
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Microbiol., 26 February 2025
Sec. Antimicrobials, Resistance and Chemotherapy
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1543509
This article is part of the Research TopicOpportunistic pathogens: pathogenesis and multi-drug resistance mechanismsView all 10 articles
Carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa (CRPA) has become a serious global health concern due to the limited treatment options. The primary resistance mechanism in CRPA involves the production of metallo-β-lactamases (MBLs), making MBL-producing P. aeruginosa a significant component of CRPA cases. To understand the prevalence of CRPA in hospitals in northern China, we conducted a preliminary screening and identification of CRPA in 143 clinical isolates of P. aeruginosa collected from various departments of a tertiary hospital between 2021 and 2023, analyzing CRPA resistance trends in certain regions of northern China during this period. We identified 71 CRPA isolates that exhibited high carbapenem resistance and phylogenetic tree analysis revealed that ST244 CRPA isolates had widely spread across various departments of the same hospital over three consecutive years. We also identified two VIM-producing isolates, PJK40 and PJK43, both of which carried the same novel VIM-type metallo-β-lactamase, VIM-92, encoded by a newly identified gene, blaVIM-92, closely related to blaVIM-24. blaVIM-92 was embedded in class 1 integrons within the Tn1403 transposon. The blaVIM-92-carrying plasmid, pPJK40, was found to resemble the pJB37 megaplasmid. The expression of VIM-92 and VIM-24 in DH5α and PAO1 revealed similar effects of the MICs of β-lactams, except for aztreonam. The high prevalence of CRPA in clinical settings, and the identification of VIM-92, highlights the urgent need for ongoing surveillance of CRPA and emerging MBL variants in P. aeruginosa.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) is a Gram-negative, opportunistic pathogen commonly associated with hospital-acquired infections, especially in immunocompromised patients and individuals with cystic fibrosis (Qin et al., 2022). Carbapenem antibiotics are often the first-line treatment for P. aeruginosa infections due to their broad antibacterial spectrum, potent activity, and rapid onset (Takahashi et al., 2021). However, the global CRPA increase has become a significant health concern. P. aeruginosa can acquire resistance to carbapenem through various mechanisms, producing carbapenemase enzymes encoded by carbapenemase genes as a primary resistance pathway (Tenover et al., 2022). To date, class A, B, and D carbapenemases have been identified in P. aeruginosa, with class B metallo-β-lactamase (MBL) enzymes, such as Verona Integron-encoded Metallo-β-lactamase (VIM), imipenemases (IMP), and New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase (NDM), being the most prevalent (Park and Koo, 2022). MBLs can hydrolyze most β-lactams, except monobactams, but remain unaffected by novel β-lactamase inhibitors such as avibactam, vaborbactam, relebactam, and nacubactam (Jean et al., 2019). Consequently, therapeutic options for infections caused by MBL-producing P. aeruginosa are substantially limited. In addition, bacterial secretion systems played a significant role in the infection and pathogenesis of CRPA. The virulence of CRPA was closely associated with its encoded secretion systems, including type I to type VI secretion systems (Wood et al., 2015). Among these, the type III secretion system (T3SS) was the most complex and virulent secretion system in CRPA, primarily involving four virulence factors: exoY, exoT, exoU, and exoS.
The VIM-type enzyme is the most prevalent MBL in Europe, with over 80 variants identified to date (Botelho et al., 2019). According to relevant literature, the detection rate of CRPA in northern China is significantly higher than in other regions, with VIM-type enzymes being more frequently detected than other types of MBLs (Wu et al., 2024). Among these, blaVIM-2 is the most frequently reported carbapenemase-encoding gene in P. aeruginosa spp. In recent years, isolates carrying novel VIM-type alleles have continuously been identified. According to recent literature, blaVIM-84, a novel VIM-type MBLs, was first reported in the IncP-2 megaplasmid of P. aeruginosa (Wang et al., 2023). This indicates the potential for the transfer and spread of blaVIM-84 in Pseudomonas species. In another study, researchers characterized a Pseudomonas monteilii (P. monteilii) isolate carrying blaVIM-84 for the first time, which conferring resistance to β-lactams (Tu et al., 2024). Genome analysis revealed that blaVIM-84 was located within a class I integron, with Tn3 surrounding. This structure suggested potential for dissemination. MBL-encoding genes are typically integrated within class I integrons and are transmitted via mobile genetic elements, which commonly embed blaVIM genes into genetic cassettes, facilitating their widespread dissemination (Zhang et al., 2023).
Zhangjiakou, in China, the location of this study, occupies a unique geographic position at the intersection of Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, and Inner Mongolia, which can contribute to different sources of infection and epidemiological patterns. The First Affiliated Hospital of Hebei North University, a tertiary hospital in Zhangjiakou, serves as a central healthcare facility, providing critical data to understand antimicrobial resistance trends in northern China. These data support regional and interregional public health collaborations and comparative studies on P. aeruginosa resistance. For this study, we collected 143 P. aeruginosa isolates from clinical specimens submitted by various departments at our hospital between January 1, 2021, and December 31, 2023. Following culture, identification, and antimicrobial susceptibility testing, we analyzed the transmission dynamics within the hospital and resistance patterns of CRPA. After excluding duplicate isolates from the same patient and sample size, we identified 71 CRPA isolates. Among these, two were VIM-producing P. aeruginosa, PJK40 and PJK43. Whole-genome sequencing revealed that the genetic sequences of these two isolates were identical, and both of them carried a new variant of VIM-2, VIM-92, with the difference of isolation sources. Therefore, to avoid redundancy, we selected PJK40, strained from lavage fluid, further analyzed the genetic characterization of this isolate, and evaluated the effect of VIM-92 on antibiotic resistance.
Clinical isolates of P. aeruginosa were obtained from patient samples at the First Affiliated Hospital of Hebei North University using selective Pseudomonas Isolation Agar plates. And then identification was confirmed using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry (Bruker Daltonik GmbH, Bremen, Germany). Data on 143 P. aeruginosa isolates, including the year of detection, department, and source of the isolates, were retrieved from the hospital’s electronic medical records.
The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of antibiotics were determined using the broth microdilution method. The antibiotics tested included Meropenem (Hanhui Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., China), Imipenem (Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., USA), Cefepime (Jiangsu Hengrui Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., China), Piperacillin (Suzhou Erye Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., China), Ceftazidime (Guangdong Jincheng Jinsu Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., China), Tazobactam (Meilunbio, China), Avibactam (MedChemExpress, USA), Aztreonam (Sigma-Aldrich, USA), Ciprofloxacin (Fluka Analytical, USA), Amikacin (Meilunbio, China), and Colistin (Sigma-Aldrich, USA). P. aeruginosa isolate ATCC 27853 and Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 700603 were used as quality control isolates. The diluted cultures were incubated overnight at 37°C, and results were interpreted according to the CLSI performance standards (30th Edition) (Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, 2020). According to the CLSI standards, CRPA were defined as P. aeruginosa exhibiting resistance to any carbapenem, including imipenem and meropenem. In this study, isolates with a MIC ≥128 were classified as highly resistant isolates (Park and Koo, 2022). The VIM alleles were identified by PCR amplification of the full ORF, using primer pairs VIM-F (5′-tgccgtagaagaacagcaag-3′) and VIM-R (5′-gcaacttcatgttatgccgc-3′). The PCR products were sequenced using Sanger sequencing.
All 71 CRPA isolates were subjected to second-generation sequencing on the Illumina HiSeq platform. Genomic DNA was extracted using the QIAamp DNA Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Sequencing was performed on the Illumina HiSeq platform, and raw reads were assembled using Shovill 0.9.0.1 Additionally, two VIM-producing isolates were selected for third-generation sequencing. For these isolates, hybrid assembly that combined Illumina and Nanopore reads was conducted with Unicycler v.0.4.8 (Wick et al., 2017). Multilocus sequence typing (MLST) was determined through PubMLST,2 and gene annotation was performed with Prokka v.1.14.6 (Seemann, 2014). ABRicate v.1.0.03 was used for the identification of resistance genes and virulence factors, while sequence alignment against the plasmid was performed using BWA-MEM (Li, 2014). Genetic sequence comparisons and visualizations were generated using Easyfig 2.2.5 and BRIG-0.95 (Alikhan et al., 2011; Sullivan et al., 2011). Based on the annotation results from Prokka, the genomic data of 71 CRPA isolates were selected for pan-genome analysis using Roary v.3.13.0 (Page et al., 2015). Phylogenetic tree construction was conducted with FastTree v.2.1.11 (Price et al., 2009) using default parameters, and the tree was visualized and annotated with features using ChiPlot (Xie et al., 2023).
Conjugation experiments were conducted using clinical isolates as donors and a rifampin-resistant derivative of P. aeruginosa PAO1 as the recipient. The selection was performed with rifampicin (300 μg/mL) and ceftazidime-avibactam (16 μg/mL). The donor and recipient bacterial colonies were cultured in 2 mL of Luria-Bertani (LB) medium and shaken at 37°C for 4 h. The isolates were mixed in LB medium in a 1:1 ratio (100 μL each). A 20 μL aliquot of the mixture was placed on a sterile 0.22-μm pore-size Millipore filter of 0.22-m size on a Mueller-Hinton (MH) agar plate and cocultured at 37°C overnight. The bacterial lawn formed on the filter was harvested, resuspended in 200 μL of LB broth, and seeded on agar containing selective antibiotics. After overnight incubation at 37°C, colonies that grew in the selective plates were confirmed by PCR amplification.
Plasmid pGK1900 was designed to express MBL genes. In brief, the oriT and traJ region from plasmid pCasPA (Chen et al., 2018), and the GmR region from plasmid pEX18Gm (Hoang et al., 1998), were amplified and recombined into the broad-host-range plasmid pACRISPR (Chen et al., 2018), which carries the pRO1600 oriV and T7 promoter. The final plasmid, pGK1900, was constructed.
The blaVIM-92 gene, along with its upstream predicted promoter (identified using Softberry),4 was amplified from the clinical isolate PJK40 and cloned into pGK1900 using the Hieff Clone Plus One Step Cloning Kit (Li et al., 2022). The resulting VIM-expressing plasmids were introduced into Escherichia coli DH5α via chemical transformation and into P. aeruginosa PAO1 by electroporation.
SPSS 20.0 and WHONET v5.6 software (WHO Collaborating Centre for Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance, Boston, MA, USA) were used to analyze the data. The counting data were expressed as the number of cases (n) and rate (%).
Between 2021 and 2023, 143 P. aeruginosa isolates were detected, of which 71 were identified as CRPA, excluding duplicate isolates from the same patient, resulting in a CRPA detection rate of 49.65%. Statistical analysis indicated a significant downward trend in the CRPA detection rate over the 3 years (Z = 1.850, p = 0.0174) (Supplementary Table S1). These 71 CRPA isolates were distributed between various departments, with the highest proportion of other departments (20 isolates, 28.17%), followed by the Respiratory Department (18 isolates, 25.35%) and the International Medical Department (14 isolates, 19.72%) (Supplementary Table S2). And the primary source of CRPA specimens was sputum, accounting for 55 isolates (77.46%), followed by lavage fluid and other sources, each with five isolates (7.04%) (Supplementary Table S3).
The CRPA isolates exhibited high resistance rates to carbapenems, with imipenem (98.59%) and meropenem (78.87%). Resistance to most cephalosporins (ceftazidime, cefepime), β-lactams (aztreonam), enzyme inhibitor complexes (piperacillin/tazobactam, ceftazidime/avibactam) and quinolones (ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin) exceeded 49%, indicating a multidrug-resistant profile. In contrast, the isolates remained relatively susceptible to amikacin and polymyxins, with resistance rates below 34%, suggesting that these agents may still be effective treatment options. During the 3-year period, the resistance rate to piperacillin-tazobactam initially declined but then increased (p < 0.05), while resistance to ceftazidime-avibactam, aztreonam, imipenem, ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, and amikacin showed a decreasing trend (p < 0.05). No statistically significant differences were observed in resistance rates to ceftazidime, cefepime, meropenem, and colistin (Table 1). MICs for 71 CRPA isolates are provided in Supplementary Table S4.
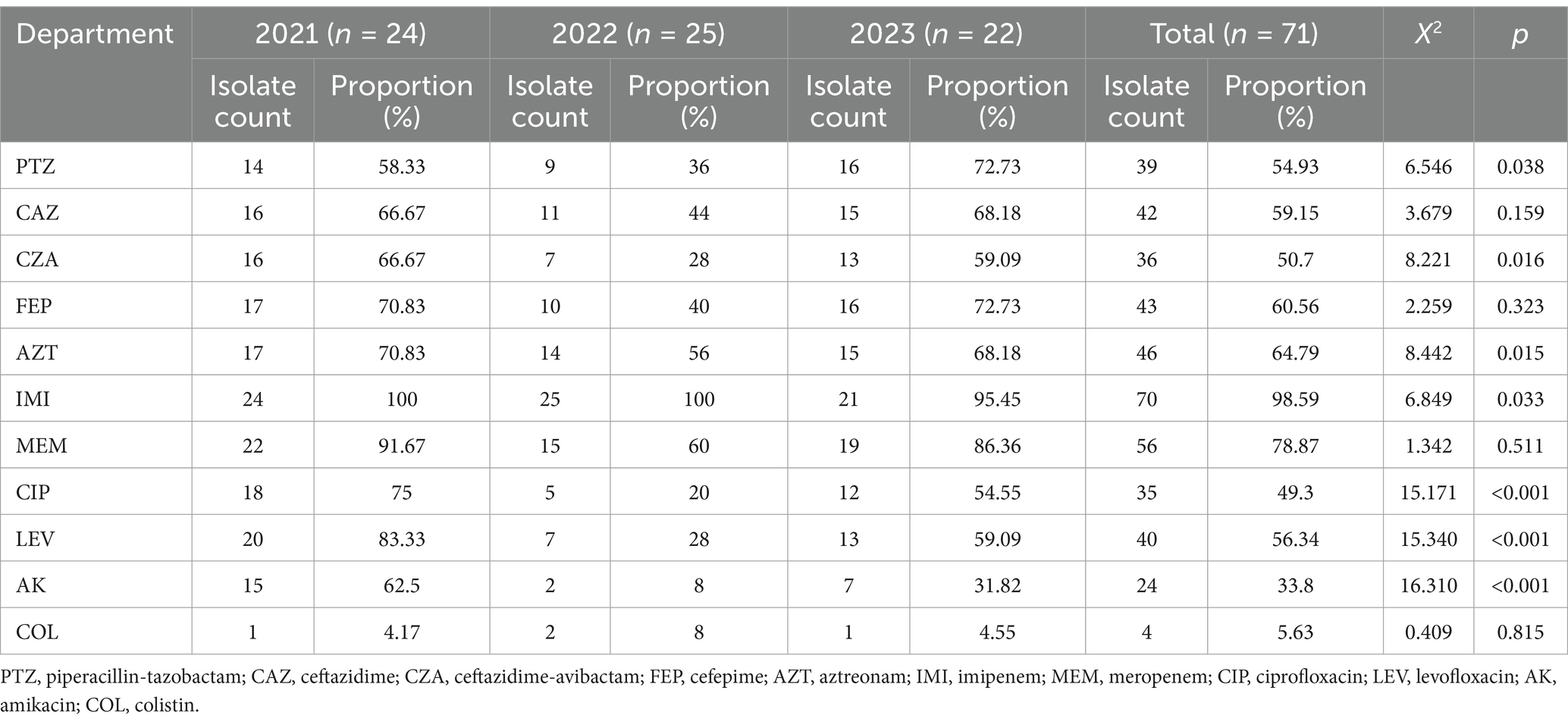
Table 1. Changes in drug resistance rates of CRPA isolates to commonly used antibiotics from 2021 to 2023.
To further understand the relationships between the 71 CRPA isolates, we constructed a phylogenetic tree based on the nucleotide composition of core genes (Figure 1). MLST is a an unambiguous, portable and nucleotide-based technique for typing bacteria using the sequences of internal fragments of (usually) seven house-keeping genes (Maiden et al., 1998; Spratt, 1999; Urwin and Maiden, 2003). Among the 71 CRPA isolates, 32 sequence types (STs) were identified, with the predominant types being ST244, ST2651, and ST3134, accounting for 29.6% (21/71), 11.3% (8/71), and 7.0% (5/71), respectively. The analysis of STs among the 71 CRPA isolates over 3 years (2021–2023) revealed distinct trends. In 2021, ST244 was the predominant type, accounting for the majority of isolates (24 isolates). In 2022, both ST3134 and ST2651 were the most prevalent types, each represented by 5 isolates. By 2023, ST244 re-emerged as the dominant type, once again constituting the largest proportion of isolates. Notably, ST1278 was prevalent in the first 2 years but disappeared in 2023. Meanwhile, ST60, ST471, and ST2651 began to emerge as significant types starting from 2022. Combined analysis of the ST types, departmental distribution, and isolation years of the 71 CRPA isolates revealed that ST244 CRPA was consistently detected across different departments of the same hospital over a three-year period. In addition, T3SS virulence factor analysis showed that the virulence factor exoT had the highest carriage rate at 100% (71/71), followed by exoS and exoY, both at 90.1% (64/71), while exoU had the lowest carriage rate at 11.3% (8/71). Notably, isolate PJK15 carried all four T3SS virulence factors, which may contribute to its high virulence potential (Supplementary Figure S2).

Figure 1. The phylogenetic tree based on the concatenated set of core genes displays the evolutionary relationships among the 71 CRPA isolates. The primary features of CRPA isolates are indicated in various colors, and the presence of T3SS virulence factors and resistance genes is represented by orange.
We predicted resistance genes in the 71 CRPA isolates and identified a total of 54 resistance genes. Among these, four carbapenemase-producing isolates, PJK2, BFP34, PJK40, and PJK43, were detected, carrying the resistance genes blaAFM, blaKPC, and blaVIM. Isolate PJK2 carried the highest number of resistance genes, with a total of 23. The distribution of shared and unique resistance genes is shown in the Supplementary Figure S1.
Bioinformatic analysis of the 71 CRPA isolates revealed mutations in the VIM alleles in two isolates. These two VIM-producing P. aeruginosa isolates were identified as PJK40 and PJK43. Sequence analysis revealed that the VIM gene sequences of the two isolates were identical, with the difference of isolation sources. Therefore, PJK40 was selected for further analysis to avoid redundancy. PJK40, carried a novel VIM allele and was isolated from a patient’s bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. Genome sequencing classified PJK40 as sequence type (ST) 207. PCR and sequencing revealed this isolate harbors a novel allele, blaVIM-92 (GenBank accession: PQ563311). In the amino acid sequence, VIM-24 has an arginine-to-leucine substitution at residue 205 (GenBank accession: HM855205.1), while VIM-92 shows a valine-to-isoleucine substitution at residue 236 (Supplementary Figure S3).
To better understand the role blaVIM-92 in conferring β-lactam resistance, blaVIM-92 was cloned in the plasmid pGK1900 and transformed into E. coli DH5α and P. aeruginosa PAO1. The effects VIM-92 on β-lactam resistance to β-lactam differed between DH5α and PAO1 (Table 2).
In DH5α, VIM-92 increased the MICs of meropenem, imipenem, piperacillin, cefepime, ceftazidime, piperacillin-tazobactam, and ceftazidime-avibactam by more than 8 times. In PAO1, the MICs of all β-lactams, except for aztreonam, increased by more than 16-fold due to the presence of VIM-92. This is expected, as VIM-92 is an MBL that does not hydrolyze aztreonam. We subsequently cloned blaVIM-24 using the same method. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing revealed minimal differences in antibiotic resistance effects between VIM-24 and VIM-92.
Whole-genome sequencing of PJK40 revealed multiple acquired resistance genes, with blaVIM-92 embedded in the plasmid pPJK40. The pPJK40 plasmid showed query coverage of 82, 81, and 79% with pJB37 (GenBank accession: KY494864.1), pWTJH36 (GenBank accession: CP104591.1), and pPUV-16 (GenBank accession: MT732194.1), respectively (Figure 2). The backbones of these homologous plasmids were similar to those of the IncP-2 plasmid pOZ176, suggesting that they belong to the same megaplasmid family (Zhang et al., 2021). The complete sequence of pPJK40 is 467,425 bp, contains 583 ORFs, and exhibits a GC content of 57%. This plasmid contains a few resistance genes organized into a gene cluster, approximately 144 to 159 kbp, which includes the blaVIM-92 gene. The differences between pPJK40, pJB37, pWTJH36, and pPUV-16 are mainly due to the presence of insertion sequences (ISs) or integrase-encoding genes, indicating that these plasmids have evolved through multiple insertions and recombination events.
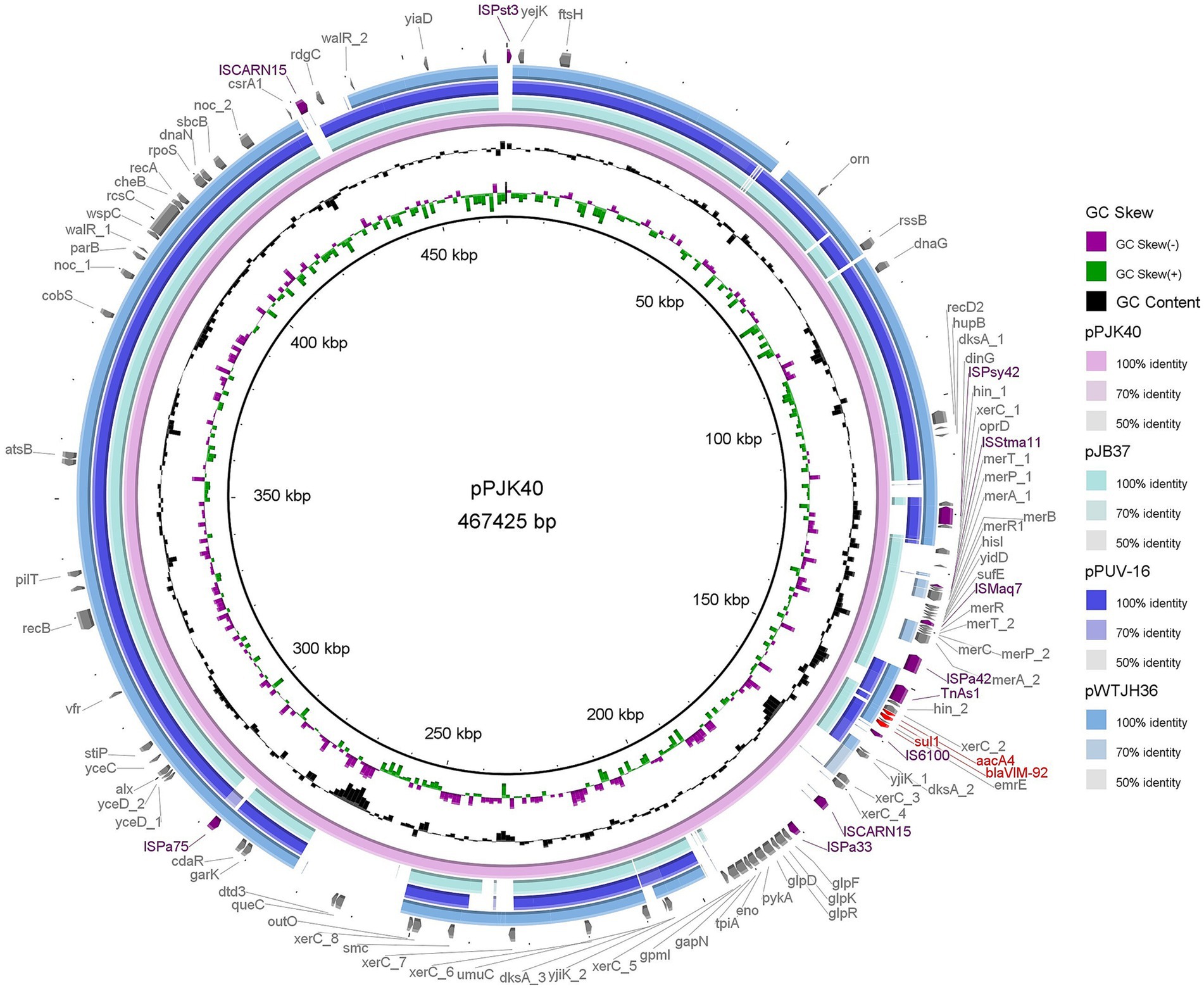
Figure 2. Comparison of pPJK40 with other plasmids. The rings represent the alignment of sequence reads from pJB37, pPUV-16, and pWTJH36 against pPJK40. Both pJB37 and pPUV-16 contain blaVIM-2, while pWTJH36 contains blaVIM-85.
Among the homologous plasmids identified in the NCBI database, pPJK40 shows the highest similarity to pJB37, the first blaVIM-2-carrying megaplasmid described in P. aeruginosa (Botelho et al., 2017). pPJK40 shares 81% query coverage and 99.97% sequence identity with pJB37, according to the BLAST analysis (Figure 3). Several conserved regions were observed between the two plasmids, reflecting a high degree of sequence similarity. The resistance gene cluster in pPJK40 spans 11,365 bp and contains multiple genetic elements and resistance genes, including blaVIM-92. The strong sequence similarity between this region and the corresponding cluster on pJB37 suggests that these plasmids share similar structural features that support the preservation and transmission of resistance genes. In particular, the insertion sequence downstream of blaVIM-92 may enhance its mobility, facilitating the spread of resistance genes across bacterial species (Figure 3).
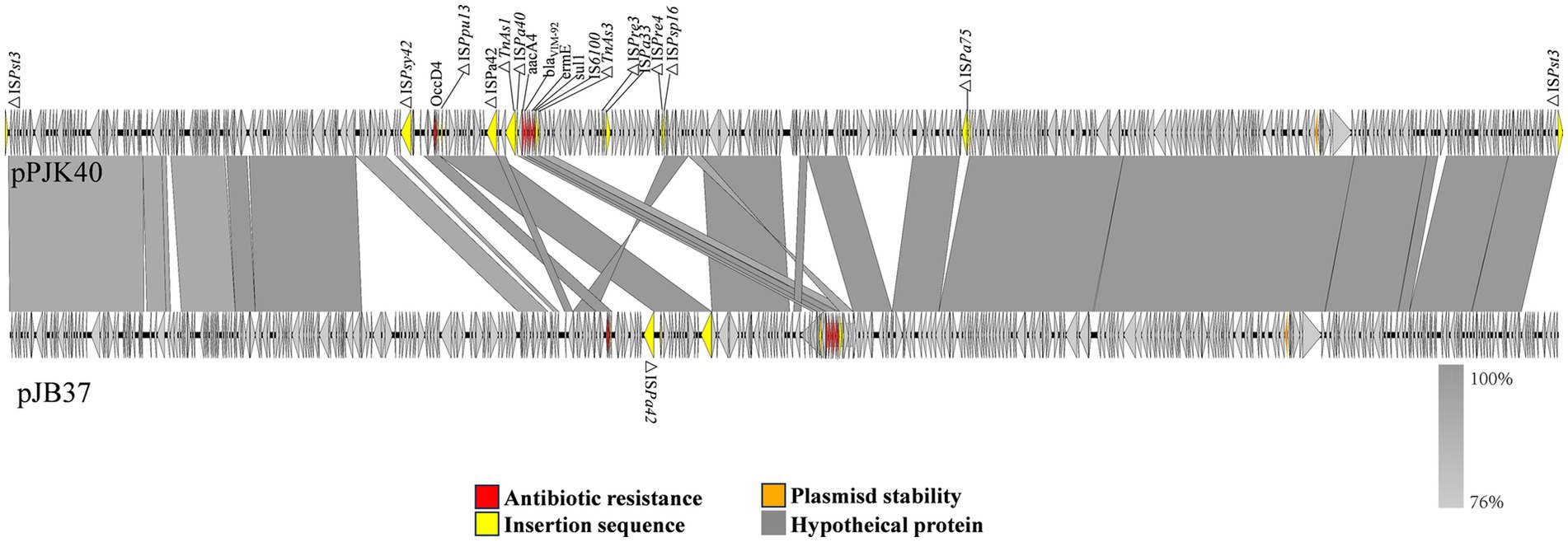
Figure 3. Comparison of pPJK40 and pJB37. The arrow direction indicates the transcription direction of each ORF. The dark yellow arrows represent mobile elements, the red arrows represent resistance genes, and the gray and blue arrows represent predicted ORFs.
Conjugation assays were conducted to assess the transferability of pPJK40. All three experiments were unsuccessful, suggesting that this plasmid is non-conjugative.
Numerous VIM alleles have been reported in P. aeruginosa (Pournaras et al., 2003; Siarkou et al., 2009). In a previous report, sequencing revealed that both blaVIM-84 (GenBank accession: ON688661.1) and blaVIM-85 (GenBank accession: ON688662.1) had a length of 801 bp and they were highly similar to blaVIM-24 (GenBank accession: HM855205), with nucleotide identities of 99.88 and 99.75%, respectively (Wang et al., 2023). In this study, according to BLASTn search, blaVIM-92 was highly similar to blaVIM-84 and blaVIM-85, with a nucleotide identity of 99.63 and 99.5%, respectively. Therefore, we selected the plasmids pWTJH2 (GenBank accession: CP104585.1), pWTJH6 (GenBank accession: CP104587.1), and pPJK40 to compare the genetic backgrounds of the VIM alleles in P. aeruginosa (Figure 4).
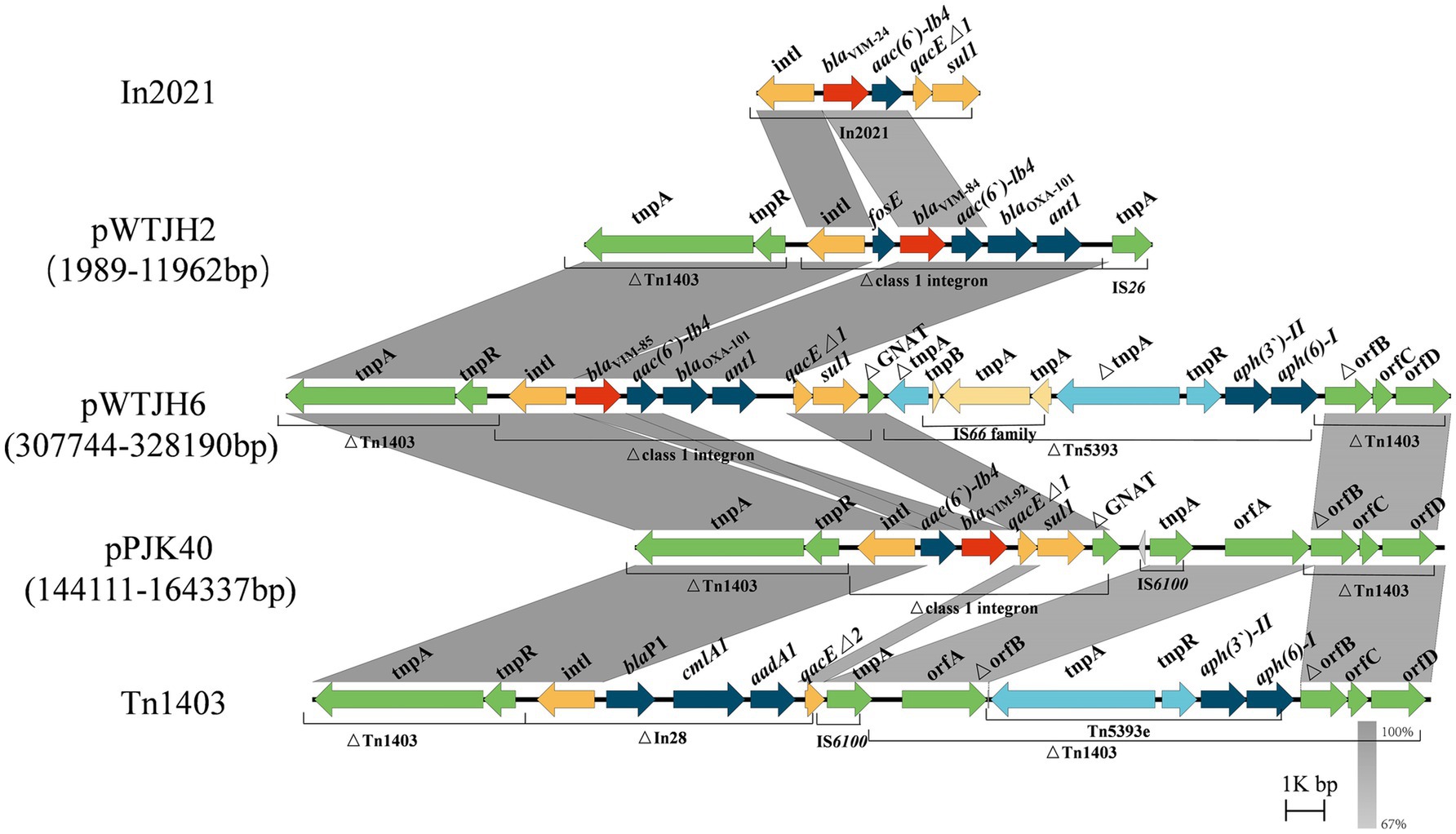
Figure 4. Comparison of the genetic environments of blaVIM. Shaded regions indicate nucleotide identity (67–100%). Red arrows represent blaVIM and other antibiotic resistance genes, shown in dark blue. The yellow, green, and light blue arrows represent structures of mobile elements.
In plasmids pWTJH2 and pWTJH6, the blaVIM-84 and blaVIM-85 genes are embedded within class 1 integrons. Similarly, in the plasmid pPJK40, the blaVIM-92 gene is also embedded in a class 1 integron. The blaVIM-84 gene is the second cassette in a class 1 integron, with the fosE gene located upstream. The downstream cassettes include aac(6′)-Ib4, blaOXA-101, and ant1 within an integron that originally carried blaVIM-24. In this integron, the qacEΔ1 and sul1 genes in the 3′ conserved segment (3’-CS) were replaced by an IS26 element.
For the blaVIM-85 genetic environment, the 3’-CS is interrupted by a gene encoding GNAT family N-acetyltransferase, clipped by the insertion of transposon Tn5393. A similar genetic structure was observed in blaVIM-92, characterized by the arrangement intI-aac(6′)-Ib4-blaVIM-92-qacEΔ1-sul1. In this configuration, blaVIM-92 is embedded within the second gene cassette of a class 1 integron, with the aac(6′)-Ib4 resistance gene positioned upstream. In particular, the downstream blaOXA-101 and ant1 genes are absent. The integron harboring blaVIM-92 was inserted into transposon Tn1403 (GenBank accession: AF313472.2), which contains a backbone with the genes tnpA, tnpR, and orfABCD, along with a class 1 integron and Tn5393. In Tn5393, the tnpA gene is interrupted by an IS66 family insertion (Stokes et al., 2007).
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is capable of quickly evolving and developing resistance to adapt to environmental conditions, especially in hospital settings. For example, studies have shown that after prolonged exposure in different hospital environments, P. aeruginosa adapts to the host environment, modulating the expression of numerous virulence factors and acquiring or developing mechanisms for antibiotic resistance, including resistance to carbapenems (Cameron et al., 2022). This adaptability is a major factor contributing to the frequent occurrence of hospital-acquired infections. In China, surveillance data from 2021 reported that P. aeruginosa accounted for 7.96% of hospital-acquired infections, highlighting its significant role in clinical settings (Yan et al., 2022). Among these, CRPA has become increasingly prevalent due to the widespread use of antibiotics. CRPA poses a major threat to public health, with its rising detection rates associated with increased morbidity and mortality (Litwin et al., 2020). Furthermore, CRPA exhibits resistance not only to carbapenems but also to multiple classes of antibiotics, severely limiting treatment options (Ning and Yang, 2022). The extensive dissemination of CRPA and its ability to transfer resistance genes to other bacteria underscore the need for effective surveillance and control measures to curb its spread and impact.
In this study, the average annual CRPA detection rate in the First Affiliated Hospital of Hebei North University from 2021 to 2023 was 16.55%, derived by averaging the overall detection rate of 46.95% over 3 years, which was comparable to the national detection rate reported for 2022 (16.6%), but slightly lower than the rate for Hebei Province in the same year (17.4%) (Yu et al., 2022). With the widespread use of antibiotics, the detection rate of P. aeruginosa resistant to multiple antibiotics is increasing yearly (Litwin et al., 2020). Due to the high mortality rate, propensity for cross-infection, and difficulty in treatment, the emergence of CRPA had made infection control in hospitals increasingly difficult. Although the detection rate of CRPA may differ across regions, its higher detection rate in specific areas, especially within local hospital environments, emphasizes the critical need for focused surveillance and control strategies (Huang et al., 2023). This difference in detection rates may be related to factors such as the hospital classification level, patient demographics, regional conditions, and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. In the present work, 71 CRPA isolates mainly came from four key departments: respiratory, the others, international medical department and the ICU. Notably, the department distribution of CRPA is largely consistent with previous reports (Li et al., 2021). Patients in these departments are often critically ill, require prolonged hospital stays, frequently undergo invasive procedures (e.g., tracheal intubation and tracheostomy), leading to Device-associated Hospital-acquired Infections (DA-HAIs) in some patients, and have multiple underlying conditions. Related studies suggested that the incidence of infections in ICU patients might have varied across different geographical regions, hospitals, and even among different ICUs within the same hospital. The types of infections, the profiles of pathogens causing these infections, and their antimicrobial susceptibility patterns also varied depending on the location (Alfouzan et al., 2021). These factors collectively facilitated the spread of CRPA. Long-term use of antibiotics and immunosuppressants compromises immune function, increasing susceptibility to CRPA infection (Rossi et al., 2021; Pettigrew et al., 2019). Many studies showed that inappropriate and irrational use of antibiotics to treat infections led to the emergence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) isolates of common bacterial isolates (Rizzo et al., 2019). This results in prolonged hospital stays, significantly increased morbidity and mortality, and contributes to the spread of CRPA. These findings demonstrate the importance of judicious use of antibiotics following antimicrobial guidelines. When performing invasive procedures on CRPA patients, strict aseptic protocols, improved surface disinfection, timely equipment replacement, and early tube removal are crucial to prevent infection. Subsequently, statistical analysis was conducted on the types of specimens, and it was found that most CRPA isolates were detected in sputum specimens, accounting for 77.46%, which is consistent with reports that CRPA is mainly strained from sputum (Gill et al., 2022). However, as P. aeruginosa is part of normal respiratory flora, it can quickly colonize the respiratory tract as an opportunistic pathogen. Thus, interpreting the results of respiratory cultures requires careful assessment to confirm infection. Previous research (Yan et al., 2022) has linked CRPA strained from sputum to higher long-term mortality, indicating that it may be a potential source of hospital-acquired infections that warrant attention.
In recent years, the detection rate of MBLs has increased significantly, with a broad distribution across bacterial species and geographic regions, making them a focal point of clinical concern (Safavi et al., 2020). MBL genes can reside on integrons, transposons, plasmids, chromosomes, or other genetic elements, and their plasmid-mediated mobility improves transferability, contributing to bacterial resistance. Clinically, carbapenems such as imipenem, meropenem, ertapenem, and doripenem are ineffective against MBLs, except for monobactams (Bush, 2001). Therefore, the presence of MBLs is likely to increase the risk of treatment failure in carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa infections. The increasing prevalence of MBLs highlights their growing significance in hospital-acquired infections, further emphasizing the urgent need for effective surveillance and control strategies to mitigate their public health impact. Among acquired MBL genotypes, blaVIM is the most prevalent, with multiple variants differentiated by gene and translated amino acid sequences. In this study, VIM-producing isolates accounted for 1.40% (2/143) of all isolates, with VIM-92-producing isolates belonging to the sequence type ST207. Although the global prevalence of ST207 may be lower than classic sequence types such as ST235 and ST111, it has been reported in some regions as an MDR isolate carrying carbapenemase genes, such as blaVIM or blaNDM (Gondal et al., 2024). ST244 CRPA was consistently detected in the same hospital over three consecutive years. This observation suggested the dissemination of ST244 isolates producing OXA-101 and PER-1 enzymes within the hospital. In the analysis of T3SS virulence factors, we identified an isolate, PJK15, which carried four virulence factors. Previous studies had generally suggested that exoU and exoS were mutually exclusive due to occupying the same chromosomal locus (Freschi et al., 2019). However, recent studies have revealed that high-risk clones co-carrying the T3SS effector genes exoS and exoU are capable of causing community-acquired infections (CAIs) in non-immunocompromised young individuals, likely due to the enhanced virulence profiles of these isolates (Song et al., 2023). In our study, we hypothesized that the coexistence of these virulence factors in PJK15 was induced by mutations triggered by environmental pressures on the isolate. The simultaneous presence of both virulence factors could potentially influence the severity of the infection and the response to treatment, highlighting the urgent need for further investigation.
We identified two P. aeruginosa isolates, PJK40 and PJK43, carrying the blaVIM-92 gene and selected PJK40 for further study in this research. This isolate exhibited elevated MICs for β-lactams, cephalosporins, and β-lactam combination agents, attributed to acquiring the resistant plasmid pPJK40. The blaVIM-92 gene is located on a pJB37-like megaplasmid of the IncP-2 family. Typically, plasmids acquire resistance genes through mobile elements, allowing their spread within and between bacterial species (Hall et al., 2022). However, the results of our conjugation experiments indicated that pPJK40 was not conjugative, likely due to its specific structural configuration, which includes the blaVIM-92 resistance gene. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing comparing PAO1 MICs expressing blaVIM-92 and blaVIM-24 indicated that blaVIM-92 confers similar or, in some cases, higher resistance to most antibiotics, except for aztreonam. This suggests that VIM-92 may be equally or more effective than VIM-24 in mediating antibiotic resistance.
In conclusion, with its unique geographic location, our study in Zhangjiakou identified 71 CRPA isolates and analyzed CRPA resistance trends in certain regions of northern China from 2021 to 2023. Among the CRPA isolates, two produced the novel metallo-β-lactamase, VIM-92. blaVIM-92 was in a pJB37-like plasmid within a distinct genetic context compared to other VIM alleles in P. aeruginosa. We also identified an isolate carrying four T3SS virulence factors simultaneously. With the continuous emergence of carbapenemase-producing P. aeruginosa, these findings highlight the importance of ongoing surveillance and comparative studies to inform effective antimicrobial stewardship and public health interventions in the northern region.
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/, PQ563311; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/, ON688661.1; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/, HM855205; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/, CP104585.1; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/, CP104587.1; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/, AF313472.2; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/, KY494864.1; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/, CP104591.1; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/, MT732194.1; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/, ON688662.1.
This study was approved for exemption from ethical review by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Hebei North University (Approval Number: K2024334). It involves a retrospective analysis of anonymized clinical data and was conducted in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution. The data were collected from clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa without any direct interaction with human participants. As the study utilized only anonymized data and did not involve any identifiable personal information, ethical approval was not required. All data were handled in compliance with local legislation and institutional requirements to ensure the protection of patient privacy.
LZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. JP: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. YL: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. HC: Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. MH: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Resources, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JT: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was financially supported by the research project “Optimization of Anti-Infective Therapy for Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Based on PK/PD Models and In Vitro Susceptibility Testing” (Grant No. ZF2025275), led by Jianhua Tang from the Department of Pharmacy, The First Hospital of Hebei North University.
We thank the staff from the Department of Infectious Diseases, Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, for their participation in this study.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1543509/full#supplementary-material
1. ^https://github.com/tseemann/shovill
2. ^https://pubmlst.org/organisms/pseudomonas-aeruginosa
Alfouzan, W., Dhar, R., Abdo, N. M., Alali, W. Q., and Rabaan, A. A. (2021). Epidemiology and microbiological profile of common healthcare associated infections among patients in the intensive care unit of a general Hospital in Kuwait: a retrospective observational study. J Epidemiol Glob Health 11, 302–309. doi: 10.2991/jegh.k.210524.001
Alikhan, N.-F., Petty, N. K., Ben Zakour, N. L., and Beatson, S. A. (2011). BLAST ring image generator (BRIG): simple prokaryote genome comparisons. BMC Genomics 12:402. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-402
Botelho, J., Grosso, F., and Peixe, L. (2019). Antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa - mechanisms, epidemiology and evolution. Drug Resist. Updat. 44:100640. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2019.07.002
Botelho, J., Grosso, F., Quinteira, S., Mabrouk, A., and Peixe, L. (2017). The complete nucleotide sequence of an IncP-2 megaplasmid unveils a mosaic architecture comprising a putative novel blaVIM-2-harbouring transposon in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 72, 2225–2229. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkx143
Bush, K. (2001). New beta-lactamases in gram-negative bacteria: diversity and impact on the selection of antimicrobial therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 32, 1085–1089. doi: 10.1086/319610
Cameron, D. R., Pitton, M., Oberhaensli, S., Schlegel, K., Prod'hom, G., Blanc, D. S., et al. (2022). Parallel evolution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa during a prolonged ICU-infection outbreak. Microbiol Spectr 10:e0274322. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02743-22
Chen, W., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y., Pi, Y., Gu, T., Song, L., et al. (2018). CRISPR/Cas9-based genome editing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and cytidine deaminase-Mediated Base editing in Pseudomonas species. iScience 6, 222–231. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2018.07.024
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (2020). Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Available at: https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/standard/CLSI%20M100-2022 (Accessed February 19, 2025).
Freschi, L., Vincent, A. T., Jeukens, J., Emond-Rheault, J.-G., Kukavica-Ibrulj, I., Dupont, M.-J., et al. (2019). The Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pan-genome provides new insights on its population structure, horizontal gene transfer, and pathogenicity. Genome Biol. Evol. 11, 109–120. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evy259
Gill, C. M., and Nicolau, D. P.ERACE-PA Global Study Group (2022). Carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: an assessment of frequency of isolation from ICU versus non-ICU, phenotypic and genotypic profiles in a multinational population of hospitalized patients. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 11:146. doi: 10.1186/s13756-022-01187-8
Gondal, A. J., Choudhry, N., Niaz, A., and Yasmin, N. (2024). Molecular analysis of Carbapenem and aminoglycoside resistance genes in Carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical strains: a challenge for tertiary care hospitals. Antibiotics 13:191. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13020191
Hall, J. P. J., Botelho, J., Cazares, A., and Baltrus, D. A. (2022). What makes a megaplasmid? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 377:20200472. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2020.0472
Hoang, T. T., Karkhoff-Schweizer, R. R., Kutchma, A. J., and Schweizer, H. P. (1998). A broad-host-range Flp-FRT recombination system for site-specific excision of chromosomally-located DNA sequences: application for isolation of unmarked Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants. Gene 212, 77–86. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(98)00130-9
Huang, W., Wei, X., Xu, G., Zhang, X., and Wang, X. (2023). Carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in critically ill children: prevalence, risk factors, and impact on outcome in a large tertiary pediatric hospital of China. Front. Public Health 11:1088262. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1088262
Jean, S. S., Gould, I. M., Lee, W. S., and Hsueh, P. R.International Society of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (ISAC) (2019). New drugs for multidrug-resistant gram-negative organisms: time for stewardship. Drugs 79, 705–714. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-01112-1
Li, H. (2014). Aligning sequence reads, clone sequences and assembly con*gs with BWA-MEM. arXiv: Genomics. doi: 10.6084/M9.FIGSHARE.963153.V1
Li, Z.-J., Wang, K.-W., Liu, B., Zang, F., Zhang, Y., Zhang, W.-H., et al. (2021). The distribution and source of MRDOs infection: a retrospective study in 8 ICUs, 2013-2019. Infect Drug Resist 14, 4983–4991. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S332196
Li, Y., Zhu, Y., Zhou, W., Chen, Z., Moran, R. A., Ke, H., et al. (2022). Alcaligenes faecalis metallo-β-lactamase in extensively drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 28, 880.e1–880.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2021.11.012
Litwin, A., Fedorowicz, O., and Duszynska, W. (2020). Characteristics of microbial factors of healthcare-associated infections including multidrug-resistant pathogens and antibiotic consumption at the university intensive care unit in Poland in the years 2011-2018. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 17:6943. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17196943
Maiden, M. C., Bygraves, J. A., Feil, E., Morelli, G., Russell, J. E., Urwin, R., et al. (1998). Multilocus sequence typing: a portable approach to the identification of clones within populations of pathogenic microorganisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 3140–3145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.6.3140
Ning, W., and Yang, J. (2022). Research hotspots and trends of Pseudomonas aeruginosa drug resistance: a study based on CiteSpace. Microbiol. China 49, 4942–4956. doi: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.220336
Page, A. J., Cummins, C. A., Hunt, M., Wong, V. K., Reuter, S., Holden, M. T. G., et al. (2015). Roary: rapid large-scale prokaryote pan genome analysis. Bioinformatics 31, 3691–3693. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv421
Park, Y., and Koo, S. H. (2022). Epidemiology, molecular characteristics, and virulence factors of Carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from patients with urinary tract infections. Infect Drug Resist 15, 141–151. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S346313
Pettigrew, M. M., Gent, J. F., Kong, Y., Halpin, A. L., Pineles, L., Harris, A. D., et al. (2019). Gastrointestinal microbiota disruption and risk of colonization with Carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in intensive care unit patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 69, 604–613. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciy936
Pournaras, S., Maniati, M., Petinaki, E., Tzouvelekis, L. S., Tsakris, A., Legakis, N. J., et al. (2003). Hospital outbreak of multiple clones of Pseudomonas aeruginosa carrying the unrelated metallo-beta-lactamase gene variants blaVIM-2 and blaVIM-4. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 51, 1409–1414. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkg239
Price, M. N., Dehal, P. S., and Arkin, A. P. (2009). FastTree: computing large minimum evolution trees with profiles instead of a distance matrix. Mol. Biol. Evol. 26, 1641–1650. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msp077
Qin, S., Xiao, W., Zhou, C., Pu, Q., Deng, X., Lan, L., et al. (2022). Pseudomonas aeruginosa: pathogenesis, virulence factors, antibiotic resistance, interaction with host, technology advances and emerging therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 7:199. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01056-1
Rizzo, K., Horwich-Scholefield, S., and Epson, E. (2019). Carbapenem and cephalosporin resistance among Enterobacteriaceae in healthcare-associated infections, California, USA1. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 25, 1389–1393. doi: 10.3201/eid2507.181938
Rossi, E., la, R., Bartell, J. A., Marvig, R. L., Haagensen, J. A. J., Sommer, L. M., et al. (2021). Pseudomonas aeruginosa adaptation and evolution in patients with cystic fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 19, 331–342. doi: 10.1038/s41579-020-00477-5
Safavi, M., Bostanshirin, N., Hajikhani, B., Yaslianifard, S., van Belkum, A., Goudarzi, M., et al. (2020). Global genotype distribution of human clinical isolates of New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae; a systematic review. J Glob Antimicrob Resist 23, 420–429. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2020.10.016
Seemann, T. (2014). Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 30, 2068–2069. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu153
Siarkou, V. I., Vitti, D., Protonotariou, E., Ikonomidis, A., and Sofianou, D. (2009). Molecular epidemiology of outbreak-related pseudomonas aeruginosa strains carrying the novel variant blaVIM-17 metallo-beta-lactamase gene. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 53, 1325–1330. doi: 10.1128/aac.01230-08
Song, Y., Mu, Y., Wong, N.-K., Yue, Z., Li, J., Yuan, M., et al. (2023). Emergence of hypervirulent Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathotypically armed with co-expressed T3SS effectors ExoS and ExoU. hLife 1, 44–56. doi: 10.1016/j.hlife.2023.02.001
Spratt, B. G. (1999). Multilocus sequence typing: molecular typing of bacterial pathogens in an era of rapid DNA sequencing and the internet. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2, 312–316. doi: 10.1016/S1369-5274(99)80054-X
Stokes, H. W., Elbourne, L. D. H., and Hall, R. M. (2007). Tn1403, a multiple-antibiotic resistance transposon made up of three distinct transposons. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51, 1827–1829. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01279-06
Sullivan, M. J., Petty, N. K., and Beatson, S. A. (2011). Easyfig: a genome comparison visualizer. Bioinformatics 27, 1009–1010. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr039
Takahashi, T., Tada, T., Shrestha, S., Hishinuma, T., Sherchan, J. B., Tohya, M., et al. (2021). Molecular characterisation of carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates in Nepal. J Glob Antimicrob Resist 26, 279–284. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2021.07.003
Tenover, F. C., Nicolau, D. P., and Gill, C. M. (2022). Carbapenemase-producing -an emerging challenge. Emerging Microbes Infections 11, 811–814. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2022.2048972
Tu, J., Liu, Y., Xu, W., Dong, X., Zhang, L., Qian, J., et al. (2024). Genome characteristics of an MDR Pseudomonas monteilii carrying a novel VIM-type β-lactamase, blaVIM-84. J Glob Antimicrob Resist 39, 199–201. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2024.09.007
Urwin, R., and Maiden, M. C. J. (2003). Multi-locus sequence typing: a tool for global epidemiology. Trends Microbiol. 11, 479–487. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2003.08.006
Wang, N., Lei, T., Zhu, Y., Li, Y., Cai, H., Zhang, P., et al. (2023). Characterization of two novel VIM-type metallo-β-lactamases, VIM-84 and VIM-85, associated with the spread of IncP-2 megaplasmids in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiol Spectr 11:e0154423. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01544-23
Wick, R. R., Judd, L. M., Gorrie, C. L., and Holt, K. E. (2017). Unicycler: resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Comput. Biol. 13:e1005595. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005595
Wood, S. J., Goldufsky, J. W., Bello, D., Masood, S., and Shafikhani, S. H. (2015). Pseudomonas aeruginosa ExoT induces mitochondrial apoptosis in target host cells in a manner that depends on its GTPase-activating protein (GAP) domain activity*. J. Biol. Chem. 290, 29063–29073. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.689950
Wu, Y., Chen, J., Zhang, G., Li, J., Wang, T., Kang, W., et al. (2024). In-vitro activities of essential antimicrobial agents including aztreonam/avibactam, eravacycline, colistin and other comparators against carbapenem-resistant bacteria with different carbapenemase genes: a multi-Centre study in China, 2021. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 64:107341. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2024.107341
Xie, J., Chen, Y., Cai, G., Cai, R., Hu, Z., and Wang, H. (2023). Tree visualization by one Table (tvBOT): a web application for visualizing, modifying and annotating phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 51, W587–W592. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad359
Yan, M., Zheng, B., Li, Y., and Lv, Y. (2022). Antimicrobial susceptibility trends among gram-negative Bacilli causing bloodstream infections: results from the China antimicrobial resistance surveillance trial (CARST) program, 2011-2020. Infect Drug Resist 15, 2325–2337. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S358788
Yu, Y., Shao, C., Gong, X., Quan, H., Liu, D., Chen, Q., et al. (2022). Antimicrobial resistance surveillance of Tigecycline-resistant strains isolated from herbivores in Northwest China. Microorganisms 10:2432. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10122432
Zhang, X., Wang, L., Li, D., Li, P., Yuan, L., Yang, F., et al. (2021). An IncP-2 plasmid sublineage associated with dissemination of blaIMP-45 among carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Emerg Microbes Infect 10, 442–449. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2021.1894903
Zhang, X., Zhu, Y., Gao, Y., Li, W., Wang, Y., and Li, Y. (2023). Evaluation and analysis of multidrug resistance- and hypervirulence-associated genes in carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains among children in an area of China for five consecutive years. Front. Microbiol. 14:1280012. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1280012
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa , epidemiological investigation, metallo-β-lactamase, VIM-92, plasmid
Citation: Zhao L, Pu J, Liu Y, Cai H, Han M, Yu Y and Tang J (2025) High prevalence of carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and identification of a novel VIM-type metallo-β-lactamase, VIM-92, in clinical isolates from northern China. Front. Microbiol. 16:1543509. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1543509
Received: 11 December 2024; Accepted: 13 February 2025;
Published: 26 February 2025.
Edited by:
Shicheng Chen, Northern Illinois University, United StatesReviewed by:
Mahmuda Yasmin, University of Dhaka, BangladeshCopyright © 2025 Zhao, Pu, Liu, Cai, Han, Yu and Tang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yunsong Yu, eXZ5czExOUB6anUuZWR1LmNu; Jianhua Tang, amh0YW5nMjAwMkB0anUuZWR1LmNu
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.