- Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Beijing Youan Hospital Affiliated with Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
Accumulating evidence indicates that patients with liver diseases exhibit distinct microbiological profiles, which can be attributed to the bidirectional relationship of the gut-liver axis. Porto-sinusoidal vascular disease (PSVD) has recently been introduced to describe a group of vascular diseases of the liver, involving the portal venules and sinusoids. Although the pathophysiology of PSVD is not yet fully understood, several predisposing conditions, including immunodeficiency, inflammatory bowel disease, abdominal bacterial infections are associated with the increasing in intestinal permeability and microbial translocation, supporting the role of altered gut microbiota and gut-derived endotoxins in PSVD etiopathogenesis. Recent studies have proposed that the gut microbiome may play a crucial role in the pathophysiology of intrahepatic vascular lesions, potentially influencing the onset and progression of PSVD in this context. This review aims to summarize the current understanding of the gut microbiome's potential role in the pathogenesis of hepatic microvascular abnormalities and thrombosis, and to briefly describe their interactions with PSVD. The insights into gut microbiota and their potential influence on the onset and progression of PSVD may pave the way for new diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic strategies.
1 Introduction
Porto-sinusoidal vascular disease (PSVD) is a rare vascular and parenchymal liver disease encompassing a spectrum of often subtle hepatic microvascular lesions and related microarchitectural abnormalities in the absence of cirrhosis in liver biopsy, regardless of the presence of portal hypertension (Premkumar and Anand, 2024). Previously, it was referred to as idiopathic non-cirrhotic portal hypertension (INCPH), characterized by the presence of portal hypertension in the absence of a clear underlying liver disease and portal vein thrombosis (PVT) (Lee et al., 2016). However, these diagnostic criteria for INCPH have certain shortcomings. INCPH excludes patients in the early stages of the disease spectrum who have not yet achieved portal hypertension but already exhibit histopathological lesions in sinusoids and portal venules (Khanna and Sarin, 2014). Similarly, nearly 40% of INCPH patients experience PVT as the disease progresses (Siramolpiwat et al., 2014). Excluding patients with PVT fails to acknowledge that PVT may be both a consequence and a contributing factor in the progression of INCPH. To address these limitations and facilitate early diagnosis, the Vascular Liver Disease Group recently introduced a novel entity named PSVD (De Gottardi et al., 2019). PSVD includes patients who meet the diagnostic criteria for INCPH but do not exhibit symptoms of portal hypertension as well as those with PVT or other causes of liver disease if the liver biopsy suggests PSVD, indicating that its prevalence may be significantly higher than that of INCPH. However, patients with PSVD are generally asymptomatic unless they present a complication typical of portal hypertension (Aggarwal et al., 2013; Kang et al., 2021). The diagnosis of PSVD remains challenging, which primarily relies on clinical signs of portal hypertension combined with specific histological features involving the porto-sinusoidal vascular abnormalities (obliterative portal venopathy, portal tract hypervascularization, and abnormal periportal vessels) as well as parenchymal abnormalities (Gioia et al., 2024; De Gottardi et al., 2022). Moreover, the pathophysiology responsible for PSVD is complex and hinders the development of treatments capable of altering the natural history of the disease. A better insight into the biological processes and pathophysiological mechanisms involved in PSVD is essential for identifying disease drivers and developing new diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
Gut microbiome plays critical roles in the development of several vascular disease phenotypes by activating vascular endothelial cells, platelets, and innate immune cells (Hasan et al., 2020). Since the liver yields most of its blood supply via the portal circulation, the hepatic microcirculation constantly encounters gut-derived components, metabolites, and signals. These factors can induce changes in the liver sinusoidal endothelium, affecting the immune partitioning of the sinusoids and influencing portal hypertension (Kiouptsi et al., 2023). Although the exact pathogenesis of PSVD remains unclear, it is hypothesized to result from injuries and occlusion of the intrahepatic portal microvasculature, leading to increased resistance to portal blood flow and subsequent presinusoidal type of portal hypertension (Jin and Choi, 2023). Predisposing conditions of PSVD are related to immune disorders, infections, prothrombotic conditions, congenital or hereditary defects, drug exposure, and inherited vascular remodeling disorders (Kmeid et al., 2021). The link between gut microbiome, portal hypertension, and predisposing conditions of PSVD have supported that gut microbiota translocation into the sinusoids may impact on the pathophysiology of PSVD (Fiordaliso et al., 2023). Research has shown that intestinal permeability and gut-derived endotoxins play an important role in the pathogenesis of PSVD by activating the immune response of the liver, trigger inflammatory reactions in the liver, and thereby affect the health of the portal vein and sinusoidal vessels (Baffy and Portincasa, 2024). Previous studies reported that intestinal relocation with Escherichia coli (E. coli) might cause recurrent septic embolization leading to endothelial damage and the obstruction of small portal veins contributing to idiopathic portal hypertension (Kono et al., 1988; Giuli et al., 2023; Sarin and Aggarwal, 1998).
Recent advances in metagenomics and bioinformatics have provided new insights into the microbial ecology in different liver diseases (Nychas et al., 2025; Parthasarathy et al., 2024; Oh et al., 2020). Emerging studies have revealed the connection of intestinal microbiome and porto-sinusoidal vascular abnormalities, as well as hepatic thrombosis. In this review, we provide an overview of current knowledge regarding the role of the gut microbiome in the pathogenesis of intrahepatic microvascular abnormalities and thrombosis formation. Additionally, this review also introduces a brief description of the state of research and perspectives on the interactions between gut microbiome and PSVD progression. The insights into gut microbiota and its potential role in PSVD will help to elucidate the mechanism by which the gut microbiota influence PSVD and provide new opportunities for its diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment.
2 The potential interlink between gut microbiome and PSVD
The human gastrointestinal tract harbors over trillions of microorganisms including bacteria, fungi, viruses, and archaea that make up the gut microbiome (Hsu and Schnabl, 2023). The gut and liver have a symbiotic relationship with gut microbiome, which is referred to as the gut-liver axis (Wang et al., 2021b). The composition and structure of gut microbiota, intestinal barrier, liver vascular system, and liver status all play crucial roles in maintaining homeostasis within this axis. Under normal physiological conditions, the intestinal barrier in the gut liver axis, including physical (gut vascular and epithelial cell tight junctions), immunological (gut-associated lymphoid tissue), and biochemical (antimicrobial peptides, secretory immunoglobulin A and mucus layer) components (Tranah et al., 2021), forms the first line of defense for human immune system, while the liver vascular microenvironment provides a second line of defense to preventing the pathogenic factors of intestinal mucosal immune response triggering the dissemination of systemic inflammatory (He et al., 2021; Seo and Shah, 2012). A perturbation of this balance causes gut dysbiosis, which not only leads to liver damage and systemic inflammation but is also related to impaired microcirculation, abnormal vascular permeability, and liver hemodynamics (Simbrunner et al., 2019).
PSVD involves abnormalities in the liver's vascular system and is likely a group of different diseases that can cause inflammation and obstruction of porto-sinusoidal vascular system affect portal venous pressure (Isidro and Zhao, 2023). Most of PSVD patients appears idiopathic portal hypertension, and relevant pathogenesis is involved in liver structural distortion fibrosis, microvascular thrombosis, dysfunction of cellular elements in the hepatic sinusoidal vascular microenvironment (Mehta et al., 2014). The portal vein is frequently exposed to intestinal microbe-associated pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), including lipopolysaccharide (LPS), antigens, as well as bacteria, and transmits them to the liver, thus eliciting negative effects on the liver (Pabst et al., 2023). Gut dysbiosis can disrupt intestinal barriers, increasing permeability causing the translocation of PAMPs into the liver through portal vein and participate in enterohepatic circulation (Spadoni et al., 2015), which results in an imbalance of the gut-liver-vascular homoeostasis, activation pro-inflammatory response in hepatic sinus and increasing hepatic vascular resistance (Liang et al., 2020), which may per se contribute to the occurrence and development of PSVD. In this section, we will review the current literature on the potential interactions between gut microbiome and PSVD, focusing on abnormal intrahepatic porto-sinusoidal vascular microenvironment and hepatic microvascular thrombosis formation.
2.1 Gut microbial dysbiosis and porto-sinusoidal microcirculatory dysfunction
The liver contains two distinct microvascular structures. One is made up of continuous endothelial cells organized within the basement membrane, forming a complete vascular structure seen in portal vein blood vessels. The other is composed of discontinuous liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs) (Xu et al., 2019). The intrahepatic porto-sinusoidal microvascular unit consists of several discrete units, primarily including portal venules, hepatic sinusoids, and central venules. LSECs constitute a natural barrier that separates the liver parenchyma from the bloodstream in the sinusoidal lumen and participate in regulating liver sinusoidal blood flow and material exchange in surrounding tissues, thereby playing a key role in maintaining hepatic microcirculatory homeostasis (Wang et al., 2021c). In addition, LSECs actively regulate intrahepatic coagulation by generating procoagulant factors, stimulating neutrophils, and interacting with platelets (Yang et al., 2017; Hilscher et al., 2019; Gracia-Sancho et al., 2021). The occurrence of PSVD is closely related to changes in the structure and function of the intrahepatic vascular microenvironment (especially liver sinusoids) accompanied by microvascular thrombosis. Portal vein collects blood from the gastrointestinal tract and first supplies it to the capillary network of hepatic sinusoids (Chopyk and Grakoui, 2020). Obstruction of the sinusoids and the resulting increase in hepatic vascular resistance to portal vein blood flow are the main causes of portal hypertension (Mcconnell and Iwakiri, 2018).
Key mechanisms of gut dysbiosis-related alterations in sinusoidal vascular include weakened gut barrier and amplified translocation of PAMPs (Seki and Brenner, 2008). LSECs express a series of scavenger receptors and toll like receptors (TLRs), which render LSECs able to mediate hepatic clearance process of PAMPs and products derived from the gastrointestinal tract (Shetty et al., 2018; Øie et al., 2020). It is well understood that LSECs are exposed to relatively high concentrations of gut-derived PAMPs in portal blood, which can activate TRLs signaling in LSECs further driving chemokine dependent changes and enhancing vasoconstrictor production, increasing portal perfusion pressure (Hilscher et al., 2019). Thus, the phenotype of LSECs exerts pivotal roles in physiological immune functions and maintains liver vascular homeostasis, including regulating porto-sinusoidal shear stress, angiogenesis, as well as hepatic sinusoidal remodeling (Marrone et al., 2016; Gola et al., 2021). LSECs typically exhibit unique phenotypic characteristics, including open fenestrae and lack of a basement membrane. Abnormalities in LSECs distort the normal architecture of the liver and play a key role in the recruitment and activation of platelets, which can lead to microthrombosis and fibrin deposition within the sinusoids (Lisman and Luyendyk, 2018; Abdelmoneim et al., 2010). LSECs capillarization is regarded as an early hallmark in the pathogenesis of portal hypertension (Iwakiri and Groszmann, 2007; Sutton et al., 2018). Meanwhile, the dysfunction of LSECs and the onset of local inflammation which causes damage to small portal vein branches, endothelial dysfunction, activation of HSCs, and hepatic micro-thrombosis, suggest central roles of LSECs in the pathophysiology and onset of PSVD (Zhang et al., 2020; Khanna and Sarin, 2019; Cerda Reyes et al., 2021). Studies have found that increased levels of gut-derived endotoxins and pro-inflammatory cytokines lead to LSECs dysfunction and vasoconstriction via activation endothelin-1 (ET-1), which plays vital roles in raising hepatic vascular resistance (Yadav et al., 2019; Gracia-Sancho et al., 2007). Bacterial infections have also been found to target LSECs, leading to a shift from their normal tolerogenic state to a pro-inflammatory state (Martin-Armas et al., 2006). PAMPS can stimulate the dedifferentiation of LSECs, driving their dysfunction and capillarization (Wilkinson et al., 2020). Leong et al. found that the loss of fenestrations in LSECs was observed in response to bacilli, specifically Bartonella bacilli (Leong et al., 1992). Furthermore, liver endothelial cell fenestrations were found to be negatively correlated with a higher abundance of Firmicutes phylum and reduced abundance of Bacteroidetes (Cogger et al., 2016). Taken together, gut microbiota-derived signals and metabolites can influence angiogenesis, transcriptional and metabolic landscape of the hepatic endothelium, thereby shaping the LSECs phenotype (Formes et al., 2021).
In addition to LSECs, other non-parenchymal cells, including hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), monocytes, and Kupffer cells (KCs), are essential for maintaining the function of the liver vascular microenvironment (Cheng et al., 2021). HSCs are wrapped around LSECs and regulate microcirculation within the hepatic sinus through the contractile function of their slender protrusions, thereby affecting the sinusoidal tone and regulating liver blood flow. Activated HSCs increase large amounts of collagen and myofibroblasts which are deposited in the Disse and sinusoidal spaces, exacerbating vascular resistance, which can lead to the distortion of liver vascular structure (Serrano et al., 2019). Additionally, activated HSCs can produce vasoactive mediators such as angiopoietin, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and increase ET-1 synthesis thereby maintaining the LSEC phenotype or regulating fenestrations, which in turn influences vascular tone and endothelial function, further contributing to hepatic vascular remodeling (Gana et al., 2016; Marrone et al., 2016). In turn, LSECs play an important role in maintaining the quiescence of HSCs and LSECs capillarization can lead to the secretion of exosomes rich in sphingosine kinase-1, promoting the activation of HSCs (Xie et al., 2012). Previous studies have revealed that the LSECs communication with HSCs facilitates sinusoidal vascular remodeling, which is an early feature of intrahepatic portal hypertension (Deleve et al., 2008; Gracia-Sancho et al., 2019, 2008). Intestinal microbiota translocation can cause the activation of HSCs and alter the cell phenotype of LSECs (Cheng et al., 2021; Corbitt et al., 2013; Stojic et al., 2023).
KCs are resident macrophages in the liver sinusoids, playing crucial roles in capturing and eliminating soluble antigens derived from gut microbes via the portal vein. In general, KCs are responsible for sensing and processing gut-derived signals reaching liver sinusoids, such as pathogens, cell fragments, and endogenous metabolites (Zhou et al., 2022b), playing essential roles in pathogen clearance and immunosuppressive features (Li et al., 2022). The expression of TLR receptors on KCs responds to gut-derived LPS exposure, ultimately promoting the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1, IL-6, IL-12, and TNF-α (Mehta et al., 2014; Płóciennikowska et al., 2015). Braedon et al. implicated the gut microbiota as a direct regulator of KCs antibacterial functions (Mcdonald et al., 2020). Moreover, KCs have abilities to enhance LSECs capillarization, resulting in a transition of LSECs morphology toward a more vascular or capillary-like state by losing fenestrations, and forming a distinctive basement membrane (Ford et al., 2015). In cirrhotic patients, KCs activation has been shown to be closely associated with the hepatic venous pressure gradient, liver disease severity, and an increased risk of venous thrombosis (Waidmann et al., 2013; Tranah et al., 2021). CD163 is a monocyte/macrophage specific membrane marker cleaved from the surface of activated macrophages as a soluble form (sCD163) (Maroto-García et al., 2023). KCs serve as the primary source of CD163 in the liver. The activation of KCs during liver fibrosis and inflammation upregulates CD163 expression and promotes the release of sCD163. Consequently, sCD163 levels demonstrate significant potential as a robust biomarker for evaluating the progression of liver fibrosis and the severity of hepatic tissue inflammation (Dultz et al., 2015). Intriguingly, activation of KCs is also observed in PSVD patients, with higher levels of KC activation markers, including soluble CD163 and the mannose receptor, compared to cirrhotic patients (Ørntoft et al., 2021).
In summary, LSECs capillarization, activation of HSCs and KCs as well as hepatic microvascular thrombosis is associated with the dysregulation of vascular homeostasis and increased intrahepatic vascular interactions, which may partly contribute to PSVD progression. Interlinks between different cell types in the porto-sinusoids involve host-produced inflammatory cytokines alongside microbial byproducts generated by the gut microbiota, which affect the hemodynamics of the intrahepatic vascular microenvironment. A deeper understanding of the crosstalk between gut dysbiosis and vascular processes has led to improved insights of the potential microbial mechanisms associated with PSVD.
2.2 Gut microbial dysbiosis and hepatic microvascular thrombosis
Coagulation disequilibrium, especially hypercoagulable states or prothrombotic conditions, has been implicated in the PSVD onset and progression (Riggio et al., 2016). Liver biopsy often reveals signs of thrombosis, including intrahepatic portal vein thickening, occlusion, and obstruction in PSVD cases (De Gottardi et al., 2022). Accumulating studies have suggested that the presence of hepatic vein thrombosis may be a common consequence of PSVD, which can be attributed to both reduced portal flow velocity and the elevated prevalence of prothrombotic risk factors (Gioia et al., 2018, 2019). Microvascular thrombosis and platelet aggregation occurring in intrahepatic portal venules and sinusoids are suggested to contribute to PSVD. The gut microbiota can regulate coagulation disorders in thromboembolism (Hasan et al., 2020). Gut dysbiosis characterized by an increased relative abundance of opportunistic pathogenic proteobacteria and fewer beneficial genera play vital roles in thrombosis-related diseases (Xiang et al., 2020; Yin et al., 2015; Yang et al., 2022). Gut microbiota also affects the hemostatic properties of hepatic microvascular endothelium through the gut–liver axis (Kiouptsi et al., 2023). An increasing number of studies have found that gut microbes, PAMPs, and microbial metabolites play important roles in shaping vascular development, affecting endothelial cell function and coagulation system activation causing thrombosis (Hasan et al., 2020; Mohammed et al., 2020). Under gut dysbiosis, gut microbe-derived components into portal-systemic circulation activating PAMPs-induced inflammatory pathways, which are related to prothrombotic states. Gut microbiota-triggered TLR-2 alters the synthesis of von Willebrand factor (vWF) by the liver endothelium and favors platelet integrin-dependent thrombus growth (Jäckel et al., 2017).
LPS, found in the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria, can influence coagulation and lead to continuous, chronic low-grade inflammation in the liver through stimulation of pattern recognition receptors and TLRs on endothelial cells and platelets, which can culminate in the production of large amounts of inflammatory cytokines and activate the coagulation cascade (An et al., 2022; Vijay, 2018; Ozinsky et al., 2000). LPS has also been reported to prime platelets to respond to activation by common agonists, promoting the expression of tissue factor and exerting prothrombin activity (Reinhardt et al., 2012). In vitro, human endothelial cells were incubated were incubated with LPS concentrations similar with those found in the peripheral circulation of liver cirrhosis, and the results showed that LPS increased the release of vWF and factor VIII (Carnevale et al., 2017). Meanwhile, LPS can decrease thrombomodulin expression in LESCs resulting in sinusoidal microthrombus formation and liver dysfunction (Kume et al., 2003). Clinical studies have also found that the imbalance of inflammatory states and gram-negative bacteria-derived products (LPS or other bacterial toxins) leads to activation of the coagulation in cirrhotic patients with PVT (Huang et al., 2023; Georgescu et al., 2023). Mechanistically, translocated LPS derived from the gut microbiota activate the immune response in the liver, triggering inflammatory reactions in the liver, thereby affecting the health of the portal vein and sinusoidal vessels (Violi et al., 2023). E. coli-derived LPS has been reported to increase liver damage by inducing macrophage and platelet activation through TLR4 pathway (Carpino et al., 2020). TLR4 is widely expressed in hepatocytes, HSCs, and KCs. Activation of the LPS-TLR4 pathway can potentially become a risk factor leading to liver diseases (Violi et al., 2023).
Previous studies have reported that intestinal translocation of E. coli might cause recurrent septic embolization resulting in histological changes similar with those seen PSVD including endothelial damage and obstruction of small portal veins (Kono et al., 1988; Sarin and Aggarwal, 1998; Giuli et al., 2023). Chronic or recurrent infections that cause intestinal antigenemia may ultimately lead to mild portal vein inflammation, resulting in pathological changes compatible with PSVD (De Gottardi et al., 2022; Harmanci and Bayraktar, 2007). In patients with coeliac disease, factors of enteric origin contribute to the obliteration of the portal venous microcirculation, suggesting that prothrombotic factors of gut origin may cause PSVD (Eapen et al., 2011). Gioia et al. found that LPS translocation and the number of TLR4+ macrophages were significantly increased in liver biopsies of patients with PSVD compared to healthy controls. Meanwhile, TLR4+ macrophages were located both in the portal tract and perisinusoidal area, regions typically altered in PSVD with the activation of LPS-TLR4 pathway in patients affected by PSVD (Gioia et al., 2023). The LPS-TLR4 pathway may also be considered a key promoter in the development of PSVD.
3 Future research direction and perspectives
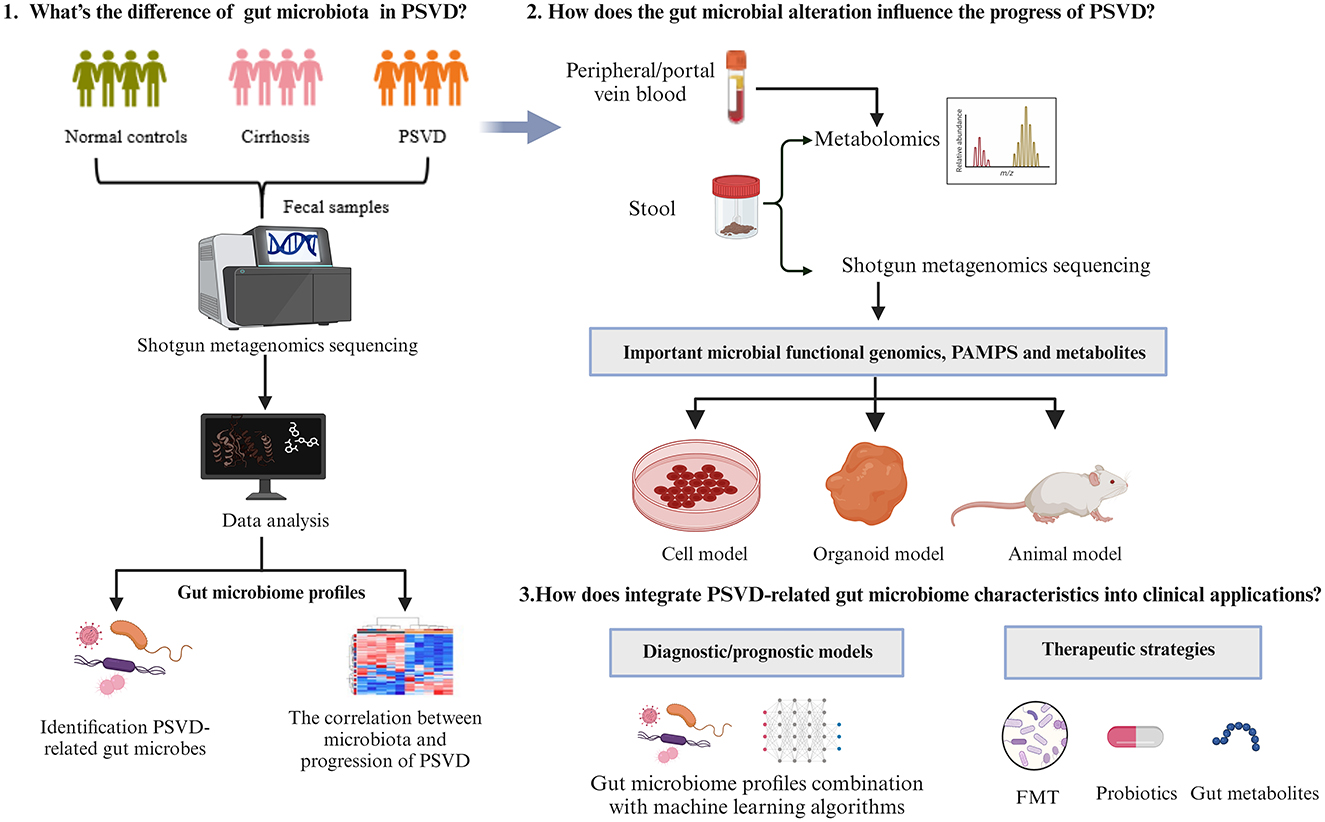
The changes in gut microbiota and its derivatives on liver pathophysiology has become widely recognized (Wang et al., 2021b; Shen et al., 2023). As the liver is directly supplied by gut-derived blood via the portal vein, the periportal areas would be the first to be exposed to gut-derived metabolites or inflammation substances (English et al., 2021), playing an important role in the function of microvasculature. Based on the extensive evidence linking gut dysbiosis with porto-sinusoidal microcirculatory abnormalities and hepatic thrombosis, it is reasonable to hypothesize that the continuous interaction between gut-derived pathogens and metabolites contributes to the pathophysiology of PSVD. However, the studies on the interactions between gut microbiome and PSVD are limited, and many questions remain unresolved (Figure 1).
A key point is to identify a core group of gut microbes associated with PSVD and to explore how gut dysbiosis impacts the structural and functional changes in in the microbiome that contribute to this condition. The most widely utilized method for classifying and phylogenetically identifying of bacterial community composition is 16S rRNA gene amplicon analysis, which allows for the differentiation of bacteria at the genus level (Rutanga et al., 2018). However, merely understanding the genus and its relative abundance is insufficient for clinical applications or mechanistic research in liver diseases, as each genus encompasses various strains that may exert different pathological or beneficial effects (Giuffrè et al., 2020). As sequencing costs continue to decrease, shotgun metagenomics is progressively replacing 16S rRNA sequencing in microbiome studies. Shotgun metagenomics can identify the composition and structure of gut microbiota—including viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites—at the species level, as well as provide insights into microbial gene expression, elucidating the functions of actively expressed genes (Valles-Colomer et al., 2023; Shakya et al., 2019). Although collecting PSVD cases in clinical practice is challenging due to the relatively low prevalence of PSVD and the complex diagnostic process, sufficient sample sizes are essential to account for the inherent inter-individual variability when using shotgun metagenomics to detect alterations in structure and composition of gut microbiota in PSVD patients. Research designs should ensure that the included PSVD patients should be diagnosed based on pathology and clinical manifestations, and that study controls consist of healthy individuals and those with other liver diseases that may be easily confused with PSVD.
Besides unraveling the alterations and interlinks of gut microbiome and PSVD, the pathogenesis of PSVD from the perspective of microbial functional genomics, PAMPs and metabolites is also a key focus requiring further research. Compared to gut microbiota, PAMPs, and microbial metabolites are more readily transported to the liver via the portal vein, where they impact liver function and contribute to liver disease. Metabolomics, which targets metabolites, provides insights into overall metabolic states and host-microbe interactions. A combination of shotgun metagenomics and metabolomics can elucidate the intricate interactions among the gut microbiome, microbial metabolites, and liver diseases. When designing studies on the relationship between gut microbiota, metabolites, and PSVD, it is vital to distinguish between metabolites produced by the host and those generated by microbial communities. Research should focus on identifying microbial metabolites closely linked to PSVD progression, emphasizing the sources of gut microbial metabolites and analyzing the interactions between these metabolites, alterations in microbial communities, and the severity of PSVD. Combining cell models and organoid models with the multi-omics techniques will facilitate functional research and mechanistic exploration targeting PSVD-related pathogenic microorganisms, PAMPs, and metabolites. As illustrated in this review, bacterial LPS accumulation in the liver can induce aberrant characteristics and functions of hepatic sinusoids, promote platelet-dependent hepatic thrombosis, and trigger inflammation, thereby contributing to the onset and progression of PSVD. In addition to LPS, several metabolites have been reported to influence vascular development, affect endothelial cell function, and activate coagulation systems, warranting further investigation, such as trimethylamine oxide (TMAO), short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), and gaseous molecules (Mohammed et al., 2020; Mitten and Baffy, 2022).
TMAO, a key gut microbiota-derived metabolite, is also associated with inflammation, vascular endothelial injury, and thrombosis (Koeth et al., 2013). Several gut microbes (such as Desulfovibrio) can degrade choline, betaine, and L-carnitine from the diet into TMA which is absorbed, transferred to the liver and eventually converted by hepatic flavin monooxygenases into TMAO (Qiu et al., 2018). TMAO acts on inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate generation in platelets can activate macrophage scavenger receptor expression through various pathways to activate the inflammatory signal pathway, resulting in the aggravation of oxidative stress, endothelial dysfunction, and thrombotic process (Wang et al., 2021a). Studies have revealed that microbial taxa associated with a high choline diet significantly increased TMAO which was positively correlated with enhanced platelet hyper-responsiveness and thrombosis risk (Mohammed et al., 2020; Skye et al., 2018). Higher levels of TMAO can increase endothelial reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and impair vascular endothelial function, which have been found to be positively correlated with thrombosis (Lässiger-Herfurth et al., 2019). Modulating the gut microbiome to target TMAO levels may represent an innovative approach for reducing the risk of thrombosis (Vinchi, 2019). The liver is the main organ responsible for TMAO production, and long-term exposure to high doses may induce chronic liver diseases by modulating inflammatory responses. Indeed, TMAO generated by the gut microbiome affects bile acid metabolism, cholesterol and sterol metabolism, and oxidative stress, promoting the development of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) (Li et al., 2021; Tan et al., 2019). Zhou et al. found that TMAO mediates the crosstalk between the gut microbiota and hepatic vascular niche to affect LSECs characteristics in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (Zhou et al., 2022a). Nevertheless, there is currently no research available on the relationships between TMAO and hepatic microvascular thrombosis.
Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), such as acetate, propionate, and butyrate, which produced through the fermentation of carbohydrate by gut bacteria, are important for maintaining intestinal motility, enterocyte viability, and tight junction integrity (Morrison and Preston, 2016; Boursier et al., 2016). SCFAs in the portal blood participate in the modulation of liver hemodynamics, and the level of circulating SCFAs is negatively related to the severity of liver disease (Koh et al., 2016). Butyric acid has been reported to be reported to inversely associated with the hepatic venous pressure gradient values, and induce inflammatory markers (TNFα and IL-6) in the hepatic, portal, and peripheral blood (Mitten and Baffy, 2022). Inflammation affecting the blood vessels activates the coagulation cascade, promoting the formation of thrombosis (Jonsson and Bäckhed, 2017).
Notably, gut microbiota utilizes carbohydrate and protein fermentation, as well as hydrocarbons to produce some gas signal molecules regulation vascular function and maintenance vasculature homeostasis, which is gradually being recognized in liver diseases. Nitric oxide (NO) and hydrogen sulfide (H2S) are the best-known gas molecules playing crucial roles in vascular signaling and other processes (Zhou et al., 2022a; Yang et al., 2023). Under normal physiological conditions, endothelial nitric oxide synthase derived NO in the blood can serve as an early marker of endothelial injury (Stanhewicz and Kenney, 2017). LSECs are specialized vascular cells located between the sinusoidal lumen and Disse space. NO is a key factor that maintains the phenotypes of LSECs. Reduced NO bioavailability is associated with liver disease progression, which induces hepatic vascular resistance, activation of HSCs, and endothelial dysfunction in LSECs (Hwang et al., 2023; Poisson et al., 2017). Simultaneously, the ability of abnormal LSECs to synthesize NO is reduced, leading to vasoconstriction, increasing intrahepatic vascular resistance, eventually inducing the development of porto-sinusoidal hypertension (Pillai et al., 2015; García-Pagán et al., 2012). Endogenous H2S have demonstrated the involvement in regulating angiogenic responses by activation the VEGF-NO pathway in HSCs participating to maintain LESCs phenotype and functional status (Yang et al., 2023). Together, ecological imbalance in the intestinal flora may promote gut microbes, gut-derived PAMPs, and microbial metabolites to act on porto-sinusoidal vascular abnormalities and hepatic microthrombosis, thus participating in the occurrence and development of PSVD (Figure 2).

Figure 2. The potential role of gut dysbiosis in the pathobiology of PSVD. Emerging evidence has demonstrated that gut dysbiosis is significantly associated with multiple predisposing conditions of PSVD, particularly immune disorders, bacterial infections and thrombophilia. Changes in gut microbiota, gut-derived bacterial products (PAMPs) and metabolites can stimulate the toll-like receptor (TLRs) signaling, leading to the activate hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), and Kupffer cells (KCs) as well as liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs) capillarization. These pathophysiological processes trigger the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and vasoactive substances, which subsequently induce vasoconstriction, elevate intrahepatic vascular resistance, and promote hepatic microvascular thrombosis, ultimately contributing to the development of portal hypertension and other pathological manifestations in PSVD.
Understanding the links between gut microbes and PSVD not only helps us better understand the pathophysiological mechanisms of PSVD, but also provides important information for clinical diagnosis and treatment. Currently, in addition to exploring the diagnostic and prognostic value of microorganisms for diseases, targeting the gut microbiota has become the focus of emerging therapies with varying success such as fecal microbiota transplantation, probiotics, selective antibiotic use, and targeted small metabolites produced by gut microbiota, such as SCFAs and TMAO (Wong and Levy, 2019; Velasquez et al., 2016). Advances in gut microbiota sequencing technology and metabolomics have made the detection of specific changes in gut microbiota and related metabolites valuable methods for non-invasive diagnostic or prognostic biomarkers of PSVD. Previous studies have identified metabolic features that clearly differentiate patients with PSVD from those with cirrhosis and portal hypertension, as well as from healthy individuals (Seijo et al., 2013, 2016). However, specific treatments to prevent disease progression in PSVD patients are currently unavailable. Therapeutic options are limited to agents addressing complications related to portal hypertension and hepatic thrombosis, which generally result in a poor prognosis. With better understanding of the interactions between gut microbial alterations and PSVD, identifying PSVD-related characteristic gut-derived microbes and metabolites may provide promising research fields for related clinical applications.
4 Conclusion
Accumulating evidence suggests that gut dysbiosis may play a pivotal role in the occurrence and progression of PSVD by promoting porto-sinusoidal abnormalities and intrahepatic thrombosis. Gut dysbiosis disrupts the homeostasis of the gut-liver axis, facilitating the translocation of gut-derived microbial components, including LPS and metabolites into the liver. These factors induce structural and functional abnormalities in LSECs, HSCs, and KCs, while simultaneously promoting intrahepatic vascular resistance and coagulation dysregulation within the hepatic sinusoids, leading to the subsequent progression of PSVD. Currently, there is still limited understanding of the direct association between gut microbiome and PSVD. Integrating gut microbiota research into the clinical management of PSVD holds significant promise for enhancing diagnostic accuracy, prognostic evaluation, and therapeutic efficacy. Future research should focus on identifying specific gut microbial signatures and metabolites associated with PSVD by utilizing advanced multi-omics approaches. Elucidating the mechanistic pathways through which gut-derived signals, especially microbial functional genomics and metabolites, influence PSVD will be crucial for developing innovative, non-invasive diagnostic tools and personalized treatment strategies for PSVD.
Author contributions
YL: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. LL: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. HD: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants from the Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission (Z221100007422002), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81970525), and the Capital Medical Development and Research Fund (2022-1-2181).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
PSVD, porto-sinusoidal vascular disease; INCPH, idiopathic non-cirrhotic portal hypertension; PVT, portal vein thrombosis; E. coli, Escherichia coli; PAPMs, pathogen-associated molecular patterns; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; LSECs, liver sinusoidal endothelial cells; TLRs, toll like receptors; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; ET-1, endothelin-1; HSCs, hepatic stellate cells; KCs, Kupffer cells; vWF, von Willebrand factor; TMAO, trimethylamine oxide; SCFAs, short-chain fatty acids; ROS, reactive oxygen species; MAFLD, metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease; NO, nitric oxide; H2S hydrogen sulfite.
References
Abdelmoneim, S. S., Talwalkar, J., Sethi, S., Kamath, P., Fathalla, M. M., Kipp, B. R., et al. (2010). A prospective pilot study of circulating endothelial cells as a potential new biomarker in portal hypertension. Liver Int. 30, 191–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2009.02132.x
Aggarwal, S., Fiel, M. I., and schiano, T. D. (2013). Obliterative portal venopathy: a clinical and histopathological review. Dig. Dis. Sci. 58, 2767–2776. doi: 10.1007/s10620-013-2736-4
An, L., Wirth, U., Koch, D., Schirren, M., Drefs, M., Koliogiannis, D., et al. (2022). The role of gut-derived lipopolysaccharides and the intestinal barrier in fatty liver diseases. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 26, 671–683. doi: 10.1007/s11605-021-05188-7
Baffy, G., and Portincasa, P. (2024). Gut microbiota and sinusoidal vasoregulation in MASLD: a portal perspective. Metabolites 14:324. doi: 10.3390/metabo14060324
Boursier, J., Mueller, O., Barret, M., Machado, M., Fizanne, L., Araujo-Perez, F., et al. (2016). The severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with gut dysbiosis and shift in the metabolic function of the gut microbiota. Hepatology 63, 764–775. doi: 10.1002/hep.28356
Carnevale, R., Raparelli, V., Nocella, C., Bartimoccia, S., Novo, M., Severino, A., et al. (2017). Gut-derived endotoxin stimulates factor VIII secretion from endothelial cells. Implications for hypercoagulability in cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 67, 950–956. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.07.002
Carpino, G., del Ben, M., Pastori, D., Carnevale, R., Baratta, F., Overi, D., et al. (2020). Increased liver localization of lipopolysaccharides in human and experimental NAFLD. Hepatology 72, 470–485. doi: 10.1002/hep.31056
Cerda Reyes, E., González-Navarro, E. A., Magaz, M., Muñoz-Sánchez, G., Diaz, A., Silva-Junior, G., et al. (2021). Autoimmune biomarkers in porto-sinusoidal vascular disease: potential role in its diagnosis and pathophysiology. Liver Int. 41, 2171–2178. doi: 10.1111/liv.14997
Cheng, Q. N., Yang, X., Wu, J. F., Ai, W. B., and Ni, Y. R. (2021). Interaction of non-parenchymal hepatocytes in the process of hepatic fibrosis (review). Mol. Med. Rep. 23:364. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12003
Chopyk, D. M., and Grakoui, A. (2020). Contribution of the intestinal microbiome and gut barrier to hepatic disorders. Gastroenterology 159, 849–863. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.04.077
Cogger, V. C., Mohamad, M., Solon-Biet, S. M., Senior, A. M., Warren, A., O'reilly, J. N., et al. (2016). Dietary macronutrients and the aging liver sinusoidal endothelial cell. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 310, H1064–H1070. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00949.2015
Corbitt, N., Kimura, S., Isse, K., Specht, S., Chedwick, L., Rosborough, B. R., et al. (2013). Gut bacteria drive Kupffer cell expansion via MAMP-mediated ICAM-1 induction on sinusoidal endothelium and influence preservation-reperfusion injury after orthotopic liver transplantation. Am. J. Pathol. 182, 180–191. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.09.010
De Gottardi, A., Rautou, P. E., Schouten, J., Rubbia-Brandt, L., Leebeek, F., Trebicka, J., et al. (2019). Porto-sinusoidal vascular disease: proposal and description of a novel entity. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 4, 399–411. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30047-0
De Gottardi, A., Sempoux, C., and Berzigotti, A. (2022). Porto-sinusoidal vascular disorder. J. Hepatol. 77, 1124–1135. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.05.033
Deleve, L. D., Wang, X., and Guo, Y. (2008). Sinusoidal endothelial cells prevent rat stellate cell activation and promote reversion to quiescence. Hepatology 48, 920–930. doi: 10.1002/hep.22351
Dultz, G., Gerber, L., Farnik, H., Berger, A., Vermehren, J., Pleli, T., et al. (2015). Soluble CD163 is an indicator of liver inflammation and fibrosis in patients chronically infected with the hepatitis B virus. J. Viral Hepat. 22, 427–432. doi: 10.1111/jvh.12309
Eapen, C. E., Nightingale, P., Hubscher, S. G., Lane, P. J., Plant, T., Velissaris, D., et al. (2011). Non-cirrhotic intrahepatic portal hypertension: associated gut diseases and prognostic factors. Dig. Dis. Sci. 56, 227–235. doi: 10.1007/s10620-010-1278-2
English, K., Bowen, D. G., and Bertolino, P. (2021). Zone defence - the gut microbiota position macrophages for optimal liver protection. Immunol. Cell. Biol. 99, 565–569. doi: 10.1111/imcb.12476
Fiordaliso, M., Marincola, G., Pala, B., Muraro, R., Mazzone, M., Di Marcantonio, M. C., et al. (2023). A narrative review on non-cirrohotic portal hypertension: not all portal hypertensions mean cirrhosis. Diagnostics 13:3263. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13203263
Ford, A. J., Jain, G., and Rajagopalan, P. (2015). Designing a fibrotic microenvironment to investigate changes in human liver sinusoidal endothelial cell function. Acta. Biomater. 24, 220–227. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2015.06.028
Formes, H., Bernardes, J. P., Mann, A., Bayer, F., Pontarollo, G., Kiouptsi, K., et al. (2021). The gut microbiota instructs the hepatic endothelial cell transcriptome. iScience 24:103092. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103092
Gana, J. C., Serrano, C. A., and Ling, S. C. (2016). Angiogenesis and portal-systemic collaterals in portal hypertension. Ann. Hepatol. 15, 303–313. doi: 10.5604/16652681.1198799
García-Pagán, J. C., Gracia-Sancho, J., and Bosch, J. (2012). Functional aspects on the pathophysiology of portal hypertension in cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 57, 458–461. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.03.007
Georgescu, D., Ancusa, O. E., Azoulay, D., Lascu, A., Ionita, I., Calamar-Popovici, D., et al. (2023). Portal vein thrombosis in patients with liver cirrhosis: what went wrong? Int. J. Gen. Med. 16, 3889–3906. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S413438
Gioia, S., Baiocchini, A., D'amati, G., Tavano, D., Ridola, L., Nardelli, S., et al. (2024). Porto-sinusoidal vascular disorder (PSVD): application of new diagnostic criteria in a multicenter cohort of patients. Dig. Liver Dis. 56, 291–296. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2023.07.023
Gioia, S., Carnevale, R., Tavano, D., Overi, D., Ridola, L., Nardelli, S., et al. (2023). Association between gut-derived endotoxins and porto-sinusoidal vascular disorder with portal hypertension. Aliment Pharmacol. Ther. 58, 1205–1216. doi: 10.1111/apt.17727
Gioia, S., Nardelli, S., Pasquale, C., Pentassuglio, I., Nicoletti, V., Aprile, F., et al. (2018). Natural history of patients with non cirrhotic portal hypertension: comparison with patients with compensated cirrhosis. Dig. Liver Dis. 50, 839–844. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2018.01.132
Gioia, S., Nardelli, S., Ridola, L., D'amati, G., and Riggio, O. (2019). Is porto sinusoidal vascular disease to be actively searched in patients with portal vein thrombosis? World J. Hepatol. 11, 613–618. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v11.i8.613
Giuffrè, M., Campigotto, M., Campisciano, G., Comar, M., and Crocè, L. S. (2020). A story of liver and gut microbes: how does the intestinal flora affect liver disease? A review of the literature. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 318, G889–G906. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00161.2019
Giuli, L., Pallozzi, M., Venturini, G., Gasbarrini, A., Ponziani, F. R., and Santopaolo, F. (2023). Molecular mechanisms underlying vascular liver diseases: focus on thrombosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24:12754. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612754
Gola, A., Dorrington, M. G., Speranza, E., Sala, C., Shih, R. M., Radtke, A. J., et al. (2021). Commensal-driven immune zonation of the liver promotes host defence. Nature 589, 131–136. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2977-2
Gracia-Sancho, J., Caparrós, E., Fernández-Iglesias, A., and Francés, R. (2021). Role of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in liver diseases. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 18, 411–431. doi: 10.1038/s41575-020-00411-3
Gracia-Sancho, J., Laviña, B., Rodríguez-Vilarrupla, A., García-Calderó, H., Bosch, J., and García-Pagán, J. C. (2007). Enhanced vasoconstrictor prostanoid production by sinusoidal endothelial cells increases portal perfusion pressure in cirrhotic rat livers. J. Hepatol. 47, 220–227. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2007.03.014
Gracia-Sancho, J., Laviña, B., Rodríguez-Vilarrupla, A., García-Calderó, H., Fernández, M., Bosch, J., et al. (2008). Increased oxidative stress in cirrhotic rat livers: a potential mechanism contributing to reduced nitric oxide bioavailability. Hepatology 47, 1248–1256. doi: 10.1002/hep.22166
Gracia-Sancho, J., Marrone, G., and Fernández-Iglesias, A. (2019). Hepatic microcirculation and mechanisms of portal hypertension. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 16, 221–234. doi: 10.1038/s41575-018-0097-3
Harmanci, O., and Bayraktar, Y. (2007). Clinical characteristics of idiopathic portal hypertension. World J. Gastroenterol. 13, 1906–1911. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i13.1906
Hasan, R. A., Koh, A. Y., and Zia, A. (2020). The gut microbiome and thromboembolism. Thromb. Res. 189, 77–87. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2020.03.003
He, L. H., Yao, D. H., Wang, L. Y., Zhang, L., and Bai, X. L. (2021). Gut microbiome-mediated alteration of immunity, inflammation, and metabolism involved in the regulation of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Front. Microbiol. 12:761836. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.761836
Hilscher, M. B., Sehrawat, T., Arab, J. P., Zeng, Z., Gao, J., Liu, M., et al. (2019). Mechanical stretch increases expression of CXCL1 in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells to recruit neutrophils, generate sinusoidal microthombi, and promote portal hypertension. Gastroenterology 157. 193–209.e9. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.03.013
Hsu, C. L., and Schnabl, B. (2023). The gut-liver axis and gut microbiota in health and liver disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 21, 719–733. doi: 10.1038/s41579-023-00904-3
Huang, X. Y., Zhang, Y. H., Yi, S. Y., Lei, L., Ma, T., Huang, R., et al. (2023). Potential contribution of the gut microbiota to the development of portal vein thrombosis in liver cirrhosis. Front. Microbiol. 14:1217338. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1217338
Hwang, J. H., Heo, W., Park, J. I., Kim, K. M., Oh, H. T., Yoo, G. D., et al. (2023). Endothelial TAZ inhibits capillarization of liver sinusoidal endothelium and damage-induced liver fibrosis via nitric oxide production. Theranostics 13, 4182–4196. doi: 10.7150/thno.83714
Isidro, R. A., and Zhao, L. (2023). Evolving understanding of noncirrhotic portal hypertension. Surg. Pathol. Clin. 16, 549–563. doi: 10.1016/j.path.2023.04.009
Iwakiri, Y., and Groszmann, R. J. (2007). Vascular endothelial dysfunction in cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 46, 927–934. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2007.02.006
Jäckel, S., Kiouptsi, K., Lillich, M., Hendrikx, T., Khandagale, A., Kollar, B., et al. (2017). Gut microbiota regulate hepatic von Willebrand factor synthesis and arterial thrombus formation via toll-like receptor-2. Blood 130, 542–553. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-11-754416
Jin, S. J., and Choi, W. M. (2023). Porto-sinusoidal vascular disease: a concise updated summary of epidemiology, pathophysiology, imaging, clinical features, and treatments. Korean J. Radiol. 24, 31–38. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2022.0668
Jonsson, A. L., and Bäckhed, F. (2017). Role of gut microbiota in atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 14, 79–87. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2016.183
Kang, J. H., Kim, D. H., Kim, S. Y., Kang, H. J., Lee, J. B., Kim, K. W., et al. (2021). Porto-sinusoidal vascular disease with portal hypertension vs. liver cirrhosis: differences in imaging features on CT and hepatobiliary contrast-enhanced MRI. Abdom. Radiol. 46, 1891–1903. doi: 10.1007/s00261-020-02831-w
Khanna, R., and Sarin, S. K. (2014). Non-cirrhotic portal hypertension - diagnosis and management. J. Hepatol. 60, 421–441. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.08.013
Khanna, R., and Sarin, S. K. (2019). Noncirrhotic portal hypertension: current and emerging perspectives. Clin. Liver Dis. 23, 781–807. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2019.07.006
Kiouptsi, K., Pontarollo, G., and Reinhardt, C. (2023). Gut microbiota and the microvasculature. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 13:a041179. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a041179
Kmeid, M., Liu, X., Ballentine, S., and Lee, H. (2021). Idiopathic non-cirrhotic portal hypertension and porto-sinusoidal vascular disease: review of current data. Gastroenterology Res. 14, 49–65. doi: 10.14740/gr1376
Koeth, R. A., Wang, Z., Levison, B. S., Buffa, J. A., Org, E., Sheehy, B. T., et al. (2013). Intestinal microbiota metabolism of L-carnitine, a nutrient in red meat, promotes atherosclerosis. Nat. Med. 19, 576–585. doi: 10.1038/nm.3145
Koh, A., De Vadder, F., Kovatcheva-Datchary, P., and Bäckhed, F. (2016). From dietary fiber to host physiology: short-chain fatty acids as key bacterial metabolites. Cell 165, 1332–1345. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.041
Kono, K., Ohnishi, K., Omata, M., Saito, M., Nakayama, T., Hatano, H., et al. (1988). Experimental portal fibrosis produced by intraportal injection of killed nonpathogenic Escherichia coli in rabbits. Gastroenterology 94, 787–796. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90255-7
Kume, M., Hayashi, T., Yuasa, H., Tanaka, H., Nishioka, J., Ido, M., et al. (2003). Bacterial lipopolysaccharide decreases thrombomodulin expression in the sinusoidal endothelial cells of rats – a possible mechanism of intrasinusoidal microthrombus formation and liver dysfunction. J. Hepatol. 38, 9–17. doi: 10.1016/S0168-8278(02)00324-0
Lässiger-Herfurth, A., Pontarollo, G., Grill, A., and Reinhardt, C. (2019). The gut microbiota in cardiovascular disease and arterial thrombosis. Microorganisms 7:691. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7120691
Lee, H., Rehman, A. U., and Fiel, M. I. (2016). Idiopathic noncirrhotic portal hypertension: an appraisal. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 50, 17–25. doi: 10.4132/jptm.2015.09.23
Leong, S. S., Cazen, R. A., Yu, G. S., Lefevre, L., and Carson, J. W. (1992). Abdominal visceral peliosis associated with bacillary angiomatosis. Ultrastructural evidence of endothelial destruction by bacilli. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 116, 866–871.
Li, W., Chang, N., and Li, L. (2022). Heterogeneity and function of Kupffer cells in liver injury. Front. Immunol. 13:940867. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.940867
Li, X., Hong, J., Wang, Y., Pei, M., Wang, L., and Gong, Z. (2021). Trimethylamine-N-Oxide pathway: a potential target for the treatment of MAFLD. Front. Mol. Biosci. 8:733507. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.733507
Liang, Q., Zhang, M., Hu, Y., Zhang, W., Zhu, P., Chen, Y., et al. (2020). Gut microbiome contributes to liver fibrosis impact on T cell receptor immune repertoire. Front. Microbiol. 11:571847. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.571847
Lisman, T., and Luyendyk, J. P. (2018). Platelets as modulators of liver diseases. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 44, 114–125. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1604091
Maroto-García, J., Martínez-Escribano, A., Delgado-Gil, V., Mañez, M., Mugueta, C., Varo, N., et al. (2023). Biochemical biomarkers for multiple sclerosis. Clin Chim Acta 548, 117471. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2023.117471
Marrone, G., Shah, V. H., and Gracia-Sancho, J. (2016). Sinusoidal communication in liver fibrosis and regeneration. J. Hepatol. 65, 608–617. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.04.018
Martin-Armas, M., Simon-Santamaria, J., Pettersen, I., Moens, U., Smedsrød, B., and Sveinbjørnsson, B. (2006). Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) is present in murine liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs) and mediates the effect of CpG-oligonucleotides. J. Hepatol. 44, 939–946. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2005.09.020
Mcconnell, M., and Iwakiri, Y. (2018). Biology of portal hypertension. Hepatol. Int. 12, 11–23. doi: 10.1007/s12072-017-9826-x
Mcdonald, B., Zucoloto, A. Z., Yu, I. L., Burkhard, R., Brown, K., Geuking, M. B., et al. (2020). Programing of an intravascular immune firewall by the gut microbiota protects against pathogen dissemination during infection. Cell. Host. Microbe. 28, 660–668.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2020.07.014
Mehta, G., Gustot, T., Mookerjee, R. P., Garcia-Pagan, J. C., Fallon, M. B., Shah, V. H., et al. (2014). Inflammation and portal hypertension - the undiscovered country. J. Hepatol. 61, 155–163. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.03.014
Mitten, E. K., and Baffy, G. (2022). Microbiota transplantation in portal hypertension: promises and pitfalls. Clin. Sci. 136, 425–429. doi: 10.1042/CS20220029
Mohammed, Y., Kootte, R. S., Kopatz, W. F., Borchers, C. H., Büller, H. R., Versteeg, H. H., et al. (2020). The intestinal microbiome potentially affects thrombin generation in human subjects. J. Thromb. Haemost. 18, 642–650. doi: 10.1111/jth.14699
Morrison, D. J., and Preston, T. (2016). Formation of short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on human metabolism. Gut Microbes 7, 189–200. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2015.1134082
Nychas, E., Marfil-Sánchez, A., Chen, X., Mirhakkak, M., Li, H., Jia, W., et al. (2025). Discovery of robust and highly specific microbiome signatures of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Microbiome 13:10. doi: 10.1186/s40168-024-01990-y
Oh, T. G., Kim, S. M., Caussy, C., Fu, T., Guo, J., Bassirian, S., et al. (2020). A Universal gut-microbiome-derived signature predicts cirrhosis. Cell Metab. 32, 878–888.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.06.005
Øie, C. I., Wolfson, D. L., Yasunori, T., Dumitriu, G., Sørensen, K. K., Mccourt, P. A., et al. (2020). Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells contribute to the uptake and degradation of entero bacterial viruses. Sci. Rep. 10:898. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-57652-0
Ørntoft, N. W., Blé, M., Baiges, A., Ferrusquia, J., Hernández-Gea, V., Turon, F., et al. (2021). Divergences in macrophage activation markers soluble CD163 and mannose receptor in patients with non-cirrhotic and cirrhotic portal hypertension. Front. Physiol. 12:649668. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.649668
Ozinsky, A., Underhill, D. M., Fontenot, J. D., Hajjar, A. M., Smith, K. D., Wilson, C. B., et al. (2000). The repertoire for pattern recognition of pathogens by the innate immune system is defined by cooperation between toll-like receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 97, 13766–13771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.250476497
Pabst, O., Hornef, M. W., Schaap, F. G., Cerovic, V., Clavel, T., and Bruns, T. (2023). Gut-liver axis: barriers and functional circuits. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 20, 447–461. doi: 10.1038/s41575-023-00771-6
Parthasarathy, G., Malhi, H., and Bajaj, J. S. (2024). Therapeutic manipulation of the microbiome in liver disease. Hepatology. doi: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000987. [Epub ahead of print].
Pillai, A. K., Andring, B., Patel, A., Trimmer, C., and Kalva, S. P. (2015). Portal hypertension: a review of portosystemic collateral pathways and endovascular interventions. Clin. Radiol. 70, 1047–1059. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2015.06.077
Płóciennikowska, A., Hromada-Judycka, A., Borzecka, K., and Kwiatkowska, K. (2015). Co-operation of TLR4 and raft proteins in LPS-induced pro-inflammatory signaling. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 72, 557–581. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1762-5
Poisson, J., Lemoinne, S., Boulanger, C., Durand, F., Moreau, R., Valla, D., et al. (2017). Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells: physiology and role in liver diseases. J. Hepatol. 66, 212–227. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.07.009
Premkumar, M., and Anand, A. C. (2024). Porto-sinusoidal vascular disease: classification and clinical relevance. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 14:101396. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2024.101396
Qiu, L., Tao, X., Xiong, H., Yu, J., and Wei, H. (2018). Lactobacillus plantarum ZDY04 exhibits a strain-specific property of lowering TMAO via the modulation of gut microbiota in mice. Food. Funct. 9, 4299–4309. doi: 10.1039/C8FO00349A
Reinhardt, C., Bergentall, M., Greiner, T. U., Schaffner, F., Ostergren-Lundén, G., Petersen, L. C., et al. (2012). Tissue factor and PAR1 promote microbiota-induced intestinal vascular remodelling. Nature 483, 627–631. doi: 10.1038/nature10893
Riggio, O., Gioia, S., Pentassuglio, I., Nicoletti, V., Valente, M., and D'amati, G. (2016). Idiopathic noncirrhotic portal hypertension: current perspectives. Hepat. Med. 8, 81–88. doi: 10.2147/HMER.S85544
Rutanga, J. P., Van Puyvelde, S., Heroes, A. S., Muvunyi, C. M., Jacobs, J., and Deborggraeve, S. (2018). 16S metagenomics for diagnosis of bloodstream infections: opportunities and pitfalls. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 18, 749–759. doi: 10.1080/14737159.2018.1498786
Sarin, S. K., and Aggarwal, S. R. (1998). Idiopathic portal hypertension. Digestion 59, 420–423. doi: 10.1159/000007502
Seijo, S., Lozano, J. J., Alonso, C., Miquel, R., Berzigotti, A., Reverter, E., et al. (2016). Metabolomics as a diagnostic tool for idiopathic non-cirrhotic portal hypertension. Liver Int. 36, 1051–1058. doi: 10.1111/liv.12972
Seijo, S., Lozano, J. J., Alonso, C., Reverter, E., Miquel, R., Abraldes, J. G., et al. (2013). Metabolomics discloses potential biomarkers for the noninvasive diagnosis of idiopathic portal hypertension. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 108, 926–932. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2013.11
Seki, E., and Brenner, D. A. (2008). Toll-like receptors and adaptor molecules in liver disease: update. Hepatology 48, 322–335. doi: 10.1002/hep.22306
Seo, Y. S., and Shah, V. H. (2012). The role of gut-liver axis in the pathogenesis of liver cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 18, 337–346. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2012.18.4.337
Serrano, C. A., Ling, S. C., Verdaguer, S., León, M., Jarufe, N., Guerra, J. F., et al. (2019). Portal angiogenesis in chronic liver disease patients correlates with portal pressure and collateral formation. Dig. Dis. 37, 498–508. doi: 10.1159/000500115
Shakya, M., Lo, C. C., and Chain, P. S. G. (2019). Advances and challenges in metatranscriptomic analysis. Front. Genet. 10:904. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00904
Shen, Y., Wu, S. D., Chen, Y., Li, X. Y., Zhu, Q., Nakayama, K., et al. (2023). Alterations in gut microbiome and metabolomics in chronic hepatitis B infection-associated liver disease and their impact on peripheral immune response. Gut Microbes. 15:2155018. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2155018
Shetty, S., Lalor, P. F., and Adams, D. H. (2018). Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells - gatekeepers of hepatic immunity. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 15, 555–567. doi: 10.1038/s41575-018-0020-y
Simbrunner, B., Mandorfer, M., Trauner, M., and Reiberger, T. (2019). Gut-liver axis signaling in portal hypertension. World J. Gastroenterol. 25, 5897–5917. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i39.5897
Siramolpiwat, S., Seijo, S., Miquel, R., Berzigotti, A., Garcia-Criado, A., Darnell, A., et al. (2014). Idiopathic portal hypertension: natural history and long-term outcome. Hepatology 59, 2276–2285. doi: 10.1002/hep.26904
Skye, S. M., Zhu, W., Romano, K. A., Guo, C. J., Wang, Z., Jia, X., et al. (2018). Microbial transplantation with human gut commensals containing cutc is sufficient to transmit enhanced platelet reactivity and thrombosis potential. Circ. Res. 123, 1164–1176. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.313142
Spadoni, I., Zagato, E., Bertocchi, A., Paolinelli, R., Hot, E., Di Sabatino, A., et al. (2015). A gut-vascular barrier controls the systemic dissemination of bacteria. Science 350, 830–834. doi: 10.1126/science.aad0135
Stanhewicz, A. E., and Kenney, W. L. (2017). Role of folic acid in nitric oxide bioavailability and vascular endothelial function. Nutr. Rev. 75, 61–70. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuw053
Stojic, J., Kukla, M., and Grgurevic, I. (2023). The intestinal microbiota in the development of chronic liver disease: current status. Diagnostics 13:2960. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13182960
Sutton, H., Dhawan, A., and Grammatikopoulos, T. (2018). Non-invasive markers of portal hypertension: appraisal of adult experience and potential utilisation in children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 66, 559–569. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000001882
Tan, X., Liu, Y., Long, J., Chen, S., Liao, G., Wu, S., et al. (2019). Trimethylamine N-oxide aggravates liver steatosis through modulation of bile acid metabolism and inhibition of farnesoid X receptor signaling in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 63:e1900257. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201900257
Tranah, T. H., Edwards, L. A., Schnabl, B., and Shawcross, D. L. (2021). Targeting the gut-liver-immune axis to treat cirrhosis. Gut 70, 982–994. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-320786
Valles-Colomer, M., Menni, C., Berry, S. E., Valdes, A. M., Spector, T. D., and Segata, N. (2023). Cardiometabolic health, diet and the gut microbiome: a meta-omics perspective. Nat. Med. 29, 551–561. doi: 10.1038/s41591-023-02260-4
Velasquez, M. T., Ramezani, A., Manal, A., and Raj, D. S. (2016). Trimethylamine N-oxide: the good, the bad and the unknown. Toxins 8:326. doi: 10.3390/toxins8110326
Vijay, K. (2018). Toll-like receptors in immunity and inflammatory diseases: past, present, and future. Int. Immunopharmacol. 59, 391–412. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.03.002
Vinchi, F. (2019). Thrombosis prevention: let's drug the microbiome! Hemasphere 3:e165. doi: 10.1097/HS9.0000000000000165
Violi, F., Nocella, C., Bartimoccia, S., Castellani, V., Carnevale, R., Pignatelli, P., et al. (2023). Gut dysbiosis-derived low-grade endotoxemia: a common soil for liver and cardiovascular disease. Kardiol. Pol. 81, 563–571. doi: 10.33963/KP.a2023.0115
Waidmann, O., Brunner, F., Herrmann, E., Zeuzem, S., Piiper, A., and Kronenberger, B. (2013). Macrophage activation is a prognostic parameter for variceal bleeding and overall survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 58, 956–961. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.01.005
Wang, B., Qiu, J., Lian, J., Yang, X., and Zhou, J. (2021a). Gut metabolite trimethylamine-N-oxide in atherosclerosis: from mechanism to therapy. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 8:723886. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.723886
Wang, R., Tang, R., Li, B., Ma, X., Schnabl, B., and Tilg, H. (2021b). Gut microbiome, liver immunology, and liver diseases. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 18, 4–17. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-00592-6
Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., Liu, Y., Xu, J., and Liu, Y. (2021c). Gut-liver axis: liver sinusoidal endothelial cells function as the hepatic barrier in colitis-induced liver injury. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 9:702890. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.702890
Wilkinson, A. L., Qurashi, M., and Shetty, S. (2020). The role of sinusoidal endothelial cells in the axis of inflammation and cancer within the liver. Front. Physiol. 11:990. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00990
Wong, A. C., and Levy, M. (2019). New approaches to microbiome-based therapies. mSystems 4:e00122. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00122-19
Xiang, L., Lou, Y., Liu, L., Liu, Y., Zhang, W., Deng, J., et al. (2020). Gut microbiotic features aiding the diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 10:587284. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.587284
Xie, G., Wang, X., Wang, L., Wang, L., Atkinson, R. D., Kanel, G. C., et al. (2012). Role of differentiation of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells in progression and regression of hepatic fibrosis in rats. Gastroenterology 142, 918–927.e6. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.12.017
Xu, M., Xu, H. H., Lin, Y., Sun, X., Wang, L. J., Fang, Z. P., et al. (2019). LECT2, a ligand for tie1, plays a crucial role in liver fibrogenesis. Cell 178, 1478–1492.e20. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.07.021
Yadav, N., Jaber, F. L., Sharma, Y., Gupta, P., Viswanathan, P., and Gupta, S. (2019). Efficient reconstitution of hepatic microvasculature by endothelin receptor antagonism in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. Hum. Gene Ther. 30, 365–377. doi: 10.1089/hum.2018.166
Yang, H., Li, N., Du, Y., Tong, C., Lü, S., Hu, J., et al. (2017). Neutrophil adhesion and crawling dynamics on liver sinusoidal endothelial cells under shear flow. Exp. Cell Res. 351, 91–99. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.01.002
Yang, H., Tan, M., Gao, Z., Wang, S., Lyu, L., and Ding, H. (2023). Role of hydrogen sulfide and hypoxia in hepatic angiogenesis of portal hypertension. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 11, 675–681.
Yang, M., Luo, P., Zhang, F., Xu, K., Feng, R., and Xu, P. (2022). Large-scale correlation analysis of deep venous thrombosis and gut microbiota. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 9:1025918. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1025918
Yin, J., Liao, S. X., He, Y., Wang, S., Xia, G. H., Liu, F. T., et al. (2015). Dysbiosis of gut microbiota with reduced trimethylamine-N-oxide level in patients with large-artery atherosclerotic stroke or transient ischemic attack. J Am Heart Assoc 4:e002699. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.115.002699
Zhang, X., Thomas, C., Schiano, T. D., Thung, S. N., Ward, S. C., and Fiel, M. I. (2020). Aberrant von Willebrand factor expression of sinusoidal endothelial cells and quiescence of hepatic stellate cells in nodular regenerative hyperplasia and obliterative portal venopathy. Histopathology 76, 959–967. doi: 10.1111/his.14083
Zhou, D., Zhang, J., Xiao, C., Mo, C., and Ding, B. S. (2022a). Trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO) mediates the crosstalk between the gut microbiota and hepatic vascular niche to alleviate liver fibrosis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Front. Immunol. 13:964477. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.964477
Keywords: porto-sinusoidal vascular disease, portal hypertension, gut-liver axis, gut microbiome, microvascular thrombosis
Citation: Li Y, Lyu L and Ding H (2025) The potential roles of gut microbiome in porto-sinusoidal vascular disease: an under-researched crossroad. Front. Microbiol. 16:1556667. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1556667
Received: 07 January 2025; Accepted: 14 February 2025;
Published: 03 March 2025.
Edited by:
Yongli Ye, Jiangnan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Gabriele Deidda, University of Padua, ItalyDinakaran Vasudevan, SKAN Research Trust, India
Copyright © 2025 Li, Lyu and Ding. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Huiguo Ding, ZGluZ2h1aWd1b0BjY211LmVkdS5jbg==
 Yangjie Li
Yangjie Li Lingna Lyu
Lingna Lyu Huiguo Ding
Huiguo Ding