
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
Front. Microbiol., 19 February 2025
Sec. Antimicrobials, Resistance and Chemotherapy
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1532231
Background: Infections by drug-resistant bacteria are a significant threat to human health worldwide although many drug-resistant bacteria are sensitive to aminoglycosides (AGs), an older class of antibiotics. AGs have played a significant role in clinical practice in recent years.
Methods: Publications from 1 January 2013 to 31 December 2023 that described clinical research of AGs were identified by searching the Web of Science Core Collection Database. Visual presentations of different bibliometric networks were prepared using VOSviewer and CiteSpace.
Results: There were 915 eligible publications and the annual number of publications increased over time. The United States had the most publications and was at the core of the cooperative network. Italy and Belgium had the highest quality publications, and many of the institutions with high yield and high research quality were in Australia. JA Roberts (University of Queensland, Australia) was the most productive author and was the author of many high-quality studies in cooperation with various other researchers. The majority of publications were in journals that focused on antibacterials, chemotherapy, and pharmacokinetics. Analysis of the most highly cited publications, references, and keywords, indicated that this research mainly focused on infections by drug-resistant bacteria, drug administration in vulnerable populations, safety, pharmacokinetics, combination therapy, and new methods of administration.
Conclusion: AGs have an increasingly important role in the treatment of infections by multidrug-resistant bacteria. Therapeutic drug monitoring should be performed in vulnerable populations, such as the elderly, children, and infants, to improve efficacy and reduce toxicity. Avoiding prolonged dosing cycles and refraining from using AGs in patients with the m.1555 A > G gene variant can significantly mitigate the risk of ototoxicity. Future studies should examine the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic targets of AGs and assess the efficacy and safety of administration by inhalation to improve efficacy and decrease risk.
Aminoglycosides (AGs) are a large class of broad-spectrum bactericidal drugs, including gentamicin, amikacin, tobramycin, streptomycin, netilmicin, and etimicin. These drugs contain one or more amino sugars bound to an amino-cyclitol ring by glycoside bond(s) and inhibit bacterial protein synthesis by binding the 16S rRNA of the 30S ribosome (Sajwan et al., 2024). Since streptomycin was first used to treat tuberculosis in 1944, clinicians have relied on AGs to treat many different infections by Gram-negative bacteria. Due to the nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity of AGs, they fell out of favor and were gradually replaced by a new generation of antibiotics, such as cephalosporins, carbapenems, and fluoroquinolones (Krause et al., 2016). However, the overuse of these newer antibiotics led to antibiotic resistance, and this has contributed to changes in the prevalence, transmission characteristics, and mechanisms of bacterial resistance, making infections by multidrug-resistant bacteria a major threat to public health (Luo et al., 2024). It is necessary for clinicians to administer antibiotics more rationally, educate the public about the overuse of antibiotics, and decrease the overuse of broad-spectrum antibiotics, such as carbapenems, to curb the spread of antibiotic resistance (Tao et al., 2024).
The development of new antibiotics and the renewed interest in older antibiotics are important measures that may aid in the treatment of drug-resistant bacteria. However, because significant time and resources are usually needed to develop new antibiotics, many clinicians have reconsidered the use of AGs because many bacteria are susceptible to this older class of drugs (Muteeb, 2023). Moreover, the combined use of AGs with other antibiotics, such as β-lactams, tigecycline, and fosfomycin, can improve their therapeutic effect, prevent subsequent infections, and reduce mortality (Guillamet et al., 2023; Darlow et al., 2021; Demirlenk et al., 2022). Plazomicin is a recently developed AG that has more potent bactericidal effects and causes fewer toxic and adverse effects, and this has led clinicians to use plazomicin for the treatment of infections by carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) (Eljaaly et al., 2019; Shaeer et al., 2019; Yan et al., 2022). Many studies have examined the clinical use of AGs during the past 10 years, but their widespread off-label use has made it challenging for researchers to follow recent developments and identify research hotspots in this field. Therefore, there is an urgent need to present a comprehensive review of the clinical applications of AGs that were reported during the last decade to inform researchers and clinicians about suitable treatment options for patients who are infected by drug-resistant bacteria.
Literature reviews are commonly used to summarize the research status of a field but, despite their value, they can be affected by subjective factors and may not provide quantitative results. Bibliometrics is the application of mathematical and statistical methods for characterization of the distribution, structure, quantitative relationships, and changes of the knowledge system of a discipline, and can provide a deeper understanding of the development and characteristics of a discipline during a defined period of time and thereby identify future research trends (Donthu et al., 2021). We performed a bibliometric analysis of the temporal and spatial relationships of clinical publications about AGs by analysis of the countries, institutions, authors, journals, highly cited publications, references, and keywords associated with these publications. Our examination of research hotspots and trends in this field provides important information for clinicians and researchers and may lead to the more rational use of AGs in the future.
The Web of Science Core Collection (WOSCC) was the data source, and the search time span was from 1 January 2013 to 31 December 2023. We used the following search formula (where TS refers to Topic and TDM refers to Therapeutic Drug Monitoring): (TS = aminoglycosides OR TS = streptomycin OR TS = neomycin OR TS = kanamycin OR TS = gentamicin OR TS = sisomicin OR TS = ribostamycin OR TS = micronomicin OR TS = spectinomycin OR TS = amikacin OR TS = netilmicin OR TS = etimicin OR TS = dibekacin OR TS = arbekacin OR TS = paromomycin OR TS = plazomicin) AND ((TS = TDM OR TS = “therapeutic drug monitoring” OR TS = “clinical pharmacokinetics” OR TS = “population pharmacokinetics”) OR ((TS = intensive care unit OR TS = children OR TS = newborn* OR TS = infant* OR TS = neonate* OR TS = adult OR TS = elderly OR TS = pediatric* OR TS = “critically ill” OR TS = “severe infection”) AND (TS = pharmacokinetics OR TS = safety OR TS = ototoxicity OR TS = nephrotoxicity OR TS = “clinical application” OR TS = “clinical effect” OR TS = effectiveness OR TS = “clinical efficacy”))).
Research articles and review articles related to the clinical study of AGs were included. The following types of articles were excluded: (i) meeting abstracts, editorial materials, early access materials, proceedings, letters, and corrections; (ii) non-English language articles; (iii) studies of animals or cells and veterinary studies; and (iv) studies unrelated to the clinical study of AGs.
The VOSviewer (version 1.6.19) was used to visualize and analyze the countries, institutions, authors, journals, highly cited publications, and co-cited references associated with the included publications. CiteSpace (version 6.2.3) was used to visualize the data and create scientific knowledge maps of keywords, and Excel 2021 was used to manage the extracted data and for statistical analysis.
Our search led to the preliminary identification of 1,497 publications, the inclusion of 915 eligible publications (697 research articles and 218 review articles) after screening (Figure 1A), and the determination of the number of publications and Total Global Citation Score (TGCS) for each year (Figure 1B). The number of publications per year generally increased over time, although there were some variations and a slight decrease since 2021. The largest number of publications was in 2021 (123), and the TGCS was highest in 2015 (2339), although there were only 67 publications that year. This indicates that the quality of publications during 2015 was particularly good and had important value for subsequent research. The sharp decline of the TGCS after 2021 is likely because of the delay from the time of publication to its citation or because studies after 2021 were less important.
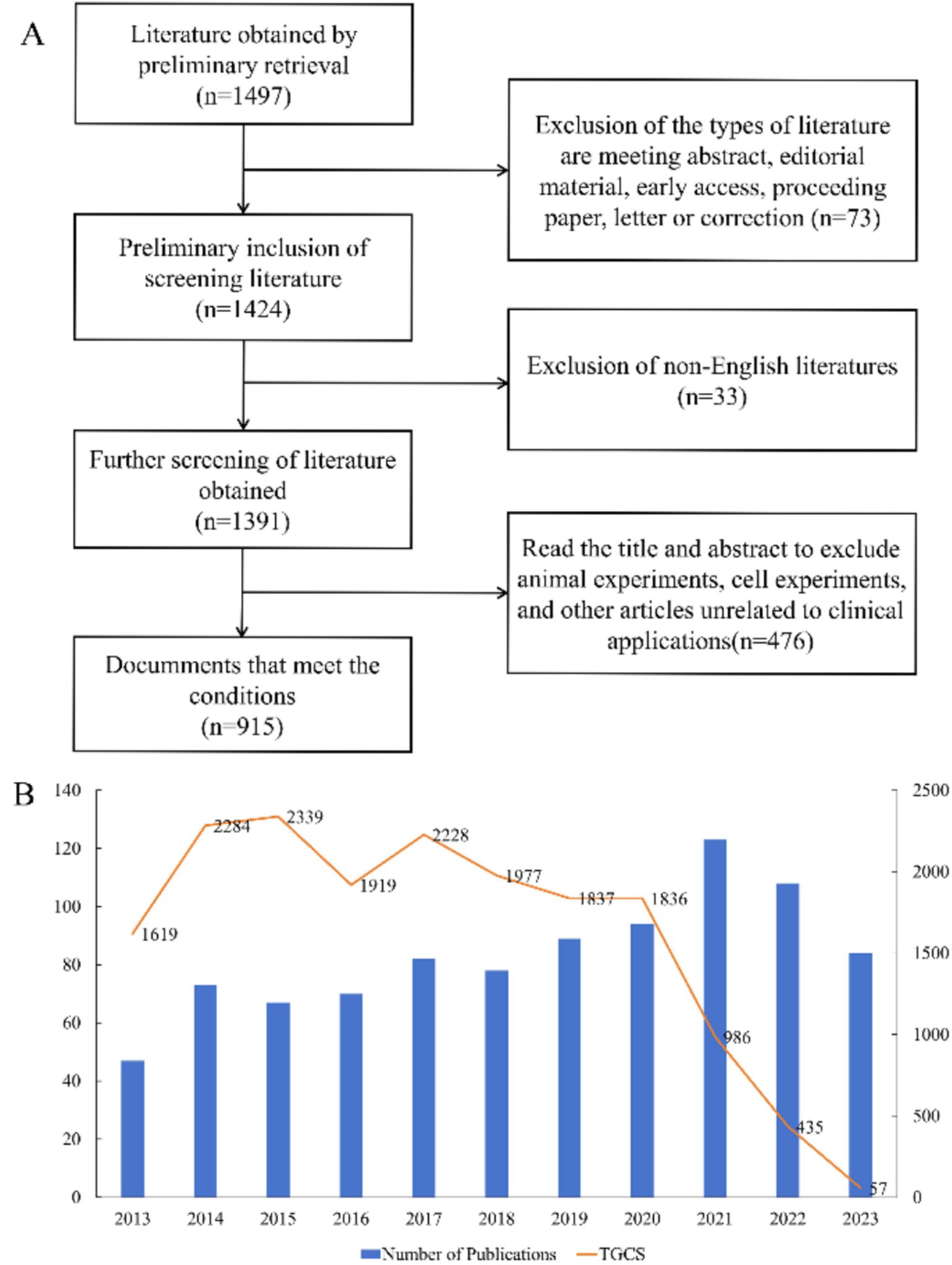
Figure 1. Overview of publications and citations. (A) Process used for literature screening. (B) Annual number of publications and Total Global Citation Score.
We identified the 10 countries with the most publications (Figure 2A), and these included the United States (260, 28.4%), several European countries, Australia (92, 10.1%), China (63, 6.9%), and Canada (45, 4.9%) (Table 1). Italy and Belgium had the highest average citations per publication (ACPP, 38.2 and 34.7 respectively), indicating that research from these two countries had the greatest value. We also identified a cooperation network among the 43 countries and regions with more than 5 publications (Figure 2B). The United States was the most centrally located country in this network, and it had cooperative relationships with most other countries, especially Australia, the Netherlands, and Belgium.
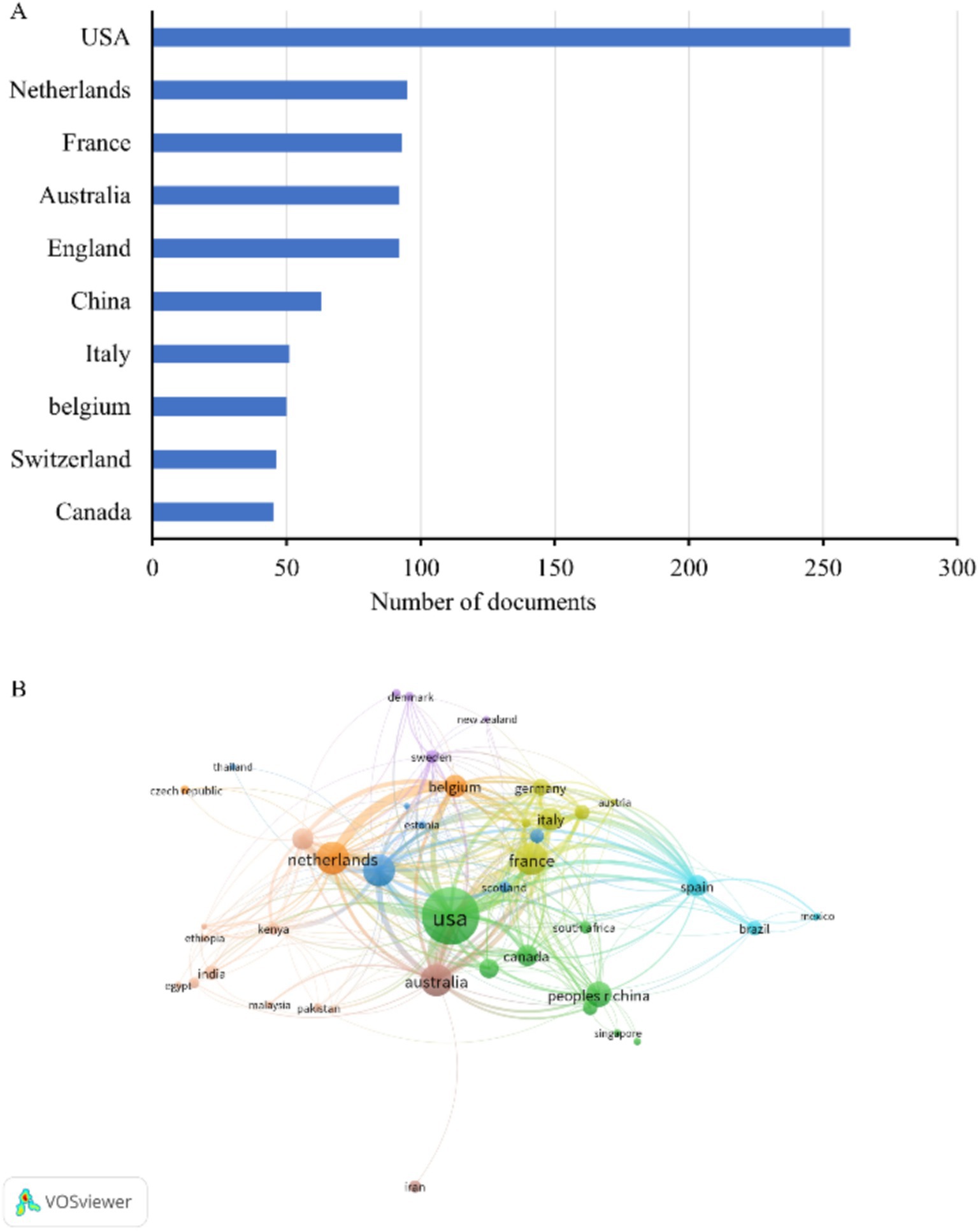
Figure 2. Publications in different countries. (A) Ten countries with the most publications. (B) Co-occurrence network of publications from different countries.
Analysis of the number of citations by different institutions showed that Australian institutions were the most productive (Table 2). The University of Queensland had the most publications (Cegielski et al., 2021). The University of Sydney and Monash University had the highest ACPP values (54.4 and 59.8, respectively), indicating that these two institutions produced the most valuable research and should be pursued for future collaborations. Analysis of the partnerships of institutions that had more than seven publications showed that the University of Queensland had the most prominent role (Figure 3) and that cooperations with the University of Queensland, Royal Brisbane and Women’s Hospital, the University of Sydney, and Monash University were most important.
The author with the most publications was JA Roberts (Australia), who had 29 publications and an ACPP of 42.4 (Table 3). Roberts mainly studied the application of AGs in critically ill patients (Jager et al., 2016; Abdul-Aziz et al., 2020; Roger et al., 2021; Roger et al., 2015; Roger et al., 2016; Bukkems et al., 2018; Roger et al., 2016; Boidin et al., 2019; Tait et al., 2022), the benefits of therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) of patients receiving AGs (Matusik et al., 2022; Abdul-Aziz et al., 2022; Imani et al., 2020), and the administration of AGs using nebulized inhalation (Solé-Lleonart et al., 2017; Rello et al., 2017; Solé-Lleonart et al., 2016). K Allegaert (Belgium) ranked second in terms of publications (Boidin et al., 2019), and he mainly studied the pharmacokinetics and dosing regimens of AGs for newborns (Smits et al., 2017; Dewandel et al., 2021; De Cock et al., 2014; Smits et al., 2015; Liu et al., 2019; Valitalo et al., 2015; Cristea et al., 2017; Allegaert et al., 2015). M Bassetti (Italy) had the highest ACPP (91.5), indicating that his research on multidrug-resistant bacteria and TDM of AGs had high quality (Abdul-Aziz et al., 2020; Niederman et al., 2020; Lodise et al., 2022; Bassetti et al., 2016). The cooperation network of authors with more than five publications (Figure 4) shows that most of the authors with a large number of publications had cooperative relationships; JA Roberts and K Allegaert were the main core authors, meaning they made the most significant contributions.
There were 915 publications published in 363 journals (Table 4), and the journals that had the most publications were Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (Satlin et al., 2011), Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (Niederman et al., 2020), and Therapeutic Drug Monitoring (Dewandel et al., 2021). However, these journals had lower ACPP values and Impact Factors based on Journal Citation Reports for 2022, suggesting that AG researchers should consider other journals to improve these metrics. The co-occurrence network of 46 journals that had more than 5 publications shows that most of the journals were related to antibacterial therapy and chemotherapy, and there were also some journals on pharmacokinetics (Figure 5A).
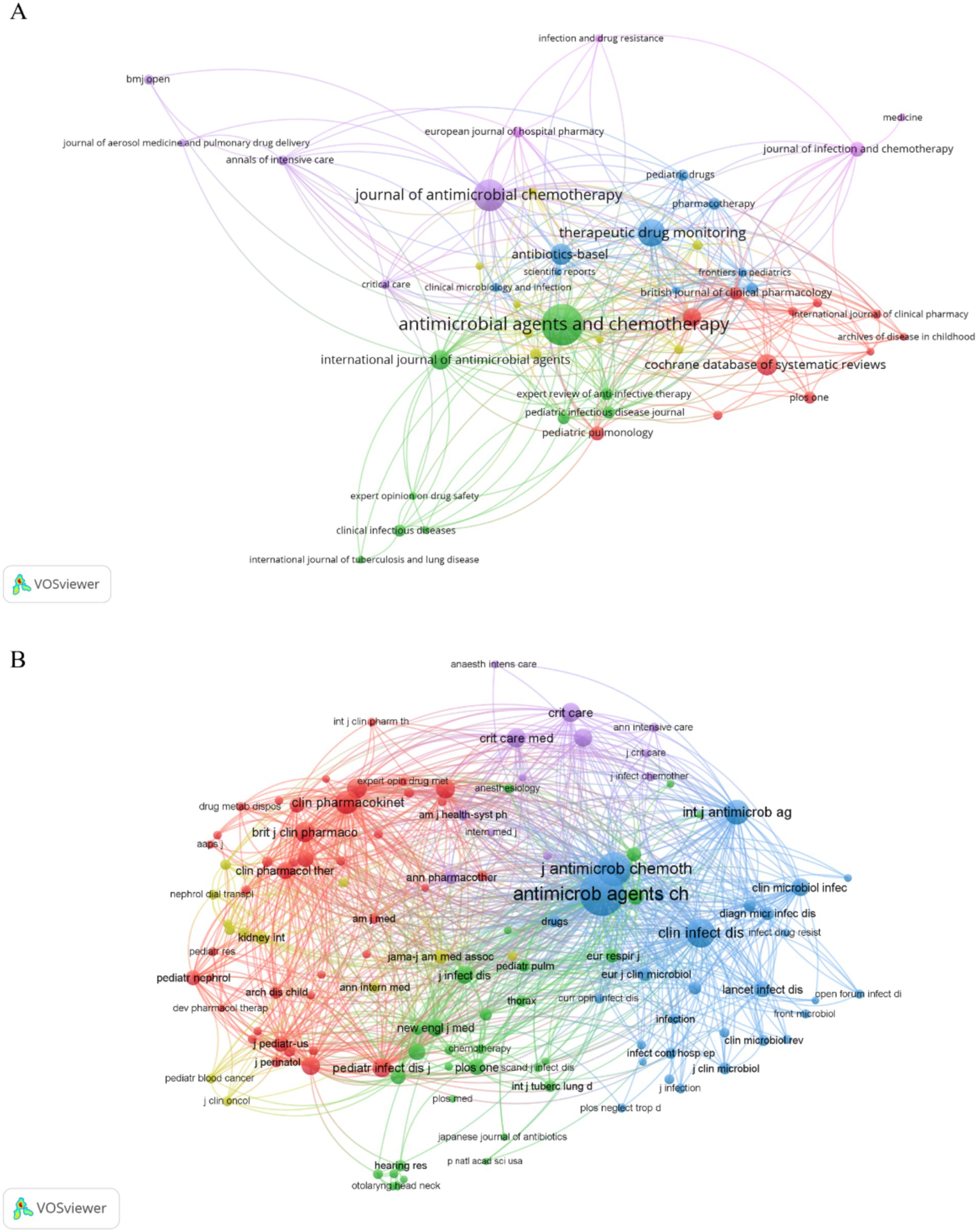
Figure 5. Journals and co-cited journals. (A) Co-occurrence network of journals. (B) Co-occurrence network of co-cited journals.
Our co-occurrence network of co-cited journals that had a minimum of 50 citations per journal (Figure 5B) showed that 124 of the 5,792 co-cited journals met this criterion. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy and Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy had core positions in this network and the top co-cited journals were Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, Clinical Infectious Diseases, International Journal of Antibiotic Agents, and Clinical Pharmacokinetics (Table 5). These top co-cited journals therefore have great value for future research in this field; however, most of these journals had IFs below 10, suggesting that future researchers should consider more influential journals.
Among all 918 publications, 82 had more than 50 citations, 156 had more than 30 citations, and the top 10 had 162 to 453 citations (Supplementary File 1). The network diagram of publications that had 30 or more citations (Figure 6A) demonstrated a central role for “Antimicrobial therapeutic drug monitoring in critically ill adult patients: a Position Paper.” This publication had 453 citations and recommended routine TDM when administering AGs to critically ill patients. Most of the highly cited publications were about therapeutic drugs and regimens used to treat drug-resistant bacteria, demonstrating that this topic is a ‘hot spot.’
References can be considered the knowledge base of a field. Publications with more citations can be considered the most significant, and a co-citation occurs when one publication cites two other publications. Our analysis of the 28,893 cited references showed that 74 publications had at least 20 citations, and we therefore identified the co-citation network of these publications (Figure 6B). The top 10 references according to the number of local citations indicated that many of these publications were relatively old, mostly before 2000 (Supplementary File 2), suggesting that recent clinical research in this field may be less important or lacking innovation. In addition, most of these studies examined dosing regimens of AGs and the effect of AGs on renal function, emphasizing that AG safety is a top priority. The article entitled “clinical response to aminoglycoside therapy: importance of the ratio of peak concentration to minimal inhibitory concentration,” by RD Moore et al. had the most local citations (124). The major result of this study is that the ratio of the peak concentration to minimum inhibitory concentration (Cmax/MIC) was significantly associated with clinical response and that the clinical response reached 85–90% when this ratio was 8–10 (Moore et al., 1987), a result that has significant value for the clinical application of AGs.
The number and evolution of keywords can reflect research ‘hot spots’ and changes in ‘hot spots,’ and may help elucidate the development of previous research and predict the development of future research. Our analysis of the top 30 keywords (Table 6) indicated the two most common keywords were “population pharmacokinetics” and “pharmacokinetics,” demonstrating an emphasis on these topics during the last decade. The top 30 keywords also include 3 different specific AGs (gentamicin, amikacin, and tobramycin), indicating that most researchers focused on these specific drugs. The other common keywords were “critically ill patients,” “children,” and “infants,” indicating a focus on these groups of patients. Several other common keywords are “resistance,” specific drug-resistant bacteria (“Pseudomonas aeruginosa” and “Klebsiella pneumoniae”), and “safety.” We also identified a network of keywords (Figure 7), in which a larger circle indicates a more common keyword, and the connection between the circles represents the appearance in the same publication.
We used CiteSpace to identify bursting keywords (those that increased over time) and presented the top 25 of these keywords (Figure 8). In this plot, a larger value indicates greater use of a keyword, the blue line represents the timing of the keyword burst, and the red line indicates the period with the strongest keyword burst. These results thus show that “renal function” had the strongest burst (5.72), followed by “hearing loss” (5.33). “Glomerular filtration rate” was the keyword with the longest-lasting burst (6 years), and three keywords—“continuous infusion,” “augmented renal clearance,” and “mortality”—have been bursting since 2023. This analysis shows that the safety of AGs, especially nephrotoxicity, was an area of active research in recent years, and may also be a ‘hot spot’ in the future.
We then performed a timeline visualization of keywords (Figure 9), in which a node in this plot represents the time when a keyword first appears. Thus, “aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity,” “kidney function,” “GFR,” “combinations,” and “model-informed precision dosing” were the core keywords during the past 2 years. These results suggest that nephrotoxicity and drug combinations were research ‘hot spots’ in this field, and are also likely to be the ‘hot spots’ in the future. Model-informed precision dosing is another recent research ‘hot spot.’ Altogether, these results suggest the need for more studies to establish an administration model for AGs by performing population pharmacokinetic studies to improve safety.
The present study is the first to use bibliometrics to analyze and visualize clinical research about AGs, and the results provide important information about the impact of recent research and guidance for future research and clinical applications. Our analysis of highly cited publications, co-cited references, and keywords showed that the main topics were drug-resistant bacteria, administration in vulnerable populations, safety, pharmacokinetics, combination therapy, and new methods of administration.
AGs are broad-spectrum antibacterial agents that have strong activity against various aerobic Gram-negative bacteria, such as Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Proteus, and Shigella. When used in combination with other antimicrobials, AGs can also increase the efficacy of treatment in patients infected by many drug-resistant bacteria, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, and Enterococcus faecium (Galani et al., 2020; Hirsch et al., 2013; Lim et al., 2008; Thy et al., 2023; Bassetti et al., 2019; Yadav et al., 2015; Moustafa et al., 2023; Al-Tulaibawi et al., 2023).
A systematic review and meta-analysis revealed that amikacin was highly effective for children infected with extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae (ESBL-PE) (Luo et al., 2023). Another meta-analysis suggested that ceftazidime combined with amikacin is the first choice for empirical treatment of cancer patients with febrile neutropenia, and that meropenem can be effective as the last defense against pathogens in these patients (Wang et al., 2021). El-Mahallawy et al. (2022) found that CRE had high resistance to colistin, that this resistance increased over time, and that AGs were the preferred drugs to decrease the use of colistin and prevent further increases of drug resistance. Cegielski et al. (2021) performed a meta-analysis and found that streptomycin and amikacin were the preferred AGs for the treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis, and the results from their drug sensitivity tests supported this practice. A cohort study that compared the effects of several drugs on the clearance of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in patients with urinary tract infections showed that AGs outperformed polymyxin B and tigecycline (Satlin et al., 2011). Stalenhoef et al. (2019) showed that intravesical instillation of gentamicin reduced the number of urinary tract infection episodes and the extent of antibiotic resistance, indicating that treatment with this AG was effective, safe, and feasible. Plazomicin is a recently developed AG and a promising alternative to carbapenems and β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitors for the treatment of complex urinary tract infections caused by multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (Bilinskaya et al., 2020).
Administering an antibiotic by inhalation can significantly increase the local concentration in the lungs while reducing the concentration in the blood and the whole body, thereby decreasing toxic and adverse effects (Bacle et al., 2021; Brodt et al., 2014; Desgrouas and Ehrmann, 2021). Therefore, inhalational administration of AGs has been a research ‘hot spot’ in recent years. Hassan et al. (2018) studied patients with hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) and ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP), comparing intravenous and inhalational amikacin. They showed that inhalational amikacin led to a higher clinical cure rate, less time in an ICU, more rapid complete recovery, and decreased nephrotoxicity. An amikacin liposome inhalation suspension (ALIS) that was designed for inhalational delivery was the first therapy approved for refractory Mycobacterium avium complex lung disease (MAC-LD) (Daley et al., 2020). A subsequent population pharmacokinetic study of ALIS showed that the systemic levels of amikacin in the serum and urine of patients with refractory non-tuberculous mycobacterial lung disease were significantly lower following daily ALIS administration than those previously reported for parenteral amikacin (Rubino et al., 2021). An international phase 3 open-label trial and an open-label extension study of patients with refractory MAC-LD demonstrated the efficacy and safety of daily ALIS when added to guideline-based therapy (Griffith et al., 2018; Winthrop et al., 2021). The United States recently approved ALIS as part of a combined antimicrobial regimen for the treatment of MAC-LD in adults who received a multi-drug background regimen for 6 or more months, whose sputum culture was not yet negative, and who had no (or only limited) alternative treatment options (Golia et al., 2020).
In addition to amikacin, there is also great interest in inhalational gentamicin and inhalational tobramycin. For example, Boisson et al. (2018) showed that inhalational (rather than intravenous) gentamicin for the treatment of patients with VAP led to a greater drug concentration in the lungs and a lower systemic concentration. Twiss et al. (2022) performed randomized controlled crossover trials of children (age 5–15 years) who had bronchiectasis and found that inhalational gentamicin decreased bacterial density in the sputum and the levels of various inflammatory factors. Another study of patients with bronchiectasis and chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection showed that inhalational tobramycin decreased the bacterial density in the sputum, shortened the hospitalization time, relieved symptoms, and prevented patient deterioration (Elborn et al., 2022). However, there are no approved inhalational forms and established dosages of gentamicin and tobramycin, indicating the need for further research on the efficacy and safety of these and other inhalational AGs.
The main adverse effects associated with AGs are irreversible ototoxicity and reversible nephrotoxicity (O'Sullivan et al., 2017), and recent studies showed that AG-associated nephrotoxicity was related to a high blood concentration and can be reduced by TDM and dose adjustment (Jayakumar et al., 2020; Alqahtani et al., 2020; Ben Romdhane et al., 2019; Mason et al., 2017). The ototoxicity of AGs can manifest as vestibular or cochlear toxicity (Prayle et al., 2010). Cochlear toxicity can cause tinnitus and/or sensorineural hearing loss and even deafness; vestibular toxicity can manifest as dizziness, nausea, nystagmus, and ataxia (Rivetti et al., 2023). Lanvers-Kaminsky et al. (2017) compared the severity of ototoxicity among different AGs and concluded that neomycin had high toxicity, gentamicin, kanamycin, and tobramycin had moderate toxicity, and amikacin and netilmicin had low toxicity. Ototoxicity may occur even when the blood concentration of an AG is within the recommended therapeutic range, and some studies have shown that the cumulative duration of AG treatment is a predictor of ototoxicity (Modongo et al., 2015; Beaubien et al., 1989). The ototoxicity of AGs is also related to certain genetic factors, in particular a variant of the mitochondrial gene 12S rRNA (Prezant et al., 1993). In particular, the m.1555A > G variant of this gene causes a conformational change in this eukaryotic subunit so that it is more similar to the bacterial subunit (16S rRNA), leading to increased off-target binding of AGs to the human gene. The effect of this increased affinity for AGs is most pronounced in hair cells of the inner ear, and this explains the increased cell damage in this region and overall ototoxicity (Qian and Guan, 2009; McDermott et al., 2022). The Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guideline recommends that individuals with this gene variant should not receive AGs unless the severity of the infection exceeds the risk of permanent hearing loss, and there is no safe or effective alternative treatment (McDermott et al., 2022). McDermott et al. (2022) developed a rapid point-of-care test for the m.1555A > G variant, and this test can be used to guide antibiotic prescriptions and prevent AG-associated ototoxicity.
AGs have a narrow therapeutic index because they can cause ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity, and patient age, weight, and renal function also impact AG metabolism and the therapeutic index (Germovsek et al., 2017). It is well known that the therapeutic effect of an AG is related to its Cmax and that a greater trough concentration (Cmin) can lead to toxicity, but the optimal PK/PD target for AGs is still under debate (Bland et al., 2018). The effects of an AG are concentration-dependent, so the Cmax/MIC ratio is related to antibacterial activity and clinical efficacy, and the clinical response can reach 85 to 95% when the Cmax/MIC ratio is 8 to 10 (Moore et al., 1987). Jayakumar et al. (2020) studied patients receiving short-term amikacin treatment and showed that the Cmax/MIC ratio can predict the time required for clinical cure and that the Cmin can predict nephrotoxicity. A meta-analysis showed that a Cmin below 2 mg/L for gentamicin and a Cmin below 10 mg/L for amikacin can reduce the risk of nephrotoxicity (Yamada et al., 2021). However, this study only consisted of two observational studies of amikacin and was not a randomized controlled trial.
TDM of AGs can help achieve the goals of safe and effective treatment (Abdul-Aziz et al., 2022). It is particularly important in patients with impaired renal function, as AGs are not metabolized and are only excreted by the kidneys. A ‘Position Paper’ from multiple clinical societies recommended routine TDM of AGs in critically ill patients (Abdul-Aziz et al., 2020), and Ben Romdhane et al. (2019) conducted a retrospective study that found dose adjustment based on TDM helped achieve a non-toxic Cmin. A simulation study showed that using saliva as an alternative matrix for non-invasive TDM was successful when using non-linear mixed-effect models combined with Bayesian optimization (Kruizinga et al., 2021). Samb et al. (2023) developed a non-invasive TDM method for measuring amikacin from saliva, showed that the results were comparable to those from plasma samples, and suggested that this method may be especially useful for premature infants or newborns who have late-onset sepsis.
Newborns, children, and the elderly are the most common users of antibacterial drugs among hospitalized patients, but dosing in these patients is difficult because they typically have diminished immune function, decreased renal function, and altered body water content. Moreover, the in vivo pharmacokinetics of amikacin have large inter-individual differences and are affected by patient age, body weight, and renal function, so individualization of dosage is usually necessary (Shi and Klotz, 2011). Recent studies showed that the administration of an AG once per day was safer and more effective than multiple doses per day (Karimzadeh et al., 2023).
TDM is essential when AGs are given to elderly patients (>75 years old) who have severe infections, and short-term treatment and avoidance of other nephrotoxic drugs can reduce the risk of nephrotoxicity in these patients (Fraisse et al., 2014). Sadeghi et al. (2018) examined the elderly and critically ill patients and found that a higher dose of amikacin and administration at more extended intervals may be more appropriate than a standard dosage of once per day. A systematic review and meta-analysis found that elderly adults had a significantly higher risk of acute kidney injury than non-elderly adults; however, the risk of acute kidney injury was similar in elderly and non-elderly adults taking AGs (Chinzowu et al., 2021). Medellín-Garibay et al. (2022) designed an initial dosing regimen of amikacin for elderly patients based on non-linear mixed effects modeling and found that consideration of body mass index (BMI) and creatinine clearance (CrCl) increased the probability of achieving efficacy and safety.
Clinicians should consider gestational age and postnatal age when developing a dosage regimen for neonates (Germovsek et al., 2017). For example, an observational study that examined a large neonatal cohort confirmed that body weight, gestational age, and postnatal age were associated with increased clearance of gentamicin and that the co-administration of dopamine significantly decreased gentamicin clearance (Fuchs et al., 2014). Compared to full-term newborns, premature infants require higher doses and longer dosing intervals of AGs to achieve the target concentration (Fuchs et al., 2014). Hodiamont et al. (2022) performed a retrospective clinical pharmacokinetic study of gentamicin and recommended that the initial dose should be based on total body weight (or adjusted body weight for obese patients), that the dose should be 7 mg/kg for adults and children over the age of 1 month (including critically ill patients), and that TDM should be used after the first administration, although they recommend against gentamicin monotherapy for the treatment of pneumonia caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. There is also evidence that obese patients with reduced renal function should receive a lower dose of gentamicin and the dosing interval should be prolonged (Smit et al., 2020); critically ill patients with hypoalbuminemia require a higher initial dose of gentamicin to achieve Cmax (Hodiamont et al., 2017); and creatinine clearance (calculated from 6-h urinary creatinine concentration) provided better predictions of Cmin in critically ill patients than serum creatinine and creatinine clearance estimated by the Cockcroft-Gault formula (Hodiamont et al., 2017).
Zazo et al. (2022) found that an extended-interval gentamicin dosing regimen (6 mg/kg q36h for term infants and 6 mg/kg q48h for preterm neonates) led to high efficacy and low toxicity, and could be used for Model-Informed Precision Dosing in neonates. Ekmen and Dogan (2021) studied newborns and found that gentamicin did not have ototoxic effects when used short term (5–7 days) with an extended dosing interval (24–48 h), and when no loop diuretics (which are often ototoxic) were co-administered. Hashiguchi et al. (2023) explored the AUC-guided dose of tobramycin for the treatment of infections by drug-resistant bacteria based on population pharmacokinetic models and suggested a lower initial dose (15, 11, 10, 8, and 7 mg/kg) according to the serum creatinine level (>90, 60–89, 45–59, 30–44, and 15–29 mL/min/1.73 m2), with TDM at the peak and 24 h after the first dose. Aquino et al. (2023) found that cancer patients needed a higher initial dose of amikacin when they received chemotherapy during the previous 30 days.
Our research demonstrated that AGs play an important role in the treatment of infections by multidrug-resistant bacteria, such as β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae and carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. TDM can improve the efficacy of AGs and reduce the occurrence of nephrotoxicity, especially in vulnerable populations, such as the elderly, children, and infants. To prevent ototoxicity, long dosing cycles should be avoided and AGs should not be given to patients with the m.1555 A > G gene variant. Inhalational administration of AGs has significant potential because it can achieve a sufficient concentration in the lungs with a reduced concentration in systemic blood. In the future, more research is needed to determine the PK/PD targets of AGs and assess the effectiveness and safety of inhalational administration to improve the efficacy of these drugs for the treatment of clinical infections.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
TZ: Conceptualization, Investigation, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. NC: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MZ: Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LL: Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BL: Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YF: Conceptualization, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZH: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CL: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Henan Province 2024 Science and Technology Development Plan (No. 242102310242).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1532231/full#supplementary-material
Abdul-Aziz, M. H., Alffenaar, J. W. C., Bassetti, M., Bracht, H., Dimopoulos, G., Marriott, D., et al. (2020). Antimicrobial therapeutic drug monitoring in critically ill adult patients: a position paper. Intensive Care Med. 46, 1127–1153. doi: 10.1007/s00134-020-06050-1
Abdul-Aziz, M. H., Brady, K., Cotta, M. O., and Roberts, J. A. (2022). Therapeutic drug monitoring of antibiotics: defining the therapeutic range. Ther. Drug Monit. 44, 19–31. doi: 10.1097/FTD.0000000000000940
Allegaert, K., Cossey, V., and van den Anker, J. N. (2015). Dosing guidelines of aminoglycosides in neonates: a balance between physiology and feasibility. Curr. Pharm. Des. 21, 5699–5704. doi: 10.2174/1381612821666150901110659
Alqahtani, S., Alhumoud, A., Abushomi, H., Alsultan, A., and Balkhi, B. (2020). Appropriate therapeutic drug monitoring of antibiotics contributed to lower nephrotoxicity. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 58, 82–88. doi: 10.5414/CP203545
Al-Tulaibawi, N. A. J., Aal-Aaboda, M., and Al-Qaesy, D. B. A. (2023). Prevalence and antibiotic sensitivity profile of Bacteria in patients with ear infections. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 17, 549–553. doi: 10.22207/JPAM.17.1.52
Aquino, M., Tinoco, M., Bicker, J., Falcao, A., Rocha, M., and Fortuna, A. (2023). Therapeutic drug monitoring of amikacin in neutropenic oncology patients. Antibiotics 12:373. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12020373
Bacle, A., Bouzillé, G., Bruyère, A., Cuggia, M., Fardel, O., and Le Corre, P. (2021). Drivers of absolute systemic bioavailability after oral pulmonary inhalation in humans. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 164, 36–53. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2021.04.014
Bassetti, M., Peghin, M., and Pecori, D. (2016). The management of multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 29, 583–594. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0000000000000314
Bassetti, M., Peghin, M., Vena, A., and Giacobbe, D. R. (2019). Treatment of infections due to MDR gram-negative bacteria. Front. Med. 6:74. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2019.00074
Beaubien, A. R., Desjardins, S., Ormsby, E., Bayne, A., Carrier, K., Cauchy, M. J., et al. (1989). Incidence of amikacin ototoxicity: a sigmoid function of total drug exposure independent of plasma levels. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 10, 234–243. doi: 10.1016/0196-0709(89)90002-1
Ben Romdhane, H., Ben Fredj, N., Chaabane, A., Ben Aicha, S., Chadly, Z., Ben Fadhel, N., et al. (2019). Interest of therapeutic drug monitoring of aminoglycosides administered by a monodose regimen. Nephrol. Ther. 15, 110–114. doi: 10.1016/j.nephro.2018.08.004
Bilinskaya, A., Linder, K. E., and Kuti, J. L. (2020). Plazomicin: an intravenous aminoglycoside antibacterial for the treatment of complicated urinary tract infections. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 18, 705–720. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2020.1759419
Bland, C. M., Pai, M. P., and Lodise, T. P. (2018). Reappraisal of contemporary pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic principles for informing aminoglycoside dosing. Pharmacotherapy 38, 1229–1238. doi: 10.1002/phar.2193
Boidin, C., Bourguignon, L., Cohen, S., Roger, C., Lefrant, J. Y., Roberts, J. A., et al. (2019). Amikacin initial dose in critically ill patients: a nonparametric approach to optimize a priori pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic target attainments in individual patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 63:e00993-19. doi: 10.1128/aac.00993-19
Boisson, M., Mimoz, O., Hadzic, M., Marchand, S., Adier, C., Couet, W., et al. (2018). Pharmacokinetics of intravenous and nebulized gentamicin in critically ill patients. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 73, 2830–2837. doi: 10.1093/jac/dky239
Brodt, A. M., Stovold, E., and Zhang, L. J. (2014). Inhaled antibiotics for stable non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis: a systematic review. Eur. Respir. J. 44, 382–393. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00018414
Bukkems, L. H., Roger, C., Hodiamont, C. J., Lefrant, J. Y., Juffermans, N. P., Roberts, J. A., et al. (2018). Predictive performance of a gentamicin population pharmacokinetic model in two western populations of critically ill patients. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 52, 218–225. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2018.04.016
Cegielski, J. P., Chan, P.-C., Lan, Z., Udwadia, Z. F., Viiklepp, P., Yim, J.-J., et al. (2021). Aminoglycosides and Capreomycin in the treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: individual patient data meta-analysis of 12 030 patients from 25 countries, 2009-2016. Clin. Infect. Dis. 73:e3929. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa621
Chinzowu, T., Roy, S., and Nishtala, P. S. (2021). Risk of antimicrobial-associated organ injury among the older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr. 21:617. doi: 10.1186/s12877-021-02512-3
Cristea, S., Smits, A., Kulo, A., Knibbe, C. A. J., van, M., Krekels, E. H. J., et al. (2017). Amikacin pharmacokinetics to optimize dosing in neonates with perinatal asphyxia treated with hypothermia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 61:e01282-17. doi: 10.1128/aac.01282-17
Daley, C. L., Iaccarino, J. M., Lange, C., Cambau, E., Wallace, R. J., Andrejak, C., et al. (2020). Treatment of nontuberculous mycobacterial pulmonary disease: an official ATS/ERS/ESCMID/IDSA clinical practice guideline. Clin. Infect. Dis. 71, 905–913. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa1125
Darlow, C. A., Docobo-Perez, F., Farrington, N., Johnson, A., McEntee, L., Unsworth, J., et al. (2021). Amikacin combined with Fosfomycin for treatment of neonatal Sepsis in the setting of highly prevalent antimicrobial resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 65:e0029321. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00293-21
De Cock, R. F. W., Allegaert, K., Sherwin, C. M. T., Nielsen, E. I., de, M., van, J., et al. (2014). A neonatal amikacin covariate model can be used to predict ontogeny of other drugs eliminated through glomerular filtration in neonates. Pharm. Res. 31, 754–767. doi: 10.1007/s11095-013-1197-y
Demirlenk, Y. M., Gücer, L. S., Uçku, D., Tanrıöver, C., Akyol, M., Kalay, Z., et al. (2022). A meta-analysis for the role of aminoglycosides and tigecyclines in combined regimens against colistin-and carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae bloodstream infections. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 41, 761–769. doi: 10.1007/s10096-022-04429-0
Desgrouas, M., and Ehrmann, S. (2021). Inhaled antibiotics during mechanical ventilation-why it will work. Ann. Transl. Med. 9:598. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-3686
Dewandel, I., Allegaert, K., Renard, M., Laenen, A., and Smits, A. (2021). Covariates of amikacin disposition in a large pediatric oncology cohort. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 59, 31–41. doi: 10.5414/CP203793
Donthu, N., Kumar, S., Mukherjee, D., Pandey, N., and Lim, W. M. (2021). How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: an overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 133, 285–296. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.04.070
Ekmen, S., and Dogan, E. (2021). Evaluation of gentamicin ototoxicity in newborn infants: a retrospective observational study. Int J Pediatr. 9, 13137–13144. doi: 10.22038/ijp.2021.55656.4383
Elborn, J. S., Blasi, F., Haworth, C. S., Ballmann, M., Tiddens, H., Murris-Espin, M., et al. (2022). Bronchiectasis and inhaled tobramycin: a literature review. Respir. Med. 192:106728:106728. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2021.106728
Eljaaly, K., Alharbi, A., Alshehri, S., Ortwine, J. K., and Pogue, J. M. (2019). Plazomicin: a novel aminoglycoside for the treatment of resistant gram-negative bacterial infections. Drugs 79, 243–269. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-1054-3
El-Mahallawy, H. A., El Swify, M., Hak, A. A., and Zafer, M. M. (2022). Increasing trends of colistin resistance in patients at high-risk of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Ann. Med. 54, 1–9. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2022.2129775
Fraisse, T., Aygon, C. G., Paccalin, M., Vitrat, V., De Wazieres, B., Baudoux, V., et al. (2014). Aminoglycosides use in patients over 75 years old. Age Ageing 43, 676–681. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afu023
Fuchs, A., Guidi, M., Giannoni, E., Werner, D., Buclin, T., Widmer, N., et al. (2014). Population pharmacokinetic study of gentamicin in a large cohort of premature and term neonates. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 78, 1090–1101. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12444
Galani, I., Papoutsaki, V., Karantani, I., Karaiskos, I., Galani, L., Adamou, P., et al. (2020). In vitro activity of ceftolozane/tazobactam alone and in combination with amikacin against MDR/XDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from Greece. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 75, 2164–2172. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkaa160
Germovsek, E., Barker, C. I., and Sharland, M. (2017). What do I need to know about aminoglycoside antibiotics? Arch. Dis. Child. Educ. Pract. Ed. 102, 89–93. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2015-309069
Golia, A., Mahmood, B., Fundora, Y., Thornby, K. A., and Chahine, E. (2020). Amikacin liposome inhalation suspension for Mycobacterium avium complex lung disease. Sr Care Pharm. 35, 162–170. doi: 10.4140/TCP.n.2020.162
Griffith, D. E., Eagle, G., Thomson, R., Aksamit, T. R., Hasegawa, N., Morimoto, K., et al. (2018). Amikacin liposome inhalation suspension for treatment-refractory lung disease caused by Mycobacterium avium complex (CONVERT). A prospective, open-label, randomized study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 198, 1559–1569. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201807-1318OC
Guillamet, M. C. V., Damulira, C., Atkinson, A., Fraser, V. J., Micek, S., and Kollef, M. H. (2023). Addition of aminoglycosides reduces recurrence of infections with multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacilli in patients with sepsis and septic shock. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 62:106913. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106913
Hashiguchi, Y., Matsumoto, N., Oda, K., Jono, H., and Saito, H. (2023). Population pharmacokinetics and AUC-guided dosing of tobramycin in the treatment of infections caused by glucose-nonfermenting gram-negative Bacteria. Clin. Ther. 45, 400–414. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2023.03.015
Hassan, N. A., Awdallah, F. F., Abbassi, M. M., and Sabry, N. A. (2018). Nebulized versus IV amikacin as adjunctive antibiotic for hospital and ventilator-acquired pneumonia Postcardiac surgeries: a randomized controlled trial. Crit. Care Med. 46, 45–52. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000002695
Hirsch, E. B., Guo, B. N., Chang, K. T., Cao, H., Ledesma, K. R., Singh, M., et al. (2013). Assessment of antimicrobial combinations for Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase-Producing K. pneumoniae. J. Infect. Dis. 207, 786–793. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jis766
Hodiamont, C. J., Juffermans, N. P., Bouman, C. S. C., de Jong, M. D., Mathot, R. A. A., and van Hest, R. M. (2017). Determinants of gentamicin concentrations in critically ill patients: a population pharmacokinetic analysis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 49, 204–211. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2016.10.022
Hodiamont, C. J., van den Broek, A. K., de Vroom, S. L., Prins, J. M., Mathôt, R. A. A., and van Hest, R. M. (2022). Clinical pharmacokinetics of gentamicin in various patient populations and consequences for optimal dosing for gram-negative infections: an updated review. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 61, 1075–1094. doi: 10.1007/s40262-022-01143-0
Imani, S., Alffenaar, J. W., Cotta, M. O., Daveson, K., van, S., Lau, C., et al. (2020). Therapeutic drug monitoring of commonly used anti-infective agents: a nationwide cross-sectional survey of Australian hospital practices. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 56:106180:106180. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106180
Jager, N. G. L., van Hest, R. M., Lipman, J., Taccone, F. S., and Roberts, J. A. (2016). Therapeutic drug monitoring of anti-infective agents in critically ill patients. Expert. Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 9, 961–979. doi: 10.1586/17512433.2016.1172209
Jayakumar, I., Mathaiyan, J., Mandal, J., Deepanjali, S., and Sreenivasan, S. K. (2020). Impact of therapeutic drug monitoring on once-daily regimen of amikacin in patients with urinary tract infection: a prospective observational study. Ther. Drug Monit. 42, 841–847. doi: 10.1097/FTD.0000000000000800
Karimzadeh, I., Abdollahpour-Alitappeh, M., Ghaffari, S., Mahi-Birjand, M., Barkhordari, A., and Alemzadeh, E. (2023). Aminoglycosides: single-or multiple-daily dosing? An updated qualitative systematic review of randomized trials on toxicity and efficacy. Curr. Mol. Med. 1358–1373. doi: 10.2174/1566524023666230801160452
Krause, K. M., Serio, A. W., Kane, T. R., and Connolly, L. E. (2016). Aminoglycosides: an overview. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 6:a027029. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a027029
Kruizinga, M. D., Stuurman, F. E., Driessen, G. J. A., Cohen, A. F., Bergmann, K. R., and van Esdonk, M. J. (2021). Theoretical performance of nonlinear mixed-effect models incorporating saliva as an alternative sampling matrix for therapeutic drug monitoring in pediatrics: a simulation study. Ther. Drug Monit. 43, 546–554. doi: 10.1097/FTD.0000000000000904
Lanvers-Kaminsky, C., Zehnhoff-Dinnesen, A. G. A., Parfitt, R., and Ciarimboli, G. (2017). Drug-induced ototoxicity: mechanisms, pharmacogenetics, and protective strategies. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 101, 491–500. doi: 10.1002/cpt.603
Lim, T. P., Ledesma, K. R., Chang, K. T., Hou, J. G., Kwa, A. L., Nikolaou, M., et al. (2008). Quantitative assessment of combination antimicrobial therapy against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 52, 2898–2904. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01309-07
Liu, X. X., Smits, A., Wang, Y. H., Renard, M., Wead, S., Kagan, R. J., et al. (2019). Impact of disease on amikacin pharmacokinetics and dosing in children. Ther. Drug Monit. 41, 44–52. doi: 10.1097/FTD.0000000000000568
Lodise, T. P., Bassetti, M., Ferrer, R., Naas, T., Niki, Y., Paterson, D. L., et al. (2022). All-cause mortality rates in adults with carbapenem-resistant gram-negative bacterial infections: a comprehensive review of pathogen-focused, prospective, randomized, interventional clinical studies. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 20, 707–719. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2022.2020099
Luo, Q. X., Lu, P., Chen, Y. B., Shen, P., Zheng, B. W., Ji, J. R., et al. (2024). ESKAPE in China: epidemiology and characteristics of antibiotic resistance. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 13:2317915. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2024.2317915
Luo, H., Xu, L. N., and Chen, Y. (2023). Drug resistance and susceptibility of amikacin in children with extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacterales: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 106:115956. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2023.115956
Mason, T., Verley, M., Gossell-Williams, M., Thorbourne, A., Walcott-Mitchell, A., Hoe, K., et al. (2017). Gentamicin therapeutic drug monitoring: importance in the hospital setting. West Ind. Med. J. 66, 324–328. doi: 10.7727/wimj.2015.603
Matusik, E., Boidin, C., Friggeri, A., Richard, J. C., Bitker, L., Roberts, J. A., et al. (2022). Therapeutic drug monitoring of antibiotic drugs in patients receiving continuous renal replacement therapy or intermittent hemodialysis: a critical review. Ther. Drug Monit. 44, 86–102. doi: 10.1097/FTD.0000000000000941
McDermott, J. H., Mahaveer, A., James, R. A., Booth, N., Turner, M., Harvey, K. E., et al. (2022). Rapid point-of-care genotyping to avoid aminoglycoside-induced ototoxicity in neonatal intensive care. JAMA Pediatr. 176, 486–492. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2022.0187
McDermott, J. H., Wolf, J., Hoshitsuki, K., Huddart, R., Caudle, K. E., Whirl-Carrillo, M., et al. (2022). Clinical Pharmacogenetics implementation consortium guideline for the use of aminoglycosides based on MT-RNR1 genotype. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 111, 366–372. doi: 10.1002/cpt.2309
Medellín-Garibay, S., Romano-Aguilar, M., Parada, A., Suárez, D., Romano-Moreno, S., Barcia, E., et al. (2022). Amikacin pharmacokinetics in elderly patients with severe infections. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 175:106219:106219. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2022.106219
Modongo, C., Pasipanodya, J. G., Zetola, N. M., Williams, S. M., Sirugo, G., and Gumbo, T. (2015). Amikacin concentrations predictive of ototoxicity in multidrug-resistant tuberculosis patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 59, 6337–6343. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01050-15
Moore, R. D., Lietman, P. S., and Smith, C. R. (1987). Clinical response to aminoglycoside therapy: importance of the ratio of peak concentration to minimal inhibitory concentration. J. Infect. Dis. 155, 93–99. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.1.93
Moustafa, N. M., Mahmoud, F. M., Khamsin, N. W. B., Almomen, F., Alali, M., Abosbaih, M., et al. (2023). Antimicrobial susceptibility of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from intensive and non-intensive care units patients: a one-year retrospective study in a tertiary healthcare hospital, Saudi Arabia. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 17, 2453–2466. doi: 10.22207/JPAM.17.4.43
Muteeb, G. (2023). Network meta-analysis of antibiotic resistance patterns in gram-negative bacterial infections: a comparative study of carbapenems, fluoroquinolones, and aminoglycosides. Front. Microbiol. 14:1304011. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1304011
Niederman, M. S., Alder, J., Bassetti, M., Boateng, F., Cao, B., Corkery, K., et al. (2020). Inhaled amikacin adjunctive to intravenous standard-of-care antibiotics in mechanically ventilated patients with gram-negative pneumonia (INHALE): a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3, superiority trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 20, 330–340. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(19)30574-2
O'Sullivan, M. E., Perez, A., Lin, R., Sajjadi, A., Ricci, A. J., and Cheng, A. G. (2017). Towards the prevention of aminoglycoside-related hearing loss. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 11:325. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2017.00325
Prayle, A., Watson, A., Fortnum, H., and Smyth, A. (2010). Side effects of aminoglycosides on the kidney, ear and balance in cystic fibrosis. Thorax 65, 654–658. doi: 10.1136/thx.2009.131532
Prezant, T. R., Agapian, J. V., Bohlman, M. C., Bu, X., Öztas, S., Qiu, W. Q., et al. (1993). Mitochondrial ribosomal RNA mutation associated with both antibiotic-induced and non-syndromic deafness. Nat. Genet. 4, 289–294. doi: 10.1038/ng0793-289
Qian, Y. P., and Guan, M. X. (2009). Interaction of aminoglycosides with human mitochondrial 12S rRNA carrying the deafness-associated mutation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 53, 4612–4618. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00965-08
Rello, J., Solé-Lleonart, C., Rouby, J. J., Chastre, J., Blot, S., Poulakou, G., et al. (2017). Use of nebulized antimicrobials for the treatment of respiratory infections in invasively mechanically ventilated adults: a position paper from the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 23, 629–639. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2017.04.011
Rivetti, S., Romano, A., Mastrangelo, S., Attinà, G., Maurizi, P., and Ruggiero, A. (2023). Aminoglycosides-related ototoxicity: mechanisms, risk factors, and prevention in pediatric patients. Pharmaceuticals 16:1353. doi: 10.3390/ph16101353
Roger, C., Louart, B., Elotmani, L., Barton, G., Escobar, L., Koulenti, D., et al. (2021). An international survey on aminoglycoside practices in critically ill patients: the AMINO III study. Ann. Intensive Care 11:49. doi: 10.1186/s13613-021-00834-4
Roger, C., Nucci, B., Louart, B., Friggeri, A., Knani, H., Evrard, A., et al. (2016). Impact of 30 mg/kg amikacin and 8 mg/kg gentamicin on serum concentrations in critically ill patients with severe sepsis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 71, 208–212. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkv291
Roger, C., Nucci, B., Molinari, N., Bastide, S., Saissi, G., Pradel, G., et al. (2015). Standard dosing of amikacin and gentamicin in critically ill patients results in variable and subtherapeutic concentrations. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 46, 21–27. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2015.02.009
Roger, C., Wallis, S. C., Muller, L., Saissi, G., Lipman, J., Lefrant, J. Y., et al. (2016). Influence of renal replacement modalities on amikacin population pharmacokinetics in critically ill patients on continuous renal replacement therapy. ASM J. CD 60, 4901–4909. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00828-16
Rubino, C. M., Onufrak, N. J., van, J., Griffith, D. E., Bhavnani, S. M., Yuen, D. W., et al. (2021). Population pharmacokinetic evaluation of amikacin liposome inhalation suspension in patients with treatment-refractory nontuberculous mycobacterial lung disease. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 46, 277–287. doi: 10.1007/s13318-020-00669-7
Sadeghi, K., Hamishehkar, H., Najmeddin, F., Ahmadi, A., Hazrati, E., Honarmand, H., et al. (2018). High-dose amikacin for achieving serum target levels in critically ill elderly patients. Infect. Drug Resist. 11, 223–228. doi: 10.2147/idr.S150839
Sajwan, R. K., Hashmi, S. Z. H., Himanshu, J. K., Kumari, A., and Solanki, P. R. (2024). Current advancement in nanomaterial-based emerging techniques for the determination of aminoglycosides antibiotics for antibiotic resistance surveillances. Mater Adv. 5, 961–985. doi: 10.1039/D3MA00632H
Samb, A., Sinkeler, F., Bijleveld, Y. A., van Kaam, A., de Haan, T. R., and Mathot, R. (2023). Therapeutic drug monitoring of amikacin in preterm and term neonates with late-onset sepsis. Can saliva samples replace plasma samples? Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 89, 3195–3203. doi: 10.1111/bcp.15823
Satlin, M. J., Kubin, C. J., Blumenthal, J. S., Cohen, A. B., Furuya, E. Y., Wilson, S. J., et al. (2011). Comparative effectiveness of aminoglycosides, Polymyxin B, and Tigecycline for clearance of Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae from urine. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 55, 5893–5899. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00387-11
Shaeer, K. M., Zmarlicka, M. T., Chahine, E. B., Piccicacco, N., and Cho, J. C. (2019). Plazomicin: a next-generation aminoglycoside. Pharmacotherapy 39, 77–93. doi: 10.1002/phar.2203
Shi, S. J., and Klotz, U. (2011). Age-related changes in pharmacokinetics. Curr. Drug Metab. 12, 601–610. doi: 10.2174/138920011796504527
Smit, C., van Schip, A. M., van Dongen, E. P. A., Brüggemann, R. J. M., Becker, M. L., and Knibbe, C. A. J. (2020). Dose recommendations for gentamicin in the real-world obese population with varying body weight and renal (dys)function. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 75, 3286–3292. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkaa312
Smits, A., De Cock, R. F. W., Allegaert, K., Vanhaesebrouck, S., Danhof, M., and Knibbe, C. A. J. (2015). Prospective evaluation of a model-based dosing regimen for amikacin in preterm and term neonates in clinical practice. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 59, 6344–6351. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01157-15
Smits, A., Kulo, A., van den Anker, J., and Allegaert, K. (2017). The amikacin research program: a stepwise approach to validate dosing regimens in neonates. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 13, 157–166. doi: 10.1080/17425255.2017.1234606
Solé-Lleonart, C., Roberts, J. A., Chastre, J., Poulakou, G., Palmer, L. B., Blot, S., et al. (2016). Global survey on nebulization of antimicrobial agents in mechanically ventilated patients: a call for international guidelines. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 22, 359–364. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2015.12.016
Solé-Lleonart, C., Rouby, J. J., Blot, S., Poulakou, G., Chastre, J., Palmer, L. B., et al. (2017). Nebulization of antiinfective agents in invasively mechanically ventilated adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Anesthesiology 126, 890–908. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000001570
Stalenhoef, J. E., van Nieuwkoop, C., Menken, P. H., Bernards, S. T., Elzevier, H. W., and van Dissel, J. T. (2019). Intravesical gentamicin treatment for recurrent urinary tract infections caused by multidrug resistant Bacteria. J. Urol. 201, 549–555. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2018.10.004
Tait, J. R., Bilal, H., Rogers, K. E., Lang, Y. Z., Kim, T. H., Zhou, J. Q., et al. (2022). Effect of different piperacillin-Tazobactam dosage regimens on synergy of the combination with tobramycin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa for the pharmacokinetics of critically ill patients in a dynamic infection model. Antibiotics 11:101. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11010101
Tao, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., Han, Y., Feng, J., Cheng, H., et al. (2024). A qualitative study of the factors impacting implementation of the national action plan to contain antimicrobial resistance (2016-2020) in medical institutions. BMC Health Serv. Res. 24:120. doi: 10.1186/s12913-023-10404-y
Thy, M., Timsit, J. F., and de Montmollin, E. (2023). Aminoglycosides for the treatment of severe infection due to resistant gram-negative pathogens. Antibiotics 12:860. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12050860
Twiss, J., Stewart, A., Gilchrist, C. A., Keelan, J. A., Metcalfe, R., and Byrnes, C. A. (2022). Randomised controlled trial of nebulised gentamicin in children with bronchiectasis. J. Paediatr. Child Health 58, 1039–1045. doi: 10.1111/jpc.15899
Valitalo, P. A. J., van, J., Allegaert, K., De Cock, R. F. W., de Hoog, M., Simons, S. H. P., et al. (2015). Novel model-based dosing guidelines for gentamicin and tobramycin in preterm and term neonates. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 70, 2074–2077. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkv052
Wang, Y., Du, Z. C., Chen, Y. D., Liu, Y. G., and Yang, Z. T. (2021). Meta-analysis: combination of meropenem vs ceftazidime and amikacin for empirical treatment of cancer patients with febrile neutropenia. Medicine 100:24883. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000024883
Winthrop, K. L., Flume, P. A., Thomson, R., Mange, K. C., Yuen, D. W., Ciesielska, M., et al. (2021). Amikacin liposome inhalation suspension for Mycobacterium avium complex lung disease a 12-month open-label extension clinical trial. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 18, 1147–1157. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202008-925OC
Yadav, R., Landersdorfer, C. B., Nation, R. L., Boyce, J. D., and Bulitta, J. B. (2015). Novel approach to optimize synergistic Carbapenem-aminoglycoside combinations against Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 59, 2286–2298. doi: 10.1128/AAC.04379-14
Yamada, T., Fujii, S., Shigemi, A., and Takesue, Y. (2021). A meta-analysis of the target trough concentration of gentamicin and amikacin for reducing the risk of nephrotoxicity. J. Infect. Chemother. 27, 256–261. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2020.09.033
Yan, K. C., Liang, B. B., Zhang, G. X. Z., Wang, J., Zhu, M., and Cai, Y. (2022). Efficacy and safety of Plazomicin in the treatment of Enterobacterales infections: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 9:429. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofac429
Keywords: bibliometric analysis, aminoglycoside antibiotics, antibiotic resistance, therapeutic drug monitoring, individualized administration
Citation: Zhao T, Chen N, Zhang M, Lin L, Lin B, Fang Y, Hua Z and Liang C (2025) Bibliometric analysis of global research on the clinical applications of aminoglycoside antibiotics: improving efficacy and decreasing risk. Front. Microbiol. 16:1532231. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1532231
Received: 21 November 2024; Accepted: 28 January 2025;
Published: 19 February 2025.
Edited by:
Benno H. Ter Kuile, University of Amsterdam, NetherlandsReviewed by:
Iordanis Kesisoglou, Laboratory Corporation of America Holdings (LabCorp), United StatesCopyright © 2025 Zhao, Chen, Zhang, Lin, Lin, Fang, Hua and Liang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Nan Chen, MTM1OTg4NzgyMzFAMTYzLmNvbQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.