- Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, New York University, 6 MetroTech Center, Brooklyn, NY, United States
Aberrant self-assembly of an intrinsically disordered protein is a pathological hallmark of protein misfolding diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases (AD and PD, respectively). In AD, the 40–42 amino acid-long extracellular peptide, β-amyloid (Aβ), self-assembles into oligomers, which eventually aggregate into fibrils. A similar self-association of the 140 amino acid-long intracellular protein, α-synuclein (αS), is responsible for the onset of PD pathology. While Aβ and αS are primarily extracellular and intracellular polypeptides, respectively, there is evidence of their colocalization and pathological overlaps of AD and PD. This evidence has raised the likelihood of synergistic, toxic protein-protein interactions between Aβ and αS. This mini review summarizes the findings of studies on Aβ-αS interactions related to enhanced oligomerization via co-assembly, aiming to provide a better understanding of the complex biology behind AD and PD and common pathological mechanisms among the major neurodegenerative diseases.
1 Introduction
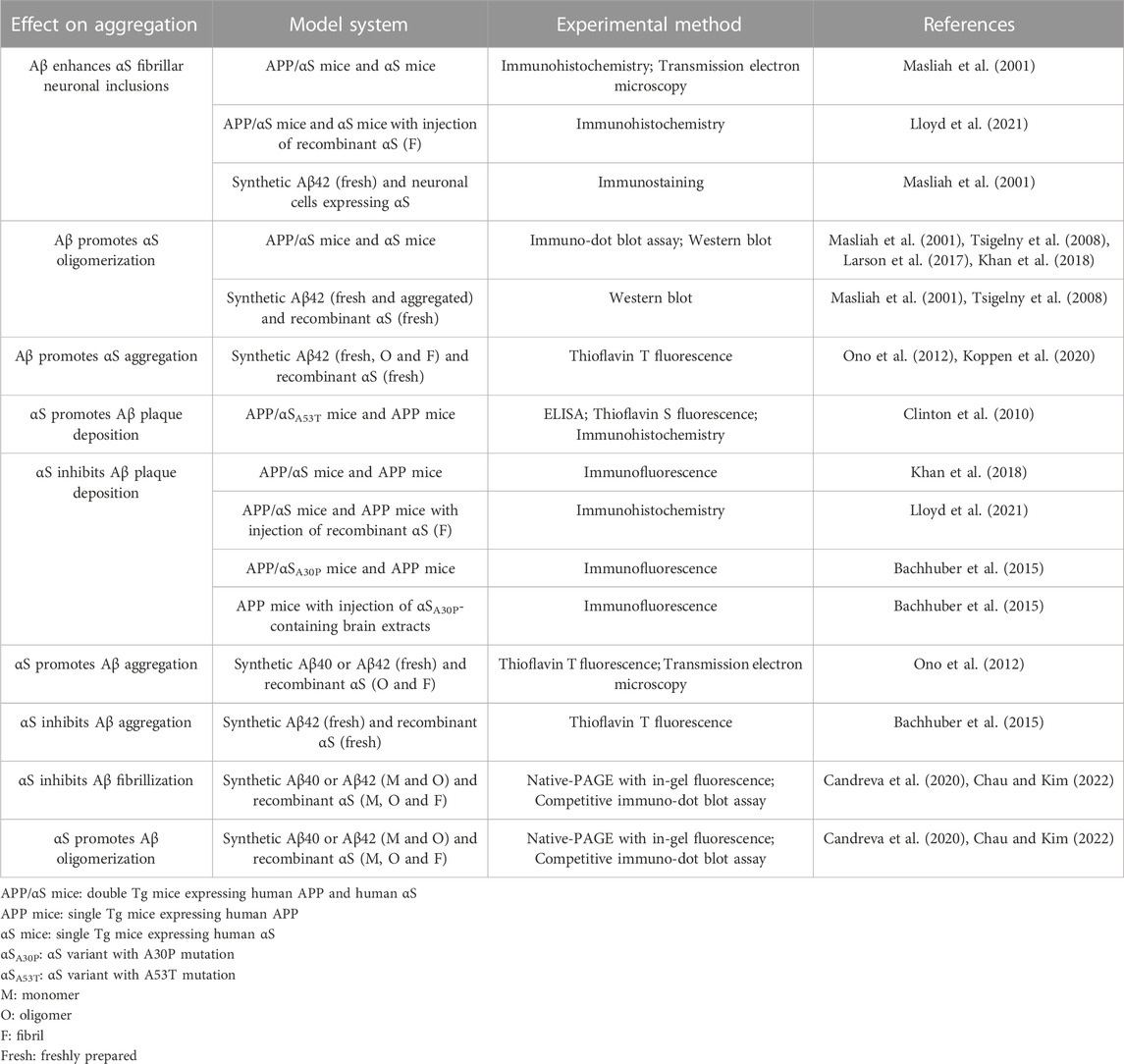
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the losses of forebrain cholinergic and hippocampal neurons (Dallaire-Theroux et al., 2017). AD pathology is caused by aggregation of the peptide, β-amyloid (Aβ), containing 40 or 42 residues (referred to as Aβ40 and Aβ42, respectively; Figure 1A) leading to the formation of extracellular amyloid plaques in the brains of AD patients (Aguzzi and O'Connor, 2010). The typical physiological ratio of Aβ40/Aβ42 is ∼9 (Qiu et al., 2015). The hydrophobic sequences of Aβ (e.g., Aβ17-21 and the C-terminus; Figure 1A) promote Aβ aggregation (Bolognesi et al., 2010; Hu et al., 2012). Aβ aggregation involves three distinct conformers (Figure 1B): monomeric Aβ spontaneously self-assembles into soluble oligomeric Aβ (Gao et al., 2020; Xiao et al., 2020), which then aggregates further to form insoluble fibrillar Aβ (Petkova et al., 2002; Luhrs et al., 2005). The primary toxic agents in AD are oligomeric rather than monomeric or fibrillar Aβ (Kayed et al., 2003; Aguzzi and O'Connor, 2010). Toxic Aβ oligomers can disrupt neuronal activity at the synapse, disturb cell membranes, cause oxidative stress, and perturb calcium homeostasis (Aguzzi and O'Connor, 2010), thereby initiating degeneration in AD (He et al., 2019). While Aβ monomers and some small Aβ oligomers are structurally disordered (Jin et al., 2011; Potapov et al., 2015), β-sheet content grows with increasing size of oligomeric Aβ (Ono et al., 2009). The major Aβ oligomeric morphologies include spherical and protofibrillar forms (Harper et al., 1997; Lasagna-Reeves et al., 2011). Aβ fibrils adopts in-register cross β-sheet structures (Petkova et al., 2002; Luhrs et al., 2005).
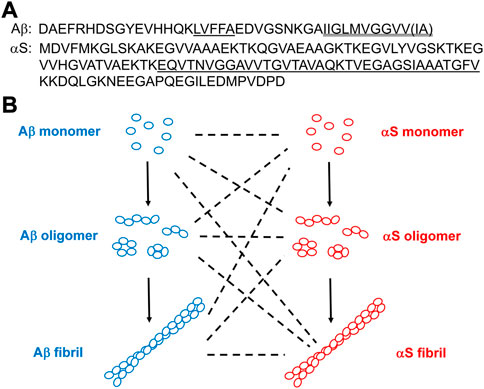
FIGURE 1. (A) Amino acid sequences of Aβ and αS. In Aβ, the hydrophobic Aβ17-21 (LVFFA) and the hydrophobic Aβ C-terminus are shown single-underlined and double-underlined, respectively. The two additional C-terminal residues of Aβ42 relative to Aβ40 are Ile-Ala shown in a parenthesis. In αS, the NAC domain is underlined. (B) Schematics of aggregations of Aβ and αS by self-assembly (solid lines) from their monomeric forms to oligomeric, and to fibrillar forms or via co-assembly (dotted lines).
The AD afflicted brain is also characterized by intraneuronal filamentous aggregates composed of phosphorylated tau (Twohig and Nielsen, 2019), a microtubule-binding protein that consists of 352–441 residues. The multiple repeat regions in tau are aggregation-prone (Jouanne et al., 2017). In AD, tau pathology generally occurs later relative to neuronal cell loss, memory deficit and Aβ plaque formation (Oddo et al., 2003) and can be induced by Aβ aggregates (Gotz et al., 2001; Vasconcelos et al., 2016).
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder after AD, and the most common movement disorder (Surmeier et al., 2017). PD is characterized by the loss of substantia nigra dopamine neurons and the presence of Lewy bodies (LB) with intracellular protein inclusions that contain the 140 residue-protein, α-synuclein (αS; Figure 1A) (Irwin et al., 2013). Hydrophobic αS 61–95, known as the non-amyloid component (NAC; Figure 1A), is critical in αS self-assembly (Giasson et al., 2001). Similar to the role of Aβ in AD, aggregation of αS is the hallmark event in PD pathology (Surmeier et al., 2017; Hijaz and Volpicelli-Daley, 2020). Self-assembly of αS monomers produces soluble αS oligomers, which eventually aggregate into fibrillar αS (Figure 1B). As is the case with Aβ in AD, oligomeric rather than monomeric or fibrillar αS is a major toxic agent in PD (Winner et al., 2011; Chen et al., 2015). Toxic αS oligomers disrupt lipid membranes (Giehm et al., 2011; Winner et al., 2011), disturb ion homeostasis (Danzer et al., 2007) and cause oxidative stress (Cremades et al., 2012). Many toxic αS oligomers are β sheet-structured and globular or pore-like in morphology (Giehm et al., 2011; Cremades et al., 2012). Also, like Aβ, monomeric αS is structurally disordered (Eliezer et al., 2001) and fibrillar αS is cross β-sheet-structured (Vilar et al., 2008).
The recent progresses in AD therapy and diagnosis have reinforced the critical role of oligomers in AD pathology, though no symptom-modifying therapeutic agents are currently available for PD (Paolini Paoletti et al., 2020). A couple of antibody-based AD drugs, aducanumab and lecanemab, have recently been approved by FDA (Walsh et al., 2021; Couzin-Frankel and Piller, 2022). Aducanumab targets Aβ aggregates, including oligomers and fibrils (Sevigny et al., 2016), whereas lecanemab does Aβ protofibrillar oligomers (van Dyck et al., 2023). These findings support that amyloid oligomers play a critical role in neurodegenerative diseases, though the efficacy of aducanumab and the safety of lecanemab are still debatable (Walsh et al., 2021; Couzin-Frankel and Piller, 2022). While oligomerizations of single amyloid proteins have been extensively examined (for example, see (Nguyen et al., 2021)), oligomer formation driven by interactions between multiple amyloid proteins (e.g., Aβ and αS) is relatively understudied, which is a major focus of this minireview.
2 Pathological synergy between AD and PD via interactions between Aβ and αS
A great deal of evidence indicates that both AD- and PD-related symptoms are detected in some patients. For example, many (∼50%) patients with AD develop LB pathology in addition to Aβ plaques and tau tangles (Irwin et al., 2013; Visanji et al., 2019). These patients exhibit faster cognitive decline and shorter lifespan compared to those with only AD pathology (Kraybill et al., 2005). Similarly, PD patients can be diagnosed with dementia (PDD) and PDD patients show more severe cognitive dysfunction than AD patients (Hamilton 2000; Irwin et al., 2013). Moreover, both dementia and parkinsonism are evident in Diffuse Lewy Body disease (DLB) (Hamilton 2000). Importunately, previous in vivo studies with transgenic (Tg) mice showed greater neuronal degeneration, stronger neuroinflammation, and more severe deficits in cognition and motor skill when Aβ and αS are both present (Larson et al., 2017; Khan et al., 2018; Lloyd et al., 2021). These findings serve as direct evidence that the synergistic connections of AD and PD pathologies are mediated by Aβ and αS (Twohig and Nielsen, 2019; Bassil et al., 2020; Murakami and Ono, 2022).
3 Oligomerization enhanced by Aβ-αS interactions: Clinical and animal studies
Strong evidence in the literature has shown that the synergistic toxic effects are associated with enhanced oligomerization via Aβ-αS interactions. For instance, the level of soluble αS oligomers is higher and amyloid plaque load is lower in human brain with AD and PD co-pathologies than in AD alone (Heyman et al., 1999; Tsigelny et al., 2008). A post-mortem analysis showed greater amounts of toxic oligomeric αS in AD brains compared to healthy controls (Larson et al., 2017). Aβ and αS co-expression in double Tg mice enhances αS oligomerization compared to single Tg mice, while reducing Aβ fibrillar plaques (Larson et al., 2017; Khan et al., 2018). Moreover, intracerebral injections of αS-containing brain extracts into AD mice inhibit Aβ deposition into fibrillar plaques, presumably increasing the quantity of Aβ oligomers (Bachhuber et al., 2015).
4 Co-localization of Aβ and αS for direct protein-protein interactions
While Aβ and αS can facilitate oligomerization of each other indirectly, for example, by enhancing protein production (Roberts et al., 2017), a large body of evidence points to direct Aβ-αS interactions as a more effective cross-talk mechanism (Ren et al., 2019). Generally, Aβ and αS are considered as extracellular and intracellular proteins, respectively. Nevertheless, a chance of these proteins being in spatial proximity is not negligible, permitting the direct protein-protein interactions. For example, expression levels of αS are high in human brain regions where AD lesions are abundant (Mandal et al., 2006). In addition, co-localization of Aβ and αS (either its NAC fragment or full-length form) was detected within fibrillar plaques (Drummond et al., 2017; Bluhm et al., 2022) in clinical and animal studies and suggested to occur in cellular compartments, such as an mitochondrion (Hashimoto et al., 2003). Aβ once produced extracellularly can be accumulated intraneuronally (LaFerla et al., 2007). Likewise, αS initially produced intracellularly can be secreted into extracellular space (Lee et al., 2005). Thus, direct protein-protein interactions between Aβ and αS occur both intracellularly and extracellularly (Masliah et al., 2001; Hashimoto et al., 2003; Tsigelny et al., 2008; Kayed et al., 2020).
5 Impact of Aβ-αS interaction on aggregation: In vivo and in vitro studies
Studies on Aβ-αS interactions in vivo would be most ideal to understand the outcome of the interactions under a biological context. Several animal and cell culture studies have reported impact of direct Aβ-αS interactions on aggregations (Table 1). For example, Aβ promotes αS oligomerization and LB inclusions in Tg mice and cultured neurons (Masliah et al., 2001; Tsigelny et al., 2008; Larson et al., 2017; Khan et al., 2018; Lloyd et al., 2021). Aβ plaque deposition can be accelerated by αS in animal studies (Clinton et al., 2010), though the opposite effects of αS were reported elsewhere (Bachhuber et al., 2015; Khan et al., 2018; Lloyd et al., 2021). Unfortunately, conformations of amyloid proteins are crucial for their associations with other amyloid proteins, internalization mechanisms and pathological effects (Peng et al., 2018; Kayed et al., 2020), yet are difficult to control in samples of biological origin (Peng et al., 2018). Similarly, the collection of brain-derived amyloid aggregates requires sample treatments that can alter aggregation state (Casali and Lanreth, 2016), for example, the use of denaturing agents (e.g., Sarkosyl) for extraction (Ren and Sahara, 2013) or acidic buffer for elution of proteins (Puangmalai et al., 2020). Moreover, isolations of Aβ and αS from biological origins suffer from low quantities and the lack of concentration controls (Casali and Lanreth, 2016).
Instead, in vitro studies with synthetic Aβ and recombinant αS might be more suitable to examine Aβ-αS interactions for several reasons: 1) synthetic Aβ and recombinant αS injections into animal models have proven effective for studying the onset, progression and outcomes of AD and PD pathologies, and their co-pathology (Bloom 2014; McAllister et al., 2020); 2) conformations and aggregation states of Aβ and αS − critical for the severity and the phenotype of pathology − are relatively easier to control and characterize in vitro than in vivo (McAllister et al., 2020), permitting an understanding of molecular outcomes from specific Aβ-αS interactions. In previous in vitro studies (Table 1), Aβ enhanced αS aggregation (Ono et al., 2012; Koppen et al., 2020), including αS oligomerization (Masliah et al., 2001; Tsigelny et al., 2008). αS can either accelerate (Ono et al., 2012) or inhibit Aβ aggregation in vitro (Bachhuber et al., 2015). Unfortunately, the intrinsic complexity associated with different conformers of Aβ and αS (i.e., monomeric, oligomeric, and fibrillar forms) has precluded the identification of exact synergistic mechanisms linked to AD, PD and their co-pathologies. Moreover, most previous studies have provided limited insight into conformer-specific Aβ-αS interactions. This limitation arose because aggregation was frequently ill-defined with no distinction between oligomerization and fibrilization. In addition, Aβ-αS interactions were often characterized under denaturing conditions (e.g., with SDS), which can introduce undesired artifacts on aggregation states, complicating data interpretation. Other histopathology and injection studies have focused on fibrils, underestimating the role of oligomers in comorbidities.
6 Conformer-specific Aβ-αS interactions: αS-assisted oligomerization of Aβ in vitro
Recent in vitro studies by Kim and coworkers have provided experimental evidence of Aβ-αS co-assembly into potentially toxic oligomers, revealing important insights into the nature of Aβ-αS interactions: excess soluble αS species (i.e., αS monomers and oligomers) prevent fibrillization of Aβ40 while enhancing oligomerization of Aβ40 (Figure 2; Table 1). Though the αS monomer concentration tested in this study was 350 μM, exceeding the physiological αS concentrations (i.e., low μM range (Wilhelm et al., 2014)), oligomeric αS at 17 μM, which is slightly above the physiological αS concentrations, was effective for enhancing Aβ oligomerization in vitro. Thus, this observation suggests a possibility of oligomeric αS seeding Aβ oligomerization in vivo. Moreover, in vivo αS concentrations can be elevated locally by various mechanisms (Owen et al., 2019), which may promote the formation of αS oligomers. Once formed, these oligomers are kinetically stable at < μM concentrations (Nag et al., 2011), available for enhancing Aβ oligomerization. In the same study, the C-terminus of Aβ40 was shown to be directly involved in interactions with αS, facilitating the formation of co-assembled oligomers. The competitive immunoassay provides evidence for binding of Aβ40 in all three forms (i.e. monomeric, oligomeric and fibrillar Aβ40) to αS fibrils via the Aβ C-terminus (Candreva et al., 2020). In addition, aggregations of αS monomers and oligomers were facilitated by Aβ40 fibrils (Candreva et al., 2020), as reported elsewhere (Ono et al., 2012). Interestingly, when judged by thioflavin T fluorescence, incorporation of αS into fibrillar Aβ40 or Aβ40 into fibrillar αS was relatively minor or slow compared to co-assembled oligomerization (Candreva et al., 2020). The implication is that Aβ40-αS interactions might occur more drastically for the formation of oligomers rather than fibrils.
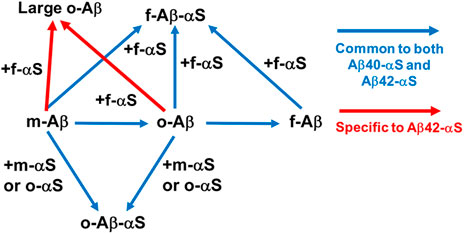
FIGURE 2. Direct Aβ-αS interaction networks. Blue arrows: common to both Aβ40-αS and Aβ42-αS (Candreva et al., 2020; Chau and Kim, 2022). Addition of αS monomers and oligomers inhibits fibrilization of monomeric (m-) and oligomeric (o-) Aβ, while promoting oligomerization of Aβ monomers and stabilizing preformed Aβ oligomers via co-assembly. Monomeric, oligomeric, and fibrillar (f-) Aβ can be incorporated into αS fibrils. Red arrows: specific to Aβ42-αS (Chau and Kim, 2022). αS fibrils partially interferes with conversion of soluble Aβ42, but not Aβ40, into insoluble aggregates, instead possibly promoting the formation of large oligomeric Aβ42.
The subsequent study showed both similarities and dissimilarities between Aβ42-αS and Aβ40-αS interactions. Specifically, while monomeric and oligomeric αS promoted oligomerization of Aβ42, similar to Aβ40, αS fibrils induced the formation of large Aβ42 oligomers - a finding unique to Aβ42 (Figure 2; Table 1) (Chau and Kim, 2022). The C-terminus of Aβ42 is primarily utilized for its interactions with αS, similar to Aβ40, yet other regions of Aβ42 (e.g., Aβ22-35) are also involved (Chau and Kim, 2022). A molecular dynamics simulation study suggested that direct Aβ42-NAC interactions induce the formation of new β-strands in Aβ42 while the NAC domain remains structurally unchanged (Atsmon-Raz and Miller, 2016). A similar structural study with Aβ and the full-length αS will provide valuable insight into the molecular determinants crucial in Aβ-αS interactions.
Overall, these studies demonstrate that Aβ and αS can directly interact to form Aβ-αS co-assembled oligomers, possibly responsible for the enhanced oligomerization in vivo when Aβ and αS co-exist. Thus, Aβ-αS interactions provide a synergistic mechanism to produce oligomeric assemblies and may have common biological consequences in AD, PD, DLB and PDD, given that amyloid oligomers are usually neurotoxic (Ahmed et al., 2010; Giehm et al., 2011).
7 Discussion
7.1 Aβ-αS interactions in a biological context
For a better understanding of pathogenic overlap between AD and PD, how the conformer-specific Aβ-αS interactions are manifested in a biological context would be a critical first step (Murakami and Ono, 2022). This biological examination would interrogate the pathological relevance of Aβ-αS interactions, closing a knowledge gap in a link among Aβ-αS co-assembly, oligomerization and synergistic toxic effects. Intracellular and extracellular co-localizations of Aβ and αS (Chinta et al., 2010; Drummond et al., 2017) raise a possibility of transportation across cell membranes of oligomers formed by Aβ-αS interactions, spreading their toxic effects (Kayed et al., 2020). Given αS’s ubiquitous and abundant expression in brain and strong innate ability to shuttle between intra- and extracellular compartments (Irwin et al., 2013), the role of αS in orchestrating a pathophysiological ensemble of AD and PD by enhancing Aβ oligomerization is of a particular therapeutic relevance (Kayed et al., 2020). Moreover, the co-assembly of Aβ and αS may facilitate circumvention of their proteolytic clearances, possibly increasing their toxic effects in vivo. Thus, a strategy to modulate the interactions would open a new therapeutic avenue, beyond targeting self-assembly of a single amyloid protein adopted by most anti-amyloid therapeutic strategies developed against AD and PD (Murakami and Ono, 2022).
7.2 Additional complexity
While Aβ-αS interactions may provide additional routes to form oligomeric species beyond aggregation of individual amyloid proteins, heterogeneity of oligomers in size, morphology, structure, and seeding ability further increases pathological complexity. Aβ and αS oligomers of biological or synthetic origins range from dimers to ∼200 mers (Breydo and Uversky, 2015) and display different morphologies, such as globular and protofibrillar shapes (Chen et al., 2015). While many Aβ and αS oligomers possess well-defined secondary structures, usually β-sheets, others are structurally disordered (Breydo and Uversky, 2015; Gao et al., 2020). Moreover, amyloid oligomers can be either on-pathway intermediates of fibrillization or off-pathway end products (Breydo and Uversky, 2015), differing in seeding ability. Inhibitions of Aβ42 fibrillization by off-pathway αS oligomers - generated by forming covalent adducts with a dopamine metabolite or a polyunsaturated fatty acid - have recently been reported (Dhakal et al., 2021), though whether the modulations lead to Aβ-αS co-assembly into oligomers remains unclear. In this study, interactions of Aβ42 with the two structurally distinct off-pathway αS oligomers were found to promote the formation of Aβ42 assemblies that differ in toxicity, suggesting the importance of αS oligomer conformation in the observed phenotypes and clinical manifestations (Dhakal et al., 2021). Thus, testing with specific subgroups of Aβ and αS oligomers for the outcomes of their interactions would further depict the heterogeneity-driven complexity of the interactions.
The Aβ-αS interaction may extend further with other amyloidogenic and non-amyloidogenic proteins, increasing the boundaries of interaction networks (Murakami and Ono, 2022). For example, tau is an intracellular amyloid protein, whose filamentous aggregates are found in the AD afflicted brain (Buee et al., 2000; Twohig and Nielsen, 2019). Tau is highly abundant as soluble monomers and does not spontaneously aggregate under the physiological condition (Jouanne et al., 2017; Visanji et al., 2019), yet its aggregation into oligomers and filaments related to neurotoxicity can be induced by Aβ following phosphorylation-dependent and independent mechanisms (Jin et al., 2011; Vasconcelos et al., 2016; Gyparaki et al., 2021). Similar to Aβ and αS, oligomeric rather than monomeric or filamentous tau is toxic (Ghag et al., 2018) and responsible for neuronal dysfunction in AD (Spires et al., 2006). αS can also induce tau aggregation in both phosphorylation-dependent (Twohig and Nielsen, 2019) and independent manners (Giasson et al., 2003). αS oligomers rather than αS monomers and fibrils catalyze tau oligomerization (Lasagna-Reeves et al., 2010) and αS and tau can promote their mutual aggregations (Giasson et al., 2003; Dasari et al., 2019). Thus, the direct Aβ-αS interactions extend further with tau through the shared release, trafficking and uptake mechanisms (Twohig and Nielsen, 2019; Visanji et al., 2019), that allow intra- and inter-cellular propagation of pathological seeds of Aβ, αS and tau (Frost et al., 2009; Irwin et al., 2013; Kayed et al., 2020), initiating an autocatalytic cycle of aggregation (Vasconcelos et al., 2016) and spreading pathology (Lloyd et al., 2021). The protein-protein interaction network centered on Aβ-αS can also extend with a non-amyloidogenic protein, such as DNA-binding protein TDP-43, known to bind to αS (Dhakal et al., 2022).
8 Conclusion
Aβ-αS interactions leading to the formation of co-assembled oligomers and their propagation are deemed responsible for pathological complexity, overlap, and heterogeneity of AD, PD and other major neurodegenerative diseases. Thus, a better understanding of Aβ-αS interactions will be required to close current knowledge gaps and point to new therapeutic strategies targeting oligomerization.
Author contributions
JRK collected materials, wrote the manuscript and approved its submission.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health [grant number R21AG049137].
Conflict of interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Aguzzi, A., and O'Connor, T. (2010). Protein aggregation diseases: Pathogenicity and therapeutic perspectives. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 9 (3), 237–248. doi:10.1038/nrd3050
Ahmed, M., Davis, J., Aucoin, D., Sato, T., Ahuja, S., Aimoto, S., et al. (2010). Structural conversion of neurotoxic amyloid-beta(1-42) oligomers to fibrils. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 17 (5), 561–567. doi:10.1038/nsmb.1799
Atsmon-Raz, Y., and Miller, Y. (2016). Non-Amyloid-β component of human α-synuclein oligomers induces formation of new Aβ oligomers: Insight into the mechanisms that link Parkinson's and alzheimer's diseases. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 7 (1), 46–55. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.5b00204
Bachhuber, T., Katzmarski, N., McCarter, J. F., Loreth, D., Tahirovic, S., Kamp, F., et al. (2015). Inhibition of amyloid-beta plaque formation by alpha-synuclein. Nat. Med. 21 (7), 802–807. doi:10.1038/nm.3885
Bassil, F., Brown, H. J., Pattabhiraman, S., Iwasyk, J. E., Maghames, C. M., Meymand, E. S., et al. (2020). Amyloid-beta (Aβ) plaques promote seeding and spreading of alpha-synuclein and tau in a mouse model of Lewy body disorders with Aβ pathology. Neuron 105 (2), 260–275. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2019.10.010
Bloom, G. S. (2014). Amyloid-beta and tau: The trigger and bullet in alzheimer disease pathogenesis. JAMA Neurol. 71 (4), 505–508. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2013.5847
Bluhm, A., Schrempel, S., Schilling, S., von Horsten, S., Schulze, A., Rossner, S., et al. (2022). Immunohistochemical demonstration of the pGlu79 alpha-synuclein fragment in alzheimer's disease and its Tg2576 mouse model. Biomolecules 12 (7), 1006. doi:10.3390/biom12071006
Bolognesi, B., Kumita, J. R., Barros, T. P., Esbjorner, E. K., Luheshi, L. M., Crowther, D. C., et al. (2010). ANS binding reveals common features of cytotoxic amyloid species. ACS Chem. Biol. 5 (8), 735–740. doi:10.1021/cb1001203
Breydo, L., and Uversky, V. N. (2015). Structural, morphological, and functional diversity of amyloid oligomers. FEBS Lett. 589, 2640–2648. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2015.07.013
Buee, L., Bussiere, T., Buee-Scherrer, V., Delacourte, A., and Hof, P. R. (2000). Tau protein isoforms, phosphorylation and role in neurodegenerative disorders. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 33 (1), 95–130. doi:10.1016/s0165-0173(00)00019-9
Candreva, J., Chau, E., Rice, M. E., and Kim, J. R. (2020). Interactions between soluble species of beta-amyloid and alpha-synuclein promote oligomerization while inhibiting fibrillization. Biochemistry 59 (4), 425–435. doi:10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00655
Casali, B. T., and Landreth, G. E. (2016). Aβ extraction from murine brain homogenates. Bio Protoc. 6 (8), e1787. doi:10.21769/BioProtoc.1787
Chau, E., and Kim, J. R. (2022). α-synuclein-assisted oligomerization of β-amyloid (1-42). Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 717, 109120. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2022.109120
Chen, S. W., Drakulic, S., Deas, E., Ouberai, M., Aprile, F. A., Arranz, R., et al. (2015). Structural characterization of toxic oligomers that are kinetically trapped during alpha-synuclein fibril formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 112 (16), E1994–E2003. doi:10.1073/pnas.1421204112
Chinta, S. J., Mallajosyula, J. K., Rane, A., and Andersen, J. K. (2010). Mitochondrial alpha-synuclein accumulation impairs complex I function in dopaminergic neurons and results in increased mitophagy in vivo. Neurosci. Lett. 486 (3), 235–239. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2010.09.061
Clinton, L. K., Blurton-Jones, M., Myczek, K., Trojanowski, J. Q., and LaFerla, F. M. (2010). Synergistic interactions between abeta, tau, and alpha-synuclein: Acceleration of neuropathology and cognitive decline. J. Neurosci. 30 (21), 7281–7289. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0490-10.2010
Couzin-Frankel, J., and Piller, C. (2022). Alzheimer's drug stirs excitement-and concerns. Science 378 (6624), 1030–1031. doi:10.1126/science.adg1899
Cremades, N., Cohen, S. I., Deas, E., Abramov, A. Y., Chen, A. Y., Orte, A., et al. (2012). Direct observation of the interconversion of normal and toxic forms of alpha-synuclein. Cell 149 (5), 1048–1059. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.037
Dallaire-Theroux, C., Callahan, B. L., Potvin, O., Saikali, S., and Duchesne, S. (2017). Radiological-pathological correlation in alzheimer's disease: Systematic review of antemortem magnetic resonance imaging findings. J. Alzheimers Dis. 57 (2), 575–601. doi:10.3233/JAD-161028
Danzer, K. M., Haasen, D., Karow, A. R., Moussaud, S., Habeck, M., Giese, A., et al. (2007). Different species of alpha-synuclein oligomers induce calcium influx and seeding. J. Neurosci. 27 (34), 9220–9232. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2617-07.2007
Dasari, A. K. R., Kayed, R., Wi, S., and Lim, K. H. (2019). Tau interacts with the C-terminal region of alpha-synuclein, promoting formation of toxic aggregates with distinct molecular conformations. Biochemistry 58 (25), 2814–2821. doi:10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00215
Dhakal, S., Robang, A. S., Bhatt, N., Puangmalai, N., Fung, L., Kayed, R., et al. (2022). Distinct neurotoxic TDP-43 fibril polymorphs are generated by heterotypic interactions with alpha-Synuclein. J. Biol. Chem. 298, 102498. doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102498
Dhakal, S., Saha, J., Wyant, C. E., and Rangachari, V. (2021). αS oligomers generated from interactions with a polyunsaturated fatty acid and a dopamine metabolite differentially interact with Aβ to enhance neurotoxicity. Acs Chem. Neurosci. 12 (21), 4153–4161. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.1c00530
Drummond, E., Nayak, S., Faustin, A., Pires, G., Hickman, R. A., Askenazi, M., et al. (2017). Proteomic differences in amyloid plaques in rapidly progressive and sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 133 (6), 933–954. doi:10.1007/s00401-017-1691-0
Eliezer, D., Kutluay, E., Bussell, R., and Browne, G. (2001). Conformational properties of alpha-synuclein in its free and lipid-associated states. J. Mol. Biol. 307 (4), 1061–1073. doi:10.1006/jmbi.2001.4538
Frost, B., Jacks, R. L., and Diamond, M. I. (2009). Propagation of tau misfolding from the outside to the inside of a cell. J. Biol. Chem. 284 (19), 12845–12852. doi:10.1074/jbc.M808759200
Gao, Y., Guo, C., Watzlawik, J. O., Randolph, P. S., Lee, E. J., Huang, D., et al. (2020). Out-of-Register parallel β-sheets and antiparallel β-sheets coexist in 150-kDa oligomers formed by amyloid-β(1-42). J. Mol. Biol. 432 (16), 4388–4407. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2020.05.018
Ghag, G., Bhatt, N., Cantu, D. V., Guerrero-Munoz, M. J., Ellsworth, A., Sengupta, U., et al. (2018). Soluble tau aggregates, not large fibrils, are the toxic species that display seeding and cross-seeding behavior. Protein Sci. 27 (11), 1901–1909. doi:10.1002/pro.3499
Giasson, B. I., Forman, M. S., Higuchi, M., Golbe, L. I., Graves, C. L., Kotzbauer, P. T., et al. (2003). Initiation and synergistic fibrillization of tau and alpha-synuclein. Science 300 (5619), 636–640. doi:10.1126/science.1082324
Giasson, B. I., Murray, I. V., Trojanowski, J. Q., and Lee, V. M. (2001). A hydrophobic stretch of 12 amino acid residues in the middle of alpha-synuclein is essential for filament assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 276 (4), 2380–2386. doi:10.1074/jbc.M008919200
Giehm, L., Svergun, D. I., Otzen, D. E., and Vestergaard, B. (2011). Low-resolution structure of a vesicle disrupting α-synuclein oligomer that accumulates during fibrillation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 108, 3246–3251. doi:10.1073/pnas.1013225108
Gotz, J., Chen, F., van Dorpe, J., and Nitsch, R. M. (2001). Formation of neurofibrillary tangles in P301l tau transgenic mice induced by Abeta 42 fibrils. Science 293 (5534), 1491–1495. doi:10.1126/science.1062097
Gyparaki, M. T., Arab, A., Sorokina, E. M., Santiago-Ruiz, A. N., Bohrer, C. H., Xiao, J., et al. (2021). Tau forms oligomeric complexes on microtubules that are distinct from tau aggregates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 118 (19), e2021461118. doi:10.1073/pnas.2021461118
Hamilton, R. L. (2000). Lewy bodies in alzheimer's disease: A neuropathological review of 145 cases using α-synuclein immunohistochemistry. Brain Pathol. 10 (3), 378–384. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3639.2000.tb00269.x
Harper, J. D., Wong, S. S., Lieber, C. M., and Lansbury, P. T. (1997). Observation of metastable Abeta amyloid protofibrils by atomic force microscopy. Chem. Biol. 4 (2), 119–125. doi:10.1016/s1074-5521(97)90255-6
Hashimoto, M., Rockenstein, E., Crews, L., and Masliah, E. (2003) Role of protein aggregation in mitochondrial dysfunction and neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. Neuromolecular Med. 4 (1-2), 21–36. doi:10.1385/Nmm:4:1-2:21
He, Y., Wei, M., Wu, Y., Qin, H., Li, W., Ma, X., et al. (2019). Amyloid beta oligomers suppress excitatory transmitter release via presynaptic depletion of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate. Nat. Commun. 10 (1), 1193. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-09114-z
Heyman, A., Fillenbaum, G. G., Gearing, M., Mirra, S. S., Welsh-Bohmer, K. A., Peterson, B., et al. (1999). Comparison of Lewy body variant of alzheimer's disease with pure alzheimer's disease: Consortium to establish a registry for alzheimer's disease, Part XIX. Neurology 52 (9), 1839–1844. doi:10.1212/wnl.52.9.1839
Hijaz, B. A., and Volpicelli-Daley, L. A. (2020). Initiation and propagation of alpha-synuclein aggregation in the nervous system. Mol. Neurodegener. 15 (1), 19. doi:10.1186/s13024-020-00368-6
Hu, Y., Zheng, H., Su, B., Hernandez, M., and Kim, J. R. (2012). Modulation of beta-amyloid aggregation by engineering the sequence connecting beta-strand forming domains. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1824 (10), 1069–1079. doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2012.06.004
Irwin, D. J., Lee, V. M., and Trojanowski, J. Q. (2013). Parkinson's disease dementia: Convergence of alpha-synuclein, tau and amyloid-beta pathologies. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 14 (9), 626–636. doi:10.1038/nrn3549
Jin, M., Shepardson, N., Yang, T., Chen, G., Walsh, D., and Selkoe, D. J. (2011). Soluble amyloid beta-protein dimers isolated from Alzheimer cortex directly induce Tau hyperphosphorylation and neuritic degeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 108 (14), 5819–5824. doi:10.1073/pnas.1017033108
Jouanne, M., Rault, S., and Voisin-Chiret, A. S. (2017). Tau protein aggregation in Alzheimer's disease: An attractive target for the development of novel therapeutic agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 139, 153–167. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.07.070
Kayed, R., Dettmer, U., and Lesne, S. E. (2020). Soluble endogenous oligomeric alpha-synuclein species in neurodegenerative diseases: Expression, spreading, and cross-talk. J. Park. Dis. 10 (3), 791–818. doi:10.3233/JPD-201965
Kayed, R., Head, E., Thompson, J. L., McIntire, T. M., Milton, S. C., Cotman, C. W., et al. (2003). Common structure of soluble amyloid oligomers implies common mechanism of pathogenesis. Science 300 (5618), 486–489. doi:10.1126/science.1079469
Khan, S. S., LaCroix, M., Boyle, G., Sherman, M. A., Brown, J. L., Amar, F., et al. (2018). Bidirectional modulation of Alzheimer phenotype by alpha-synuclein in mice and primary neurons. Acta Neuropathol. 136 (4), 589–605. doi:10.1007/s00401-018-1886-z
Koppen, J., Schulze, A., Machner, L., Wermann, M., Eichentopf, R., Guthardt, M., et al. (2020). Amyloid-beta peptides trigger aggregation of alpha-synuclein in vitro. Molecules 25 (3), 580. doi:10.3390/molecules25030580
Kraybill, M. L., Larson, E. B., Tsuang, D. W., Teri, L., McCormick, W. C., Bowen, J. D., et al. (2005). Cognitive differences in dementia patients with autopsy-verified AD, Lewy body pathology, or both. Neurology 64 (12), 2069–2073. doi:10.1212/01.WNL.0000165987.89198.65
LaFerla, F. M., Green, K. N., and Oddo, S. (2007). Intracellular amyloid-beta in Alzheimer's disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 8 (7), 499–509. doi:10.1038/nrn2168
Larson, M. E., Greimel, S. J., Amar, F., LaCroix, M., Boyle, G., Sherman, M. A., et al. (2017). Selective lowering of synapsins induced by oligomeric alpha-synuclein exacerbates memory deficits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 114 (23), E4648–E4657. doi:10.1073/pnas.1704698114
Lasagna-Reeves, C. A., Castillo-Carranza, D. L., Guerrero-Muoz, M. J., Jackson, G. R., and Kayed, R. (2010). Preparation and characterization of neurotoxic tau oligomers. Biochemistry 49 (47), 10039–10041. doi:10.1021/bi1016233
Lasagna-Reeves, C. A., Glabe, C. G., and Kayed, R. (2011). Amyloid-beta annular protofibrils evade fibrillar fate in Alzheimer disease brain. J. Biol. Chem. 286 (25), 22122–22130. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.236257
Lee, H. J., Patel, S., and Lee, S. J. (2005). Intravesicular localization and exocytosis of alpha-synuclein and its aggregates. J. Neurosci. 25 (25), 6016–6024. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0692-05.2005
Lloyd, G. M., Dhillon, J. S., Gorion, K. M., Riffe, C., Fromholt, S. E., Xia, Y., et al. (2021). Collusion of α-Synuclein and Aβ aggravating co-morbidities in a novel prion-type mouse model. Mol. Neurodegener. 16 (1), 63. doi:10.1186/s13024-021-00486-9
Luhrs, T., Ritter, C., Adrian, M., Riek-Loher, D., Bohrmann, B., Dobeli, H., et al. (2005). 3D structure of Alzheimer's amyloid-beta(1-42) fibrils. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 102 (48), 17342–17347. doi:10.1073/pnas.0506723102
Mandal, P. K., Pettegrew, J. W., Masliah, E., Hamilton, R. L., and Mandal, R. (2006). Interaction between abeta peptide and alpha synuclein: Molecular mechanisms in overlapping pathology of alzheimer's and Parkinson's in dementia with Lewy body disease. Neurochem. Res. 31 (9), 1153–1162. doi:10.1007/s11064-006-9140-9
Masliah, E., Rockenstein, E., Veinbergs, I., Sagara, Y., Mallory, M., Hashimoto, M., et al. (2001). beta-amyloid peptides enhance alpha-synuclein accumulation and neuronal deficits in a transgenic mouse model linking Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 98 (21), 12245–12250. doi:10.1073/pnas.211412398
McAllister, B. B., Lacoursiere, S. G., Sutherland, R. J., and Mohajerani, M. H. (2020). Intracerebral seeding of amyloid-beta and tau pathology in mice: Factors underlying prion-like spreading and comparisons with alpha-synuclein. Neurosci. Biobehav Rev. 112, 1–27. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2020.01.026
Murakami, K., and Ono, K. (2022). Interactions of amyloid coaggregates with biomolecules and its relevance to neurodegeneration. FASEB J. 36 (9), e22493. doi:10.1096/fj.202200235R
Nag, S., Sarkar, B., Bandyopadhyay, A., Sahoo, B., Sreenivasan, V. K., Kombrabail, M., et al. (2011). Nature of the amyloid-beta monomer and the monomer-oligomer equilibrium. J. Biol. Chem. 286 (16), 13827–13833. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.199885
Nguyen, P. H., Ramamoorthy, A., Sahoo, B. R., Zheng, J., Faller, P., Straub, J. E., et al. (2021). Amyloid oligomers: A joint experimental/computational perspective on alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, type II diabetes, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Chem. Rev. 121 (4), 2545–2647. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c01122
Oddo, S., Caccamo, A., Shepherd, J. D., Murphy, M. P., Golde, T. E., Kayed, R., et al. (2003). Triple-transgenic model of alzheimer's disease with plaques and tangles: Intracellular abeta and synaptic dysfunction. Neuron 39 (3), 409–421. doi:10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00434-3
Ono, K., Condron, M. M., and Teplow, D. B. (2009). Structure-neurotoxicity relationships of amyloid beta-protein oligomers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 106 (35), 14745–14750. doi:10.1073/pnas.0905127106
Ono, K., Takahashi, R., Ikeda, T., and Yamada, M. (2012). Cross-seeding effects of amyloid beta-protein and alpha-synuclein. J. Neurochem. 122 (5), 883–890. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2012.07847.x
Owen, M. C., Gnutt, D., Gao, M., Warmlander, S., Jarvet, J., Graslund, A., et al. (2019). Effects of in vivo conditions on amyloid aggregation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 48 (14), 3946–3996. doi:10.1039/c8cs00034d
Paolini Paoletti, F., Gaetani, L., and Parnetti, L. (2020). The challenge of disease-modifying therapies in Parkinson's disease: Role of CSF biomarkers. Biomolecules 10 (2), 335. doi:10.3390/biom10020335
Peng, C., Gathagan, R. J., Covell, D. J., Medellin, C., Stieber, A., Robinson, J. L., et al. (2018). Cellular milieu imparts distinct pathological alpha-synuclein strains in alpha-synucleinopathies. Nature 557 (7706), 558–563. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0104-4
Petkova, A. T., Ishii, Y., Balbach, J. J., Antzutkin, O. N., Leapman, R. D., Delaglio, F., et al. (2002). A structural model for Alzheimer's beta -amyloid fibrils based on experimental constraints from solid state NMR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 99 (26), 16742–16747. doi:10.1073/pnas.262663499
Potapov, A., Yau, W. M., Ghirlando, R., Thurber, K. R., and Tycko, R. (2015). Successive stages of amyloid-beta self-assembly characterized by solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance with dynamic nuclear polarization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137 (25), 8294–8307. doi:10.1021/jacs.5b04843
Puangmalai, N., Bhatt, N., Montalbano, M., Sengupta, U., Gaikwad, S., Ventura, F., et al. (2020). Internalization mechanisms of brain-derived tau oligomers from patients with Alzheimer's disease, progressive supranuclear palsy and dementia with Lewy bodies. Cell Death Dis. 11 (5), 314. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-2503-3
Qiu, T., Liu, Q., Chen, Y. X., Zhao, Y. F., and Li, Y. M. (2015). Aβ42 and Aβ40: Similarities and differences. J. Pept. Sci. 21 (7), 522–529. doi:10.1002/psc.2789
Ren, B., Zhang, Y., Zhang, M., Liu, Y., Zhang, D., Gong, X., et al. (2019). Fundamentals of cross-seeding of amyloid proteins: An introduction. J. Mater Chem. B 7 (46), 7267–7282. doi:10.1039/c9tb01871a
Ren, Y., and Sahara, N. (2013). Characteristics of tau oligomers. Front. Neurol. 4, 102. doi:10.3389/fneur.2013.00102
Roberts, H. L., Schneider, B. L., and Brown, D. R. (2017). α-Synuclein increases β-amyloid secretion by promoting β-/γ-secretase processing of APP. PLoS One 12 (2), e0171925. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0171925
Sevigny, J., Chiao, P., Bussiere, T., Weinreb, P. H., Williams, L., Maier, M., et al. (2016). The antibody aducanumab reduces Aβ plaques in Alzheimer's disease. Nature 537 (7618), 50–56. doi:10.1038/nature19323
Spires, T. L., Orne, J. D., SantaCruz, K., Pitstick, R., Carlson, G. A., Ashe, K. H., et al. (2006). Region-specific dissociation of neuronal loss and neurofibrillary pathology in a mouse model of tauopathy. Am. J. Pathol. 168 (5), 1598–1607. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2006.050840
Surmeier, D. J., Obeso, J. A., and Halliday, G. M. (2017). Selective neuronal vulnerability in Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 18 (2), 101–113. doi:10.1038/nrn.2016.178
Tsigelny, I. F., Crews, L., Desplats, P., Shaked, G. M., Sharikov, Y., Mizuno, H., et al. (2008). Mechanisms of hybrid oligomer formation in the pathogenesis of combined Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. PLoS One 3 (9), e3135. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0003135
Twohig, D., and Nielsen, H. M. (2019). α-synuclein in the pathophysiology of Alzheimer's disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 14 (1), 23. doi:10.1186/s13024-019-0320-x
van Dyck, C. H., Swanson, C. J., Aisen, P., Bateman, R. J., Chen, C., Gee, M., et al. (2023). Lecanemab in early alzheimer's disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 388 (1), 9–21. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2212948
Vasconcelos, B., Stancu, I. C., Buist, A., Bird, M., Wang, P., Vanoosthuyse, A., et al. (2016). Heterotypic seeding of Tau fibrillization by pre-aggregated Abeta provides potent seeds for prion-like seeding and propagation of Tau-pathology in vivo. Acta Neuropathol. 131 (4), 549–569. doi:10.1007/s00401-015-1525-x
Vilar, M., Chou, H. T., Luhrs, T., Maji, S. K., Riek-Loher, D., Verel, R., et al. (2008). The fold of alpha-synuclein fibrils. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105 (25), 8637–8642. doi:10.1073/pnas.0712179105
Visanji, N. P., Lang, A. E., and Kovacs, G. G. (2019). Beyond the synucleinopathies: Alpha synuclein as a driving force in neurodegenerative comorbidities. Transl. Neurodegener. 8, 28. doi:10.1186/s40035-019-0172-x
Walsh, S., Merrick, R., Milne, R., and Brayne, C. (2021). Aducanumab for Alzheimer's disease? BMJ 374, n1682. doi:10.1136/bmj.n1682
Wilhelm, B. G., Mandad, S., Truckenbrodt, S., Krohnert, K., Schafer, C., Rammner, B., et al. (2014). Composition of isolated synaptic boutons reveals the amounts of vesicle trafficking proteins. Science 344 (6187), 1023–1028. doi:10.1126/science.1252884
Winner, B., Jappelli, R., Maji, S. K., Desplats, P. A., Boyer, L., Aigner, S., et al. (2011). In vivo demonstration that alpha-synuclein oligomers are toxic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 108 (10), 4194–4199. doi:10.1073/pnas.1100976108
Keywords: alpha-synuclein, aggregation, beta-amyloid, oligomer, protein-protein interaction
Citation: Kim JR (2023) Oligomerization by co-assembly of β-amyloid and α-synuclein. Front. Mol. Biosci. 10:1153839. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1153839
Received: 30 January 2023; Accepted: 07 March 2023;
Published: 20 March 2023.
Edited by:
Neville Vassallo, University of Malta, MaltaCopyright © 2023 Kim. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jin Ryoun Kim, amluLmtpbUBueXUuZWR1
 Jin Ryoun Kim
Jin Ryoun Kim