
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Microbiol. , 04 March 2025
Sec. Microbial Physiology and Metabolism
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1551625
 Xiaoyu Liu1†
Xiaoyu Liu1† Sihai Geng1,2,3†
Sihai Geng1,2,3† Daoyou Ye1
Daoyou Ye1 Wenhua Xu1
Wenhua Xu1 Yidi Zheng1
Yidi Zheng1 Fangji Wang1
Fangji Wang1 Jianpeng Lei1
Jianpeng Lei1 Ying Wu4
Ying Wu4 Haibin Jiang4
Haibin Jiang4 Ying Hu1
Ying Hu1 Dafu Chen1,2,3
Dafu Chen1,2,3 Tizhen Yan5
Tizhen Yan5 Rui Guo1,2,3*
Rui Guo1,2,3* Jianfeng Qiu1,2,3*
Jianfeng Qiu1,2,3*Ascosphaera apis, a specialized fungal pathogen, causes lethal infection in honeybee larvae. miRNA-like small RNAs (milRNAs) are fungal small non-coding RNAs similar to miRNAs, which have been shown to regulate fungal hyphal growth, spore formation, and pathogenesis. Based on the transcriptome data, differentially expressed miRNA-like RNAs (DEmilRNAs) in A. apis infecting the Apis cerana cerana worker 4-, 5-, and 6-day-old larvae (Aa-4, Aa-5, and Aa-6) were screened and subjected to trend analysis, followed by target prediction and annotation as well as investigation of regulatory networks, with a focus on sub-networks relative to MAPK signaling pathway, glycerolipid metabolism, superoxide dismutase, and enzymes related to chitin synthesis and degradation. A total of 606 milRNAs, with a length distribution ranging from 18 nt to 25 nt, were identified. The first nucleotide of these milRNAs presented a bias toward U, and the bias patterns across bases of milRNAs were similar in the aforementioned three groups. There were 253 milRNAs, of which 68 up-and 54 down-regulated milRNAs shared by these groups. Additionally, the expression and sequences of three milRNAs were validated by stem-loop RT-PCR and Sanger sequencing. Trend analysis indicated that 79 DEmilRNAs were classified into three significant profiles (Profile4, Profile6, and Profile7). Target mRNAs of DEmilRNAs in these three significant profiles were engaged in 42 GO terms such as localization, antioxidant activity, and nucleoid. These targets were also involved in 120 KEGG pathways including lysine biosynthesis, pyruvate metabolism, and biosynthesis of antibiotics. Further investigation suggested that DEmilRNA-targeted mRNAs were associated with the MAPK signaling pathway, glycerolipid metabolism, superoxide dismutase, and enzymes related to chitin synthesis and degradation. Moreover, the binding relationships between aap-milR10516-x and ChsD as well as between aap-milR-2478-y and mkh1 were confirmed utilizing a combination of dual-luciferase reporter gene assay and RT-qPCR. Our data not only provide new insights into the A. apis proliferation and invasion, but also lay a basis for illustrating the DEmilRNA-modulated mechanisms underlying the A. apis infection.
Ascosphaera apis is a lethal fungal pathogen that exclusively invades honeybee larvae, giving rise to chalkbrood disease, which causes severe damage to bee health and sharp decline of colony population as well as productivity (Aronstein and Murray, 2010) A. apis spores are ingested orally with food by honeybee larvae and germinate at a low level in the lumen of the midgut, the septum between the midgut and the hindgut disappears at the pre-pupal stage, the spores enter the hindgut with the food residues and germinate violently upon the stimulation of oxygen, and the fungal mycelium rapidly develops and penetrate the intestinal wall and then the body wall, the mycelia pierce from the end of larvae and finally covered the entire larvae, generating a white or black chalkbrood mummy (Aronstein and Murray, 2010). A. apis has been verified to infect not only Apis mellifera larvae and bumblebee queens (Maxfield-Taylor et al., 2015), but also larvae of Apis cerana worker as well as drone.
In past decades, miRNAs have been discovered in diverse animals (Grimson et al., 2008), plants (Llave et al., 2002), and microorganisms (Chen et al., 2014; Nersisyan et al., 2020) and confirmed to play essential roles in numerous processes such as growth (DeVeale et al., 2021), development (Pei et al., 2023), metabolism (Agbu and Carthew, 2021), and immunity (Kim et al., 2017; Asgari, 2013). With the development of deep sequencing technology and relevant bioinformatics, a substantial amount of miRNA-like small RNAs (milRNAs) in fungi have been identified and documented (Lee et al., 2010; Huang and Evans, 2016; Lau et al., 2018). Previously, mixed samples of A. apis mycelium and spores were prepared followed by sequencing of corresponding cDNA libraries using small RNA-seq technology, a total of 118 milRNAs were predicted and found to play a potential regulatory part in the material and energy metabolism as well as MAPK signaling pathway (Guo et al., 2018). Accumulating evidence has demonstrated that milRNAs are engaged in the modulation of fungal mycelium growth, spore formation, and pathogenesis (Li et al., 2017; Lin et al., 2016; Guo et al., 2019). For instance, Villalobos-Escobedo et al. (2022) found that Trichoderma atroviride milRNAs could regulate hyphal regeneration by post-transcriptionally regulating cellular signaling processes involving phosphorylation events. Li et al. (2017) reported that mro-miR-33 promoted spore formation in Metarhizium robertsii through negative modulation of brlA, a key gene responsible for asexual spore production in filamentous fungi. Previous studies on pathogenic milRNAs were mainly associated with fungi infecting plants. Two milRNAs in Rhizoctonia solani, Rhi-milR-16, and Rhi-milR-92, were engaged in the degradation of host cell walls and antifungal compounds by regulating the expression of target genes relative to various pathogenic factors (Lin et al., 2016). Comparatively, due to a lack of relevant research, little is known about the role of milRNAs in the fungal infection of insects. Cui et al. (2019) discovered that bba-milR1, a miRNA-like RNA in Beauveria bassiana, could suppress host immunity by silencing the expression of the Toll receptor ligand Spätzle 4 (Spz4) gene in mosquitoes. Recently, Fan et al. (2024) identified 974 milRNAs in A. apis infecting Apis mellifera ligustica worker larvae, and found that DEmilRNAs included in four significant trends potentially modulated the expression of the target genes encoding secondary metabolite-associated enzymes, virulence factors, and MAPK signaling pathway.
Apis cerana, a bee species widely distributed in Asian countries such as China, Japan, and North Korea, is well-known for its long foraging period, ability to utilize scattered nectar sources, tolerance to low temperature, and strong disease resistance (Mi and Tan, 2007; Zhang et al., 2008; Qin et al., 2016), making it indispensable for maintaining ecosystem stability and promoting the apicultural development.
Following deep sequencing of cDNA libraries from A. apis-and un-inoculated gut tissues of A. cerana worker larvae annotated, we previously gained high-quality transcriptome datasets including both A. cerana-and A. apis-derived data. Here, trend analysis of DEmilRNAs in A. apis during the infection process was performed, followed by annotation of DEmilRNA-targeted mRNAs and in-depth investigation of the regulatory network associated with MAPK signaling pathway, glycerolipid metabolism, superoxide dismutase, and enzymes related to chitin synthesis and degradation, and further, the relationships between two DEmilRNAs and corresponding target mRNAs were verified using molecular approach. Our findings could not only provide novel insights into the A. apis proliferation and invasion, but also lay a foundation for clarifying the milRNA-mediated mechanisms underlying the A. apis infection of A. cerana larvae. Also, this work will offer candidates for functional dissection and promising targets for diagnosis and control of chalkbrood.
Apis cerana worker larvae were obtained from three colonies reared by the Host-Pathogen Interaction and Precision Medicine research team, College of Bee Science and Biomedicine, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (119.2369° E, 26.08279° N). The larvae were cultured at 35.0 ± 0.5°C and 90% relative humidity (RH), and fed with an artificial diet every 24 h. A. apis (Fuzhou strain) was isolated by our laboratory (Maxfield-Taylor et al., 2015) and conserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (NO. 40895).
Following the protocol developed by our lab, the A. apis spores were purified (Du et al., 2019; Guo et al., 2019a). The fresh spores were counted using a hemocytometer. In the treatment group, 3-day-old larvae (n = 3) were each fed 50 μL of the artificial diet containing spores with a final concentration of 1 × 107 spores/mL. In the control group, 3-day-old larvae (n = 3) were each fed 50 μL of the artificial diet without spores. The larvae in these two groups were placed in two separate constant temperature and humidity chambers, and reared at 35.0 ± 0.5°C and 90% RH. After the larvae consumed the diet, a fresh diet without spores was added, thereafter fresh diet was added every 24 h. At 4, 5, and 6 day-old, 9 larvae in each group were dissected and the gut tissues were placed in RNA-Free Eppendorf (EP) tubes. The prepared gut samples were frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80°C. The experiment was performed in triplicates.
The sRNA-seq was prepared according to the established protocol, followed by total RNA isolation, cDNA library construction, sRNA-seq, and strict quality control of raw data (Chen et al., 2020). The gut tissues of A. apis-inoculated A. c. cerana worker 4-, 5-, and 6-day-old larvae (Aa-4, Aa-5, and Aa-6 group) were dissected and then subjected to total RNA isolation and cDNA library construction, followed by sRNA-seq and data quality control, there were three biological replicates of the A. apis-inoculated larval gut samples (Guo et al., 2019b; Xiong et al., 2020). The raw data are available in the NCBI SRA database under the BioProject number: PRJNA565611.
Quality control was performed on the raw reads by: (1) filtering out reads with more than one base having a quality value below 20; (2) removing reads containing unknown bases (N); (3) filtering out 3′ or 5′ adapter sequences and discarding reads shorter than 18 bp; (4) filtering reads containing poly-A tails. The resulting clean reads were used for subsequent analysis. Clean reads were aligned against the GenBank database1 and the Rfam database2 using the Blastall tool, and reads aligning with rRNA, scRNA, snoRNA, snRNA, and tRNA were excluded.
The clean tags were, respectively, aligned to the GenBank database,3 RFAM database,4 ribosome database,5 and A. apis reference genome (assembly AAP 1.0) by using the Blast tool to remove possible rRNA, scRNA, snoRNA, snRNA, tRNA, and those aligned clean tags to genomic exon, intron, and repeat regions (Xiong et al., 2020). Subsequently, the unaligned clean tags were compared with milRNA precursor sequences in the miRBase database6 to identify known milRNA sequences. Further, the unannotated tags were mapped to the A. apis reference genome (assembly AAP 1.0) using the Mireap_v0.2 software, and novel milRNA candidates were identified according to their genomic positions and hairpin structures. The TPM (tags per million) algorithm is utilized to normalize the expression level of all milRNAs. Furtherly, the length distribution and first nucleotide bias of milRNAs in the Aa-4, Aa-5, and Aa-6 groups were identified which were plotted using the GraphPad Prism 7 software.
First, the miRNA was analyzed differentially using the edgeR software with |log2(fold change)| > 1 and p < 0.05. Among them, the fold change in expression level between Aa-4 vs. Aa-5, Aa-4 vs. Aa-6, and Aa-5 vs. Aa-6 comparison groups were determined according to the following formula: (TPM in Aa-5)/(TPM in Aa-4) or (TPM in Aa-6)/(TPM in Aa-5) (Fan et al., 2024). Subsequently, Short Time-series Expression Miner (STEM) software (Ernst and Bar-Joseph, 2006) to analyze the trend of the total DEmilRNAs, with p < 0.05 as the significant threshold. The default parameters were as follows: The maximum unit change of the model profiles between time points was 1, the maximum number of output maps was 20, and the minimum fold change ratio of DEmilRNA was not less than 2.0. The results were exported from the STEM software and significant profiles were selected.
Three software, RNAhybrid (v2.1.2) + svm_light (v6.01) (Enright et al., 2003), Miranda (v3.3a) (Krüger and Rehmsmeier, 2006), and Target Scan (Version:7.0) (Allen et al., 2005), were employed to predict the target mRNA of the DEmilRNAs, and the intersection of the three prediction results was regarded as a reliable set of target mRNAs. Subsequently screening obtained the targeted binding relationship with ΔG < −17 kcal/mol for subsequent analysis. Next, these target mRNAs were mapped to the GO7 and KEGG8 databases to gain corresponding annotations using the relevant tool in the Omicshare platform,9 with the default parameters. Finally, the different functional terms and KEGG pathways were presented through the Omicshare platform (see Footnote 9).
In collaboration with the annotations in KEGG databases as well as relevant documentation (Asl et al., 2021), those target mRNAs associated with MAPK signaling pathway, virulence factor, and glycerolipid metabolism and corresponding DEmilRNAs were screened followed by construction of sub-networks, which were visualized by the Cytoscape v.3.2.1 software (Smoot et al., 2011).
Randomly selected 3 milRNAs (milR-31-x, milR-7977-x, and milR-9993-y) for Stem-loop RT-PCR and Sanger sequencing. Then, specific Stem-loop primers and upstream primers (F) as well as universal downstream primers (R) were designed and synthesized by Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) (Supplementary Table S1). According to the method of Fan et al. (2024), total RNA was extracted using RNA extraction kit (Permoga, LS1040, China), followed by reverse transcription with Stem-loop primers. The resulting cDNA were used as templates for PCR amplification (Yeasen, 10102ES08, China). The products were then subjected to electrophoresis on a 1.5% agarose gel. Next, the target fragment was recovered, ligated with pMD-19 T vector (TaKaRa, 6,013, China), and transformed into E. coli DH5α (Tiangen, CB101-01, China). The single colony was transferred to the LB liquid medium to culture for 12 h, and a bit of bacterial liquid was then taken to conduct PCR confirmation. The bacterial liquid with a positive signal was sent to Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) for Sanger sequencing.
RT-qPCR detection was performed on a QuantStudio 3 fluorescent quantitative PCR system (ABI, Los Angeles, CA, United States), following the conditions: 95°C for 5 min; 95°C for 30s; 60°C for 30 s; 40 cycles.; melting curve program default system settings. The reaction system was as follows: 10 μL of SYBR Green Dye (Yeasen, 11202ES08, China), 1 μL each of upstream and downstream primers (2.5 μmol/L) (Table 1) as well as cDNA templates, and the DEPC treatment water was replenished to 20 μL. The 5.8S rRNA gene (GeneBank accession number: NR_178140) was used as the internal reference. The relative expression level of each DEmilRNA and target mRNAs was calculated by using the 2−ΔΔCt method (Ha and Kim, 2014). Each reaction was conducted with at least three samples in parallel and was repeated three times.
The mimic and the negative control mimic (Mimic-NC) were commissioned to be synthesized by Shanghai Jimar Pharmaceutical Technology Company. The potential binding site sequences of milRNA and targeted genes were predicted by the software and cloned into the pmirGLO vectors. The mutant sequences of the above binding sites were designed and cloned into the pmirGLO vectors, and the bacterial fluids were sent to Sango Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co. for Sanger sequencing. The correctly sequenced bacterial fluids were transferred to fresh LB liquid medium. The plasmids were extracted using the Endotoxin Removal Plasmid Extraction Kit (Beijing AllStyle Gold Biotechnology Co., Ltd.).
HEK-293T cells were spread into 48-well cell culture plates and then placed into a 37°C incubator to continue incubation for 24 h, so that the cell density reached 90–95%. Cell transfection experiments were performed according to the instructions of Hieff Trans® Liposomal Transfection Reagent (Yeasen, 40802ES02, China). Each group was transfected with 200 ng of plasmid and 20 pmol Mimics or Mimic-NC. After the transfection was completed and incubated for 24 h, the firefly fluoresceinase and kidney fluoresceinase were detected on a GloMax chemiluminescence detector using a dual-luciferase kit (Yeasen, 11402ES60, China), and the firefly fluoresceinase/kidney fluoresceinase ratio was calculated to obtain the relative expression folds. The experiment was repeated three times.
GraphPad Prism version 10 (GraphPad, San Diego, CA, United States) was used for graph construction and statistical analysis. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed using the one-way ANOVA or Two-way ANOVA, Tukey’s multiple comparisons (ns, p > 0.05; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001).
On average, 13119026.7, 11,905,316, and 10,773,889 raw reads were identified from the Aa-4, Aa-5, and Aa-6 groups, respectively. After quality control, the clean reads of Aa-4, Aa-5, and Aa-6 groups were 12537258.3, 11,494,486, and 10,399,091, respectively, accounting for 95.56, 96.55, and 96.52% of the raw reads. In addition, the mapping ratios were 7.66, 5.11, and 6.43%, respectively (Table 1).
In the Aa-4 group, 398 milRNAs were identified, including 396 known and 2 novel ones. A total of 431 milRNAs were detected in the Aa-5 group, including 396 known and 35 novel ones. Additionally, 387 milRNA, including 330 known and 57 novel milRNAs, were found in the Aa-6 group (Figure 1A). Venn analysis indicated that 253 milRNAs were shared by the Aa-4, Aa-5, and Aa-6 groups, whereas there were 86, 86, and 77 specific milRNAs, respectively (Figure 1B). As shown in Figure 1C, these shared milRNAs displayed various expression trends during the process of A. apis infection, with 68 (54) milRNAs showing a continuous up-regulation (down-regulation) trend (Supplementary Figure S1).
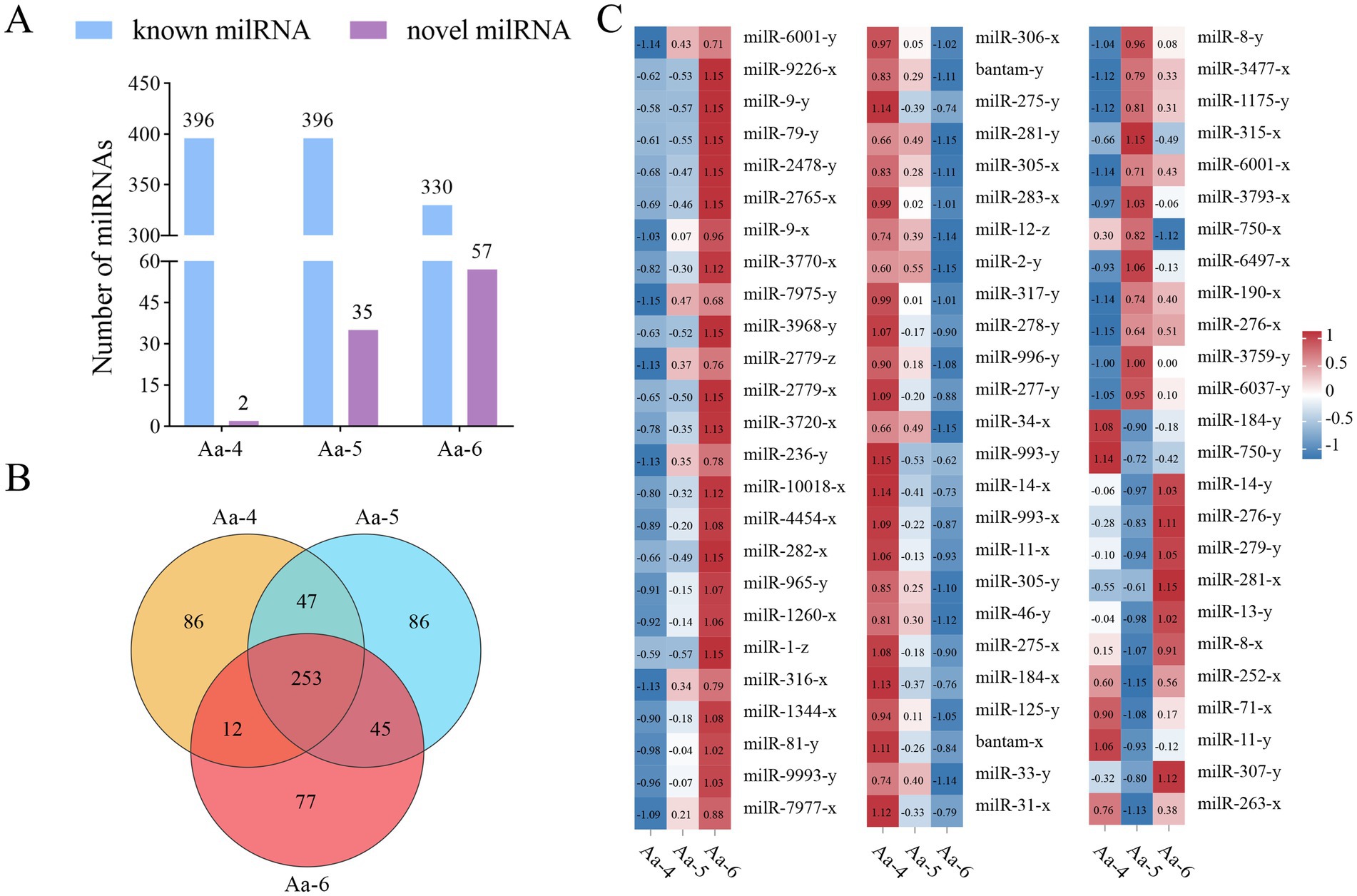
Figure 1. Number statistics, Venn diagram, and expression clustering of A. apis milRNAs. (A) Statistics of known and novel milRNAs in three different groups; (B) Venn diagram of milRNAs in three different groups; (C) Heat map of expression clustering of shared milRNAs by different groups.
Agarose gel electrophoresis demonstrated that the fragments with expected sizes (approximately 100 bp) were amplified from aap-milR-31-x, aap-milR-7977-x, and aap-milR-9993-y (Figure 2A). Sanger sequencing suggested that the sequences of amplified fragments were consistent with those in the transcriptome sequencing data, verifying the authenticity of their sequences (Figure 2B).
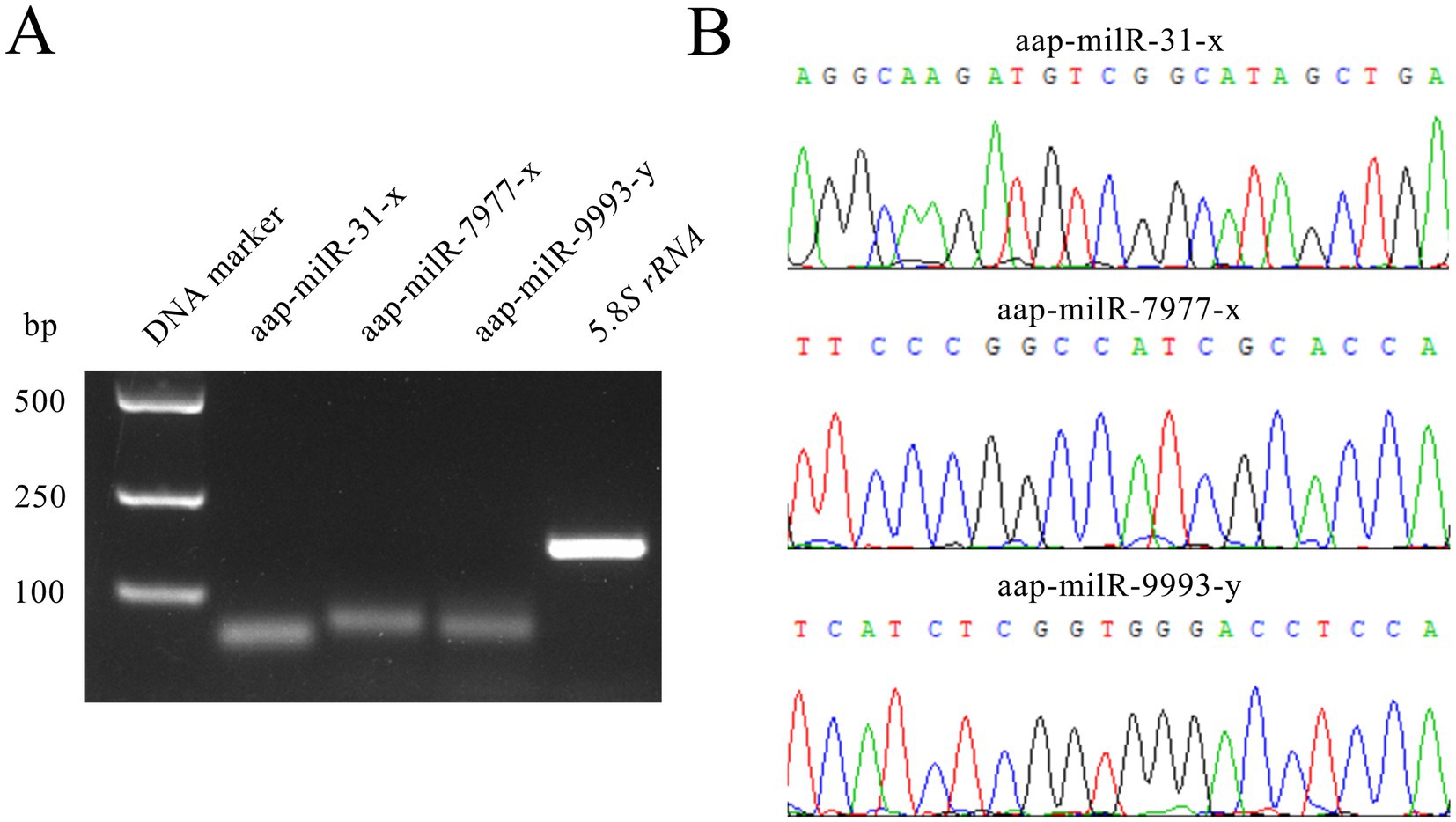
Figure 2. Molecular validation of expression and sequences of A. apis milRNAs. (A) Agarose gel electrophoresis for the amplification products from Stem-loop RT-PCR of aap-milR-31-x, aap-milR-7977-x, and aap-milR-9993-y; (B) Peak diagrams of Sanger sequencing of the amplified fragments from aap-milR-31-x, aap-milR-7977-x, and aap-milR-9993-y.
In the Aa-4, Aa-5, and Aa-6 groups, aap-milR-31-x, aap-milR-7977-x, and aap-milR-9993-y were, respectively, identified, their length distribution were ranged from 18 nt to 25 nt, with the most milRNAs distributed in 22 nt (Figure 3A). In addition, the first base of milRNAs was always biased toward U (Figure 3B), and milRNAs exhibited various base biases at each base (Figure 3C).
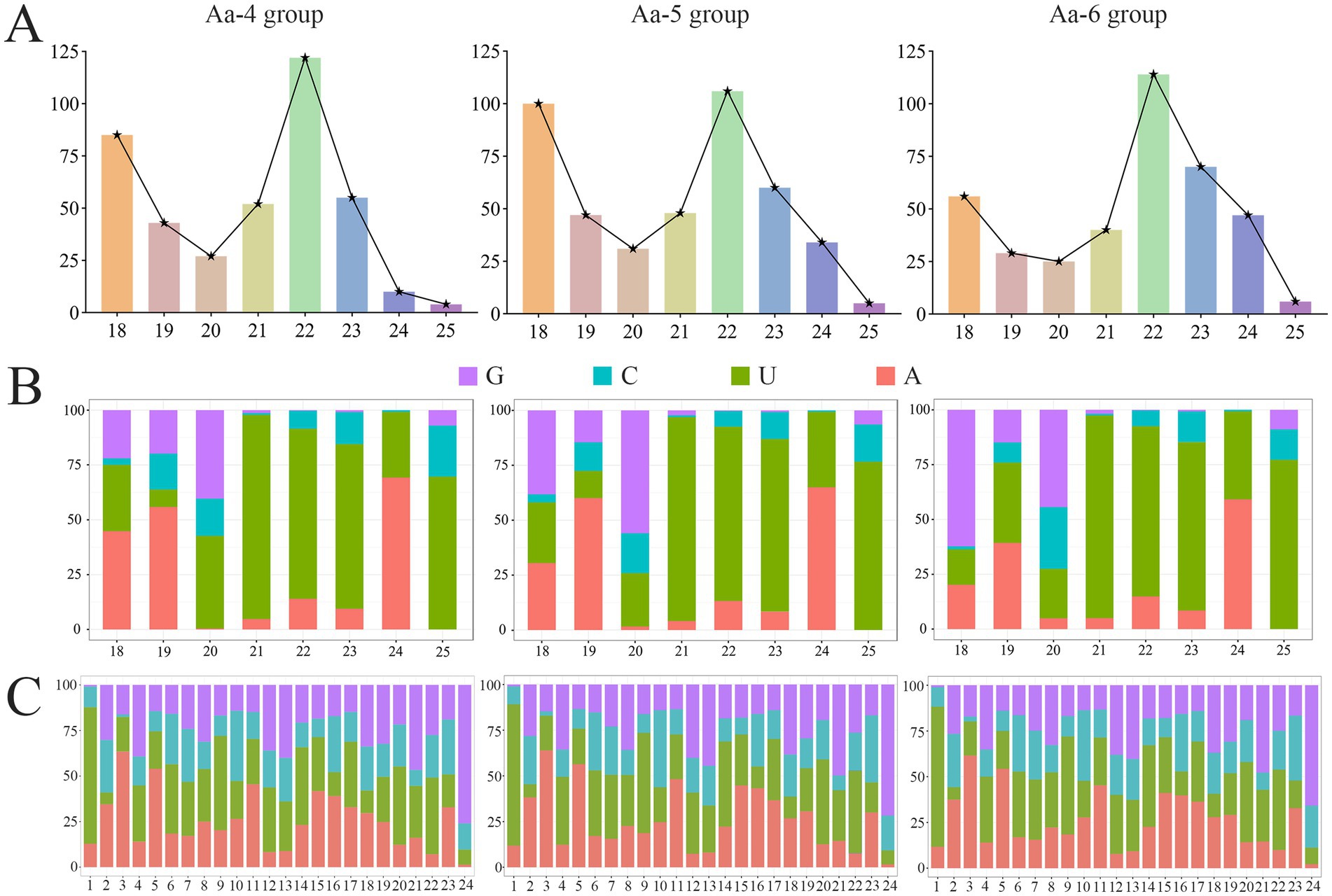
Figure 3. The structural property of milRNAs identified in 4-, 5-, and 6-day-old larval guts infected by A. apis. (A) Length distribution of milRNAs; (B) First base bias of milRNAs; (C) Base bias of milRNAs at each base.
Following trend analysis, 113 milRNAs were divided into 8 profiles, including three significant profiles (profile4, profile6, and profile7). There were 29, 18, and 32 milRNAs included in profile4, profile6, and profile7, further targeting 4,457, 4,469, and 3,353 mRNA, respectively (Figure 4).
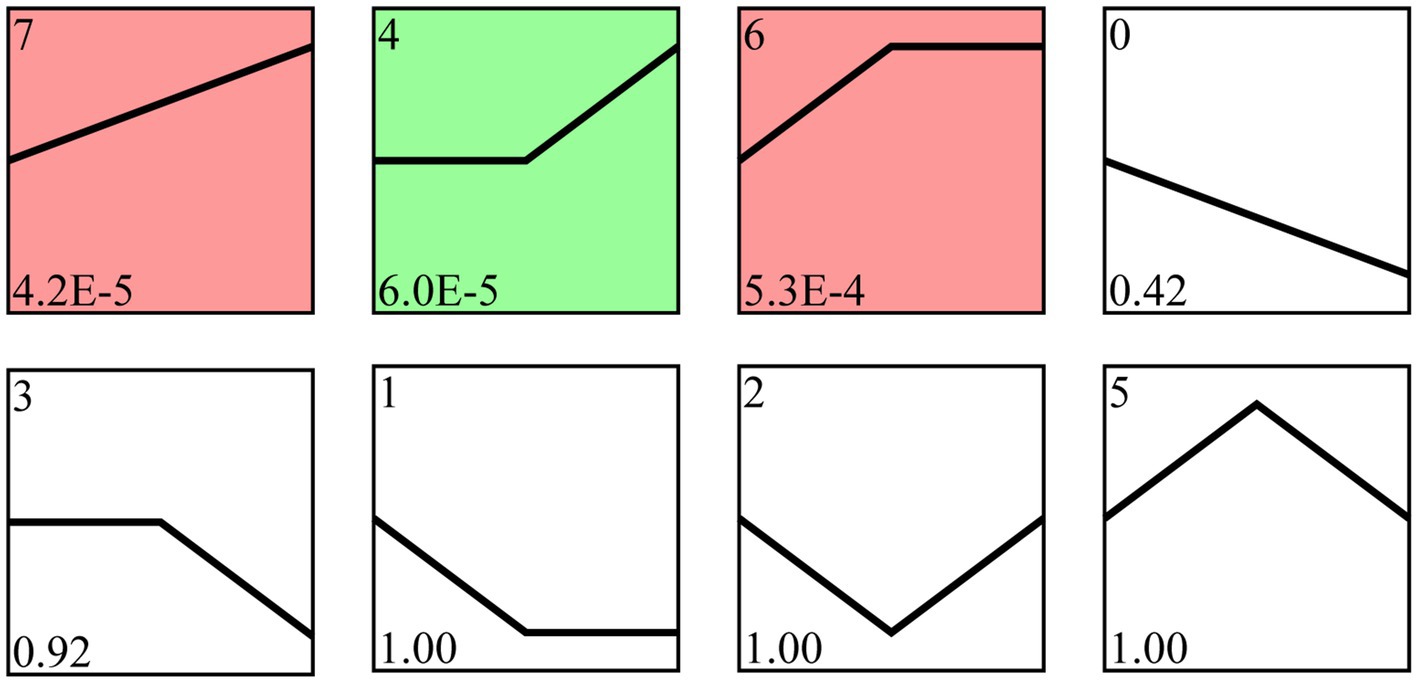
Figure 4. Trend analysis of A. apis milRNAs. Colorful squares represent significant trends, while colorless squares represent non-significant trends; the numbers located in the upper left of each square indicate different trends, whereas those located in the lower left of each square indicate the p value of each trend.
It’s found that 4,457 target mRNAs in profile4 were annotated to 42 functional terms in the GO database, including 19 Biological Process terms (localization, single-organism process, and cellular process, etc.), 11 Molecular Function terms (transporter activity, catalytic activity, and binding, etc.), and 12 Cellular Component terms (membrane, cell, and cell part, etc.), the proportions of these three terms were as follows: 45.2, 26.2, and 28.6% (Figure 5, see also Supplementary Table S2); 4,469 target mRNAs in profile6 were involved in 42 functional terms including 45.2% Biological Process terms (19 types), 26.2% Molecular Function terms (11 types), and 28.6% Cellular Component terms (12 types) (Figure 5, see also Supplementary Table S3), while 3,275 targets in profile7 were associated with 41 terms including 46.3% Biological Process terms (19 types), 24.4% Molecular Function terms (10 types), and 29.3% Cellular Component terms (12 types) (Figure 5, see also Supplementary Table S4).
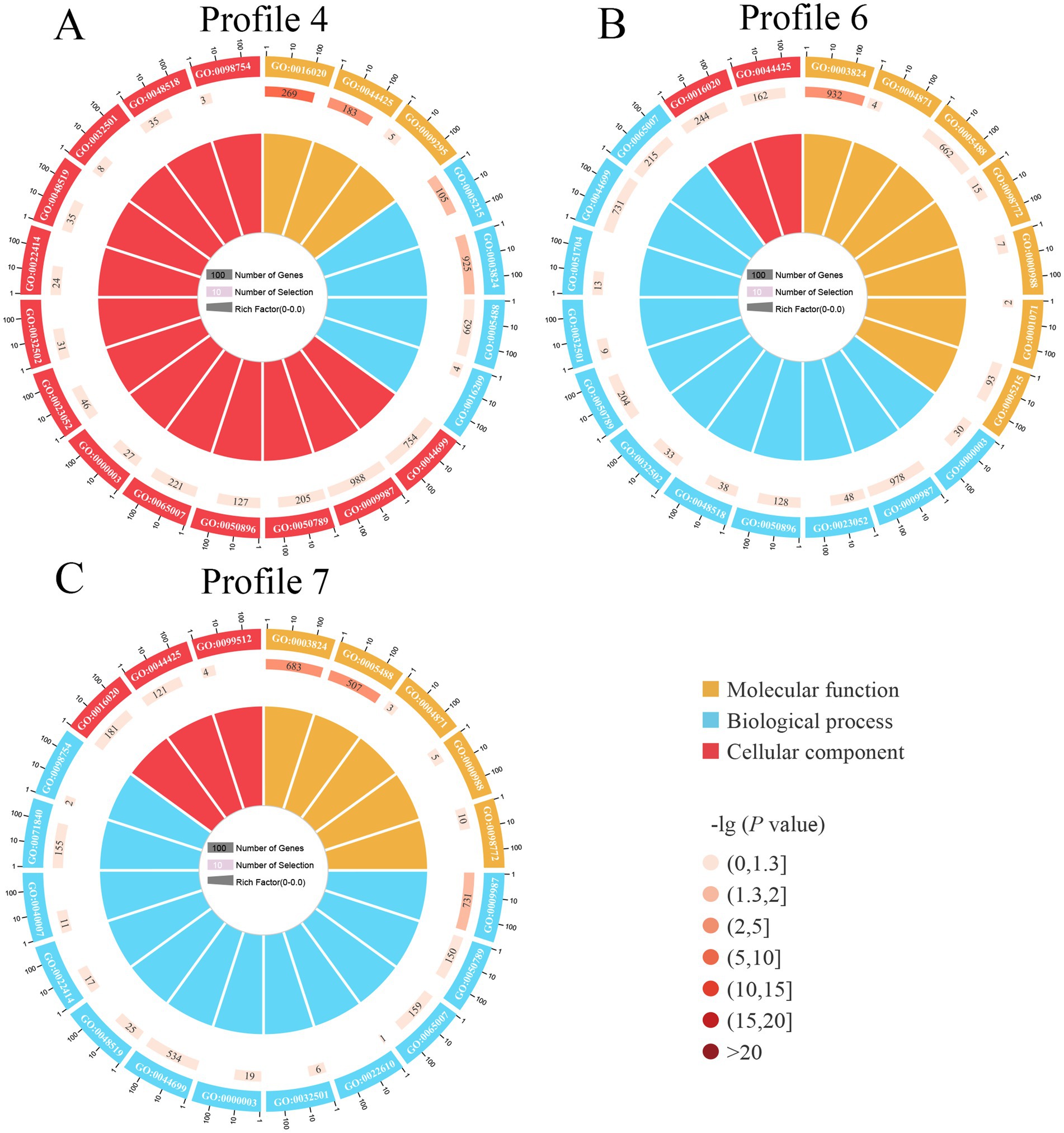
Figure 5. Loop diagrams of GO terms enriched by target mRNAs of A. apis milRNAs within 3 significant trends including profile4 (A), profile6 (B), and profile7 (C).
In contrast to GO annotation, KEGG enrichment focused on pathway-level interactions and regulation of genes in biological systems. Here, 120 KEGG pathways were enriched by 4,457 target mRNAs of DEmilRNAs in profile 4, such as lysine biosynthesis, phosphatidylinositol signaling system, and pyruvate metabolism (Figure 6, see also Supplementary Table S5), 4,469 target mRNAs of DEmilRNAs in profile 6 were involved in 119 pathways like glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchor biosynthesis, galactose metabolism, and endocytosis (Figure 6, see also Supplementary Table S6), whereas 3,275 target mRNAs of DEmilRNAs in profile7 were relevant to 118 pathways including biosynthesis of antibiotics, tryptophan metabolism, and sphingolipid metabolism (Figure 6, see also Supplementary Table S7).
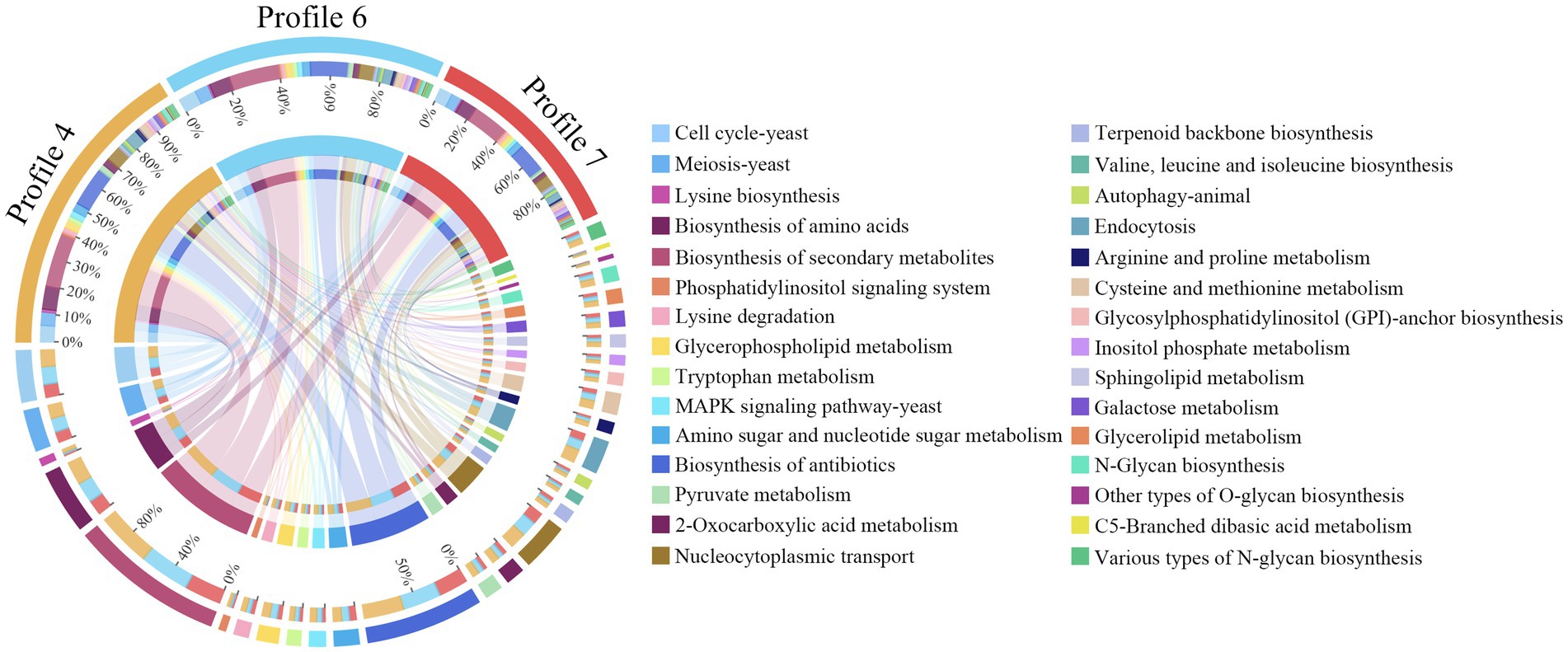
Figure 6. Chord diagrams of KEGG pathways enriched by A. apis milRNA-targeted mRNAs in 3 significant trends. The scale value represents the proportion of the corresponding color label. The line in the middle indicated the presence of pathways in a Profile, and the thicker the line segment, the more genes could be annotated to the pathway.
It’s detected that 25, 27, and 15 DEmilRNAs in profile 4, profile 6, and profile 7 could target 25 mRNAs (mkh1, rhoA, and hog1, etc.) related to the MAPK signaling pathway (Supplementary Figure S2). Specifically, 16 DEmilRNAs in profile 4, 19 DEmilRNAs in profile 6, and 11 DEmilRNAs in profile 7 could target 21 glycerolipid metabolism-relevant mRNAs such as aglA, aglD, and gar1 (Supplementary Figure S3). A total of 63 DEmilRNAs could target 18 virulence factor-relevant mRNAs (Figure 7). In detail, 6, 8, and 5 milRNAs were observed to target 6 superoxide dismutase-encoding mRNAs, including Na+/H+ antiporter Nha1 (SOD22), Cation/H+ exchanger (SOD2), and Cu, Zn superoxide dismutase SOD1 (sodA) (Figure 7A). Additionally, 17, 17, and 10 milRNAs were found to target 12 mRNAs related to chitin synthesis and degradation in profile 4, profile 6, and profile 7, such as chitin synthase class VI (chsD), chitin synthase (chsC), and endochitinase 1 (chiB) (Figure 7B). Furthermore, it’s noticed that several milRNAs, such as aap-milR-3720-x, aap-milR-4120-x, and aap-milR-4451-y, can target more than 1 mRNA (Figure 7).
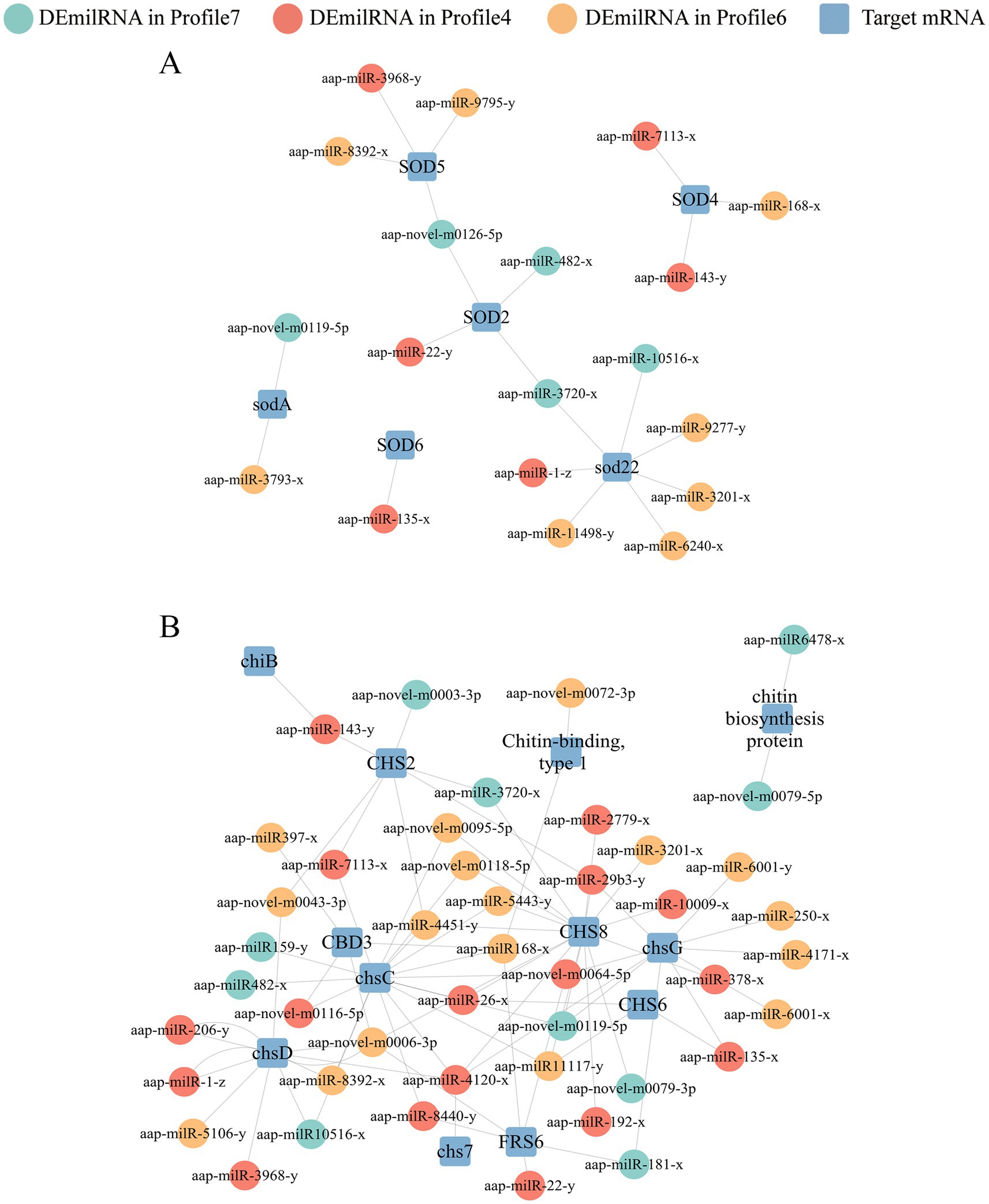

Figure 7. Regulatory networks between A. apis DEmilRNAs in significant trends and target mRNAs associated with virulence factors. (A) Regulatory network of milRNAs-targeted superoxide dismutase-encoding mRNAs; (B) Regulatory network of milRNAs-targeted enzymes related to chitin synthesis and degradation-encoding mRNAs.
Here, recombinant plasmids pmirGLO-ChsD/mkh1-wt and pmirGLO-ChsD/mkh1-mut were successfully constructed, as shown in Figures 8A,D. Dual-luciferase reporter gene assay suggested that the luciferase activities in the wt co-transfection groups were significantly decreased as compared to that in the corresponding control groups; comparatively, in both two mut co-transfection groups, the luciferase activities were non-significantly different in comparison with those in the corresponding mut control group (Figures 8B,E). These results together were indicative of the binding relationships between aap-milR10516-x and ChsD as well as between aap-milR-2478-y and mkh1.
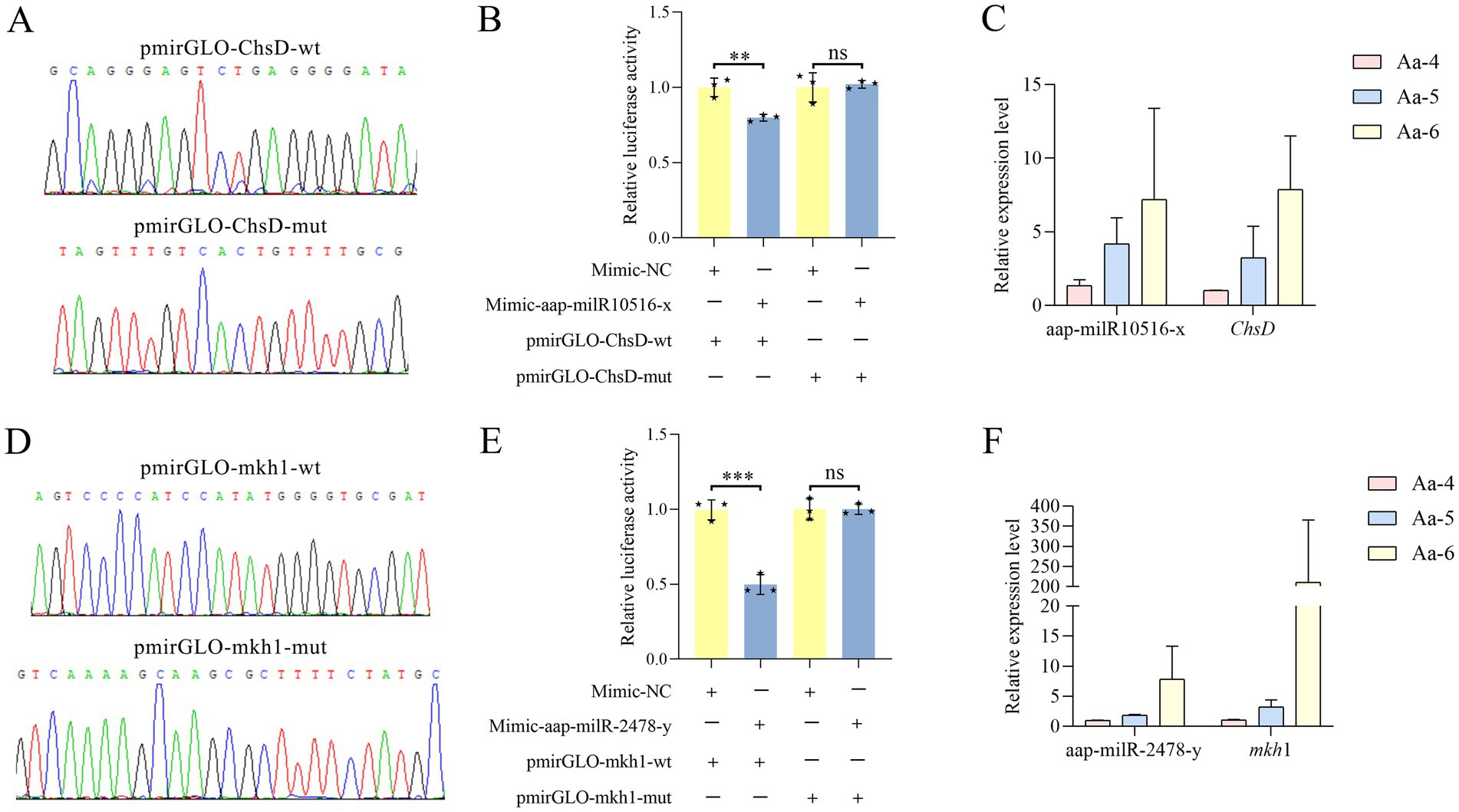
Figure 8. Validation of binding relationships between ChsD and aap-milR10516-x and between mkh1 and aap-milR-2478-y. (A) Peak diagram of Sanger sequencing of the amplified binding sites. (B) Dual-luciferase reporter gene assay of the binding relationship between aap-milR10516-x and ChsD. (C) RT-qPCR detection of aap-milR10516-x and ChsD. (D) Peak diagram of Sanger sequencing of the mutated binding sites. (E) Dual-luciferase reporter gene assay binding relationship between aap-milR-2478-y and mkh1. (F) RT-qPCR detection of aap-milR-2478-y and mkh1. The dual-luciferase assay data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) and analyzed by two-sided Student’s t-test; ns, p > 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.
RT-qPCR results demonstrated that in the 4-, 5-, and 6-day-old larval guts infected by A. apis the expression level between aap-milR-2478-y and mkh1 was positively correlated, and a similar relationship was also observed between aap-milR10516-x and ChsD (Figures 8C,F).
To facilitate infection, pathogens typically deliver biomacromolecules such as effector proteins, nucleic acids, and toxins into the host. In recent years, it has been demonstrated that milRNAs can participate in regulating fungal spore formation (Zhou et al., 2012; Zeng et al., 2018; Zhang E. et al., 2022; Zhang W. D. et al., 2022). Zhang et al. reported that milRNAs can influence the morphology and structure of Metarhizium acridum spores (Zhang E. et al., 2022; Zhang W. D. et al., 2022). A. apis specifically infects honeybee larvae and has developed specific infection patterns through long-term coevolution with its host (Li et al., 2012). However, current understanding of the pathogenic mechanisms of A. apis is limited to histological and biochemical levels, lacking in-depth elucidation at the molecular level. In this work, we for the first time conducted a comprehensive analysis and exploration of milRNAs in A. apis spores during the infection process, including their abundance, structural features, expression profiles, target mRNAs, and regulatory networks, based on high-quality sRNA-seq data. This study provides a foundation for understanding the mechanisms of A. apis infection in the Asian honeybee larvae mediated by milRNAs and offers a new perspective for the prevention and control of chalkbrood disease in honeybees.
Here, we identified a total of 398, 431, and 387 milRNAs ranging in length from 18 to 25 nt, with the highest number of milRNAs found at a length of 22 nt (Figures 3A,B). The first nucleotide of these milRNAs is predominantly U (Figure 3C), and their structural features are highly similar to milRNAs discovered in various fungi such as Coprinopsis cinerea (Lau et al., 2018), Curvularia lunata (Liu et al., 2016), Penicillium marneffei (Lau et al., 2013), as well as in animals and plants like honeybees and cotton (Li et al., 2019; Xiong et al., 2018). The 253 shared milRNAs among the three groups exhibited varying expression patterns during the infection process of A. apis (Figure 1C). It’s inferred that these common milRNAs are likely to play essential roles during the whole process of A. apis infection, hence deserving more attention and further investigation.
In recent years, utilizing STEM software for trend analysis has been widely applied in diverse species, such as Columba livia (Wang et al., 2020), Bos grunniens (Liu et al., 2023), Solenopsis Invicta (Wu et al., 2023), and Chilo suppressalis (Bao et al., 2022). Wu et al. (2023) analyzed the DEGs of Metarhizium anisopliae during S. invicta infection by using STEM software and discovered that M. Anisopliae inhibited the immune response of S. invicta in the early stage but activated the host immune response in the later stage. Based on the trend analysis, Wang et al. (2020) analyzed the DEmiRNAs in the liver of C. livia at different developmental stages and found these DEmiRNAs with different expression patterns through enrichment analysis of target mRNAs might play critical roles in response to growth factors, cellular morphogenesis, and glandular development. In this current work, trend analysis revealed that 79 milRNAs in A. apis invading the Asian honeybee worker larvae could be classified into three significant trends: Profile4, Profile6, and Profile7 (Figure 4). The GO term analysis of their target mRNAs mainly included functional terms such as localization, antioxidant activity, and nucleoid (Figure 5). Enriched KEGG pathways primarily included lysine biosynthesis, pyruvate metabolism, and biosynthesis of antibiotics (Figure 6). These targets were implicated in pathogen activation.
In fungi, glycerolipid metabolism is involved in lots of biological processes, such as cell division and growth, energy metabolism, and membrane biogenesis (Henry et al., 2014; Henry et al., 2012). Nosema ceranae, another widespread fungal disease of honey bees, has been shown to cause energy stress on the host (Mayack and Naug, 2009). Here, the results showing 11, 16, and 19 DEmilRNAs in Profile4, Profile6, and Profile7, respectively, could target 21 glycerolipid metabolism-encoding mRNAs (Supplementary Figure S3), which suggested that these DEmilRNAs possibly regulated the energy metabolism through their related target mRNAs.
Moreover, a total of 67 DEmilRNAs were detected to target 25 mRNAs engaged in the MAPK signaling pathway (Supplementary Figure S2). After being stimulated by external environmental factors, pathogenic fungi can initiate complex and conserved signal transduction cascades, leading to changes in the expression of downstream target mRNAs (Lange et al., 1999). The MAPK signaling pathway plays a crucial role in modulating various biological processes in fungi, including spore formation (Zhao et al., 2007), virulence levels (Igbaria et al., 2008), reproduction (Chen et al., 2016), and pathogenicity (Rodríguez-Peña et al., 2010). Chen et al. (2016) investigated the complete complementarity of the MAPK cascade components in Metarhizium robertsii and found that the Hog1 and Slt2-MAPK cascades contributed to pathogenicity, and the Fus3-MAPK cascade was indispensable for the fungal pathogenesis. Chen et al. (2017) observed that 48 DEGs in A. apis were enriched in the MAPK signaling pathway during the infection of A. m. ligustica larvae, and their expression levels significantly increased with prolonged fungal pathogen stress. However, for the A. apis infecting A. c. cerana larvae, Guo et al. (2017) found that 11 DEGs enriched in the MAPK signaling pathway displayed a downward trend. Here, 15, 25, and 27 DEmilRNAs (eg. aap-milR-3720-x, aap-milR-1-z, and aap-milR-6001-y) were observed to bind to 25 target mRNAs associated with the MAPK signaling pathway of A. apis in profile7, profile4, and profile6, respectively (Supplementary Figure S2). It speculated that these DEmilRNAs of A. apis may act as pathogenic factors involved in regulating the MAPK signaling pathway of A. apis, and participated in the process of A. apis infecting the A. cerana worker larvae.
During the infection of honeybee larvae by A. apis in the gut, the pathogen is capable of secreting various enzymes such as chitinases, proteases, lipases, and secondary metabolites, which act as virulence factors to influence and bypass the host’s immune defense system (Aronstein and Murray, 2010). Chitin synthase was an important virulence factor of entomopathogenic fungi, participating in the synthesis of fungal cell walls and play a key part in maintaining fungal cell morphology, stress resistance, pathogenicity, and other aspects (Fiorin et al., 2018). It also cooperated with other virulence factors such as proteases, then degraded the insect’s peritrophic membrane and cuticle (Leger, 1996). In the present study, 10, 17, and 17 DEmilRNAs from profile7, profile4, and profile6 could target enzymes related to chitin synthesis and degradation gene-encoding mRNAs, such as aap-milR-3968-y, aap-milR-1-z and aap-milR-3201-x (Figure 7B). This suggested that these DEmiRNAs could affect the pathogenesis of A. apis through regulating the expression of enzymes related to chitin synthesis and degradation genes. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) were a ubiquitous family of enzymes widely discovered in animals (Miao and St Clair, 2009), plants (Gill et al., 2015), and microorganisms (Brioukhanov and Netrusov, 2004). Previous studies have demonstrated that SOD in fungi could affect virulence (Papapostolou and Georgiou, 2010; Fréalle et al., 2005). Martchenko et al. (2004) reported that SOD5 was a virulence factor for Candida albicans and was important for fungal survival against the oxidative attack of macrophages and neutrophils. Here, 6 dismutase gene-encoding mRNAs were detected to be targeted by 5, 6, and 8 DEmilRNAs in profile7, profile4, and profile6 (Figure 7A). This indicated that the relevant DEmilRNAs could affect the virulence of A. apis the modulation of their target mRNAs. ChsD is one of the fungal chitin synthase genes and play an important role in maintaining fungal morphology. Chitin synthesized by the ChsD-encoded isozyme contributes to the rigidity of the walls of germinating conidia, the rigidity of hyphae subapical region and conidiophore vesicles (Specht et al., 1996). mkh1 is an important gene involved in the MAPK signaling pathway. The positive regulatory relationship between milR10516-x and ChsD as well as between milR-2478-y and mkh1 were validated through RT-qPCR and dual-luciferase reporter gene assays. miRNAs achieve degradation or translation inhibition primarily by targeting the 3’UTR of mRNA transcripts in the cytoplasm. The miRNAs are still considered as repressors of gene expression in the mainstream view. However, there is growing evidence of non-canonical novel role in the nucleus of miRNAs, acting as activators or silencing of target gene transcription through miRNA-promoter interaction (Sarkar and Kumar, 2025). Studies have shown that mir-23a and miR-23b directly target Hmgn2, promoting transcriptional activation at several gene promoters, including the amelogenin gene promoter (Eliason et al., 2022). miR-24-1 activates gene transcription by targeting enhancers. When the enhancer sequence is removed, the activation is completely eliminated. In addition, miR-24-1 activates enhancer RNA expression, alters histone modification, and increases enrichment of p300 and RNA Pol II at the enhancer locus (Xiao et al., 2017). In our past studies of another fungal pathogen Nosema ceranae, we found that the structure of N. ceanae mRNAs were very simple, and almost all mRNAs lack a 3’UTR structure (Zhang E. et al., 2022; Zhang W. D. et al., 2022). Similarly, as a microorganism, A. apis has a very simple structure, perhaps this is what causes A. apis milRNAs to positively regulate genes. This not only proved the authenticity of sequencing data, but also provided two candidate DEmilRNA/mRNA axes for further in-depth research on the function of milRNA during the infection of A. cerana by A. apis.
In conclusion, a total of 606 A. apis milRNAs were discovered, with lengths ranging from 18 nt to 25 nt. Among these, 253 milRNAs were shared by A. apis infecting 4-, 5-, and 6-day-old larvae (Figure 1B). These common milRNAs exhibited different expression patterns during the infection process, with 68 milRNAs upregulated and 54 ones downregulated (Figure 1C). Furthermore, the expression of three milRNAs was validated. 79 milRNAs of A. apis could be classified into three significant trends (Profile4, Profile6, and Profile7), and these DEmilRNAs mainly targeted mRNAs associated with glycerol metabolism, mRNAs in the MAPK signaling pathway, and mRNAs encoding virulence factors like enzymes related to chitin synthesis and degradation and superoxide dismutase. The positive regulatory relationship between milR10516-x and ChsD as well as between milR-2478-y and mkh1 were verified (Figure 8). These findings not only lay a foundation for understanding the mechanism of A. apis infection in the Asian honeybee larvae mediated by milRNAs, but also offer new insights into the prevention and control of chalkbrood disease in honeybees (Figure 9).
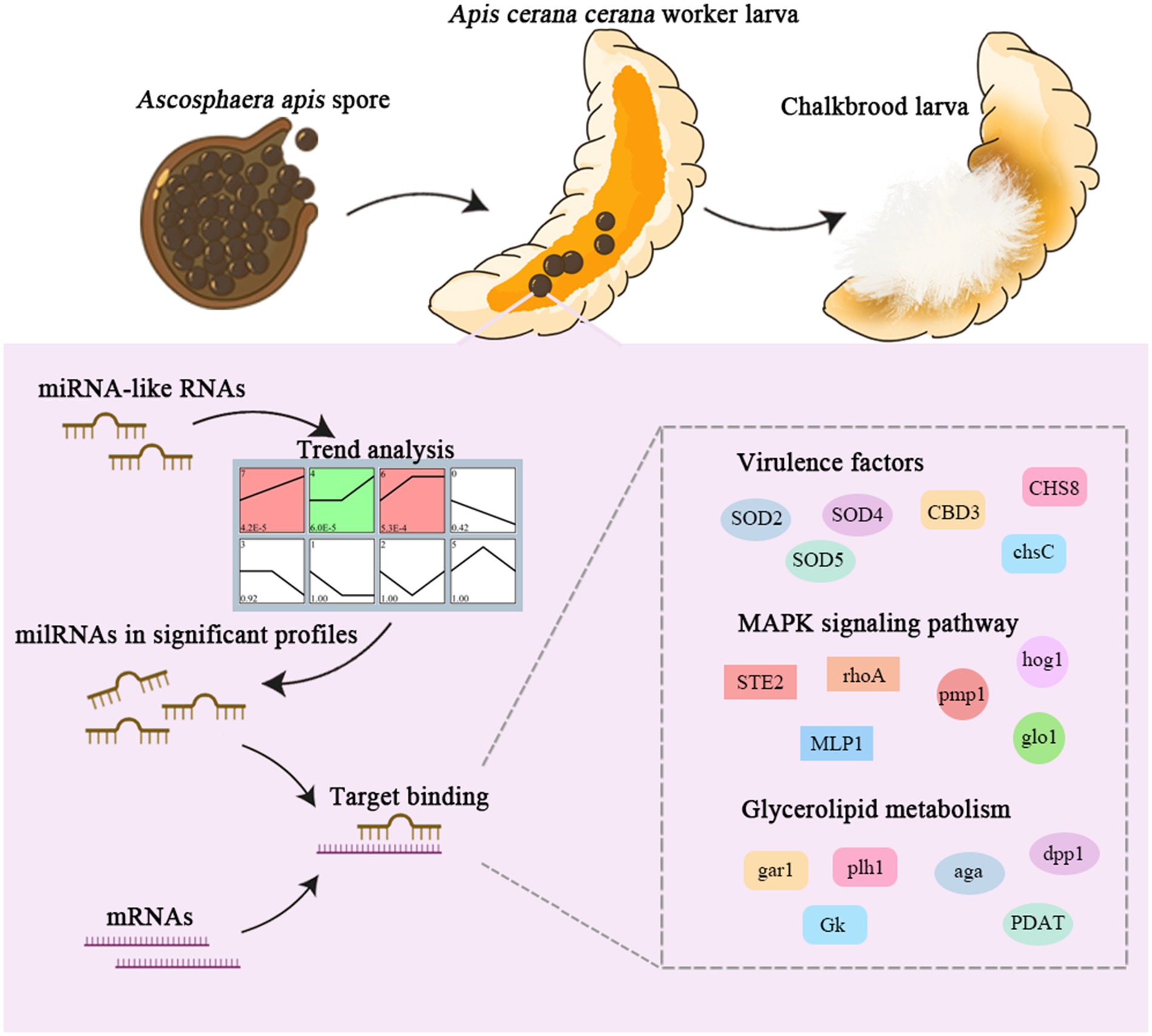
Figure 9. A hypothetical working model of milRNA regulation in A. apis infecting the A. c. cerana larvae.
Raw data generated from RNA-seq are available in the NCBI SRA database under the BioProject number PRJNA565611.
XL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SG: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. DY: Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. WX: Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. YZ: Validation, Writing – original draft. FW: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. JL: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. YW: Data curation, Writing – original draft. HJ: Data curation, Writing – original draft. YH: Data curation, Writing – original draft. DC: Data curation, Writing – original draft. TY: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – original draft. RG: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JQ: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32172792 and 32372943), the Earmarked Fund for China Agriculture Research System (CARS-44-KXJ7), the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (2022J01133 and 2023J01447), the Master Supervisor Team Fund of Fujian.
All authors thank the reviewers and editors for their constructive comments and recommendations.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1551625/full#supplementary-material
1. ^https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/
3. ^http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Web/Genbank/
5. ^http://oberon.fvms.ugent.be:8080/rRNA/lsu/index.html
Agbu, P., and Carthew, R. W. (2021). Micro RNA-mediated regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 22, 425–438. doi: 10.1038/s41580-021-00354-w
Allen, E., Xie, Z., Gustafson, A. M., and Carrington, J. C. (2005). microRNA-directed phasing during trans-acting siRNA biogenesis in plants. Cell 121, 207–221. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.04.004
Aronstein, K., and Murray, K. D. (2010). Chalkbrood disease in honey bees. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 103, S20–S29. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2009.06.018
Asgari, S. (2013). MicroRNA functions in insects. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 43, 388–397. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2012.10.005
Asl, E. R., Amini, M., Najafi, S., Mansoori, B., Mokhtarzadeh, A., Mohammadi, A., et al. (2021). Interplay between MAPK/ERK signaling pathway and MicroRNAs: a crucial mechanism regulating cancer cell metabolism and tumor progression. Life Sci. 278:119499. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119499
Bao, H., Zhu, H., Yu, P., Luo, G., Zhang, R., Yue, Q., et al. (2022). Time-series transcriptomic analysis reveals the molecular profiles of diapause termination induced by Long photo-periods and high temperature in Chilo suppressalis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23:12322. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012322
Brioukhanov, A. L., and Netrusov, A. I. (2004). Catalase and superoxide dismutase: distribution, proper-ties, and physiological role in cells of strict anaerobes. Biochemistry (Mosc) 69, 949–962. doi: 10.1023/B:BIRY.0000043537.04115.d9
Chen, H., Du, Y., Zhu, Z., Xiong, C., Zheng, Y., Chen, D., et al. (2020). Transcriptome data of control and Ascosphaera apis infected Apis mellifera ligustica larval guts. Data Brief 29:105264. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2020.105264
Chen, D. F., Guo, R., Xiong, C. L., Liang, Q., Zheng, Y. Z., Xu, X. J., et al. (2017). Transcriptomic analysis of Ascosphaera apis stressing larval gut of Apis mellifera ligustica (Hyemenoptera:Apidae). Acta Entomol. Sin. 60, 401–411. doi: 10.16380/j.kcxb.2017.04.005 (In Chinese)
Chen, R., Jiang, N., Jiang, Q., Sun, X., Wang, Y., Zhang, H., et al. (2014). Exploring mi-croRNA-like small RNAs in the filamentous fungus Fusarium oxysporum. PLoS One 9:e104956. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104956
Chen, X., Xu, C., Qian, Y., Liu, R., Zhang, Q., Zeng, G., et al. (2016). MAPK cascade-mediated regulation of pathogenicity, conidiation and tolerance to abiotic stresses in the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium robertsii. Environ. Microbiol. 18, 1048–1062. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.13198
Cui, C., Wang, Y., Liu, J., Zhao, J., Sun, P., and Wang, S. (2019). A fungal pathogen deploys a small silencing RNA that attenuates mosquito immunity and facilitates infection. Nat. Commun. 10:4298. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12323-1
DeVeale, B., Swindlehurst-Chan, J., and Blelloch, R. (2021). The roles of microRNAs in mouse development. Nat. Rev. Genet. 22, 307–323. doi: 10.1038/s41576-020-00309-5
Du, Y., Tong, X. Y., Zhou, D. D., Chen, D. F., Xiong, C. L., Zheng, Y. Z., et al. (2019). MicroRNA responses in the larval gut of Apis cerana cerana to Ascosphaera apis stress. Acta Microbiol Sin. 59, 1747–1764. doi: 10.13343/j.cnki.wsxb.20180401 (In Chinese)
Eliason, S., Su, D., Pinho, F., Sun, Z., Zhang, Z., Li, X., et al. (2022). HMGN2 represses gene transcription via interaction with transcription factors Lef-1 and Pitx2 during amelogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 298:102295. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102295
Enright, A. J., John, B., Gaul, U., Tuschl, T., Sander, C., and Marks, D. S. (2003). MicroRNA targets in drosophila. Genome Biol. 5:R1. doi: 10.1186/gb-2003-5-1-r1
Ernst, J., and Bar-Joseph, Z. (2006). STEM: a tool for the analysis of short time series gene expression data. BMC Bioinformatics 7:191. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-191
Fan, X., Gao, X., Zang, H., Liu, Z., Jing, X., Liu, X., et al. (2024). Transcriptional dynamics and regulatory function of milRNAs in Ascosphaera apis invading Apis mellifera larvae. Front. Microbiol. 15:1355035. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1355035
Fiorin, G. L., Sanchéz-Vallet, A., Thomazella, D. P. T., do Prado, P. F. V., do Nascimento, L. C., Figueira, A. V. O., et al. (2018). Suppression of plant immunity by fungal Chitinase-like effectors. Curr. Biol. 28, 3023–3030.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.07.055
Fréalle, E., Noël, C., Viscogliosi, E., Camus, D., Dei-Cas, E., and Delhaes, L. (2005). Manganese superoxide dismutase in pathogenic fungi: an issue with pathophysiological and phylogenetic involvements. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 45, 411–422. doi: 10.1016/j.femsim.2005.06.003
Gill, S. S., Anjum, N. A., Gill, R., Yadav, S., Hasanuzzaman, M., Fujita, M., et al. (2015). Superoxide dismutase—mentor of abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 22, 10375–10394. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-4532-5
Grimson, A., Srivastava, M., Fahey, B., Woodcroft, B. J., Chiang, H. R., King, N., et al. (2008). Early origins and evolution of microRNAs and Piwi-interacting RNAs in animals. Nature 455, 1193–1197. doi: 10.1038/nature07415
Guo, R., Chen, D., Diao, Q., Xiong, C., Zheng, Y., and Hou, C. (2019a). Transcriptomic investigation of immune responses of the Apis cerana cerana larval gut infected by Ascosphaera apis. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 166:107210. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2019.107210
Guo, R., Chen, D. F., Huang, Z. T., Liang, Q., Xiong, C. L., Xu, X. J., et al. (2017). Transcriptome analysis of Ascosphaera apis stressing larval gut of Apis cerana cerana. Acta Microbiol Sin. 57, 1865–1878. doi: 10.13343/j.cnki.wsxb.20160551 (In Chinese)
Guo, R., Du, Y., Zhou, N. H., Liu, S. Y., Xiong, C. L., Zheng, Y. Z., et al. (2019b). Comprehensive analysis of differentially expressed microRNAs and their target genes in the larval gut of Apis mellifera ligustica during the late stage of Ascosphaera apis stress. Acta Entomol. Sin. 62, 49–60. doi: 10.16380/j.kcxb.2019.01.006 (In Chinese)
Guo, R., Wang, H. P., Chen, H. Z., Xiong, C. L., Zheng, Y. Z., Fu, Z. M., et al. (2018). Identification of Ascosphaera apis microRNAs and investigation of their regulation networks. Acta Microbiol Sin. 58, 1077–1089. doi: 10.13343/j.cnki.wsxb.20170535 (In Chinese)
Guo, M. W., Yang, P., Zhang, J. B., Liu, G., Yuan, Q. S., He, W. J., et al. (2019). Expression of microRNA-like RNA-2 (Fgmil-2) and bioH1 from a single transcript in Fusarium graminearum are inversely correlated to regulate biotin synthesis during vegetative growth and host infection. Mol. Plant Pathol. 20, 1574–1581. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12859
Ha, M., and Kim, V. N. (2014). Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 15, 509–524. doi: 10.1038/nrm3838
Henry, S. A., Gaspar, M. L., and Jesch, S. A. (2014). The response to inositol: regulation of glycerolipid metabolism and stress response signaling in yeast. Chem. Phys. Lipids 180, 23–43. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2013.12.013
Henry, S. A., Kohlwein, S. D., and Carman, G. M. (2012). Metabolism and regulation of glycerolipids in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 190, 317–349. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.130286
Huang, Q., and Evans, J. D. (2016). Identification of microRNA-like small RNAs from fungal parasite Nosema ceranae. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 133, 107–109. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2015.12.005
Igbaria, A., Lev, S., Rose, M. S., Lee, B. N., Hadar, R., Degani, O., et al. (2008). Distinct and combined roles of the MAP kinases of Cochliobolus heterostrophus in virulence and stress responses. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 21, 769–780. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-21-6-0769
Kim, J. K., Kim, T. S., Basu, J., and Jo, E. K. (2017). MicroRNA in innate immunity and autophagy during mycobacterial infection. Cell. Microbiol. 19:e12687. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12687
Krüger, J., and Rehmsmeier, M. (2006). RNAhybrid: MicroRNA target prediction easy, fast and flexi-ble. Nucleic Acids Res. 34, W451–W454. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl243
Lange, R., Wagner, C., de Saizieu, A., Flint, N., Molnos, J., Stieger, M., et al. (1999). Domain organization and molecular characterization of 13 two-component systems identified by genome sequencing of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Gene 237, 223–234. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1119(99)00266-8
Lau, A. Y. T., Cheng, X., Cheng, C. K., Nong, W., Cheung, M. K., Chan, R. H., et al. (2018). Discovery of microRNA-like RNAs during early fruiting body development in the model mushroom Coprinopsis cinerea. PLoS One 13:e0198234. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198234
Lau, S. K., Chow, W. N., Wong, A. Y., Yeung, J. M., Bao, J., Zhang, N., et al. (2013). Identification of microRNA-like RNAs in mycelial and yeast phases of the thermal dimorphic fungus Penicillium marneffei. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 7:e2398. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002398
Lee, H. C., Li, L., Gu, W., Xue, Z., Crosthwaite, S. K., Pertsemlidis, A., et al. (2010). Diverse pathways generate microRNA-like RNAs and dicer-independent small interfering RNAs in fungi. Mol. Cell 38, 803–814. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.04.005
Leger, R. J. (1996). The role of cuticle-degrading proteases in fungal pathogenesis of insects. J. Can. Bot 73, 1119–1125.
Li, Q., Cui, C. L., Song, H. S., and Wang, S. B. (2017). The effects of mro-miR-33 on the conidial production in Metarhizium robertsii. Mycosystema 36, 671–678. doi: 10.13346/j.mycosystema.160248 (In Chinese)
Li, J., Hull, J. J., Liang, S., Wang, Q., Chen, L., Zhang, Q., et al. (2019). Genome-wide analysis of cotton miRNAs during whitefly infestation offers new insights into plant-herbivore interaction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20:5357. doi: 10.3390/ijms20215357
Li, J. H., Zheng, Z. Y., and Chen, D. F. (2012). Factors influencing Ascosphaera apis infection on hon-eybee larvae and observation on the infection process. Acta Entomol. Sin. 55, 790–797. doi: 10.16380/j.kcxb.2012.55.7.790797 (In Chinese)
Lin, R., He, L., He, J., Qin, P., Wang, Y., Deng, Q., et al. (2016). Comprehensive analysis of microRNA-Seq and target mRNAs of rice sheath blight pathogen provides new insights into pathogenic regulatory mechanisms. DNA Res. 23, 415–425. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dsw024
Liu, T., Hu, J., Zuo, Y., Jin, Y., and Hou, J. (2016). Identification of microRNA-like RNAs from curvularia lunata associated with maize leaf spot by bioinformation analysis and deep sequencing. Mol. Gen. Genomics. 291, 587–596. doi: 10.1007/s00438-015-1128-1
Liu, Y., Min, Q., Tang, J., Yang, L., Meng, X., Peng, T., et al. (2023). Transcriptome profiling in rumen, reticulum, omasum, and abomasum tissues during the developmental transition of pre-ruminant to the ruminant in yaks. Front. Vet. Sci. 10:1204706. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1204706
Llave, C., Kasschau, K. D., Rector, M. A., and Carrington, J. C. (2002). Endogenous and silencing-associated small RNAs in plants. Plant Cell 14, 1605–1619. doi: 10.1105/tpc.003210
Martchenko, M., Alarco, A. M., Harcus, D., and Whiteway, M. (2004). Superoxide dismutases in Candida albicans: transcriptional regulation and functional characterization of the hyphal-induced SOD5 gene. Mol. Biol. Cell 15, 456–467. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e03-03-0179
Maxfield-Taylor, S. A., Mujic, A. B., and Rao, S. (2015). First detection of the larval chalkbrood disease pathogen Ascosphaera apis (Ascomycota: Eurotiomycetes: Ascosphaerales) in adult bum-ble bees. PLoS One 10:e0124868. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124868
Mayack, C., and Naug, D. (2009). Energetic stress in the honeybee Apis mellifera from Nosema ceranae infection. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 100, 185–188. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2008.12.001
Mi, J. L., and Tan, K. (2007). Research Progress of Apis cerana taxonomy in China. Apicult. China 7:13-14+16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0412-4367.2007.07.004 (In Chinese)
Miao, L., and St Clair, D. K. (2009). Regulation of superoxide dismutase genes: implications in disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 47, 344–356. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.05.018
Nersisyan, S., Engibaryan, N., Gorbonos, A., Kirdey, K., Makhonin, A., and Tonevitsky, A. (2020). Potential role of cellular miRNAs in coronavirus-host interplay. PeerJ 8:e9994. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9994
Papapostolou, I., and Georgiou, C. D. (2010). Superoxide radical induces sclerotial differentiation in filamentous phytopathogenic fungi: a superoxide dismutase mimetics study. Microbiology (Reading) 156, 960–966. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.034579-0
Pei, L. L., Zhang, L. L., Liu, X., and Jiang, J. (2023). Role of microRNA miR171 in plant development. PeerJ 11:e15632. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15632
Qin, M., Wang, H. F., Liu, Z. G., Wang, Y., and Xu, B. H. (2016). Research progress on insect resistance to cold and its mechanism. Apicult. China 68, 21–24. doi: 10.26914/c.cnkihy.2016.004655 (In Chinese)
Rodríguez-Peña, J. M., García, R., Nombela, C., and Arroyo, J. (2010). The high-osmolarity glycerol (HOG) and cell wall integrity (CWI) signalling pathways interplay: a yeast dialogue be-tween MAPK routes. Yeast 27, 495–502. doi: 10.1002/yea.1792
Sarkar, N., and Kumar, A. (2025). Paradigm shift: microRNAs interact with target gene promoters to cause transcriptional gene activation or silencing. Exp. Cell Res. 444:114372. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2024.114372
Smoot, M. E., Ono, K., Ruscheinski, J., Wang, P. L., and Ideker, T. (2011). Cytoscape 2.8: new features for data integration and network visualization. Bioinformatics 27, 431–432. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq675
Specht, C. A., Liu, Y., Robbins, P. W., Bulawa, C. E., Iartchouk, N., Winter, K. R., et al. (1996). The chsD and chsE genes of Aspergillus nidulans and their roles in chitin synthesis. Fungal Genet. Biol. 20, 153–167. doi: 10.1006/fgbi.1996.0030
Villalobos-Escobedo, J. M., Martínez-Hernández, J. P., Pelagio-Flores, R., González-De la Rosa, P. M., Carreras-Villaseñor, N., Abreu-Goodger, C., et al. (2022). Trichoderma atroviride hyphal regeneration and condition depend on cell-signaling processes regulated by a microRNA-like RNA. Microb. Genom. 8:mgen000869. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000869
Wang, X., Yan, P., Liu, L., Luo, Y., Zhao, L., Liu, H., et al. (2020). MicroRNA expression profiling reveals potential roles for mi-croRNA in the liver during pigeon (Columba livia) development. Poult. Sci. 99, 6378–6389. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2020.09.039
Wu, H., Xu, Y., Zafar, J., Mandal, S., Lin, L., Lu, Y., et al. (2023). Tran-scriptomic analysis reveals the impact of the biopesticide Metarhizium anisopliae on the immune system of major workers in Solenopsis invicta. Insects 14:701. doi: 10.3390/insects14080701
Xiao, M., Li, J., Li, W., Wang, Y., Wu, F., Xi, Y., et al. (2017). MicroRNAs activate gene transcription epigenetically as an enhancer trigger. RNA Biol. 14, 1326–1334. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1112487
Xiong, C. L., Du, Y., Chen, D. F., Zheng, Y. Z., Fu, Z. M., Wang, H. P., et al. (2018). Bioinformatic prediction and analysis of miRNAs in the Apis mellifera ligustica larval gut. Chin. J. Appl. Entomol. 55, 1023–1033. doi: 10.7679/j.issn.2095-1353.2018.124 (In Chinese)
Xiong, C. L., Du, Y., Feng, R. R., Jiang, H. B., Shi, X. Y., Wang, H. P., et al. (2020). Differential expression pattern and regulation network of microRNAs in Ascosphaera apis in-vading Apis cerana cerana 6-day-old larvae. Acta Microbiol Sin. 60, 992–1009. doi: 10.13343/j.cnki.wsxb.20190421 (In Chinese)
Zeng, W., Wang, J., Wang, Y., Lin, J., Fu, Y., Xie, J., et al. (2018). Dicer-like proteins regulate sexual development via the biogenesis of Perithecium-specific MicroRNAs in a plant pathogenic fungus Fusarium graminearum. Front. Microbiol. 9:818. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00818
Zhang, C. X., Tang, X. D., and Cheng, J. A. (2008). The utilization and industrialization of insect re-sources in China. Entomol. Res. 38, S38–S47. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-5967.2008.00173.x
Zhang, E., Zhang, J., Zhao, R., Lu, Y., Yin, X., Lan, X., et al. (2022). Role of MicroRNA-like RNAs in the regulation of spore morphological differences in the Entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium acridum. Pol. J. Microbiol. 71, 309–324. doi: 10.33073/pjm-2022-028
Zhang, W. D., Zhao, H. D., Sun, M. H., Yu, K. J., Guo, Y. L., Zhu, L. R., et al. (2022). Identification and analysis of microRNAs in Nosema ceranae spores. Acta Microbiol Sin. 65, 708–717. doi: 10.16380/j.kcxb.2022.06.006 (In Chinese)
Zhao, X., Mehrabi, R., and Xu, J. R. (2007). Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways and fungal pathogenesis. Eukaryot. Cell 6, 1701–1714. doi: 10.1128/EC.00216-07
Keywords: chalkbrood, Ascosphaera apis, Apis cerana, milRNA, target mRNA, regulatory network
Citation: Liu X, Geng S, Ye D, Xu W, Zheng Y, Wang F, Lei J, Wu Y, Jiang H, Hu Y, Chen D, Yan T, Guo R and Qiu J (2025) Global discovery, expression pattern, and regulatory role of miRNA-like RNAs in Ascosphaera apis infecting the Asian honeybee larvae. Front. Microbiol. 16:1551625. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1551625
Received: 26 December 2024; Accepted: 19 February 2025;
Published: 04 March 2025.
Edited by:
Minu Chaudhuri, Meharry Medical College, United StatesReviewed by:
Rui Pang, South China Agricultural University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Liu, Geng, Ye, Xu, Zheng, Wang, Lei, Wu, Jiang, Hu, Chen, Yan, Guo and Qiu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rui Guo, cnVpZ3VvQGZhZnUuZWR1LmNu; Jianfeng Qiu, amZxaXVAZmFmdS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.