- 1State Key Laboratory of North China Crop Improvement and Regulation/College of Plant Protection, Hebei Agricultural University, Baoding, China
- 2Key Laboratory of Hebei Province for Plant Physiology and Molecular Pathology, Baoding, China
To clarify the roles of glycoside hydrolase 3 (GH3) family genes in the growth, development, and pathogenicity of Fusarium verticillioides, GH3 family genes were identified in the genome by bioinformatics software, and their expression levels in the infection process of F. verticillioides were analyzed using transcriptome data. The FvGH3-6 gene was knocked out and complemented via genetic transformation to explore the role of F. verticillioides. The results demonstrated that a total of 19 GH3 family genes were identified in the genome of F. verticillioides, which were located on 11 chromosomes, encoding amino acids ranging from 559 to 1,034, with relative molecular weights between 61.20 and 113.97 kDa, and containing 1–6 exons. Transcriptome data indicated that during the infection of maize kernels by F. verticillioides, the expression of nine genes, including FvGH3-6, was upregulated at different stages. Knockout of the FvGH3-6 gene did not impact the mycelial growth rate of F. verticillioides but reduced the sporulation ability. Compared with the wild type, the pathogenicity of FvGH3-6 knockout mutants towards maize grains and stems was weakened. The above results suggest that the glycoside hydrolase gene family participates in the pathogenicity of F. verticillioides, and the FvGH3-6 gene plays a significant role in the conidia production and pathogenicity of F. verticillioides.
1 Introduction
Maize (Zea mays) is China’s top grain and feed crop. With the advancement of science and technology and the improvement of planting technology, maize production has increased significantly. Nevertheless, diseases continue to impair the yield and quality of maize. F. verticillioides has the capability to infiltrate maize via natural apertures and wounds. Seeds harboring F. verticillioides are also apt to trigger systemic infections within maize, thereby giving rise to a variety of maize diseases, notably ear rot and stem rot (Blacutt et al., 2018). In recent years, relevant research has shown that F. verticillioides spreads widely. The maize ear rot disease caused by this pathogen has now surfaced in multiple countries, such as South Africa, Mexico, Brazil, Canada, Germany, and India (Logrieco et al., 2021; Van et al., 2007). In China, it predominantly appears in key maize-producing areas such as Northeast, North China, and the Huang-Huai-Hai regions (Sun et al., 2017; Logrieco et al., 2021). Diseases induced by F. verticillioides, including maize ear rot and stalk rot, demand attention due to their substantial influence on maize yield (Hurni et al., 2015; Mei et al., 2023; Njeru et al., 2023). At the onset of maize ear rot, white mycelium emerges at the ear’s apex. In severe scenarios, it may trigger ear abscission and result in a 30–50% decline in maize yield, or even total crop failure (Yu et al., 2017). Based on Munkvold and Carlton (1997) research, if maize in the field is infected by F. verticillioides, 80% of the seeds will ultimately be, 80% of the seeds will ultimately be contaminated. Maize diseases induced by F. verticillioides present substantial threats. These diseases not only diminish maize yield but also yield toxic secondary metabolites—fumonisins, which pose a grave peril to the well-being of humans and animals and the security of food and feed (Pienaar et al., 1981). Corn ear rot frequently manifests itself during the late growth phase, and the execution of pesticidal control protocols proves to be considerably arduous. In the wake of the proliferation of mechanized maize harvesting, the mechanical excision of diseased ears becomes challenging, frequently culminating in a commingled harvest with healthy ears, thereby impacting the storage quality and market value of maize (Guo et al., 2023). Meanwhile, F. verticillioides is capable of instigating stalk rot in maize, leading to the degeneration of both stalks and leaves. In severe scenarios, lodging is prone to transpire, which erects impediments to mechanized harvesting and incurs significant economic losses in agricultural production (Ding et al., 2023; Marin et al., 2013). Consequently, it is of utmost urgency to undertake a profound exploration of the pathogenic mechanism of F. verticillioides and identify the pivotal pathogenic genes so as to establish a theoretical underpinning for the scientific and effective prevention and control of maize diseases.
The glycoside hydrolase (GH) family represents a crucial class of enzymes in vivo, playing a significant role in the hydrolysis of diverse glycosidic bonds. Among them, the GH3 family is predominantly composed of β-glucosidase (β-D-Glucosidase, EC 3.2.1.21). The function of β-glucosidase involves hydrolyzing the non-reducing β-D-glucosidase bond at the substrate’s terminus, simultaneously releasing β-D-glucose and the corresponding ligand (Pan and Luo, 2006). To date, the majority of identified β-glucosidases belong to the GH1 and GH3 families. Notably, numerous fungal-derived β-glucosidases are classified into the GH3 family. In contrast, β-glucosidases from the GH2, GH5, GH16, GH30, GH39, and GH116 families have received relatively little attention in the literature (Ferrara et al., 2014; Qi et al., 2008; Sansenya et al., 2015; Suzuki et al., 2013). β-glucosidase is widely distributed in organisms and performs diverse functions across archaea, fungi, and eukaryotes. It participates in a variety of biological processes and metabolic pathways, exerting crucial impacts on organisms. For instance, it is involved in biomass conversion in microorganisms, lignin and cell wall oligosaccharide catabolism, and the decomposition of exogenous glycosidic lipids in animals. Moreover, β-glucosidase plays significant roles in plant self-defense mechanisms and plant interactions with microorganisms and insects (Ketudat Cairns and Esen, 2010; Morant et al., 2008). In a previous study, during the infection of apple trees by Valsa mali, the β-glucosidase gene VmGluI showed a remarkable up-regulation (Li et al., 2017). The knockout of VmGlu2 was associated with reduced β-glucosidase activity and toxin levels, which in turn led to a decrease in the pathogenicity of Valsa mali (Huang et al., 2021). Similarly, knocking out the β-glucosidase gene Foglu1 in Fusarium oxysporum f.sp.conglutinan resulted in a reduction of the pathogen’s pathogenicity to cabbage (Wang et al., 2023). Additionally, the knockout of the pxo04104 gene by Xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzae caused a decline in its pathogenicity to rice and a reduction in the mutant’s osmotic resistance, indicating a positive correlation between the gene and the pathogen’s pathogenicity (Tian et al., 2017). F. verticillioides, a phytopathogenic fungus, lacks specialized cellular structures like appressoria and haustoria, which are typically employed by certain pathogens to adhere to and penetrate plant cells. Nevertheless, it is capable of secreting a series of cell wall—degrading enzymes (CWDEs). These enzymes play a crucial role in effectively degrading the components of the plant cell wall, facilitating the fungus’s invasion and nutrient acquisition within the host plant. β-glucosidase is among the key CWDEs. In F. verticillioides, the functions of β-glucosidase genes belonging to the GH3 family remain unreported to date.
In the present study, we identified the genes within the GH3 family of F. verticillioides and analyzed their expression levels. Additionally, we focused on elucidating the functions of the differentially expressed β-glucosidase gene FvGH3-6. This was done to uncover its roles in the growth and development of F. verticillioides, as well as in the pathogenesis of maize when infected by this fungus. Understanding the functions of FvGH3-6 holds great significance for exploring the pathogenic mechanisms of diseases caused by F. verticillioides. The insights gained from this research can serve as a theoretical foundation for developing more effective strategies for agricultural disease control, aiming to mitigate the damage caused by this pathogen to maize crops.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Plants, strains, and culture conditions
Fusarium verticillioides 7600 strain was provided by Gu Qin from Nanjing Agricultural University. The plasmid pUCATPH containing hygromycin (HPH) fragment, complementary plasmid pHZ100, and maize B73 were provided by Hebei Key Laboratory of Plant Physiology and Molecular Pathology. The F. verticillioides 7600 strain was cultured on potato dextrose agar medium (PDA) in the darkness at 25°C.
2.2 Methods
2.2.1 Gene identification and bioinformatics analysis of GH3 gene family in F. verticillioides
The genomic sequence of F. verticillioides 7600 (ASM14955v1.59) was downloaded from the Ensemble Fungi database,1 and the members of the GH3 gene family were screened out from the genomic sequence of F. verticillioides 7600 by Hidden Markov Model (HMM). The genes containing the conserved domain (PFAM accession number: PF00933, PF01915) of GH3 protein were screened and identified by the online tool InterPro.2 The physical and chemical properties of the protein sequence of the GH3 family of F. verticillioides were analyzed using the online website ExPASy.3 The gene location and structure were further explored with TBtools (Version 2.154), with all parameters set to default values. The online database WoLF PSORT4 was used to predict the subcellular localization of GH3 family members. The phylogenetic tree was constructed using MEGA 7.0 software and the Neighbor-Joining (NJ) method. Bootstrap was repeatedly set to 1, 000, and other parameters were the default values of the system.
2.2.2 Transcriptome analysis of GH3 gene family in F. verticillioides
To screen for the key GH3 genes involved in the growth, development, and pathogenicity of F. verticillioides, we analyzed the expression levels of GH3 family member genes during different infection stages through transcriptome data and selected genes with significantly upregulated expression levels during the infection process. Meanwhile, the total RNA of F. verticillioides mycelia and pathogen—host interaction samples was extracted following the total RNA extraction protocol provided by the miRcute miRNA Extraction and Isolation Kit (Tiangen, Beijing, China). The isolated RNA was stored at −80°C for subsequent studies. cDNA was synthesized by reverse transcription using the PrimeScript™ RT reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser (TaKaRa, Beijing, China). qPCR primers were designed using Primer Premier 5 software. The Actin gene of F. verticillioides was used as the internal reference gene. Real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR (qPCR) analysis was conducted using the Super EvaGreen qPCR Master Mix Kit. The relative expression levels of genes with significantly upregulated expression in the transcriptome were measured. The samples tested included F. verticillioides—infected maize kernels at 4 hpi, 12 hpi, and 72 hpi, and the in vitro—cultured mycelia of F. verticillioides grown on PDA for 3 days.
2.2.3 The generation of GH3 family gene knockout mutants and complementary strains
Based on the transcriptome gene expression levels described in Section 2.2.2, the key gene FvGH3-6, which was significantly up-regulated during infection, was selected to construct knockout mutants and complementary strains. Primers (Supplementary Table S1) were designed by Primer Premier 5.0. The fusion gene fragments required for knockout transformation were obtained by fusion PCR. Mycelia cultured on a PDA plate at 25°C in the dark for 4 days were collected. The DNA of F. verticillioides was extracted using the CTAB method and served as a template for PCR amplification. The upstream arm of FvGH3-6 was amplified using primer 1F/1R to obtain fragment 1. The downstream arm was amplified using primer 2F/2R to obtain fragment 2. The HPH fragment was amplified using primer HPH-F / HPH-R with pUCATPH plasmid as a template, and fragment 3 was obtained. Fragments 1, 2, and 3 were fused based according to the principle of homologous recombination. Using the method described by Müller (1999), the fusion fragments were introduced into the F. verticillioides 7600 strain via 40% PEG-mediated protoplast transformation. Using the cDNA of F. verticillioides as a template, we amplified the cDNA fragment of the FvGH3-6 CDS sequence devoid of the stop codon. The amplified fragment was ligated to the pHZ100 plasmid through seamless cloning in accordance with the principle of homologous recombination to generate the complementary vector. These constructs were reintroduced into the respective mutant strains. Complemented strains were selected on G418-containing mediums.
The wild type strains and mutant strains were cultured on a PDA plate at 25°C in the dark for 4 days. DNA was extracted using the CTAB method. The extracted DNA served as a template, and four pairs of primers were used for PCR detection. When no band was detected for the target gene fragment while the other three fragments could be successfully amplified with the correct bands, the knockout mutant was deemed to have been obtained. Two pairs of primers were used to verify the gene complemented transformants. The aminoglycoside phosphotransferase (APH) fragment and FvGH3-6 target gene were detected, separately. qPCR was used to determine the gene expression levels of the positive transformants. Total RNA was isolated from the mycelium using the Column Fungal Total RNA Extraction and Purification Kit (Sangon Biotech, Shanghai, China). Subsequently, cDNA was synthesized via reverse transcription using the PrimeScript® Reverse Transcription Kit (Takara, Beijing, China) following the manufacturer’s instructions. The Actin gene of F. verticillioides served as the internal reference gene. The relative expression of each gene was calculated by the 2−ΔΔCt method, and each reaction contained 3 biological replicates.
2.2.4 Analysis of growth and development ability of mutant strains
The samples were collected from the edge of colonies with a diameter of 5 mm of wild-type (WT) strains and mutant strains. Subsequently, they were cultured on PDA plates at 25°C in the dark for 4 days. The colony diameter was then measured and photographed using the cross method. The growth inhibition rate was calculated as follows: (growth diameter of WT—growth diameter of knockout mutant strains) / (growth diameter of WT—5 mm). For this test, three independent biological replicates were established. Additionally, five bacterial cakes with a diameter of 8 mm were, respectively, obtained from the WT and mutant strains and added into 100 mL of CMC liquid medium. The mixtures were incubated at 25°C with shaking at 175 rpm to induce sporulation. After 4 days of culture, the number of conidia was counted, and three independent biological replicates were set up.
2.2.5 Determination of the sensitivity of mutant strains to environmental stress
To explore the growth of gene deletion mutant strains and complemented mutant strains in different stress environments, two stress factors, namely 0.05% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and 100 μg/mL Congo red (CR), were established. We inoculated three 5 mm diameter fungal cakes of WT strains, knockout mutant strains, and complemented mutant strains on PDA plates containing different stress agents. After culturing in the dark at 25°C and a relative humidity of 60–70% for 5 days, the growth rate of the colony was recorded and the diameter was measured to calculate the growth inhibition rate. Three independent biological replicates were set up.
2.2.6 Determination of pathogenicity of mutant strains
To assess the impact of knocking out the FvGH3-6 gene on the pathogenicity of F. verticillioides, conidia from the WT and knockout mutant strains were used to infect maize kernels and maize stalks. The concentration of the spore suspension was 1 × 106 conidia/mL. The sterile syringe needle gently scratched the endosperm of corn kernels, and each kernel was injected with 15 μL of spore suspension. The corn kernels were cultured in dark and humid conditions at 25 ° C for 3 days. In addition, living maize plants at the 10-leaf stage were injected with 200 μL spore suspension on the third stem node near the ground of live maize. The wound was wrapped with autoclaved absorbent cotton and gauze to prevent contamination by exogenous bacteria. After the inoculated maize stems grew in the field environment for 12 days, a multispectral measurement system was employed to photograph the inoculated and diseased areas. Finally, the relative lesion area was calculated.
2.2.7 Effects of different carbon source conditions on the growth of mutant strains
β-glucosidase is an important component of cellulose hydrolase, which can hydrolyze the cellooligosaccharides and cellobiose produced by hydrolysis into glucose (Liu et al., 2022). To explore whether the knockout of the FvGH3-6 gene affects its ability to hydrolyze cellulose. The mycelial growth of WT and knockout mutant strains under different carbon source conditions was determined, and three carbon sources were selected, namely glucose, cellobiose, and CMC (sodium carboxymethyl cellulose). Three 5 mm diameter fungal cakes of WT and knockout mutant strains were collected and inoculated on the medium containing different carbon sources. After 5 days of culture at 25°C in darkness, with relative humidity of 60–70%, the growth state of the colony was recorded and the diameter was measured. Three independent biological replicates were set up in the experiment.
2.2.8 Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS software (Version 26.0) and GraphPad Prism software (Version 9.5). The unpaired t-test and one-way analysis of variance were employed to conduct significance tests for differences. Asterisks and different letters indicate statistically significant differences (p < 0.05).
3 Results
3.1 GH3 family members of F. verticillioides
Based on the genome data of F. verticillioides, 19 GH3 family genes were successfully screened and identified, and they were numbered FvGH3-1 ~ FvGH3-19 according to their location on the chromosome. The 19 genes of the GH3 family were distributed on 11 chromosomes. Which encoding amino acids ranging from 559 to 1,034. The proteins encoded by them, and the relative molecular weight ranged from 61.20 to 113.97 kDa. Among them, FvGH3-8 encoded the greatest number of amino acids, corresponding to a molecular weight of merely 61.20 kDa. FvGH3-6 encoded the greatest number of amino acids, corresponding to a molecular weight of 113.97 kDa. Isoelectric points ranged from 4.76 to 6.22, all less than 7. The GH3 protein of F. verticillioides were acidic proteins, of which the lowest isoelectric point was at 4.76, while the highest isoelectric point was at 6.22. The instability coefficients of the GH3 proteins of F. verticillioides ranged from 26.33 to 43.05, and the instability coefficients of most of the proteins of F. verticillioides GH3 family genes were lower than 40, indicating that the proteins encoded by this family of genes were mostly stabilized proteins. Only FvGH3-4, FvGH3-7, and FvGH3-14 exhibited instability coefficients higher than 40, which were unstable proteins. The results of subcellular localization showed that 12 FvGH3 members were localized in the cytoplasm, 5 in the extracellular, and 2 in the cytoskeleton (Supplementary Table S2). The phylogenetic tree of the 19 GH3 family proteins of F. verticillioides was constructed by MEGA7 software. According to the similarity of amino acid sequences, the phylogenetic tree can be divided into three groups (Figure 1A). To explore the conserved protein motifs of GH3 family members. Tbtools was used to predict the conserved motifs of FvGH3 family members. The results showed that among the 20 conserved motifs, motif 1, motif 3, motif 10, motif 11, and motif 16 were widely present in the 19 GH3 proteins. FvGH3-8 and FvGH3-15 contained only 11 motifs, and the other genes had more motifs (Figure 1B). The gene structure of GH3 family members was analyzed and visualized by Tbtools. The number of exons among GH3 family genes varies significantly (Supplementary Table S2), and GH3 family members are composed of 1–6 exons (Figure 1C).
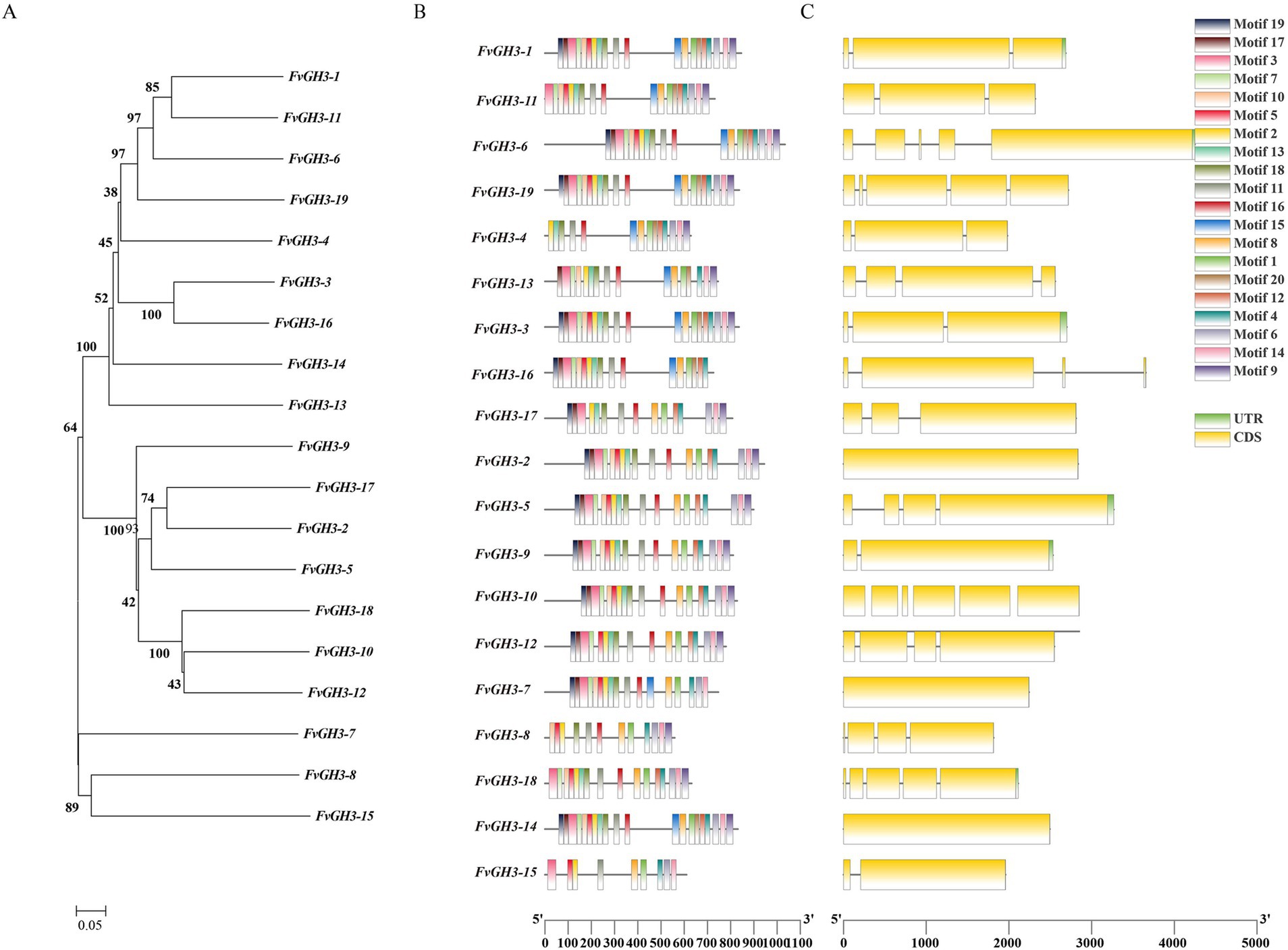
Figure 1. Bioinformatics analysis of GH3 gene family in F. verticillioides. (A) Phylogenetic tree; (B) analysis of amino acid conserved motifs; (C) gene structure.
3.2 Expression patterns of FvGH3 family genes
To screen for the key GH3 genes involved in the pathogenesis of F. verticillioides, the transcriptome data of pathogen samples at the infection stages of 4 hpi, 12 hpi, and 72 hpi, and the in vitro cultured mycelia of F. verticillioides grown on PDA for 3 days was used. Subsequently, a heatmap of the expression patterns of FvGH3 gene family members during the infection stages was drawn. Our study revealed that, compared with the in vitro—cultured mycelium of F. verticillioides that had been cultured on PDA for 3 days and the samples at 4 hpi of the pathogen, the relative expression levels of FvGH3-1, FvGH3-2, FvGH3-3, FvGH3-4, FvGH3-5, FvGH3-6, FvGH3-7, FvGH3-9, and FvGH3-14 in the GH3 gene family of F. verticillioides at 72 hpi increased significantly. Two genes, FvGH3-11 and FvGH3-13, exhibited inverse expression patterns. Moreover, the other eight genes remained unexpressed during the infection process (Figure 2A). Therefore, we conducted qPCR analysis for the nine genes whose expression levels were up-regulated during the infection period. qPCR was performed on maize kernel samples at 4 hpi, 12 hpi, and 72 hpi after F. verticillioides infestation and on F. verticillioides mycelium cultured for 3 days. Results showed these nine genes were up-regulated during the infestation period. Specifically, the relative expression of FvGH3-3 was highest at 12 hpi. The relative expression of the other eight genes gradually increased as the infestation time extended, and the highest relative expression was observed at 72 hpi (Figure 2B). FvGH3-6 had the highest relative expression during infestation, therefore, the FvCH3-6 gene was finally selected to construct knockout mutant strains and complementary mutant strains to analyze the function of the GH3 family.
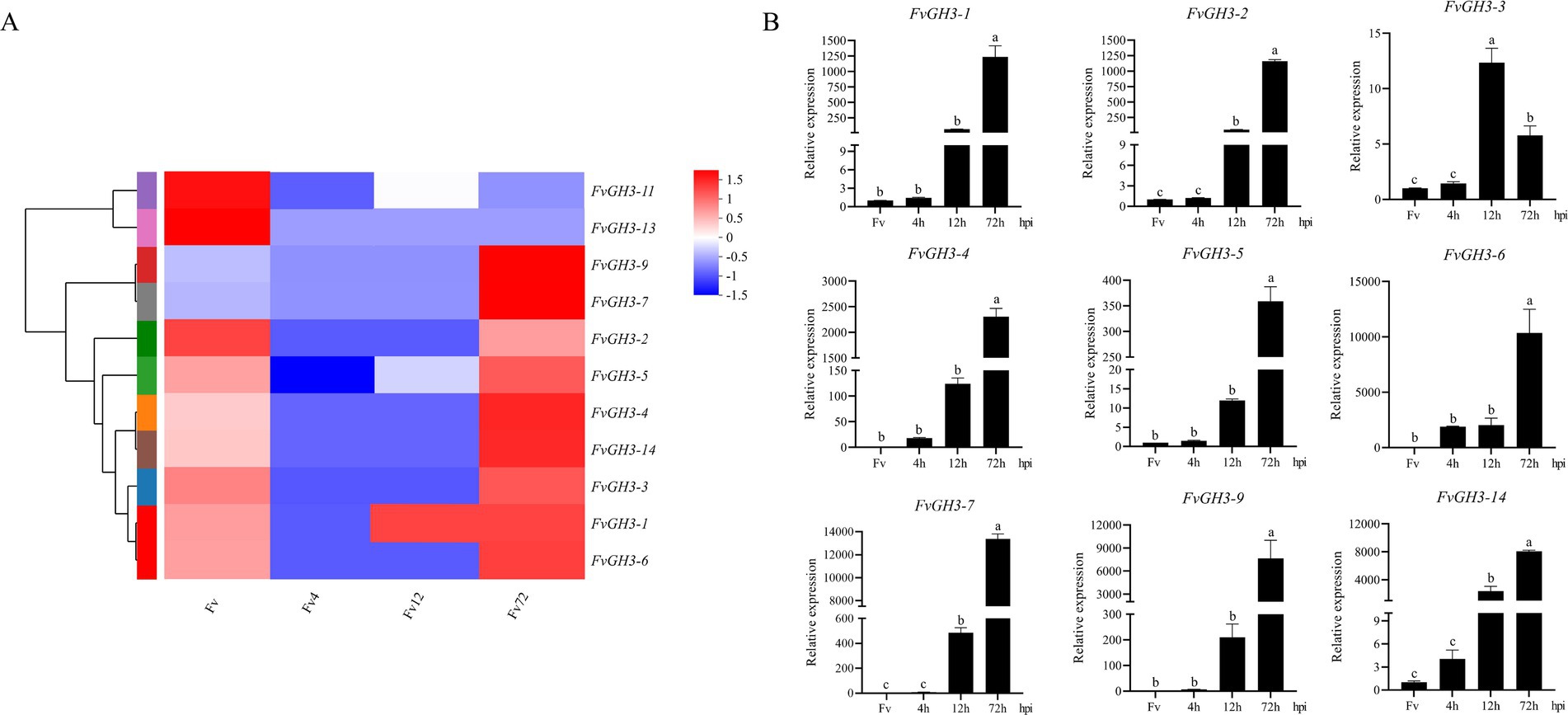
Figure 2. Gene expression of F. verticillioides GH3 family members during infection of maize kernels. (A) Heatmap of the expression pattern of the GH3 family of F. verticillioides during the infection period, (B) Validation of the expression levels of the GH3 family of F. verticillioides during the infection period by qPCR. Data in the figure are mean ± SE. Different lowercase letters showed significant differences by one-way analysis of variance (p < 0.05). hpi, hours post inoculation. The colored bar on the right indicates the gene expression levels. The redder the color, the higher the expression level, and vice versa.
3.3 Acquisition of FvGH3-6 knockout mutants and complementary strains
By PCR, we verified the target gene fragment of the knockout transformants exhibiting stable hygromycin resistance, and this verification demonstrated the absence of the target gene in the mutants (Figures 3A–G). Subsequently, we employed qPCR for the detection of the FvGH3-6 gene expression level in the knockout mutants and found that the target gene expression level was significantly reduced (Figure 3H). These results suggest the successful generation of the FvGH3-6 gene knockout mutants. We then introduced the complementation vector into the protoplasts of the knockout strain, resulting in the generation of the complementation mutant strains. PCR-based verification of the generated complementation transformants validated the presence of the FvGH3-6 gene and the APH gene in the complementation strains (Figure 4A). Subsequently, qPCR was employed for assessing the FvGH3-6 gene expression level in the complementation mutant strains (Figure 4B), and the target gene had restored the WT gene expression level. These results suggest the successful generation of the FvGH3-6 gene complementation mutants.

Figure 3. Identification of F. verticillioides FvGH3-6 gene knockout mutant strain PCR and qPCR. (A,B) The upstream and downstream homologous arms of the FvGH3-6 gene were amplified; (C) Amplification of hygromycin fragment containing promoter in pUCATPH plasmid; (D) Fusion fragment; (E–G) Validation of the target gene fragment by PCR; (H) The expression level of FvGH3-6 gene in knockout mutants was detected by qPCR. M1: 2,000 bp marker; M2: 5,000 bp marker; 1: wild type; 2: negative control; 3: ∆FvGH3-6. Data in the figure are mean ± SE in H. ** indicates significant difference by t-test (p < 0.01).
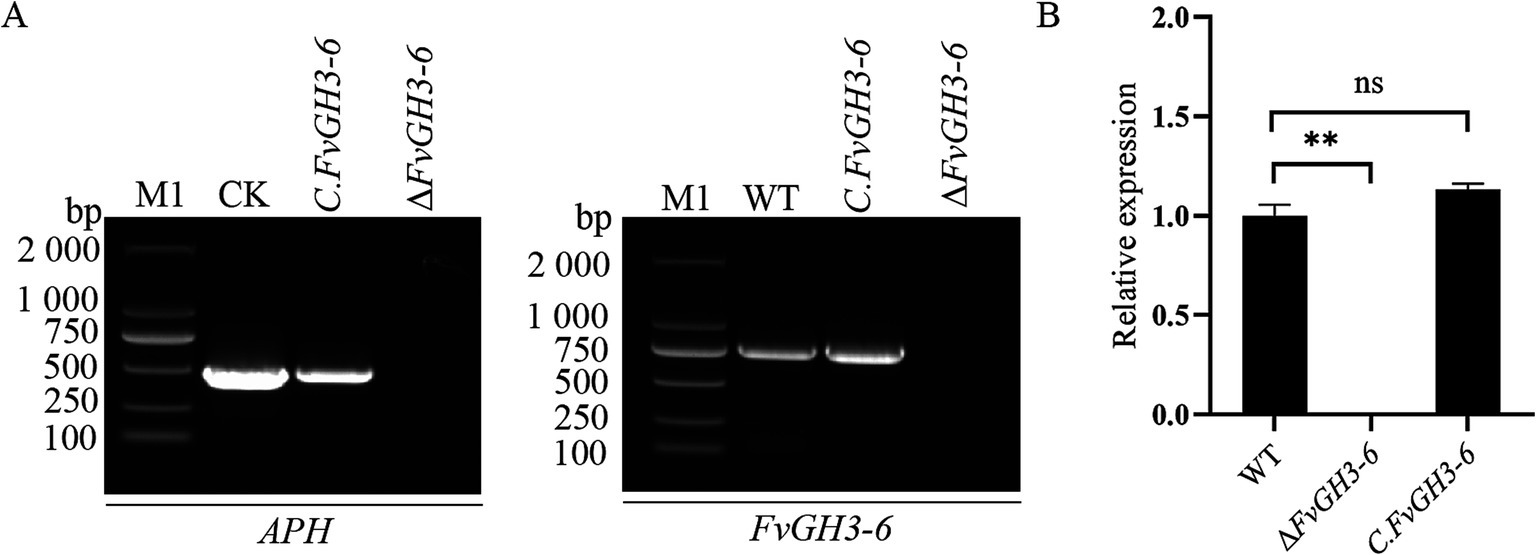
Figure 4. Identification of F. verticillioides FvGH3-6 gene complemented mutant strain PCR (A) and qPCR (B). (A) The FvGH3-6 gene and APH gene were verified by PCR; (B) The expression level of the FvGH3-6 gene in the complemented mutant was detected by qPCR. M1: 2,000 bp marker; WT: wild type; ∆FvGH3-6: gene knockout mutant; CK: pHZ100 plasmid; C. FvGH3-6: complemented mutant; APH: aminoglycoside phosphotransferase. Data in the figure are mean ± SE in B. ** indicates significant difference by t-test (p < 0.01), ns indicates no significant difference (p > 0.05).
3.4 FvGH3-6 affected the pathogenicity of F. verticillioides to maize grain and stem
The WT and the mutant ΔFvGH3-6 were inoculated onto maize seeds and stems to detect the effect of gene knockout on the pathogenicity of maize. The results showed that compared with the WT, the relative lesion area of maize kernels and stems after inoculation with the ΔFvGH3-6 strain was smaller (Figure 5A). Compared with the WT, the lesion area of maize kernels inoculated with the ΔFvGH3-6 strain decreased significantly by 20.66% (Figure 5B), and the lesion area of maize stems inoculated with the ΔFvGH3-6 strain decreased significantly by 28.72% (Figure 5C). These results indicate that the knockout of the FvGH3-6 gene led to a significant decrease in the pathogenicity of the pathogen. Additionally, they suggest that FvGH3-6 plays a crucial role in the pathogenicity of F. verticillioides.
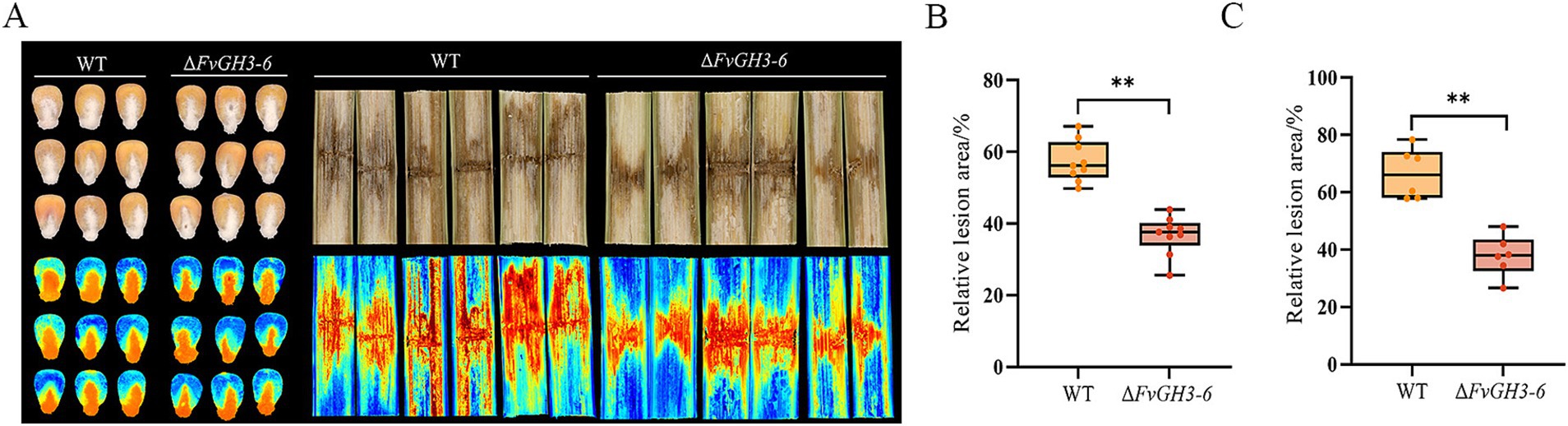
Figure 5. The symptoms of maize kernels and stems (A) and the relative lesion area in maize kernels (B) and stems (C) of FvGH3-6 gene knockout mutants of F. verticillioides. Data in the figure are mean ± SE in (A, B). ** indicates significant difference by t-test (p < 0.01).
3.5 FvGH3-6 affected the growth, development and stress resistance of F. verticillioides
An analysis was conducted on the phenotype and growth rate of the mutants. It was observed that there was no significant difference in the colony morphology between the mutants and the WT (Figure 6A), and the growth rate was not affected as well (Figure 6B). However, the conidia production of the knockout mutant strain ΔFvGH3-6 decreased, exhibiting a 26.9% reduction in comparison with that of the WT. In contrast, no significant difference was detected in the conidia production of the complemented strain C. FvGH3-6 relative to that of the WT (Figure 6C). The result indicates that FvGH3-6 affects the sporulation ability.
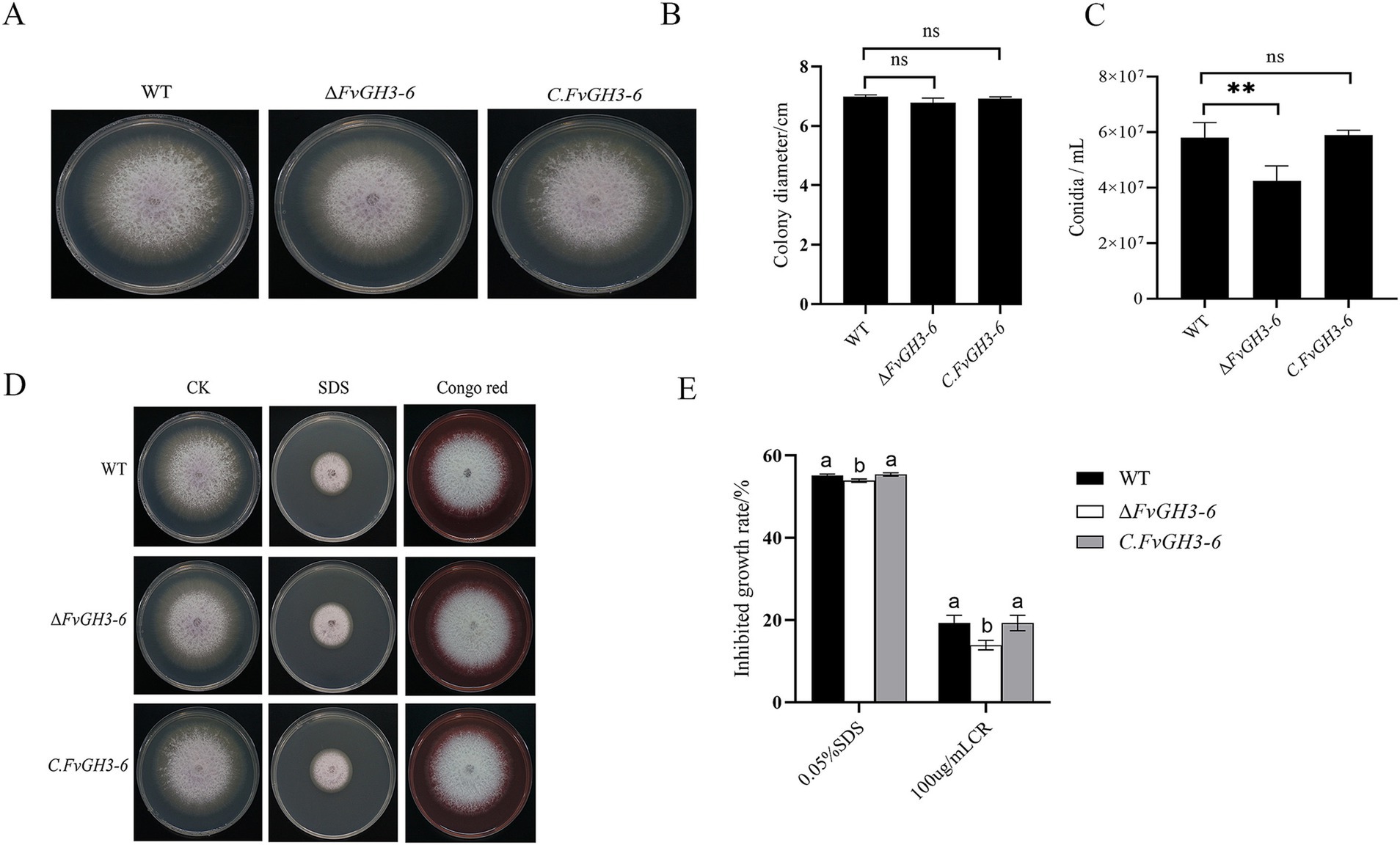
Figure 6. The growth phenotypes of the FvGH3-6 gene knockout mutant strain and complemented strain in F. verticillioides are presented here. (A,B) The growth phenotypes and diameters of the mutants after 4 days of growth on PDA. (C) The conidiospore production of the mutants. (D,E) The growth status of the mutants on PDA media supplemented with different stress agents. Data in the figure are presented as the mean ± SE. “**” indicates a significant difference (p < 0.01) as determined by the t-test, while “ns” indicates no significant difference (p > 0.05). Columns with different letters represent significant differences at p < 0.05.
We assessed the effects of cell wall-disrupting agents on the growth of the ΔFvGH3-6 mutant strain (Figures 6D,E). The growth inhibition rates of the knockout mutant ΔFvGH3-6 under SDS and CR treatments were 53.92 and 13.92%, respectively, both of which were significantly lower than those of the WT. The deletion of the FvGH3-6 gene resulted in an enhanced resistance to the fungal cell wall inhibitors CR and SDS. This indicates that FvGH3-6 affects the cell wall synthesis of F. verticillioides.
3.6 FvGH3-6 exhibits no significant effect on the utilization of carbon sources of F. verticillioides
The WT and mutant strain ΔFvGH3-6 were cultured under different carbon source conditions, and the effect of gene knockout on carbon source utilization ability was detected through the measurement of mycelial growth (Figure 7A). The results showed no significant difference in mycelial growth between WT and mutant strain ΔFvGH3-6 on the medium containing glucose, cellobiose, and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose as individual carbon sources. These results suggested that the deletion of the FvGH3-6 gene did not affect the utilization capacity of the strain to cellobiose and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (Figure 7B).
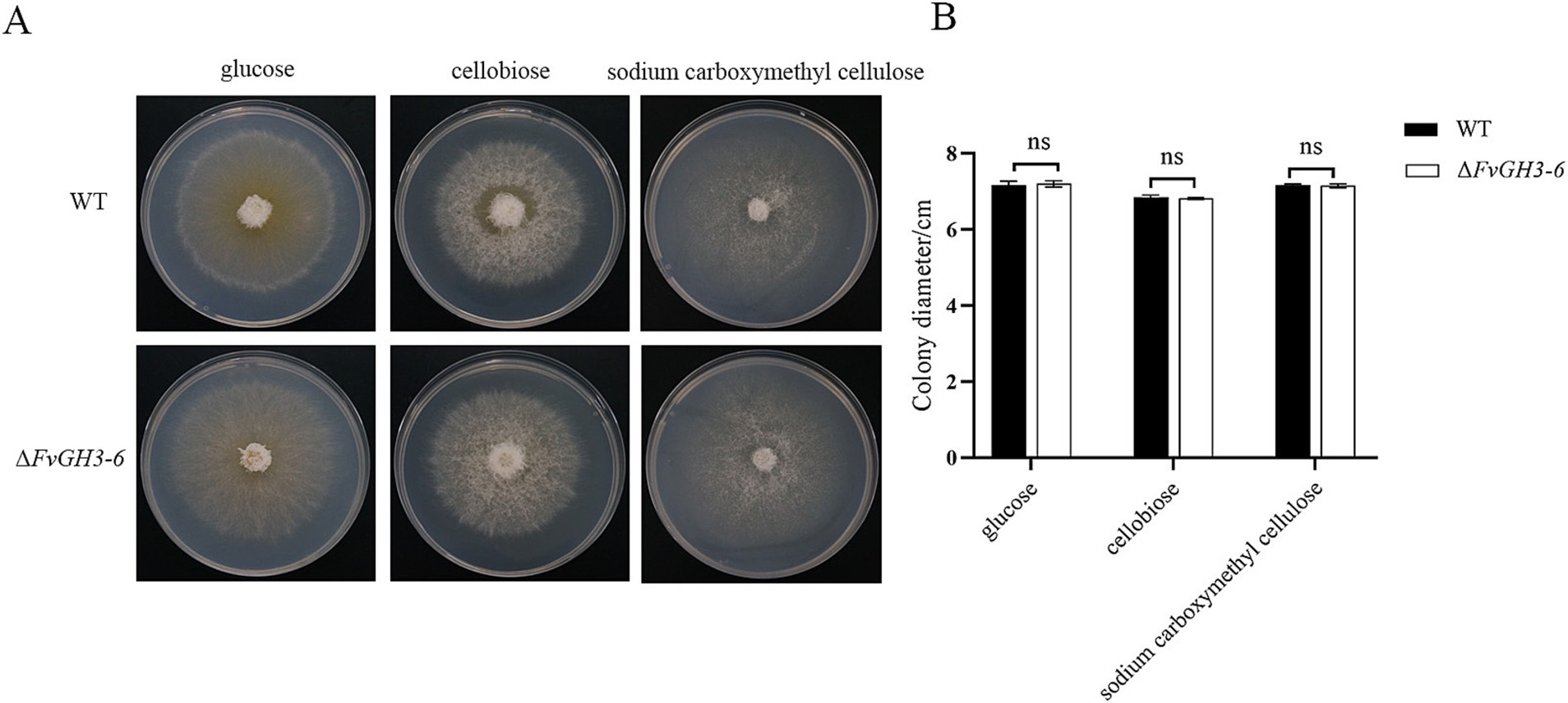
Figure 7. Growth of F. verticillioides wild-type and FvGH3-6 gene knockout mutant strain on media with different carbon sources added. (A) Colony phenotype diagram, (B) Colony growth diameter. Data in the figure are mean ± SE. ** indicates a significant difference by t-test (p < 0.01), ns indicates no significant difference (p > 0.05).
4 Discussion
GH is a large class of hydrolases that act on different carbohydrate substrates and play a variety of roles. As a common β-glucosidase, GH3 has a large number of family members in organisms. Previous studies reported that 13 GH3 family genes were screened from the whole genome of Dendrobium officinale, and the expression patterns of these family genes were significantly different in different tissues and treatments (Li et al., 2024). Fungi also possess a large number of GH3 family genes. Aspergillus niger harbors 11 genes belonging to the GH3 family, which possess potential β-glucosidase functions (Pel et al., 2007). Researchers screened and identified 16 GH3 gene family members from the genome of Aspergillus aculeatus, and the expression levels of these members under cellulose induction were in line with the changes in extracellular β-glucosidase activity (Li and Wang, 2023). The genome of Neurospora crassa contains seven β-glucosidase genes, gh1-1, gh3-1 ~ gh3-6, belonging to the GH1 and GH3 families. These genes encode proteins that play important roles in the degradation of cellulose (Galagan et al., 2003; Wu et al., 2013; Zhang et al., 2024). According to the amino acid sequence homology, our research identified that there were a total of 19 GH3 family genes in the genome of F. verticillioides, distributed on 11 chromosomes, and all these genes contained the typical domain of the CH3 family. However, the functions of these genes remain unclear. As the corn diseases caused by F. verticillioides have become increasingly severe, we focused on the role of GH3 family genes in pathogen infection. In this study, transcriptional screening was performed at the transcriptional level. We observed that during the infection of maize kernels by F. verticillioides, as the infection time elapsed, the expression levels of nine GH3 gene family members increased significantly, indicating that multiple genes of the GH3 family were involved in the pathogenic process of F. verticillioides and might play an important role therein.
The integrity of the fungal cell wall plays a pivotal role in the life process of fungi. On the one hand, it is crucial for fungi to successfully infect host cells, as it can maintain the inherent shape of fungal cells and precisely regulate the interactions between fungal cells and the complex external environment (Cabib et al., 2001). On the other hand, the continuous process of cell wall remodeling is also a necessary condition for ensuring the normal growth and development of fungi (Bowman and Free, 2006). Numerous research examples have highlighted the profound impacts of cell wall-related genes on fungal characteristics. In Neostagonosporella sichuanesis, through in-depth investigation, our research ascertained that the ΔNsxyn1 and ΔNsxyn2 strains exhibited extremely significant sensitivity when faced with cell wall stressors (Liu et al., 2024), which clearly revealed the close association between the deletion of relevant genes and the cell wall stress response. Similarly, in the research field of Aspergillus fumigatus, the edeA deletion mutant was confirmed to have a substantially increased sensitivity to cell wall-disrupting agents, fully indicating that EdeA plays an indispensable and crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the cell wall of A. fumigatus (Dai et al., 2024). Further focusing on the research object F. verticillioides, the connection between its GH family genes and cell wall characteristics has gradually emerged. For example, after knocking out the FvGH16-2 gene of F. verticillioides, the sensitivity of the mutant to cell wall inhibitors CFW and CR increased significantly, consequently resulting in the impairment of the integrity and functionality of the fungal cell wall (Ren et al., 2024). In the paper, after the knockout of the FvGH3-6 gene of F. verticillioides, the resistance of the mutant to cell wall inhibitors CR and SDS was enhanced, indicating that FvGH3-6 exerted a significant influence on the integrity and function of the cell wall of F. verticillioides.
The production of conidia is a crucial stage in the life cycle of pathogens. Therefore, it is widely believed that inhibiting conidia formation is presumed to mitigate or proficiently regulate the occurrence of diseases. However, the relationship between conidia and the pathogenicity of pathogens remains unclear. In a previous study, the deletion of transcription factors FvMbp1 and FvSwi6 severely affected the growth rate of the pathogen and the number of conidia produced. Meanwhile, the virulence on maize stalks and ears also decreased significantly (Huang et al., 2024). In a previous study, the deletion of VmE02, encoding the pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP), demonstrated attenuated conidiation but not the attenuation of virulence (Nie et al., 2019). The deletion mutant of VmGlu2 exhibited a normal growth rate but significantly reduced pycnidia formation and pathogenicity (Huang et al., 2021). In this study, the ΔFvGH3-6 mutant showed a normal growth rate, decreased conidia production, and reduced pathogenicity. These results suggest that the production of conidia in pathogens is not necessarily related to the growth rate and virulence.
For fungi to infect plants, they must traverse the plant cell wall, which is an important barrier for plants to resist pathogen attack. Many scholars regard the ability of fungi to destroy plant tissue structure during infection as an important criterion for judging whether they are pathogenic (Marie et al., 2000). GH has been reported to be closely related to the pathogenicity of plant pathogenic fungi. It can release nutrients and enhance the permeability of mycelium by hydrolyzing carbohydrates in the plant cell wall, such as cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin, to promote the infection of host plants by pathogenic bacteria (Han and Xu, 2017). In Penicillium expansum, the deletion of β-glucosidase 1b (eglB), a member of the glycoside hydrolase family, resulted in a reduction in the growth of fungal hyphae, a decrease in the ability of P. expansum to produce spores and patulin, and a decrease in pathogenicity to pears (Xu et al., 2024). Upon knockout of the glycoside hydrolase family FvGH16-2 gene of F. verticillioides, the pathogenicity of F. verticillioides to maize grains and stems was attenuated (Ren et al., 2024). The deletion of VmGluI and VmGlu2 resulted in a reduction in the infectivity of V. mali (Huang et al., 2021; Li et al., 2017). The results demonstrated that the knockout of the FvGH3-6 gene resulted in a significant decrease in the pathogenicity of F. verticillioides to maize grains and stems, indicating that this gene affected the pathogenicity of F. verticillioides and played significant roles in plant-pathogen interaction. Numerous reports have indicated that the GH3 family is involved in the degradation of cellobiose and cellulose (Liu et al., 2022; Singhania et al., 2013). Similar to the case when glucose was used as a carbon source, the growth rate of the F. verticillioides mutant with the FvGH3-6 gene knocked out was comparable to that of the WT in media containing cellobiose or sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, indicating that the deletion of the FvGH3-6 gene did not affect the ability of the strain to degrade cellulose. Therefore, the effect of FvGH3-6 on the pathogen’s pathogenicity is regulated by a more complex mechanism, and the function of FvGH3-6 in the interaction between maize and F. verticillioides remains to be further studied.
Currently, biocontrol agents and chemical fungicides have been used to mitigate the occurrence of maize ear rot. However, the problem of drug resistance is becoming increasingly severe. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct in-depth research on the pathogenic mechanism of F. verticillioides and develop new and highly effective fungicides thereon to prevent the epidemic of this disease. In this study, the knockout of the FvGH3-6 gene affected the pathogenicity of F. verticillioides, and this gene may potentially serve as a molecular target for fungicides to prevent the occurrence of the disease.
5 Conclusion
In summary, this study preliminarily analyzed the basic situation of the GH3 family of F. verticillioides, and analyzed the biological functions of the significantly up-regulated FvGH3-6 gene in the growth, development, and pathogenicity of F. verticillioides, which provided theoretical support for further in-depth study of the role of F. verticillioides in growth, development and pathogenicity, and provided a theoretical basis for scientific and effective prevention and control of maize diseases.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
XZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. PD: Writing – review & editing. SS: Writing – review & editing. MS: Writing – review & editing. NL: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. ZC: Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. JD: Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Modern Agricultural Industrial Technology System (CARS-02), the Independent Project of the State Key Laboratory of Crop Improvement and Regulation in North China (NCCIR2024ZZ-17), and the Key Research and Development Program of Hebei Province (20326502D).
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Mr. Gu Qin of Nanjing Agricultural University for donating Fusarium verticillioides 7600 strain for the experiment.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1543210/full#supplementary-material
Footnotes
1. ^https://fungi.ensembl.org/index.html
2. ^https://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/
References
Blacutt, A. A., Gold, S. E., Voss, K. A., Gao, M., and Glenn, A. E. (2018). Fusarium verticillioides: advancements in understanding the toxicity, virulence, and niche adaptations of a model mycotoxigenic pathogen of maize. Phytopathology 108, 312–326. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-06-17-0203-RVW
Bowman, S. M., and Free, S. J. (2006). The structure and synthesis of the fungal cell wall. BioEssays 28, 799–808. doi: 10.1002/bies.20441
Cabib, E., Roh, D. H., Schmidt, M., Crotti, L. B., and Varma, A. (2001). The yeast cell wall and septum as paradigms of cell growth and morphogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 19679–19682. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R000031200
Dai, M., Liu, X., Goldman, G. H., Lu, L., and Zhang, S. (2024). The EH domain-containing protein, EdeA, is involved in endocytosis, cell wall integrity, and pathogenicity in Aspergillus fumigatus. mSphere 9:e0005724. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00057-24
Ding, X. H., Song, Z. S., Jiang, X. D., Fu, K. Y., Wang, X. W., Tursun, A., et al. (2023). Isolation and identification of dominant pathogens causing maize stalk rot in the irrigated maize producing areas in Xinjiang oases. J. Plant Prot. 50, 733–743. doi: 10.13802/j.cnki.zwbhxb.2023.2021211
Ferrara, M. C., Cobucci-Ponzano, B., Carpentieri, A., Henrissat, B., Rossi, M., Amoresano, A., et al. (2014). The identification and molecular characterization of the first archaeal bifunctional exo-β-glucosidase/N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase demonstrate that family GH116 is made of three functionally distinct subfamilies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1840, 367–377. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.09.022
Galagan, J. E., Calvo, S. E., Borkovich, K. A., Selker, E. U., Read, N. D., Jaffe, D., et al. (2003). The genome sequence of the filamentous fungus Neurospora crassa. Nature 422, 859–868. doi: 10.1038/nature01554
Guo, Z. F., Wang, S. H., Liu, J. C., Liu, A. P., and Li, W. X. (2023). Genetic analysis of Fusarium verticillioides ear rot in maize. China Seed Industry. 10, 61–65. doi: 10.19462/j.cnki.1671-895x.2023.10.018
Han, C. Z., and Xu, X. (2017). Advance in functional research of secreted protein and CAZymes in plant pathogenic filamentous fungus. J. Nanjing For. Univ. 41, 152–160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2006.201607045
Huang, Y., Chen, J., Xia, H., Gao, Z., Gu, Q., Liu, W., et al. (2024). FvMbp1-Swi6 complex regulates vegetative growth, stress tolerance, and virulence in Fusarium verticillioides. J. Hazard. Mater. 473:134576. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.134576
Huang, Y., Yu, C., Sun, C., Saleem, M., Li, P., Li, B., et al. (2021). β-Glucosidase VmGlu2 contributes to the virulence of Valsa Mali in apple tree. Front. Microbiol. 12:695112. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.695112
Hurni, S., Scheuermann, D., Krattinger, S. G., Kessel, B., Wicker, T., Herren, G., et al. (2015). The maize disease resistance gene Htn1 against northern corn leaf blight encodes a wall-associated receptor-like kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 112, 8780–8785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1502522112
Ketudat Cairns, J. R., and Esen, A. (2010). β-Glucosidases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 67, 3389–3405. doi: 10.1007/s00018-010-0399-2
Li, Y. P., Jin, F. L., Huang, Z. G., Zhang, T., Duan, X. J., Jiang, W., et al. (2024). Identification and expression pattern analysis of glycoside hydrolase GH3 gene family in Dendrobium officinale. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis 36, 790–799. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20230502
Li, T., Lian, S., Li, B. H., Liang, W. X., and Wang, C. X. (2017). Molecular cloning and expression analysis of β-glucosidase gene from Valsa mali var.mali. Acta Agric. Boreali Sin. 32, 78–84. doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.2017.06.012
Li, C., and Wang, Y. (2023). Bioinformatics and expression analyses of glycoside hydrolase 3 genes in Trichoderma asperellum. Microbiol. China 50, 1–12. doi: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.220480
Liu, L., Li, C., Liang, F., Han, S., Li, S., Yang, C., et al. (2024). Global characterization of GH11 family xylanases genes in Neostagonosporella sichuanensis and functional analysis of Nsxyn1 and Nsxyn2. Front. Microbiol. 15:1507998. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1507998
Liu, X. H., Shen, F. F., Shi, P. J., and Liu, H. Q. (2022). Expression and characterization of a bifunctional thermal β-glucosidase IuBgl3 from thermophilic archaeon Infirmifilum uzonense. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 38, 4644–4657. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.220191
Logrieco, A., Battilani, P., Leggieri, M. C., Jiang, Y., Haesaert, G., Lanubile, A., et al. (2021). Perspectives on global mycotoxin issues and management from the MycoKey maize working group. Plant Dis. 105, 525–537. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-06-20-1322-FE
Marie, T., Georges, B., and Bernard, D. (2000). Cell wall degrading enzymes, inhibitory proteins, and oligosaccharides participate in the molecular dialogue between plants and pathogens. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 38, 157–163. doi: 10.1016/S0981-9428(00)00161-3
Marin, S., Ramos, A. J., Cano-Sancho, G., and Sanchis, V. (2013). Mycotoxins: occurrence, toxicology, and exposure assessment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 60, 218–237. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.07.047
Mei, J., Zhou, S., and Liu, W. (2023). Gene-for-gene-mediated resistance to southern corn rust in maize. Trends Plant Sci. 28, 255–258. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2022.12.002
Morant, A. V., Jørgensen, K., Jørgensen, C., Paquette, S. M., Sánchez-Pérez, R., Møller, B. L., et al. (2008). beta-Glucosidases as detonators of plant chemical defense. Phytochemistry 69, 1795–1813. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2008.03.006
Müller, U. (1999). Ten years of gene targeting: targeted mouse mutants, from vector design to phenotype analysis. Mech. Dev. 82, 3–21. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4773(99)00021-0
Munkvold, G. P., and Carlton, W. M. (1997). Influence of inoculation method on systemic fusarium moniliforme infection of maize plants grown from infected seeds. Plant Dis. 81, 211–216. doi: 10.1094/PDIS.1997.81.2.211
Nie, J., Yin, Z., Li, Z., Wu, Y., and Huang, L. (2019). A small cysteine-rich protein from two kingdoms of microbes is recognized as a novel pathogen-associated molecular pattern. New Phytol. 222, 995–1011. doi: 10.1111/nph.15631
Njeru, F., Wambua, A., Muge, E., Haesaert, G., Gettemans, J., and Misinzo, G. (2023). Major biotic stresses affecting maize production in Kenya and their implications for food security. PeerJ 11:e15685. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15685
Pan, L. H., and Luo, J. P. (2006). Advance in research and application of β-D-glucosidase. Food Sci. 49, 803–807. doi: 10.1093/jimb/kuac027
Pel, H. J., de Winde, J. H., Archer, D. B., Dyer, P. S., Hofmann, G., Schaap, P. J., et al. (2007). Genome sequencing and analysis of the versatile cell factory Aspergillus niger CBS 513.88. Nat. Biotechnol. 25, 221–231. doi: 10.1038/nbt1282
Pienaar, J. G., Kellerman, T. S., and Marasas, W. F. (1981). Field outbreaks of leukoencephalomalacia in horses consuming maize infected by Fusarium verticillioides (= F. Moniliforme) in South Africa. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 52, 21–24.
Qi, M., Jun, H. S., and Forsberg, C. W. (2008). Cel9D, an atypical 1,4-beta-D-glucan glucohydrolase from Fibrobacter succinogenes: characteristics, catalytic residues, and synergistic interactions with other cellulases. J. Bacteriol. 190, 1976–1984. doi: 10.1128/JB.01667-07
Ren, Z. G., Liu, N., Chen, Y., Sun, M. L., Cao, Z. Y., and Dong, J. G. (2024). The glycoside hydrolase gene FvGH16-2 is involved in the growth and pathogenicity of mycotoxigenic fungus Fusarium verticillioides. J. Plant Prot. 51, 342–351. doi: 10.13802/j.cnki.zwbhxb.2024.2023080
Sansenya, S., Mutoh, R., Charoenwattanasatien, R., Kurisu, G., and Ketudat Cairns, J. R. (2015). Expression and crystallization of a bacterial glycoside hydrolase family 116 β-glucosidase from Thermoanaerobacterium xylanolyticum. Acta Crystallogr. F Struct. Biol. Commun. 71, 41–44. doi: 10.1107/S2053230X14025461
Singhania, R. R., Patel, A. K., Sukumaran, R. K., Larroche, C., and Pandey, A. (2013). Role and significance of beta-glucosidases in the hydrolysis of cellulose for bioethanol production. Bioresour. Technol. 127, 500–507. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.09.012
Sun, H., Zhang, H. J., Guo, N., Shi, J., Chen, D., and Ma, H. X. (2017). Isolation and identification of pathogens causing maize ear rot in Huang-Huai-Hai summer corn region. J. Plant Prot. 44, 796–802. doi: 10.13802/j.cnki.zwbhxb.2017.2016078
Suzuki, K., Sumitani, J., Nam, Y. W., Nishimaki, T., Tani, S., Wakagi, T., et al. (2013). Crystal structures of glycoside hydrolase family 3 β-glucosidase 1 from aspergillus aculeatus. Biochem. J. 452, 211–221. doi: 10.1042/BJ20130054
Tian, C., Duan, J. N., Li, J. C., Ni, Z., Luo, J., Han, Q., et al. (2017). Preliminary analysis of the function of pxo04104 gene in Xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzae. Genom. Appl. Biol. 36, 1588–1593. doi: 10.13417/j.gab.036.001588
Van, E., Schothorst, R., and Jonker, M. (2007). Regu-lations relating to mycotoxins in food: perspectives in aglobal and European context. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 389, 147–157. doi: 10.1007/s00216-007-1317-9
Wang, T., Wang, B. X., Li, S. Y., Wei, J., and Li, E. F. (2023). Functional study of a β-glucosidase Foglu1 in Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Conglutinans. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis 35, 373–382. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2023.02.15
Wu, W., Kasuga, T., Xiong, X., Ma, D., and Fan, Z. (2013). Location and contribution of individual β-glucosidase from Neurospora crassa to total β-glucosidase activity. Arch. Microbiol. 195, 823–829. doi: 10.1007/s00203-013-0931-5
Xu, M., Godana, E. A., Li, J., Deng, Y., Ma, Y., Ya, H., et al. (2024). Infection of postharvest pear by Penicillium expansum is facilitated by the glycoside hydrolase (eglB) gene. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 410:110465. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2023.110465
Yu, C., Saravanakumar, K., Xia, H., Gao, J. X., Fu, K. H., Sun, J. N., et al. (2017). Occurrence and virulence of fusarium spp. associated with stalk rot of maize in North-East China. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 98, 1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.pmpp.2016.12.004
Keywords: Fusarium verticillioides, glycoside hydrolase 3, expression pattern, functional analysis, pathogenicity
Citation: Zhang X, Duan P, Shi S, Sun M, Liu N, Cao Z and Dong J (2025) Global characterization of GH3 family glycoside hydrolase genes in Fusarium verticillioides and functional analysis of FvGH3-6. Front. Microbiol. 16:1543210. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1543210
Edited by:
Abhijeet Shankar Kashyap, National Bureau of Agriculturally Important Microorganisms (ICAR), IndiaReviewed by:
Amit Kumar Kesharwani, Washington State University, United StatesVishal Srivastava, Cleveland Clinic, United States
Deepanshu Jayaswal, Indian Institute of Seed Science, India
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Duan, Shi, Sun, Liu, Cao and Dong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhiyan Cao, Y2FvemhpeWFuQGhlYmF1LmVkdS5jbg==; Jingao Dong, ZG9uZ2ppbmdhb0AxMjYuY29t
 Xiaojie Zhang
Xiaojie Zhang Pengliang Duan1,2
Pengliang Duan1,2 Manli Sun
Manli Sun Ning Liu
Ning Liu Zhiyan Cao
Zhiyan Cao Jingao Dong
Jingao Dong