
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
Front. Microbiol. , 19 February 2025
Sec. Microbiological Chemistry and Geomicrobiology
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1546852
This article is part of the Research Topic Mineral Solubilizing Microorganisms (MSM) and Their Applications in Nutrient Bioavailability, Bioweathering and Bioremediation, Vol III View all 11 articles
Phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms (PSM) play a crucial role in promoting crop growth by enhancing phosphorus supply and reducing phosphorus loss in soil. However, a comprehensive bibliometric overview of the research landscape on PSM in agricultural applications has been lacking. This study conducts a bibliometric analysis to explore global research trends, key contributors, and collaborative networks in the application of PSM in ecological restoration, providing valuable insights for future research. A total of 1,662 documents from the Web of Science Core Collection, spanning from 1984 to 2024, were extracted and analyzed using Bibliometrix and CiteSpace software. The findings reveal a period of rapid growth in this field since 2018. Initially, research focused on microbial soil nutrients, such as phosphate rock and Azospirillum brasilense. Current research hotspots have shifted towards topics like drought and salt stress, as well as productivity, reflecting an increasing emphasis on mitigating the impacts of global warming and environmental changes. China and India lead in research output, contributing 36.67% of the total articles. The Indian Council of Agricultural Research published the highest number of articles. Future research on PSM should emphasize their role in enhancing nutrient uptake, improving soil health, and mitigating environmental stresses, supporting sustainable agriculture and ecological restoration. This bibliometric analysis of 1,162 articles by 7,454 authors from 101 countries highlights critical advances at the intersection of soil microbiology, sustainable land management, and climate change adaptation. These findings provide a foundation for addressing global challenges like soil degradation, nutrient cycling, and food security, aligning with the Sustainable Development Goals.
Phosphorus is a critical macronutrient essential for plant growth and development, playing a pivotal role in various processes including energy transfer, photosynthesis, and nutrient cycling (Kamerlin et al., 2013; Majeed et al., 2023). Despite its significance, phosphorus often acts as a limiting factor in numerous terrestrial ecosystems, primarily due to its existence in forms that are not readily available to plants (Syers et al., 2008; Rawat et al., 2021). Global estimates indicate that approximately 40% of the world’s agricultural soils suffer from phosphorus deficiency, which negatively impacts both food production and ecosystem health (Vance et al., 2003). This limitation severely hampers soil productivity and the capacity for ecosystem recovery, posing a significant challenge to sustainable land management and ecological restoration efforts (Xiao et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2023). In regions where phosphorus depletion is most acute, soil fertility often declines by over 50%, thereby greatly restricting the potential for ecosystem recovery (Huang et al., 2012; Qin et al., 2023). A promising approach to address phosphorus deficiency in soils involves the utilization of phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms (PSM) (Richardson and Simpson, 2011). As a crucial component of soil microbiota, PSM can convert insoluble soil phosphorus into plant-accessible forms through their metabolites (organic acids, phosphatases) or via synergistic interactions within microbial communities (Richardson et al., 2009; Alori et al., 2017; Rawat et al., 2021). This not only improves phosphorus uptake by plants, but also accelerates nutrient cycling, enhances soil structure, and supports broader ecosystem functions by accelerating nutrient cycling and improving the bioavailability of critical minerals, making it a key strategy for sustainable ecosystem management (Rajwar et al., 2018).
The role of PSM in ecological restoration has gained prominence due to their capacity to enhance nutrient cycling, stimulate plant growth, and aid biodiversity recovery in degraded ecosystems (Liang et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2023). By improving phosphorus availability in the soil, By increasing phosphorus bioavailability, PSM contribute to critical ecosystem services, such as improving soil stability, supporting vegetation regrowth, and enhancing carbon sequestration (Sun et al., 2023; Chen et al., 2024). These attributes align closely with global efforts to address land degradation and promote sustainable land management (Hussain et al., 2019; Silva et al., 2023; Gurav et al., 2024). Furthermore, In the context of global warming, PSM have shown significant potential to help ecosystems adapt to changing climatic conditions by enhancing nutrient cycling under stress conditions, such as drought and heat (Aqeel et al., 2023). This ability to maintain or restore ecosystem functions under climate change is crucial for increasing ecosystem resilience, ensuring food security, and mitigating climate-related impacts on ecosystems (Rawat et al., 2021).
While the ecological and agricultural importance of PSM has been extensively studied (Lambers, 2022; Iftikhar et al., 2024), a systematic and comprehensive global analysis of this research domain remains largely unexplored (Alori et al., 2017; Ampese et al., 2022). Existing studies often neglect the evolving research priorities and their implications for land management and ecosystem restoration, limiting a holistic understanding of PSM’s role in sustainability. Bibliometrics involves the quantitative analysis of academic publications and their citation data to comprehend patterns and developments in scientific knowledge dissemination (Garfield, 1972; Aria and Cuccurullo, 2017; Ampese et al., 2022; Montazeri et al., 2023). Its primary objectives include measuring research output impact, evaluating academic contributions of institutions or individuals, identifying research trends, and monitoring the evolution of scholarly domains (Glänzel, 2003; Wang et al., 2024). A fundamental tool in bibliometrics is citation analysis, which assesses the significance of research based on citation frequency (Van Raan, 1997). Collaboration network analysis elucidates relationships among scholars, facilitating understanding of scientific cooperation and knowledge dissemination patterns (Aria and Cuccurullo, 2017). Beyond identifying research hotspots, bibliometrics tracks disciplinary development, providing empirical support for research evaluation, academic management, and policy formulation, ultimately contributing to the optimal allocation of research resources (Egghe and Rousseau, 1990; Hirsch, 2010).
This study aims to conduct a bibliometric analysis on the application of PSM in ecological restoration, utilizing data from the Web of Science Core Collection, covering literature from 1984 to 2024. Through an examination of publication trends, author collaborations, keyword co-occurrence, and geographic distribution, this research endeavors to map the development of PSM research within the context of ecological restoration. The findings aim to provide a comprehensive landscape of PSM research, identifying significant contributors, uncovering emerging themes, and pinpointing underexplored areas that can guide future ecological restoration strategies. This analysis intends to provide researchers and practitioners with insights for more effective utilization of PSM in ecological restoration efforts.
As shown in Figure 1, This study was conducted according to the PRISMA 2020 guideline (Page et al., 2021). The search was conducted in “Web of Science Core Collection,” with “All” selected in “Editions.” The search query focused primarily on “Phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms,” and the data retrieval strategies were designed as follows: TS = (“phosphor-releas*” OR “phosphor-solubili*” OR “phosphate-releas*” OR “phosphate-solubili*” OR “phosphor-mobiliz*” OR “phosphate-mobiliz*” OR “phosphor releas*” OR “phosphor solubili*” OR “phosphate releas*” OR “phosphate solubili*” OR “phosphor mobiliz*” OR “phosphate mobiliz*”) AND TS = (microorganism* OR microb* OR bacteria* OR Fungi OR Fungus) AND TS = (ecolog* OR ecosystem* OR environment* OR nutrient* OR fertilit*) AND TS = (rehabilit* OR restor* OR improve* OR remedia* OR bioremedia* OR sustainab* OR manage*). The data used in this study can be accessed through Mendeley Data (Mendeley Data, V2, doi:10.17632/xrp4hp58gs.2).
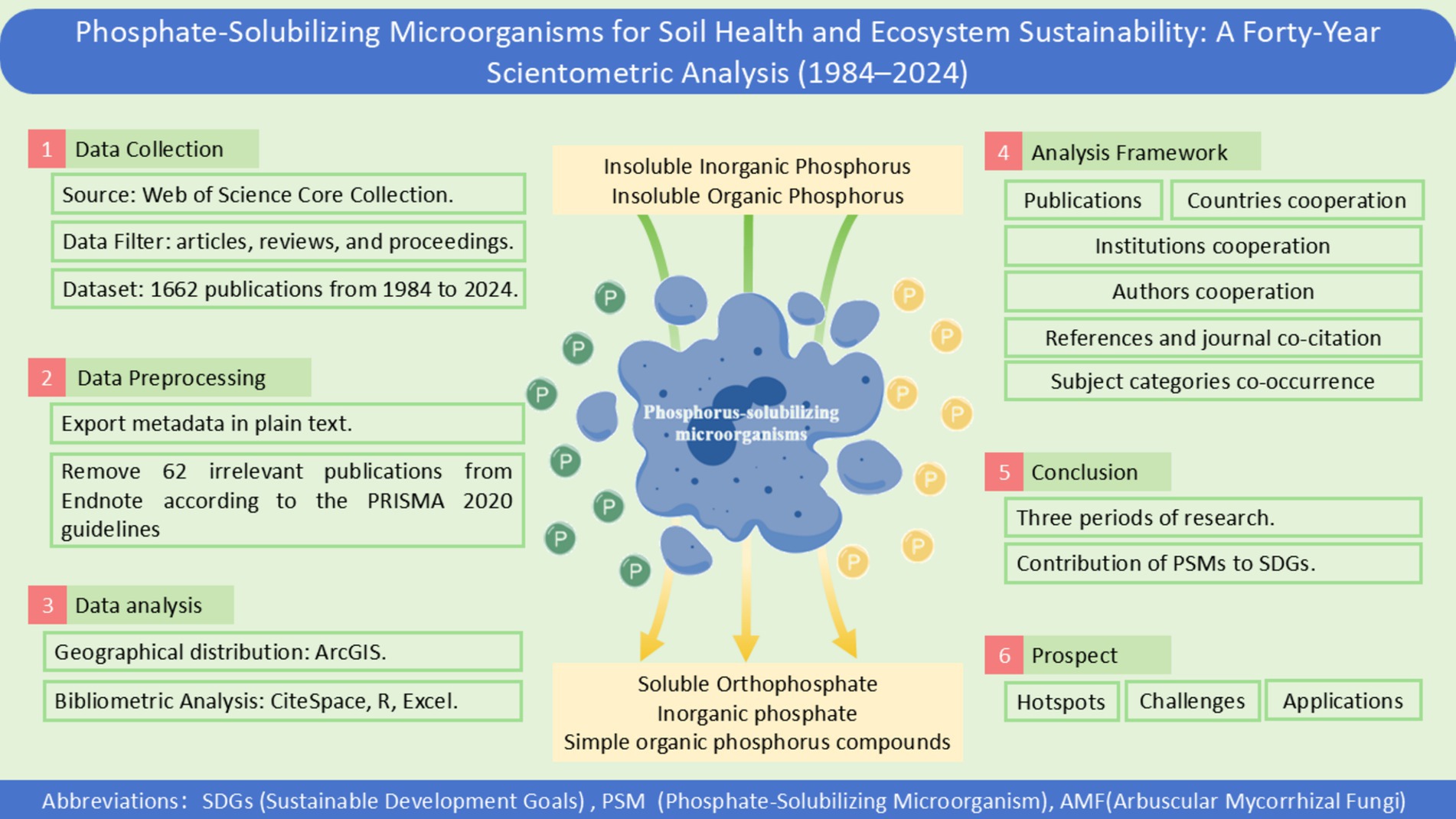
Figure 1. Bibliometric analysis flow of this study. Abbreviation in this study: SDGs (Sustainable Development Goals), PSM (Propensity Score Matching) and AMF (Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi).
This initial query yielded 1,378 English publications on December 31, 2023, covering the period from January 1, 1994, to December 31, 2023. An additional search was conducted on December 9, 2024, extending the dataset to 1,662 publications. After screening the records (Figure 1), 47 records were excluded due to incomplete bibliographic information, such as missing author names, publication dates, or other essential details necessary for proper analysis. Following full-text review, 15 records were excluded because they were not relevant to the content of the study.
To analyze the retrieved data comprehensively, this study utilized CiteSpace (6.3.R1 Advanced), Bibliometrix R-package (Aria and Cuccurullo, 2017), and Microsoft Excel 2021. These tools were selected based on their established effectiveness in conducting co-occurrence analysis, collaboration network mapping, and visualizing research trends. CiteSpace was used for co-citation and keyword co-occurrence analyses, identifying research hotspots and trends over time (Chen and Leydesdorff, 2014; Chen, 2017). These analyses revealed correlations between literature, emerging frontiers, and thematic developments (Chen, 2006; Montazeri et al., 2023; Du and Li, 2024). CiteSpace’s algorithms were also applied to assess keyword characteristics, where node size indicated frequency, and link thickness reflected co-occurrence strength (Li et al., 2023). Key nodes (centrality >0.1) were identified as critical to connecting research themes, and the burstiness indicator highlighted emerging research trends and hotspots (Guo and Yao, 2024). Pajek complemented this by processing large-scale network data, enabling visualization of collaboration and citation networks (Batagelj and Mrvar, 2004). ArcGIS facilitated spatial analyses to map research distributions and academic cooperation patterns (Borge-Holthoefer and Moreno, 2012). Bibliometrix provided a robust platform for bibliometric analysis, integrating data transformation, analysis, and visualization (Aria and Cuccurullo, 2017).
However, bibliometric methods may introduce certain biases. Data source selection can lead to sample bias, as reliance on databases like Web of Science or Scopus may overlook non-English and regional studies (Alois, 2024). Additionally, keyword extraction and classification involve subjectivity, where handling synonyms and polysemes can affect results (Liu et al., 2021). Overemphasis on highly cited papers may also overshadow emerging or niche research areas and these biases can impact the accurate identification of research hotspots and trends (Larivière, 2010). In this study, all the literature data have been optimized to avoid the above problems.
The number of publications indicates the total count of papers published within a specific research field over a designated period, and fluctuations in this number can signify development trends within that field (Pan et al., 2024). The corpus of publications, as shown in Figure 2 (a), primarily comprised articles (1367), followed by reviews (233), and proceedings papers (17). The publication trend can be divided into three stages (1984–2008, 2009–2017, 2018 to present) as illustrated in Figure 2 (b). In the first stage, the quantity of publications was relatively low and grew slowly. The annual number of publications remained in single digits to approximately 10. The first two articles were published in 1984 and 1991, representing the initial stage of the PSM studies. During this period, the research field was gradually building and the growth was steady but modest, reflecting the early development phase of the field. From 2008, the number of publications began to gradually increase. By 2017, the number of publications exceeded 50. The years 2006 and 2009 exhibited two small “peaks,” with growth rates of 90.91 and 116.67%, respectively. These peaks indicate periods of increased research activity and interest in the field. The growth during this period was more pronounced compared to the initial stage. From 2018 onwards, the number of publications increased significantly. The peak number of publications was reached in 2021 and 2022, at nearly 160. In 2019, the number of publications increased by 58.06% compared to 2018, and in 2021, it increased by 38.46% compared to 2020. This sharp increase in publications reflects the rapid growth of research in the field, driven by advancements in technology, increased funding, and a growing recognition of the importance of PSM studies in addressing contemporary challenges.
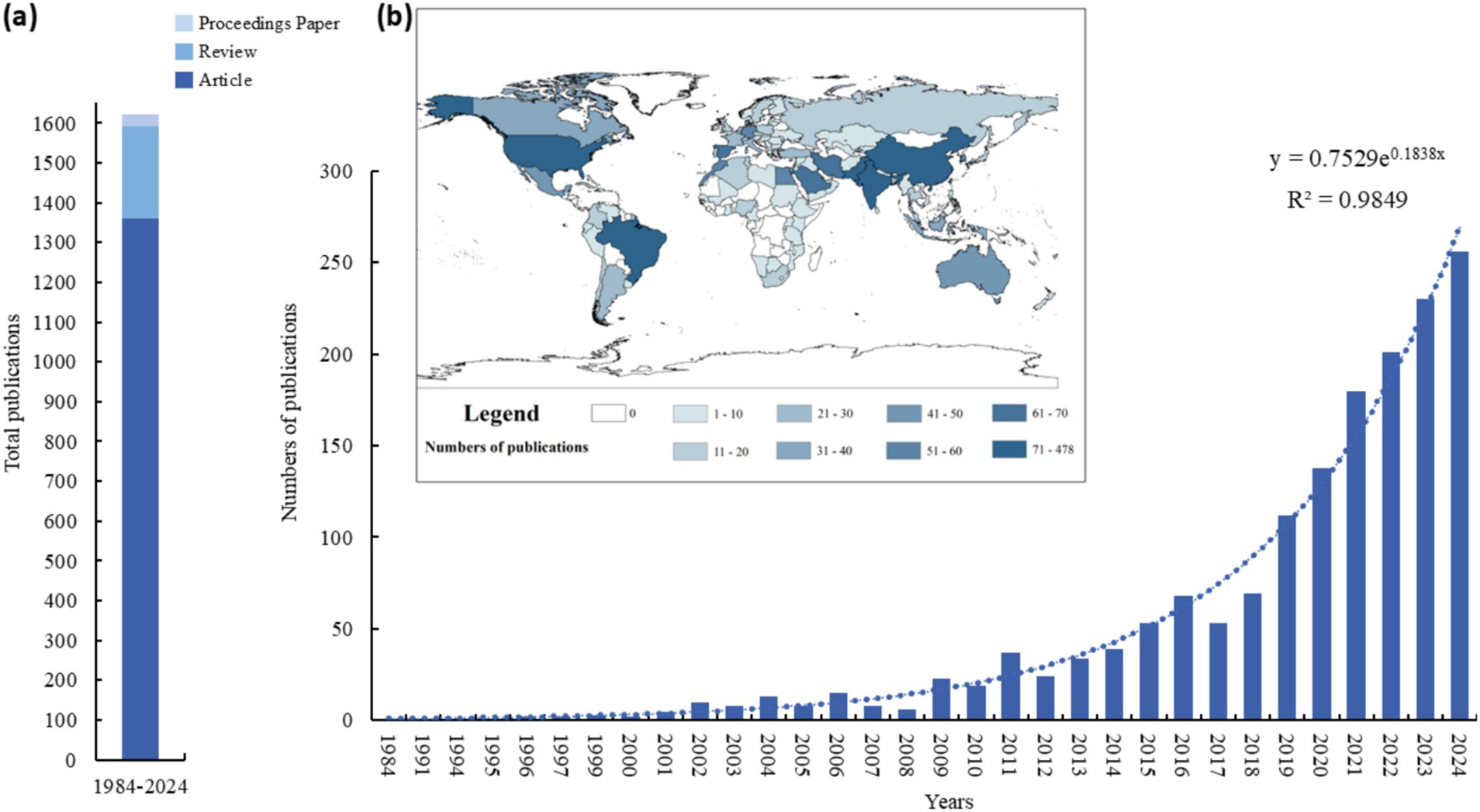
Figure 2. Publication output in the field of PSM from 1984 to 2023. (A) Stack chart of total publications. (B) Annual and cumulative number of publications and geographic visualizations.
Based on the cumulative number of publications per year, an equation for fitting the curve can be derived: y = 0.7529e0.1838x, R2 = 0.9849, demonstrating excellent fitting properties and conforming to the Price curve. This trend is particularly evident in recent years, with research potentially related to ecological restoration and PSM garnering increasing attention.
From a bibliometric perspective, 101 countries have conducted research on PSM, and 21 countries have published more than 20 articles each. Supplementary Table S1 lists the top 20 countries by number of published papers. Three countries have surpassed the threshold of 100 publications, collectively accounting for 41.47% of the total publications. India leads with 478 publications, closely followed by China with 349. Notably, India initiated research in this field earlier, and the first two articles published in 1984 and 1991 were both from India. Pakistan ranks third with 130 publications.
In the collaboration network shown in Figure 3, India, China, and Pakistan are prominently positioned with larger nodes, signifying their high publication output. India’s dominant role is further emphasized by its extensive connections with numerous countries, reflecting strong international collaborations. China also exhibits robust collaborative links, particularly with the USA, Germany, and Australia, highlighting research partnerships. France’s high centrality suggests it acts as a key bridge in the network, facilitating collaboration between other major research hubs. Countries like Germany, Iran, and South Korea display moderate centrality, implying active participation but with less influence compared to France and the USA. Clusters of closely connected countries are evident, such as the collaborations between European nations (France, Germany, Spain, and Italy) and between Asian countries (India, China, Pakistan, and Bangladesh). These clusters suggest regional research networks that complement broader international collaborations. Overall, the visualization in Figure 3 demonstrates a well-integrated global research network on PSM, characterized by strong bilateral and multilateral partnerships. This interconnected framework facilitates knowledge sharing and accelerates advancements in sustainable agricultural technologies and ecosystem restoration initiatives.
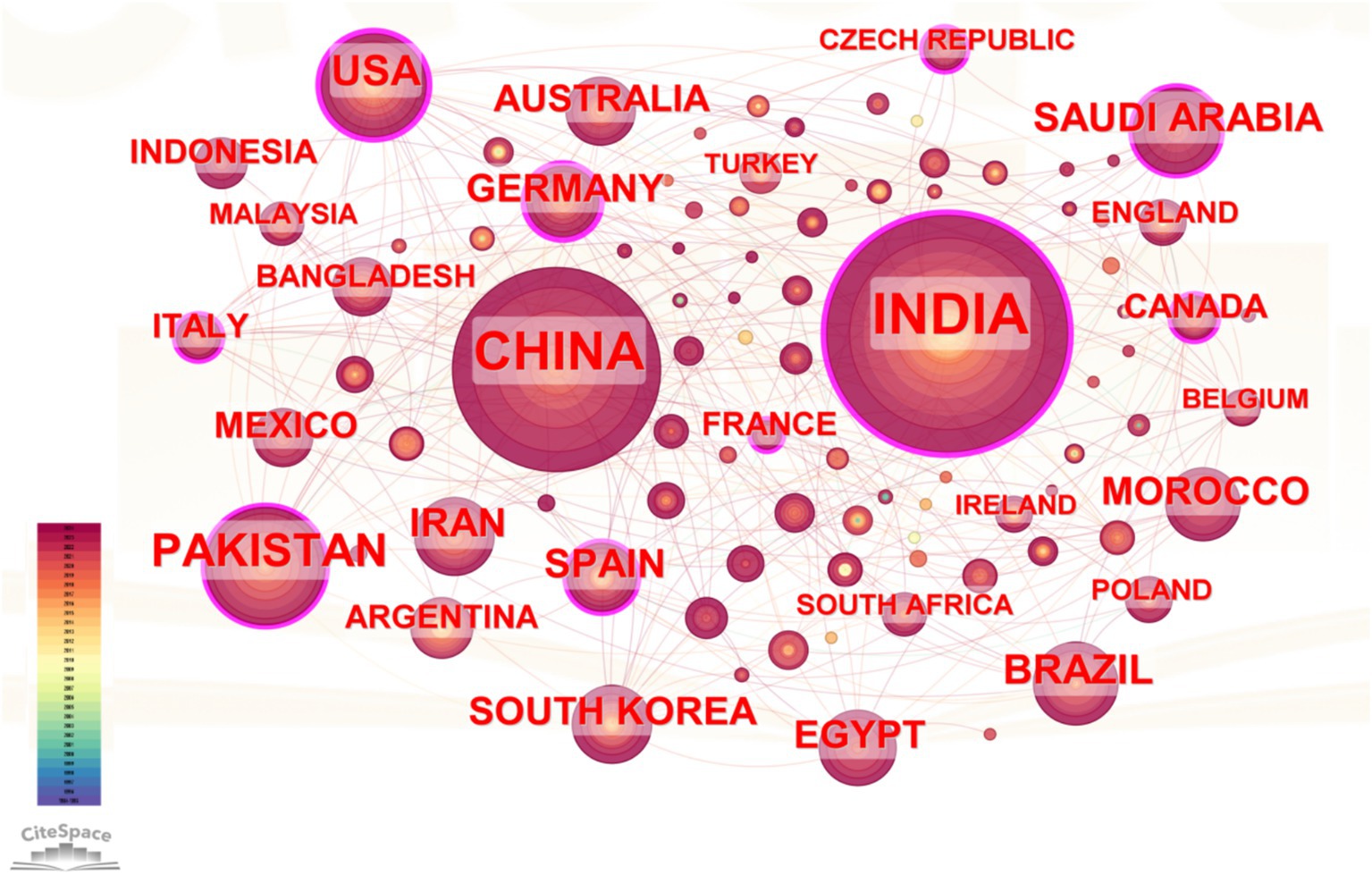
Figure 3. Map of country cooperation network analysis of PSM publications. Nodes represent countries involved in the collaboration network, with size indicating their level of participation. Colors reflect collaboration frequency, with darker nodes showing more active partnerships. Lines represent collaborations between countries, with thicker lines indicating stronger or more frequent ties.
Co-occurrence network analysis of research topics in the field of PSM and national collaborations reveal seven distinct thematic clusters (Supplementary Figure S1), showing connections between countries and research themes. Cluster #0 (soil fertility), dominated by India and Australia, focuses on improving soil nutrient availability. Cluster #1 (growth-promoting rhizobacteria), linked to Pakistan and Brazil, emphasizes enhancing plant growth. Cluster #2 (oil palm tree), represented by Indonesia, explores PSM applications in tropical agriculture. Cluster #3 (calcareous soil), involving Pakistan and Spain, addresses challenges in alkaline soils. Cluster #4 (phosphorus deficiency), associated with China and the USA, investigates solutions for phosphorus scarcity. Cluster #5 (unlocking agro-ecosystem sustainability), connected to Italy and France, focuses on sustainable farming, while Cluster #7 (environmental remediation), linked to Germany, highlights PSM’ role in restoring degraded environments. This network reflects the global collaboration in advancing PSM research for sustainable agriculture.
The distribution of collaboration and beneficial contribution among diverse institutions in the research field is analyzed using CiteSpace. In the selection criteria, the scale factor k = 5. The analysis revealed that 2097 institutions published research articles in the field of PSM, and the top 20 institutions with the highest number of publications are presented in Supplementary Figure S2. The results indicate that the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (India) ranks first with 111 papers, followed by the Egyptian Knowledge Bank (Egypt) and Chinese Academy of Sciences (China), each with more than 40 publications. Among the top 20 institutions in terms of publication count, India leads with 259, followed by China with 74 and Morocco with 55. The three institutions with the highest centrality are Bahauddin Zakariya University (Pakistan), Huazhong Agricultural University (China), and Al Azhar University (Egypt), suggesting their relatively high comprehensive influence in this field.
The collaborative network of research institutions in the field of PSM highlight the relationship and contributions of key institutions (Figure 4). The full names, abbreviations and countries of these institutions are shown in Table 1. Cluster #0 (Cropping System) is dominated by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (India) and the Indian Agricultural Research Institute (India), which play central roles in advancing sustainable farming practices. Cluster #1 (Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria) features close collaboration between the Chinese Academy of Sciences (China) and the University of Agriculture Faisalabad (Pakistan), emphasizing research on microbial solutions for nutrient availability. In Cluster #2 (Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi), institutions like the Spanish National Research Council (Spain) and the Zaidin Experimental Station (Spain) showcase strong cross-regional collaboration on soil–plant interactions. Similarly, Cluster #5 (Nutrient Management) highlights partnerships between King Saud University (Saudi Arabia) and Punjab Agricultural University (India), focusing on optimizing nutrient use efficiency. These thematic clusters illustrate both the diversity of research directions and the interconnected nature of global collaboration in PSM research, with institutions working together to address critical agricultural and environmental challenges.
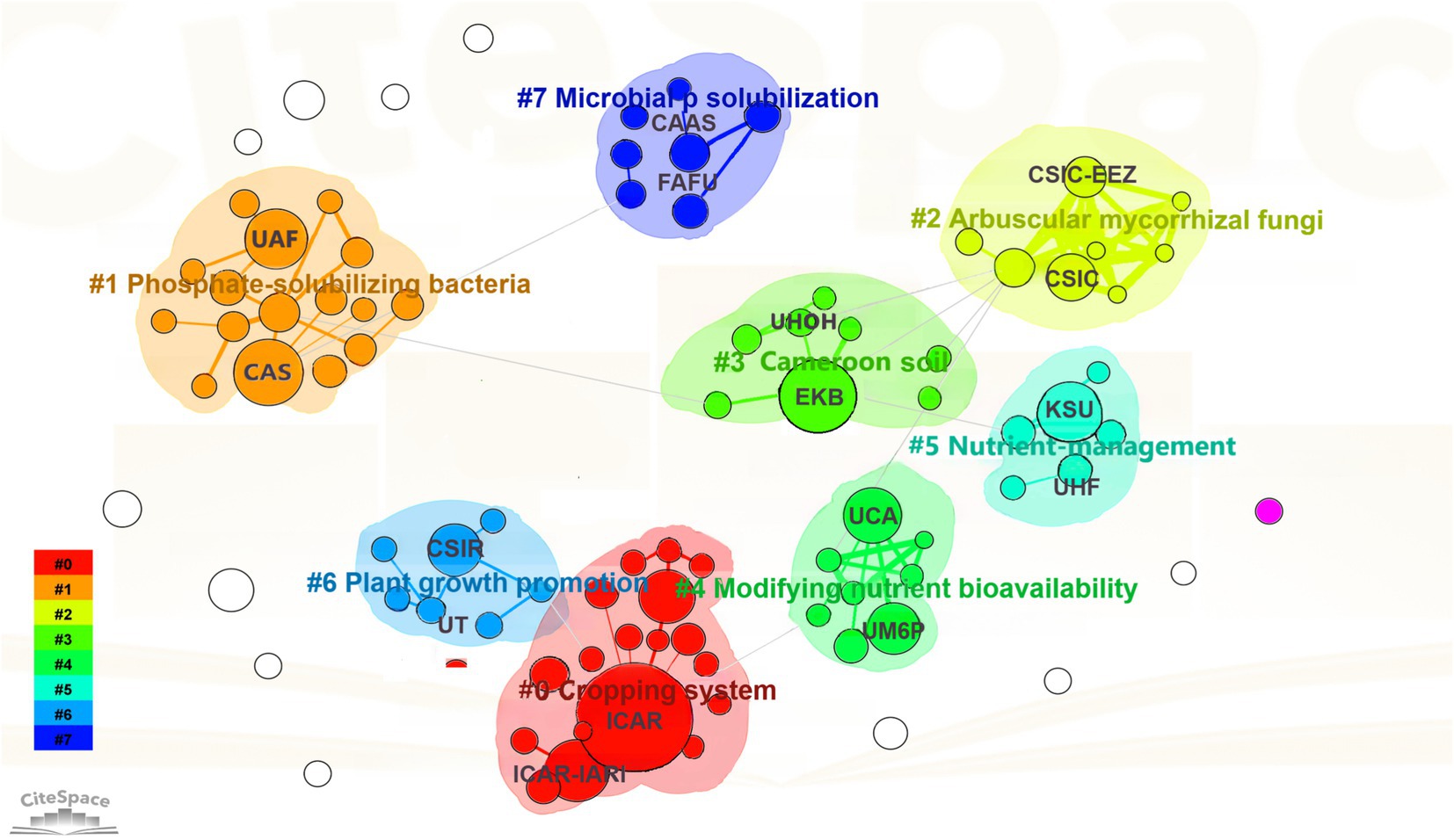
Figure 4. Map of collaborative network of global institutions. Colors represent different research clusters. Nodes indicate research institutions, with node size reflecting their influence, and edges represent collaboration links between institutions.
The author cooperation analysis in PSM research highlights the significant contributions and collaborative efforts of key researchers in the field (Supplementary Table S2). Hassan Etesami stands out with the highest number of publications (13) and citations (854), reflecting his central role and influence in advancing PSM studies. Adnane Bargaz (11 publications, 729 citations) and Yadav Ajar Nath (10 publications, 387 citations) are also prominent contributors, indicating active involvement in this research area. Highly cited authors such as Bernard R. Glick (1,484 citations) and Youssef Zeroual (641 citations) underscore the impactful nature of their work, despite slightly fewer publications. The data suggests a network of researchers with diverse expertise, working collaboratively to address critical challenges in the PSM domain. Emerging contributors like Olubukola Oluranti Babalola, Divjot Kour, and Hossein Ali Alikhani also highlight the growing international interest in this field. The distribution of publications and citations demonstrates a balance between well-established and newer authors, emphasizing the importance of both individual impact and collaborative synergy in driving innovation and knowledge dissemination in PSM research.
Figure 5 depicts the co-occurrence network of keywords in PSM research, providing a visual representation of the field’s intellectual structure. In this network, each node corresponds to a specific keyword, with node size proportional to its frequency of occurrence in the literature (Chen, 2020). The color gradient of the nodes indicates the temporal distribution of studies, where darker red shades represent more recent research (Sabe et al., 2022). The links between nodes signify co-occurrence relationships, with thicker lines denoting stronger associations (Chen, 2020). The network highlights several core research keywords, as evidenced by the larger nodes, including “phosphate solubilizing bacteria,” “plant growth,” and “rhizosphere. “These keywords represent foundational areas of focus within PSM research. The strong connection between “phosphorus,” “rhizosphere,” and “microorganisms” suggests a sustained research emphasis on microbial-mediated phosphorus solubilization processes in the soil environment. Additionally, the association between “growth promotion” and “diversity” with mechanisms such as “nitrogen fixation” and “inoculation” reflects the integration of multifunctional microbial strategies that enhancing plant growth and nutrient acquisition. Emerging research fronts are evident in the increasing occurrence of keywords such as “nutrient uptake,” “growth promotion,” and “sustainable agriculture,” indicating a shift towards the practical application of PSM in sustainable crop production systems. The prominence of terms like “biological control” and “plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria” further underscores the expanding interest in leveraging microbial diversity for improving soil fertility and plant health.
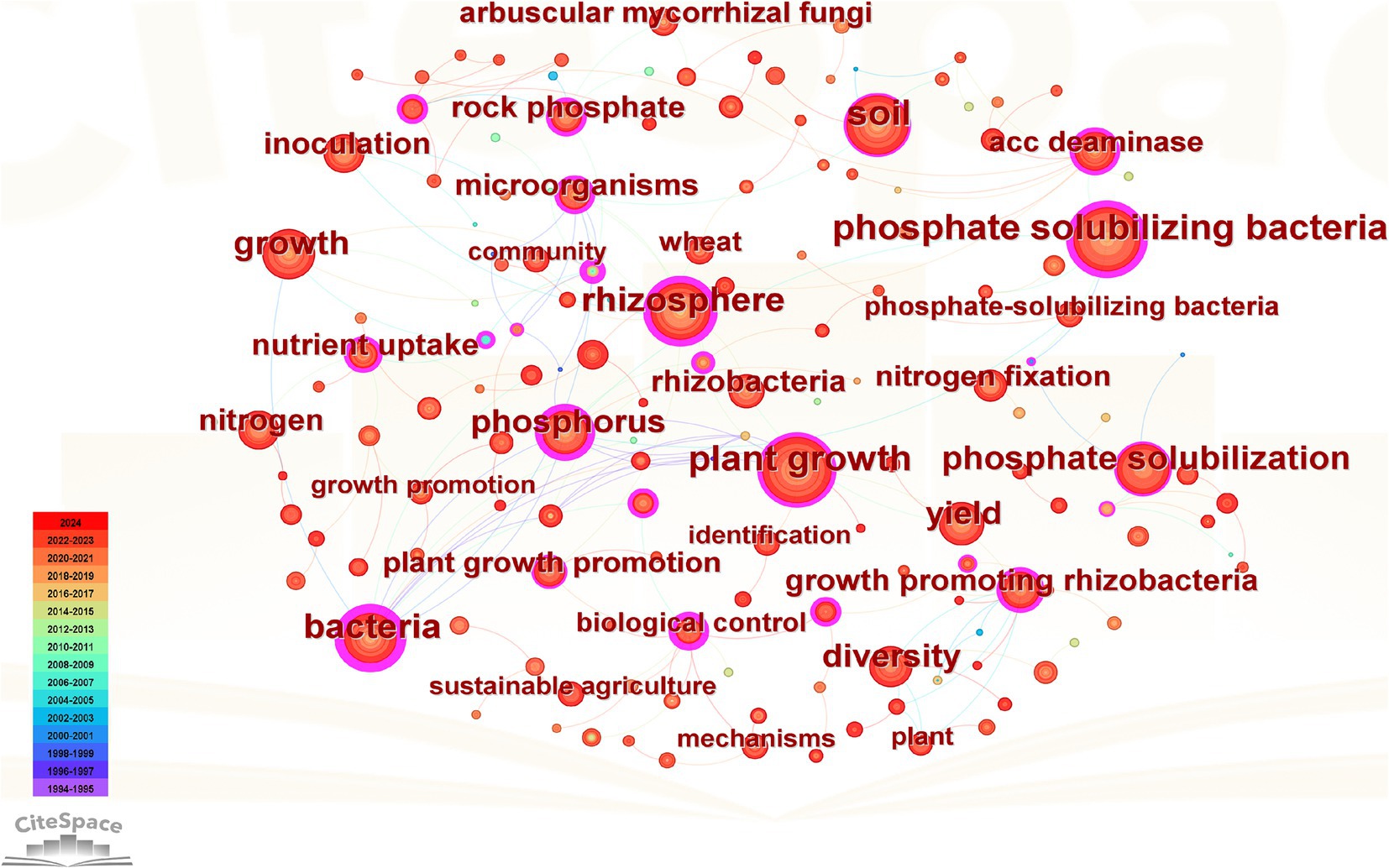
Figure 5. Co-occurrence network of core keywords. Each node represents a keyword, with the node size indicating its frequency of occurrence in the literature. The color of the nodes reflects the timeline of publication. Lines represent co-occurrence relationships.
Owing to the lengthy interval between the first two papers published in 1984 and 1991, a connection was made with other literature. Consequently, these two documents were not incorporated in the following analysis. Figure 6 offers a comprehensive view of the evolution of research hotspots in agricultural and environmental microbiology from 1990 to 2024, highlighting the development of key topics within the field. Early research themes, such as “organic acids,” “plant growth promotion,” and “sustainable agriculture,” emerge as prominent areas, reflecting a long-standing focus on improving agricultural productivity and sustainability. The figure also reveals the interconnected nature of research, with topics like “phosphate-solubilizing bacteria” and “nitrogen fixation” closely linked, emphasizing the crucial role of microbial processes in nutrient cycling for soil fertility. As the timeline progresses, new clusters, such as “accdeaminase” and “plant growth-promoting bacteria,” signal a shift towards mechanistic studies exploring molecular pathways involved in plant stress tolerance and growth promotion. Additionally, keywords like “phytoremediation” and “community structure” indicate a growing interest in the environmental applications of plant growth-promoting microbes, especially for soil health and pollution remediation. The color gradient, transitioning from purple (early years) to yellow (recent years), visually represents the timeline of research development, highlighting when certain topics gained prominence (Chen, 2017; Chen and Song, 2019). Clusters like “bacterial community” and “rock phosphate” further emphasize the critical role of soil microbes and microbial diversity in enhancing soil health and phosphorus availability, which are vital for sustainable agricultural practices. Overall, this visualization provides a detailed overview of how research within soil microbiology and plant growth has evolved, focusing on microbial processes, soil health, and environmental concerns, alongside mechanistic studies aimed at addressing global agricultural challenges like climate change and soil degradation.
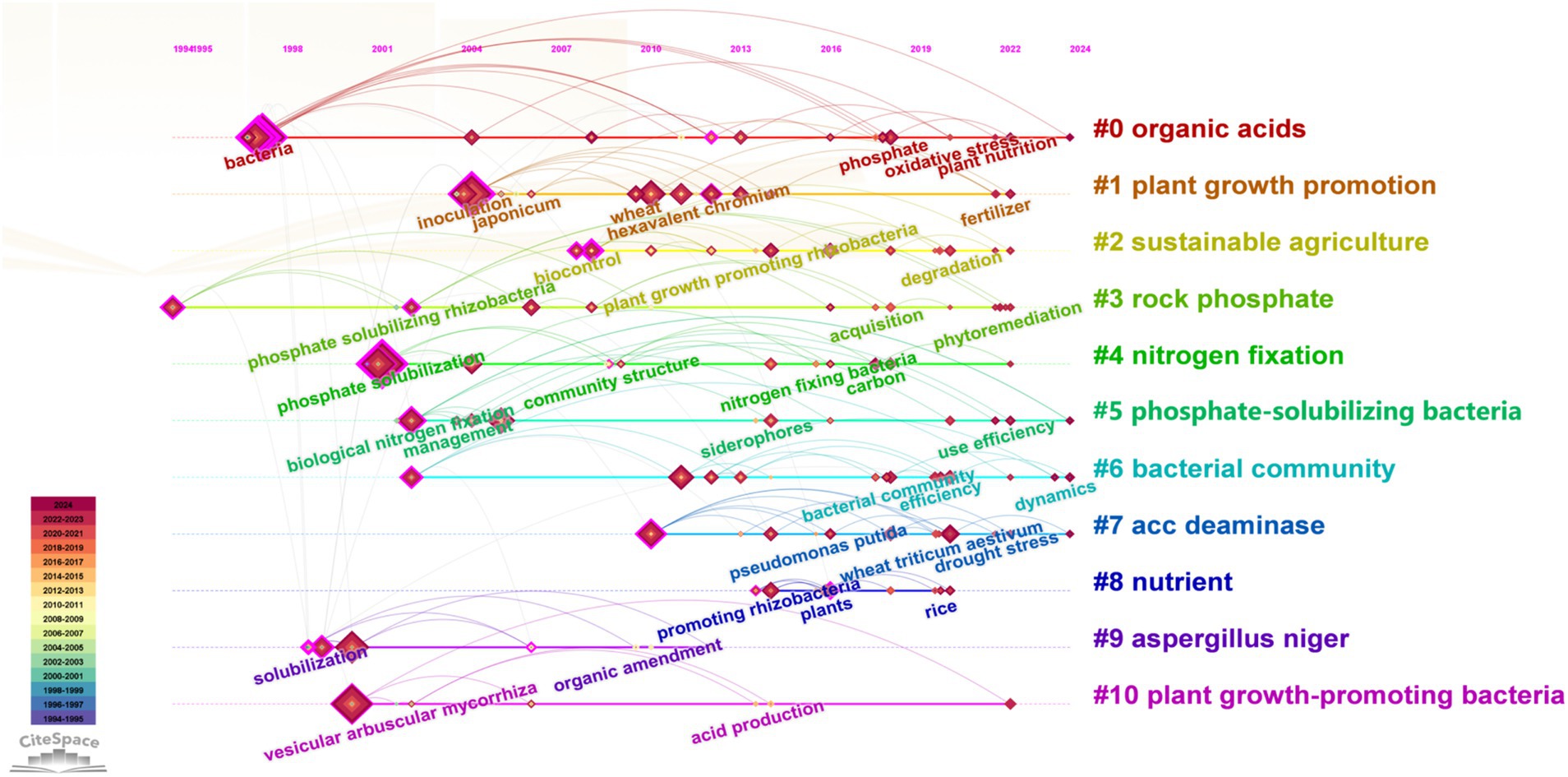
Figure 6. Keyword co-occurrence network timeline. The larger nodes represent high-frequency keywords in these fields, indicating the significant influence of these topics over the past few decades. The different colored lines illustrate the connections and interdisciplinary research between various themes.
Figure 7 illustrates the 25 keywords with the strongest Citation Bursts in the academic literature. Adjacent to each keyword is the year of its citation surge, intensity, start and end times, and the corresponding time period (Hou et al., 2018). Each keyword is accompanied by its surge year, intensity, duration, and corresponding time period. Early bursts like “nutrition” (1997) and “Aspergillus niger” (1999) reflect sustained interest in microbial roles in plant nutrient uptake, using traditional microbiological methods. Keywords from the early 2000s, such as “nutrient uptake” and “rhizosphere,” indicate growing research on plant-microbe interactions, transitioning towards molecular techniques. Later bursts like “arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi” (2006) and “azospirillum brasilense” (2010) highlight increased focus on beneficial fungi and nitrogen-fixing bacteria, enhanced by metagenomics and sequencing technologies. Recent bursts, including “promoting rhizobacteria” (2014) and “nitrogen fixation” (2016), signal a shift towards microbial solutions for soil fertility and crop yields, utilizing omics technologies. Keywords like “microbial biomass” (2018) and “solubilization” (2019) emphasize microbial roles in phosphate solubilization, supported by advanced analytical methods. The most recent bursts, such as “gene expression” and “induced systemic resistance” (2020–2024), suggest a focus on molecular mechanisms of plant-microbe interactions, often using gene-editing technologies like CRISPR. Overall, the data highlights a shift in PSM research from basic functions to applied solutions, with increasing attention on enhancing soil health and sustainable farming through microbial interventions. This evolution from conventional to advanced techniques offers insights into modern approaches suitable for current and future studies.
The top 10 co-citation articles in PSM research filed are listed in Table 2. The most influential article, “Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria and their role in plant growth promotion” by Rodríguez and Fraga (1999), with 3,321 co-citation, underscores its foundational role in linking PSM to plant growth enhancement. Sharma et al. (2013) work on sustainable phosphorus management, ranks second with 2,816 citations, highlighting the pivotal role of PSM in addressing phosphorus deficiency in agricultural soils. Other significant studies, such as Nautiyal (1999) and Pikovskaya (1948), focus on an efficient microbiological growth medium and microbial contributions to soil nutrient mobilization, achieving 2,291 and 2,158 citations, respectively. These articles collectively demonstrate high total link strengths, with values exceeding 1900, indicating their substantial connectivity and influence within the research community. Top 20 journals by number of publications from 1,622 articles are listed in Supplementary Table S3. A total of 1,622 articles were published across 472 journals, with 40 journals publishing more than 10 articles, as illustrated in Supplementary Figure S3.
The co-occurrence analysis of subject categories contributes to the advancement of research frontiers and the identification of interdisciplinary characteristics within specific knowledge fields (Li et al., 2019). Utilizing cluster analysis in CiteSpace software, we identified that research on PSM is both multidisciplinary and interdisciplinary (Figure 8), generating seven distinct clusters. This research encompasses various fields, including medicine, research and experimental, horticulture, physics, engineering environment, water resources, agronomy, biotechnology and applied microbiology, oceanography, chemistry, plant sciences, and ecology.

Figure 8. Subject co-occurrence analysis in the scientific research field of PSM. Different colors represent distinct clusters research themes. Each color typically indicates a specific area of study.
Research on PSM from 1984 to 2024 illustrates a remarkable evolution in focus, with growing contributions from diverse institutions and countries, reflecting regional priorities and global challenges. Early studies primarily focused on the fundamental mechanisms of phosphate solubilization. Rodríguez and Fraga (1999) emphasized that the secretion of organic acids, such as citric and oxalic acids, is a key mechanism, as these acids lower soil pH and promote phosphate solubilization. Illmer and Schinner (1992) demonstrated that environmental conditions (e.g., pH, temperature, and carbon sources) significantly influence the efficiency of bacterial phosphate solubilization. Kim et al. (1997) identified acid phosphatase and phospholipase as crucial enzymes for the mineralization of organic phosphorus, converting it into plant-available forms. Further molecular studies revealed that certain bacteria (e.g., Pseudomonas) possess genes regulating the synthesis of organic acids and extracellular enzyme secretion, which are controlled by environmental phosphate levels (Goldstein, 1986). Additionally, microbial interactions, such as the synergistic relationship between phosphate-solubilizing bacteria and AMF, can enhance plant phosphorus uptake (Zheng et al., 2024; García-Berumen et al., 2025). These studies, conducted primarily in Europe and North America, laid a theoretical foundation for developing PSM-based microbial fertilizers. Despite the limited number of publications and modest growth in the field, studies explored the mode of action of PSM (Toro et al., 1997), their diversity (De Souza et al., 2000), and their interactions with plant roots (Sharma, 2003).
In the following decades, PSM research expanded globally, with notable contributions from countries like India, China, and Brazil. Key institutions, including the Indian Council of Agricultural Research and the Chinese Academy of Sciences, advanced PSM applications in agriculture and soil management. Studies emphasized PSM synergies with other microorganisms. Kohler et al. (2007) and Egamberdiyeva and Höflich (2003) highlighted interactions with AMF and plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria, demonstrating enhanced nutrient uptake and plant growth, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions. During this period, policy support in many countries began to emerge, recognizing the role of biofertilizers in sustainable agriculture. For instance, India’s National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture and China’s Green Development Policy encouraged the use of biofertilizers like PSM to improve soil fertility and reduce chemical fertilizer dependency (Jianbo Shen et al., 2024; Kaur et al., 2024).
Thematic priorities diversified to address nutrient management, ecosystem restoration, and microbial interactions. Research focused on PSM roles in improving soil health, plant growth, and productivity under environmental stress (Rodríguez and Fraga, 1999; Khan et al., 2007). Some studies demonstrated field applications for phosphorus-deficient soils, further supporting the potential of PSM in improving soil fertility and aiding in the bioremediation of heavy metal contamination, particularly lead, cadmium, and chromium (Sharma et al., 2013; Guo et al., 2021a; Guo et al., 2021b; Li et al., 2022). Recent studies have expanded this understanding by examining PSM performance across diverse ecosystems, climates, and soil types. For instance, PSM applications in arid and semi-arid regions have shown promise in mitigating drought stress and enhancing soil fertility (Rodríguez and Fraga, 1999). In saline soils, certain halotolerant PSM strains have effectively solubilized phosphorus, contributing to plant resilience and productivity (Kushwaha et al., 2024). Similarly, PSM adapted to acidic soils have improved phosphorus availability and crop yields in tropical regions (Khan et al., 2007). Synergistic interactions with other microbes, such as nitrogen-fixing bacteria (Zaidi et al., 2009) and potassium-solubilizing microorganisms (Yadav, 2022), improved soil nutrient bioavailability and supported ecological restoration on a larger scale. These research advancements aligned with global policy initiatives, such as the European Union’s Farm to Fork Strategy, which promotes sustainable agricultural practices by supporting microbial fertilizers through funding and regulatory frameworks (Kour et al., 2020; Dasgupta et al., 2021).
The post-2020 period has seen a global shift in PSM research, driven by pressing challenges such as climate change, environmental stresses, and the need for ecological resilience. This trend is marked by growing contributions from countries like India, China, and the United States, with key institutions such as the Indian Institute of Soil Science, the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, and the United States Department of Agriculture advancing this field. Some research on PSM has concentrated on their utilization in alleviating environmental stresses induced by climate change, particularly under drought and salt conditions (Kumari et al., 2023); the cooperative interactions between PSM and other microorganisms, enhancing nutrient acquisition and pathogen resistance in crops (Phour and Sindhu, 2023); genomic and metabolomic investigations to elucidate phosphate solubilization mechanisms and identify highly efficient strains (Kumari et al., 2023). In addition, through collaborative efforts between academia and industry, progress has been made in industrial applications that promote psm in sustainable agricultural practices (Phour and Sindhu, 2023). This has a positive impact on soil health and the carbon cycle and can contribute to the sustainable development of agro-ecosystems. Moreover, public-private partnerships have facilitated the commercialization of PSM-based products, bridging scientific research and practical agricultural applications (Verma et al., 2019). However, challenges such as production standardization, quality control, and regulatory disparities across regions must be addressed to maximize PSM’s potential in sustainable agriculture (Gopalakrishnan et al., 2015).
Significant progress has been made in the study of PSM from 1984 to 2024, but several challenges remain, particularly concerning their integration into sustainable ecosystem management. Key issues include: (1) limited understanding of molecular and enzymatic mechanisms underlying phosphate solubilization (Rodríguez and Fraga, 1999; Raghothama and Karthikeyan, 2005). (2) The environmental adaptability of PSM remains a critical yet insufficiently explored area, particularly given their variable performance across diverse ecosystems, climatic conditions, and soil types. The underlying mechanisms by which temperature fluctuations, soil pH, moisture levels, and nutrient availability affect PSM survival, colonization, and phosphate-solubilizing efficiency have not been thoroughly elucidated (Alori et al., 2017). (3) underdeveloped multifunctional traits, such as nitrogen fixation and plant growth promotion (Adesemoye et al., 2009). (4) Insufficient research on PSM interactions with soil microbes, particularly in nutrient cycling and ecosystem stability (Richardson and Simpson, 2011; Bashan et al., 2013). (5) Research on the long-term stability and ecological safety of PSM is limited, particularly regarding their impact on native microbial communities and soil functions (Vassilev et al., 2013). (6) Inconsistent policies and regulations across regions hinder the large-scale commercialization and adoption of PSM-based biofertilizers. The absence of unified standards for production quality, application methods, and environmental safety creates barriers to industry adoption and farmer use (Yadav and Yadav, 2024). Addressing these challenges will be vital for advancing PSM-based solutions for sustainable agriculture and ecosystem restoration.
This bibliometric study analyzed 1,662 publications on PSM spanning 1984–2024, revealing distinct evolutionary phases in research focus and applications. The initial phase (1984–2008) concentrated on isolating and characterizing PSM, emphasizing their biochemical mechanisms for phosphorus solubilization. The subsequent period (2009–2017), the research expanded to agricultural applications, exploring PSM as biofertilizers within organic farming systems. The recent phase (2018 to present) reflects an increased focus on ecological restoration, soil pollution control, and their role in addressing global challenges such as climate change and nutrient resource recycling.
Despite significant progress, challenges in PSM remain, such as limited understanding of their mechanisms across environments, poor integration of genomic and metabolic analyses, and inconsistent field outcomes due to environmental factors. Future research should focus on: (1) Unraveling Functional Mechanisms: Using omics approaches to uncover metabolic pathways and regulatory networks involved in phosphate solubilization. (2) Environmental Adaptability: Investigating PSM resilience and adaptability under varying environmental stresses, such as drought, salinity, and extreme temperatures, to ensure consistent field performance. (3) Multifunctional Microbial Design: Engineering PSM with additional functionalities such as nitrogen fixation and stress tolerance using advanced biotechnological tools. (4) Microbial Interactions: Exploring how PSM influence and are influenced by native soil microbiomes to maintain ecological balance. (5) Biofertilizer Development: Focusing on scalable production technologies, formulation stability, and delivery methods to improve the commercial viability of PSM-based biofertilizers. (6) Policy and Research Integration: Promoting interdisciplinary research and policy integration to support the sustainable application of PSMs in agriculture and ecological restoration. By expanding research in these directions, PSM can be more effectively harnessed to address global challenges such as soil degradation, food insecurity, and climate change. This comprehensive approach will support resilient agricultural systems and accelerate progress toward global sustainability targets.
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found at: https://data.mendeley.com/drafts/xrp4hp58gs.
YL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft. YK: Data curation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. MG: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. HZ: Writing – review & editing. YY: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. HH: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFF0803100), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31901177), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (20720240090).
The authors would like to thank TopEdit (www.topeditsci.com) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1546852/full#supplementary-material
Adesemoye, A. O., Torbert, H. A., and Kloepper, J. W. (2009). Plant growth-promoting Rhizobacteria allow reduced application rates of chemical fertilizers. Microb. Ecol. 58, 921–929. doi: 10.1007/s00248-009-9531-y
Alois, M. (2024). Bibliometrics: application opportunities and limitations. Intech Open. Ch. 1, 1–170. doi: 10.5772/intechopen.1005292
Alori, E. T., Glick, B. R., and Babalola, O. O. (2017). Microbial phosphorus Solubilization and its potential for use in sustainable agriculture. Front. Microbiol. 8, 1–8. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00971
Ampese, L. C., Sganzerla, W. G., Di Domenico Ziero, H., Mudhoo, A., Martins, G., and Forster-Carneiro, T. (2022). Research progress, trends, and updates on anaerobic digestion technology: A bibliometric analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 331:130004. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.130004
Aqeel, M., Ran, J., Hu, W., Irshad, M. K., Dong, L., Akram, M. A., et al. (2023). Plant-soil-microbe interactions in maintaining ecosystem stability and coordinated turnover under changing environmental conditions. Chemosphere 318:137924. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.137924
Aria, M., and Cuccurullo, C. (2017). Bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Informet. 11, 959–975. doi: 10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007
Bashan, Y., Kamnev, A. A., and de-Bashan, L. E. (2013). Tricalcium phosphate is inappropriate as a universal selection factor for isolating and testing phosphate-solubilizing bacteria that enhance plant growth: a proposal for an alternative procedure. Biol. Fertil. Soils 49, 465–479. doi: 10.1007/s00374-012-0737-7
Batagelj, V., and Mrvar, A. (2004). Pajek - analysis and visualization of large networks. Graph Drawing Software. 2265, 77–103. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-18638-7_4
Borge-Holthoefer, J., and Moreno, Y. (2012). Absence of influential spreaders in rumor dynamics. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 85:026116. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.85.026116
Chen, C. (2006). CiteSpace II: detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 57, 359–377. doi: 10.1002/asi.20317
Chen, C. (2017). Science mapping: A systematic review of the literature. J. Data Information Sci. 2, 1–40. doi: 10.1515/jdis-2017-0006
Chen, C. (2020). A glimpse of the first eight months of the COVID-19 literature on Microsoft academic graph: themes, citation contexts, and uncertainties. Front. Res. Metrics Analytics 5:7286. doi: 10.3389/frma.2020.607286
Chen, H., Jiang, H., Nazhafati, M., Li, L., and Jiang, J. (2023). Biochar: An effective measure to strengthen phosphorus solubilizing microorganisms for remediation of heavy metal pollution in soil. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 11:7166. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1127166
Chen, C., and Leydesdorff, L. (2014). Patterns of connections and movements in dual-map overlays: A new method of publication portfolio analysis. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 65, 334–351. doi: 10.1002/asi.22968
Chen, Y. P., Pd, R., Bhagwath, A., Shen, F.-T., Lai, W.-A., and Young, C. (2006). Phosphate solubilizing bacteria from subtropical soil and their tricalcium phosphate solubilizing abilities. Appl. Soil Ecol. 34, 33–41. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2005.12.002
Chen, C., and Song, M. (2019). Visualizing a field of research: A methodology of systematic scientometric reviews. PLoS One 14:e0223994. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223994
Chen, M., Song, X., Liu, L., Jing, Z., Miao, J., Ding, X., et al. (2024). Response of soil organic carbon stability and sequestration to long-term phosphorus application: insight from a 9-year field experiment in saline alkaline paddy soil. Plant Soil 496, 415–429. doi: 10.1007/s11104-023-06371-2
Dasgupta, D., Kumar, K., Miglani, R., Mishra, R., Panda, A. K., and Bisht, S. S. (2021). Chapter 1- microbial biofertilizers: recent trends and future outlook. Recent Advancement Microbial Biotechnol. 1–26. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-822098-6.00001-x
De Souza, M., Nair, S., and Chandramohan, D. (2000). Phosphate solubilizing bacteria around Indian peninsula. Indian J. Marine Sci. 29, 48–51.
Du, C., and Li, Z. (2024). Bibliometric analysis and systematic review of fluoride-containing wastewater treatment: development, hotspots and future perspectives. J. Environ. Manag. 370:122564. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.122564
Egamberdiyeva, D., and Höflich, G. (2003). Influence of growth-promoting bacteria on the growth of wheat in different soils and temperatures. Soil Biol. Biochem. 35, 973–978. doi: 10.1016/S0038-0717(03)00158-5
Egghe, L., and Rousseau, R. (1990). Introduction to Informetrics: Quantitative methods in library : Documentation and Information Science. ed. R. Rousseau (Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Documentation and Information Science).
García-Berumen, J. A., Flores de la Torre, J. A., de los Santos-Villalobos, S., Espinoza-Canales, A., Echavarría-Cháirez, F. G., and Gutiérrez-Bañuelos, H. (2025). Phosphorus dynamics and sustainable agriculture: the role of microbial solubilization and innovations in nutrient management. Curr. Res. Microbial Sci. 8:100326. doi: 10.1016/j.crmicr.2024.100326
Garfield, E. (1972). Citation analysis as a tool in journal evaluation. Science 178, 471–479. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4060.471
Glänzel, W. (2003). Bibliometrics as a research field: A course on theory and application of bibliometric indicators. Lexington, MA, USA: Course Handouts.
Glick, B. R. (2012). Plant growth-promoting Bacteria: mechanisms and applications. Scientifica 2012:963401, 1–15. doi: 10.6064/2012/963401
Goldstein, A. H. (1986). Bacterial solubilization of mineral phosphates: historical perspective and future prospects. Am. J. Altern. Agric. 1, 51–57. doi: 10.1017/S0889189300000886
Gopalakrishnan, S., Sathya, A., Vijayabharathi, R., Varshney, R. K., Gowda, C. L. L., and Krishnamurthy, L. (2015). Plant growth promoting rhizobia: challenges and opportunities. Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobia 5, 355–377. doi: 10.1007/s13205-014-0241-x
Gordon, S. A., and Weber, R. P. (1951). Colorimetric estimation of indoleacetic acid. Plant Physiol. 26, 192–195. doi: 10.1104/pp.26.1.192
Guo, S., Xiao, C., Zheng, Y., Li, Y., and Chi, R. (2021a). Removal and potential mechanisms of Cr (VI) contamination in phosphate mining wasteland by isolated Bacillus megatherium PMW-03. J. Clean. Prod. 322:129062. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129062
Guo, S., Xiao, C., Zhou, N., and Chi, R. (2021b). Speciation, toxicity, microbial remediation and phytoremediation of soil chromium contamination. Environ. Chem. Lett. 19, 1413–1431. doi: 10.1007/s10311-020-01114-6
Guo, Q., and Yao, P. (2024). Bibliometric review of carbon peak with CiteSpace: evolution, trends, and framework. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 31, 13592–13608. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-32008-7
Gurav, P. P., Kollah, B., Shirale, A. O., Yadav, D. K., Mohanty, S. R., Babu, S., et al. (2024). Phosphorus solubilizing microorganisms: a technique for enhancing phosphorus use efficiency. J. Plant Nutr. 47, 3906–3920. doi: 10.1080/01904167.2024.2388798
Hirsch, J. E. (2010). An index to quantify an individual’s scientific research output that takes into account the effect of multiple coauthorship. Scientometrics 85, 741–754. doi: 10.1007/s11192-010-0193-9
Hou, J., Yang, X., and Chen, C. (2018). Emerging trends and new developments in information science: a document co-citation analysis (2009–2016). Scientometrics 115, 869–892. doi: 10.1007/s11192-018-2695-9
Huang, L., Baumgartl, T., and Mulligan, D. (2012). Is rhizosphere remediation sufficient for sustainable revegetation of mine tailings? Ann. Bot. 110, 223–238. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcs115
Hussain, A., Adnan, M., Iqbal, S., Fahad, S., Saeed, M., Mian, I. A., et al. (2019). Combining phosphorus (P) with phosphate solubilizing bacteria (PSB) improved wheat yield and P uptake in alkaline soil. Pure Appl. Biol. 8, 1809–1817. doi: 10.19045/bspab.2019.80124
Iftikhar, A., Farooq, R., Akhtar, M., Khalid, H., Hussain, N., Ali, Q., et al. (2024). Ecological and sustainable implications of phosphorous-solubilizing microorganisms in soil. Discover Applied Sci. 6:33. doi: 10.1007/s42452-024-05683-x
Illmer, P., and Schinner, F. (1992). Solubilization of inorganic phosphates by microorganisms isolated from forest soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 24, 389–395. doi: 10.1016/0038-0717(92)90199-8
Jianbo Shen, Q. Z., Hou, Y., Cong, W.-F., Wen, X., Jiuliang, X., An, Z., et al. (2024). Agriculture green development in China: insights and advances. Front. Agr. Sci. Eng. 19. doi: 10.15302/j-fase-2024535
Kamerlin, S. C. L., Sharma, P. K., Prasad, R. B., and Warshel, A. (2013). Why nature really chose phosphate. Q. Rev. Biophys. 46, 1–132. doi: 10.1017/S0033583512000157
Kaur, H., Mir, R. A., Hussain, S. J., Prasad, B., Kumar, P., Aloo, B. N., et al. (2024). Prospects of phosphate solubilizing microorganisms in sustainable agriculture. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 40:291. doi: 10.1007/s11274-024-04086-9
Khan, M. S., Zaidi, A., and Wani, P. A. (2007). Role of phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms in sustainable agriculture — A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 27, 29–43. doi: 10.1051/agro:2006011
Kim, K. Y., McDonald, G. A., and Jordan, D. (1997). Solubilization of hydroxyapatite by Enterobacter agglomerans and cloned Escherichia coli in culture medium. Biol. Fertil. Soils 24, 347–352. doi: 10.1007/s003740050256
Kohler, J., Caravaca, F., Carrasco, L., and Roldán, A. (2007). Interactions between a plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium, an AM fungus and a phosphate-solubilising fungus in the rhizosphere of Lactuca sativa. Appl. Soil Ecol. 35, 480–487. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2006.10.006
Kour, D., Rana, K. L., Yadav, A. N., Yadav, N., Kumar, M., Kumar, V., et al. (2020). Microbial biofertilizers: bioresources and eco-friendly technologies for agricultural and environmental sustainability. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 23:101487. doi: 10.1016/j.bcab.2019.101487
Kumari, A., Dash, M., Singh, S. K., Jagadesh, M., Mathpal, B., Mishra, P. K., et al. (2023). Soil microbes: a natural solution for mitigating the impact of climate change. Environ. Monit. Assess. 195:1436. doi: 10.1007/s10661-023-11988-y
Kushwaha, M., Mishra, A., Shankar, S., Goel, D., Joshi, S., and Ram, S. (2024). “Chapter 32- plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria for sustainable agriculture: recent progress and challenges” in Role of green chemistry in ecosystem restoration to achieve environmental sustainability. Elsevier, 333–342.
Lambers, H. (2022). Phosphorus acquisition and utilization in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 73, 17–42. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-102720-125738
Larivière, V. (2010). “The limits of bibliometrics for the analysis of the social sciences and humanities literature,” in Advances in Pollution Research. World social science report 2009/2010. Elsevier.
Li, Y., Guo, S., Zheng, Y., Yu, J., Chi, R., and Xiao, C. (2022). Bioimmobilization of lead in phosphate mining wasteland by isolated strain Citrobacter farmeri CFI-01. Environ. Pollut. 307:119485. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119485
Li, C., Ji, X., and Luo, X. (2019). Phytoremediation of heavy metal pollution: A bibliometric and Scientometric analysis from 1989 to 2018. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 16:4475. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16234755
Li, X., Nan, H., Jiang, H., Wang, H., and Wang, C. (2023). Research trends on phosphorus removal from wastewater: A review and bibliometric analysis from 2000 to 2022. J. Water Process Eng. 55:104201. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2023.104201
Liang, J.-L., Liu, J., Jia, P., Yang, T. T., Zeng, Q. W., Zhang, S. C., et al. (2020). Novel phosphate-solubilizing bacteria enhance soil phosphorus cycling following ecological restoration of land degraded by mining. ISME J. 14, 1600–1613. doi: 10.1038/s41396-020-0632-4
Liu, H., Li, X., and Wang, S. (2021). A bibliometric analysis of 30 years of platform research: developing the research agenda for platforms, the associated technologies and social impacts. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 169:120827. doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2021.120827
Majeed, A., Khan, M. B., Dawood, A., Ul-Allah, S., and Hussain, M. (2023). Phosphorus application improved fodder yield, phosphorus use efficiency and economic returns of different pearl millet genotypes. Soil Environ. 42, 236–246. doi: 10.25252/se/2023/243172
Montazeri, A., Mohammadi, S., Hesari, P. M., Ghaemi, M., Riazi, H., and Sheikhi-Mobarakeh, Z. (2023). Preliminary guideline for reporting bibliometric reviews of the biomedical literature (BIBLIO): a minimum requirements. Syst. Rev. 12:239. doi: 10.1186/s13643-023-02410-2
Murphy, J., and Riley, J. P. (1962). A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 27, 31–36. doi: 10.1016/S0003-2670(00)88444-5
Nautiyal, C. S. (1999). An efficient microbiological growth medium for screening phosphate solubilizing microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 170, 265–270. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1999.tb13383.x
Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., et al. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 10:89. doi: 10.1186/s13643-021-01626-4
Pan, B. G., Zhang, F. T., Zhu, X. Q., Huang, L., Wu, Y., Tang, J. Q., et al. (2024). Global trends and hotspots evolution in soil microplastic pollution research: A bibliometric analysis based on the web of science. Ecol. Indic. 161:111974. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2024.111974
Phour, M., and Sindhu, S. S. (2023). Soil salinity and climate change: microbiome-based strategies for mitigation of salt stress to sustainable agriculture. Climate Change Microbiome Dynamics 12, 191–243. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-21079-2_13
Pikovskaya, R. I. (1948). Mobilization of phosphorus in soil in connection with the vital activity of some microbial species: Environmental Science, Biology. Moscow, Russia: Mikrobiologiya, 17, 362–370.
Qin, S., Zhang, H., He, Y., Chen, Z., Yao, L., and Han, H. (2023). Improving radish phosphorus utilization efficiency and inhibiting cd and Pb uptake by using heavy metal-immobilizing and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 868:161685. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.161685
Raghothama, K. G., and Karthikeyan, A. S. (2005). Phosphate acquisition. Plant Soil 274, 37–49. doi: 10.1007/s11104-004-2005-6
Rajwar, J., Chandra, R., Suyal, D. C., Tomer, S., Kumar, S., and Goel, R. (2018). Comparative phosphate solubilizing efficiency of psychrotolerant Pseudomonas jesenii MP1 and Acinetobacter sp. ST02 against chickpea for sustainable hill agriculture. Biologia 73, 793–802. doi: 10.2478/s11756-018-0089-3
Rawat, P., Das, S., Shankhdhar, D., and Shankhdhar, S. C. (2021). Phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms: mechanism and their role in phosphate Solubilization and uptake. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 21, 49–68. doi: 10.1007/s42729-020-00342-7
Richardson, A. E., Barea, J.-M., McNeill, A. M., and Prigent-Combaret, C. (2009). Acquisition of phosphorus and nitrogen in the rhizosphere and plant growth promotion by microorganisms. Plant Soil 321, 305–339. doi: 10.1007/s11104-009-9895-2
Richardson, A. E., and Simpson, R. J. (2011). Soil microorganisms mediating phosphorus availability update on microbial phosphorus. Plant Physiol. 156, 989–996. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.175448
Rodríguez, H., and Fraga, R. (1999). Phosphate solubilizing bacteria and their role in plant growth promotion. Biotechnol. Adv. 17, 319–339. doi: 10.1016/S0734-9750(99)00014-2
Sabe, M., Pillinger, T., Kaiser, S., Chen, C., Taipale, H., Tanskanen, A., et al. (2022). Half a century of research on antipsychotics and schizophrenia: A scientometric study of hotspots, nodes, bursts, and trends. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 136:104608. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2022.104608
Schwyn, B., and Neilands, J. B. (1987). Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal. Biochem. 160, 47–56. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90612-9
Sharma, S. N. (2003). Effect of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria on efficiency of Mussoorie rockphosphate in rice-wheat cropping system. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 73, 478–481.
Sharma, S. B., Sayyed, R. Z., Trivedi, M. H., and Gobi, T. A. (2013). Phosphate solubilizing microbes: sustainable approach for managing phosphorus deficiency in agricultural soils. Springerplus 2:587. doi: 10.1186/2193-1801-2-587
Silva, L. I. D., Pereira, M. C., Carvalho, A. M. X. D., Buttrós, V. H., Pasqual, M., and Dória, J. (2023). Phosphorus-solubilizing microorganisms: A key to sustainable agriculture. Agriculture 13:462. doi: 10.3390/agriculture13020462
Sun, J., Lu, X., Chen, G., Luo, N., Zhang, Q., and Li, X. (2023). Biochar promotes soil aggregate stability and associated organic carbon sequestration and regulates microbial community structures in Mollisols from Northeast China. Soil 9, 261–275. doi: 10.5194/soil-9-261-2023
Syers, J. K., Johnston, A. E., and Curtin, D. (2008). “Efficiency of soil and fertilizer phosphorus use. Reconciling changing concepts of soil phosphorus behaviour with agronomic information,” in FAO Fertilizer and Plant Nutrition Bulletin 18. Rome: Food Agricultural Organization of the United Nations.
Toro, M., Azcon, R., and Barea, J. M. (1997). Improvement of arbuscular mycorrhiza development by inoculation of soil with phosphate-solubilizing rhizobacteria to improve rock phosphate bioavailability (P-32) and nutrient cycling. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63, 4408–4412. doi: 10.1128/aem.63.11.4408-4412.1997
Van Raan, A. F. J. (1997). Scientometrics: state-of-the-art. Scientometrics 38, 205–218. doi: 10.1007/BF02461131
Vance, C. P., Uhde-Stone, C., and Allan, D. L. (2003). Phosphorus acquisition and use: critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource. New Phytol. 157, 423–447. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00695.x
Vassilev, N., Martos, E., Mendes, G., Martos, V., and Vassileva, M. (2013). Biochar of animal origin: a sustainable solution to the global problem of high-grade rock phosphate scarcity? J. Sci. Food Agric. 93, 1799–1804. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.6130
Verma, M., Mishra, J., and Arora, N. K. (2019). Plant growth-promoting Rhizobacteria: diversity and applications. Environ. Biotechnol. 6, 129–173. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-7284-0_6
Wang, C., Deng, L., Zhang, Y., Zhao, M., Liang, M., Lee, L.-C., et al. (2024). Farmland phytoremediation in bibliometric analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 351:119971. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.119971
Wang, Z., Zheng, Y., Peng, J., Zhou, F., Yu, J., Chi, R., et al. (2023). Mechanisms of combined bioremediation by phosphate-solubilizing fungus and plants and its effects on cadmium contamination in phosphate-mining wastelands. J. Environ. Manag. 346:118983. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.118983
Xiao, C., Guo, S., Wang, Q., and Chi, R. (2021). Enhanced reduction of lead bioavailability in phosphate mining wasteland soil by a phosphate-solubilizing strain of Pseudomonas sp., LA, coupled with ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) and sonchus (Sonchus oleraceus L.). Environ. Pollut. 274:116572. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116572
Yadav, A. N. (2022). Potassium-solubilizing microorganisms for agricultural sustainability. Journal of applied biology & amp. Biotechnology, 1–4. doi: 10.7324/jabb.2022.105ed
Yadav, A., and Yadav, K. (2024). Challenges and opportunities in biofertilizer commercialization. SVOA Microbiol. 5, 01–14. doi: 10.58624/SVOAMB.2024.05.037
Zaidi, A., Khan, M. S., Ahemad, M., and Oves, M. (2009). Plant growth promotion by phosphate solubilizing bacteria. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 56, 263–284. doi: 10.1556/AMicr.56.2009.3.6
Keywords: phosphorus availability, ecological restoration, crop growth, global research trends, sustainable agriculture, microbial soil nutrients
Citation: Lei Y, Kuai Y, Guo M, Zhang H, Yuan Y and Hong H (2025) Phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms for soil health and ecosystem sustainability: a forty-year scientometric analysis (1984–2024). Front. Microbiol. 16:1546852. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1546852
Received: 17 December 2024; Accepted: 03 February 2025;
Published: 19 February 2025.
Edited by:
Maqshoof Ahmad, The Islamia University of Bahawalpur, PakistanReviewed by:
Sumera Yasmin, National Institute for Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering, PakistanCopyright © 2025 Lei, Kuai, Guo, Zhang, Yuan and Hong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yuan Yuan, eXVhbjk0MEAxNjMuY29t; Hualong Hong, aG9uZ2hsQHhtdS5lZHUuY24=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.