
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Microbiol. , 14 March 2025
Sec. Microorganisms in Vertebrate Digestive Systems
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1559119
 Jingjun Zhu1†
Jingjun Zhu1† Fei Peng1†
Fei Peng1† Huixin Yang2†
Huixin Yang2† Jing Luo1
Jing Luo1 Li Zhang1
Li Zhang1 Xiaolong Chen1
Xiaolong Chen1 Huazhi Liao1
Huazhi Liao1 Hao Lei1
Hao Lei1 Shuai Liu3
Shuai Liu3 Tingqian Yang1,4
Tingqian Yang1,4 Guanghua Luo1*
Guanghua Luo1* Guodong Chen3*
Guodong Chen3* Heng Zhao1*
Heng Zhao1*Sarcopenia refers to the decline in skeletal muscle mass and function. Due to its increased mortality rate and severe disability, the clinical importance of sarcopenia is becoming increasingly prominent. Although the exact cause of sarcopenia is not fully understood, the gut microbiota (GM) plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of sarcopenia, and increasing evidence suggests that gut dysbiosis may be associated with disease development. In the past few decades, the use of probiotics has surged, few studies have explored their impact on sarcopenia prevention and treatment. Lactobacillus probiotics are commonly used for gut health and immune support, but their mechanism in sarcopenia via the gut-muscle axis remains uncertain. This review highlights the treatment challenges, GM’s role in sarcopenia, and the potential of Lactobacillus as an adjunct therapy. In addition, we also discuss the possible mechanisms by which Lactobacillus affect muscle function, such as alleviating inflammatory states, clearing excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS), improving skeletal muscle metabolism, enhancing intestinal barrier function and modulating the gut microbiota and its metabolites. These mechanisms may collectively contribute to the preservation of muscle mass and function, offering a promising avenue for advancing microbial therapies for sarcopenia.
Sarcopenia, as defined by the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People (EWGSOP), refers to a decline in muscle mass and function in terms of strength or performance (Cruz-Jentoft et al., 2019). Due to the aging of the body, muscle mass and strength naturally decrease. In individuals with sarcopenia, this process accelerates significantly, leading to a rapid deterioration in muscle function and eventual development of muscle atrophy. These changes result in a decline in mobility, increasing susceptibility to falls, fractures, disability, and even rising mortality rate (Gomes et al., 2017; Walston, 2012). With the aggravation of population aging and the change of lifestyle, the prevalence of sarcopenia shows a rising trend year by year. Significantly, the prevalence of sarcopenia is approximately 10%–50% in people aged ≥ 60 years, which has become a serious challenge for global health (Witham and Aihie Sayer, 2016). Therefore, the prevention and intervention of sarcopenia are crucial to mitigating its progression and reducing the risk of severe conditions and complications.
It is challenging to ensure timely diagnosis and intervention for sarcopenia. The effectiveness of medications is often limited, and this may even cause side effects. Moreover, the expensive treatment costs combined with individual differences have led to varying outcomes in rehabilitation and nutritional interventions (Cho et al., 2022). Encouragingly, the innovative theory of the gut-muscle axis has become a focal point of research in the scientific community, with its potential to revolutionize our understanding of the interaction between gut health and muscles. According to the “Gut-muscle axis Hypothesis,” muscle function and metabolism largely depend on the quantity and structure of the gut microbiota. It suggests that gut microbes could become potential biological targets for the prevention and therapy of muscle-related disorders such as sarcopenia and muscle atrophy (Ticinesi et al., 2017). Multiple lines of evidence indicate the interaction between gut microbiota and skeletal muscle (Kang et al., 2021; Lahiri et al., 2019; Manickam et al., 2018; Qiu et al., 2021). Hence interventions targeting gut microbiota imbalance, such as dietary changes, supplements, and active compounds, may alleviate sarcopenia. Understanding how the gut microbiota regulates muscle function is especially crucial for enhancing patients’ mobility and strength.
Lactobacillus, an important bacterium within the Firmicutes phylum, has attracted significant interest due to its prominent presence in the gut microbiota. Its subgroups have been suggested to influence the progression of sarcopenia, showing protective effects in studies conducted on mice, cells, and humans (Kim et al., 2023; Lee et al., 2023; Ni et al., 2019; Rondanelli et al., 2022). Despite the promising potential of Lactobacillus, to the best of our knowledge, a clear and comprehensive review of its specific mechanisms of action in sarcopenia remains absent. Consequently, we elaborate the role of Lactobacillus in sarcopenia, attempting to provide new insights into potential mechanism for developing effective therapies for sarcopenia.
Currently, though non-pharmacological treatment such as exercise and nutritional interventions are still the first-line treatment for sarcopenia. Clinicians, pharmaceutist, researchers, etc. have made arduous explorations of drugs for treating sarcopenia. Unfortunately, due to the complex pathogenesis of sarcopenia, there is still no specific drugs approved for treating sarcopenia. Some drugs used in clinical practice to treat other diseases may benefit muscles and expand their use for sarcopenia. Although these drugs have shown good clinical efficacy in treatment, several adverse outcomes that may arise after treating sarcopenia cannot be ignored. For example, Testosterone promotes muscle cell proliferation via the Ras/MEK/ERK pathway and increases muscle mass and strength (De Spiegeleer et al., 2018), but the treatment risks include thrombosis, sleep apnea, and cancer (Morley, 2016). Selective androgen receptor molecules (SARMs) may lead to severe liver and kidney damage, and also result in testicular shrinkage and male infertility (Efimenko et al., 2022). In addition, prolonged administration of myostatin inhibition (MI) may result in raising the risk of cardiovascular disease (Campbell et al., 2017). Growth Hormone (GH) supplementation increases muscle mass but does not enhance strength or function (Papadakis et al., 1996), and is relatively more expensive than other sarcopenia medications (Liu et al., 2007). Overall, there is no safe or effective treatment plan for the medication used to treat sarcopenia. How to innovate and optimize the safety and efficacy of treatment in clinical practice, while ensuring they are affordable for patients with sarcopenia, remains a critical issue that needs to be addressed.
The gut-muscle axis represents a crucial biological mechanism, highlighting the pivotal contribution of gut microbes in maintaining overall lean mass, skeletal muscle mass, and bodily functions. In recent years, considerable valuable results on the gut-muscle axis have been revealed (Liu Y. et al., 2023). First, germ-free mice, which lacked a gut microbiota showed a more pronounced reduction in muscle mass, quality, and neuromuscular performance compared to pathogen-free mice that had a gut microbiota (Lahiri et al., 2019). Second, mice treated with antibiotics experienced increased muscle atrophy, which was associated with an imbalance in gut microbiota and lower levels of ileal fibroblast growth factor 15 (FGF15) were observed, while administering FGF19 effectively reversed muscle atrophy (Manickam et al., 2018; Qiu et al., 2021). Third, sarcopenia patients showed a higher abundance of Lactobacillus compared to healthy controls and a decrease of Eubacterium, Lachnospira, Fusicatenibacter, and Roseburia genera (Kang et al., 2021). Notably, probiotics are defined as “living microorganisms” by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), which exert their beneficial effects in the human body by inhibiting the proliferation of pathogenic microbes, generating bioactive compounds, and sustaining a balanced local micro-environment (Hill et al., 2014). Lactobacillus is the most researched and commonly utilized probiotic that has been applied in the commercial field for a long time, which can survive in the acidic environment of the gastrointestinal tract (Corcoran et al., 2005). Importantly, the majority of Lactobacillus’ subspecies have benefits for gut health, particularly with the potential to help the host restore muscle mass and function.
For example, it has been observed that the conditioned medium (CM) from L. rhamnosus JY02 reduced myotube atrophy caused by dexamethasone (DEX) and lowered the expression of muscle degradation markers, MuRF1 and atrogin-1, in C2C12 cells. Meanwhile, L. rhamnosus JY02 supplement could enhance the expression of muscle-enhancing markers such as MHC Iβ, MHC IIα, and Myo-D, decreases the levels of muscle degradation markers, and mitigates muscle atrophy symptoms in a murine model (Lee et al., 2023). Moreover, Lactobacillus casei LC122 increased the mass of quadriceps femoris (QM) and gastrocnemius (GM) muscles, and enhanced muscle strength and function in aged mice (Ni et al., 2019). These results sparked tremendous interest, suggesting that priority consideration may be involved in opting for Lactobacillus probiotics as an adjunct treatment for sarcopenia, and motivated us to explore the underlying mechanisms. The relief of the inflammatory state, the clearance of excess reactive oxygen species, the improvement of skeletal muscle metabolism, the regulation of gut microbiota and its metabolites has been identified as a potential mechanism through which Lactobacillus can alleviate sarcopenia (Chen L. et al., 2022; He et al., 2023; Hor et al., 2021; Yan et al., 2019) (Figure 1). These findings can not only provide new ideas for the treatment of sarcopenia, but also further deepen our understanding of the role of Lactobacillus in the gut-muscle axis.
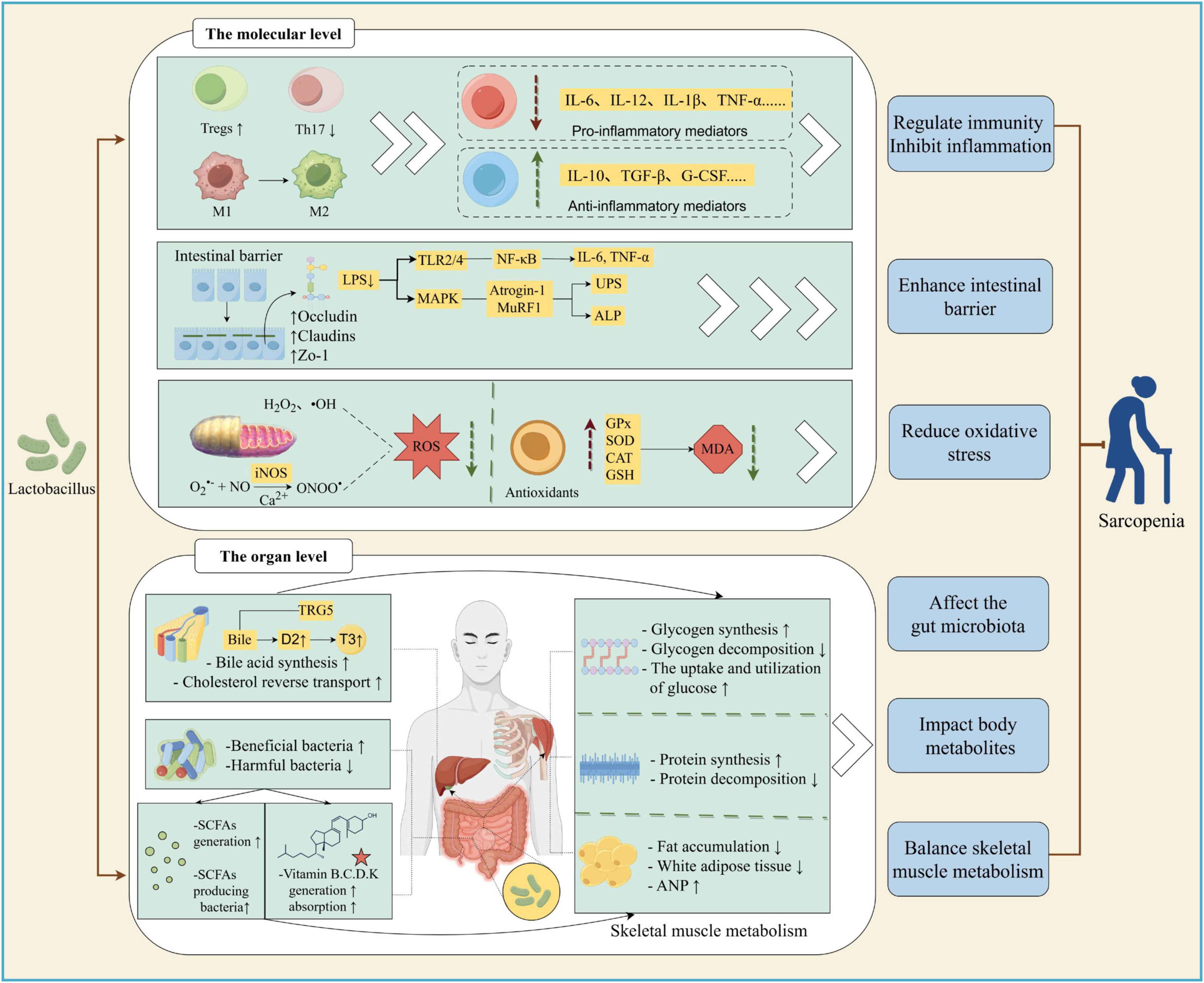
Figure 1. Possible mechanism of Lactobacillus alleviating sarcopenia. Lactobacillus can alleviate sarcopenia in various ways. (1) At molecular level, lactobacilli alter the phenotype and quantity of immune cells; enhancing gut barrier affects MAPK and NF-KB signaling pathway, thereby reducing the level of inflammatory factors. It can also regulate the level of antioxidant enzymes, thereby reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) and malondialdehyde (MDA), inhibiting Nitric Oxide (NO) production, alleviating oxidative stress, and ameliorating sarcopenia. (2) At tissue level, Lactobacillus can increase skeletal muscle glycogen synthesis; reduce glycogen decomposition; promote protein synthesis; reduce protein decompositon and fat accumulation; increase beneficial bacteria and reduce harmful bacteria in the intestine; increase glucose utilization in fat and muscle groups. In addition, Lactobacillus increases the number of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) producing bacteria, enhances bile acid synthesis and Cholesterol reverse transport, promotes the production and absorption of vitamins, thereby showing therapeutic activity against sarcopenia. M1, M1 macrophages; M2, M2 macrophages; Tregs, Regulatory T cells; Th17, T helper cell 17 (Created with figdraw.com).
Lactobacillus, a gram of gram-positive anaerobic bacteria recognized for its capacity to ferment glucose and other sugars to generate lactic acid. Classified within the Firmicutes phylum, it falls under the Bacillus class, Lactobacillales order, and Lactobacillus family. It encompasses several subspecies including Lactobacillus fermentum (L. fermentum), Lactobacillus plantarum (L. plantarum), Lactobacillus salivarius (L. salivarius), Lactobacillus acidophilus (L. acidophilus), Lactobacillus rhamnosus (L. rhamnosus), etc (Heeney et al., 2018). It is estimated that this genus is believed to represent roughly 0.3% and 6% among the total bacterial population within the human colon and duodenum, respectively (Almonacid et al., 2019; Nistal et al., 2016). Among the over 200 known lactobacilli species, only a few have been consistently and frequently interacted with the human gastrointestinal tract. However, the number of discovered species has significantly increased recently, with more than 50 lactobacilli species now being repeatedly verified in the feces of healthy volunteers (Rossi et al., 2016). Among them, the most abundant lactobacilli species primarily include L. casei, Lactobacillus delbrueckii (L. delbrueckii), L. rhamnosus, L. plantarum, Lactobacillus mushroomorum (L. mushroomorum).
It has been demonstrated that a positive correlation existed between the levels of gut Lactobacillus and skeletal muscle mass index. In the elderly, it has been shown that the proportion of certain gut microbiota in patients with sarcopenia has changed, with a significant decrease in the proportion of Lactobacilli, Bacteroidetes, and Prevotella, along with an increases in Escherichia coli (Lou et al., 2024). In the gut of accelerated aging mice, the enriched bacterial genera, including Odoribacter, Oscillibacter, and Anaerotruncus, were found to be negatively correlated with muscle and mitochondrial function. At the same time, these bacteria were positively correlated with pro-inflammatory cytokines and negatively correlated with anti-inflammatory cytokines (Chen L. et al., 2022). Lactobacillus can restore the composition and beta diversity of intestinal microbiota, which may be one of the ways to play a therapeutic role in sarcopenia (Picca et al., 2019). For example, L. paracasei, can increase the populations of Akermaceae and Deinococcaceae, which are associated with muscle weight and Myosin Heavy Chain (MyHC) expression. In contrast, it can reduce the populations of Odobacteraceae and certain members of Deinococcaceae, which are associated with elevated levels of Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and Muscle RING-Finger 1 (MuRF1) expression (Baek et al., 2023). In addition to increasing beneficial gut bacteria, Lactobacillus can enhance epithelial integrity through adequate colonization, making it less susceptible to infections by harmful bacteria such as Bacteroides, Escherichia, and Shigella, as well as their translocation into the intestinal lumen (Karczewski et al., 2010). It also has the ability to provide nutritional support (SCFAs, vitamins, amino acids, and amines, etc.) and lower the pH value of the intestinal cavity, thereby preventing the colonization of harmful bacteria and maintaining the gut microbiota balance (Hong et al., 2018). Consequently, the role of Lactobacillus in preserving balance in gut environments should not be underestimated.
When the gut microbiota balance of sarcopenia patients was in a state of disorder, their gut immune microenvironment was also disrupted. As the primary defense against microbiota, the intestinal mucosa contains a variety of immune cells, which work together to preserve immune homeostasis in both the peripheral blood and the intestinal mucosal environment. Imbalance in the gut microbiota can lead to abnormal activation of the immune system and a state of chronic inflammation (Zheng et al., 2020). The process of muscle wasting during aging can be exacerbated by abnormalities in the immune system, while the chronic low-grade inflammation caused by immune is considered one of the pivotal factor contributing to sarcopenia (Saini et al., 2016). Lactobacillus may modulate excessive activation of intestinal and systemic inflammatory responses from various angles by altering the number, recruitment, and differentiation of immune cells, thereby limiting the progression and worsening of sarcopenia.
Lactobacillus may alleviate symptoms of muscle atrophy by restoring the quantity and proportion of altered immune cells. Firstly, Lactobacillus reuteri enhanced anti-inflammatory force, hindered pro-inflammatory power, and inhibited muscle atrophy by restoring impaired systemic immunosuppressive function through upregulating the Treg/Th17 ratio. The transcription factor Foxp3 regulates Treg development, while the activity of Tregs is modulated by IL-35 and IL-10. Respectively, L. reuteri not only restored the levels of T lymphocytes (CD3γ), Th1 lymphocytes (Tbet), and Th17 lymphocytes (IL-17A) but also maintain levels of Foxp3 and IL-10 to raise the frequency of Tregs in tissue (Bindels et al., 2016). Besides L. reuteri, L. rhamnosus was also effective in impacting the relative abundance of immune cells due to it could repair and maintain intestinal barrier function by upregulating the levels of TJs and GLP-2, ultimately regulating Th17/Treg and related cytokine levels in mesenteric lymph nodes (Guo et al., 2023).
In addition to changing the quantity and proportions of various immune cells, the immune cell phenotype was also induced changes to regulate the inflammatory by Lactobacillus. The changes in macrophage immune metabolism are related to muscle wasting symptoms. In the context of skeletal muscle functional metabolic disorders, the phenotype of macrophages changes from M2 (anti-inflammatory) to M1 (pro-inflammatory) (Liu N. et al., 2023). M1 and M2 represent two phenotypes in macrophages with completely opposite functions, The former is characterized by high expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-1β, IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α, while the latter predominantly produces anti-inflammatory cytokines like IL-10 and TGF-β (Shapouri-Moghaddam et al., 2018). L. rhamnosus GroEL modulates macrophage phenotype to relieve the inflammatory pressure in muscle by inhibiting markers associated with M1-like macrophages and upregulating M2-like macrophage markers (Dias et al., 2021). Apart from the change in macrophage markers, L. rhamnosus GG can also significantly decrease the mRNA expression of MCP-1 and CD11c, associated with monocyte recruitment and M1 macrophage activation, thereby suppressing the infiltration and activation of M1 cells (Park et al., 2015).
From a dialectical perspective, a correlation existed between the distribution of immune cells and the production of inflammatory cytokines. With numerous immune cells releasing inflammatory cytokines, these cytokines may in turn hinder their recruitment and function. Many experiments have demonstrated that Lactobacillus can alter inflammatory cytokine levels. L. casei Shirota (LcS), boosted the levels of IL-10 and short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), suppressed macrophage production of TNF-α and lowered TNF-α levels (Chen L. et al., 2022). Moreover, other Lactobacillus strains exhibit similar effects. L. reuteri, L. acidophilus, L. fermentum, L. brevis and L. rhamnosus enhanced IL-10 levels while decreasing TNF-α expression (Archer et al., 2021; Peña and Versalovic, 2003). Meanwhile, Lactobacillus upregulated the expression of anti-inflammatory mediators. A multifunctional factor involved in immune modulation, G-CSF, which exhibited a negative correlation with inflammation-promoting mediators like TNF-α, IL-12 and IL-23, which were proven to have potential in skeletal muscle repair and regeneration (Wright et al., 2017). L. reuteri and L. gasseri escalated the expression of G-CSF and reduced markers of atrophy including Atrogin-1, MuRF1, LC3, and Cathepsin L. Increasing IL-10 decreased the generation of pro-inflammatory factors like IFN-γ and IL-2/IL-1β, which alleviated the inflammatory response and inhibiting the progression of sarcopenia (Bindels et al., 2012).
Oxidative stress is closely related to cell damage and aging (Marzetti et al., 2013). Reactive oxygen species (ROS), primarily composed of superoxide anions, hydrogen peroxide, and hydroxyl radicals, are crucial components of the neutrophils antibacterial library. Excessive ROS can lead to oxidative stress in muscle tissue with activating intracellular signaling pathways involved in sarcopenia (Bonetto et al., 2009). Oxidative stress can induce lipid and protein oxidation, disrupt the composition and structural integrity of muscle cell membranes, thereby leading to a decline in skeletal muscle function (König et al., 2001). Thus, managing oxidative stress could be an effective approach to treating sarcopenia.
Various studies have verified the high antioxidant capacity of Lactobacillus strains. The antioxidant properties of Lactobacillus are closely associated with its ability to scavenge reactive oxygen species and increase antioxidant levels (Lin and Chang, 2000). Firstly, L. paracasei can promote the expression of antioxidant-associated genes superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT), inhibits the oxidation process, and prevents inflammation (Lin et al., 2021). L. fermentum not only upregulates the expression of antioxidant genes, but also eliminates peroxides in tissues through glutathione peroxidase (GPx) activity to alleviate oxidative stress that damages muscles and protect muscle (Hor et al., 2021). Secondly, L. plantarum has the ability to modulate the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) signaling pathway, thereby enhancing the body’s antioxidant capacity and reducing the levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), a biomarker of oxidative stress (Chen Q. et al., 2022). Thirdly, mitochondria serve as key sites for ROS production. Dysfunctional mitochondria increases inflammation and ROS that are strongly linked to sarcopenia (Picca et al., 2018), which may also be a new target for Lactobacillus therapy. L. plantarum can regulate mitochondrial biogenesis, including PGC1 α, SIRT1, NRF1, and TFAM prevent mitochondrial dysfunction to reduce inflammation and ROS production, ultimately mitigating sarcopenia in the aging mouse model (Chen et al., 2019). Additionally, Lactobacillus strains play a significant role in combating muscle aging by modulating AMPK activity and mitochondrial regulation related genes. As a key regulator of cellular energy balance, AMPK not only modulates mitochondrial dynamics but also helps counteract oxidative stress by reducing energy expenditure and conserving resources, thereby promoting the restoration of muscle function. Through this pathway, they influence the expression of the p53 gene, which encodes a tumor suppressor protein. P53 is an important marker for senescence caused by telomere stress and regulates critical processes such as cell cycle arrest, DNA repair, apoptosis, and cellular aging (Qian and Chen, 2013). Specifically, these strains (such as LP-0291 and LF-DR9) can reduce the expression of the p53 gene in local gastrocnemius and tibialis muscles, which is associated with the activation of AMPK. This series of mechanisms provides effective support in resisting aging, highlighting the significant potential of Lactobacillus strains in relief of oxidative stress (Hor et al., 2019).
Additionally, excessive NO can break the balance of intracellular redox and trigger inflammatory reactions, resulting in muscle tissue damage and atrophy (Kaminski and Andrade, 2001). NO is a key player in muscle tissue inflammation, injury, and atrophy, as verified in animal research (Hall et al., 2011). Lactobacillus alleviates oxidative stress by indirectly or directly inhibiting the production of NO. L. plantarum down-regulates the expression level of the syncytin-1, nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and TNF-α gene present in skeletal muscle, restores overall energy balance in muscle tissue of animals and reduces the oxidative response (Yi et al., 2021). Beside, arginine deaminase, an enzyme found in L. brevis, aids in the inhibition of NO is produced by competing with NOS for arginine, its common substrate, and metabolizing it into citrulline and ammonia (Zhang et al., 2014). Moreover, Lactobacillus can not only restore normal NO and GSH levels, but also stimulate the proliferation of myogenic stellate cells; thus having an anti-aging-related myopathy effect (Abdel-Halim et al., 2023).
Skeletal muscle is a vital organ for glucose metabolism, and the composition of the gut microbiome influences glycogen storage in muscles. Microbiome dysregulation can reduce muscle glucose utilization, leading to insufficient glycogen reserves, which in turn affects muscle function and quality, accelerating muscle atrophy (Daily and Park, 2022). Lactobacillus may directly or indirectly affect glucose metabolism, thereby improving muscle function. In the liver, GSK-3 β is a serine/threonine kinase that can inhibit glycogen synthase (GS) activity, and L. acidophilus can downregulate the expression of GSK-3 β and increase glycogen synthesis (Yan et al., 2019). As the main metabolites of Lactobacillus and other gut microbiota, SCFAs have been proven to promote the synthesis of muscle glycogen (Fushimi and Sato, 2005). Regarding glycogen consumption, fermented milk enriched with probiotics that contains L. acidophilus and L. casei could reduce fasting blood glucose (FBG) and HbA1c levels, stimulate muscle glucose absorption (Hu et al., 2017).
Sarcopenia is often accompanied by insulin resistance and both are mutually pathogenic, resulting in a vicious cycle (Liu and Zhu, 2023). Lactobacillus strains contribute to a decrease in insulin resistance, consequently againsting the progression of sarcopenia. Glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) in skeletal muscle can mediate insulin-stimulated glucose uptake (Herman and Kahn, 2006). In mice with diet-induced obesity, the administration of Lactobacillus lowered insulin resistance and improved glucose tolerance, potentially by alleviating endoplasmic reticulum stress in skeletal muscle, inhibiting macrophage activation, and enhancing GLUT4 expression (Tabuchi et al., 2003). Furthermore, a mixture of probiotic content L. rhamnosus, L. acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum regulated insulin signal transduction in muscles, improving insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance in obese mice. This strategy fully restored Akt phosphorylation levels in muscle tissue while significantly reducing the relative amounts of TNF-α and IL-6 transcripts (Bagarolli et al., 2017).
Skeletal muscle serve as a storage site for amino acids stored in the form of proteins (Baskin et al., 2015). The balance between the synthesis of skeletal muscle proteins (MPS) and the breakdown of muscle proteins (MPB) is crucial for skeletal muscle phenotype, mass and function (Schiaffino et al., 2013). Increasing protein degradation and reducing protein synthesis is the main mechanism of muscle atrophy in sarcopenia (Sartori et al., 2021). Dysbiosis in the gut microbiota can lead to increased gut barrier permeability, endotoxin translocation, and insulin resistance, resulting in impaired muscle protein synthesis. Supplementing with L. plantarum can regulate gut microbiota dysbiosis, reduce the expression of muscle atrophy markers such as Atrogin-1 and LC3 protein in mice, and promote muscle protein synthesis (Chen et al., 2016). L. plantarum and L. rhamnosus not just modulate the structure of gut microbiota and its metabolites, but regulating the expression of protein synthesis genes mTOR and S6K in skeletal muscle, ultimately enhancing nitrogen metabolism in the weaned piglets (He et al., 2023). In addition, whey protein fermented with L. gasseri prevented dexamethasone (DEX)-induced muscle atrophy by stimulating myogenesis and protein synthesis through activation of the IGF-1-PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, reducing protein breakdown via FOXO-mediated modulation of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway (UPP) and autophagy lysosomal pathway (ALP). Specifically, it prevented the increase in mRNA and protein expression of in UPP related molecules atrogin-1/MAFbx and MuRF1, as well as those of ALP related molecules LC3, calpain L, and BNI (Jang et al., 2023). L. paracasei also exert beneficial effects on skeletal muscle by modulating key signaling pathways involved in muscle protein homeostasis. Specifically, these probiotics inhibit FOXO3a activation, which in turn suppresses the expression of MuRF1 and MAFbx/Atrogin-1, two E3 ubiquitin ligases that regulate ubiquitin-mediated skeletal muscle protein degradation. Additionally, probiotics inhibit NF-κB activation, a pathway known to promote muscle atrophy (Zhong et al., 2023). There by enhancing AKT and mTOR activation, pathways that play a central role in promoting myogenic gene expression and protein synthesis. This dual action reducing protein degradation and enhancing protein synthesis leads to an increase in MyHC (myosin heavy chain) expression, a key marker of muscle differentiation and contractile function. Together, these mechanisms contribute to the preservation of muscle mass, strength, and function (He et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2024). Collectively, these findings indicate that Lactobacillus show the potential to prevent muscle atrophy and promote overall muscle protein homeostasis.
Clinically, sarcopenia is often accompanied by obesity, which can further promote the occurrence of sarcopenia (Tardif et al., 2014). This type of obese muscle atrophy includes intramuscular fat accumulation and muscle fibrosis. Abnormal accumulation of lipids in the body will accelerate muscle atrophy and muscle steatosis (Vial et al., 2020). Skeletal muscle lipid metabolism is also regulated by lactobacilli. Animal experiments have found that the increase in skeletal muscle fat content in rats fed with a high-fat high-sucrose (HFS) diet may be related to a decrease in the relative abundance of Lactobacillus and Prevotella (Collins et al., 2016). L. plantarum can improve lipid oxidation by increasing the mRNA expression of lipid oxidation genes, including CPT1, ACOX1, and MCAD, and reduce lipid synthesis by activating the SIRT1-PGC-1 alpha pathway, leading to reduction of fat accumulation (Kwon et al., 2020). Additionally, supplementing with L. plantarum can reduce white adipose tissue without weight gain, enhance muscle mass, and increase the number of type I fibers related to exercise endurance in the gastrocnemius muscle, thereby preventing muscle atrophy caused by muscle function degradation (Chen et al., 2016).
Adiponectin (APN) is the most abundantly expressed human body adipokine, having a role in resisting inflammation and regulating muscles (Krause et al., 2019). A meta-analysis on the association between adiponectin level and sarcopenia has shown that individuals with sarcopenia had lower adiponectin levels compared to those without sarcopenia (Komici et al., 2021). APN may activate signals by binding to T-cadherin, thereby promoting muscle regeneration and resisting muscle atrophy (Tanaka et al., 2019). L. rhamnosus effectively increases insulin sensitivity and reduces lipid accumulation by stimulating APN secretion and AMPK activation, while upregulating expression genes involved in fatty acid oxidation, such as PPAR-a, CPT1, and ACOX in the liver and skeletal muscle of HFD mice (Kim et al., 2013). Interestingly, measurements of total body fat, fat deposition, and lipid levels in diet-induced obese mice showed no difference between the control group and mice supplemented with Lactobacillus acidophilus (Arora et al., 2012). Therefore, the efficacy of a Lactobacillus is highly strain-specific. Diverse strains of lactobacilli have different effects and ways on lipid metabolism, which may explain differences in the results of studies using various strains.
SCFAs is primarily consisting of acetic, propionic, and butyric acids, which are produced by specific anaerobic colon bacteria to decompose carbohydrates. These SCFAs are vital in supporting gut homeostasis, glucose, protein and lipid metabolism, immune system, and body inflammatory response (Tan et al., 2014). Current studies propose that SCFAs can participate in muscle regulation through the following pathways (Figure 2): (1) SCFAs are able to attach to free fatty acid receptors 2 and 3 (FFAR2/3), enhancing glucose metabolism and IGF-1 release. IGF-1 activates the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling cascade, supporting muscle protein synthesis and phosphorylates FoxO to prevent muscle protein breakdown (Pekmez et al., 2019). (2) SCFAs increase mitochondrial adenylate activating proteins. AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) enhances the activity of carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT-1), leading to increased fatty acid oxidation. (3) Regulation is carried out via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1α), which functions as an activator for numerous nuclear receptors and transcription factors, regulating the expression of CPT-1 to increase fatty acid oxidation (Zong et al., 2002). In mouse models, the positive effects of CPT-1 and PGC-1α on muscle mass have been confirmed, showing their ability to inhibit muscle atrophy (Hénique et al., 2015). (4) SCFAs passively diffuse into cells to inhibit HDACs, which possess key roles in the function and metabolism of skeletal muscle, affecting the development and differentiation of muscle cells by regulating the acetylation status of myogenic regulatory factors such as MyoD, MEF2 and Myogenin. This involves the promotion of skeletal muscle atrophy, inhibition of mitochondrial synthesis, and regulation of glucose and lipid oxidation processes (Tian et al., 2020).
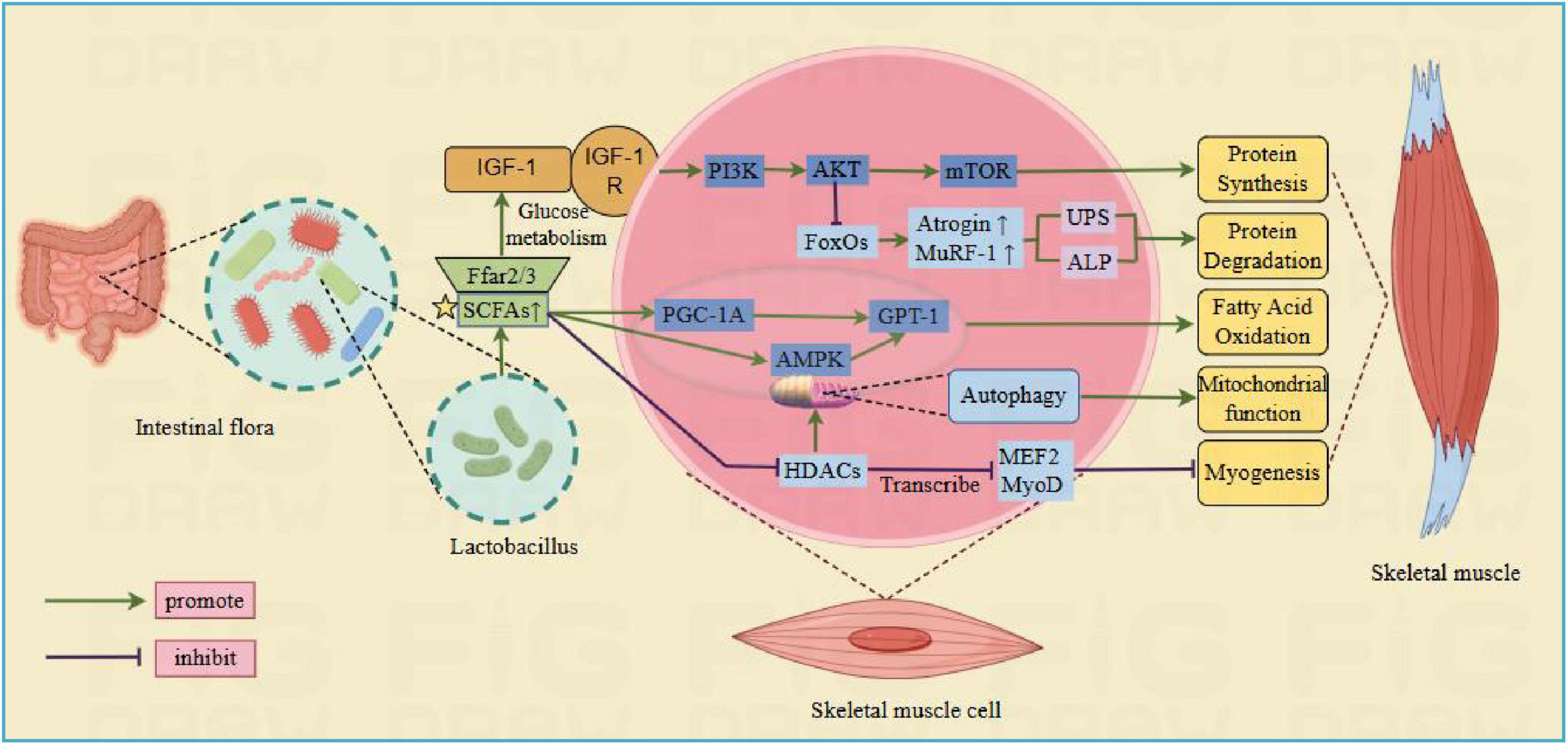
Figure 2. Lactobacillus regulate skeletal muscle pathways through short-chain fatty acids. Ffar2/3, free fatty acid receptors 2 and 3; IGF-1, insulin like growth factor; IGF1R, IGF-1 membrane receptor; MTOR, rapamycin target protein; CPT-1, carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1; PGC-1α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol kinase; AMPK, adenylate activated protein kinase; FoxO, forked transcription factor; MuRF-1, muscle specific ring finger protein 1; Atrogin, human muscle atrophy protein Fbox; HDAC, histone deacetylase; MEF2, myocyte enhancer factor 2; MyoD, myogenic differentiation antigen (Created with figdraw.com).
Beneficial gut bacteria, including Lactobacillus, Bifidobacteria, Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Actinobacteria and Enterococcus faecalis, promote the production of SCFAs, which regulate skeletal muscle metabolism and muscle fiber phenotype through the gut-muscle axis, indirectly influencing muscle health (Anachad et al., 2023). Lactobacillus are key growth factors for gut bacteria that produce short chain fatty acids. They not only produce acetic acid on its own, but also regulate the bacteria that produce SCFA in the intestine, promoting the mutual transformation of SCFA through cross fertilization. For example, bacteria that produce butyric acid can increase SCFA levels by utilizing lactic acid and acetic acid (Morrison et al., 2006). The concentrations of acetate, propionate, and butyrate in the cecal contents of mice significantly increased after oral supplementation of L. plantarum. In acetate-producing bacteria, there was a significant increase in the abundance of members from the Peptococcaceae family and the Ruminococcaceae genus UCG-004. Furthermore, there is a significant rise in the abundance of bacteria producing butyrate, particularly members of the Lachnospiraceae family. This leads to improve SCFAs levels and relieve sarcopenia. Meanwhile, the presence of L. plantarum increased the abundance of beneficial SCFA producing bacteria and significantly reduced the number of intestinal pathogenic bacteria (such as Proteobacteria and Enterobacteriaceae) (Lee C.-C. et al., 2021).
The vast majority of ongoing research aims to quantify the levels of SCFA influenced by LAB. Nevertheless, its effect on muscle is complex. In addition to concentration, further research is needed into the individuals and the ratio. Different SCFAs mediated by Lactobacillus have different effects on muscle fibers. Propionic acid shows a positive association with the ratio of type I muscle fibers, but the cross-sectional area of type I muscle fibers is negatively correlated with the ratio of type IIb muscle fibers. The ratio of butyric acid to IIa type muscle fibers is positively correlated (Liu T. et al., 2023). In the intestine, the molar ratio of acetic, propionic, and butyric acids is roughly 60:20:20, respectively (Markowiak-Kopeć and Śliżewska, 2020). In vitro studies have shown that SCFAs exhibit a dose-dependent effect, and glucose uptake in C2C12 myotubes varies in different proportions of combinations. Single SCFA does not increase glucose uptake (Otten et al., 2023). Moreover, although lactic acid may not fall under the category of SCFAs, it is an essential compound generated by Lactobacillus and a critical precursor for the production of SCFAs. The link between lactic acid and muscle atrophy needs to be further explored.
A healthy intestinal barrier function can reduce inflammation and promote nutrient absorption, thereby helping to prevent the occurrence of sarcopenia (Baumgart and Dignass, 2002). The gut mechanical barrier, as the first line of defense against the penetration of harmful substances and pathogens (such as lipopolysaccharide) into the body, is primarily consisted of small cells that form a protective layer over the intestinal epithelium, interconnected by adherens junctions (AJs) and tight junctions (TJs). This intricate network serves as the principal determinant of paracellular permeability within the gastrointestinal tract (Drolia and Bhunia, 2019). Tight junctions (TJs) contain transmembrane proteins, including occludin and claudins, as well as peripheral membrane proteins like ZO (occlusive zone protein) as important complexes for sealing the space between Intestinal Epithelial Cells (IEC), maintaining cell polarity, and sustaining the osmotic function of the intestinal barrier. Dysfunction of the intestinal barrier can cause bacteria and their metabolites (such as LPS) in the intestine to leak out and enter the bloodstream.
LPS, including lipid A, core oligosaccharides, and O antigen, is a strong endotoxin present in the outer membrane of Gram negative bacteria. When excessive LPS is transferred to the systemic circulation and increases plasma LPS levels, it can trigger inflammation, thereby facilitating the onset and progression of sarcopenia (Bindels and Delzenne, 2013). Due to the expression of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) by skeletal muscle cells, they can identify a variety of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (Boyd et al., 2006). Nuclear factor κB (NF-κB), the transcription factor involved in muscle-specific activation, induces sarcopenia, thereby triggering the toll-like receptors/NF-κB pathway (Thoma and Lightfoot, 2018). Therefore, upon recognition of LPS from gut bacteria by TLR4 on skeletal muscle cells, nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) is activated, leading to the production of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) (Barton and Medzhitov, 2003). The IL-6 secreted by macrophages and T-cells is involved in the inhibition of protein synthesis (Haddad et al., 2005), and the TNF-a producted by macrophages induces protein degradation and apoptosis in cells during the initial stages of stress response (Li et al., 2005). Another pathway shown that LPS promotes the expression of Atrogin-1 and MuRF1 genes via MAPK activation, activating both the UPS and autophagy-lysosome pathways, leading to skeletal muscle protein degradation (Ronnebaum et al., 2014).
Lactobacillus hold a pivotal role in repairing and preserving the intestinal barrier function, maintaining intestinal homeostasis, which affect the occurrence and progression of muscle atrophy. It can protect the gut barrier by stimulating the proliferation of intestinal epithelial cells and the expression of TJ protein related growth factors, and balance inflammatory factors through changing downstream signaling pathways after specific recognition of receptors. TJs were observed downregulated in early-weaned piglets infected with Escherichia coli k88, leading to increased permeability of the intestinal mucosa. However, the administration of L. casei salvaged this disaster. L. casei showed a remarkable ability to reinstate the expression of TJs, such as ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-1 in piglets, and enhanced the intestinal structure. Furthermore, L. casei can also promote the regeneration and repair of intestinal mucosal epithelial cells by enhancing their proliferation, thus protecting the integrity of intestinal epithelial tissue. Simultaneously it increased the thickness of intestinal muscles and the height of villi, further improving the overall health of the intestine (Wang et al., 2019). As a probiotic mixture consisting of Plant Lactobacillus and Fermented Lactobacillus, which has been proven to have the ability to increase TJs expression and reduce the levels of LPS in their plasma in high-fat diet-fed mice. It also can enhance GLP-1 levels, alleviate endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, improve peripheral insulin sensitivity, and increase skeletal muscle mass (Balakumar et al., 2018).
In terms of inhibiting LPS induced inflammatory factors, L. rhamnosus (LGG) exhibited anti-inflammatory effects in the gastrointestinal tract. Certain Lactobacillus species demonstrated a specific ability to mitigate LPS-induced inflammatory damage in mouse models (Petrof et al., 2009). In human smooth muscle cell (SMC), the protective effect of LGG against LPS-induced damage is mediated by inhibiting phosphorylation in both NF-κB subunits and suppressing the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6 upon activation of surface TLR2, whose expression is reduced following exposure to LGG. Furthermore, LGG also reinstates the secretion levels of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 (Ammoscato et al., 2013).
BAs, including chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) and cholic acid (CA), are endogenously synthesized in the liver from cholesterol. After undergoing lipid digestion and absorption in the duodenum, the lipids journey to the distal ileum and the proximal colon. Here, they undergo a transformation into free bile acids, facilitated by the action of gut bacteria and bile salt hydrolase (BSH). A small portion of BA that has not entered the enterohepatic circulation is metabolized by gut microorganisms in the colon, producing non-conjugated bile acids and secondary bile acids through isomerization and dehydroxylation (Cai et al., 2022). Previous studies have shown that the level of 12α-hydroxylated cholic acid (such as deoxycholic acid) is negatively correlated with skeletal muscle volume. In contrast, the level of non-12α-hydroxylated cholic acid (such as chenodeoxycholic acid) is positively correlated with skeletal muscle volume (Kobayashi et al., 2017). It has been also revealed that low-dose ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) blocks the production of cancer induced reactive oxygen species through the PKC signaling pathway, thereby inhibiting transcription factors AP-1 and NF-κ B, leading to the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-α and reducing the consumption of cachexia (e.g., fat and skeletal muscle tissue loss) (Tschirner et al., 2012).
Lactobacillus can modulate BAs metabolism and affect its gastrointestinal transport. LAB possess bile acids hydrolase, which exhibits tolerance and deconjugation activity toward BAs, allowing them to survive and exert bile acids dissociation ability (Hernández-Gómez et al., 2021). Joyce et al. (2014) demonstrated the importance of gut microbiota in bile acid metabolism and systemic gene expression. Mice treated with Lactobacillus plantarum exhibited enhanced expression levels of genes related to bile acid synthesis and reverse cholesterol transport in the liver. Additionally, the expression of the bile acid receptor TRG5 was increased in the liver, ileum, and skeletal muscle of mice treated with L. plantarum (Kwon et al., 2020). The binding of bile acid with TGR5 can enhance D2 activity (Watanabe et al., 2006), resulting in elevated T3 levels in skeletal muscle cells, thereby facilitating the development and regeneration of skeletal muscle (Mullur et al., 2014). Whereas, given the significant differences in bile acid profiles between mice and humans, further studies will be necessary to determine the correlation between bile acids, gut microbiota and muscle atrophy in humans. Accordingly, exploring the underlying mechanisms still remains many challenges (Figure 3).
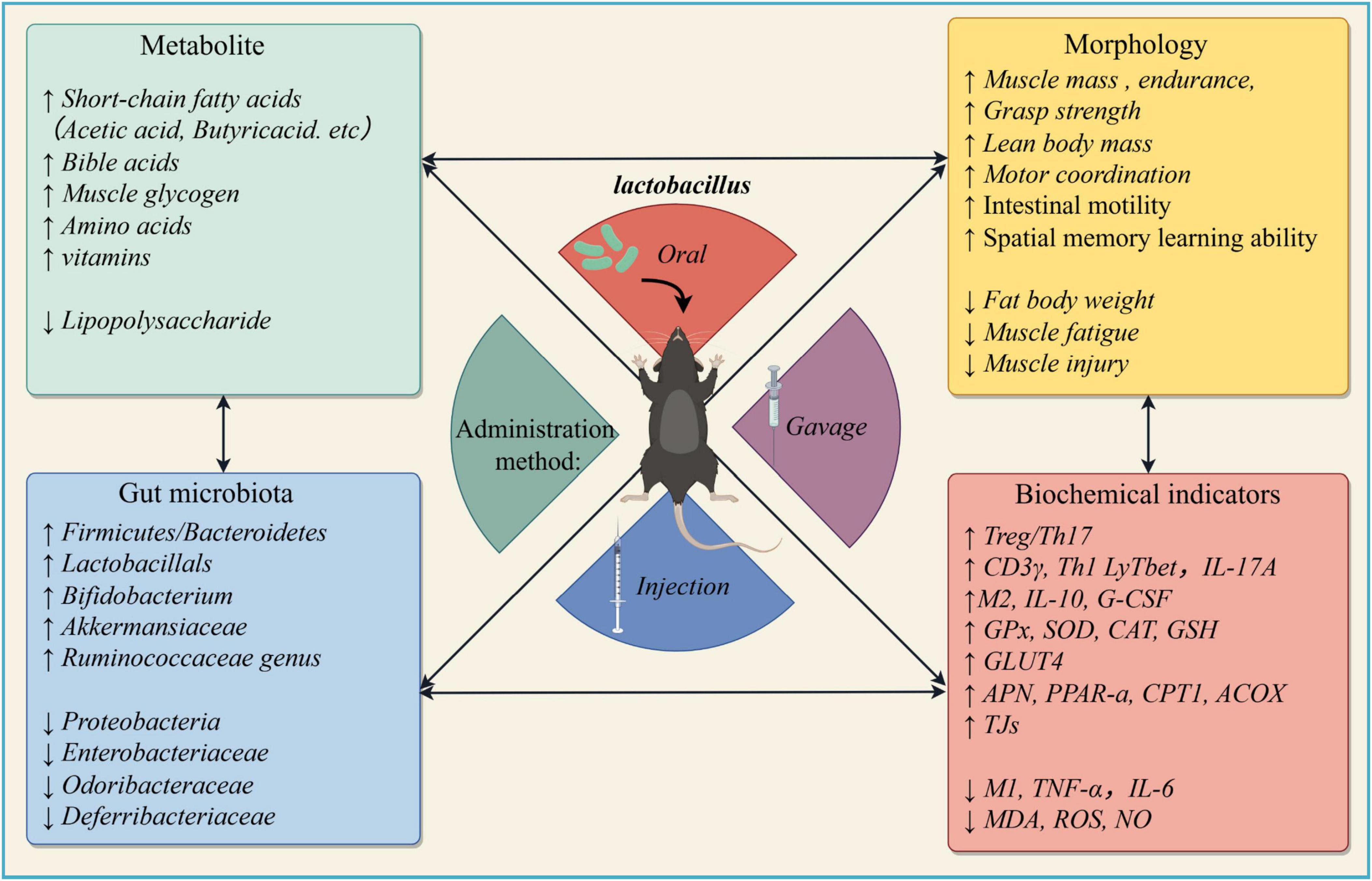
Figure 3. Clinical findings of muscle atrophy mice/rat models after Lactobacillus intervention (Created with figdraw.com)).
A balanced gut microbiota such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium can delivers essential vitamins, including B-vitamins B3, B5, B6, B7, B12, folate, and vitamin K. There is an inextricable link between various vitamins and sarcopenia, with adequate vitamin intake being crucial for maintaining muscle mass and function, The production of these compounds by gut microbiota can enter the systemic circulation and ultimately affect skeletal muscle cells, particularly in the case of vitamin D (Bauer et al., 2013; Uchitomi et al., 2020). Low plasma vitamin B12 and vitamin D has been observed in elderly patients with sarcopenia (Ates Bulut et al., 2017). Lactobacillus can influence the production, absorption, and metabolism of vitamins, thereby preventing sarcopenia. It can regulate skeletal muscle synthesis and metabolism by restoring a normal gut microbiome, producing folate and vitamin B12. This process helps prevent oxidative stress and endothelial damage caused by hyperhomocysteinemia, thereby preventing skeletal muscle dysfunction (Langille et al., 2014). Similarly, Lactobacillus strains can also influence vitamin D levels. Study found that L. reuteri NCIMB 30242 may promote vitamin D absorption by increasing liver 25-hydroxylase activity or 7-dehydrocholesterol (7-DHC) concentration, thereby leading to an increase in the production of 25(OH)D (Jones et al., 2013). Research has also found that L. rhamnosus GG and L. plantarum are capable of increasing the expression of the vitamin D receptor (VDR) protein in both mouse and human intestinal epithelial cells while enhancing its transcriptional activity. By activating the VDR signaling pathway, these probiotics ultimately promote vitamin D absorption and the expression of its target genes, such as the antimicrobial peptide cathelicidin, thereby exerting anti-inflammatory effects (Wu et al., 2015). In another study, it was also found that L. rhamnosus GG can promote gut absorption of cholecalciferol, and increase 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 levels by upregulating the protein levels of vitamin D transporters in senile osteoporosis, thereby affecting the absorption of vitamin D and treating osteoporosis (Cheng et al., 2022). Many studies have demonstrated a highly significant link between sarcopenia and osteoporosis, with both conditions share similar pathological mechanisms (Wang et al., 2024). This gave rise to the term “osteosarcopenia.” Although current research on Lactobacillus is either focused on osteoporosis (Bose and Sharan, 2024; Guo et al., 2023; Huang et al., 2022) or sarcopenia (Kim et al., 2023; Lee et al., 2023; Ni et al., 2019; Rondanelli et al., 2022). Considering the strong association and shared pathophysiology between osteoporosis and sarcopenia, Lactobacillus, due to its ability to enhance vitamin D production, absorption, promote vitamin D metabolism, and improve calcium utilization, presents great potential in the treatment of osteosarcopenia.
The gut microbiota is essential for maintaining overall human health and preventing diseases. Table 1 lists more detail on the actual effectiveness of each strain. In recent years, direct supplementation of Lactobacillus has gradually become a suitable treatment option to prevent or alleviate sarcopenia and improve patient quality of life, which is considered as an effective means of assisting or replacing traditional drug therapy. Several randomized controlled trials have substantiated the efficacy of various probiotics, with a particular emphasis on Lactobacillus. These studies have been conducted across diverse populations, focusing notably on adult and elderly individuals suffering from sarcopenia. In terms of promoting muscle health, L. plantarum PL-02 and LY-66 has demonstrated benefits in increasing muscle mass and reducing body fat accumulation, which can help mitigate myosteatosis, muscle steatosis is a key factor contributing to sarcopenia, thereby effectively preventing its progression (Lee et al., 2024). Long-term and excessive exercise can lead to microdamage of muscle fibers and inflammatory responses. Patients may develop muscle dysfunction/insufficiency, and a small proportion may even suffer from muscle atrophy (Rubio-Arias et al., 2019). Supplementing Lactobacillus can effectively alleviate these adverse conditions. Two capsules (3 × 1010 CFU/capsule) of L. plantarum PS128 administered each morning and evening before meals for four weeks reduced muscle damage (i.e., myoglobin, LDH, and CPK), significantly elevated the antioxidation indicator SOD, and reduced muscle inflammation response of marathon runners (Fu et al., 2021). The same dose of L. plantarum TWK10 administered over 6 weeks reduced muscle fatigue and improved endurance. In terms of body composition, the administration of TWK10 resulted in favorable changes in body composition (body fat, bodyweight, muscle weight, BMI). Particularly in the high-dose group, a significant decrease in body fat and increases in muscle mass was observed in healthy participants without professional athletic training (Huang et al., 2019).
With aging, muscle mass and function gradually decline in the elderly population, making them more susceptible to sarcopenia. In this context, Lactobacillus can play a significant role by reducing muscle fat infiltration, improving metabolic processes, and exerting anti-inflammatory effects, thereby effectively slowing down the progression of sarcopenia. In obese or metabolic syndrome patients, where muscle fat infiltration is more prevalent due to altered lipid metabolism, Lactobacillus can help regulate body composition and improve lipid metabolism. Additionally, for individuals engaged in intense physical training, such as athletes or fitness enthusiasts, supplementation with Lactobacillus offers benefits in alleviating exercise-related muscle damage while maintaining overall muscle health. This is particularly important for those who are consistently subjected to high-intensity workouts that may contribute to muscle strain and inflammation. These effects not only mitigate the risk of sarcopenia but also support overall metabolic health in these populations.
The ability of Lactobacillus to improve muscle function and quality can serve as a preventive measure. Similarly, these capabilities, such as enhancing muscle protein synthesis and reducing inflammation, also play a therapeutic role in alleviating sarcopenia symptoms in elderly or chronic disease patients. Twice daily administration of whey protein fermented by L. casei DK211 in capsule ingested (37 g per group) an 8-week period of consumption treatment increased levels of branched chain amino acids in plasma, and improved muscle protein synthesis, especially muscle strength and exercise performance in 48 middle-aged healthy males relative to the placebo-treated control group (Kim et al., 2023). In the same vein, another study with a similar L. casei treatment protocol on elderly subjects with sarcopenia found analogous changes, while reduced inflammation in the muscle tissue and restored muscle function after administration of a new food composed of omega-3 fatty acids, leucine and probiotic L. paracasei PS23 (Rondanelli et al., 2022). In addition, it was found that supplementing TWK10 for 6 weeks possess a trend of enhancing muscle mass, grip strength, lower limb muscle strength, gait speed and balance in Frail Older Adults. The effect became even more pronounced as the supplementation duration extends to the 18th week (Lee M.-C. et al., 2021). The above studies that demonstrate how Lactobacillus supplementation can both prevent muscle wasting in at-risk populations and aid in recovery in individuals already experiencing sarcopenia.
While Lactobacillus strains show promise in mitigating sarcopenia, current research still has notable limitations that need to be addressed. Lactobacillus-mediated microbiota and metabolites perform an essential foundational role. Currently, the majority of studies still rely on 16S sequencing technology to determine the classification information of microbial communities, which may reduce the precision of specific categories and ignore the role of fungus and viruses from the gut microbiota. Such an integrated approach could reveal additional factors that contribute to sarcopenia, paving the way for novel therapeutic interventions that target a broader spectrum of the microbiome. Therefore, subsequent research should incorporate fungi and viruses in the intestines to provide a thorough analysis of key microorganisms that might interact with Lactobacillus to mitigate sarcopenia. For instance, shotgun metagenomic sequencing technology that can investigate species level and microbial community functional changes at a more detailed classification level (Ma et al., 2020). Furthermore, the connection between specific bacterial communities and substance metabolism is not yet fully understood, with most research primarily identifying correlations. In the future, in vitro fermentation simulations, biosensor technology should be applied to detect the generation of metabolites and their influence on sarcopenia.
Although Lactobacillus strains are generally recognized as safe and widely used, mild gastrointestinal symptoms such as bloating and gas are occasionally reported. In certain cases, especially in individuals with compromised immune systems, Lactobacillus may overgrow and cause bacterial translocation. This involves the migration of bacteria from the gut to other parts of the body, such as the bloodstream or internal organs, potentially leading to infections and even rare cases of systemic infections including bacteremia, have occurred (Doron and Snydman, 2015; Sanders et al., 2016). Give to this, it is need to develop personalized probiotic formulations, tailored to an individual’s health status, microbiome composition, and specific needs, can optimize benefits and minimize adverse effects by ensuring that the selected Lactobacillus strains are compatible with each individual’s gut microbiome. Due to different strains of Lactobacillus exhibit varying safety profiles and functional properties such as Lactobacillus hilgardii X1B, which produces putrescine and agmatine through arginine and ornithine, may be harmful to the human body, especially at high concentrations, which may cause hypertension, allergic reactions, or combine with nitrite to form carcinogenic nitrosamines (Arena and Manca de Nadra, 2001). Therefore, careful strain selection is crucial. For example, strains with a long history of safe use, such as L. rhamnosus GG or L. plantarum may be preferred for certain populations. Though different strains share many similarities, the unique characteristics of different subspecies result in variations in the anti-sarcopenic properties and functional components of each stain (Baek et al., 2023). Thus, combining the utilization of different strains of Lactobacillus to develop more efficient probiotics or to jointly use Lactobacillus with other probiotics or prebiotics, it may be possible to reduce the required dosage of Lactobacillus, thereby minimizing the risk of adverse effects. In recent years, newly emerged microorganisms, including Akkermansia muciniphila, Ruminococcus gnavus, and others, may be regarded as powerful candidates to deliver a partnership with Lactobacillus. However, the effectiveness of Lactobacillus in clinical applications is still hindered by issues such as low vitality and low bioavailability in the gastrointestinal process. As we focus on the combination, an effective delivery method seems to double our efforts with half the effort. Emerging nanotechnology can design various forms of nanoparticles (NPs) have been designed for probiotics/prebiotics/symbiotics or their different combinations, facilitating the efficient coupling of probiotics with intestinal mucosal tissues and ensuring their orderly targeted release (Dangi et al., 2023). Moreover, a new packaging method for probiotics method [encapsulate a single bacterium with Gum arabic (GA) and Maltodextrin] tremendously increase the survivability of Lactobacillus acidophilus under the gastrointestinal conditions (Arepally et al., 2020).
We summarized the potential mechanisms of Lactobacillus in treating sarcopenia, which demonstrated that Lactobacillus play both direct and indirect roles in alleviating the symptoms of sarcopenia. Specifically, Lactobacillus play a pivotal role in regulating immunity, inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress, hosting metabolism, balancing skeletal muscle metabolism and adjusting gut microecology, all of which interact with each other and protect muscle mass and function in sarcopenia. Although there are medications available for treating other clinical conditions that can be used for sarcopenia, their safety and efficacy remains limited, especially in patients with severe sarcopenia. In contrast, Lactobacillus offers a more effective treatment with fewer side effects and lower cost burden. This review demonstrated that Lactobacillus has the potential to become a promising option for the treatment of sarcopenia.
JZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. FP: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. HY: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. JL: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. LZ: Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. XC: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. HuL: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. HaL: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. SL: Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. TY: Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. GL: Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. GC: Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. HZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
The authors declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 2023JJ30552 to HZ. Grant No. 2025JJ81045 to FP), the Hunan Provincial Science and Technology Innovation Program of China (Grant No. 2017SK50203 to HZ), The College Student Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Project of the University of South China (Grant No. 20200021001 to SL), the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province [Joint Project of Science and Health (Grant No. 2021JJ70039 to GC), University of South China Clinical Research 4310 Program (Grant No. 20224310NHYCG01 to GC)], the Hunan Provincial Innovation Foundation For Postgraduate (Grant No. CX20200971 to TY), and the Scientific Research Project of Health Commission Of Hunan Province (Grant No. 202109040556 to HuL, Grant No. 202209014251 to XC, Grant No. D202309019457 to HaL, and Grant No. B202309018212 to GL).
We would like to thank the senior management of The University of South China for their constant support and guidance.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abdel-Halim, N., Farrag, E., Hammad, M., Habotta, O., and Hassan, H. (2023). Probiotics attenuate myopathic changes in aging rats via activation of the myogenic stellate cells. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins Online ahead of print. doi: 10.1007/s12602-023-10202-2
Almonacid, D., Kraal, L., Ossandon, F., Budovskaya, Y., Cardenas, J., Bik, E., et al. (2019). 16S rRNA gene sequencing and healthy reference ranges for 28 clinically relevant microbial taxa from the human gut microbiome. PLoS One 14:e0212474. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176555
Ammoscato, F., Scirocco, A., Altomare, A., Matarrese, P., Petitta, C., Ascione, B., et al. (2013). Lactobacillus rhamnosus protects human colonic muscle from pathogen lipopolysaccharide-induced damage. Neurogastroent. Motil. 25, 984–e777.
Anachad, O., Taouil, A., Taha, W., Bennis, F., and Chegdani, F. (2023). The implication of short-chain fatty acids in obesity and diabetes. Microbiol. Insights 16:11786361231162720.
Archer, A., Muthukumar, S., and Halami, P. (2021). Lactobacillus fermentum MCC2759 and MCC2760 alleviate inflammation and intestinal function in high-fat diet-fed and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 13, 1068–1080.
Arena, M., and Manca de Nadra, M. C. (2001). Biogenic amine production by Lactobacillus. J. Appl. Microbiol. 90, 158–162.
Arepally, D., Reddy, R., and Goswami, T. (2020). Encapsulation of lactobacillus acidophilus NCDC 016 cells by spray drying: Characterization, survival after in vitro digestion, and storage stability. Food Funct. 11, 8694–8706. doi: 10.1039/d0fo01394c
Arora, T., Anastasovska, J., Gibson, G., Tuohy, K., Sharma, R., Bell, J., et al. (2012). Effect of lactobacillus acidophilus NCDC 13 supplementation on the progression of obesity in diet-induced obese mice. Br. J. Nutr. 108, 1382–1389. doi: 10.1017/S0007114511006957
Ates Bulut, E., Soysal, P., Aydin, A., Dokuzlar, O., Kocyigit, S., and Isik, A. (2017). Vitamin B12 deficiency might be related to sarcopenia in older adults. Exp. Gerontol. 95, 136–140.
Baek, J., Shin, Y., Ma, X., Park, H., Hwang, Y., and Kim, D. (2023). Bifidobacterium bifidum and lactobacillus paracasei alleviate sarcopenia and cognitive impairment in aged mice by regulating gut microbiota-mediated AKT, NF-κB, and FOXO3a signaling pathways. Immun. Ageing A 20:56. doi: 10.1186/s12979-023-00381-5
Bagarolli, R., Tobar, N., Oliveira, A., Araújo, T., Carvalho, B., Rocha, G., et al. (2017). Probiotics modulate gut microbiota and improve insulin sensitivity in DIO mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 50, 16–25. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2017.08.006
Balakumar, M., Prabhu, D., Sathishkumar, C., Prabu, P., Rokana, N., Kumar, R., et al. (2018). Improvement in glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity by probiotic strains of indian gut origin in high-fat diet-fed C57BL/6J mice. Eur. J. Nutr. 57, 279–295. doi: 10.1007/s00394-016-1317-7
Barton, G., and Medzhitov, R. (2003). Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. Science 300, 1524–1525.
Baskin, K., Winders, B., and Olson, E. (2015). Muscle as a ‘mediator’ of systemic metabolism. Cell. Metab. 21, 237–248.
Bauer, J., Biolo, G., Cederholm, T., Cesari, M., Cruz-Jentoft, A., Morley, J., et al. (2013). Evidence-based recommendations for optimal dietary protein intake in older people: A position paper from the PROT-AGE Study Group. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 14, 542–559. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2013.05.021
Baumgart, D., and Dignass, A. (2002). Intestinal barrier function. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 5, 685–694.
Bindels, L., and Delzenne, N. (2013). Muscle wasting: The gut microbiota as a new therapeutic target? Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 45, 2186–2190.
Bindels, L., Beck, R., Schakman, O., Martin, J., De Backer, F., Sohet, F., et al. (2012). Restoring specific lactobacilli levels decreases inflammation and muscle atrophy markers in an acute leukemia mouse model. PLoS One 7:e37971. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037971
Bindels, L., Neyrinck, A., Claus, S., Le Roy, C., Grangette, C., Pot, B., et al. (2016). Synbiotic approach restores intestinal homeostasis and prolongs survival in leukaemic mice with cachexia. ISME J. 10, 1456–1470. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2015.209
Bonetto, A., Penna, F., Muscaritoli, M., Minero, V., Rossi Fanelli, F., Baccino, F., et al. (2009). Are antioxidants useful for treating skeletal muscle atrophy? Free Radical Biol. Med. 47, 906–916.
Bose, S., and Sharan, K. (2024). Effect of probiotics on postmenopausal bone health: A preclinical meta-analysis. Br. J. Nutr. 131, 567–580. doi: 10.1017/S0007114523002362
Boyd, J., Divangahi, M., Yahiaoui, L., Gvozdic, D., Qureshi, S., and Petrof, B. (2006). Toll-like receptors differentially regulate CC and CXC chemokines in skeletal muscle via NF-kappaB and calcineurin. Infect. Immun. 74, 6829–6838. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00286-06
Cai, J., Sun, L., and Gonzalez, F. (2022). Gut microbiota-derived bile acids in intestinal immunity, inflammation, and tumorigenesis. Cell. Host. Microbe 30, 289–300.
Campbell, C., McMillan, H., Mah, J., Tarnopolsky, M., Selby, K., McClure, T., et al. (2017). Myostatin inhibitor ACE-031 treatment of ambulatory boys with duchenne muscular dystrophy: Results of a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Muscle Nerve 55, 458–464. doi: 10.1002/mus.25268
Chen, L., Chang, S., Chang, H., Wu, C., Pan, C., Chang, C., et al. (2022). Probiotic supplementation attenuates age-related sarcopenia via the gut-muscle axis in SAMP8 mice. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 13, 515–531. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12849
Chen, L., Huang, S., Huang, K., Hsu, C., Yang, K., Li, L., et al. (2019). Lactobacillus paracasei PS23 decelerated age-related muscle loss by ensuring mitochondrial function in SAMP8 mice. Aging 11, 756–770. doi: 10.18632/aging.101782
Chen, Q., Liu, C., Zhang, Y., Wang, S., and Li, F. (2022). Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum KSFY01 on the exercise capacity of D-galactose-induced oxidative stress-aged mice. Front. Microbiol. 13:1030833. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1030833
Chen, Y., Wei, L., Chiu, Y., Hsu, Y., Tsai, T., Wang, M., et al. (2016). Lactobacillus plantarum TWK10 supplementation improves exercise performance and increases muscle mass in mice. Nutrients 8:205.
Cheng, J., Zhai, J., Zhong, W., Zhao, J., Zhou, L., and Wang, B. (2022). Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG promotes intestinal vitamin D absorption by upregulating vitamin D transporters in senile osteoporosis. Calcif. Tissue Int. 111, 162–170. doi: 10.1007/s00223-022-00975-z
Cho, M., Lee, S., and Song, S.-K. (2022). A review of sarcopenia pathophysiology, diagnosis, treatment and future direction. J. Korean Med. Sci. 37:e146.
Collins, K., Paul, H., Hart, D., Reimer, R., Smith, I., Rios, J., et al. (2016). A high-fat high-sucrose diet rapidly alters muscle integrity, inflammation and gut microbiota in Male rats. Sci. Rep. 6:37278. doi: 10.1038/srep37278
Corcoran, B., Stanton, C., Fitzgerald, G., and Ross, R. (2005). Survival of probiotic lactobacilli in acidic environments is enhanced in the presence of metabolizable sugars. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71, 3060–3067. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.6.3060-3067.2005
Cruz-Jentoft, A., Bahat, G., Bauer, J., Boirie, Y., Bruyère, O., Cederholm, T., et al. (2019). Sarcopenia: Revised european consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 48, 16–31.
Daily, J., and Park, S. (2022). Sarcopenia is a cause and consequence of metabolic dysregulation in aging humans: Effects of gut dysbiosis, glucose dysregulation, diet and lifestyle. Cells 11:338. doi: 10.3390/cells11030338
Dangi, P., Chaudhary, N., Chaudhary, V., Virdi, A., Kajla, P., Khanna, P., et al. (2023). Nanotechnology impacting probiotics and prebiotics: A paradigm shift in nutraceuticals technology. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 388:110083. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2022.110083
De Spiegeleer, A., Beckwée, D., Bautmans, I., and Petrovic, M. (2018). Sarcopenia guidelines development group of the belgian society of gerontology and geriatrics (BSGG). Pharmacological interventions to improve muscle mass, muscle strength and physical performance in older people: An umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Drugs Aging 35, 719–734. doi: 10.1007/s40266-018-0566-y
Dias, A., Douhard, R., Hermetet, F., Regimbeau, M., Lopez, T., Gonzalez, D., et al. (2021). Lactobacillus stress protein GroEL prevents colonic inflammation. J. Gastroenterol. 56, 442–455. doi: 10.1007/s00535-021-01774-3
Drolia, R., and Bhunia, A. (2019). Crossing the intestinal barrier via listeria adhesion protein and internalin A. Trends Microbiol. 27, 408–425.
Efimenko, I., Valancy, D., Dubin, J., and Ramasamy, R. (2022). Adverse effects and potential benefits among selective androgen receptor modulators users: A cross-sectional survey. Int. J. Impot. Res. 34, 757–761. doi: 10.1038/s41443-021-00465-0
Farida, E., Nuraida, L., Giriwono, P., and Jenie, B. (2020). Lactobacillus rhamnosus reduces blood glucose level through downregulation of gluconeogenesis gene expression in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Int. J. Food Sci. 2020:6108575. doi: 10.1155/2020/6108575
Fu, S., Tseng, W., Tseng, K., Lai, C., Tsai, Y., Tai, H., et al. (2021). Effect of daily oral lactobacillus plantarum PS128 on exercise capacity recovery after a half-marathon. Nutrients 13:4023. doi: 10.3390/nu13114023
Fushimi, T., and Sato, Y. (2005). Effect of acetic acid feeding on the circadian changes in glycogen and metabolites of glucose and lipid in liver and skeletal muscle of rats. Br. J. Nutr. 94, 714–719. doi: 10.1079/bjn20051545
Gomes, M., Martinez, P., Pagan, L., Damatto, R., Cezar, M., Lima, A., et al. (2017). Skeletal muscle aging: Influence of oxidative stress and physical exercise. Oncotarget 8, 20428–20440.
Guo, M., Liu, H., Yu, Y., Zhu, X., Xie, H., Wei, C., et al. (2023). Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG ameliorates osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats by regulating the Th17/treg balance and gut microbiota structure. Gut Microbes 15:2190304. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2190304
Haddad, F., Zaldivar, F., Cooper, D., and Adams, G. R. (2005). IL-6-induced skeletal muscle atrophy. J. Appl. Physiol. 98, 911–917.
Hall, D., Ma, J., Marco, S., and Gallouzi, I. (2011). Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in muscle wasting syndrome, sarcopenia, and cachexia. Aging 3, 702–715. doi: 10.18632/aging.100358
He, F., Jin, X., Wang, C., Hu, J., Su, S., Zhao, L., et al. (2023). Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG ATCC53103 and lactobacillus plantarum JL01 improved nitrogen metabolism in weaned piglets by regulating the intestinal flora structure and portal vein metabolites. Front. Microbiol. 14:1200594. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1200594
Heeney, D., Gareau, M., and Marco, M. (2018). Intestinal lactobacillus in health and disease, a driver or just along for the ride? Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 49, 140–147.
Hénique, C., Mansouri, A., Vavrova, E., Lenoir, V., Ferry, A., Esnous, C., et al. (2015). Increasing mitochondrial muscle fatty acid oxidation induces skeletal muscle remodeling toward an oxidative phenotype. FASEB J. 29, 2473–2483.
Herman, M., and Kahn, B. (2006). Glucose transport and sensing in the maintenance of glucose homeostasis and metabolic harmony. J. Clin. Invest. 116, 1767–1775. doi: 10.1172/JCI29027
Hernández-Gómez, J., López-Bonilla, A., Trejo-Tapia, G., Ávila-Reyes, S., Jiménez-Aparicio, A., and Hernández-Sánchez, H. (2021). In vitro bile salt hydrolase (BSH) activity screening of different probiotic microorganisms. Foods 10:674. doi: 10.3390/foods10030674
Hill, C., Guarner, F., Reid, G., Gibson, G., Merenstein, D., Pot, B., et al. (2014). Expert consensus document. The international scientific association for probiotics and prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 11, 506–514.
Hong, S., Kim, J., Bae, H., Ham, J., Yoo, J., Chung, K., et al. (2018). Selection and characterization of broad-spectrum antibacterial substance-producing lactobacillus curvatus PA40 as a potential probiotic for feed additives. Anim. Sci. J. Nihon Chikusan Gakkaiho 89, 1459–1467. doi: 10.1111/asj.13047
Hor, Y., Ooi, C., Khoo, B., Choi, S., Seeni, A., Shamsuddin, S., et al. (2019). Lactobacillus strains alleviated aging symptoms and aging-induced metabolic disorders in aged rats. J. Med. Food 22, 1–13. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2018.4229
Hor, Y., Ooi, C., Lew, L., Jaafar, M., Lau, A., Lee, B., et al. (2021). The molecular mechanisms of probiotic strains in improving ageing bone and muscle of d-galactose-induced ageing rats. J. Appl. Microbiol. 130, 1307–1322. doi: 10.1111/jam.14776
Hu, Y., Zhou, F., Yuan, Y., and Xu, Y. (2017). Effects of probiotics supplement in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of randomized trials. Med. Clin. Barcelona 148, 362–370.
Huang, R., Liu, P., Bai, Y., Huang, J., Pan, R., Li, H., et al. (2022). Changes in the gut microbiota of osteoporosis patients based on 16S rRNA gene sequencing: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B. 23, 1002–1013. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2200344
Huang, W., Lee, M., Lee, C., Ng, K., Hsu, Y., Tsai, T., et al. (2019). Effect of lactobacillus plantarum TWK10 on exercise physiological adaptation, performance, and body composition in healthy humans. Nutrients 11:2836. doi: 10.3390/nu11112836
Jang, J., Joung, J., Pack, S., and Oh, N. (2023). Preventive effect of fermented whey protein mediated by Lactobacillus gasseri IM13 via the PI3K/AKT/FOXO pathway in muscle atrophy. J. Dairy Sci. 107, 2606–2619. doi: 10.3168/jds.2023-24027
Jones, M., Martoni, C., and Prakash, S. (2013). Oral supplementation with probiotic L. reuteri NCIMB 30242 increases mean circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D: A post hoc analysis of a randomized controlled trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 98, 2944–2951. doi: 10.1210/jc.2012-4262
Joyce, S., MacSharry, J., Casey, P., Kinsella, M., Murphy, E., Shanahan, F., et al. (2014). Regulation of host weight gain and lipid metabolism by bacterial bile acid modification in the gut. PNAS 111, 7421–7426. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1323599111
Kaminski, H., and Andrade, F. (2001). Nitric oxide: Biologic effects on muscle and role in muscle diseases. Neuromuscul. Disord. 11, 517–524.
Kang, L., Li, P., Wang, D., Wang, T., Hao, D., and Qu, X. (2021). Alterations in intestinal microbiota diversity, composition, and function in patients with sarcopenia. Sci. Rep. 11:4628.
Karczewski, J., Troost, F., Konings, I., Dekker, J., Kleerebezem, M., Brummer, R., et al. (2010). Regulation of human epithelial tight junction proteins by lactobacillus plantarum in vivo and protective effects on the epithelial barrier. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 298, G851–G859. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00327.2009
Kim, C., Jeon, Y., Yoo, D., Kim, K., Jeong, H., Kim, B., et al. (2023). Fermented whey protein supplementation improves muscular strength, muscle parameters, and physical performance in middle-aged korean adults: An 8-week double blind randomized controlled trial. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 43, 512–530. doi: 10.5851/kosfa.2023.e14
Kim, S., Park, K., Kim, B., Kim, E., and Hyun, C. (2013). Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG improves insulin sensitivity and reduces adiposity in high-fat diet-fed mice through enhancement of adiponectin production. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 431, 258–263. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.12.121
Kobayashi, Y., Hara, N., Sugimoto, R., Mifuji-Moroka, R., Tanaka, H., Eguchi, A., et al. (2017). The associations between circulating bile acids and the muscle volume in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Intern. Med. 56, 755–762. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.56.7796
Komici, K., Dello Iacono, A., De Luca, A., Perrotta, F., Bencivenga, L., Rengo, G., et al. (2021). Adiponectin and sarcopenia: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 12:576619. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.576619
König, D., Wagner, K., Elmadfa, I., and Berg, A. (2001). Exercise and oxidative stress: Significance of antioxidants with reference to inflammatory, muscular, and systemic stress. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 7, 108–133.
Krause, M., Milne, K., and Hawke, T. (2019). Adiponectin-consideration for its role in skeletal muscle health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20:1528. doi: 10.3390/ijms20071528
Kwon, J., Kim, B., Lee, C., Joung, H., Kim, B., Choi, I., et al. (2020). Comprehensive amelioration of high-fat diet-induced metabolic dysfunctions through activation of the PGC-1α pathway by probiotics treatment in mice. PLoS One 15:e0228932. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228932
Lahiri, S., Kim, H., Garcia-Perez, I., Reza, M., Martin, K., Kundu, P., et al. (2019). The gut microbiota influences skeletal muscle mass and function in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 11:eaan5662.
Langille, M., Meehan, C., Koenig, J., Dhanani, A., Rose, R., Howlett, S., et al. (2014). Microbial shifts in the aging mouse gut. Microbiome 2:50.
Lee, C.-C., Liao, Y.-C., Lee, M.-C., Lin, K.-J., Hsu, H.-Y., Chiou, S.-Y., et al. (2021). Lactobacillus plantarum TWK10 attenuates aging-associated muscle weakness, bone loss, and cognitive impairment by modulating the gut microbiome in mice. Front. Nutr. 8:708096. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.708096
Lee, J., Kang, M., Yoo, J., Lee, S., Kang, M., Yun, B., et al. (2023). Lactobacillus rhamnosus JY02 ameliorates sarcopenia by anti-atrophic effects in a dexamethasone-induced cellular and murine model. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 33, 915–925. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2303.03001
Lee, K., Kim, J., Park, S., Shim, J.-J., and Lee, J.-L. (2021). Lactobacillus plantarum HY7715 ameliorates sarcopenia by improving skeletal muscle mass and function in aged Balb/c mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22:10023. doi: 10.3390/ijms221810023
Lee, M., Hsu, Y., Chen, M., Kuo, Y., Lin, J., Hsu, Y., et al. (2024). Efficacy of lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis LY-66 and lactobacillus plantarum PL-02 in enhancing explosive strength and endurance: A randomized, double-blinded clinical trial. Nutrients 16:1921. doi: 10.3390/nu16121921
Lee, M.-C., Tu, Y.-T., Lee, C.-C., Tsai, S.-C., Hsu, H.-Y., and Tsai, T.-Y. (2021). Lactobacillus plantarum TWK10 improves muscle mass and functional performance in frail older adults: A randomized, double-blind clinical trial. Microorganisms 9:1466. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9071466
Li, Y., Chen, Y., John, J., Moylan, J., Jin, B., Mann, D., et al. (2005). TNF-alpha acts via p38 MAPK to stimulate expression of the ubiquitin ligase atrogin1/MAFbx in skeletal muscle. FASEB J. 19, 362–370. doi: 10.1096/fj.04-2364com
Lin, M., and Chang, F. (2000). Antioxidative effect of intestinal bacteria bifidobacterium longum ATCC 15708 and lactobacillus acidophilus ATCC 4356. Digest. Dis. Sci. 45, 1617–1622. doi: 10.1023/a:1005577330695
Lin, S., Tsai, Y., Chen, Y., Wang, M., Chen, C., Lin, W., et al. (2021). An examination of lactobacillus paracasei GKS6 and bifidobacterium lactis GKK2 isolated from infant feces in an aged mouse model. Evid. Based Complement Altern. Med. 2021:6692363. doi: 10.1155/2021/6692363
Liu, H., Bravata, D., Olkin, I., Nayak, S., Roberts, B., Garber, A., et al. (2007). Systematic review: The safety and efficacy of growth hormone in the healthy elderly. Ann. Intern. Med. 146, 104–115.
Liu, N., Butcher, J., Nakano, A., and Del Campo, A. (2023). Changes in macrophage immunometabolism as a marker of skeletal muscle dysfunction across the lifespan. Aging 15, 4035–4050. doi: 10.18632/aging.204750
Liu, T., Bai, Y., Wang, C., Zhang, T., Su, R., Wang, B., et al. (2023). Effects of probiotics supplementation on the intestinal metabolites, Muscle fiber properties, and meat quality of sunit lamb. Anim. Open Access J MDPI 13:762. doi: 10.3390/ani13040762
Liu, Y., Xu, L., Yang, Z., Wang, D., Li, T., Yang, F., et al. (2023). Gut-muscle axis and sepsis-induced myopathy: The potential role of gut microbiota. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 163:114837. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114837
Liu, Z., and Zhu, C. (2023). Causal relationship between insulin resistance and sarcopenia. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 15:46.
Lou, J., Wang, Q., Wan, X., and Cheng, J. (2024). Changes and correlation analysis of intestinal microflora composition, inflammatory index, and skeletal muscle mass in elderly patients with sarcopenia. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 24, 140–146. doi: 10.1111/ggi.14661
Ma, C., Wasti, S., Huang, S., Zhang, Z., Mishra, R., Jiang, S., et al. (2020). The gut microbiome stability is altered by probiotic ingestion and improved by the continuous supplementation of galactooligosaccharide. Gut Microbes 12:1785252. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1785252
Manickam, R., Oh, H., Tan, C., Paramalingam, E., and Wahli, W. (2018). Metronidazole causes skeletal muscle atrophy and modulates muscle chronometabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19:2418. doi: 10.3390/ijms19082418
Markowiak-Kopeć, P., and Śliżewska, K. (2020). The effect of probiotics on the production of short-chain fatty acids by human intestinal microbiome. Nutrients 12:1107.
Marzetti, E., Calvani, R., Cesari, M., Buford, T., Lorenzi, M., Behnke, B., et al. (2013). Mitochondrial dysfunction and sarcopenia of aging: From signaling pathways to clinical trials. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 45, 2288–2301. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.06.024
Morley, J. (2016). Pharmacologic options for the treatment of sarcopenia. Calcif. Tissue Int. 98, 319–333.
Morrison, D., Mackay, W., Edwards, C., Preston, T., Dodson, B., and Weaver, L. (2006). Butyrate production from oligofructose fermentation by the human faecal flora: What is the contribution of extracellular acetate and lactate? Br. J. Nutr. 96, 570–577.
Mullur, R., Liu, Y., and Brent, G. (2014). Thyroid hormone regulation of metabolism. Physiol. Rev. 94, 355–382.
Ni, Y., Yang, X., Zheng, L., Wang, Z., Wu, L., Jiang, J., et al. (2019). Lactobacillus and bifidobacterium improves physiological function and cognitive ability in aged mice by the regulation of gut microbiota. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 63:e1900603. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201900603
Nistal, E., Caminero, A., Herrán, A., Pérez-Andres, J., Vivas, S., Ruiz de Morales, J. M., et al. (2016). Study of duodenal bacterial communities by 16S rRNA gene analysis in adults with active celiac disease vs non-celiac disease controls. J. Appl. Microbiol. 120, 1691–1700. doi: 10.1111/jam.13111
Otten, B., Sthijns, M., and Troost, F. J. (2023). A combination of acetate, propionate, and butyrate increases glucose uptake in C2C12 myotubes. Nutrients 15:946. doi: 10.3390/nu15040946
Papadakis, M., Grady, D., Black, D., Tierney, M., Gooding, G., Schambelan, M., et al. (1996). Growth hormone replacement in healthy older men improves body composition but not functional ability. Ann. Intern. Med. 124, 708–716.
Park, K., Kim, B., and Hyun, C. (2015). Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG improves glucose tolerance through alleviating ER stress and suppressing macrophage activation in db/db mice. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 56, 240–246. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.14-116
Pekmez, C., Dragsted, L., and Brahe, L. (2019). Gut microbiota alterations and dietary modulation in childhood malnutrition - the role of short chain fatty acids. Clin. Nutr. 38, 615–630. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2018.02.014
Peña, J., and Versalovic, J. (2003). Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG decreases TNF-alpha production in lipopolysaccharide-activated murine macrophages by a contact-independent mechanism. Cell Microbiol. 5, 277–285. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-5822.2003.t01-1-00275.x
Petrof, E., Claud, E., Sun, J., Abramova, T., Guo, Y., Waypa, T., et al. (2009). Bacteria-free solution derived from lactobacillus plantarum inhibits multiple NF-kappaB pathways and inhibits proteasome function. Nes. Nutr. Ws. 15, 1537–1547. doi: 10.1002/ibd.20930
Picca, A., Fanelli, F., Calvani, R., Mulè, G., Pesce, V., Sisto, A., et al. (2018). Gut dysbiosis and muscle aging: Searching for novel targets against sarcopenia. Mediators Inflammation 2018:7026198. doi: 10.1155/2018/7026198
Picca, A., Ponziani, F., Calvani, R., Marini, F., Biancolillo, A., Coelho-Junior, H., et al. (2019). Gut microbial, inflammatory and metabolic signatures in older people with physical frailty and sarcopenia: Results from the BIOSPHERE study. Nutrients 12:65. doi: 10.3390/nu12010065
Qian, Y., and Chen, X. (2013). Senescence regulation by the p53 protein family. Methods Mol. Biol. 965, 37–61.
Qiu, Y., Yu, J., Li, Y., Yang, F., Yu, H., Xue, M., et al. (2021). Depletion of gut microbiota induces skeletal muscle atrophy by FXR-FGF15/19 signalling. Ann. Med. 53, 508–522. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2021.1900593
Rondanelli, M., Gasparri, C., Barrile, G., Battaglia, S., Cavioni, A., Giusti, R., et al. (2022). Effectiveness of a novel food composed of leucine, omega-3 fatty acids and probiotic lactobacillus paracasei PS23 for the treatment of sarcopenia in elderly subjects: A 2-month randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Nutrients 14:4566. doi: 10.3390/nu14214566
Ronnebaum, S., Patterson, C., and Schisler, J. (2014). Minireview: Hey U(PS): Metabolic and proteolytic homeostasis linked via AMPK and the ubiquitin proteasome system. Mol. Endocrinol. 28, 1602–1615. doi: 10.1210/me.2014-1180
Rossi, M., Martínez-Martínez, D., Amaretti, A., Ulrici, A., Raimondi, S., and Moya, A. (2016). Mining metagenomic whole genome sequences revealed subdominant but constant lactobacillus population in the human gut microbiota. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 8, 399–406. doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.12405
Rubio-Arias, J. Á, Ávila-Gandía, V., López-Román, F. J., Soto-Méndez, F., Alcaraz, P. E., and Ramos-Campo, D. J. (2019). Muscle damage and inflammation biomarkers after two ultra-endurance mountain races of different distances: 54km vs 111km. Physiol. Behav. 205, 51–57. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2018.10.002
Saini, J., McPhee, J., Al-Dabbagh, S., Stewart, C., and Al-Shanti, N. (2016). Regenerative function of immune system: Modulation of muscle stem cells. Ageing Res. Rev. 27, 67–76.
Sanders, M., Merenstein, D., Ouwehand, A., Reid, G., Salminen, S., Cabana, M., et al. (2016). Probiotic use in at-risk populations. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 56, 680–686.
Sartori, R., Romanello, V., and Sandri, M. (2021). Mechanisms of muscle atrophy and hypertrophy: Implications in health and disease. Nat. Commun. 12:330.
Schiaffino, S., Dyar, K., Ciciliot, S., Blaauw, B., and Sandri, M. (2013). Mechanisms regulating skeletal muscle growth and atrophy. FEBS J. 280, 4294–4314.
Shapouri-Moghaddam, A., Mohammadian, S., Vazini, H., Taghadosi, M., Esmaeili, S., Mardani, F., et al. (2018). Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J. Cell. Physiol. 233, 6425–6440.
Tabuchi, M., Ozaki, M., Tamura, A., Yamada, N., Ishida, T., Hosoda, M., et al. (2003). Antidiabetic effect of lactobacillus GG in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 67, 1421–1424.
Tan, J., McKenzie, C., Potamitis, M., Thorburn, A., Mackay, C., and Macia, L. (2014). The role of short-chain fatty acids in health and disease. Adv. Immunol. 121, 91–119.
Tanaka, Y., Kita, S., Nishizawa, H., Fukuda, S., Fujishima, Y., Obata, Y., et al. (2019). Adiponectin promotes muscle regeneration through binding to T-cadherin. Sci. Rep. 9:16. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-37115-3
Tardif, N., Salles, J., Guillet, C., Tordjman, J., Reggio, S., Landrier, J., et al. (2014). Muscle ectopic fat deposition contributes to anabolic resistance in obese sarcopenic old rats through eIF2α activation. Aging Cell. 13, 1001–1011. doi: 10.1111/acel.12263
Thoma, A., and Lightfoot, A. P. (2018). NF-kB and inflammatory cytokine signalling: Role in skeletal muscle atrophy. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1088, 267–279.
Tian, H., Liu, S., Ren, J., Lee, J., Wang, R., and Chen, P. (2020). Role of histone deacetylases in skeletal muscle physiology and systemic energy homeostasis: Implications for metabolic diseases and therapy. Front. Physiol. 11:949. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00949
Ticinesi, A., Lauretani, F., Milani, C., Nouvenne, A., Tana, C., Del Rio, D., et al. (2017). Aging gut microbiota at the cross-road between nutrition, physical frailty, and sarcopenia: Is there a gut–muscle axis? Nutrients 9:1303. doi: 10.3390/nu9121303
Tschirner, A., von Haehling, S., Palus, S., Doehner, W., Anker, S., and Springer, J. (2012). Ursodeoxycholic acid treatment in a rat model of cancer cachexia. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 3, 31–36. doi: 10.1007/s13539-011-0044-4
Uchitomi, R., Oyabu, M., and Kamei, Y. (2020). Vitamin D and sarcopenia: Potential of vitamin D supplementation in sarcopenia prevention and treatment. Nutrients 12:3189.
Vial, G., Coudy-Gandilhon, C., Pinel, A., Wauquier, F., Chevenet, C., Béchet, D., et al. (2020). Lipid accumulation and mitochondrial abnormalities are associated with fiber atrophy in the skeletal muscle of rats with collagen-induced arthritis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell. Biol. Lipids 1865:158574. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2019.158574
Wang, Q., Peng, F., Yang, J., Chen, X., Peng, Z., Zhang, M., et al. (2024). MicroRNAs regulate the vicious cycle of vascular calcification-osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Mol. Biol. Rep. 51:622. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09550-1
Wang, Y., Yan, X., Zhang, W., Liu, Y., Han, D., Teng, K., et al. (2019). Lactobacillus casei zhang prevents jejunal epithelial damage to early-weaned piglets induced by escherichia coli K88 via regulation of intestinal mucosal integrity, tight junction proteins and immune factor expression. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 29, 863–876. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1903.03054
Watanabe, M., Houten, S., Mataki, C., Christoffolete, M., Kim, B., Sato, H., et al. (2006). Bile acids induce energy expenditure by promoting intracellular thyroid hormone activation. Nature 439, 484–489. doi: 10.1038/nature04330
Witham, M., and Aihie Sayer, A. (2016). Introduction to the age and ageing sarcopenia collection. Age Ageing 45, 752–753. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afw145
Wright, C., Ward, A., and Russell, A. (2017). Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and its potential application for skeletal muscle repair and regeneration. Mediators Inflammation 2017:7517350.
Wu, S., Yoon, S., Zhang, Y., Lu, R., Xia, Y., Wan, J., et al. (2015). Vitamin D receptor pathway is required for probiotic protection in colitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 309, G341–G349. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00105.2015
Yan, F., Li, N., Shi, J., Li, H., Yue, Y., Jiao, W., et al. (2019). Lactobacillus acidophilus alleviates type 2 diabetes by regulating hepatic glucose, lipid metabolism and gut microbiota in mice. Food Funct. 10, 5804–5815. doi: 10.1039/c9fo01062a
Yi, R., Feng, M., Chen, Q., Long, X., Park, K., and Zhao, X. (2021). The effect of lactobacillus plantarum CQPC02 on fatigue and biochemical oxidation levels in a mouse model of physical exhaustion. Front. Nutr. 8:641544. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.641544
Zhang, Y., Guo, X., Guo, J., He, Q., Li, H., Song, Y., et al. (2014). Lactobacillus casei reduces susceptibility to type 2 diabetes via microbiota-mediated body chloride ion influx. Sci. Rep. 4:5654. doi: 10.1038/srep05654
Zhang, Y., Li, T., Liu, Y., Wang, C., Wang, D., Xu, L., et al. (2024). Gsdmd knockout alleviates sepsis-associated skeletal muscle atrophy by inhibiting il18/ampk signaling. Shock 62, 565–573. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000002430
Zheng, D., Liwinski, T., and Elinav, E. (2020). Interaction between microbiota and immunity in health and disease. Cell. Res. 30, 492–506.
Zhong, Q., Zheng, K., Li, W., An, K., Liu, Y., Xiao, X., et al. (2023). Post-translational regulation of muscle growth, muscle aging and sarcopenia. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 14, 1212–1227.
Keywords: sarcopenia, gut-muscle axis, gut microbiota, Lactobacillus, muscle
Citation: Zhu J, Peng F, Yang H, Luo J, Zhang L, Chen X, Liao H, Lei H, Liu S, Yang T, Luo G, Chen G and Zhao H (2025) Probiotics and muscle health: the impact of Lactobacillus on sarcopenia through the gut-muscle axis. Front. Microbiol. 16:1559119. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1559119
Received: 13 January 2025; Accepted: 24 February 2025;
Published: 14 March 2025.
Edited by:
Haibo Shi, South China University of Technology, ChinaReviewed by:
Yuchang Wang, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Zhu, Peng, Yang, Luo, Zhang, Chen, Liao, Lei, Liu, Yang, Luo, Chen and Zhao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Heng Zhao, YW5nZXJoOUAxMjYuY29t; Guodong Chen, Y2hlbmd1b2RvbmdAdXNjLmVkdS5jbg==; Guanghua Luo, MTU3OTgzOTk4MTRAcXEuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.