- 1First School of Clinical Medicine, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, China
- 2Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, China
- 3Department of Psychiatry, Wenzhou Seventh People’s Hospital, Wenzhou, China
- 4Department of Neurology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, China
Introduction: A growing body of evidence suggests a potential connection between myocardial infarction (MI) and lung cancer (LC). However, the underlying pathogenesis and molecular mechanisms remain unclear. This research aims to identify common genes and pathways between MI and LC through bioinformatics analysis.
Methods: Two public datasets (GSE166780 and GSE8569) were analyzed to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs). Common DEGs were enriched using Gene Ontology (GO) and the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG). Hub genes were identified and their diagnostic performance was evaluated. Gene co-expression networks, as well as regulatory networks involving miRNA-hub genes and TF-hub genes, were also constructed. Finally, candidate drugs were predicted.
Results: Among the datasets, 34 common trend DEGs were identified. Enrichment analysis linked these DEGs to key biological processes, cellular components, and molecular functions. Eight hub genes (CEBPA, TGFBR2, EZH2, JUNB, JUN, FOS, PLAU, COL1A1) were identified, demonstrating promising diagnostic accuracy. Key transcription factors associated with these hub genes include SP1, ESR1, CREB1, ETS1, NFKB1, and RELA, while key miRNAs include hsa-mir-101-3p, hsa-mir-124-3p, hsa-mir-29c-3p, hsa-mir-93-5p, and hsa-mir-155-5p. Additionally, potential therapeutic drugs were identified, with zoledronic acid anhydrous showing potential value in reducing the co-occurrence of the two diseases.
Discussion: This study identified eight common signature genes shared between NSCLC and AMI. Validation datasets confirmed the diagnostic value of key hub genes COL1A1 and PLAU. These findings suggest that shared hub genes may serve as novel therapeutic targets for patients with both diseases. Ten candidate drugs were predicted, with zoledronic acid showing potential for targeting dual hub genes, offering a promising therapeutic approach for the comorbidity of lung cancer and myocardial infarction.
1 Introduction
Lung cancer (LC), a leading cause of cancer-related death globally (Shtivelman et al., 2014), encompasses small cell lung cancer (SCLC) as well as non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), which includes lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), lung squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC), and large cell carcinoma (Sahu et al., 2023). NSCLC accounts for approximately 85% of all LC diagnoses (Stolz et al., 2022). Though studies in epidemiology have clearly demonstrated that cigarette smoke (CS) exposure contributes to the risk of NSCLC (Hecht, 1999), and many studies have focused on identifying specific targets for NSCLC, such as PIK3CA (Yamamoto et al., 2008), PDGFRA (Ramos et al., 2009), EPHA2 (Psilopatis et al., 2022), etc., the precise etiology and pathogenesis remain elusive.
Myocardial infarction (MI) is a form of cardiac injury caused by inadequate blood supply and oxygen deprivation (Murphy and Goldberg, 2022), usually associated with the ongoing development of arterial plaque over time. The main pathological characteristic is the impairment of endothelial function (Zhang et al., 2024). Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is the main factor contributing to deaths among cardiovascular diseases, with increasing incidence and fatality rates (Huang et al., 2024). Studies have revealed associations between MI and processes such as pyroptosis, apoptosis, and PAN apoptosis (Chang et al., 2024).
There are certain associations between MI and LC. Firstly, these two diseases share common risk factors such as smoking (Ambrose and Barua, 2004) and personality type (Nagano et al., 2001). In terms of epidemiology, patients with lung malignancies show an increased incidence of cardiovascular (CV) events (Mitchell et al., 2023). Additionally, recent studies have shown that the heart, especially myocardial mesenchymal stromal cells, releases extracellular vesicles with tumor characteristics after MI, and their tumor-promoting effects have a greater impact on LC (Caller et al., 2024). This provides further evidence for the link between MI and LC. The side effects of NSCLC treatment also have a certain impact. Platinum is associated with the occurrence of AMI, and tyrosine kinase inhibitors have shown certain cardiotoxicity (Chang et al., 2023). It is reported that the incidence of vascular events in patients with NSCLC treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors cannot be ignored (Giustozzi et al., 2021). It is worth noting that NSCLC and AMI share some common pathogenesis. As for the inflammatory response, the occurrence and development of AMI is closely related to abnormal inflammatory cells (Sun et al., 2024) and persistent inflammation will increase the risk of lung cancer (Elsayed, 2024). In addition, oxidative stress (Di Carlo and Sorrentino, 2024; Guo et al., 2024), vascular remodeling and endothelial dysfunction (Li et al., 2023; Meng et al., 2021) are involved in the pathogenesis of both diseases. However, the specific pathogenesis and molecular mechanisms underlying the association between MI and LC have not yet been fully understood.
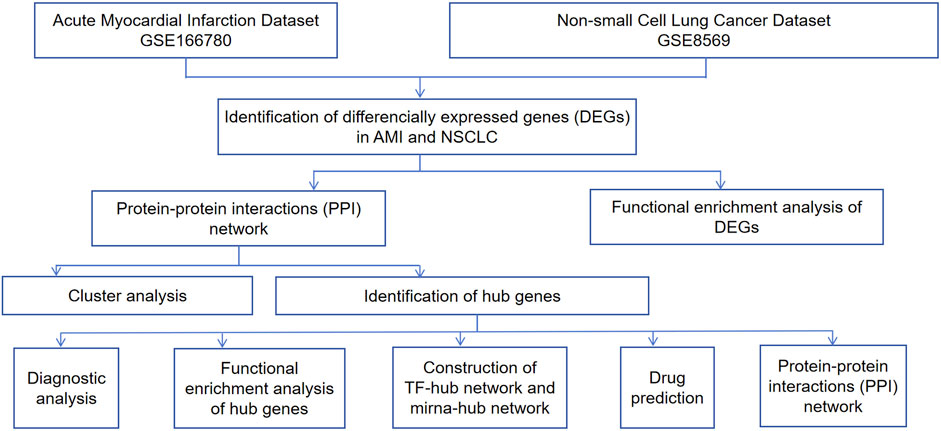
Microarray technology and network-based analysis provide valuable insights into gene expression profiles across various cancers. In this research, we performed a bioinformatics analysis to detect shared molecular mechanism-based biomarkers (CEBPA, TGFBR2, EZH2, JUNB, JUN, FOS, PLAU, COL1A1) between NSCLC and AMI, validating their correlation and identifying candidate drugs targeting hub genes. These hub genes may be involved in the onset and progression of AMI and NSCLC through inflammatory response, oxidative stress, apoptosis, and related signaling pathways. In NSCLC and AMI, COL1A1 is involved through EMT and arterial dissection, while PLAU contributes through tumor invasiveness and macrophage function, each separately. Notably, COL1A1 and PLAU are dual targets of zoledronic acid anhydrous, a drug proven in previous experiments to reduce cancer mortality and the incidence of cardiovascular events. Our study suggests that zoledronic acid anhydrous has promising potential in the combined treatment of AMI and NSCLC. This study offers insights into the formulation of dual-purpose preventative and therapeutic approaches. The research process is illustrated in Figure 1.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Data collection
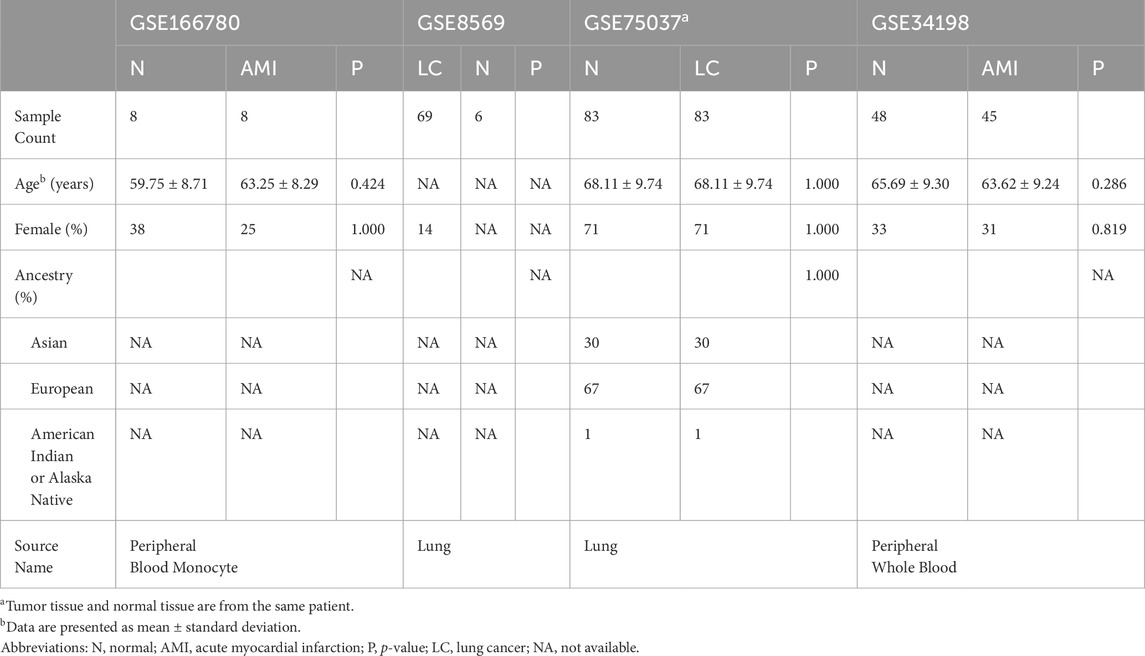
The Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) is the largest and most comprehensive public gene expression data resource (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/). We used the keywords “lung cancer” and “myocardial infarction” to identify datasets related to NSCLC and MI. The selected datasets were based on the following criteria: they must cover both cases and controls, samples must be from human subjects, and they must provide original information for subsequent analysis. Finally, we chose the NSCLC-related dataset GSE8569 and the AMI-related dataset GSE166780 for subsequent research. Furthermore, we included the NSCLC-related dataset GSE75037 and the AMI-related dataset GSE34198 for validation. Detailed information on these datasets is provided in Table 1.
2.2 Identification of differentially expressed genes (DEGs)
The online analysis tool GEO2R was utilized to identify DEGs, using screening criteria of |log2(FC)| > 1 and p < 0.05. DEGs specific to NSCLC and AMI were obtained by comparing gene expression profiles between NSCLC cancer cells and normal cells, as well as between peripheral blood samples from AMI patients and normal peripheral blood samples. The Venn diagram tool of the Xiantao Academic Platform (https://www.xiantaozi.com) was used to find the common DEGs of the two diseases. The results were visualized using volcano plots, box plots, and Venn diagrams.
2.3 Enrichment analysis of DEGs
First, the common DEGs were converted to gene IDs, followed by gene enrichment analysis. Gene Ontology (GO) analysis, encompassing biological processes (BP), molecular function (MF), and cellular component (CC), is a widely used gene annotation bioinformatics tool. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) provides comprehensive information on genomes, biological pathways, diseases, and chemicals. Using the clusterProfiler package in RStudio, we conducted GO functional enrichment and KEGG pathway analyses on the common DEGs. The ggplot2 package was used to visualize the data. The filtering condition was set at p < 0.05.
2.4 Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network construction
We used the STRING database (https://cn.string-db.org/) to construct a PPI network for the co-expressed DEGs in NSCLC and AMI. The minimum interaction score was set to 0.400 and the FDR stringency for filtering was set to 0.500 to identify interactions among protein-coding genes. Then, we processed the data using Cytoscape 3.10.2, clustered the gene network using the “MCODE” plug-in, identified key subnetwork modules, and performed cluster analysis. Hub genes were determined using the cytohubba method (Degree, EPC, MCC, and MNC). We constructed a hub gene expression network using the GeneMANIA database (http://www.genemania.org/).
2.5 Diagnostic significance of hub genes
We further investigated the importance of key genes as potential biomarkers. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was employed to assess the sensitivity and specificity of our selected target genes. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) was used to evaluate the results.
2.6 Construction of miRNA-hub gene network and TF-hub gene network
The online database NetworkAnalyst 3.0 (https://www.networkanalyst.ca/) was used to construct the miRNA-hub and TF-hub networks of hub genes to describe the associations between hub genes, miRNA, and TF. The selected TF-gene interaction database was ENCODE, using criteria of peak intensity signal <500 and the predicted regulatory potential score <1. The miRNA-gene interaction data were collected from miRTarBase.
2.7 Drug prediction based on hub genes
We searched DGIdb (https://dgidb.genome.wustl.edu), a database for exploring known and potential drug-gene interactions, to identify candidate drugs associated with the hub genes.
2.8 Statistical analyses
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS version 27. Clinical characteristics were compared using Student’s t-test, Pearson Chi-Square test or Fisher’s exact test, as appropriate. A two-sided p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Identification of DEGs
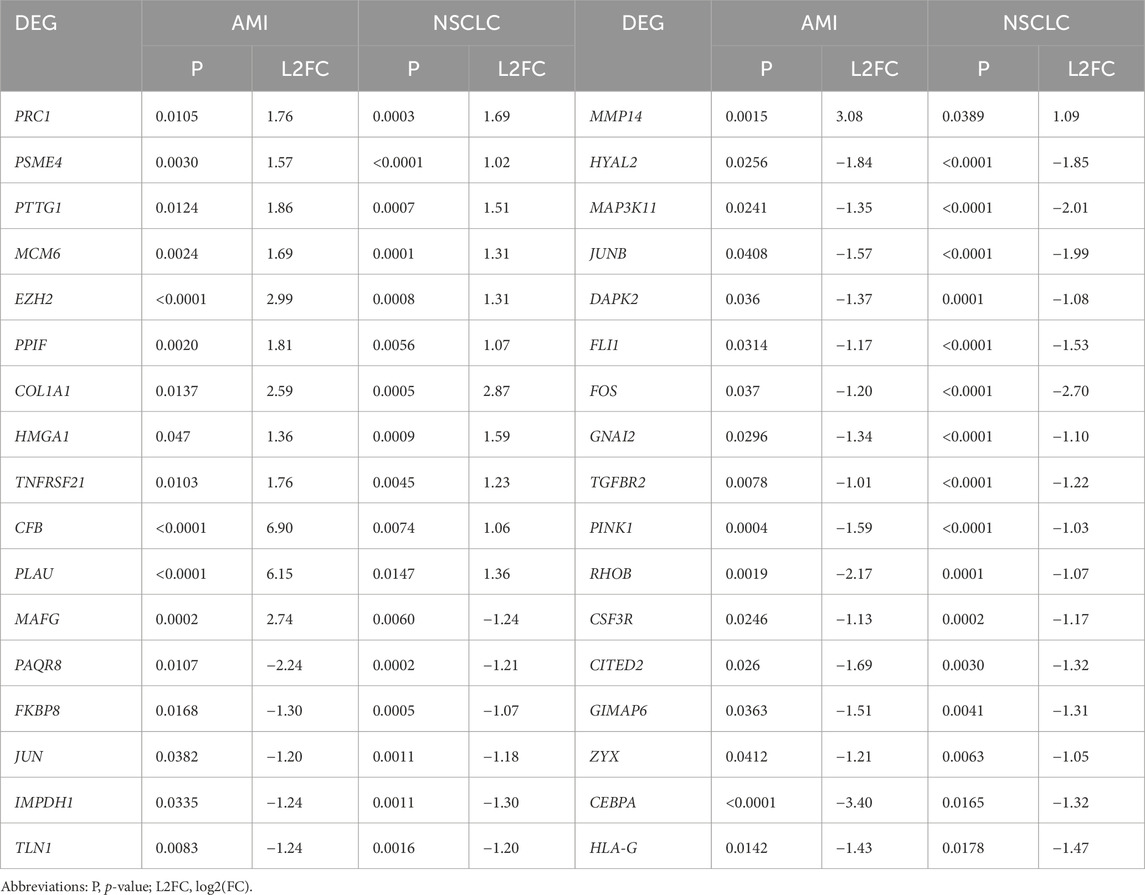
The AMI-related dataset GSE166780 contains 8 normal and 8 AMI samples, while the NSCLC-related dataset GSE8569 includes 69 NSCLC and 6 normal samples. We compared the gene expression of AMI and normal samples in GSE166780 and identified 3060 AMI DEGs, including 1,498 upregulated genes and 1,223 downregulated genes (Figures 2A, C). Similarly, we compared the gene expression of normal and NSCLC samples in GSE8569 and identified 678 NSCLC DEGs, including 182 upregulated genes and 359 downregulated genes (Figures 2B, D). Through the Venn diagram, 13 co-upregulated DEGs and 21 co-downregulated DEGs were filtered out (Figures 2E, F). The co-expressed genes and their corresponding p-values are listed in Table 2.
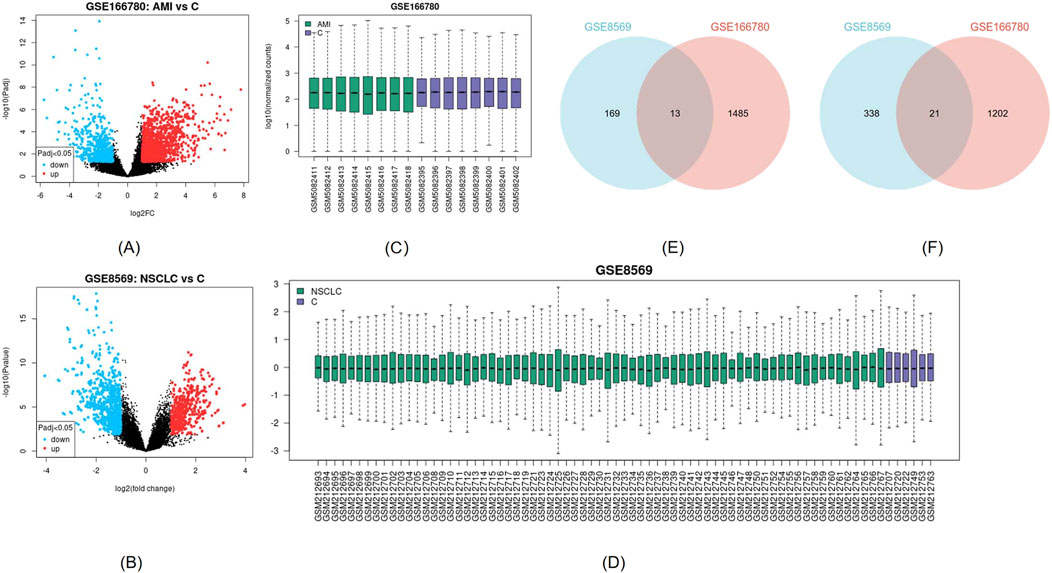
Figure 2. (A, B) Visualization of DEGs of GSE166780 and GSE8569 using volcano plots, blue represents downregulation, red represents upregulation (|log2(FC)|>1, p < 0.05) (C, D) Visualization of GSE166780 and GSE8569 using box plots (E) Co-expressed upregulated differentially expressed genes (DEGs) of GSE166780 and GSE8569 (|log2(FC)|>1, p < 0.05) (F) Co-expressed downregulated DEGs of GSE166780 and GSE8569 (|log2(FC)|>1, p < 0.05).
3.2 Functional annotation analysis of DEGs
GO and KEGG analysis were conducted on 34 co-expressed DEGs in NSCLC and AMI, and the outcomes are depicted in Figure 3. Concerning the BP, DEGs were significantly concentrated in “response to oxidative stress” and “response to reactive oxygen species.” In terms of CC, DEGs were enriched in “RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex,” “focal adhesion,” and “cell-substrate junction.” For MF, DEGs are enriched in “DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific,” and “DNA-binding transcription activator activity.” KEGG analysis revealed that DEGs were enriched in “Human T-cell leukemia virus 1 infection” and “Relaxin signaling pathway.”
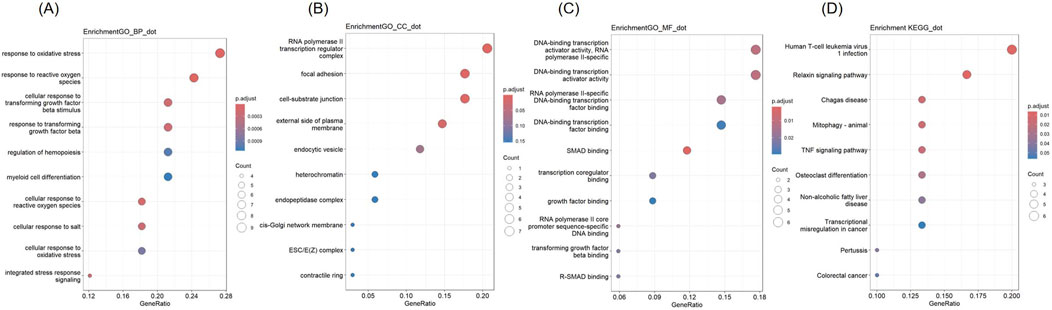
Figure 3. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis of DEGs (A) Biological Processes (B) Cellular Component (C) Molecular Function (D) KEGG.
3.3 PPI network analysis, cluster analysis, and identification of hub genes
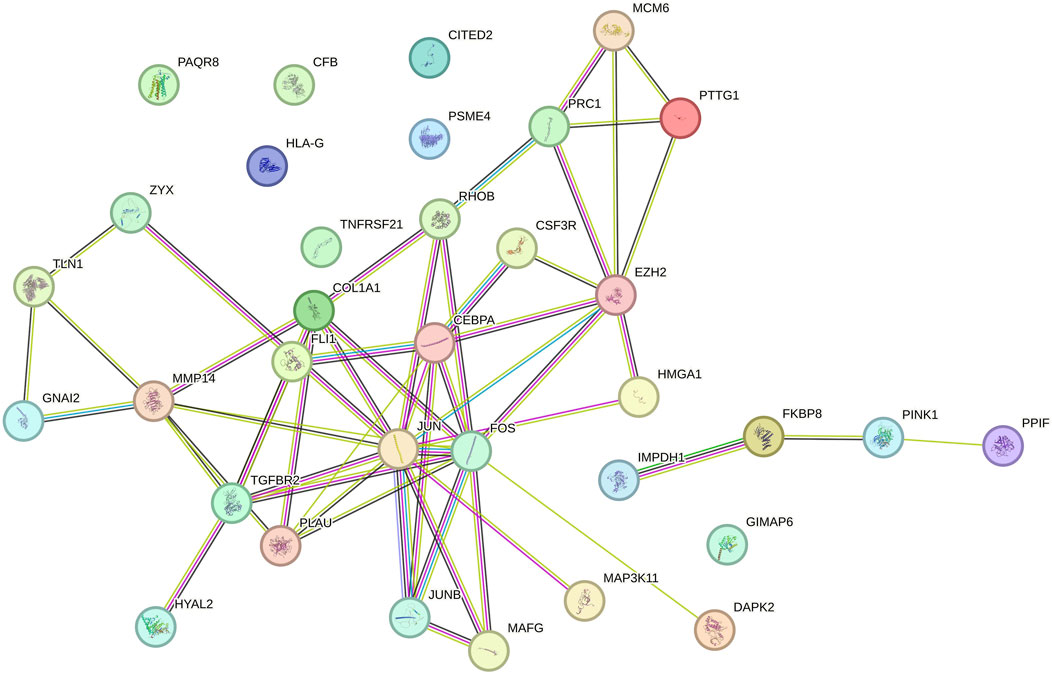
We analyzed 34 shared DEGs using the STRING online database (Figure 4) and imported the data into Cytoscape for visualization. After removing isolated points, the PPI of the shared DEGs is illustrated in Figure 5A, with 27 nodes and 53 edges. Additionally, we employed the MCODE plug-in to identify crucial gene cluster modules and discovered 2 clusters. Cluster 1 contains 6 nodes and 14 edges with a score of 5.6. Cluster 2 includes 3 nodes and 3 edges with a score of 3 (Figures 5B, C). To identify hub genes, we used the CytoHubba plug-in. By taking the intersection of the four algorithms, we identified 8 hub proteins: CEBPA, TGFBR2, EZH2, JUNB, JUN, FOS, PLAU and COL1A1 (Figure 6). In the NSCLC and AMI datasets, EZH2, COL1A1 and PLAU were upregulated, and CEBPA, TGFBR2, JUN, JUNB and FOS were downregulated.
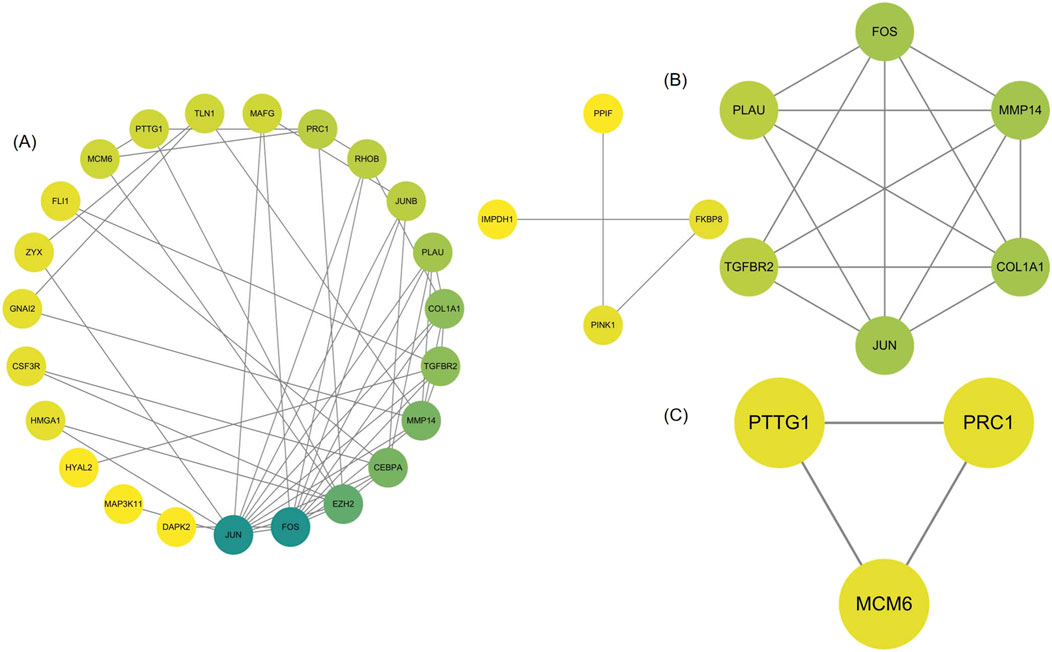
Figure 5. (A) PPI network of common DEGs visualized using Cytoscape (B, C) MCODE plugin shows that cluster 1 contains 6 nodes and 14 edges with a score of 5.6. Cluster 2 contains 3 nodes and 3 edges with a score of 3.
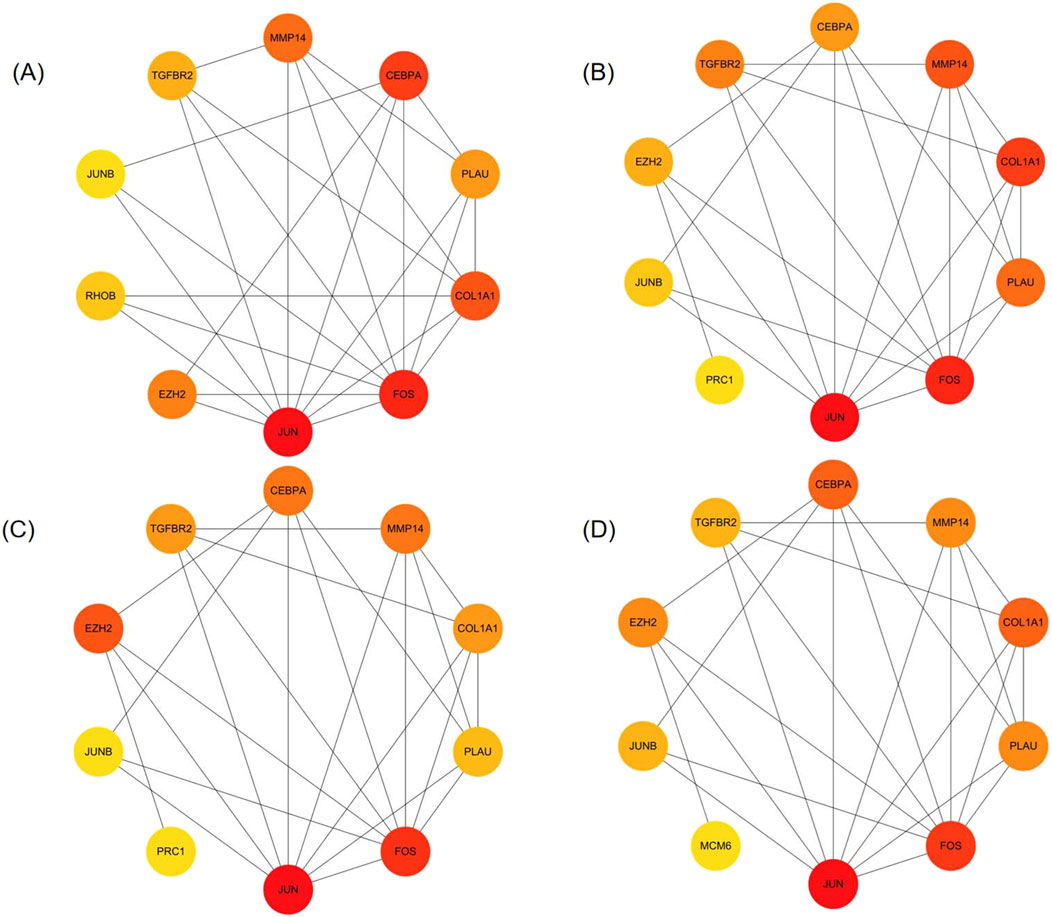
Figure 6. Identification of hub genes (A–D) The top 10 genes in the PPI network were sorted by Degree, MCC, EPC, and MNC respectively. The 8 hub genes identified are CEBPA, TGFBR2, EZH2, JUNB, JUN, FOS, PLAU, COL1A1.
3.4 Enrichment analysis of hub genes
GO and KEGG analyses were conducted (Figure 7). The hub genes were mainly related to “integrated stress response signaling,” “cellular response to salt,” “cellular response to metal iron,” “response to reactive oxygen species” “cellular response to inorganic substance,” “myeloid leukocyte differentiation,” “cellular response to transforming growth factor beta” in BP terms. In CC terms, they were predominantly associated with the “RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex.” In MF terms, they were mainly related to “DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific,” “DNA-binding transcription activator activity,” “SMAD binding,” “RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding,” and “DNA-binding transcription factor binding.” In KEGG analysis, they were enriched in “Relaxin signaling pathway,” and “Osteoclast differentiation.”
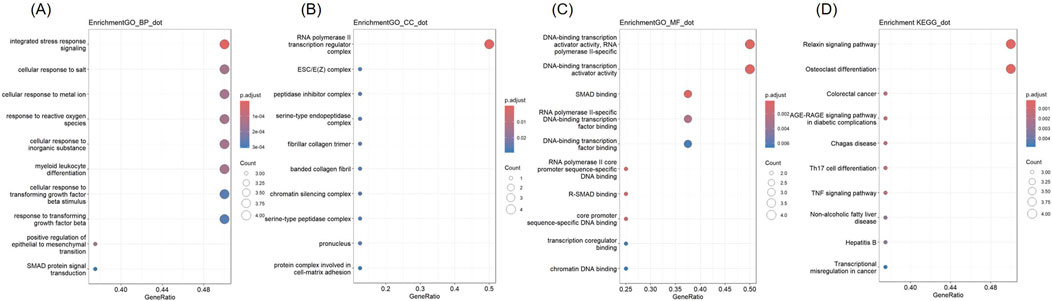
Figure 7. GO and KEGG analysis of Hub genes (A) Biological Processes (B) Cellular Component (C) Molecular Function (D) KEGG.
3.5 PPI analysis of hub genes
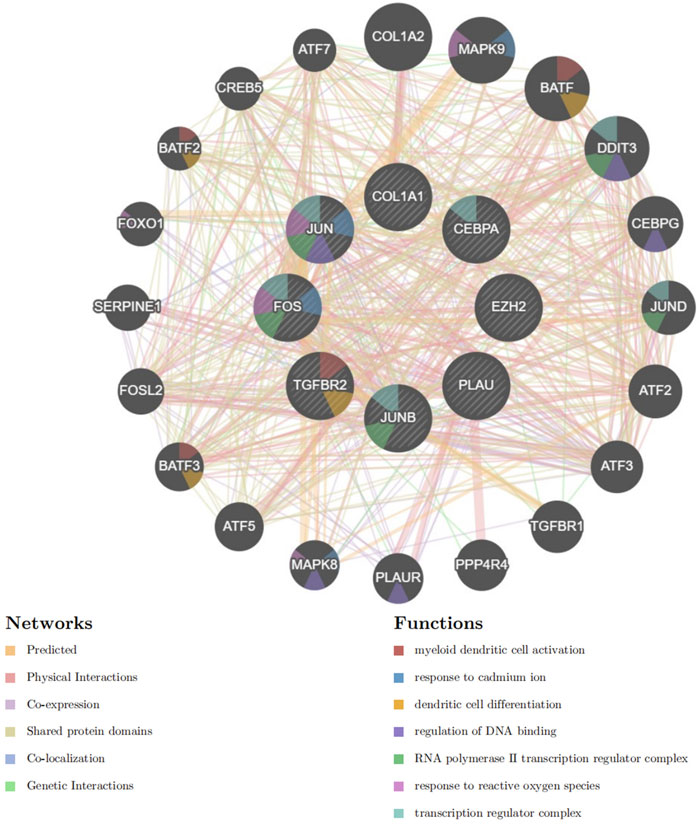
Based on GeneMANIA, PPI analysis was performed on 8 hub genes and 20 cross genes (Figure 8). Among them, predicted accounted for 32.57%, physical Interactions for 28.18%, co-expression for 28.02%, shared protein domains for 10.32%, co-localization for 0.73% and genetic interactionsfor 0.18%. The primary biological roles of this network pertain to the myeloid dendritic cell activation, response to cadmium ion, dendritic cell differentiation, regulation of DNA binding, RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex, response to reactive oxygen species and transcription regulator complex.
3.6 Diagnostic significance of hub genes
According to the ROC curve developed by the eight candidate hub genes, we evaluated the specificity and sensitivity of each gene for diagnosis (Figure 9). We calculated the AUC of each item, among which the AUCs of COL1A1, JUN, EZH2, FOS, PLAU, CEBPA, TGFBR2, and JUNB in the NSCLC-related dataset were 0.925, 0.879, 0.937, 0.935, 0.906, 0.853, 0.957, and 0.957, respectively. The AUCs of COL1A1, JUN, EZH2, FOS, PLAU, CEBPA, TGFBR2, and JUNB in the AMI-related dataset were 0.625, 0.922, 0.922, 0.859, 0.859, 1.000, 0.984, and 0.859, respectively. These genes have high diagnostic value for both NSCLC and AMI. Among them, the AUC of EZH2 and TGFBR2 were greater than 0.9 in both diseases, showing high diagnostic efficacy. In the validation dataset of NSCLC, the AUCs of COL1A1, CEBPA, PLAU, JUNB, JUN, TGFBR2, FOS, and EZH2 were 0.946, 0.794, 0.725, 0.836, 0.859, 0.985, 0.862, and 0.905, respectively. In the validation dataset of AMI, the AUCs of COL1A1, CEBPA, PLAU, JUNB, JUN, TGFBR2, FOS, and EZH2 were 0.739, 0.570, 0.860, 0.671, 0.716, 0.679, 0.592, and 0.642, respectively. In both validation datasets, COL1A1, PLAU, JUNB, JUN, TGFBR2, and EZH2 maintained high diagnostic efficacy.
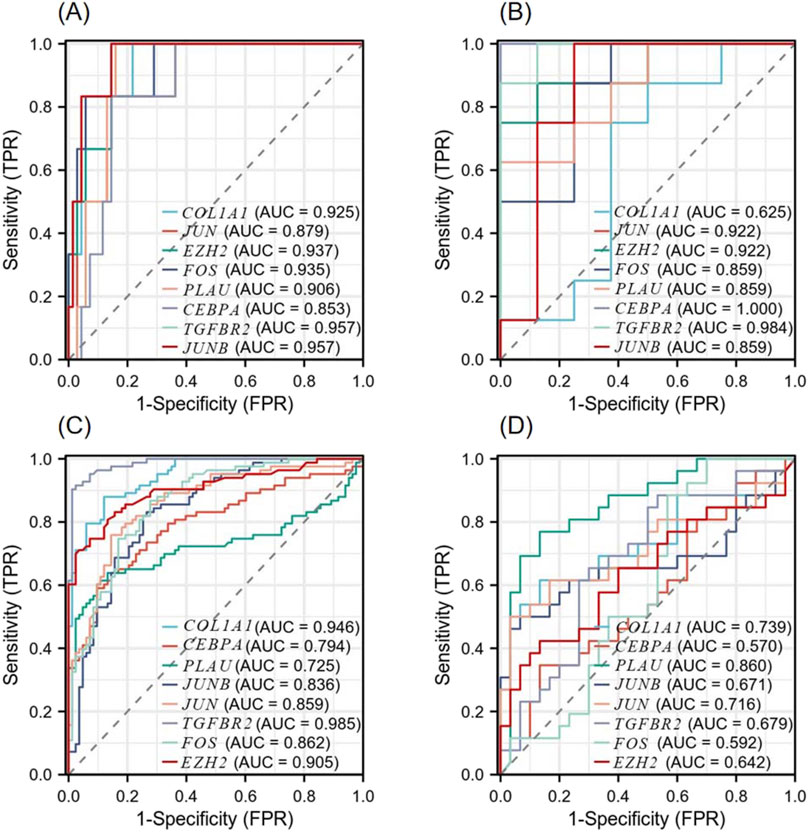
Figure 9. Diagnostic Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves of 8 co-expressed hub genes (A) ROC curve of the hub gene in the GSE8569 dataset. (B) ROC curve of the hub gene in the GSE166780 dataset. (C) ROC curve of the hub gene in the GSE75037 dataset. (D) ROC curve of the hub gene in the GSE34198 dataset.
3.7 Construction of TF-hub gene network and miRNA-hub gene network
We used NetworkAnalyst 3.0 software to construct the TF-Hub genes and miRNA-Hub genes regulatory networks. The TF-Hub network consists of 100 nodes and 121 edges, and the miRNA-Hub network has 358 nodes and 407 edges. We found that in the TF-Hub network, SP1 interacts with TGFBR2, FOS, PLAU, and COL1A1. ESR1 regulates FOS, JUN, and JUNB. CREB1 regulates PLAU, JUN, and FOS. ETS1 interacts with COL1A1, TGFBR2, and PLAU. Notably, NFKB1 and RELA simultaneously regulate COL1A1, JUNB and PLAU (Figure 10A). In the miRNA-Hub network, hsa-mir-101-3p interacts with 4 genes, including JUN, EZH2, TGFBR2 and FOS. Hsa-mir-124-3p targets EZH2, COL1A1, and CEBPA. Hsa-mir-29c-3p targets JUN, FOS, and COL1A1. Hsa-mir-93-5p targets JUN, TGFBR2, and EZH2. Hsa-mir-155-5p targets JUN, JUNB, and FOS (Figure 10B).
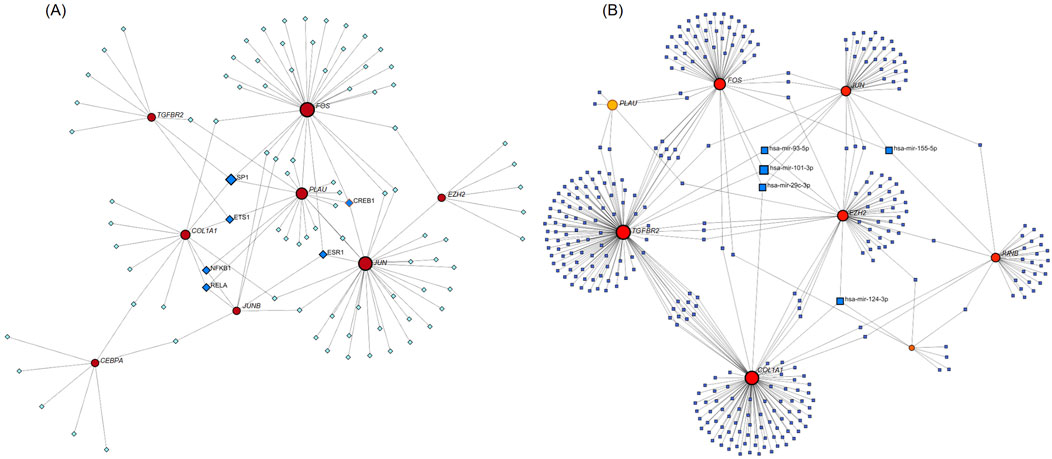
Figure 10. (A) TF-Hub genes network, circles are hub genes, and squares are TFs. (B) miRNA-Hub genes network, circles are hub genes, and squares are miRNAs.
3.8 Identification of drug candidates
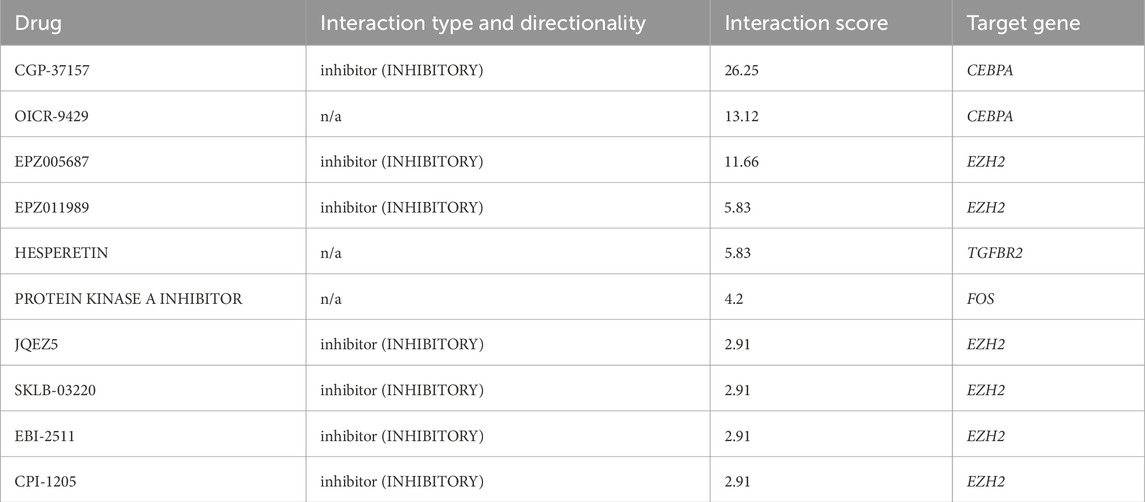
To investigate gene-drug interactions, 8 validated hub genes were submitted to the DGIdb database, and the results were visualized in Cytoscape (Figure 11). A total of 145 drugs were identified, and the top ten were CGP-37157, OICR-9429, EPZ005687, EPZ011989, HESPERETIN, PROTEIN KINASE A INHIBITOR, JQEZ5, SKLB-03220, EBI-2511, CPI-1205 (Table 3). It is worth noting that zoledronic acid anhydrous and antibiotic are connected with two hub genes.
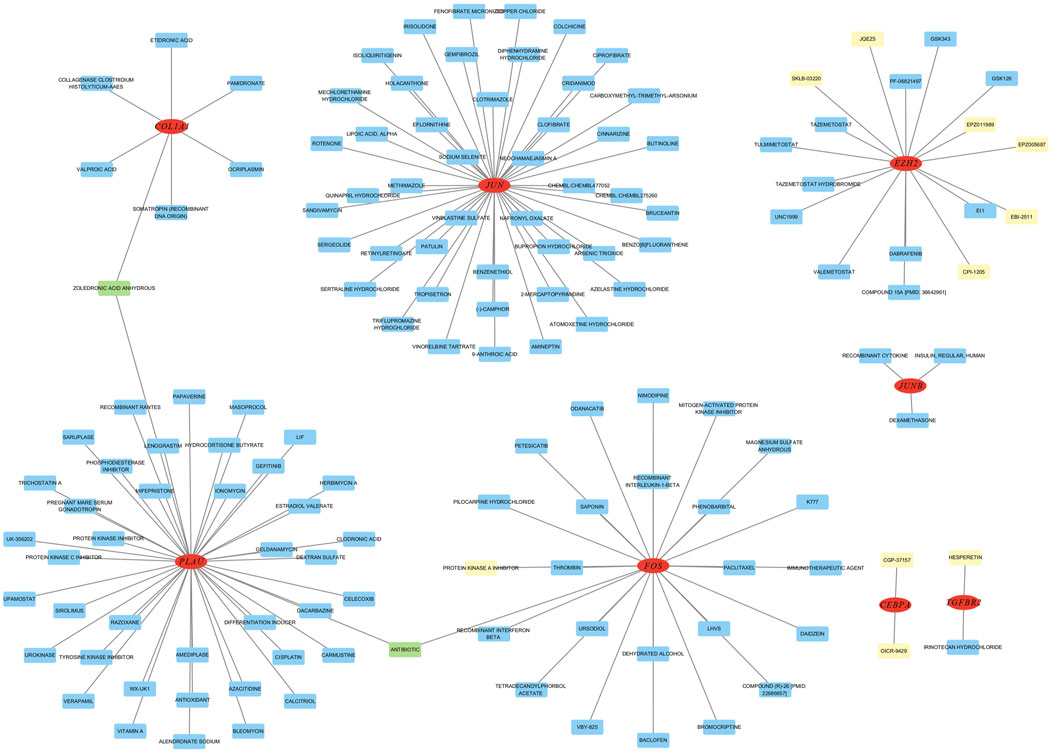
Figure 11. Analysis of hub genes on DGibd, a sum of 145 drugs were discovered. Red indicates hub genes, yellow indicates the top ten drugs, green indicates drugs connected with two genes, and blue indicates other potential drugs.
4 Discussion
Previous studies have demonstrated an inverse relationship between cardiovascular disease and cancer. The mechanism behind this relationship is not fully understood. Still, it may be associated with circulating microRNAs, extracellular vesicles, cardiac-derived mediators, along with pathways associated with inflammatory responses, clonal hematopoiesis, and oxygen deprivation (Aboumsallem et al., 2020). Several studies have indicated an increased risk of cancer in patients with MI (Hasin et al., 2016; Rinde et al., 2017). Research into the common mechanisms between MI and cancer has gained attention recently (Yuan et al., 2023; Meijers et al., 2018). However, limited studies have explored the shared genetic underpinnings between NSCLC and AMI at the genetic level. Our study has examined the molecular biological roles and common pathways of NSCLC and AMI, offering insights for the development of dual-purpose prevention and therapy strategies.
In this study, we utilized bioinformatics tools to identify 34 common DEGs between an NSCLC dataset and an AMI dataset. GO analysis of these DEGs revealed their association with “response to reactive oxygen species,” “response to oxidative stress,” “RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex,” “focal adhesion,” “cell-substrate junction,” “RNA polymerase II-specific DNA binding transcription factor binding,” “DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific.” KEGG analysis revealed that these DEGs were linked to pathways involving “Human T-cell leukemia virus 1 infection,” and “Relaxin signaling pathway.”
We developed a PPI network of DEGs and detected 8 hub genes, namely, CEBPA, TGFBR2, EZH2, JUNB, JUN, FOS, PLAU and COL1A1. In both datasets, EZH2, COL1A1 and PLAU were upregulated, while CEBPA, TGFBR2, JUN, JUNB and FOS were downregulated.
COL1A1 encodes the pro-α1 chain of type I collagen, a fibrillogenic collagen found abundantly in bone, cornea, dermis, and tendon. It has been recognized as a predictive biomarker for LUAD, and its increased expression has been observed in LC tissue samples, consistent with our findings (Dong et al., 2023). EMT and fibroblast-myofibroblast-myofibroblast transition (FMT) are involved in the initiation and progression of cancer (Ribatti et al., 2020), and studies have demonstrated that fibroblasts with high levels of COL1A1 are related to EMT (Wang et al., 2022). This means that highly expressed COL1A1 may participate in the onset and progression of LC by participating in the EMT process. Spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD) constitutes a non-atherosclerotic etiology for AMI (Saw et al., 2017). Studies have linked COL1A1 to the formation of arterial dissection (Zekavat et al., 2022), which may explain the association between AMI and COL1A1. Some studies have also pointed out that type I collagen’s effective deposition is crucial for the healing process after MI (Nong et al., 2011). More research is still needed to elucidate the underlying mechanism.
CEBPA contributes to the development, expansion, metabolic functions, and immune responses (Newman and Keating, 2003). It has been reported to be downregulated in various solid tumors, including liver, breast cancer, and LC (Lourenco and Coffer, 2017), similar to our findings. CEBPα is reported to act as a key factor in preserving the stability of the epithelial cell layer by suppressing the transcription of vital mesenchymal markers, which in turn stops the initiation of tumors driven by the EMT process (Lourenco et al., 2020). Studies have shown that therapeutic upregulation of CEBPA leads to inactivation of immunosuppressive myeloid cells and has effective anti-tumor responses in different tumor models and cancer patients (Hashimoto et al., 2021). Furthermore, some scholars have demonstrated that JAM-A activates CEBPα and induces the transcription of the claudin-5 gene, which plays a key role in maintaining the vascular barrier (Kakogiannos et al., 2020). However, there are a few reports that deviate from this trend (Zhu et al., 2024), and it is reported that CEBPA can promote LOXL2 and LOXL3 transcription and stabilize BCL-2, thereby enhancing the proliferation and metastasis of LC cells in vitro (Fan et al., 2024). In short, the function of CEBPA in the genesis and progression of tumors still needs further confirmation. In cardiac research, studies have revealed that the C/EBP family’s transcription factors (TFs) are activated in the epicardium upon receiving developmental prompts and injury indicators. They collaborate with HOX, MEIS, and Grainyhead TFs to clarify the genomic program directing embryonic gene transcription in the epicardium (Huang et al., 2012). However, the relationship between CEBPA and AMI has not been fully elucidated.
FOS is a member of the FOS gene family. The protein encoded by FOS can form the TF complex AP-1 with the Jun family proteins through the leucine zipper and is vital in signal transduction, cell proliferation, and differentiation (Li et al., 2024). A study has shown that the levels of c-fos and c-jun in tumor tissues of NSCLC cases are lower than those in adjacent normal tissues (Levin et al., 1994). It is reported that FOS is downregulated in cases of heart failure (HF) after MI as well (Hu et al., 2023). Our results similarly found that FOS was downregulated in both diseases. However, some reports show the opposite. As a target for miR-101A, overexpression of FOS can lead to aggravated myocardial fibrosis after MI (Pan et al., 2012), and inhibition of Fos/AP-1 can reduce inflammatory response and cardiac dysfunction (Zhuang et al., 2022). At the same time, miR-29b-3p mitigates cardiac fibrosis following infarction by directly targeting FOS (Xue et al., 2020). Studies have also found that focusing on c-fos may be a supplementary treatment approach to hinder and diminish metastasis in LUAD patients carrying SNP BRMS1v2 A273V/A273V (Liu et al., 2022). Therefore, the association between the FOS gene and the two diseases requires further study.
JUN is a potential oncogene of avian sarcoma virus 17. Dysregulation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway is critical in the progression of LC and several other cancer types (Braicu et al., 2019). The c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway, one of the MAPK pathways, is involved in various cellular functions in tumor development, including proliferation, differentiation, survival, and apoptosis (Johnson and Lapadat, 2002). Mesothelin (MSLN) promotes the level and activation of MET through the JNK signaling pathway, enabling cancer cells to disrupt tight junctions and the integrity of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), thus penetrating the barrier (Xia et al., 2024). Studies have also demonstrated that c-Jun is essential for coordinating the developmental processes of cardiac cells during their early stages (Su et al., 2023). Activation of JNK has been linked to myocardial injury, left ventricular remodeling (LVR), and HF after MI (Plotnikov et al., 2023). In our study, JUN was downregulated in both AMI and NSCLC, which may be related to these mechanisms and thus supporting these findings to a certain extent.
EZH2 is an important catalytic protein and is part of the polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) family. In our study, EZH2 was upregulated in both diseases. Previous studies have demonstrated that EZH2 is elevated in ischemic hearts (Zhao et al., 2021). In the context of MI, inhibition of EZH2-induced cardiac recruitment and enhanced activity of non-classical monocytes accelerates the resolution of inflammation and reduces infarct scar expansion, thereby contributing to decreased cardiac remodeling and dysfunction after MI (Rondeaux et al., 2023). Exosomal miR-25-3p from mesenchymal stem cells reduces MI by inhibiting EZH2 (Peng et al., 2020). EZH2 is a target of SETD1A, which maintains cancer stem cell properties by triggering Wnt/β-catenin pathway activity (Wang R. et al., 2021). It has been proposed that inhibition of EZH2 combined with inhibition of PI3K is a possible combination therapy against LC with PIK3CA alteration or overexpression (Chen et al., 2022). Previous studies have shown that BMSC-exo-miR-30b-5 can regulate the development of NSCLC by targeting EZH2 (Wu et al., 2023).
PLAU is a urokinase plasminogen activator known for its role in cancer invasiveness, positioning it as a central figure in cancer metastasis and related invasion processes, including attachment, movement, and infiltration (Han et al., 2005; Sliva, 2008). Our results showed that PLAU was upregulated in both diseases. PLAU is closely associated with mutations in the tumor suppressor gene TP53, which prevents the occurrence of anoikis (Barta et al., 2020). PLAU has been associated with a wide range of biological and pathological mechanisms, covering chemotaxis, adhesion processes, migration and growth (Chavakis et al., 2002). Overexpression of PLAU positively regulates the growth and colony formation of NSCLC cells (Zheng et al., 2024). Elevated PLAU levels in macrophages accelerate atherosclerosis and blockage of the coronary arteries (Cozen et al., 2004).
TGFBR2, a central component of the TGF-β pathway, is often deleted during carcinogenesis in numerous cancer types, including NSCLC (Wang et al., 2007), and functions as an effective tumor suppressor in NSCLC (Lo Sardo et al., 2021). We found that TGFBR2 was downregulated in NSCLC and AMI. Masaki Ikeuchi et al. revealed that activation of TGF-β provides protective benefits against early ischemic heart damage. However, if its expression persists, the beneficial effects may be compromised, leading to LVR and failure after MI (Ikeuchi et al., 2004). Conversely, a study has demonstrated the potential benefits of targeting TGFBR2 in alleviating MI-like symptoms in vivo and in vitro (Wang X. et al., 2021).
JUNB belongs to the family of activator protein-1 (AP-1) TFs and binds to specific sequences in the cis-regulatory domains of target genes, regulating multiple biological mechanisms encompassing cell division, cell growth, and programmed cell death. It has been reported that JUNB exhibited a substantial decrease in its mRNA and protein levels in cardiac tissues of HF mice (Yan et al., 2018). However, another study demonstrated that during early myocardial ischemia (EMI), JUNB increases in the nuclei of cardiomyocytes in both in vivo models and in human myocardium (Aljakna et al., 2018). The andrographolide can inhibit tumor growth and invasion of NSCLC by upregulating HLJ1, a novel tumor suppressor, through activation of JUNB (Lai et al., 2013). In this study, JUNB was downregulated in both diseases. In conclusion, research on the relationship between JUNB and these two diseases is limited, and more follow-up studies are needed.
GeneMANIA-based PPI analysis indicated that the primary biological functions of the hub genes and their interconnected genes are related to the myeloid dendritic cell activation, response to cadmium ion, dendritic cell differentiation, regulation of DNA binding, RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex, response to reactive oxygen species and transcription regulator complex. Reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced cardiomyocyte injury is critical for the pathogenesis of various heart diseases and involves multiple genes, TFs, and oxidation-sensitive signaling pathways (Li et al., 2013). MI and LC are both associated with oxidative stress. The cross-linking of cysteine residues 1,078 and 2,991 is essential for the redox control of the cardiac ryanodine receptor (RyR) (Nikolaienko et al., 2023). NOP56 and mTOR cooperate to maintain homeostasis in response to oxidative stress and significantly enhance cell death in KRAS mutant tumor cells (Yang et al., 2022).
ROC curve analysis was employed to assess the diagnostic efficacy of key genes, revealing their high diagnostic value for both NSCLC and AMI. Among these, EZH2 and TGFBR2 exhibited AUCs greater than 0.9 in both diseases. These findings underscore the significant roles of COL1A1, JUN, EZH2, FOS, PLAU, CEBPA, TGFBR2, and JUNB in the development of NSCLC and AMI. Subsequently, we used validation datasets to verify the diagnostic efficacy of hub genes and COL1A1, PLAU, JUNB, JUN, TGFBR2 as well as EZH2 maintaining high diagnostic efficacy. This further screened out genes with greater diagnostic value.
NetworkAnalyst was used to construct related miRNA-hub networks and TF-hub networks. The five most active miRNAs interacting with hub genes are hsa-mir-101-3p, hsa-mir-124-3p, hsa-mir-29c-3p, hsa-mir-93-5p, and hsa-mir-155-5p. The 6 TFs that predominantly interact with hub genes are SP1, ESR1, CREB1, ETS1, NFKB1, and RELA. These miRNAs and TFs could be correlated with the initiation and progression of NSCLC and AMI.
Previous studies have linked many of these miRNAs to the development of LC and AMI. For instance, miR-101-3p downregulation in cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) increases vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) secretion, promoting LC metastasis via the Akt/eNOS pathway (Guo et al., 2021). Conversely, overexpression of miR-101a-3p can enhance cardiac function after MI (Li et al., 2019). In NSCLC, miR-124-3p markedly suppresses metastasis via exosomal transport and intracellular PI3K/AKT signaling (Zhu et al., 2023). Inhibition of miR-124-3p may activate the FGF21/CREB/PGC1α pathway, reducing cardiomyocyte apoptosis and improving oxidative stress and inflammatory responses (Wei et al., 2021). miR-29c-3p suppresses the activity of Mitochondrial fission regulator 1 (MTFR1), thereby inhibiting the progression of lung adenocarcinoma via the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway (Li et al., 2021). miR-93-5p is often overexpressed in NSCLC and acts as an oncogene by inhibiting the tumor suppressor activities of PTEN and RB1 (Yang et al., 2018). The suppression of miR-155-5p rejuvenates senescent mesenchymal stem cells, thereby augmenting their cardioprotective effects post-myocardial infarction (Hong et al., 2020). Also, it can mediate the inhibition of radiotherapy in NSCLC (Zhu et al., 2019). In conclusion, these miRNAs are closely associated with both NSCLC and AMI.
There are also studies proving that predicted TFs are related to NSCLC and AMI. For example, HIF1α-SP1 interaction can promote the development of NSCLC (Wu et al., 2022). KN-93 enhances fatty acid oxidation in MI via the HDAC4-SP1 axis (Zhao et al., 2024). ESR1 expression serves as an independent prognostic indicator in metastatic NSCLC (Atmaca et al., 2014). ESR1 encodes the nuclear receptor ERα, which leads to a reduction in infarct size, inflammatory response, and oxidative stress in animal models (Puzianowska-Kuznicka, 2012). Inactivation of CREB1 may confer cisplatin resistance in metastatic NSCLC (Kim et al., 2019). ETS1 mediates the initiation of gene expression patterns that result from the RAS/MAPK signaling pathway (Plotnik and Hollenhorst, 2017). The rs28362491 ins/del variation of the NFKB1 gene is linked to a higher likelihood of MI and increased severity of coronary artery disease (Luo et al., 2020). MUC3A interacts with RELA to activate the NFκB pathway (Sun et al., 2021). In summary, these TFs could contribute to the onset and progression of the two diseases.
We used DGibd to predict dual-use drugs for AMI and NSCLC. A total of 145 candidate drugs were retrieved, of which the top ten scores were CGP-37157, OICR-9429, EPZ005687, EPZ011989, HESPERETIN, PROTEIN KINASE A INHIBITOR, JQEZ5, SKLB-03220, EBI-2511, and CPI-1205. Notably, zoledronic acid anhydrous and antibiotic target two hub genes. Zoledronic acid anhydrous targets PLAU and COL1A1, which are the two genes with the highest diagnostic value identified in our study. This offers a new perspective on the dual-use treatment of the two diseases. Some studies proved that zoledronic acid anhydrous may affect COL1A1 expression. Specifically, treatment with bisphosphonates, including zoledronic acid anhydrous, inhibits expression levels of the COL1A1 chains of type-I collagen in oral fibroblasts (Ravosa et al., 2011). A study indicates that women who received zoledronic acid treatment experienced fewer vascular events, lower cancer rates, and a tendency towards reduced mortality (Reid et al., 2020). This greatly confirms our view that zoledronic acid can be used in a dual-use treatment strategy for NSCLC and AMI. Zoledronic acid has also been reported to boost the effectiveness of immunotherapy in NSCLC (Zheng et al., 2022). This is a significant finding, as it suggests that zoledronic acid anhydrous could be a valuable adjunct to current immunotherapeutic approaches, potentially improving patient outcomes. Additionally, some antibiotics have been shown to affect COL1A1 expression. The transgenes integrated at the COL1A1 locus have demonstrated strong transgenerational inheritance of epigenetic alterations caused by fetal exposure to doxycycline (Wan et al., 2013), which is a tetracycline antibiotic. Scholars also found that the expression of COL1A1 was significantly reduced in the rabbit model of benign tracheal stenosis treated with penicillin (Enyuan et al., 2018). However, it is reported that antibiotics can decrease the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in NSCLC treatment (Qiu et al., 2022). Therefore, the role of antibiotics in NSCLC remains to be determined. Evidence also suggests that among the top ten ranked drugs, some possess the potential for application in the treatment of both diseases. Some scholars have discovered that hesperetin regulates the inflammatory response caused by AMI in mouse models (Meng et al., 2018). Protein kinase A (PKA) inhibition enhances susceptibility to ferroptosis in NSCLC cells and could improve the efficacy of ferroptosis inhibitors in the treatment of NSCLC patients (Shan et al., 2023). The effects of these drugs on the two diseases warrant further investigation. Our results provide further ideas for drug therapy of the two diseases.
In summary, we comprehensively analyzed public databases and gene expression microarray data from NSCLC and AMI patients and healthy controls. We identified eight common signature genes (CEBPA, TGFBR2, EZH2, JUNB, JUN, FOS, PLAU, COL1A1) and their co-regulated pathways between NSCLC and AMI. All eight common signature genes have high diagnostic value, among which EZH2 and TGFBR2 perform well. In the validation datasets, COL1A1, PLAU, JUNB, JUN, TGFBR2, and EZH2 retain their high diagnostic effect. Undoubtedly, detecting shared hub genes and pathways in NSCLC and AMI provides new insights into potential therapeutic targets for patients with both diseases and this finding may facilitate the diagnosis of LC-related MI. Among these genes, COL1A1 may be involved in the occurrence and progression of the two diseases by participating in the EMT process and the formation of arterial dissection separately. Meanwhile, the association of PLAU with these two diseases may be related to tumor invasiveness and macrophage activity, respectively. We also constructed miRNA-hub and TF-hub networks, in which five miRNAs and 6 TFs were found to be active in the network. These miRNAs and TFs are implicated in various cellular processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and immune responses, which are critical to the development and progression of both NSCLC and AMI. Furthermore, we predicted potential drugs based on common targets and obtained ten candidate drugs, providing more treatment options for related diseases. It is worth emphasizing that zoledronic acid targets two hub genes simultaneously and has shown in past experiments that it can reduce the risk of both cancer and cardiovascular disease. Therefore, our research suggests that zoledronic acid anhydrous may have great therapeutic prospects as a treatment for the comorbidity of lung cancer and myocardial infarction.
However, this study’s limitations involve the need for further experimental validation of the shared hub genes and pathways identified in AMI and NSCLC. There is no specific relationship among the selected datasets. If patients with AMI who also have NSCLC were included as the research subjects, the results might be more representative. Additionally, the diagnosis of NSCLC and AMI should not rely solely on these signature genes and pathways but also needs to consider clinical symptoms and laboratory tests. Also, the availability of extensive and valuable public datasets for AMI and NSCLC is somewhat limited, highlighting the need for additional data in future studies to substantiate our findings.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=gse166780 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE8569.
Author contributions
HZ: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft. JW: Resources, Software, Writing–review and editing. YZ: Methodology, Writing–review and editing. XH: Data curation, Validation, Writing–review and editing. LW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Aboumsallem, J. P., Moslehi, J., and de Boer, R. A. (2020). Reverse cardio-oncology: cancer development in patients with cardiovascular disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 9 (2), e013754. doi:10.1161/JAHA.119.013754
Aljakna, A., Fracasso, T., and Sabatasso, S. (2018). Molecular tissue changes in early myocardial ischemia: from pathophysiology to the identification of new diagnostic markers. Int. J. Leg. Med. 132 (2), 425–438. doi:10.1007/s00414-017-1750-z
Ambrose, J. A., and Barua, R. S. (2004). The pathophysiology of cigarette smoking and cardiovascular disease: an update. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 43 (10), 1731–1737. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2003.12.047
Atmaca, A., Al-Batran, S. E., Wirtz, R. M., Werner, D., Zirlik, S., Wiest, G., et al. (2014). The validation of estrogen receptor 1 mRNA expression as a predictor of outcome in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Cancer 134 (10), 2314–2321. doi:10.1002/ijc.28571
Barta, J. A., Pauley, K., Kossenkov, A. V., and McMahon, S. B. (2020). The lung-enriched p53 mutants V157F and R158L/P regulate a gain of function transcriptome in lung cancer. Carcinogenesis 41 (1), 67–77. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgz087
Braicu, C., Buse, M., Busuioc, C., Drula, R., Gulei, D., Raduly, L., et al. (2019). A comprehensive review on MAPK: a promising therapeutic target in cancer. Cancers (Basel) 11 (10), 1618. doi:10.3390/cancers11101618
Caller, T., Rotem, I., Shaihov-Teper, O., Lendengolts, D., Schary, Y., Shai, R., et al. (2024). Small extracellular vesicles from infarcted and failing heart accelerate tumor growth. Circulation 149 (22), 1729–1748. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.123.066911
Chang, W. T., Lin, H. W., Chang, T. C., Lin, S. H., and Li, Y. H. (2023). Assessment of tyrosine kinase inhibitors and survival and cardiovascular outcomes of patients with non-small cell lung cancer in taiwan. JAMA Netw. Open 6 (5), e2313824. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.13824
Chang, X., Wang, B., Zhao, Y., Deng, B., Liu, P., and Wang, Y. (2024). The role of IFI16 in regulating PANoptosis and implication in heart diseases. Cell Death Discov. 10 (1), 204. doi:10.1038/s41420-024-01978-5
Chauhan, S. J., Thyagarajan, A., Chen, Y., Travers, J. B., and Sahu, R. P. (2020). Platelet-Activating factor-receptor signaling mediates targeted therapies-induced microvesicle particles release in lung cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (22), 8517. doi:10.3390/ijms21228517
Chavakis, T., Kanse, S. M., May, A. E., and Preissner, K. T. (2002). Haemostatic factors occupy new territory: the role of the urokinase receptor system and kininogen in inflammation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 30 (2), 168–173. doi:10.1042/0300-5127:0300168
Chen, F., Liu, J., Song, X., DuCote, T. J., Byrd, A. L., Wang, C., et al. (2022). EZH2 inhibition confers PIK3CA-driven lung tumors enhanced sensitivity to PI3K inhibition. Cancer Lett. 524, 151–160. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2021.10.010
Cozen, A. E., Moriwaki, H., Kremen, M., DeYoung, M. B., Dichek, H. L., Slezicki, K. I., et al. (2004). Macrophage-targeted overexpression of urokinase causes accelerated atherosclerosis, coronary artery occlusions, and premature death. Circulation 109 (17), 2129–2135. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000127369.24127.03
Di Carlo, E., and Sorrentino, C. (2024). Oxidative stress and age-related tumors. Antioxidants (Basel) 13 (9), 1109. doi:10.3390/antiox13091109
Dong, L., Fu, L., Zhu, T., Wu, Y., Li, Z., Ding, J., et al. (2023). A five-collagen-based risk model in lung adenocarcinoma: prognostic significance and immune landscape. Front. Oncol. 13, 1180723. doi:10.3389/fonc.2023.1180723
Elsayed, N. (2024). Selective imaging, gene, and therapeutic delivery using PEGylated and pH-Sensitive nanoparticles for enhanced lung disorder treatment. Int. J. Pharm. 666, 124819. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2024.124819
Enyuan, Q., Mingpeng, X., Luoman, G., Jinghua, G., Yu, L., Wentao, L., et al. (2018). Erythromycin combined with corticosteroid reduced inflammation and modified trauma-induced tracheal stenosis in a rabbit model. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 12, 1753466618773707. doi:10.1177/1753466618773707
Fan, L., Jiang, W., Chen, C., Gao, H., Shi, J., and Wang, D. (2024). CEBPA facilitates LOXL2 and LOXL3 transcription to promote BCL-2 stability and thus enhances the growth and metastasis of lung carcinoma cells in vitro. Exp. Cell Res. 435 (2), 113937. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2024.113937
Giustozzi, M., Becattini, C., Roila, F., Agnelli, G., and Mandala, M. (2021). Vascular events with immune checkpoint inhibitors in melanoma or non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Treat. Rev. 100, 102280. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2021.102280
Guo, X., Chen, M., Cao, L., Hu, Y., Li, X., Zhang, Q., et al. (2021). Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer cells via miR-101-3p mediated VEGFA secretion and AKT/eNOS pathway. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 764151. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.764151
Guo, Z., Tian, Y., Liu, N., Chen, Y., Chen, X., Yuan, G., et al. (2024). Mitochondrial stress as a central player in the pathogenesis of hypoxia-related myocardial dysfunction: new insights. Int. J. Med. Sci. 21 (13), 2502–2509. doi:10.7150/ijms.99359
Han, B., Nakamura, M., Mori, I., Nakamura, Y., and Kakudo, K. (2005). Urokinase-type plasminogen activator system and breast cancer (Review). Oncol. Rep. 14 (1), 105–112. doi:10.3892/or.14.1.105
Hashimoto, A., Sarker, D., Reebye, V., Jarvis, S., Sodergren, M. H., Kossenkov, A., et al. (2021). Upregulation of C/EBPα inhibits suppressive activity of myeloid cells and potentiates antitumor response in mice and patients with cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 27 (21), 5961–5978. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-0986
Hasin, T., Gerber, Y., Weston, S. A., Jiang, R., Killian, J. M., Manemann, S. M., et al. (2016). Heart failure after myocardial infarction is associated with increased risk of cancer. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 68 (3), 265–271. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2016.04.053
Hecht, S. S. (1999). Tobacco smoke carcinogens and lung cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 91 (14), 1194–1210. doi:10.1093/jnci/91.14.1194
Hong, Y., He, H., Jiang, G., Zhang, H., Tao, W., Ding, Y., et al. (2020). miR-155-5p inhibition rejuvenates aged mesenchymal stem cells and enhances cardioprotection following infarction. Aging Cell 19 (4), e13128. doi:10.1111/acel.13128
Hu, Y., Chen, X., Mei, X., Luo, Z., Wu, H., Zhang, H., et al. (2023). Identification of diagnostic immune-related gene biomarkers for predicting heart failure after acute myocardial infarction. Open Med. (Wars) 18 (1), 20230878. doi:10.1515/med-2023-0878
Huang, G. N., Thatcher, J. E., McAnally, J., Kong, Y., Qi, X., Tan, W., et al. (2012). C/EBP transcription factors mediate epicardial activation during heart development and injury. Science 338 (6114), 1599–1603. doi:10.1126/science.1229765
Huang, X., Bai, S., and Luo, Y. (2024). Advances in research on biomarkers associated with acute myocardial infarction: a review. Med. Baltim. 103 (15), e37793. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000037793
Ikeuchi, M., Tsutsui, H., Shiomi, T., Matsusaka, H., Matsushima, S., Wen, J., et al. (2004). Inhibition of TGF-beta signaling exacerbates early cardiac dysfunction but prevents late remodeling after infarction. Cardiovasc Res. 64 (3), 526–535. doi:10.1016/j.cardiores.2004.07.017
Johnson, G. L., and Lapadat, R. (2002). Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and p38 protein kinases. Science 298 (5600), 1911–1912. doi:10.1126/science.1072682
Kakogiannos, N., Ferrari, L., Giampietro, C., Scalise, A. A., Maderna, C., Rava, M., et al. (2020). JAM-A acts via C/EBP-α to promote claudin-5 expression and enhance endothelial barrier function. Circ. Res. 127 (8), 1056–1073. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.316742
Kim, I. K., McCutcheon, J. N., Rao, G., Liu, S. V., Pommier, Y., Skrzypski, M., et al. (2019). Acquired SETD2 mutation and impaired CREB1 activation confer cisplatin resistance in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 38 (2), 180–193. doi:10.1038/s41388-018-0429-3
Lai, Y. H., Yu, S. L., Chen, H. Y., Wang, C. C., Chen, H. W., and Chen, J. J. (2013). The HLJ1-targeting drug screening identified Chinese herb andrographolide that can suppress tumour growth and invasion in non-small-cell lung cancer. Carcinogenesis 34 (5), 1069–1080. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgt005
Levin, W. J., Casey, G., Ramos, J. C., Arboleda, M. J., Reissmann, P. T., and Slamon, D. J. (1994). Tumor suppressor and immediate early transcription factor genes in non-small cell lung cancer. Chest 106 (6 Suppl. l), 372S–6S. doi:10.1378/chest.106.6.372s
Li, B., Li, Y., Chen, S., Wang, Y., and Zheng, Y. (2023). VEGF mimetic peptide-conjugated nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging and therapy of myocardial infarction. J. Control Release 360, 44–56. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.06.017
Li, X., Kong, M., Jiang, D., Qian, J., Duan, Q., and Dong, A. (2013). MicroRNA-150 aggravates H2O2-induced cardiac myocyte injury by down-regulating c-myb gene. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. (Shanghai) 45 (9), 734–741. doi:10.1093/abbs/gmt067
Li, X., Wu, W., He, H., Guan, L., Chen, G., Lin, Z., et al. (2024). Analysis and validation of hub genes in neutrophil extracellular traps for the long-term prognosis of myocardial infarction. Gene 914, 148369. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2024.148369
Li, X., Zhang, S., Wa, M., Liu, Z., and Hu, S. (2019). MicroRNA-101 protects against cardiac remodeling following myocardial infarction via downregulation of runt-related transcription factor 1. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 8 (23), e013112. doi:10.1161/JAHA.119.013112
Li, Y., Liu, Y., Jin, K., Dong, R., Gao, C., Si, L., et al. (2021). Negatively regulated by miR-29c-3p, MTFR1 promotes the progression and glycolysis in lung adenocarcinoma via the AMPK/mTOR signalling pathway. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 771824. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.771824
Liu, Y., Chudgar, N., Mastrogiacomo, B., He, D., Lankadasari, M. B., Bapat, S., et al. (2022). A germline SNP in BRMS1 predisposes patients with lung adenocarcinoma to metastasis and can be ameliorated by targeting c-fos. Sci. Transl. Med. 14 (665), eabo1050. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.abo1050
Lo Sardo, F., Pulito, C., Sacconi, A., Korita, E., Sudol, M., Strano, S., et al. (2021). YAP/TAZ and EZH2 synergize to impair tumor suppressor activity of TGFBR2 in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 500, 51–63. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2020.11.037
Lourenco, A. R., and Coffer, P. J. (2017). A tumor suppressor role for C/EBPα in solid tumors: more than fat and blood. Oncogene 36 (37), 5221–5230. doi:10.1038/onc.2017.151
Lourenco, A. R., Roukens, M. G., Seinstra, D., Frederiks, C. L., Pals, C. E., Vervoort, S. J., et al. (2020). C/EBPɑ is crucial determinant of epithelial maintenance by preventing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Commun. 11 (1), 785. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-14556-x
Luo, J. Y., Li, Y. H., Fang, B. B., Tian, T., Liu, F., Li, X. M., et al. (2020). NFKB1 gene rs28362491 ins/del variation is associated with higher susceptibility to myocardial infarction in a Chinese Han population. Sci. Rep. 10 (1), 19518. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-72877-9
Meijers, W. C., Maglione, M., Bakker, S. J. L., Oberhuber, R., Kieneker, L. M., de Jong, S., et al. (2018). Heart failure stimulates tumor growth by circulating factors. Circulation 138 (7), 678–691. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.030816
Meng, C., Guo, Z., Li, D., Li, H., He, J., Wen, D., et al. (2018). Preventive effect of hesperidin modulates inflammatory responses and antioxidant status following acute myocardial infarction through the expression of PPAR-gamma and Bcl-2 in model mice. Mol. Med. Rep. 17 (1), 1261–1268. doi:10.3892/mmr.2017.7981
Meng, Y. M., Jiang, X., Zhao, X., Meng, Q., Wu, S., Chen, Y., et al. (2021). Hexokinase 2-driven glycolysis in pericytes activates their contractility leading to tumor blood vessel abnormalities. Nat. Commun. 12 (1), 6011. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-26259-y
Mitchell, J. D., Laurie, M., Xia, Q., Dreyfus, B., Jain, N., Jain, A., et al. (2023). Risk profiles and incidence of cardiovascular events across different cancer types. ESMO Open 8 (6), 101830. doi:10.1016/j.esmoop.2023.101830
Murphy, A., and Goldberg, S. (2022). Mechanical complications of myocardial infarction. Am. J. Med. 135 (12), 1401–1409. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2022.08.017
Nagano, J., Sudo, N., Kubo, C., and Kono, S. (2001). Lung cancer, myocardial infarction, and the Grossarth-Maticek personality types: a case-control study in Fukuoka, Japan. J. Epidemiol. 11 (6), 281–287. doi:10.2188/jea.11.281
Newman, J. R., and Keating, A. E. (2003). Comprehensive identification of human bZIP interactions with coiled-coil arrays. Science 300 (5628), 2097–2101. doi:10.1126/science.1084648
Nikolaienko, R., Bovo, E., Kahn, D., Gracia, R., Jamrozik, T., and Zima, A. V. (2023). Cysteines 1078 and 2991 cross-linking plays a critical role in redox regulation of cardiac ryanodine receptor (RyR). Nat. Commun. 14 (1), 4498. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-40268-z
Nong, Z., O’Neil, C., Lei, M., Gros, R., Watson, A., Rizkalla, A., et al. (2011). Type I collagen cleavage is essential for effective fibrotic repair after myocardial infarction. Am. J. Pathol. 179 (5), 2189–2198. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.07.017
Pan, Z., Sun, X., Shan, H., Wang, N., Wang, J., Ren, J., et al. (2012). MicroRNA-101 inhibited postinfarct cardiac fibrosis and improved left ventricular compliance via the FBJ osteosarcoma oncogene/transforming growth factor-β1 pathway. Circulation 126 (7), 840–850. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.094524
Peng, Y., Zhao, J. L., Peng, Z. Y., Xu, W. F., and Yu, G. L. (2020). Exosomal miR-25-3p from mesenchymal stem cells alleviates myocardial infarction by targeting pro-apoptotic proteins and EZH2. Cell Death Dis. 11 (5), 317. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-2545-6
Plotnik, J. P., and Hollenhorst, P. C. (2017). Interaction with ZMYND11 mediates opposing roles of Ras-responsive transcription factors ETS1 and ETS2. Nucleic Acids Res. 45 (8), 4452–4462. doi:10.1093/nar/gkx039
Plotnikov, M. B., Chernysheva, G. A., Smol’yakova, V. I., Aliev, O. I., Fomina, T. I., Sandrikina, L. A., et al. (2023). Cardioprotective effects of a selective c-jun N-terminal kinase inhibitor in a rat model of myocardial infarction. Biomedicines 11 (3), 714. doi:10.3390/biomedicines11030714
Psilopatis, I., Karniadakis, I., Danos, K. S., Vrettou, K., Michaelidou, K., Mavridis, K., et al. (2022). May EPH/ephrin targeting revolutionize lung cancer treatment? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (1), 93. doi:10.3390/ijms24010093
Puzianowska-Kuznicka, M. (2012). ESR1 in myocardial infarction. Clin. Chim. Acta 413 (1-2), 81–87. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2011.10.028
Qiu, H., Ma, Q. G., Chen, X. T., Wen, X., Zhang, N., Liu, W. M., et al. (2022). Different classes of antibiotics exhibit disparate negative impacts on the therapeutic efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients. Am. J. Cancer Res. 12 (7), 3175–3184.
Ramos, A. H., Dutt, A., Mermel, C., Perner, S., Cho, J., Lafargue, C. J., et al. (2009). Amplification of chromosomal segment 4q12 in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 8 (21), 2042–2050. doi:10.4161/cbt.8.21.9764
Ravosa, M. J., Ning, J., Liu, Y., and Stack, M. S. (2011). Bisphosphonate effects on the behaviour of oral epithelial cells and oral fibroblasts. Arch. Oral Biol. 56 (5), 491–498. doi:10.1016/j.archoralbio.2010.11.003
Reid, I. R., Horne, A. M., Mihov, B., Stewart, A., Garratt, E., Bastin, S., et al. (2020). Effects of zoledronate on cancer, cardiac events, and mortality in osteopenic older women. J. Bone Min. Res. 35 (1), 20–27. doi:10.1002/jbmr.3860
Ribatti, D., Tamma, R., and Annese, T. (2020). Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer: a historical overview. Transl. Oncol. 13 (6), 100773. doi:10.1016/j.tranon.2020.100773
Rinde, L. B., Smabrekke, B., Hald, E. M., Brodin, E. E., Njolstad, I., Mathiesen, E. B., et al. (2017). Myocardial infarction and future risk of cancer in the general population-the Tromso Study. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 32 (3), 193–201. doi:10.1007/s10654-017-0231-5
Rondeaux, J., Groussard, D., Renet, S., Tardif, V., Dumesnil, A., Chu, A., et al. (2023). Ezh2 emerges as an epigenetic checkpoint regulator during monocyte differentiation limiting cardiac dysfunction post-MI. Nat. Commun. 14 (1), 4461. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-40186-0
Sahu, P., Donovan, C., Paudel, K. R., Pickles, S., Chimankar, V., Kim, R. Y., et al. (2023). Pre-clinical lung squamous cell carcinoma mouse models to identify novel biomarkers and therapeutic interventions. Front. Oncol. 13, 1260411. doi:10.3389/fonc.2023.1260411
Saw, J., Humphries, K., Aymong, E., Sedlak, T., Prakash, R., Starovoytov, A., et al. (2017). Spontaneous coronary artery dissection: clinical outcomes and risk of recurrence. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 70 (9), 1148–1158. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2017.06.053
Shan, G., Bi, G., Zhao, G., Liang, J., Bian, Y., Zhang, H., et al. (2023). Inhibition of PKA/CREB1 pathway confers sensitivity to ferroptosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Respir. Res. 24 (1), 277. doi:10.1186/s12931-023-02567-3
Shtivelman, E., Hensing, T., Simon, G. R., Dennis, P. A., Otterson, G. A., Bueno, R., et al. (2014). Molecular pathways and therapeutic targets in lung cancer. Oncotarget 5 (6), 1392–1433. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.1891
Sliva, D. (2008). Suppression of cancer invasiveness by dietary compounds. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 8 (7), 677–688. doi:10.2174/138955708784567412
Stolz, D., Mkorombindo, T., Schumann, D. M., Agusti, A., Ash, S. Y., Bafadhel, M., et al. (2022). Towards the elimination of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a Lancet Commission. Lancet 400 (10356), 921–972. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01273-9
Su, L., Zhang, G., Jiang, L., Chi, C., Bai, B., and Kang, K. (2023). The role of c-Jun for beating cardiomycyte formation in prepared embryonic body. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 14 (1), 371. doi:10.1186/s13287-023-03544-9
Sun, H., Liu, H., Li, J., Kou, J., and Yang, C. (2024). Analysis of the clinical predictive value of the novel inflammatory indices SII, SIRI, MHR and NHR in patients with acute myocardial infarction and their extent of coronary artery disease. J. Inflamm. Res. 17, 7325–7338. doi:10.2147/JIR.S479253
Sun, Y., Sun, X., You, C., Ma, S., Luo, Y., Peng, S., et al. (2021). MUC3A promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression via activating the NFκB pathway and attenuates radiosensitivity. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 17 (10), 2523–2536. doi:10.7150/ijbs.59430
Wan, M., Gu, H., Wang, J., Huang, H., Zhao, J., Kaundal, R. K., et al. (2013). Inducible mouse models illuminate parameters influencing epigenetic inheritance. Development 140 (4), 843–852. doi:10.1242/dev.088229
Wang, J., Zhang, L., Luo, L., He, P., Xiong, A., Jiang, M., et al. (2022). Characterizing cellular heterogeneity in fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis by single-cell transcriptional analysis. Cell Death Discov. 8 (1), 38. doi:10.1038/s41420-022-00831-x
Wang, J. C., Su, C. C., Xu, J. B., Chen, L. Z., Hu, X. H., Wang, G. Y., et al. (2007). Novel microdeletion in the transforming growth factor beta type II receptor gene is associated with giant and large cell variants of nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 46 (2), 192–201. doi:10.1002/gcc.20400
Wang, R., Liu, J., Li, K., Yang, G., Chen, S., Wu, J., et al. (2021a). An SETD1A/Wnt/β-catenin feedback loop promotes NSCLC development. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 40 (1), 318. doi:10.1186/s13046-021-02119-x
Wang, X., Zhu, Y., Wu, C., Liu, W., He, Y., and Yang, Q. (2021b). Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes carry MicroRNA-671 to alleviate myocardial infarction through inactivating the TGFBR2/smad2 Axis. Inflammation 44 (5), 1815–1830. doi:10.1007/s10753-021-01460-9
Wei, Y. J., Wang, J. F., Cheng, F., Xu, H. J., Chen, J. J., Xiong, J., et al. (2021). miR-124-3p targeted SIRT1 to regulate cell apoptosis, inflammatory response, and oxidative stress in acute myocardial infarction in rats via modulation of the FGF21/CREB/PGC1α pathway. J. Physiol. Biochem. 77 (4), 577–587. doi:10.1007/s13105-021-00822-z
Wu, D., Chen, T., Zhao, X., Huang, D., Huang, J., Huang, Y., et al. (2022). HIF1α-SP1 interaction disrupts the circ-0001875/miR-31-5p/SP1 regulatory loop under a hypoxic microenvironment and promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 41 (1), 156. doi:10.1186/s13046-022-02336-y
Wu, T., Tian, Q., Liu, R., Xu, K., Shi, S., Zhang, X., et al. (2023). Inhibitory role of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosome in non-small-cell lung cancer: microRNA-30b-5p, EZH2 and PI3K/AKT pathway. J. Cell Mol. Med. 27 (22), 3526–3538. doi:10.1111/jcmm.17933
Xia, S., Duan, W., Xu, M., Li, M., Tang, M., Wei, S., et al. (2024). Mesothelin promotes brain metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer by activating MET. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 43 (1), 103. doi:10.1186/s13046-024-03015-w
Xue, Y., Fan, X., Yang, R., Jiao, Y., and Li, Y. (2020). miR-29b-3p inhibits post-infarct cardiac fibrosis by targeting FOS. Biosci. Rep. 40 (9). doi:10.1042/BSR20201227
Yamamoto, H., Shigematsu, H., Nomura, M., Lockwood, W. W., Sato, M., Okumura, N., et al. (2008). PIK3CA mutations and copy number gains in human lung cancers. Cancer Res. 68 (17), 6913–6921. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5084
Yan, M., Yang, S., Meng, F., Zhao, Z., Tian, Z., and Yang, P. (2018). MicroRNA 199a-5p induces apoptosis by targeting JunB. Sci. Rep. 8 (1), 6699. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-24932-9
Yang, W., Bai, J., Liu, D., Wang, S., Zhao, N., Che, R., et al. (2018). MiR-93-5p up-regulation is involved in non-small cell lung cancer cells proliferation and migration and poor prognosis. Gene 647, 13–20. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2018.01.024
Yang, Z., Liang, S. Q., Zhao, L., Yang, H., Marti, T. M., Hegedus, B., et al. (2022). Metabolic synthetic lethality by targeting NOP56 and mTOR in KRAS-mutant lung cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 41 (1), 25. doi:10.1186/s13046-022-02240-5
Yuan, Y., Mei, Z., Qu, Z., Li, G., Yu, S., Liu, Y., et al. (2023). Exosomes secreted from cardiomyocytes suppress the sensitivity of tumor ferroptosis in ischemic heart failure. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 8 (1), 121. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01336-4
Zekavat, S. M., Chou, E. L., Zekavat, M., Pampana, A., Paruchuri, K., Lino Cardenas, C. L., et al. (2022). Fibrillar collagen variants in spontaneous coronary artery dissection. JAMA Cardiol. 7 (4), 396–406. doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2022.0001
Zhang, Y., Yu, W., Zhang, L., and Li, P. (2024). Nanozyme-based visual diagnosis and therapeutics for myocardial infarction: the application and strategy. J. Adv. Res. doi:10.1016/j.jare.2024.04.019
Zhao, J., Li, L., Wang, X., and Shen, J. (2024). KN-93 promotes HDAC4 nucleus translocation to promote fatty acid oxidation in myocardial infarction. Exp. Cell Res. 438 (2), 114050. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2024.114050
Zhao, L., You, T., Lu, Y., Lin, S., Li, F., and Xu, H. (2021). Elevated EZH2 in ischemic heart disease epigenetically mediates suppression of Na(V)1.5 expression. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 153, 95–103. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2020.12.012
Zheng, Y., Wang, P. P., Fu, Y., Chen, Y. Y., and Ding, Z. Y. (2022). Zoledronic acid enhances the efficacy of immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Int. Immunopharmacol. 110, 109030. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109030
Zheng, Y., Zhang, L., Zhang, K., Wu, S., Wang, C., Huang, R., et al. (2024). PLAU promotes growth and attenuates cisplatin chemosensitivity in ARID1A-depleted non-small cell lung cancer through interaction with TM4SF1. Biol. Direct 19 (1), 7. doi:10.1186/s13062-024-00452-7
Zhu, J., Zhu, X., Shi, C., Li, Q., Jiang, Y., Chen, X., et al. (2024). Integrative analysis of aging-related genes reveals CEBPA as a novel therapeutic target in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 24 (1), 267. doi:10.1186/s12935-024-03457-4
Zhu, L., Xue, F., Cui, Y., Liu, S., Li, G., Li, J., et al. (2019). miR-155-5p and miR-760 mediate radiation therapy suppressed malignancy of non-small cell lung cancer cells. Biofactors 45 (3), 393–400. doi:10.1002/biof.1500
Zhu, Q., Zhang, Y., Li, M., Zhang, Y., Zhang, H., Chen, J., et al. (2023). MiR-124-3p impedes the metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer via extracellular exosome transport and intracellular PI3K/AKT signaling. Biomark. Res. 11 (1), 1. doi:10.1186/s40364-022-00441-w
Keywords: non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), acute myocardial infarction (AMI), differentially expressed genes (DEGs), hub genes, bioinformatics analysis
Citation: Zheng H, Wang J, Zheng Y, Hong X and Wang L (2024) Identification of genetic associations between acute myocardial infarction and non-small cell lung cancer. Front. Mol. Biosci. 11:1502509. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1502509
Received: 27 September 2024; Accepted: 19 November 2024;
Published: 06 December 2024.
Edited by:
Giuseppe Bronte, University of Ferrara, ItalyReviewed by:
Laura Duran-Lozano, Vall d’Hebron Institute of Oncology (VHIO), SpainFlorentina Duica, Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Romania
Copyright © 2024 Zheng, Wang, Zheng, Hong and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Luxi Wang, d2FuZ2x1eGlAd211LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Hao Zheng
Hao Zheng Jie Wang2,3†
Jie Wang2,3† Yijia Zheng
Yijia Zheng Luxi Wang
Luxi Wang