- 1West China Hospital, Sichuan University/West China School of Nursing, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
- 2Department of Critical Care Medicine, West China Hospital, Sichuan University/West China School of Nursing, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
Objectives: Dysphagia is a common complication in stroke patients, widely affecting recovery and quality of life after stroke. The objective of this systematic review is to identify the gaps that between evidence and practice by critically assessing the quality of clinical practice guidelines (CPGs) for management of dysphagia in stroke.
Methods: We systematically searched academic databases and guideline repositories between January 1, 2014, and August 1, 2023. The Appraisal of Guidelines for Research and Evaluation (AGREE II) instrument was used by two authors to independently assess CPG quality.
Results: In a total of 14 CPGs included, we identified that three CPGs obtained a final evaluation of “high quality,” nine CPGs achieved “moderate quality” and two CPGs received “low quality.” The domain of “scope and purpose” achieved the highest mean score (91.1%) and the highest median (IQR) of 91.7% (86.1, 94.4%), while the domain of “applicability” received the lowest mean score (55.8%) and the lowest median (IQR) of 55.4% (43.2, 75.5%).
Conclusion: The CPG development group should pay more attention to improving the methodological quality according to the AGREE II instrument, especially in the domain of “applicability” and “stakeholder involvement;” and each item should be refined as much as possible.
1 Introduction
Globally, stroke remained the second-leading cause of death and the third-leading cause of death and disability combined in 2019 (1, 2). Dysphagia is a common complication in stroke patients, widely affecting recovery and quality of life after stroke and increasing mortality risk through increased risk of dehydration, malnutrition and pneumonia (3). The incidence of dysphagia varies widely depending on the method of assessment, compared with clinical assessment (30–55%) and video rheology (64–78%), a lower incidence was detected using initial screening tools (37–43%) (4). However, managing dysphagia correctly and effectively can shorten hospital stays, reduce the risk of death, and decrease healthcare costs (5, 6).
Clinical practice guidelines (CPGs) are a type of declaration that include evidence-informed recommendations aimed at optimizing patient care that are informed by a systematic review of evidence and an assessment of the benefits and harms of alternative care options (4). To date, a number of CPGs have been developed and updated with the aim of ensuring optimal dysphagia management of stroke patients. CPGs would contribute to improving the quality of health care, for example, providing evidence for clinicians to make decisions about patient care and determining appropriate medical criteria, thereby identifying gaps between evidence and practice (7). Nevertheless, hospital personnel adherence to evidence-based stroke care is limited (8), translating evidence into clinical practice is challenging, and implementation of these CPGs in clinical practice remains suboptimal (9, 10).
The quality of the CPGs has a direct impact on utilization (11, 12), and the purpose of this study was to assess the quality of guidelines for managing poststroke dysphagia. Therefore, we used the Appraisal of Guidelines for Research and Evaluation II (AGREE II) instrument (13) to evaluate the quality of CPGs for dysphagia management after stroke, which may be helpful in identifying the potential factors that impact the quality of CPGs. The findings would illustrate the gaps between evidence-based guidelines and clinical practice and attempt to explore potential measures of improvement.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Search strategy
A comprehensive literature search was conducted by two authors to identify CPGs for the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of dysphagia after acute stroke between January 1, 2014, and August 1, 2023. The following databases were searched: PubMed, Web of Science and EMBASE, Clinical Practice Guidelines, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, National Guideline Clearinghouse, World Health Organization, Scottish Intercollegiate Guideline Network, New Zealand Guidelines Group and BMJ Best Practice. Search strategies were tailored according to each database (The specific search strategy is displayed in Supplementary File 1). All results were imported into EndNote (Version.X9.2), where duplicates were removed. A third author resolved any disagreements.
2.2 Eligibility criteria
The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) International and national CPGs published on the management of dysphagia after acute stroke; (2) Published or updated from January 1, 2014 to August 1, 2023; (3) Published in English; and (4) Guidelines focused on adult patients. The excluded criteria were as follows: (1) Guideline-related interpretation, application evaluation or brief versions, etc.; (2) Full text not available; and (3) Guidelines under development or withdrawal.
2.3 Data screening and extraction
The titles and abstracts of all search results were screened by two authors before checking the full text. In addition, two authors scanned the reference lists of the confirmed papers to identify more relevant CGPs. Then, they extracted the characteristics of the CPGs including year, developer, grading system, country/region, target population, and multidisciplinary team using a predesigned standardized data extraction form.
2.4 Quality assessment
The quality of the 14 CPGs was appraised by two authors trained using the AGREE II instrument, which is a reliable tool that is widely used to assess the quality of CPGs (13). AGREE II consists of 23 items organized into six domains and two overall assessment portions. Each item was scored from 1 to 7 (1 = strongly disagree, 7 = strongly agree). Prior to the formal assessment, we discussed the assessment criteria based on the AGREE II manual and training tools to maintain a consistent understanding of each item. After scoring, we organized the CPGs and randomly cross-checked 10% (14) to ensure consistency between authors, especially for items with wide variations in scoring.
The standardized scores for each domain were computed based on the achievement scores (13), as follows: The maximum possible score of domain = 7 (strongly agree) × number of items × number of evaluators; a minimum possible score of domain = 1 (strongly disagree) × the number of items x the number of evaluators. The standardized scores = (obtained score ─ minimum possible score)/(maximum possible score ─ minimum possible score) × 100%.
The AGREE II manual does not offer any advice on how to explain the scores. In accordance with previous studies (15, 16), if a CPG scored above 70% on six domains, it was classified as ‘high quality’; if a CPG scored above 70% on three to five domains, it was classified as ‘moderate quality’; and if a CPG scored less than 70% on ≥ two domains, it was classified as ‘low quality’.
2.5 Statistical analysis
All data were analyzed using IBM SPSS Statistics Version 26.0 software and Microsoft Excel 2021. Mean, median and interquartile range (IQR) were computed for the domain scores. The intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was computed to measure the interrater agreement when performing a quality appraisal of the CPGs among the two appraisers to ensure the reliability of our conclusions. The level of ICC was classified according to commonly cited cutoffs: poor (< 0.50), fair (0.50–0.75), good (0.75–0.90) or excellent (0.90–1.00) (17).
3 Results
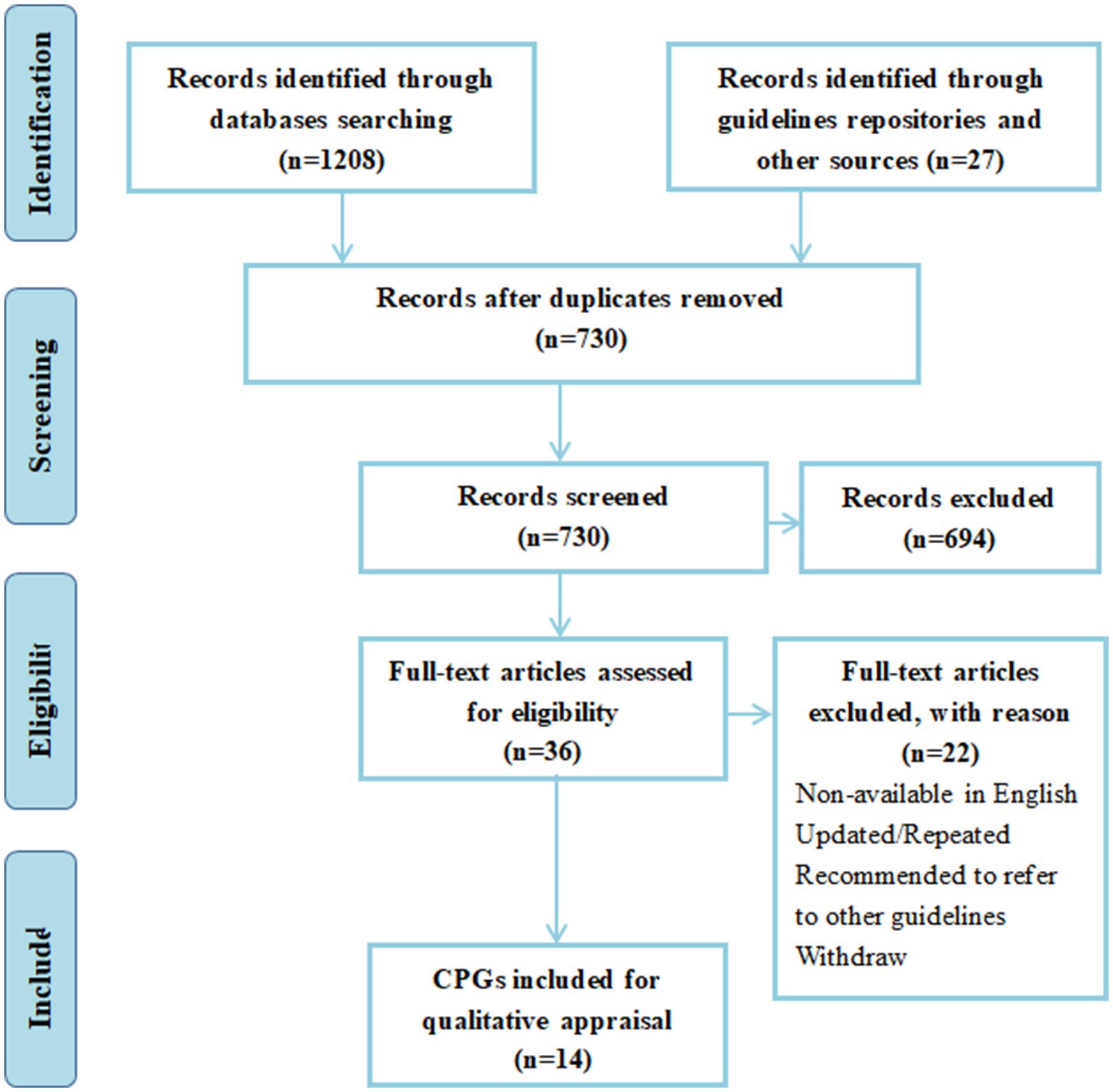
A total of 1,208 titles and abstracts were generated through database and manual searches. After deleting duplicates, 730 articles were filtered by title and abstract. A total of 36 full-text CPGs were screened for eligibility, and 14 CPGs were included in our systematic review. Figure 1 provides the PRISMA flow chart (18). Table 1 shows the general characteristics of the CPGs included in the analysis. Regarding geographical distribution, six of them are from Europe, the US and Canada all have two CPGs each, while Brazil, China, Turkey, Australia and New Zealand have only one.
3.1 Quality of CPGs according to the AGREE II domains
Table 2 reports the ICC score, overall quality and recommendation comments of all CPGs. In total, 14 CPGs were included, only three CPGs were found to be of high quality with all domains reaching a score higher than 70%, nine CPGs were graded as moderate quality and the remaining two were classified as low quality. The evaluation results of the two appraisers were reliably consistent, with ICCs (95% CI) ranging from 0.75 (0.48, 0.88) to 0.90 (0.82, 0.99).
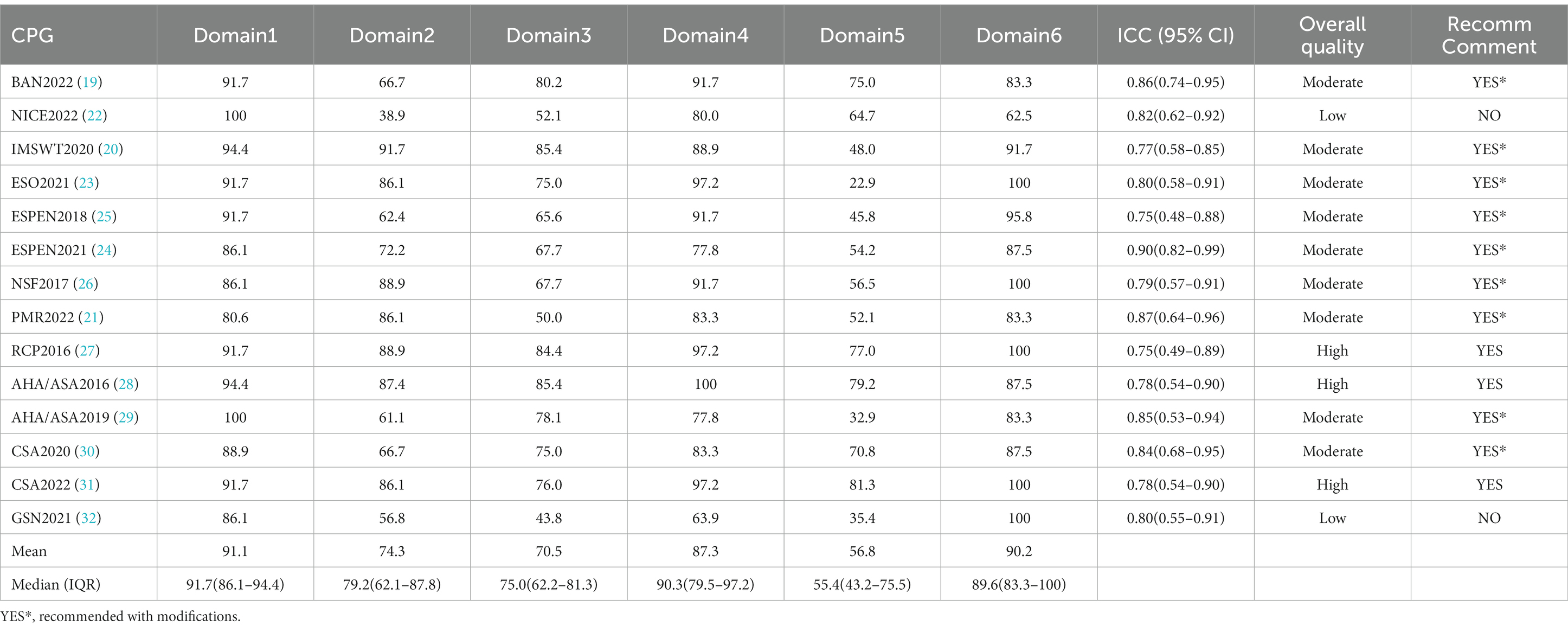
Table 2. Appraisal of Guidelines for Research and Evaluation (AGREE) II version result for clinical practice guidelines.
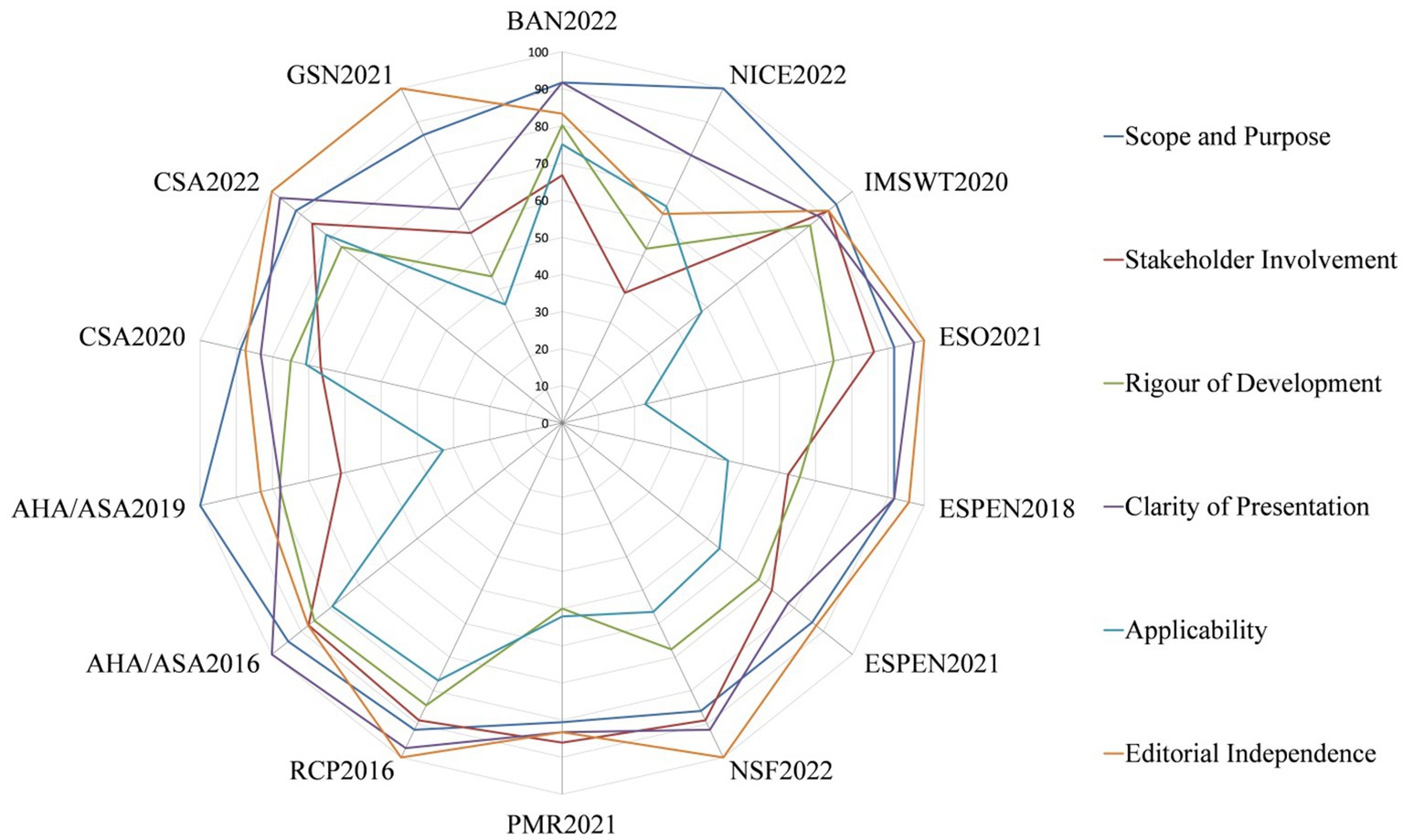
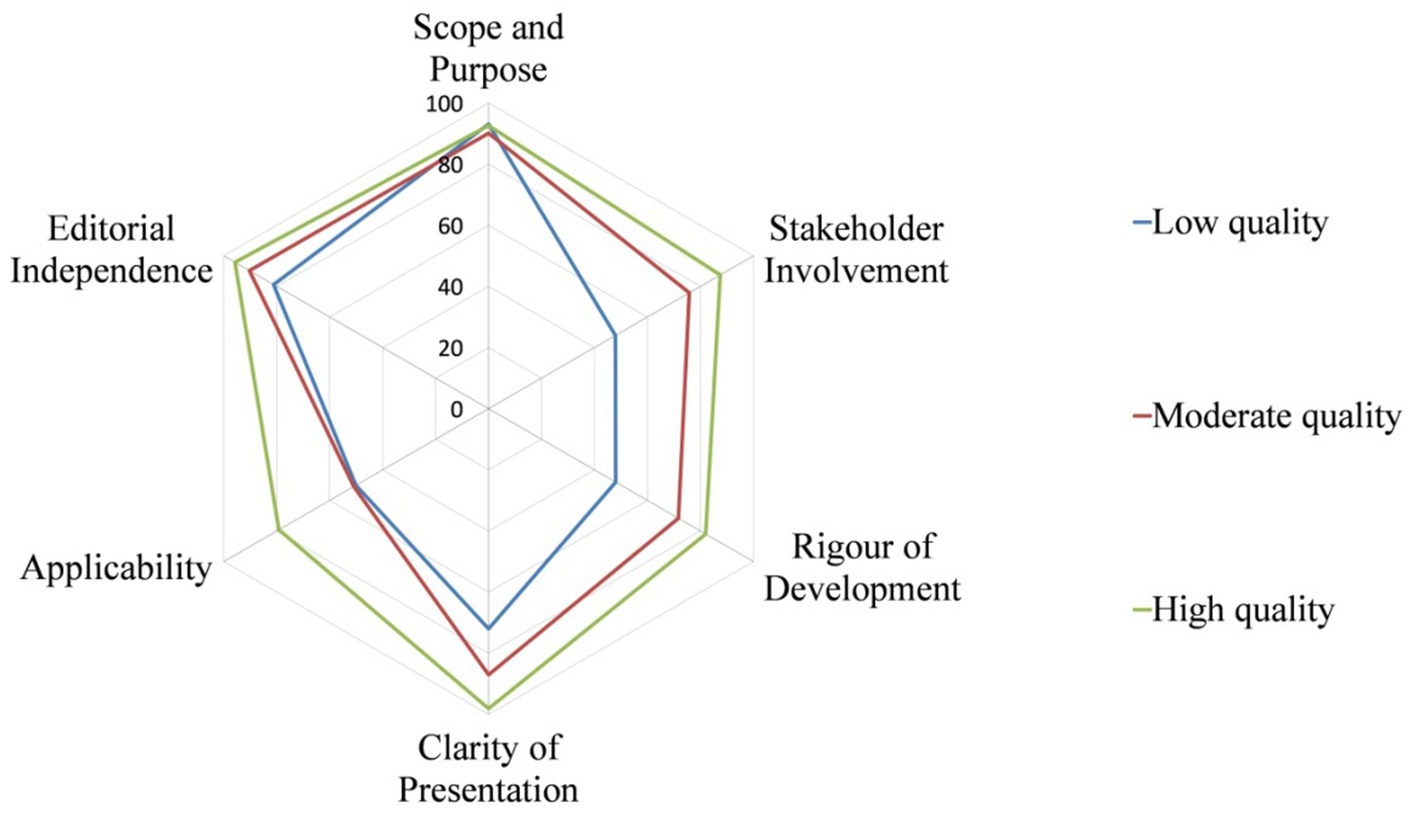
The quality of CPGs evaluated by AGREE II varied widely, not only between guidelines, but also between domains within guidelines. Figure 2 shows the score distribution of the 6 domains among the 14 CPGs. Figure 3 shows the mean score of each domain for all CPGs sorted by quality classification.
3.1.1 Scope and purpose
The domain of “scope and purpose” obtained the highest mean (91.1%) and the highest median (IQR) score of 91.7% (86.1, 94.4%). Moreover, all guidelines achieved over 70% in this domain, but only two of them had a maximum score of 100% (22, 29).
3.1.2 Stakeholder involvement
The standardized scores in this domain ranged from 38.9 to 91.7%, with nine of 14 CPGs scoring above 70%. Most of the poor scores are due to the views and preferences of the target population (patients, public, etc.) have not been sought (22, 32).
3.1.3 Rigor of development
Regarding the standardized scores in this domain, the mean was 70.5%, and the median (IQR) was 75.0% (62.2, 81.3%). GSN2021 (32) obtained the lowest scores (43.8%). Most CPGs lacked clarity in describing all stages of the methodological development or did not provide a procedure for updating the guidelines.
3.1.4 Clarity of presentation
In this domain, the mean score was 87.3%, and the median (IQR) was 90.3% (79.5, 97.2%). Six CPGs received above 90%. In contrast, GSN2021 (32) obtained the lowest score of 63.9%, which means that the guideline development group did not present recommendations clearly.
3.1.5 Applicability
This domain yielded the lowest mean score of 56.8% and the lowest median (IQR) score of 55.4% (43.2, 75.5%). Five CPGs scored more than 70% (19, 27–29, 31), but only CSA2022 (31) scored above 80%, whereas the other guidelines described certain items in the domain unsatisfactorily.
3.1.6 Editorial independence
In this domain, the mean was 90.2%, and the median (IQR) was 89.6% (83.3, 100%). Five CPGs (23, 26, 27, 31, 32) received full marks in this domain, with the exception of NICE2022 (22), which did not explicitly provide information on editorial independence and the competing interests of members of the CPG development group have not been recorded and addressed.
4 Discussion
The present study proposes a critical review that evaluates the quality of 14 CPGs developed to manage dysphagia in acute stroke using the AGREE II tool (13). Depending on our results, the quality of CPGs evaluated by AGREE II varied significantly, not only between guidelines, but also between domains within guidelines. RCP2016 (27), AHA/ASA2016 (28) and CSA2022 (31) were classified as high quality and thus were recommended based on the AGREE II tool. Among the domains, “scope and purpose” obtained the highest mean score of 91.1% and the highest median (IQR) score of 91.7% (86.1, 94.4%), while “applicability” yielded the lowest mean score of 56.8% and the lowest median (IQR) score of 55.4% (43.2, 75.5%).
Based on the AGREE II reported items, the domain of “applicability” performed the worst, which is consistent with other quality assessment results of CPGs in different healthcare topics (33, 34). Many CPGs failed to identify and describe the potential facilitators, barriers and advice or tools on how the recommendations can be put into practice. This may be one of the reasons why clinical implementation is not as effective as it could be (9, 35). To address this issue, we find that implementation science approaches are feasible, and a quality improvement intervention that includes online educational videos, mobile health technology, simplified versions of the guidelines manual, audits and feedback, is recommended to improve the CPG adherence of medical staff and patients, user awareness and CPG uptake (36–39).
Regarding the domain of “stakeholder involvement,” some CPGs did not clearly describe the guideline development group or the views and preferences of the target population (patients, public, etc.) were not been sought. During the development of CPGs, patients and a variety of stakeholders, such as clinicians of all types, insurance payers and funders, health policy decision makers, and experts should be involved in the development of CPGs to set priorities, ensure feasibility, and promote distribution and compliance (6, 40, 41).
Most of the CPGs lacked clarity in describing the crucial stages of the methodological development, especially in external review and procedure for updating, which is important for transparency and applicability (42). In addition, guidelines would benefit from a more prescriptive and standardized evidence-based approach to developing recommendations and avoiding the use of ambiguous recommendations. Two of the included CPGs [IMSWT2020 (20), CSA2022 (31)] used the AGREE II tool during the external review and development phase. Although IMSWT2020 (20) used the AGREE II instrument, high quality is still not achieved in the domain of applicability. Therefore, the AGREE II instrument should be considered in the process of planning, developing and publishing CPGs for guideline development groups (13). Our results were largely similar to the results of CPG quality appraisal in different clinical topics (43–45), indicating that the problems in CPG development have some commonality. The CPG development group should pay more attention to improving the methodological quality according to the AGREE II instrument, and each item should be refined as much as possible (16, 42).
In addition to focusing on improving the transparency and methodological rigor of the guideline development process, the quality of guidelines is more dependent on high-quality evidence. However, most of the recommendations in the above guidelines are based on low to moderate quality evidence, and even some of them are not based on evidence. More high-quality evidence is needed for the management of post-stroke dysphagia, such as how to select instruments to evaluate swallowing with sensory tests (29), rational dietary programs (24), and effective therapies (31), which are extremely important for improving the quality of care for patients with post-stroke dysphagia.
Our study has several strengths. First, before the formal assessment, two assessors discussed the appraisal criteria according to the AGREE II manual and training tools to maintain the understanding of each item in line with each other. After scoring, the CPGs were collated with a randomized 10% cross-check (14) to ensure consistency between authors, especially for the items with significantly different scores. Furthermore, to the best of our knowledge, this is the first study that compares and evaluates the quality of CPGs in the nutritional management of stroke patients.
Due to language or publication restrictions, our review is limited to CPGs written in English, and excluding CPGs written in other languages may introduce bias. Furthermore, AGREE II does not provide an explicit cutoff to distinguish between high quality, moderate quality, and low quality CPGs. We defined them based on previous studies, but we are not exempt from misinterpretation that may derive from heterogeneity in the formulation and wording of recommendations. In addition, it is worth noting that in this study, only the critical appraisal of the quality development of the guidelines was performed, without any assessment of the quality of the guidelines’ content.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
S-LG: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. C-QL: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. Q-HH: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. X-RD: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. Y-WL: Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Methodology. KL: Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program (grant number 2018YFC2001805).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2023.1310133/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Feigin, VL, Stark, BA, Johnson, CO, Roth, GA, Bisignano, C, and Abady, GG. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. Lancet Neurol. (2021) 20:795–820. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00252-0
2. Campbell, BCV, and Khatri, P. Stroke. Lancet. (2020) 396:129–42. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31179-X
3. Labeit, B, Michou, E, Hamdy, S, Trapl-Grundschober, M, Suntrup-Krueger, S, Muhle, P, et al. The assessment of dysphagia after stroke: state of the art and future directions. Lancet Neurol. (2023) 22:858–70. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(23)00153-9
4. Jiang, L, Zhang, W, Qian, L, and Wang, C. Clinical practice guideline appraisal and algorithm development to identify recommendations related to nursing practice for post-stroke dysphagia. J Clin Nurs. (2023) 32:6089–100. doi: 10.1111/jocn.16737
5. Feng, W. Diagnosis of post-stroke dysphagia: towards better treatment. Lancet Neurol. (2023) 22:778–9. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(23)00292-2
6. Lowther, HJ, Harrison, J, Hill, JE, Gaskins, NJ, Lazo, KC, Clegg, AJ, et al. The effectiveness of quality improvement collaboratives in improving stroke care and the facilitators and barriers to their implementation: a systematic review. Implement Sci. (2021) 16:95. doi: 10.1186/s13012-021-01162-8
7. Alonso-Coello, P, Irfan, A, Solà, I, Gich, I, Delgado-Noguera, M, Rigau, D, et al. The quality of clinical practice guidelines over the last two decades: a systematic review of guideline appraisal studies. Qual Saf Health Care. (2010) 19:e58. doi: 10.1136/qshc.2010.042077
8. Wang, Y, Li, Z, Zhao, X, Wang, C, Wang, X, Wang, D, et al. Effect of a multifaceted quality improvement intervention on hospital personnel adherence to performance measures in patients with acute ischemic stroke in China: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. (2018) 320:245–54. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.8802
9. Machline-Carrion, MJ, Santucci, EV, Damiani, LP, Bahit, MC, Málaga, G, Pontes-Neto, OM, et al. Effect of a quality improvement intervention on adherence to therapies for patients with acute ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack: a cluster randomized clinical trial. JAMA Neurol. (2019) 76:932–41. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.1012
10. Hill, MD, Kamal, N, and Jeerakathil, T. Bridging the evidence-to-practice gap in stroke care. JAMA. (2018) 320:236–7. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.8803
11. Sanders, JO, Bozic, KJ, Glassman, SD, Jevsevar, DS, and Weber, KL. Clinical practice guidelines: their use, misuse, and future directions. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. (2014) 22:135–44. doi: 10.5435/JAAOS-22-03-135
12. Sarkies, MN, Jones, LK, Gidding, SS, and Watts, GF. Improving clinical practice guidelines with implementation science. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2022) 19:3–4. doi: 10.1038/s41569-021-00645-x
13. Brouwers, MC, Kho, ME, Browman, GP, Burgers, JS, Cluzeau, F, Feder, G, et al. Agree ii: advancing guideline development, reporting and evaluation in health care. CMAJ. (2010) 182:E839–42. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.090449
14. Harrison, CL, Teede, H, Khan, N, Lim, S, Chauhan, A, Drakeley, S, et al. Weight management across preconception, pregnancy, and postpartum: a systematic review and quality appraisal of international clinical practice guidelines. Obes Rev. (2021) 22:e13310. doi: 10.1111/obr.13310
15. Bakaloudi, DR, Chrysoula, L, Poulia, KA, Dounousi, E, Liakopoulos, V, and Chourdakis, M. Agreeing on nutritional Management of Patients with Ckd-a quality appraisal of the available guidelines. Nutrients. (2021) 13:624. doi: 10.3390/nu13020624
16. Muñoz-Manrique, C, Ancira-Moreno, M, Burrola-Méndez, S, Omaña-Guzmán, I, Hoyos-Loya, E, Hernández-Cordero, S, et al. Quality appraisal of nutritional guidelines to prevent, diagnose, and treat malnutrition in all its forms during pregnancy. Nutrients. (2022) 14:4579. doi: 10.3390/nu14214579
17. Ten Hove, D, Jorgensen, TD, and Van Der Ark, LA. Updated guidelines on selecting an intraclass correlation coefficient for interrater reliability, with applications to incomplete observational designs. Psychol Methods. (2022). 10.1037/met0000516. doi: 10.1037/met0000516 [Epub ahead of print].
18. Page, MJ, Moher, D, Bossuyt, PM, Boutron, I, Hoffmann, TC, Mulrow, CD, et al. Prisma 2020 explanation and elaboration: updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. (2021) 372:n160. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n160
19. Minelli, C, Luvizutto, GJ, Cacho, RO, Neves, LO, Magalhães, SCSA, Pedatella, MTA, et al. Brazilian practice guidelines for stroke rehabilitation: part ii. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. (2022) 80:741–58. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-1757692
20. Ni, X, Lin, H, Li, H, Liao, W, Luo, X, Wu, D, et al. Evidence‐based practice guideline on integrative medicine for stroke working team, neurology chapter of China Association of Chinese Medicine, neurology Committee of Guangdong Provincial Association of Chinese medicine, and stroke Committee of Guangdong Provincial Association of Chinese integrative medicine evidence-based practice guideline on integrative medicine for stroke 2019. J Evid Based Med. (2020) 13:137–52. doi: 10.1111/jebm.12386
21. Umay, E, Eyigor, S, Ertekin, C, Unlu, Z, Selcuk, B, Bahat, G, et al. Best practice recommendations for stroke patients with dysphagia: a Delphi-based consensus study of experts in Turkey-part I: management, diagnosis, and follow-up. Dysphagia. (2022) 37:217–36. doi: 10.1007/s00455-021-10273-9
22. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence: Guidelines. Stroke and transient ischaemic attack in over 16s: Diagnosis and initial management. London: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (Nice) (2022).
23. Dziewas, R, Michou, E, Trapl-Grundschober, M, Lal, A, Arsava, EM, Bath, PM, et al. European stroke organisation and European Society for Swallowing Disorders guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of post-stroke dysphagia. Eur Stroke J. (2021) 6:Lxxxix. doi: 10.1177/23969873211039721
24. Thibault, R, Abbasoglu, O, Ioannou, E, Meija, L, Ottens-Oussoren, K, Pichard, C, et al. Espen guideline on hospital nutrition. Clin Nutr. (2021) 40:5684–709. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2021.09.039
25. Burgos, R, Bretón, I, Cereda, E, Desport, JC, Dziewas, R, Genton, L, et al. Espen guideline clinical nutrition in neurology. Clin Nutr. (2018) 37:354–96. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2017.09.003
26. National Stroke Foundation. (2017). Australian and New Zealand living clinical guidelines for stroke management. Available at: https://app.magicapp.org/#/guideline/We8wOn/section/Ekykvl.
27. Royal College of Physicians Rpc. National clinical guideline for stroke. (2016). Available at: https://www.strokeaudit.org/Guideline/Full-Guideline.aspx
28. Winstein, CJ, Stein, J, Arena, R, Bates, B, Cherney, LR, Cramer, SC, et al. Guidelines for adult stroke rehabilitation and recovery: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. (2016) 47:e98–e169. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000098
29. Powers, WJ, Rabinstein, AA, Ackerson, T, Adeoye, OM, Bambakidis, NC, Becker, K, et al. Guidelines for the early Management of Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. (2019) 50:e344–418. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000211
30. Teasell, R, Salbach, N M, and Foley, N Canadian stroke best practice recommendations: Rehabilitation, recovery, and community participation following stroke. Part one: Rehabilitation and recovery following stroke. 6th Edition. Int J Stroke. (2020), 15: 763–788. doi: 10.1177/1747493019897843
31. Heran, M, Lindsay, P, and Gubitz, G. Canadian stroke best practice recommendations: acute stroke management, practice guidelines update. Can J Neurol Sci. (2022) 2022:1–31. doi: 10.1017/cjn.2022.344
32. Dziewas, R, Allescher, HD, Aroyo, I, Bartolome, G, Beilenhoff, U, Bohlender, J, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of neurogenic dysphagia - S1 guideline of the German Society of Neurology. Neurol Res Pract. (2021) 3:23. doi: 10.1186/s42466-021-00122-3
33. Li, HY, Wang, J, Wang, T, and Wang, HS. Management of venous thromboembolism in pediatric patients: quality assessment of clinical practice guidelines and variations in recommendations. Thromb Res. (2023) 226:107–16. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2023.04.022
34. Pat, JJ, Witte, LPW, Steffens, MG, Vernooij, RWM, Marcelissen, TAT, Fuentes, P, et al. Quality appraisal of clinical guidelines for recurrent urinary tract infections using agree ii: a systematic review. Int Urogynecol J. (2022) 33:1059–70. doi: 10.1007/s00192-022-05089-6
35. Hwang, F, Boardingham, C, Walther, S, Jacob, M, Hidalgo, A, Gandhi, CD, et al. Establishing goals of Care for Patients with Stroke and Feeding Problems: an interdisciplinary trigger-based continuous quality improvement project. J Pain Symptom Manage. (2018) 56:588–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2018.06.010
36. Abboud, J, Abdel Rahman, A, Kahale, L, Dempster, M, and Adair, P. Prevention of health care associated venous thromboembolism through implementing Vte prevention clinical practice guidelines in hospitalized medical patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Implement Sci. (2020) 15:49. doi: 10.1186/s13012-020-01008-9
37. Kahn, SR, Morrison, DR, Diendéré, G, Piché, A, Filion, KB, Klil-Drori, AJ, et al. Interventions for implementation of thromboprophylaxis in hospitalized patients at risk for venous thromboembolism. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2018) 4:Cd008201. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008201.pub3
38. Pai, M, Lloyd, NS, Cheng, J, Thabane, L, Spencer, FA, Cook, DJ, et al. Strategies to enhance venous thromboprophylaxis in hospitalized medical patients (sentry): a pilot cluster randomized trial. Implement Sci. (2013) 8:1. doi: 10.1186/1748-5908-8-1
39. Gebreyohannes, EA, Salter, SM, Chalmers, L, Bereznicki, L, and Lee, K. Reasons for non-adherence to thromboprophylaxis prescribing guidelines in atrial fibrillation in Western Australia: a qualitative descriptive study of general practitioners' views. Thromb Res. (2021) 208:83–91. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2021.10.025
40. Allida, S, House, A, and Hackett, ML. Pharmaceutical interventions for emotionalism after stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2022) 11:Cd003690. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003690.pub5
41. Lindsay, MP, Gierman, N, Harris, JE, Arthur, G, Teed, ME, Mountain, A, et al. People with lived experience at the Centre of Canadian Stroke Best Practice Recommendations: a model for guideline developers. J Patient Exp. (2020) 7:951–6. doi: 10.1177/2374373520956538
42. Andrade, R, Pereira, R, and Van Cingel, R. How should clinicians rehabilitate patients after Acl reconstruction? A systematic review of clinical practice guidelines (Cpgs) with a focus on quality appraisal (agree ii). Br J Sports Med. (2020) 54:512–9. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2018-100310
43. Cui, N, Zhang, Y, Li, Q, Tang, J, Li, Y, Zhang, H, et al. Quality appraisal of guidelines on physical restraints in intensive care units: a systematic review. Intensive Crit Care Nurs. (2022) 70:103193. doi: 10.1016/j.iccn.2021.103193
44. Zhang, J, Xu, J, Zhang, W, Jiang, M, Liu, J, Xu, L, et al. Quality appraisal of guidelines on Cancer-associated thrombosis using agree ii instrument and analysis of current status of new Oral anticoagulants. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. (2019) 25:107602961984656. doi: 10.1177/1076029619846562
Keywords: stroke, dysphagia, clinical practice guidelines, AGREE II, quality appraisal
Citation: Gao S-L, Liu C-Q, Han Q-H, Dai X-R, Liu Y-W and Li K (2023) Quality appraisal of clinical practice guidelines for the management of Dysphagia after acute stroke. Front. Neurol. 14:1310133. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1310133
Edited by:
Masahiro Nakamori, Hiroshima University, JapanReviewed by:
Bruno J. Weder, University of Bern, SwitzerlandMani Abdul Karim, XIM University, India
Copyright © 2023 Gao, Liu, Han, Dai, Liu and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ka Li, bGlrYTEyN0AxMjYuY29t; Yi-Wen Liu, bGl1eWl3ZW4zQDE2My5jb20=
 Shi-Lin Gao
Shi-Lin Gao Chang-Qing Liu1
Chang-Qing Liu1