
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Nanotechnol., 27 November 2024
Sec. Biomedical Nanotechnology
Volume 6 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnano.2024.1490980
Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) exhibit great promise in cancer therapy and drug delivery due to their unique physicochemical properties. The utilization of plant extracts and phytochemicals for the synthesis of AuNPs offers a simple, rapid, eco-friendly, and cost-effective alternative. This review provides an in-depth analysis of the role of plant-mediated AuNPs in cancer treatment, focusing on their core mechanisms, drug delivery applications, and future potential. It emphasizes the advantages of green synthesis methods for cancer therapy, detailing the processes involved and highlighting various plants used for nanoparticle biosynthesis. The review also explores the anti-cancer effects of plant-mediated AuNPs, such as their ability to selectively target cancer cells and induce apoptosis, supported by both in vitro and in vivo studies. Additionally, the application of these nanoparticles in targeted drug delivery for cancer therapy is examined. The review addresses biocompatibility and toxicity concerns, providing insights into the safety of these nanoparticles. Future research directions and challenges are discussed to overcome current limitations and maximize their clinical applicability. In summary, plant-mediated AuNPs offer a sustainable and effective approach for cancer therapy and drug delivery, with their green synthesis and diverse anti-cancer properties highlighting their potential. Further research is essential to fully realize their clinical benefits.
A medical condition known as cancer is characterized by abnormal development of cells or tissues. It is challenging to combat cancer, especially when developing treatments for tumors that are rapidly proliferating (Shunmugam et al., 2021). The International Agency for Research Cancer (IARC) estimates that one in five people acquires cancer in their lifetime worldwide. The GLOBACAN is an online database that provides the global cancer statistics data. According to GLOBACAN 2020 data, there were approximately 19.3 million new cancer cases and 10 million cancer-related deaths worldwide. Recently, lung and prostate cancer have been the most common among men, while women most frequently face colorectal, lung, cervical, and thyroid cancers (Sung et al., 2021). The 2023 report from the American Cancer Society and the National Centre for Health Statistics recorded 1,958,310 new cancer cases and 609,820 cancer deaths in the United States (Siegel et al., 2023). Traditional cancer treatments such as surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation have been shown to pose significant risks to human health. Therefore, targeted drug delivery combined with controlled release technology, which is more efficient and harmful-free, is needed in place of current approaches (Rajeshkumar, 2016).
Nanotechnology is being employed in medicine to create novel antibacterial and anti-cancer medicines to provide more effective cancer therapies and prevention methods. Since the early 2000s, extensive research has focused on the use of nanoparticles as a promising approach for cancer treatment. Currently, there is significant interest in the synthesis of metal nanoparticles, particularly gold nanoparticles, due to their superior biological compatibility and low toxicity. Their photophysical and optical properties make gold nanoparticles valuable for chemotherapy and cancer diagnostics. Gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) offer several advantages over other nanoparticles in cancer therapy. Their biocompatibility, minimal toxicity, and size tunability make them ideal candidates for drug delivery systems. Au NPs have strong optical and physical properties, making them highly effective for diagnostic imaging and therapeutic applications such as photothermal therapy and radiosensitization. Furthermore, Au NPs can be functionalized with various targeting ligands, enhancing their selectivity and enabling precise delivery to cancer cells, minimizing damage to healthy tissues. Their ability to act as diagnostic and therapeutic agents (“theranostics”) further enhances their versatility in cancer treatment. Recent studies highlight the growing focus on gold nanoparticles for their potential to work synergistically with immunotherapy. This combination shows significant promise in improving early cancer diagnosis and enhancing overall treatment outcomes by boosting immune responses and offering better control over tumor progression (Goddard et al., 2020; Sultana et al., 2023). AuNPs demonstrate significant antimicrobial activity, effectively inhibiting various pathogens and biofilm formation, making them promising as alternative antimicrobials. Moreover, their wound healing potential is evident in enhanced cell migration and proliferation, aiding tissue repair and offering anti-inflammatory benefits. AuNPs also show great promise in biosensing and diagnostics due to their unique optical properties, enabling sensitive detection of biomolecules for early disease diagnosis (Mikhailova, 2021).
The synthesis of gold nanoparticles can be achieved through physical, chemical, and biological methods, including the use of plants and microorganisms. In comparison to other methods, plant-mediated nanoparticle production is preferred because it allows for the utilization of physiologically active plant components as essential raw materials (Rana et al., 2023). Furthermore, this method does not necessitate labor-intensive intracellular manufacturing procedures, numerous purifications, or the upkeep of microbial cells (Tomar and Garg, 2013; Hanan et al., 2018). Several studies have been reported on the use of plants and their part extracts for gold nanoparticle synthesis and their potential activities as anticancer agents. The gold nanoparticles synthesized using Tecoma capensis (L.) leaf extract have shown potent anticancer activity against the growth and proliferation of human breast cancer cell lines (Hosny et al., 2022). It has been studied that the spherical-shaped gold nanoparticles synthesized using Dracocephalum kotschyi leaf extract possessed great anticancer activity against HeLa and K562 cell lines (Dorosti and Jamshidi, 2016). The plants Marsdenia tenacissima, Halymenia dilate, Nerium oleander, Lonicera japonica, Pleuropterus multiflorous, and Dendropanax morbifera have also been found to synthesize gold nanoparticles with anticancer characteristics (Sun et al., 2019; Vinosha et al., 2019; Barai et al., 2018; Patil et al., 2019; Castro-Aceituno et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2016). This study intends to highlight the overall synthesis of plant-mediated gold nanoparticles, their anticancer properties in both in vitro and in vivo settings, and the mechanisms involved. Additionally, the study emphasizes the drug delivery potential, biocompatibility, and toxicity of synthesized gold nanoparticles, while also discussing their future prospects and associated obstacles.
The process of synthesizing gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) using plants and their extracts (Figure 1) has attracted significant interest owing to their distinctive properties and diverse applications, particularly in the field of medicine. This type of synthesis approach is facile, cost-effective, and eco-friendly, in that the particles can act as sensors, catalysts, etc. with regulated crystal growth and stability. The biochemical compounds found in the plant extract act as agents that reduce, stabilize, and cap the gold nanoparticles during their synthesis. These include proteins, carbohydrates, organic acids, enzymes, flavonoids, phenolics, alkaloids, vitamins, etc. These biomolecules are essential for converting chloroaurate ions into metallic gold and for stabilizing them at the nanoscale. Gold nanoparticles synthesized from plant extracts typically range in size from 1 to 100 nm and predominantly exhibit a spherical morphology. However, triangular, oval, hexagonal, polygonal, irregular, or rod-shaped particles were also found (Sargazi et al., 2022; Dash et al., 2022). The selection of plant extract, its concentration, the type and amount of precursor or salt, pH level of the medium, incubation temperature, and reaction duration are critical factors influencing the quantity, specific shape, and size of the synthesized nanoparticles. (Teimouri et al., 2018). For example, a previous study used Eucalyptus globulus Labill bark aqueous extract to examine the different factors responsible for the shape and size of synthesized gold nanoparticles. The results concluded that the pH of the medium and concentration of the extract are the primary key factors for the controlled size and shape of the synthesized nanoparticles. However, the temperature and reaction time showed moderate effects on their morphology. According to this work, several experimental conditions can affect the shape and size of greenly synthesized AuNPs (Pinto et al., 2017). In another study, gold nanoparticles were synthesized using Cucurbita pepo leaf extract at relatively low temperatures (70°C). The results indicated that the shape and size of the nanoparticles were related to the concentration of chlorophylls and carotenoids in the extracts. The Transmission electron microscopy results showed the development of anisotropic nanoparticles with lower gold concentration whereas a large production of monodisperse AuNPs with sizes between 10 and 15 nm is encouraged by higher concentrations (Gonnelli et al., 2018).
There are Various methods have been reported for the plant-mediated synthesis of gold nanoparticles such as the use of aqueous extracts, enzymatic reduction, microwave-assisted, ultrasonication, and solar irradiation (Table 1). Aqueous gold salt solutions, such as chloroauric acid (HAuCl4), are combined with plant extracts, which are commonly derived from leaves, stems, or roots. The reduction of gold ions is facilitated by phytochemicals present in plant extracts. For instance, the aqueous extract of Momordica cochinchinensis rhizome has been used as a reducing and stabilizing agent in the synthesis of gold nanoparticles at room temperature. When 1 mL of the extract was added to 20 mL of a 0.01 mM gold solution, it reduced the gold ions, resulting in the formation of gold nanoparticles. UV-visible spectroscopy results confirmed the color change to ruby red, indicating the excitation of surface plasmon resonance in the nanoparticles. The FTIR spectrum revealed the presence of phenolic acids and flavonoids, which are responsible for reducing and stabilizing the nanoparticles. These compounds facilitate the conversion of precursor gold ions into small metal ions (Lakshmanan et al., 2016). The aqueous peel extract of Garcinia mangostana and the bark extract of Mimusops elengi have also been reported as effective reducing and stabilizing agents for the synthesis of gold nanoparticles. When combined with an aqueous gold solution, these extracts facilitated the reduction of gold ions, forming gold nanoparticles. FTIR spectrum analysis confirmed the presence of benzophenones, anthocyanins, polyphenols, and flavonoids which served as both reducing and stabilizing agents. Furthermore, gold nanoparticles mediated by M. elengi bark extract have been utilized as strong catalysts for reducing 3-nitrophenol and 4-nitrophenol in water at room temperature (Xin Lee et al., 2016; Majumdar et al., 2016) Figure 2 is showing the physiochemical characteristics of plant mediated gold nanoparticles synthesized using leaf extract of Moringa oleifera. In the process, 4 mL of the extract was mixed with 20 mL of gold chloride solution, leading to a noticeable color change, signifying the formation of AuNPs. The nanoparticles, with sizes ranging from 14 to 30 nm, were characterized using techniques like TEM and DLS, confirming their spherical morphology and stable size distribution. The characterization data highlights these features. Additionally, UV-Vis spectroscopy displayed a surface plasmon resonance peak between 520–540 nm, confirming nanoparticle formation. The AuNPs also showed effective biological and photocatalytic activities, making them potential candidates for diverse applications (Boruah et al., 2021).Microwave irradiation is one of the rapid, facile, and laid-back techniques for the formation of plant-mediated gold nanoparticles. When compared to conventional heating methods, microwave assistance offers many advantages including quicker reaction times, faster reaction rates, better product yields, and lower energy consumption. In this method, the plant extracts are combined with a gold-containing salt solution and microwave irradiated which results in rapid synthesis of AuNPs (Punnoose et al., 2021). Recently, Mimosa diplotricha leaf extract has been employed for the microwave-assisted synthesis of AuNPs. In this process, 10 mL of the leaf extract was combined with 90 mL of a 1 mM auric trichloride solution and subjected to microwaving in a standard domestic oven. The results showed that with 1 min of microwave heating the light-colored blend changes to violet color. The presence of the characteristic peak at 548 nm indicated the complete reduction of gold ions (Au3+ to Au0). Also, the FTIR spectroscopy confirms the presence of phenolic groups in the leaf extract (Punnoose and Mathew, 2022). Similar to this, it has also been claimed that Jatropha curcas, Myristica fragrans, green tea, Caesalpinia sappan, Oroxylum indicum, and aloe leaf extract all contributed to the formation of gold nanoparticles. Moreover, the phytoconstituents present in the extracts functioned as capping, reducing, and stabilizing agents (Francis et al., 2018; Punnoose et al., 2021; Serdar and Kılınç, 2023; Thanayutsiri et al., 2023; Worakitjaroenphon et al., 2023; Parimala et al., 2022). Ultrasonication is one of the most efficient methods for the production of small-sized nanoparticles. In this method, the ultrasonicated waves promote the reduction of gold ions by the plant extracts. Recently, gold nanoparticles with ultrasonic assistance were made using Citrus sinensis peel extract. It was observed that the use of ultrasound reduced the distribution and size of the synthesized NPs while enhancing their yield and stability. Additionally, hesperidin was identified as the primary reducing agent for the NPs (Gao et al., 2022). The leaf extract of Nothapodytes foetida has been utilized for the ultrasonication-assisted synthesis of gold nanoparticles. This process resulted in the formation of spherical and crystalline nanoparticles with diameters ranging from 5 to 30 nm. The nanoparticles exhibited excellent stability, attributed to their negative zeta potential (Susanna et al., 2023). The flower extract of Clitoria ternatea has been documented for the synthesis of gold nanoparticles via ultrasonication, serving as a reducing agent in the process. By using ultrasound irradiation, small-size nanoparticles formed with a size range of 18–50 nm in a short time (Fatimah et al., 2020). Considering ultrasonication can control particle size and improve stability, it is the most effective approach for creating homogenous AuNPs in plant-mediated synthesis. Citrus sinensis and N. foetida extracts show that this technique efficiently reduces size distribution and produces very uniform nanoparticles in the 5–30 nm range.
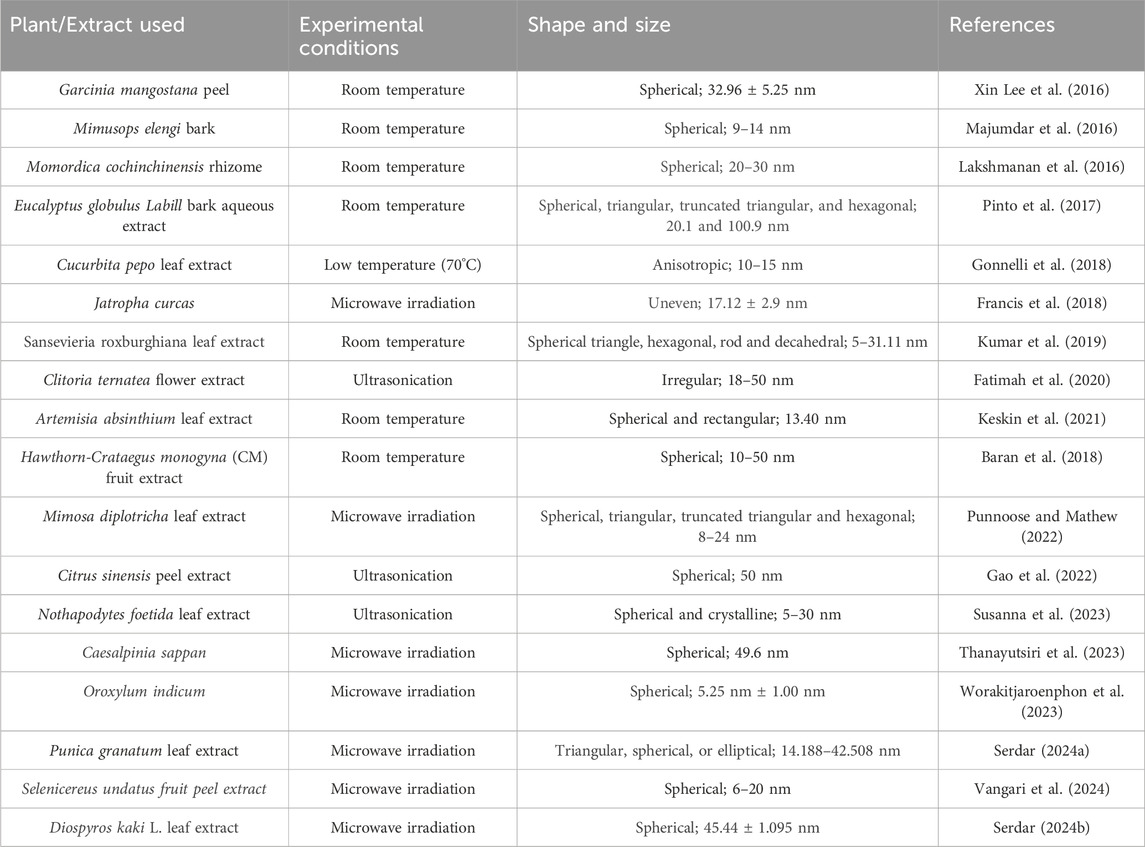
Table 1. Synthesis and characterization of plant-mediated gold nanoparticles using different methods.
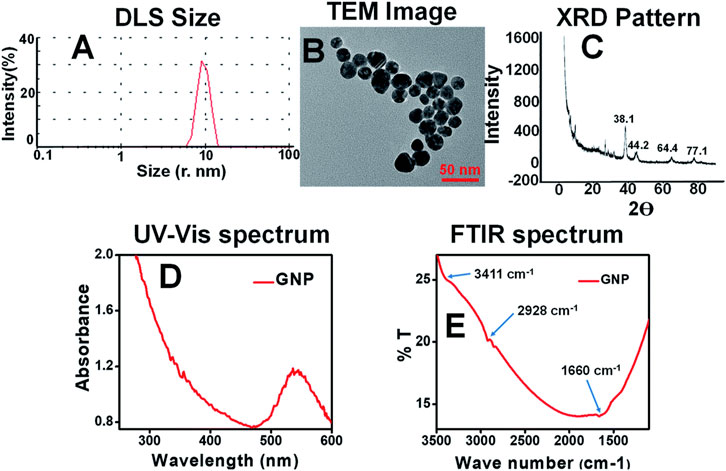
Figure 2. Characterization images of Plant mediated synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Moringa oleifera leaf extract (A) DLS; (B) TEM; (C) XRD; (D) UV-Visible; (E) FTIR (Boruah et al., 2021).
Several potential anticancer mechanisms of green-synthesized NPs have been identified. These mechanisms include selective targeting, induction of apoptosis, inhibition of angiogenesis, generation of reactive oxygen species, mitochondrial dysfunction, enhancement of drug delivery, and photothermal therapy (Figure 3) (Bharadwaj et al., 2021). Several publications suggest that gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) exhibit various interactions with cells, with numerous researchers documenting the internalization of AuNPs by cellular entities. The surface properties of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) play a crucial role in the process of cellular internalization. The cellular uptake and internalization of AuNPs can be accredited to the electrostatic attraction resulting from the opposing charges exhibited by AuNPs and the cell membrane. Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) possess positive charges, whereas the membranes of cancer and normal cells consist of lipids, particularly phosphate groups, which are negatively charged (Gong et al., 2015; Albanese et al., 2012). Moreover, certain research has indicated that the internalization of gold nanoparticles occurs via the process of endocytosis (Cui et al., 2012). Once inside the mitochondria, they follow various pathways that impact the electron transport chain, induce structural damage, activate NADPH enzymes, and depolarize mitochondrial membranes (Xia et al., 2006; Sun et al., 2018). In malignant cells, AuNPs increase intracellular ROS levels which leads to permanent oxidative harm, DNA degradation, and cellular demise through several routes such as apoptosis, autophagy, or necroptosis (Redza-Dutordoir and Averill-Bates, 2016). Gold nanoparticles (AuNP) have been found to induce mitochondrial malfunction and trigger apoptosis through a caspase-dependent pathway. The mitochondria are the primary cellular organelles that experience damage during apoptosis mediated by reactive oxygen species (ROS). As a result of oxidative stress and membrane permeabilization, mitochondria have been observed to release specific cell death-related chemicals into the cytosol and nucleus, including cytochrome-c, Apoptosis-Inducing Factor (AIF), and Endonuclease G (ENDO-G) (Zorov et al., 2014; Wang and Youle, 2009).
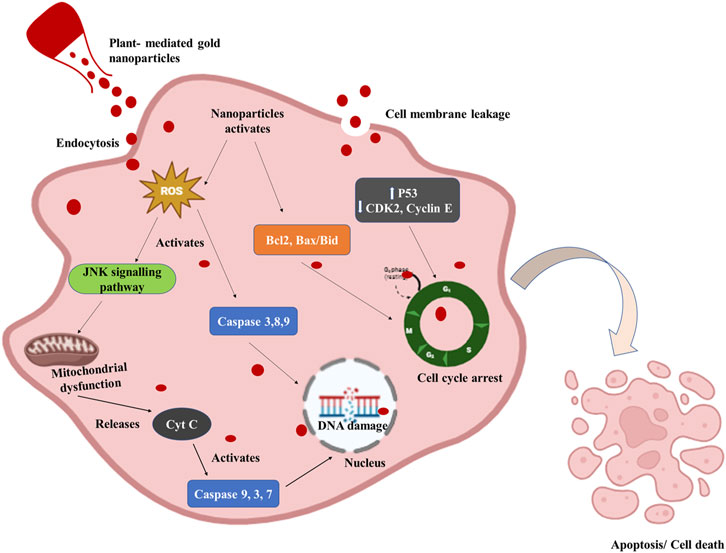
Figure 3. Diagrammatic representation of the anticancer mechanism of plant-mediated gold nanoparticles. Gold nanoparticles enter the cell through endocytosis or cellular internalization and activate the Reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction and DNA damage by activation of caspases cause apoptosis or cell death in cancer cells. P53 expression is elevated while CDK2, Cyclin E, and P53 expression are decreased by AuNPs. Additionally, it increases the expression of the bax/bcl2 apoptotic gene, which ultimately causes G0/G1 phase cell-cycle arrest.
One of the studies demonstrated the anticancer effect of M. tenacissima-mediated gold nanoparticles against lung cancer cells. The gold nanoparticles triggered apoptosis in cancer cells by down-regulating the expression of Bid and Bcl-2, while up-regulating the expression of caspase-8, caspase-9, caspase-3, and Bax (Sun et al., 2019). In a recent study, gold nanoparticles mediated by Tecoma capensis (L.) induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells, leading to cell shrinkage or cell death. The synthesized nanoparticles penetrate the cell membrane, interact with, and disrupt other biomolecules like proteins, nucleic acids, and other compounds (Hosny et al., 2022). AuNPs produced by plants can cause cancer cells to produce reactive oxygen species (ROS). High ROS concentrations can damage biological components, induce oxidative stress, and eventually result in cell death. The gold nanoparticles synthesized using the Syzygium aromaticum extract induced apoptosis in the SUDHL-4 cell lines through ROS production (Parida et al., 2014). Similarly, the Rhus chinensis mediated gold nanoparticles induced apoptosis to the Adenocarcinoma (MKN-28), Hepatocellular carcinoma (Hep3B), and Osteosarcoma (MG-63) cells through the DNA fragmentation or DNA damage (Patil et al., 2017). Furthermore, M. oleifera-mediated AuNPs induced caspase-mediated cell death in A549 cells, as indicated by elevated activities of caspase-9 and caspase-3/7, a substantial decrease in ATP levels, and a significant increase in the protein concentrations of p53 and Bax (Tiloke et al., 2016). The gold nanoparticles synthesized using Cynodon dactylon aqueous extract have shown probable anticancer activity against human breast cancer cells and are nontoxic to normal cells. The inhibitory effect was found to be dose-dependent, with green-synthesized AuNPs exhibiting an IC50 value of 31.34 μg/mL. Post-treatment, ROS levels increased, leading to programmed cell death in MCF-7 cancer cells. Results from rhodamine staining, AO/EtBr staining, and DAPI labeling indicated significant mitochondrial membrane damage and DNA fragmentation, suggesting apoptosis in the cancer cell lines (Vinayagam et al., 2021). Another study was conducted that showed the environment-friendly efficacy of Commiphora wightii-mediated AuNPs against human cancer cell lines. The results of in vitro cytotoxicity assays showed cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase, which subsequently triggered apoptosis (Uzma et al., 2020). Moreover, through surface modification, AuNPs can attach to other materials covalently or non-covalently. Molecules can adhere to AuNPs non-covalently by a variety of interactions, including particular binding affinities, electrostatic interactions, and hydrophobic interactions. That’s why gold nanoparticles are also used as transporters for anticancer drugs. They can deliver the chemotherapeutic drugs directly to the targeted tumour site which further reduces the risk of systematic toxicity of the drug. The Punica granutum fruit peel extract-mediated monodispersed AuNPs have been used as carriers for targeted drug delivery for MCF-7 cancer cell lines. The synthesized nanoparticles functionalized with folic acid showed in vitro cytotoxicity in the cancer cells via DNA fragmentation and induced G0/G1-phase cell cycle arrest. These findings imply that p21WAF1-induced G1-phase cell cycle arrest and growth suppression in MCF-7 must be mediated through the JNK/ERK signaling pathway (Ganeshkumar et al., 2013). Gold nanoparticles mediated by Vitex negundo were synthesized using leaf extract as a reducing agent and Arabic gum as a stabilizing agent. Folic acid was subsequently added to the nanoparticles to specifically target A549 lung cancer cells. It was found that the folic acid functionalized nanoparticles increased the cytotoxic effect by targeting the cells and also raised the epirubicin uptake by the cancer cells (Renuga Devi et al., 2015). Another study examined the potential of pectin-mediated AuNPs as chemotherapeutic medication carriers in drug delivery systems. Pectin, a natural polysaccharide, functions as both a reducing and stabilizing agent. In vitro assays demonstrated that doxorubicin (DOX) loaded onto pectin-derived AuNPs (pec-AuNPs) exhibited a significantly greater lethal effect on breast cancer cells compared to DOX alone. The study also suggested that AuNPs decorated with chitosan-folic acid could serve as biocompatible nanocarriers for delivering cancer-specific medications (Devendiran et al., 2016).
The process by which new blood vessels are produced is called angiogenesis. One method for depriving tumors of nutrition and oxygen is to inhibit angiogenesis. AuNPs may hinder the angiogenesis-related signaling pathways. An in vitro study investigated the impact of gold nanoparticles synthesized using Mangifera indica seed extract on human gastric cancer cells. The gold nanoparticles demonstrated significant anticancer properties by disrupting the cell membrane and inducing cell cycle arrest. Furthermore, an in vivo study done on chick embryos concluded that the antiangiogenic effect of synthesized gold nanoparticles by targeting the Ang-1 and Tie2 pathways (Vimalraj et al., 2018).
AuNPs with maximal absorption in the visible or near-infrared region absorb light and produce heat. This characteristic can be used in photothermal therapy, which uses light-induced heating of AuNPs to specifically target and kill cancer cells. Spherical solid gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) exhibiting a diameter above 50 nm, owing to their pronounced near-infrared (NIR) absorption capabilities, are frequently observed in photothermal therapy (Mishra et al., 2016). An aqueous method was used to produce NIR-absorbing anisotropic gold nanoparticles, utilizing cocoa extract as a reducing and stabilizing agent. These gold nanoparticles were then subjected to density gradient centrifugation to enhance their near-infrared (NIR) absorption within the 800–1,000 nm wavelength range. In vitro results demonstrated significant anticancer effects at concentrations up to 200 μg/mL against MDA-MB231, L929, A431, and NIH-3T3 cell lines. Also, Cell death was observed in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells when exposed to irradiation from a femtosecond laser operating at a wavelength of 800 nm and a low power density of 6 W/cm2 (Fazal et al., 2014). In one of the studies, apigenin-coated AuNPs with a diameter of 19.1 nm were synthesized and showed a significant photothermal effect on cancerous cells by inducing apoptosis. Based on the obtained findings, the application of in vitro photothermal therapy (PTT) for a duration of 3 min, using apigenin-coated gold nanoparticles at a concentration of 128 μg/mL, results in around 50% mortality rate for both mouse fibroblastic and colorectal cancer cells (Amini et al., 2021). Recently, rutin-mediated gold nanoparticles coupled with laser radiation have been used to check out their photothermal effect against breast cancer cell lines. Rutin, a highly abundant flavonoid glycoside found in R. graveolens L., was utilized as a reducing and capping agent in the study. The findings demonstrated that Au NPs produced using Rutin, in combination with laser radiation (150 J/cm2 for 300 s), exhibited a significant and effective photothermal therapy (PTT) anticancer effect on MCF-7 cells (Shabani et al., 2023). Conclusively, AuNPs with a size between 30 and 50 nm are excellent for cancer therapy. The increased permeability and retention (EPR) effect helps this size, which facilitates better drug transport, less systemic toxicity, and better tumor accumulation. This family of AuNPs further enhances photothermal therapy, providing increased therapeutic efficacy and tumor-targeting efficiency.
Several studies have documented the in vitro anticancer efficacy of plant-mediated AuNPs on various cancer cell lines, including lung, breast, prostate, colon, and ovarian cancer, and some latest examples have been listed in Table 2 and Figure 4 (Hoshyar et al., 2016; Anand et al., 2015; Abel et al., 2016; Vinay et al., 2021; Chen et al., 2021). These nanoparticles have demonstrated promising effects by inhibiting cell growth, causing cell cycle arrest, inducing apoptosis, and blocking various signaling pathways essential for tumor development. Also, this is a safe and targeted method for cancer therapy because of their special physicochemical characteristics, such as their high surface area-to-volume ratio, biocompatibility, and capacity to be functionalized with a variety of targeted molecules. Along with their small size, they have improved permeability and retention (EPR) in tumor tissues, which improves therapeutic efficacy, reduces systemic toxicity, and enables for targeted drug administration. Additionally, AuNPs can be utilized in photothermal therapy, which uses light absorption and conversion to heat to kill cancer cells. Furthermore, AuNPs provide a dual therapeutic and diagnostic (theranostic) platform by acting as diagnostic tools in biosensing and imaging. In a study by (Khan et al., 2016), the gold nanoparticles synthesized using the Dimocarpus longan fruit juice showed in vitro cytotoxicity against the MCF-7 breast cancer cell line. When exposed to synthesized gold nanoparticles, breast cancer cells showed morphological alterations, suppressed cell proliferation, and finally clumped together and died. In another study, gold nanoparticles synthesized using a combination of Carica papaya and Catharanthus roseus leaf extracts demonstrated cytotoxic effects against the Hepatoblastoma cell line (HepG2) and the human breast cancer cell line (MCF-7). The gold nanoparticles exhibited a high percentage of cell death, achieving 98.1% and 97.5% at a concentration of 250 μg/mL, respectively (Muthukumar et al., 2016). Moreover, the synthesized gold nanoparticles using Elettaria cardamomum seed extract and Actinidia Deliciosa have been also reported for their significant cytotoxic effect against HeLa and HCT116 colon cancer cell lines. The biogenic nanoparticles cause cell shrinkage and granulation in the cytoplasm and cause apoptosis in the tumor cells (Rajan et al., 2017; Naraginti and Li, 2017).
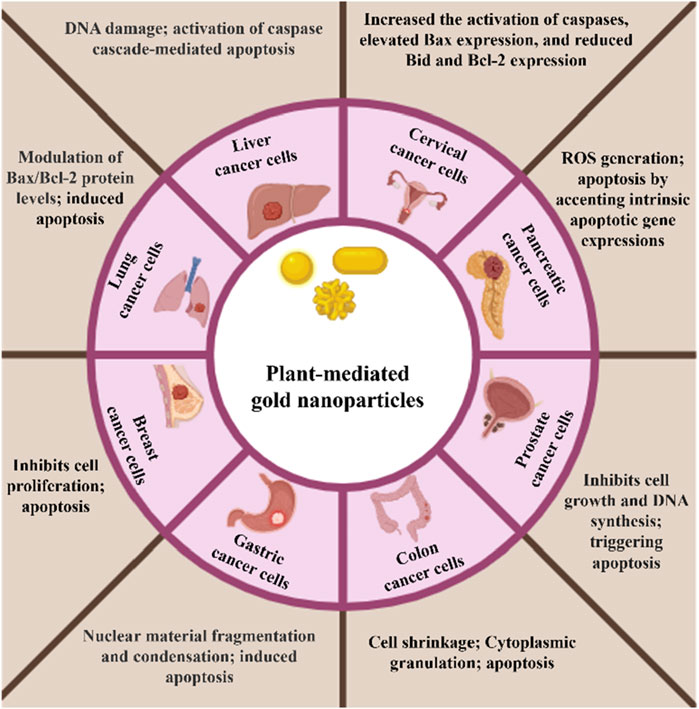
Figure 4. Schematic representation of in vitro anticancer effect of plant-mediated gold nanoparticles on different cell lines.
Conducting in vivo investigations on plant-mediated gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) is necessary for knowing their potential applications and assuring their safety in various fields such as medicine, agriculture, and remediation of the environment. These studies frequently evaluate factors including animal overall survival rates, metastasis prevention, and tumor growth inhibition. However, some publications have documented in vivo experiments using both male and female mouse models which have been listed in table 3. Recently, Female C57BL/6 mice were administered 2 mg/kg of spherical, 30 nm-sized Dendrobium officinale gold nanoparticles for in vivo testing. The results showed potential antitumor activity without any toxicity and used as a new nanomedicine for liver cancer (Zhao W. et al., 2021). Another study investigated the effect of administering gold nanoparticles produced by Pseudobulbus Cremastrae seu Pleiones on female C57BL/6 mice at a dosage of 20 mg/kg. The AuNPs had a spherical shape, characterized by an average diameter of 30.4 ± 3.36 nm. It was observed that the synthesized nanoparticles exhibited not only little toxicity but also enhanced the immune-mediated antitumor response. This finding suggests that these nanoparticles have the potential to act as a promising and effective therapeutic agent for liver cancer (Zhu et al., 2022). Moreover, the Cirsium japonicum-mediated gold nanoparticles exhibited both spherical and polygonal forms, with sizes ranging from 6 to 38 nm. The activity percentages of these nanoparticles were evaluated in male nude mice at different doses, specifically 2.5, 5, and 10 mg/kg. The resulting activity percentages were found to be 31.59%, 47.45%, and 62.49%, respectively (Mi et al., 2022). In a study by (Mukherjee et al., 2016), the researchers investigated the green synthesis, characterization, and toxicity of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) and their potential for delivering the anticancer drug doxorubicin in a mouse model. The study utilized a green synthesis approach to produce monodispersed AuNPs using an undisclosed plant source. The synthesized AuNPs were monodispersed, indicating a uniform size distribution. The in vivo study was conducted using a mouse model to evaluate the toxicity and biodistribution of the synthesized AuNPs. The study also explored the potential of the synthesized AuNPs as a delivery system for the anticancer drug doxorubicin, where the AuNPs were loaded with doxorubicin and administered to the mouse model. The toxicity of the synthesized AuNPs was assessed in the mouse model, and the biodistribution of the AuNPs was investigated to determine their distribution in various organs and tissues. In a study by (Zhao P. et al., 2021), the researchers investigated the green synthesis of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) using Dendrobium officinale and its anticancer effect on liver cancer. The study utilized a green synthesis approach to produce spherical AuNPs with a size of 30 nm using D. officinale, a medicinal plant known for its therapeutic properties. The in vivo study was conducted using female C57BL/6 mice, and the AuNPs were administered at a dose of 2 mg/kg. The results showed that the synthesized AuNPs exhibited potential antitumor activity without any toxicity, suggesting their potential as a new nanomedicine for liver cancer treatment. The in vivo studies on plant-mediated gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) demonstrate their potential as promising therapeutic agents for various types of cancer. The studies utilized green synthesis approaches to produce AuNPs using different plant sources, resulting in varying shapes and sizes. In vivo experiments conducted in mouse models evaluated the antitumor activity, toxicity, and immune response of the synthesized AuNPs at different doses. The results suggest that plant-mediated AuNPs exhibit dose-dependent antitumor activity, with minimal toxicity and enhanced immune response, making them promising candidates for cancer therapy. However, further research is needed to fully understand their safety, efficacy, and underlying mechanisms of action in various cancer types and to optimize their synthesis and characterization for clinical applications.
Biomolecules such as receptors, proteins, carbohydrates, and polyphenolic compounds can be conjugated to AuNPs via surface modification techniques. This modification grants AuNPs specific functionalities such as nano-bioconjugates, rendering them suitable for applications in biomedicine, particularly targeted drug delivery (Lee et al., 2008). As a result, they can specifically target tumor cells through receptor-mediated endocytosis, a process known as active targeting (Fadeel and Garcia-Bennett, 2010; Sezgin et al., 2008). Furthermore, nanoparticles synthesized biosynthetically are naturally coated with biomolecules extracted from plants, which can act as carriers for delivering biomolecules. Due to their large surface area, AuNPs have significant conjugation capabilities and can bind with various chemical compounds, including drugs and other biomolecules. Therefore, AuNPs synthesized through biological methods can be modified by biological peptides from plant extracts, serving as natural connectors for delivering drugs to specific cells or tissues (Heegaard et al., 2007). Moreover, the biocompatibility of AuNPs synthesized through green methods extends to both normal and abnormal cells, rendering them indispensable as carriers for drug delivery. Utilizing these green-synthesized AuNPs, a drug delivery system (DDS) based on gold has been developed, incorporating the FDA-approved anticancer drug doxorubicin. This system has demonstrated superior therapeutic efficacy compared to the drug administered alone. The heightened effectiveness of the DDS may stem from increased specificity, as well as enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effects (Patra and Baek, 2015). Here are some potential drug delivery applications of PM-AuNPs.
Targeting ligands, such as aptamers, peptides, or antibodies, can be functionalized on AuNPs to deliver medications to sick cells or tissues. Plant-derived biomolecules can be added to plant-mediated AuNPs to provide targeted drug delivery, boost therapeutic efficacy, and reduce side effects. In one study, mono-dispersed PAuNPs were synthesized using Punica granatum fruit peel extract without surfactants or external energy which were formed within 60 s. Casein was employed to conjugate PAuNPs for functionalization with folic acid, targeting cancer cells. These functionalized PAuNPs have the potential to enhance therapeutic efficacy while minimizing side effects in targeted cancer drug delivery. Toxicity analysis in zebrafish embryos indicated minimal toxicity for PAuNPs, 5-Fluorouracil (5-Fu), and 5Fu@PAuNPs. In vitro cytotoxicity testing against MCF-7 cells revealed significantly lower IC50 values for 5Fu@PAuNPs-Fa compared to free 5-Fu. Results from in vitro drug release, cytotoxicity, and therapeutic efficacy studies suggest that 5-Fu@PAuNPs-Fa could serve as a promising carrier for targeting breast cancer (Ganeshkumar et al., 2013). Moreover, Gold nanoparticles were synthesized using Peltophorum pterocarpum leaf extract, demonstrating stability and biocompatibility. These nanoparticles loaded with doxorubicin were developed as a drug delivery system, demonstrating significant inhibition of cancer cell proliferation in laboratory studies and suppression of tumor growth in animal models. Cellular uptake and release of the drug were faster with the nanoconjugated form. In vivo toxicity studies in mice showed no adverse effects, suggesting the potential for this drug-delivery system as a cost-effective cancer treatment (Mukherjee et al., 2016). One more study utilized a green chemistry method to rapidly synthesize gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) within 30 s using Limonia acidissima L. fruit extract. These AuNPs were subsequently coupled with epirubicin (EPI) and activated folic acid (FA) for targeted drug delivery. Stability tests conducted in vitro demonstrated the nanoparticles’ stability under physiological conditions. Evaluation of cytotoxicity against MCF-7 cells revealed that EPI-FA-AuNPs achieved 50% growth inhibition (IC50) at a lower concentration than free EPI. Flow cytometry analysis showed a notable decrease in G2/M cells following treatment with EPI-FA-AuNPs, corroborated by molecular apoptosis studies using Western blotting. Overall, the results indicate that EPI-FA-AuNPs exhibit enhanced regression of tumor cells compared to free EPI (Kumar et al., 2016). Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) were produced utilizing V. negundo leaves for reduction and Arabic gum for stabilization. Subsequently, folic acid was incorporated onto the nanoparticles to target A549 lung cancer cells. The utilization of natural gum demonstrated superior outcomes in terms of drug release, cytotoxicity, and therapeutic effectiveness (Renuga Devi et al., 2015).
Many medications are subject to poor solubility, which reduces their bioavailability and therapeutic effectiveness. Through encapsulation or the formation of drug-AuNP complexes, plant-mediated AuNPs can act as carriers to enhance the solubility of hydrophobic medicines, hence increasing their administration and uptake. The study investigates enhancing the dispersion of metal-free phthalocyanine (H2Pc) in aqueous solutions for photodynamic therapy (PDT) using biosynthetic gold nanoparticles (Au NPs). Gold nanoparticles are synthesized using Potatoes (Solanum tuberosum) extract in a single step. H2Pc is conjugated to the surface of Au NPs through secondary amine groups. The disappearance of the secondary amine absorption band in Pc-Au nanoconjugates compared to H2Pc confirms the dispersion of H2Pc on Au NP surfaces. In vitro studies on buffalo epithelial cells reveal that both biosynthetic Au NPs and Pc-Au nanoconjugates are biocompatible, unlike chemically synthesized Au NPs. This research introduces the use of water-suspended H2Pc for PDT and other phototherapeutic applications for the first time (Alexeree et al., 2017).
By utilising a variety of stimuli-responsive processes, such as pH, temperature, or light, AuNPs can be designed to release pharmaceuticals in a controlled way. Natural molecules from plant extracts can be included via plant-mediated synthesis techniques, and these compounds can act as stimuli-responsive triggers for medication release. By allowing for spatiotemporal control over medication release, this method lowers systemic toxicity and enhances therapeutic results. Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) with sizes ranging from 30 to 40 nm were synthesized using A. hirsutus leaf extract as a reducing agent under microwave irradiation lasting from 60 to 360 s. These capped AuNPs were effectively conjugated with activated folic acid (FA) and chlorambucil (CHL), an anticancer drug. Confirmation of AuNPs-FA-CHL formation was achieved through various characterization techniques including X-ray diffraction, UV-visible spectroscopy, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, and transmission electron microscopy imaging. The bioconjugated AuNPs exhibited potent anticancer activity against human cancer cell lines (HeLa, RKO, and A549), while sparing normal epithelial cells (Vero). Remarkably, AuNPs-FA-CHL demonstrated enhanced toxicity towards cancer cells compared to AuNPs or CHL alone. Furthermore, drug release was optimized at a tumor-specific pH of 5.3. (Vijayashree et al., 2017).
AuNPs are good candidates for imaging and therapeutic applications due to their unique optical characteristics. AuNPs with adjustable optical characteristics can be created by plant-mediated synthesis techniques, enabling simultaneous drug delivery and multimodal imaging (such as surface-enhanced Raman scattering and photoacoustic imaging). Personalized medicine is made possible by this integrated approach, which allows for real-time monitoring of therapy response and drug administration. N a study, barley leaf extract was used to biologically synthesize gold nanoparticles (BL-Au NPs) acting as both a reducing agent and stabilizer, employing a rapid, straightforward, environmentally friendly, and cost-effective method. Characterization techniques including TEM, UV-vis spectroscopy, and FTIR confirmed the successful synthesis of BL-Au NPs. The biological components from the barley leaf extract coating the Au NPs provided the desired colloidal stability and biocompatibility, supported by stability and toxicity assays. Importantly, BL-Au NPs exhibited superior X-ray attenuation and enhanced CT imaging properties compared to traditional contrast agents in both in vitro and in vivo studies. In conclusion, BL-Au NPs show potential as a valuable CT imaging contrast agent for biomedical applications (Xue et al., 2021). Research has shown that extracts from Hubertia ambavilla and Hypericum lanceolatum have been utilized to produce shell-like hybrid flavonoid-gold nanoparticles (NPs) complexes, with sizes ranging from approximately 15 nm–40 nm in flower-shaped diameter. These complexes serve a dual role in nano theranostics, combining plasmonic phototherapy for cancer treatment with X-ray-based computed tomography for imaging purposes (Morel et al., 2017). In a prior study, gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) synthesized using cinnamon have demonstrated efficacy as a diagnostic agent for both in vitro and in vivo imaging. These AuNPs are biocompatible and pure, rendering them suitable for in vivo applications. In vitro studies showed uptake of cinnamon-AuNPs in MCF-7 cells, and PC-3 with detection facilitated by photoacoustic signals. Furthermore, biodistribution studies in normal mice indicated that these AuNPs accumulated in the lungs, underscoring their potential as targeted contrast agents for imaging purposes (Chanda et al., 2011). Furthermore, fluorescently labeled gold nanoparticles (AuNPs-OX) were synthesized using Olax scandens leaf extract. These nanoparticles were applied to breast (MCF-7), lung (A549), and colon (COLO 205) cancer cells, facilitating the identification of cancerous cells. AuNPs-OX displayed strong red fluorescence within cancer cells, distinguishing them from cells treated with the aqueous leaf extract alone (Mukherjee et al., 2013).
To provide synergistic therapeutic effects, AuNPs can be loaded with a variety of therapeutic agents, including nucleic acids, chemotherapeutic medications, and photothermal agents. The co-delivery of several medications or therapeutic agents is made possible by plant-mediated synthesis techniques, which provide a flexible platform for combination therapy approaches that focus on various disease-progression pathways. This strategy can defeat drug resistance and enhance the effectiveness of treatment for many illnesses, such as infectious and cancerous disorders. In one study, Cyclopia intermedia (HB) and mangiferin (MGF), a xanthonoid known for its various biological activities including anti-tumor properties, were utilized in the synthesis of HB-AuNPs and MGF-AuNPs, respectively. The study also highlights a potential synergistic effect between doxorubicin and HB-AuNPs derived from C. intermedia, as well as between DOX and MGF-AuNPs derived from MGF. The cytotoxicity of HB-AuNPs and MGF-AuNPs was assessed on human colon (Caco-2), prostate (PC-3), and glioblastoma (U87) cancer cells, as well as normal breast epithelial (MCF-12A) cells using the MTT assay. The results indicate that both HB-AuNPs and MGF-AuNPs demonstrate relatively low cytotoxicity in these cells. However, when combined with doxorubicin, the cytotoxicity of doxorubicin was significantly enhanced (Aboyewa et al., 2021). Recently, AuNPs were synthesized using two aqueous extracts obtained from Ziziphus spina-christi leaves and Cordia myxa L. leaves. The efficacy of these gold nanoparticles as an anti-breast cancer agent was assessed against the MCF-7 cell line, in conjunction with near-infrared radiation (NIR) at 808 nm. It was observed that radiation enhances the therapeutic properties of gold nanoparticles by swiftly converting absorbed light into heat through non-radiative processes. The combined application of AuNP extracts with NIR irradiation demonstrates significant anti-cancer activity against breast cancer cells, exhibiting dose and time-dependent effects. Additionally, this combined treatment results in a notable increase in apoptotic induction within these cells, attributed to the elevated temperature achieved through photothermal therapy (PTT). Hence, the utilization of combination therapies holds promise as a viable approach for the treatment of cancers and other ailments (Abed et al., 2023).
In another investigation, an aqueous extract from Nyctanthes arbortristis Linn (NAT) was employed alongside doxorubicin-conjugated gold nanoparticles to evaluate their effectiveness in inducing cell death in breast cancer cells resistant to Paclitaxel. The combination of NAT and doxorubicin loaded onto AuNPs demonstrated improved stability and stimulated ferritinophagy in PacR/MCF-7 stem cells. These results suggest that AuNP-NAT, in conjunction with a low dose of AuNP-Doxorubicin nanoconjugate, could represent a potent anti-neoplastic treatment targeting the necroptosis-autophagy pathway. This approach has the potential to mitigate the adverse side effects associated with conventional chemotherapy drugs (Chittineedi et al., 2023).
Through comprehensive assessments encompassing biocompatibility, physicochemical properties, dosage, exposure routes, and environmental fate, researchers strive to elucidate the intricate nuances surrounding the safety profile of these nanomaterials, particularly in the context of medical applications.
In conducting compatibility studies, researchers delve into the intricate interplay between plant-mediated AuNPs and biological systems. Employing a diverse array of in vitro and in vivo models, investigations aim to elucidate the impacts of AuNPs on cellular function, organ systems, and overall health. These studies not only shed light on the biocompatibility of AuNPs but also serve to identify potential mechanisms underlying any observed effects, thus facilitating informed decision-making regarding their biomedical utility. Furthermore, the physicochemical properties of AuNPs serve as critical determinants of their biocompatibility and toxicity profiles. Through meticulous characterization utilizing advanced techniques such as transmission electron microscopy (TEM), dynamic light scattering (DLS), and zeta potential analysis, researchers unravel the intricate morphological and surface characteristics of AuNPs. By scrutinizing parameters such as size, shape, surface charge, and coating composition, researchers gain invaluable insights into the factors governing the interactions between AuNPs and biological entities, thereby informing strategies for enhancing their compatibility and mitigating potential adverse effects. Dosage and exposure routes represent additional dimensions that warrant meticulous scrutiny in assessing the safety profile of plant-mediated AuNPs for medical applications. Studies systematically explore the effects of varying concentrations and exposure durations across diverse biological systems, encompassing routes such as oral, inhalation, and dermal exposure. Through meticulous experimentation, researchers aim to delineate the dose-response relationships and ascertain threshold levels beyond which adverse effects may manifest, thus facilitating the establishment of guidelines for safe usage in medical settings. Moreover, the biodegradation and environmental fate of plant-mediated AuNPs represent critical facets that necessitate thorough investigation to comprehensively assess their safety profile. By scrutinizing factors such as persistence, transformation, and potential accumulation in ecosystems, researchers gain insights into the long-term environmental implications of AuNP utilization. Furthermore, elucidating the interactions of AuNPs with environmental matrices and biota enables a holistic understanding of their ecological footprint, thereby informing strategies for minimizing environmental impact.
In essence, the amalgamation of compatibility studies, physicochemical characterization, dosage assessment, and environmental fate analysis culminates in a comprehensive evaluation of the safety profile of plant-mediated AuNPs for medical use. Green-synthesized gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) have emerged as a fascinating field of study within biomedical research, offering a myriad of potential applications owing to their eco-friendly production methods and unique properties. These nanoparticles, synthesized using plant extracts, have attracted considerable attention for their biocompatibility and therapeutic potential across diverse areas such as drug delivery, imaging, cancer therapy, and antibacterial treatments. Unlike their chemically synthesized counterparts, green-synthesized AuNPs exhibit reduced cytotoxicity and improved compatibility with biological systems, positioning them as promising candidates for safer and more effective biomedical interventions. A seminal study by (Rónavári et al., 2021) illuminated the superior biocompatibility of plant-mediated AuNPs compared to chemically synthesized counterparts. Their investigation revealed that AuNPs synthesized via green methods displayed reduced cytotoxic effects on mammalian cell lines while demonstrating efficacy in inhibiting the growth of cancer cells, all while exerting minimal toxicity to normal cells. This pivotal research underscored the therapeutic promise of green-synthesized AuNPs, positioning them as viable options for various biomedical applications.
The eco-friendly synthesis of AuNPs utilizing plant extracts offers numerous advantages (Patil and Chandrasekaran, 2020). elucidated the stability and reduced toxicity of biogenic AuNPs, attributing these qualities to the natural capping agents present in plant extracts. These agents serve to prevent nanoparticle aggregation and enhance cellular uptake without inducing harm, thereby enhancing the overall biocompatibility of the nanoparticles. Additionally (Roy et al., 2022), expounded upon the enhanced biocompatibility and stability of biogenic AuNPs, advocating for their utility across a broad spectrum of biomedical applications, including drug delivery and imaging. Critical to the advancement of green-synthesized AuNPs for clinical use is the comprehensive assessment of their safety profile emphasizes the significance of standardized protocols in evaluating the biocompatibility and cytotoxicity of AuNPs. Generally, green-synthesized nanoparticles exhibit lower cytotoxicity and higher biocompatibility compared to their chemically synthesized counterparts, rendering them safer for medical applications (Bailly et al., 2019). conducted in-depth in vivo evaluations elucidating the safety, biodistribution, and pharmacokinetics of AuNPs, revealing minimal adverse effects and effective clearance mechanisms. The functionalization of AuNPs further augments their stability and biocompatibility. Moreover, studies by (Akkam et al., 2023) delved into the fate and toxicity of green-synthesized AuNPs in animal models, revealing minimal toxicity and effective clearance mechanisms, particularly by the liver and spleen. In the realm of cancer therapy, AuNPs offer unparalleled advantages. Furthermore (Akouibaa et al., 2024), delved into the fate and toxicity of green-synthesized AuNPs in albino mice, offering valuable insights into their biocompatibility and distribution within living organisms. This research provides crucial information for understanding the systemic effects of AuNPs and assessing their safety for clinical use (Table 4). (Pannerselvam et al., 2020) prepared gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) from ten Cassia species, with C. roxburghii producing the most efficient and stable AuNPs. Optimal conditions were pH 7.0, 37°C, 1.0 mL of C. roxburghii leaf extract, and 1.0 mM HAuCl4, resulting in ∼50 nm particles stable for 12 months. In-vivo safety was tested by intravenous injection in male Wistar albino rats. No significant changes were observed in body weight, hematological and biochemical parameters, or histopathology of vital organs. The highest accumulation was in the spleen, least in the brain. The AuNPs were biocompatible with no adverse effects noted, but long-term bioaccumulation needs further study (Pannerselvam et al., 2020). One of the study reported the green synthesis of stable, well-characterized gold nanoparticles (CAuNP) using Calotropis gigantea floral extract and investigated their in vivo biocompatibility compared to commercial AuNPs in a zebrafish embryo model. The LC50 of CAuNPs was 69 ± 12 μg/mL, compared to 52 ± 6 μg/mL for commercial AuNPs. Gold nanoparticles caused concentration-dependent morphological abnormalities and acute cellular and molecular effects. Both experimental and computational analyses showed nanotoxicity due to oxidative stress, leading to apoptosis through interactions with Sod1, He1a, and tp53 mRNA and proteins. This study highlighted the nanotoxicity of gold nanoparticles and suggested the potential of green synthesis methods for future production (Verma et al., 2018). In one of the studies, gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) were biosynthesized using leaf tissue from Isodon excisus (Maxim.) Kudo (IE). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images revealed that the AuNPs had sizes ranging from 10 to 100 nm and exhibited polygonal, triangular, and hexagonal shapes. Additionally, the cytotoxicity of IE-AuNPs on human keratinocytes (HaCaT cells) was evaluated, showing that the IE-AuNPs, at a concentration of 50 μg/mL, did not exhibit any cytotoxic effects on HaCaT cells (Dhandapani et al., 2023).
The field of plant-mediated gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) faces several multifaceted challenges and limitations across synthesis, characterization, and application stages. Inconsistencies in synthesis arise due to the variability in biochemical composition of plant extracts, which can change based on factors such as plant species, part used, age, and growing conditions. This leads to variations in size, shape, and yield of the nanoparticles, posing a significant hurdle for large-scale production and ensuring reproducibility. The complexity of plant extracts, containing a mixture of bioactive compounds like proteins and polyphenols, complicates the understanding and control of the synthesis process, making it difficult to optimize conditions for desired nanoparticle properties.
Stability and shelf-life of plant-mediated AuNPs present another challenge, as these nanoparticles are prone to aggregation and changes in physicochemical properties over time, affecting their efficacy in applications. Ensuring long-term stability without compromising biocompatibility is crucial. Additionally, scaling up production from laboratory to industrial scale while maintaining quality and consistency requires the development of new protocols and technologies capable of handling the increased volume and complexity. Concerns about biocompatibility and potential toxicity of AuNPs remain significant. Although plant-mediated synthesis is generally considered more environmentally friendly and less toxic than chemical methods, thorough understanding of interactions with biological systems is necessary. Comprehensive toxicity studies are essential to ensure safe use, particularly in biomedical applications like cancer treatment. Furthermore, evaluating the environmental impact of AuNPs, including their fate and behavior in ecosystems, is critical to prevent bioaccumulation and unintended harm to non-target organisms.
Despite these challenges, plant-mediated AuNPs hold substantial potential. Their unique properties, including biocompatibility, ease of functionalization, and enhanced permeability and retention in tumor tissues, make them suitable for these uses. In cancer theranostics, AuNPs can act as both therapeutic and diagnostic agents. They can be engineered to target tumors specifically, reducing side effects and improving treatment efficacy. For diagnostics, AuNPs enhance imaging techniques such as MRI, CT scans, and photoacoustic imaging, enabling high-resolution images and early tumor detection. Moreover, the optical characteristics of AuNPs, including surface plasmon resonance, render them suitable for photothermal therapy (PTT). During PTT, AuNPs accumulate at tumor sites and convert near-infrared light into heat, effectively destroying cancer cells. This approach provides a targeted and non-invasive treatment option with minimal impact on healthy tissues.
Future research must address several key areas to fully realize the clinical potential of plant-mediated AuNPs. Standardization and optimization of the synthesis process are critical to achieving consistent size, shape, and functional properties. Researchers should focus on standardizing the phytosynthesis process by optimizing parameters such as plant species, extraction methods, and reaction conditions to ensure reproducibility and scalability. Comprehensive toxicity studies are essential to understand the long-term effects on human health, including the biodistribution, metabolism, and excretion of these nanoparticles. Further research is also needed to elucidate the exact mechanisms by which plant extracts facilitate AuNP formation, which can lead to more controlled and efficient synthesis methods.
Assessing the environmental impact of increasing AuNP production and use is also crucial. This includes studying their biodegradability and ecological effects to develop strategies for minimizing environmental footprints. Interdisciplinary collaboration among chemists, biologists, medical researchers, and environmental scientists will be vital in overcoming these challenges and accelerating the translation of laboratory findings into clinical and industrial applications. By addressing these areas, researchers can pave the way for the safe and effective clinical use of plant-mediated AuNPs, harnessing their full potential for various biomedical applications.
The green synthesis of AuNPs using plant extracts has emerged as a transformative approach in cancer research, offering numerous significant findings and implications. This eco-friendly and sustainable method leverages the natural reducing and stabilizing agents present in plants, resulting in the production of biocompatible nanoparticles that exhibit potent anticancer properties. These plant-mediated AuNPs have demonstrated remarkable efficacy in inhibiting cancer cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis across various cancer cell lines, showcasing their potential as effective anticancer agents. The unique optical and electronic properties of these AuNPs, derived from their nanoscale dimensions and surface characteristics, enhance their utility in both therapeutic and diagnostic applications. For instance, in cancer diagnostics, these nanoparticles improve the sensitivity and specificity of imaging techniques such as MRI, CT scans, and photoacoustic imaging. This capability allows for more accurate tumor detection and monitoring, facilitating early diagnosis and precise treatment planning.
In therapeutic applications, plant-mediated AuNPs have shown great promise in enhancing the delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs. By conjugating these nanoparticles with anticancer drugs, targeted delivery to tumor cells is achieved, increasing the drugs’ therapeutic efficacy while minimizing systemic side effects. Additionally, these nanoparticles play a critical role in advanced treatment modalities such as photothermal therapy (PTT) and photodynamic therapy (PDT). In PTT, the AuNPs absorb near-infrared light and convert it into heat, effectively killing cancer cells localized in the tumor. When combined with PDT, which involves light-activated drugs producing reactive oxygen species to destroy cancer cells, the overall therapeutic outcome is significantly improved, offering a synergistic effect with minimal damage to surrounding healthy tissues. Moreover, the integration of plant-mediated AuNPs in immunotherapy is an exciting avenue for future research. These nanoparticles can be engineered to deliver immunomodulatory agents directly to the tumor microenvironment, enhancing the body’s immune response against cancer cells and potentially improving the effectiveness of existing immunotherapies. The dual functionality of these AuNPs in combating both cancer and other diseases further underscores their broad-spectrum applicability. For example, studies have shown that these nanoparticles not only exhibit anticancer activity but also possess antimicrobial properties, making them versatile tools in the fight against various health challenges.
Henceforth, the green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using plant extracts represents a significant advancement in cancer research. This approach offers a sustainable, biocompatible, and multifunctional platform for developing innovative cancer therapies. The continued exploration and optimization of these biogenic synthesis methods hold great promise for enhancing the efficacy and safety of cancer treatments, paving the way for their integration into clinical practice. As research progresses, the potential for these nanoparticles to revolutionize cancer therapy and diagnostics becomes increasingly apparent, highlighting the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration in realizing their full potential.
Nisha: Investigation, Writing–original draft. RK: Investigation, Writing–original draft. AnS: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing–original draft. AK: Conceptualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. AmS: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. GK: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
We would like to express our genuine appreciation to Lovely Professional University, GNA University and National Medical College and Teaching Hospital for creating an academic atmosphere and offering resources that greatly supported the successful culmination of this in-depth review paper.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abed, A. S., Khalaf, Y. H., and Mohammed, A. M. (2023). Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles as an effective opportunity for cancer treatment. Results Chem. 5, 100848. doi:10.1016/J.RECHEM.2023.100848
Abel, E. E., John Poonga, P. R., and Panicker, S. G. (2016). Characterization and in vitro studies on anticancer, antioxidant activity against colon cancer cell line of gold nanoparticles capped with Cassia tora SM leaf extract. Appl. Nanosci. Switz. 6, 121–129. doi:10.1007/s13204-015-0422-x
Aboyewa, J. A., Sibuyi, N. R. S., Meyer, M., and Oguntibeju, O. O. (2021). Gold nanoparticles synthesized using extracts of cyclopia intermedia, commonly known as honeybush, amplify the cytotoxic effects of doxorubicin. Nanomaterials 11, 132. doi:10.3390/NANO11010132
Adebayo, V. A., Adewale, O. B., Anadozie, S. O., Osukoya, O. A., Obafemi, T. O., Adewumi, D. F., et al. (2023). GC-MS analysis of aqueous extract of Nymphaea lotus and ameliorative potential of its biosynthesized gold nanoparticles against cadmium-induced kidney damage in rats. Heliyon 9, e17124. doi:10.1016/J.HELIYON.2023.E17124
Adewale, O. B., Anadozie, S. O., Potts-Johnson, S. S., Onwuelu, J. O., Obafemi, T. O., Osukoya, O. A., et al. (2020). Investigation of bioactive compounds in Crassocephalum rubens leaf and in vitro anticancer activity of its biosynthesized gold nanoparticles. Biotechnol. Rep. 28, e00560. doi:10.1016/J.BTRE.2020.E00560
Akkam, N., Aljabali, A. A. A., Akkam, Y., Abo Alrob, O., Al-Trad, B., Alzoubi, H., et al. (2023). Investigating the fate and toxicity of green synthesized gold nanoparticles in albino mice. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 49, 508–520. doi:10.1080/03639045.2023.2243334
Akouibaa, A., Masrour, R., Mordane, S., Benhamou, M., El Assyry, A., and Derouiche, A. (2024). Optical and thermo-plasmonic properties of spherical and hollow gold nanoparticles injected in cell organelles. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 95, 105559. doi:10.1016/J.JDDST.2024.105559
Albanese, A., Tang, P. S., and Chan, W. C. W. (2012). The effect of nanoparticle size, shape, and surface chemistry on biological systems. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 14, 1–16. doi:10.1146/ANNUREV-BIOENG-071811-150124
Alexeree, S. M. I., Sliem, M. A., EL-Balshy, R. M., Amin, R. M., and Harith, M. A. (2017). Exploiting biosynthetic gold nanoparticles for improving the aqueous solubility of metal-free phthalocyanine as biocompatible PDT agent. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 76, 727–734. doi:10.1016/J.MSEC.2017.03.129
Al-Radadi, N. S. (2021). Green biosynthesis of flaxseed gold nanoparticles (Au-NPs) as potent anti-cancer agent against breast cancer cells. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 25, 101243. doi:10.1016/J.JSCS.2021.101243
Amini, S. M., Mohammadi, E., Askarian-amiri, S., Azizi, Y., Shakeri-zadeh, A., and Neshastehriz, A. (2021). Investigating the in vitro photothermal effect of green synthesized apigenin-coated gold nanoparticle on colorectal carcinoma. IET Nanobiotechnol 15, 329–337. doi:10.1049/NBT2.12016
Anadozie, S. O., Effiom, D. O., Adewale, O. B., Jude, J., Zosela, I., Akawa, O. B., et al. (2023). Hibiscus sabdariffa synthesized gold nanoparticles ameliorate aluminum chloride induced memory deficits through inhibition of COX-2/BACE-1 mRNA expression in rats. Arabian J. Chem. 16, 104604. doi:10.1016/J.ARABJC.2023.104604
Anand, K., Gengan, R. M., Phulukdaree, A., and Chuturgoon, A. (2015). Agroforestry waste Moringa oleifera petals mediated green synthesis of gold nanoparticles and their anti-cancer and catalytic activity. J. Industrial Eng. Chem. 21, 1105–1111. doi:10.1016/J.JIEC.2014.05.021
Arumugam, G., and Nirmala, M. (2020). Characterization of green synthesized gold nanoparticles from Nigella sativa oil and evaluation of its antibacterial and anticancer activity. J. Crit. Rev. 7, 1664–1679. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/372744228 (Accessed June 6, 2024).
Arvindganth, R., and Kathiravan, G. (2019). Biogenic synthesis of gold nanoparticle from enicostema axillare and their in vitro cytotoxicity study against MCF-7 cell line. Bionanoscience 9, 839–847. doi:10.1007/s12668-019-00656-6
Asl, S. S., Tafvizi, F., and Noorbazargan, H. (2022). Biogenic synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Satureja rechingeri Jamzad: a potential anticancer agent against cisplatin-resistant A2780CP ovarian cancer cells. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30 (8 30), 20168–20184. doi:10.1007/S11356-022-23507-6
Bailly, A. L., Correard, F., Popov, A., Tselikov, G., Chaspoul, F., Appay, R., et al. (2019). In vivo evaluation of safety, biodistribution and pharmacokinetics of laser-synthesized gold nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 9 (1 9), 12890–12912. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-48748-3
Balashanmugam, P., Mosachristas, K., and Kowsalya, E. (2018). In vitro cytotoxicity and antioxidant evaluation of biogenic synthesized gold nanoparticles from marsilea quadrifolia on lung and ovarian cancer cells. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. 10, 153–158. doi:10.22159/IJAP.2018V10I5.27999
Balasubramanian, S., Kala, S. M. J., and Pushparaj, T. L. (2020). Biogenic synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Jasminum auriculatum leaf extract and their catalytic, antimicrobial and anticancer activities. J. Drug Delivery Sci. Technol. 57, 101620. doi:10.1016/j.jddst.2020.101620
Barai, A. C., Paul, K., Dey, A., Manna, S., Roy, S., Bag, B. G., et al. (2018). Green synthesis of Nerium oleander-conjugated gold nanoparticles and study of its in vitro anticancer activity on MCF-7 cell lines and catalytic activity. Nano Converg. 5, 10–19. doi:10.1186/s40580-018-0142-5
Bawazeer, S., Rauf, A., Nawaz, T., Khalil, A. A., Javed, M. S., Muhammad, N., et al. (2021). Punica granatum peel extracts mediated the green synthesis of gold nanoparticles and their detailed in vivo biological activities. Green Process. Synthesis 10, 882–892. doi:10.1515/gps-2021-0080
Bharadwaj, K. K., Rabha, B., Pati, S., Sarkar, T., Choudhury, B. K., Barman, A., et al. (2021). Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using plant extracts as beneficial prospect for cancer theranostics. Molecules 26, 6389. doi:10.3390/MOLECULES26216389
Bin-Jumah, M. N., Al-Abdan, M., Al-Basher, G., and Alarifi, S. (2020). Molecular mechanism of cytotoxicity, genotoxicity, and anticancer potential of green gold nanoparticles on human liver normal and cancerous cells. Dose-Response 18, 155932582091215. doi:10.1177/1559325820912154
Botteon, C. E. A., Silva, L. B., Ccana-Ccapatinta, G. V., Silva, T. S., Ambrosio, S. R., Veneziani, R. C. S., et al. (2021). Biosynthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles using Brazilian red propolis and evaluation of its antimicrobial and anticancer activities. Sci. Rep. 11 (111), 1974. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-81281-w
Castro-Aceituno, V., Abbai, R., Moon, S. S., Ahn, S., Mathiyalagan, R., Kim, Y. J., et al. (2017). Pleuropterus multiflorus (Hasuo) mediated straightforward eco-friendly synthesis of silver, gold nanoparticles and evaluation of their anti-cancer activity on A549 lung cancer cell line. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 93, 995–1003. doi:10.1016/J.BIOPHA.2017.07.040
Chanda, N., Shukla, R., Zambre, A., Mekapothula, S., Kulkarni, R. R., Katti, K., et al. (2011). An effective strategy for the synthesis of biocompatible gold nanoparticles using cinnamon phytochemicals for phantom CT imaging and photoacoustic detection of cancerous cells. Pharm. Res. 28, 279–291. doi:10.1007/s11095-010-0276-6
Chen, J., Li, Y., Fang, G., Cao, Z., Shang, Y., Alfarraj, S., et al. (2021). Green synthesis, characterization, cytotoxicity, antioxidant, and anti-human ovarian cancer activities of Curcumae kwangsiensis leaf aqueous extract green-synthesized gold nanoparticles. Arabian J. Chem. 14, 103000. doi:10.1016/J.ARABJC.2021.103000
Chittineedi, P., Pandrangi, S. L., Neira Mosquera, J. A., Sánchez Llaguno, S. N., and Mohiddin, G. J. (2023). Aqueous Nyctanthes arbortristis and doxorubicin conjugated gold nanoparticles synergistically induced mTOR-dependent autophagy-mediated ferritinophagy in paclitaxel-resistant breast cancer stem cells. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1201319. doi:10.3389/FPHAR.2023.1201319
Cui, W., Li, J., Zhang, Y., Rong, H., Lu, W., and Jiang, L. (2012). Effects of aggregation and the surface properties of gold nanoparticles on cytotoxicity and cell growth. Nanomedicine 8, 46–53. doi:10.1016/J.NANO.2011.05.005
Dash, S. S., Sen, I. K., and Dash, S. K. (2022). A review on the plant extract mediated green syntheses of gold nanoparticles and its anti-microbial, anti-cancer and catalytic applications. Int. Nano Lett. 12, 47–66. doi:10.1007/s40089-021-00358-6
Datkhile, K. D., Durgavale, P. P., Patil, M. N., Jagdale, N. J., and Deshmukh, V. N. (2020). Biosynthesis, characterization and evaluation of biological properties of biogenic gold nanoparticles synthesized using Nothapodytes foetida leaf extract. Nanosci. and Nanotechnology-Asia 11, 84–96. doi:10.2174/2210681210666200225112002
Datkhile, K. D., Patil, S. R., Durgawale, P. P., Patil, M. N., Hinge, D. D., Jagdale, N. J., et al. (2021). Biogenic synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Argemone mexicana L. and their cytotoxic and genotoxic effects on human colon cancer cell line (HCT-15). J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 19, 9–11. doi:10.1186/s43141-020-00113-y
Devendiran, R. M., Chinnaiyan, S. kumar, Yadav, N. K., Moorthy, G. K., Ramanathan, G., Singaravelu, S., et al. (2016). Green synthesis of folic acid-conjugated gold nanoparticles with pectin as reducing/stabilizing agent for cancer theranostics. RSC Adv. 6, 29757–29768. doi:10.1039/C6RA01698G
Dey, A., Yogamoorthy, A., and Sundarapandian, S. (2018). Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles and evaluation of its cytotoxic property against colon cancer cell line. 4(6) 1–17. Res. J. Life Sci. Bioinform Pharm. Chem. Sci.
Dhandapani, S., Wang, R., cheol Hwang, K., Kim, H., and Kim, Y. J. (2023). Exploring the potential anti-inflammatory effect of biosynthesized gold nanoparticles using Isodon excisus leaf tissue in human keratinocytes. Arabian J. Chem. 16, 105113. doi:10.1016/J.ARABJC.2023.105113
Dorosti, N., and Jamshidi, F. (2016). Plant-mediated gold nanoparticles by Dracocephalum kotschyi as anticholinesterase agent: synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of anticancer and antibacterial activity. J. Appl. Biomed. 14, 235–245. doi:10.1016/J.JAB.2016.03.001
El-Borady, O. M., Ayat, M. S., Shabrawy, M. A., and Millet, P. (2020). Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Parsley leaves extract and their applications as an alternative catalytic, antioxidant, anticancer, and antibacterial agents. Adv. Powder Technol. 31, 4390–4400. doi:10.1016/J.APT.2020.09.017
El-Rafie, H. M., El-Aziz, S. M. A., and Zahran, M. K. (2023). In vitro cytotoxicity against breast cancer using biogenically synthesized gold and iron oxide nanoparticles derived from the hydroethanolic extract of Salvia officinalis L. Chem. Pap. 77, 361–373. doi:10.1007/s11696-022-02464-x
Fadeel, B., and Garcia-Bennett, A. E. (2010). Better safe than sorry: understanding the toxicological properties of inorganic nanoparticles manufactured for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 62, 362–374. doi:10.1016/J.ADDR.2009.11.008
Fatimah, I., Hidayat, H., Nugroho, B. H., and Husein, S. (2020). Ultrasound-assisted biosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles using Clitoria ternatea flower. S Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 34, 97–106. doi:10.1016/J.SAJCE.2020.06.007
Fazal, S., Jayasree, A., Sasidharan, S., Koyakutty, M., Nair, S. V., and Menon, D. (2014). Green synthesis of anisotropic gold nanoparticles for photothermal therapy of cancer. ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces 6, 8080–8089. doi:10.1021/am500302t
Francis, S., Koshy, E., and Mathew, B. (2018). Microwave aided synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles and their antioxidant, antimicrobial and catalytic potentials. J. Nanostructures 8, 55–66. doi:10.22052/JNS.2018.01.007
Ganeshkumar, M., Sathishkumar, M., Ponrasu, T., Dinesh, M. G., and Suguna, L. (2013). Spontaneous ultra fast synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Punica granatum for cancer targeted drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 106, 208–216. doi:10.1016/J.COLSURFB.2013.01.035
Gao, L., Mei, S., Ma, H., and Chen, X. (2022). Ultrasound-assisted green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using citrus peel extract and their enhanced anti-inflammatory activity. Ultrason. Sonochem 83, 105940. doi:10.1016/J.ULTSONCH.2022.105940
Geetha, R., Ashokkumar, T., Tamilselvan, S., Govindaraju, K., Sadiq, M., and Singaravelu, G. (2013). Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles and their anticancer activity. Cancer Nanotechnol. 4, 91–98. doi:10.1007/s12645-013-0040-9
Goddard, Z. R., Marín, M. J., Russell, D. A., and Searcey, M. (2020). Active targeting of gold nanoparticles as cancer therapeutics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 49 (23), 8774–8789. doi:10.1039/d0cs01121e
Gong, N., Chen, S., Jin, S., Zhang, J., Wang, P. C., and Liang, X.-J. (2015). Effects of the physicochemical properties of gold nanostructures on cellular internalization. Regen. Biomater. 2, 273–280. doi:10.1093/RB/RBV024
Gonnelli, C., Giordano, C., Fontani, U., Salvatici, M. C., and Ristori, S. (2018). Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles from extracts of Cucurbita pepo L. Leaves: insights on the role of plant ageing. Lect. Notes Bioeng., 155–164. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-62027-5_14
Hanan, N. A., Chiu, H. I., Ramachandran, M. R., Tung, W. H., Mohamad Zain, N. N., Yahaya, N., et al. (2018). Cytotoxicity of plant-mediated synthesis of metallic nanoparticles: a systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 1725. doi:10.3390/IJMS19061725
Heegaard, P. M. H., Boas, U., and Otzen, D. E. (2007). Dendrimer effects on peptide and protein fibrillation. Macromol. Biosci. 7, 1047–1059. doi:10.1002/MABI.200700051
Hoshyar, R., Khayati, G. R., Poorgholami, M., and Kaykhaii, M. (2016). A novel green one-step synthesis of gold nanoparticles using crocin and their anti-cancer activities. J. Photochem Photobiol. B 159, 237–242. doi:10.1016/J.JPHOTOBIOL.2016.03.056
Hosny, M., and Fawzy, M. (2021). Instantaneous phytosynthesis of gold nanoparticles via Persicaria salicifolia leaf extract, and their medical applications. Adv. Powder Technol. 32, 2891–2904. doi:10.1016/J.APT.2021.06.004
Hosny, M., Fawzy, M., El-Badry, Y. A., Hussein, E. E., and Eltaweil, A. S. (2022). Plant-assisted synthesis of gold nanoparticles for photocatalytic, anticancer, and antioxidant applications. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 26, 101419. doi:10.1016/J.JSCS.2022.101419
Ismail, E. H., Saqer, A. M. A., Assirey, E., Naqvi, A., and Okasha, R. M. (2018). Successful green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using a corchorus olitorius extract and their antiproliferative effect in cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 2612. doi:10.3390/IJMS19092612
Ke, Y., Al Aboody, M. S., Alturaiki, W., Alsagaby, S. A., Alfaiz, F. A., Veeraraghavan, V. P., et al. (2019). Photosynthesized gold nanoparticles from Catharanthus roseus induces caspase-mediated apoptosis in cervical cancer cells (HeLa). Artif. Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 47, 1938–1946. doi:10.1080/21691401.2019.1614017
Keskin, C., Atalar, M. N., Firat Baran, M., and Baran, A. (2021). Environmentally friendly rapid synthesis of gold nanoparticles from Artemisia absinthium plant extract and application of antimicrobial activities. J. Inst. Sci. Technol. 11 (1), 365–375. doi:10.21597/jist.779169
Khan, A. U., Yuan, Q., Wei, Y., Khan, S. U., Tahir, K., Khan, Z. U. H., et al. (2016). Longan fruit juice mediated synthesis of uniformly dispersed spherical AuNPs: cytotoxicity against human breast cancer cell line MCF-7, antioxidant and fluorescent properties. RSC Adv. 6, 23775–23782. doi:10.1039/C5RA27100B
Khandanlou, R., Murthy, V., Saranath, D., and Damani, H. (2018). Synthesis and characterization of gold-conjugated Backhousia citriodora nanoparticles and their anticancer activity against MCF-7 breast and HepG2 liver cancer cell lines. J. Mater Sci. 53, 3106–3118. doi:10.1007/s10853-017-1756-4
Klekotko, M., Matczyszyn, K., Siednienko, J., Olesiak-Banska, J., Pawlik, K., and Samoc, M. (2015). Bio-mediated synthesis, characterization and cytotoxicity of gold nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17, 29014–29019. doi:10.1039/C5CP01619C
Kumar, C. S., Mahesh, A., Antoniraj, M. G., Vaidevi, S., and Ruckmani, K. (2016). Ultrafast synthesis of stabilized gold nanoparticles using aqueous fruit extract of Limonia acidissima L. and conjugated epirubicin: targeted drug delivery for treatment of breast cancer. RSC Adv. 6, 26874–26882. doi:10.1039/C6RA01482H
Kumar, I., Mondal, M., Meyappan, V., and Sakthivel, N. (2019). Green one-pot synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Sansevieria roxburghiana leaf extract for the catalytic degradation of toxic organic pollutants. Mater. Res. Bull. 117, 18–27. doi:10.1016/j.materresbull.2019.04.029
Kumari, S., kumari, P., Panda, P. K., Pramanik, N., Verma, S. K., and Mallick, M. A. (2019). Molecular aspect of phytofabrication of gold nanoparticle from Andrographis peniculata photosystem II and their in vivo biological effect on embryonic zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 11, 100201. doi:10.1016/J.ENMM.2018.100201
Lakshmanan, A., Umamaheswari, C., and Nagarajan, N. S. (2016). A facile phyto-mediated synthesis of gold nanoparticles using aqueous extract of Momordica cochinchinensis rhizome and their biological activities. J. Nanosci. Technol. 2, 76–80. Available at: www.jacsdirectory.com/jnst (Accessed June 6, 2024).
Lee, H., Lee, K., Kim, I. K., and Park, T. G. (2008). Synthesis, characterization, and in vivo diagnostic applications of hyaluronic acid immobilized gold nanoprobes. Biomaterials 29, 4709–4718. doi:10.1016/J.BIOMATERIALS.2008.08.038
Li, W., Liu, R., Pei, Q., Shou, T., Zhang, W., and Hu, J. (2019). Curcuma wenyujin. Int. J. Nanomedicine 14, 4091–4103. doi:10.2147/IJN.S203222
Lubis, K., Chudapongse, N., Doan, H. V., and Weeranantanapan, O. (2018). Characterization of biocompatible gold nanoparticles synthesized by using curcuma xanthorrhiza and their catalytic activity. Curr. Nanosci. 16, 214–225. doi:10.2174/1573413715666181128142258
Majumdar, R., Bag, B. G., and Ghosh, P. (2016). Mimusops elengi bark extract mediated green synthesis of gold nanoparticles and study of its catalytic activity. Appl. Nanosci. Switz. 6, 521–528. doi:10.1007/s13204-015-0454-2
Malaikolundhan, H., Mookkan, G., Krishnamoorthi, G., Matheswaran, N., Alsawalha, M., and Veeraraghavan, V. P. (2020). Anticarcinogenic effect of gold nanoparticles synthesized from Albizia lebbeck on HCT-116 colon cancer cell lines. Artif. Cells, Nanomed., Biotechnol. 48 (1), 1206–1213. doi:10.1080/21691401.2020.1814313
Mi, X. J., Park, H. R., Dhandapani, S., Lee, S., and Kim, Y. J. (2022). Biologically synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Cirsium japonicum var. maackii extract and the study of anti-cancer properties on AGS gastric cancer cells. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 18, 5809–5826. doi:10.7150/IJBS.77734
Mikhailova, E. O. (2021). Gold nanoparticles: biosynthesis and potential of biomedical application. J. Funct. Biomaterials 12 (4), 70. doi:10.3390/jfb12040070
Mishra, P., Ray, S., Sinha, S., Das, B., Khan, M. I., Behera, S. K., et al. (2016). Facile bio-synthesis of gold nanoparticles by using extract of Hibiscus sabdariffa and evaluation of its cytotoxicity against U87 glioblastoma cells under hyperglycemic condition. Biochem. Eng. J. 105, 264–272. doi:10.1016/J.BEJ.2015.09.021
Mobaraki, F., Momeni, M., Taghavizadeh Yazdi, M. E., Meshkat, Z., Silanian Toosi, M., and Hosseini, S. M. (2021). Plant-derived synthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles: investigation of its antioxidant and anticancer activity against human testicular embryonic carcinoma stem cells. Process Biochem. 111, 167–177. doi:10.1016/J.PROCBIO.2021.09.010
Morel, A.-L., Giraud, S., Bialecki, A., Moustaoui, H., de La Chapelle, M. L., and Spadavecchia, J. (2017). Green extraction of endemic plants to synthesize gold nanoparticles for theranostic applications. Front. Laboratory Med. 1, 158–171. doi:10.1016/J.FLM.2017.10.003
Mousavi-Kouhi, S. M., Beyk-Khormizi, A., Mohammadzadeh, V., Ashna, M., Es-haghi, A., Mashreghi, M., et al. (2022). Biological synthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles using Verbascum speciosum Schrad. and cytotoxicity properties toward HepG2 cancer cell line. Res. Chem. Intermed. 48, 167–178. doi:10.1007/s11164-021-04600-w
Mukherjee, S., Sau, S., Madhuri, D., Bollu, V. S., Madhusudana, K., Sreedhar, B., et al. (2016). Green synthesis and characterization of monodispersed gold nanoparticles: toxicity study, delivery of doxorubicin and its bio-distribution in mouse model. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 12, 165–181. doi:10.1166/JBN.2016.2141
Mukherjee, S., Vinothkumar, B., Prashanthi, S., Bangal, P. R., Sreedhar, B., and Patra, C. R. (2013). Potential therapeutic and diagnostic applications of one-step in situ biosynthesized gold nanoconjugates (2-in-1 system) in cancer treatment. RSC Adv. 3, 2318–2329. doi:10.1039/C2RA22299J
Muthukumar, T., Sambandam, B., Aravinthan, A., Sastry, T. P., and Kim, J. H. (2016). Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles and their enhanced synergistic antitumor activity using HepG2 and MCF7 cells and its antibacterial effects. Process Biochem. 51, 384–391. doi:10.1016/J.PROCBIO.2015.12.017
Naraginti, S., and Li, Y. (2017). Preliminary investigation of catalytic, antioxidant, anticancer and bactericidal activity of green synthesized silver and gold nanoparticles using Actinidia deliciosa. J. Photochem Photobiol. B 170, 225–234. doi:10.1016/J.JPHOTOBIOL.2017.03.023
Pannerselvam, B., Devanathadesikan, V., Alagumuthu, T. S., Kanth, S. V., and Thangavelu, K. P. (2020). Assessment of in-vivo biocompatibility evaluation of phytogenic gold nanoparticles on Wistar albino male rats. IET Nanobiotechnol 14, 314–324. doi:10.1049/IET-NBT.2019.0116
Parida, U. K., Biswal, S. K., and Bindhani, B. K. (2014). Green synthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles: study of its biological mechanism in human SUDHL-4 cell line. Adv. Biol. Chem. 04, 360–375. doi:10.4236/ABC.2014.46041
Parimala, L., Ramapriya, L., and Santhanalakshmi, J. (2022). Aloe leaf extract and microwave assisted green synthesis of gold nanoparticles and its catalytic activity on reductive degradation of methyl red. AIP Conf. Proc. 2446. doi:10.1063/5.0108582/2824282
Patil, M. P., Bayaraa, E., Subedi, P., Piad, L. L. A., Tarte, N. H., and Kim, G.Do (2019). Biogenic synthesis, characterization of gold nanoparticles using Lonicera japonica and their anticancer activity on HeLa cells. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 51, 83–90. doi:10.1016/J.JDDST.2019.02.021
Patil, M. P., Jin, X., Simeon, N. C., Palma, J., Kim, D., Ngabire, D., et al. (2018). Anticancer activity of Sasa borealis leaf extract-mediated gold nanoparticles. Artif. Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 46, 82–88. doi:10.1080/21691401.2017.1293675
Patil, M. P., Ngabire, D., Thi, H. H. P., Kim, M.Do, and Kim, G.Do (2017). Eco-friendly synthesis of gold nanoparticles and evaluation of their cytotoxic activity on cancer cells. J. Clust. Sci. 28, 119–132. doi:10.1007/s10876-016-1051-6
Patil, S., and Chandrasekaran, R. (2020). Biogenic nanoparticles: a comprehensive perspective in synthesis, characterization, application and its challenges. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 18, 67. doi:10.1186/S43141-020-00081-3
Patra, J. K., and Baek, K. H. (2015). Novel green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Citrullus lanatus rind and investigation of proteasome inhibitory activity, antibacterial, and antioxidant potential. Int. J. Nanomedicine 10, 7253–7264. doi:10.2147/IJN.S95483
Pechyen, C., Ponsanti, K., Tangnorawich, B., and Ngernyuang, N. (2021). Waste fruit peel – mediated green synthesis of biocompatible gold nanoparticles. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 14, 2982–2991. doi:10.1016/J.JMRT.2021.08.111
Perveen, K., Husain, F. M., Qais, F. A., Khan, A., Razak, S., Afsar, T., et al. (2021). Microwave-assisted rapid green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using seed extract of trachyspermum ammi: ROS mediated biofilm inhibition and anticancer activity. Biomolecules 11, 197. doi:10.3390/BIOM11020197
Pinto, R. J. B., Lucas, J. M. F., Morais, M. P., Santos, S. A. O., Silvestre, A. J. D., Marques, P. A. A. P., et al. (2017). Demystifying the morphology and size control on the biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using Eucalyptus globulus bark extract. Ind. Crops Prod. 105, 83–92. doi:10.1016/J.INDCROP.2017.05.003
Priya, M. R. K., and Iyer, P. R. (2020). Antiproliferative effects on tumor cells of the synthesized gold nanoparticles against Hep2 liver cancer cell line. Egypt. Liver J. 10, 1–12. doi:10.1186/S43066-020-0017-4/FIGURES/7
Punnoose, M. S., Bijimol, D., Abraham, T., Plathanam, N. J., and Mathew, B. (2021). Green synthesized unmodified silver nanoparticles as reproducible dual sensor for mercuric ions and catalyst to abate environmental pollutants. Bionanoscience 11, 739–754. doi:10.1007/s12668-021-00883-w
Punnoose, M. S., and Mathew, B. (2022). Microwave-assisted green synthesis of Cyanthillium cinereum mediated gold nanoparticles: evaluation of its antibacterial, anticancer and catalytic degradation efficacy. Res. Chem. Intermed. 48, 1025–1044. doi:10.1007/s11164-021-04641-1
Qian, L., Su, W., Wang, Y., Dang, M., Zhang, W., and Wang, C. (2019). Synthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles from aqueous leaf extract of Alternanthera sessilis and its anticancer activity on cervical cancer cells (HeLa). Artif. Cells, Nanomed., Biotechnol. 47 (1), 1173–1180. doi:10.1080/21691401.2018.1549064
Rabori, M. S., Karimabad, M. N. O. R. O. O. Z. I., and Hajizadeh, M. R. (2021). Facile, low-cost and rapid phytosynthesis of stable and eco-friendly gold nanoparticles using green walnut shell and study of their anticancer potential. World Cancer Res. J. 8. doi:10.32113/WCRJ_20217_2037
Rajan, A., Rajan, A. R., and Philip, D. (2017). Elettaria cardamomum seed mediated rapid synthesis of gold nanoparticles and its biological activities. OpenNano 2, 1–8. doi:10.1016/J.ONANO.2016.11.002
Rajeshkumar, S. (2016). Anticancer activity of eco-friendly gold nanoparticles against lung and liver cancer cells. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 14, 195–202. doi:10.1016/J.JGEB.2016.05.007
Rana, N., Singh, S. K., Banu, N. A., Hjazi, A., Vamanu, E., and Singh, M. P. (2023). The ethnopharmacological properties of green-engineered metallic nanoparticles against metabolic disorders. Medicina 59, 1022–1059. doi:10.3390/MEDICINA59061022
Redza-Dutordoir, M., and Averill-Bates, D. A. (2016). Activation of apoptosis signalling pathways by reactive oxygen species. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1863, 2977–2992. doi:10.1016/J.BBAMCR.2016.09.012
Renuga Devi, P., Senthil Kumar, C., Selvamani, P., Subramanian, N., and Ruckmani, K. (2015). Synthesis and characterization of Arabic gum capped gold nanoparticles for tumor-targeted drug delivery. Mater Lett. 139, 241–244. doi:10.1016/J.MATLET.2014.10.010
Rodríguez-León, E., Rodríguez-Vázquez, B. E., Martínez-Higuera, A., Rodríguez-Beas, C., Larios-Rodríguez, E., Navarro, R. E., et al. (2019). Synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Mimosa tenuiflora extract, assessments of cytotoxicity, cellular uptake, and catalysis. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 14, 334. doi:10.1186/S11671-019-3158-9
Rónavári, A., Igaz, N., Adamecz, D. I., Szerencsés, B., Molnar, C., Kónya, Z., et al. (2021). Green silver and gold nanoparticles: biological synthesis approaches and potentials for biomedical applications. Molecules 26 (4), 844. doi:10.3390/MOLECULES26040844
Roy, A., Pandit, C., Gacem, A., Alqahtani, M. S., Bilal, M., Islam, S., et al. (2022). Biologically derived gold nanoparticles and their applications. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2022, 8184217. doi:10.1155/2022/8184217
Saqr, A.Al, Khafagy, E. S., Alalaiwe, A., Aldawsari, M. F., Alshahrani, S. M., Anwer, M. K., et al. (2021). Synthesis of gold nanoparticles by using green machinery: characterization and in vitro toxicity. Nanomaterials 11, 1–14. doi:10.3390/NANO11030808
Sargazi, S., Laraib, U., Er, S., Rahdar, A., Hassanisaadi, M., Zafar, M. N., et al. (2022). Application of green gold nanoparticles in cancer therapy and diagnosis. Nanomaterials 12, 1102–1112. doi:10.3390/NANO12071102
Serdar, G. (2024a). Biosynthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles using microwave-assisted technology from pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) leaf extract produced by the method of supercritical fluid extraction (SFE). Plasmonics 19, 2233–2243. doi:10.1007/s11468-024-02312-6
Serdar, G. (2024b). Gold nanoparticles biosynthesis through green synthesis mediated by leaf extract from Diospyros kaki L.(Persimmon) using the microwave extraction method. Plasmonics 19, 2813–2823. doi:10.1007/s11468-024-02294-5
Serdar, G., and Kılınç, G. G. (2023). Microwave assisted production and characterization of gold nanoparticles using green tea and catechin extracts obtained by supercritical extraction method. Chem. Pap. 77, 5155–5167. doi:10.1007/s11696-023-02851-y
Sezgin, E., Karataş, F., Çam, D., Sur, İ., Sayin, İ., Avci, E., et al. (2008). Interaction of gold nanoparticles with living cells. Sigma 26, 227–246.
Shabani, L., Kasaee, S. R., Chelliapan, S., Abbasi, M., Khajehzadeh, H., Dehghani, F. S., et al. (2023). An investigation into green synthesis of Ru template gold nanoparticles and the in vitro photothermal effect on the MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line. Appl. Phys. A Mater Sci. Process 129, 564. doi:10.1007/s00339-023-06832-6
Shunmugam, R., Renukadevi Balusamy, S., Kumar, V., Menon, S., Lakshmi, T., and Perumalsamy, H. (2021). Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using marine microbe (Vibrio alginolyticus) and its anticancer and antioxidant analysis. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 33, 101260. doi:10.1016/J.JKSUS.2020.101260
Sibuyi, N. R. S., Thipe, V. C., Panjtan-Amiri, K., Meyer, M., and Katti, K. V. (2021). Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Acai berry and Elderberry extracts and investigation of their effect on prostate and pancreatic cancer cells. Nanobiomedicine (Rij) 8, 1849543521995310–1849543521995318. doi:10.1177/1849543521995310
Siegel, R. L., Miller, K. D., Wagle, N. S., and Jemal, A. (2023). Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 73, 17–48. doi:10.3322/CAAC.21763
Sultana, R., Yadav, D., Puranik, N., Chavda, V., Kim, J., and Song, M. (2023). A review on the use of gold nanoparticles in cancer treatment. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. Former. Curr. Med. Chemistry-Anti-Cancer Agents 23 (20), 2171–2182. doi:10.2174/0118715206268664231004040210
Sun, B., Hu, N., Han, L., Pi, Y., Gao, Y., and Chen, K. (2019). Anticancer activity of green synthesised gold nanoparticles from Marsdenia tenacissima inhibits A549 cell proliferation through the apoptotic pathway. Artif. Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 47, 4012–4019. doi:10.1080/21691401.2019.1575844
Sun, H., Liu, Y., Bai, X., Zhou, X., Zhou, H., Liu, S., et al. (2018). Induction of oxidative stress and sensitization of cancer cells to paclitaxel by gold nanoparticles with different charge densities and hydrophobicities. J. Mater Chem. B 6, 1633–1639. doi:10.1039/C7TB03153J
Sung, H., Ferlay, J., Siegel, R. L., Laversanne, M., Soerjomataram, I., Jemal, A., et al. (2021). Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 71, 209–249. doi:10.3322/CAAC.21660
Susanna, D., Balakrishnan, R. M., and Ponnan Ettiyappan, J. (2023). Ultrasonication-assisted green synthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles from Nothapodytes foetida: an assessment of their antioxidant, antibacterial, anticancer and wound healing potential. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 87, 104740. doi:10.1016/J.JDDST.2023.104740
Teimouri, M., Khosravi-Nejad, F., Attar, F., Saboury, A. A., Kostova, I., Benelli, G., et al. (2018). Gold nanoparticles fabrication by plant extracts: synthesis, characterization, degradation of 4-nitrophenol from industrial wastewater, and insecticidal activity – a review. J. Clean. Prod. 184, 740–753. doi:10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2018.02.268
Thanayutsiri, T., Patrojanasophon, P., Opanasopit, P., Ngawhirunpat, T., Laiwattanapaisal, W., and Rojanarata, T. (2023). Rapid and efficient microwave-assisted extraction of Caesalpinia sappan Linn. heartwood and subsequent synthesis of gold nanoparticles. Green Process. Synthesis 12. doi:10.1515/gps-2022-8109
Tiloke, C., Phulukdaree, A., Anand, K., Gengan, R. M., and Chuturgoon, A. A. (2016). Moringa oleifera gold nanoparticles modulate oncogenes, tumor suppressor genes, and caspase-9 splice variants in A549 cells. J. Cell Biochem. 117, 2302–2314. doi:10.1002/JCB.25528
Tomar, A., and Garg, G. (2013). Short review on application of gold nanoparticles. Glob. J. Pharmacol. 7, 34–38. doi:10.5829/IDOSI.GJP.2013.7.1.66173
Uzma, M., Sunayana, N., Raghavendra, V. B., Madhu, C. S., Shanmuganathan, R., and Brindhadevi, K. (2020). Biogenic synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Commiphora wightii and their cytotoxic effects on breast cancer cell line (MCF-7). Process Biochem. 92, 269–276. doi:10.1016/J.PROCBIO.2020.01.019
Vandarkuzhali, S. A. A., Karthikeyan, G., and Pachamuthu, M. P. (2021). Microwave assisted biosynthesis of Borassus flabellifer fruit mediated silver and gold nanoparticles for dye reduction, antibacterial and anticancer activity. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 9, 106411. doi:10.1016/J.JECE.2021.106411
Valsalam, S., Agastian, P., Esmail, G. A., Ghilan, A. K. M., Al-Dhabi, N. A., and Arasu, M. V. (2019). Biosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles using Musa acuminata colla flower and its pharmaceutical activity against bacteria and anticancer efficacy. J. Photochem. Photobiol., B 201, 111670. doi:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.111670
Vangari, V., Reddy, P. R., Rao, L. N., Mohammed, A., and Reddy, A. P. (2024). Microwave-assisted synthesis of Au nanoparticles using fruit peel waste: antioxidant activity and catalytic reduction of malachite green. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal., 1–13. doi:10.1007/s11144-024-02726-7
Verma, S. K., Jha, E., Panda, P. K., Kumari, P., Pramanik, N., Kumari, S., et al. (2018). Molecular investigation to RNA and protein based interaction induced in vivo biocompatibility of phytofabricated AuNP with embryonic zebrafish. Artif. Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 46, S671–S684. doi:10.1080/21691401.2018.1505746
Vijayakumar, S. (2019). Eco-friendly synthesis of gold nanoparticles using fruit extracts and in vitro anticancer studies. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 23, 753–761. doi:10.1016/J.JSCS.2018.12.002
Vijayakumar, S., Vaseeharan, B., Malaikozhundan, B., Gopi, N., Ekambaram, P., Pachaiappan, R., et al. (2017). Therapeutic effects of gold nanoparticles synthesized using Musa paradisiaca peel extract against multiple antibiotic resistant Enterococcus faecalis biofilms and human lung cancer cells (A549). Microb. Pathog. 102, 173–183. doi:10.1016/J.MICPATH.2016.11.029
Vijayan, R., Joseph, S., and Mathew, B. (2018). Indigofera tinctoria leaf extract mediated green synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles and assessment of their anticancer, antimicrobial, antioxidant and catalytic properties. Artif. Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 46, 861–871. doi:10.1080/21691401.2017.1345930
Vijayashree, I. S., Niranjana, P., Prabhu, G., Sureshbabu, V. V., and Manjanna, J. (2017). Conjugation of Au nanoparticles with chlorambucil for improved anticancer activity. J. Clust. Sci. 28, 133–148. doi:10.1007/s10876-016-1053-4
Vimalraj, S., Ashokkumar, T., and Saravanan, S. (2018). Biogenic gold nanoparticles synthesis mediated by Mangifera indica seed aqueous extracts exhibits antibacterial, anticancer and anti-angiogenic properties. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 105, 440–448. doi:10.1016/J.BIOPHA.2018.05.151
Vinay, S. P., Sumedha, H. N., Shashank, M., Nagaraju, G., and Chandrasekhar, N. (2021). In-vitro antibacterial, antioxidant and cytotoxic potential of gold nanoparticles synthesized using novel Elaeocarpus ganitrus seeds extract. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 6, 127–133. doi:10.1016/J.JSAMD.2020.09.008
Vinayagam, R., Santhoshkumar, M., Lee, K. E., David, E., and Kang, S. G. (2021). Bioengineered gold nanoparticles using Cynodon dactylon extract and its cytotoxicity and antibacterial activities. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 44, 1253–1262. doi:10.1007/s00449-021-02527-5
Vinosha, M., Palanisamy, S., Muthukrishnan, R., Selvam, S., Kannapiran, E., You, S. G., et al. (2019). Biogenic synthesis of gold nanoparticles from Halymenia dilatata for pharmaceutical applications: antioxidant, anti-cancer and antibacterial activities. Process Biochem. 85, 219–229. doi:10.1016/J.PROCBIO.2019.07.013
Wang, C., Mathiyalagan, R., Kim, Y. J., Castro-Aceituno, V., Singh, P., Ahn, S., et al. (2016). Rapid green synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles using Dendropanax morbifera leaf extract and their anticancer activities. Int. J. Nanomedicine 11, 3691–3701. doi:10.2147/IJN.S97181
Wang, C., and Youle, R. J. (2009). The role of mitochondria in apoptosis. Annu. Rev. Genet. 43, 95–118. doi:10.1146/annurev-genet-102108-134850
Wang, L., Xu, J., Yan, Y., Liu, H., Karunakaran, T., and Li, F. (2019). Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles from Scutellaria barbata and its anticancer activity in pancreatic cancer cell (PANC-1). Artif. Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 47, 1617–1627. doi:10.1080/21691401.2019.1594862
Worakitjaroenphon, S., Shanmugam, P., Boonyuen, S., Smith, S. M., and Chookamnerd, K. (2023). Green synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles using Oroxylum indicum plant extract for catalytic and antimicrobial activity. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. doi:10.1007/S13399-023-04734-4
Wu, T., Duan, X., Hu, C., Wu, C., Chen, X., Huang, J., et al. (2019). Synthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles from Abies spectabilis extract and its anticancer activity on bladder cancer T24 cells. Artif. Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 47, 512–523. doi:10.1080/21691401.2018.1560305
Xia, T., Kovochich, M., Brant, J., Hotze, M., Sempf, J., Oberley, T., et al. (2006). Comparison of the abilities of ambient and manufactured nanoparticles to induce cellular toxicity according to an oxidative stress paradigm. Nano Lett. 6, 1794–1807. doi:10.1021/nl061025k
Xin Lee, K., Shameli, K., Miyake, M., Kuwano, N., Bt Ahmad Khairudin, N. B., Bt Mohamad, S. E., et al. (2016). Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using aqueous extract of Garcinia mangostana fruit peels. J. Nanomater 2016, 1–7. doi:10.1155/2016/8489094
Xue, N. C., Zhou, C. H., Chu, Z. Y., Chen, L. N., and Jia, N. Q. (2021). Barley leaves mediated biosynthesis of Au nanomaterials as a potential contrast agent for computed tomography imaging. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 64, 433–440. doi:10.1007/s11431-019-1546-3
Yang, N., Weihong, L., and Hao, L. (2014). Biosynthesis of Au nanoparticles using agricultural waste mango peel extract and its in vitro cytotoxic effect on two normal cells. Mater Lett. 134, 67–70. doi:10.1016/J.MATLET.2014.07.025
Yang, Z., Liu, Z., Zhu, J., Xu, J., Pu, Y., and Bao, Y. (2022). Green synthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles from Pholiota adiposa and their anticancer effects on hepatic carcinoma. Drug Deliv. 29, 997–1006. doi:10.1080/10717544.2022.2056664
Yun, R., Li, Y., Zhang, X., and Cong, X. qiang (2020). Eco friendly fabrication of gold nanoclusters and their induction of cardiomyocyte apoptosis after intratracheal instillation in rats. J. Clust. Sci. 31, 851–860. doi:10.1007/s10876-019-01692-8
Zangeneh, M. M., and Zangeneh, A. (2020). Novel green synthesis of Hibiscus sabdariffa flower extract conjugated gold nanoparticles with excellent anti-acute myeloid leukemia effect in comparison to daunorubicin in a leukemic rodent model. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 34, e5271. doi:10.1002/AOC.5271
Zhang, X., Tan, Z., Jia, K., Zhang, W., and Dang, M. (2019). Rabdosia rubescens Linn: green synthesis of gold nanoparticles and their anticancer effects against human lung cancer cells A549. Artif. Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 47, 2171–2178. doi:10.1080/21691401.2019.1620249
Zhao, P., El-kott, A., Ahmed, A. E., Khames, A., and Zein, M. A. (2021a). Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) using Tribulus terrestris extract: investigation of its catalytic activity in the oxidation of sulfides to sulfoxides and study of its anti-acute leukemia activity. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 131, 108781. doi:10.1016/J.INOCHE.2021.108781
Zhao, W., Li, J., Zhong, C., Zhang, X., and Bao, Y. (2021b). Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles from Dendrobium officinale and its anticancer effect on liver cancer. Drug Deliv. 28, 985–994. doi:10.1080/10717544.2021.1921079
Zheng, Y., Zhang, J., Zhang, R., Luo, Z., Wang, C., and Shi, S. (2019). Gold nano particles synthesized from Magnolia officinalis and anticancer activity in A549 lung cancer cells. Artif. Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 47, 3101–3109. doi:10.1080/21691401.2019.1645152
Zhu, J., Liu, Z., Pu, Y., Xu, J., Zhang, S., and Bao, Y. (2022). Green synthesized gold nanoparticles from Pseudobulbus Cremastrae seu Pleiones show efficacy against hepatic carcinoma potentially through immunoregulation. Drug Deliv. 29, 1983–1993. doi:10.1080/10717544.2022.2092238
Keywords: gold nanoparticles, plant mediated, mechanism of action, anticancer, drug delivery, toxicity
Citation: Nisha , Sachan RSK, Singh A, Karnwal A, Shidiki A and Kumar G (2024) Plant-mediated gold nanoparticles in cancer therapy: exploring anti-cancer mechanisms, drug delivery applications, and future prospects. Front. Nanotechnol. 6:1490980. doi: 10.3389/fnano.2024.1490980
Received: 06 September 2024; Accepted: 08 November 2024;
Published: 27 November 2024.
Edited by:
Sumaira Anjum, Kinnaird College for Women University, PakistanReviewed by:
Yuvaraj Haldorai, PSG College of Arts and Science, IndiaCopyright © 2024 Nisha, Sachan, Singh, Karnwal, Shidiki and Kumar. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Amrullah Shidiki, YW1hcnVsbGFoc2lkaGlxaWUyNEBnbWFpbC5jb20=; Gaurav Kumar, Z2F1cmF2LjE5NDU0QGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==, Z2F1cmF2a3IwMUBnbWFpbC5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.