
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CASE REPORT article
Front. Neurol., 26 January 2023
Sec. Dementia and Neurodegenerative Diseases
Volume 14 - 2023 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2023.1099077
This article is part of the Research TopicDementia and Neurodegenerative Diseases – Case Report Collection 2022View all 25 articles
Background: Nitrous oxide (N2O) is an increasingly popular recreational drug. N2O irreversibly disturbs the metabolism of vitamin B12, resulting in a functional deficiency. Vitamin B12 is vital for myelin synthesis and its deficiency primarily produces neurological complications. Inhaling N2O is more common and neurological complications are more evident than before.
Case presentation: We report a young man who developed progressive limb numbness and unsteady walking after N2O abuse. The dominant diagnosis was subacute combined degeneration of the spinal cord (SCD). The patient was admitted to the hospital and given adenosylcobalamin treatment, but his symptoms progressed significantly from before and he developed acute cognitive impairment. After methylprednisolone combined with vitamin B12 treatment, symptoms significantly improved.
Conclusion: Clinicians need to understand the presentation and treatment of SCD caused by N2O abuse. When symptoms progress despite conventional vitamin B12 therapy, the combination of methylprednisolone and vitamin B12 may be considered.
Nitrous oxide (N2O), also called “laughing gas,” is a colorless gas with a sweet taste and good stability. Its role as an inhaled anesthetic is primarily in dental and labor analgesia. Because laughing gas inhalation can produce euphoria, it is widely prevalent among young people who are blindly seeking excitement. Long-term abuse can cause severe neurological complications. In recent years, Smoking laughing gas has become increasingly popular, and as a result, neurological complications will be more evident than before. This case reports an adolescent patient with central and peripheral nervous system involvement and acute cognitive decline caused by long-term inhalation of N2O. The patient's condition changes and treatment options are described in detail to improve clinicians' awareness of recreational N2O abuse.
An 18-year-old man was admitted to the emergency center with progressive numbness in the limbs for 10 days. The patient developed numbness in both feet, which gradually progressed proximal end, with numbness in both lower limbs and hands, a sense of girdle in the front chest and abdomen, and a feeling of soreness in the back. After 3 days of admission, the patient's condition progressed significantly compared with the previous. He presented with acute cognitive impairment and weakness in both lower extremities. Without support, he could not walk or stand.
The patient had a history of inhaling N2O for 6 months (N2O canned, 2 L/can, 2–8 L can be used at a time), 3–4 times/week. The last time he consumed about 10 L was significantly increased compared to the previous time.
Clear consciousness, slow language, decreased calculation and orientation, recent memory decline (cannot recall what you ate for breakfast), blunt response and no abnormality were found in the examination of twelve pairs of cranial nerves. The muscle strength of both upper limbs was grade 4, and the muscle strength of both lower limbs was grade 3, the muscle tension was slightly increased, bilateral superficial paresthesias, the sense of position and vibration of both feet were weakened, needle-punching in both feet, inaccurate finger-nose test, unstable heel and knee shin, positive Romberg's sign, weakened tendon reflexes on both sides, involuntary stretch-like movements of both upper extremities, skin scratch test positive, no elicitation of bilateral Barthel's sign and no abnormal meningeal irritation sign.
Homocysteine 58.9 μmol/L (normal value 5–15 μmol/L), vitamin B12 (>1,144.0 pg/ml; normal value 200–900 pg/ml considered to be related to taking drugs before admission), folic acid 17.39 nmol/L (normal value is 7–45.1 nmol/L), and no abnormality was found in the rest.
MRI of the spinal cord showed the diffuse high signal of the T2W1 sequence (Figure 1A) and the posterior cord of the spinal cord was mainly involved in the axial image, showing an “inverted V sign” (Figure 1B). There were no apparent abnormalities in the thoracic and lumbar spine. There was no obvious abnormality in the head MRI.
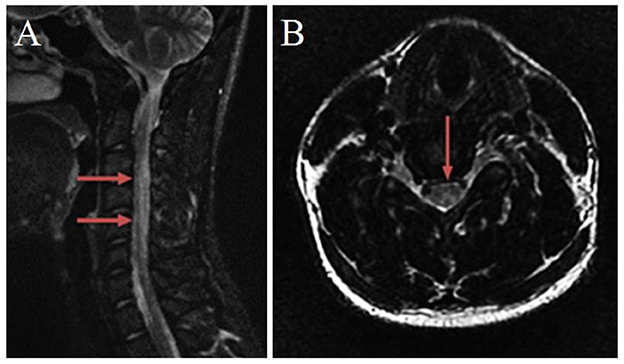
Figure 1. Magnetic resonance imaging of the cervical spinal cord. (A) T2-weighted sagittal image, from C2 to C7 spinal cord hyperintensity. (B) T2-weighted axial image, an “inverted V-sign” was shown.
Peripheral nerve injury, the lower extremities became more significantly involved than the upper extremities.
The Mini-Mental State Examination Scale (MMSE) scored 18 points (5 points for orientation, 1 point for calculation, 5 points for memory, and 7 points for language ability).
Treatment was given with intramuscular Adenosylcobalamin (1.5 mg/day), and symptoms were further aggravation. The patient was given intramuscular injections of Adenosylcobalamin combined with Methylprednisolone intravenous infusion (500 mg/day for a 5-day course). Adenosylcobalamin (1.5 mg/day) was administered intramuscularly for 10 days. After 7 days of treatment, the patient's chest discomfort in the front, back soreness and numbness in limbs improved, and the orientation, calculation, and mental were improved. The patient was hospitalized for a total of 10 days. At the time of discharge, the muscle strength of his extremities was better than before. The muscle strength of his lower extremities was Grade 4, and that of his upper extremities was Grade 5. Oral medication and rehabilitation after discharge. After 1 month, the patient could walk independently. The Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) scored 27 points (8 points for orientation, 4 points for calculation, 6 points for memory, and 9 points for language ability). After 3 months of follow-up, the patient's limb numbness was significantly improved, and his daily life was not affected.
Neurological complications from N2O inhalation have been rare before. In recent years, more N2O abuse complications have been reported. Inhaling N2O can create a relaxing feeling and is relatively easy to obtain. There are rich ways to buy it in the market and the price is low. More young people relax and indulge by inhaling large amounts of laughing gas. However, they are not aware of the possible side effects of inhaling. The extent of N2O abuse is often difficult to quantify accurately, most people hide their history of N2O use, so N2O abuse is often severely underestimated.
To date, the poisoning mechanism of N2O has not been fully elucidated. Methylcobalamin in vitamin B12 converts homocysteine to methionine, and S-adenosylmethionine, a metabolite of methionine, is irreplaceable for the formation and maintenance of myelin sheaths. Vitamin B12 deficiency leads to impaired myelin synthesis and methylation of myelin proteins (1), causing neural demyelination changes. N2O interferes with the metabolic pathway of vitamin B12 by irreversibly oxidizing the cobalt element of vitamin B12, leading to a decrease in vitamin B12 (2) and ultimately impaired myelin synthesis and neurological complications. N2O interferes with the metabolism of intracellular vitamin B12, while serology tests the level of extracellular vitamin B12. In the early stages of the disease, in people with a normal diet or with self-supplementation of vitamin B12, serum levels of Vit B12 may be normal, but the increase of homocysteine can indirectly reflect the lack of in vivo vitamin B12 functionality (3).
The patient has been inhaling laughing gas for 6 months, and the body does not have enough stored vitamin B12. The patient once took vitamin B12 drugs orally, which increased the level of vitamin B12 in the blood. Therefore, the serum vitamin B12 test was beyond the normal range. And the last time, he inhaled a huge amount of N2O, which caused N2O toxicity.
The patient had decreased sense of position and vibration of the feet, involving the lamella and wedge tracts, and developed sensory ataxia. The patient's walking instability, inaccurate finger-nose test, and positive Romberg's sign suggest that the lesion involves the spinocerebellar tract. The diffusivity of N2O is good, after inhalation, the partial pressure of oxygen in the alveoli can be reduced quickly, resulting in the reduction of oxygen delivered to the brain, resulting in brain hypoxia (4). The patient's muscle tone was slightly increased on admission, accompanied by involuntary stretch-like movements of both upper limbs, which may be related to the extrapyramidal symptoms of basal ganglia hypoxia after a large amount of N2O inhalation. The previous literature reported generalized dystonia and involuntary movements for patients with N2O abuse, which disappeared after vitamin B12 supplementation, suggesting that dyskinesia may be related to neurotoxicity (5).
The patient, in this case, has decreased calculation, spatial and temporal orientation and decreased memory, which is considered to be related to the cognitive dysfunction caused by N2O inhalation. Dreyfus et al. (6) reported 2 cases of anesthesiologists with prolonged exposure to N2O who experienced cognitive declines such as unresponsiveness, memory loss, and distraction. After stopping work and receiving professional treatment, the appeal symptoms were relieved. Shen et al. (7) described a patient with acute cognitive decline due to long-term inhalation of N2O who recovered well after adequate vitamin B12 supplementation.
According to the patient's N2O abuse history, clinical manifestations and signs, elevated homocysteine, MRI showed an inverted “V” sign, EMG showed limb nerve damage, N2O abuse-induced SCD and acute cognitive impairment were diagnosed.
There is no specific treatment protocol for neurotoxicity due to N2O abuse and it is mainly based on previous reports in the literature. In our case, the patient's clinical symptoms significantly progressed despite vitamin B12 supplementation. Hormones can alleviate spinal cord edema and also have neuroprotective effects, so we used hormones in combination with vitamin B12 to rapidly reverse the neurological damage caused by N2O abuse. Previous studies have proposed that methylprednisolone decreases desynovial myelination and axonal damage (8). It also promotes the survival of neurons and supports myelin regeneration (9). Early rehabilitation is also essential for the recovery of nerve function and can vastly reduce the extent of nerve damage (10). When there is abnormal mental behavior, we should also pay attention to effective psychological counseling, give patients active psychological support treatment, encourage patients to stay away from N2O, and develop healthy work and living habits.
In short, the clinical manifestations caused by long-term inhalation of N2O are different. Clinicians should have sufficient knowledge of the clinical manifestations and treatment of N2O toxicity. Clinically, when patients complain of neurological complications such as numbness of limbs, unstable walking, and weakness of limbs, especially in adolescents, clinicians should inquire whether they have a history of inhaling N2O. The young patient with acute cognitive impairment should be associated with the possibility of N2O poisoning. When symptoms progress despite treatment with vitamin B12 supplementation, a combination of methylprednisolone and vitamin B12 may be considered.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
HW: data analysis, interpretation, and drafting of the manuscript. HH, LX, and NJ: critical revision of the manuscript. XZ: study concept and design and critical revision of the manuscript. KX: study concept and design and study supervision. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
We thank the participant of the study.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Zheng D, Ba F, Bi G, Guo Y, Gao Y, Li W. The sharp rise of neurological disorders associated with recreational nitrous oxide use in China: a single-center experience and a brief review of Chinese literature. J Neurol. (2020) 267:422–9. doi: 10.1007/s00415-019-09600-w
2. van Amsterdam J, Nabben T, van den Brink W. Recreational nitrous oxide use: Prevalence and risks. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. (2015) 73:790–6. doi: 10.1016/j.yrtph.2015.10.017
3. Hathout L, El-Saden S. Nitrous oxide-induced B12 deficiency myelopathy: Perspectives on the clinical biochemistry of vitamin B12. J Neurol Sci. (2011) 301:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2010.10.033
4. Brodsky JB, Cohen EN. Adverse effects of nitrous oxide. Med Toxicol. (1986) 1:362–74. doi: 10.1007/BF03259849
5. Chen HJ, Huang CS. Nitrous oxide-induced subacute combined degeneration presenting with dystonia and pseudoathetosis: a case report. Acta Neurol Taiwan. (2016) 25:50–5.
6. Dreyfus E, Tramoni E, Lehucher-Michel MP. Persistent cognitive functioning deficits in operating rooms: two cases. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. (2008) 82:125–30. doi: 10.1007/s00420-008-0302-8
7. Shen Q, Lu H, Wang H, Xu Y. Acute cognitive disorder as the initial manifestation of nitrous oxide abusing: a case report. Neurol Sci. (2021) 42:755–6. doi: 10.1007/s10072-019-04183-w
8. Yilmaz C, Karali K, Fodelianaki G, Gravanis A, Chavakis T, Charalampopoulos I, et al. Neurosteroids as regulators of neuroinflammation. Front Neuroendocrinol. (2019) 55:100788. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2019.100788
9. Guennoun R. Progesterone in the brain: hormone, neurosteroid and neuroprotectant. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:15. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155271
Keywords: nitrous oxide, subacute combined degeneration of the spinal cord, cognitive decline, vitamin B12, methylprednisolone
Citation: Wu H, Huang H, Xu L, Ji N, Zhou X and Xie K (2023) Case report: Subacute combined degeneration of the spinal cord due to nitrous oxide abuse. Front. Neurol. 14:1099077. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1099077
Received: 15 November 2022; Accepted: 10 January 2023;
Published: 26 January 2023.
Edited by:
Bruce Miller, University of California, San Francisco, United StatesReviewed by:
Marta Waliszewska-Prosół, Wroclaw Medical University, PolandCopyright © 2023 Wu, Huang, Xu, Ji, Zhou and Xie. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xinyu Zhou,  emhvdXh5MDcxMkAxMjYuY29t; Kang Xie,
emhvdXh5MDcxMkAxMjYuY29t; Kang Xie,  NzYwMDIwMjIwMDM1QHh6aG11LmVkdS5jbg==
NzYwMDIwMjIwMDM1QHh6aG11LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.