- 1Faculty of Pharmacy, Van Lang University, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
- 2Faculty of Pharmacy, HUTECH University, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
Nanoparticulate delivery systems have been attracting attention in pharmaceutical sciences for enhanced drug bioavailability and targeted delivery. Specifically, these systems can enhance the solubility of poorly water-soluble drugs, protect therapeutic agents from degradation, prolong circulation time in the body, control drug release, and facilitate the precise targeting of drugs to specific tissues or cells. However, once administered into the body, nanoparticles often encounter significant challenges that can affect their efficacy and safety, such as issues with stability, biocompatibility, and targeting. The surface properties of nanoparticles are one of the most important features as they can greatly influence the interactions between nanoparticles themselves and between nanoparticles and biological targets. Key surface characteristics, such as charge, hydrophobicity, and the presence of functional groups, determine how nanoparticles behave in biological environments, thereby influencing their stability, cellular uptake, and ability to avoid immune clearance. Modification of the nanoparticle surface has been shown to be an effective approach to modulate the physicochemical and biological properties of nanoparticles, achieving desired therapeutic efficacy in vivo. This review aims to summarize recent advances in surface decoration of nanoparticles, with an emphasis on improved colloidal and biological stability, reduced toxicity, and enhanced drug targeting. The challenges and future perspectives of nanoparticle surface modification approaches are also discussed.
1 Introduction
Nanoparticles are generally defined as particles with diameters ranging from 1 to 100 nm; however, in the field of pharmaceutics and medicine, submicron particles are also termed nanoparticles (Wu et al., 2011). The use of nanoparticles in drug delivery is driven by their ability to improve the solubility and/or stability of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), thereby enhancing drug bioavailability. Nanoparticles can also be designed to release their payload in a controlled manner over a prolonged period, allowing for sustained drug release and reducing the frequency of dosing. Additionally, nanoparticles can be engineered to achieve targeted delivery, thereby minimizing side effects and enhancing the drug efficacy. Their small size facilitates the penetration through biological barriers, enabling efficient targeting of tissues and cells (Sharma et al., 2018).
There are different types of nanoparticles, including polymeric nanoparticles, lipid-based nanoparticles, inorganic nanoparticles, and biological nanoparticles. Each type possesses specific characteristics that can be employed for various drug delivery purposes (Yetisgin et al., 2020). Polymeric nanoparticles can be synthesized from a variety of natural or synthetic materials, offering diverse structures and characteristics. They can be manufactured using different techniques including emulsification, nanoprecipitation, ionic gelation, and microfluidics. Therapeutics can be encapsulated within, entrapped in, conjugated to, or bound to the nanoparticle surface, allowing delivery of various payloads including hydrophobic and hydrophilic compounds with differing molecular weights (Zielińska et al., 2020). Polymeric nanoparticles are excellent for drug delivery due to their water solubility, biocompatibility, and storage stability. However, they can pose risks of particle aggregation and toxicity (Beach et al., 2024). Lipid-based nanoparticles typically feature spherical structures with one or more lipid bilayers encapsulating an aqueous core. They offer numerous advantages such as simplicity in formulation, self-assembly, biocompatibility, high bioavailability, and the ability to carry large payloads. Their physicochemical properties can be controlled to modulate biological characteristics. The most common lipid-based nanoparticles are liposomes and lipid nanoparticles (Mehta et al., 2023). Inorganic materials, such as gold, iron, and silica, are used to create nanostructured materials for drug delivery, diagnostics, and imaging. These nanoparticles can be precisely engineered in various sizes, structures, and geometries (Mitchell et al., 2021). Biological nanoparticles, often derived from natural biological materials, such as proteins, lipids, and polysaccharides, exhibit inherent biocompatibility and biodegradability. These nanoparticles can be engineered to carry therapeutic agents, enhancing drug delivery by leveraging their natural cellular interactions. Common examples include exosomes, virus-like particles, and protein-based nanoparticles (Stanley, 2014).
Upon administration into the body, nanoparticles often face significant challenges that can compromise their efficacy and safety, including stability, biocompatibility, and targetability. Stability is a major challenge in nanoparticle-based drug delivery. Once administered, nanoparticles must remain stable in the bloodstream long enough to reach their target site. However, nanoparticles frequently encounter physical stability issues, primarily due to aggregation driven by van der Waals forces or hydrophobic interactions. This aggregation leads to particle clumping and sedimentation, which alters the size distribution of the nanoparticles and results in unpredictable behavior in biological environments (Wu et al., 2011). In addition to physical instability, biological instability of nanoparticles is another concern, typically caused by the adsorption of biomolecules, including proteins, lipids, and enzymes, onto the particle surface. This adsorption can alter the surface properties of nanoparticles, modifying their interactions with cells and leading to rapid clearance by the mononuclear phagocyte system (MPS). The biological instability of nanoparticles could also be attributed to enzymatic degradation that compromises the structural integrity of nanoparticles (Guerrini et al., 2018). The instability can lead to a reduction in the therapeutic effectiveness of the drug and can also cause unintended toxicity. Another challenge associated with nanoparticles is their limited biocompatibility, which can result in toxicity following administration. Nanoparticle-induced toxicity may stem from either the incompatible nature of the material or the small size of the nanoparticle. The latter factor can lead to strong interactions between nanoparticles and biological systems, potentially inducing toxicity. Parameters influencing nanoparticle toxicity include composition, size, shape, surface charge, and propensity for aggregation (Kyriakides et al., 2021). A significant concern with nanoparticles is their inability to specifically target tissues and cells. Physiological barriers, such as the immune system and the blood-brain barrier, prevent nanoparticles from selectively accumulating in target cells or tissues. Consequently, nanoparticles may exhibit suboptimal specificity, leading to a substantial portion of the therapeutic payload being distributed to non-target sites. This non-specific distribution can lead to off-target effects and reduced therapeutic efficacy (Debbage, 2009).
To address the issues associated with nanoparticles, a potential approach is to modify the nanoparticle surface, altering their physicochemical properties and bioactivity. For instance, functionalizing the nanoparticle surface with polymers such as polyethylene glycol (PEG) significantly improves stability by preventing aggregation and protein adsorption, thereby maintaining consistent size distribution and prolonging circulation time in biological environments—an effect known as stealth coating (Choi et al., 2003). Doxil® is the first approved PEGylated liposome loaded with doxorubicin for the treatment of some cancer types. The PEGylated liposome increased the drug bioavailability by 90-fold compared to the free drug and demonstrated a prolonged circulation half-life (Gabizon et al., 2003). Alternatively, surface modification of nanoparticles with chitosan can induce a positive surface charge, facilitating robust electrostatic interactions between the nanoparticles and mucin. This process extends the residence time of nanoparticles at the target site, consequently enhancing drug absorption (Gupta et al., 2011; Vieira et al., 2018). Additionally, surface modifications can mitigate toxicity by using biocompatible coatings that shield the nanoparticles from eliciting adverse immune responses and minimize interactions with non-target cells (Gamucci et al., 2014). In recent years, there has been a shift towards utilizing more specific and complex ligands for surface modification to improve targeting specificity. Nanoparticles can be conjugated with ligands, such as antibodies, peptides, or small molecules, that recognize and bind to specific receptors on the cell membrane, thereby facilitating uptake by target cells and enabling controlled drug release. This targeted approach, known as active coating, enhances the accumulation of nanoparticles in diseased tissues while reducing off-target effects and systemic toxicity (Patel et al., 2019). This underscores the necessity for continued development of surface decoration approaches to overcome the challenges of nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems as well as maximize their therapeutic potential. Recent studies have investigated surface modifications of various types of nanoparticles for both stealth and active coating purposes, as summarized in Table 1.
The purpose of this review paper is to explore and elucidate the significant advancements in the surface modification of nanoparticles. This paper focuses on the mechanism and approaches of surface modification to enhance physicochemical and biological stability, enable targeted delivery, and improve biocompatibility. By examining these key areas, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current strategies and technologies employed to optimize nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems for increased efficacy and safety.
2 Impact of surface on nanoparticle properties
The surface properties of nanoparticles are paramount in dictating their physicochemical and biological behavior, which in turn significantly impacts their effectiveness in drug delivery applications. The physicochemical properties of the nanoparticles, namely, the particle size, surface charge, hydrophobicity, and the presence of functional groups, can influence the stability, solubility, dispersibility, drug release rate, and toxicity of nanoparticles.
2.1 Particle size and surface charge
The particle size and surface charge of nanoparticles are critical determinants of their physicochemical and biological properties. Particle size affects several key aspects, including the stability, biodistribution, and cellular uptake of nanoparticles. Small nanoparticles, typically in the range of 10–100 nm, can penetrate tissues more effectively and are less likely to be recognized and cleared by the reticuloendothelial system (RES), allowing for prolonged circulation time and enhanced accumulation at target sites. However, very small nanoparticles with less than 10 nm in size might exhibit rapid renal clearance, reducing their therapeutic efficacy (Sadat et al., 2016). Surface charge, on the other hand, plays a pivotal role in the interaction of nanoparticles with biological membranes and proteins. Positively charged nanoparticles often demonstrate enhanced cellular uptake due to the electrostatic attraction to the negatively charged cell membranes but may also exhibit higher toxicity and be rapidly cleared from the bloodstream due to opsonization and uptake by the RES. Negatively charged or neutral nanoparticles typically exhibit reduced protein adsorption and lower clearance rates, resulting in prolonged circulation time but potentially reduced cellular uptake (He et al., 2010).
2.2 Hydrophobicity
Hydrophilic surfaces tend to exhibit better dispersion in aqueous media, while hydrophobic-surfaced nanoparticles tend to aggregate due to their tendency to minimize contact with water molecules, which can lead to reduced stability and poor dispersion in biological fluids. This aggregation can hinder their ability to circulate effectively within the bloodstream and reach target sites (Sinani et al., 2005). Biologically, the hydrophobicity of nanoparticles plays a crucial role in their interaction with biological membranes and proteins. Hydrophobic surfaces can enhance the adsorption of plasma proteins, leading to opsonization and subsequent clearance by the RES, thereby reducing circulation time and limiting therapeutic efficacy (Verma and Stellacci, 2010). However, hydrophobic nanoparticles can also facilitate the encapsulation and controlled release of hydrophobic drugs, which are often challenging to deliver due to their poor solubility in water (Wischke and Schwendeman, 2008).
2.3 Surface functional groups
The incorporation of various functional groups can tailor the surface characteristics of nanoparticles, such as hydrophilicity, charge, and reactivity. Hydrophilic functional groups, such as hydroxyl or carboxyl groups, can enhance the solubility and physical stability of nanoparticles in biological fluids. Charged functional groups, whether positive (e.g., amine groups) or negative (e.g., carboxyl groups), significantly impact the surface charge of nanoparticles, resulting in changes in their physicochemical and biological properties (Verma and Stellacci, 2010). Functional groups can also be used to conjugate targeting ligands, such as antibodies, peptides, or small molecules, to the nanoparticle surface, thereby enabling active targeting of specific cells or tissues and improving therapeutic efficacy while minimizing off-target effects (Friedman et al., 2013).
3 Surface modification
To immobilize functionalities or ligands on the surface of nanoparticles, various approaches have been developed, which can be generally classified into two categories, i.e., covalent conjugation and non-covalent interactions (Moku et al., 2019). These two surface modification strategies are graphically demonstrated in Figure 1.
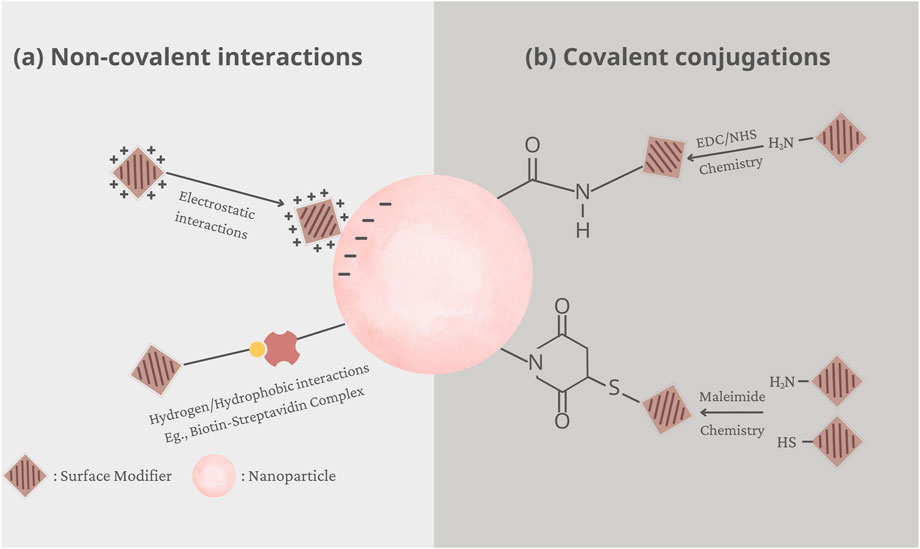
Figure 1. Graphical demonstration of two surface modification strategies: (A) electrostatic interactions and (B) covalent conjugations.
Covalent conjugation is a widely used method, which involves chemical immobilization of the functionalised moiety, such as the ligand or polymer, to the surface of nanoparticles. However, this process requires the presence of functional groups on the surface that can facilitate the attachment of functionalised moieties. A variety of functional groups have been immobilized onto the surface of nanoparticles, including carboxylic acids, amines, thiols, alcohols, or maleimides. For instance, 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) is a common coupling reagent that converts carboxyl or phosphate groups into amine-reactive forms, often in combination with N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) or sulfo-NHS to stabilize intermediates and enhance efficiency (Alcantara et al., 2024). Alternatively, maleimide coupling, which involves reactions between a primary amine and a thiol, or between two thiols, is also a prevalent technique for surface modification (Lee et al., 2020).
Noncovalent interactions offer another avenue for ligand attachment, showcasing the versatility of surface functionalization techniques. This method relies on the interplay of attractive forces between nanoparticle surfaces and functionalized moieties, encompassing electrostatic interactions, hydrogen bonding, hydrophobic interactions, and van der Waals forces. One prominent example is the biotin-(strept)avidin system, a paradigm of strong and specific molecular recognition. Avidin or streptavidin, proteins with a high affinity for biotin, form robust complexes, allowing for stable nanoparticle surface functionalization (Ehsani et al., 2021). Additionally, electrostatic interactions between oppositely charged species present another mechanism for stable ligand immobilization. By harnessing the inherent electrical properties of nanoparticles and ligands, electrostatic interactions can drive efficient binding, leading to effective surface modification (Nguyen et al., 2020). Furthermore, physical adsorption, facilitated by hydrogen bonding or hydrophobic interactions, offers a non-invasive approach for ligand attachment. For example, hydrophobically-modified dextran was physically adsorbed onto the surface of polystyrene nanoparticles via hydrophobic interactions (Delgado et al., 2000).
4 Surface modification for enhanced nanoparticle stability
The small size and high surface area of nanoparticles result in a strong tendency to adhere to each other and form aggregates, compromising their physical stability in biological fluids. This aggregation significantly reduces the circulation time of nanoparticles within the body, therefore limiting their pharmacological effectiveness. Additionally, nanoparticles tend to form a protein corona on their surface while circulating throughout the body, which alters their biological identity and impacts their biodistribution and targeting efficiency. Specifically, this protein corona can trigger the capture of nanoparticles by macrophages, thereby reducing the biological half-life. To address these challenges, surface modification of nanoparticles has emerged as a widely studied and effective strategy. Altering the surface properties of nanoparticles makes it possible to enhance nanoparticle stability, prevent agglomeration, and prolong circulation time.
4.1 Surface modification for stabilization of nanoparticles
Nanoparticles generally exhibit lower stability in aqueous media and biological fluids compared to microparticles due to several factors, which includes (Hotze et al., 2010):
- Size effect: Smaller particles have higher surface energy, making them more prone to agglomeration to reduce system free energy.
- Surface area to volume ratio: Nanoparticles have a higher surface area to volume ratio, increasing susceptibility to interactions and aggregation.
- Van der Waals forces: These forces are more significant at the nanoscale, causing nanoparticles to aggregate when in contact with each other or with the medium.
- Brownian motion: Pronounced Brownian motion in nanoparticles leads to collisions and aggregation.
- Electrostatic interactions: Nanoparticles may exhibit stronger electrostatic interactions with ions or molecules in the medium, influencing stability through attraction or repulsion.
These factors contribute to the reduced physical stability of nanoparticles in the liquid medium. Aoki et al. performed a study on the in vivo toxicity of high-dose intravenous nano-hydroxyapatite to Wistar rats and found that the observed health issues in the rats were due to nanoparticle aggregation, which caused drug blockage in pulmonary capillaries (Aoki et al., 2000). Other studies have also shown that nanoparticle aggregation can lead to diseases and toxicity in animals (Xie et al., 2010; Moore et al., 2013; Moore, 2014). These studies highlight the importance of stabilizing nanoparticles in biological fluids for enhanced drug bioavailability and reduced toxicity. Surface modification is one of the most effective methods used to improve nanoparticle stability. Materials used for surface modification of nanoparticles can be broadly classified into macromolecules and small molecules, each offering distinct advantages depending on the application’s specific requirements. The distinction between macromolecules and small molecules is primarily based on molecular mass. Macromolecules are molecules with a high molecular weight, typically greater than 1 kDa, and are often large, complex structures formed by the polymerization of monomers through covalent bonds (Dkhar et al., 2022). In contrast, small molecules generally have a molecular weight ranging from 0.1 to 1 kDa (Chhabra, 2021). This difference in molecular weight also leads to differing characteristics in how they bind to the surface of nanoparticles.
4.1.1 Macromolecules
Macromolecules, such as polymers, polysaccharides, lipids, proteins, antibodies, or nucleic acids (aptamers), are frequently used for surface modification due to their large size and ability to introduce multiple functional groups. In general, macromolecules can be coated on nanoparticles via the formation of chemical bonds between biomolecules and the substrate surface either directly, through a spacer, or by noncovalent adsorption (Moku et al., 2019).
4.1.1.1 Polymers
One of the effective methods to stabilize nanoparticles in biological fluids is to use polymeric ligands. Polymeric ligands provide a short physical barrier to the mutual interactions between nanoparticles. Many types of polymeric ligands have been used, but the most popular one is PEG because of its popularity and biocompatibility. Another reason for using PEG is the hydrophilic nature of this polymer. PEG forms a hydration layer around the nanoparticles, generating a repulsive force that prevents the nanoparticles from agglomeration. This steric stabilization enhances the stability of nanoparticles in biological fluids. Furthermore, PEG increases the stability of polymeric nanoparticles during storage and in aqueous dispersions by reducing the tendency of particles to aggregate (Suk et al., 2016). The distance between nanoparticles increases as the PEG chain length increases, thereby enhancing the steric repulsion of PEG and preventing the aggregation of nanoparticles (Shi et al., 2021). Kostiv et al. demonstrated that coating PEG-2000 to the surface of Fe3O4 and SiO2 nanoparticles increased the biocompatibility and stability of these particles (Kostiv et al., 2017). Cyclic PEG, prepared through the etherification of PEG-3000, can also be used to modify the surface of gold nanoparticles, which significantly improved the nanoparticle’s colloidal stability at 85°C for 48 h (Wang et al., 2020b). In addition to PEG, other polymers have also been used for steric stabilization of nanoparticles, including natural polymers (e.g., alginate, chitosan) and synthetic polymers (e.g., polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP)). Jin Soon Han et al. used PEI (polyethylenimine) and PAA (polyacrylic acid) for surface functionalisation of Fe3O4 nanoparticles, resulting in reduced particle size distribution, mean particle size, and polydispersity index (PDI) compared to uncoated nanoparticles. The zeta potential increased by approximately tenfold, leading to electrostatic repulsion and reduced nanoparticle aggregation in suspension. Thus, PEI and PAA surface attachment significantly improved nanoparticle stability in the dispersion system (Han et al., 2018). Another work by Sabzi et al. modified the surface of Fe₃O₄ nanoparticles with PVA (72 kDa) and PEG-6000. The coated nanoparticles exhibited good colloidal stability in water for 72 h, while the uncoated nanoparticles showed agglomeration (Sabzi Dizajyekan et al., 2024).
4.1.1.2 Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides or glycans are molecules that selectively bind to proteins and are essential for signaling between cells. An important property of glycans is their selectivity for specific cell types through carbohydrate receptors, which can be maintained regardless of the media used. The disadvantage of the glycan method is the complex chemical process on the surface of the nanoparticles. The stabilisation effect of polysaccharides when decorated onto the surface of nanoparticles is due to their steric protection, which prevents protein adsorption and uptake by macrophages (Lemarchand et al., 2004). For instance, Garcia et al. used thiol-terminated glycoconjugates either N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) or disaccharide lactose to functionalize Au nanorods. The nanoparticles showed good stability in the standard cell culture medium (Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium, DMEM) supplemented with 10% FBS for 2 h at 37°C (Garcia et al., 2015). Yang et al. studied the surface modification of nanoparticles using heparosan polysaccharide (HEP) to produce colloidally stable HEP-conjugated gold nanoparticles. The resulting nanoparticles exhibited good stability in saline solutions with 0.3–0.7 M NaCl and within a pH range of 1.5–7 over a period of 4 days. The stability of the HEP-conjugated gold nanoparticles was also retained after six repeated centrifugation and washing cycles with water and PBS (Yang et al., 2022).
4.1.1.3 Lipids
Another strategy used to improve the stability of nanoparticles in biological fluids is to use lipids as a coating layer for nanoparticles. The most important advantage of the lipid layer is to create a thin and uniform shell covering the nanoparticles, so it does not significantly change the hydrodynamic diameter of the nanoparticles. Besides, the uniformity of the lipid layer also helps the nanoparticles to be less susceptible to protein adsorption, making them more stable in biological fluids. However, media such as cultures containing high concentrations of cysteine or glutathione have been reported to cause aggregation of lipid-coated nanoparticles. Another downside of the lipid coating method is that they are not made from covalent bonds on the nanoparticle surfaces, so they are less durable and easy to separate. Natural phospholipids such as phosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidylserine, phosphatidic acid, phosphatidylethanolamine and their synthetic counterparts are often used to coat the surface of polymeric nanoparticles (Mandal et al., 2013). Bhowmik et al. simulated the cell membrane by using a lipid bilayer composed of POPC (1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine), POPG (1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3 phosphoglycerol), and cholesterol. The coated nanoparticle suspension was shown to be highly stable in both PBS (pH 7.4) and 100 mM NaCl (Bhowmik et al., 2015). Märkl et al. utilized the phospholipid bilayer to coat the small core-shell upconversion nanoparticles of 12 nm, which demonstrated good colloidal stability in various media, including phosphate buffer (pH 7.4), high ionic saline solution (138 mM NaCl) and cell culture media supplemented with 5% fetal bovine serum (FBS) for 96 h (Märkl et al., 2020).
4.1.1.4 Proteins
The formation of a protein corona can cause nanoparticles to become unstable and more susceptible to uptake by macrophages. Prior studies have, however, shown that coating nanoparticles with proteins enhances their stability in biological fluids. The protein coating, which contains many charged groups, helps stabilize the nanoparticles by maintaining their charge balance, thereby improving their spatial stability and reducing aggregation. Additionally, the protein coating creates a hydration layer around the nanoparticles, which prevents them from being absorbed by other free proteins, further enhancing their stability. Serum albumin is particularly suitable for this application because it carries cysteine groups that are highly reactive with the nanoparticle surface. Proteins can also be used to coat the surface of nanoparticles using the ligand exchange method, which involves replacing existing surface-bound ligands on the nanoparticles with protein molecules. Tebbe et al. investigated the ligand exchange of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) with bovine serum albumin (BSA) for gold nanorods. The obtained nanoparticles were demonstrated to be stable in biological media such as PBS or DMEM over a large pH range (pH 2−12). These nanoparticles could be freeze-dried and then redispersed in PBS without compromising their particle size (Tebbe et al., 2015). Chanana et al. used various proteins, i.e., insulin, β-lactoglobulin, and bovine serum albumin, to coat gold nanoparticles (Chanana et al., 2013). The colloidal stability of gold nanoparticles was tested by dispersing them in PBS (pH 7.4) with and without proteolytic enzymes (proteases), followed by incubation at 37°C for 3 days. The results showed that the nanoparticles remained stable at pH 7.4 throughout the incubation period. Bychkova et al. used bovine serum albumin (BSA), human serum albumin (HAS), and thrombin (TR) to coat magnetic nanoparticles. The obtained nanoparticles were stable in PBS at pH 6.5 (BSA, HSA) or pH 7.3 (TR) in the presence of hydrogen peroxide (Bychkova et al., 2013). Wenck et al. coated magnetic nanoparticles with casein, which resulted in enhanced colloidal stability compared to uncoated nanoparticles. This was evidenced by no change in particle size or magnetic behavior after incubation in solutions of NaCl, Ca(CH₃COO)₂ (NH₄)₂SO₄, and MgSO₄ for 18 h (Wenck et al., 2024).
4.1.1.5 Aptamers
Aptamers are short sequences of DNA, RNA, XNA (i.e., xeno nucleic acids, a synthetic alternative to the natural nucleic acids DNA and RNA) or artificial peptides that bind to a specific target molecule or a family of target molecules. Aptamers can be considered natural antibodies, which can be used to replace antibodies in some applications such as identifying pathological markers or used in targeted therapy. Attaching aptamers to the surface of nanoparticles also renders these particles more stable and intact in biological fluids (Abdelkawi et al., 2023). Aptamers can be directly attached to the surface of nanoparticles via the thiol linkage (Catala et al., 2016). The disadvantage of the aptamer attachment method is the rarity and difficulty of obtaining this material (Guerrini et al., 2018). Delaviz et al. used cyanogen bromide in a sodium bicarbonate buffer to activate the hydroxyl groups of starch-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles and couple them with amino groups of aptamers (Delaviz et al., 2015). Additionally, Nair’s group used a similar approach anchoring amino-modified aptamers onto carboxylated dextran-stabilized magnetic nanoparticles via EDC chemistry (Nair et al., 2010). In both above studies, aptamer functionalized magnetic nanoparticles have been shown to be stable in PBS upon incubation at 37°C for an hour.
4.1.2 Small molecule ligands
Small molecules, such as surfactants, ligands, and small organic compounds, stabilize the nanoparticles through various mechanisms, such as reducing surface tension or modifying surface charge. The major advantages of using a small molecule as the targeting ligand over macromolecules are their stability, ease of conjugation with nanoparticles, and low cost. The drawbacks associated with the use of small molecules as targeting ligands include the lack of an efficient approach to identify such ligands and their lower specificity and affinity for surface receptors on the target cells (Moku et al., 2019).
4.1.2.1 Zwitterionic ligands
Zwitterionic ligands are molecules containing two or more functional groups carrying different positive and negative charges, but the total charge of the molecule is 0. Zwitterionic ligands, such as carboxybetaines or sulfobetaines, show a variety of positively and negatively charged groups allowing for the modulation of charge densities to optimize solubility and to avoid the interactions of the protein corona (Sanita et al., 2020). Because of this structure, zwitterionic ligands are less sensitive to solvents with high ionic concentrations. Therefore, zwitterionic ligands are good candidates for surface modification of nanoparticles and helping them stable in biological fluids. In addition, coating nanoparticles with zwitterionic ligands has been shown to produce nanoparticles with much smaller hydrodynamic diameters and lower degrees of opsonization compared to the corresponding polymers. Despite many advantages, zwitterionic ligands are not popular and the synthesis process is quite complicated. In addition, zwitterionic ligands are sensitive to pH changes, which increases the adsorption of proteins onto nanoparticles. Zhan et al. synthesized two compact multicoordinating (lipoic acid-appended) zwitterion ligands for the capping of luminescent quantum dots. The obtained quantum dots were tested for long-term colloidal stability in PBS at differing pH (pH 4-13), with the presence of excess electrolyte (1 and 2 M NaCl). The data obtained indicated that quantum dots photoligated with the zwitterion ligand were stable in those conditions for at least 2 months of storage at 4°C (Zhan et al., 2013). Wei et al. synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles via thermal decomposition of Fe(CO)5 in dioctyl ether, then decorated the nanoparticle surface with the water-soluble zwitterionic dopamine sulfonate. These synthesized nanoparticles were highly stable in PBS (pH 7.4) over one-month of storage at room temperature, as evidenced by no significant changes in particle size and surface charge (Wei et al., 2012). Khunsuk et al. developed lipid nanoparticles by conjugating 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (DPPE) with an antifouling zwitterionic polymer, poly (2-methyacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine) (PMPC). The obtained nanoparticles suspended in 150 mM HEPES buffer were spherical with a diameter of 144–255 nm, neutral in charge, and stable at 4°C for up to 28 days (Khunsuk et al., 2023). However, the absorption and biodistribution of nanoparticles may be affected by the surface charge distribution of zwitterionic nanoparticles. Han et al. demonstrated that zwitterionic nanoparticles with a positively charged outer layer are more sensitive to protein interactions than those with a negatively charged outer layer (Han et al., 2013).
4.1.2.2 Mercaptoalkyl acid ligands
Mercaptoalkyl acid ligands are commonly used to decorate the surface of nanoparticles due to their strong affinity for metal surfaces. These ligands contain thiol (-SH) binding to metal atoms and carboxyl (-COOH) offering sites for further functionalization (Limongi et al., 2019). 11-Mercaptoundecanoic acid (MUA) is one of the most used mercaptoalkyl acid ligands for surface modification. Although MUA is less stable compared to other ligands, it can form a thin, single layer on the surface of nanoparticles. This layer provides effective protection and helps stabilize the nanoparticles in biological fluids. For instance, gold nanoparticles modified by MUA had good colloidal stability, which was proven by no changes in its colloidal state following multiple centrifugation steps at 20,000 ×g (Schulz et al., 2016). MUA molecules are usually short providing just a slight increase in the hydrodynamic diameter of the nanoparticles compared to PEG. This makes MUA inferior to PEG in terms of colloidal stability of nanosystems, but helps the nanoparticles to have lower degrees of opsonization, resulting in longer blood circulation time and the capability to escape from the capture by the phagocytic system (Guerrini et al., 2018).
4.2 Surface modification on enhancement the circulation time of nanoparticles–stealth effect
An important characteristic of an effective delivery system is its ability to stay in systemic circulation for a prolonged period. Phagocytic uptake by macrophages is the primary mechanism of particle clearance from systemic circulation. Stable nanoparticles are those that can circulate in the body for an extended period without being engulfed by macrophages. Most unprotected nanoparticles, regardless of their material composition, can be cleared from the blood circulation by the phagocytic system within seconds to minutes after introduction into the body (Fam et al., 2020). Modification of the nanoparticle surface with different types of molecules makes the nanoparticles “invisible” to cells of the immune system and not captured by macrophages. For this purpose, the researchers used hydrophilic polymers that bind water molecules, which creates a barrier on the nanoparticle surface. This water layer plays a role in reducing the interactions of nanoparticles with opsonin receptors and/or macrophages leading to reduced clearance of nanoparticles in the blood (Sanita et al., 2020). Hydrophilic polymers are often used as stealth coatings such as PEG, PVP, PVA, polyaminoacids, or poloxamer (Knop et al., 2010). PEG is a hydrophilic and neutral polymer that helps form barrier layers on the nanoparticle surface, leading to steric blocking, low opsonization and high blood circulation time (Papi et al., 2017). Lipka et al. demonstrated that gold nanoparticles (∼5 nm) modified with PEG-10000 had a prolonged blood circulation time compared to uncoated nanoparticles in an in vivo study in rats. Twenty-4 hours after intravenous injection, over 18% of the coated nanoparticles remained in the blood, compared to just 0.1% of the uncoated ones (Lipka et al., 2010). The prolonged circulation time achieved by PEGylation of the nanoparticle surface has been shown to translate into an improved therapeutic effect in cancer treatment, as demonstrated in more recent studies using different types of nanoparticles (Kang et al., 2020; Mukherjee et al., 2020; Teng et al., 2020). In addition to PEG, other surface-modified materials have also been used to increase the circulation time of nanoparticles in the blood, such as chitosan, dextran, hyaluronic acid, or heparin (Abd Ellah and Abouelmagd, 2017). For instance, Miao et al. modified the surface of lipid nanoparticles with chitosan-grafted polyhydroxy polymer (PEO-PPO-PEO), which was shown to effectively reduce immunoglobulin adsorption onto the nanoparticles, leading to extended blood circulation in vivo (Miao et al., 2024). Another work by Simon et al. utilised polyoxazolines to modify the surface of liposomes and extracellular vesicles (EVs), which also results in increased blood circulation time in an in vivo biodistribution study in mice (Simon et al., 2025).
5 Surface modification for drug targeting
To enhance bioactivity and minimize side effects of drugs, several surface modification strategies have been developed to enable targeted delivery. The concept of drug targeting was first suggested by Paul Ehrlich in the early 20th century and has been considered a “magic bullet” that can precisely reach biological targets. In principle, the formulations must be able to enter the target site, then selectively accumulate and elicit therapeutic actions (Hirsjarvi et al., 2011). Drug targeting is particularly valuable in the case of using highly toxic chemotherapeutics in cancer treatment because it can reduce cytotoxicity and immunogenic responses in healthy tissues. Furthermore, the dosage, frequency of administration, and cost of therapy will be reduced thanks to targeting efficiency (Hirsjarvi et al., 2011). There are two types of drug targeting, known as passive targeting and active targeting. Passive targeting, which was first discovered and applied in drug delivery, is based on the physiological features of the targeted area, particularly the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect of the leaky vasculature in solid tumours. This is a pathophysiological phenomenon in which the intravascular structure is not structurally intact and complete due to the rapid growth of tumour cells. Such a condition unintentionally helps nanoparticles of 100–200 nm in size readily go through wide fenestrations between defective endothelial cells and accumulate in the tumour environment. Furthermore, tumour tissues usually lack effective lymphatic drainage, which keeps nanomedicine staying longer at the tumour site (Wu, 2021; Sun et al., 2022). While passive targeting is mainly applied in cancer treatment, active targeting can be utilized for a wider variety of disease settings, such as neurological disorders (Xu et al., 2021; Annu et al., 2022), osteoporosis (Niu et al., 2022), pulmonary diseases (Azarmi et al., 2008; Deng Z. et al., 2021) or cardiovascular diseases (Flores et al., 2019) in addition to cancer. For active targeting, nanomedicine is decorated with ligands that have high affinity to specific receptors over-expressed in targeted tissues. This approach utilizes the selective interactions between ligands and receptors, the receptor-mediated cellular uptake and transport to facilitate intended biodistribution. Common nanocarriers employed for active targeting include monoclonal antibodies (Tsao et al., 2021), liposomes (Liu et al., 2021), polymeric micelles (Kotta et al., 2022), polymeric nanoparticles (Begines et al., 2020), and mesoporous inorganic nanoparticles (Parra-Nieto et al., 2021). Figure 2 illustrates the mechanisms of passive and active targeting of nanoparticles to tumours. The main difference between these two mechanisms is that active targeting utilizes interactions between nanoparticles and over-expressed receptors on cancer cells and vascular endothelial cells, thereby enhancing nanoparticle accumulation in the tumour. In contrast, passive targeting does not involve receptor interactions but relies on the EPR effect of tumour vasculature, allowing for a higher concentration of nanoparticles in the tumour compared to other tissues.
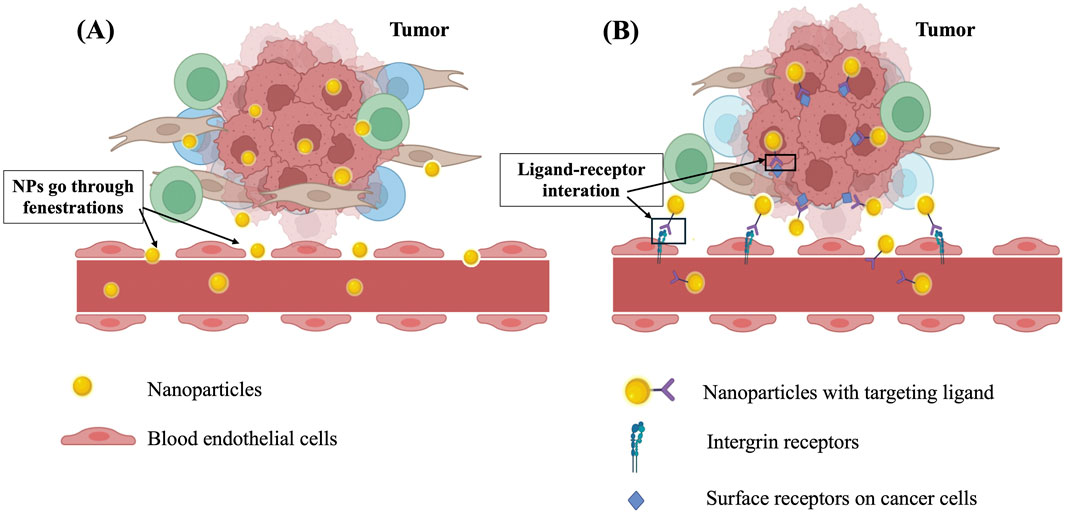
Figure 2. The mechanism of action of (A) passive targeting based on EPR effect and (B) active targeting based on interactions between targeting ligand and receptors.
In addition to the aforementioned drug delivery systems, stimuli-responsive prodrugs has been recently explored to control the drug release at the site of action, thereby enhancing drug perfusion into the tumour microenvironment (Rahim et al., 2021). Stimuli-responsive drug delivery systems contain “sensitive” moieties that undergo changes in response to exogenous (i.e., light, temperature, ultrasound) or endogenous (i.e., pH, redox potential, enzymes) stimuli at the target site (Majumder and Minko, 2021). An example of an exogenous-triggered system is thermosensitive liposome, which can increase its lipid bilayer permeability under heating to a temperature above the average transition temperature of the lipid mixture (Dou et al., 2017). ThermoDox®, the first commercialized thermosensitive liposome contains a lysolipid component (i.e., 1-stearoyl-2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidylcholine (MSPC or S-lyso-PC)) that becomes porous and releases approximately 80% of doxorubicin within 20 s upon heating to 42°C at the tumour site (Dou et al., 2017). pH-responsive prodrugs are systems belonging to endogenous triggered nanoplatforms. These systems contain either acid-cleavable linkers or ionizable groups that are stable at physiological pH 7.4 but susceptible to acidic pH. As a result, such prodrugs are degraded under the acidic condition in the tumour microenvironment (pH 6.5 – 7.0), leading to drug release at the targeted milieu (Xie et al., 2020).
5.1 Surface modification for passive targeting to the tumour
To achieve passive targeting, the physicochemical properties of nanomedicines should be favorable for the EPR effect. In the 1970s, Alec Bangham investigated the first liposome product as drug carriers, but researchers found that liposomes were quickly cleared by the RES, accumulating in the liver and spleen within minutes and reducing passive targeting effectiveness. PEGylation has emerged as a pivotal strategy for enhancing passive targeting in drug delivery systems. This modification imparts a hydrophilic stealth coating to the nanoparticles, significantly increasing their circulation time in the bloodstream by reducing opsonization and subsequent clearance by the MPS. The extended circulation time allows for enhanced accumulation of nanoparticles in tumour tissues through the EPR effect (Jokerst et al., 2011; Vllasaliu et al., 2014). In 1995, the first PEGylated nanomedicine was licensed to the market for the treatment of metastatic ovarian and breast cancer by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA), named Caelyx/Doxil® developed by Liposome Technology Inc., and recently sold by Johnson & Johnson. This product is doxorubicin-loaded liposome with a size less than 100 nm and stabilized with DSPE-PEG-2000 (Barenholz, 2012). Compared to the uncoated doxorubicin-loaded liposomes that were quickly cleared from human plasma before reaching the tumour, Doxil® circulates in the blood for up to 36 h and facilitates passive targeting to the tumour extended to 3-7 days (Barenholz, 2012). Following the success of PEGylated nano-liposomes, Genexol®, a product of Samyang Pharmaceuticals containing PEGylated poly (D, L-lactide) micelles loaded with paclitaxel, was approved in Korea in 2007 for the treatment of breast cancer and small cell lung cancer. This product demonstrated targeted biodistribution to malignant tissues, resulting in reduced toxicities of paclitaxel and promoted antitumour effect (Werner et al., 2013). The approval of these two PEGylated nano-products on the market for cancer treatment has strongly demonstrated the tumour targeting effect of PEGylation. Besides liposomes and micelles, the PEGylation technology has also been extensively studied on a wide range of nanocarriers. Studies on the tumour-directed effects of PEGylation in the past 5 years include research on solid lipid nanoparticles (Arduino et al., 2020; Smith et al., 2020; Korake et al., 2023), polymeric nanoparticles (Baião et al., 2020; Bobde et al., 2020; Guo et al., 2020), inorganic nanoparticles (Samadian et al., 2020; Sadalage et al., 2021), and dendrimers (Yadav et al., 2023) for cancer therapy. For instance, 5-fluorouracil-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles composed of PEGylated lipids and surfactants demonstrated a significant inhibition on tumour growth in mice bearing subcutaneous colorectal cancer cells, compared to the free form of 5-fluorouracil. At a dose of 20 mg/kg, 5-fluorouracil-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles remarkably suppressed HER2 receptor expression without causing toxicity in kidney and liver cells. This effect could be attributed to the passive targeting of the tumour due to PEGylation (Smith et al., 2020).
5.2 Surface modification for active targeting
While the EPR effect facilitates passive targeting of nanoparticles, it is often insufficient for achieving optimal therapeutic outcomes due to the heterogeneous and variable nature of tumour vasculature. To address the limitations of passive targeting, active targeting mechanisms have been developed, which are based on the selective and specific interactions of targeting ligands with specific receptors over-expressed in the target tissues. Attaching these targeting ligands to the surface of nanoformulations helps enhance targeting efficiency, increase cellular uptake and reach a wider range of targets than passive targeting. It is feasible to graft both PEG chains and targeting ligands on the surface to achieve both passive and active targeting effects. The common targeting moieties used in prior studies include transferrin, peptides, antibodies, carbohydrates, and aptamers (Vllasaliu et al., 2014).
5.2.1 Transferrin
Transferrin is a serum β-globulin with reversible binding properties to iron, first isolated by Schade and Caroline in 1946 (Giansanti et al., 2016). Transferrin plays an important role in transport and uptake of iron in the cells, and keeps the balance between the release of iron by RES and the absorption of iron by the bone marrow. When iron binds to transferrin, it will be transported by transferrin to the bone marrow to produce hemoglobin and part of red blood cells. In drug delivery, transferrin has been attached on the surface of nanoformulations to promote the interaction with the transferrin receptor 1 (TfR1), also known as CD-71 receptors, which are abundantly expressed in many types of maglinant cells. After binding to the receptors, the cellular uptake of these nano-formulations is improved through the receptor-mediated endocytosis pathway. Several nanocarriers, including polymeric micelles (Sun et al., 2020), dendrimers (Hu et al., 2020), polymeric nanoparticles (Zhang et al., 2021), nanocomplexes (Su et al., 2022) and liposomes (dos Santos Rodrigues et al., 2020; Fernandes et al., 2021; Mojarad-Jabali et al., 2022) have been successfully grafted with the transferrin ligand. Nanoformulations attached with transferrin showed a great cytotoxicity effect in several types of cancer cells in vitro and in vivo, including human breast carcinoma MCF-7ADR cells (Gao et al., 2017), human alveolar cancer cell lines (Singh et al., 2016), HepG2 human hepatoma cell line (Zhang et al., 2016), colon cancer cell line (Varshosaz et al., 2017), and glioblastoma cells (Jhaveri et al., 2018; Sandbhor et al., 2022). Among the aforementioned cancer cells, brain tumour cells receive the most attention due to the significant challenge of delivering drugs across the blood-brain barrier. Thanks to the abundance of transferrin receptors in brain endothelial cells, the nanoformulations attached with transferrin becomes a potential cargo for glioblastoma treatment (Ramalho et al., 2022). For example, quercetin lipid nanoparticles attached with transferrin showed enhanced brain permeability on human cerebral microvascular endothelial cells and offered great benefits on reverting amyloid-beta fibrillation in Alzheimer´s disease in vitro (Pinheiro et al., 2020). Alternatively, a curcumin–loaded solid lipid nanoparticle modified with transferrin also demonstrated an enhanced permeability across blood-brain barrier, providing greater efficacy on neuroprotection (Neves et al., 2021).
5.2.2 Peptides - tumour-homing peptides and cell-penetrating peptides
Tumour-homing peptides, particularly those containing the RGD (arginine-glycine-aspartic acid) motif, have emerged as a powerful tool for targeted cancer therapy. The RGD sequence is known for its strong affinity to integrins, especially αvβ3 and αvβ5 integrins, which are overexpressed on the surface of tumour cells and tumour vasculature. These integrins play a crucial role in tumour growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis by mediating cell adhesion and signaling. Nanoparticles modified with peptides containing the RGD motif, such as iRGD (CRGDKGPDC), on the surface can specifically bind to these integrins, thereby facilitating the targeted delivery to the tumour (Wang et al., 2014a). Previous studies have prepared liposomes, solid lipid nanoparticles and polymeric micelles attached with the RGD motif-containing peptide, which have shown enhancement in drug accumulation in tumour cells (Dubey et al., 2004; Wang et al., 2009; Sanati et al., 2023). For liposomes, the RGD peptides are typically conjugated to PEG-linked lipid ingredients prior to the formation of liposomes. For instance, liposomes can be prepared using distearoylphosphatidylcholine (DSPC), cholesterol and distearoylphosphatidylethanolamine–polyethyleneglycol–RGD peptide conjugate (DSPE–PEG–RGD) in a molar ratio of 56:39:5. This cyclic RGD-PEG-liposome formulation was significantly more effective against both primary and metastatic tumours than the non-targeted PEGylated liposome (Dubey et al., 2004). In another study, cyclic RGD molecules containing a free amine group (-NH2) were conjugated with DSPE-PEG2000-COOH via EDC/NHS chemistry to form cRGD-modified solid lipid nanoparticles. The cellular uptake studies of these cRGD-SLN on U87MG glioma cells has shown an enhancement in the uptake efficiency compared to the uncoated nanoparticles. The surface modification with cRGD is therefore considered an important factor in promoting the antitumour activity of solid lipid nanoparticles on malignant glioblastoma cells (Wang et al., 2021b). In addition to its benefits in cancer treatment, the tumour-targeting effect of RGD also offers diagnostic applications. Polydopamine nanospheres, which are utilized in photothermal imaging due to their high absorbance in the near-infrared region, were modified with RGD to target ανβ3 integrin-overexpressing tumour cells, thereby successfully enhancing the visualization of tumour position and borders in vivo (Liu et al., 2023).
Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs), also known as peptide transduction domains, are short peptides that are able to pass through a wide range of tissues and cell membranes. The internalization mechanism of CPPs occurs via either direct penetration through the cell membrane or through the endocytosis and macropinocytosis pathways, but not through interactions with specific receptors (Palm-Apergi et al., 2012). There are nearly 20 types of CPPs that have been tested in preclinical and clinical studies for their transporting capability into cells, including transactivator of transcription (TAT) protein of HIV-1, short arginine-rich sequence of TAT, penetratin pAntp (43-58), and polyarginines. Most of them comprise 5 – 30 amino acids, which are either cationic, amphiphilic, or hydrophobic (Guidotti et al., 2017). Thanks to these unique properties, CPPs have been used as surface ligands of nanomedicines to increase their ability to penetrate into target cells. This enhanced cellular uptake can address the limitation that although nano-carriers can reach the tumour environment via the EPR effect, they are not able to enter the cells (Desale et al., 2021). The first attempt of producing CPP-NP conjugates was described by Weissleder et al. in 1999, who reported a 100-fold higher internalization into lymphocytes compared to nonmodified particles (Josephson et al., 1999). Since then, numerous efforts have been made to conjugate CPP with mesoporous silica nanoparticles (Shadmani et al., 2023), liposomes (Yu et al., 2021), or hybrid magnetic nanoparticles (Zhang W. et al., 2020). CPP is also known as an emerging tool for the delivery of mRNA, siRNA, and pDNA, as it can improve endosomal escape efficiency and modulate endocytosis pathways in dendritic cells (Falato et al., 2021; Kurrikoff et al., 2021; Yokoo et al., 2021). This capability is crucial because, upon internalization, nucleic acid-based therapeutics often become trapped within endosomes, leading to their degradation and reduced therapeutic efficacy. CPPs facilitate the disruption of endosomal membranes, allowing the therapeutic cargo to escape into the cytoplasm where it can exert its intended biological function. For instance, the addition of CPP to poly (lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) nanoparticles containing pDNA enhanced the internalization and endosomal escape in Beas-2B and A549 cells, making the NP–DNA–CPP delivery system a promising approach for gene delivery to the lung (Gomes dos Reis et al., 2020).
5.2.3 Monoclonal antibodies (mAb) and antibody fragment (Fab)
Monoclonal antibodies (mAb) are large, Y-shaped glycoproteins, which are divided into two domains, the upper part is the Fab fragment and the lower part is the Fc fragment. The antigen binding site, known as the variable region, is at the top of the Fab fragment to specifically recognize and bind to the antigen. mAbs and Fab fragments are extensively studied for active targeting, especially tumour targeting. In addition, single-chain variable fragments (scFv), minibodies, diabodies, and nanobodies are other variants also used in drug targeting (Sanna et al., 2014). The choice of ligands depends on the compatibility between the structure and size of the ligand in the drug delivery system, and the features of the target tissues. Particularly, to target cancerous tissues that often over-express epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFR) and epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER-2 receptor), nanocarriers can be grafted with EGFR antibodies or HER2 antibodies on the surface to enhance the accumulation of nanocarriers in the tumour environment. For example, PLGA nanoparticles loaded with the anticancer agent, camptothecin was conjugated with mAb against EGFR (cetuximab) showed the targeting distribution of nanoparticles to mutant KRAS PANC-1 tumours and reduced tumour growth in vivo (McDaid et al., 2019). Besides tumour treatment, the targeting effect of antibodies is also useful for breast cancer imaging at the early stage. Recently, 5-poly (amidoamine) dendrimers conjugated with gold nanoparticles, chelated gadolinium, and anti-human HER-2 antibody (trastuzumab) enhanced MRI signal intensity by ∼ 20% and improved CT resolution and contrast by two-fold (Chen et al., 2020).
5.2.4 Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are highly biocompatible and have low immunogenicity as ligands for active targeting. Among ligands such as dextran, mannose, and hyaluronic acid (HA), HA is widely studied in drug delivery systems. HA is an anionic, nonsulfated glycosaminoglycan, widely distributed in the extracellular matrix and recognized as a natural ligand for CD44, a cell surface adhesion molecule that is overexpressed in cancer cells, particularly in tumour-initiating cells (Wang et al., 2014a). Nanomedicine modified with HA is thus a potential targeted delivery system to tumour cells including liposomes (Park et al., 2014), mesoporous silica nanoparticles (Yu et al., 2013), and solid lipid nanoparticles (Shen et al., 2015). Recently, a biocompatible glycosaminoglycan layer of hyaluronic acid was attached to the surface of gene-loaded nanoparticles to selectively interact with CD44 receptors and thus increase the biodistribution of nanoparticles into cancer cells (Zhang et al., 2020a).
5.2.5 Aptamers
Aptamers are 3D conformations of DNA or RNA oligonucleotides that are potentially used as therapeutic agents in clinical applications or as targeting ligands to enhance active targeted delivery (Gao et al., 2022). Aptamers are commonly conjugated with potent chemical drugs or biological medicines via cleavable linkers, which can be broken down to release the payloads upon exposure to environmental conditions such as low acidic pH, high redox, or high enzymatic activity. The aptamer AS1411 was conjugated to proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs) to improve tumour-specific targeting. In an MCF-7 xenograft model, imaging assays showed that 8 h after administration, a high concentration of aptamer-modified PROTACs was observed in tumour tissues, while no signal was detected from the unmodified PROTACs. This result demonstrated the targeting effect of the aptamer in vivo distribution to breast cancer cells (He et al., 2021).
6 Applications of surface modifications on nanoparticle toxicity
Surface altering techniques have been employed extensively to reduce the toxicity of nanoparticles since the translation of nanomedicine from bench to bedside has encountered many toxicity-related problems. The harmful effects of nanoparticles predominantly depend on their physical and chemical properties, including dimensions, configuration, surface area, electric charge, catalytic potential, and coatings (Sukhanova et al., 2018). Aiming to reduce the toxicity of nanoparticles, one must first and foremost carefully examine the surface charges of nanoparticles. Naturally, cell membranes exhibit negative charges because of the lipid bilayer. Thus, nanoparticles with positive surface charges or zeta potential could interact with the cell membranes. Many studies have indeed demonstrated higher toxicity of positively charged nanoparticles compared to neutral or negatively charged counterparts (Kedmi et al., 2010; Jones et al., 2012; Hühn et al., 2013; Bozich et al., 2014). Wang et al. modified the surface charge of injected nano drug vehicles containing doxorubicin, a positively charged drug, to negative by utilizing poly (carboxybetaine methacrylate) (pCBMA) and negatively charged monomer sodium methacrylate (SMA). This strategy effectively mitigated toxicity, enhanced resistance to non-specific protein adsorption, and prolonged circulation time (Wang et al., 2014b). In the intestinal epithelial cell model, surface charge modification has also been demonstrated to reduce cytotoxicity, and between two factors, size and surface charge, the latter plays a more decisive role in the interaction of nanoparticles with these cell models (Bannunah et al., 2014). Surface charge modification not only decreases cytotoxicity of the nanoparticles but also enhances their haemocompatibility. Generally, cationic particles or polymers induce more adverse effects on blood cells and coagulation processes (Boas and Heegaard, 2004). Aisina et al. indicated that cationic polyamidoamine dendrimers prolonged prothrombin time and decreased endogenous thrombin generation, whereas anionic dendrimers did not impact these factors. Thus, cationic dendrimers exhibit a more pronounced inhibition of the overall hemostatic potential in plasma compared to anionic dendrimers (Aisina et al., 2020).
Another emerging approach to tackle toxicity-related challenges is to employ highly biocompatible molecules to coat the surface of nanoparticles. Commonly used coating moieties range from synthetic derivatives (e.g., PEG, silica, dextran) to nature-inspired derivatives (e.g., chitosan, red blood cell membrane, albumin) (Table 2). To illustrate, surface modification of zinc oxide nanoparticles with ε-polylysine (ε-PL) via mussel-inspired methods and “Michael addition” reactions significantly reduces toxicity, as indicated by improved cell viability at a high concentration (500 μg/mL) (Luo et al., 2023). The surface modification strategy can also mitigate the toxicity of nanoparticles by enhancing immunocompatibility. To evade detection by the immune system, nanoparticle surface can be modified with various molecules, commonly hydrophilic polymers, which form a protective shield by binding water molecules. This outermost water layer diminishes interactions with opsonins and macrophage receptors, thus rendering nanoparticles invisible to immune system cells (Pinzaru et al., 2018).
7 Summary, challenges and future directions of surface modifications on drug delivery
In recent decades, there has been a growing interest in developing strategies for surface modification of nanoparticles for drug delivery purposes (Priya et al., 2023). A wide range of ligands have been used to reduce toxicity, improve stability, and enhance drug bioavailability (Newhouse et al., 2023). By harnessing the specific interactions between the surface ligands of nanoparticles and receptors overexpressed on target cells, the modified nanoparticles can be customized to actively target these cells and enhance cellular internalisation (Ying et al., 2022; Priya et al., 2023).
While surface modifications of nanoparticles offer significant promise for drug delivery, numerous challenges persist in this field (Gessner, 2021). First, the orientation and density of ligands on the nanoparticle surface are critical factors in affecting cellular uptake. The modification of nanoparticles with large molecules can significantly increase nanoparticle size and affect cellular uptake. Therefore, it is essential to examine the size distribution and morphology of modified nanoparticles to identify changes and their impact on cellular uptake. Secondly, the effectiveness of surface modification largely depends on the type of ligands and the methods employed to incorporate them onto the nanoparticle surface. Therefore, ligands should be carefully screened, and selecting an appropriate method is crucial for achieving effective modification. Thirdly, the non-covalent bonds between the nanoparticles and ligands are susceptible to changes in environmental conditions, including temperature, pH, and ionic strength. Therefore, it is essential to investigate the stability of surface-modified nanoparticles under various physiological conditions to ensure their integrity (Zou et al., 2023). Fourthly, during the functionalisation process, some ligands may undergo changes in their three-dimensional structure. This could potentially compromise the targeting ability of active ligands. Fifthly, the fate of modified nanoparticles in the body, including their absorption, biodistribution, metabolism, and excretion, requires thorough investigation to assess their delivery to target tissues or organs (Maheshwari et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2020b). Finally, it is essential to assess the biocompatibility, toxicity, and long-term effects of surface-modified nanoparticles on the body. This evaluation should include thorough assessments of adverse reactions and immunogenic responses resulting from the surface modifications (Kozma et al., 2020b; Duong, 2023). For instance, the production of anti-PEG antibodies in response to PEG exposure may increase clearance from the body and reduce the efficacy of the nanoparticles (Kozma et al., 2020a).
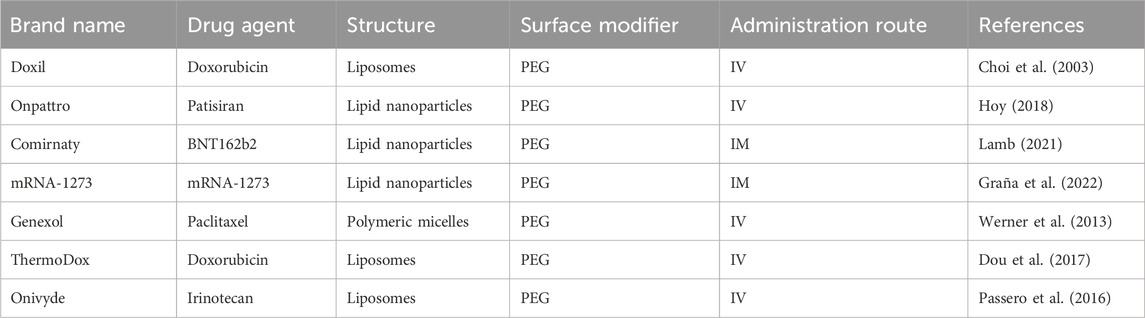
The regulatory approval process for nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems, including those with surface modifications, involves rigorous evaluation by the US FDA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA). These agencies assess different factors to ensure the safety, efficacy, and quality of the product. For instance, the pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of the drug can be altered after surface modification of the nanoparticles and should be evaluated. The modification can lead to an extended half-life and reduced immunogenicity (Gabizon et al., 2003). Therefore, a thorough investigation should be conducted to understand potential long-term effects, including immunogenic reactions to the ligands. Several detailed characterisations of the surface modifications may be required, including studies on the stability of the modification in the bloodstream and the potential for interactions with other components in the body. Through these comprehensive preclinical studies, the nanoparticles with surface modifications must demonstrate safety and efficacy before they proceed to clinical trials. The regulatory review will also focus on the reproducibility of the surface modification process and the consistency of the nanoparticle production. This involves strict adherence to Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) and thorough documentation to ensure the final product maintains its intended characteristics. Variations in surface decoration could lead to inconsistent therapeutic outcomes or unexpected side effects. Once the preclinical data demonstrate the safety, efficacy, and reproducibility of the surface-modified nanoparticles, they will be evaluated in the clinical phases. Some surface-modified nanoparticles have led to successful clinical outcomes (Table 3), such as Doxil (Choi et al., 2003), Genexol (Werner et al., 2013), Onivyde (Passero et al., 2016), ThermoDox (Dou et al., 2017), Onpattro (Hoy, 2018), Comirnaty (Lamb, 2021), and mRNA-1273 (Graña et al., 2022). However, some clinical trials may fail due to unexpected immune responses, off-target effects, or insufficient targeting specificity. On the other hand, the outcomes of these trials may influence regulatory guidelines, pushing for more detailed preclinical testing and more models to predict clinical behavior.
Currently, several clinical trials involving surface-modified nanoparticles in tumour immunotherapy are underway. For example, surface-modified liposomes targeting mucinous glycoprotein-1 (MUC1) have been investigated for their potential to induce T-cell immune responses in managing non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) (NCT00409188) (Butts et al., 2014), colon carcinoma (NCT01462513), rectal cancer (NCT01507103), and prostate cancer (NCT01496131) (Chen and Cong, 2023). These trials highlight the promising role of surface modification of nanoparticles in drug delivery, offering enhanced biocompatibility, stability, uptake, and targeting ability. During the development of surface-modified nanoparticles, it is essential to evaluate their impact on nanoparticle size distribution, morphology, stability, toxicity, and in vivo fate. In the coming years, we anticipate a surge in research on surface-modified nanoparticles, especially in the field of cancer immunotherapy. Future investigations will likely prioritize the utilisation of a wide range of ligands with tailored properties to target specific cells or tissues effectively. Furthermore, comprehensive biodistribution studies will be conducted to validate the efficacy of the designed surface-modified nanoparticles. Another promising trend is multi-functionalisation, where nanoparticles are engineered to carry multiple functional groups, allowing for the attachment of targeting ligands, imaging agents, and therapeutic molecules on the same nanoparticle. This trend is particularly important for creating drug delivery systems that can simultaneously diagnose and treat diseases, which are often referred to as theranostic nanoparticles (Hosseini et al., 2023). We anticipate more advances in the adoption of bioinspired and biomimetic approaches to develop nanoparticles that mimic natural biological processes. For instance, coating nanoparticles with cell membranes or utilizing endogenous molecules for surface decoration can enhance biocompatibility and reduce immune system recognition, thereby prolonging circulation time and improving the therapeutic index. These bioinspired nanoparticles can better navigate the complex biological environment, increasing their efficiency in targeting specific tissues (Chen et al., 2019). We also expect the future advancement of surface-modified nanoparticles for nose-to-brain delivery. Given the direct anatomical link between the nasal cavity and the central nervous system, nanoparticles administered intranasally have the potential to penetrate the central nervous system (Nguyen and Maeng, 2022). Surface modification of nanoparticles with mucoadhesive polymers can prolong the residence times of the nanoparticles in the nasal cavity, consequently enhancing drug absorption and accumulation in the brain (Singh et al., 2018; Qureshi et al., 2019; Kaur et al., 2021). The utilisation of Angiopep-2, a peptide capable of traversing the blood-brain barrier, in the modification of nanoparticles enables their transportation from the bloodstream to the brain (Wei et al., 2018; Duong et al., 2023). This represents another promising application for future development in surface-modified nanoparticles.
Author contributions
P-DL: Conceptualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. K-NL: Conceptualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. H-LP: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. HuN: Supervision, Writing–review and editing. V-AD: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. HiN: Conceptualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing, Visualization, Resources, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdelkawi, A., Slim, A., Zinoune, Z., and Pathak, Y. (2023). Surface modification of metallic nanoparticles for targeting drugs. Coatings 13 (9), 1660. doi:10.3390/coatings13091660
Abd Ellah, N. H., and Abouelmagd, S. A. (2017). Surface functionalization of polymeric nanoparticles for tumor drug delivery: approaches and challenges. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 14 (2), 201–214. doi:10.1080/17425247.2016.1213238
Aisina, R., Mukhametova, L., and Ivanova, E. (2020). Influence cationic and anionic PAMAM dendrimers of low generation on selected hemostatic parameters in vitro. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 109, 110605. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2019.110605
Alcantara, K. P., Malabanan, J. W. T., Vajragupta, O., Rojsitthisak, P., and Rojsitthisak, P. (2024). A promising strategy of surface-modified nanoparticles targeting CXCR4 for precision cancer therapy. J. Drug Target. 32, 587–605. doi:10.1080/1061186x.2024.2345235
Annesi, F., Pane, A., Pezzi, L., Pagliusi, P., Losso, M. A., Stamile, B., et al. (2021). Biocompatible and biomimetic keratin capped Au nanoparticles enable the inactivation of mesophilic bacteria via photo-thermal therapy. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 625, 126950. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126950
Annu, , Sartaj, A., Qamar, Z., Md, S., Alhakamy, N. A., Baboota, S., et al. (2022). An insight to brain targeting utilizing polymeric nanoparticles: effective treatment modalities for neurological disorders and brain tumor. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 10, 788128. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2022.788128
Aoki, H., Aoki, H., Kutsuno, T., Li, W., and Niwa, M. (2000). An in vivo study on the reaction of hydroxyapatite-sol injected into blood. J. Mater Sci. Mater Med. 11 (2), 67–72. doi:10.1023/a:1008993814033
Arduino, I., Depalo, N., Re, F., Dal Magro, R., Panniello, A., Margiotta, N., et al. (2020). PEGylated solid lipid nanoparticles for brain delivery of lipophilic kiteplatin Pt (IV) prodrugs: an in vitro study. Int. J. Pharm. 583, 119351. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.119351
Azarmi, S., Roa, W. H., and Löbenberg, R. (2008). Targeted delivery of nanoparticles for the treatment of lung diseases. Adv. drug Deliv. Rev. 60 (8), 863–875. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2007.11.006
Baião, A., Sousa, F., Oliveira, A. V., Oliveira, C., and Sarmento, B. (2020). Effective intracellular delivery of bevacizumab via PEGylated polymeric nanoparticles targeting the CD44v6 receptor in colon cancer cells. Biomaterials Sci. 8 (13), 3720–3729. doi:10.1039/d0bm00556h
Balas, M., Ciobanu, C. S., Burtea, C., Stan, M. S., Bezirtzoglou, E., Predoi, D., et al. (2017). Synthesis, characterization, and toxicity evaluation of dextran-coated iron oxide nanoparticles. Metals 7 (2), 63. doi:10.3390/met7020063
Balenzano, G., Racaniello, G. F., Panzarino, M. D., Knoll, P., Truszkowska, M., Laquintana, V., et al. (2024). S-protected thiolated surfactants enhancing surface properties of lipid-based nanocarriers. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 95, 105540. doi:10.1016/j.jddst.2024.105540
Bannunah, A. M., Vllasaliu, D., Lord, J., and Stolnik, S. (2014). Mechanisms of nanoparticle internalization and transport across an intestinal epithelial cell model: effect of size and surface charge. Mol. Pharm. 11 (12), 4363–4373. doi:10.1021/mp500439c
Barenholz, Y. C. (2012). Doxil® — the first FDA-approved nano-drug: lessons learned. J. Control. release 160 (2), 117–134. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.03.020
Barnaud, L., Fukuhara, S., Pava, M., Carrasco, M., Aviñó, A., Eritja, R., et al. (2024). Surface decoration of PLGA nanoparticles enables efficient transport of floxuridine oligomers into mammalian cells. React. Funct. Polym. 202, 105959. doi:10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2024.105959
Beach, M. A., Nayanathara, U., Gao, Y., Zhang, C., Xiong, Y., Wang, Y., et al. (2024). Polymeric nanoparticles for drug delivery. Chem. Rev. 124 (9), 5505–5616. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00705
Begines, B., Ortiz, T., Pérez-Aranda, M., Martínez, G., Merinero, M., Argüelles-Arias, F., et al. (2020). Polymeric nanoparticles for drug delivery: recent developments and future prospects. Nanomaterials 10 (7), 1403. doi:10.3390/nano10071403
Bhowmik, D., Mote, K. R., MacLaughlin, C. M., Biswas, N., Chandra, B., Basu, J. K., et al. (2015). Cell-membrane-mimicking lipid-coated nanoparticles confer Raman enhancement to membrane proteins and reveal membrane-attached amyloid-β conformation. ACS Nano 9 (9), 9070–9077. doi:10.1021/acsnano.5b03175
Boas, U., and Heegaard, P. M. H. (2004). Dendrimers in drug research. Chem. Soc. Rev. 33 (1), 43–63. doi:10.1039/b309043b
Bobde, Y., Biswas, S., and Ghosh, B. (2020). PEGylated N-(2 hydroxypropyl) methacrylamide-doxorubicin conjugate as pH-responsive polymeric nanoparticles for cancer therapy. React. Funct. Polym. 151, 104561. doi:10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2020.104561
Bozich, J., Lohse, S., Torelli, M., Murphy, C., Hamers, R., and Klaper, R. (2014). Surface chemistry, charge and ligand type impact the toxicity of gold nanoparticles to Daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Nano 1 (3), 260–270. doi:10.1039/c4en00006d
Butts, C., Socinski, M. A., Mitchell, P. L., Thatcher, N., Havel, L., Krzakowski, M., et al. (2014). Tecemotide (L-BLP25) versus placebo after chemoradiotherapy for stage III non-small-cell lung cancer (START): a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 15 (1), 59–68. doi:10.1016/s1470-2045(13)70510-2
Bychkova, A., Sorokina, O., Pronkin, P., Tatikolov, A., Kovarski, A., and Rosenfeld, M. (2013). “Protein-coated magnetic nanoparticles: creation and investigation,” in Proceedings of the international conference nanomaterials: applications and properties (Sumy, Ukraine: Sumy State University Publishing).
Catala, C., Mir-Simon, B., Feng, X., Cardozo, C., Pazos-Perez, N., Pazos, E., et al. (2016). Online SERS quantification of Staphylococcus aureus and the application to diagnostics in human fluids. Adv. Mater. Technol. 1 (8). doi:10.1002/admt.201600163
Chanana, M., Rivera Gil, P., Correa-Duarte, M. A., Liz-Marzan, L. M., and Parak, W. J. (2013). Physicochemical properties of protein-coated gold nanoparticles in biological fluids and cells before and after proteolytic digestion. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 52 (15), 4179–4183. doi:10.1002/anie.201208019
Chen, B., Li, F., Zhu, X. K., Xie, W., Hu, X., Zan, M. H., et al. (2021). Highly biocompatible and recyclable biomimetic nanoparticles for antibiotic-resistant bacteria infection. Biomaterials Sci. 9 (3), 826–834. doi:10.1039/d0bm01397h
Chen, J., and Cong, X. (2023). Surface-engineered nanoparticles in cancer immune response and immunotherapy: current status and future prospects. Biomed. & Pharmacother. 157, 113998. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113998
Chen, J. S., Chen, J., Bhattacharjee, S., Cao, Z., Wang, H., Swanson, S. D., et al. (2020). Functionalized nanoparticles with targeted antibody to enhance imaging of breast cancer in vivo. J. Nanobiotechnology 18, 135–139. doi:10.1186/s12951-020-00695-2
Chen, Z., Wang, Z., and Gu, Z. (2019). Bioinspired and biomimetic nanomedicines. Acc. Chem. Res. 52 (5), 1255–1264. doi:10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00079
Chhabra, M. (2021). “Biological therapeutic modalities,” in Translational biotechnology (Elsevier), 137–164.
Chiu, J. Z. S., Castillo, A. M., Tucker, I. G., Radunskaya, A. E., and McDowell, A. (2022). Modeling the interaction of polymeric nanoparticles functionalized with cell penetrating peptides at the nano-bio interface. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 217, 112626. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2022.112626
Choi, S. W., Kim, W. S., and Kim, J. H. (2003). Surface modification of functional nanoparticles for controlled drug delivery. J. Dispersion Sci. Technol. 24 (3-4), 475–487. doi:10.1081/dis-120021803
Debbage, P. J. C. p.d. (2009). Targeted drugs and nanomedicine: present and future. Curr. Pharm. Des. 15 (2), 153–172. doi:10.2174/138161209787002870
Delaviz, N., Gill, P., Ajami, A., and Aarabi, M. (2015). Aptamer-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles for the efficient removal of HCV particles from human plasma samples. RSC Adv. 5 (97), 79433–79439. doi:10.1039/c5ra12209k
Delgado, A. D. S., Leonard, M., and Dellacherie, E. (2000). Surface modification of polystyrene nanoparticles using dextrans and dextran–POE copolymers: polymer adsorption and colloidal characterization. J. Biomaterials Sci. 11 (12), 1395–1410. doi:10.1163/156856200744309
De Lorenzi, F., Rizzo, L. Y., Daware, R., Motta, A., Baues, M., Bartneck, M., et al. (2023). Profiling target engagement and cellular uptake of cRGD-decorated clinical-stage core-crosslinked polymeric micelles. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 13 (5), 1195–1211. doi:10.1007/s13346-022-01204-8
Deng, X., Zhao, J., Liu, K., Wu, C., and Liang, F. (2021a). Stealth PEGylated chitosan polyelectrolyte complex nanoparticles as drug delivery carrier. J. Biomaterials Sci. 32 (11), 1387–1405. doi:10.1080/09205063.2021.1918043
Deng, Z., Kalin, G. T., Shi, D., and Kalinichenko, V. V. (2021b). Nanoparticle delivery systems with cell-specific targeting for pulmonary diseases. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 64 (3), 292–307. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2020-0306tr
de Oliveira, G. M. T., de Oliveira, E. M. N., Pereira, T. C. B., Papaléo, R. M., and Bogo, M. R. (2017). Implications of exposure to dextran-coated and uncoated iron oxide nanoparticles to developmental toxicity in zebrafish. J. Nanoparticle Res. 19 (12), 389. doi:10.1007/s11051-017-4074-5
Desale, K., Kuche, K., and Jain, S. (2021). Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs): an overview of applications for improving the potential of nanotherapeutics. Biomaterials Sci. 9 (4), 1153–1188. doi:10.1039/d0bm01755h
Dkhar, D. S., Kumari, R., Mahapatra, S., Divya, , Kumar, R., Tripathi, T., et al. (2022). Antibody-receptor bioengineering and its implications in designing bioelectronic devices. Int J Biol Macromol 218. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 218, 225–242. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.07.109
dos Santos Rodrigues, B., Kanekiyo, T., and Singh, J. (2020). In vitro and in vivo characterization of CPP and transferrin modified liposomes encapsulating pDNA. Nanomedicine Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 28, 102225. doi:10.1016/j.nano.2020.102225
Dou, Y., Hynynen, K., and Allen, C. (2017). To heat or not to heat: challenges with clinical translation of thermosensitive liposomes. J. Control. release 249, 63–73. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.01.025
Dubey, P. K., Mishra, V., Jain, S., Mahor, S., and Vyas, S. (2004). Liposomes modified with cyclic RGD peptide for tumor targeting. J. drug Target. 12 (5), 257–264. doi:10.1080/10611860410001728040
Duong, V.-A. (2023). Polymer surface treatments for drug delivery and wound healing. Appl. Sci. 13 (16), 9054. doi:10.3390/app13169054
Duong, V.-A., Nguyen, T.-T.-L., and Maeng, H.-J. (2023). Recent advances in intranasal liposomes for drug, gene, and vaccine delivery. Pharmaceutics 15 (1), 207. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics15010207
Ehsani, G., Farahnak, M., Norouzian, D., and Ehsani, P. (2021). Immobilization of recombinant lysostaphin on nanoparticle through biotin–streptavidin conjugation technology as a geometrical progressed confrontation against Staphylococcus aureus infection. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 68 (5), 1058–1066. doi:10.1002/bab.2025
Falato, L., Gestin, M., and Langel, Ü. (2021). Cell-penetrating peptides delivering siRNAs: an overview. Des. Deliv. SiRNA Ther. 2282, 329–352. doi:10.1007/978-1-0716-1298-9_18
Fam, S. Y., Chee, C. F., Yong, C. Y., Ho, K. L., Mariatulqabtiah, A. R., and Tan, W. S. (2020). Stealth coating of nanoparticles in drug-delivery systems. Nanomater. (Basel) 10 (4), 787. doi:10.3390/nano10040787
Farooq, A., Shukur, A., Astley, C., Tosheva, L., Kelly, P., Whitehead, D., et al. (2018). Titania coating of mesoporous silica nanoparticles for improved biocompatibility and drug release within blood vessels. Acta Biomater. 76, 208–216. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2018.06.024
Fernandes, M. A., Eloy, J. O., Luiz, M. T., Junior, S. L. R., Borges, J. C., de la Fuente, L. R., et al. (2021). Transferrin-functionalized liposomes for docetaxel delivery to prostate cancer cells. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 611, 125806. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.125806
Flores, A. M., Ye, J., Jarr, K.-U., Hosseini-Nassab, N., Smith, B. R., and Leeper, N. J. (2019). Nanoparticle therapy for vascular diseases. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, Vasc. Biol. 39 (4), 635–646. doi:10.1161/atvbaha.118.311569
Friedman, A., Claypool, S., and Liu, R. (2013). The smart targeting of nanoparticles. Curr. Pharm. Des. 19 (35), 6315–6329. doi:10.2174/13816128113199990375
Fu, S., Liang, M., Wang, Y., Cui, L., Gao, C., Chu, X., et al. (2019). Dual-modified novel biomimetic nanocarriers improve targeting and therapeutic efficacy in glioma. ACS Appl. Mater. & Interfaces 11 (2), 1841–1854. doi:10.1021/acsami.8b18664
Gabizon, A., Shmeeda, H., and Barenholz, Y. (2003). Pharmacokinetics of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 42 (5), 419–436. doi:10.2165/00003088-200342050-00002
Gamucci, O., Bertero, A., Gagliardi, M., and Bardi, G. (2014). Biomedical nanoparticles: overview of their surface immune-compatibility. Coatings 4 (1), 139–159. doi:10.3390/coatings4010139
Gao, F., Yin, J., Chen, Y., Guo, C., Hu, H., and Su, J. (2022). Recent advances in aptamer-based targeted drug delivery systems for cancer therapy. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 10, 972933. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2022.972933
Gao, W., Ye, G., Duan, X., Yang, X., and Yang, V. C. (2017). Transferrin receptor-targeted pH-sensitive micellar system for diminution of drug resistance and targetable delivery in multidrug-resistant breast cancer. Int. J. Nanomedicine Vol. 12, 1047–1064. doi:10.2147/ijn.s115215
Garcia, I., Sanchez-Iglesias, A., Henriksen-Lacey, M., Grzelczak, M., Penades, S., and Liz-Marzan, L. M. (2015). Glycans as biofunctional ligands for gold nanorods: stability and targeting in protein-rich media. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137 (10), 3686–3692. doi:10.1021/jacs.5b01001
Gessner, I. (2021). Optimizing nanoparticle design and surface modification toward clinical translation. MRS Bull. 46 (7), 643–649. doi:10.1557/s43577-021-00132-1
Giansanti, F., Panella, G., Leboffe, L., and Antonini, G. (2016). Lactoferrin from milk: nutraceutical and pharmacological properties. Pharmaceuticals 9 (4), 61. doi:10.3390/ph9040061
Gomes dos Reis, L., Lee, W.-H., Svolos, M., Moir, L. M., Jaber, R., Engel, A., et al. (2020). Delivery of pDNA to lung epithelial cells using PLGA nanoparticles formulated with a cell-penetrating peptide: understanding the intracellular fate. Drug Dev. Industrial Pharm. 46 (3), 427–442. doi:10.1080/03639045.2020.1724134
Gomez–Caballero, L. F., Pichardo-Molina, J. L., Briones, J., Oyarzún, S., Denardin, J. C., and Basurto-Islas, G. (2023). Facile synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles at room temperature coated with meso-2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid for improved biocompatibility. J. Nanoparticle Res. 25 (4), 66. doi:10.1007/s11051-023-05711-8
Gounani, Z., Asadollahi, M. A., Meyer, R. L., and Arpanaei, A. (2018). Loading of polymyxin B onto anionic mesoporous silica nanoparticles retains antibacterial activity and enhances biocompatibility. Int. J. Pharm. 537 (1), 148–161. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.12.039
Graña, C., Ghosn, L., Evrenoglou, T., Jarde, A., Minozzi, S., Bergman, H., et al. (2022). Efficacy and safety of COVID-19 vaccines. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 12 (12), Cd015477. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd015477
Guerrini, L., Alvarez-Puebla, R. A., and Pazos-Perez, N. (2018). Surface modifications of nanoparticles for stability in biological fluids. Mater. (Basel) 11 (7), 1154. doi:10.3390/ma11071154
Guidotti, G., Brambilla, L., and Rossi, D. (2017). Cell-penetrating peptides: from basic research to clinics. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 38 (4), 406–424. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2017.01.003
Guo, L., Huang, Z., Huang, L., Liang, J., Wang, P., Zhao, L., et al. (2021). Surface-modified engineered exosomes attenuated cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by targeting the delivery of quercetin towards impaired neurons. J. Nanobiotechnology 19 (1), 141. doi:10.1186/s12951-021-00879-4
Guo, W., Chen, M., Yang, Y., Ge, G., Tang, L., He, S., et al. (2023). Biocompatibility and biological effects of surface-modified conjugated polymer nanoparticles. , 28(5), 2034, doi:10.3390/molecules28052034
Guo, Z., Sui, J., Ma, M., Hu, J., Sun, Y., Yang, L., et al. (2020). pH-Responsive charge switchable PEGylated ε-poly-l-lysine polymeric nanoparticles-assisted combination therapy for improving breast cancer treatment. J. Control. Release 326, 350–364. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.07.030
Gupta, N. K., Tomar, P., Sharma, V., and Dixit, V. K. (2011). Development and characterization of chitosan coated poly-(ɛ-caprolactone) nanoparticulate system for effective immunization against influenza. Vaccine 29 (48), 9026–9037. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.09.033
Han, H. S., Martin, J. D., Lee, J., Harris, D. K., Fukumura, D., Jain, R. K., et al. (2013). Spatial charge configuration regulates nanoparticle transport and binding behavior in vivo. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 52 (5), 1414–1419. doi:10.1002/anie.201208331
Han, J. S., An, G. S., Park, B. G., and Choi, S.-C. (2018). The influence of functionalization of the Fe3O4 nanoparticle on its dispersion property. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 55 (1), 80–84. doi:10.4191/kcers.2018.55.1.01
Han, N., Wang, Y., Bai, J., Liu, J., Wang, Y., Gao, Y., et al. (2016). Facile synthesis of the lipid bilayer coated mesoporous silica nanocomposites and their application in drug delivery. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 219, 209–218. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2015.08.006
Han, Y., Gao, C., Wang, H., Sun, J., Liang, M., Feng, Y., et al. (2021). Macrophage membrane-coated nanocarriers Co-Modified by RVG29 and TPP improve brain neuronal mitochondria-targeting and therapeutic efficacy in Alzheimer's disease mice. Bioact. Mater. 6 (2), 529–542. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.08.017
He, C., Hu, Y., Yin, L., Tang, C., and Yin, C. (2010). Effects of particle size and surface charge on cellular uptake and biodistribution of polymeric nanoparticles. Biomaterials 31 (13), 3657–3666. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.01.065
He, S., Gao, F., Ma, J., Ma, H., Dong, G., and Sheng, C. (2021). Aptamer-protac conjugates (apcs) for tumor-specific targeting in breast cancer. Angew. Chem. 133 (43), 23487–23493. doi:10.1002/ange.202107347
Hirsjarvi, S., Passirani, C., and Benoit, J.-P. (2011). Passive and active tumour targeting with nanocarriers. Curr. drug Discov. Technol. 8 (3), 188–196. doi:10.2174/157016311796798991
Hosseini, N. F., Amini, R., Ramezani, M., Saidijam, M., Hashemi, S. M., and Najafi, R. (2022). AS1411 aptamer-functionalized exosomes in the targeted delivery of doxorubicin in fighting colorectal cancer. Biomed. & Pharmacother. 155, 113690. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113690
Hosseini, S. M., Mohammadnejad, J., Salamat, S., Beiram Zadeh, Z., Tanhaei, M., and Ramakrishna, S. (2023). Theranostic polymeric nanoparticles as a new approach in cancer therapy and diagnosis: a review. Mater. Today Chem. 29, 101400. doi:10.1016/j.mtchem.2023.101400
Hotze, E. M., Phenrat, T., and Lowry, G. V. (2010). Nanoparticle aggregation: challenges to understanding transport and reactivity in the environment. J. Environ. Qual. 39 (6), 1909–1924. doi:10.2134/jeq2009.0462
Hoy, S. M. (2018). Patisiran: first global approval. Drugs 78 (15), 1625–1631. doi:10.1007/s40265-018-0983-6
Hu, Q., Wang, Y., Xu, L., Chen, D., and Cheng, L. (2020). Transferrin conjugated pH-and redox-responsive poly (amidoamine) dendrimer conjugate as an efficient drug delivery carrier for cancer therapy. Int. J. nanomedicine Vol. 15, 2751–2764. doi:10.2147/ijn.s238536
Hühn, D., Kantner, K., Geidel, C., Brandholt, S., De Cock, I., Soenen, S. J. H., et al. (2013). Polymer-coated nanoparticles interacting with proteins and cells: focusing on the sign of the net charge. ACS Nano 7 (4), 3253–3263. doi:10.1021/nn3059295
Jhaveri, A., Deshpande, P., Pattni, B., and Torchilin, V. (2018). Transferrin-targeted, resveratrol-loaded liposomes for the treatment of glioblastoma. J. Control. release 277, 89–101. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.03.006
Jokerst, J. V., Lobovkina, T., Zare, R. N., and Gambhir, S. S. (2011). Nanoparticle PEGylation for imaging and therapy. Nanomedicine 6 (4), 715–728. doi:10.2217/nnm.11.19
Jones, C. F., Campbell, R. A., Brooks, A. E., Assemi, S., Tadjiki, S., Thiagarajan, G., et al. (2012). Cationic PAMAM dendrimers aggressively initiate blood clot formation. ACS Nano 6 (11), 9900–9910. doi:10.1021/nn303472r
Josephson, L., Tung, C.-H., Moore, A., and Weissleder, R. (1999). High-efficiency intracellular magnetic labeling with novel superparamagnetic-Tat peptide conjugates. Bioconjugate Chem. 10 (2), 186–191. doi:10.1021/bc980125h
Kang, H., Rho, S., Stiles, W. R., Hu, S., Baek, Y., Hwang, D. W., et al. (2020). Size-Dependent EPR effect of polymeric nanoparticles on tumor targeting. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 9 (1), 1901223. doi:10.1002/adhm.201901223
Kaur, R., Gorki, V., Singh, G., Kaur, R., Katare, O. P., Nirmalan, N., et al. (2021). Intranasal delivery of polymer-anchored lipid nanoconstructs of artemether-lumefantrine in Plasmodium berghei ANKA murine model. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 61, 102114. doi:10.1016/j.jddst.2020.102114
Kedmi, R., Ben-Arie, N., and Peer, D. (2010). The systemic toxicity of positively charged lipid nanoparticles and the role of Toll-like receptor 4 in immune activation. Biomaterials 31 (26), 6867–6875. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.05.027
Khunsuk, P. O., Pongma, C., Palaga, T., and Hoven, V. P. (2023). Zwitterionic polymer-decorated lipid nanoparticles for mRNA delivery in mammalian cells. Biomacromolecules 24 (12), 5654–5665. doi:10.1021/acs.biomac.3c00649
Knop, K., Hoogenboom, R., Fischer, D., and Schubert, U. S. (2010). Poly(ethylene glycol) in drug delivery: pros and cons as well as potential alternatives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 49 (36), 6288–6308. doi:10.1002/anie.200902672
Korake, S., Bothiraja, C., and Pawar, A. (2023). Design, development, and in-vitro/in-vivo evaluation of docetaxel-loaded PEGylated solid lipid nanoparticles in prostate cancer therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 189, 15–27. doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2023.05.020
Kostiv, U., Patsula, V., Šlouf, M., Pongrac, I. M., Škokić, S., Radmilović, M. D., et al. (2017). Physico-chemical characteristics, biocompatibility, and MRI applicability of novel monodisperse PEG-modified magnetic Fe3O4&SiO2 core–shell nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 7 (15), 8786–8797. doi:10.1039/c7ra00224f
Kotta, S., Aldawsari, H. M., Badr-Eldin, S. M., Nair, A. B., and Yt, K. (2022). Progress in polymeric micelles for drug delivery applications. Pharmaceutics 14 (8), 1636. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics14081636
Kozma, G. T., Shimizu, T., Ishida, T., and Szebeni, J. (2020a). Anti-PEG antibodies: properties, formation, testing and role in adverse immune reactions to PEGylated nano-biopharmaceuticals. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 154-155, 163–175. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2020.07.024
Kozma, G. T., Shimizu, T., Ishida, T., and Szebeni, J. (2020b). Anti-PEG antibodies: properties, formation, testing and role in adverse immune reactions to PEGylated nano-biopharmaceuticals. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 154-155, 163–175. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2020.07.024
Kurrikoff, K., Vunk, B., and Langel, Ü. (2021). Status update in the use of cell-penetrating peptides for the delivery of macromolecular therapeutics. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 21 (3), 361–370. doi:10.1080/14712598.2021.1823368
Kyriakides, T. R., Raj, A., Tseng, T. H., Xiao, H., Nguyen, R., Mohammed, F. S., et al. (2021). Biocompatibility of nanomaterials and their immunological properties. Biomed. Mater 16 (4), 042005. doi:10.1088/1748-605x/abe5fa
Lamb, Y. N. (2021). BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine: first approval. Drugs 81 (4), 495–501. doi:10.1007/s40265-021-01480-7
Lee, J. C., Donahue, N. D., Mao, A. S., Karim, A., Komarneni, M., Thomas, E. E., et al. (2020). Exploring maleimide-based nanoparticle surface engineering to control cellular interactions. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 3 (3), 2421–2429. doi:10.1021/acsanm.9b02541
Lemarchand, C., Gref, R., and Couvreur, P. (2004). Polysaccharide-decorated nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 58 (2), 327–341. doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2004.02.016
Limongi, T., Canta, M., Racca, L., Ancona, A., Tritta, S., Vighetto, V., et al. (2019). Improving dispersal of therapeutic nanoparticles in the human body. Nanomedicine 14 (7), 797–801. doi:10.2217/nnm-2019-0070
Lin, M. H., Lai, P.-S., Chang, L.-C., Huang, W.-C., Lee, M.-H., Chen, K.-T., et al. (2021). Characterization and optimization of chitosan-coated polybutylcyanoacrylate nanoparticles for the transfection-guided neural differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (16), 8741. doi:10.3390/ijms22168741
Lipka, J., Semmler-Behnke, M., Sperling, R. A., Wenk, A., Takenaka, S., Schleh, C., et al. (2010). Biodistribution of PEG-modified gold nanoparticles following intratracheal instillation and intravenous injection. Biomaterials 31 (25), 6574–6581. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.05.009
Liu, H., Han, Y., Wang, T., Zhang, H., Xu, Q., Yuan, J., et al. (2020a). Targeting microglia for therapy of Parkinson’s disease by using biomimetic ultrasmall nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 142 (52), 21730–21742. doi:10.1021/jacs.0c09390
Liu, X., Tang, I., Wainberg, Z. A., and Meng, H. (2020b). Safety considerations of cancer nanomedicine-A key step toward translation. Small 16 (36), e2000673. doi:10.1002/smll.202000673
Liu, X., Wang, F., Liu, L., Li, T., Zhong, X., Lin, H., et al. (2023). Functionalized polydopamine nanospheres as in situ spray for photothermal image-guided tumor precise surgical resection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 222, 114995. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2022.114995
Liu, X., Zhang, H., Chang, L., Yu, B., Liu, Q., Wu, J., et al. (2015). Human-like collagen protein-coated magnetic nanoparticles with high magnetic hyperthermia performance and improved biocompatibility. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 10 (1), 28. doi:10.1186/s11671-015-0752-3
Liu, Y., Bravo, K. M. C., and Liu, J. (2021). Targeted liposomal drug delivery: a nanoscience and biophysical perspective. Nanoscale Horizons 6 (2), 78–94. doi:10.1039/d0nh00605j
Luo, J., Liu, J., Yao, H., Li, Z., and Wei, J. (2023). An efficient method to improve the dispersion and biocompatibility of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Dispersion Sci. Technol. 0 (0), 1–8. doi:10.1080/01932691.2023.2289620
Ma, J., Zhang, S., Liu, J., Liu, F., Du, F., Li, M., et al. (2019). Targeted drug delivery to stroke via chemotactic recruitment of nanoparticles coated with membrane of engineered neural stem cells. Small 15 (35), e1902011. doi:10.1002/smll.201902011
Maheshwari, R., Raval, N., and Tekade, R. K. (2019). Surface modification of biomedically essential nanoparticles employing polymer coating. Methods Mol. Biol. 2000, 191–201. doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-9516-5_13
Majumder, J., and Minko, T. (2021). Multifunctional and stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for targeted therapeutic delivery. Expert Opin. drug Deliv. 18 (2), 205–227. doi:10.1080/17425247.2021.1828339
Malabanan, J. W. T., Alcantara, K. P., Jantaratana, P., Pan, Y., Nalinratana, N., Vajragupta, O., et al. (2023). Enhancing physicochemical properties and biocompatibility of hollow porous iron oxide nanoparticles through polymer-based surface modifications. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 6 (12), 5426–5441. doi:10.1021/acsabm.3c00657
Mandal, B., Bhattacharjee, H., Mittal, N., Sah, H., Balabathula, P., Thoma, L. A., et al. (2013). Core-shell-type lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles as a drug delivery platform. Nanomedicine 9 (4), 474–491. doi:10.1016/j.nano.2012.11.010
Manuja, A., Kumar, B., Athira, S., Sarkar, P., Riyesh, T., Kumar, N., et al. (2022). Zinc oxide nanoparticles encapsulated in polysaccharides alginate/gum acacia and iron oxide nanomatrices show enhanced biocompatibility and permeability to intestinal barrier. Food Hydrocoll. Health 2, 100050. doi:10.1016/j.fhfh.2021.100050
Märkl, S., Schroter, A., and Hirsch, T. (2020). Small and bright water-protected upconversion nanoparticles with long-time stability in complex, aqueous media by phospholipid membrane coating. Nano Lett. 20 (12), 8620–8625. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c03327
McDaid, W. J., Greene, M. K., Johnston, M. C., Pollheimer, E., Smyth, P., McLaughlin, K., et al. (2019). Repurposing of Cetuximab in antibody-directed chemotherapy-loaded nanoparticles in EGFR therapy-resistant pancreatic tumours. Nanoscale 11 (42), 20261–20273. doi:10.1039/c9nr07257h
Mehta, M., Bui, T. A., Yang, X., Aksoy, Y., Goldys, E. M., and Deng, W. (2023). Lipid-based nanoparticles for drug/gene delivery: an overview of the production techniques and difficulties encountered in their industrial development. ACS Mater. Au 3 (6), 600–619. doi:10.1021/acsmaterialsau.3c00032
Miao, Y., Li, L., Wang, Y., Wang, J., Zhou, Y., Guo, L., et al. (2024). Regulating protein corona on nanovesicles by glycosylated polyhydroxy polymer modification for efficient drug delivery. Nat. Commun. 15 (1), 1159. doi:10.1038/s41467-024-45254-7
Mitchell, M. J., Billingsley, M. M., Haley, R. M., Wechsler, M. E., Peppas, N. A., and Langer, R. (2021). Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 20 (2), 101–124. doi:10.1038/s41573-020-0090-8
Mojarad-Jabali, S., Mahdinloo, S., Farshbaf, M., Sarfraz, M., Fatahi, Y., Atyabi, F., et al. (2022). Transferrin receptor-mediated liposomal drug delivery: recent trends in targeted therapy of cancer. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 19 (6), 685–705. doi:10.1080/17425247.2022.2083106
Moku, G., Gopalsamuthiram, V. R., Hoye, T. R., and Panyam, J. (2019). “Surface modification of nanoparticles: methods and applications,” in Surface modification of polymers, 317–346.
Moore, T. (2014). Polymer-coated hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for the delivery of statins. J. Nanomedicine & Nanotechnol. 05 (05). doi:10.4172/2157-7439.1000237
Moore, T. L., Pitzer, J. E., Podila, R., Wang, X., Lewis, R. L., Grimes, S. W., et al. (2013). Multifunctional polymer-coated carbon nanotubes for safe drug delivery. Part Part Syst. Charact. 30 (4), 365–373. doi:10.1002/ppsc.201200145
Mukherjee, S., Kotcherlakota, R., Haque, S., Bhattacharya, D., Kumar, J. M., Chakravarty, S., et al. (2020). Improved delivery of doxorubicin using rationally designed PEGylated platinum nanoparticles for the treatment of melanoma. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 108, 110375. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2019.110375
Nair, B. G., Nagaoka, Y., Morimoto, H., Yoshida, Y., Maekawa, T., and Sakthi Kumar, D. (2010). Aptamer conjugated magnetic nanoparticles as nanosurgeons. Nanotechnology 21 (45), 455102. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/21/45/455102
Navarro-Palomares, E., González-Saiz, P., Renero-Lecuna, C., Martín-Rodríguez, R., Aguado, F., González-Alonso, D., et al. (2020). Dye-doped biodegradable nanoparticle SiO2 coating on zinc- and iron-oxide nanoparticles to improve biocompatibility and for in vivo imaging studies. Nanoscale 12 (10), 6164–6175. doi:10.1039/c9nr08743e
Neves, A., Van der Putten, L., Queiroz, J., Pinheiro, M., and Reis, S. (2021). Transferrin-functionalized lipid nanoparticles for curcumin brain delivery. J. Biotechnol. 331, 108–117. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2021.03.010
Newhouse, R., Nelissen, E., El-Shakankery, K. H., Rogozińska, E., Bain, E., Veiga, S., et al. (2023). Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin for relapsed epithelial ovarian cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 7 (7), Cd006910. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd006910.pub3
Ngema, L. M., Adeyemi, S. A., Marimuthu, T., Ubanako, P. N., Ngwa, W., and Choonara, Y. E. (2023). Surface immobilization of anti-VEGF peptide on SPIONs for antiangiogenic and targeted delivery of paclitaxel in non-small-cell lung carcinoma. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 6 (7), 2747–2759. doi:10.1021/acsabm.3c00224
Nguyen, H.-V. T., Tran, V. H., Vong, L. B., Tran, T. T. N., Tran, N. H. T., Huynh, L. T., et al. (2024). Enhancing camptothecin loading and release control through physical surface modification of organosilica nanoparticles with polyethylene glycol. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 699, 134802. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2024.134802
Nguyen, N. T., Dao, T. H., Truong, T. T., Nguyen, T. M. T., and Pham, T. D. (2020). Adsorption characteristic of ciprofloxacin antibiotic onto synthesized alpha alumina nanoparticles with surface modification by polyanion. J. Mol. Liq. 309, 113150. doi:10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113150
Nguyen, T.-T.-L., and Maeng, H.-J. (2022). Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of intranasal solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers for nose-to-brain delivery. Pharmaceutics 14 (3), 572. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics14030572
Nisha, R., Kumar, P., Kumar, U., Mishra, N., Maurya, P., Singh, P., et al. (2022). Assessment of hyaluronic acid-modified imatinib mesylate cubosomes through CD44 targeted drug delivery in NDEA-induced hepatic carcinoma. Int. J. Pharm. 622, 121848. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.121848
Niu, Y., Yang, Y., Yang, Z., Wang, X., Zhang, P., Lv, L., et al. (2022). Aptamer-immobilized bone-targeting nanoparticles in situ reduce sclerostin for osteoporosis treatment. Nano Today 45, 101529. doi:10.1016/j.nantod.2022.101529
Notabi, M. K., Arnspang, E. C., and Andersen, M. Ø. (2021). Antibody conjugated lipid nanoparticles as a targeted drug delivery system for hydrophobic pharmaceuticals. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 161, 105777. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2021.105777
Palm-Apergi, C., Lönn, P., and Dowdy, S. F. (2012). Do cell-penetrating peptides actually “penetrate” cellular membranes? Mol. Ther. 20 (4), 695–697. doi:10.1038/mt.2012.40
Papi, M., Caputo, D., Palmieri, V., Coppola, R., Palchetti, S., Bugli, F., et al. (2017). Clinically approved PEGylated nanoparticles are covered by a protein corona that boosts the uptake by cancer cells. Nanoscale 9 (29), 10327–10334. doi:10.1039/c7nr03042h
Park, J.-H., Cho, H.-J., Yoon, H. Y., Yoon, I.-S., Ko, S.-H., Shim, J.-S., et al. (2014). Hyaluronic acid derivative-coated nanohybrid liposomes for cancer imaging and drug delivery. J. Control. Release 174, 98–108. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.11.016
Parra-Nieto, J., Del Cid, M. A. G., de Cárcer, I. A., and Baeza, A. (2021). Inorganic porous nanoparticles for drug delivery in antitumoral therapy. Biotechnol. J. 16 (2), 2000150. doi:10.1002/biot.202000150
Passero, F. C., Grapsa, D., Syrigos, K. N., and Saif, M. W. (2016). The safety and efficacy of Onivyde (irinotecan liposome injection) for the treatment of metastatic pancreatic cancer following gemcitabine-based therapy. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 16 (7), 697–703. doi:10.1080/14737140.2016.1192471
Patel, P., Hanini, A., Shah, A., Patel, D., Patel, S., Bhatt, P., et al. (2019). “Surface modification of nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery,” in Surface modification of nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. Editor Y. V. Pathak (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 19–31.
Peng, Y., Song, C., Yang, C., Guo, Q., and Yao, M. (2017). Low molecular weight chitosan-coated silver nanoparticles are effective for the treatment of MRSA-infected wounds. Int. J. Nanomedicine 12, 295–304. doi:10.2147/ijn.s122357
Pinheiro, R., Granja, A., Loureiro, J. A., Pereira, M., Pinheiro, M., Neves, A. R., et al. (2020). Quercetin lipid nanoparticles functionalized with transferrin for Alzheimer's disease. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 148, 105314. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105314
Pinzaru, I., Coricovac, D., Dehelean, C., Moacă, E.-A., Mioc, M., Baderca, F., et al. (2018). Stable PEG-coated silver nanoparticles - a comprehensive toxicological profile. Food Chem. Toxicol. An Int. J. Publ. Br. Industrial Biol. Res. Assoc. 111, 546–556. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2017.11.051
Pongrac, I. M., Dobrivojević, M., Ahmed, L. B., Babič, M., Šlouf, M., Horák, D., et al. (2016). Improved biocompatibility and efficient labeling of neural stem cells with poly(L-lysine)-coated maghemite nanoparticles. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 7 (1), 926–936. doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.84
Pramanik, N., De, T., Sharma, P., Alakesh, A., Jagirdar, S. K., Rangarajan, A., et al. (2022). Surface-coated cerium nanoparticles to improve chemotherapeutic delivery to tumor cells. ACS Omega 7 (36), 31651–31657. doi:10.1021/acsomega.2c00062
Priya, S., Desai, V. M., and Singhvi, G. (2023). Surface modification of lipid-based nanocarriers: a potential approach to enhance targeted drug delivery. ACS Omega 8 (1), 74–86. doi:10.1021/acsomega.2c05976
Qie, Y., Yuan, H., von Roemeling, C. A., Chen, Y., Liu, X., Shih, K. D., et al. (2016). Surface modification of nanoparticles enables selective evasion of phagocytic clearance by distinct macrophage phenotypes. Sci. Rep. 6 (1), 26269. doi:10.1038/srep26269
Qureshi, M., Aqil, M., Imam, S. S., Ahad, A., and Sultana, Y. (2019). Formulation and evaluation of neuroactive drug loaded chitosan nanoparticle for nose to brain delivery: in-vitro characterization and in-vivo behavior study. Curr. Drug Deliv. 16 (2), 123–135. doi:10.2174/1567201815666181011121750
Rahim, M. A., Jan, N., Khan, S., Shah, H., Madni, A., Khan, A., et al. (2021). Recent advancements in stimuli responsive drug delivery platforms for active and passive cancer targeting. Cancers 13 (4), 670. doi:10.3390/cancers13040670
Ramalho, M. J., Loureiro, J. A., Coelho, M. A., and Pereira, M. C. (2022). Transferrin receptor-targeted nanocarriers: overcoming barriers to treat glioblastoma. Pharmaceutics 14 (2), 279. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics14020279
Sabzi Dizajyekan, B., Jafari, A., Vafaie-Sefti, M., Saber, R., and Fakhroueian, Z. (2024). Preparation of stable colloidal dispersion of surface modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles for magnetic heating applications. Sci. Rep. 14 (1), 1296. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-51801-5
Sadalage, P. S., Patil, R. V., Havaldar, D. V., Gavade, S. S., Santos, A. C., and Pawar, K. D. (2021). Optimally biosynthesized, PEGylated gold nanoparticles functionalized with quercetin and camptothecin enhance potential anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer and anti-angiogenic activities. J. nanobiotechnology 19, 84–17. doi:10.1186/s12951-021-00836-1
Sadat, S. M. A., Jahan, S. T., and Haddadi, A. (2016). Effects of size and surface charge of polymeric nanoparticles on in vitro and in vivo applications. J. Biomaterials Nanobiotechnology 7(2), 18. doi:10.4236/jbnb.2016.72011
Samadian, H., Mohammad-Rezaei, R., Jahanban-Esfahlan, R., Massoumi, B., Abbasian, M., Jafarizad, A., et al. (2020). A de novo theranostic nanomedicine composed of PEGylated graphene oxide and gold nanoparticles for cancer therapy. J. Mater. Res. 35 (4), 430–441. doi:10.1557/jmr.2020.3
Sanati, M., Afshari, A. R., Aminyavari, S., Kesharwani, P., Jamialahmadi, T., and Sahebkar, A. (2023). RGD-engineered nanoparticles as an innovative drug delivery system in cancer therapy. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 84, 104562. doi:10.1016/j.jddst.2023.104562
Sandbhor, P., Goda, J., Mohanty, B., Chaudhari, P., Dutt, S., and Banerjee, R. (2022). Non-invasive transferrin targeted nanovesicles sensitize resistant glioblastoma multiforme tumors and improve survival in orthotopic mouse models. Nanoscale 14 (1), 108–126. doi:10.1039/d1nr05460k
Sanita, G., Carrese, B., and Lamberti, A. (2020). Nanoparticle surface functionalization: how to improve biocompatibility and cellular internalization. Front. Mol. Biosci. 7, 587012. doi:10.3389/fmolb.2020.587012
Sanna, V., Pala, N., and Sechi, M. (2014). Targeted therapy using nanotechnology: focus on cancer. Int. J. nanomedicine 9, 467–483. doi:10.2147/ijn.s36654
Schulz, F., Dahl, G. T., Besztejan, S., Schroer, M. A., Lehmkühler, F., Grübel, G., et al. (2016). Ligand layer engineering to control stability and interfacial properties of nanoparticles. Langmuir 32 (31), 7897–7907. doi:10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b01704
Shadmani, N., Makvandi, P., Parsa, M., Azadi, A., Nedaei, K., Mozafari, N., et al. (2023). Enhancing methotrexate delivery in the brain by mesoporous silica nanoparticles functionalized with cell-penetrating peptide using in vivo and ex vivo monitoring. Mol. Pharm. 20 (3), 1531–1548. doi:10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.2c00755
Sharma, D., Sharma, N., Pathak, M., Agrawala, P. K., Basu, M., and Ojha, H. (2018). “Chapter 2 - nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems: challenges and opportunities,” in Drug targeting and stimuli sensitive drug delivery systems. Editor A. M. Grumezescu (Norwich, United States: William Andrew Publishing), 39–79.
Shaterabadi, Z., Nabiyouni, G., and Soleymani, M. (2017). High impact of in situ dextran coating on biocompatibility, stability and magnetic properties of iron oxide nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 75, 947–956. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2017.02.143
Shen, H., Shi, S., Zhang, Z., Gong, T., and Sun, X. (2015). Coating solid lipid nanoparticles with hyaluronic acid enhances antitumor activity against melanoma stem-like cells. Theranostics 5 (7), 755–771. doi:10.7150/thno.10804
Shi, L., Zhang, J., Zhao, M., Tang, S., Cheng, X., Zhang, W., et al. (2021). Effects of polyethylene glycol on the surface of nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. Nanoscale 13 (24), 10748–10764. doi:10.1039/d1nr02065j
Shukla, S., Jadaun, A., Arora, V., Sinha, R. K., Biyani, N., and Jain, V. K. (2015). In vitro toxicity assessment of chitosan oligosaccharide coated iron oxide nanoparticles. Toxicol. Rep. 2, 27–39. doi:10.1016/j.toxrep.2014.11.002
Simon, L., Constanzo, J., Terraza-Aguirre, C., Ibn Elfekih, Z., Berthelot, J., Benkhaled, B. T., et al. (2025). Surface modification of extracellular vesicles with polyoxazolines to enhance their plasma stability and tumor accumulation. Biomaterials 313, 122748. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2024.122748
Sinani, V. A., Gheith, M. K., Yaroslavov, A. A., Rakhnyanskaya, A. A., Sun, K., Mamedov, A. A., et al. (2005). Aqueous dispersions of single-wall and multiwall carbon nanotubes with designed amphiphilic polycations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127 (10), 3463–3472. doi:10.1021/ja045670+
Singh, R. P., Sharma, G., Singh, S., Patne, S. C., Pandey, B. L., Koch, B., et al. (2016). Effects of transferrin conjugated multi-walled carbon nanotubes in lung cancer delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 67, 313–325. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2016.05.013
Singh, S. K., Hidau, M. K., Gautam, S., Gupta, K., Singh, K. P., Singh, S. K., et al. (2018). Glycol chitosan functionalized asenapine nanostructured lipid carriers for targeted brain delivery: pharmacokinetic and teratogenic assessment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 108, 1092–1100. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.11.031
Smith, T., Affram, K., Nottingham, E. L., Han, B., Amissah, F., Krishnan, S., et al. (2020). Application of smart solid lipid nanoparticles to enhance the efficacy of 5-fluorouracil in the treatment of colorectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 10 (1), 16989. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-73218-6
Stanley, S. (2014). Biological nanoparticles and their influence on organisms. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 28, 69–74. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2013.11.014
Su, J., Yao, Z., Chen, Z., Zhou, S., Wang, Z., Xia, H., et al. (2022). TfR aptamer enhanced blood-brain barrier penetration of biomimetic nanocomplexes for intracellular transglutaminase 2 imaging and silencing in glioma. Small 18 (40), 2203448. doi:10.1002/smll.202203448
Suk, J. S., Xu, Q., Kim, N., Hanes, J., and Ensign, L. M. (2016). PEGylation as a strategy for improving nanoparticle-based drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 99 (Pt A), 28–51. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2015.09.012
Sukhanova, A., Bozrova, S., Sokolov, P., Berestovoy, M., Karaulov, A., and Nabiev, I. (2018). Dependence of nanoparticle toxicity on their physical and chemical properties. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 13 (1), 44. doi:10.1186/s11671-018-2457-x
Sun, P., Xiao, Y., Di, Q., Ma, W., Ma, X., Wang, Q., et al. (2020). Transferrin receptor-targeted PEG-PLA polymeric micelles for chemotherapy against glioblastoma multiforme. Int. J. Nanomedicine 15, 6673–6687. doi:10.2147/ijn.s257459
Sun, R., Xiang, J., Zhou, Q., Piao, Y., Tang, J., Shao, S., et al. (2022). The tumor EPR effect for cancer drug delivery: current status, limitations, and alternatives. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 191, 114614. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2022.114614
Tang, W., Yang, Y., Yang, L., Tang, M., Chen, Y., and Li, C. (2021). Macrophage membrane-mediated targeted drug delivery for treatment of spinal cord injury regardless of the macrophage polarization states. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 16 (4), 459–470. doi:10.1016/j.ajps.2021.03.005
Tebbe, M., Kuttner, C., Mannel, M., Fery, A., and Chanana, M. (2015). Colloidally stable and surfactant-free protein-coated gold nanorods in biological media. ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces 7 (10), 5984–5991. doi:10.1021/acsami.5b00335
Teng, C., Chai, Z., Yuan, Z., Ren, L., Lin, C., Yan, Z., et al. (2020). Desirable PEGylation for improving tumor selectivity of hyaluronic acid-based nanoparticles via low hepatic captured, long circulation times and CD44 receptor-mediated tumor targeting. Nanomedicine Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 24, 102105. doi:10.1016/j.nano.2019.102105
Toy, R., Pradhan, P., Ramesh, V., Di Paolo, N. C., Lash, B., Liu, J., et al. (2019). Modification of primary amines to higher order amines reduces in vivo hematological and immunotoxicity of cationic nanocarriers through TLR4 and complement pathways. Biomaterials 225, 119512. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119512
Tsao, L.-C., Force, J., and Hartman, Z. C. (2021). Mechanisms of therapeutic antitumor monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Res. 81 (18), 4641–4651. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-21-1109
Unterweger, H., Janko, C., Schwarz, M., Dézsi, L., Urbanics, R., Matuszak, J., et al. (2017). Non-immunogenic dextran-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: a biocompatible, size-tunable contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging. Int. J. Nanomedicine 12, 5223–5238. doi:10.2147/ijn.s138108
Varshosaz, J., Riahi, S., Ghassami, E., and Jahanian-Najafabadi, A. (2017). Transferrin-targeted poly (butylene adipate)/terephthalate nanoparticles for targeted delivery of 5-fluorouracil in HT29 colorectal cancer cell line. J. Bioact. compatible Polym. 32 (5), 503–527. doi:10.1177/0883911517690756
Verma, A., and Stellacci, F. (2010). Effect of surface properties on nanoparticle–cell interactions. Small 6 (1), 12–21. doi:10.1002/smll.200901158
Vieira, A. C. C., Chaves, L. L., Pinheiro, S., Pinto, S., Pinheiro, M., Lima, S. C., et al. (2018). Mucoadhesive chitosan-coated solid lipid nanoparticles for better management of tuberculosis. Int. J. Pharm. 536 (1), 478–485. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.11.071
Vllasaliu, D., Fowler, R., and Stolnik, S. (2014). PEGylated nanomedicines: recent progress and remaining concerns. Expert Opin. drug Deliv. 11 (1), 139–154. doi:10.1517/17425247.2014.866651
Wang, C., Kimura, K., Li, J., Richardson, J. J., Naito, M., Miyata, K., et al. (2021a). Polydopamine-mediated surface functionalization of exosomes. ChemNanoMat 7 (6), 592–595. doi:10.1002/cnma.202100078
Wang, C., Wu, B., Wu, Y., Song, X., Zhang, S., and Liu, Z. (2020a). Camouflaging nanoparticles with brain metastatic tumor cell membranes: a new strategy to traverse blood–brain barrier for imaging and therapy of brain tumors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30 (14), 1909369. doi:10.1002/adfm.201909369
Wang, L., Wang, X., Shen, L., Alrobaian, M., Panda, S. K., Almasmoum, H. A., et al. (2021b). Paclitaxel and naringenin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles surface modified with cyclic peptides with improved tumor targeting ability in glioblastoma multiforme. Biomed. & Pharmacother. 138, 111461. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111461
Wang, X., Li, S., Shi, Y., Chuan, X., Li, J., Zhong, T., et al. (2014a). The development of site-specific drug delivery nanocarriers based on receptor mediation. J. Control. release 193, 139–153. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.05.028
Wang, Y., Quinsaat, J. E. Q., Ono, T., Maeki, M., Tokeshi, M., Isono, T., et al. (2020b). Enhanced dispersion stability of gold nanoparticles by the physisorption of cyclic poly(ethylene glycol). Nat. Commun. 11 (1), 6089. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19947-8
Wang, Y., Wang, X., Zhang, Y., Yang, S., Wang, J., Zhang, X., et al. (2009). RGD-modified polymeric micelles as potential carriers for targeted delivery to integrin-overexpressing tumor vasculature and tumor cells. J. drug Target. 17 (6), 459–467. doi:10.1080/10611860902974085
Wang, Z., Ma, G., Zhang, J., Lin, W., Ji, F., Bernards, M. T., et al. (2014b). Development of zwitterionic polymer-based doxorubicin conjugates: tuning the surface charge to prolong the circulation and reduce toxicity. Langmuir 30 (13), 3764–3774. doi:10.1021/la5000765
Wei, H., Insin, N., Lee, J., Han, H. S., Cordero, J. M., Liu, W., et al. (2012). Compact zwitterion-coated iron oxide nanoparticles for biological applications. Nano Lett. 12 (1), 22–25. doi:10.1021/nl202721q
Wei, H., Liu, T., Jiang, N., Zhou, K., Yang, K., Ning, W., et al. (2018). A novel delivery system of cyclovirobuxine D for brain targeting: angiopep-conjugated polysorbate 80-coated liposomes via intranasal administration. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 14 (7), 1252–1262. doi:10.1166/jbn.2018.2581
Wenck, C., Meier, N., Heinrich, E., Grützner, V., Wiekhorst, F., and Bleul, R. J. R. a. (2024). Design and characterisation of casein coated and drug loaded magnetic nanoparticles for theranostic applications. RSC Adv. 14 (36), 26388–26399. doi:10.1039/d4ra02626h
Werner, M. E., Cummings, N. D., Sethi, M., Wang, E. C., Sukumar, R., Moore, D. T., et al. (2013). Preclinical evaluation of Genexol-PM, a nanoparticle formulation of paclitaxel, as a novel radiosensitizer for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 86 (3), 463–468. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.02.009
Wischke, C., and Schwendeman, S. P. (2008). Principles of encapsulating hydrophobic drugs in PLA/PLGA microparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 364 (2), 298–327. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2008.04.042
Wu, J. (2021). The enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect: the significance of the concept and methods to enhance its application. J. personalized Med. 11 (8), 771. doi:10.3390/jpm11080771
Wu, L., Zhang, J., and Watanabe, W. (2011). Physical and chemical stability of drug nanoparticles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 63 (6), 456–469. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2011.02.001
Wu, Q., Miao, T., Feng, T., Yang, C., Guo, Y., and Li, H. (2018). Dextran-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles activate the MAPK pathway in human primary monocyte cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 18 (1), 564–570. doi:10.3892/mmr.2018.8972
Xie, A., Hanif, S., Ouyang, J., Tang, Z., Kong, N., Kim, N. Y., et al. (2020). Stimuli-responsive prodrug-based cancer nanomedicine. EBioMedicine 56, 102821. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102821
Xie, G., Sun, J., Zhong, G., Shi, L., and Zhang, D. (2010). Biodistribution and toxicity of intravenously administered silica nanoparticles in mice. Arch. Toxicol. 84 (3), 183–190. doi:10.1007/s00204-009-0488-x
Xu, Y., Zhao, M., Zhou, D., Zheng, T., and Zhang, H. (2021). The application of multifunctional nanomaterials in Alzheimer’s disease: a potential theranostics strategy. Biomed. & Pharmacother. 137, 111360. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111360
Yadav, D., Semwal, B. C., and Dewangan, H. K. (2023). Grafting, characterization and enhancement of therapeutic activity of berberine loaded PEGylated PAMAM dendrimer for cancerous cell. J. biomaterials Sci. 34, 1053–1066. doi:10.1080/09205063.2022.2155782
Yang, W., Wang, L., Fang, M., Sheth, V., Zhang, Y., Holden, A. M., et al. (2022). Nanoparticle surface engineering with heparosan polysaccharide reduces serum protein adsorption and enhances cellular uptake. Nano Lett. 22 (5), 2103–2111. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.2c00349
Yetisgin, A. A., Cetinel, S., Zuvin, M., Kosar, A., and Kutlu, O. (2020). Therapeutic nanoparticles and their targeted delivery applications. Molecules 25 (9), 2193. doi:10.3390/molecules25092193
Ying, N., Lin, X., Xie, M., and Zeng, D. (2022). Effect of surface ligand modification on the properties of anti-tumor nanocarrier. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 220, 112944. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2022.112944
Yokoo, H., Oba, M., and Uchida, S. (2021). Cell-penetrating peptides: emerging tools for mRNA delivery. Pharmaceutics 14 (1), 78. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics14010078
Yu, M., Jambhrunkar, S., Thorn, P., Chen, J., Gu, W., and Yu, C. (2013). Hyaluronic acid modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery to CD44-overexpressing cancer cells. Nanoscale 5 (1), 178–183. doi:10.1039/c2nr32145a
Yu, Y., Zu, C., He, D., Li, Y., Chen, Q., Chen, Q., et al. (2021). pH-dependent reversibly activatable cell-penetrating peptides improve the antitumor effect of artemisinin-loaded liposomes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 586, 391–403. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2020.10.103
Zahednezhad, F., Shahbazi Mojarrad, J., Zakeri-Milani, P., Baradaran, B., Mahmoudian, M., Sarfraz, M., et al. (2021). Surface modification with cholesteryl acetyl carnitine, a novel cationic agent, elevates cancer cell uptake of the PEGylated liposomes. Int. J. Pharm. 609, 121148. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.121148
Zhan, N., Palui, G., Grise, H., Tang, H., Alabugin, I., and Mattoussi, H. (2013). Combining ligand design with photoligation to provide compact, colloidally stable, and easy to conjugate quantum dots. ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces 5 (8), 2861–2869. doi:10.1021/am302788q
Zhang, H., Liu, J., Chen, Q., and Mi, P. (2020a). Ligand-installed anti-VEGF genomic nanocarriers for effective gene therapy of primary and metastatic tumors. J. Control. Release 320, 314–327. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.01.026
Zhang, W., Mehta, A., Tong, Z., Esser, L., and Voelcker, N. H. (2021). Development of polymeric nanoparticles for blood–brain barrier transfer—strategies and challenges. Adv. Sci. 8 (10), 2003937. doi:10.1002/advs.202003937
Zhang, W., Taheri-Ledari, R., Hajizadeh, Z., Zolfaghari, E., Ahghari, M. R., Maleki, A., et al. (2020b). Enhanced activity of vancomycin by encapsulation in hybrid magnetic nanoparticles conjugated to a cell-penetrating peptide. Nanoscale 12 (6), 3855–3870. doi:10.1039/c9nr09687f
Zhang, X., He, J., Qiao, L., Wang, Z., Zheng, Q., Xiong, C., et al. (2022). 3D printed PCLA scaffold with nano-hydroxyapatite coating doped green tea EGCG promotes bone growth and inhibits multidrug-resistant bacteria colonization. Cell Prolif. 55 (10), e13289. doi:10.1111/cpr.13289
Zhang, X., Li, J., and Yan, M. (2016). Targeted hepatocellular carcinoma therapy: transferrin modified, self-assembled polymeric nanomedicine for co-delivery of cisplatin and doxorubicin. Drug Dev. Industrial Pharm. 42 (10), 1590–1599. doi:10.3109/03639045.2016.1160103
Zielińska, A., Carreiró, F., Oliveira, A. M., Neves, A., Pires, B., Venkatesh, D. N., et al. (2020). Polymeric nanoparticles: production, characterization, toxicology and ecotoxicology. Molecules 25 (16), 3731. doi:10.3390/molecules25163731
Keywords: nanoparticles, surface modification, targeted delivery, stability, toxicity
Citation: Ly P-D, Ly K-N, Phan H-L, Nguyen HHT, Duong V-A and Nguyen HV (2024) Recent advances in surface decoration of nanoparticles in drug delivery. Front. Nanotechnol. 6:1456939. doi: 10.3389/fnano.2024.1456939
Received: 29 June 2024; Accepted: 27 September 2024;
Published: 11 October 2024.
Edited by:
Long Binh Vong, Vietnam National University, Ho Chi Minh City, VietnamReviewed by:
Anisha Dsouza, Harvard Medical School, United StatesZahraa S. Al-Ahmady, Nottingham Trent University, United Kingdom
Lekshmi Rethi, Taipei Medical University, Taiwan
Copyright © 2024 Ly, Ly, Phan, Nguyen, Duong and Nguyen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hien V. Nguyen, aGllbi5udkB2bHUuZWR1LnZu
 Phuong-Dung Ly1
Phuong-Dung Ly1 Van-An Duong
Van-An Duong Hien V. Nguyen
Hien V. Nguyen