- 1Department of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics, Bushehr Branch, Islamic Azad University, Bushehr, Iran
- 2Applied Virology Research Center, Biomedicine Technologies Institute, Baqiyatallah University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
- 3Department of Fisheries and Natural Resources, Bushehr Branch, Islamic Azad University, Bushehr, Iran
Introduction: Ulcerative colitis (UC), a common gastrointestinal disorder in affluent nations, involves chronic intestinal mucosal inflammation. This research investigated the effects of combined probiotic treatment of Lactobacillus casei (L. casei) and mesalazine on disease activity index and inflammatory factors in the UC model.
Methods: 20 male BALB/c mice were utilized and divided into four groups. To induce UC, all groups received 100 μL of 4% acetic acid (AA) intra-rectally. The first group received phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (as a control group), the second group was treated with L. casei, the third group was treated with mesalazine and, the fourth group was treated with L. casei and mesalazine. Treatment with L. Casei and mesalazine commenced after the manifestation of symptoms resulting from UC induction. Finally, the mice were euthanized and the disease activity index, myeloperoxidase activity, nitric oxide rate, cytokines level (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α) and, gene expression (iNOS, COX-2, and cytokines) were evaluated.
Results: The combined treatment of L. casei and mesalazine led to a significant decrease in the levels of NO, MPO and inflammatory cytokines. In addition, the expression of cytokines, iNOS and COX-2 genes decreased in mice treated with the combination.
Discussion: This study shows that combined treatment of L. casei and mesalazine improves of experimental UC, which can be attributed to the anti-inflammatory properties of L. casei and mesalazine. In conclusion, this combination therapy can be considered a suitable option for the management of UC.
Introduction
Ulcerative colitis (UC), a recurrent and ongoing form of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), has unique characteristics related to inflammation and localization. UC typically commences in the rectum and remains confined to the colon (Makević et al., 2023). IBD has a complex etiology involving disruptions in physiology, microbiology, immunology, and genetics (Bermudez-Brito et al., 2012). The intestinal bacterial flora, mucosal immune dysregulation, and genetic susceptibility contribute to the development of IBD, resulting in various signs consisting of abdominal pain, diarrhea, and rectal bleeding. Additionally, this condition can also cause extra-intestinal manifestations (Ohlsson, 2022). The best treatments for UC involve using corticosteroids, aminosalicylates, and immunosuppressants. However, the severe side effects of these drugs limit their long-term use. Some medications may lead to severe adverse effects, including gastrointestinal disturbances, pancreatitis, liver and kidney disorders, and gastrointestinal ulcers. Mesalazine, also known as aminosalicylic acid, is the first-line treatment for IBD and is the primary treatment for mild to moderate UC. It works by inhibiting lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase intermediates, as well as IL-1, IL-2, and tumor necrosis factor-α, effectively controlling active inflammation and promoting intestinal tissue healing (Iacucci et al., 2010). However, many patients do not respond well to this treatment. If inflammation is not controlled, individuals with UC are at risk of developing colorectal cancer (Bohm et al., 2020). Extensive research focuses on modulating beneficial microbes to alter the balance of gut bacteria, reduce inflammation, and prevent relapses in UC (Cristofori et al., 2021). Probiotics, notably Lactobacillus species, are a pivotal constituent of the intestinal microflora (Qin et al., 2022). An imbalance in gut microorganisms and improper recognition of commensal bacteria by the immune system have been associated with illnesses such as IBD (Santana et al., 2022). Specific probiotic bacteria have shown potential to provoke protective anti-inflammatory responses and reduce colitis development in animal models, demonstrating promise for managing chronic UC in humans (Guo and Lv, 2023). Among these, L. casei, a commensal bacterium, is naturally present in the gut of healthy individuals (Xu et al., 2020). Recent investigations have revealed the efficacy of certain probiotics in improving lifestyles for IBD cases, highlighting the significance of the human intestinal microbiota and its functions, including protection against pathogenic microbes and regulation of epithelial innate immunity (Roy and Dhaneshwar, 2023). Dysbiosis is commonly associated with IBD, underlining the influence of microbial balance or imbalance in disease pathogenesis (Stolfi et al., 2022). Evidence indicates that the presence of commensal enteric bacteria and their byproducts influences the progression of IBD, underscoring the potential of probiotics to enhance intestinal diversity and alleviate symptoms in individuals with IBD (Štofilová et al., 2022). These probiotics, capable of suppressing inflammation or activating innate immunity, present therapeutic potential in restoring the host’s gut microbiota (Kaur and Ali, 2022). Moreover, probiotic microorganisms generate lactic acid and lactate, which can impede the growth of detrimental organisms and exhibit an anti-inflammatory impact on the gastrointestinal tract (Sun et al., 2021). Pathogenic bacteria can activate TLR4, which can cause a disruption in the gut barrier and lead to allergen translocation within the intestinal mucosa. As a result, pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1ß, and IL-6 may be produced (Kaur and Ali, 2022). The progressive nature of this disease and the costs associated with its treatments pose a growing economic burden on health systems globally (Zhao et al., 2021). This research aims to investigate the effects of combined treatment with L. casei and mesalazine on several aspects of inflammation in the UC model.
Materials and methods
Experimental model
The study utilized male BALB/c mice, aged 6–8 weeks and weighing between 25 and 30 g, obtained from the Baqiyatullah University of Medical Sciences (BMSU) animal care facility. These mice were housed in controlled environments with a regular day-night cycle, a temperature of 23°C ± 2°C, and appropriate humidity levels. They had unrestricted access to food and water. The study procedure was approved by the Baqiyatullah University of Medical Sciences Research Ethics Committee (Approval ID: IR.BMSU.AEC.1400.001).
Lactobacillus casei culture
The BMSU provided a probiotic species L. casei ATCC: 393, which was cultivated on Man- Rogosa-Sharpe agar and kept anaerobically at 37°C for 72 h. After adjusting the probiotic strain’s concentration of 109 CFU, PBS was used two times for washing.
Acetic acid-induced ulcerative colitis
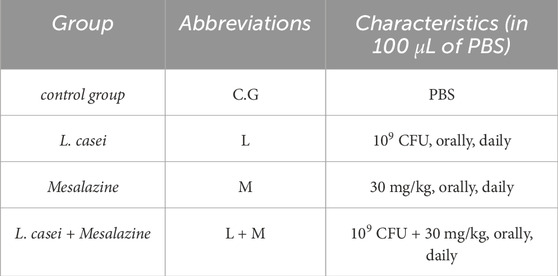
In the process of inducing UC, before the intrarectally administration of AA, the mice were provided unrestricted access to water while undergoing a 36-h fasting period. Following the fasting period, 100 µL of a 4% AA solution was injected into the rectum several times. After the injection, the mice were maintained in a slantwise position for 30 s. Ten days after the last injection and following the onset of symptoms (Diarrhea and bloody stools) of the disease, the treatment began. The research involved 20 male BALB/c mice that were randomly allocated into four equal groups: control group (PBS, orally, daily), L. casei (109 CFU, orally, daily), mesalazine (30 mg/mL, orally, daily), and L. casei + Mesalazine (109 CFU + 30 mg/kg, orally, daily) in 100 µL PBS (Table 1) (Gheibi et al., 2018). After 1 month of treatment, the mice were euthanized, and the intestine and spleen tissues were isolated for analysis (Herias et al., 2005).
Homogenization of intestine tissue
The mice were euthanized using ketamine (100 mg/kg) and xylazine (10 mg/kg). Approximately 2 cm of distal intestine tissue was excised, opened, and washed with PBS to remove feces and visible fat. Then it was homogenized in a saline solution that was ten times more in volume and kept at a very low temperature. This mixture was further centrifuged at 10,000 × g at 4°C for 10 min (Mashhouri et al., 2020).
Disease activity index (DAI)
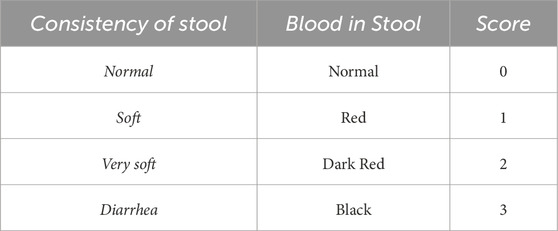
To calculate DAI in mice, stool consistency and blood in stool severity were recorded and the individual scores for each parameter provided a quantitative measure of the severity of colitis (Table 2) (Mashhouri et al., 2020).
Macroscopic and microscopic assessments
Colon tissue samples were taken and histological evaluations were performed. 10% formalin solution was used to fix the samples. After sectioning, they were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). Scoring for measurements was done by an impartial observer (Table 3). Histopathological evaluations were scored on a scale from 0 to 4. Scores for each parameter were summed to determine the overall severity of tissue damage (Gheibi et al., 2018).
Measuring MPO assessment
MPO is often used as a biochemical marker to determine the presence of granulocytes, specifically neutrophil infiltration in gastrointestinal tissues. To measure the MPO activity level, a previously described method was adopted (Mashhouri et al., 2020). The sample was homogenized and mixed with H2O2 and TMB solution. The mixture was then assessed for absorbance at 450 nm with a reference of 620 nm on a microplate reader. After incubating the samples at 37°C for 15 min, the reaction was stopped using H2SO4 and absorbance was measured again. The MPO activity was determined based on the difference in absorbance concerning the standard curve of HRP. The results were presented as millunits per milliliter (mU/mL).
NO activity assessment
To quantify the NO concentration within colonic tissues, the Griess reagent, a commonly utilized colorimetric method, was employed. Specifically, 50 µL of Griess reagent (composed of 0.1 per cent sulfanilamide, 3 per cent phosphoric acid, and 0.1 per cent naphthyl ethylenediamine) was mixed with an equal amount of homogenized colonic tissue. This mixture underwent incubation in darkness at 25°C for 10 min. Subsequently, the amount of absorbance at 540 nm was measured. Analysis of nitric oxide concentration in colon tissue samples involved correlating absorbance values with the sodium nitrite standard curve (Mashhouri et al., 2020).
Cytokines assay
To quantify the levels of IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6 ELISA kits from the Peprotech Company were used. The evaluation of culture supernatants followed the instructions and guidelines provided by the manufacturer (Jahantigh et al., 2023).
Inflammatory genes and cytokines expression
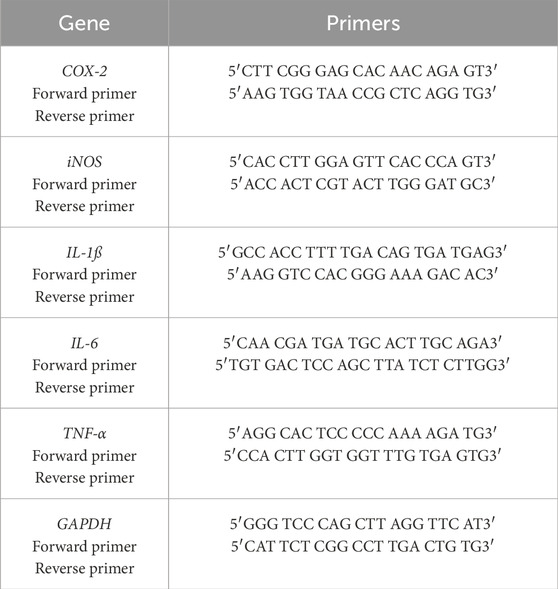
Using the Pars Tous kit and the manufacturer’s instructions, colon tissue was subjected to RNA extraction. Subsequently, cDNA synthesis was conducted. To amplify the IL-1β, IL-6, COX-2, TNF-α, and iNOS genes in mice, unique primer sequences for the forward and reverse were designed utilizing Oligo7 primer design software and validated via the NCBI website. The housekeeping gene Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was utilized with the primer set outlined in Table 4. The RT-PCR procedure consisted of forty Polymerase Chain Reaction cycles after a 30-s initial denaturing step at 95°C (Tehranipour et al., 2018).
Statistics analysis
The statistical data were presented as Mean ± SEM. The Kruskal–Wallis test was used to compare score differences among various groups. In the case of non-parametric values (discontinuous ranks associated with disease severity), the Mann-Whitney U test with Bonferroni correction was employed. For continuous data, a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted along with Dunnett’s post hoc test after confirming their normal distribution through the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Any significance level below p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Molecular data analyses were done using REST (2009) software, and other analyses were performed using SPSS (ver. 24). All graphs were created using Graph Pad Prism (ver. 8) software.
Results
Disease activity index and microscopic assay
Figure 1A shows the disease activity index. The control group had the highest values, while the combined treatment group had the lowest. Significant statistical differences were observed between all treatment’s groups, except between the L. casei and mesalazine groups, and between the mesalazine and combined treatment groups.
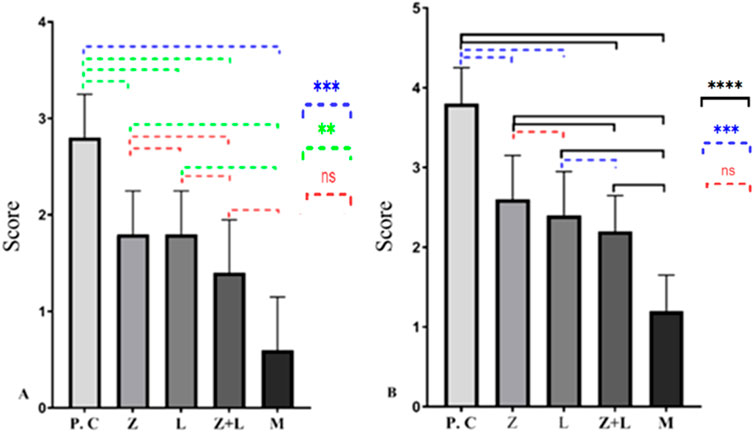
Figure 1. Macroscopic and microscopic condition of all treatments and control group. (A) Disease Activity Index. (B) Tissue damage. (* indicates p < 0.05, ** indicates p < 0.01, *** indicates p < 0.001, **** indicates p < 0.0001), (C.G: control group, L: L. casei, M: Mesalazine, L + M: L. casei + Mesalazine).
Microscopic evaluation of slides (Figure 1B) show extensive mucosal damage in the control group, with over 90% necrotic and destroyed features in the colon’s epithelial layer. In healthy mice, normal tissue structure was observed, including the intestinal wall, crypts, muscular layer, mucous layer, Lieberkühn glands, submucosa, simple columnar epithelial tissue and connective tissue. In the untreated group, pathological changes were observed in the intestinal tissue structure, including disruption of the crypt structure and breakdown of the epithelial lining. Lieberkühn’s glands were somewhat undefined. Increased muscle tissue thickness and leukocyte infiltration were noted. There was a significant decrease in goblet cells, with signs of a repair in certain areas due to the prolonged process. The group that received L. casei showed slight improvement in intestinal tissue, with some presence of Lieberkühn glands and positive changes in goblet cells. The combined treatment group showed less tissue damage, with most parts of the intestine repaired, appearing somewhat similar to healthy mice.
MPO and NO activity
Based on the data presented in Figures 2A, B, the production of MPO and NO in the intestinal tissue of all treated mice was significantly reduced compared to the control group. Also, single-agent and two-agent treatment groups showed a statistically significant difference, and the two-agent treatment group showed the lowest levels of MPO and NO compared to all the studied groups.
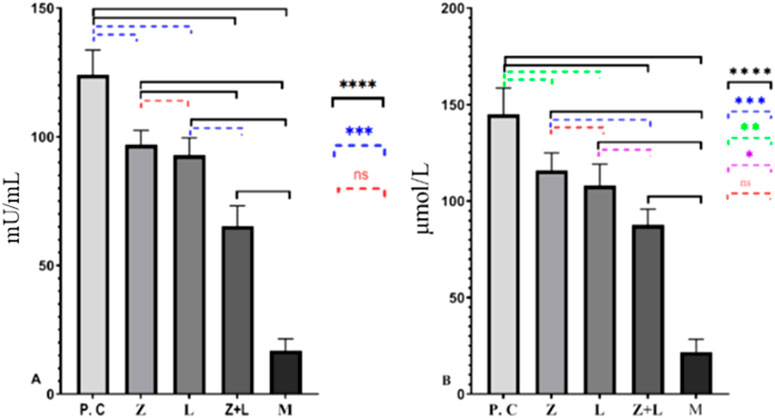
Figure 2. (A) Levels of MPO and (B) NO in the colon tissue of the study groups. In both figures, a significant statistical difference was seen between the studied groups. (* indicates p < 0.05, ** indicates p < 0.01, *** indicates p < 0.001, **** indicates p < 0.0001), (C.G: control group, L: L. casei, M: Mesalazine, L + M: L. casei + Mesalazine).
Cytokines
According to Figure 3, in the untreated colitis group, the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines increased significantly compared to the single-factor and two-factor treatment groups. Also, a statistically significant difference was seen between the single-agent and two-agent treatment groups, and the lowest production values of inflammatory cytokines were observed in the two-agent treatment group.
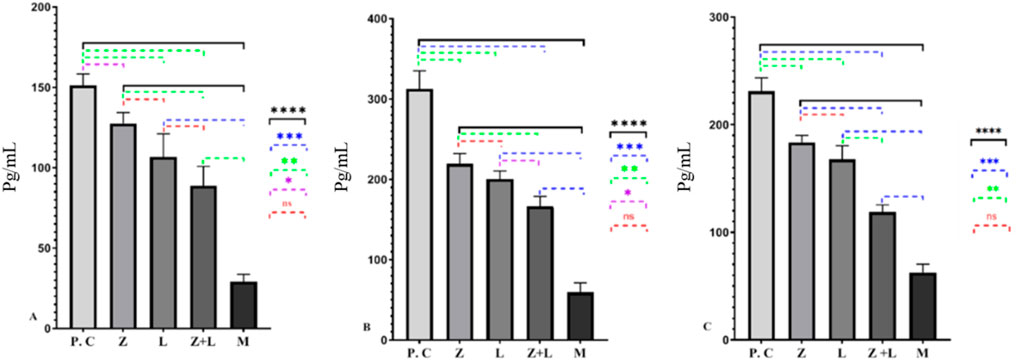
Figure 3. (A) The amount of IL-1ß, (B) The amount of IL-6, and (C) The amount of TNF-α cytokines production in different studied groups, for every group under study, a statistically significant difference was seen. (* indicates p < 0.05, ** indicates p < 0.01, *** indicates p < 0.001, **** indicates p < 0.0001), (C.G: control group, L: L. casei, M: Mesalazine, L + M: L. casei + Mesalazine).
Cytokines, iNOS and, COX-2 genes expression
The expression levels of the genes IL-1ß, IL-6, TNF-α, iNOS, and COX-2 were analyzed in different study groups using RT-PCR. The results presented in Figure 4 show a significant increase in these cytokines and genes in the control group. A significant reduction in expression levels was observed in all treatment groups compared to the control group. The lowest expression level was observed in the group treated with mesalazine. According to Figure 4, all treatment groups showed a statistically significant difference in the expression levels of IL-1ß and IL-6. However, in the L. casei treatment group, the expression levels of TNF-α, iNOS, and COX-2 did not show a statistically significant difference. Additionally, the expression levels of all genes in the groups receiving mesalazine and L. casei + mesalazine showed a significant reduction compared to the control group, And the expression levels of the genes in these two groups were approximately the same.
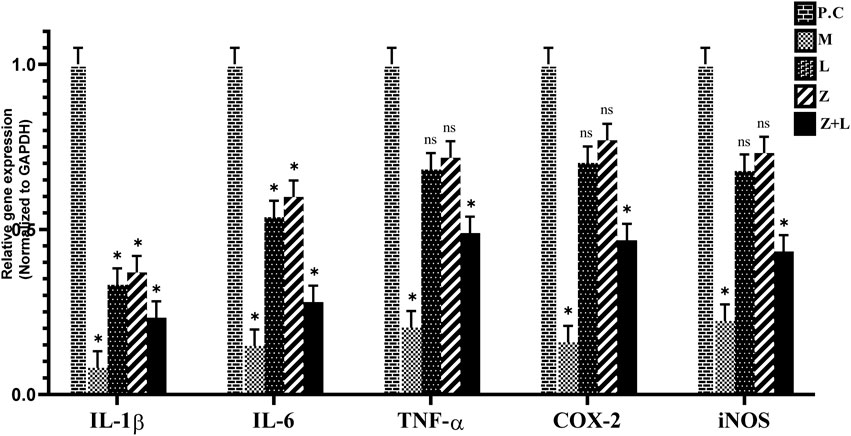
Figure 4. Relative expression diagram of IL-1ß, IL-6, TNF-α, COX-2, and iNOS genes in different study groups than the control group (C.G: control group, L: L. casei, M: Mesalazine, L + M: L. casei + Mesalazine).
Discussion
Animal models used for studying the immune response within the intestine have proven valuable in understanding IBD. This investigation specifically focuses on examining the effects of treatment with probiotic L. casei, mesalazine, and their combination on mice with UC. The findings showed that using L. casei probiotic and mesalazine reduced inflammation induced by colitis in mice. Additionally, it led to a significant decrease in disease activity index, the production of NO, MPO, inflammatory cytokine synthesis and expression, as well as COX-2 and iNOS genes. These results indicate that probiotic bacteria have the potential to reduce AA-induced damage (treatment was started after the onset of inflammation) (O’mahony et al., 2001). A study suggests that UC may be caused by gut microbiota. Clinical trials confirm that probiotics can help by changing the gut microbiota (Fedorak, 2009). One factor involved in managing and avoiding UC is the integrity of the intestinal mucosa. Known for their efficacy, probiotic strains like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium actively contribute to this stabilization (Saniabadi et al., 2014). Evidence supports the beneficial effects of probiotics, including their role in lowering cancer risk, functioning as antioxidants, and offering relief for UC (Argyri et al., 2013). Currently, probiotics are beneficial for autoimmune and digestive disorders (Sarowska et al., 2013). According to Je et al.'s research, probiotics can improve the function of the intestinal barrier and immune system as well as promote the survival of intestinal epithelial cells by inducing the generation of cytokines (Je et al., 2018). Evidence supports the widespread utilization of Lactobacillus as a supplement in foods owing to its advantageous impact on the host. These advantages encompass immune system modulation, anti-inflammatory traits, and antioxidant capabilities (Hu et al., 2020). In the study by Lin et al., research confirms the antioxidant potential of Lactobacillus. Numerous studies have illustrated how components of Lactobacillus can mitigate the harm induced by oxidative stress, particularly in cases like UC (Lin and Chang, 2000). Several mechanisms have been identified. These actions encompass the modulation of gut microbiota, fortification of the function of the intestinal barrier, shielding the gastrointestinal epithelium from pathogenic intrusion, and bolstering immune functionality. In mice, oral treatment of L. casei ATCC 393 decreased intestinal damage from dextran sodium sulfate, according to research by Bellavia et al. In addition, research results show that the histological changes caused by TNBS are improved by oral consumption of L. casei (Bellavia et al., 2014). The L. casei probiotic utilized in Dong et al.'s study concurrently triggered the expression of both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines (Dong et al., 2012). According to the survey by Hussein et al., the consumption of probiotics reversed the massive architectural damage of the colon wall caused by acetic acid, which is evident by the restoration of the typical structure of the colon wall in H&E stained sections (Hussein et al., 2023). Some limitations in our study should be discussed. One of the limitations of the study was the high mortality of animals due to perforation of their intestines.
In 2008, Amany and Eman showed that the combination of the probiotic L. acidophilus with olsalazine resulted in significant improvement compared to using the probiotic or olsalazine as monotherapy. This improvement led to a reduction in diarrhea and rectal bleeding, along with a significant decrease in the Disease Activity Index (DAI) and inflammatory markers (Abdin and Saeid, 2008). Additionally, Tursi and colleagues in 2004 demonstrated that the combination of balsalazide and VSL#3 is a very good choice for treating active ulcerative colitis, instead of using balsalazide alone or mesalazine (Tursi et al., 2004). In 2010, Tursi and colleagues found that VSL#3 supplementation after 8 weeks was able to reduce disease activity scores in patients affected by relapsing mild to moderate UC who were concurrently under treatment with 5-ASA and/or immunosuppressants (Tursi et al., 2010). In the study by Palumbo et al., all UC patients treated with combination therapy (mesalazine + Ligilactobacillus salivarius, L. acidophilus, and Bifidobacterium bifidus BGN4) showed improvement in the Disease Activity Index and reduced stool frequency, with endoscopic pictures showing improvement in gut mucosa signs compared to controls who received only mesalazine. These findings are consistent with our results, indicating that combination therapy improves clinical outcomes (Palumbo et al., 2016). Tursi et al. (2013) discovered that administering mesalazine and Lactobacillus casei concurrently proved to be more successful than a placebo in enhancing the recovery of patients experiencing symptomatic and uncomplicated diverticular disease (Tursi et al., 2013). Our study highlights the potential of Combined treatment with mesalazine and L. casei as a promising approach for UC. Using a model induced by acetic acid, we observed the effectiveness of L. casei and mesalazine in alleviating inflammation and shielding the intestinal tissue from damage. Notably, a substantial reduction in crucial inflammatory markers, including NO, MPO, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, were evident after treatment with L. casei and mesalazine. Additionally, the downregulation of pro-inflammatory genes such as IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, iNOS, and COX-2 further supports its therapeutic potential. These findings suggest the simultaneous use of L. casei and mesalazine is an effective treatment for managing this inflammatory condition.
However, additional research is imperative to explore its therapeutic advantages, safety profile, and long-term implications.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
No human studies are presented in the manuscript. The animal studies were reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Baqiyatallah University of Medical Sciences (BMSU) (code: IR.BMSU.AEC.1400.001). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent was obtained from the owners for the participation of their animals in this study. No potentially identifiable images or data are presented in this study.
Author contributions
SB: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Validation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. NB: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. HE: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. JM: Resources, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. MF: Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
This study is a component of Shabnam Bahrami's. thesis, and the authors wish to acknowledge with gratitude those who assisted in the research process.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdin, A. A., and Saeid, E. M. (2008). An experimental study on ulcerative colitis as a potential target for probiotic therapy by Lactobacillus acidophilus with or without “olsalazine”. J. Crohn's Colitis 2 (4), 296–303. doi:10.1016/j.crohns.2008.04.002
Argyri, A. A., Zoumpopoulou, G., Karatzas, K.-A. G., Tsakalidou, E., Nychas, G.-J. E., Panagou, E. Z., et al. (2013). Selection of potential probiotic lactic acid bacteria from fermented olives by in vitro tests. Food Microbiol. 33 (2), 282–291. doi:10.1016/j.fm.2012.10.005
Bellavia, M., Rappa, F., Brecchia, G., Tomasello, G., Leone, A., Spatola, G., et al. (2014). Lactobacillus casei and bifidobacterium lactis supplementation reduces tissue damage of intestinal mucosa and liver after 2, 4, 6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid treatment in mice. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. agents 28 (2), 251–261.
Bermudez-Brito, M., Plaza-Díaz, J., Muñoz-Quezada, S., Gómez-Llorente, C., and Gil, A. (2012). Probiotic mechanisms of action. Ann. Nutr. Metabolism 61 (2), 160–174. doi:10.1159/000342079
Bohm, M., Xu, R., Zhang, Y., Varma, S., Fischer, M., Kochhar, G., et al. (2020). Comparative safety and effectiveness of vedolizumab to tumour necrosis factor antagonist therapy for Crohn's disease. Alimentary Pharmacol. and Ther. 52 (4), 669–681. doi:10.1111/apt.15921
Cristofori, F., Dargenio, V. N., Dargenio, C., Miniello, V. L., Barone, M., and Francavilla, R. (2021). Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of probiotics in gut inflammation: a door to the body. Front. Immunol. 12, 578386. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.578386
Dong, H., Rowland, I., and Yaqoob, P. (2012). Comparative effects of six probiotic strains on immune function in vitro. Br. J. Nutr. 108 (3), 459–470. doi:10.1017/S0007114511005824
Fedorak, R. N. (2009). Probiotics in ulcerative colitis. Probiotics Pediatr. Med., 181–194. doi:10.1007/978-1-60327-289-6_13
Gheibi, S., Hashemi, S. R., Karimipour, M., Motlagh, B. M., and Ghaleh, H. E. G. (2018). Synergistic effects of hydro extract of jujube fruit in combination with Mesalazine (orally) and Asacol (intra-colonic) administration in ameliorating animal model of ulcerative colitis. J. Coloproctology (Rio de Janeiro) 38, 275–282. doi:10.1016/j.jcol.2018.05.008
Guo, N., and Lv, Ll (2023). Mechanistic insights into the role of probiotics in modulating immune cells in ulcerative colitis. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 11 (10), e1045. doi:10.1002/iid3.1045
Herias, M., Koninkx, J., Vos, J., In't Veld, J. H., and Van Dijk, J. (2005). Probiotic effects of Lactobacillus casei on DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in mice. Int. J. food Microbiol. 103 (2), 143–155. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2004.11.032
Hu, T., Wang, H., Xiang, C., Mu, J., and Zhao, X. (2020). Preventive effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus XY27 on DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in mice. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 14, 5645–5657. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S284422
Hussein, M. N., Abdelhamid, Z., Elmarakby, D., and Fares, A. E. (2023). Assessment of the prophylactic effect of probiotics in an experimental model of ulcerative colitis in male albino rat: histological and immunohistochemical study. Egypt. J. Histology 46 (1), 33–48. doi:10.21608/ejh.2021.95675.1562
Iacucci, M., de Silva, S., and Ghosh, S. (2010). Mesalazine in inflammatory bowel disease: a trendy topic once again? Can. J. Gastroenterology Hepatology 24, 127–133. doi:10.1155/2010/586092
Jahantigh, M., Froushani, S. M. A., and Ahangaran, N. A. (2023). Benefits of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells primed with estradiol in alleviating collagen-induced arthritis. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 26 (4), 400–407. doi:10.22038/IJBMS.2023.68112.14882
Je, I.-G., Lee, D.-G., Jeong, D.-G., Hong, D., Yoon, J.-M., Moon, J. S., et al. (2018). The probiotic, ID-JPL934, attenuates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice through inhibition of proinflammatory cytokines expression. J. Med. food 21 (9), 858–865. doi:10.1089/jmf.2017.4152
Kaur, H., and Ali, S. A. (2022). Probiotics and gut microbiota: mechanistic insights into gut immune homeostasis through TLR pathway regulation. Food and Funct. 13 (14), 7423–7447. doi:10.1039/D2FO00911K
Lin, M.-Y., and Chang, F.-J. (2000). Antioxidative effect of intestinal bacteria Bifidobacterium longum ATCC 15708 and Lactobacillus acidophilus ATCC 4356. Dig. Dis. Sci. 45, 1617–1622. doi:10.1023/A:1005577330695
Makević, V., Milovanovich, I. D., Popovac, N., Janković, R., Trajković, J., Vuković, A., et al. (2023). Fractal parameters as independent biomarkers in the early diagnosis of pediatric onset inflammatory bowel disease. Fractal Fract. 7 (8), 619. doi:10.3390/fractalfract7080619
Mashhouri, S., Froushani, S. M. A., and Tehrani, A. A. (2020). Non-adherent bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate clinical manifestations and inflammation in an experimental model of ulcerative colitis in rats. Iran. J. Med. Sci. 45 (5), 341–351. doi:10.30476/ijms.2020.72514.0
Ohlsson, B. (2022). Extraintestinal manifestations in irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterology 15, 17562848221114558. doi:10.1177/17562848221114558
O’mahony, L., Feeney, M., O'halloran, S., Murphy, L., Kiely, B., Fitzgibbon, J., et al. (2001). Probiotic impact on microbial flora, inflammation and tumour development in IL-10 knockout mice. Alimentary Pharmacol. and Ther. 15 (8), 1219–1225. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2036.2001.01027.x
Palumbo, V. D., Romeo, M., Marino Gammazza, A., Carini, F., Damiani, P., Damiano, G., et al. (2016). The long-term effects of probiotics in the therapy of ulcerative colitis: a clinical study. Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky. Olomouc Czech Repub. 160 (3), 372–377. doi:10.5507/bp.2016.044
Qin, D., Ma, Y., Wang, Y., Hou, X., and Yu, L. (2022). Contribution of Lactobacilli on intestinal mucosal barrier and diseases: perspectives and challenges of Lactobacillus casei. Life 12 (11), 1910. doi:10.3390/life12111910
Roy, S., and Dhaneshwar, S. (2023). Role of prebiotics, probiotics, and synbiotics in management of inflammatory bowel disease: current perspectives. World J. Gastroenterology 29 (14), 2078–2100. doi:10.3748/wjg.v29.i14.2078
Saniabadi, A. R., Tanaka, T., Ohmori, T., Sawada, K., Yamamoto, T., and Hanai, H. (2014). Treating inflammatory bowel disease by adsorptive leucocytapheresis: a desire to treat without drugs. World J. Gastroenterology WJG 20 (29), 9699–9715. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.9699
Santana, P. T., Rosas, S. L. B., Ribeiro, B. E., Marinho, Y., and de Souza, H. S. (2022). Dysbiosis in inflammatory bowel disease: pathogenic role and potential therapeutic targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (7), 3464. doi:10.3390/ijms23073464
Sarowska, J., Choroszy-Król, I., Regulska-Ilow, B., Frej-Madrzak, M., and Jama-Kmiecik, A. (2013). The therapeutic effect of probiotic bacteria on gastrointestinal diseases. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 22 (5), 759–766.
Štofilová, J., Kvaková, M., Kamlárová, A., Hijová, E., Bertková, I., and Guľašová, Z. (2022). Probiotic-based intervention in the treatment of ulcerative colitis: conventional and new approaches. Biomedicines 10 (9), 2236. doi:10.3390/biomedicines10092236
Stolfi, C., Maresca, C., Monteleone, G., and Laudisi, F. (2022). Implication of intestinal barrier dysfunction in gut dysbiosis and diseases. Biomedicines 10 (2), 289. doi:10.3390/biomedicines10020289
Sun, S., Xu, X., Liang, L., Wang, X., Bai, X., Zhu, L., et al. (2021). Lactic acid-producing probiotic Saccharomyces cerevisiae attenuates ulcerative colitis via suppressing macrophage pyroptosis and modulating gut microbiota. Front. Immunol. 12, 777665. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.777665
Tehranipour, M., Emamyian, M. Z., Vaezi, G. H., and Nejad Shahrokh Abadi, K. (2018). The effect of aqueous extract of Cichorium intybus L. stem on the biochemical parameters of serum and urine in male rats with nephrolithiasis. Iran. J. Biol. Sci. 13 (3), 53–61.
Tursi, A., Brandimarte, G., Elisei, W., Picchio, M., Forti, G., Pianese, G., et al. (2013). Randomised clinical trial: mesalazine and/or probiotics in maintaining remission of symptomatic uncomplicated diverticular disease--a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled study. Alimentary Pharmacol. and Ther. 38 (7), 741–751. doi:10.1111/apt.12463
Tursi, A., Brandimarte, G., Giorgetti, G. M., Forti, G., Modeo, M. E., and Gigliobianco, A. (2004). Low-dose balsalazide plus a high-potency probiotic preparation is more effective than balsalazide alone or mesalazine in the treatment of acute mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis. Med. Sci. Monit. 10 (11), PI126–PI131.
Tursi, A., Brandimarte, G., Papa, A., Giglio, A., Elisei, W., Giorgetti, G. M., et al. (2010). Treatment of relapsing mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis with the probiotic VSL# 3 as adjunctive to a standard pharmaceutical treatment: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Official J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterology| ACG. 105 (10), 2218–2227. doi:10.1038/ajg.2010.218
Xu, C., Yan, S., Guo, Y., Qiao, L., Ma, L., Dou, X., et al. (2020). Lactobacillus casei ATCC 393 alleviates Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction via TLRs/mast cells pathway. Life Sci. 244, 117281. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117281
Keywords: inflammatory cytokine, inflammation, Lactobacillus casei, mesalazine, probiotic, ulcerative colitis
Citation: Bahrami S, Babaei N, Esmaeili Gouvarchin Ghaleh H, Mohajeri Borazjani J and Farzanehpour M (2024) Investigating the effects of combined treatment of mesalazine with Lactobacillus casei in the experimental model of ulcerative colitis. Front. Mol. Biosci. 11:1456053. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1456053
Received: 04 July 2024; Accepted: 13 September 2024;
Published: 03 October 2024.
Edited by:
Ilaria Laudadio, Sapienza University of Rome, ItalyReviewed by:
Juan Andrés De Paula, Italian Hospital of Buenos Aires, ArgentinaAntonio Tursi, Azienda Sanitaria Localedella Provincia di Barletta Andri Trani (ASL BT), Italy
Copyright © 2024 Bahrami, Babaei, Esmaeili Gouvarchin Ghaleh, Mohajeri Borazjani and Farzanehpour. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hadi Esmaeili Gouvarchin Ghaleh, aC5zbWFpbGk2OUB5YWhvby5jb20=
†ORCID: Shabnam Bahrami, https://orcid.org/0009-0008-0772-6927; Nahid Babaei, https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6459-0116; Hadi Esmaeili Gouvarchin Ghaleh, orcid.org/0000-0001-8562-2295; Jaleh Mohajeri Borazjani, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7612-0397; Mahdieh Farzanehpour, https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2134-1061
 Shabnam Bahrami1†
Shabnam Bahrami1† Hadi Esmaeili Gouvarchin Ghaleh
Hadi Esmaeili Gouvarchin Ghaleh