
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Neurol. , 29 March 2018
Sec. Movement Disorders
Volume 9 - 2018 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2018.00213
 Lucia Corrado1
Lucia Corrado1 Fabiola De Marchi2
Fabiola De Marchi2 Sara Tunesi3,4
Sara Tunesi3,4 Gaia Donata Oggioni2,5
Gaia Donata Oggioni2,5 Miryam Carecchio2
Miryam Carecchio2 Luca Magistrelli2
Luca Magistrelli2 Silvana Tesei6
Silvana Tesei6 Giulio Riboldazzi5
Giulio Riboldazzi5 Alessio Di Fonzo7
Alessio Di Fonzo7 Clarissa Locci1
Clarissa Locci1 Ilaria Trezzi7
Ilaria Trezzi7 Roberta Zangaglia8
Roberta Zangaglia8 Cristina Cereda9
Cristina Cereda9 Sandra D’Alfonso1
Sandra D’Alfonso1 Corrado Magnani3
Corrado Magnani3 Giacomo P. Comi7
Giacomo P. Comi7 Giorgio Bono5
Giorgio Bono5 Claudio Pacchetti8
Claudio Pacchetti8 Roberto Cantello2
Roberto Cantello2 Stefano Goldwurm6
Stefano Goldwurm6 Cristoforo Comi2*
Cristoforo Comi2*
Background: Alpha-synuclein is a constituent of Lewy bodies and mutations of its gene cause familial Parkinson’s disease (PD). A previous study showed that a variant of the alpha-synuclein gene (SNCA), namely the 263 bp allele of Rep1 was associated with faster motor progression in PD. On the contrary, a recent report failed to detect a detrimental effect of Rep1 263 on both motor and cognitive outcomes in PD. Aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of the Rep1 variants on disease progression in PD patients.
Methods: We recruited and genotyped for SNCA Rep1 426 PD patients with age at onset ≥40 years and disease duration ≥4 years. We then analyzed frequency and time of occurrence of wearing-off, dyskinesia, freezing of gait, visual hallucinations, and dementia using a multivariate Cox’s proportional hazards regression model.
Results: SNCA Rep1 263 carriers showed significantly increased risk of both dementia (HR = 3.03) and visual hallucinations (HR = 2.69) compared to 263 non-carriers. Risk of motor complications did not differ in the two groups.
Conclusion: SNCA Rep1 263 allele is associated with a worse cognitive outcome in PD.
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the second most frequent neurodegenerative disease (1), and is clinically characterized by the presence of asymmetric motor signs, including resting tremor, rigidity, and bradykinesia (2). Nonetheless, non-motor symptoms, such as mood deflection, anosmia, and sleep disturbances may also be present and can at times pre-date motor impairment (3). As disease progresses, further disabling symptoms appear, such as posture and gait impairment on the motor side, and cognitive decline and hallucinations in the non-motor domain (4, 5).
Parkinson’s disease neuropathology is characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons and the presence of Lewy bodies (LBs) in surviving neurons (6, 7). LBs contain fibrils composed of alpha-synuclein, a small protein involved in synaptic vesicle trafficking and neurotransmitter release (7), but also in more widespread functions, including the triggering of neuroinflammatory processes (8). Duplication and triplication of alpha-synuclein gene (SNCA) cause dominant early-onset PD, suggesting that overexpression of wild-type alpha-synuclein is sufficient to cause the disease (9). The amount of alpha-synuclein is relevant in sporadic disease as well, since its expression is higher in brain tissue from PD patients compared to control tissue (10). Furthermore, genome-wide association studies revealed that SNCA variations are associated with sporadic PD development (11).
Variations in the complex microsatellite D4S3481 (known as Rep-1), located approximately 10 kb upstream of the translational start of SNCA, have been reported to increase PD risk. SNCA Rep1 is essentially triallelic (259, 261, and 263 base pairs in length) and a meta-analysis of association studies showed higher frequency of 263 bp allele in cases compared to controls (12). Furthermore, the 259 bp allele was found to be associated with a decreased risk of PD, being more frequent in controls than in cases, whereas no relevant effect was observed for the 261 bp allele (12). To date, data on the role of SNCA common variants in PD progression are conflicting. Ritz et al. analyzed 232 PD patients and found that the risk of faster motor decline, assessed by UPDRS, was fourfold increased in carriers of the Rep1 263 bp promoter variant (13). Thereafter, a study in which outcome was measured in terms of life expectancy, did not detect any association between SNCA Rep1 genotypes and risk of death in 6,154 PD cases (14). More recently, Markopoulou et al. (15) analyzed the correlation between SNCA Rep1 genotypes and both motor and cognitive outcomes, assessed by telephone interview, in a large cohort of PD patients. Surprisingly, they found an opposite role of the microsatellite variants, with shorter alleles providing worse outcomes.
On this background, the aim of our study was to investigate the effect of SNCA Rep1 on disease progression in a cohort of Italian PD patients, clinically characterized through the collection of solid and reliable milestones of disease evolution.
426 patients (249 males) with PD (2) were enrolled according to the following inclusion criteria: age at onset ≥40 years, longitudinal follow-up ≥ 4 years. All patients were of Italian origin and were enrolled at the following Movement Disorders Centers: (1) University of Piemonte Orientale, Novara, (2) University of Insubria, Varese, (3) IRCCS Foundation Ca’ Granda Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico, Dino Ferrari Center, Neuroscience Section, University of Milan, (4) C. Mondino National Institute of Neurology Foundation, IRCCS, Pavia, (5) Parkinson Institute, ASST Gaetano Pini-CTO, Milan. The Parkinson Institute cohort (144 patients) had been previously analyzed in both a case-control study assessing the role of SNCA variants in PD susceptibility (16) and in the collaborative GEO-PD study on survival (14).
Patients who had at least one first- or second degree relative with a diagnosis of primary parkinsonism, and/or age at onset ≤50 years and/or peculiar clinical features had been previously analyzed to exclude pathogenic mutations of known PD-related genes (SNCA, LRRK2, Parkin, PINK1, and DJ-1) according to EFNS guidelines (17).
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of Piemonte Orientale (identification code 65/16). Patients were included in the study after having read and signed an informed consent form for research purpose.
All recruited patients had been longitudinally evaluated every 6 months at each center by a team of neurologist’s expert in movement disorders. The mean follow-up duration was 11.3 years. Clinical records were retrospectively analyzed taking into consideration only variables that had been assessed in each center. Agreement was found on the following parameters: gender, age at onset, disease duration, and family history. Furthermore, the presence and time of onset of the following motor and non-motor complications was recorded: wearing-off, dyskinesia, freezing of gait, visual hallucinations, and dementia. Dementia was diagnosed with a comprehensive cognitive evaluation according to MDS criteria (18).
Genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral blood using standard procedures. We analyzed the microsatellite SNCA Rep1 in the entire cohort (426 subjects). The SNCA Rep1 region was amplified through PCR from genomic DNA using the primer pair: 5′-GACTGGCCCAAGATTAACCA-3′ (fluorescently labeled with 6-FAM) and 5′-CCTGGCATATTTGATTGCAA-3′. PCR products were resolved by capillary electrophoresis on an ABI-3130XL DNA Analyzer (Applied Biosystem, Foster City, CA, USA) using GeenScan-500 ROX (Applied Biosystem) as molecular weight marker. Allelic sizes were assessed using the GeneMapper 4.0 software.
To confirm the accuracy of the genotyping method, we sequenced several individuals representative of each genotype as standard samples.
Allelic distribution was assessed for Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) with Fisher’s exact test.
SNCA Rep1 was analyzed using a dominant genetic model (e.g., subjects 263 carriers vs 263 non-carriers) as previously described (13).
Continuous variables were reported as median and 25th and 75th percentile, categorical variables were presented as frequencies (counts) and percentages. Allelic frequencies and family history were compared with the χ2 test, differences between age at onset and disease duration were assessed with Mann–Whitney U test.
The influence of the SNCA variant carrier status on disease natural history was investigated performing time-to-event analysis: wearing-off, dyskinesia, freezing of gait, visual hallucinations, and dementia were considered as separate outcomes. Every patient contributed time of observation from disease onset to complication under study or the last assessment. Individual analyses were performed for each complication under study and cumulative incidences were estimated using the Kaplan–Meier (KM) methods. Log-rank test was used to examine univariate association with outcome. Multivariate Cox’s proportional hazards (PHs) regression model was fitted to obtain the hazard ratio (HR) for SNCA variant carrier status adjusted by gender, age at PD onset, and recruitment center.
Proportional hazard model was assessed by regression scaled Schoenfeld residuals against the log time. All p-values are two-tailed and the significance cut-off was p < 0.05. Statistical analysis was performed using STATA v14.
Demographic and clinical features of the 426 PD patients are summarized in Table 1.
Observed frequencies of SNCA Rep1 genotypes were in HWE (p = 0.19) (Table S1 in Supplementary Material).
Disease duration and family history did not differ significantly between Rep1 263 carriers (n = 44) and 263 non-carriers (n = 382) (p = 0.088, Mann–Whitney U test, and p = 0.797, χ2 test). On the contrary, the former group showed significantly earlier age at onset compared to the latter (p = 0.016, Mann–Whitney U test) (Table S2 in Supplementary Material).
Furthermore, we performed a Kaplan–Meyer survival analysis to compare the probability of developing each complication over time in 263 carriers vs 263 non-carriers (Figure 1; Figure S1 in Supplementary Material). At 10 years from onset, cumulative incidence of dementia was higher in carriers than in non-carriers (26.39 vs 12.94%, log-rank test p = 0.001; Table 2). Similar findings were also observed for visual hallucinations and wearing-off (24.48 vs 15.01% and 65.33 vs 53.02%, log-rank test p = 0.0037 and p = 0.028 respectively; Table 2).
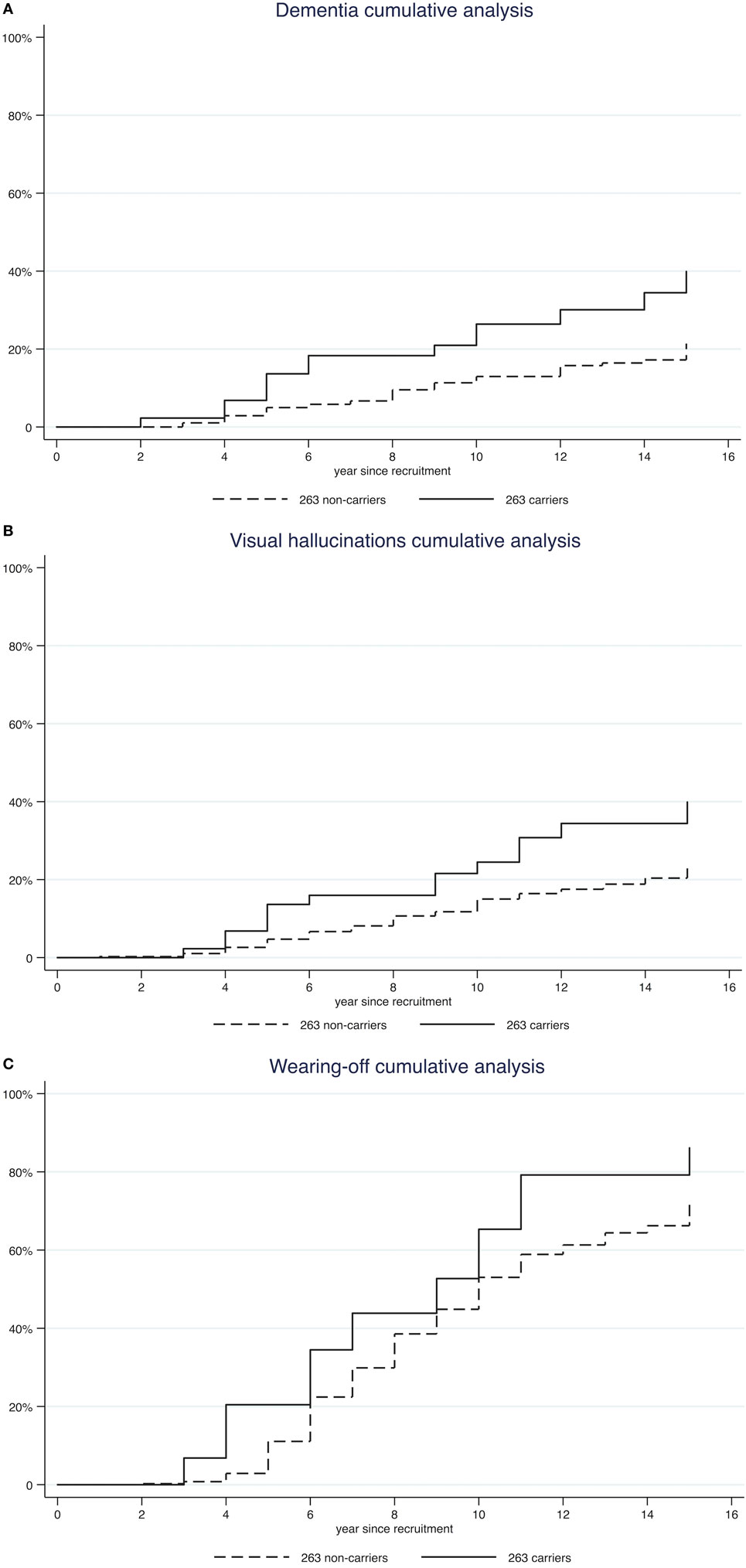
Figure 1. Kaplan–Meyer survival analysis of complications [dementia panel (A); visual hallucinations panel (B); wearing-off panel (C)].
Finally, after applying a multivariate Cox regression model adjusting by gender, age at disease onset, and recruitment center, a statistically significant difference persisted for dementia and visual hallucinations, but not for wearing-off. In detail, we found that 263 carriers had a 3.03-fold higher risk of dementia, a 2.69-fold higher risk of visual hallucinations, and a 1.26-fold higher risk of wearing-off compared to non-carriers (p < 0.001, p = 0.001, and 0.236, respectively; Table 3).
This study showed for the first time that Rep1 polymorphic variants of the SNCA gene influence non-motor evolution in PD. In patients carrying the SNCA Rep1 263 allele, the risk of developing dementia and visual hallucinations is increased by 3.03 and 2.69, respectively, compared to patients carrying shorter Rep1 variants. With regards to motor progression, Rep1 263 carriers display a slightly increased cumulative incidence of wearing-off, compared to non-carriers, even though such difference was not statistically significant in multivariate regression.
To date, there is strong evidence supporting a genetic component in PD susceptibility. On the contrary, few studies have addressed the role of disease modifying genes (19, 20, 21). This might be due, at least in part, to the difficulty in collecting data on disease evolution compared to recording disease development. Consistently, large collaborative studies aimed at tracking PD progression are ongoing (22, 23). In our study, we chose to include only patients with longitudinal follow-up and accurate information regarding the main motor and non-motor complications, putting together a well characterized population of 426 patients.
The cognitive features of 263 carriers recalled that of familial PD caused by rare pathogenic SNCA multiplications, in which progression is faster compared to sporadic PD (24). It is known that such mutations cause alpha-synuclein overproduction through increased mRNA expression (25). With regards to the possible effect of the length of Rep1 microsatellite on alpha-synuclein expression, conflicting data were reported. Chiba-Falek et al. detected a threefold increase of alpha-synuclein expression with longer compared to shorter Rep1 alleles in a cellular model (26). Furthermore, alpha-synuclein mRNA varied 1.7-fold in transgenic mice carrying the different Rep1 alleles (27). These findings were further supported by Fuchs et al. who detected a correlation between protein level in blood and Rep1 genotypes (28). Intriguingly, a recent report remarked that plasma alpha-synuclein levels may predict cognitive decline in PD (29). On the contrary, Soldner et al. suggested that neither the deletion of the entire Rep1 repeat sequence nor the presence of the three different length alleles (including 263 bp) were able to influence significantly SNCA expression. Nonetheless, the authors themselves underline that their findings might have been influenced by the cellular model analyzed, which only allows to detect early events (30). For such reasons, a robust biologic relationship between the 263 allele and PD progression still has to be confirmed.
Our study is the first to investigate the correlation between SNCA polymorphisms and PD progression in the European population. On the contrary, two Northern American studies, the first on 233 patients and the second on 1,098 patients, were published in 2012 and 2014, respectively (12, 13).
In the first study, a faster motor progression in PD patients carrying at least one Rep1 263 was reported (13). As regards, motor progression in Rep1 263 carriers, our findings display a trend similar to that of Ritz et al. (13), even though our data lose statistical significance in the multivariate regression model. Nonetheless, it should be noted that discrepancies might be related to substantial methodological differences. In fact, Ritz et al. (13) studied a cohort of 233 PD patients for a relatively short follow-up (5.1 years) and measured motor progression with the motor section of UPDRS. This score: (a) Does not weigh the different motor signs, (b) does not evaluate cognitive and neuropsychiatric complications, (c) is strongly influenced by treatment, and (d) shows a relevant inter-rater variability (31). On the other hand, our study of Rep1 SNPs included a larger population (426 patients) with a mean follow-up of 11.3 years. Progression was measured through clinical milestones, which are reliable measures of patients’ status, especially when multicenter studies are concerned.
A second report was published in 2014 by Markopoulou et al. (15). In this study, authors failed to detect a detrimental effect of Rep1 263 allele on PD progression. On the contrary, they found that patients carrying longer Rep1 alleles had a better motor outcome and a similar trend was observed for cognitive outcome, even though without statistical significance. In this case too, important differences between the two studies might account for the discordant results. First, our clinical data were collected through direct examination of patients, whereas cognitive data included in the report by Markopoulou et al. (15) were collected through telephonic interviews. Second, the biological effect of Rep1 microsatellite might differ among subjects, especially when a different ethnic background is involved. In fact, Rep1 is a complex microsatellite characterized by a mixed dinucleotide composition. Alleles with the same size could have different composition and it was reported that two alleles with the same length, but different dinucleotide composition might have different functional effects on the promoter activity (26). Finally, the way data are presented in the two studies makes results difficult to compare. In fact, Markopoulou et al. (15) aggregated patients carrying two different genotypes (261–261 and 259–263) in a unique very large group, thus losing the impact of the 263 allele.
Our study found a significant and biologically plausible correlation between SNCA Rep1 263 allele and the risk of development of dementia and visual hallucinations in a cohort of Italian PD patients. Future studies recruiting larger populations and assessing correlations between in vivo markers of pathology, such as cerebrospinal fluid, MRI, or PET findings, and genetic variations are mandatory to replicate our findings (32). Moreover, a thorough assessment of further clinical features, such as hyposmia and REM behavior disorder in the genetic subgroups may add relevant information on the determinants of progression (33). Early identification of patients at high risk of complications has relevant implications in terms of both prognosis and disease modifying therapy.
This study was carried out in accordance with the recommendations of the local Ethics Committee with written informed consent from all subjects. All subjects gave written informed consent in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The protocol was approved by the local Ethics Committee.
(1) Research project: A. Conception, B. Organization, C. Execution; (2) Statistical analysis: A. Design, B. Execution, C. Review and Critique; and (3) Manuscript: A. Writing of the first draft, B. Review and critique. LC: 1A, 1C, and 3A. FDM: 1B, 1C, and 3A. STu: 2A, 2B. GDO: 1C. MC: 1C. LM: 1C. STe: 1C. GR: 1C. ADF: 1C, 3B. CL: 1C. IT: 1C. RZ: 1C. CCe: 1C. SDA: 3B. CM: 2A. GPC: 3B. GB: 3B. CP: 1B, 3B. RC: 3B. SG: 1B, 3B. CCo: 1A, 1B, 2C, and 3B.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
This research was supported by the University of Piemonte Orientale, “Fondi di Ricerca Dipartimentale” and by AriSLA (REPEATALS grant). SG received grants from Italian Telethon Foundation: grant no. GTB12001B “Parkinson Institute Biobank” (2012–17). SG is coordinator of the Italian consortium of the COURAGE-PD (COmprehensive Unbiased Risk factor Assessment for Genetics and Environment in PD) funded by JPND (The EU Joint Program – Neurodegenerative Disease Research). CCo received a research grant from the Borghi Foundation, Brebbia (VA), Italy.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2018.00213/full#supplementary-material.
Figure S1. Kaplan–Meyer survival analysis of complications [dyskinesia panel (B); freezing of gait panel (A)].
Table S1. Genotype distribution frequencies.
Table S2. Age at PD onset, disease duration and family history for 263 carriers and 263 non-carriers.
1. Wirdefeldt K, Adami HO, Cole P, Trichopoulos D, Mandel J. Epidemiology and etiology of Parkinson’s disease: a review of the evidence. Eur J Epidemiol (2011) 26:S1–58. doi:10.1007/s10654-011-9581-6
2. Gelb DJ, Oliver E, Gilman S. Diagnostic criteria for Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol (1999) 56:33–9. doi:10.1001/archneur.56.1.33
3. Chaudhuri KR, Odin P, Antonini A, Martinez-Martin P. Parkinson’s disease: the non-motor issues. Parkinsonism Relat Disord (2011) 17:717–23. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2011.02.018
4. De Marchi F, Carecchio M, Cantello R, Comi C. Predicting cognitive decline in Parkinson’s disease: can we ask the genes? Front Neurol (2014) 5:224. doi:10.3389/fneur.2014.00224
5. Kalia LV, Lang AE. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet (2015) 386:896–912. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61393-3
6. Comi C, Magistrelli L, Oggioni GD, Carecchio M, Fleetwood T, Cantello R, et al. Peripheral nervous system involvement in Parkinson’s disease: evidence and controversies. Parkinsonism Relat Disord (2014) 20:1329–34. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2014.10.010
7. Tofaris GK, Spillantini MG. Alpha-synuclein dysfunction in Lewy body diseases. Mov Disord (2005) 20:S37–44. doi:10.1002/mds.20538
8. Cappellano G, Carecchio M, Fleetwood T, Magistrelli L, Cantello R, Dianzani U, et al. Immunity and inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Am J Neurodegener Dis (2013) 2:89–107.
9. Ibáñez P, Bonnet AM, Débarges B, Lohmann E, Tison F, Pollak P, et al. Causal relation between alpha-synuclein gene duplication and familial Parkinson’s disease. Lancet (2004) 364:1169–71. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)17104-3
10. Gründemann J, Schlaudraff F, Haeckel O, Liss B. Elevated alpha-synuclein mRNA levels in individual UV-laser-microdissected dopaminergic substantia nigra neurons in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Nucleic Acids Res (2008) 36:e38. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn084
11. Maraganore DM, de Andrade M, Lesnick TG, Strain KJ, Farrer MJ, Rocca WA, et al. High-resolution whole-genome association study of Parkinson disease. Am J Hum Genet (2005) 77:685–93. doi:10.1086/496902
12. Maraganore DM, de Andrade M, Elbaz A, Farrer MJ, Ioannidis JP, Krüger R, et al. Collaborative analysis of alpha-synuclein gene promoter variability and Parkinson disease. JAMA (2006) 296:661–70. doi:10.1001/jama.296.6.661
13. Ritz B, Rhodes SL, Bordelon Y, Bronstein J. α-Synuclein genetic variants predict faster motor symptom progression in idiopathic Parkinson disease. PLoS One (2012) 7:e36199. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0036199
14. Chung SJ, Biernacka JM, Armasu SM, Anderson K, Frigerio R, Aasly JO, et al. α-Synuclein repeat variants and survival in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord (2014) 29:1053–7. doi:10.1002/mds.25841
15. Markopoulou K, Biernacka JM, Armasu SM, Anderson KJ, Ahlskog JE, Chase BA, et al. Does α-synuclein have a dual and opposing effect in preclinical vs. clinical Parkinson’s disease? Parkinsonism Relat Disord (2014) 20:584–9. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2014.02.021
16. Trotta L, Guella I, Soldà G, Sironi F, Tesei S, Canesi M, et al. SNCA and MAPT genes: independent and joint effects in Parkinson disease in the Italian population. Parkinsonism Relat Disord (2012) 18:257–62. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2011.10.014
17. Berardelli A, Wenning GK, Antonini A, Berg D, Bloem BR, Bonifati V, et al. EFNS/MDS-ES/ENS [corrected] recommendations for the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Neurol (2013) 20:16–34. doi:10.1111/ene.12022
18. Dubois B, Burn D, Goetz C, Aarsland D, Brown RG, Broe GA, et al. Diagnostic procedures for Parkinson’s disease dementia: recommendations from the movement disorder society task force. Mov Disord (2007) 22:2314–24. doi:10.1002/mds.21844
19. Comi C, Ferrari M, Marino F, Magistrelli L, Cantello R, Riboldazzi G, et al. Polymorphisms of dopamine receptor genes and risk of L-Dopa-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson’s disease. Int J Mol Sci (2017) 24:18. doi:10.3390/ijms18020242
20. Ferrari M, Comi C, Marino F, Magistrelli L, De Marchi F, Cantello R, et al. Polymorphisms of dopamine receptor genes and risk of visual hallucinations in Parkinson’s patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol (2016) 72:1335–41. doi:10.1007/s00228-016-2111-4
21. Zheng J, Yang X, Zhao Q, Tian S, Huang H, Chen Y, et al. Festination correlates with SNCA polymorphism in chinese patients with Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsons Dis (2017) 2017:3176805. doi:10.1155/2017/3176805
22. Ffytche DH, Pereira JB, Ballard C, Chaudhuri KR, Weintraub D, Aarsland D. Risk factors for early psychosis in PD: insights from the Parkinson’s progression markers initiative. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry (2017) 88:325–31. doi:10.1136/jnnp-2016-314832
23. Malek N, Swallow DM, Grosset KA, Lawton MA, Marrinan SL, Lehn AC, et al. Tracking Parkinson’s: study design and baseline patient data. J Parkinsons Dis (2015) 5:947–59. doi:10.3233/JPD-150662
24. Farrer M, Kachergus J, Forno L, Lincoln S, Wang DS, Hulihan M, et al. Comparison of kindreds with parkinsonism and alpha-synuclein genomic multiplications. Ann Neurol (2004) 55:174–9. doi:10.1002/ana.10846
25. Miller DW, Hague SM, Clarimon J, Baptista M, Gwinn-Hardy K, Cookson MR, et al. Alpha-synuclein in blood and brain from familial Parkinson disease with SNCA locus triplication. Neurology (2004) 62:1835–8. doi:10.1212/01.WNL.0000127517.33208.F4
26. Chiba-Falek O, Nussbaum RL. Effect of allelic variation at the NACP-Rep1 repeat upstream of the alpha-synuclein gene (SNCA) on transcription in a cell culture luciferase reporter system. Hum Mol Genet (2001) 10:3101–9. doi:10.1093/hmg/10.26.3101
27. Cronin KD, Ge D, Manninger P, Linnertz C, Rossoshek A, Orrison BM, et al. Expansion of the Parkinson disease-associated SNCA-Rep1 allele upregulates human alpha-synuclein in transgenic mouse brain. Hum Mol Genet (2009) 18:3274–85. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddp265
28. Fuchs J, Tichopad A, Golub Y, Munz M, Schweitzer KJ, Wolf B, et al. Genetic variability in the SNCA gene influences alpha-synuclein levels in the blood and brain. FASEB J (2008) 22:1327–34. doi:10.1096/fj.07-9348com
29. Lin CH, Yang SY, Horng HE, Yang CC, Chieh JJ, Chen HH, et al. Plasma α-synuclein predicts cognitive decline in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry (2017) 88:818–24. doi:10.1136/jnnp-2016-314857
30. Soldner F, Stelzer Y, Shivalila CS, Abraham BJ, Latourelle JC, Barrasa MI, et al. Parkinson-associated risk variant in distal enhancer of α-synuclein modulates target gene expression. Nature (2016) 533:95–9. doi:10.1038/nature17939
31. Grill S, Weuve J, Weisskopf MG. Predicting outcomes in Parkinson’s disease: comparison of simple motor performance measures and the unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale-III. J Parkinsons Dis (2011) 1:287–98. doi:10.3233/JPD-2011-11016
32. Sharma S, Moon CS, Khogali A, Haidous A, Chabenne A, Ojo C, et al. Biomarkers in Parkinson’s disease (recent update). Neurochem Int (2013) 63:201–29. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2013.06.005
Keywords: dementia, hallucinations, genetic markers, disease progression, Parkinson’s disease
Citation: Corrado L, De Marchi F, Tunesi S, Oggioni GD, Carecchio M, Magistrelli L, Tesei S, Riboldazzi G, Di Fonzo A, Locci C, Trezzi I, Zangaglia R, Cereda C, D’Alfonso S, Magnani C, Comi GP, Bono G, Pacchetti C, Cantello R, Goldwurm S and Comi C (2018) The Length of SNCA Rep1 Microsatellite May Influence Cognitive Evolution in Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 9:213. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00213
Received: 17 December 2017; Accepted: 19 March 2018;
Published: 29 March 2018
Edited by:
Giuseppe De Michele, University of Naples Federico II, ItalyReviewed by:
Gennaro Pagano, King’s College London, United KingdomCopyright: © 2018 Corrado, De Marchi, Tunesi, Oggioni, Carecchio, Magistrelli, Tesei, Riboldazzi, Di Fonzo, Locci, Trezzi, Zangaglia, Cereda, D’Alfonso, Magnani, Comi, Bono, Pacchetti, Cantello, Goldwurm and Comi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Cristoforo Comi, Y29taUBtZWQudW5pdXBvLml0
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.