- 1School of Biotechnology, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, Jiangsu, China
- 2Laboratory of Food Perception Science, Science Center for Future Foods, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, Jiangsu, China
G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) subtypes within the hypothalamus play a pivotal role in maintaining body homeostasis, particularly in the regulation of food intake and energy metabolism. This review provides an overview of classical loss and gain-of-function studies on GPCRs related to feeding and metabolism, with a focus on emerging cell-type-specific investigations. These studies reveal that diverse GPCR-expressing neuronal populations are intricately linked to feeding and energy balance. We also discuss recent findings that highlight the interaction of distinct peptide-GPCR systems in modulating complex feeding behaviors.
Introduction
The global rise in obesity and associated metabolic disorders, largely due to unhealthy lifestyles and excessive consumption of energy-dense foods, presents a significant health challenge (Simpson et al., 2015; NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC), 2016; Baak, 2023; Lingvay, 2024). Addressing this issue requires a comprehensive understanding of the central mechanisms that drive overeating (Schwartz et al., 2000; Rossi and Stuber, 2018; Zimmerman and Knight, 2020). G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), a vast family of seven-transmembrane receptor proteins (Hilger et al., 2019), have emerged as pivotal targets for numerous pharmacological interventions for metabolic diseases, including obesity and diabetes (Liu et al., 2024).
The hypothalamus, a critical brain region essential for the regulation of feeding and metabolism (Coll et al., 2007; Brüning and Fenselau, 2023), is enriched with GPCRs related to these functions (Sobrino Crespo et al., 2014; Krashes et al., 2016; Kabahizi et al., 2022). Recent advancements in GPCR drug development have shown promise in treating obesity. For example, semaglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonist, has demonstrated reliable weight loss effects in treating obesity and diabetes (Knudsen and Lau, 2019; Davies et al., 2021). Similarly, melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) agonist, setmelanotide, is effective for the treatment of genetic forms of obesity (Clément et al., 2020; Markham, 2021; Clément et al., 2018; Haws et al., 2020). Expanding our knowledge of GPCR functions in the hypothalamus is fundamental for the future improvement of GPCR drugs for metabolic syndrome.
In this review, we focus on key GPCRs and their associated neurons within the hypothalamus that are crucial for feeding and metabolism, including GLP-1 receptor, melanocortin receptor, neuropeptide Y receptor, corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor, and oxytocin receptor. By presenting the current understanding of the complex roles and interactions between peptide-GPCR systems in the hypothalamus, we aim to offer new insights into the future development of anti-obesity medications.
GLP-1 receptors
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptors (GLP-1Rs) have become a key target in obesity treatment, garnering significant attention. Semaglutide and Liraglutide, developed as long-acting GLP-1R agonists, have shown dramatic weight loss effects in treating metabolic disorders, including obesity and type 2 diabetes (Knudsen and Lau, 2019). Moreover, a meta-analysis study demonstrates that administration of GLP-1 receptor agonists in diabetes patients exhibits slightly better effects on blood glucose control compared with insulin therapy (Abd El Aziz et al., 2016).
In central, GLP-1Rs are heavily expressed in the hypothalamus, including the arcuate nucleus (ARC), paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus (PVH), and dorsomedial hypothalamus (DMH; Gu et al., 2013; Cork et al., 2015). Electrophysiology study has shown that the application of GLP-1R agonist exendin-4, significantly enhances the action potential (AP) firing rate of ARCGLP-1R neurons. Furthermore, activation of these neurons, performed by the excitatory DREADD hM3Dq, results in a notable suppression of food intake without significant changes in blood glucose or insulin levels (Singh, 2022). GLP-1R neurons in the PVH receive projections from the NTS, activation of glucagon (Gcg) neurons in the NTS inhibits feeding behaviors, while deletion of PVHGLP-1R neurons increases food intake and decreases locomotor activities, leading to obesity (Liu et al., 2017). In another study, it is reported that the activity of PVHGLP-1R neurons increase temporarily during refeeding and chemogenetic activation of these neurons also significantly reduce appetite (Li et al., 2019).
GLP-1Rs in the DMH also play a crucial role in metabolism and are suggested to be a major target for GLP-1R agonist drugs (Figure 1). Chemogenetic activation of GLP-1R neurons in the DMH, innervated by NTSGcg neurons, reduces blood glucose levels, whereas ablation of GLP-1R in the DMH elevates them, suggesting that the endogenous GLP-1 system is crucial for maintaining blood glucose balance (Huang et al., 2022). Recent findings also implicate DMHGLP-1R neurons are involved in pre-ingestive satiation (Kim et al., 2024), indicated by an increased self-reported satiation index in human after semaglutide administration. Optogenetic inhibition of DMHGLP-1R neurons reduces feeding motivation in fasted mice, while activation of the same neurons increases appetite. Furthermore, in vivo calcium imaging reveals that a subset of DMHGLP-1R neurons is tuned to response during food seeking, supporting the hypothesis that these neurons encode the pre-ingestive satiation. In addition, ARCAgRP neurons are identified as the downstream target of DMHGLP-1R neurons to elicit satiation. Collectively, these observations strengthened the reliability of GLP-1R agonist-based drug therapies for obesity.
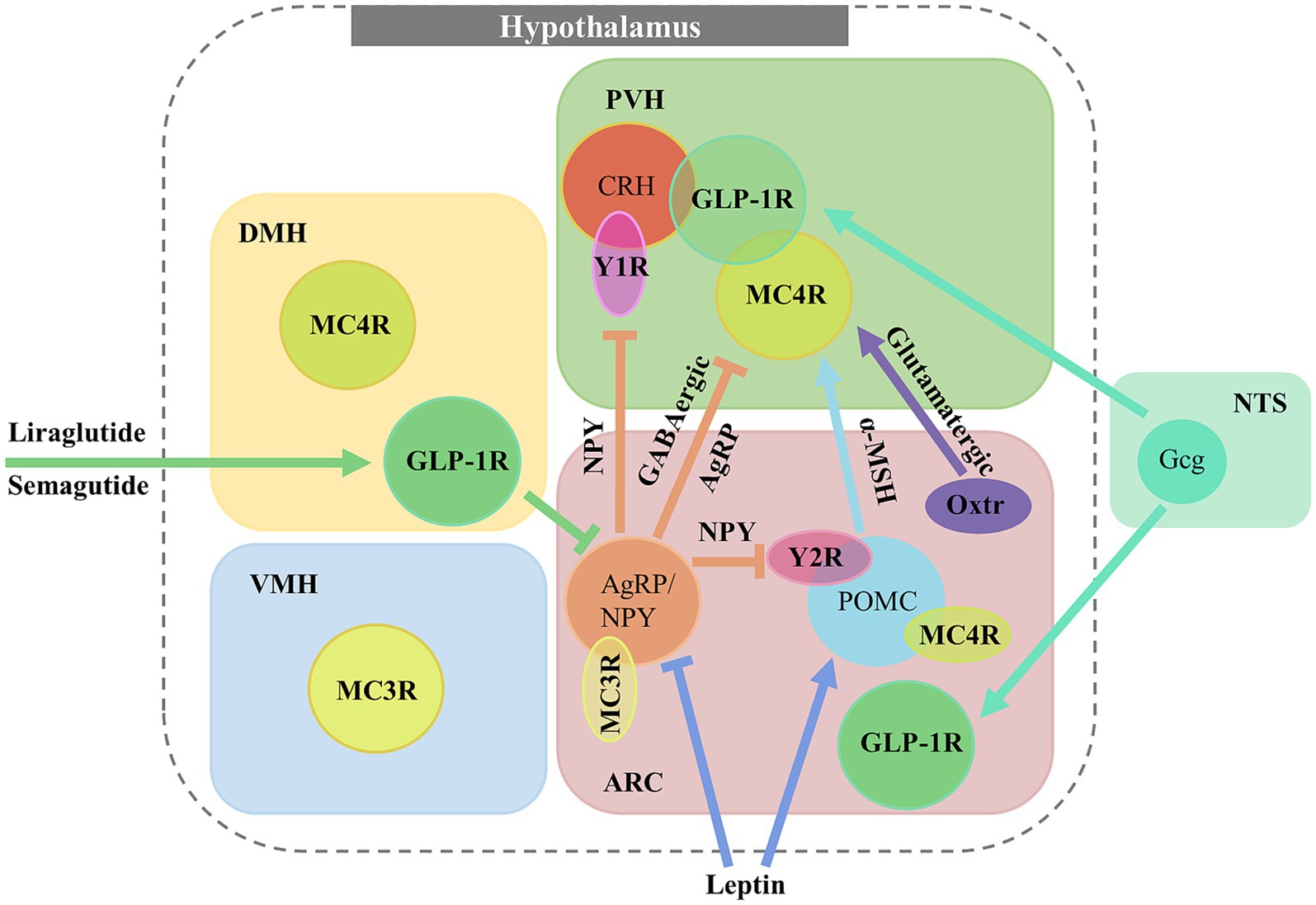
Figure 1. GPCR expression in hypothalamus and neural networks for regulating feeding and metabolism. GLP-1R and MC4R are differentially expressed in numerous hypothalamic areas, distributed in PVH, DMH, VMH or ARC. GLP-1R neurons in PVH and ARC are activated by endogenous GLP-1 from NTSGcg neurons while DMHGLP-1R neurons are activated by GLP-1R agonist drugs (Liraglutide and Semagutide). Leptin signaling activates POMC neurons but inhibits in AgRP neurons. PVHMC4R neurons are activated by α-MSH from POMC neurons and inhibited by AgRP neurons. In the ARC, AgRP neurons inhibit NPY2R in POMC neurons and NPY1R on PVHCRH neurons by release of NPY.
Melanocortin receptors
Melanocortin receptors (MCRs), particularly the melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R), are crucial GPCR in regulating physiological metabolic processes (Sweeney et al., 2023). The recent approval of Setmelanotide, an MC4R agonist, for treating obesity caused by deficiencies in proopiomelanocortin (POMC), proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 1 (PCSK1), or Leptin Receptor (Markham, 2021), has heightened scientific interest in the effects of MCRs on feeding and energy balance (Table 1).
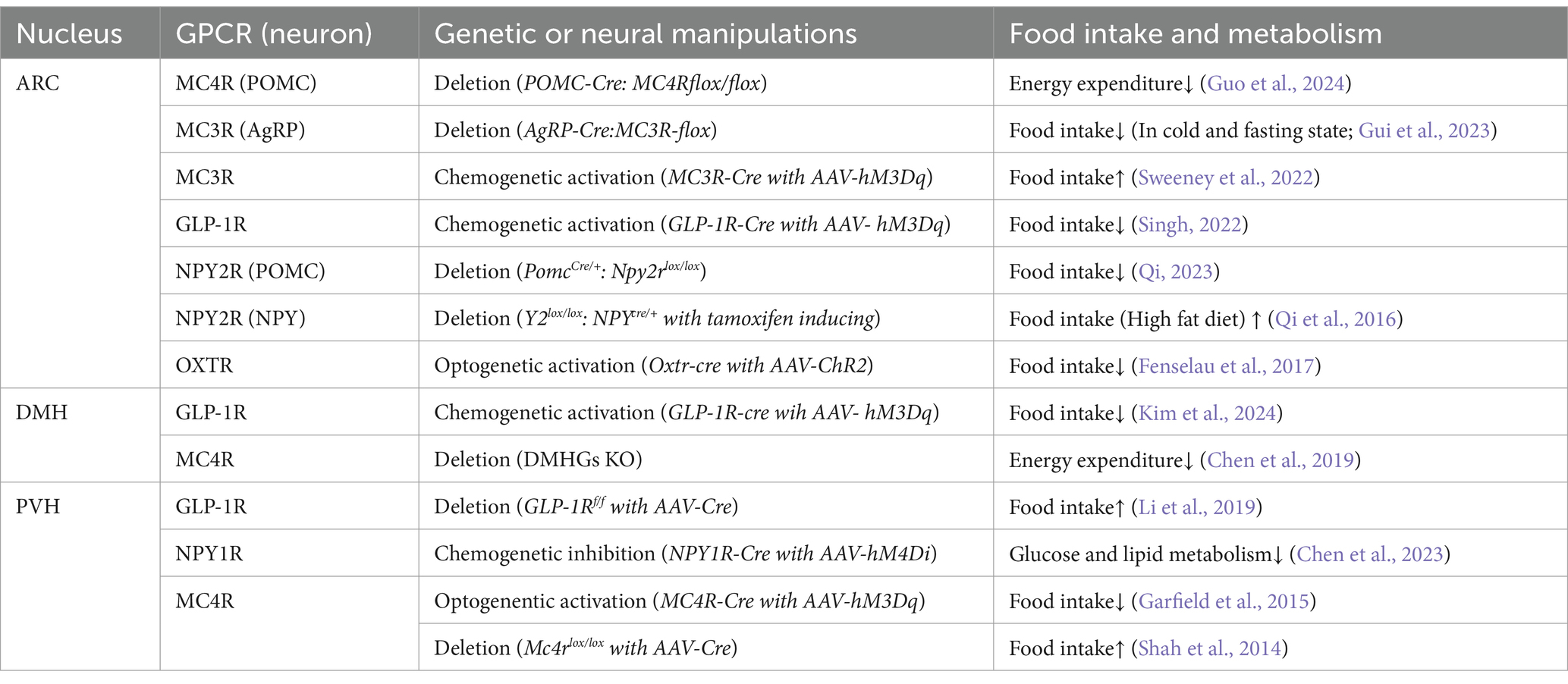
Table 1. Cell-specific manipulations of GPCR expressing neurons and their impact on food intake and metabolism.
Among numerous MCR from type1 to type5, MC3R and MC4R are expressed in the brain (Dib et al., 2017), with significant dense distributions in the hypothalamus (Catania, 2010). Both receptors play a pivotal role in feeding and energy homeostasis (Anderson et al., 2016; Butler et al., 2000). MC3R deficient mice show increased fat mass, reduced lean mass and higher feed efficiency than wild-type mice (Chen et al., 2000). MC3R knockout mice display an obese phenotype, restoring MC3R signaling in ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus (VMH) Steroidogenic Factor-1(SF-1) neurons, which are involved in the regulation of blood glucose and fat metabolism (Coutinho et al., 2017; Rashid et al., 2023), results in a partial rescue by attenuating changes in fat mass and markedly improving metabolic homeostasis (Begriche et al., 2011). Furthermore, VMHMC3R neurons are sensitive to glucose changes, and their activation promotes glucose disposal (Sutton et al., 2021). Besides the VMH, MC3Rs are also expressed in ARCAgRP neurons (Sweeney et al., 2023), and MC3R signals are required for the activation of AgRP neurons by fasting. Food intake during refeeding following overnight fasting is significantly lower in MC3R knockout mice compared to normal mice, with a decline in c-Fos expression in AgRP neurons (Gui et al., 2023). Another study indicates that MC3R knockout mice exhibit enhanced anorexia. Chemogenetic activation of AgRPMC3R neurons increases feeding, while MC3R specific antagonist C11 inhibits food intake (Sweeney et al., 2022), suggesting that MC3R in the ARC is a potential pharmacological target for anorexia.
MC4R is primarily expressed in the CNS in a distinct set of nuclei from MC3R, predominantly in the PVH (Sweeney et al., 2023). Notably, MC3R is expressed pre-synaptically in AgRP neurons, from which it acts to regulate the release of GABA onto PVHMC4R neurons (Ghamari-Langroudi et al., 2018). The absence of MC4R in PVH leads to hyperphagia (Shah et al., 2014), energy imbalance, increased fat mass, and glucose disorders (Krashes et al., 2016). Electrophysiological studies show significantly increased activity of PVHMC4R neurons when exposed to α-MSH, an MC4R agonist from POMC neurons (Fenselau et al., 2017). In contrast, optogenetic activation of ARCAgRP neurons that project to PVHMC4R increases feeding, while chemogenetic activation of the neural pathway from PVHMC4R to lateral parabrachial nucleus (LPBN) significantly reduces food intake (Garfield et al., 2015; Figure 1). Besides, chemogenetic inhibition of PVHMC4R neurons leads to increased food intake in energy-sufficient states (Sayar-Atasoy et al., 2023), indicating that PVHMC4R neurons encode satiety. α-MSH released from POMC neurons can persistently elevates cAMP level in PVHMC4R neurons, which in turn induces satiety and decreases food intake during feeding (Zhang, 2024). Specific ablation of MC4R in ARCPOMC neurons also leads to obesity, decreased energy expenditure, and impaired insulin sensitivity. Kir2.1, an inwardly rectifying potassium channel, mediates MC4R function in the ARCPOMC neurons. Knockdown of Kir2.1 in MC4R-deficient mice partially restores energy balance and insulin sensitivity (Guo et al., 2024). The DMHMC4R neurons also connect to brown adipose tissue (BAT) via rostral raphe pallidus (rRPa) in brainstem, and its sympathetic innervation generates thermogenesis. Disruption of MC4R or Gαs signaling in the DMH impairs basal and cold-stimulated SNS outflow to BAT, leading to reduced thermogenesis and energy expenditure (Chen et al., 2019).
NPY receptors
The neuropeptide Y receptors (NPYRs) are a family of GPCRs that respond to the neuropeptide Y, peptide YY, and pancreatic polypeptide. Centrally, NPY receptors are extensively distributed in the hypothalamus, with NPY1, NPY2, and NPY5 receptors being the primary binding targets of endogenous NPY and implicated in the regulation of food intake (Balasubramaniam, 2002; Mercer et al., 2011; Parker and Balasubramaniam, 2008).
In ARC, NPY1R and NPY2R are expressed in both AgRP and POMC neurons, and it is reported that POMC neurons could receive central NPY from AgRP neurons (Cowley et al., 2001). In slice patch clamp study, NPY2R agonists inhibit NPY release from ARCNPY neurons (King et al., 1999). Moreover, the mRNA expression of NPY2R in AgRP neurons is elevated in fasted mice, while no significant difference is observed for NPY1R. On the contrary, when mice were exposed to a high-fat diet, both NPY1R and 2R mRNA levels decreased in POMC neurons and loss of NPY2R in POMC neurons significantly reduces food intake (Qi, 2023). Previous studies suggest that specific NPY2R deletion in postnatal onset NPY neurons did not significantly affect spontaneous food intake but increase fasting-induced food intake (Qi et al., 2016). NPY1R deletion slightly induces increasing in body temperature and significantly increasing body weight but no significantly change in food intake (Kushi et al., 1998). Another recent study indicates that NPY in AgRP neurons modulates food intake via NPY1R and energy expenditure via the NPY2R pathway. In an AgRP neuron-specific NPY deletion mouse model, re-introduction of NPY1R signaling by selective NPY1R agonists increases feeding and Respiratory Quotient (RQ), while NPY2R selective agonist administration elevates energy expenditure and locomotion (Qi et al., 2022).
In addition to ARC, NPY receptors are also expressed in PVH (Fetissov et al., 2004). Early immunostaining studies suggest that some PVH neurons expressing NPY1R receive projections from AgRP neurons (Broberger et al., 1999). This finding has been further substantiated by the Calcium and RNA multiplexed Activity analysis (CaRMA) technique, which confirms the expression of NPY1R in PVH neurons and highlights the strong correlation between their activity and feeding behavior as well as physiological state (Xu et al., 2020). Activation of ARCAgRP-PVH pathway has been shown to increase food intake in mice, and blocking NPY1R with a selective antagonist significantly reduces food intake (Atasoy et al., 2012).
CRH and OXT receptors
Neuroendocrine systems are essential for regulating body homeostasis, including blood pressure, blood glucose level, metabolism. Here, we introduce the CRH-CRHR (Corticotropin-releasing Factor Receptor) and Oxytocin-OXTR (Oxytocin Receptor) system within the PVH based on current findings for their role in regulating food intake.
CRH neurons are enriched in the PVH and function as the apex of the HPA axis, known for the stress response (Swaab et al., 2005). Corticotropin Releasing hormone (CRH) is released from these neurons, binds to CRH receptors on the pituitary gland (Daniel, 1976), triggers ACTH release, and eventually increase blood corticosterone level, a process suggested to alter feeding behaviors (Adam and Epel, 2007; Qi et al., 2020; Jiang and Tong, 2022). Recent in vivo calcium imaging for CRH neuron confirmed that these neurons are sensitive to stressors, and their activities could be suppressed by food reward (Yuan et al., 2019; Kim et al., 2019), suggesting that the CRH-CRHR system may function as a hub for regulating feeding behaviors under stress. Moreover, activation of PVHCRH neurons or AMPK modulates macronutrient preference in mice (Okamoto et al., 2018). Disrupted PVHCRH neuron responsiveness by clamping at high or low levels similarly contributes to diet-induced obesity (Zhu et al., 2020).
CRH receptors have two main subtypes: CRHR1 and CRHR2 (Aguilera et al., 2004). CRHR1 is associated with stress perception and is the primary subtype in the pituitary that receives CRH from the PVH (Ramot et al., 2017). Acute stress increases c-Fos expression in CRHR1 positive cells in the PVH, and chronic stress causes an attenuation in the gene expression of CRH1R (Bonaz and Rivest, 1998). Although CRHR1 KO mice do not show change in total food intake but exhibit a change in circadian rhythm, increase oxygen consumption and promote resistance to diet-induced obesity (Sakamoto et al., 2013). CRHR2 in the hypothalamus is also suggested to regulate feeding in different ways under acute or chronic stress (Qi et al., 2020). Following acute stress, CRH binding to CRHR2 reduces NPY expression while increases POMC expression, inhibit feeding.
OXT receptors in the hypothalamus are closely linked with learning, stress, and social behavior (Liu et al., 2023; Osakada et al., 2024), and recent research highlights their roles in feeding behavior and energy metabolism (Kerem and Lawson, 2021). Intracerebroventricular oxytocin activates LepR in hypothalamus, reducing food intake, especially in males (Liu et al., 2020). The paraventricular nucleus (PVH) houses many OXT and OXTR neurons, and their interactions are crucial for the regulating of feeding and body weight (Maejima et al., 2024). Notably, Oxytocin are also reported to regulate fat accumulation, OXTR-deficient mice show an increase of white adipose Tissue (WAT) and a decrease of body temperature compared with controls (Takayanagi et al., 2008), implying that the absence of OXTR might increase the likelihood for overweight and obesity.
OXTR are potential targets for anti-obesity drugs (Niu et al., 2021; Kerem and Lawson, 2021). Peripheral oxytocin binds to receptors on vagus nerve endings (Jurek and Neumann, 2018), signaling to the NTS in the brainstem, which then activates the oxytocin system in the PVH to suppress appetite. Optogenetic activation of ARCOXTR-PVH terminals significantly reduces food intake and produces satiety (Fenselau et al., 2017). However, OXTR does not appear to have a significant effect on energy expenditure, as there is no significant alteration in energy expenditure and RQ in male OXTR knockout mice (Kasahara et al., 2013).
Interaction within distinct peptide-GPCR systems and other appetite regulating modules in the hypothalamus
We have discussed numerous peptide-GPCR systems and their functions in the regulation of feeding and metabolism (Table 1). These appetite-related GPCRs are often expressed in AgRP neurons and POMC neurons, which are known to encode opposing internal states (Van De Wall et al., 2008), representing hunger and satiety. Moreover, genes encoding different peptides or GPCRs are also co-expressed in the same neuron populations in the hypothalamus, identified by immunohistology, in situ hybridization, or more recent single cell RNA-seq analysis (Steuernagel et al., 2022; Figure 1). These properties enable potential interactions between distinct peptide-GPCR systems and other appetite regulating modules.
PVH is considered as an important nucleus for such interaction as it contains a plenty of neuropeptides and GPCR expressing neural populations. Previous anterograde tracing study suggests that CRH neurons that express NPY1R in PVH serve as a direct downstream target of NPY neurons in ARC (Li et al., 2000). Recent RNAscope data indicates a considerable overlap of GLP-1R, MC4R, CRH and OXT expressing in PVH, particularly MC4R, CRH, and OXT neurons show high levels of GLP-1R expression (Li et al., 2019), implying that these neurons might receive regulation from central GLP-1. Another study shows that NPY released from AgRP neurons in ARC acts on PVHNPY1R neurons, which in turn activate adjacent PVHCRH neurons to enhance of lipid and glucose metabolism (Chen et al., 2023). In addition, CRHRs are expressed in a proportion of oxytocin neurons in PVH (Ugartemendia et al., 2022), suggesting that CRH and oxytocin system may constitute a reciprocal regulation for stress-induced changes in feeding.
Peptide-GPCR interactions also exist in another important appetite regulating module, known as the leptin and its receptor, LepR (Patterson et al., 2011; Friedman, 2019; Rossi, 2023). Leptin released from peripheral adipocytes could across the blood–brain barrier and function on LepR expressing hypothalamic neurons to regulate energy metabolism (Allison and Myers, 2014; Butiaeva et al., 2021; Duquenne et al., 2022). In the lateral hypothalamic area (LH), MC3R neurons modulate locomotor activity, energy expenditure, and adiposity, and a proportion of these neurons overlap with LHLepR neurons, suggesting that MC3R neurons might receive leptin signals to synergistically modulate energy balance (Pei et al., 2019). In addition, single-cell RNA sequencing and fluorescent ISH data indicate that there are a large number of neurons co-express GLP-1R and LepR in DMH and ARC (Rupp et al., 2023). Loss of the leptin receptors in LepRGLP-1R neurons provoke hyperphagic obesity without impairing energy expenditure. In contrast, restoration of GLP-1R expression in LepRGLP-1R neurons in GLP-1R-null mice enable inhibition of food intake by the GLP-1R agonist, liraglutide. These data suggest that melanocortin, leptin and GLP-1 system may collaborate to regulate feeding and energy homeostasis through specific neural populations.
Besides the direct interactions within neuropeptide and GPCR co-expressing neurons, probably via specific neuronal populations or neural circuits, leptin signals in ARC could also indirectly influence MC4R functions in the PVH, which is described as a part of central leptin–melanocortin pathway. Leptin activates POMC but inhibits AgRP neurons (Friedman, 2019), thus modulates the function of their downstream target PVHMC4R neurons. Furthermore, leptin administration upregulates POMC gene expression and downregulates AgRP and NPY gene expression (Casanueva and Dieguez, 1999; Seoane-Collazo et al., 2020). In addition, it is reported that diminished AgRP signals to the PVHMC4R neurons and elevated α-MSH from POMC neurons reduce food intake and enhance satiety (Deem et al., 2022).
Conclusion and perspectives
In the hypothalamus, GPCR-expressing neurons regulate feeding behavior and energy homeostasis in many aspects. Distinct peptide-GPCR systems are not only operated independently in the brain, these signals are also integrated, which in turn modulate complex feeding behaviors in distinct internal states. Understanding these mechanisms is beneficial for developing novel therapeutic drugs and strategies for obesity induced metabolic disorders.
Author contributions
TQ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. OF: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (32400838), Basic Research Program of Jiangsu (BK20231046), and the Wuxi Science and Technology Development Fund Project of China (K20221017).
Acknowledgments
We thank the member of the Fu laboratory, Liaorihong Zhao, for comments and revision on the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abd El Aziz, M. S., Kahle, M., Meier, J. J., and Nauck, M. A. (2016). A meta-analysis comparing clinical effects of short- or long-acting GLP-1 receptor agonists versus insulin treatment from head-to-head studies in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 19, 216–227. doi: 10.1111/dom.12804
Adam, T. C., and Epel, E. S. (2007). Stress, eating and the reward system. Physiol. Behav. 91, 449–458. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2007.04.011
Aguilera, G., Nikodemova, M., Wynn, P. C., and Catt, K. J. (2004). Corticotropin releasing hormone receptors: two decades later. Peptides 25, 319–329. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2004.02.002
Allison, M. B., and Myers, M. G. (2014). 20 YEARS OF LEPTIN: connecting leptin signaling to biological function. J. Endocrinol. 223, T25–T35. doi: 10.1530/JOE-14-0404
Anderson, E. J. P., Çakir, I., Carrington, S. J., Cone, R. D., Ghamari-Langroudi, M., Gillyard, T., et al. (2016). 60 YEARS OF POMC: regulation of feeding and energy homeostasis by α-MSH. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 56, T157–T174. doi: 10.1530/JME-16-0014
Atasoy, D., Betley, J. N., Su, H. H., and Sternson, S. M. (2012). Deconstruction of a neural circuit for hunger. Nature 488, 172–177. doi: 10.1038/nature11270
Baak, M. A. (2023). Obesity-induced and weight-loss-induced physiological factors affecting weight regain. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 19, 655–670. doi: 10.1038/s41574-023-00887-4
Balasubramaniam, A. (2002). Clinical potentials of neuropeptide Y family of hormones. Am. J. Surg. 183, 430–434. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9610(02)00803-6
Begriche, K., Levasseur, P. R., Zhang, J., Rossi, J., Skorupa, D., Solt, L. A., et al. (2011). Genetic dissection of the functions of the Melanocortin-3 receptor, a seven-transmembrane G-protein-coupled receptor, suggests roles for central and peripheral receptors in energy. Homeostasis. 286, 40771–40781. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.278374
Bonaz, B., and Rivest, S. (1998). Effect of a chronic stress on CRF neuronal activity and expression of its type 1 receptor in the rat brain. Am. J. Phys. 275, R1438–R1449. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1998.275.5.R1438
Broberger, C., Visser, T. J., Kuhar, M. J., and Hökfelt, T. (1999). Neuropeptide Y innervation and neuropeptide-Y-Y1-receptor-expressing neurons in the paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus of the mouse. Neuroendocrinology 70, 295–305. doi: 10.1159/000054490
Brüning, J. C., and Fenselau, H. (2023). Integrative neurocircuits that control metabolism and food intake. Science 381:eabl7398. doi: 10.1126/science.abl7398
Butiaeva, L. I., Slutzki, T., Swick, H. E., Bourguignon, C., Robins, S. C., Liu, X., et al. (2021). Leptin receptor-expressing pericytes mediate access of hypothalamic feeding centers to circulating leptin. Cell Metab. 33, 1433–1448.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.05.017
Butler, A. A., Kesterson, R. A., Khong, K., Cullen, M. J., Pelleymounter, M. A., Dekoning, J., et al. (2000). A unique metabolic syndrome causes obesity in the melanocortin-3 receptor-deficient mouse. Endocrinology 141, 3518–3521. doi: 10.1210/endo.141.9.7791
Casanueva, F. F., and Dieguez, C. (1999). Neuroendocrine regulation and actions of leptin. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 20, 317–363. doi: 10.1006/frne.1999.0187
Catania, A. (2010). Melanocortins: Multiple actions and therapeutic potential. New York, NY: Springer New York.
Chen, A. S., Marsh, D. J., Trumbauer, M. E., Frazier, E. G., Guan, X.-M., Yu, H., et al. (2000). Inactivation of the mouse melanocortin-3 receptor results in increased fat mass and reduced lean body mass. Nat. Genet. 26, 97–102. doi: 10.1038/79254
Chen, W., Mehlkop, O., Scharn, A., Nolte, H., Klemm, P., Henschke, S., et al. (2023). Nutrient-sensing AgRP neurons relay control of liver autophagy during energy deprivation. Cell Metab. 35, 786–806.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.03.019
Chen, M., Wilson, E. A., Cui, Z., Sun, H., Shrestha, Y. B., Podyma, B., et al. (2019). Gsa deficiency in the dorsomedial hypothalamus leads to obesity, hyperphagia, and reduced thermogenesis associated with impaired leptin signaling. Mol Metab. 25, 142–153. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2019.04.005
Clément, K., Biebermann, H., Farooqi, I. S., Van Der Ploeg, L., Wolters, B., Poitou, C., et al. (2018). MC4R agonism promotes durable weight loss in patients with leptin receptor deficiency. Nat. Med. 24, 551–555. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0015-9
Clément, K., Van Den Akker, E., Argente, J., Bahm, A., Chung, W. K., Connors, H., et al. (2020). Efficacy and safety of setmelanotide, an MC4R agonist, in individuals with severe obesity due to LEPR or POMC deficiency: single-arm, open-label, multicentre, phase 3 trials. Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinol 8, 960–970. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30364-8
Coll, A. P., Farooqi, I. S., and O’Rahilly, S. (2007). The hormonal control of food intake. Cell 129, 251–262. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.04.001
Cork, S. C., Richards, J. E., Holt, M. K., Gribble, F. M., Reimann, F., and Trapp, S. (2015). Distribution and characterisation of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor expressing cells in the mouse brain. Molecular Metabolism 4, 718–731. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2015.07.008
Coutinho, E. A., Okamoto, S., Ishikawa, A. W., Yokota, S., Wada, N., Hirabayashi, T., et al. (2017). Activation of SF1 neurons in the ventromedial hypothalamus by DREADD technology increases insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues. Diabetes 66, 2372–2386. doi: 10.2337/db16-1344
Cowley, M. A., Smart, J. L., Rubinstein, M., Cerdán, M. G., Diano, S., Horvath, T. L., et al. (2001). Leptin activates anorexigenic POMC neurons through a neural network in the arcuate nucleus. Nature 411, 480–484. doi: 10.1038/35078085
Daniel, P. M. (1976). Anatomy of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. J. Clin. Pathol. 7, 1–7. doi: 10.1136/jcp.s1-7.1.1
Davies, M., Færch, L., Jeppesen, O. K., Pakseresht, A., Pedersen, S. D., Perreault, L., et al. (2021). Semaglutide 2·4 mg once a week in adults with overweight or obesity, and type 2 diabetes (STEP 2): a randomised, double-blind, double-dummy, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 397, 971–984. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00213-0
Deem, J. D., Faber, C. L., and Morton, G. J. (2022). AgRP neurons: regulators of feeding, energy expenditure, and behavior. FEBS J. 289, 2362–2381. doi: 10.1111/febs.16176
Dib, L., San-Jose, L. M., Ducrest, A.-L., Salamin, N., and Roulin, A. (2017). Selection on the major color gene Melanocortin-1-receptor shaped the evolution of the Melanocortin system genes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18:2618. doi: 10.3390/ijms18122618
Duquenne, M., Folgueira, C., Bourouh, C., Millet, M., Silva, A., Clasadonte, J., et al. (2022). Leptin brain entry via a tanycytic LepR: EGFR shuttle controls lipid metabolism and pancreas function. Nat. Metab. 3, 1071–1090. doi: 10.1038/s42255-021-00432-5
Fenselau, H., Campbell, J. N., Verstegen, A. M. J., Madara, J. C., Xu, J., Shah, B. P., et al. (2017). A rapidly acting glutamatergic ARC→PVH satiety circuit postsynaptically regulated by α-MSH. Nat. Neurosci. 20, 42–51. doi: 10.1038/nn.4442
Fetissov, S. O., Kopp, J., and Hökfelt, T. (2004). Distribution of NPY receptors in the hypothalamus. Neuropeptides 38, 175–188. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2004.05.009
Friedman, J. M. (2019). Leptin and the endocrine control of energy balance. Nat. Metab. 1, 754–764. doi: 10.1038/s42255-019-0095-y
Garfield, A. S., Li, C., Madara, J. C., Shah, B. P., Webber, E., Steger, J. S., et al. (2015). A neural basis for melanocortin-4 receptor–regulated appetite. Nat. Neurosci. 18, 863–871. doi: 10.1038/nn.4011
Ghamari-Langroudi, M., Cakir, I., Lippert, R. N., Sweeney, P., Litt, M. J., Ellacott, K. L. J., et al. (2018). Regulation of energy rheostasis by the melanocortin-3 receptor. Sci. Adv. 4:eaat0866. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aat0866
Gu, G., Roland, B., Tomaselli, K., Dolman, C. S., Lowe, C., and Heilig, J. S. (2013). Glucagon-like peptide-1 in the rat brain: distribution of expression and functional implication. J. Comp. Neurol. 521, 2235–2261. doi: 10.1002/cne.23282
Gui, Y., Dahir, N. S., Wu, Y., Downing, G., Sweeney, P., and Cone, R. D. (2023). Melanocortin-3 receptor expression in AgRP neurons is required for normal activation of the neurons in response to energy deficiency. Cell Rep. 42:113188. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113188
Guo, H., Xin, Y., Wang, S., Zhang, X., Ren, Y., Qiao, B., et al. (2024). Hypothalamic POMC neuron-specific knockout of MC4R affects insulin sensitivity by regulating Kir2.1. Mol. Med. 30:34. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00804-z
Haws, R., Bs, K. F., Stewart, M., Msn, S. B., Yuan, G., Yanovski, J., et al. (2020). Effect of setmelanotide, a melanocortin‐4 receptor agonist, on obesity in Bardet‐Biedl syndrome. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 22, 2133–2140. doi: 10.1111/dom.14133
Hilger, D., Masureel, M., and Kobilka, B. K. (2019). Structure and dynamics of GPCR signaling complexes. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 25, 4–12. doi: 10.1038/s41594-017-0011-7
Huang, Z., Liu, L., Zhang, J., Conde, K., Phansalkar, J., Li, Z., et al. (2022). Glucose-sensing glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor neurons in the dorsomedial hypothalamus regulate glucose metabolism. Sci. Adv. 8:eabn5345. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abn5345
Jiang, Z., and Tong, Q. (2022). Hypothalamic CRH neurons: a crossroad between stress and metabolism. Current Opinion in Endocrine and Metabolic Res 26:100384. doi: 10.1016/j.coemr.2022.100384
Jurek, B., and Neumann, I. D. (2018). The oxytocin receptor: from intracellular signaling to behavior. Physiol. Rev. 98, 1805–1908. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00031.2017
Kabahizi, A., Wallace, B., Lieu, L., Chau, D., Dong, Y., Hwang, E., et al. (2022). Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) signalling in the brain: from neural circuits and metabolism to therapeutics. British J Pharmacol 179, 600–624. doi: 10.1111/bph.15682
Kasahara, Y., Sato, K., Takayanagi, Y., Mizukami, H., Ozawa, K., Hidema, S., et al. (2013). Oxytocin receptor in the hypothalamus is sufficient to rescue Normal thermoregulatory function in male oxytocin receptor knockout mice. Endocrinology 154, 4305–4315. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-2206
Kerem, L., and Lawson, E. A. (2021). The effects of oxytocin on appetite regulation, food intake and metabolism in humans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22:7737. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147737
Kim, J., Lee, S., Fang, Y.-Y., Shin, A., Park, S., Hashikawa, K., et al. (2019). Rapid, biphasic CRF neuronal responses encode positive and negative valence. Nat. Neurosci. 22, 576–585. doi: 10.1038/s41593-019-0342-2
Kim, K. S., Park, J. S., Hwang, E., Park, M. J., Shin, H. Y., Lee, Y. H., et al. (2024). GLP-1 increases preingestive satiation via hypothalamic circuits in mice and humans. Science 385, 438–446. doi: 10.1126/science.adj2537
King, P. J., Widdowson, P. S., Doods, H. N., and Williams, G. (1999). Regulation of neuropeptide Y release by neuropeptide Y receptor ligands and Calcium Channel antagonists in hypothalamic slices. J. Neurochem. 73, 641–646. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1999.0730641.x
Knudsen, L. B., and Lau, J. (2019). The discovery and development of Liraglutide and Semaglutide. Front. Endocrinol. 10:155. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00155
Krashes, M. J., Lowell, B. B., and Garfield, A. S. (2016). Melanocortin-4 receptor–regulated energy homeostasis. Nat. Neurosci. 19, 206–219. doi: 10.1038/nn.4202
Kushi, A., Sasai, H., Koizumi, H., Takeda, N., Yokoyama, M., and Nakamura, M. (1998). Obesity and mild hyperinsulinemia found in neuropeptide Y-Y1 receptor-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 15659–15664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.26.15659
Li, C., Chen, P., and Smith, M. S. (2000). Corticotropin releasing hormone neurons in the paraventricular nucleus are direct targets for neuropeptide Y neurons in the arcuate nucleus: an anterograde tracing study. Brain Res. 854, 122–129. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(99)02324-0
Li, C., Navarrete, J., Liang-Guallpa, J., Lu, C., Funderburk, S. C., Chang, R. B., et al. (2019). Defined paraventricular hypothalamic populations exhibit differential responses to food contingent on caloric state. Cell Metab. 29, 681–694.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.10.016
Liu, S., Anderson, P. J., Rajagopal, S., Lefkowitz, R. J., and Rockman, H. A. (2024). G protein-coupled receptors: a century of research and discovery. Circ. Res. 135, 174–197. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.124.323067
Liu, J., Conde, K., Zhang, P., Lilascharoen, V., Xu, Z., Lim, B. K., et al. (2017). Enhanced AMPA receptor trafficking mediates the Anorexigenic effect of endogenous glucagon-like Peptide-1 in the paraventricular hypothalamus. Neuron 96, 897–909.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.09.042
Liu, C. M., Davis, E. A., Suarez, A. N., Wood, R. I., Noble, E. E., and Kanoski, S. E. (2020). Sex differences and estrous influences on oxytocin control of food intake. Neuroscience 447, 63–73. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.10.020
Liu, Y., Shan, L., Liu, T., Li, J., Chen, Y., Sun, C., et al. (2023). Molecular and cellular mechanisms of the first social relationship: a conserved role of 5-HT from mice to monkeys, upstream of oxytocin. Neuron 111, 1468–1485.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2023.02.010
Maejima, Y., Yokota, S., Hidema, S., Nishimori, K., De Wet, H., and Shimomura, K. (2024). Systemic co-Administration of Low-Dose Oxytocin and Glucagon-like Peptide 1 additively decreases food intake and body weight. Neuroendocrinology 114, 639–657. doi: 10.1159/000538792
Markham, A. (2021). Setmelanotide: first approval. Drugs 81, 397–403. doi: 10.1007/s40265-021-01470-9
Mercer, R. E., Chee, M. J. S., and Colmers, W. F. (2011). The role of NPY in hypothalamic mediated food intake. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 32, 398–415. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2011.06.001
NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC) (2016). Trends in adult body-mass index in 200 countries from 1975 to 2014: a pooled analysis of 1698 population-based measurement studies with 19·2 million participants. Lancet 387, 1377–1396. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30054-X
Niu, J., Tong, J., and Blevins, J. E. (2021). Oxytocin as an anti-obesity treatment. Front. Neurosci. 15:743546. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.743546
Okamoto, S., Sato, T., Tateyama, M., Kageyama, H., Maejima, Y., Nakata, M., et al. (2018). Activation of AMPK-regulated CRH neurons in the PVH is sufficient and necessary to induce dietary preference for carbohydrate over fat. Cell Rep. 22, 706–721. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.11.102
Osakada, T., Yan, R., Jiang, Y., Wei, D., Tabuchi, R., Dai, B., et al. (2024). A dedicated hypothalamic oxytocin circuit controls aversive social learning. Nature 626, 347–356. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06958-w
Parker, S. L., and Balasubramaniam, A. (2008). Neuropeptide Y Y2 receptor in health and disease. British J Pharmacol 153, 420–431. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707445
Patterson, C. M., Leshan, R. L., Jones, J. C., and Myers, M. G. (2011). Molecular mapping of mouse brain regions innervated by leptin receptor-expressing cells. Brain Res. 1378, 18–28. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2011.01.010
Pei, H., Patterson, C. M., Sutton, A. K., Burnett, K. H., Myers, M. G., and Olson, D. P. (2019). Lateral hypothalamic Mc3R-expressing neurons modulate locomotor activity, energy expenditure, and adiposity in male mice. Endocrinology 160, 343–358. doi: 10.1210/en.2018-00747
Qi, Y. (2023). Agrp-negative arcuate NPY neurons drive feeding under positive energy balance via altering leptin responsiveness in POMC neurons. Cell Metab. 35, 979–995.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.04.020
Qi, Y., Fu, M., and Herzog, H. (2016). Y2 receptor signalling in NPY neurons controls bone formation and fasting induced feeding but not spontaneous feeding. Neuropeptides 55, 91–97. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2015.09.009
Qi, Y., Lee, N. J., Ip, C. K., Enriquez, R., Tasan, R., Zhang, L., et al. (2022). NPY derived from AGRP neurons controls feeding via Y1 and energy expenditure and food foraging behaviour via Y2 signalling. Molecular Metabolism 59:101455. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2022.101455
Qi, J., Zhang, X., Li, Y., Xu, S., Wang, M., Chen, H., et al. (2020). The suppression effects of feeding and mechanisms in CRF system of animals. Gene 733:144363. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144363
Ramot, A., Jiang, Z., Tian, J.-B., Nahum, T., Kuperman, Y., Justice, N., et al. (2017). Hypothalamic CRFR1 is essential for HPA axis regulation following chronic stress. Nat. Neurosci. 20, 385–388. doi: 10.1038/nn.4491
Rashid, M., Kondoh, K., Palfalvi, G., Nakajima, K., and Minokoshi, Y. (2023). Inhibition of high-fat diet-induced inflammatory responses in adipose tissue by SF1-expressing neurons of the ventromedial hypothalamus. Cell Rep. 42:112627. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112627
Rossi, M. A. (2023). Control of energy homeostasis by the lateral hypothalamic area. Trends Neurosci. 46, 738–749. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2023.05.010
Rossi, M. A., and Stuber, G. D. (2018). Overlapping brain circuits for homeostatic and hedonic feeding. Cell Metab. 27, 42–56. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.09.021
Rupp, A. C., Tomlinson, A. J., Affinati, A. H., Yacawych, W. T., Duensing, A. M., Lindsley, S. R., et al. (2023). Suppression of food intake by Glp1r/Lepr-coexpressing neurons prevents obesity in mouse models. J. Clin. Invest. 133:e157515. doi: 10.1172/JCI157515
Sakamoto, R., Matsubara, E., Nomura, M., Wang, L., Kawahara, Y., Yanase, T., et al. (2013). Roles for corticotropin-releasing factor receptor type 1 in energy homeostasis in mice. Metabolism 62, 1739–1748. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.08.005
Sayar-Atasoy, N., Laule, C., Aklan, I., Kim, H., Yavuz, Y., Ates, T., et al. (2023). Adrenergic modulation of melanocortin pathway by hunger signals. Nat. Commun. 14:6602. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42362-8
Schwartz, M. W., Woods, S. C., Porte, D., Seeley, R. J., and Baskin, D. G. (2000). Central nervous system control of food intake. Nature 404, 661–671. doi: 10.1038/35007534
Seoane-Collazo, P., Martínez-Sánchez, N., Milbank, E., and Contreras, C. (2020). Incendiary leptin. Nutrients 12:472. doi: 10.3390/nu12020472
Shah, B. P., Vong, L., Olson, D. P., Koda, S., Krashes, M. J., Ye, C., et al. (2014). MC4R-expressing glutamatergic neurons in the paraventricular hypothalamus regulate feeding and are synaptically connected to the parabrachial nucleus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 111, 13193–13198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1407843111
Simpson, S. J., Le Couteur, D. G., and Raubenheimer, D. (2015). Putting the balance Back in diet. Cell 161, 18–23. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.02.033
Singh, I. (2022). Activation of arcuate nucleus glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor-expressing neurons suppresses food intake. Cell Biosci. 12:178. doi: 10.1186/s13578-022-00914-3
Sobrino Crespo, C., Perianes Cachero, A., Puebla Jiménez, L., Barrios, V., and Arilla, F. E. (2014). Peptides and food intake. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 5:58. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2014.00058
Steuernagel, L., Lam, B. Y. H., Klemm, P., Dowsett, G. K. C., Bauder, C. A., Tadross, J. A., et al. (2022). HypoMap—a unified single-cell gene expression atlas of the murine hypothalamus. Nat. Metab. 4, 1402–1419. doi: 10.1038/s42255-022-00657-y
Sutton, A. K., Goforth, P. B., Gonzalez, I. E., Dell, J., Pei, H., Jr, M. G. M., et al. (2021). Melanocortin 3 receptor-expressing neurons in the ventromedial hypothalamus promote glucose disposal. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 118:e2103090118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2103090118
Swaab, D. F., Bao, A.-M., and Lucassen, P. J. (2005). The stress system in the human brain in depression and neurodegeneration. Ageing Res. Rev. 4, 141–194. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2005.03.003
Sweeney, P., Bedenbaugh, M. N., Maldonado, J., Pan, P., Fowler, K., Williams, S. Y., et al. (2022). The melanocortin-3 receptor is a pharmacological target for the regulation of anorexia. Sci. Transl. Med. 13:eabd6434. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abd6434
Sweeney, P., Gimenez, L. E., Hernandez, C. C., and Cone, R. D. (2023). Targeting the central melanocortin system for the treatment of metabolic disorders. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 19, 507–519. doi: 10.1038/s41574-023-00855-y
Takayanagi, Y., Kasahara, Y., Onaka, T., Takahashi, N., Kawada, T., and Nishimori, K. (2008). Oxytocin receptor-de¢cient mice developed late-onset obesity. Neuroreport 19, 951–955. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0b013e3283021ca9
Ugartemendia, L., De Guzman, R. M., Cai, J., Rajamanickam, S., Jiang, Z., Tao, J., et al. (2022). A subpopulation of oxytocin neurons initiate expression of CRF receptor 1 (CRFR1) in females post parturition. Psychoneuroendocrinology 145:105918. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2022.105918
Van De Wall, E., Leshan, R., Xu, A. W., Balthasar, N., Coppari, R., Liu, S. M., et al. (2008). Collective and individual functions of leptin receptor modulated neurons controlling metabolism and ingestion. Endocrinology 149, 1773–1785. doi: 10.1210/en.2007-1132
Xu, S., Yang, H., Menon, V., Lemire, A. L., Wang, L., Henry, F. E., et al. (2020). Behavioral state coding by molecularly defined paraventricular hypothalamic cell type ensembles. Science 370:eabb 2494. doi: 10.1126/science.abb2494
Yuan, Y., Wu, W., Chen, M., Cai, F., Fan, C., Shen, W., et al. (2019). Reward inhibits paraventricular CRH neurons to relieve stress. Curr. Biol. 29, 1243–1251.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.02.048
Zhang, S. X. (2024). Stochastic neuropeptide signals compete to calibrate the rate of satiation. Nature 637, 137–144. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-08164-8
Zhu, C., Xu, Y., Jiang, Z., Tian, J. B., Cassidy, R. M., Cai, Z., et al. (2020). Disrupted hypothalamic CRH neuron responsiveness contributes to diet-induced obesity. EMBO Rep. 21:e49210. doi: 10.15252/embr.201949210
Keywords: hypothalamus, GPCR (G protein coupled receptor), GLP-1 receptor, melanocortin receptor, NPY receptor, food intake, metabolism
Citation: Qiu T and Fu O (2025) GPCRs in hypothalamic neurons and their roles in controlling food intake and metabolism. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 18:1536577. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2025.1536577
Edited by:
Doreen Thor, Leipzig University, GermanyReviewed by:
Giulia Baldini, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Qiu and Fu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ou Fu, ZnVvdTEwMzFAamlhbmduYW4uZWR1LmNu
 Tian Qiu
Tian Qiu Ou Fu
Ou Fu