiopia. A simple random sampling technique was used to select the patients’ charts. Hence, the sampling frame was a registry of trauma patient data registered in Excel from July 2019 to July 2023. Finally, computer-generated random numbers were used to enroll all the study units (n = 1,029) from the Excel registry of total trauma patients (n = 8,820) who visited the Yanet Trauma and Surgery Specialized Center from July 2019 to July 2023.
2.7 Variables
2.7.1 Dependent variables
• Traumatic head injury
2.7.2 Independent variables
Socio-demographic Factors: Age, Sex, Residence.
Mechanism of injury: RTA, fall down accident, Burn, Fall down object, Assault (Fighting, bullet injury). Clinical characteristics: Epilepsy, psychiatric illness, DM, HTN.
2.8 Data collection tool and procedures
2.8.1 Data collection tool and data collection procedures
The data collection tool was adapted from the WHO on injury surveillance (21) and the literature, modified to fit the study context after pretesting at Hawassa referral hospital, which was not included in the present study. The questionnaires consisted of five sections, including socio-demographic variables, physical factors, personal factors, RTAs, and clinical factors.
2.8.2 Data collection procedures
Before data collection was carried out, the final version of the structured tool was designed by using the Kobo collection toolbox. Then, two trained professional nurses were recruited as data collectors. These two nurses extracted data from the registry system by randomly selected patients who had a follow-up from 2019 to 2023 under the supervision of the data manager and hospital administrators who were trained for this purpose. The researchers rechecked if there was an incomplete and inconsistent abstraction from the chart every day; if an incomplete checklist was found, we sent it back to the data collectors for correction.
2.9 Data quality assurance
To maintain the quality of the data, a pretest was performed on 35 trauma patients at the emergency unit of Hawassa University Comprehensive Specialized Hospital. After the pretest, some revisions were made to the questionnaires, and modifications were made to the skipping pattern. Finally, the pretested Kobo toolbox was used to collect the data. One day of training was given to the data collectors and supervisors. Furthermore, the principal investigator and supervisors supervised the daily process of data collection and provided necessary corrective measures.
2.10 Data processing and analysis
The gathered information was downloaded as Excel and SPSS labels, and it was then exported to SPSS version 27 for analysis. For continuous variables, descriptive statistics such as means and standard deviations were computed; for categorical variables, tables and graphs show frequencies and percentages. Binary logistic regression analysis was used to identify risk variables for head injuries. Therefore, factors in the bivariate analysis with p-values less than 0.25 were deemed potential candidates for multivariate analysis. Authors also considered certain criteria for the multivariate analysis, took adequate sample size for the analysis, as we know that inadequate sample sizes may lead to unreliable results, especially in multivariate analyses with multiple predictors. We verified the variables were presented and sufficient completed for each observation. Besides, authors checked outliers, normality, and p-value < 0.25 and also checked multicollinearity among predictor.
In addition, the multivariate binary logistic regression model included a backward likelihood ratio to control for confounding variables. A head injury was deemed to be predicted if the p- value was less than 0.05 at the 95% confidence range. Furthermore, the Hosmer and Lemeshow test was used to assess the model’s fitness; a P- value of more than 0.05 was seen as indicating a good model fit. Additionally, multicollinearity was tested using the variance inflation factor (VIF) had less than 10.
2.11 Operational definitions
Head injury was defined as patients who experienced traumatic scalp and/or skull injuries with or without traumatic brain injury (22). It is refer to a change in brain function that may cause convulsion, coma, and altered level of consciousness called traumatic brain injury (22).
Conservative management: a patient who experienced traumatic scalp or skull injury with or without traumatic brain injury and was treated without any surgical procedure.
3 Results
3.1 Socio-demographic characteristics
In our study, we included 1,029 research respondents for the final analysis. The mean age of the respondents was 35.82 ± 18.53 years. The majority (70.9%, n = 730) of the study participants were male. Furthermore, the majority (72.6%, n = 747) of the participants were urban residents. Considering the referral history of more than half of the study participants, 55.3% (n = 564) had a referral history, and the majority (73.5%, n = 338) of the study respondents were referred from governmental health institutions (Table 1).

Table 1. Admission characteristics of study participants who visited the Yanet Trauma and Surgery Specialized Center from July 2019 to July 2023.
3.2 Admission characteristics of the study participants
The majority of traumas were occurred due to fall-down accidents (38.5%) and road traffic accidents (37.1%). About (85.2%, n = 877) of the respondents were presented with Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) scores ranging from 13 to 15 at admission. Furthermore, the greater proportion of respondents presented with normal vital signs, with percentages of 79.9% (n = 822), 84.8% (n = 873), and 97.3% (n = 1,001) for blood pressure, pulse, and temperature, respectively (Table 1).
3.3 Clinical conditions of the patients
Regarding clinical condition, about 58.8% (n = 605) of the research respondents were outpatients. In addition, 13.75% (n = 141) of the study participants presented with poly trauma, and more than half (58.2%, n = 82) of them injured their extremities. In addition, almost one-third (32.9%, n = 339) of the study participants presented with bone fractures. Medical comorbidities and visceral organ injury were present in 4.3% (n = 44) and 4.7% (n = 48) of the study participants, respectively. Among the investigated modalities, the most common were X-ray (58.2%, n = 599), followed by head computed tomography (CT) (52.2%, n = 537) and electrocardiogram (ECG) (13.4%, n = 138) (Table 2).
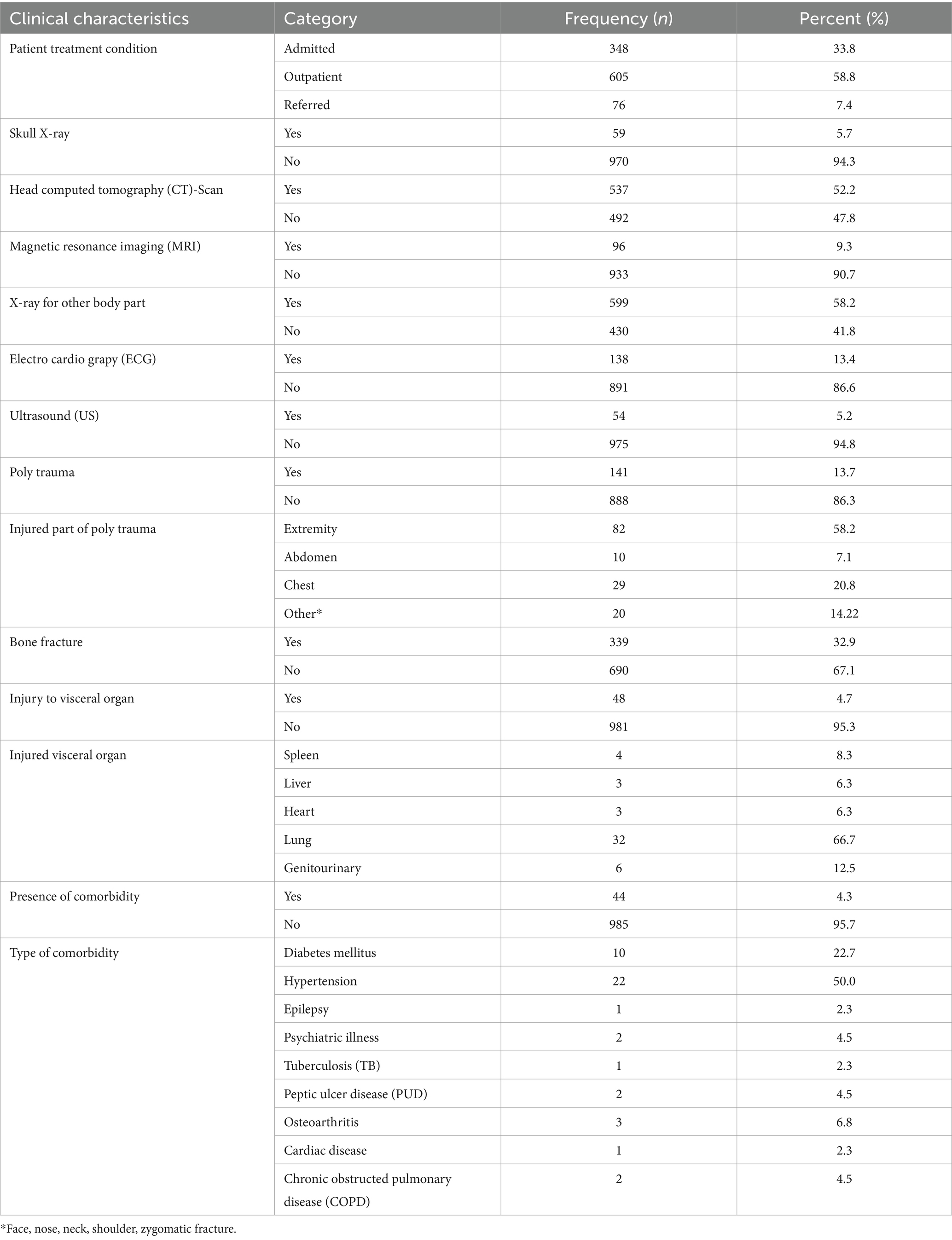
Table 2. Clinical characteristics of the study participants who visited the Yanet Trauma and Surgery Specialized Center from July 2019 to July 2023.
3.4 Incidence of head injury
In the 5 years, 1,029 injured patient followed 2,302 person-days. The incidence density rate of head injury was 14.03/100 person-days. The cumulative incidence of head injury among trauma patients was 31.4% [95% CI (29.5–34%)].The most common type of head injury was brain contusion (38.1%, n = 123), followed by epidural hematoma (EDH) (33.1%, n = 107), skull fracture (15.8%, n = 51) and intracerebral hematoma (ICH) (13.0%, n = 42). Furthermore, only 5.6% (n = 57) and 1.7% (n = 18) of the study participants developed trauma-related complications and hospital-acquired infections, respectively (Figure 1).
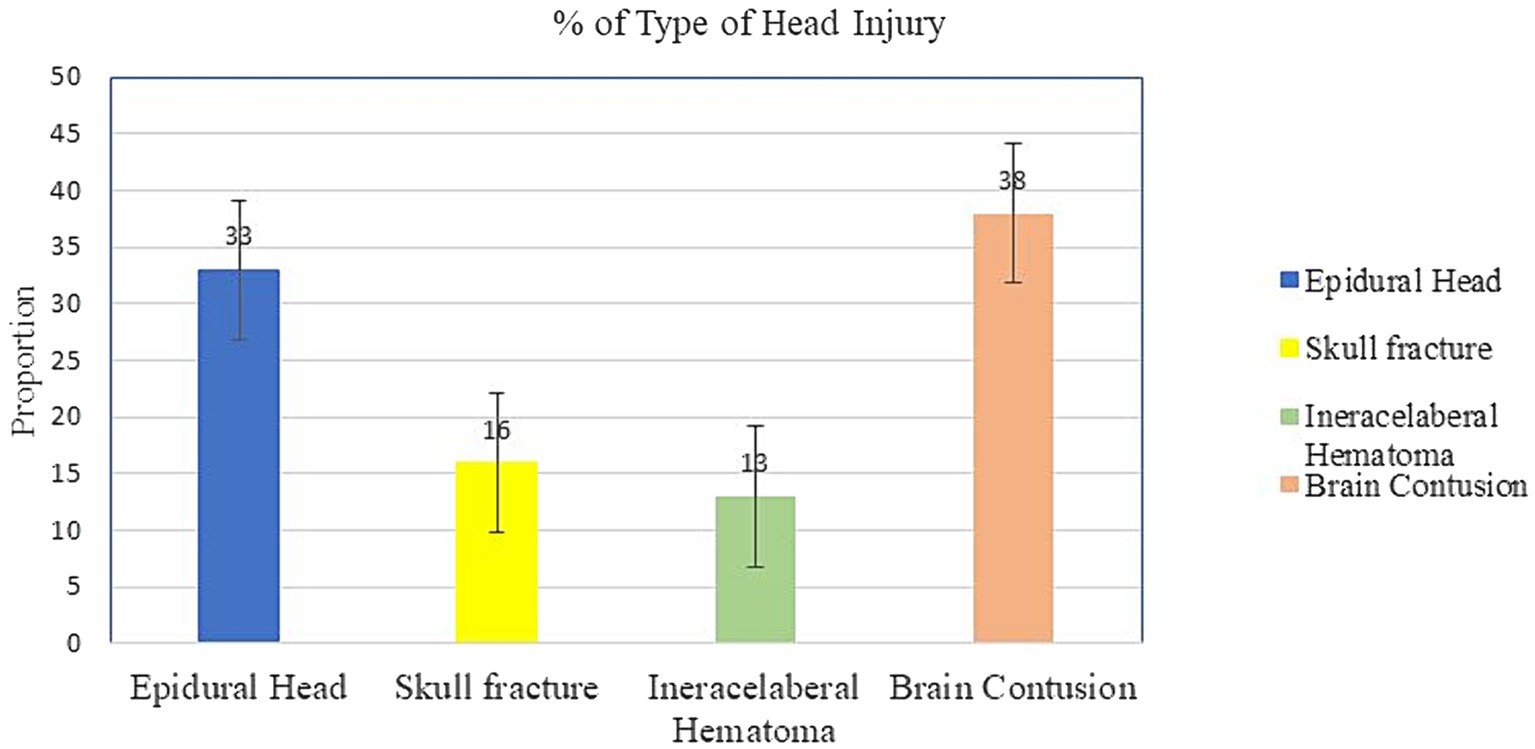
Figure 1. Type of head injury among study respondents from trauma patients who visited the Yanet Trauma and Surgery Specialized Center from July 2019 to July 2023.
3.5 Head injury complication and management
Overall, 15 (5.5%) of the patients developed posttraumatic seizures, 13 (1.3%) developed aspiration pneumonia, 7 (0.7%) developed skin contusions, 7 (0.7%) developed extremity paralysis, 5 (0.5%) developed post-traumatic meningitis, and 4 (0.4%) underwent amputation. Regarding management, 180 (55.7%) of the patients were managed with medication (conservative management), and 143 (44.3%) of the head-injured patients were managed with surgery (Table 3).
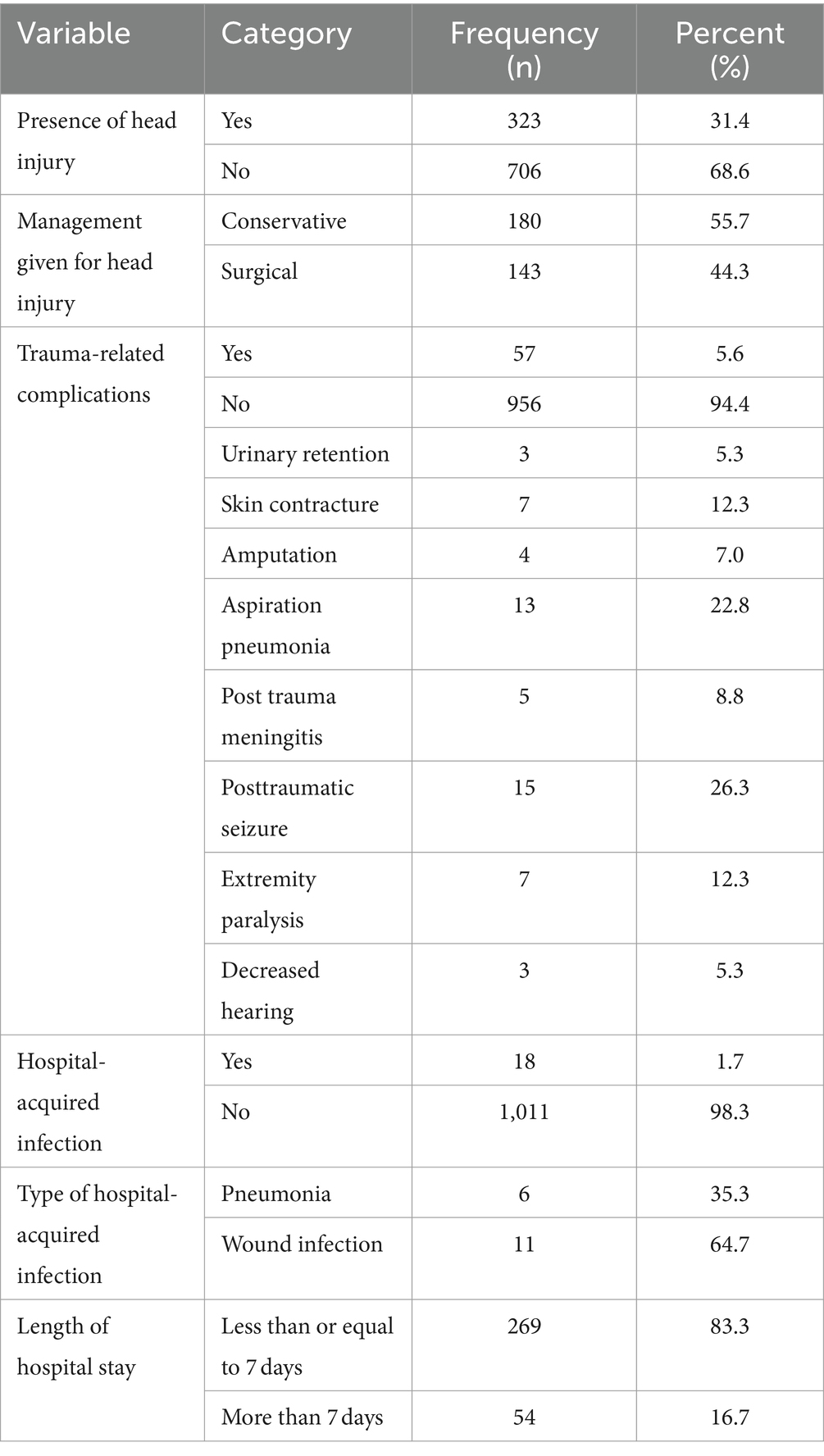
Table 3. Incidence, management, and trauma-related complications of head injury among study participants from trauma patients who visited the Yanet Trauma and Surgery Specialized Center from July 2019 to July 2023.
3.6 Head injury outcome
Among the total admitted patients, almost one-quarter of the respondents (242, 23.3%) were cured and returned home, 59 (5.7%) were referred to higher facilities due to complications, 5 (0.5%) had no improvement and reported no improvement, and the remaining 17 (1.7%) of the admitted patients died. The mean (±SD) number of patients who stayed in the trauma center was 4.46 (± 5.11), and the maximum number of stay days was 56 (Table 3).
3.7 Predictors of head injury
According to the bivariate analysis, seven variables were significantly associated with head injury at a significance level less than 0.25. Hence, sex, residence, place of trauma, fall-down accident, road traffic accident, assault, and comorbidity were the seven independent candidate variables for multivariable analysis.
After adjusting for confounders through the backward stepwise likelihood ratio in multivariate binary logistic regression, four variables showed a statistically significant association with head injury among trauma patients, namely, residence, RTA, assault, and comorbidity.
The odds of head injury were almost 2 times greater among rural residents than among urban residents (AOR = 1.6; 95% CI: 1.18–2.16). Furthermore, the odds of head injury were almost 6 times greater for road traffic accidents than for other means of injury (AOR = 5.5; 95% CI: 2.27–13.34). Similarly, the odds of head injury were 3.4 times greater for the assault mode than for the other means of injury (AOR = 3.4; 95% CI: 1.35–8.37). Finally, the odds of head injury were 2.2 times greater among patients with comorbidities of chronic disease than among their counterparts (AOR = 2.2; 95% CI: 1.13–4.18) (Table 4).
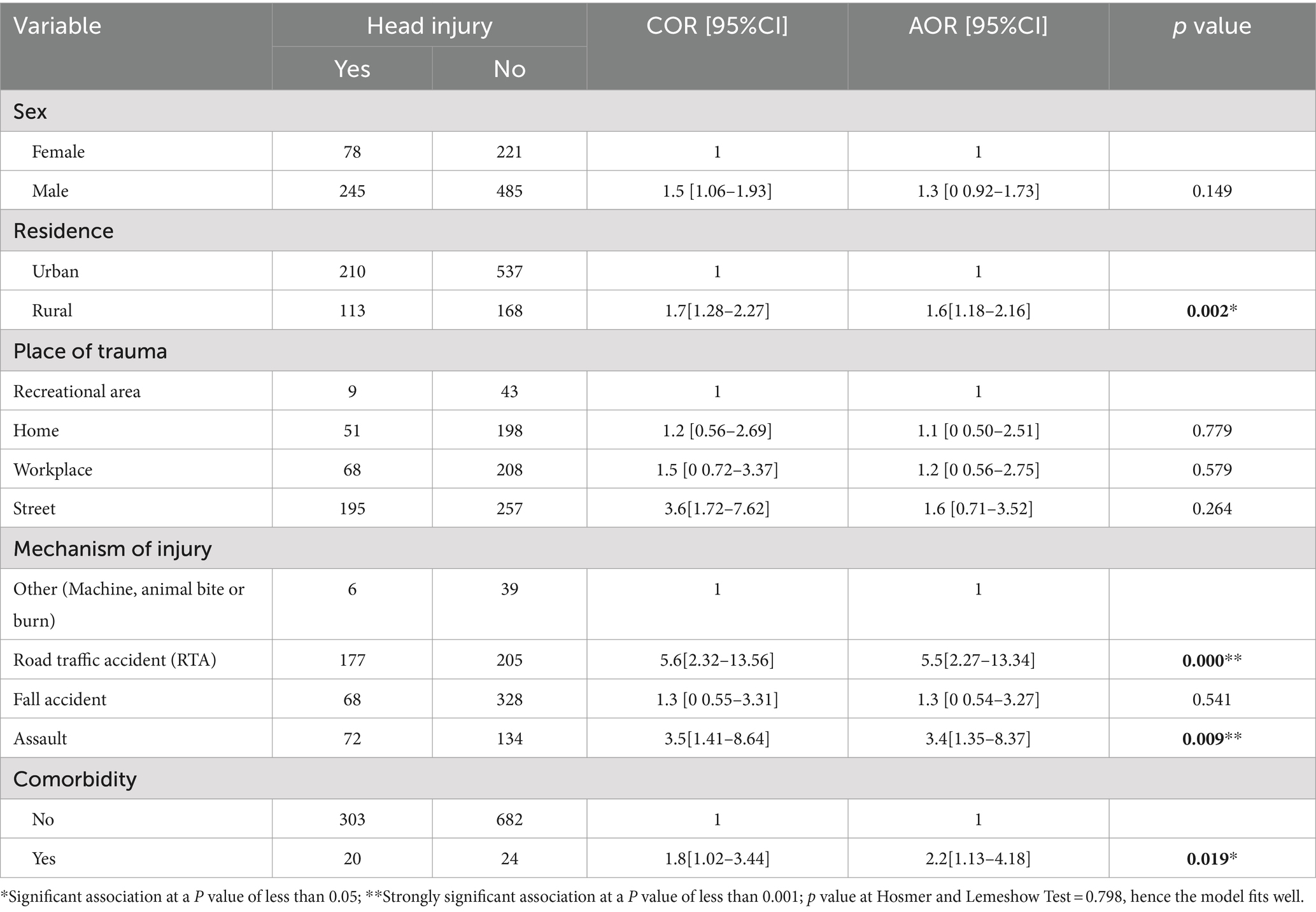
Table 4. Factors associated with head injury among study participants from trauma patients who visited the Yanet Trauma and Surgery Specialized Center from July 2019 to July 2023.
4 Discussion
4.1 Overall description of the study
In this retrospective health facility cohort study, we measured the incidence, risk factors, and outcomes of traumatic head injury among trauma patients who visited the Yanet Trauma and Surgery Specialized Centre, Ethiopia, in 2023. Over 5 years, 1,029 injured patients were followed for 2,302 person-days. The incidence density rate of head injury was 14.03/100 person-days. The cumulative incidence of head injury among trauma patients was 31.4% [95% CI (29.5–34%)], which was a substantially higher burden. This result was in line with earlier research from Ethiopia (32.1%) (23) and Nigeria (33.8%) (24). On the other hand, our analysis found a higher incidence than a prior research on (12.4%) (25). This discrepancy may have occurred for a variety of reasons, including variations in socioeconomic level, lifestyle characteristics, research design, patient context, and that may raise the risk of head injury.
The most common type of head injury was brain contusion (38.1%), followed by epidural hematoma (33.1%), skull fracture (15.8%), and intracerebral hematoma (13.0%). This finding was comparable with the existing evidence (26–28). Head injuries may occur for a variety of causes. Head injuries can vary based on the type and severity of the impact. For example, a head injury caused by a fall from a height may differ from one caused by a direct blow to the head in a sports-related incident. The force, angle, and speed of the impact can all influence the nature and severity of the injury.
4.2 Clinical conditions of the patients
According to this study, 141 (13.75%) of the study respondents presented with poly trauma, and more than half (82 (58.2%) of them) presented with poly trauma. In addition, almost one-third (32.9%, n = 339) of the study participants presented with a bone fracture. This finding was consistent with a study conducted in South Africa (29–31). The timeliness and quality of medical care following a head injury can affect its subsequent development and impact. Variations in access to medical facilities, expertise of healthcare providers, and availability of diagnostic tools can contribute to differences in outcomes for individuals with head injuries.
Regarding complications, 15 (5.5%) of the patients developed post traumatic seizures, 13 (1.3%) developed aspiration pneumonia, 7 (0.7%) developed skin contusions, 7 (0.7%) developed extremity paralysis, 5 (0.5%) developed post trauma meningitis, and 4 (0.4%) underwent amputation. These findings are comparable with the documented evidence elsewhere (32–34) indicating that head injury patients experienced other medical and mental health complications during their long-term course and life after injury. The sudden deceleration or direct blows to the head can cause concussions, fractures, contusions, and other types of head injuries.
Our study shows us, the most common investigated modalities used during were X-ray, followed by head computed tomography (CT) and electrocardiogram (ECG). According to existing research, neurosurgical and diagnostic procedures were frequently predicated on identifying shifts in clinical indications and symptoms in the years prior to CT scanning. The patient had an intrusive, hazardous angiography to confirm a diagnosis, with a propensity to delay the procedure until the patient was in critical condition. If digital biomarkers such as hard fall detection are standardized and utilized as a means to notify paramedics to an unresponsive trauma patient, the existing lag in TBI incidence and hospitalization can be eliminated (35).
4.3 Risk factors associated with head injury
Considering the factors associated with head injury, socio-demographic characteristics such as rural residence (AOR = 1.6), mechanisms of injury such as RTA (AOR = 5.5) and assault (AOR = 3.4), and comorbidity of chronic disease (AOR = 2.2) were identified as independent predictors of head injury. Thus, the incidence of head injury among rural residents was 60% greater than that among urban residents. This was consistent with the findings of previous studies (20, 36, 37), where traumatic head injuries were more common in rural areas than in urban areas. There are various reasons why rural individuals may have more head injuries than urban ones. Some of the possible reason could be: (a) Rural communities may have restricted access to healthcare services such as hospitals and trauma centers. Delays in seeking early medical treatment after a head injury may result in worse results, (b) Rural populations may be more prone to work in sectors such as agriculture, forestry, or construction, which have a greater risk of head injuries caused by heavy equipment, falls, or blunt force trauma. (c) Rural inhabitants may have to drive greater distances to receive critical services, increasing their chances of being involved in car accidents that result in brain injuries. Poor road conditions and inadequate public transit choices in rural locations may also lead to increased accident rates.
In our study, road traffic accidents and assaults were significantly associated with head injuries. Hence, the prevalence of head injury associated with RTAs and assault (interpersonal violence) was 5.5 and 3.4 times greater, respectively, than that associated with other mechanisms of injury. This finding is also comparable with findings from North Central Ethiopia (20) and Northwest Ethiopia (38). Nevertheless, a research conducted in Australia (1) revealed contrasting results, since the majority of head injuries were attributed to sports and leisure activities rather than road traffic accidents (RTAs) and assault. RTA and assaults may lead to several forms of injury, including ejection from a vehicle, impact with a solid surface, or being hit by a weapon or object. These several mechanisms worsen the intricacy and severity of brain traumas endured.
Furthermore, comorbidities of chronic disease had a significant correlation between these factors and brain injury. Therefore, the incidence of head injury in individuals with comorbidities of chronic illness was 2.2 times higher compared to those without such conditions. The greater incidence of accidents and susceptibility to various consequences among people with chronic conditions may account for this observation. This result was corroborated by studies in Ethiopia (39). Individuals with pre-existing medical conditions, such as epilepsy or neurodegenerative disorders, may be more susceptible to certain types of head injuries or experience different outcomes compared to those without these conditions.
Regarding the clinical condition of the trauma patients, 13.75% (n = 141) of the study participants presented with poly trauma, and almost one-third (32.9%) of the study participants presented with bone fractures. This figure was in line with a study performed in the Amhara region, Ethiopia (39). In road traffic incidents, vehicle passengers or pedestrians may not be wearing seat belts, helmets, or other protective gear that may assist lessen the risk of head injuries. Victims of attack may be unable to defend themselves against direct strikes to the head.
4.4 Outcomes of head injury
Consecutively, the majority (74.9%) of the study participants had good or improved discharge outcomes. This could be because timely management of head trauma before patients develop secondary brain injury and the use of surgical intervention based on CT scan diagnosis reduce the occurrence of unfavorable outcomes. Furthermore, in the current study, only 16.7% of the study participants had lived for more than 7 days. Therefore, this result implies the need for close follow-up of trauma patients, and the availability of a functional neurosurgery department and strong referral systems in the study area were the main reasons. Hence, these factors have a significant impact on the expected outcome or recovery time for trauma patients. This finding was in line with findings from a study in Nekemte Referral Hospital, Oromia, Ethiopia (40), where the proportion of favorable discharge outcomes was 74.9% (40). Moreover, the current research documented on the trends in mild traumatic brain injury treatment of all types of TBI prior demonstrating the need for improved care specific to mild TBI patients (41). Therefore, the outcomes of head injuries can vary widely depending on the severity of the injury, the specific type of head trauma, the individual’s age and overall health, and the timeliness and quality of medical intervention.
4.5 Methodological comparison
The majority of the exiting study were cross-sectional study (42–45) design that measured prevalence of the head injury has lack of temporal relationships. However, the recent study used 5 year observational retrospective cohort study design that helped to outline how data was collected, analyzed, and interpreted. Validity, Reliability, Sample size and representativeness, Validation of measurement tools, Control of confounding variables were considerer to respond research questions. This study had similar methodological issue with the previous study (46–49).
5 Strengths and limitations
This study used an adequate and representative sample size to address the research questions. Moreover, data were collected with digital form in kobo with smart phone. However, the limitations of study were retrospective nature of the study design and the lack of data on alcohol consumption and smoking status.
6 Conclusion
The incidence of head injury in this study ranged from one to three, which is a significant public health concern in the study setting. In addition, rural residence, RTA, assault, and comorbidity of chronic disease were identified as independent predictors of head injury. Therefore, policy makers and partners should focus on tailored strategies such as wearing protecting helmets, practice safe driving with seatbelt while in a vehicle, maintain a safe environment, avoid risky behaviors such as excessive drinking/drug use or smoking, consult a healthcare provider for screening and early treatment of comorbidity are very essential to mitigate the risk of head injury.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the ethical clearance was secured from the Yanet-Liyana College of Health Sciences of the ethical review committee (with Ref # of LHC/YLCHS/OGL/995/15 and Date: 20/11/2023 GC). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
TaA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. TsA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Yanet Trauma and Surgical Specialist Centre management teams and all the staff for their permission for data collection for this study, and we would also like to extend our warm appreciation to our data collectors who took part in the data collection. We are grateful to the Yanet-liyana College of Health Ethical Committee for our ethical document approval and support letter provisions for this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Amaranath, JE, Ramanan, M, Reagh, J, Saekang, E, Prasad, N, Chaseling, R, et al. Epidemiology of traumatic head injury from a major paediatric trauma Centre in New South Wales. Austr ANZ J Surg. (2014) 84:424–8. doi: 10.1111/ans.12445
2. Global, regional, and national burden of traumatic brain injury and spinal cord injury, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2016. Lancet Neurol. (2019) 18:56–87. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30415-0
3. Dewan, MC, Rattani, A, Gupta, S, Baticulon, RE, Hung, YC, Punchak, M, et al. Estimating the global incidence of traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg. (2018) 130:1080–97. doi: 10.3171/2017.10.JNS17352
4. Godwin, EE, Kreutzer, JS, Arango-Lasprilla, JC, and Lehan, TJ. Marriage after brain injury: review, analysis, and research recommendations. J Head Trauma Rehabil. (2011) 26:43–55. doi: 10.1097/HTR.0b013e3182048f54
5. Roozenbeek, B, Maas, AI, and Menon, DK. Changing patterns in the epidemiology of traumatic brain injury. Nat Rev Neurol. (2013) 9:231–6. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2013.22
6. Aenderl, I, Gashaw, T, Siebeck, M, and Mutschler, W. Head injury-a neglected public health problem: a four-month prospective study at Jimma University specialized hospital, Ethiopia. Ethiop J Health Sci. (2014) 24:27–34. doi: 10.4314/ejhs.v24i1.4
7. Abate, SM, Abafita, BJ, and Bekele, T. Journal pre-proof the prevalence of traumatic brain injury among trauma patients in Ethiopia: Systematic review and meta-analysis. The Annals African Surgery (2021) 18:10–15. doi: 10.4314/aas.v18i1.3
8. Hyder, AA, Wunderlich, CA, Puvanachandra, P, Gururaj, G, and Kobusingye, OC. The impact of traumatic brain injuries: a global perspective. Neuro Rehabi. (2007) 22:341–53.
9. Sharma, B, and Lawrence, DW. Top-cited articles in traumatic brain injury. Front Hum Neurosci. (2014) 8:879. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2014.00879
10. Feigin, VL, Nichols, E, Alam, T, Bannick, MS, Beghi, E, Blake, N, et al. Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2016. Lancet Neurol. (2019) 18:459–80. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30499-X
11. Bryan-Hancock, C, and Harrison, J. The global burden of traumatic brain injury: preliminary results from the global burden of disease project. Inj Prev. (2010) 16:A17. doi: 10.1136/ip.2010.029215.61
12. Nguyen, R, Fiest, KM, McChesney, J, Kwon, CS, Jette, N, Frolkis, AD, et al. The international incidence of traumatic brain injury: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Can J Neurol Sci. (2016) 43:774–85. doi: 10.1017/cjn.2016.290
13. Blennow, K, Brody, DL, Kochanek, PM, Levin, H, McKee, A, Ribbers, GM, et al. Traumatic brain injuries. Nat Rev Dis Prim. (2016) 2:1–19. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2016.84
14. Wagner, AK, Franzese, K, Weppner, JL, Kwasnica, C, Galang, GN, Edinger, J, et al. 43 - Traumatic Brain Injury. In: DX Cifu, editor. Braddom’s Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation (Sixth Edition). Elsevier (2021). p. 916–953.
15. Rosyidi, RM, Priyanto, B, Laraswati, NKP, Islam, AA, Hatta, M, Bukhari, A, et al. Characteristics and clinical outcome of traumatic brain injury in Lombok. Indonesia Interdiscip Neurosurg. (2019) 18:100470. doi: 10.1016/j.inat.2019.04.015
16. Qureshi, JS, Ohm, R, Rajala, H, Mabedi, C, Sadr-Azodi, O, Andrén-Sandberg, Å, et al. Head injury triage in a sub Saharan African urban population. Int J Surg. (2013) 11:265–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2013.01.011
17. Tesfaw, A, Eshetu, M, Dagnaw, F, Fenta, E, Gelaw, M, Mihret, G, et al. Prevalence of head injury among trauma patients at Debre Tabor comprehensive specialized hospital. North Central Ethiopia Open Access Surg. (2021) 14:47–54. doi: 10.2147/OAS.S321404
18. Van Tulder, R, Rodrigues, SB, Mirza, H, and Sexsmith, K. The UN’s sustainable development goals: can multinational enterprises lead the decade of action? J Int Bus Policy. (2021) 4:1–21. doi: 10.1057/s42214-020-00095-1
19. Walle, TA, Tiruneh, BT, and Bashah, DT. Prevalence of head injury and associated factors among trauma patients visiting surgical emergency department of Gondar University Referral Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia 2016. Across-sectional study. Int J Africa Nur Sci. (2018) 9:57–61. doi: 10.1016/j.ijans.2018.08.002
20. Tesfaw, A, Eshetu, M, Teshome, F, Fenta, E, Gelaw, M, Mihret, G, et al. Prevalence of head injury among trauma patients at Debre Tabor comprehensive specialized hospital, north Central Ethiopia. Open Access Surgery. (2021) 14:47–54.
21. Holder, Y, Peden, M, and Krug, E, (Eds.). Injury surveillance guidelines. Geneva: World Health Organization (2001).
22. Ghandour, H, Abbas, H, Al-Hajj, S, El Sayed, M, Harati, H, Kabbani, S, et al. Traumatic brain injury patient characteristics and outcomes in Lebanon: a multicenter retrospective cohort study. J Glob Health Reports. (2022) 6:1–12. doi: 10.29392/001c.32364
23. Eshete, A, and Taye, F. Magnitude of severe head injury and its associated factors among head injury patients in Gedeo zone, southern Ethiopia: a two-year retrospective study. Ethiop J Health Sci. (2018) 28:323–30. doi: 10.4314/ejhs.v28i3.10
24. Jasper, U, Opara, M, Pyiki, E, and Akinrolie, O. The epidemiology of hospital-referred head injury in northern Nigeria. J Scient Res Rep. (2014) 3:2055–64. doi: 10.9734/JSRR/2014/9645
25. Kool, B, Raj, N, Wainiqolo, I, Kafoa, B, McCaig, E, and Ameratunga, S. Hospitalised and fatal head injuries in Viti Levu, Fiji: findings from an island-wide trauma registry (TRIP 4). Neuroepidemiology. (2012) 38:179–85. doi: 10.1159/000337261
26. Sidpra, J, Jeelani, NUO, Ong, J, Birch, W, and Mankad, K. Skull fractures in abusive head trauma: a single Centre experience and review of the literature. Childs Nerv Syst. (2021) 37:919–29. doi: 10.1007/s00381-020-04870-6
27. Griswold, DP, Fernandez, L, and Rubiano, AM. Traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage: a scoping review. J Neurotrauma. (2022) 39:35–48. doi: 10.1089/neu.2021.0007
28. Kowalski, RG, Hammond, FM, Weintraub, AH, Nakase-Richardson, R, Zafonte, RD, Whyte, J, et al. Recovery of consciousness and functional outcome in moderate and severe traumatic brain injury. JAMA Neurol. (2021) 78:548–57. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2021.0084
29. Bashir, AA, Kong, VY, Weale, RD, Bruce, JL, Laing, GL, Bekker, W, et al. Quantifying the burden of trauma imaging on the CT scan service at a major trauma Centre in South Africa. S Afr J Surg. (2019) 57:48–53. doi: 10.17159/2078-5151/2019/v57n2a2836
30. Swenson, TL, Izmaylov, M, and Swenson, BR. Head Trauma. J Emerg Med. (2022) 62:128. doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2021.09.021
31. Hofman, M, Andruszkow, H, Kobbe, P, Poeze, M, and Hildebrand, F. Incidence of post-traumatic pneumonia in poly-traumatized patients: identifying the role of traumatic brain injury and chest trauma. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. (2020) 46:11–9. doi: 10.1007/s00068-019-01179-1
32. Hammond, FM, Corrigan, JD, Ketchum, JM, Malec, JF, Dams-OʼConnor, K, Hart, T, et al. Prevalence of medical and psychiatric comorbidities following traumatic brain injury. J Head Trauma Rehabil. (2019) 34:E1–e10. doi: 10.1097/HTR.0000000000000465
33. Sudhakar, SK, Sridhar, S, Char, S, Pandya, K, and Mehta, K. Prevalence of comorbidities post mild traumatic brain injuries: a traumatic brain injury model systems study. Front Hum Neurosci. (2023) 17:1158483. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2023.1158483
34. Hanscom, M, and Loane, DJ. Shea-Donohue T: brain-gut axis dysfunction in the pathogenesis of traumatic brain injury. J Clin Invest. (2021) 131:1–15. doi: 10.1172/JCI143777
35. Nishimura, K, Cordeiro, JG, Ahmed, AI, Yokobori, S, and Gajavelli, S. Advances in traumatic brain injury biomarkers. Cureus. (2022) 14:e23804. doi: 10.7759/cureus.23804
36. Daugherty, J, Sarmiento, K, Waltzman, D, and Xu, L. Traumatic brain injury-related hospitalizations and deaths in urban and rural Counties-2017. Ann Emerg Med. (2022) 79:288–296.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2021.09.433
37. Yue, JK, Upadhyayula, PS, Avalos, LN, Phelps, RRL, Suen, CG, and Cage, TA. Concussion and mild-traumatic brain injury in rural settings: epidemiology and specific health care considerations. J Neurosci Rural Pract. (2020) 11:023–33. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-3402581
38. Ayele, TA, Zeleke, BM, Tessema, GA, and Melak, MF. Magnitude and patterns of injuries among patients in Gondar University hospital, Northwest Ethiopia: an institutional-based study. Open Access Surg. (2017) 10:25–31. doi: 10.2147/OAS.S126043
39. Solomon, GM, Terefe, B, Asfaw, MG, and Liyew, B. Outcomes and associated factors of traumatic brain injury among adult patients treated in Amhara regional state comprehensive specialized hospitals. BMC Emerg Med. (2023) 23:109. doi: 10.1186/s12873-023-00859-x
40. Kumara, M, and Dhugasa, M. Factors affecting traumatic brain injury outcome among patients treated for head injury at surgical side, in Nekemte referral hospital, Oromia. Ethiopia J Spine Neuroscience. (2020) 1:1–13. doi: 10.14302/issn.2694-1201.jsn-20-3554
41. Krueger, EM, DiGiorgio, AM, Jagid, J, Cordeiro, JG, and Farhat, H. Current trends in mild traumatic brain injury. Cureus. (2021) 13:e18434. doi: 10.7759/cureus.18434
42. Asmamaw, Y, Yitayal, M, Debie, A, and Handebo, S. The costs of traumatic head injury and associated factors at University of Gondar Specialized Referral Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia. BMC Public Health. (2019) 19:1399. doi: 10.1186/s12889-019-7800-3
43. Cociu, S, Hamann, CJ, Cebanu, S, Cazacu-Stratu, A, Coman, MA, and Peek-Asa, C. Traumatic head injuries in Moldova: a cross-sectional analysis of medical registry data. Folia Med. (2023) 65:775–82. doi: 10.3897/folmed.65.e91262
44. Hagos, A, Tedla, F, Tadele, A, and Zewdie, A. Pattern and outcome of traumatic brain injury, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: a cross-sectional hospital-based study. Ethiop J Health Sci. (2022) 32:343–50. doi: 10.4314/ejhs.v32i2.15
45. Du, Q, Liu, C, Liu, Y, Li, J, Gong, X, Zhang, Q, et al. Investigation of long-term symptoms and influencing factors in patients with mild traumatic brain injury: a cross-sectional study. Int Emerg Nurs. (2023) 69:101313. doi: 10.1016/j.ienj.2023.101313
46. Uchiyama, M, Mori, K, Abe, T, and Imaki, S. Risk factors for clinically important traumatic brain injury in minor head injury in older people. Am J Emerg Med. (2024) 80:156–61. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2024.04.003
47. Katayama, Y, Kitamura, T, Kiyohara, K, Sado, J, Hirose, T, Matsuyama, T, et al. Factors associated with posttraumatic meningitis among traumatic head injury patients: a nationwide study in Japan. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. (2021) 47:251–9. doi: 10.1007/s00068-019-01224-z
48. Barrett, JW, Williams, J, Skene, SS, Griggs, JE, Bootland, D, Leung, J, et al. Head injury in older adults presenting to the ambulance service: who do we convey to the emergency department, and what clinical variables are associated with an intracranial bleed? A retrospective case-control study. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. (2023) 31:65. doi: 10.1186/s13049-023-01138-1
Keywords: head injury, incidence, risk factor, trauma, Sidama Ethiopia
Citation: Abebe T, Alemu T and Sorato MM (2024) Incidence, risk factors and outcomes of traumatic head injury among trauma patients visited at the Yanet Trauma and Surgery Specialized Centre, Sidama region, Hawassa, Ethiopia: cohort study. Front. Neurol. 15:1431999. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1431999
Edited by:
Renato Anghinah, University of São Paulo, BrazilReviewed by:
Diogo Haddad Santos, Santa Casa of São Paulo, BrazilJoacir Graciolli Cordeiro, University of Miami, United States
Copyright © 2024 Abebe, Alemu and Sorato. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tsegaye Alemu, dHNlZ2F5ZWE0OUBnbWFpbC5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Tadelech Abebe1†
Tadelech Abebe1† Tsegaye Alemu
Tsegaye Alemu Mende Mensa Sorato
Mende Mensa Sorato