
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Microbiomes, 09 April 2025
Sec. Host and Microbe Associations
Volume 4 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/frmbi.2025.1567462
Alfalfa forms and rumen degradable starch (RDS) levels in diets can profoundly affect growth performance and rumen fermentation patterns, this influence may result in variations in rumen microbiota. However, the effects of RDS levels on methanogenic and fungal communities in alfalfa hay (AH) or alfalfa silage (AS) diets, and the interaction between methanogens and fungi with growth performance and rumen fermentation patterns, remain unknown. In this study, a 2 × 2 factorial design resulted in four diets: two alfalfa forms (AH and AS) and two RDS levels (LR: 14.85% DM RDS; and HR: 20.21% DM RDS). We used 32 female Suffolk sheep for the experiment. On day 75 (including a 15-day transition period and a 60-day trial period), rumen content was collected after slaughter to examine the ruminal methanogens and fungi. The AHHR diet reduced the methanogen Chao 1 index compared to the AS diets (P < 0.05), and the Shannon index was lower than in the ASLR diet (P < 0.05). The fungi Chao 1 index was higher in the AH diets than in the ASHR diet (P < 0.05), and the fungi Shannon index was higher in the LR diets than in the HR diets (P < 0.05). The relative abundance of Aspergillus in the AHLR diet was significantly higher than in the AS diets (P < 0.01), and the relative abundance of Occultifur and Meyerozyma were decreased in the AH diets than in the AS diets (P < 0.05). The LEfSe analysis showed that Methanobrevibacter_sp_YE315 and Methanobrevibacter_sp_AbM4 were enriched in the ASLR diet, while Methanobrevibacter_millerae was enriched in the ASHR diet. For the fungal biomarkers, the AHLR diet included Aspergillus, Metschnikowia, and unclassified_f:Stachybotryaceae; the AHHR diet included stachybotrys, Stemphylium, and Cystobasidium; the ASLR diet included unclassified_k:Fungi, Trichothecium, and Psathyrella; and the ASHR diet included Alfaria. The correlation analysis results showed the relative abundance of Methanobrevibacter, Methanoculleus, Penicillium, Cladosporium, and Exophiala and the concentrations of isobutyrate and isovalerate, which may provide deeper insights into the previously observed differences.
Alfalfa is an important roughage for ruminant feed due to its excellent amino acid profile and low lignocellulose content. Haymaking and ensiling are the most frequent forms of processing alfalfa (Wayne et al., 2020; Radovic et al., 2009; Sun et al., 2023). Ensiling is an anaerobic microbial-based fermentation process dominated by lactic acid bacteria, which produce lactic acid and volatile fatty acids (VFAs) necessary for pH decline and the inhibition of harmful microorganisms (Jiang et al., 2020). Furthermore, environmental conditions that develop during ensiling favor the proliferation of the phylum Firmicutes (Yang et al., 2020). This leads to variations in the microbiota of alfalfa silages (AS) compared to alfalfa hay (AH), and these changes further alter the microbial community in the rumen. For instance, silage treatment disrupts the structure of plant lignocellulosic materials through anaerobic fungi. The abundance of cellulolytic microorganisms was increased after feeding a fermented diet (He et al., 2023), and the gastrointestinal microbial community undergoes changes (Xu et al., 2023). Our previous studies have shown that AS diets increased amino acid degradation and the abundance of associated bacteria in the rumen of sheep (Guo et al., 2025), implying that AS had the potential to alter rumen microbiota.
Livestock contributes approximately 14.5% of global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, with enteric methane (CH4) emissions accounting for up to 40% of livestock’s GHG emissions (Eugène et al., 2021). CH4 is one of the fermentation products produced by archaea utilizing carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrogen (H2), accounting for approximately 2%–12% of the host’s ingested feed energy lost. Nearly all the archaea identified are methanogens known to be resident in the rumen (Johnson and Johnson, 1995), and the abundance of methanogens has a positive correlation with methane emissions (Wallace et al., 2015; Niu et al., 2020). Current research shows that the effect of feeding AH or AS on ruminal methane emissions in ruminants appears to be slight. Gislon et al. (2020) demonstrated that methane production per unit of feed intake and milk production was not different in cows fed AH or AS and in the case of dairy goats (Fernández et al., 2019). In vitro tests have found similar results. Getachew et al. (2004) found no difference in gas production between AH and AS using in vitro techniques. Xue et al. (2020) evaluated in vitro rumen methane production responses to different forage ratios of AH and AS. The results indicate that methane production at 48 h was greater for silages compared to hays. However, the above experiments did not determine the methanogens.
Rumen fungi are considered to play key roles in the degradation of plant lignocellulosic materials. The average abundances indicate that fungi represent 10% to 20% of the rumen microbiota (Elekwachi et al., 2017). After ensiling, most aerobic fungi genera were killed and/or inhibited, and only a few anaerobic fungi genera are present along with lactic acid bacteria to secrete extracellular enzymes to degrade cell walls (Jiang et al., 2020; Jia et al., 2024). Microbial-rich silage feeding is generally considered to alter the rumen microbial community (Akin et al., 1988). Although many studies have examined the effects on rumen fermentation parameters (Hristov et al., 2001; Beauchemin et al., 1997) and bacterial community (Guo et al., 2025) in AH or AS diets, the effects on fungi were unknown.
Starch is a major component of cereals and the primary energy source for the fattening of ruminants. Corn and wheat have been important diet sources for ruminant and non-ruminant animals due to their high production yields and high starch content (Li et al., 2019; Ma et al., 2022). Wheat, a cereal with a high rumen degradable starch (RDS) content, is commonly included in the diets of Australian dairy cows (Moate et al., 2017; Shen et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2024). The starch degradation rate of wheat is 24.8% higher than that of corn (Ferraretto et al., 2013). Studies have shown that increasing dietary RDS improves feed efficiency (Jin et al., 2023; Karim et al., 2008), optimizes the digestion of carbohydrates and protein (Moate et al., 2017; Gao et al., 2024), reduces methane emissions (Savin et al., 2022), and increases protein flow to the small intestine (Zhang et al., 2024; Plascencia et al., 2018). In addition, increased dietary RDS alters the diversity and abundance of rumen bacteria (Jiang et al., 2020; Guo et al., 2025a; Li et al., 2024). However, analyses of methanogens and fungi were still lacking in these experiments. Methanogens and fungi have a certain symbiotic relationship, and fungal degradation fiber provides an H2 substrate for methanogens, which promotes their reproduction. Therefore, a joint analysis of methanogens and fungi may provide a better understanding of the effects of phenotypic variables. We hypothesized that dietary alfalfa forms and RDS levels will result in different rumen methanogens and fungi communities in sheep, and that these microbial differences will explain the previously observed differences in growth performance and rumen fermentation.
All animal procedures were conducted according to protocols approved by the Animal Welfare and Ethics Committee of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University (NND2024053). This study was carried out at the Experimental Farm of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, located in Tumurt Left Banner, Hohhot, China. As part of a previous study (Guo et al., 2025a), a total of 32 female Suffolk sheep with similar weights (initial weight 27.28 ± 3.4 kg) and aged 3 months were randomly assigned to four dietary treatments in a completely randomized design (n = 8 per treatment). Four diets were designed with 2 × 2 factors: two alfalfa forms (AH: alfalfa hay; AS: alfalfa silage) and two RDS levels (LR: 14.85%DM RDS; and HR: 20.21%DM RDS). Alfalfa hay (AH) and alfalfa silage (AS) were determined based on the results of Ainslie et al. (2014). The RDS level was determined based on the results of Guo et al. (2025b). The treatment diets were formulated to be isocaloric and isonitrogenous and met the NYT816-2021 recommendations (Tables 1, 2). Sheep were housed in an outdoor rearing system in individual pens (1.0 × 1.0 m2) bedded with sand. The experimental period was 75 days, including a 15-day transition period and a 60-day trial period. Sheep were fed twice daily at 09:00 and 16:00 as Total Mixed Ration (TMR) for ad libitum intake. Rumen contents were collected after slaughter and stored at −80°C to examine the ruminal methanogens and fungi.
Metagenomic DNA was extracted from each rumen sample using the E.Z.N.A.® soil DNA Kit (Omega Biotek, Norcross, GA, USA), following the manufacturer’s instructions. The hypervariable V4 region of the methanogens’ 16S rRNA gene and the fungal internal transcribed spacer were amplified by PCR using a T100 Thermal Cycler. The methanogens primers used in the current study were MLfF-F: 5´-GGTGGTGTMGGATTCACACARTAYGCWACAGC-3´ and MLfF-R:5´-TTCATTGCRTAGTTWGGRTAGTT-3´. The fungal primers used in the current study were ITS1-1F-F: 5′-CTTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA-3′ and ITS1-1F-R: 5′-GCTGCGTTCTTCATCGATGC-3′. The amplification system (20 μL) was as follows: 4 µL 5×FastPfu Buffer, 2 µL 2.5 mmol/L dNTPs, 0.4 µL forward primers (5 mmol/L), 0.8 µL reverse primers (5 mmol/L), 0.2 µL BSA, template DNA 10 ng, and make up ddH2O to 20 µL. The steps of PCR amplification were as described previously (Guo et al., 2025a). PCR products were recovered by gel extraction in AquaPōr LM low-melt agarose (National Diagnostics, Atlanta, GA) using the Zymoclean Gel DNA Recovery Kit (Zymo Research, Irvine, CA). After the constructed library was quantified by Qubit and real-time PCR, sequencing was performed using the Illumina NovaSeq 6,000 sequencing platform.
The amplicon sequences were quality-controlled and merged by FASTP (version 0.19.6) and FLASH (version 1.2.7), respectively. Briefly, amplicon sequence denoising, merging, and chimeric sequence removal were conducted as described previously (Li et al., 2024) using the DADA2 plugin at a 97% sequence similarity threshold in Uparse software. Bioinformatic analysis of the rumen methanogens and fungi was carried out using the Majorbio Cloud platform (https://cloud.majorbio.com, accessed on 28 September 2024). QIIME2 software (v.1.8.0) was used to assess alpha diversity measurements including Chao 1 and Shannon indices, with significant differences analyzed using the Wilcox rank sum test. QIIME2 software assessed beta diversity measurements including principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) based on Bray–Curtis dissimilarities and relative abundance, with significant differences analyzed using analysis of similarity (ANOSIM). The software Linear discriminant analysis Effect Size (LEfSe) (Version 1.0) was used to analyze the effects of different diet treatments of rumen methanogens and fungi. Only microbial communities’ linear discriminant analysis (LDA) score values greater than 3.0 were identified as specific microbiota unique to the diet treatments. Spearman’s rank correlation analyzed the relationship between the rumen methanogens and the top 10 fungi at the genus level, with a coefficient of > |0.4|, P < 0.05 considered significant. The rumen methanogens and fungal sequencing data of this study are available in the NCBI SRA database with the BioProject ID: PRJNA1236662.
The methanogen and fungi data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA using statistical analysis software SAS (Version 9.2, SAS Institute Inc. Cary, NC, USA). Duncan’s multiple range test (DMRT) was conducted to evaluate the differences among the treatments, along with the mixed model procedure in SAS. The model included alfalfa forms (AS: AH), RDS levels (LR: HR), and the two-way interaction between alfalfa forms and RDS levels, and was considered significant at P < 0.05 and extremely significant at P < 0.01. Data were presented as averages.
Methanogen relative abundance, fungal relative abundance, and the relationship between methanogens and fungi in relation to growth performance and rumen fermentation parameters were assessed using Spearman’s rank correlation, with a coefficient of > |0.4|, p < 0.05 considered significant.
For our methanogen alpha diversity analysis, the Chao 1 index was higher in the AS diets compared to the AHHR diet (P < 0.05). Similarly, the Shannon index was higher in the ASLR diet compared to the AHHR diet (P < 0.05) (Figures 1A, B). These results suggest that there were more lowly abundant methanogen genera in the AS diets and a co-occurrence of highly abundant methanogen genera in the ASLR diet. However, beta diversity analysis revealed that the Bray–Curtis dissimilarities in the methanogen communities were similar among the four diets (Figure 1C).
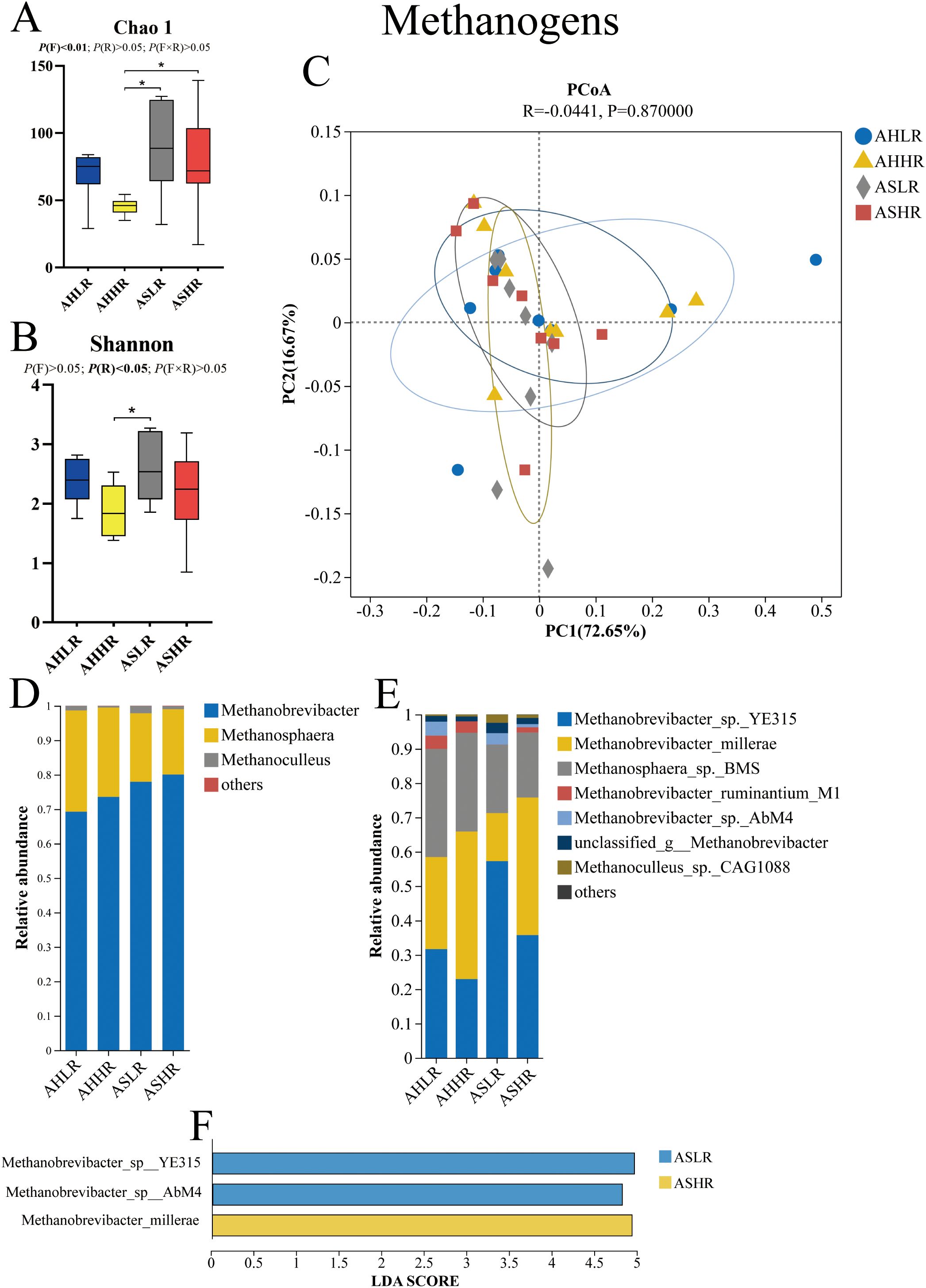
Figure 1. Dietary alfalfa forms and RDS levels altered methanogen communities in the rumen of sheep. (A) Chao 1 index of alpha diversity under genus level. (B) Shannon index of alpha diversity under genus level. (C) Principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) at the genus level. (D) Methanogens taxa averaged at the genus level. (E) Methanogen taxa averaged at the species level. (F) LEfSe analysis of methanogen at the species level for different treatments. AHLR, alfalfa hay and low (14.85% DM) RDS; AHHR, alfalfa hay and high (20.21% DM) RDS; ASLR, alfalfa silage and low (14.85% DM) RDS; ASHR, alfalfa silage and high (20.21% DM) RDS. * means a significant difference P < 0.05. P (F) = alfalfa hay versus alfalfa silage (AH vs. AS); P (R) = low (14.85% DM) RDS versus high (20.21% DM) RDS; P (F×R) = alfalfa forms by RDS levels interaction.
All methanogens were identified as belonging to the Euryarchaeota phylum, including three genera of Euryarchaeota present in all of the samples, with Methanobrevibacter being more prevalent (69.25%–80.05%) than Methanosphaera (18.96%–29.42%) and Methanoculleus (0.5%–2.11%). There was no significant difference in the relative abundance of these three genera among the four diets (P > 0.05) (Figure 1D; Table 3). At the species level, Methanobrevibacter_sp._YE315 (31.68%–57.25%), Methanobrevibacter_millerae (14.02%–26.78%), and Methanosphaera_sp._BMS (19.9%–35.77%) dominated the methanogen communities, accounting for at least 90% of the methanogen species present (Figure 1E). LEfSe analysis results showed that Methanobrevibacter_sp_YE315 and Methanobrevibacter_sp_AbM4 were enriched in the ASLR diet, while Methanobrevibacter_millerae was higher in the ASHR diet (Figure 1F). There was no enrichment of methanogen in AH diets.
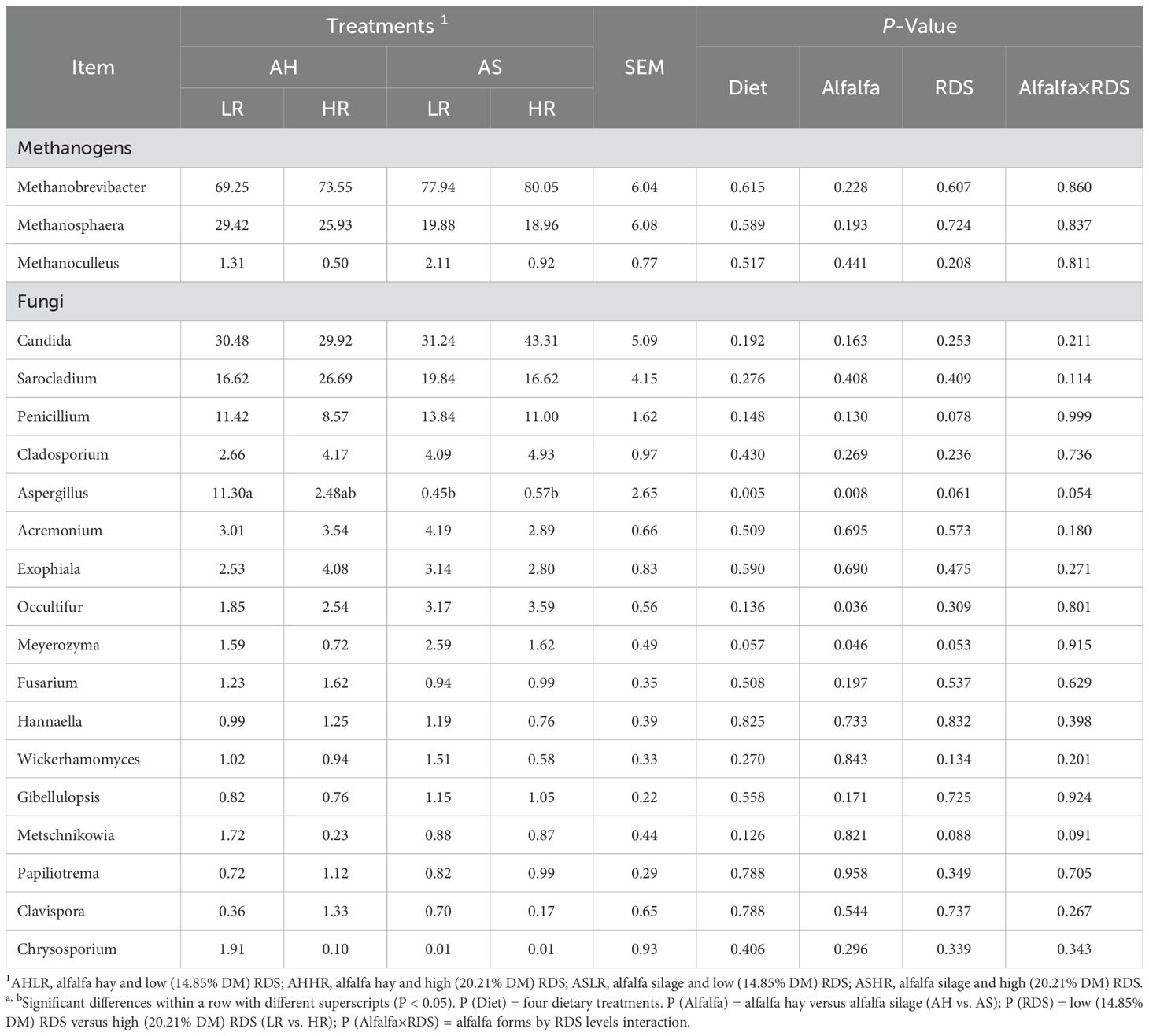
Table 3. Effect of dietary alfalfa forms and RDS levels on rumen relative abundance of methanogens and fungi at the genus level in sheep.
In our fungal alpha diversity analysis, the Chao 1 index was higher in the AH diets compared to the ASHR diet (P < 0.05). Additionally, the Shannon index was higher in the AHLR diet compared to the HR diets (P < 0.05). Furthermore, the Shannon index was also higher in the ASLR diet compared to the AHHR (P < 0.05) (Figures 2A, B). These results suggest that the AS diets contained a greater number of lowly abundant fungal genera compared to the ASHR diet, while the LR diets exhibited a higher diversity and co-occurrence of highly abundant fungal genera. However, the beta diversity analysis revealed that Bray–Curtis dissimilarities in the fungal community were similar among the four diets (Figure 2C).
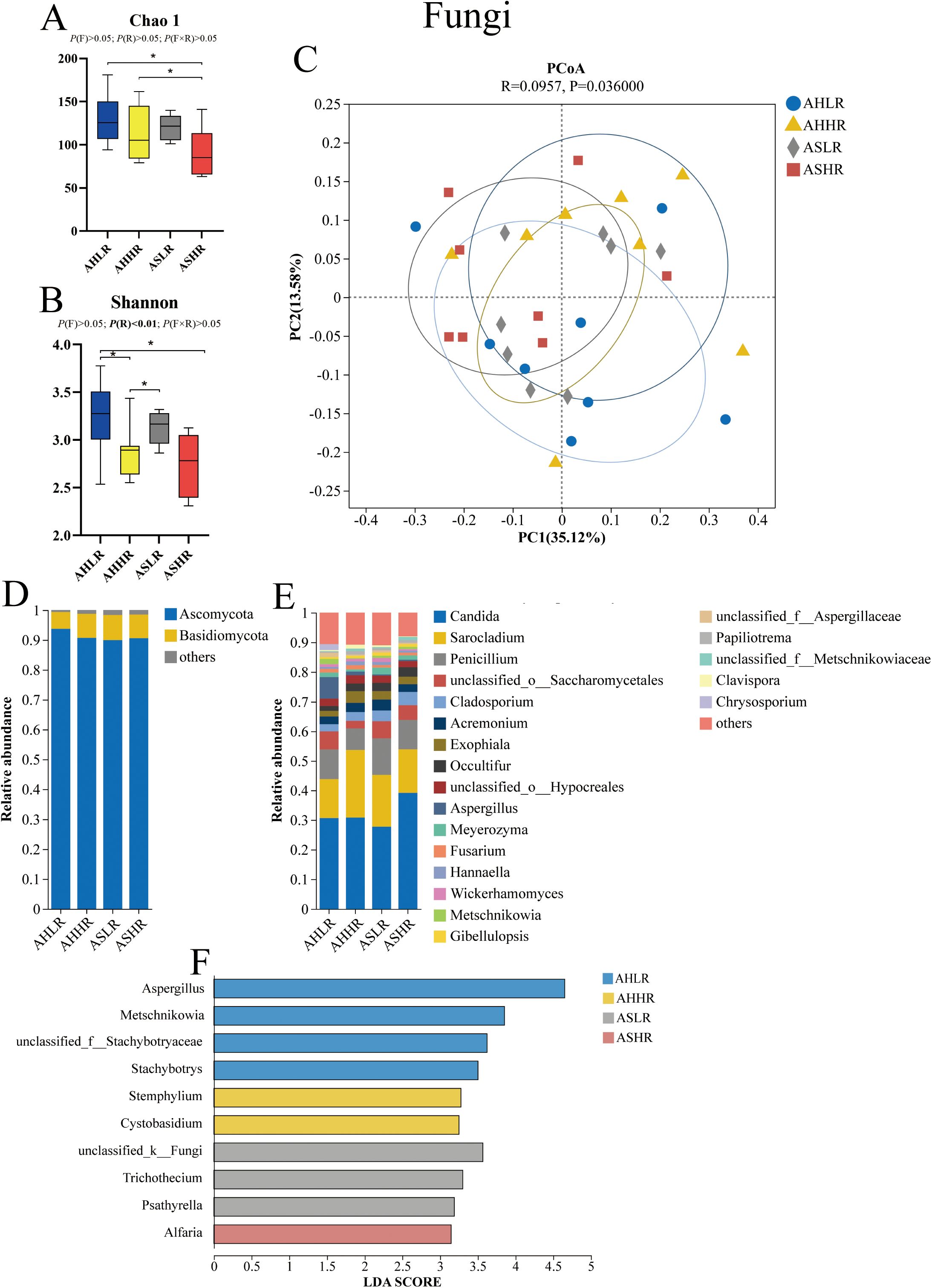
Figure 2. Dietary alfalfa forms and RDS levels altered rumen fungal communities in the rumen of sheep. (A) Chao 1 index of alpha diversity at the genus level. (B) Shannon index of alpha diversity at the genus level. (C) Principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) at the genus level. (D) Fungi taxa averaged at the phylum level. (E) Fungi taxa averaged at the genus level. (F) LEfSe analysis of fungi at the genus level for different treatments. AHLR, alfalfa hay and low (14.85% DM) RDS; AHHR, alfalfa hay and high (20.21% DM) RDS; ASLR, alfalfa silage and low (14.85% DM) RDS; ASHR, alfalfa silage and high (20.21% DM) RDS. * means a significant difference P < 0.05. P (F) = alfalfa hay versus alfalfa silage (AH vs. AS); P (R) = low (14.85% DM) RDS versus high (20.21% DM)RDS; P (F×R) = alfalfa forms by RDS levels interaction.
The Ascomycota (89.95%–93.73%) and Basidiomycota (5.63%–8.42%) were the dominant phyla of fungi across all diets. These included five genera: Candida (29.92%–43.31%), Sarocladium (16.62%–26.69%), Penicillium (8.57%–13.84%), Cladosporium (2.66%–4.93%), and Aspergillus (0.45%–11.30%), which accounted for at least 70% of the fungi genera present (Figures 2D, E). The relative abundance of Aspergillus was higher in the AHLR diet than in the AS diets (P < 0.01). In contrast, the relative abundance of Occultifur and Meyerozyma were decreased in the AH diet compared to the AS diets (P < 0.05) (Table 3). Additionally, LEfSe analysis revealed four (Aspergillus, Metschnikowia, unclassified_f:Stachybotryaceae, and stachybotrys), two (Stemphylium and Cystobasidium), three (unclassified_k:Fungi, Trichothecium, and Psathyrella), and one (Alfaria) fungi taxa significantly associated with AHLR, AHHR, ASLR, and ASHR diets, respectively (Figure 2F).
The correlations within methanogens at the genus level were analyzed using triangular heatmaps, which revealed that the relative abundance of Methanobrevibacter was negatively correlated with Methanosphaera (P < 0.01). Among the top 10 fungi at the genus level, Candida showed a negative correlation with Sarocladium (P < 0.01) and Exophiala (P < 0.05). Furthermore, Penicillium, Cladosporium, and Exophiala showed positive correlations among themselves (P < 0.01). Aspergillus was also negatively associated with Occultifur (P < 0.01) (Figure 3).
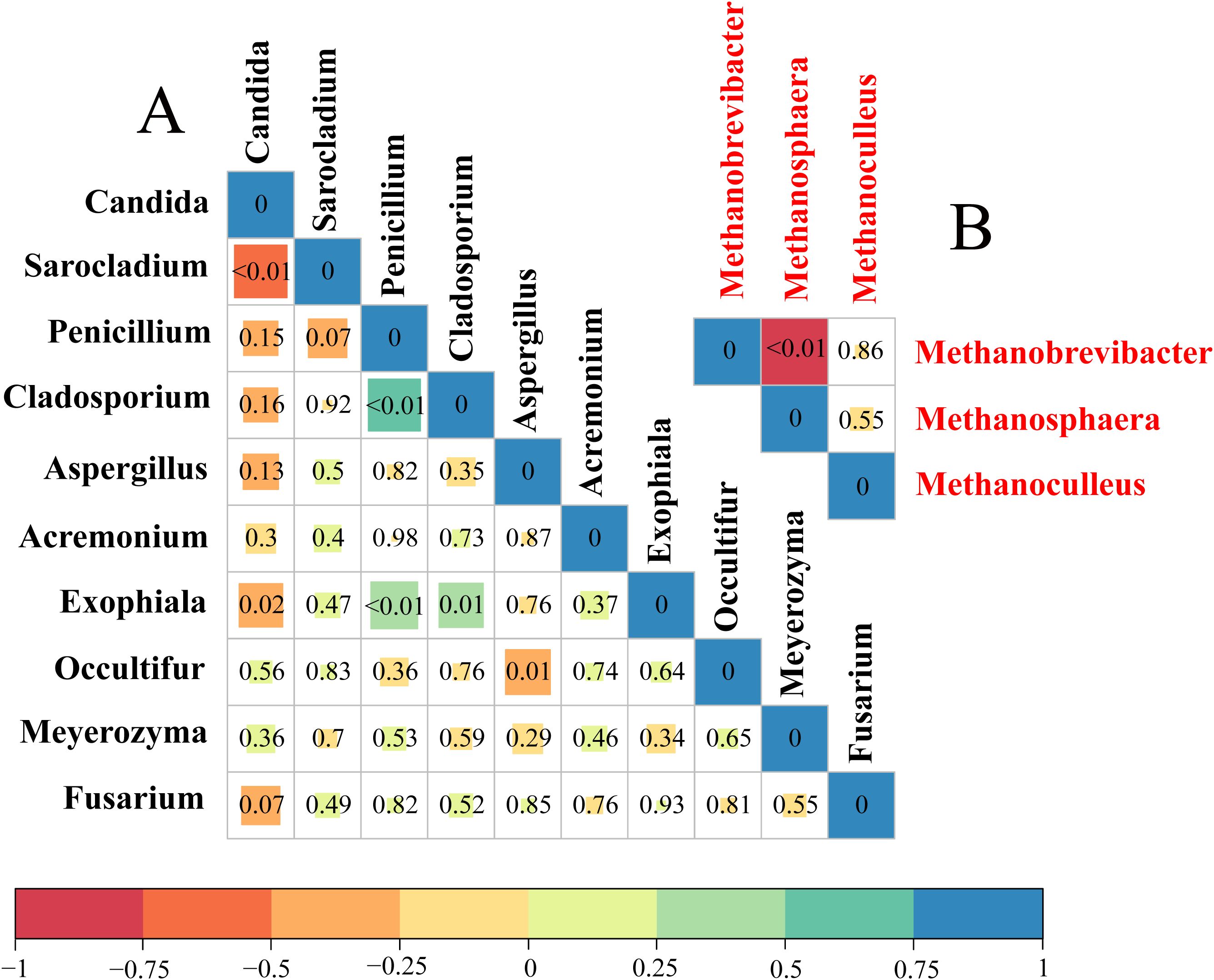
Figure 3. The correlations among the relative abundance of methanogen genera (red) and among the relative abundance of fungal genera (black) in different treatment diets. (A) Triangular heatmap of fungi. (B) Triangular heatmap of methanogens. The correlation is shown by Spearman’s rank correlation, ranging from −1 to 1, and represented by red (perfect negative correlation) to blue (perfect positive correlation).
Heatmap correlation analysis was employed to determine correlations between the relative abundance of microorganisms (methanogens and top 10 fungal genera) and growth performance and rumen fermentation parameters (Supplementary Material, Supplementary Table S1; Guo et al., 2025a; Figure 4). At the alpha diversity level, the Chao 1 index (P < 0.01) and the Shannon index (P < 0.05) of methanogens were negatively correlated with bacterial protein (BCP), respectively. Furthermore, the fungal Shannon index displayed a negative correlation with average daily gain (ADG) (P < 0.05) and positive correlation with isovalerate (P < 0.01) and lactic acid (P < 0.05). At the methanogen genus level, the relative abundance of Methanobrevibacter showed a positive correlation with isovalerate (P < 0.05). Methanosphaera was negatively correlated with isobutyrate and isovalerate (P < 0.05). Moreover, Methanoculleus exhibited a negative correlation with BCP (P < 0.01) and positive correlations with isobutyrate (P < 0.01) and isovalerate (P < 0.05). At the fungal genus level, Candida was negatively correlated with isovalerate (P < 0.05). Penicillium displayed negative correlations with BCP (P < 0.05) and propionate (P < 0.01) while showing positive correlations with isobutyrate (P < 0.05) and isovalerate (P < 0.01). Cladosporium exhibited negative correlations with propionate (P < 0.01), valerate, and total volatile fatty acids (TVFA) (P < 0.05). Aspergillus was positively correlated with F: G (P < 0.05) and lactic acid (P < 0.01) while showing a negative correlation with NH3-N (P < 0.05). Exophiala demonstrated negative correlations with acetate, propionate, butyrate, valerate, and TVFA (P < 0.01). Meyerozyma was negatively correlated with daily matter intake (DMI) (P < 0.05) and positively correlated with acetate (P < 0.01). In addition, Fusarium had a negative association with BCP (P < 0.01).
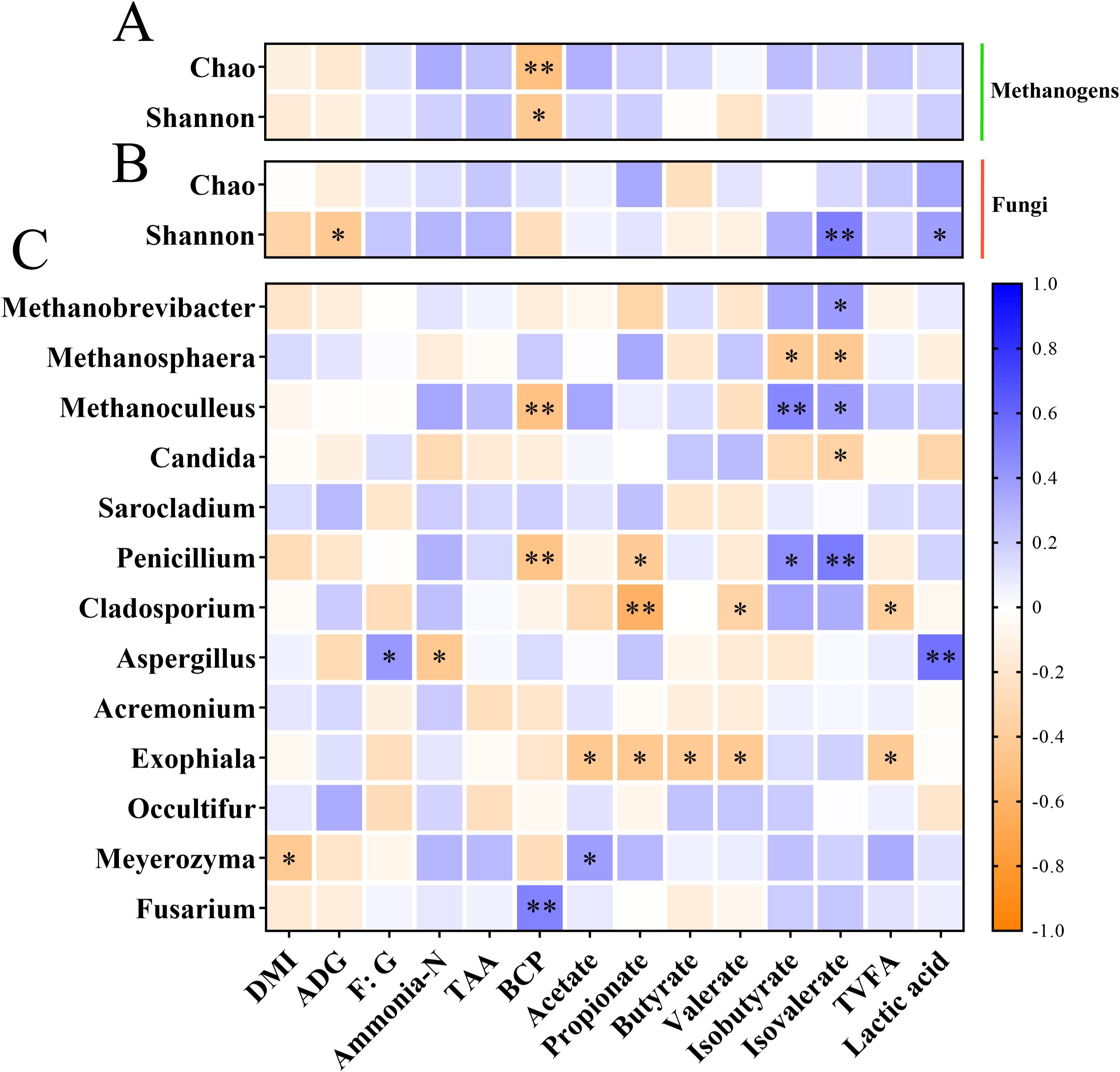
Figure 4. The relationship between methanogens and fungi and growth performance and rumen fermentation parameters. (A) Heat map of the relationship between the methanogen alpha diversity index and growth performance and rumen fermentation parameters. (B) Heat map of the relationship between the fungal alpha diversity and growth performance and rumen fermentation parameters. (C) Heat map of the relationship between the relative abundances of methanogens and fungi at the genus level and growth performance and rumen fermentation parameters. * and ** indicate significant differences at P < 0.05 and P < 0.01, respectively. ADG, average daily gain; DMI, daily matter intake; F:G, feed to gain ratio; TAA, total amino acid; BCP, bacterial protein; TVFA, total volatile fatty acids.
Dietary forage and concentrate are the most important factors influencing growth performance, mainly by affecting rumen fermentation parameters and microbial community. In our previous study, all four diets altered rumen fermentation parameters and bacterial communities, yet only the HR diets improved growth performance. Therefore, understanding the effects of dietary alfalfa forms and RDS levels on rumen methanogens and fungal communities can aid in identifying differences in growth performance and rumen fermentation parameters. In this study, the Chao 1 and Shannon indices of methanogens in the AHHR diet were lower compared to those in the ASLR diet, and similarly, the Shannon index for fungi was also lower in the AHHR diet. The diversity of rumen methanogens and fungi in sheep was significantly different among the four diet treatments. Additionally, we identified taxa of methanogens and fungi that might be associated with rumen VFAs.
Archaea account for 2%–4% of rumen microbes, with 98% of them being methanogens (Li et al., 2024). Methanobacteria produce CH4 by regulating the partial pressure of H2, promoting digestion in the rumen. However, the CH4 production is known to result in a loss of dietary energy for the host and contribute to the greenhouse effect. Our results show that the relative abundance of methanogens in the AHHR diet was lower than in the AS diets. This may be due to the few methanogens after ensiling that were still present, as increasing RDS in the AS diets can decrease the diversity of methanogens. After anaerobic fermentation of plant lignocellulosic materials, lactic acid, formate, and acetic acid are produced, and these substrates are conducive to Methanosaeta growth. Although the acidic environments after silage reduced Methanobacteria relative abundance from 14% to 4%, it was still higher than that of hay (Zhao et al., 2016). The results of in vitro rumen studies found that greater 48h gas and methane production were observed in alfalfa silage than in alfalfa hay (Zhang et al., 2024). In addition, previous studies have established that increasing wheat in the diet decreased CH4 production (Moate et al., 2017). However, the effects of the above experiments on methanogens remain unknown. Savin et al. (2022) found that a wheat diet reduced rumen pH and H2 for CH4 generation, resulting in lower CH4 production and a relative abundance of Methanobacteria. These results may indicate that the AHHR diet has lower methane production than the AS diet due to the relative abundance of methanogens, which has also been correlated with higher levels of methane emissions (Wallace et al., 2015). There was little impact of diet on the methanogen genera. In the present study, the genera Methanobrevibacter, Methanosphaera, and Methanoculleus were the dominant archaea in the four diets and were similarly distributed, which is consistent with a previous study (Thirumalaisamy et al., 2022). Methanobrevibacter and Methanosphaera belong to Methanobacteria class, which usually account for more than 90% of methanogen 16S rRNA gene reads. Methanoculleus belongs to the Methanomicrobia class. Methanobrevibacter and Methanoculleus perform methanogenesis from CO2 with H2 and formate, while Methanosphaera uses H2 and methanol for methanogenesis (Garcia et al., 2000). In addition, we explored the methanogen biomarkers (at the species level) in different diets using LEfSe analysis. Methanobrevibacter_sp_YE315 and Methanobrevibacter_sp_AbM4 were abundant in the ASLR diet and Methanobrevibacter_millerae was abundant in the ASHR diet. This may be due to differences in rumen fermentation pH and pathways (Savin et al., 2022). Dong et al. (2019) reported that butyrate was positively related to Methanobrevibacter_sp_AbM4.
The changes in the fungal community in the rumen have seldom been described in the literature when feeding alfalfa forms or RDS diet, thus, our data fill this gap. Fungi are known to play a key role in the degradation of plant lignocellulosic materials through the production of enzymes (Elekwachi et al., 2017; Gruninger et al., 2014). Fungal counts are usually low before feeding AH, while AS can reach 7.74×107mL-1 (Chen et al., 2021). However, we found that the relative abundance of fungi was higher in the AH diets than in the ASHR diet in the rumen, and diversity was higher in the LR diets than in the HR diets. This indicates that the growth of fungi was promoted by more lignin substrates in the AH diets, and inhibited by the low pH or other ensiling products in the AS diets (Shen et al., 2020). Although a high RDS diet usually reduces rumen pH (Li et al., 2014), rumen pH in our same study did not show a difference (Guo et al., 2025a). At the level of fungal phylum, our research found that Ascomycota and Basidiomycota are the major fungi in the rumen of sheep, in line with our results (Wei et al., 2024; Han et al., 2019). At the genus level of fungi, the current results are not in agreement with previous findings in sheep. Kittelmann et al. (2013) reported that Neocallimastix (28%), Piromyces (20%), Orpinomyces (12%), BlackRhino (8%), Caecomyces (8%), and Cyllamyces (5%) were the predominant anaerobic fungal genera in the rumen. In addition, Han et al. (2019) reported that Neocallimastix was the most abundant anaerobic fungal genus in the rumen. However, our findings showed that the predominant fungi detected were from the genera Candida, Sarocladium, and Penicillium, which collectively accounted for more than 50% of the fungal genus reads and have the same function as degrading fibers. Aspergillus was the only fungal genus with a higher relative abundance in the sheep fed the AHLR diet compared to the AS diets, indicating that the high fiber and low RDS promoted the proliferation of Aspergillus, which are mainly involved in the degradation of lignin (Nidhina et al., 2017). In addition, we explored the fungal biomarkers in the four diets using LEfSe analysis. We found that the different diets significantly affected the rumen fungal community. Specifically, the specific fungal biomarkers in the AHLR diet were Aspergillus, Metschnikowia, unclassified_f:Stachybotryaceae, and Stachybotrys; Stemphylium and Cystobasidium in the AHHR diet; unclassified_k:Fungi, Trichothecium, and Psathyrella in the ASLR diet; and Alfaria in the ASHR diet. Among them, the strong fiber degradation function of Aspergillus in the rumen has been reported (Nidhina et al., 2017; Tulsani et al., 2022), however, the function of most other fungi in the rumen is still unknown.
The triangular heat map shows the internal relationships among the methanogens. Our findings revealed that the relative abundance of Methanobrevibacter was negatively correlated with Methanosphaera in all diets, which is due to different methanogenesis pathway competition for H2 within the rumen (Li et al., 2024; Garcia et al., 2000). For fungi, Penicillium, Cladosporium, and Exophiala showed positive correlations among themselves. These fungi can degrade carbohydrates to produce formic acid, H2, and CO2, which in turn promotes the growth of Methanobrevibacter in the rumen (Han et al., 2019). Moreover, Candida was negatively associated with Sarocladium, as both can degrade lignocelluloses (Marrero et al., 2015; Hou et al., 2019). Those with comparable nutrition patterns may compete with each other (Johnston et al., 2019). Additionally, Aspergillus had a negative association with Occultifur. These results indicate that there is always a strong pattern of association among methanogens and fungi despite perturbations in dietary changes.
We integrated the changes in methanogens and fungi with the phenotypic characteristics previously observed. The methanogen Chao 1 and Shannon indexes had a negative correlation with BCP, suggesting that the proliferation of rumen microbiota may have reduced the relative abundance of low-abundance methanogens (Tian et al., 2023). The fungal Shannon index was negatively correlated with ADG. This again proves that microbiota interactions could be more important to ecosystem functioning than microbiota diversity in high feed efficiency ecosystems (Wang et al., 2023). In addition, Methanobrevibacter, Methanoculleus, and Penicillium exhibited a positive correlation with branched-chain VFAs, which indicates extensive degradation of AS protein and fiber, with amino acids and fibers degrading to form branched-chain VFAs and formic acid, respectively (Guo et al., 2025a; Wang et al., 2024). Meanwhile, the relative abundance of Methanobacteria was higher in the AS diets in the current study (Chao 1 index). Formate is not only a substrate that increases Methanobacteria growth but also Penicillium growth (Wang et al., 2019). Cladosporium and Exophiala also exhibited a negative correlation with VFAs. Many researchers have indicated that the enzymatic action of anaerobic rumen fungi forms VFAs, along with CO2 and H2 as fermentation endproducts (Bhagat et al., 2023). Thus, the methanogens and fungi have a certain symbiotic relationship. After the substrate was depleted and the VFAs concentration increased, the growth of fungi was inhibited. Although our study provided new insights into the effects of different alfalfa forms and RDS levels on rumen methanogens and fungi, future research is needed to determine their functional role and interaction relationships using metagenomic sequencing techniques, and such information can provide greater insights into how diets affect performance.
The present findings showed RDS levels altered rumen richness and diversity of methanogens and fungi in sheep fed AH or AS. The increased level of RDS in the AH diets reduced the methanogen Chao 1 index compared to the AS diets, and the Shannon index was reduced compared to the ASLR diet. The AH diet fungi Chao 1 index was higher than the ASHR diet, and the LR diets’ Shannon index was higher than the HR diets. Some species and genera were also affected differently by the four dietary treatments. The correlation analysis found some genera (Methanobrevibacter, Methanoculleus, Penicillium, Cladosporium, and Exophiala) were positively correlated with our previously observed concentrations of isobutyrate and isovalerate, and may provide greater insights into the previously observed differences.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
The animal study was approved by the Experimental Animal Welfare and Ethics Committee, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University. All animal procedures were conducted according to the “Laboratory Animal Guideline for Ethical Review of Animal Welfare” National Standard of the People’s Republic of China (GB/T 35892-2018). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
WG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MN: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. SL: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. KL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – review & editing. HD: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Conceptualization, Investigation, Software, Writing – review & editing. RN: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. YL: Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the Project on Standardization of Healthy livestock and Poultry breeding and Harmless Treatment of livestock andpoultry Waste in horqin youyi zhongqi (2022YFXZ0027), the Program for Innovative Research Team in Universities of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (NMGIRT2322), the basic scientific research business fee project for universities directly under the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (BR22-13-02), and the Inner Mongolia Agricultural University landmark achievement project (BZX202211).
The authors are grateful to Meila Na, Shuwei Liu, Kenan Li, Haidong Du, and Jing Zhang for their assistance in the data and sample collection and laboratory analysis and to Professor Renhua Na, Yu Zhang, and Yulan Liu for the experimental design and financial support.
Author YL was employed by the company Inner Mongolia Zhamuqin Agriculture and Animal Husbandry Technology Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frmbi.2025.1567462/full#supplementary-material
ADG, Average daily gain; AH, Alfalfa hay; AS, Alfalfa silage; AHLR, Alfalfa hay and low (14.85%DM) rumen degradable starch group; AHHR, Alfalfa hay and high (20.21%DM) rumen degradable starch group; ASLR, Alfalfa silage and low (14.85%DM) rumen degradable starch group; ASHR, Alfalfa silage and high (20.21%DM) rumen degradable starch group; BCP, Bacterial protein; DM, Dry matter; DMI, Dry matter intake; F:G, Feed to gain; RDS, Rumen-degradable starch; NH3-N, Ammonia-N; TAA, total amino acids; TVFA, Total volatile fatty acid; VFA, Volatile fatty acid.
Ainslie S. J., Fox D. G., Perry T. C. (1992). Management systems for Holstein steers that utilize alfalfa silage and improve carcass value. J. Anim. Sci. 70, 9, 2643–2651.
Akin D. E., Borneman W. S., Windham W. R. (1988). Rumen fungi: Morphological types from Georgia cattle and the attack on forage cell walls. Biosystems 21, 385–391. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(88)90037-8
Beauchemin K. A., Rode L. M., Eliason M. V. (1997). Chewing activities and milk production of dairy cows fed alfalfa as hay, silage, or dried cubes of hay or silage. J. Dairy Sci. 80, 324–333. doi: 10.3168/jds.s0022-0302(97)75942-3
Bhagat N. R., Kumar S., Kumari R., Bharti V. K. (2023). A review on rumen anaerobic fungi, current understanding on carbohydrate fermentation and roughages digestion in ruminants. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 59. doi: 10.1134/s0003683823030043
Chen L., Bao X., Guo G., Huo W., Xu Q., Wang C., et al. (2021). Effects of hydrolysable tannin with or without condensed tannin on alfalfa silage fermentation characteristics and in vitro ruminal methane production, fermentation patterns, and microbiota. Animals 11, 1967. doi: 10.3390/ani11071967
Dong L. F., Ma N. J., Tu Y., Diao Q. Y. (2019). Weaning methods affect ruminal methanogenic archaea composition and diversity in Holstein calves. J. Integr. Agric. 18, 146–158. doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(18)62120-3
Elekwachi O. C., Wang Z., Wu X. F., Rabee A., Forster R. J. (2017). Total rRNA-Seq Analysis Gives Insight into Bacterial, Fungal, Protozoal and Archaeal Communities in the Rumen Using an Optimized RNA Isolation Method. Front. Microbiol. 8, 1814. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01814
Eugène M., Klumpp K., Sauvant D. (2021). Methane mitigating options with forages fed to ruminants. Grass Forage Sci. 2, 196–204. doi: 10.1111/gfs.12540
Fernández C., Gomis-Tena J., Hernández A., Saiz J. (2019). An Open-circuit indirect calorimetry head hood system for measuring methane emission and energy metabolism in small ruminants. Animals 9, 380. doi: 10.3390/ani9060380
Ferraretto L. F., Crump P. M., Shaver R. D. (2013). Effect of cereal grain type and corn grain harvesting and processing methods on intake, digestion, and milk production by dairy cows through a meta-analysis. J. Dairy Sci. 96, 533–550. doi: 10.3168/jds.2012-5932
Gao Z. H., Raza S. H. A., Ma B. Y., Zhang F. S., Wang Z. Y., Hou S. Z., et al. (2024). Effects of dietary wheat supplementation levels on growth performance, rumen bacterial community and fermentation parameters in Chinese Tibetan Sheep. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 108, 470–479. doi: 10.1111/jpn.v108.2
Garcia J. L., Patel B. K., Ollivier B. (2000). Taxonomic, phylogenetic, and ecological diversity of methanogenic Archaea. Anaerobe 6, 205–226. doi: 10.1006/anae.2000.0345
Getachew G., Robinson P. H., DePeters E. J., Taylor S. J. (2004). Relationships between chemical composition, dry matter degradation and in vitro gas production of several ruminant feeds. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 111, 57–71. doi: 10.1016/S0377-8401(03)00217-7
Gislon G., Colombini S., Borreani G., Crovetto G. M., Sandrucci A., Galassi G., et al. (2020). Milk production, methane emissions, nitrogen, and energy balance of cows fed diets based on different forage systems. J. Dairy Sci. 103, 8048–8061. doi: 10.3168/jds.2019-18134
Gruninger R. J., Puniya A. K., Callaghan T. M., Edwards J. E., Youssef N., Dagar S. S., et al. (2014). Anaerobic fungi (phylum Neocallimastigomycota), advances in understanding their taxonomy, life cycle, ecology, role and biotechnological potential. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 90, 1–17. doi: 10.1111/fem.2014.90.issue-1
Guo W., Liu Y., Na M., Zhang Y., Na R. (2025b). Effects of rumen-degradable starch levels on in vitro rumen fermentation and microbial protein synthesis in alfalfa silage. Fermentation 11, 106. doi: 10.3390/fermentation11020106
Guo W. L., Na M. L., Liu S. W., Li K. N., Du H. D., Zhang J., et al. (2025a). Rumen-degradable starch improves rumen fermentation, function, and growth performance by altering bacteria and its metabolome in sheep fed alfalfa hay or silage. Animals 15, 34. doi: 10.3390/ani15010034
Han X., Li B., Wang X., Chen Y., Yang Y. (2019). Effect of dietary concentrate to forage ratios on ruminal bacterial and anaerobic fungal populations of cashmere goats. Anaerobe 59, 118–125. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2019.06.010
He G. X., Chen C., Mei S. H., Chen Z., Zhang R., Zhang T. T., et al. (2023). Partially alternative feeding with fermented distillers’ Grains modulates gastrointestinal flora and metabolic profile in guanling cattle. Animals 13, 3437. doi: 10.3390/ani13223437
Hou Y. M., Zhang X., Zhang N. N., Naklumpa W., Zhao W. Y., Liang X. F., et al. (2019). Genera Acremonium and Sarocladium cause brown spot on bagged apple fruit in China. Plant Dis. 103, 1889–1901. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-10-18-1794-RE
Hristov A. N., Huhtanen P., Rode L. M., Acharya S. N., McAllister T. A. (2001). Comparison of the ruminal metabolism of nitrogen from 15N-labeled alfalfa preserved as hay or as silage. J. Dairy Sci. 84, 2738–2750. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(01)74728-5
Jia T. T., Luo Y., Wang L., Yu Z. (2024). Effect of soil contamination and additives on fermentative profile, microbial community and iron bioaccessibility of alfalfa silage. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 11, 55. doi: 10.1186/s40538-024-00578-w
Jiang D., Li B. N., Zheng M. L., Niu D. Z., Zuo S. S., Xu C. C. (2020). Effects of Pediococcus pentosaceus on fermentation, aerobic stability and microbial communities during ensiling and aerobic spoilage of total mixed ration silage containing alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Grassland Sci. 66, 215–224. doi: 10.1111/grs.12272
Jin C. J., Su X. J., Wang P. Y., Liang Z. Q., Lei X. J., Bai H. X., et al. (2023). Effects of rumen degradable starch on growth performance, carcass, rumen fermentation, and ruminal VFA absorption in growing goats. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 299, 115618. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2023.115618
Johnson K. A., Johnson D. E. (1995). Methane emissions from cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 73, 2483–2492. doi: 10.2527/1995.7382483x
Johnston S. R., Hiscox J., Savoury M., Boddy L., Weightman A. J. (2019). Highly competitive fungi manipulate bacterial communities in decomposing beech wood. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 95. doi: 10.1093/femsec/fiy225
Karim S. A., Chaturvedi O. H., Verma D. L., Tripathi M. K. (2008). Nutritional value of animal feed grade wheat as replacement for maize in lamb feeding for mutton production. J. Sci. Food Agric. 87, 2447–2455. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.2942
Kittelmann S., Seedorf H., Walters W. A., Clemente J. C., Knight R., Gordon J. I., et al. (2013). Simultaneous amplicon sequencing to explore co-occurrence patterns of bacterial, archaeal and eukaryotic microorganisms in rumen microbial communities. PloS One 2, e47879. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047879
Li K., Du H., Guo W., Na M., Na R. (2024). Alfalfa supplementation timing changes the rumen archaeal and fungal community composition and colonization in pre-weaning lambs. Front. Microbiol. 15, 1380322. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1380322
Li S., Lei Y., Zhang Y., Liu J., Shi X., Jia H., et al. (2019). Rational trade-offs between yield increase and ferti-lizer inputs are essential for sustainable intensification, A case study in wheat-maize cropping systems in China. Sci. Total Environ. 20, 328–336. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.085
Li F., Yang X. J., Cao Y. C., Li S. X., Sun F. F. (2014). Effects of dietary effective fiber to rumen degradable starch ratios on the risk of sub-acute ruminal acidosis and rumen content fatty acids composition in dairy goat. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 189. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2013.12.011
Ma X., Li Z., Zhang Y. (2022). Effects of the partial substitution of corn with wheat or barley on the growth performance, blood antioxidant capacity, intestinal health and fecal microbial composition of growing pigs. Antioxidants 11, 1614. doi: 10.3390/antiox11081614
Marrero Y., Castillo Y., Ruiz O., Burrola E., , Claudio. A. (2015). Feeding of yeast (Candida spp.) improves in vitro ruminal fermentation of fibrous substrates. J. Integr. Agric. 14, 514–519. doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(14)60830-3
Moate P. J., Williams S. R., Jacobs J. L., Hannah M. C., Beauchemin K. A., Eckard R. J., et al. (2017). Wheat is more potent than corn or barley for dietary mitigation of enteric methane emissions from dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 100, 7139–7153. doi: 10.3168/jds.2016-12482
Nidhina N., Bhavya M. L., Bhaskar N., Muthukumar S. P., Murthy P. S. (2017). Aflatoxin production by Aspergillus flavus in rumen liquor and its implications. Food Ctrl 71, 26–31. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.05.051
Niu W. J., Wang H. B., He Y., Qiu Q. H., Shao T. Q., Cao B. H., et al. (2020). Comparative analysis of wheat hay and silage in methane production, fermentation characteristics and microbiota using in vitro rumen cultures. Appl. Sci. 10, 8456. doi: 10.3390/app10238456
Plascencia A., González V., Víctor M., Zinn R. A. (2018). Comparative effects of grain source on digestion characteristics of finishing diets for feedlot cattle, Steam_flaked corn, barley, wheat, and oats. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 98, 794–800. doi: 10.1139/cjas-2018-0018
Radovic J., Sokolovic D., Markovic J. (2009). Alfalfa-most important perennial forage legume in animal husbandry. Biotechnol. Anim. Husb 25, 465–475. doi: 10.2298/BAH0906465R
Savin K. W., Moate P. J., Williams S. R. O., Bath C., Hemsworth J., Wang J. H., et al. (2022). Dietary wheat and reduced methane yield are linked to rumen microbiome changes in dairy cows. PloS One 17, 268157. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0268157
Shen J., Zheng L., Chen X., Han X., Cao Y., Yao J. (2020). Metagenomic analyses of microbial and carbohydrate-active enzymes in the rumen of dairy goats fed different rumen degradable starch. Front. Microbiol. 20, 1003. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01003
Sun J., Wang J., Bai C., Zhao J., Yun Y., Yu Z., et al. (2023). Natural fermentation quality, bacteria, and functional profiles of three cuttings of alfalfa silage in a year in Inner Mongolia, China. Front. Microbiol. 14, 1083620. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1083620
Thirumalaisamy G., Malik P. K., Trivedi S., Kolte A. P., Bhatta R. (2022). Effect of long-term supplementation with silkworm pupae oil on the methane yield, ruminal protozoa, and archaea community in sheep. Front. Microbiol. 13, 780073. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.780073
Tian G., Zhang X., Hao X., Zhang J., Naklumpa W., Zhao W. Y., et al. (2023). Effects of curcumin on growth performance, ruminal fermentation, rumen microbial protein synthesis, and serum antioxidant capacity in housed growing lambs. Animals 13, 1439. doi: 10.3390/ani13091439
Tulsani N. J., Jakhesara S. J., Hinsu A. T., Jyotsana B., Dafale N. A., Patil N. V., et al. (2022). Genome analysis and CAZy repertoire of a novel fungus Aspergillus sydowii C6d with lignocellulolytic ability isolated from camel rumen. Elec J. Biotechnol. 59, 36–45. doi: 10.1016/j.ejbt.2022.06.004
Wallace R. J., Rooke J. A., Mckain N., Duthie C.-A., Hyslop J. J., Ross D. W., et al. (2015). The rumen microbial metagenome associated with high methane production in cattle. BMC Genomics 16, 839. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-2032-0
Wang D. D., Chen L. Y., Tang G. F., Yu J. J., Chen J., Li Z. J., et al. (2023). Multi-omics revealed the long-term effect of ruminal keystone bacteria and the microbial metabolome on lactation performance in adult dairy goats. Microbiome 11, 215. doi: 10.1186/s40168-023-01652-5
Wang H., Fu J., Wu X., Wang Y., Li W., Huang Y., et al. (2024). Effects of dietary protein level and rumen-protected methionine and lysine on growth performance, rumen fermentation and serum indexes for yaks. Animals 14, 1751. doi: 10.3390/ani14121751
Wang G., Wang X. X., Wang T., Gulik W. V., Noorman H. J., Zhang Y. P., et al. (2019). Comparative fluxome and metabolome analysis of formate as an auxiliary substrate for penicillin production in glucose-limited cultivation of penicillium chrysogenum. Biotechnol. J. 14. doi: 10.1002/biot.201900009
Wayne K. C., Matthew S. A., Burney A. K. (2020). Storage characteristics and nutritive value of moist large-round bales of alfalfa or alfalfa–grass hay treated with a propionic acid–based preservative. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 36, 455–470. doi: 10.15232/aas.2020-02024
Wei H., Liu J., Liu M., Zhang H., Chen Y. (2024). Rumen fermentation and microbial diversity of sheep fed a high-concentrate diet supplemented with hydroethanolic extract of walnut green husks. Anim. Biosci 37, 655–667. doi: 10.5713/ab.23.0213
Xu Y., Aung M., Sun Z. Y., Zhou Y. Q., Xue T. H., Cheng X. M., et al. (2023). Ensiling of rice straw enhances the nutritive quality, improves average daily gain, reduces in vitro methane production and increases ruminal bacterial diversity in growing Hu lambs. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 295, 115513. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2022.115513
Xue Z., Liu N., Wang Y., Yang H., Wei Y., Moriel P., et al. (2020). Combining orchardgrass and alfalfa, effects of forage ratios on in vitro rumen degradation and fermentation characteristics of silage compared with hay. Animals 10, 59. doi: 10.3390/ani10010059
Yang F. Y., Wang Y. P., Zhao S. S., Wang Y. (2020). Lactobacillus plantarum inoculants delay spoilage of high moisture alfalfa silages by regulating bacterial community composition. Front. Microbiol. 11, 1989. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01989
Zhang Z. A., Wang L., Li Q. W., Li F., Ma Z. Y., Li F. D., et al. (2024). Effects of dietary forage neutral detergent fiber and rumen degradable starch ratios on chewing activity, ruminal fermentation, ruminal microbes and nutrient digestibility of Hu sheep fed a pelleted total mixed ration. J. Anim. Sci. 3, 102. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae100
Keywords: alfalfa hay, alfalfa silage, rumen degradable starch, rumen, methanogens, fungi
Citation: Guo W, Na M, Liu S, Li K, Du H, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Na R and Liu Y (2025) Relationships between rumen methanogens and fungal communities and their response to changes in alfalfa forms and starch in sheep diets. Front. Microbiomes 4:1567462. doi: 10.3389/frmbi.2025.1567462
Received: 27 January 2025; Accepted: 19 March 2025;
Published: 09 April 2025.
Edited by:
Jesús Muñoz-Rojas, Meritorious Autonomous University of Puebla, MexicoReviewed by:
Julia María Alatorre Cruz, Meritorious Autonomous University of Puebla, MexicoCopyright © 2025 Guo, Na, Liu, Li, Du, Zhang, Zhang, Na and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Renhua Na, bmFyZW5odWFsYW9zaGlAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Yulan Liu, bGl1eXVsYW43Njk0NDAyNjVAMTYzLmNvbQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.