
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
MINI REVIEW article
Front. Mol. Neurosci., 27 March 2025
Sec. Methods and Model Organisms
Volume 18 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2025.1552885
This article is part of the Research TopicMulti-modality tools and applications in functional and mechanistic exploration in nervous systemsView all 5 articles
A traumatic injury to the nervous system has significant consequences for mammals, including long-term disability, loss of functions, and neuropathic pain. In contrast to mammals, zebrafish (Danio rerio) exhibits a markedly enhanced neuroregenerative capacity, which can be attributed to the phenomenon of adult neurogenesis and to the distinctive characteristics of the inflammatory response at the injury site. The post-traumatic recovery of zebrafish under different experimental injury conditions was demonstrated in numerous studies, which has substantially advanced our understanding of the cellular and molecular mechanisms of neuroregeneration in this animal. In view of the significant differences in molecular mechanisms depending on the injury site, lesion severity, and harmful agents, selecting an appropriate model for investigations is of paramount importance. This review discusses some approaches to modeling neural injury in zebrafish and considers the effect of cellular interactions in post-traumatic neurogenesis, with focus on the animal’s age and the specific damaging factor that may be used to select an optimum model for certain nervous system lesions.
In recent years, the zebrafish (Danio rerio) has become a promising model for neuroscience research, both in normal conditions and in disease modeling. The number of articles on this topic has dramatically increased over the past decade.
Eggs, early embryos, and larvae are optically transparent. This transparency allows detection of fluorescent proteins, in particular in cells of transgenic fish (Choe et al., 2021), e.g., the development and migration of Schwann cells (Cunningham and Monk, 2018). In post-traumatic, Tau-linked conditions in Tau-GFP reporter zebrafish (Alyenbaawi et al., 2021), the vital fluorescent dyes can be used as makers in early developmental stages to analyze behavior of single cells (Cunningham and Monk, 2018; Bensimon-Brito et al., 2016). Transparent strains of adult fish (Casper and Crystal) are available for in vivo imaging in various research fields (Antinucci and Hindges, 2016).
From a morphological viewpoint, zebrafish is a valuable model across vertebrates due to its conserved nervous system parts. Both zebrafish and mammals possess a tripartite brain structure consisting of a forebrain, a midbrain, and a hindbrain (Saleem and Kannan, 2018). A similarity of gene expression patterns, neurotransmitters, receptors, and regional connectivity within well-defined substructures exists between fish and mammals (Kozol et al., 2016). Moreover, zebrafish exhibits fast neural development, with major central nervous system (CNS) regions being recognizable at approximately 24 hpf and most cell type circuits and nuclei being functional by 3 days post-fertilization (dpf) and continuing to grow and differentiate thereafter (Kaslin and Ganz, 2020). It was also shown that the developmental changes of gene expression patterns in the brain of a 40–59-yr-old human and that of a 1–2-yr-old zebrafish are somewhat similar (Nakajima et al., 2021). It is noteworthy that the cognitive function also declines with age in zebrafish, a phenomenon that is attributed to subtle changes in cellular and synaptic integrity (Adams and Kafaligonul, 2018).
Zebrafish is a valuable model for regeneration studies due to its high regenerative capacity. This animal can successfully regenerate fin, heart, pancreas, liver, kidney, skin, hair cells of lateral line, and CNS (Marques et al., 2019). A differences between zebrafish and mammals is the presence of multiple neurogenic niches in the CNS even in adult individuals (Zupanc and Sîrbulescu, 2011; Kizil et al., 2012; Schmidt et al., 2013). The zones of constitutive neurogenesis that exist in the zebrafish’s CNS throughout life are located in different parts of the brain, in contrast to rodents whose proliferative activity in the brain is found in two major areas (Diotel et al., 2020). Previous studies showed that a spinal cord injury can effectively regenerate in larvae within approximately 48 h (Ohnmacht et al., 2016), while it takes 4–8 weeks for adult zebrafish to regenerate motor neurons at the injury site (Reimer et al., 2008). Moreover, zebrafish can regenerate various neural tissues including the retina (Sherpa et al., 2008), optic nerves (Harvey et al., 2023), vagal nerves (Isabella et al., 2021), other peripheral nerves (Ceci et al., 2014; Bremer et al., 2017), and the brain (Zupanc, 2006; Kishimoto et al., 2012; Pose-Méndez et al., 2023). Following a damage to neural structures in zebrafish, certain cell populations provide rapid proliferation and replacement of dead cells. These include radial glia cells (Kroehne et al., 2011), neurogenic progenitor cells (Kizil et al., 2012), and oligodendrocyte precursor cells (Tsata et al., 2020). In the retina, Müller glia have been shown to undergo reprogrammed to regenerate retinal neurons (Lahne et al., 2020). Contrary to observations on mammals, zebrafish does not exhibit extensive glial scarring following CNS injury. The lack of scarring creates a permissive environment favorable for axonal regrowth and tissue repair (Mokalled et al., 2016). The cellular and molecular mechanisms of this process can be translated to mammals. Therefore, the use of zebrafish as a model organism for nervous system research is highly promising and provides many new opportunities for extending our knowledge of neural regeneration and for disease modeling.
Zebrafish is suitable for research purposes at all ages, with larvae and sexually mature animals (6–8 months post-fertilization) being the most commonly used in neuroregeneration studies. However, depending on the specific objectives of the experiment, juvenile and older animals can also be selected. The transparency of larvae facilitates visualization at the cellular level, enabling observation of glial cell and neuronal behavior in transgenic reporter lines, assessment of neuronal excitation (calcium imaging), and analysis of axonogenesis (Hecker et al., 2020) and synaptogenesis in a living organism. Additionally, it allows rapid screening of pharmacological substances and their effect on labelled cells. Despite the possibility to study fundamental behavioral responses, the behavioral repertoire in larvae is, however, not as extensive as that in adults.
Adult zebrafish possesses the fully developed immune and endocrine systems, thus, providing the opportunity to elucidate neuroimmune interactions and the effect of sex on neuroregeneration. Furthermore, the phases of regeneration can be more clearly distinguished in adult animals, and, due to their more complex behavior compared to larvae, the functional recovery or lack thereof of memory, learning ability, and social behavior can also be assessed. Adult zebrafish suits well for studying the ageing processes and their effect on the regenerative response, which can provide valuable clues for translational research.
In this review, we discuss traumatic injury modeling, both local and systemic, in zebrafish. The methods for chemical and genetic ablation of certain cell populations and stroke modeling are too extensive to fit the scope of this review. The most common approaches to modeling neural injuries are shown in Figure 1.
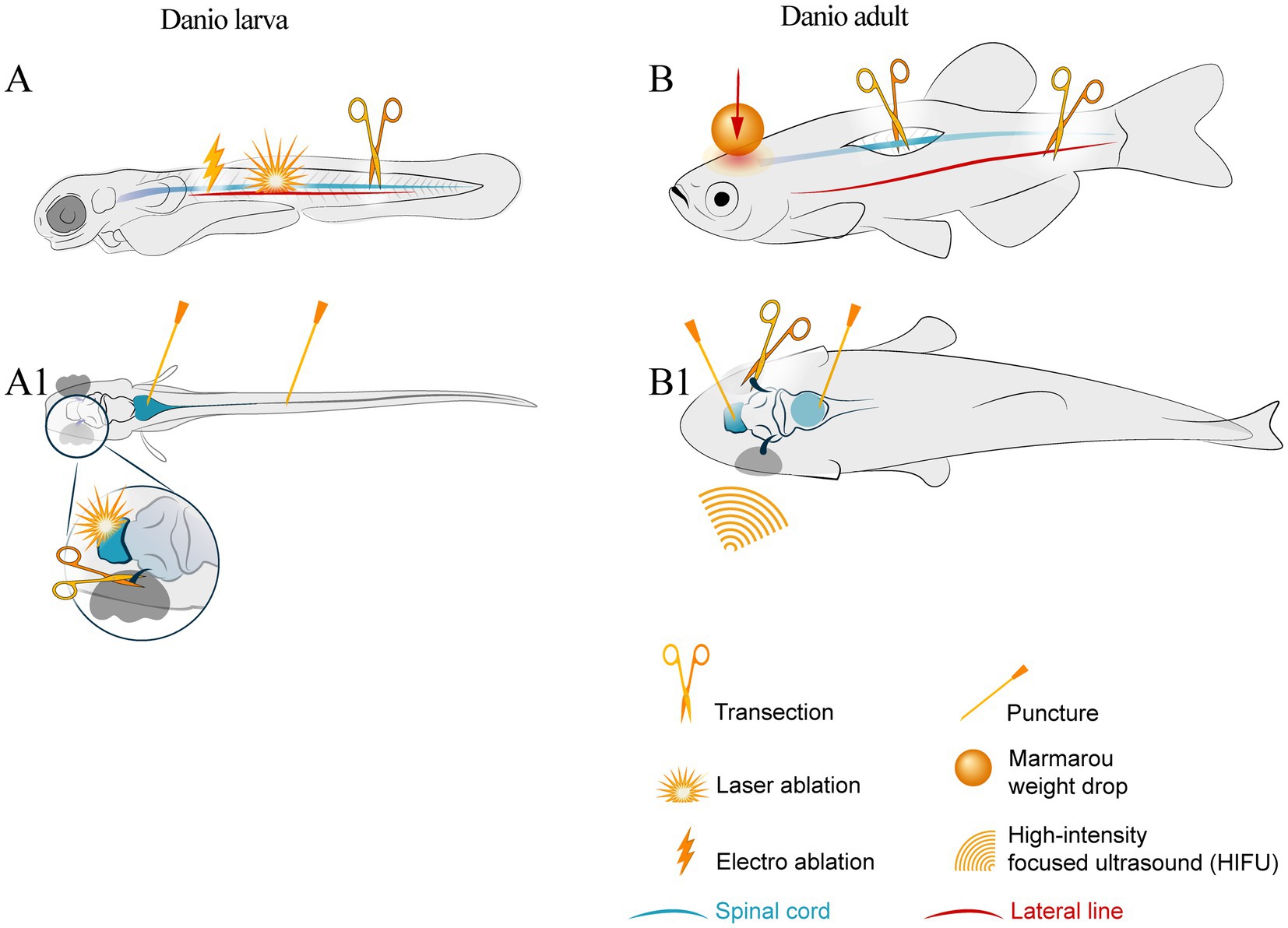
Figure 1. Schematic of injury sites in larval and adult zebrafish. The notation keys of injury types are presented in the bottom right corner. (A) larval lateral view; symbols show laser ablation of the cells in the central nervous system, electro-ablation of the lateral line axons, transection of the spinal cord by the edged tool. (A1) larval dorsal view with symbols indicating brain stem and spinal cord puncture trauma and optic nerve transection. (B) adult lateral view and (B1) adult dorsal view with symbols of spinal cord and optic nerve transection, lateral line axotomy, stab wound of the brain areas, and whole brain trauma by Marmarou weight drop and high intensity ultrasound.
The closed head trauma model in zebrafish is inflicted in different ways. It closely mimics a clinical situation with loss of consciousness, seizures, brain edema, and hemorrhage. With variations in impact force, it is possible to obtain scalable models of closed head trauma, from slight concussion to severe brain damage. In some investigations, it was caused in adult wild-type AB zebrafish using pulsed high intensity focused ultrasound (pHIFU). Two modes of pHIFU were set up, behavior tests were performed (Novel Tank test and Shoaling Test), and protein expression changes in the brain tissue were assessed. The post-injury changes were shown to be dose-dependent (McCutcheon et al., 2017).
Another method for traumatic brain injury in adult zebrafish is based on head injury with dropped weight. This model was designed for rodents (Marmarou et al., 1994).
This approach was applied to create a reproducible cost-effective traumatic brain injury model in adult zebrafish and analyze the gene expression and signaling pathways involved in post-traumatic recovery (Maheras et al., 2018).
Mild modifications were made to circumvent skull damage in the experimental animals. For this, adult wild-type AB, Tg[nestin:GFP], Tg[gfap:EGFP] transgenic lines, and albino and roy; mitfa mutant lines of zebrafish were used. In that study, behavior tests were performed, gross pathology examination carried out, cell apoptosis and proliferation examined, and the Sonic hedgehog pathway in post-traumatic regeneration in the cerebellum demonstrated (Hentig et al., 2021b).
These methods are not suitable for larvae due to their small size. Nevertheless, some approaches were made for close head trauma modeling in early developmental stages of zebrafish. One of them was used to detect abnormal Tau protein in Tg[Tau4R-GFP] larvae after traumatic brain injury (TBI). In that study, the post-traumatic hemorrhage in Tg(gata1a:DsRed) larvae was assessed, and bursts of neuronal excitation during TBI causing seizures in Tg(elavl3:CaMPARI)ua3144 larvae were documented. The method can be described as follows: zebrafish larvae (in their typical liquid growth medium) were loaded into a syringe with a closed valve stopper. A hit was applied on the plunger to produce a pressure wave comparable to shock waves experienced in the case of human blast injury. The study showed a correlation between the seizure intensity and the accumulation of abnormal Tau protein aggregates in the post-traumatic period (Alyenbaawi et al., 2021).
Another approach to closed head trauma modeling in larvae is the “concussion machine”: a cylindrical capsule filled with the E3 medium, which moves fast and stops abruptly (Beppi et al., 2022). The TBI caused by this method is milder than that in the above-described case. Nevertheless, behavioral changes were observed in that study.
For local open head trauma modeling, a stab wound is typically inflicted. A fine, sterile needle or glass capillary is inserted into a certain brain region of anesthetized fish: the telencephalon (Kishimoto et al., 2012; Kim et al., 2020; Lübke et al., 2022), optic tectum (Gan et al., 2020; Ueda et al., 2018; Shimizu et al., 2018), cerebellum (Wu et al., 2014), or hindbrain (Hannah et al., 2012). Local injury is caused to study cell apoptosis (Anand et al., 2021), proliferation (Kishimoto et al., 2012; Baumgart et al., 2012; März et al., 2011), signaling pathways (Kishimoto et al., 2012; Shimizu et al., 2018; Wu et al., 2014), and gene expression in the damaged zone (Kizil et al., 2012; Anand et al., 2021; Yin et al., 2018).
Stab wound has been sufficiently well developed for investigating post-traumatic neurogenesis and cellular crosstalk in the mature brain (März et al., 2011; Schmidt et al., 2014). While this technique is commonly applied to adult zebrafish, it has also demonstrated reproducible results on fish larvae (Gan et al., 2020). Study of post-traumatic neuroregeneration in zebrafish is particularly intriguing due to the age-related changes that occur on tissue, cellular, and subcellular levels and can begin 1 year post-fertilization (Van Houcke et al., 2021).
The spinal cord and peripheral nerves can be considered as linear structures. Thus, transection with scissors and crushing with jeweler forceps can be made to induce traumatic injuries in these regions, as described in Supplementary Table 1. Since the spinal cord is a component of the CNS, and nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system (PNS), these structures exhibit significant differences in cell composition and regeneration processes.
Spinal cord injury modeling protocols have actively been applied to both adult and larval zebrafish over the past 25 years. In case of adult animals, the typical transection localizations are at the level of brainstem/spinal cord transition zone (Becker et al., 1998), 3.5–4.0 mm caudally of the brainstem/spinal cord transition zone at the level of the 8th–9th vertebrae (Becker et al., 1998; Vajn et al., 2014), and at the level of dorsal fin, which corresponds to the 15th–16th vertebrae (Hui et al., 2014). For motor neuron activity research, traumatic injury can be applied at the level of the 24th vertebra (Stil and Drapeau, 2016). In larval zebrafish, the spinal cord can be transected with a needle (Ohnmacht et al., 2016; John et al., 2022; Hossainian et al., 2022) or a “glass scalpel” made from broken glass capillary (Briona and Dorsky, 2014).
Extensive research has been conducted on the spinal cord regeneration in zebrafish, and the regeneration process studied in sufficient detail.
To elucidate the axonal regeneration in the PNS, studies focused on large visible nerves: the optic nerve, posterior lateral line, and vagal nerve (Harvey et al., 2023; Isabella et al., 2021; Graciarena et al., 2014). Axotomy protocol was also designed for laser ablation of trigeminal nerve axons in larvae (O’Brien et al., 2009), single dorsal root ganglion axons (Nichols and Smith, 2020), and for motor nerve transection (Rosenberg et al., 2012). These studies also considered neuron–glia interactions (Ceci et al., 2014; Graciarena et al., 2014) and metabolomic changes in optic nerve regeneration (Meehan et al., 2023). Various methods were employed to model spinal cord injury, including transection using a needle in larval zebrafish (Harvey et al., 2023), transection using a glass capillary in adult and aged zebrafish (Graciarena et al., 2014), nerve crush using fine forceps (Meehan et al., 2023; Diekmann et al., 2015), laser axotomy (Isabella et al., 2021), and electroablation (Ceci et al., 2014; Moya-Díaz et al., 2014).
In the case of nerve crush method, a mechanical force is applied to a nerve without severing it completely, thus, preserving its complete structural integrity. This method ensures continuity of the surrounding connective tissue, thereby creating a favorable environment for enhanced regeneration. In the case of nerve transection, the nerve is completely severed, resulting in a more profound damage. When both axons and connective tissues are severed, this typically leads to a more complex healing process.
Electroablation represents a noteworthy approach to focal cell ablation and axotomy. The use of microelectrodes allows ablation of single lateral-line mechanosensory neuromasts and posterior lateral-line axons in larval and adult zebrafish, thereby providing the opportunity to observe neuroregeneration in damaged tissues (Moya-Díaz et al., 2014). Two modes of electroablation can be applied: radiofrequency (thermal protein coagulation in damaged tissue) (Widmann, 2009) and irreversible electroporation of membranes of damaged cells without thermal damage to tissue (Thomson et al., 2015), which is typically used for treatment of large animals and humans. It is relevant to note that the use of electroablation in zebrafish for traumatic injury research is still a relatively novel technique, which requires further investigation to fully understand its potential and limitations. Nonetheless, the opportunity to induce precise and focal injuries in zebrafish using electroablation provides a valuable tool for studying the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying the post-traumatic neuroregeneration in the CNS and PNS.
Laser ablation is another noninvasive technique for neural damage that has been applied to zebrafish larvae (Liu and Fetcho, 1999; Roeser and Baier, 2003; Muto and Kawakami, 2018) due to their optical transparency and the clear visibility of structures to be ablated. However, this technique can also be used for adult fish (Tikhonova et al., 2022). For precise laser ablation using the two-photon excitation microscopy, cells to be ablated should be distinguished based on their optical characteristics. This requires distinct cell labeling with vital stains (Liu and Fetcho, 1999) or fluorescent protein expression in transgenic zebrafish (Roeser and Baier, 2003; Muto and Kawakami, 2018; Hiyoshi et al., 2021; Xiao et al., 2022). This method is useful for identifying the functions of specific cell populations in a particular body area or even single cells. For adult fish, a diode laser can be used, which, with proper tuning of focal distance and laser power, induces focal injuries, with above-located tissues remaining intact (Tikhonova et al., 2022). However, this approach has some disadvantages, including the high cost of equipment required and the time-consuming procedure in case where many cells are to be ablated.
Zebrafish has been found as an exceptionally useful model for studying retinal injury and subsequent regeneration due to its remarkable capacity to regenerate retinal neurons after damage. The following approaches can be used to investigate retinal regeneration: laser-induced injury (DiCicco et al., 2014), chemical lesions, e.g., intravitreal injections of ouabain (Barrett et al., 2022), physical damage by poking with a needle to make a stub wound injury (Sharma and Ramachandran, 2019) or stab wound technique (Senut et al., 2004), thermal injury (Bernardos et al., 2005), or combined approaches. A range of mechanical models of retinal injury in zebrafish have been shown to offer valuable clues into the mechanisms of retinal regeneration. However, these models have distinct advantages and disadvantages. Needle poke and stab wound injuries, e.g., while creating uniform and localized lesions, can give also variable results due to individual differences in reaction. In contrast, laser-induced injuries offer high precision but necessitate specialized equipment, and heat-induced injuries permit controlled severity, while, however, causing non-specific damages. It is, therefore, essential to take these advantages and disadvantages into account when selecting the most appropriate model for addressing specific research issues related to retinal regeneration.
To summarize the overview of approaches to modelling nervous system injuries, the following conclusions can be drawn. The models of closed head injury in adult fish are the closest to the situations observed in clinical practice. The key advantage of the pHIFU method consists in non-invasive and scalable injuries caused. This allows researchers to model a wide spectrum of TBI severities without causing mechanical skull damage. However, it requires specialized equipment and expertise, which potentially limits availability. Conversely, the dropped weight method offers simplicity and cost-effectiveness, facilitating reproducible results without the need for advanced equipment. However, it is less precise than pHIFU, as controlling the force and localization of the injury is more challenging. Both methods have contributed substantially to understanding TBI in zebrafish. The pHIFU model is particularly suited for studies requiring precise control over injury severity and localization such as dose–response analyses of molecular pathways. Conversely, the simplicity of the latter makes it a perfect choice for large-scale studies investigating into genetic and cellular mechanisms.
Whilst it is not yet technically feasible to model isolated closed head injuries in zebrafish larvae, it is possible to induce shock wave-induced injury that involves the entire body. The above-described approaches also allow potential assessment of the embryonic nervous system injury and the consequences for body development. The transparency of zebrafish larvae makes it possible to detect cellular damage, hemorrhages, and accumulation of aggregates of abnormal proteins. Furthermore, the use of transgenic reporter lines such as Tg(plvap:EGFP) (Umans et al., 2017) gives an opportunity for detection of alterations in the brain microcirculation and the blood–brain barrier and their subsequent effect on the animal’s development.
Stab wound, electroablation, and laser ablation are the techniques that permit the evaluation of the specificity of the response to injury in specific regions of the nervous system. However, the translational potential of such interventions is limited. While stab wound provides the simulation of open brain injury in a specific brain region with subsequent inflammation of the tissues along the wound channel, electro- and laser ablation are more suitable for the study of compensatory mechanisms after the loss of parts of the nervous system or specific neurons, for elucidating the formation of new neuronal pathways, behavioral changes, and for identification of new interactions between specific parts of the nervous system and other systems of the body. Furthermore, stab wound is an appropriate model to study the cellular and molecular features of nervous system regeneration in a particular area of the nervous system in animals of different ages. This may be important in the further development of therapeutic strategies for mammals.
Although surgical spinal cord transection has not provided simulation of the clinical scenario in humans, this experimental model remains a common classic technique employed in both zebrafish (Becker et al., 1998) and rodent models (Kjell and Olson, 2016). This approach has yielded substantial data on the characteristics of spinal cord regeneration in zebrafish, thus, facilitating the development of therapeutic strategies for mammals, including cell therapy and utilization of the neurotrophic factors. Further studies on this model may clarify the influence of epigenetic regulation on spinal cord regeneration in animals of different ages and the influence of pharmacological agents on regeneration.
It is evident that both nerve crush and transection injuries, modelled in zebrafish, can give rise to divergent regenerative outcomes and mechanisms. Nerve crush has been shown to result in faster and more effective regeneration due to the preservation of supportive structures. Conversely, nerve transection has been demonstrated to pose greater challenges for recovery due to complete disruption of the nerve architecture. Understanding these differences is crucial for designing effective therapeutic strategies for nerve injuries in zebrafish models and for potential applications in humans.
The organism’s response to a nervous system injury is a multifaceted process involving diverse cell populations including neurons, radial glia, oligodendrocytes, microglia, Schwann cells in the PNS, fibroblasts, pericytes, blood cells (in particular neutrophils and macrophages), and mast cells. Such an intricate response necessitates coordinated interactions of multiple cell types.
In one of the studies, zebrafish larvae at 3 dpf exhibited a remarkable capacity for motor function recovery within 48 h following spinal cord transection. Their individual motor neuron axons commenced entering the injury site as early as 12 h post-transection, with a substantial presence of regenerated axons observed by the 36-h mark (Ohnmacht et al., 2016). An extended period of proliferative activity was recorded at 5 dpf. Nonetheless, by 9 days post-injury (dpi), detectable neuronal presence was already observed within the damaged area (Anguita-Salinas et al., 2019). The results of studies with spinal cord electroablation in zebrafish larvae are generally consistent with those with mechanical transection of this structure, although there are differences in the timing of the inflammatory response between these experimental techniques (Anguita-Salinas et al., 2019).
In the adult zebrafish model, an immediate inflammatory response to spinal cord injury is manifested within hours post-injury, and the proliferative activity becomes apparent at 3 dpi (Hui et al., 2014). The spinal cord tissue remodeling is observed for three to 4 weeks, ultimately culminating in the functional recovery around the six-week mark (Becker et al., 2005). Despite this recovery of functional integrity within 42 dpi, up to 50% of axonal tracts located rostrally of the injury site remain unrepaired, and the deficiency of axonal myelination suggests incomplete regeneration. Of particular note is that even at 1 year post-injury, the spinal cord tissue in adult zebrafish cannot fully regenerate its anatomical integrity and myelination to the pre-injury level (Tsata et al., 2020).
Following damage, microglia actively aggregate at the injury site in adult zebrafish. The increase in cell number is related to migration and proliferation processes (März et al., 2011). In the context of spinal cord injury in zebrafish larvae, microglia are activated within the injury zone and are involved in phagocytosis of cellular debris (Morsch et al., 2015). Moreover, due to the disruption of the blood–brain barrier, bone marrow-derived macrophages also aggregate in the injury zone (Hui et al., 2010), with the primary function being to clear cellular debris and modulate the local inflammatory response.
A distinct population of stress-resistant cells is present along the wound edges in the case of spinal cord injury in zebrafish larvae. These cells can be categorized into subtypes associated with radial glia and neuronal progenitor cells. They are capable of differentiating into neurons that bridge the wound edges during the regeneration process. Furthermore, cells located on the rostral side of the lesion exhibit caveolin-1 expression, which augments the regenerative response and fosters axon growth in that region (Zeng et al., 2021).
Glial cells have been identified as the most actively proliferating cell population in the spinal cord injury model (Goldshmit et al., 2012). Member A of the acidic nuclear phosphoprotein 32 (ANP32a) enhance the motor neuron and ependymo-radial glia cell proliferation following post-spinal cord injury in zebrafish larvae (Lee et al., 2022). Significant radial glia proliferation and subsequent neurogenesis in the spinal cord of zebrafish larvae has also been noted (Briona et al., 2015).
After spinal cord injury in adult zebrafish, the number of oligodendrocyte bodies and myelin sheaths in the lesion site becomes reduced. Apoptotic cell death can be detected as early as 4 h post-injury (hpi). Oligodendrocyte progenitor cells in the spinal cord exhibit dynamic changes in morphology within the first 3 dpi, including the increase in size, the formation of long branching outgrowths, and the increased proliferative activity in response to experimental injury (Tsata et al., 2020). It has also been found that olig2-positive oligodendrocyte precursors, which do not express myelin basic protein (MBP), aggregate in the stab wound area in the damaged telencephalon hemisphere. Although their proliferation is not very active, it suggests migration to the injury site, albeit temporarily, because this phenomenon is not observed after 35 days (März et al., 2011).
The expression of olig2 in the ventromedial region of the spinal cord in adult zebrafish significantly increases at 2 weeks post-injury, and these olig2-positive cells subsequently differentiate into hb9+ motor neurons (Reimer et al., 2009). After a stab wound to the telencephalon hemisphere, an increase in mdka expression is observed in quiescent radial glia cells of the damaged hemisphere in response to the injury, thus, indicating its role in the regulation of stem cell behavior (Lübke et al., 2022).
Such a stab wound also causes a slight decrease in GFAP expression in radial glia cell processes at 1 dpi, followed by a gradual increase from 3 to 14 dpi. The number of S100B-positive cells (radial glia cell bodies) also gradually increases from 8 dpi. GFAP-positive fibers in the injured hemisphere form hypertrophic swellings resembling cell bodies without nuclei, similar in appearance. Active proliferation of cells, including radial glia, is observed in the ventricular region of the damaged hemisphere (März et al., 2011). The radial glia’s ability to divide decreases with the animal’s age even in post-traumatic conditions. However, the formation of neuroblasts and subsequent neurogenesis appear to remain largely unaffected (Edelmann et al., 2013).
In zebrafish larvae, if an injury is inflicted to the spinal cord at 5 dpf, V2a interneuron bodies can be observed at the injury site as early as 9 dpi. These neurons exhibit the ability to receive signals from motor neurons and generate action potentials; however, they display distinct morphological and functional characteristics compared to mature V2a neurons. The persistence of these differences throughout the animal’s lifespan after the injury remains unclear (Vasudevan et al., 2021).
Regeneration of Mauthner cell axons post-laser ablation depends on the distance from the soma where the axon is severed, which is possibly regulated by regeneration-associated genes (RAGs). Although previous studies suggested incomplete functional recovery of these neurons post-injury, a successful regenerative response was observed with cAMP treatment following laser ablation in zebrafish larvae (Hecker et al., 2020).
A study highlighted the critical role of pdgfrb + cells in the structural repair of axons post-spinal cord injury in zebrafish larvae and adults. A marked expansion of the pdgfrb + cell population occurs around 7 dpi, coinciding in time with the initiation of axonal recovery after the injury (Tsata et al., 2021).
In adult zebrafish, the expression of hb-egfa significantly increases within the first 2 weeks post-spinal cord injury. Impairment of this factor was shown to negatively affect the axonal bridging between the injury edges and the post-traumatic neurogenesis (Cigliola et al., 2023).
After cerebellar injury in adult zebrafish, regeneration is primarily driven by neuroepithelial cells in the dorsal part of the ventricular zone, with radial glia cells playing a secondary role. Since the latter cells respond to injury, they are unable to be fully recruited to the lost cell population in the adult cerebellum. In juvenile fish, cerebellar regeneration is complete, leading to the regeneration of all damaged cell types (Kaslin et al., 2017).
A model of blunt-force head trauma in adult fish induces diffuse changes in the brain, with apoptosis-type neuronal death occurring predominantly in regions with high neuronal density. Constitutive neurogenic niches exhibit enhanced proliferative activity in response to the blunt force trauma, correlating with its severity. The proliferative response across the neuroaxis increases in a severity-dependent manner (Hentig et al., 2021a).
As shown in one of the studies, the expression profiles of various signaling pathways associated with cell death, developmental and proliferation signals, inflammatory response, neuronal differentiation, and axon guidance undergo dynamic changes at different stages following spinal cord injury in zebrafish (Hui et al., 2014). Figure 2 shows a schematic representation of the signaling pathways and cell populations involved in neuroregeneration in zebrafish.
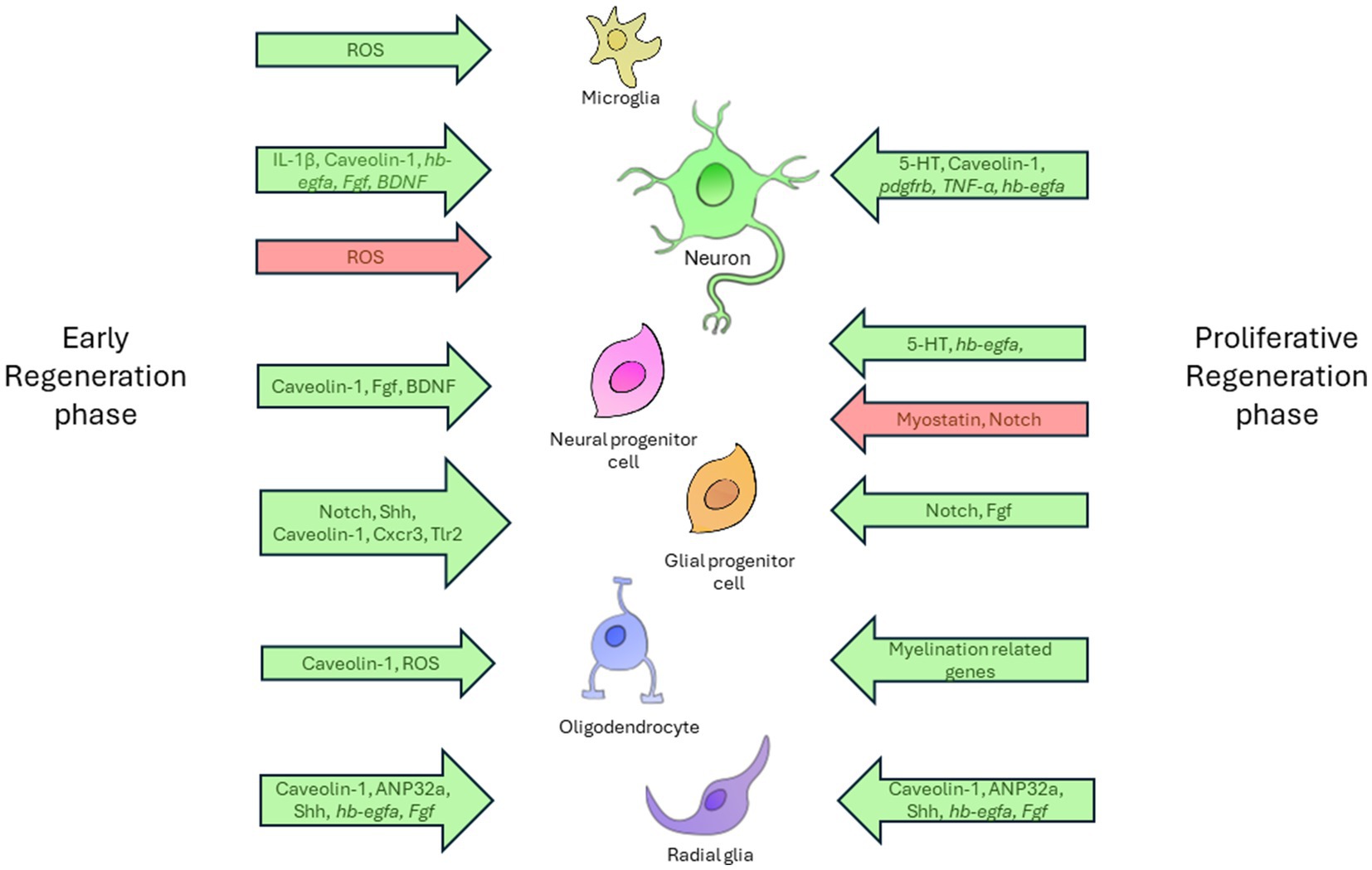
Figure 2. The diagram demonstrates complex relationships between diverse cell types and the regulatory factors involved in the nervous system regeneration in zebrafish. The regenerative process is provisionally divided into two distinct phases: the early phase and the proliferative phase. Each phase is characterized by specific cellular activities. The diagram shows the principal cell types involved in regeneration, including microglia, neurons, neuronal and glial progenitor cells, radial glia, and oligodendrocytes. The relationships between these cells and the influencing factors are illustrated using arrows that indicate the direction and nature of the factors’ effects. Permissive factors, which facilitate cellular processes, are designated by green arrows. These factors are instrumental in driving essential regenerative actions, including cell activation, axon growth, differentiation, and proliferation. In contrast, inhibitory factors, which impede these processes, are designated by red arrows. Factors located on the left of the timeline are associated with the early phase of regeneration and exert their effect at the initial stages of the cellular response. Those situated on the right correspond to the proliferative phase, where they regulate the later stages of regeneration, including cellular growth and differentiation.
According to numerous studies, signaling pathways associated with the initial development of the organism are activated in response to damage. Therefore, the Wnt/β-catenin signaling plays a crucial role in early stages of regeneration, when it is directly linked to p53, MAPK, Fox-O, mTor, and apoptosis (Briona et al., 2015; Demirci et al., 2020), and in a later proliferative phase (Strand et al., 2016). The Wnt signaling pathway has a significant effect on the proliferation and differentiation of radial glia at the injury site, both in the early post-traumatic phase and in the proliferative phase of CNS regeneration (Shimizu et al., 2018). Wnt also influences axonogenesis by modifying the composition of extracellular matrix (Wehner et al., 2017). It is also worth noting that Wnt/β-catenin plays a crucial role in the process of retinal regeneration following traumatic injury in zebrafish (Meyers et al., 2012).
The Shh signaling pathway is critical for regeneration and important for both local and systemic neural damage. After stab wound injury in adult fish, the upregulation of Shh activates the proliferation of radial glia cells in the optic tectum. However, this process inhibits their differentiation into neurons (Ueda et al., 2018). Shh is activated in the cerebellum of adult zebrafish after blunt forced injury within the first few hours post-injury. However, by 60 hpi, it returns to the pre-injury expression level (Hentig et al., 2021b). After spinal cord injury in adult fish, Shh is significantly higher expressed in ependymo-radial glia in the ventral part of the spinal canal compared to control animals. This expression changes dynamically over time (Reimer et al., 2009). Shh activation has an anti-edematous and anti-inflammatory effect and reduces seizure activity in adult zebrafish with systemic traumatic brain injury (Hentig et al., 2021a).
Notch signaling, when overexpressed, influences the post-traumatic neurogenesis in the adult fish spinal cord by significantly reducing the number of new neurons (Dias et al., 2012). Histone deacetylases 1 and 3, in synergy with Notch, reduce the proliferative activity of radial glia and increase the post-traumatic neurogenesis in the optic tectum. This is achieved by affecting the expression of her4.1 and her6 (Kiyooka et al., 2020).
Various members of the FGF family influence the neurogenesis and axonogenesis in the zebrafish nervous system following experimental injury. Studies have demonstrated that FGF2, FGF3, and FGF8 are involved in the stimulation of neuronal progenitor cell proliferation, neurite outgrowth, and glial cell morphogenesis, thereby promoting axon repair after injury (Goldshmit et al., 2018). The interaction between the Wnt/β-catenin and FGF signaling pathways enhances proliferation and differentiation during neuromast regeneration in zebrafish, promoting the production of hair cells and supporting cells after injury (Tang et al., 2019). Overall, FGF signaling acts as a key player in the organization of neurogenesis and axon repair processes in zebrafish, demonstrating its importance in stimulating efficient neurogenesis and axon growth.
Post-traumatic inflammation plays a crucial role in the post-transection spinal cord regeneration in both larval (Keatinge et al., 2021) and adult zebrafish (Saraswathy et al., 2022). Of particular note is the activation of TGF-β signaling pathways such as those in dorsal SOX2 positive progenitors in adults (Saraswathy et al., 2022), which appears to be one of a key factor in the successful spinal cord regeneration in larvae (Keatinge et al., 2021).
The myostatin expression is detected in SOX2 progenitor cells between days 7 and 14 after spinal cord injury. This factor is crucial for restoration of the functional characteristics of the spinal cord, but it has no effect on the restoration of the axonal structure or the formation of the glial bridge between the wound edges. Furthermore, it has been found to reduce the differentiation of progenitor cells into neurons in the dorsal part of the injury zone (Saraswathy et al., 2022).
In the process of regeneration (6–11 dpi), a significant increase in contactin-2 expression is observed following spinal cord transection in adult zebrafish. This has been found to be positively correlated with axon regrowth and functional recovery in injured animals. The same correlation is recorded from axons of nMLF neurons. Therefore, one can assume that proteins of the contact in family may exert a significant effect on the recovery of neural tissue post-injury (Lin et al., 2012).
Additionally, it has been demonstrated that the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression in the telencephalon of adult zebrafish markedly increases at the 1-day mark following injury, which is then followed by a gradual decline at the 15-day mark. It is noteworthy that the expression of this protein differs from that observed after injury in rats. In zebrafish, it is significantly expressed in the injured hemisphere, whereas in mammals, it is expressed in the contralateral hemisphere. The authors associate this observation with the formation of glial scars in rats (Cacialli et al., 2018). The role of BDNF in the continuous regeneration and turnover of structures such as the “rosette” in the retina and taste buds of juvenile and adult teleosts has been demonstrated, and its importance in maintaining the functionality of sensory organs emphasized (Aragona et al., 2022). The above findings suggest that this factor may influence not only constitutive but also regenerative neurogenesis in different parts of the nervous system and may be a potential therapeutic agent to facilitate neuroregeneration.
The “bystander effect” in neurotrauma refers to the influence of injured neurons on neighboring, uninjured cells. In adult zebrafish, this effect assumes a pivotal significance in the context of spinal cord injury (SCI) and various forms of neural damage.
Calcium imaging techniques have revealed an elevation in resting calcium levels within motoneurons (pMNs) post-injury, indicating a disruption in calcium homeostasis during the regenerative process. This alteration is further correlated with a pronounced upregulation of Calretinin expression, thereby implying an essential role for this protein in the buffering of intracellular calcium concentrations.
Furthermore, the expression levels of connexin 35/36 have been observed to increase post-injury, indicating a potential enhancement in gap junction-mediated intercellular communication among neurons. These findings underscore the fundamental importance of intercellular and biochemical signaling processes in the preservation of neuronal integrity and facilitation of recovery. Subsequent investigations should explore in greater depth the molecular pathways implicated in the bystander effect to more thoroughly elucidate the mechanisms underlying neuroprotection and regeneration (Pedroni et al., 2024).
The zebrafish (D. rerio) represents a valuable vertebrate model to study the nervous system. This organism has a number of advantages due to its morphological resemblance with mammals and regenerative abilities, which makes it a suitable choice for investigating a variety of traumatic injuries to the nervous system. Furthermore, both zebrafish larvae and adults can be used in the neuronal damage and neurogenesis research, providing a lot of opportunities for experimentation. In addition, this animal model offers a broad range of tools for disease modeling purposes. A variety of transgenic animal strains are currently available, and even double transgenic lines can be obtained to facilitate studies.
Like other model organisms, zebrafish has some limitations: its small size restricts applicability of such technologies as fMRI and EEG. Furthermore, zebrafish cannot perform cognitive tasks such as those set up for more complex animals. Nevertheless, the use of this fish in research markedly reduces costs and accelerates data acquisition. The regenerative abilities of zebrafish facilitate investigation of the fundamental mechanisms underlying the nervous system regeneration and potentially provide a basis for the development of therapies to treat injuries in various regions of the mammalian brain and spinal cord.
Zebrafish research has provided significant insights into neural regeneration, with, however, many issues to be addressed, which suggests the necessity of further studies. Despite the identification of the major signaling pathways involved in the nervous system regeneration in zebrafish, questions still remain as to their interactions during various stages of post-traumatic regeneration, in particular in aged individuals. Epigenetic modifications may also be of substantial significance, with DNA methylation patterns and non-coding RNAs exhibiting considerable variation between zebrafish (including various age and sex groups) and species with lower regenerative capacities.
While the responses of sensory and motor neurons to injury models have been extensively investigated, there have been a limited number of studies focused on the regeneration of interneurons and the re-establishment of the normal architecture of intricate neuronal networks. This should be subject to further investigation.
Environmental factors may also exert considerable effect on the regenerative capacities of organisms. A promising domain of investigation is the effects of these factors on the rate and completeness of regeneration. Furthermore, only very few studies have conducted long-term observations of animals to evaluate the morphological and functional alterations of cells within the regeneration zone and associated regions of the nervous system, which may be regarded as a promising subject for future research.
LM: Visualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. VD: Visualization, Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was financially supported by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation (Agreement No. 075-15-2022-301).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnmol.2025.1552885/full#supplementary-material
Adams, M. M., and Kafaligonul, H. (2018). Zebrafish—a model organism for studying the neurobiological mechanisms underlying cognitive brain aging and use of potential interventions. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 6:135. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2018.00135
Alyenbaawi, H., Kanyo, R., Locskai, L. F., Kamali-Jamil, R., DuVal, M. G., Bai, Q., et al. (2021). Seizures are a druggable mechanistic link between TBI and subsequent tauopathy. eLife 10:e58744. doi: 10.7554/eLife.58744
Anand, S. K., Sahu, M. R., and Mondal, A. C. (2021). Induction of oxidative stress and apoptosis in the injured brain: potential relevance to brain regeneration in zebrafish. Mol. Biol. Rep. 48, 5099–5108. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06506-7
Anguita-Salinas, C., Sánchez, M., Morales, R. A., Ceci, M. L., Rojas-Benítez, D., and Allende, M. L. (2019). Cellular dynamics during spinal cord regeneration in larval zebrafish. Dev. Neurosci. 41, 112–122. doi: 10.1159/000500185
Antinucci, P., and Hindges, R. (2016). A crystal-clear zebrafish for in vivo imaging. Sci. Rep. 6:29490. doi: 10.1038/srep29490
Aragona, M., Porcino, C., Guerrera, M. C., Montalbano, G., Laurà, R., Cometa, M., et al. (2022). The BDNF/TrkB Neurotrophin system in the sensory organs of zebrafish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23:2621. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052621
Barrett, L. M., Mitchell, D. M., Meighan, P. C., Varnum, M. D., and Stenkamp, D. L. (2022). Dynamic functional and structural remodeling during retinal regeneration in zebrafish. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 15:1070509. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.1070509
Baumgart, E. V., Barbosa, J. S., Bally-cuif, L., Götz, M., and Ninkovic, J. (2012). Stab wound injury of the zebrafish telencephalon: a model for comparative analysis of reactive gliosis. Glia 60, 343–357. doi: 10.1002/glia.22269
Becker, T., Bernhardt, R. R., Reinhard, E., Wullimann, M. F., Tongiorgi, E., and Schachner, M. (1998). Readiness of zebrafish brain neurons to regenerate a spinal axon correlates with differential expression of specific cell recognition molecules. J. Neurosci. 18, 5789–5803. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-15-05789.1998
Becker, T., Lieberoth, B. C., Becker, C. G., and Schachner, M. (2005). Differences in the regenerative response of neuronal cell populations and indications for plasticity in intraspinal neurons after spinal cord transection in adult zebrafish. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 30, 265–278. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2005.07.008
Bensimon-Brito, A., Cardeira, J., Dionísio, G., Huysseune, A., Cancela, M. L., and Witten, P. E. (2016). Revisiting in vivo staining with alizarin red S - a valuable approach to analyse zebrafish skeletal mineralization during development and regeneration. BMC Dev. Biol. 16:2. doi: 10.1186/s12861-016-0102-4
Beppi, C., Penner, M., Straumann, D., and Bögli, S. Y. (2022). A non-invasive biomechanical model of mild TBI in larval zebrafish. PLoS One 17:e0268901. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0268901
Bernardos, R. L., Barthel, L. K., and Raymond, P. A. (2005). Localized retinal regeneration following thermal lesions in adult zebrafish. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 46:5327.
Bremer, J., Skinner, J., and Granato, M. (2017). A small molecule screen identifies in vivo modulators of peripheral nerve regeneration in zebrafish. PLoS One 12:e0178854. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178854
Briona, L. K., and Dorsky, R. I. (2014). Radial glial progenitors repair the zebrafish spinal cord following transection. Exp. Neurol. 256, 81–92. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.03.017
Briona, L. K., Poulain, F. E., Mosimann, C., and Dorsky, R. I. (2015). Wnt/ß-catenin signaling is required for radial glial neurogenesis following spinal cord injury. Dev. Biol. 403, 15–21. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2015.03.025
Cacialli, P., D’angelo, L., Kah, O., Coumailleau, P., Gueguen, M., Pellegrini, E., et al. (2018). Neuronal expression of brain derived neurotrophic factor in the injured telencephalon of adult zebrafish. J. Comp. Neurol. 526, 569–582. doi: 10.1002/cne.24352
Ceci, M. L., Mardones-Krsulovic, C., Sánchez, M., Valdivia, L. E., and Allende, M. L. (2014). Axon-Schwann cell interactions during peripheral nerve regeneration in zebrafish larvae. Neural Develop. 9:22. doi: 10.1186/1749-8104-9-22
Choe, C. P., Choi, S.-Y., Kee, Y., Kim, M. J., Kim, S.-H., Lee, Y., et al. (2021). Transgenic fluorescent zebrafish lines that have revolutionized biomedical research. Lab. Anim. Res. 37:26. doi: 10.1186/s42826-021-00103-2
Cigliola, V., Shoffner, A., Lee, N., Ou, J., Gonzalez, T. J., Hoque, J., et al. (2023). Spinal cord repair is modulated by the neurogenic factor Hb-egf under direction of a regeneration-associated enhancer. Nat. Commun. 14:4857. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40486-5
Cunningham, R. L., and Monk, K. R. (2018). “Live imaging of Schwann cell development in zebrafish” in Schwann cells, methods in molecular biology. eds. P. V. Monje and H. A. Kim (New York, New York, NY: Springer), 401–405.
Demirci, Y., Cucun, G., Poyraz, Y. K., Mohammed, S., Heger, G., Papatheodorou, I., et al. (2020). Comparative transcriptome analysis of the regenerating zebrafish telencephalon unravels a resource with key pathways during two early stages and activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling at the early wound healing stage. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 8:584604. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.584604
Dias, T. B., Yang, Y.-J., Ogai, K., Becker, T., and Becker, C. G. (2012). Notch signaling controls generation of motor neurons in the lesioned spinal cord of adult zebrafish. J. Neurosci. 32, 3245–3252. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6398-11.2012
DiCicco, R. M., Bell, B. A., Kaul, C., Hollyfield, J. G., Anand-Apte, B., Perkins, B. D., et al. (2014). Retinal regeneration following OCT-guided laser injury in zebrafish. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 55, 6281–6288. doi: 10.1167/iovs.14-14724
Diekmann, H., Kalbhen, P., and Fischer, D. (2015). Characterization of optic nerve regeneration using transgenic zebrafish. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 9:118. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00118
Diotel, N., Lübke, L., Strähle, U., and Rastegar, S. (2020). Common and distinct features of adult neurogenesis and regeneration in the telencephalon of zebrafish and mammals. Front. Neurosci. 14:568930. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.568930
Edelmann, K., Glashauser, L., Sprungala, S., Hesl, B., Fritschle, M., Ninkovic, J., et al. (2013). Increased radial glia quiescence, decreased reactivation upon injury and unaltered neuroblast behavior underlie decreased neurogenesis in the aging zebrafish telencephalon. J. Comp. Neurol. 521, 3099–3115. doi: 10.1002/cne.23347
Gan, D., Wu, S., Chen, B., and Zhang, J. (2020). Application of the zebrafish traumatic brain injury model in assessing cerebral inflammation. Zebrafish 17, 73–82. doi: 10.1089/zeb.2019.1793
Goldshmit, Y., Sztal, T. E., Jusuf, P. R., Hall, T. E., Nguyen-Chi, M., and Currie, P. D. (2012). Fgf-dependent glial cell bridges facilitate spinal cord regeneration in zebrafish. J. Neurosci. 32, 7477–7492. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0758-12.2012
Goldshmit, Y., Tang, J. K. K. Y., Siegel, A. L., Nguyen, P. D., Kaslin, J., Currie, P. D., et al. (2018). Different Fgfs have distinct roles in regulating neurogenesis after spinal cord injury in zebrafish. Neural Develop. 13:24. doi: 10.1186/s13064-018-0122-9
Graciarena, M., Dambly-Chaudière, C., and Ghysen, A. (2014). Dynamics of axonal regeneration in adult and aging zebrafish reveal the promoting effect of a first lesion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 111, 1610–1615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1319405111
Hannah, R. M., Smith, A., and Yin, V. P. (2012). An open-head traumatic brain injury model in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Bull. MDI Biol. Lab. 2012:51.
Harvey, B. M., Baxter, M., and Granato, M. (2023). “Assaying optic nerve regeneration in larval zebrafish” in Axon regeneration, methods in molecular biology. eds. A. J. Udvadia and J. B. Antczak (US, New York, NY: Springer), 191–203.
Hecker, A., Anger, P., Braaker, P. N., Schulze, W., and Schuster, S. (2020). High-resolution mapping of injury-site dependent functional recovery in a single axon in zebrafish. Commun. Biol. 3:307. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-1034-x
Hentig, J., Campbell, L. J., Cloghessy, K., Lee, M., Boggess, W., and Hyde, D. R. (2021a). Prophylactic activation of Shh signaling attenuates TBI-induced seizures in zebrafish by modulating glutamate excitotoxicity through Eaat2a. Biomedicines 10:32. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10010032
Hentig, J., Cloghessy, K., Lahne, M., Jung, Y. J., Petersen, R. A., Morris, A. C., et al. (2021b). Zebrafish blunt-force TBI induces Heterogenous injury pathologies that mimic human TBI and responds with sonic hedgehog-dependent cell proliferation across the Neuroaxis. Biomedicines 9:861. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9080861
Hiyoshi, K., Saito, K., Fukuda, N., Matsuzaki, T., Yoshikawa, H. Y., and Tsuda, S. (2021). Two-photon laser ablation and in vivo wide-field imaging of inferior olive neurons revealed the recovery of Olivocerebellar circuits in zebrafish. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18:8357. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18168357
Hossainian, D., Shao, E., Jiao, B., Ilin, V. A., Parris, R. S., Zhou, Y., et al. (2022). Quantification of functional recovery in a larval zebrafish model of spinal cord injury. J. Neurosci. Res. 100, 2044–2054. doi: 10.1002/jnr.25118
Hui, S. P., Dutta, A., and Ghosh, S. (2010). Cellular response after crush injury in adult zebrafish spinal cord. Dev. Dyn. 239, 2962–2979. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.22438
Hui, S. P., Sengupta, D., Lee, S. G. P., Sen, T., Kundu, S., Mathavan, S., et al. (2014). Genome wide expression profiling during spinal cord regeneration identifies comprehensive cellular responses in zebrafish. PLoS One 9:e84212. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084212
Isabella, A. J., Stonick, J. A., Dubrulle, J., and Moens, C. B. (2021). Intrinsic positional memory guides target-specific axon regeneration in the zebrafish vagus nerve. Development 148:dev199706. doi: 10.1242/dev.199706
John, N., Kolb, J., and Wehner, D. (2022). Mechanical spinal cord transection in larval zebrafish and subsequent whole-mount histological processing. STAR Protoc. 3:101093. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2021.101093
Kaslin, J., and Ganz, J. (2020). “Zebrafish nervous systems” in The zebrafish in biomedical research. eds. S. C. Cartner, J. S. Eisen, and G. E. Sanders (London: Academic Press), 181–189.
Kaslin, J., Kroehne, V., Ganz, J., Hans, S., and Brand, M. (2017). Correction: distinct roles of neuroepithelial-like and radial glia-like progenitor cells in cerebellar regeneration. Development 144:3388. doi: 10.1242/dev.158600
Keatinge, M., Tsarouchas, T. M., Munir, T., Porter, N. J., Larraz, J., Gianni, D., et al. (2021). CRISPR gRNA phenotypic screening in zebrafish reveals pro-regenerative genes in spinal cord injury. PLoS Genet. 17:e1009515. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009515
Kim, H.-K., Lee, D., Kim, E., Jeong, I., Kim, S., Kim, B.-J., et al. (2020). Notch signaling controls oligodendrocyte regeneration in the injured telencephalon of adult zebrafish. Exp. Neurobiol. 29, 417–424. doi: 10.5607/en20050
Kishimoto, N., Shimizu, K., and Sawamoto, K. (2012). Neuronal regeneration in a zebrafish model of adult brain injury. Dis. Model. Mech. 5, 200–209. doi: 10.1242/dmm.007336
Kiyooka, M., Shimizu, Y., and Ohshima, T. (2020). Histone deacetylase inhibition promotes regenerative neurogenesis after stab wound injury in the adult zebrafish optic tectum. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 529, 366–371. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.06.025
Kizil, C., Kaslin, J., Kroehne, V., and Brand, M. (2012). Adult neurogenesis and brain regeneration in zebrafish. Dev. Neurobiol. 72, 429–461. doi: 10.1002/dneu.20918
Kjell, J., and Olson, L. (2016). Rat models of spinal cord injury: from pathology to potential therapies. Dis. Model. Mech. 9, 1125–1137. doi: 10.1242/dmm.025833
Kozol, R. A., Abrams, A. J., James, D. M., Buglo, E., Yan, Q., and Dallman, J. E. (2016). Function over form: modeling groups of inherited neurological conditions in zebrafish. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 9:55. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2016.00055
Kroehne, V., Freudenreich, D., Hans, S., Kaslin, J., and Brand, M. (2011). Regeneration of the adult zebrafish brain from neurogenic radial glia-type progenitors. Development 138, 4831–4841. doi: 10.1242/dev.072587
Lahne, M., Nagashima, M., Hyde, D. R., and Hitchcock, P. F. (2020). Reprogramming Müller glia to regenerate retinal neurons. Annu. Rev. Vis. Sci. 6, 171–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev-vision-121219-081808
Lee, H. C., Lai, W. L., Lin, C. Y., Zeng, C. W., Sheu, J. C., Chou, T. B., et al. (2022). Anp32a promotes neuronal regeneration after spinal cord injury of zebrafish embryos. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23:15921. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415921
Lin, J. F., Pan, H. C., Ma, L. P., Shen, Y. Q., and Schachner, M. (2012). The cell neural adhesion molecule Contactin-2 (TAG-1) is beneficial for functional recovery after spinal cord injury in adult zebrafish. PLoS One 7:e52376. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052376
Liu, K. S., and Fetcho, J. R. (1999). Laser ablations reveal functional relationships of segmental hindbrain neurons in zebrafish. Neuron 23, 325–335. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80783-7
Lübke, L., Zhang, G., Strähle, U., and Rastegar, S. (2022). Mdka expression is associated with quiescent neural stem cells during constitutive and reactive neurogenesis in the adult zebrafish telencephalon. Brain Sci. 12:284. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12020284
Maheras, A. L., Dix, B., Carmo, O. M. S., Young, A. E., Gill, V. N., Sun, J. L., et al. (2018). Genetic pathways of Neuroregeneration in a novel mild traumatic brain injury model in adult zebrafish. Eneuro 5:ENEURO.0208–17.2017. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0208-17.2017
Marmarou, A., Foda, M. A. A.-E., Brink, W. V. D., Campbell, J., Kita, H., and Demetriadou, K. (1994). A new model of diffuse brain injury in rats: part I: pathophysiology and biomechanics. J. Neurosurg. 80, 291–300. doi: 10.3171/jns.1994.80.2.0291
Marques, I. J., Lupi, E., and Mercader, N. (2019). Model systems for regeneration: zebrafish. Development 146:dev167692. doi: 10.1242/dev.167692
März, M., Schmidt, R., Rastegar, S., and Strähle, U. (2011). Regenerative response following stab injury in the adult zebrafish telencephalon. Dev. Dyn. 240, 2221–2231. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.22710
McCutcheon, V., Park, E., Liu, E., Sobhebidari, P., Tavakkoli, J., Wen, X.-Y., et al. (2017). A novel model of traumatic brain injury in adult zebrafish demonstrates response to injury and treatment comparable with mammalian models. J. Neurotrauma 34, 1382–1393. doi: 10.1089/neu.2016.4497
Meehan, S. D., Hu, M., Veldman, M. B., and Bhattacharya, S. K. (2023). Metabolomics dataset of zebrafish optic nerve regeneration after injury. Data Brief 48:109102. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2023.109102
Meyers, J. R., Hu, L., Moses, A., Kaboli, K., Papandrea, A., and Raymond, P. A. (2012). β-Catenin/Wnt signaling controls progenitor fate in the developing and regenerating zebrafish retina. Neural Develop. 7:30. doi: 10.1186/1749-8104-7-30
Mokalled, M. H., Patra, C., Dickson, A. L., Endo, T., Stainier, D. Y. R., and Poss, K. D. (2016). Injury-induced ctgfa directs glial bridging and spinal cord regeneration in zebrafish. Science 354, 630–634. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf2679
Morsch, M., Radford, R., Lee, A., Don, E. K., Badrock, A. P., Hall, T. E., et al. (2015). In vivo characterization of microglial engulfment of dying neurons in the zebrafish spinal cord. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 9:321. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00321
Moya-Díaz, J., Peña, O. A., Sánchez, M., Ureta, D. A., Reynaert, N. G., Anguita-Salinas, C., et al. (2014). Electroablation: a method for neurectomy and localized tissue injury. BMC Dev. Biol. 14:7. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-14-7
Muto, A., and Kawakami, K. (2018). Ablation of a neuronal population using a two-photon laser and its assessment using calcium imaging and behavioral recording in zebrafish larvae. J. Vis. Exp. 136:57485. doi: 10.3791/57485
Nakajima, R., Hagihara, H., and Miyakawa, T. (2021). Similarities of developmental gene expression changes in the brain between human and experimental animals: rhesus monkey, mouse, zebrafish, and Drosophila. Mol. Brain 14:135. doi: 10.1186/s13041-021-00840-4
Nichols, E. L., and Smith, C. J. (2020). Functional regeneration of the sensory root via axonal invasion. Cell Rep. 30, 9–17.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.12.008
O’Brien, G. S., Martin, S. M., Söllner, C., Wright, G. J., Becker, C. G., Portera-Cailliau, C., et al. (2009). Developmentally regulated impediments to skin Reinnervation by injured peripheral sensory axon terminals. Curr. Biol. 19, 2086–2090. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.10.051
Ohnmacht, J., Yang, Y., Maurer, G. W., Barreiro-Iglesias, A., Tsarouchas, T. M., Wehner, D., et al. (2016). Spinal motor neurons are regenerated after mechanical lesion and genetic ablation in larval zebrafish. Development 143, 1464–1474. doi: 10.1242/dev.129155
Pedroni, A., Dai, Y.-W. E., Lafouasse, L., Chang, W., Srivastava, I., Del Vecchio, L., et al. (2024). Neuroprotective gap-junction-mediated bystander transformations in the adult zebrafish spinal cord after injury. Nat. Commun. 15:4331. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48729-9
Pose-Méndez, S., Schramm, P., Winter, B., Meier, J. C., Ampatzis, K., and Köster, R. W. (2023). Lifelong regeneration of cerebellar Purkinje cells after induced cell ablation in zebrafish. eLife 12:e79672. doi: 10.7554/eLife.79672
Reimer, M. M., Kuscha, V., Wyatt, C., Sörensen, I., Frank, R. E., Knüwer, M., et al. (2009). Sonic hedgehog is a polarized signal for motor neuron regeneration in adult zebrafish. J. Neurosci. 29, 15073–15082. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4748-09.2009
Reimer, M. M., Sörensen, I., Kuscha, V., Frank, R. E., Liu, C., Becker, C. G., et al. (2008). Motor Neuron Regeneration in Adult Zebrafish. J. Neurosci. 28, 8510–8516. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1189-08.2008
Roeser, T., and Baier, H. (2003). Visuomotor behaviors in larval zebrafish after GFP-guided laser ablation of the optic tectum. J. Neurosci. 23, 3726–3734. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-09-03726.2003
Rosenberg, A. F., Wolman, M. A., Franzini-Armstrong, C., and Granato, M. (2012). In vivo nerve–macrophage interactions following peripheral nerve injury. J. Neurosci. 32, 3898–3909. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5225-11.2012
Saleem, S., and Kannan, R. R. (2018). Zebrafish: an emerging real-time model system to study Alzheimer’s disease and neurospecific drug discovery. Cell Death Discov. 4:45. doi: 10.1038/s41420-018-0109-7
Saraswathy, V. M., Zhou, L., McAdow, A. R., Burris, B., Dogra, D., Reischauer, S., et al. (2022). Myostatin is a negative regulator of adult neurogenesis after spinal cord injury in zebrafish. Cell Rep. 41:111705. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111705
Schmidt, R., Beil, T., Strähle, U., and Rastegar, S. (2014). Stab wound injury of the zebrafish adult telencephalon: a method to investigate vertebrate brain neurogenesis and regeneration. J. Vis. Exp. 51753:e51753. doi: 10.3791/51753
Schmidt, R., Strähle, U., and Scholpp, S. (2013). Neurogenesis in zebrafish – from embryo to adult. Neural Develop. 8:3. doi: 10.1186/1749-8104-8-3
Senut, M.-C., Gulati-Leekha, A., and Goldman, D. (2004). An element in the α1-tubulin promoter is necessary for retinal expression during optic nerve regeneration but not after eye injury in the adult zebrafish. J. Neurosci. 24, 7663–7673. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2281-04.2004
Sharma, P., and Ramachandran, R. (2019). Retina injury and retina tissue preparation to study regeneration in zebrafish. Bio Protoc. 9:e3466. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3466
Sherpa, T., Fimbel, S. M., Mallory, D. E., Maaswinkel, H., Spritzer, S. D., Sand, J. A., et al. (2008). Ganglion cell regeneration following whole-retina destruction in zebrafish. Dev. Neurobiol. 68, 166–181. doi: 10.1002/dneu.20568
Shimizu, Y., Ueda, Y., and Ohshima, T. (2018). Wnt signaling regulates proliferation and differentiation of radial glia in regenerative processes after stab injury in the optic tectum of adult zebrafish. Glia 66, 1382–1394. doi: 10.1002/glia.23311
Stil, A., and Drapeau, P. (2016). Neuronal labeling patterns in the spinal cord of adult transgenic zebrafish. Dev. Neurobiol. 76, 642–660. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22350
Strand, N. S., Hoi, K. K., Phan, T. M. T., Ray, C. A., Berndt, J. D., and Moon, R. T. (2016). Wnt/β-catenin signaling promotes regeneration after adult zebrafish spinal cord injury. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 477, 952–956. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.07.006
Tang, D., He, Y., Li, W., and Li, H. (2019). Wnt/β-catenin interacts with the FGF pathway to promote proliferation and regenerative cell proliferation in the zebrafish lateral line neuromast. Exp. Mol. Med. 51, 1–16. doi: 10.1038/s12276-019-0247-x
Thomson, K. R., Kavnoudias, H., and Neal, R. E. (2015). Introduction to irreversible electroporation—principles and techniques. Tech. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 18, 128–134. doi: 10.1053/j.tvir.2015.06.002
Tikhonova, M. A., Maslov, N. A., Bashirzade, A. A., Nehoroshev, E. V., Babchenko, V. Y., Chizhova, N. D., et al. (2022). A novel laser-based zebrafish model for studying traumatic brain injury and its molecular targets. Pharmaceutics 14:1751. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14081751
Tsata, V., Kroehne, V., Wehner, D., Rost, F., Lange, C., Hoppe, C., et al. (2020). Reactive oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (re-)myelinate the regenerating zebrafish spinal cord. Development 147:dev193946. doi: 10.1242/dev.193946
Tsata, V., Möllmert, S., Schweitzer, C., Kolb, J., Möckel, C., Böhm, B., et al. (2021). A switch in pdgfrb cell-derived ECM composition prevents inhibitory scarring and promotes axon regeneration in the zebrafish spinal cord. Dev. Cell 56, 509–524.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2020.12.009
Ueda, Y., Shimizu, Y., Shimizu, N., Ishitani, T., and Ohshima, T. (2018). Involvement of sonic hedgehog and notch signaling in regenerative neurogenesis in adult zebrafish optic tectum after stab injury. J. Comp. Neurol. 526, 2360–2372. doi: 10.1002/cne.24489
Umans, R. A., Henson, H. E., Mu, F., Parupalli, C., Ju, B., Peters, J. L., et al. (2017). CNS angiogenesis and barriergenesis occur simultaneously. Dev. Biol. 425, 101–108. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.03.017
Vajn, K., Suler, D., Plunkett, J. A., and Oudega, M. (2014). Temporal profile of endogenous anatomical repair and functional recovery following spinal cord injury in adult zebrafish. PLoS One 9:e105857. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105857
Van Houcke, J., Mariën, V., Zandecki, C., Seuntjens, E., Ayana, R., and Arckens, L. (2021). Modeling Neuroregeneration and Neurorepair in an aging context: the power of a teleost model. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9:619197. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.619197
Vasudevan, D., Liu, Y.-C., Barrios, J. P., Wheeler, M. K., Douglass, A. D., and Dorsky, R. I. (2021). Regenerated interneurons integrate into locomotor circuitry following spinal cord injury. Exp. Neurol. 342:113737. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2021.113737
Wehner, D., Tsarouchas, T. M., Michael, A., Haase, C., Weidinger, G., Reimer, M. M., et al. (2017). Wnt signaling controls pro-regenerative collagen XII in functional spinal cord regeneration in zebrafish. Nat. Commun. 8:126. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00143-0
Widmann, G. (2009). Tumour ablation: technical aspects. Cancer Imaging 9, S63–S67. doi: 10.1102/1470-7330.2009.9026
Wu, C.-C., Tsai, T.-H., Chang, C., Lee, T.-T., Lin, C., Cheng, I. H.-J., et al. (2014). On the crucial cerebellar wound healing-related pathways and their cross-talks after traumatic brain injury in Danio rerio. PLoS One 9:e97902. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097902
Xiao, Y., Petrucco, L., Hoodless, L. J., Portugues, R., and Czopka, T. (2022). Oligodendrocyte precursor cells sculpt the visual system by regulating axonal remodeling. Nat. Neurosci. 25, 280–284. doi: 10.1038/s41593-022-01023-7
Yin, G., Du, M., Li, R., Li, K., Huang, X., Duan, D., et al. (2018). Glia maturation factor beta is required for reactive gliosis after traumatic brain injury in zebrafish. Exp. Neurol. 305, 129–138. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2018.04.008
Zeng, C.-W., Kamei, Y., Shigenobu, S., Sheu, J.-C., and Tsai, H.-J. (2021). Injury-induced Cavl-expressing cells at lesion rostral side play major roles in spinal cord regeneration. Open Biol. 11:200304. doi: 10.1098/rsob.200304
Zupanc, G. K. H. (2006). Neurogenesis and neuronal regeneration in the adult fish brain. J. Comp. Physiol. A 192, 649–670. doi: 10.1007/s00359-006-0104-y
Keywords: zebrafish, neuroregeneration, traumatic neural injury model, posttraumatic cellular interactions, post-traumatic neurogenesis
Citation: Murashova L and Dyachuk V (2025) Modeling traumatic brain and neural injuries: insights from zebrafish. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 18:1552885. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2025.1552885
Received: 29 December 2024; Accepted: 07 March 2025;
Published: 27 March 2025.
Edited by:
Zhaoyu Li, Brain Institute, University of Queensland, AustraliaReviewed by:
Anna Jazwinska, Université de Fribourg, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2025 Murashova and Dyachuk. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Vyacheslav Dyachuk, c2xhdmFkODNAZ21haWwuY29t
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.