
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Neurol. , 07 May 2018
Sec. Neurotrauma
Volume 9 - 2018 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2018.00285
This article is part of the Research Topic An Update on Cognitive Neuroscience and Neurorehabilitation: From Bench to Clinic View all 6 articles
 Ahreum Baek1,2†
Ahreum Baek1,2† Eun Jee Park3†
Eun Jee Park3† Soo Yeon Kim4
Soo Yeon Kim4 Bae-Geun Nam2,5
Bae-Geun Nam2,5 Ji Hyun Kim1
Ji Hyun Kim1 Sang Woo Jun6
Sang Woo Jun6 Sung Hoon Kim1*
Sung Hoon Kim1* Sung-Rae Cho2,5,7,8,9*
Sung-Rae Cho2,5,7,8,9*
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) can be used in various neurological disorders. However, neurobiological mechanism of rTMS is not well known. Therefore, in this study, we examined the global gene expression patterns depending on different frequencies of repetitive magnetic stimulation (rMS) in both undifferentiated and differentiated Neuro-2a cells to generate a comprehensive view of the biological mechanisms. The Neuro-2a cells were randomly divided into three groups—the sham (no active stimulation) group, the low-frequency (0.5 Hz stimulation) group, and high-frequency (10 Hz stimulation) group—and were stimulated 10 min for 3 days. The low- and high-frequency groups of rMS on Neuro-2a cells were characterized by transcriptome array. Differentially expressed genes were analyzed using the Database of Annotation Visualization and Integrated Discovery program, which yielded a Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway. Amphetamine addiction pathway, circadian entrainment pathway, long-term potentiation (LTP) pathway, neurotrophin signaling pathway, prolactin signaling pathway, and cholinergic synapse pathway were significantly enriched in high-frequency group compared with low-frequency group. Among these pathways, LTP pathway is relevant to rMS, thus the genes that were involved in LTP pathway were validated by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction and western blotting. The expression of glutamate ionotropic receptor N-methyl d-aspartate 1, calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) δ, and CaMKIIα was increased, and the expression of CaMKIIγ was decreased in high-frequency group. These genes can activate the calcium (Ca2+)–CaMKII–cAMP-response element-binding protein (CREB) pathway. Furthermore, high-frequency rMS induced phosphorylation of CREB, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) transcription via activation of Ca2+–CaMKII–CREB pathway. In conclusion, high-frequency rMS enhances the expression of BDNF by activating Ca2+–CaMKII–CREB pathway in the Neuro-2a cells. These findings may help clarify further therapeutic mechanisms of rTMS.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a non-invasive tool that allows electrical stimulation of the nervous system and could be an ideal treatment tool due to its ability to modify brain plasticity (1). TMS can generate an electric current in the central nervous system by making short 100 μs biphasic electromagnetic pulse (2, 3). When given at regular frequencies, it is termed repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) (3).
Several studies reported that changes in rTMS frequency and stimulation patterns resulted in varying long-term effects (4, 5). High-frequency stimulation (>3 Hz) stimulated cortical excitability and generally resulted in an effect that share similar aspects with long-term potentiation (LTP). In comparision, low frequency stimulation (≤1 Hz) reduced cortical excitability and induced a reduction in synaptic efficiency which were similar to long-term depression (4, 5). Various stimulation parameters such as intensity, frequency, overall patterns of stimulation, and periods determine the functional effects of rTMS on cortical excitability (6, 7). However, the neural mechanisms related with various stimulation parameters of rTMS remain unclear.
rTMS is a safe, painless, and non-invasive brain stimulation method that has been recently gaining focus as a neurorehabilitation tool with therapeutic ability (8). rTMS has been used in various neurological diseases to provide relief and reduce chronic pain (9–13). Motor symptoms in patients with Parkinson’s disease and dystonia can be ameliorated by high-frequency rTMS treatment (14–16). In stroke patients, high-frequency rTMS can increase ipsilesional cortical excitability to improve paretic limb function (17–19). Also, high-frequency rTMS may be a promising effective and safe modality in frontal cortex for Alzheimer’s disease (20). Furthermore, in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) production may play a role by regulating with neuronal activity by rTMS in primary motor cortex (21). However, the precise therapeutic mechanisms of rTMS are still unknown.
In this study, we aimed to investigate the global gene expression patterns depending on different frequencies of repetitive magnetic stimulation (rMS) in both undifferentiated and differentiated Neuro-2a cells with multiple properties of neurons (22–25) to provide a comprehensive view of the neurobiological mechanisms. Achieving our goals, transcriptome analysis, to quantify the expression levels of individual transcripts, and possible comparison (26, 27), were conducted to compare the effect of high-frequency and low-frequency rMS in the Neuro-2a cells. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) of high-frequency compared with low-frequency rMS were analyzed with bioinformatics tool to identify relevant cellular signaling pathways and examine the expression level to elucidate the neurobiological mechanisms.
Neuro-2a cells were obtained from American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA). Neuro-2a cells were maintained in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM; Hyclone, Logan, UT, USA) with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Serum Source International, Charlotte, NC, USA) and 1% penicillin–streptomycin solution (Gibco, Rockville, MD, USA) in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2 and 95% air at 37°C (Figure 1A). It has been reported that Neuro-2a cells are differentiated by retinoic acid (RA) treatment (28–30). According to our previous study (25), differentiated Neuro-2a cells were maintained in DMEM with 2% FBS and 20 µM of RA for 4 days in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2 and 95% air at 37°C (Figure 1B). Cells were observed under microscope and photographed using a Nikon Eclipse TS100 microscope (Nikon, Melville, NY, USA). Cells were harvested at 80% confluence using 0.25% trypsin–EDTA (Gibco). Cells were seeded on new plates and the growth medium was replaced every 2–3 days.
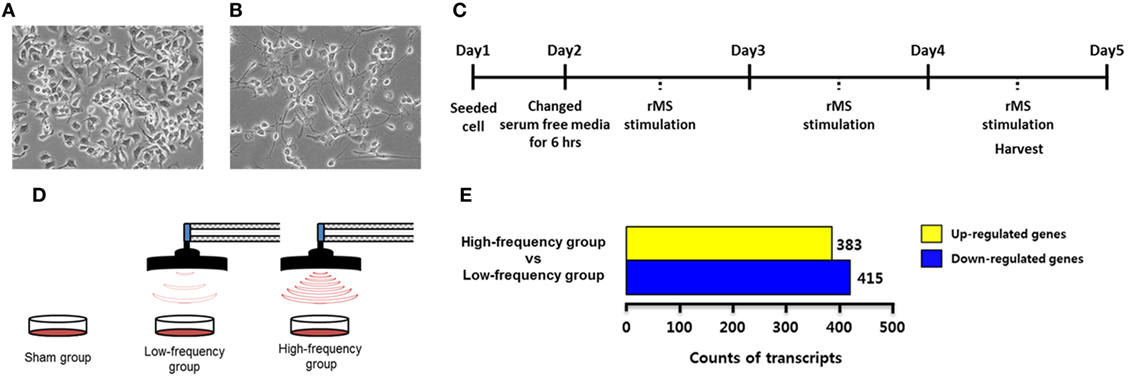
Figure 1. Experimental design and transcriptome analysis. (A) Undifferentiated Neuro-2a cells. (B) Neuro-2a cells were differentiated for 4 days with 2% fetal bovine serum and retinoic acid in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium. (C) A timeline of the experimental procedures. (D) A scheme of repetitive magnetic stimulation (rMS) treatment in Neuro-2a cells. The cultured cells were divided into the sham group, the low-frequency group, and the high-frequency groups and were each stimulated over 3 days. (E) Bar graphs show the number of differentially expressed genes with fold change ≥ |1.5| in the high-frequency group compared with the low-frequency group.
In each experiment, Neuro-2a cells were rendered quiescent for 6 h by the addition of DMEM without FBS in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2 and 95% air at 37°C. Then, the cells were replaced by the growth medium and stimulated with customized rMS (Bicon-1000Pro, Mcube Technology, Seoul, Korea) as indicated in our previous studies (3, 25). To clarify the design of the experiment, the distance between the center of the magnetic coil (70 mm diameter) and the culture dish was approximately 1.0 cm. Cultured cells were divided into three groups (N = 5 dishes/group) as follows: the sham group (exposed to rMS but no active stimulation for 10 min), the low-frequency group (0.5 Hz stimulation for 10 min), and the high-frequency group (10 Hz stimulation for 10 min). All groups were stimulated over the course of 3 days for a duration of 10 min/day. After 3 days of stimulation, cells were harvested with 0.25% trypsin–EDTA (Gibco) as described earlier. The experimental scheme is shown in Figures 1C,D.
By using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA), RNA was isolated from the cell pellets by following the manufacturer’s instructions. The Nanodrop spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) was used to confirm the quality and quantity of isolated RNA.
RNA sequencing between high-frequency group and low-frequency group in Neuro-2a cells was performed by Macrogen Inc. (Seoul, Korea) to provide a comparison. The procedures have been detailed previously (31–34).
The lists of significant differentially expressed genes (DEGs) for the high-frequency group compared with low-frequency group were submitted to the Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery (DAVID v6.8; http://david.abcc.ncifcrf.gov/) via the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways analysis with fold change ≥ |1.5|.
To validate transcriptome analysis results, qRT-PCR was conducted with the sham groups in Neuro-2a cells as control. Following the manufacturer’s instruction for ReverTra Ace® qPCR RT Master Mix with gDNA Remover (Toyobo, Osaka, Japan), RNA were reverse-transcribed into cDNA. In a StepOnePlus Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA), the mRNA expression for genes of interest was validated with qPCRBIO SyGreen Mix Hi-ROX (PCR BIOSYSTEMS, London, UK). Gene expression analysis was conducted by the 2−ΔΔCt method (35). Primers used for qRT-PCR are listed in Table 1.
To confirm the protein expression of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII), phospho-cAMP response element binding protein (p-CREB), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and ACTIN, western blot was conducted with the sham group in Neuro-2a cells. To isolated total protein, cell pellets were homogenized and dissolved using radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer (Thermo Scientific) containing protease and phosphatase inhibitors (Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA). Total proteins were quantified by the Quick StartTM Bradford 1× Dye Reagent (BIO-RAD, Hercules, CA, USA). The samples were denatured and separated by 4–12% Bis–Tris gels (Invitrogen, Eugene, OR, USA) in 1× NuPage MES SDS Running Buffer (Invitrogen). Proteins were transferred onto a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane (Invitrogen) by 20% methanol (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) in NuPage Transfer Buffer (Invitrogen). Membranes were blocked and then incubated overnight at 4°C with anti-CaMKII (1:1,000 dilution, Abcam), anti-p-CREB (1:1,000 dilution, Santa Cruz Biotechnology), anti-BDNF (1:1,000 dilution, Abcam), and anti-ACTIN (1:5,000 dilution, Santacruz) antibodies. The next day, blots were washed three times with 1× TBS plus Tween 20 (Biosesang, Sungnam, Korea) and incubated at room temperature for 1 h with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies (1:4,000 dilution, Santa Cruz). After the blots were washed three times with TBS plus Tween 20 (Biosesang), proteins were visualized with the following enhanced chemiluminescence detection systems: AmershamTM ECLTM Western Blotting Detection Reagent (GE Healthcare, Little Chalfont, UK) and West-Q Pico ECL solution (GenDEPOT, Houston, TX, USA). Quantification of relative protein expression using Multi Gauge (v3.0) software (Fujifilm, Tokyo, Japan).
All data were expressed as means ± standard error of the mean (SEM), and all experiments were repeated at least three times with three technical replicates in each group. Statistical analyses were conducted using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) for Windows version 23.0, IBM Corporation (Armonk, NY, USA). Data were analyzed with one-way analysis of variance, followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test and with statistically significant p-value < 0.05.
To identify DEGs associated with the high-frequency group compared with the low-frequency group, we conducted transcriptome analysis by RNA sequencing. A total of 21,567 transcripts were differentially expressed from the high-frequency group compared with the low-frequency group as shown in Table S1 in Supplementary Material. In the high-frequency group, 383 transcripts were 1.5-fold higher and 415 transcripts were 1.5-fold lower compared with the low-frequency group (Figure 1E; Table S2 in Supplementary Material).
DEGs of the high-frequency group compared with the low-frequency group were classified based on KEGG pathways using the DAVID Gene Functional Classification Tool. Statistically significant enriched KEGG pathways specific to the high-frequency group compared with the low-frequency group are presented in Table 2 (p < 0.01).
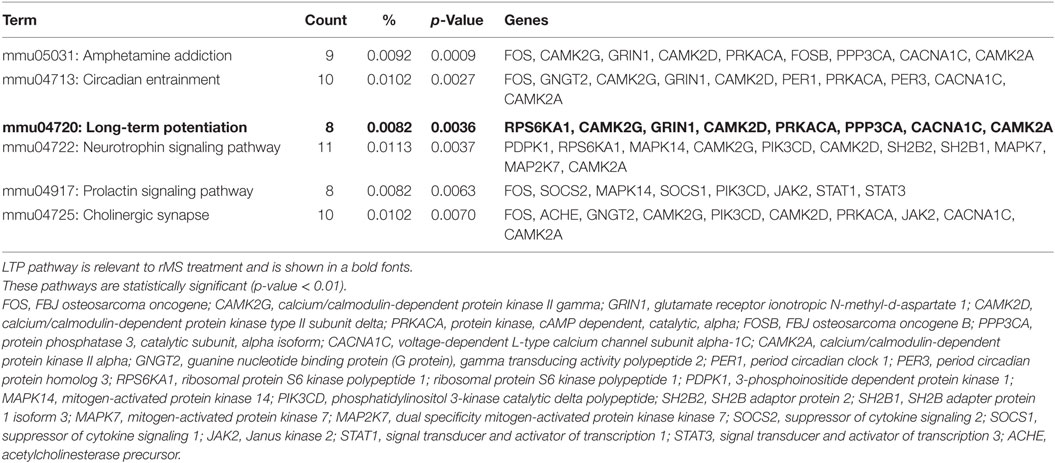
Table 2. The enriched Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathways in high-frequency group compared with low-frequency group.
According to the previous studies, among several pathways, mmu04720; LTP pathway was modulated by rTMS (4, 8, 36, 37). Glutamate ionotropic receptor N-methyl d-aspartate 1 (GRIN1), CaMKIIδ, ribosomal protein S6 kinase polypeptide 1, and CaMKIIα were significantly upregulated in the LTP pathway. In addition, CaMKIIγ, protein phosphatase 3 catalytic subunit alpha, protein kinase cAMP dependent catalytic alpha, and voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1C were significantly downregulated in the LTP pathway. Therefore, we focused on the genes that are involved in the LTP pathway.
qRT-PCR and western blot were conducted with the sham groups in Neuro-2a cells as control to validate the RNA sequencing results which identified the expression of the genes that were involved in the LTP pathway. According to the results of qRT-PCR, there were no significant changes in the low-frequency group compared with the sham group in undifferentiated Neuro-2a cells (Figure 2A). When the high-frequency group was compared with the sham group in undifferentiated Neuro-2a cells, the expression of GRIN1, CaMKIIδ, and CaMKIIα was significantly increased while CaMKIIγ expression was a significantly decreased (Figure 2A). Likewise, when the high-frequency group was compared with the low-frequency group in undifferentiated Neuro-2a cells, the expression of GRIN1, CaMKIIδ, and CaMKIIα was also significantly increased while CaMKIIγ expression was significantly decreased (Figure 2A).
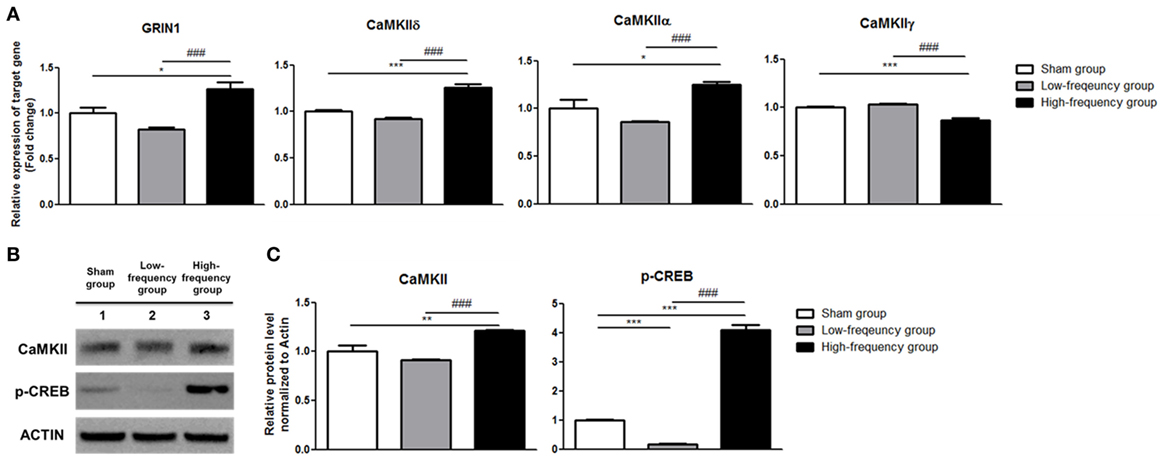
Figure 2. Validation of mRNA expression and protein quantification using qRT-PCR and western blot analysis in undifferentiated Neuro-2a cells. (A) The relative mRNA expression of target genes was normalized by sham expression and was calculated using the 2−ΔΔCt method by qRT-PCR. All results are expressed as means ± SEM. (B) Western blot analysis was performed using antibodies against calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII), phospho-cAMP response element binding (p-CREB), and actin (a control). All results are expressed as means ± SEM. (C) Comparison of relative protein expression for CaMKII, p-CREB, and actin (a control) with Multi Guage (v3.0) software (Fujifilm). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 comparison with the sham group in undifferentiated Neuro-2a cells. ###p < 0.001 comparison with the low-frequency group in undifferentiated Neuro-2a cells.
In the same manner, there were not any significant changes in the low-frequency group compared with the sham group in differentiated Neuro-2a cells (Figure 3A). The expression of GRIN1, CaMKIIδ, and CaMKIIα was significantly increased in the high-frequency group compared with the sham group or low-frequency group in differentiated Neuro-2a cells (Figure 3A). On the other hand, CaMKIIγ expression was a significantly decreased in the high-frequency group compared with either the sham or the low-frequency group in differentiated Neuro-2a cells (Figure 3A).
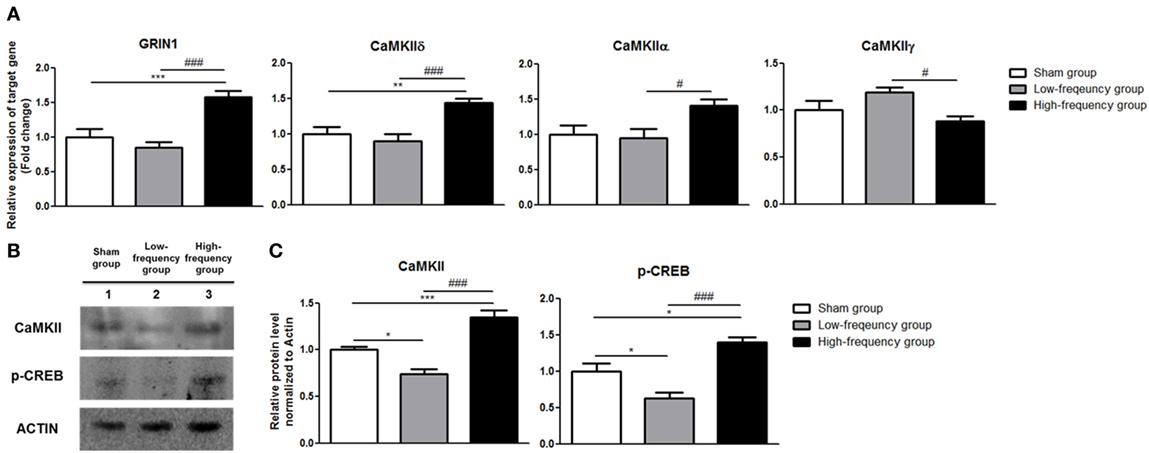
Figure 3. Validation of mRNA expression and protein quantification using qRT-PCR and western blot analysis in differentiated Neuro-2a cells. (A) The relative expression of target genes was normalized by sham expression and was calculated using the 2−ΔΔCt method by qRT-PCR during neuronal differentiation of Neuro-2a cells. (B) Western blot analysis was performed with calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII), phospho-cAMP response element binding (p-CREB), and actin (as a control) antibodies in the Neuro-2a cells. (C) Comparison of relative protein expression for CaMKII, p-CREB, and actin (a control) in differentiated Neuro-2a cells using Multi Guage (v3.0) software (Fujifilm). All results are expressed as means ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 comparison with the sham group in differentiated Neuro-2a cells. #p < 0.05 and ###p < 0.001 comparison with the low-frequency group in the Neuro-2a cells.
GRIN1, CaMKIIδ, CaMKIIα, and CaMKIIγ are involved in Ca2+–CaMKII signaling pathway (38, 39). Especially CaMKII activation induced CREB phosphorylation (40, 41). We hypothesized that these genes, which were involved in Ca2+-CaMKII-CREB pathway, induce p-CREB by the activation of Ca2+–CaMKII–CREB pathway with high-frequency rMS.
Therefore, CaMKII and p-CREB protein expression levels were identified by western blot analysis. The protein expression of the CaMKII and p-CREB was significantly increased in the high-frequency group when compared with either the sham or the low-frequency group in undifferentiated Neuro-2a cells, respectively (Figures 2B,C). Furthermore, when the high-frequency group was compared with the low-frequency group in undifferentiated Neuro-2a cells, the protein expression was statistically increased (Figures 2B,C).
Likewise, the protein expression of CaMKII and p-CREB was significantly increased in the high-frequency group compared with either the sham or the low-frequency group in differentiated Neuro-2a cells, respectively (Figures 3B,C).
These data suggest that Ca2+–CaMKII–CREB pathway is activated by high-frequency rMS in both undifferentiated and differentiated Neuro-2a cells.
Recently, it was reported that the Ca2+–CaMKII–CREB pathway plays a vital role in BDNF transcription (41, 42). Therefore, we confirmed BDNF expression by qRT-PCR and western blotting. In the low-frequency group as compared with the sham group, mRNA and protein expression of BDNF were decreased in undifferentiated Neuro-2a cells (Figure 4). However, when the high-frequency group was compared with the sham group in undifferentiated Neuro-2a cells, mRNA and protein expression of BDNF significantly increased (Figure 4). Furthermore, when the high-frequency group was compared with the low-frequency group, mRNA and protein expression of BDNF were also significantly increased in undifferentiated Neuro-2a cells (Figure 4).
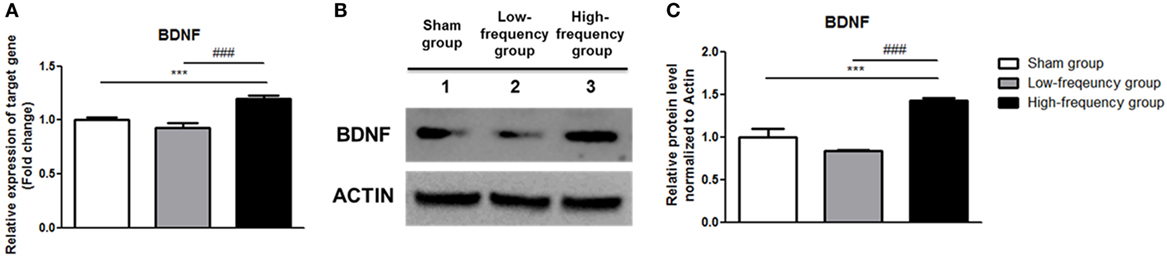
Figure 4. Repetitive magnetic stimulation treatment increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression in undifferentiated Neuro-2a cells. (A) The relative mRNA expression of BDNF was normalized by sham expression and was calculated using the 2−ΔΔCt method by qRT-PCR. All results are expressed as means ± SEM. (B) Western blot analysis was performed using antibodies against BDNF, and actin (a control). (C) Comparison of relative protein expression for BDNF and actin (a control) with Multi Guage (v3.0) software (Fujifilm). All results are expressed as means ± SEM. ***p < 0.001 comparison with the sham group in undifferentiated Neuro-2a cells. ###p < 0.001 comparison with the low-frequency group in undifferentiated Neuro-2a cells.
In the same manner, the mRNA and protein expression of BDNF was significantly increased in the high-frequency group compared with either the sham or the low-frequency group in differentiated Neuro-2a cells, respectively (Figure 5).
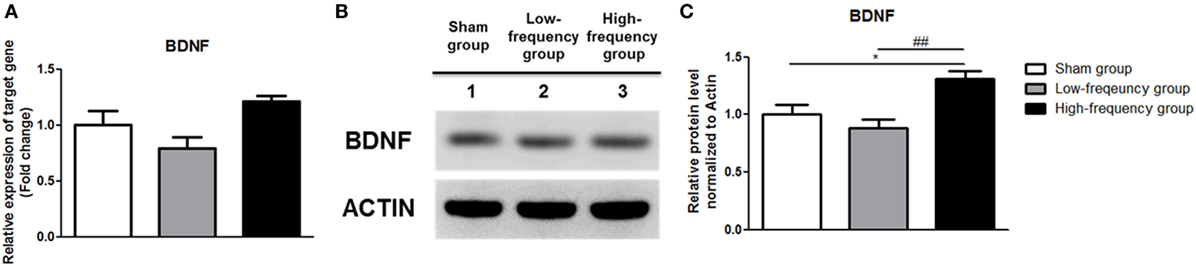
Figure 5. Repetitive magnetic stimulation treatment increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression in differentiated Neuro-2a cells. (A) The relative expression of BDNF was normalized by sham expression and was calculated using the 2−ΔΔCt method by qRT-PCR during neuronal differentiation of Neuro-2a cells. (B) Western blot analysis was performed using BDNF, and actin (as a control) antibodies in the Neuro-2a cells. (C) Comparison of relative protein expression for BDNF and actin (a control) in differentiated Neuro-2a cells with Multi Guage (v3.0) software (Fujifilm). All results are expressed as means ± SEM. ***p < 0.001 comparison with the sham group in differentiated Neuro-2a cells. ###p < 0.001 comparison with the low-frequency group in the Neuro-2a cells.
Taken together, BDNF expression is increased by Ca2+–CaMKII–CREB pathway activation in both undifferentiated and differentiated Neuro-2a cells.
It has been established that different frequencies for rTMS techniques can produce different modulatory effects (5). In this study, we examined global gene expression patterns by different frequencies of rMS in both undifferentiated and differentiated Neuro-2a cells.
In this study, LTP pathway is a significant pathway which is enriched in high-frequency group compared with low-frequency group in undifferentiated Neuro-2a cells. With its ability to endure functional enhancement of synaptic connections, or structural modification of neuronal connectivity, LTP pathway is a critical process for learning and memory (43) and has been relevant in rTMS treatment (4, 8, 36, 37). In the previous study, LTP pathway was significantly increased in the high-frequency stimulation compared with the sham (44) and had long-lasting increase in synaptic efficiency as a result of the high-frequency stimulation of afferent fibers (36). In this study, we validated that the genes such as GRIN1, CaMKIIδ, CaMKIIα, and CaMKIIγ were involved in LTP pathway by high-frequency rMS in both undifferentiated and differentiated Neuro-2a cells.
GRINI, one of the subunits of the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors (NMDARs), which were part of a large multiprotein complex (45), was upregulated in the high-frequency rMS in both undifferentiated and differentiated Neuro-2a cells. NMDARs, which are part of a large multiprotein complex, possess a large part in normal development and function, including synaptic plasticity, neural development, learning, and memory (46). NMDAR activity mediates CaMKII translocation to the postsynaptic density where it is maintained through a direct interaction with the C-terminal tail of the NMDAR complex (47). CaMKII is a calmodulin-dependent protein kinase that plays a crucial role in learning and memory by mediating a wide variety of intercellular responses (48, 49). There are four CaMKII isoform termed as CaMKIIα, CaMKIIβ, CaMKIIδ, and CaMKIIγ (50) that regulate calcium channel activity and gene expression (51–53). CaMKIIα, one of the major part of CaMKII, plays a critical role in hippocampal LTP and spatial learning (54, 55). CaMKIIγ is regarded one of the inhibitors of CaMKII functions (56). It also can regulate inhibitory synapses to lead long-term inhibitory synaptic plasticity (57). Taken together, Ca2+–CaMKII pathway is increased by high-frequency rMS in both undifferentiated and differentiated Neuro-2a cells.
Multiple signaling cascades are related in phosphorylation of CREB, including the activation of CaMKII. CaMKII has been implicated strongly in memory formation of various species as a key regulator of gene expression (41, 58–61). CREB cannot only be activated by various kinases through electrical activity, neurotransmitters, hormones, and neurotrophins, but also can promote the expression of many cAMP response elements (CREs) containing genes (62). In this study, we suggest that Ca2+–CaMKII–CREB pathway is activated by high-frequency rMS in both undifferentiated and differentiated Neuro-2a cells.
In the previous study, BDNF transcription and neurite outgrowth were increased through Ca2+–CaMKII–CREB pathway by ES in cultured rat postnatal dorsal root ganglion neurons (41). BDNF promotes neuronal survival through both inactivation of the elements that take role in cell death machinery and activation of the transcription factor, CREB (63). In addition, BDNF is a crucial protein which aids the development, differentiation, maintenance, and plasticity of brain function (64). It has been proven through several experiments that by enhancing the expression of glutamate neurotransmitters and BDNF, rTMS has the ability to regulate neuroplasticity (5, 65–67). In this study, BDNF expression is up-regulated via Ca2+–CaMKII–CREB pathway activation through high-frequency rMS in both undifferentiated and differentiated Neuro-2a cells.
Our finding suggests that the LTP pathway was confirmed to be a relevant enriched KEGG pathway by high-frequency rMS in Neuro-2a cells. In addition, high-frequency rMS activated the Ca2+–CaMKII–CREB signaling pathway, and the expression of p-CREB and BDNF was increased through the Ca2+–CaMKII–CREB signaling pathway in both undifferentiated and differentiated Neuro-2a cells (Figure 6).
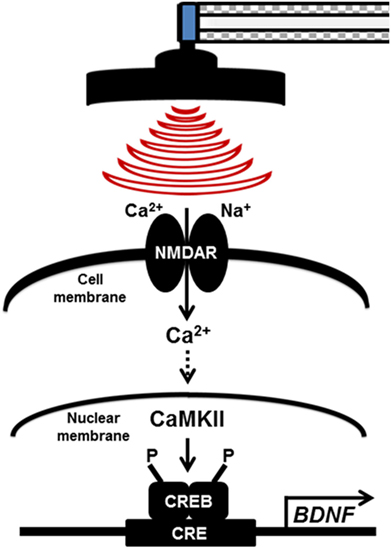
Figure 6. Potential therapeutic mechanisms for high-frequency repetitive magnetic stimulation (rMS) in both undifferentiated and differentiated Neuro-2a cells. The long-term potentiation pathway was confirmed to be an enriched relevant Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway in high-frequency rMS stimulation in both undifferentiated and differentiated Neuro-2a cells. In addition, high-frequency rMS can activate the Ca2+–calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII)–cAMP-response element-binding protein (CREB) signaling pathway. In addition, phospho-CREB and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression was increased via activation of the Ca2+–CaMKII–CREB signaling pathway in both undifferentiated and differentiated Neuro-2a cells. NMDAR, N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors; CaMKII, Ca2+–calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II; CREB, cAMP-response element-binding protein; CRE, cAMP-response element; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor.
There are several limitations in this study. Our data are focused on normal condition of undifferentiated and differentiated Neuro-2a cells, which are widely used in neurological and neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease (68, 69), Parkinson’s disease (70, 71), and stroke (25, 72, 73). Therefore, in the further investigation, work on applying the mechanism, proved through this study, in various disease models to provide a cure for neurological and neurodegenerative disorders will be done. In addition to the application on various disease models, we plan to clarify the accurate therapeutic mechanism of rTMS through the application of this mechanism in vivo and on induced pluripotent stem cell/embryonic stem cells in the further studies to be done.
The findings in this study will provide a better understanding of the neurobiological mechanisms of neuroplasticity, through the usage of different frequencies of rTMS, and a basic information for clinical application. It will provide a comprehensive view of further therapeutic mechanisms of rTMS.
AB contributed to study conception and design, collection, and/or assembly of data and manuscript writing. EJP contributed to collect and/or assembly of data and manuscript writing. SYK contributed to manuscript writing and English editing. B-GN, JHK, and SWJ contributed to collect and/or assembly of data. SHK and S-RC contributed to data analysis and interpretation, manuscript writing, and project supervision. All the authors read and approved the manuscript.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
This research was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea (2015M3A9B4067068 and 2017R1D1A1B03028855) and the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (HI16C1012 and HI16C1176).
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2018.00285/full#supplementary-material.
Table S1. Raw data for 21,567 differentially expressed transcripts.
Table S2. Raw data for 798 differentially expressed transcripts.
1. Kapoor A. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy for post-stroke non-fluent aphasia: a critical review. Top Stroke Rehabil (2017) 24(7):547–53. doi:10.1080/10749357.2017.1331417
2. Muller-Dahlhaus F, Vlachos A. Unraveling the cellular and molecular mechanisms of repetitive magnetic stimulation. Front Mol Neurosci (2013) 6:50. doi:10.3389/fnmol.2013.00050
3. Lee JY, Park HJ, Kim JH, Cho BP, Cho SR, Kim SH. Effects of low- and high-frequency repetitive magnetic stimulation on neuronal cell proliferation and growth factor expression: a preliminary report. Neurosci Lett (2015) 604:167–72. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2015.07.038
4. Gersner R, Kravetz E, Feil J, Pell G, Zangen A. Long-term effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on markers for neuroplasticity: differential outcomes in anesthetized and awake animals. J Neurosci (2011) 31:7521–6. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6751-10.2011
5. Luo J, Zheng H, Zhang L, Zhang Q, Li L, Pei Z, et al. High-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) improves functional recovery by enhancing neurogenesis and activating BDNF/TrkB signaling in ischemic rats. Int J Mol Sci (2017) 18:455. doi:10.3390/ijms18020455
6. Ma J, Zhang Z, Kang L, Geng D, Wang Y, Wang M, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) influences spatial cognition and modulates hippocampal structural synaptic plasticity in aging mice. Exp Gerontol (2014) 58:256–68. doi:10.1016/j.exger.2014.08.011
7. Ljubisavljevic MR, Javid A, Oommen J, Parekh K, Nagelkerke N, Shehab S, et al. The effects of different repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) protocols on cortical gene expression in a rat model of cerebral ischemic-reperfusion injury. PLoS One (2015) 10:e0139892. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0139892
8. Vlachos A, Muller-Dahlhaus F, Rosskopp J, Lenz M, Ziemann U, Deller T. Repetitive magnetic stimulation induces functional and structural plasticity of excitatory postsynapses in mouse organotypic hippocampal slice cultures. J Neurosci (2012) 32:17514–23. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0409-12.2012
9. Lefaucheur JP, Drouot X, Menard-Lefaucheur I, Zerah F, Bendib B, Cesaro P, et al. Neurogenic pain relief by repetitive transcranial magnetic cortical stimulation depends on the origin and the site of pain. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry (2004) 75:612–6. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2003.022236
10. Leo RJ, Latif T. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) in experimentally induced and chronic neuropathic pain: a review. J Pain (2007) 8:453–9. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2007.01.009
11. Lefaucheur JP, Andre-Obadia N, Antal A, Ayache SS, Baeken C, Benninger DH, et al. Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS). Clin Neurophysiol (2014) 125:2150–206. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2014.05.021
12. Nardone R, Holler Y, Leis S, Holler P, Thon N, Thomschewski A, et al. Invasive and non-invasive brain stimulation for treatment of neuropathic pain in patients with spinal cord injury: a review. J Spinal Cord Med (2014) 37:19–31. doi:10.1179/2045772313Y.0000000140
13. Lu H, Kobilo T, Robertson C, Tong S, Celnik P, Pelled G. Transcranial magnetic stimulation facilitates neurorehabilitation after pediatric traumatic brain injury. Sci Rep (2015) 5:14769. doi:10.1038/srep14769
14. Arias-Carrion O. Basic mechanisms of rTMS: implications in Parkinson’s disease. Int Arch Med (2008) 1:2. doi:10.1186/1755-7682-1-2
15. Wu AD, Fregni F, Simon DK, Deblieck C, Pascual-Leone A. Noninvasive brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease and dystonia. Neurotherapeutics (2008) 5:345–61. doi:10.1016/j.nurt.2008.02.002
16. Zamir O, Gunraj C, Ni Z, Mazzella F, Chen R. Effects of theta burst stimulation on motor cortex excitability in Parkinson’s disease. Neurophysiol Clin (2012) 123:815–21. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2011.07.051
17. Khedr EM, Ahmed MA, Fathy N, Rothwell JC. Therapeutic trial of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation after acute ischemic stroke. Neurology (2005) 65:466–8. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000173067.84247.36
18. Kim YH, You SH, Ko MH, Park JW, Lee KH, Jang SH, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation-induced corticomotor excitability and associated motor skill acquisition in chronic stroke. Stroke (2006) 37:1471–6. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000221233.55497.51
19. Brodie SM, Meehan S, Borich MR, Boyd LA. 5 Hz repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation over the ipsilesional sensory cortex enhances motor learning after stroke. Front Hum Neurosci (2014) 8:143. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2014.00143
20. Bentwich J, Dobronevsky E, Aichenbaum S, Shorer R, Peretz R, Khaigrekht M, et al. Beneficial effect of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation combined with cognitive training for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: a proof of concept study. J Neural Transm (2011) 118:463–71. doi:10.1007/s00702-010-0578-1
21. Angelucci F, Oliviero A, Pilato F, Saturno E, Dileone M, Versace V, et al. Transcranial magnetic stimulation and BDNF plasma levels in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuroreport (2004) 15:717–20. doi:10.1097/00001756-200403220-00029
22. Cashman NR, Durham HD, Blusztajan JK, Oda K, Tabira T, Shaw IT, et al. Neuroblastoma X spinal-cord (Nsc) hybrid cell-lines resemble developing motor neurons. Dev Dyn (1992) 194:209–21. doi:10.1002/aja.1001940306
23. Pasinelli P, Borchelt DR, Houseweart MK, Cleveland DW, Brown RH. Caspase-1 is activated in neural cells and tissue with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-associated mutations in copper-zinc superoxide dismutase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (1998) 95:15763–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.26.15763
24. Tremblay RG, Sikorska M, Sandhu JK, Lanthier P, Ribecco-Lutkiewicz M, Bani-Yaghoub M. Differentiation of mouse Neuro 2A cells into dopamine neurons. J Neurosci Methods (2010) 186:60–7. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2009.11.004
25. Baek A, Kim JH, Pyo S, Jung J-H, Park EJ, Kim SH, et al. The differential effects of repetitive magnetic stimulation in an in vitro neuronal model of ischemia/reperfusion injury. Front Neurol (2018) 9:50. doi:10.3389/fneur.2018.00050
26. Trapnell C, Roberts A, Goff L, Pertea G, Kim D, Kelley DR, et al. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat Protoc (2012) 7:562–78. doi:10.1038/nprot.2012.016
27. Rajkumar AP, Qvist P, Lazarus R, Lescai F, Ju J, Nyegaard M, et al. Experimental validation of methods for differential gene expression analysis and sample pooling in RNA-seq. BMC Genomics (2015) 16:548. doi:10.1186/s12864-015-1767-y
28. Tsuji S, Yamashita T, Tanaka M, Nagai Y. Synthetic Sialyl compounds as well as natural gangliosides induce neuritogenesis in a mouse neuro-blastoma cell-line (Neuro2a). J Neurochem (1988) 50:414–23. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb02928.x
29. Riboni L, Prinetti A, Bassi R, Caminiti A, Tettamanti G. A mediator role of ceramide in the regulation of neuroblastoma Neuro2a cell-differentiation. J Biol Chem (1995) 270:26868–75. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.45.26868
30. Yanaka N, Nogusa Y, Fujioka Y, Yamashita Y, Kato N. Involvement of membrane protein GDE2 in retinoic acid-induced neurite formation in Neuro2A cells. FEBS Lett (2007) 581:712–8. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2007.01.035
31. Kim MS, Yu JH, Lee MY, Kim AL, Jo MH, Kim M, et al. Differential expression of extracellular matrix and adhesion molecules in fetal-origin amniotic epithelial cells of preeclamptic pregnancy. PLoS One (2016) 11:e0156038. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0156038
32. Won YH, Lee MY, Choi YC, Ha Y, Kim H, Kim DY, et al. Elucidation of relevant neuroinflammation mechanisms using gene expression profiling in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PLoS One (2016) 11:e0165290. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0165290
33. Baek A, Cho SR, Kim SH. Elucidation of gene expression patterns in the brain after spinal cord injury. Cell Transplant (2017) 26:1286–300. doi:10.1177/0963689717715822
34. Baek A, Kim M, Kim SH, Cho SR, Kim HJ. Anti-inflammatory effect of DNA polymeric molecules in a cell model of osteoarthritis. Inflammation (2018) 41:677–88. doi:10.1007/s10753-017-0722-2
35. Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(T)(-Delta Delta C) method. Methods (2001) 25:402–8. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
36. Ogiue-Ikeda M, Kawato S, Ueno S. The effect of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on long-term potentiation in rat hippocampus depends on stimulus intensity. Brain Res (2003) 993:222–6. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2003.09.009
37. Tang A, Thickbroom G, Rodger J. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the brain: mechanisms from animal and experimental models. Neuroscientist (2015) 23:82–94. doi:10.1177/1073858415618897
38. Thalhammer A, Rudhard Y, Tigaret CM, Volynski KE, Rusakov DA, Schoepfer R. CaMKII translocation requires local NMDA receptor-mediated Ca2+ signaling. EMBO J (2006) 25:5873–83. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601420
39. Medvedev S, Stein P, Schultz RM. Specificity of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases in mouse egg activation. Cell Cycle (2014) 13:1482–8. doi:10.4161/cc.28432
40. Sheng M, Thompson MA, Greenberg ME. CREB: a Ca(2+)-regulated transcription factor phosphorylated by calmodulin-dependent kinases. Science (1991) 252:1427–30. doi:10.1126/science.1646483
41. Yan X, Liu J, Ye Z, Huang J, He F, Xiao W, et al. CaMKII-mediated CREB phosphorylation is involved in Ca2+-induced BDNF mRNA transcription and neurite outgrowth promoted by electrical stimulation. PLoS One (2016) 11:e0162784. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0162784
42. Lonze BE, Ginty DD. Function and regulation of CREB family transcription factors in the nervous system. Neuron (2002) 35:605–23. doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(02)00828-0
43. Monte-Silva K, Kuo MF, Hessenthaler S, Fresnoza S, Liebetanz D, Paulus W, et al. Induction of late LTP-like plasticity in the human motor cortex by repeated non-invasive brain stimulation. Brain Stimul (2013) 6:424–32. doi:10.1016/j.brs.2012.04.011
44. Shang Y, Wang X, Shang X, Zhang H, Liu Z, Yin T, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation effectively facilitates spatial cognition and synaptic plasticity associated with increasing the levels of BDNF and synaptic proteins in Wistar rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem (2016) 134(Pt B):369–78. doi:10.1016/j.nlm.2016.08.016
45. Diana MC, Santoro ML, Xavier G, Santos CM, Spindola LN, Moretti PN, et al. Low expression of Gria1 and Grin1 glutamate receptors in the nucleus accumbens of spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). Psychiatry Res (2015) 229:690–4. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2015.08.021
46. Chen W, Shieh C, Swanger SA, Tankovic A, Au M, Mcguire M, et al. GRIN1 mutation associated with intellectual disability alters NMDA receptor trafficking and function. J Hum Genet (2017) 62:589–97. doi:10.1038/jhg.2017.19
47. Bustos FJ, Jury N, Martinez P, Ampuero E, Campos M, Abarzua S, et al. NMDA receptor subunit composition controls dendritogenesis of hippocampal neurons through CAMKII, CREB-P, and H3K27ac. J Cell Physiol (2017) 232:3677–92. doi:10.1002/jcp.25843
48. Schulman H, Hanson PI. Multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein-kinase. Neurochem Res (1993) 18:65–77. doi:10.1007/BF00966924
49. Kennedy MB. Signal transduction molecules at the glutamatergic postsynaptic membrane. Brain Res Rev (1998) 26:243–57. doi:10.1016/S0165-0173(97)00043-X
50. Saddouk FZ, Ginnan R, Singer HA. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in vascular smooth muscle. Adv Pharmacol (2017) 78:171–202. doi:10.1016/bs.apha.2016.08.003
51. Chin ER. Role of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinases in skeletal muscle plasticity. J Appl Physiol (1985) (2005) 99:414–23. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00015.2005
52. Rose AJ, Alsted TJ, Kobbero JB, Richter EA. Regulation and function of Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II of fast-twitch rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol (2007) 580:993–1005. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2006.127464
53. Tavi P, Westerblad H. The role of in vivo Ca2+ signals acting on Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent proteins for skeletal muscle plasticity. J Physiol (2011) 589:5021–31. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2011.212860
54. Soderling TR. CaM-kinases: modulators of synaptic plasticity. Curr Opin Neurobiol (2000) 10:375–80. doi:10.1016/S0959-4388(00)00090-8
55. Lisman J, Schulman H, Cline H. The molecular basis of CaMKII function in synaptic and behavioural memory. Nat Rev Neurosci (2002) 3:175–90. doi:10.1038/nrn753
56. Liu XB, Murray KD. Neuronal excitability and calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type II: location, location, location. Epilepsia (2012) 53(Suppl 1):45–52. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2012.03474.x
57. Houston CM, He Q, Smart TG. CaMKII phosphorylation of the GABA(A) receptor: receptor subtype- and synapse-specific modulation. J Physiol (2009) 587:2115–25. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2009.171603
58. Sun PQ, Enslen H, Myung PS, Maurer RA. Differential activation of Creb by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein-kinases type-II and type-IV involves phosphorylation of a site that negatively regulates activity. Genes Dev (1994) 8:2527–39. doi:10.1101/gad.8.21.2527
59. Wu GY, Deisseroth K, Tsien RW. Activity-dependent CREB phosphorylation: convergence of a fast, sensitive calmodulin kinase pathway and a slow, less sensitive mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2001) 98:2808–13. doi:10.1073/pnas.051634198
60. Wu XL, McMurray CT. Calmodulin kinase II attenuation of gene transcription by preventing cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) dimerization and binding of the CREB-binding protein. J Biol Chem (2001) 276:1735–41. doi:10.1074/jbc.M006727200
61. Ma H, Groth RD, Cohen SM, Emery JF, Li BX, Hoedt E, et al. gamma CaMKII shuttles Ca2+/CaM to the nucleus to trigger CREB phosphorylation and gene expression. Cell (2014) 159:281–94. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.019
62. Muller M, Cardenas C, Mei L, Cheung KH, Foskett JK. Constitutive cAMP response element binding protein (CREB) activation by Alzheimer’s disease presenilin-driven inositol trisphosphate receptor (InsP3R) Ca2+ signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2011) 108:13293–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.1109297108
63. West AE, Chen WG, Dalva MB, Dolmetsch RE, Kornhauser JM, Shaywitz AJ, et al. Calcium regulation of neuronal gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2001) 98:11024–31. doi:10.1073/pnas.191352298
64. Min D, Guo F, Zhu S, Xu X, Mao X, Cao Y, et al. The alterations of Ca2+/calmodulin/CaMKII/CaV1.2 signaling in experimental models of Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. Neurosci Lett (2013) 538:60–5. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2013.02.001
65. Wang HY, Crupi D, Liu JJ, Stucky A, Cruciata G, Di Rocco A, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation enhances BDNF-TrkB signaling in both brain and lymphocyte. J Neurosci (2011) 31:11044–54. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2125-11.2011
66. Lee JY, Kim SH, Ko AR, Lee JS, Yu JH, Seo JH, et al. Therapeutic effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in an animal model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res (2013) 1537:290–302. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2013.08.051
67. Niimi M, Hashimoto K, Kakuda W, Miyano S, Momosaki R, Ishima T, et al. Role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in beneficial effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for upper limb hemiparesis after stroke. PLoS One (2016) 11:e0152241. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0152241
68. Rajendran L, Honsho M, Zahn TR, Keller P, Geiger KD, Verkade P, et al. Alzheimer’s disease beta-amyloid peptides are released in association with exosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2006) 103:11172–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.0603838103
69. Yan YF, Gong K, Ma T, Zhang LH, Zhao NM, Zhang XF, et al. Protective effect of edaravone against Alzheimer’s disease-relevant insults in neuroblastoma N2a cells. Neurosci Lett (2012) 531:160–5. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2012.10.043
70. Lundius EG, Stroth N, Vukojevic V, Terenius L, Svenningsson P. Functional GPR37 trafficking protects against toxicity induced by 6-OHDA, MPP+ or rotenone in a catecholaminergic cell line. J Neurochem (2013) 124:410–7. doi:10.1111/jnc.12081
71. Jing HR, Wang SX, Wang M, Fu WL, Zhang C, Xu DG. Isobavachalcone attenuates MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease in mice by inhibition of microglial activation through NF-kappa B pathway. PLoS One (2017) 12:e0169560. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0169560
72. Guo YC, Wang JF, Wang ZQ, Yang Y, Wang XM, Duan QH. Melatonin protects N2a against ischemia/reperfusion injury through autophagy enhancement. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci (2010) 30:1–7. doi:10.1007/s11596-010-0101-9
Keywords: repetitive magnetic stimulation, low-frequency, high-frequency, Ca2+–calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II–cAMP-response element-binding protein pathway, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, Neuro-2a cells
Citation: Baek A, Park EJ, Kim SY, Nam B-G, Kim JH, Jun SW, Kim SH and Cho S-R (2018) High-Frequency Repetitive Magnetic Stimulation Enhances the Expression of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Through Activation of Ca2+–Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II–cAMP-Response Element-Binding Protein Pathway. Front. Neurol. 9:285. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00285
Received: 08 October 2017; Accepted: 12 April 2018;
Published: 07 May 2018
Edited by:
Vassilis E. Koliatsos, Johns Hopkins University, United StatesReviewed by:
Francisco Capani, University of Buenos Aires, ArgentinaCopyright: © 2018 Baek, Park, Kim, Nam, Kim, Jun, Kim and Cho. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sung Hoon Kim, a2ltcmVoYWJAeW9uc2VpLmFjLmty;
Sung-Rae Cho, c3JjaG85MThAeXVocy5hYw==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work.
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.