- 1School of Food Science and Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
- 2Guangdong Key Laboratory of Food Intelligent Manufacturing, Foshan University, Foshan, Guangdong, China
- 3Overseas Expertise Introduction Centre for Discipline Innovation of Food Nutrition and Human Health (111 Centre), Guangzhou, China
- 4Department of Food Science and Technology, Khwaja Fareed University of Engineering and Information Technology, Punjab, Pakistan
- 5Food Technology Department, Faculty of Agriculture, Benha University, Qalyubia, Egypt
- 6Department of Genetics and Genetic Engineering, Faculty of Agriculture, Benha University, Qalyubia, Egypt
A Corrigendum on
Phenotype-based drug screening: An in vivo strategy to classify and identify the chemical compounds modulating zebrafish M-cell regeneration
by Kumari A, Zeng X-A, Rahaman A, Farooq MA, Huang Y, Alee M, Yao R, Ali M, Khalifa I and Badr O (2022). Front. Mol. Biosci. 9:984461. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.984461
In the published article, there was an error in the legend for Tables 3, 4 as published. The corrected table legends appear below.
TABLE 3 Table representing binding affinity and inhibition constant for the interaction of four drugs with SOCS3.
TABLE 4 Table representing binding affinity and inhibition constant for the interaction of four drugs with PTEN.
In the published article, there was an error in Table 1 and Figure 3 as published. Table 1 and its caption were duplicated in Figure 3. The corrected Figure 3 and its caption appear below.
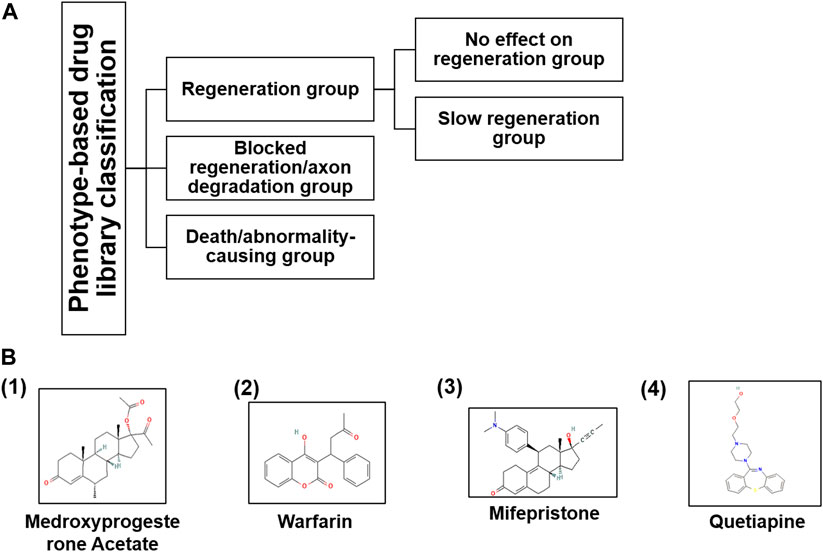
FIGURE 3. (A) Based on the phenotypic responses of M-cells upon drug treatment, we classified the entire library into three categories along with sub-categories and (B) their chemical structures taken from PubChem (nih.gov) database.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: phenotype drug screening (PDS), regeneration, zebrafish, axon, M-cell
Citation: Kumari A, Zeng X-A, Rahaman A, Farooq MA, Huang Y, Alee M, Yao R, Ali M, Khalifa I and Badr O (2023) Corrigendum: Phenotype-based drug screening: An in vivo strategy to classify and identify the chemical compounds modulating zebrafish M-cell regeneration. Front. Mol. Biosci. 9:1081922. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1081922
Received: 27 October 2022; Accepted: 28 December 2022;
Published: 16 January 2023.
Approved by:
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2023 Kumari, Zeng, Rahaman, Farooq, Huang, Alee, Yao, Ali, Khalifa and Badr. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xin-An Zeng, eGF6ZW5nQHNjdXQuZWR1LmNu; Abdul Rahaman, cmFoYW1hbl9rbmFiZHVsQHltYWlsLmNvbQ==; Ibrahim Khalifa, aWJyYWhpZW0ua2hhbGlmYUBmYWdyLmJ1LmVkdS5lZw==
 Ankita Kumari
Ankita Kumari Xin-An Zeng
Xin-An Zeng Abdul Rahaman
Abdul Rahaman Muhammad Adil Farooq
Muhammad Adil Farooq Yanyan Huang
Yanyan Huang Mahafooj Alee
Mahafooj Alee Runyu Yao1,3
Runyu Yao1,3 Murtaza Ali
Murtaza Ali Ibrahim Khalifa
Ibrahim Khalifa Omnia Badr
Omnia Badr