
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
BRIEF RESEARCH REPORT article
Front. Neurol., 08 November 2024
Sec. Neurogenetics
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2024.1428076
This article is part of the Research TopicGenetics in Rare Neurological Diseases: From Discovery to Targeted TreatmentView all 12 articles
The P4HTM gene encodes a transmembrane prolyl 4-hydroxylase, which is responsible for the degradation of hypoxia-inducible transcription factors (HIF) under normoxia. Clinically, biallelic P4HTM variants have been identified in patients with hypotonia, hypoventilation, intellectual disabilities, dysautonomia, epilepsy, and eye abnormalities (HIDEA syndrome). Seizure was one of the most prominent symptoms. However, the clinical features of patients with epilepsy associated with P4HTM variants remain unclear. In this report, we describe a one-month-old infant with HIDEA syndrome caused by compound heterozygous P4HTM variants (c.300dupG/p.Gly103Argfs*22 and c.488C > T/p.Ala163Val). The infant presented with clonic seizures of focal onset that responded well to valproate, but with profound intellectual disability and global developmental delay at the last follow-up at 3 years old. A review of the existing literature indicates that seizures in this population typically begin early in infancy, manifest in multiple types, and are relatively well controlled. Epilepsy seemed unrelated to developmental outcomes or disease progression. Valproate, which has HIF-1α inhibiting properties, may be a promising treatment avenue for this population.
The P4HTM gene (OMIM* 614584) encodes a transmembrane prolyl 4-hydroxylase (P4H-TM), which is involved in the degradation of hypoxia-inducible transcription factors (HIF) under normoxia (1). The P4H-TM protein is ubiquitously expressed during embryonic, juvenile, and adult stages, with the highest levels in the brain and eye (2). Clinically, biallelic variants in P4HTM have been reported to cause hypotonia, hypoventilation, impaired intellectual development, dysautonomia, epilepsy, and eye abnormalities (HIDEA syndrome, OMIM# 618493) (3–7). Seizures were observed in up to 57% (17 out of 30) of the cases (8). However, there are limited reports describing epilepsy in patients with P4HTM variants, and the clinical features of epilepsy in this population remain unclear.
This report presents a case of early-onset epilepsy associated with HIDEA syndrome due to P4HTM variants, provides a comprehensive review of the existing literature on the epileptic characteristics, and discusses potential treatment strategies.
A one-month-old male infant presented with recurrent clonic seizures, without signs of lip cyanosis, tachycardia, upward eye rolling, or drooling. A single episode of seizures lasted approximately 50 s and occurred three to five times per day. The infant was delivered at term, with a birth weight of 3.25 kg, and had a history of neonatal pneumonia. There was no family history of epilepsy or genetic disorders. Physical examination revealed hypotonia and roving eye movements (Supplementary Video S1). Laboratory tests, including full blood count, electrolytes, glucose, lactate, ammonia, liver and renal function tests, metabolic assessments, and brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), were all normal. Video electroencephalogram (EEG) revealed delayed maturation, multifocal discharges during both wakefulness and sleep, and captured a clonic seizure with focal onset (Figures 1A,B). According to the criteria of the Commission on Classification and Terminology of the ILAE, the infant was diagnosed with focal clonic seizures with retained awareness (9). Valproate was initiated at a dosage of 18.5 mg/kg/day for seizure control. Following subsequent titration, the infant became seizure-free at a maintenance dose of 26 mg/kg/day. At the last follow-up, the three-year-old child exhibited effective seizure control with valproate treatment, along with significant developmental delay and functioning at the level of a newborn. There was no evidence of hypoventilation, respiratory problems, obesity, or dysautonomia.
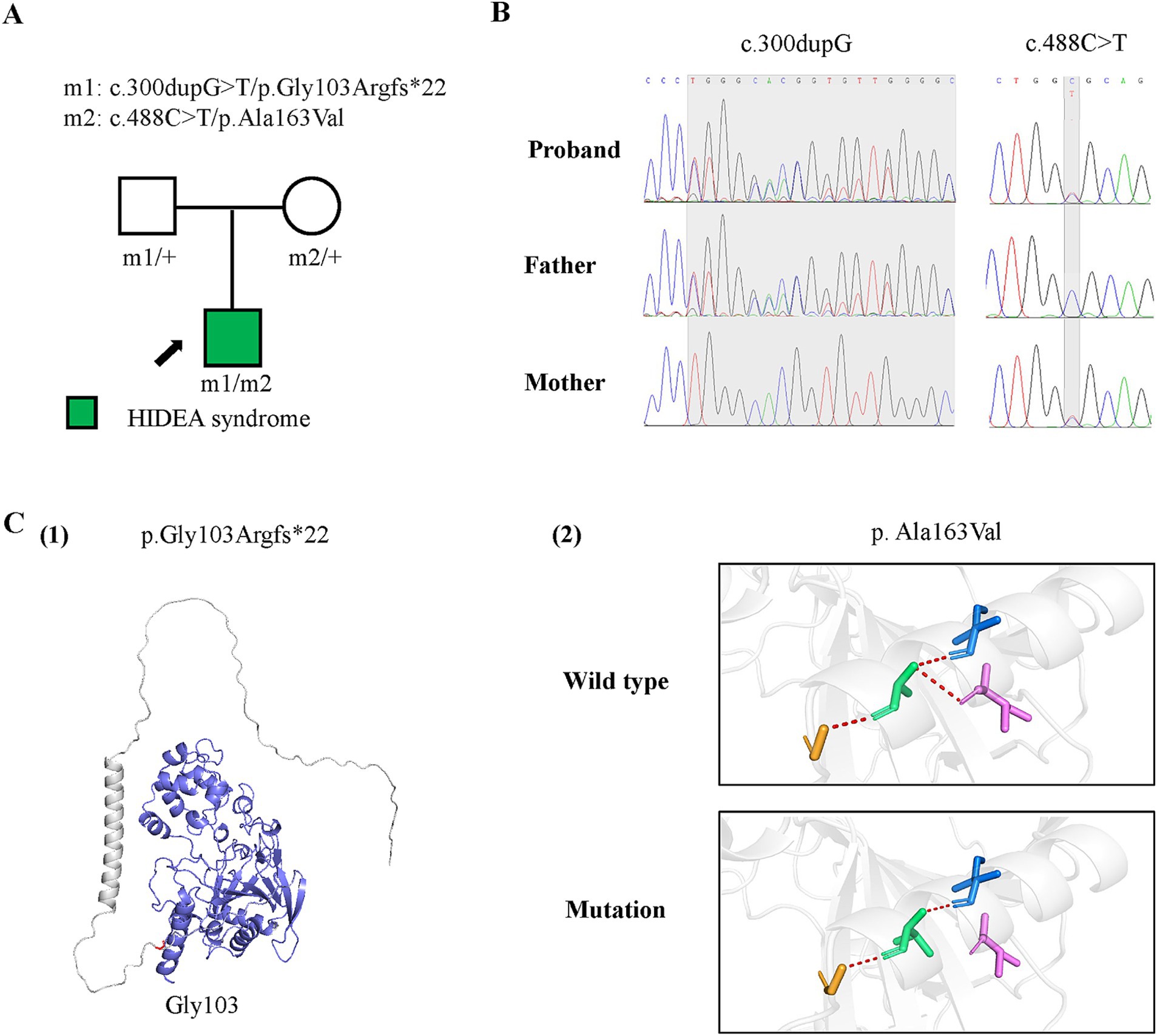
Figure 1. Genetic data of the case with P4HTM variants and molecular effect of the variants on P4H-TM protein. (A) Pedigrees of the case with P4HTM and their corresponding phenotypes. (B) DNA sequence chromatogram of the P4HTM variants. The gray regions indicate the positions of the variants. (C) Protein structure change and hydrogen bond changes of the variants from the present study. (1) The amino acid p.Gly163 is shown in red, and the deleted region in blue. (2) Hydrogen bond change of the p. Ala163Val variant.
To determine the underlying cause, genomic DNA was extracted from the proband’s and parents’ peripheral blood for trio-based whole exome sequencing. Target genes were captured by probe hybridization and enriched based on the IDT xGen Exome Research Panel. Sequence reads were aligned to the GRCh38/hg38 reference genome. Variant annotation was conducted using ANNOVAR software. Pathogenic variants were screened for their presence in exonic regions, non-synonymous mutations, and a frequency of less than 5% in databases such as ExAC, 1,000 Genomes, and gnomAD. Variants were further evaluated using databases such as dbSNP, OMIM, HGMD, and ClinVar. Sanger sequencing was used to verify variants in the proband and parents. Protein modeling was performed using AlphaFold web tool and visualization using PyMOL Molecular Graphics System 2.3.2 software.
A pair of compound heterozygous frameshift and missense variants of the P4HTM gene were identified, including a paternally inherited c.300dupG/p.Gly103Argfs*22 and a maternally inherited c.488C > T/p.Ala163Val (Figures 2A,B; transcript NM_177939.3). According to the ACMG guidelines, the p.Gly103Argfs*22 variant was classified as a variant of likely pathogenic (PVSI+PM2), and the p.Ala163Val variant was classified as having uncertain significance (PM2 + PM3 + PP3) (10). However, the biallelic variants had no or less than 0.0005 frequency in the gnomAD database and had not been reported previously. The p.Gly103Argfs*22 and p.Ala163Val variants were all predicted to be deleterious by in silico tools and altered protein structure or hydrogen bonding with surrounding residues (Figures 1C). These results suggest that P4HTM is the potential pathogenic gene associated with HIDEA syndrome in this patient.
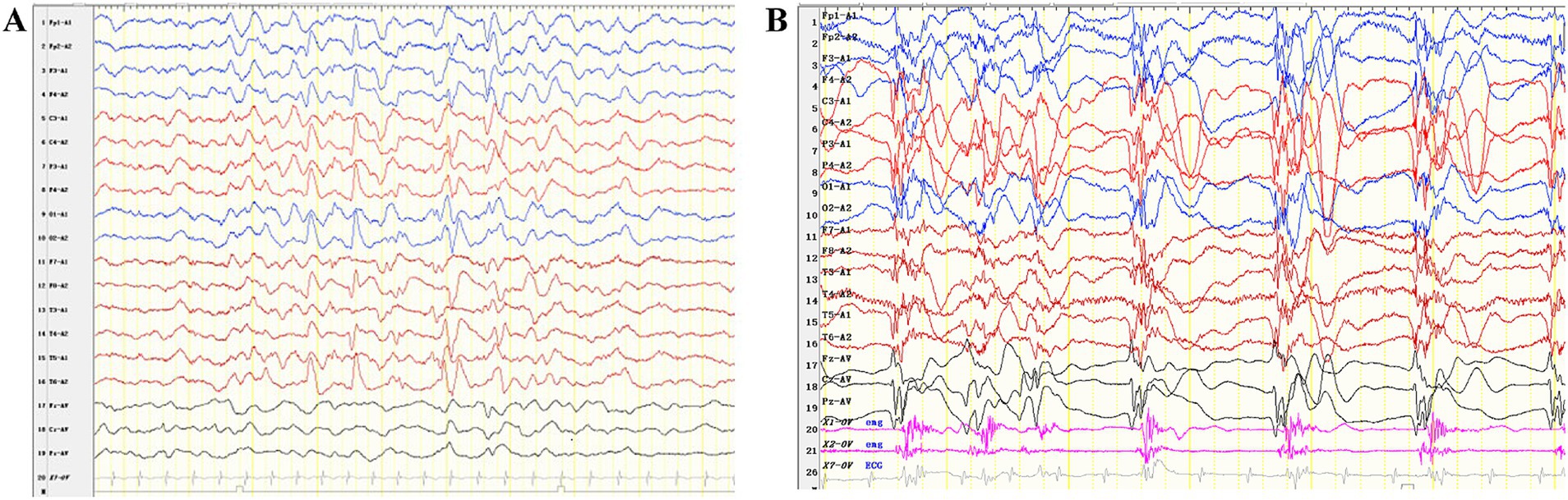
Figure 2. Interictal and ictal EEG recordings of the patient with P4HTM variants. (A) Interictal EEG of the case indicated multifocal discharges. (B) The ictal EEG shows generalized slow waves or polyspike-slow waves, along with rhythmic firing of myoelectric activity.
A literature search was conducted on PubMed and Google Scholar up to April 1, 2024, using the terms “P4HTM” or “HIDEA.” Articles describing seizures were reviewed, and a summary of the clinical and genetic profiles of the patients is presented in Table 1.
The P4HTM gene, located on chromosome 3p21.31, encodes P4H-TM, which is primarily expressed during the embryonic stage, particularly in the brain, emphasizing its critical role in early brain development (2). Clinically, biallelic variants in P4HTM gene have been reported to cause HIDEA syndrome (3–6, 8). In the present study, the infant exhibited profound global developmental delay, epilepsy, hypotonia, and abnormal eye movements after birth. Subsequently, a pair of compound heterozygous P4HTM variants was identified in the patient. One variant was classified as likely pathogenic, while the other was classified as of uncertain significance in accordance with the ACMG guidelines. However, the identified compound heterozygous P4HTM variants had no or low allele frequencies in the general population, were predicted to be damaging by in silico tools, and altered protein structure or affected hydrogen bonding. Based on the clinical presentations and genetic findings, the patient was diagnosed with HIDEA syndrome.
Seizure was a prominent symptom of HIDEA syndrome. A total of seven homozygous and three compound heterozygous pathogenic P4HTM variants were identified in 18 patients with epilepsy from 11 families (Table 1) (3, 4, 7, 8). The available data indicate that the onset of seizures varied from birth to 6 months among seven patients, with four patients exhibiting onset within the first 3 months. This finding is consistent with the predominant expression of P4H-TM in the fetal brain. However, two exceptions were noted: one patient had seizure onset at 22 years of age, while another experienced a single episode at 2.5 years. The observed seizures were of various types, including focal in four patients, generalized tonic–clonic, tonic, and atonic seizures, and epileptic spasms, each observed in one patient. Seven patients exhibited normal results, and two patients had structural abnormalities on brain MRI, including generalized brain atrophy and enlargement of the ventricles and subarachnoid space. Interictal EEG revealed background abnormalities in four cases, multifocal spikes in three cases, and focal discharges in two cases. The most frequently administered drugs were valproate and phenobarbital, each prescribed to three patients, while lamotrigine, vigabatrin, carbamazepine, and topiramate were each prescribed to one patient. Five patients received monotherapy, while two patients were treated with combination therapy including carbamazepine and valproate for one patient, and topiramate and valproate for the other. The seven cases with detailed seizure descriptions either achieved seizure freedom or responded well to anti-seizure medications.
Homozygous and heterozygous c.1073G > A variants identified in three pedigrees suggested that the c.1073G > A variant may be a hotspot variant (3, 4, 8). Despite harboring identical biallelic P4HTM variants (homozygous c.1073G > A, c.949delG, and heterozygous c.482A > C and c.286dupC), patients from the same family exhibited variable symptoms, with some experiencing seizures while others did not (3–5), suggesting that the disease phenotype may be influenced by additional genetic and environmental factors. The seizures observed in patients with HIDEA syndrome associated with P4HTM variants were effectively controlled, with no cases of drug-resistant epilepsy. These findings indicate that early-onset epilepsy induced by P4HTM variants cannot be classified as developmental and epileptic encephalopathy. However, despite early seizure freedom in seven cases, six patients exhibited profound or severe intellectual disability and global developmental delay, with four being nonverbal and two unable to walk. Additionally, in the population with HIDEA syndrome without epilepsy, some patients still had severe or profound intellectual disability/global developmental delay, were nonverbal, did not walk, and died in early childhood (3–6, 11). The presence or absence of seizures and their control were not correlated with either developmental outcomes or the progression of HIDEA syndrome.
In mice, homozygous deletion of p4htm results in an improper folding of the corresponding protein and overlapping phenotypic features with HIDEA patients with biallelic P4HTM variants, suggesting a loss-of-function disease mechanism (3, 4, 12). Thus, the compound heterozygous P4HTM variants identified in this patient with HIDEA syndrome may potentially be loss-of-function. Although the exact mechanism of P4H-TM in HIDEA syndrome remains unclear, it is known that P4H-TM acts on the hydroxylation of the HIF α protein, which is localized in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane and plays a key role in the response of cells to hypoxia (1). Knockdown of endogenous p4htm in neuroblastoma cells has been shown to increase HIF-1a protein levels in normoxia, and p4htm is induced by hypoxia in a cell type-specific manner (1). It is postulated that the disruption of HIF-1a within the endoplasmic reticulum may result in an imbalance in protein homeostasis under hypoxia, consequently triggering neuronal apoptosis. Abnormal HIF-1α levels have also been reported in some primary genetic mitochondrial diseases (13). Hay et al. observed mitochondrial dysfunction in patients with P4HTM-associated HIDEA syndrome and suggested that HIDEA syndrome may be a potential primary mitochondrial disorder (6).
Given the limited molecular understanding of the clinical symptoms associated with HIDEA syndrome, devising therapeutic strategies remains challenging. Nevertheless, targeting HIF-1α inhibitors may be a potential approach to prevent disease progression. Preclinical studies have demonstrated that the inhibition of HIF-1α activity has a significant impact on tumor growth (14, 15). Valproic acid, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, maintained the self-renewal of mouse embryonic stem cells under hypoxic conditions in vitro by suppressing HIF-1α, and downregulated the expression of HIF-1α in human retinal Müller cells under hypoxic conditions (16, 17). In patients with epilepsy associated with P4HTM variants, the only two individuals who received combination therapy were both treated with valproate and survived (3, 4, 7). In addition to seizure control, the present patient began valproate treatment early in life despite exhibiting profound intellectual disability and global developmental delay, as well as being nonverbal and unable to walk. Notably, the patient did not develop hypoventilation, obesity, or dysautonomia of thermoregulation, suggesting that valproate may also play a role in ameliorating other symptoms of HIDEA syndrome. Certainly, the effect of HIF-1α inhibitors including valproate in this population needs to be further confirmed.
In conclusion, the seizures observed in the patients with biallelic P4HTM variant-associated HIDEA syndrome are typically of infantile onset, variable in type, and relatively well controlled. Epilepsy does not appear to be associated with developmental outcome or disease progression. Valproate, which has the role of inhibiting HIF-1α, may be a promising treatment option.
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available because the data are not publicly available due to privacy or ethical restrictions. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to aGVuYWk2MTgzQDE2My5jb20=.
The studies involving humans were approved by Chengdu Women’s and Children’s Central Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual (s), and minor (s)’ legal guardian/next of kin, for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Y-JW: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. S-XL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. W-GH: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. L-LZ: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. ML: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. J-LC: Investigation, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (No. 2023JDKP0070) and the Chengdu Medical Research Program (No. 2023013). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, and decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript.
The help of patients and clinicians in participating in this work are greatly appreciated.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2024.1428076/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Video S1 | Aberrant eye movements in patients with P4HTM variants.
1. Koivunen, P, Tiainen, P, Hyvärinen, J, Williams, KE, Sormunen, R, Klaus, SJ, et al. An endoplasmic reticulum transmembrane prolyl 4-hydroxylase is induced by hypoxia and acts on hypoxia-inducible factor α. J Biol Chem. (2007) 282:30544–52. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M704988200
2. Wu, C, Orozco, C, Boyer, J, Leglise, M, Goodale, J, Batalov, S, et al. BioGPS: an extensible and customizable portal for querying and organizing gene annotation resources. Genome Biol. (2009) 10:R130. doi: 10.1186/gb-2009-10-11-r130
3. Rahikkala, E, Myllykoski, M, Hinttala, R, Vieira, P, Nayebzadeh, N, Weiss, S, et al. Biallelic loss-of-function P4HTM gene variants cause hypotonia, hypoventilation, intellectual disability, dysautonomia, epilepsy, and eye abnormalities (HIDEA syndrome). Genet Med. (2019) 21:2355–63. doi: 10.1038/s41436-019-0503-4
4. Kaasinen, E, Rahikkala, E, Koivunen, P, Miettinen, S, Wamelink, MMC, Aavikko, M, et al. Clinical characterization, genetic mapping and whole-genome sequence analysis of a novel autosomal recessive intellectual disability syndrome. Eur J Med Genet. (2014) 57:543–51. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2014.07.002
5. Maddirevula, S, Ben-Omran, T, AlMureikhi, M, Eyaid, W, Arabi, H, Alkuraya, H, et al. Further delineation of HIDEA syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. (2020) 182:2999–3006. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.61885
6. Hay, E, Wilson, LC, Hoskins, B, Samuels, M, Munot, P, and Rahman, S. Biallelic P4HTM variants associated with HIDEA syndrome and mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I deficiency. Eur J Hum Genet. (2021) 29:1536–41. doi: 10.1038/s41431-021-00932-8
7. Järvelä, I, Määttä, T, Acharya, A, Leppälä, J, Jhangiani, SN, Arvio, M, et al. Exome sequencing reveals predominantly de novo variants in disorders with intellectual disability (ID) in the founder population of Finland. Hum Genet. (2021) 140:1011–29. doi: 10.1007/s00439-021-02268-1
8. Kraatari-Tiri, M, Soikkonen, L, Myllykoski, M, Jamshidi, Y, Karimiani, EG, Komulainen-Ebrahim, J, et al. HIDEA syndrome is caused by biallelic, pathogenic, rare or founder P4HTM variants impacting the active site or the overall stability of the P4H-TM protein. Clin Genet. (2022) 102:444–50. doi: 10.1111/cge.14203
9. Object . Operational classification of seizure types by the international league against epilepsy: position paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. (2024) Available at: https://core.ac.uk/reader/195302650?utm_source=linkout (Accessed October 8, 2024).
10. Richards, S, Aziz, N, Bale, S, Bick, D, Das, S, Gastier-Foster, J, et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. (2015) 17:405–24. doi: 10.1038/gim.2015.30
11. Lim, AM, Tan, PL, Visruthan, NK, Fong, N, Viegelmann, GC, and Tan, YH. HIDEA syndrome: a rare cause of congenital hypoventilation in a premature infant. Pediatr Pulmonol. (2022) 57:1826–9. doi: 10.1002/ppul.25966
12. Ala-Nisula, T, Halmetoja, R, Leinonen, H, Kurkela, M, Lipponen, H-R, Sakko, S, et al. Metabolic characteristics of transmembrane prolyl 4-hydroxylase (P4H-TM) deficient mice. Pflüg Arch Eur J Physiol. (2024) 476:1339–51. doi: 10.1007/s00424-024-02920-5
13. Mukaneza, Y, Cohen, A, Rivard, M-È, Tardif, J, Deschênes, S, Ruiz, M, et al. mTORC1 is required for expression of LRPPRC and cytochrome-c oxidase but not HIF-1α in Leigh syndrome French Canadian type patient fibroblasts. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2019) 317:C58–67. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00160.2017
14. Ban, HS, Uto, Y, Won, M, and Nakamura, H. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) inhibitors: a patent survey (2011-2015). Expert Opin Ther Pat. (2016) 26:309–22. doi: 10.1517/13543776.2016.1146252
15. Semenza, GL . Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. (2003) 3:721–32. doi: 10.1038/nrc1187
16. Kim, YJ, Park, SJ, Kim, NR, and Chin, HS. Effects of histone deacetylase inhibitor (Valproic acid) on the expression of hypoxia-inducible Factor-1 alpha in human retinal Müller cells. Korean J Ophthalmol. (2017) 31:80–5. doi: 10.3341/kjo.2017.31.1.80
Keywords: P4HTM gene, epilepsy, HIDEA syndrome, HIF-1α inhibitor, valproate, case report, review
Citation: Wang Y-J, Li S-X, Hu W-G, Zhao L-L, Lan M and Chen J-L (2024) Clinical characteristics of patients with P4HTM variant-associated epilepsy and therapeutic exploration: a case report and literature review. Front. Neurol. 15:1428076. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1428076
Received: 05 May 2024; Accepted: 23 October 2024;
Published: 08 November 2024.
Edited by:
Huifang Shang, Sichuan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Bharatendu Chandra, The University of Iowa, United StatesCopyright © 2024 Wang, Li, Hu, Zhao, Lan and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Si-Xiu Li, aGVuYWk2MTgzQDE2My5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.