- 1Department of Materials Science, University of Milano-Bicocca, Milano, Italy
- 2NANOMIB, Center for Biomedical Nanomedicine, University of Milano-Bicocca, Milano, Italy
- 3Department of Biotechnology and Biosciences, University of Milano-Bicocca, Milano, Italy
- 4Department of Physics, University of Milano-Bicocca, Milano, Italy
Hospitals and other healthcare facilities harbor a complex interplay of microbial pathogens. The correct understanding of pathogens distribution and evolution is therefore crucial for infections control and for the design of effective prevention strategies. In parallel, the integration of cutting-edge nanotechnologies for the early detection and monitoring of these specific target pathogens is considered the most effective approach to face nosocomial infections. In this context, point-of-care (POC) testing, also known as near-patient testing, is becoming increasingly important. In this review we provide a systematic insight into the recent scientific and technological advances in pathogen detection that explore advanced nanotechnologies to realize devices and nanobiosensors, with improved selectivity and sensitivity. In particular, we report on the most diffused and affordable nanotechnologies developed and still developing for POC testing, with the aim to increase the sensitivity, speed and accuracy of pathogens detection in different environments, from intensive care units to outside the laboratory and hospital settings. The text is sub-divided in several sections, each one focused on different type of nanomaterials and techniques actually employed.
1 Introduction
Infectious diseases are disorders caused by live pathogens such as bacteria, viruses and parasites and are capable of rapid transmission among human or animal vectors by inoculation, airborne or waterborne transmission (van Seventer et al., 2017). In particular, during the twenty-first century a wave of infectious diseases had a devastating impact on our health, wellness and lifestyle. Deaths from emerging and re-emerging infections presage a possible new era of infectious disease, defined by outbreaks of emerging, re-emerging and endemic pathogens that spread rapidly, facilitated by global connectivity and shifts in range due to climate change. In particular, the recent and rapid diffusion of the severe acute respiratory COVID-19 syndrome showed the need of modern science in rapidly countering threats from emerging pathogens (Baker et al., 2022). To date, there are three different and concurrent strategies for managing infectious diseases: 1) controlling the sources of infection, 2) interrupting transmission routes, and 3) protecting susceptible people. Among these strategies, the COVID-19 case has emphasized the importance of the infection source control at the point-of-care (POC) level, i.e., in close proximity to patients (Wang et al., 2021). The required POC testing, defined as a smart strategy for real-time, rapid, accurate detection in the proximity of patient care, can be conducted at home or where patents are treated and supported by clinicians such as in hospitals and other healthcare environments. These locations, which includes three type of people, namely, staff, patients, and visitors, must be spaces where in clinicians and the medical equipment used can safely operate and, importantly, where patient must be preserved from additional risks (Suleyman et al., 2018). This latter point is a critical issues. Indeed, patients are vulnerable hosts due to immunosuppressive conditions, disruptions of their skin and mucous membranes, medications, and extremes of age. Moreover, the healthcare facility design, the multitude of life-saving invasive procedures involving complex equipment, the close proximity of patients who are carriers of transmissible microorganisms, and frequent contact with healthcare staff, who may themselves be transmitters of organisms, can provide an ideal environment for the propagation of infectious agents.
More in detail, the number and types of microorganisms present in the healthcare environment are influenced by several factors, including the number of people, degree of activity, the amount of moisture, the presence of material capable of supporting microbial growth, the rate at which airborne organisms are removed, and the type of surface and its orientation (i.e., horizontal or vertical) (Sehulster et al., 2003). Several nosocomial pathogens (such as Enterococcus, Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Acinetobacter, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas, Serratia, Shigella, Mycobacterium and Clostridium), have been shown to persist in the healthcare environment for several hours, days, or months, mostly on surfaces, and for hours on hands, with endospores typically lasting longer than vegetative bacteria (Kramer et al., 2006). These microorganisms are difficult to eradicate and serve as vehicles for transmission and spread in the hospital setting. In this way, cross-transmission of pathogens can occur via the hands of healthcare workers, who become contaminated directly from patient contact or indirectly by touching contaminated surfaces. Less commonly, a patient can be also colonized by direct contact with a contaminated environmental surface (Pittet et al., 2006). For these reasons, microorganisms in the healthcare environment must be detected on surfaces, in air and in water.
1.1 Surfaces
Environmental surfaces are defined as surfaces that do not come into direct contact with patients during care and are divided into two parts: medical equipment surfaces, such as knobs or handles on haemodialysis machines, X-ray machines, and instrument carts; and housekeeping surfaces such as floors, walls, and table tops (Suleyman et al., 2018). Although microbiologically contaminated surfaces can serve as reservoirs for potential pathogens, these surfaces are not generally associated with direct transmission of infection to either staff or patients. The transfer of microorganisms from environmental surfaces to patients is largely via hand contact with the surface (Sehulster et al., 2003).
1.2 Air
Exposure to airborne pathogens can cause respiratory infections either directly or indirectly. Direct transmission involves exposure to aerosolized droplets from oral or nasal secretions in infected individuals. These infectious particles are usually >5 μm in size and tend to fall out of the air quickly. Pathogenic microorganisms spread via direct transmission include influenza virus, rhinoviruses, adenoviruses, and respiratory syncytial virus (Suleyman et al., 2018). Indirect transmission involves the spread of airborne infections via droplet nuclei or residuals of droplets. When suspended in air, droplets desiccate and produce droplet nuclei or particles ranging from 1 to 5 μm in size that contain potentially viable microorganisms, remain suspended indefinitely in the air, and are dispersed over long distances by air currents. Examples of pathogens that can be spread via droplet nuclei include Mycobacterium tuberculosis, varicella-zoster virus, measles virus, and smallpox virus. The spores of Aspergillus, which resist desiccation, have a diameter of 2–3.5 μm, can remain airborne indefinitely, and travel long distance (Suleyman et al., 2018).
1.3 Water
Unsafe water supply affects human health, causing contagious diseases. Pathogenic microorganisms detected in the water samples of river, groundwater and drinking water can be categorised into bacteria (e.g., Salmonella typhi, Vibrio cholera and Shigella), viruses (e.g., Poliovirus) and protozoa (e.g., Giardia lambia and Cryptosporidium). Patients can be exposed to these pathogens through direct (hydrotherapy) and indirect contact (improperly reprocessed medical devices), ingestion and aspiration of contaminated water, and inhalation of aerosols dispersed from water sources. Hence, minimizing the exposure of deadly diseases is important by providing early warning detections on the presence of pathogens (Zulkifli et al., 2018).
In light of these considerations, an effective control of the infection source in healthcare facilities requires the early detection of environmental pathogens and calls for the development of rapid, sensitive and accurate detection methods. In this context, clinical microbiology diagnostic testing are traditionally relied to use time-consuming methods based on pathogen culture and identification or detection of specific antigens, antibodies or nucleic acids of infectious pathogens (Figure 1). (Wang et al., 2021) These times are too long to prevent the spread of microorganism and the evolution of pathogen diagnostic assays is moving from conventional cell culture-based techniques to modern immunological molecular diagnostics and now to biosensors (Tram et al., 2016). The transition to molecular methods such as PCR, isothermal amplification reaction, gene chip technology and high-throughput sequencing technology, has significantly improved the time to result, the sensitivity and the specificity; however, these methods show several limitations: first, nucleic acid extraction and purification steps in molecular diagnostic techniques are cumbersome. Second, most molecular diagnostic reagents require low-temperature transport and storage, which increases the cost of molecular diagnostics and hinders their application in remote or resource-limited areas. Finally, molecular diagnostic techniques such as qPCR, dPCR and sequencing are instrument-dependent, meaning that rapid on-site detection of pathogens can be difficult in resource-limited settings (Liu et al., 2023a). In this regards, the recent developments in nanotechnology have greatly influenced medical and analytical sciences to increase sensitivity, specificity and provide simple detection mechanism near patients, both inside the hospitals and away from healthcare facilities. In particular, nanomaterial-based biosensors show enhanced sensitivity, rapid response time and reduced cross-contamination issues (Fu et al., 2024). These advantages can potentially facilitate the construction of device for pathogens detection. In this context, an ideal device, should be simple and able to work with small volumes of biological, clinical, or chemical samples, to decrease the medical expenses, experimental steps, and analytical time. In the last decade, numerous techniques have been developed for the purpose of pathogen detection, but only a few have made it to the market for real-world applications. In addition, even more recently artificially intelligent (AI) technology has emerged as a focal point in medical image-based diagnostics and its application will revolutionize the interpretation and analysis of complex medical images. Several recent studies in medical diagnostics have emphasized the reduction times by integrating deep learning techniques (Ozyoruk et al., 2022; Vilar and Saiz, 2023). Lee et al. (2024) recently proposed an innovative and rapid deep learning-assisted predictive diagnostics that integrates a time-series deep learning architecture and AI-based verification, for the enhanced result analysis (Lee et al., 2024). This approach is applicable to both infectious diseases and non-infectious biomarkers and reduces assay time to just 1–2 min. In this review we would like to provide a systematic insight into the most recent, diffused and affordable nanotechnologies developed and still developing with the aim to increase the sensitivity, speed and accuracy of pathogens detection by POC testing in different environments, from intensive care units, to general wards, from medical waiting rooms to patients' homes. To this aim, the text comprises several sections each one focused on various types of nanomaterials and techniques actually employed in the most advanced nanobiosensors.
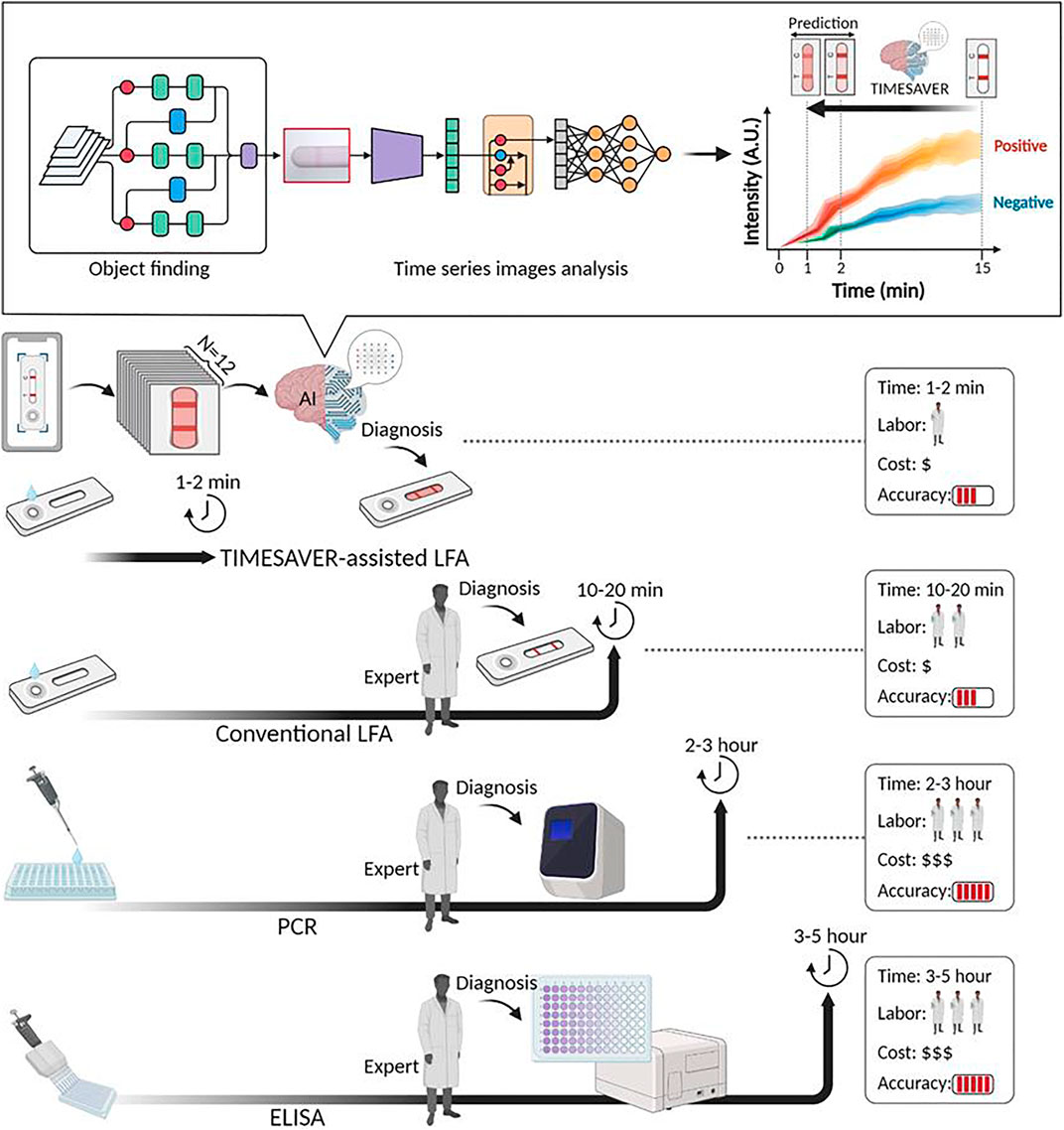
Figure 1. Schematic representation of Time-Efficient Immunoassay with Smart AI-based Verification (TIMESAVER) impact on commercialized diagnostic tools: LFA, PCR, ELISA along with their performance metrics, including time, labour, cost, and accuracy. Adapted from Ref (Lee et al., 2024). Copyright 2024@Springer Nature.
2 POC testing technologies
Specifically, the POC testing indicate a smart strategy for real-time, rapid, accurate detection in the proximity of patient care (Lippi et al., 2010). The World Health Organization (WHO) coined the acronym “ASSURED” in 2006 for the fundamental criterions of POC testing: Affordable, Sensitive, Specific, User-friendly, Rapid and robust, Equipment-free, and Deliverable to end user (Tram et al., 2016). Recently, the advancement of the digital age has led to a revision of the ASSURED criteria to REASSURED with the addition of two criteria: Real-time connectivity and Ease of specimen collection (Otoo and Schlappi, 2022). To emphasize the importance of these principles, it should be noted that the closer a POC test gets to meet the REASSURED criteria, the greater the chance to get a larger share of the POC market. Traditional infectious disease–related POC testing typically provides results in 15–20 min but even results available in <1 h from the time of specimen receipt are useful in patient management. The benefits of having results immediately available for patient care are obvious: a timely response can reduce patient anxiety, allow the provider to initiate appropriate therapy immediately if needed, and reduce the need for follow-up visits that add to patient burden and rising healthcare costs. Moreover, rapid testing results can ensure the optimal use of limited healthcare sources by determining which patients need to be in isolation due to potential transmissible pathogens and can play a significant role in interrupting a community-based transmission of pathogens (Samuel, 2020). Recently, the COVID-19 pandemic has intensified the development of POC tests for the diagnosis of pathogens infections, which have been globally used every day in hospitals, workplaces, airports, and people’s homes. Among various technologies on which these diagnostics are based at the moment, it is believed that only two technologies, namely, the microfluidic paper-based Analytical Devices (µPADs) and the Lateral Flow Assay (LFA) have the potential to meet all the REASSURED criteria.
2.1 Microfluidic paper-based analytical devices
Microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (µPADs) are powerful tools for POC testing, biosensing, environmental monitoring, and forensic investigations, since they are inexpensive devices fabricated in miniaturized sizes, ensuring better portability, lower cost and biological compatibility (Abdollahi-Aghdam et al., 2018). The µPADs have received rapid development over the last decade (Martinez et al., 2007). Like traditional microfluidic devices made from silicone, glass or polymers, paper-based microfluidic devices are portable, process small volumes of fluids, and can perform multiplexed assays. The capillary properties of paper provided by the cellulose network eliminate the necessity of pumping methods. In addition, they are simple to fabricate without cleanroom facilities, they are made from inexpensive and readily available materials, and do not require computer-controlled pumps to operate. These characteristics make paper-based microfluidics more accessible to researchers across disciplines and an ideal platform for the development of POC diagnostic tests (Abdollahi-Aghdam et al., 2018). Microfluidic paper-based analytical devices can be fabricated by using 2D or 3D methods, to transport fluids in both horizontal and vertical dimensions depending on complexity of the diagnostic application (Xia et al., 2016; Coluccio et al., 2020; Schilling et al., 2013; Chen et al., 2021). These devices can be associated with several detection methods such as fluorometric, electrochemical, chemiluminescence, and Raman spectroscopy, (Martinez et al., 2007; Kim et al., 2018a), even if the colorimetric technique is the most diffuse (Pradela-Filho et al., 2023).
A colorimetric sensor detects analytes through colour changes that can be visually observed (Figure 2). Paper is an excellent substrate for this type of detection due to its white background, contrasting with the colour appearance (Harpaz et al., 2020; Pradela-Filho et al., 2023). Different strategies can be applied for colour formation, including enzymatic reactions, redox indicators, nanoparticles formation, and acid/base indicators. The next step immediately after colour formation is the readout process, which can be done by the naked eye, especially considering qualitative tests with YES/NO output originated by a colour change due to the presence or absence of the analyte. It is also possible to perform quantitative data acquisition by constructing a calibration curve, where the colour intensity is proportional to the analytes concentration. In this case, office scanners or smartphones are required to digitize the images, which are processed in specialized software by decomposing the images into primary colours, known as RGB (red, green, blue), or secondary colours CMYK (cyan, magenta, yellow and black), among other systems (Davidson et al., 2021). The µPADs based on colorimetric detections are a good fit for POC tests regarding numerous applications, such as diabetes, (Pomili et al., 2021), pregnancy, (Rahbar et al., 2021), pathogens detections like human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), and SARS-CoV-2 for COVID-19 diagnosis, (Chowdury and Khalid, 2021), Escherichia coli (E. coli) infection (Sun et al., 2020).
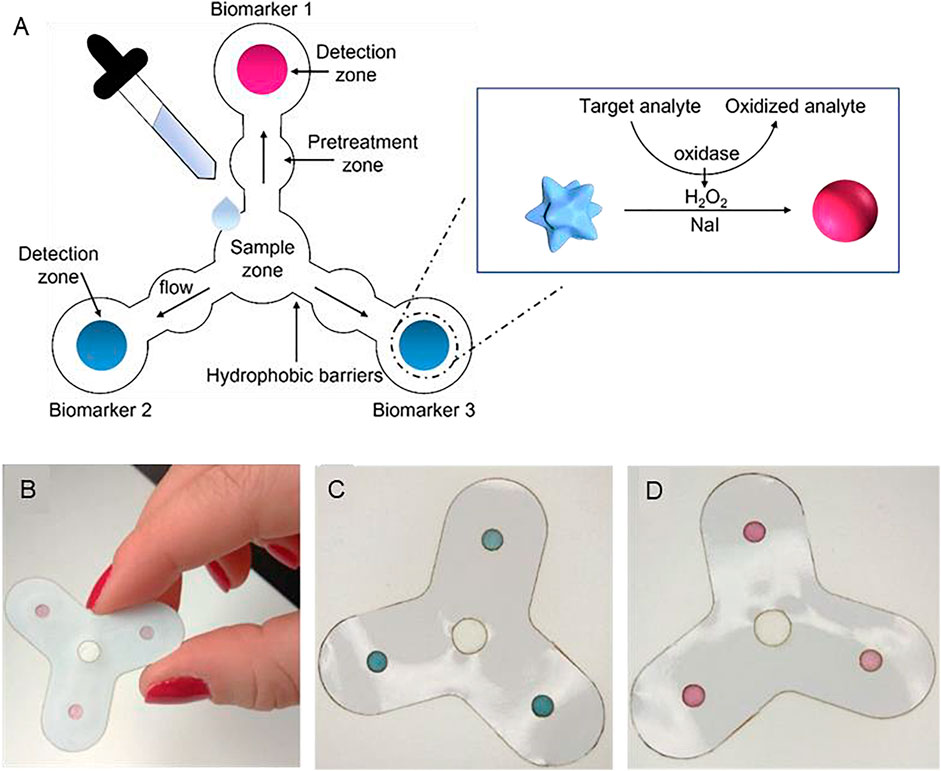
Figure 2. (A) Schematic illustration of a paper-based multiplexed colorimetric device for the simultaneous detection of salivary biomarkers. A drop of saliva deposited in the sample zone passes through the pre-treatment zones, where it is mixed with the deposited halogen (NaI), after which it reaches the detection zones with the blue suspension of MGNPs, functionalized with a layer of three oxidase enzymes, one for each sensing area. The inset shows the colorimetric detection strategy based on the colour change from blue to pink in presence of non-physiological levels of the target analyte. (B) Photograph of the final device embedded in the PVC mask. (C) Image of the device immediately after the deposition of the saliva sample and (D) after the duration of the test (10 min). Adapted from Ref (Pomili et al., 2021). Copyright 2021@MDPI Biosensors.
2.2 Lateral flow assay
Lateral flow assay (LFA) is one of the most commercialized POC testing method for detection and quantification of different analytes from a variety of biological samples: such as blood, urine and saliva. LFA offers in a simple manner, a one-step detection, without the need of washing steps and a relatively short development time, low-cost production, and low sample volume requirements (Naghdi et al., 2023; Omidfar et al., 2023). Most commercially available LFAs offer qualitative or semi-quantitative analyses and require dedicated tools for the quantitative analysis of biomarkers. Qualitative analysis refers to a screening or preliminary assay that defines the presence or absence of a target analyte in a sample. For example, in pregnancy tests, a simple binary readout is enough to indicate either a positive or negative result. Quantitative examination is the ability to determine the exact amount of the analyte in a sample environment and express it as a numerical value in appropriate units, which can be performed via the use of reader systems with simple operating procedures. Validation of analytical methods and qualitative analysis are required to achieve a reliable calibration curve (Wu et al., 2022a). As shown in Figure 3, LFA is composed of several elements: a sample pad, a conjugate pad, a reaction membrane (typically nitrocellulose) and an absorbent pad. All the components are assembled together supported by a plastic backing card. The liquid sample, containing the target analyte, is added to the sample pad and moves under capillary force through the overlapping area of the sample pad and conjugate pad, where a specific conjugate for the test has been immobilized, and then through the reaction membrane, with the test and control lines reagents. LFAs require a small sample volume to generate qualitative, semi-quantitative, or quantitative results within 5–15 min, which is often related to an optical signal produced at the test line (Nuntawong et al., 2022; Nan et al., 2023). Depending on the type of target analytes, there are different forms of detection: namely, sandwich and competitive detections.
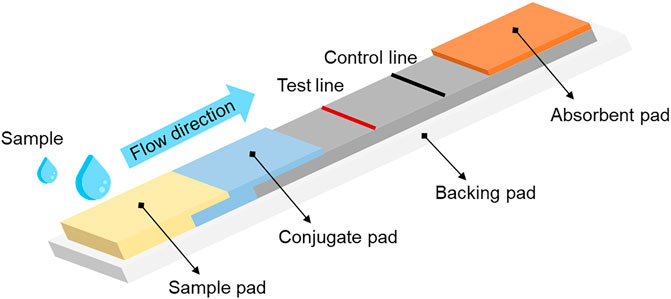
Figure 3. Basic architecture of a lateral flow assay (LFA) device, which includes a sample pad, a conjugate pad, a reaction membrane and an absorbent pad.
2.2.1 Sandwich immunoassay
The sandwich assay Figure 4A is the mainly used test for pathogens detection. In this device, the conjugate pad contains labelled conjugated antibodies. These antibodies will bind a specific epitope of the target analyte in the sample. After the conjugate pad, the sample moves towards the test line and the control line on the membrane. An antibody specific for another epitope of the analyte is applied to the test line and another antibody that captures the labelled conjugated antibody is applied to the control line. If there is analyte in the sample, it will be captured between the two antibodies, forming a sandwich and producing a positive signal in the test line. For this reason, this assay is only suitable for analytes with more than one binding site that can be captured by two antibodies at the same time. If no analyte is present, no signal is observed. Sandwich assays result in a signal intensity on the test line that is directly proportional to the amount of analyte present in the sample (Bahadır and Sezgintürk, 2016).
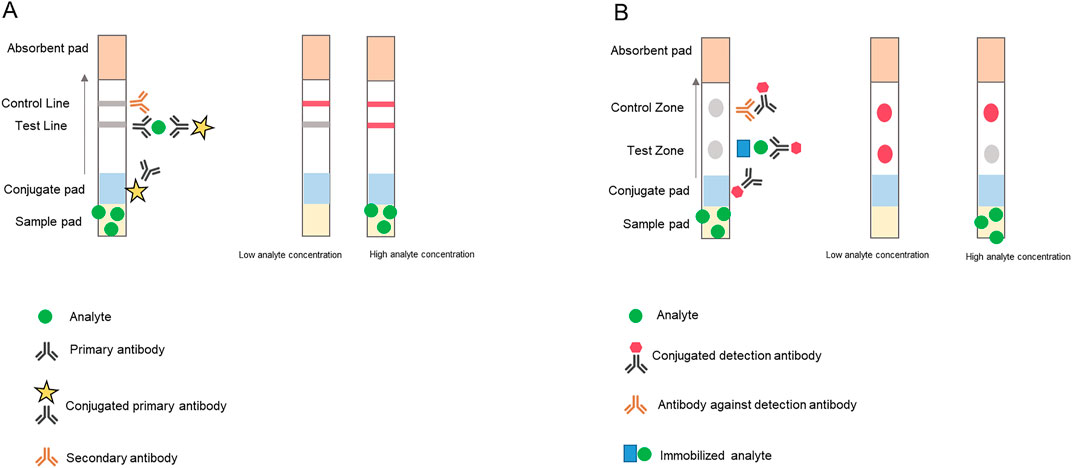
Figure 4. (A) Sandwich and (B) competitive architecture of the most common LFA devices. Sandwich assays is used for analytes with two antigen binding sites: if there is analyte in the sample, it will be captured between the two antibodies, forming a sandwich. The signal intensity on the test line is directly proportional to the amount of analyte in the sample. In the competitive format, the conjugate pad contains labeled test antibodies that bind to the analyte and move with the fluid flow, similar to a sandwich assay. But molecules on the test line contain a binding site that mimics the target, which means that only unbound labeled antibodies will be captured. As a result, an higher concentration of the analyte would result in a weaker signal at the test zone. The control zone contains capture antibodies that bind all labeled test antibodies, whether or not they are bound to the target. A line will appear regardless of the presence of the analyte. Adapted from Ref (Teerinen et al., 2014). Copyright 2014@Springer Nature.
2.2.2 Competitive immunoassay
In a competitive assay, the conjugate pad contains labelled antibodies that bind the target and move with the fluid flow, similar to a sandwich assay. However, the test line contains a molecule with a binding site that mimics the target, which means that only unbound labelled antibodies will be captured. As a result, the test line signal becomes more intense at lower concentrations of target molecule in the sample. On the other hand, the control zone contains specific capture antibodies that bind all labeled test antibodies, whether or not they are bound to the target. A line will appear regardless of the presence of the target in the sample, which signal intensity will be higher with increasing concentrations of the target (Figure 4B). There are two typical layouts of the competitive assay. In the first layout, the labelled molecule that is the same as the target analyte is coated on the conjugate pad. The primary antibody is coated at the test line while another antibody to the label molecule is dispensed. When the sample contains the analyte, it flows towards the test line with the labelled molecule. At the test line, the labelled molecule competes with the analyte in the sample. When the analyte in the sample is captured by the antibody first, the labelled molecule would not bind to the antibody. A higher concentration of the analyte in the sample would result in a weaker signal at the test line. In the second layout, the labelled antibody is immobilized on the conjugate pad. When the sample containing the analyte reaches the conjugate pad, the labelled antibody binds to the analyte. As the sample flows to the test line, there will be fewer labelled antibodies for the pre-immobilized analyte, resulting in a weaker signal at the test line (Nuntawong et al., 2022; Koczula and Gallotta, 2016).
2.2.3 Multiplex immunoassay
Multiplex LFA systems (Figure 5) have been studied for detecting multiple pathogens, with the advantage of saving time and samples compared to a single test. Multiplex detection can be performed on a single strip, on multiple strips, or on a microarray (Anfossi et al., 2019). In the single strip device multiple specific antibodies are immobilized in different positions on the strip, so different pathogens are captured by their specific antibodies and show their colours on their specific positions. Several individual strips can be arranged in a special holder, also designed as to collect one sample and distribute it between several strips or microarrays. The sample flows in parallel on each strip, which in turn can hold one or more test lines. The advantages of this approach rely on the large multiplexing capability and on the absence of reciprocal interference between assays that happen independently on individual strips. Indeed, each assay can be developed singularly and then put together, without requiring any further optimization (Anfossi et al., 2019; Hong et al., 2010).
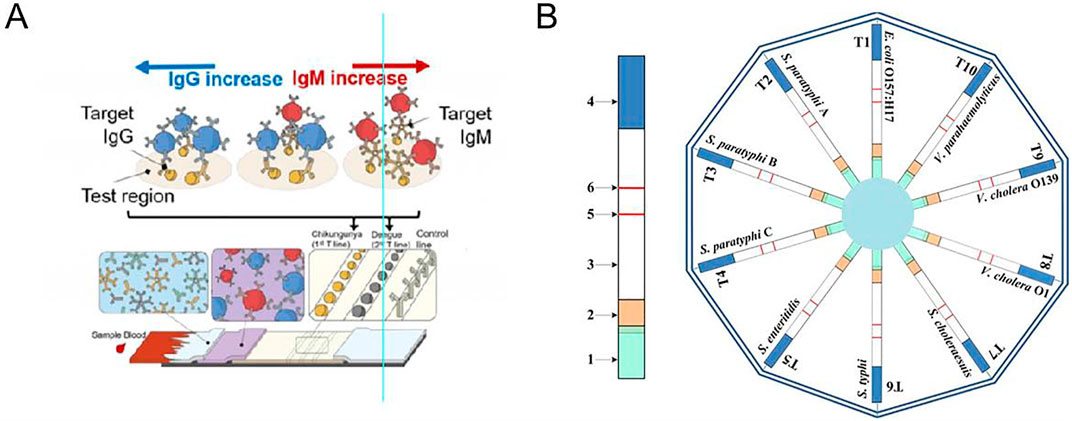
Figure 5. Devices for multiple pathogens detection: (A) multiplex detection format on one test strip. (B) Multiplex detection format on multiple test strips. Adapted from Ref (Nan et al., 2023). Copyright 2023 @ The Royal Society of Chemistry.
3 Nanotechnologies for POC testing
As described above, POC tests generate an optical signal from strongly coloured or luminescent motifs that are bound to test lines on a white nitrocellulose strip. This signal can be read by eye (qualitative or semi-quantitative) or by an optical reader (quantitative). To maximize the sensitivity of the test, each binding event between an analyte and the reporter luminescent label should produce the strongest signal possible. Several type of luminescent labels are actually employed, such as fluorescent conjugated dyes and colloidal semiconductor quantum dots, as well as larger metal nanoparticles and hybrid nanomaterials. These latter are usually relatively large system that typically provide a stronger signal per binding event, but their size must be limited to enable the easy flow through the nitrocellulose membrane maximizing the opportunity to bind to the test line. Thus, particles that are between 20 nm and 500 nm in diameter are typically selected for use in LFA.
3.1 Fluorescent conjugated dyes
Within the different types of the fluorescent reporters, organic fluorescent dyes are commonly used in commercial POC devices. The era of synthetic organic dyes commenced in 1871 with fluorescein and its more stable derivatives, such as fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) (Figure 6A), followed by rhodamine (tetramethyl rhodamine isothiocyanate, TRITC) (Figure 6B) dyes in 1887. The evolution has continued progressively with development of dyes exhibiting superior performance (Zeng et al., 2023; Sajid et al., 2015). These aromatic molecules are typically covalently bound or electrostatically attached to biological recognition elements, such as antibodies, to ensure stable, fast and strong response in a presence of a target (Fang et al., 2019). Conjugated dyes are able to provide low-cost rapid detection of biological targets with a high selectivity and sensitivity. Typically, these dyes exhibit bright emissions in dilute solutions, yet when present at high concentrations, they undergo aggregation-caused quenching. For example, Rhodamine 6G, among the most photostable traditional dyes available, can emit only approximately 106 photons before undergoing irreversible photobleaching, making it insufficient for long-term single-molecule fluorescence tracking.
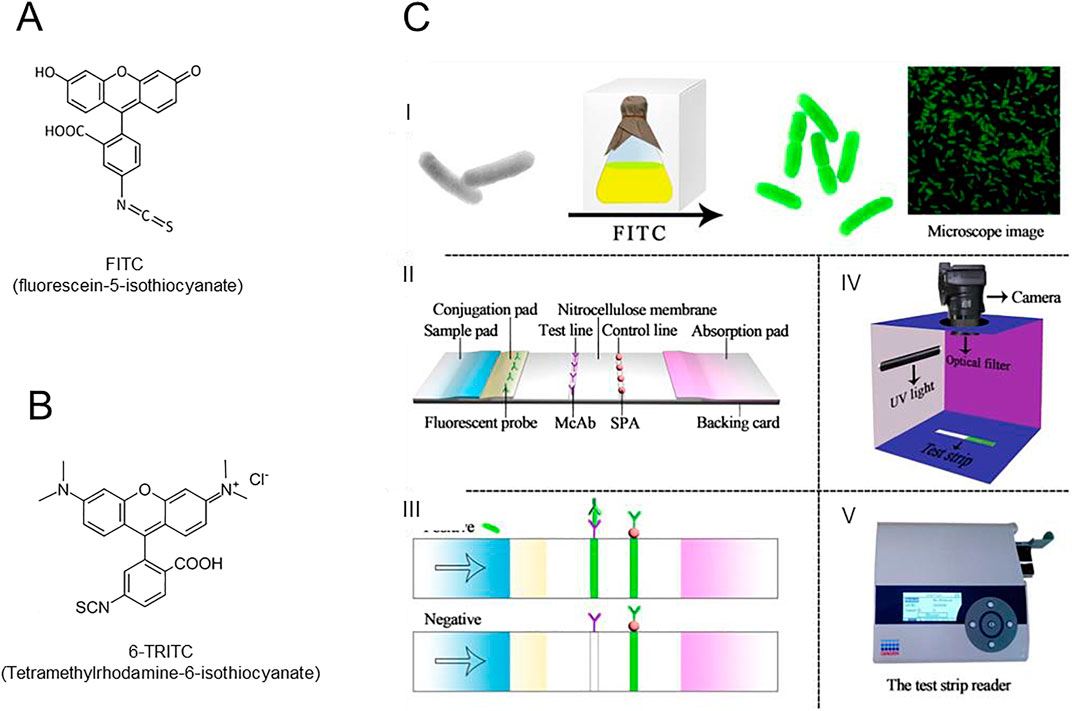
Figure 6. (A) structure of FITC (fluorescein-5-isothiocyanate); (B) structure of 6-TRITC (Tetramethylrhodamine-6-isothiocyanate; (C) Schematic diagram of the principle for the detection of E. coli O157:H7 and the typically results of the dual FITC LFA. Copyright 2016 @Elsevier.
Fluorescent organic dyes show versatility when used to detect presence of pathogens directly or indirectly. In the first case, synthetic organic fluorophore is attached to the negatively charged bacterial cell wall. Numerous works, including review papers, have been published over the years, highlighting the application of direct fluorescent labelling of pathogens for various techniques (Butcher and Weissman, 1980; Yoon et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2023b). Wang et al. (2016a) used direct fluorescent labeling strategy of some bacterial cells, including E. coli and Staphylococcus aureus (S.aureus), to get prompt fluorescence response for contaminated water and liquid samples (Wang et al., 2016a). In another work done by Guo et al. (2021), self-luminous bacteria were used as bifunctional probe for both selective recognition and fluorescent pathogen sensing in milk (Guo et al., 2021). Three common organic fluorescent dyes of HcM, FITC, and RhB were used to tag different bacteria before their inactivation and selective optical detection by multiplexed competitive immunosensor, which was complete within 10h. Indirect approach is considered more reliable for a rapid visual detection tests development. Examples of bioprobe which consists of an organic fluorophore unit and a biomarker target unit to detect bacteria are more common in the literature, since in the traditional POC approach the bioreceptor plays crucial role in effective sensitive recognition of the pathogens. Upon conjugation with bacterial target agent, these biosensors become powerful tool, providing faster and selective optical response with lower limits of detection. Already in 1993 Noriyuki et al. reported the development of a device for simultaneous detection (FITC conjugated with monoclonal antibody, Ab) and removal by bacterial magnetic particles (BMP) of E. coli microbial cells (Nakamura et al., 1993). In this work, it was demonstrated, how sedimentation of bacteria/FITC-Ab-BMP complexes, e.g., the increase in bacterial concentration, decreases the fluorescent signal coming from the synthetic fluorophore. In the early 2000s, alternatives to traditional dyes has been implemented and tested into the existing fluoroimmunoassays. Anderson and Nerurkar have explored the application of relatively novel for that time Alexa dye, as an alternative to Cy5 (Anderson and Nerurkar, 2002). In particular, Alexa Fluor 647 showed good performance as a fluorescent label for antibodies in sandwich immunoassay due to the limited quenching characteristics. In 2016 Song and co-workers reported a novel signal amplification LFIA for the detection of E. coli O157:H7 in food samples (Song et al., 2016). For the first time, FITC conjugated antibody detection system was introduced to LFIA system and was 10-fold more sensitive than nanogold-based analogue strip. The use of fluorescent proteins for the rapid pathogen detection has also been reported by several groups (Guk et al., 2024; Li et al., 2017).
One of the major limitations of conventional fluorescent molecules is that only a few or even one dye can be linked to a receptor, limiting the overall signal outcome. When compared to novel fluorescent inorganic/hybrid nanoparticles, traditional organic dyes in most of the cases lose out to brighter, more stable and better performing alternatives (Grazon et al., 2022). In order to improve stability by overcoming aggregation-induced quenching and increase the degree of labelling, common fluorescent dyes are supported by non-fluorescent carriers, with silica nanobeads and latex nanoparticles being the most used ones (Zhang et al., 2019a). Large surface-to-volume ratio of these nanocarriers facilitates the attachment of multiple dyes, thus making the labeling efficient. Moreover, beads in general play barrier role and protect photo and chemosensitive organic fluorophores from the surrounding environment, thus minimizing degradation and photobleaching (Yan et al., 2007). These dye-loaded nanoparticles can be fine-tuned by adjusting both the particle size and the concentration of loaded dyes. Moreover, the surface properties of these nanoparticles can be manipulated by chemically incorporating functional groups (Yan et al., 2007; Ananda et al., 2021; Sifana et al., 2024; Ge et al., 2021; Montalti et al., 2014). To give an example, LFA-based sensor where FITC and Ry(bpy)-doped silica nanoparticles were used to detect bacterial pathogens Salmonella spp. and E. coli O157 (Rajendran et al., 2014).
Moreover, various fluorophores can be incorporated into the polymer matrix, to achieve the final dye-loaded latex particle which exhibits good dispersion and stability, as well as high fluorescence intensities (Pellach et al., 2012; Liu et al., 2009). Development of PS (polystyrene nanobeads)-based probe for the rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 was reported by S.E. Seo and his team (Seo et al., 2023). They used the swelling-shrinking method to encapsulate large Stokes shift fluorophore Single Benzene (SB) within the matrix of carboxyl-functionalized PS bead and further conjugated SB@PS by EDC-NHS coupling with antibody. LFA strips based on the newly developed fluorescent probe for the detection of COVID-19 showed limit of detection values hundred times lower than the AuNP-based LFA under the same conditions. Some other examples of dye carriers are also available, since the research is in constant development (Pashazadeh-Panahi et al., 2021; Larsen and Wojtas, 2017). For all of the above mentioned examples of nanosupports, the actual degree of labeling will vary depending on the specific conjugation/encapsulation method and conditions, on the properties of the carrier and the organic dye itself. Properties can be tuned to increase sensitivity and signal intensity for various diagnostic applications.
In conclusion, fluorescent dyes are still frequently incorporated in the standard POC devices and in particular in LFA screening tests, although they have certain drawbacks, because of their practicality, particularly their ease of conjugation, availability in a wide range of colors and compatibility with different detection systems (Figure 6C). To name several frequently used fluorophores, commercial Alexa®, eFluor®, Dylight® and several other families of labels from the main chemical product suppliers are available for purchase. Moreover, some of them are provided in a “ready-to-use” conjugated state with antibodies and other bioreceptors and can be tailored by manufacturer upon request for a specific application.
3.2 Colloidal semiconductor quantum dots
QDs are semiconductor nanostructures, having unique optical and electronic properties as they have a small size along with a high surface area, and they show interesting phenomena such as a narrow emission peak, size-dependent emission wavelength, and broad excitation range (Ubbelohde et al., 2012). As the sensitivity of QDs detection is higher than that in other organic dyes, they have become attractive fluorophores, thus facilitating cellular imaging and quantitative cellular analysis with the help of other fluorescent probes. In addition, their surface modification is easily achievable (Singh et al., 2020). The advantages for using QDs over fluorescent dyes includes basically higher photostability and size-tunable fluorescence emission. The QDs based sensors are easy to use, give rapid result and are portable as compared to laboratory-based tests. Generally, colloidal gold is used in the LFA tests but due to the limited sensitivity and cost, QD-based LFA tests are developed which are economical, are highly sensitive and gives the rapid result apart from the other advantages it has as mentioned earlier (Yang et al., 2010). The use of QDs as a reporter in sandwich LFAs requires two antibodies wherein both the conjugate and capture antibodies are specific to the target of interest. Conjugate antibodies labelled with QDs are immobilised on the conjugate pad to enable measurable fluorescence detection. Meanwhile, on a nitrocellulose membrane, capture antibodies are immobilised to capture the target of interest, forming the QD-labelled antibody–target–antibody complex. This complex produces a bright fluorescent band in response to ultraviolet excitation. Similarly, QDs can also be used in competitive LFAs format by functionalising the nanoparticles with reaction antibodies or analytes on the conjugate pad (Uzhytchak et al., 2020).
For example, Yang et al. (2010) described the development of a novel fluorescent POC test method suitable for the rapid on-the site screening of syphilis. The method was designed to combine the rapidness of LFA and sensitiveness of fluorescence-based methods (Yang et al., 2010). QDs can also be employed as reporters in fluorescence immunochromatographic assays in order to enhance their sensitivity and specificity. The rapid and accurate detection of biomarkers, such as antigens and proteins, in body fluids is very important for clinical diagnosis and treatment programs. In this context Cheng et al. (2014) described the QD and immunochromatographic test strips assay for the rapid and quantitative detection of C-reactive protein (CRP) which is the inflammation marker and helps in the risk assessment of the cardiovascular diseases. Similarly, Zhou et al. (2019) described the faster QDs POC fluorescence immunoassay detection method for high-sensitivity cardiac troponin (Zhou et al., 2019). A QD-LFA device based on a double-antibody sandwich format labelled with core–shell quantum dots (CdSe/ZnS) coupled with streptavidin was developed for the detection of M. tuberculosis fprA proteins (Cimaglia et al., 2012). Li et al. (2012) demonstrated a novel method for detecting avian influenza virus (AIV) using highly luminescent quantum dots as a signal probe.
3.3 Noble metals and metal-oxide nanoparticles
Noble metals nanoparticles (NMNPs) have been used for POC testing for decades. When illuminated with specific wavelengths, they undergo coherent oscillations of surface electrons, a phenomenon known as localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) (Sardar et al., 2009). Moreover, the plasmon state can decay via radiative and non-radiative pathways, providing an enhancement of the electric field in the near-field regime or leading to particle heating. The light scattering properties of NMNPs allow their extensive exploitation as colorimetric, LSPR or surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) contrast agents, (Wang et al., 2021; Bouzin et al., 2015; Nasrollahpour and Khalilzadeh, 2024; Usman et al., 2023), while their non-radiative relaxation, resulting in the release of thermal energy, provides phothermal-based pathogen detection and eradication. Plasmonic-based biosensors represent an advanced technology that enables the miniaturization of biosensors, thus improving detection throughput and reducing operational costs by exploiting the plasmon properties of NMNP (Park et al., 2022). The most known example might be the lateral flow assay where gold NPs are usually utilized as colorimetric label (Quesada-González and Merkoçi, 2015). Over-the-counter pregnancy tests and the recent COVID-19 antigen rapid tests are representative examples of the LFA where gold NPs (AuNP) are used. Notably, the detectable signal from NMNPs can be fine-tuned and optimized by controlling their physicochemical parameters, such as size, shape and elemental composition, therefore in recent years, other nano-biosensors based NMNPs, including silver (Ag), platinum (Pt), palladium (Pd), rhodium (Rh), iridium (Ir), and ruthenium (Ru) have emerged as a class of effective and versatile POC testing technology (Luciano et al., 2022).
3.3.1 Gold NP for colorimetric detection
The core mechanism underlying the construction of colorimetric strategies based on AuNPs primarily depends on distance-dependent LSPR energy with ultimately set the optical absorption properties of the NPs and therefore the naked eyes observed colour (Sardar et al., 2009). Usually, a color change is due to a redshift in the UV-Vis spectrum following variations in the microenvironment conditions that can trigger NP aggregation or dispersion, thus artificially modulating the size of the NPs, that move from a dispersed population to and aggregate form showing a different absorption wavelength of the LSPR mode.
By exploiting the colour change as the analytical signal in response to an external stimulus-induced aggregation and their excellent biocompatibility, colorimetric biosensors based on AuNPs have been used for various types of pathogen detection (Yang et al., 2023; Aithal et al., 2022; Martinez-Liu et al., 2022; Xue et al., 2022; Zheng et al., 2018; Geng et al., 2022; Gopal et al., 2022). Moreover, beside simple electrostatic interactions, AuNPs can be effectively functionalized with biomolecules to improve their labeling selectivity (Yang et al., 2023). For example, antibody-AuNP bioconjugates and aptamer-modified probes are extensively used in pathogen detection, primarily for E. coli, S. aureus, and Salmonella typhimurium (S. typhimurium) (Yang et al., 2023; Abbas et al., 2023) Paper-based devices can be therefore designed to exploit the rapid and simple application of colorimetric detection. For example, Ju et al. developed p-mercaptophenylboronic acid-modified AuNPs to establish a new capture-antibody-independent LFA method for bacteria detection (Wu et al., 2022b) with an excellent linear response range. Shafiee et al. (2015) created an ultrasensitive device for detecting E. coli and S. aureus. Here, AuNPs were functionalized with various recognition agents, resulting in a color transition following aggregation due to bacteria binding. Moreover, multiplexing and sensitivity were demonstrated as both E. coli and S. aureus were tested simultaneously, resulting in color changes specific to the binding agents present in the solution (Zheng et al., 2019). Recently, Somvanshi et al. (2022) reported the simultaneous detection of E. coli O157:H7 and S. typhimurium in a paper-based microfluidic device, (Zhang et al., 2022; Lee et al., 2023; Baker et al., 2020), where aptamer-decorated AuNPs were attached to the surface of polystyrene microparticles to enhance the stability and sensitivity of the colorimetric system. The LFAs methods have been lately developed to detect also SARS-CoV-2 antigens, as well as IgG and IgM antibodies specific to the virus. (Kim et al., 2021; Lee et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2021; Zou et al., 2021; Lew et al., 2021; Spicuzza et al., 2023; He et al., 2023; Huang et al., 2020). The SARS-CoV-2 nucleoprotein was immobilized on an analytical membrane to capture samples, while anti-human IgM was labeled with AuNPs to serve as the detection reporter. Further optimized colorimetric LFAs enable to achieve a detection accuracy of 100% for 19 clinical samples (Cavalera et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2022; Lee et al., 2023).
3.3.2 SPR-based detection
The SPR has been widely exploited for detecting viruses and bacteria (Nath et al., 2020; Singh, 2017; Soler et al., 2019; Park et al., 2022; Abbas et al., 2023; Wen et al., 2022). The plasmon is generated by an evanescent wave formed at the interface between two dielectric surfaces with differing refractive indices. SPR biosensors generally utilize a thin metal film—commonly gold, silver, or aluminum—onto which biorecognition elements such as antibodies or aptamers are attached (Nath et al., 2020; Nguyen et al., 2015). When pathogens bind to the recognition elements on the metal surface, the refractive index of the medium changes, altering the propagation of the surface plasmons. This change in refractive index is detected by either monitoring the shift in the resonance angle or the excitation wavelength shift (Yesudasu et al., 2021; Shrivastav et al., 2021). When metallic nanostructures are incorporated in these biosensors, a LSPR is obtained (Soler et al., 2019). In this case, the extinction wavelength peak is monitored to detect changes in the refractive index at the nanoparticle surface.
The development of optical biosensor chips based on SPR and LSPR for POC devices is attracting considerable interest, because they are label-free biosensing techniques offering real-time operation, robustness, precision, and high sensitivity (Masson, 2020; Sharafeldin and Davis, 2021; Rasheed et al., 2024) for detection of bacteria, (Wang S. et al., 2016; Tokel et al., 2015; Yoo et al., 2015; Maphanga et al., 2023; Özgür et al., 2020; Hyeon et al., 2021; Pardoux et al., 2019; Erdem et al., 2019), viruses, (Yoo et al., 2020; Qatamin et al., 2019; Nguyen et al., 2016; Huang et al., 2024; Lee et al., 2019; Omar et al., 2019; Qiu et al., 2020; Jahanshahi et al., 2014; Omar et al., 2020; Vázquez-Guardado et al., 2021), and fungi (Stoia et al., 2024). For example, Gür et al. (2019) developed an SPR nanosensor using AuNPs for the rapid and sensitive detection of E. coli exploiting Cu(II) ions to provide interaction between bacterial cell wall and amine functionalized AuNPs. As an alternative to metals, Kaushik et al. used a molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) functionalized fiber optic SPR immunosensor for sensitive detection of E. coli. They successfully achieved rapid (15-min) bacteria quantification.
Numerous articles have been recently published about the SPR-Based sensors for Early Screening of SARS-CoV2 (Basso et al., 2021; Liang et al., 2022; Cady et al., 2021; Fendi et al., 2023) and other viral Infection such as HIV, (Sarcina et al., 2021; Li et al., 2019; Diao et al., 2018), Hepatitis B, (Riedel et al., 2016; Choi et al., 2014), and avian influenza virus (AIV) H5N1detection (Bai et al., 2012; Estmer Nilsson et al., 2010; Zhao et al., 2016a; Shrivastav et al., 2021; Lepage et al., 2013). For example, Bai et al. reported the development of an SPR-based biosensor for the detection of avian influenza virus (Bai et al., 2012). The sensing device was obtained by means of streptavidin–biotin binding by immobilizing biotinylated aptamer over a streptavidin-coated gold surface. Regarding SARS-CoV-2 detection, Bong et al. (2020) developed a gold-based SPR sensor fabricated by binding antibodies on the gold chip sensor, which was the base of the SPR platform. Yano et al. (2022) reported a nanoparticle-enhanced SPR sensing of SARS-CoV-2 N protein at fM levels by exploiting 150 nm diameter AuNPs. These NPs exhibited a detection sensitivity a full order of magnitude higher than those commonly exploited for SARS-CoV-2 N protein.
3.3.3 NMNP for SERS-based detection
Thanks to last decade effective miniaturization and optimization of electronic and optical components to fabricates compact devices, the development of optical biosensor chips based on SPR and LSPR for POC devices is now attracting considerable interest, because they offer real-time operation, precision, and high sensitivity for detection of pathogens (Murugan et al., 2020). In particular, SERS has gained significant attention in pathogen detection and identification, mostly due to its high sensitivity, high resolution, rapid data acquisition, and spectroscopic fingerprinting capabilities (Beeram et al., 2023; Usman et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2023c; Zhou et al., 2020; Tan et al., 2023; Hang et al., 2024). The SERS typically leverages localized LSPR in metallic nanostructures to significantly amplify the weak Raman signal to overcome sensitivity limitations found in conventional optical measurement methods (Zhou et al., 2020; Le Ru et al., 2007; Sharma et al., 2012). The enhancement primarily arises from two mechanisms: electromagnetic enhancement and chemical enhancement (Pilot et al., 2019). The first includes two key components, namely, LSPR and hot spots, while the second occurs due to charge-transfer mechanisms between the NPs and the analyte. The SERS efficiency is influenced by several factors such as the type of plasmonic material, choice of wavelength, surface coverage of molecules, and concentration of the analyte (Le Ru et al., 2007). Noble metals such as gold, silver and copper, along with their alloys, are commonly used in SERS due to the tunability of their LSPR in the visible and IR regions, inertness, sensitivity (Sharma et al., 2012; Li et al., 2023a). Detection methods can be categorized into label-free and label-based approaches (Ng et al., 2017; Grubisha et al., 2003). In label-based SERS bioassays, signal amplification is achieved using Raman reporter-labeled SERS nanotags as optical labels, which generate strong plasmonic signals (Cheng et al., 2017). In contrast, the label-free approach directly analyzes the SERS signals emitted by the target molecules without using SERS nanotags (Liu et al., 2017). Then, a statistical method, such as chemometrics or machine learning, is employed to analyze the data (dos Santos et al., 2023). A recently developed SERS-based test platform has demonstrated significant potential for pathogen detection. Zhang et al. (2015) successfully differentiated between two types of bacteria, S. typhimurium and S. aureus, using gold nanoparticles modified with specific aptamers for each pathogen. Additionally, different bacterial species such as S. typhi, E. coli, and L. mono were identified using SERS with Fe3O4@Au nanoparticles in real-world samples, including saliva and urine (Zhou et al., 2021).
Evolved SERS-based LFA strip devices have been specifically developed for POC applications, (Tran et al., 2019), exploiting Raman reporter-labeled gold nanoparticles as SERS nanotags instead of conventional AuNPs. This approach not only confirms the presence of the target analyte through the color change on the test line but also allows for quantitative analysis based on the intensity of the SERS signal, resulting in devices with enhanced sensitivity (Chen et al., 2020; Yu et al., 2024). Moreover, Chen et al. (2024) created a SERS-based LFA device for the simultaneous detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and E. coli O157:H7 using magnetic nanoparticles coated with a rough gold shell, demonstrating excellent specificity and reproducibility. Furthermore, to enhance the sensitivity of the SERS-LFA strip, Huang et al. (2023) took advantage of nanomaterials composed of three metals (Huang et al., 2023) to synthesize urchin-shaped Au–Ag@Pt nanoparticles, used as SERS nanotags. The authors were able to simultaneously detect three types of bacteria (E. coli, S. aureus, and P. aeruginosa) in blood, demonstrating also the utility of the synthesized nanoparticles for colorimetric, photothermal and catalytic applications in LFA assays.
3.3.4 Nanomaterials for photothermal-based pathogen detection
Significant progress has been made in developing sophisticated photothermometric detection techniques (Wang et al., 2021; Wei et al., 2021; Sarathkumar et al., 2023; Gu et al., 2024). Despite the advancements in a variety of colorimetric, fluorescent, and electrochemical sensors for diagnosing diseases, managing health, and monitoring the environment, these conventional methods often exhibit significant drawbacks, such as high background noise, stringent timing and spatial requirements, complex procedures, and high expenses, which considerably restrict their practical use. As an alternative, the use of photothermometric sensors employing various photothermal materials has shown promise in overcoming these limitations. These sensors are advantageous because they are portable, cost-effective, offer high resolution, and provide precise control over time and space, paving the way for broader applications and positioning them at the cutting edge of POC testing for various analytes. Moreover, photothermal signals, which can be generated with just a visible or near-infrared (NIR) laser and a simple temperature measuring device, are both affordable and straightforward, making them ideal for home self-testing and use in resource-limited settings (Sarathkumar et al., 2023; Cui et al., 2023; Dediu et al., 2023).
Recently, many LFA detection systems have harnessed the thermal responsiveness of tracer AuNPs to external stimuli (Pengcheng et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2019b; Pisetsky et al., 2024) enhancing the detection sensitivity of commercial devices for pathogens like influenza A, malaria, and Clostridium difficile (Song et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2019b) Qin et al. achieved a substantial increase in the sensitivity of AuNP-based LFA by exploiting thermal contrast for detection with provided a sensitivity ca. 30 times higher than that of traditional colorimetric detection. It was demonstrated that the LFA sensitivity could be boosted by up to 104 times by incorporating nanostructures such as Au nanorods, which are characterized by superior light-to-heat conversion capabilities (Qin et al., 2012). Indeed, the photothermal behavior of these nanomaterials depends on their shape, which can be modified though multiple synthesis techniques (Cui et al., 2023; Wei et al., 2021; Li et al., 2023b). Branched Au nanostructures, which exhibit higher photothermal activity compared to spherical nanoparticles, have been shown to enhance multimodal capabilities for precise and quantitative diagnostics (Wu et al., 2023). Thus, NMNPs and nanostructures can be used as effective multifunctional labels with colorimetric, Raman, and photothermal properties. For example, a dual-function nano-plasmonic and photothermal method was crafted by Qiu et al. (2020) for the detection of the SARS-CoV-2 virus protein and other viruses. This method used Au nanoislands functionalized with complementary DNA gene receptors to selectively detect the SARS-CoV-2 virus gene sequence through in situ nucleic acid hybridization, triggered by the heat generated from the Au nanoislands. This sensing prototype is based on LSRP and photothermal effects.
Notably, the temperature readout has also been converted into other detectable signals like pressure, fluorescence, resistance, and bioluminescence to improve the selectivity and sensitivity of pathogen detection (Su et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2022; Li et al., 2022). For example, Kim et al. (2018b) developed a straightforward sensing platform for sensitive and selective bacteria detection by taking advantage of the bioluminescence from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) mediated by Au NRs-photothermal lysis (Kim et al., 2018b). Moreover, nanoparticle heating induced by laser can lead to rapid thermal contraction and expansion of the surrounding medium, generating acoustic signals. Zhao and colleagues exploited this photoacoustic signal to develop an LFA strip based on AuNPs for highly sensitive detection of cryptococcal antigen, reaching low noise and strong signal despite the requirement of a sophisticated expensive equipment (Zhao et al., 2016b).
Besides NMNPs, other type of inorganic nanomaterials with excellent photothermal effects have been developed and optimized to improve the selectivity and sensitivity for pathogen detection (Wei et al., 2021; Ghosh et al., 2022). Magnetic nanomaterials such as iron oxide nanoparticles have recently been proposed for photothermometric sensing platforms since they can effectively convert light energy into heat energy. Zhang et al. (2018) introduced a photothermal detection technique using immunomagnetic nanomaterials for the efficient identification of S. typhimurium (Zhang et al., 2018). Leveraging the advantages of antibodies and thermal detectors, this photothermometric sensor demonstrated high sensitivity and excellent specificity for detecting targeted pathogenic bacteria, simplifying the operational steps and reducing the analysis time. Moreover, inorganic composites exploiting QD and metal compounds have been proposed to construct thermometric assays. For instance, Wang et al. demonstrated that Fe3O4-CuS nanostructures possess a robust capability to capture bacteria and generate an exceptionally strong photothermal effect for signaling their presence (Dong et al., 2018). Building on this result, they developed a photothermal immunoassay strip with a dual-signal readout, which enabled highly sensitive detection of E. coli. Recently, new 2D nanomaterials have attracted increasing interest due to their distinctive physical, chemical and biological properties (Ma et al., 2020; Dong et al., 2018). Transition metal sulfide nanomaterials, notable for their extensive surface area and robust photothermal effects, have shown considerable promise across various rapid detection techniques (Liu et al., 2023d). In particular, photothermal lateral flow immunoassays based MoS2 have been developed for identifying S. typhimurium, offering both color and temperature readouts (Lu et al., 2021; Du et al., 2020). Additionally, a photothermal LFA based on rhenium diselenide (ReSe2) nanosheets was integrated with a smartphone, a portable laser, and a thermal imager to devise a comprehensive, point-of-care device. This device efficiently detects human anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein IgG antibodies with the thermal signal sensitivity being 108 times greater than that of the colorimetric signal, demonstrating the device utility, characterized by its low cost, ease of use, and versatility (Figure 7). Importantly, to address the diverse requirements of POC testing that rely on photothermal readouts, there is growing interest in exploiting inorganic photothermal composites to develop multifunctional platforms. These platforms are designed not only to detect but also to efficiently eradicate pathogenic bacteria. Indeed, recent advancements have concentrated on creating plasmonic metals and hybrid inorganic nanostructures for antimicrobial purposes by capitalizing on the photothermal effect (Huo et al., 2021; Yan et al., 2023; Lin et al., 2023; Santos et al., 2016; Santos et al., 2016; Ray et al., 2012; Zhao et al., 2023; Grisoli et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2023d). This approach successfully contributed to inactivate a wide array of bacterial strains by generating heat that disrupts cellular membranes, inactivates proteins and leads to photothermal ablation.
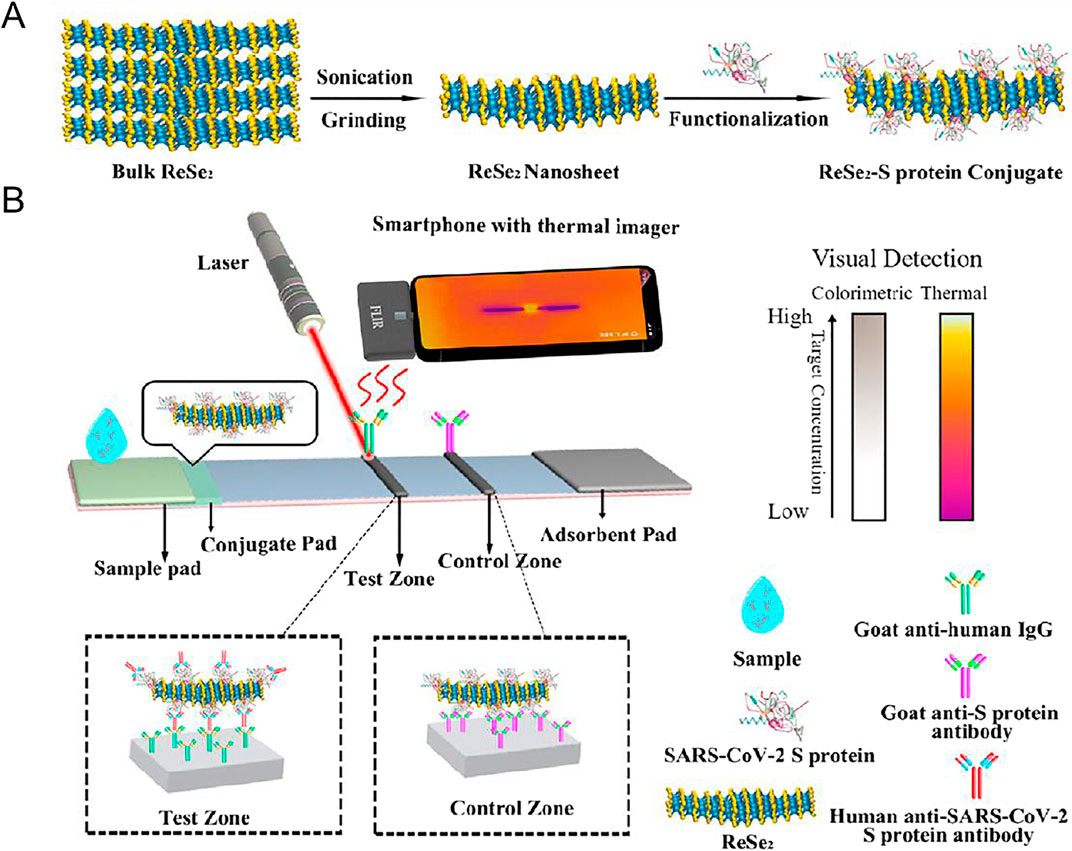
Figure 7. (A) Schematic representation of preparation of ReSe2 nanosheet fuunctionalized with SARS-CoV-2 S protein; (B) detection scheme of photothermal LFA for SARS-CoV-2. Adapted from Ref (Grisoli et al., 2021). Copyright@2023American Chemical Society.
4 Conclusion and perspectives
To summarize, here we reviewed the integration of nanotechnologies and pathogens detection in POC devices, pointing out how the unique physicochemical properties of nanoparticles have led to the development of all nanobiosensors discussed. In the Table 1 we summarize the most representative type of nanomaterials and their technological application in biosensors actually employed. The application of nanotechnologies to the production of POC brings several advantages such as increased sensitivity, miniaturization, multiplexing capabilities, improved specificity, enhanced imaging and visualization, and paves the way to personalized medicine. Importantly, the recent global pandemic has clearly highlighted the need to develop miniaturized diagnostic devices that can be used at home by a non-technical operator and, at the same time, as control devices in hospital environments at risk of contamination from pathogens. This approach would be indeed crucial in supporting the healthcare system in containing infections and allowing for immediate clinical decision-making. The application of POC devices, selected ad hoc to quickly detect the most widespread pathogens in hospital settings and potentially dangerous to the health of patients, companions and staff, could become a daily routine on a par with the cleaning and disinfection of environments and equipment. In this way, the control of contamination and the spread of pathogens can be effectively guaranteed. Although traditional methods for detecting pathogens could exhibit adequate sensitivity, their speed, flexibility and costs fall short of effectively addressing a significant outbreak. The POC approach appears at the sole strategy able to handle such situations quickly and with operative demands on a large scale. Even if further studies are still ongoing to ensure the accuracy and the reliability of nanobiosensors in agreement with regulatory agency demands for hospital validation, only the successful integration of nanotechnologies and their properties can be a real resource for the design of efficient, yet easy-to-use pathogen detection and identification tests for clinical environment surveillance with POC devices. Based on the reviewed literature and considering the quick technological advancement required for application, among the various types of nanotechnologies and systems used for the development of POC tests, multiplex LFA systems is probably be the most convenient choice to efficiently detect numerous pathogens simultaneously. These devices are easy to use and show results very quickly. They are made of FDA approved materials and ensure greater sensitivity and accuracy. Indeed, the few commercially-available POC assays based on nanotechnologies are based on LFA to detect coronaviruses specific antigens or antibodies, (Hou et al., 2023), because this platform effectively allows to respect the ASSURED criteria described above.
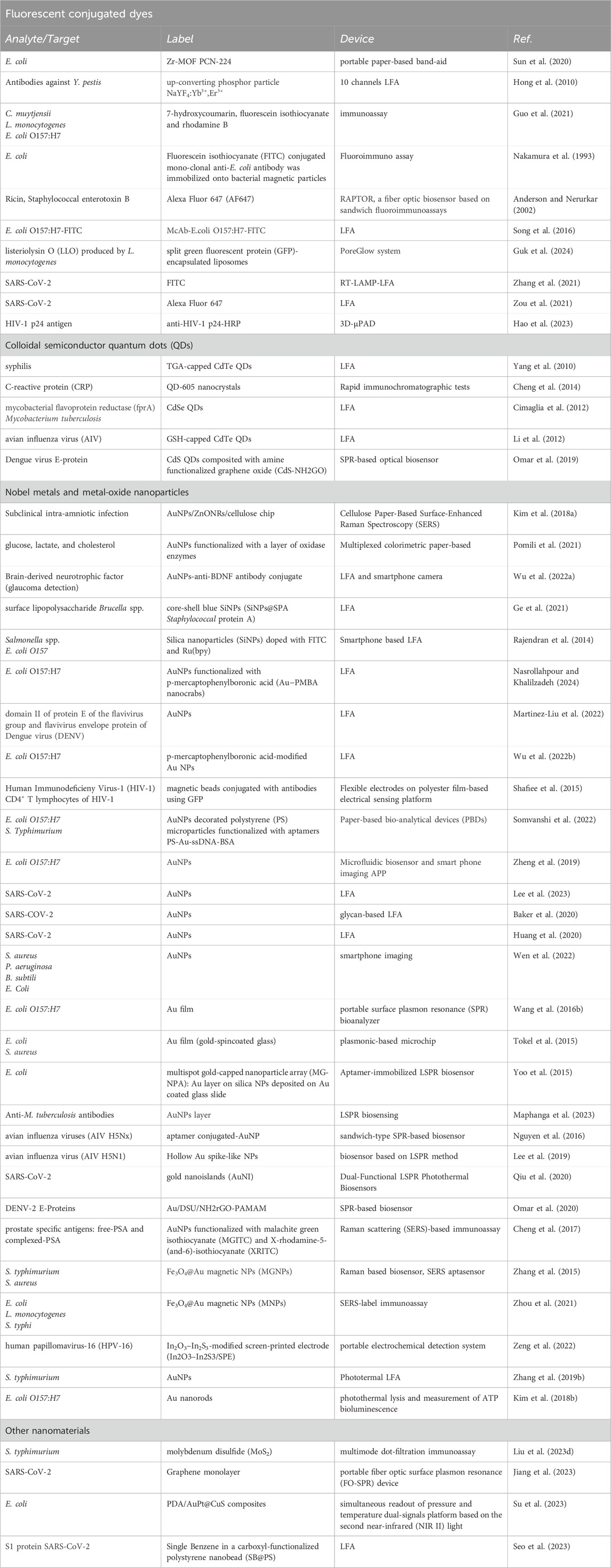
Table 1. Representative type of nanomaterials and their technological application in biosensors currently employed in nanobiosensors.
These devices, as well as other well-known traditional POC assays such as glucometers based on electrochemistry, could in principle be improved to discriminate simultaneously or with greater sensitivity between different pathogens or analytes using dedicated nanotechnology as described above. However, there are still some shortcomings that need to be addressed in real-world applications; for example, some devices only work with buffers and certain environments, not in and not in real samples, and signal readout requires special equipment. Some platforms focus on sensitivity and accuracy while showing very poor versatility to adapt to other different analytes. In some cases, simplicity is also neglected, where still too sophisticated approaches are required or where multiple analysis targets result in complex redout data matrices that are difficult to recognize and, most importantly, can generate false-positive results. For these reasons, only a few platforms have reached the preclinical stage to test real samples. Much effort is still needed to achieve clinically approved devices that can be operated by different people in different environments with a sufficiently high degree of reproducibility to obtain a real, widely used POC device. Therefore, research in this field must focus not only on finding new proof-of-principle materials and nanotechnology applications, but also, with the help of clinicians and engineers, must point out new strategies and designs to realize practical platforms suitable for the clinical setting.
Author contributions
VS: Data curation, Investigation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. AA: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. LB: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. AB: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. AC: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. SF: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. EK: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. RL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Supervision, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. LM: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. HM: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. AP: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Supervision, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. AR: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. GT: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. FT: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. MC: Validation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision. LS: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. AM: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was funded by the National Plan for NRRP Complementary Investments (PNC, established with the decree-law 6 May 2021, n. 59, converted by law n. 101 of 2021) in the call for the funding of research initiatives for technologies and innovative trajectories in the health and care sectors (Directorial Decree n. 931 of 06-06-2022)–project n. PNC0000003–AdvaNced Technologies for Human-centrEd Medicine (project acronym: ANTHEM). This work reflects only the authors’ views and opinions, neither the Ministry for University and Research nor the European Commission can be considered responsible for them.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abbas, N., Song, S., Chang, M.-S., and Chun, M.-S. (2023). Point-of-Care diagnostic devices for detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 using microfluidic systems: a focused review. Biosens. (Basel). 13 (7), 741. doi:10.3390/bios13070741
Abdollahi-Aghdam, A., Majidi, M. R., and Omidi, Y. (2018). Microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (µPADs) for fast and ultrasensitive sensing of biomarkers and monitoring of diseases. Bioimpacts 8 (4), 237–240. doi:10.15171/bi.2018.26
Aithal, S., Mishriki, S., Gupta, R., Sahu, R. P., Botos, G., Tanvir, S., et al. (2022). SARS-CoV-2 detection with aptamer-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Talanta 236, 122841. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122841
Ananda, P. D. K. P., Tillekaratne, A., Hettiarachchi, C., and Lalichchandran, N. (2021). Sensitive detection of E. coli using bioconjugated fluorescent silica nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 6, 100159. doi:10.1016/j.apsadv.2021.100159
Anderson, G. P., and Nerurkar, N. L. (2002). Improved fluoroimmunoassays using the dye Alexa Fluor 647 with the RAPTOR, a fiber optic biosensor. J. Immunol. Methods 271 (1), 17–24. doi:10.1016/s0022-1759(02)00327-7
Anfossi, L., Di Nardo, F., Cavalera, S., Giovannoli, C., and Baggiani, C. (2019). Multiplex lateral flow immunoassay: an overview of strategies towards high-throughput point-of-need testing. Biosens. (Basel). 9 (1), 2. doi:10.3390/bios9010002
Bahadır, E. B., and Sezgintürk, M. K. (2016). Lateral flow assays: principles, designs and labels. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 82, 286–306. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2016.06.006
Bai, H., Wang, R., Hargis, B., Lu, H., and Li, Y. (2012). A SPR aptasensor for detection of avian influenza virus H5N1. Sensors (Basel) 12 (9), 12506–12518. doi:10.3390/s120912506
Baker, A. N., Richards, S.-J., Guy, C. S., Congdon, T. R., Hasan, M., Zwetsloot, A. J., et al. (2020). The SARS-COV-2 spike protein binds sialic acids and enables rapid detection in a lateral flow point of care diagnostic device. ACS Central Sci. 6 (11), 2046–2052. doi:10.1021/acscentsci.0c00855
Baker, R. E., Mahmud, A. S., Miller, I. F., Rajeev, M., Rasambainarivo, F., Rice, B. L., et al. (2022). Infectious disease in an era of global change. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 20 (4), 193–205. doi:10.1038/s41579-021-00639-z
Basso, C. R., Malossi, C. D., Haisi, A., de Albuquerque Pedrosa, V., Barbosa, A. N., Grotto, R. T., et al. (2021). Fast and reliable detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies based on surface plasmon resonance. Anal. Methods 13 (29), 3297–3306. doi:10.1039/d1ay00737h
Beeram, R., Vepa, K. R., and Soma, V. R. (2023). Recent trends in SERS-based plasmonic sensors for disease diagnostics, biomolecules detection, and machine learning techniques. Biomol. Detect. Mach. Learn. Tech. 13 (3), 328. doi:10.3390/bios13030328
Bong, J.-H., Kim, T.-H., Jung, J., Lee, S. J., Sung, J. S., Lee, C. K., et al. (2020). Pig sera-derived anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in surface plasmon resonance biosensors. BioChip J. 14 (4), 358–368. doi:10.1007/s13206-020-4404-z
Bouzin, M., Sironi, L., Chirico, G., D’Alfonso, L., Inverso, D., Pallavicini, P., et al. (2015). An intermittent model for intracellular motions of gold nanostars by k-space scattering image correlation. Biophysical J. 109 (11), 2246–2258. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2015.10.025
Butcher, E. C., and Weissman, I. L. (1980). Direct fluorescent labeling of cells with fluorescein or rhodamine isothiocyanate. I. Technical aspects. J. Immunol. Methods 37 (2), 97–108. doi:10.1016/0022-1759(80)90195-7
Cady, N. C., Tokranova, N., Minor, A., Nikvand, N., Strle, K., Lee, W. T., et al. (2021). Multiplexed detection and quantification of human antibody response to COVID-19 infection using a plasmon enhanced biosensor platform. Biosens. Bioelectron. 171, 112679. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2020.112679
Cavalera, S., Colitti, B., Rosati, S., Ferrara, G., Bertolotti, L., Nogarol, C., et al. (2021). A multi-target lateral flow immunoassay enabling the specific and sensitive detection of total antibodies to SARS COV-2. Talanta 223, 121737. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121737
Chen, C.-A., Yuan, H., Chen, C.-W., Chien, Y.-S., Sheng, W.-H., and Chen, C.-F. (2021). An electricity- and instrument-free infectious disease sensor based on a 3D origami paper-based analytical device. Lab a Chip 21 (10), 1908–1915. doi:10.1039/d1lc00079a
Chen, H., Das, A., Bi, L., Choi, N., Moon, J.-I., Wu, Y., et al. (2020). Recent advances in surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based microdevices for point-of-care diagnosis of viruses and bacteria. Nanoscale 12 (42), 21560–21570. doi:10.1039/d0nr06340a
Chen, J., Liu, X., Liu, Z., Ma, J., Han, J., Sun, Y., et al. (2024). Ultrasensitive SERS biosensor for synchronous detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa via Cecropin 1-functionalized magnetic tags-based lateral flow assay. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 409, 135598. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2024.135598
Cheng, X., Pu, X., Jun, P., Zhu, X., Zhu, D., and Chen, M. (2014). Rapid and quantitative detection of C-reactive protein using quantum dots and immunochromatographic test strips. Int. J. Nanomedicine 9, 5619–5626. doi:10.2147/ijn.s74751
Cheng, Z., Choi, N., Wang, R., Lee, S., Moon, K. C., Yoon, S.-Y., et al. (2017). Simultaneous detection of dual prostate specific antigens using surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based immunoassay for accurate diagnosis of prostate cancer. ACS Nano 11 (5), 4926–4933. doi:10.1021/acsnano.7b01536
Choi, Y.-H., Lee, G.-Y., Ko, H., Chang, Y. W., Kang, M.-J., and Pyun, J.-C. (2014). Development of SPR biosensor for the detection of human hepatitis B virus using plasma-treated parylene-N film. Biosens. Bioelectron. 56, 286–294. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2014.01.035
Chowdury, M. A., and Khalid, F. (2021). Application of microfluidic paper-based analytical device (μPAD) to detect COVID-19 in energy deprived countries. Int. J. Energy Res. 45 (12), 18275–18280. doi:10.1002/er.6958
Cimaglia, F., Aliverti, A., Chiesa, M., Poltronieri, P., De Lorenzis, E., Santino, A., et al. (2012). Quantum dots nanoparticle-based lateral flow assay for rapid detection of Mycobacterium species using anti-FprA antibodies. Nanotechnol. Dev. 2 (1), e5. doi:10.4081/nd.2012.e5
Coluccio, M. L., Pullano, S. A., Vismara, M. F. M., Coppedè, N., Perozziello, G., Candeloro, P., et al. (2020). Emerging designs of electronic devices in biomedicine. Micromachines (Basel). 11 (2), 123. doi:10.3390/mi11020123
Cui, X., Ruan, Q., Zhuo, X., Xia, X., Hu, J., Fu, R., et al. (2023). Photothermal nanomaterials: a powerful light-to-heat converter. Chem. Rev. 123 (11), 6891–6952. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00159
Davidson, J. L., Wang, J., Maruthamuthu, M. K., Dextre, A., Pascual-Garrigos, A., Mohan, S., et al. (2021). A paper-based colorimetric molecular test for SARS-CoV-2 in saliva. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 9, 100076. doi:10.1016/j.biosx.2021.100076
Dediu, V., Ghitman, J., Gradisteanu Pircalabioru, G., Chan, K. H., Iliescu, F. S., and Iliescu, C. (2023). Trends in photothermal nanostructures for antimicrobial applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (11), 9375. doi:10.3390/ijms24119375
Diao, W., Tang, M., Ding, S., Li, X., Cheng, W., Mo, F., et al. (2018). Highly sensitive surface plasmon resonance biosensor for the detection of HIV-related DNA based on dynamic and structural DNA nanodevices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 100, 228–234. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2017.08.042
Dong, R., Zhang, T., and Feng, X. (2018). Interface-assisted synthesis of 2D materials: trend and challenges. Chem. Rev. 118 (13), 6189–6235. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00056
dos Santos, D. P., Sena, M. M., Almeida, M. R., Mazali, I. O., Olivieri, A. C., and Villa, J. E. L. (2023). Unraveling surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy results through chemometrics and machine learning: principles, progress, and trends. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 415 (18), 3945–3966. doi:10.1007/s00216-023-04620-y
Du, S., Lu, Z., Gao, L., Ge, Y., Xu, X., and Zhang, H. (2020). Salmonella typhimurium detector based on the intrinsic peroxidase-like activity and photothermal effect of MoS2. Microchim. Acta 187 (11), 627. doi:10.1007/s00604-020-04600-4
Erdem, Ö., Saylan, Y., Cihangir, N., and Denizli, A. (2019). Molecularly imprinted nanoparticles based plasmonic sensors for real-time Enterococcus faecalis detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 126, 608–614. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2018.11.030
Estmer Nilsson, C., Abbas, S., Bennemo, M., Larsson, A., Hämäläinen, M. D., and Frostell-Karlsson, Å. (2010). A novel assay for influenza virus quantification using surface plasmon resonance. Vaccine 28 (3), 759–766. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.10.070
Fang, X., Zheng, Y., Duan, Y., Liu, Y., and Zhong, W. (2019). Recent advances in design of fluorescence-based assays for high-throughput screening. Anal. Chem. 91 (1), 482–504. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.8b05303
Fendi, F. W. S., Mukhtar, W. M., and Abdullah, M. (2023). Surface plasmon resonance sensor for Covid-19 detection: a review on plasmonic materials. Sensors Actuators A Phys. 362, 114617. doi:10.1016/j.sna.2023.114617
Fu, Y., Liu, T., Wang, H., Wang, Z., Hou, L., Jiang, J., et al. (2024). Applications of nanomaterial technology in biosensing. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 9 (2), 100694. doi:10.1016/j.jsamd.2024.100694
Ge, L., Wang, D., Lian, F., Zhao, J., Wang, Y., Zhao, Y., et al. (2021). Lateral flow immunoassay for visible detection of human brucellosis based on blue silica nanoparticles, 8.
Geng, H., Vilms Pedersen, S., Ma, Y., Haghighi, T., Dai, H., Howes, P. D., et al. (2022). Noble metal nanoparticle biosensors: from fundamental studies toward point-of-care diagnostics. Accounts Chem. Res. 55 (5), 593–604. doi:10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00598
Ghosh, S., Nag, M., Lahiri, D., Mukherjee, D., Garai, S., and Ray, R. R. (2022). “Chapter 20 - advanced nanomaterials for point-of-care diagnosis and therapy,” in Advanced nanomaterials for point of care diagnosis and therapy. Editors S. Dave, J. Das, and S. Ghosh (Elsevier), 423–450.
Gopal, A., Yan, L., Kashif, S., Munshi, T., Roy, V. A. L., Voelcker, N. H., et al. (2022). Biosensors and point-of-care devices for bacterial detection: rapid diagnostics informing antibiotic therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater 11 (3), 2101546. doi:10.1002/adhm.202101546
Grazon, C., Chern, M., Lally, P., Baer, R. C., Fan, A., Lecommandoux, S., et al. (2022). The quantum dot vs. organic dye conundrum for ratiometric FRET-based biosensors: which one would you chose?††Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: list of oligonucleotides, MALDI-TOF and SDS-PAGE gels of TF, additional absorption and emission spectra of the different biosensors and fluorescent species, TEM images of QD, DNA–QD characterization, data analysis. Chem. Sci. 13 (22), 6715–6731. doi:10.1039/d1sc06921g
Grisoli, P., De Vita, L., Milanese, C., Taglietti, A., Diaz Fernandez, Y., Bouzin, M., et al. (2021). PVA films with mixed silver nanoparticles and gold nanostars for intrinsic and photothermal antibacterial action. Nanomater. (Basel). 11 (6), 1387. doi:10.3390/nano11061387
Grubisha, D. S., Lipert, R. J., Park, H.-Y., Driskell, J., and Porter, M. D. (2003). Femtomolar detection of prostate-specific antigen: an immunoassay based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering and immunogold labels. Anal. Chem. 75 (21), 5936–5943. doi:10.1021/ac034356f
Gu, X., Tang, Q., Kang, X., Ji, H., Shi, X., Shi, L., et al. (2024). A portable CRISPR-Cas12a triggered photothermal biosensor for sensitive and visual detection of Staphylococcus aureus and Listeria monocytogenes. Talanta 271, 125678. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2024.125678
Guk, K., Yi, S., Kim, H., Kim, S., Lim, E.-K., Kang, T., et al. (2024). PoreGlow: a split green fluorescent protein-based system for rapid detection of Listeria monocytogenes. Food Chem. 438, 138043. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.138043
Guo, Y., Zhou, Y., Fu, J., Fang, H., Li, Y., Huang, X., et al. (2021). A self-luminous bifunctional bacteria directed fluorescent immunosensor for the simultaneous detection and quantification of three pathogens in milk. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 338, 129757. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2021.129757
Gür, S. D., Bakhshpour, M., and Denizli, A. (2019). Selective detection of Escherichia coli caused UTIs with surface imprinted plasmonic nanoscale sensor. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 104, 109869. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2019.109869
Hang, Y., Wang, A., and Wu, N. (2024). Plasmonic silver and gold nanoparticles: shape- and structure-modulated plasmonic functionality for point-of-caring sensing, bio-imaging and medical therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 53 (6), 2932–2971. doi:10.1039/d3cs00793f
Hao, W., Huang, Y., Wang, L., Liang, J., Yang, S., Su, L., et al. (2023). Smartphone-based photothermal lateral flow immunoassay using rhenium diselenide nanosheet. ACS Appl. Mater. and Interfaces 15 (7), 9665–9674. doi:10.1021/acsami.2c22616
Harpaz, D., Eltzov, E., Ng, T. S. E., Marks, R. S., and Tok, A. I. Y. (2020). Enhanced colorimetric signal for accurate signal detection in paper-based biosensors. Diagn. (Basel). 10 (1), 28. doi:10.3390/diagnostics10010028
He, J., Zhu, S., Zhou, J., Jiang, W., Yin, L., Su, L., et al. (2023). Rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2: the gradual boom of lateral flow immunoassay. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 10, 1090281. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2022.1090281
Hong, W., Huang, L., Wang, H., Qu, J., Guo, Z., Xie, C., et al. (2010). Development of an up-converting phosphor technology-based 10-channel lateral flow assay for profiling antibodies against Yersinia pestis. J. Microbiol. Methods 83 (2), 133–140. doi:10.1016/j.mimet.2010.08.005
Hou, F., Sun, S., Abdullah, S. W., Tang, Y., Li, X., and Guo, H. (2023). The application of nanoparticles in point-of-care testing (POCT) immunoassays. Anal. Methods 15, 2154–2180. doi:10.1039/d3ay00182b
Huang, C., Wen, T., Shi, F.-J., Zeng, X.-Y., and Jiao, Y.-J. (2020). Rapid detection of IgM antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 virus via colloidal gold nanoparticle-based lateral-flow assay. ACS Omega 5 (21), 12550–12556. doi:10.1021/acsomega.0c01554
Huang, X., Chen, L., Zhi, W., Zeng, R., Ji, G., Cai, H., et al. (2023). Urchin-shaped Au–Ag@Pt sensor integrated lateral flow immunoassay for multimodal detection and specific discrimination of clinical multiple bacterial infections. Anal. Chem. 95 (35), 13101–13112. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.3c01631
Huang, Y.-C., Wang, S.-F., Chen, B.-C., Yang, Z.-S., Li, M.-C., Wu, X.-Y., et al. (2024). Towards cost-effective and lightweight surface plasmon resonance biosensing for H5N1 avian influenza virus detection: integration of novel near-infrared organic photodetectors. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 400, 134898. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2023.134898
Huo, J., Jia, Q., Huang, H., Zhang, J., Li, P., Dong, X., et al. (2021). Emerging photothermal-derived multimodal synergistic therapy in combating bacterial infections. Chem. Soc. Rev. 50 (15), 8762–8789. doi:10.1039/d1cs00074h
Hyeon, S. H., Lim, W. K., and Shin, H. J. (2021). Novel surface plasmon resonance biosensor that uses full-length Det7 phage tail protein for rapid and selective detection of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 68 (1), 5–12. doi:10.1002/bab.1883
Jahanshahi, P., Zalnezhad, E., Sekaran, S. D., and Adikan, F. R. M. (2014). Rapid immunoglobulin M-based dengue diagnostic test using surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Sci. Rep. 4 (1), 3851. doi:10.1038/srep03851
Jiang, S., Qian, S., Zhu, S., Lu, J., Hu, Y., Zhang, C., et al. (2023). A point-of-care testing device utilizing graphene-enhanced fiber optic SPR sensor for real-time detection of infectious pathogens. Biosens. (Basel). 13 (12), 1029. doi:10.3390/bios13121029
Kim, H.-Y., Lee, J.-H., Kim, M. J., Park, S. C., Choi, M., Lee, W., et al. (2021). Development of a SARS-CoV-2-specific biosensor for antigen detection using scFv-Fc fusion proteins. Biosens. Bioelectron. 175, 112868. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2020.112868
Kim, S. U., Jo, E.-J., Noh, Y., Mun, H., Ahn, Y.-D., and Kim, M.-G. (2018b). Adenosine triphosphate bioluminescence-based bacteria detection using targeted photothermal lysis by gold nanorods. Anal. Chem. 90 (17), 10171–10178. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.8b00254
Kim, W., Lee, S. H., Kim, J. H., Ahn, Y. J., Kim, Y.-H., Yu, J. S., et al. (2018a). Paper-based surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for diagnosing prenatal diseases in women. ACS Nano 12 (7), 7100–7108. doi:10.1021/acsnano.8b02917
Koczula, K. M., and Gallotta, A. J. E. i. b. (2016). Lateral flow assays. Essays Biochem. 60 (1), 111–120. doi:10.1042/ebc20150012
Kramer, A., Schwebke, I., and Kampf, G. (2006). How long do nosocomial pathogens persist on inanimate surfaces? A systematic review. BMC Infect. Dis. 6 (1), 130. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-6-130
Larsen, R. W., and Wojtas, L. (2017). Photophysical properties of [Ru(2,2′-bipyridine)3]2+ encapsulated within the Uio-66 zirconium based metal organic framework. J. Solid State Chem. 247, 77–82. doi:10.1016/j.jssc.2016.12.028
Lee, A. S., Kim, S. M., Kim, K. R., Park, C., Lee, D.-G., Heo, H. R., et al. (2023). A colorimetric lateral flow immunoassay based on oriented antibody immobilization for sensitive detection of SARS-CoV-2. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 379, 133245. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2022.133245
Lee, J.-H., Choi, M., Jung, Y., Lee, S. K., Lee, C.-S., Kim, J., et al. (2021). A novel rapid detection for SARS-CoV-2 spike 1 antigens using human angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). Biosens. Bioelectron. 171, 112715. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2020.112715
Lee, S., Park, J. S., Woo, H., Yoo, Y. K., Lee, D., Chung, S., et al. (2024). Rapid deep learning-assisted predictive diagnostics for point-of-care testing. Nat. Commun. 15 (1), 1695. doi:10.1038/s41467-024-46069-2
Lee, T., Kim, G. H., Kim, S. M., Hong, K., Kim, Y., Park, C., et al. (2019). Label-free localized surface plasmon resonance biosensor composed of multi-functional DNA 3 way junction on hollow Au spike-like nanoparticles (HAuSN) for avian influenza virus detection. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 182, 110341. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.06.070
Lepage, D., Jiménez, A., Beauvais, J., and Dubowski, J. J. (2013). Real-time detection of influenza A virus using semiconductor nanophotonics. Light Sci. and Appl. 2 (4), e62. doi:10.1038/lsa.2013.18
Le Ru, E. C., Blackie, E., Meyer, M., and Etchegoin, P. G. (2007). Surface enhanced Raman scattering enhancement factors: a comprehensive study. J. Phys. Chem. C 111 (37), 13794–13803. doi:10.1021/jp0687908
Lew, T. T. S., Aung, K. M. M., Ow, S. Y., Amrun, S. N., Sutarlie, L., Ng, L. F. P., et al. (2021). Epitope-functionalized gold nanoparticles for rapid and selective detection of SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies. ACS Nano 15 (7), 12286–12297. doi:10.1021/acsnano.1c04091
Li, J., Zhang, Y., Wang, X., Zhang, S., Tan, Q., Hu, B., et al. (2023b). Engineering entropy-driven nanomachine-mediated morphological evolution of anisotropic silver triangular nanoplates for colorimetric and photothermal biosensing. Anal. Chem. 95 (32), 12032–12038. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.3c01888
Li, L., Yang, H., Li, L., Tan, X., Ge, S., Zhang, L., et al. (2022). Photothermal-reagent-triggered visual thermoresponsive and quantized photoelectrochemical dual-signal assay. ACS Sensors 7 (8), 2429–2437. doi:10.1021/acssensors.2c01162
Li, P., Müller, M., Chang, M. W., Frettlöh, M., and Schönherr, H. (2017). Encapsulation of autoinducer sensing reporter bacteria in reinforced alginate-based microbeads. ACS Appl. Mater. and Interfaces 9 (27), 22321–22331. doi:10.1021/acsami.7b07166
Li, Q., Huo, H., Wu, Y., Chen, L., Su, L., Zhang, X., et al. (2023a). Design and synthesis of SERS materials for in vivo molecular imaging and biosensing. Adv. Sci. (Weinh). 10 (8), 2202051. doi:10.1002/advs.202202051
Li, X., Lu, D., Sheng, Z., Chen, K., Guo, X., Jin, M., et al. (2012). A fast and sensitive immunoassay of avian influenza virus based on label-free quantum dot probe and lateral flow test strip. Talanta 100, 1–6. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2012.08.041
Li, Z., Leustean, L., Inci, F., Zheng, M., Demirci, U., and Wang, S. (2019). Plasmonic-based platforms for diagnosis of infectious diseases at the point-of-care. Biotechnol. Adv. 37 (8), 107440. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2019.107440
Liang, J., Zhang, W., Qin, Y., Li, Y., Liu, G. L., and Hu, W. (2022). Applying machine learning with localized surface plasmon resonance sensors to detect SARS-CoV-2 particles. Biosensors 12 (3), 173. doi:10.3390/bios12030173
Lin, X., Ibarlucea, B., Peng, T., Shen, R., Li, P., and Zhang, P. (2023). Two birds with one stone: a multifunctional nanoplatform for photothermal sensitive detection and real-time inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus with NIR responsive Cu2−XSe@Van NPs. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 381, 133475. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2023.133475
Lippi, G., Plebani, M., Favaloro, E. J., and Trenti, T. (2010). Laboratory testing in pharmacies. Clin. Chem. Laboratory. Med. 48 (7), 943–953. doi:10.1515/cclm.2010.184
Liu, F., Chen, S., Zou, Y., Jiao, Y., and Tang, Y. (2023b). A simple and efficient fluorescent labeling method in Staphylococcus aureus for real-time tracking of invasive bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 14, 1128638. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2023.1128638
Liu, H., Xing, F., Zhou, Y., Yu, P., Xu, J., Luo, R., et al. (2023d). Nanomaterials-based photothermal therapies for antibacterial applications. Mater. and Des. 233, 112231. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2023.112231
Liu, L., Ma, W., Wang, X., and Li, S. (2023c). Recent progress of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for bacteria detection. Biosensors 13 (3), 350. doi:10.3390/bios13030350
Liu, Q., Jin, X., Cheng, J., Zhou, H., Zhang, Y., and Dai, Y. (2023a). Advances in the application of molecular diagnostic techniques for the detection of infectious disease pathogens (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 27 (5), 104. doi:10.3892/mmr.2023.12991
Liu, Q.-H., Liu, J., Guo, J.-C., Yan, X.-L., Wang, D.-H., Chen, L., et al. (2009). Preparation of polystyrene fluorescent microspheres based on some fluorescent labels. J. Mater. Chem. 19 (14), 2018–2025. doi:10.1039/b816963b
Liu, Y., Zhou, H., Hu, Z., Yu, G., Yang, D., and Zhao, J. (2017). Label and label-free based surface-enhanced Raman scattering for pathogen bacteria detection: a review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 94, 131–140. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2017.02.032
Lu, L., Ge, Y., Wang, X., Lu, Z., Wang, T., Zhang, H., et al. (2021). Rapid and sensitive multimode detection of Salmonella typhimurium based on the photothermal effect and peroxidase-like activity of MoS2@Au nanocomposite. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 326, 128807. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2020.128807
Luciano, K., Wang, X., Liu, Y., Eyler, G., Qin, Z., and Xia, X. (2022). Noble metal nanoparticles for point-of-care testing: recent advancements and social impacts. Bioeng. (Basel). 9 (11), 666. doi:10.3390/bioengineering9110666
Ma, B., Martín, C., Kurapati, R., and Bianco, A. (2020). Degradation-by-design: how chemical functionalization enhances the biodegradability and safety of 2D materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 49 (17), 6224–6247. doi:10.1039/c9cs00822e
Maphanga, C., Manoto, S., Ombinda-Lemboumba, S., Ismail, Y., and Mthunzi-Kufa, P. (2023). Localized surface plasmon resonance biosensing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis biomarker for TB diagnosis. Sens. Bio-Sensing Res. 39, 100545. doi:10.1016/j.sbsr.2022.100545
Martinez, A. W., Phillips, S. T., Butte, M. J., and Whitesides, G. M. (2007). Patterned paper as a platform for inexpensive, low-volume, portable bioassays. Portable Bioassays 46 (8), 1318–1320. doi:10.1002/anie.200603817
Martinez-Liu, C., Machain-Williams, C., Martinez-Acuña, N., Lozano-Sepulveda, S., Galan-Huerta, K., Arellanos-Soto, D., et al. (2022). Development of a rapid gold nanoparticle-based lateral flow immunoassay for the detection of dengue virus. Biosens. (Basel) 12 (7), 495. doi:10.3390/bios12070495
Masson, J.-F. (2020). Portable and field-deployed surface plasmon resonance and plasmonic sensors. Analyst 145 (11), 3776–3800. doi:10.1039/d0an00316f
Montalti, M., Prodi, L., Rampazzo, E., and Zaccheroni, N. (2014). Dye-doped silica nanoparticles as luminescent organized systems for nanomedicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43 (12), 4243–4268. doi:10.1039/c3cs60433k
Murugan, D., Bhatia, H., Sai, V. V. R., and Satija, J. (2020). P-FAB: a fiber-optic biosensor device for rapid detection of COVID-19. Trans. Indian Natl. Acad. Eng. 5 (2), 211–215. doi:10.1007/s41403-020-00122-w
Naghdi, T., Ardalan, S., Asghari Adib, Z., Sharifi, A. R., and Golmohammadi, H. (2023). Moving toward smart biomedical sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 223, 115009. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2022.115009
Nakamura, N., Burgess, J. G., Yagiuda, K., Kudo, S., Sakaguchi, T., and Matsunaga, T. (1993). Detection and removal of Escherichia coli using fluorescein isothiocyanate conjugated monoclonal antibody immobilized on bacterial magnetic particles. Anal. Chem. 65 (15), 2036–2039. doi:10.1021/ac00063a018
Nan, X., Yao, X., Yang, L., and Cui, Y. (2023). Lateral flow assay of pathogenic viruses and bacteria in healthcare. Analyst 148 (19), 4573–4590. doi:10.1039/d3an00719g
Nasrollahpour, H., and Khalilzadeh, B. (2024). Naked eye biosensors for pathogen monitoring. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 171, 117499. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2023.117499
Nath, P., Kabir, A., Khoubafarin Doust, S., Kreais, Z. J., and Ray, A. (2020). Detection of bacterial and viral pathogens using photonic point-of-care devices. Diagnostics 10 (10), 841. doi:10.3390/diagnostics10100841
Ng, S. P., Qiu, G., Ding, N., Lu, X., and Wu, C.-M. L. (2017). Label-free detection of 3-nitro-l-tyrosine with nickel-doped graphene localized surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 89, 468–476. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2016.04.017
Nguyen, H. H., Park, J., Kang, S., and Kim, M. (2015). Surface plasmon resonance: a versatile technique for biosensor applications. Sensors (Basel). 15 (5), 10481–10510. doi:10.3390/s150510481
Nguyen, V.-T., Seo, H. B., Kim, B. C., Kim, S. K., Song, C.-S., and Gu, M. B. (2016). Highly sensitive sandwich-type SPR based detection of whole H5Nx viruses using a pair of aptamers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 86, 293–300. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2016.06.064
Nuntawong, P., Putalun, W., Tanaka, H., Morimoto, S., and Sakamoto, S. (2022). Lateral flow immunoassay for small-molecules detection in phytoproducts: a review. J. Nat. Med. 76 (3), 521–545. doi:10.1007/s11418-022-01605-6
Omar, N. A. S., Fen, Y. W., Abdullah, J., Mustapha Kamil, Y., Daniyal, W. M. E. M. M., Sadrolhosseini, A. R., et al. (2020). Sensitive detection of dengue virus type 2 E-proteins signals using self-assembled monolayers/reduced graphene oxide-PAMAM dendrimer thin film-SPR optical sensor. Sci. Rep. 10 (1), 2374. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-59388-3
Omar, N. A. S., Fen, Y. W., Abdullah, J., Zaid, M. H. M., Daniyal, W. M. E. M. M., and Mahdi, M. A. (2019). Sensitive surface plasmon resonance performance of cadmium sulfide quantum dots-amine functionalized graphene oxide based thin film towards dengue virus E-protein. Opt. and Laser Technol. 114, 204–208. doi:10.1016/j.optlastec.2019.01.038
Omidfar, K., Riahi, F., and Kashanian, S. (2023). Lateral flow assay: a summary of recent progress for improving assay performance. Biosens. (Basel). 13 (9), 837. doi:10.3390/bios13090837
Otoo, J. A., and Schlappi, T. S. (2022). REASSURED multiplex diagnostics: a critical review and forecast. Biosens. (Basel). 12 (2), 124. doi:10.3390/bios12020124
Özgür, E., Topçu, A. A., Yılmaz, E., and Denizli, A. (2020). Surface plasmon resonance based biomimetic sensor for urinary tract infections. Talanta 212, 120778. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2020.120778
Ozyoruk, K. B., Can, S., Darbaz, B., Başak, K., Demir, D., Gokceler, G. I., et al. (2022). A deep-learning model for transforming the style of tissue images from cryosectioned to formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 6 (12), 1407–1419. doi:10.1038/s41551-022-00952-9
Pardoux, É., Roux, A., Mathey, R., Boturyn, D., and Roupioz, Y. (2019). Antimicrobial peptide arrays for wide spectrum sensing of pathogenic bacteria. Talanta 203, 322–327. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2019.05.062
Park, J.-H., Cho, Y.-W., and Kim, T.-H. (2022). Recent advances in surface plasmon resonance sensors for sensitive optical detection of pathogens. Biosens. (Basel). 12 (3), 180. doi:10.3390/bios12030180
Pashazadeh-Panahi, P., Belali, S., Sohrabi, H., Oroojalian, F., Hashemzaei, M., Mokhtarzadeh, A., et al. (2021). Metal-organic frameworks conjugated with biomolecules as efficient platforms for development of biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 141, 116285. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2021.116285
Pellach, M., Goldshtein, J., Ziv-Polat, O., and Margel, S. (2012). Functionalised, photostable, fluorescent polystyrene nanoparticles of narrow size-distribution. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 228 (1), 60–67. doi:10.1016/j.jphotochem.2011.11.012
Pengcheng, W., Jiaren, S., Caixia, S., Wanchao, Z., Jianjun, D., and Yanmin, J. (2023). Recent advances of lateral flow immunoassay for bacterial detection: capture-antibody-independent strategies and high-sensitivity detection technologies. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 166, 117203. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2023.117203
Pilot, R., Signorini, R., Durante, C., Orian, L., Bhamidipati, M., and Fabris, L. (2019). A review on surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Biosens. (Basel) 9 (2), 57. doi:10.3390/bios9020057
Pisetsky, W., Budny, P., and Müller, T. J. J. (2024). Synthesis and photophysical properties of luminescent phenothiazinyl merocyanine substituted polyacetylenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 63 (4), e202316246. doi:10.1002/anie.202316246
Pittet, D., Allegranzi, B., Sax, H., Dharan, S., Pessoa-Silva, C. L., Donaldson, L., et al. (2006). Evidence-based model for hand transmission during patient care and the role of improved practices. Lancet Infect. Dis. 6 (10), 641–652. doi:10.1016/s1473-3099(06)70600-4
Pomili, T., Donati, P., and Pompa, P. P. (2021). Paper-based multiplexed colorimetric device for the simultaneous detection of salivary biomarkers. Biosens. (Basel). 11 (11), 443. doi:10.3390/bios11110443
Pradela-Filho, L. A., Veloso, W. B., Arantes, I. V. S., Gongoni, J. L. M., de Farias, D. M., Araujo, D. A. G., et al. (2023). Paper-based analytical devices for point-of-need applications. Microchim. Acta 190 (5), 179. doi:10.1007/s00604-023-05764-5
Qatamin, A. H., Ghithan, J. H., Moreno, M., Nunn, B. M., Jones, K. B., Zamborini, F. P., et al. (2019). Detection of influenza virus by electrochemical surface plasmon resonance under potential modulation. Appl. Opt. 58 (11), 2839–2844. doi:10.1364/ao.58.002839
Qin, Z., Chan, W. C. W., Boulware, D. R., Akkin, T., Butler, E. K., and Bischof, J. C. (2012). Significantly improved analytical sensitivity of lateral flow immunoassays by using thermal contrast. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51 (18), 4358–4361. doi:10.1002/anie.201200997
Qiu, G., Gai, Z., Tao, Y., Schmitt, J., Kullak-Ublick, G. A., and Wang, J. (2020). Dual-functional plasmonic photothermal biosensors for highly accurate severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 detection. ACS Nano 14 (5), 5268–5277. doi:10.1021/acsnano.0c02439
Quesada-González, D., and Merkoçi, A. (2015). Nanoparticle-based lateral flow biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 73, 47–63. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2015.05.050
Rahbar, M., Zou, S., Baharfar, M., and Liu, G. (2021). A customized microfluidic paper-based platform for colorimetric immunosensing: demonstrated via hCG assay for pregnancy test. Biosens. (Basel). 11 (12), 474. doi:10.3390/bios11120474
Rajendran, V. K., Bakthavathsalam, P., and Jaffar Ali, B. M. (2014). Smartphone based bacterial detection using biofunctionalized fluorescent nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 181 (15), 1815–1821. doi:10.1007/s00604-014-1242-5
Rasheed, S., Kanwal, T., Ahmad, N., Fatima, B., Najam-ul-Haq, M., and Hussain, D. (2024). Advances and challenges in portable optical biosensors for onsite detection and point-of-care diagnostics. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 173, 117640. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2024.117640
Ray, P. C., Khan, S. A., Singh, A. K., Senapati, D., and Fan, Z. (2012). Nanomaterials for targeted detection and photothermal killing of bacteria. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41 (8), 3193–3209. doi:10.1039/c2cs15340h
Riedel, T., Surman, F., Hageneder, S., Pop-Georgievski, O., Noehammer, C., Hofner, M., et al. (2016). Hepatitis B plasmonic biosensor for the analysis of clinical serum samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 85, 272–279. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2016.05.014
Sajid, M., Kawde, A.-N., and Daud, M. (2015). Designs, formats and applications of lateral flow assay: a literature review. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 19 (6), 689–705. doi:10.1016/j.jscs.2014.09.001
Samuel, L. (2020). Point-of-Care testing in microbiology. Clin. Laboratory Med. 40 (4), 483–494. doi:10.1016/j.cll.2020.08.006
Santos, G., Ibañez de Santi Ferrara, F., Zhao, F., Rodrigues, D., and Shih, W.-C. (2016). Photothermal inactivation of bacteria on plasmonic nanostructures, 9724. San Francisco, CA: SPIE, 97240D. doi:10.1117/12.2213191
Sarathkumar, E., Anjana, R. S., and Jayasree, R. S. (2023). Nanoarchitectonics of photothermal materials to enhance the sensitivity of lateral flow assays. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 14, 988–1003. doi:10.3762/bjnano.14.82
Sarcina, L., Mangiatordi, G. F., Torricelli, F., Bollella, P., Gounani, Z., Österbacka, R., et al. (2021). Surface plasmon resonance assay for label-free and selective detection of HIV-1 p24 protein. Biosens. (Basel) 11 (6), 180. doi:10.3390/bios11060180
Sardar, R., Funston, A. M., Mulvaney, P., and Murray, R. W. (2009). Gold nanoparticles: past, present, and future. Langmuir 25 (24), 13840–13851. doi:10.1021/la9019475
Schilling, K. M., Jauregui, D., and Martinez, A. W. (2013). Paper and toner three-dimensional fluidic devices: programming fluid flow to improve point-of-care diagnostics. Lab a Chip 13 (4), 628–631. doi:10.1039/c2lc40984d
Sehulster, L., Chinn, R. Y., Arduino, M. J., Carpenter, J., Donlan, R., Ashford, D., et al. (2003). Guidelines for environmental infection control in health-care facilities. Recommendations of CDC and the healthcare infection control practices advisory committee (HICPAC). MMWR. Recomm. Rep. 52 (10), 1–42.
Seo, S. E., Ryu, E., Kim, J., Shin, C. J., and Kwon, O. S. (2023). Fluorophore-encapsulated nanobeads for on-site, rapid, and sensitive lateral flow assay. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 381, 133364. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2023.133364
Shafiee, H., Asghar, W., Inci, F., Yuksekkaya, M., Jahangir, M., Zhang, M. H., et al. (2015). Paper and flexible substrates as materials for biosensing platforms to detect multiple biotargets. Sci. Rep. 5 (1), 8719. doi:10.1038/srep08719
Sharafeldin, M., and Davis, J. J. (2021). Point of care sensors for infectious pathogens. Anal. Chem. 93 (1), 184–197. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.0c04677
Sharma, B., Frontiera, R. R., Henry, A.-I., Ringe, E., and Van Duyne, R. P. (2012). SERS: materials, applications, and the future. Mater. Today 15 (1), 16–25. doi:10.1016/s1369-7021(12)70017-2
Shrivastav, A. M., Cvelbar, U., and Abdulhalim, I. (2021). A comprehensive review on plasmonic-based biosensors used in viral diagnostics. Commun. Biol. 4 (1), 70. doi:10.1038/s42003-020-01615-8
Sifana, N. O., Melyna, , Septiani, N. L. W., Septama, A. W., Manurung, R. V., Yuliarto, B., et al. (2024). Detection of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus using vancomycin conjugated silica-based fluorescent nanoprobe. Spectrochimica Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 307, 123643. doi:10.1016/j.saa.2023.123643
Singh, P. (2017). “Surface plasmon resonance: a boon for viral diagnostics,” in Reference module in life sciences (Elsevier).
Singh, S., Dhawan, A., Karhana, S., Bhat, M., and Dinda, A. K. (2020). Quantum dots: an emerging tool for point-of-care testing. Micromachines 11 (12), 1058. doi:10.3390/mi11121058
Soler, M., Huertas, C. S., and Lechuga, L. M. (2019). Label-free plasmonic biosensors for point-of-care diagnostics: a review. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagnostics 19 (1), 71–81. doi:10.1080/14737159.2019.1554435
Somvanshi, S. B., Ulloa, A. M., Zhao, M., Liang, Q., Barui, A. K., Lucas, A., et al. (2022). Microfluidic paper-based aptasensor devices for multiplexed detection of pathogenic bacteria. Biosens. Bioelectron. 207, 114214. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2022.114214
Song, C., Liu, J., Li, J., and Liu, Q. (2016). Dual FITC lateral flow immunoassay for sensitive detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in food samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 85, 734–739. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2016.05.057
Song, M., Hong, S., and Lee, L. P. (2023). Multiplexed ultrasensitive sample-to-answer RT-LAMP chip for the identification of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza viruses. Viruses 35 (10), 2207138. doi:10.1002/adma.202207138
Spicuzza, L., Campagna, D., Di Maria, C., Sciacca, E., Mancuso, S., Vancheri, C., et al. (2023). An update on lateral flow immunoassay for the rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. AIMS Microbiol. 9 (2), 375–401. doi:10.3934/microbiol.2023020
Stoia, D., De Sio, L., Petronella, F., and Focsan, M. (2024). Recent advances towards point-of-care devices for fungal detection: emphasizing the role of plasmonic nanomaterials in current and future technologies. Biosens. Bioelectron. 255, 116243. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2024.116243
Su, L., Liu, B., Su, Y., and Tang, D. (2023). NIR II light response-based PDA/AuPt@CuS composites: simultaneous readout of temperature and pressure sensing strategy for portable detection of pathogenic bacteria. Talanta 260, 124629. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2023.124629
Suleyman, G., Alangaden, G., and Bardossy, A. C. (2018). The role of environmental contamination in the transmission of nosocomial pathogens and healthcare-associated infections. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 20 (6), 12. doi:10.1007/s11908-018-0620-2
Sun, Y., Zhao, C., Niu, J., Ren, J., and Qu, X. (2020). Colorimetric band-aids for point-of-care sensing and treating bacterial infection. ACS Central Sci. 6 (2), 207–212. doi:10.1021/acscentsci.9b01104
Tan, L., Effah, C. Y., He, S., Drokow, E. K., Agboyibor, C., Sangmor, A., et al. (2023). Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy: a novel diagnostic method for pathogenic organisms. Vib. Spectrosc. 127, 103560. doi:10.1016/j.vibspec.2023.103560
Teerinen, T., Lappalainen, T., and Erho, T. (2014). A paper-based lateral flow assay for morphine. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 406 (24), 5955–5965. doi:10.1007/s00216-014-8001-7
Tokel, O., Yildiz, U. H., Inci, F., Durmus, N. G., Ekiz, O. O., Turker, B., et al. (2015). Portable microfluidic integrated plasmonic platform for pathogen detection. Sci. Rep. 5 (1), 9152. doi:10.1038/srep09152
Tram, D. T. N., Wang, H., Sugiarto, S., Li, T., Ang, W. H., Lee, C., et al. (2016). Advances in nanomaterials and their applications in point of care (POC) devices for the diagnosis of infectious diseases. Biotechnol. Adv. 34 (8), 1275–1288. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2016.09.003
Tran, V., Walkenfort, B., König, M., Salehi, M., Schlücker, S., and Rapid, (2019). Rapid, quantitative, and ultrasensitive point-of-care testing: a portable SERS reader for lateral flow assays in clinical Chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58 (2), 442–446. doi:10.1002/anie.201810917
Ubbelohde, N., Fricke, C., Flindt, C., Hohls, F., and Haug, R. J. (2012). Measurement of finite-frequency current statistics in a single-electron transistor. Nat. Commun. 3 (1), 612. doi:10.1038/ncomms1620
Usman, M., Tang, J.-W., Li, F., Lai, J.-X., Liu, Q.-H., Liu, W., et al. (2023). Recent advances in surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy for bacterial pathogen identifications. J. Adv. Res. 51, 91–107. doi:10.1016/j.jare.2022.11.010
Uzhytchak, M., Smolková, B., Lunova, M., Jirsa, M., Frtús, A., Kubinová, Š., et al. (2020). Iron oxide nanoparticle-induced autophagic flux is regulated by interplay between p53-mTOR Axis and bcl-2 signaling in hepatic cells. Cells 9 (4), 1015. doi:10.3390/cells9041015
van Seventer, J. M., and Hochberg, N. S. (2017). “Principles of infectious diseases: transmission, diagnosis, prevention, and control,” in International encyclopedia of public health. Editor S. R. Quah Second Edition (Oxford: Academic Press), 22–39.
Vázquez-Guardado, A., Mehta, F., Jimenez, B., Biswas, A., Ray, K., Baksh, A., et al. (2021). DNA-modified plasmonic sensor for the direct detection of virus biomarkers from the blood. Nano Lett. 21 (18), 7505–7511. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c01609
Vilar, J. M. G., and Saiz, L. (2023). Dynamics-informed deconvolutional neural networks for super-resolution identification of regime changes in epidemiological time series. Sci. Adv. 9 (28), eadf0673. doi:10.1126/sciadv.adf0673
Wang, C., Liu, M., Wang, Z., Li, S., Deng, Y., and He, N. (2021). Point-of-care diagnostics for infectious diseases: from methods to devices. Nano Today 37, 101092. doi:10.1016/j.nantod.2021.101092
Wang, S., Xie, J., Jiang, M., Chang, K., Chen, R., Ma, L., et al. (2016b). The development of a portable SPR bioanalyzer for sensitive detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Sensors 16 (11), 1856. doi:10.3390/s16111856
Wang, Y., Jiang, C., Wen, G., Zhang, X., Luo, Y., Qin, A., et al. (2016a). A sensitive fluorescence method for detection of E. Coli using rhodamine 6G dyeing. Luminescence 31 (4), 972–977. doi:10.1002/bio.3060
Wei, M., Rao, H., Niu, Z., Xue, X., Luo, M., Zhang, X., et al. (2021). Breaking the time and space limitation of point-of-care testing strategies: photothermometric sensors based on different photothermal agents and materials. Coord. Chem. Rev. 447, 214149. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2021.214149
Wen, J., Zhu, Y., Liu, J., and He, D. (2022). Smartphone-based surface plasmon resonance sensing platform for rapid detection of bacteria. RSC Adv. 12 (21), 13045–13051. doi:10.1039/d2ra01788a
Wu, P., Xue, F., Zuo, W., Yang, J., Liu, X., Jiang, H., et al. (2022b). A universal bacterial catcher Au–PMBA-Nanocrab-Based lateral flow immunoassay for rapid pathogens detection. Anal. Chem. 94 (10), 4277–4285. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.1c04909
Wu, P., Zuo, W., Wang, Y., Yuan, Q., Yang, J., Liu, X., et al. (2023). Multimodal capture − antibody-independent lateral flow immunoassay based on AuNF − PMBA for point-of-care diagnosis of bacterial urinary tract infections. Chem. Eng. J. 451, 139021. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2022.139021
Wu, Y., Hu, Y., Jiang, N., Anantharanjit, R., Yetisen, A. K., and Cordeiro, M. F. (2022a). Quantitative brain-derived neurotrophic factor lateral flow assay for point-of-care detection of glaucoma. Lab a Chip 22 (18), 3521–3532. doi:10.1039/d2lc00431c
Xia, Y., Si, J., and Li, Z. (2016). Fabrication techniques for microfluidic paper-based analytical devices and their applications for biological testing: a review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 77, 774–789. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2015.10.032
Xue, J.-W., Wang, R., Yang, J.-Y., Wang, L.-X., Cao, Y., Li, H.-D., et al. (2022). Sensitive plasmonic ELISA assay based on butyrylcholinesterase catalyzed hydrolysis for the detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 365, 131948. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2022.131948
Yan, J., Estévez, M. C., Smith, J. E., Wang, K., He, X., Wang, L., et al. (2007). Dye-doped nanoparticles for bioanalysis. Nano Today 2 (3), 44–50. doi:10.1016/s1748-0132(07)70086-5
Yan, Z., Wang, D., and Gao, Y. (2023). Nanomaterials for the treatment of bacterial infection by photothermal/photodynamic synergism. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 11, 1192960. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2023.1192960
Yang, H., He, Q., Lin, M., Ji, L., Zhang, L., Xiao, H., et al. (2022). Multifunctional Au@Pt@Ag NPs with color-photothermal-Raman properties for multimodal lateral flow immunoassay. J. Hazard. Mater. 435, 129082. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129082
Yang, H., Li, D., He, R., Guo, Q., Wang, K., Zhang, X., et al. (2010). A novel quantum dots–based point of care test for syphilis. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 5 (5), 875–881. doi:10.1007/s11671-010-9578-1
Yang, J., Wang, X., Sun, Y., Chen, B., Hu, F., Guo, C., et al. (2023). Recent advances in colorimetric sensors based on gold nanoparticles for pathogen detection. Biosens. (Basel). 13 (1), 29. doi:10.3390/bios13010029
Yano, T.-a., Kajisa, T., Ono, M., Miyasaka, Y., Hasegawa, Y., Saito, A., et al. (2022). Ultrasensitive detection of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein using large gold nanoparticle-enhanced surface plasmon resonance. Sci. Rep. 12 (1), 1060. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-05036-x
Yesudasu, V., Pradhan, H. S., and Pandya, R. J. (2021). Recent progress in surface plasmon resonance based sensors: a comprehensive review. Heliyon 7 (3), e06321. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06321
Yoo, H., Shin, J., Sim, J., Cho, H., and Hong, S. (2020). Reusable surface plasmon resonance biosensor chip for the detection of H1N1 influenza virus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 168, 112561. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2020.112561
Yoo, S. M., Kim, D.-K., and Lee, S. Y. (2015). Aptamer-functionalized localized surface plasmon resonance sensor for the multiplexed detection of different bacterial species. Talanta 132, 112–117. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2014.09.003
Yoon, S. A., Park, S. Y., Cha, Y., Gopala, L., and Lee, M. H. (2021). Strategies of detecting bacteria using fluorescence-based dyes. Front. Chem. 9, 743923. doi:10.3389/fchem.2021.743923
Yu, X., Park, S., Lee, S., Joo, S.-W., and Choo, J. (2024). Microfluidics for disease diagnostics based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection. Nano Converg. 11 (1), 17. doi:10.1186/s40580-024-00424-7
Zeng, R., Gong, H., Li, Y., Li, Y., Lin, W., Tang, D., et al. (2022). CRISPR-Cas12a-Derived photoelectrochemical biosensor for point-of-care diagnosis of nucleic acid. Anal. Chem. 94 (20), 7442–7448. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.2c01373
Zeng, S., Liu, X., Kafuti, Y. S., Kim, H., Wang, J., Peng, X., et al. (2023). Fluorescent dyes based on rhodamine derivatives for bioimaging and therapeutics: recent progress, challenges, and prospects. Chem. Soc. Rev. 52 (16), 5607–5651. doi:10.1039/d2cs00799a
Zhang, C., Zheng, T., Wang, H., Chen, W., Huang, X., Liang, J., et al. (2021). Rapid one-pot detection of SARS-CoV-2 based on a lateral flow assay in clinical samples. Anal. Chem. 93 (7), 3325–3330. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.0c05059
Zhang, D., Du, S., Su, S., Wang, Y., and Zhang, H. (2019b). Rapid detection method and portable device based on the photothermal effect of gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 123, 19–24. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2018.09.039
Zhang, H., Ma, X., Liu, Y., Duan, N., Wu, S., Wang, Z., et al. (2015). Gold nanoparticles enhanced SERS aptasensor for the simultaneous detection of Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 74, 872–877. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2015.07.033
Zhang, J., Shikha, S., Mei, Q., Liu, J., and Zhang, Y. (2019a). Fluorescent microbeads for point-of-care testing: a review. Microchim. Acta 186 (6), 361. doi:10.1007/s00604-019-3449-y
Zhang, Y., Chai, Y., Hu, Z., Xu, Z., Li, M., Chen, X., et al. (2022). Recent progress on rapid lateral flow assay-based early diagnosis of COVID-19. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 10, 866368. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2022.866368
Zhang, Z., Wang, Q., Han, L., Du, S., Yu, H., and Zhang, H. (2018). Rapid and sensitive detection of Salmonella typhimurium based on the photothermal effect of magnetic nanomaterials. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 268, 188–194. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2018.04.043
Zhao, X., Tsao, Y.-C., Lee, F.-J., Tsai, W.-H., Wang, C.-H., Chuang, T.-L., et al. (2016a). Optical fiber sensor based on surface plasmon resonance for rapid detection of avian influenza virus subtype H6: initial studies. J. Virological Methods 233, 15–22. doi:10.1016/j.jviromet.2016.03.007
Zhao, Y., Huang, Y., Zhao, X., McClelland, J. F., and Lu, M. (2016b). Nanoparticle-based photoacoustic analysis for highly sensitive lateral flow assays. Nanoscale 8, 19204–19210. doi:10.1039/c6nr05312b
Zhao, Y., Wang, Y., Wang, X., Qi, R., and Yuan, H. (2023). Recent progress of photothermal therapy based on conjugated nanomaterials in combating microbial infections. Nanomater. (Basel). 13 (15), 2269. doi:10.3390/nano13152269
Zheng, L., Cai, G., Wang, S., Liao, M., Li, Y., and Lin, J. (2019). A microfluidic colorimetric biosensor for rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 using gold nanoparticle aggregation and smart phone imaging. Biosens. Bioelectron. 124-125, 143–149. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2018.10.006
Zheng, L., Qi, P., and Zhang, D. (2018). A simple, rapid and cost-effective colorimetric assay based on the 4-mercaptophenylboronic acid functionalized silver nanoparticles for bacteria monitoring. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 260, 983–989. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2018.01.115
Zhou, P., Liu, H., Gong, L., Tang, B., Shi, Y., Yang, C., et al. (2019). A faster detection method for high-sensitivity cardiac troponin—POCT quantum dot fluorescence immunoassay. J. Thorac. Dis. 11 (4), 1506–1513. doi:10.21037/jtd.2019.03.25
Zhou, X., Hu, Z., Yang, D., Xie, S., Jiang, Z., Niessner, R., et al. (2020). Bacteria detection: from powerful SERS to its advanced compatible techniques. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 7 (23), 2001739. doi:10.1002/advs.202001739
Zhou, Z., Xiao, R., Cheng, S., Wang, S., Shi, L., Wang, C., et al. (2021). A universal SERS-label immunoassay for pathogen bacteria detection based on Fe3O4@Au-aptamer separation and antibody-protein A orientation recognition. Anal. Chim. Acta 1160, 338421. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2021.338421
Zou, M., Su, F., Zhang, R., Jiang, X., Xiao, H., Yan, X., et al. (2021). Rapid point-of-care testing for SARS-CoV-2 virus nucleic acid detection by an isothermal and nonenzymatic Signal amplification system coupled with a lateral flow immunoassay strip. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 342, 129899. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2021.129899
Keywords: nanotechnology, nanobiosensors, pathogens, point-of-care, pathogens detection
Citation: Secchi V, Armanni A, Barbieri L, Bruno A, Colombo A, Fumagalli S, Kukushkina EA, Lorenzi R, Marchesi L, Moukham H, Paleari A, Ronchi A, Tomaino G, Tripodi F, Colombo M, Sironi L and Monguzzi A (2025) Advanced techniques and nanotechnologies for point-of-care testing. Front. Nanotechnol. 6:1465429. doi: 10.3389/fnano.2024.1465429
Received: 16 July 2024; Accepted: 27 December 2024;
Published: 15 January 2025.
Edited by:
Giulio Fracasso, University of Padova, ItalyReviewed by:
Snehasis Bhakta, Cooch Behar College, IndiaJorge Ricardo Mejía-Salazar, National Institute of Telecommunications, Brazil
Copyright © 2025 Secchi, Armanni, Barbieri, Bruno, Colombo, Fumagalli, Kukushkina, Lorenzi, Marchesi, Moukham, Paleari, Ronchi, Tomaino, Tripodi, Colombo, Sironi and Monguzzi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Miriam Colombo, bWlyaWFtLmNvbG9tYm9AdW5pbWliLml0JiN4MDIwMGE7; Laura Sironi, bGF1cmEuc2lyb25pQHVuaW1pYi5pdCYjeDAyMDBhOw==; Angelo Monguzzi, YW5nZWxvLm1vbmd1enppQHVuaW1pYi5pdA==
 Valeria Secchi1,2
Valeria Secchi1,2 Linda Barbieri
Linda Barbieri Antonia Bruno
Antonia Bruno Farida Tripodi
Farida Tripodi Miriam Colombo
Miriam Colombo Laura Sironi
Laura Sironi Angelo Monguzzi
Angelo Monguzzi