- 1School of Public Health, The Key Laboratory of Environmental Pollution Monitoring and Disease Control, Ministry of Education, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang, China
- 2Laboratory of Bacterial Disease, Experimental Center, Guizhou Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Guiyang, China
Background: The emergence of extensively drug-resistant (XDR) Salmonella in humans poses a significant public health and therapeutic challenge. However, limited data are available on XDR Salmonella isolates from Guizhou province, China. This study aimed to investigate the molecular epidemiology and resistance patterns of XDR Salmonella isolates from clinical samples in this region.
Methods: A total of 931 Salmonella isolates were screened for XDR isolates through antimicrobial susceptibility testing. These XDR isolates were subjected to whole-genome sequencing (WGS) and bioinformatic analysis to further systematically investigating the molecular epidemiology and resistance patterns of XDR Salmonella isolates.
Results: Between 2019 and 2023, 931 Salmonella isolates were collected from clinical samples in Guizhou. Of these isolates, 51 (5.5%) were identified as XDR and classified into 16 serovars. Among the serovars, 15 corresponded to a specific sequence type, except for S. Typhimurium serovars. The predominant serovars, S. 1,4,[5],12:i:-, S. Enteritidis, and S. Kentucky, were divided into ST34, ST11, and ST198, respectively. Genomic analysis showed that all XDR isolates harbored at least eight antimicrobial resistance genes (ARGs) and multidrug efflux pumps. Highly prevalent point mutations in gyrA (D87 and S83) and parC (S80I) were detected, along with eight plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance (PMQR) genes. The qnrS1 gene was the most common (43.1%), followed by oqxA, aac-(6′)-lb-cr variant, qnrB4, qnrS2, qnrA1, qepA2, and oqxB. The predominant β-lactamase gene was blaTEM-1 (54.9%), and blaCTX-M-55 (35.3%) was the most prevalent extended-spectrum β-lactamase subtype. Notably, blaNDM-1 gene was identified for the first time in Salmonella from Guizhou, and one S. 1,4,[5],12:i:- isolate contained the mcr-1.1 gene. ARGs profiles varied by serovars, with S. 1,4,[5],12:i:- isolates carrying the highest number. Ten plasmid types were identified, predominantly IncHI2/IncHI2A (47.5%). Key resistance genes such as tetA, PMQR, blaCTX-M, mcr-1.1, and blaNDM-1 were located on IncHI2/IncHI2A plasmids. Notably, 75.0% of the conjugative plasmids belonged to IncHI2/IncHI2A, indicating that horizontal gene transfer through conjugation facilitates ARGs dissemination. Core genome multilocus sequence typing (cgMLST) analysis revealed significant genetic diversity, with 39 core genome sequence types (cgSTs) identified and no evidence of outbreaks.
Conclusion: The rising prevalence of XDR Salmonella in Guizhou province is concerning. Initial whole-genome sequencing (WGS) data provide critical insights for understanding and controlling XDR Salmonella infections, aiding public health officials in identifying emerging threats and trends.
1 Introduction
Non-typhoidal Salmonella (NTS) has emerged as a leading cause of infectious diarrhea globally, underscoring its significance as both a foodborne and zoonotic pathogen. Reports indicated an alarming prevalence of NTS invasive disease, with an estimated 535,000 cases and 77,500 deaths attributed to this pathogen in 2017 alone, which indicated a mean all-age case fatality rate of approximately 14.5% (GBD 2017 Non-Typhoidal Salmonella Invasive Disease Collaborators, 2019). In the United States, the annual incidence was staggering, with around 1.35 million cases of NTS reported, resulting in approximately 26,500 hospitalizations and 420 fatalities (Lewis et al., 2023). In recent years, certain high-income countries like the United States, Australia, and Sweden have reported outbreaks of foodborne diseases (Ford et al., 2023; Kerr et al., 2022; Jansson Mörk et al., 2022). Additionally, Europe ranked NTS as the second most common zoonosis (European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC), 2023), while data from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) revealed that up to 80% of bacterial foodborne illnesses stem from Salmonella, highlighting its pervasive role in public health crises across various regions (Hu et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2021). In Guizhou province, food poisoning incidents attributable to Salmonella are common, underscoring the pathogen’s status as the leading cause of foodborne illness and infectious diarrhea in the region (Wei et al., 2023; Zhou et al., 2024). Studies have identified Salmonella as a prevalent etiological agent in diarrheal diseases across Guizhou province, revealing a significant public health threat that necessitates urgent attention and intervention.
The clinical manifestations of salmonellosis generally include diarrhea, fever, abdominal cramps, and vomiting, illustrating that while the disease is often self-limiting, certain populations—particularly those with compromised immune systems—are susceptible to severe complications (Wang Z. et al., 2024). While antimicrobial treatment was frequently unnecessary in most cases, its importance escalates in severe infections, especially amongvulnerable populations. Alarmingly, the global rise of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) poses a significant threat, with XDR Salmonella isolates emerging across multiple countries, including China, Australia, Italy, and Egypt (Chen et al., 2022; Liu B. et al., 2024; Cummins et al., 2020; Russo et al., 2022; Algammal et al., 2023; Sallam et al., 2024). The prevalence of XDR Salmonella, drastically limited treatment options and exacerbated clinical outcomes, emphasizing an urgent need for comprehensive understanding of the molecular mechanisms that underpin antibiotic resistance. In Guizhou province, China, the situation is particularly critical, as evidenced by a multidrug resistance rate of 86.7% among clinical Salmonella isolates from 2013 to 2017, with 4.4% categorized as extensively drug-resistant (Wei et al., 2023). Recent study on food revealed that a significant proportion of Salmonella isolates from retail food sources exhibited resistance to multiple antibiotic classes (Zhou et al., 2024). These data highlights the importance of understanding the underlying resistance mechanisms that facilitate the survival and proliferation of Salmonella. However, the available literature was lacking in comprehensive analyses of the molecular epidemiological characteristics and prevalence of resistance genes among clinical XDR Salmonella isolates in Guizhou. The gap in information limited the development of effective intervention strategies.
This study aimed to fill this critical gap by systematically investigating the molecular epidemiology and resistance patterns of XDR Salmonella isolates from clinical samples in Guizhou province. By exploring the incidence rates of resistance genes in clinical isolates, the findings served as a pivotal reference for public health strategies to prevent and manage Salmonella infections. Furthermore, this research informed the judicious use of antimicrobial therapies, contributing to efforts to mitigate the burgeoning public health challenge of antimicrobial resistance.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 XDR Salmonella isolate, serotyping and antimicrobial susceptibility testing
A surveillance program specifically targeting non-typhoidal Salmonella was implemented based on laboratory analyses. A total of 931 Salmonella isolates were identified from stool samples collected from diarrhea patients in 109 hospitals across six cities and three prefectures of Guizhou province between January 1, 2019 and December 31, 2023, as described previously (Wu et al., 2025). These isolates were distributed in Guiyang (n = 164), Zunyi (n = 148), Liupanshui (n = 90), Anshun (n = 45), Bijie (n = 33), Tongren (n = 258), Qiandongnan (n = 72), Qiannan (n = 89), and Qianxinan (n = 32). Additionally, the Salmonella isolates were dispatched to the bacterial laboratory of the Guizhou Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention for further identification and analysis. The serovars of Salmonella isolates were determined using the slide agglutination method according to the Kauffmann-White-Le Minor scheme (Grimont and Weill, 2007; Guibourdenche et al., 2010). Antimicrobial susceptibility testing was conducted and interpreted using the broth microdilution method, following the Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute guidelines (CLSI, 2023) (Supplementary Data S1). The following antimicrobials were tested using customized antimicrobial susceptibility test plate CHNENF (Thermo Fisher Scientific, America): (i) chloramphenicol (C), (ii) sulfonamides: trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (SXT), (iii) quinolones: nalidixic acid (NA), ciprofloxacin (CIP), (iv) macrolides: azithromycin (AZM), (v) aminoglycosides: streptomycin (STS), amikacin (AMK), (vi) tetracyclines: tetracycline (TE), tigecycline (TGC), (vii) cephems: cefotaxime (CTX), ceftazidime (CAZ), (vii) β-lactamase inhibitor: ceftazidime/avibactam (CZA), ampicillin/sulbactam (SAM), (ix) carbapenems: ertapenem (ETP), meropenem (MEM), (x) penicillin: ampicillin (AM), (xi) lipopeptide: colistin (CL). Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 was used for quality control. Sterile saline solution was used as the negative control group. XDR Salmonella was defined as non-susceptibility to at least one agent in all but two or fewer antimicrobial categories (Magiorakos et al., 2012). Antimicrobial resistance, including antimicrobial resistance rates and resistance profiles of XDR Salmonella isolates, was analyzed using Whonet 2023 software.1
2.2 DNA extraction and whole genome sequencing
Genomic DNA extraction was performed for XDR Salmonella isolates using the magnetic bacteria genomic DNA kit (Baiju Technologies, China). The extracted DNA was precisely quantified with the Qubit 4 Fluorometer (Thermo-Scientific, Waltham, United States) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. High-quality genomic DNA were further conducted for the subsequent ligation step. Adapter ligation and clean-up of sequences were performed using the SQK-NBD114.24 kit. After that, sequencing was carried out on the long-read Oxford Nanopore GridION platform (Nanopore Technologies, United Kingdom). High-coverage data were generated for downstream analyses. Species identification was performed using Kraken 2 V2.1.2,2 whole genome assembly was conducted with Flye V2.8.3,3 and the assembly was polished using medaka V1.6.0,4 which resulted in the generation of a complete genome sequence.
2.3 MLST analysis, serovars prediction, ARGs identification, and plasmid characterization
The serovars and multi-locus sequence typing (MLST) of XDR Salmonella isolates were predicted using SeqSero 2 V1.1.05 and MLST V2.0.6 The complete genomic sequences of XDR Salmonella isolates were aligned with the Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Gene Database (CARD)7 to obtain the resistance genes. Plasmids were predicted using PlasFlow V1.1,8 and the replicon family of the predicted plasmids was determined using PlasmidFinder V2.1.9 To precisely know the location of ARGs, we submitted the identified plasmid sequences and chromosomal sequences separately to the CARD for obtaining the corresponding ARGs. The transferability was predicted using VR profile 2 (Wang et al., 2022). Batch analysis of XDR Salmonella plasmids was conducted using oriTfinder to ascertain the presence or absence of oriTs, relaxase genes, T4CP genes, and T4SS gene clusters (Li et al., 2018). Moreover, the oriT, relaxase, and T4CP genes type were identified by referring to the oriTDB database.10 In addition, T4SS genes cluster types were classified according to the SecReT4 database.11
2.4 Core genome multilocus sequence typing (cgMLST) analysis
The gene sequences of XDR Salmonella isolates from Guizhou province were screened and analyzed using cgMLST finder V1.2.012 to assess the core genome multi-locus sequence typing (cgMLST) locus dataset. A Maximum Likelihood (ML) tree was constructed with IQtree V2.3.513 and visualized using the TVBOT online website14 (Xie et al., 2023) to create a binary image for comparative analysis of resistance.
3 Result
3.1 Antimicrobial resistance
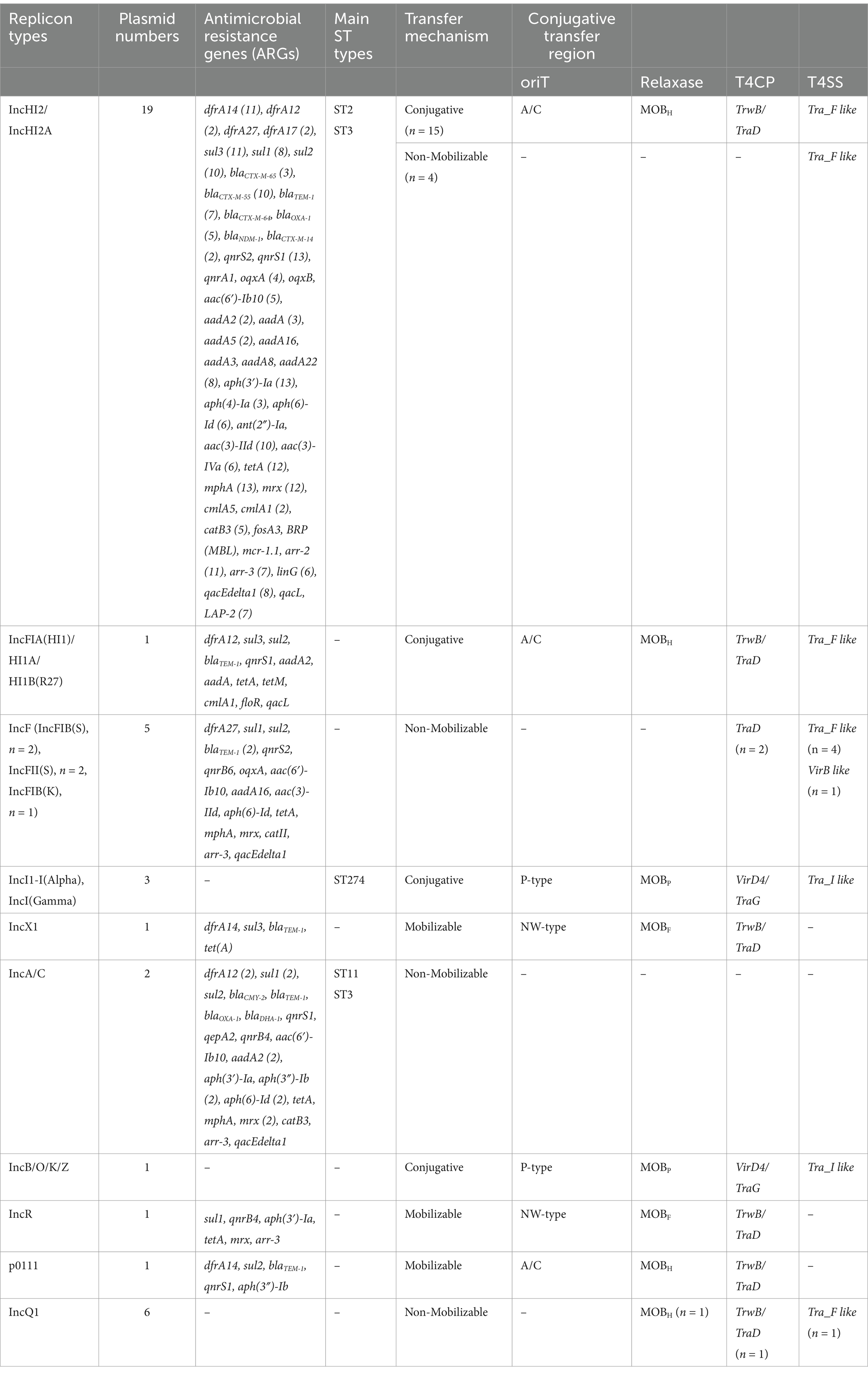
In total, 51 (5.5%; 51/931) Salmonella isolates exhibited XDR in Guizhou province, China, with being resistant to at least nine classes of antibiotics. All XDR Salmonella isolates showed 100% resistance to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, streptomycin, tetracycline, ampicillin, and cefotaxime, and high resistance rates to chloramphenicol (98.0%), ampicillin/sulbactam (98.0%), azithromycin (99.2%), and ceftazidime (74.5%). Additionally, over 84% of isolates displayed resistance to ciprofloxacin and nalidixic acid. Notably, approximately 15.7% of isolates were resistant to colistin, while no resistance was observed for tigecycline, ceftazidime/avibactam, ertapenem, and meropenem (Figure 1A). Thirteen distinct antimicrobial resistance patterns were identified among these isolates, with the most prevalent pattern being C-SXT-CIP-NA-AZM-STS-TE-AM-CTX-CAZ-SAM (47.1%; 24/51) (Figure 1A and Supplementary Data S2). The analysis of XDR in clinical Salmonella isolates from nine cities in Guizhou between 2019 and 2023 revealed that the highest proportion of XDR isolates was in Zunyi at 35.3% (18/51), followed by Liupanshui (15.7%) and Guiyang (13.7%) (Figure 1B). Notably, the prevalence of XDR gradually increased from 3.8 to 7.4% between 2019 and 2023, with the exception of 2022 (Figure 1C).
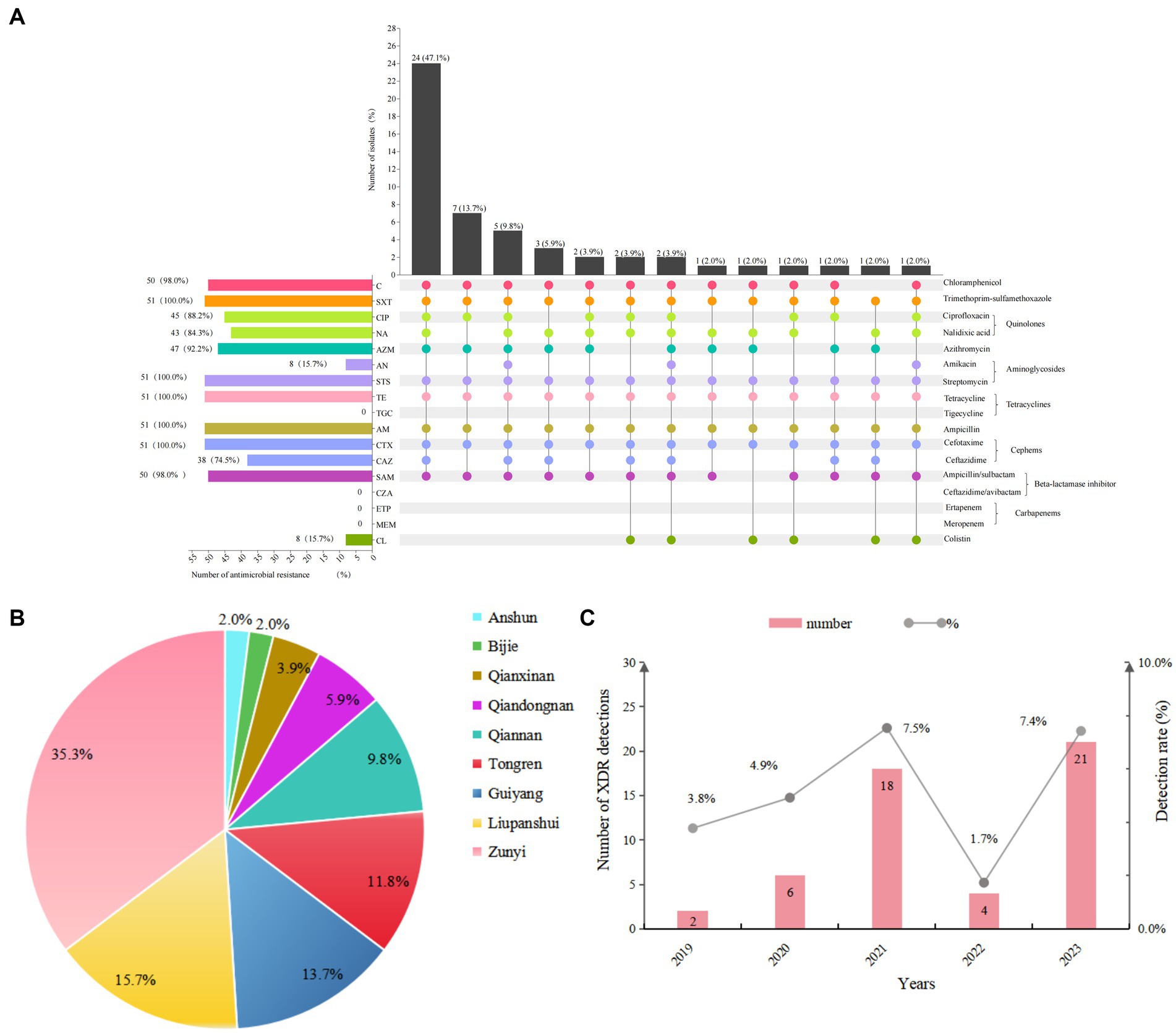
Figure 1. Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) phenotypes of 51 XDR Salmonella isolates. (A) The antibiotic resistance profiles of XDR Salmonella isolates were visualized using an UpSet plot. In the combination matrix positioned beneath the primary bar chart, individual columns corresponded to distinct AMR phenotypic profiles. Each colored dot within these columns represented resistance to a specific antimicrobial agent, with unique color coding different antimicrobial. The vertical bar chart displayed the total number of isolates exhibiting particular resistance combinations, while the horizontal bar chart displayed the prevalence of resistance for each antimicrobial agent. (B) Pie chart depicted the distribution of XDR Salmonella isolates from nine cities in Guizhou province. (C) Bar plot showed the detection rates of XDR Salmonella isolates from 2019 to 2023.
3.2 Genomic characterization of XDR Salmonella isolates
A comprehensive WGS analysis was conducted on 51 XDR Salmonella isolates from Guizhou province. The basic genomic information and characteristics of these XDR Salmonella isolates were presented in Supplementary Data S3. Analysis of the genomic features revealed that the genomes of the 51 XDR Salmonella isolates ranged in size from 4.7 Mb to 5.4 Mb, with a guanine-cytosine (GC) content spanning from 51.71 to 52.30%. Additionally, the N50 values of these isolates fell within the range of 4,650,029 bp to 5,041,259 bp for the XDR isolates.
3.3 Serovar prediction, sequence type, and antimicrobial resistance pattern
Based on WGS data of 51 XDR Salmonella, 16 distinct serovars were identified. The most prevalent serovar was S. 1,4,[5],12:i:- (29.4%), followed by S. Enteritidis (15.7%) and S. Kentucky (13.7%) (Figure 2A). Moreover, the isolates were classified into 16 sequence types (STs), with ST34 (31.4%), ST11 (15.7%), and ST198 (13.7%) being the most common. Among the 16 distinct serovars, 15 serovars were linked to a specific ST type, except for S. Typhimurium, which included one ST34 isolate and four ST19 isolates (Figure 2A). Upon comparing antibiotic resistance phenotypes, it was observed that S. 1,4,[5],12:i:- isolates exhibited the broadest range of resistance rates, varying from 13.3 to 100.0%. Notably, colistin resistance was most pronounced in S. Enteritidis isolates, reaching 62.5%, while amikacin resistance was most prevalent in S. Kentucky at 57.1% (Figure 2B).
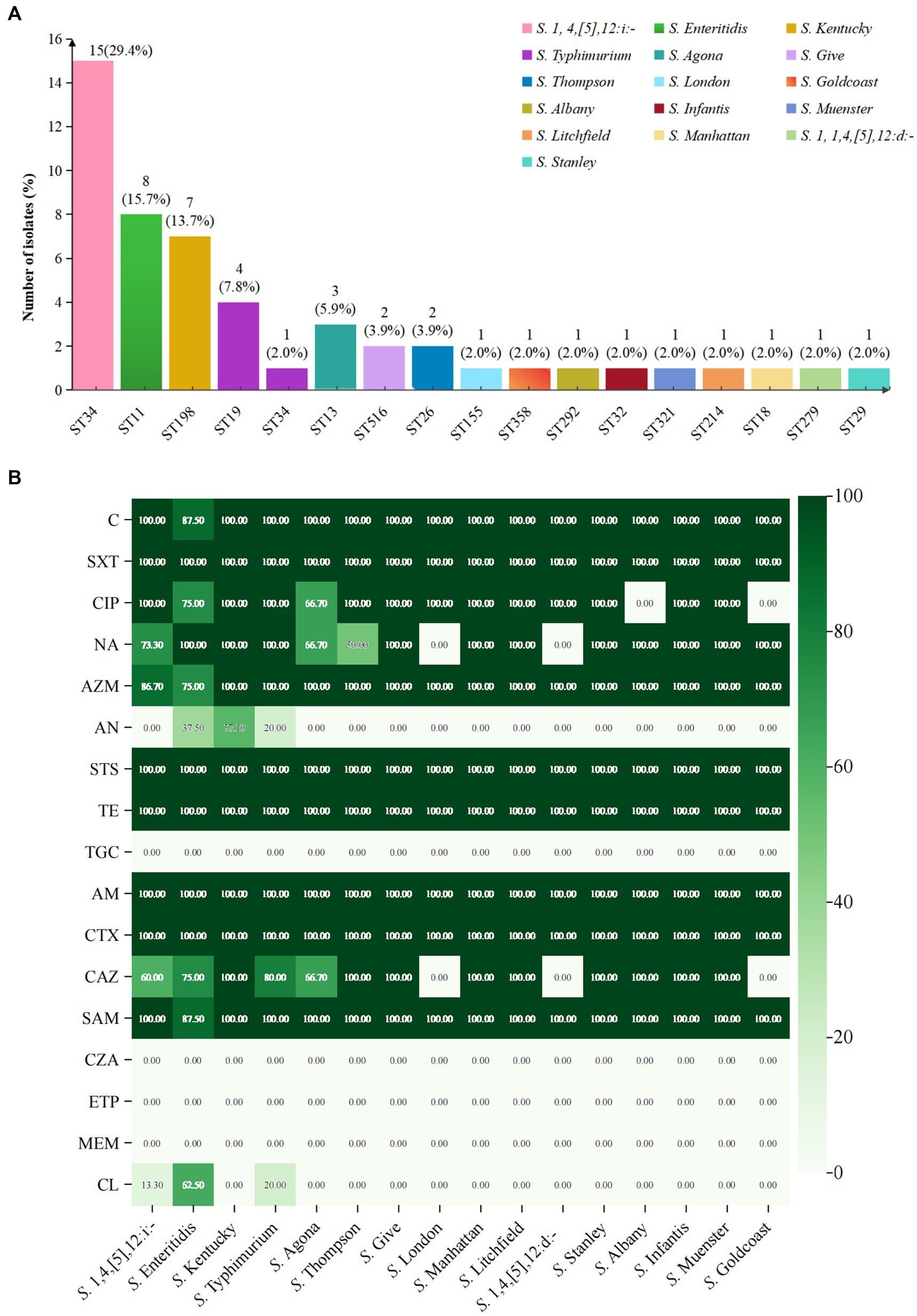
Figure 2. Analysis of serovars, STs, and antimicrobial resistance of 51 XDR Salmonella isolates. (A) Serovar prediction and MLST of 51 XDR Salmonella isolates. (B) The heatmap depicted the distribution of antimicrobial resistance across different serovars. The shades of color corresponded to the number of antimicrobial resistance isolates. Dark green indicated a high resistance rate, while white denoted the absence of resistance in that serovar.
The analysis of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) patterns revealed distinct profiles among Salmonella serovars. S. 1,4,[5],12:i:- isolates displayed five unique AMR patterns, with the predominant pattern C-SXT-CTX-CAZ-TE-CIP-NA-AZM-STS-AM-SAM (53.3%) (Supplementary Data S2). In contrast to S. 1,4,[5],12:i:- isolates which demonstrated extensive multidrug resistance patterns, other serovars including S. Kentucky, S. Typhimurium, S. Agona, and S. Thompson exhibited comparatively fewer resistance profiles. All remaining analyzed serovars displayed a singular resistance pattern.
3.4 Associated antimicrobial resistance genes of XDR Salmonella isolates
3.4.1 Distribution of antimicrobial resistance genes in 51 XDR Salmonella isolates
Whole genome analysis of 51 XDR Salmonella isolates revealed 105 ARGs, including clinically significant point mutations in two chromosomal targets (gyrA and parC). These genetic determinants conferred resistance to 15 antimicrobial classes (Figure 3). Notably, 12 isolates harbored mutations in quinolone resistance-determining regions (QRDRs), with amino acid substitutions identified in both gyrA and parC subunits. These specific mutations were associated with reduced susceptibility to fluoroquinolones, a critically important class of antimicrobials in clinical practice. For gyrA gene, the identified amino acid substitutions were S83F (15.7%), D87N (11.8%), D87G (5.9%), and D87Y (2.0%). For parC gene, the S80I substitution was observed in 11.8% of isolates. Additionally, eight PMQR genes were identified, with the qnrS being the most prevalent (47.1%). The subtypes of the qnrS gene were qnrS1 (43.1%) and qnrS2 (3.9%). Other detected PMQR genes included qnrB4 (5.9%), qnrA1 (2.0%), qepA2 (2.0%), oqxA (9.8%), and oqxB (2.0%), along with a variant of the aminoglycoside acetyltransferase gene aac-(6′)-lb-cr (7.8%). Moreover, various efflux pump resistance genes were detected in these isolates, such as emrB (100%), emrR (98%), and mdtK (98%). We found 21 ARGs associated with aminoglycoside resistance in 2.0 to 100% of these isolates. The kdpE gene was present in all isolates, while the aac(6′)-Iaa was present in 62.7%. For tetracycline resistance, related genes were identified in 86.3% (44/51) of the isolates. The tetA gene was present in over 54.9% of the isolates, while tetB and tetR were found in 23.5%, respectively. Regarding β-lactam resistance, 12 resistant genes were detected, with 78.4% (40/51) of the isolates carrying at least one β-lactam resistance gene. The most common was blaTEM-1 (54.9%). Additionally, the blaCTX-M gene was detected in 49.0% of the isolates, with four subtypes identified: blaCTX-M-55 (35.3%), blaCTX-M-65 (7.8%), blaCTX-M-14 (3.9%), and blaCTX-M-64 (2.0%). The blaDHA gene was detected in 5.9% of the isolates, with subtypes of blaDHA-1 (3.9%) and blaDHA-15 (2.0%). The blaOXA-1 gene was detected in 15.7% of the isolates, including S. 1,4,[5],12:i:-, S. Typhimurium, S. Kentucky, S. Thompson, and S. Stanley. We also identified the blaCMY-2 gene in one S. Thompson isolate. Notably, the blaNDM-1 gene was first detected in one S. Typhimurium isolate from Guizhou province. For macrolide resistance, the mphA and mrx genes are closely associated with azithromycin resistance, showing the detection rates at 43.1 and 39.2%, respectively. Both mphA and mrx genes were found to co-exist in 35.3% of the isolates. Additionally, we detected the ermB, msrE, and mphE genes, each at a rate of 2%. The most frequently identified sulfonamide resistance gene was dfrA14, which was present in 39.2% of the isolates. Additionally, the detection rates for the sul1, sul2, and sul3 genes all exceeded 30%. Among the five phenicol genes examined, catB3 was prevalent in 13.7% of the isolates, while the cmlA gene was detected in 11.8%. Furthermore, the subtypes of these resistance genes included cmlA1 (7.8%) and cmlA5 (3.9%). A gene that confers resistance to colistin, known as mcr-1.1, was identified in one S. 1,4,[5],12:i:- isolate. Besides, genes associated with resistance to fosfomycin, specifically fosA3 and fosA7, were detected in 11.8 and 5.9% of isolates, respectively. Our study also revealed 18 multidrug resistance genes, with 11 of these genes found in all isolates (Figure 3B).
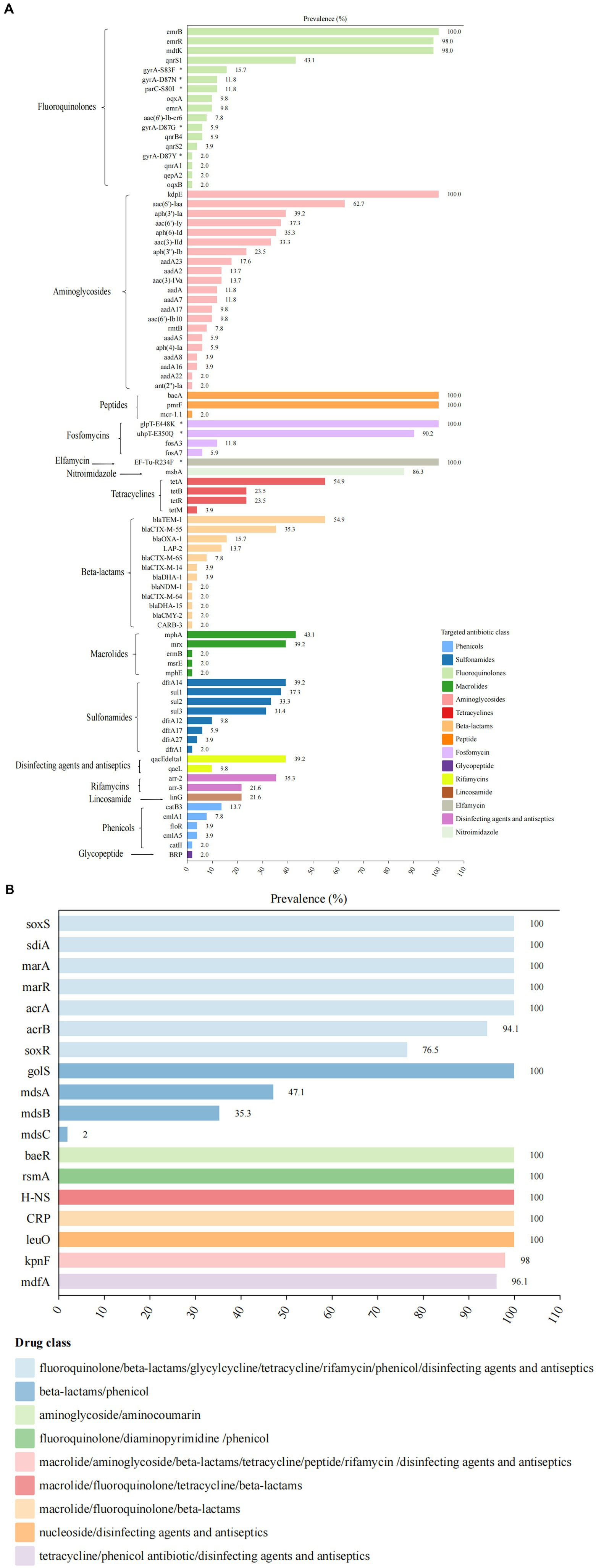
Figure 3. Antimicrobial resistance determinants among 51 XDR Salmonella isolates. (A) The distribution of ARGs and associated amino acid mutations, with corresponding genetic elements listed on the left vertical axis. The adjacent bar chart quantified their percentages, stratified by antimicrobial class through color-coded categorization. (B) Multidrug resistance genetic determinants present gene targets along the left margin. The accompanying visualization employs chromatic differentiation to demonstrate the proportional representation of MDR-associated genetic elements within the study.
3.4.2 The prevalence of ARGs in the top four common serovars
In our analysis, we compared the prevalence of ARGs among the four most common serovars of XDR Salmonella isolates (Figure 4), including S. 1,4,[5],12:i:-, S. Enteritidis, S. Kentucky, and S. Typhimurium. We observed significant polymorphisms in the ARGs across S. 1,4,[5],12:i:-, S. Kentucky, and S. Typhimurium. Regarding sulfonamide resistance, both S. 1,4,[5],12:i:- and S. Typhimurium harbored the sul1, sul2, and sul3 genes. The sul2 gene was predominant in S. 1,4,[5],12:i:- (66.7%), while sul1 was dominant gene in S. Typhimurium (60.0%). In contrast, S. Enteritidis exclusively possessed the sulfonamide resistance gene dfrA17 and did not contain the sul1, sul2, or sul3 genes. All S. Kentucky isolates carried the sul1 gene, with some also carrying the sul2 gene.
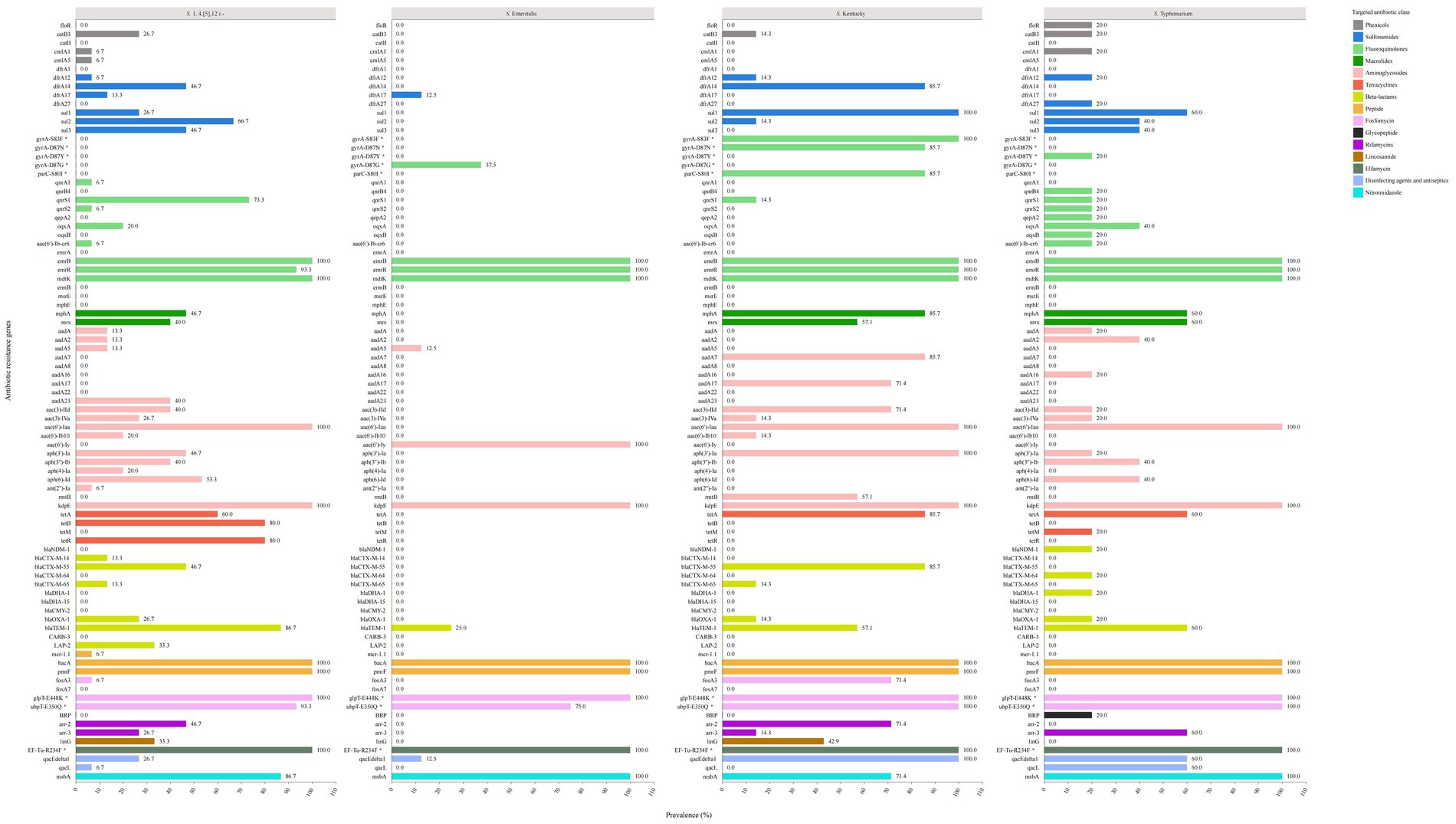
Figure 4. The prevalence of genetic determinants of antibiotic resistance in the top four common serovars of XDR Salmonella.
For fluoroquinolone (FQ) resistance, S. 1,4,[5],12:i:- exhibited five PMQR genes, with qnrS1 (73.3%) being the predominant gene. Among S. Enteritidis isolates, 37.5% showed the gyrA-D87G point mutation without any additional PMQR genes, including qnr, oqx, and aac(6′)-Ib-cr. Notably, S. Kentucky isolates displayed three types of point mutations: 100% had gyrA-S83F, 85.7% had gyrA-D87N, and 85.7% had parC-S80I mutation. Furthermore, 14.3% of the S. Kentucky isolates carried the qnrS1 gene. In contrast, S. Typhimurium isolates showed different patterns: 20.0% had the gyrA-D87Y point mutation, while another 20.0% carried a combination of PMQR genes, including qnrB4, qnrS1, qnrS2, qepA2, oqxB, and aac(6′)-Ib-cr. Additionally, 40.0% of the isolates carried the oqxA gene.
For macrolide resistance, S. 1,4,[5],12:i:-, S. Kentucky, and S. Typhimurium isolates contained the mphA and mrx genes, while none of the S. Enteritidis isolates carried these genes.
Regarding aminoglycoside resistance genes, S. 1,4,[5],12:i:- isolates harbored 14 genes. The most prevalent were aac(6′)-Iaa (100%) and kdpE (100%), followed by aph(6)-Id (53.3%), aph(3′)-Ia (46.7%), aac(3)-IId (40.0%), aph(3′)-Ib (40.0%), and aadA23 (40.0%). In comparison, the S. Enteritidis isolates exhibited only three related genes. The S. Kentucky and S. Typhimurium isolates presented nine and ten genes, respectively. All S. Kentucky isolates carried the aac(6′)-Iaa, kdpE, and aph(3′)-Ia genes, while all S. Typhimurium isolates contained the aac(6′)-Iaa and kdpE genes.
For tetracycline resistance genes, S. 1,4,[5],12:i:- isolates showed a prevalence of 60.0% for the tetA gene and 80.0% for both the tetB and tetR genes. S. Enteritidis isolates did not possess any tetracycline resistance genes. Among S. Kentucky isolates, tetA was the predominant gene (85.7%), while S. Typhimurium isolates exhibited the tetA gene (60.0%) along with the tetM gene (20.0%).
Concerning β-lactam resistance genes, S. 1,4,[5],12:i:- isolates were found to harbor six different genes, with blaTEM-1 being the most prevalent (86.7%), followed by blaCTX-M-55 (46.7%). In contrast, S. Enteritidis isolates carried only blaTEM-1 (25.0%). S. Kentucky isolates exhibited a diverse array of β-lactam resistance genes, including blaCTX-M-55 (85.7%), blaTEM-1 (57.1%), blaCTX-M-65 (14.3%), and blaOXA-1 (14.3%). For S. Typhimurium isolates, the most prevalent β-lactam resistance gene was blaTEM-1 (60.0%), followed by blaCTX-M-64 (20.0%), blaDHA-1 (20.0%), blaOXA-1 (25%), and blaNDM-1 (20.0%).
3.5 Characterization of plasmids
In this study, 40 plasmids were identified in 51 XDR Salmonella isolates (Table 1). Of these isolates, 28 (54.9%) isolates contained at least one plasmid, while 23 (45.1%) had no plasmids. The 40 identified plasmids were classified into ten different categories: A (IncA), B (IncB/O/K/Z), C (IncC), H (IncHI2/IncHI2A), I (IncI1, IncI1-I), F (IncFII, IncFIB, IncFIA), Q (IncQ1), R (IncR), X (IncX1), and p0111. The most commonly found plasmid replicon was IncHI2/IncHI2A, present in 19 isolates (47.5%), followed by IncQ1 in six isolates (15.0%). Notably, one S. Goldcoast isolate carried a hybrid plasmid replicon, IncFIA(HI1)-HI1A-HI1B(R27), while one S. Litchfield isolate contained a hybrid plasmid replicon of type IncB/O/K/Z. Among the predominant serovar of the XDR Salmonella isolates, 15 S. 1,4,[5],12:i:- isolates exhibited the presence of IncHI2/IncHI2A (73.3%; 11/15), IncQ1 (33.3%; 5/15), and p0111 (6.7%; 1/15) plasmid replicons. Of the 40 plasmids identified, 20 were classified as conjugative, three as mobilizable, and the remaining as nontransferable. The most prevalent conjugative plasmid was IncHI2/IncHI2A (75.0%; 15/20), followed by IncI (15.0%; 3/20).
3.6 The distribution of ARGs located on chromosomes and plasmids
A total of 105 ARGs were identified in this study. Among these, 58 genes were located on plasmids, while 83 ARGs were found on chromosomes (Figure 5). In total, 45 ARGs were present in 20 conjugative plasmids. Of the 40 plasmids identified, 28 harbored at least one ARG, with a maximum of 20 genes present in a single plasmid (Supplementary Data S4). The plasmid genomes displayed an overrepresentation of ARGs, including tetA, PMQR genes, aph(3′)-Ia, aadA2, mphA, mrx, sul1-3, dfrA14, and blaTEM-1. Notably, several ARGs were found in both chromosomal and plasmid genomes, such as blaTEM-1, tetA, aph (6)-Id, blaCTX-M-55, and mphA. Among the 25 blaCTX-M positive isolates, blaCTX-M-55 was present in 10 of these isolates, while blaCTX-M-65 was found in three isolates, both located on IncHI2/IncHI2A plasmids. Additionally, 12 of these isolates contained conjugative plasmids. A significant finding was that specific ARGs were found in duplicate copies on distinct plasmids within the same isolate. For example, isolate SM2023030 exhibited two copies of the genes sul1, mrx, and qacEdelta1, whereas isolate SM2023155 had two copies of the gene aph(3′)-Ia on distinct plasmids. Moreover, the plasmid SM2021073-p1 carried the gene mcr-1.1 along with 20 additional resistance genes, marking it the IncHI2/IncHI2A plasmid with the highest number of identified resistance genes in this study. Importantly, the resistance gene blaNDM-1 located on an IncHI2/IncHI2A plasmid, was first detected in one S. Typhimurium isolate (SM2021168) from Guizhou province. This plasmid also carried 18 other resistance genes, including oqxA/B, tetA, sul1-3, mphA. Additionally, the IncFIA(HI1)-HI1A-HI1B(R27) plasmid contained both the tetA and tetM genes, which was the only plasmid in this study to carry two tetracycline resistance genes. It was also noteworthy that one S. Thompson isolate, SM2023030, identified the blaCMY-2 gene on its IncC plasmid.
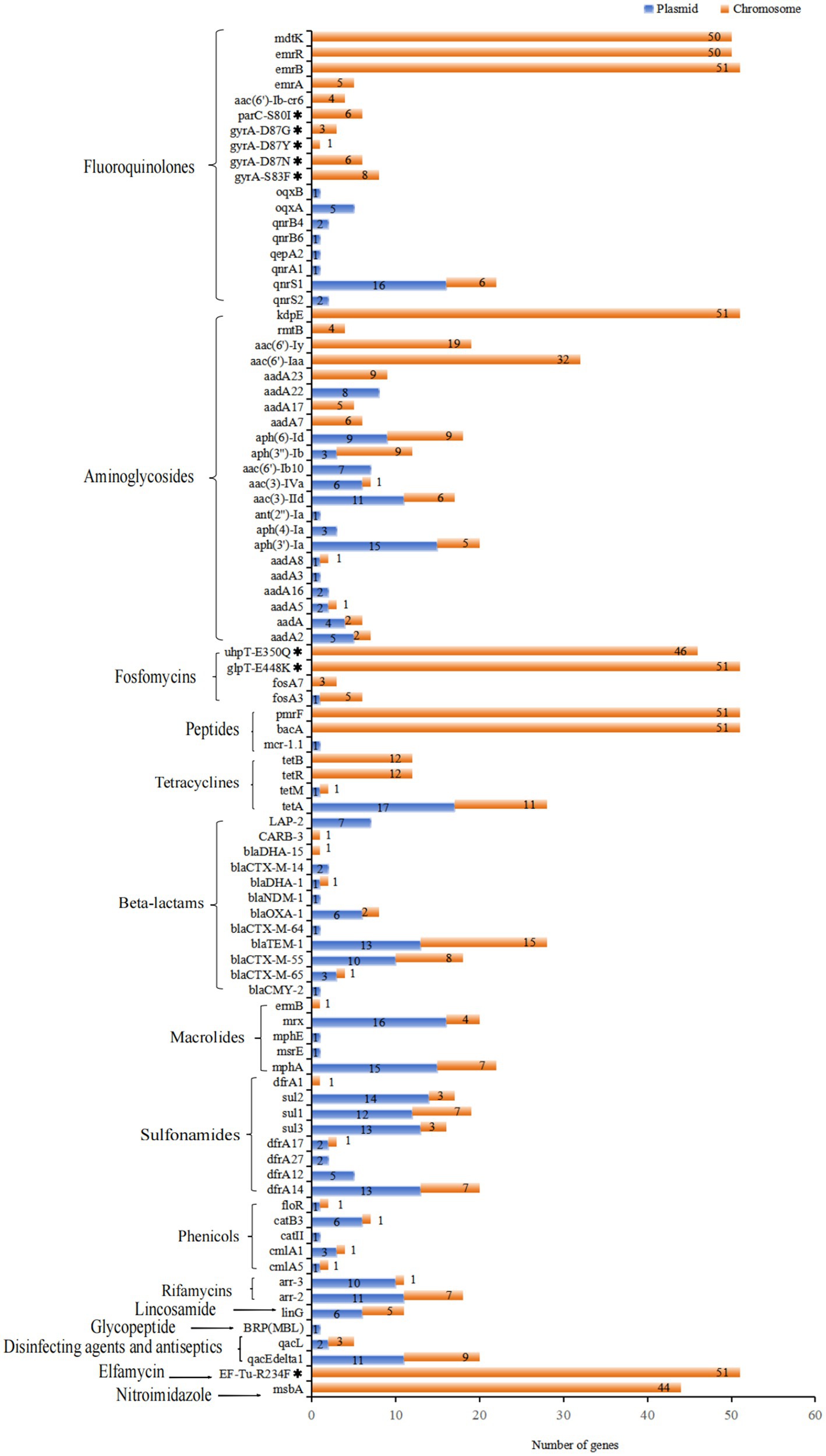
Figure 5. Distribution of ARGs and associated amino acid mutations located on chromosomes and plasmids of 51 XDR Salmonella isolates, targeting specific antimicrobial agents. Notably, 18 multidrug resistance genes were all located on chromosomal DNA, which did not show in this figure.
3.7 CgMLST cluster analysis of XDR Salmonella in Guizhou
The cgMLST clustering tree was constructed based on differences in the core genomes of the isolates, as well as an analysis of their background information, antimicrobial resistance patterns, and the classification of associated resistance genes in the 51 XDR isolates (Figure 6). The cgMLST analysis revealed that 51 XDR Salmonella isolates from Guizhou were divided into 39 cgSTs. Among these, seven cgSTs contained more than two isolates. Cluster analysis of all isolates based on cgSTs indicated that isolates of the same serovar were likely homologous. Notably, the S. 1,4,[5],12:i:- and S. Typhimurium isolates exhibited similar genomic relatedness on the phylogenetic tree. Isolates of S. Stanley, S. Litchfield, S. Typhimurium, and S. 1,4,[5],12:i:- were clustered together in the same clade. Sixteen ST34 isolates were divided into 10 cgSTs, with the dominant type being cgST190343 (25%, 4/16). Additionally, three cgSTs contained more than two isolates. Four cgST190343 isolates, SM2023071, SM2023101, SM2023107, and SM2023108, showed identical resistance profiles and carried the IncHI2/IncHI2A plasmids. These IncHI2/IncHI2A plasmids were found to possess genes such as dfrA14, sul3, sul2, blaCTX-M-55, blaTEM-1, qnrS1, aadA22, aph(3′)-Ia, aac(3)-IId, aph(6)-Id, tetA, mphA, arr2, linG, and LAP2 genes, suggesting that these isolates may have originated from the same source of infection. Among the four cgST190343 isolates, geographical distribution analysis revealed one isolate originated from Qiannan Autonomous prefecture while three were clustered in Zunyi city, indicating possible inter-regional dissemination of this isolate. Furthermore, the two cgST90701 S. 1,4,[5],12:i:- isolates, SM2023134 and SM2023141, exhibited identical antimicrobial resistance profiles and harbored concordant resistance determinants, implying a shared infection origin.
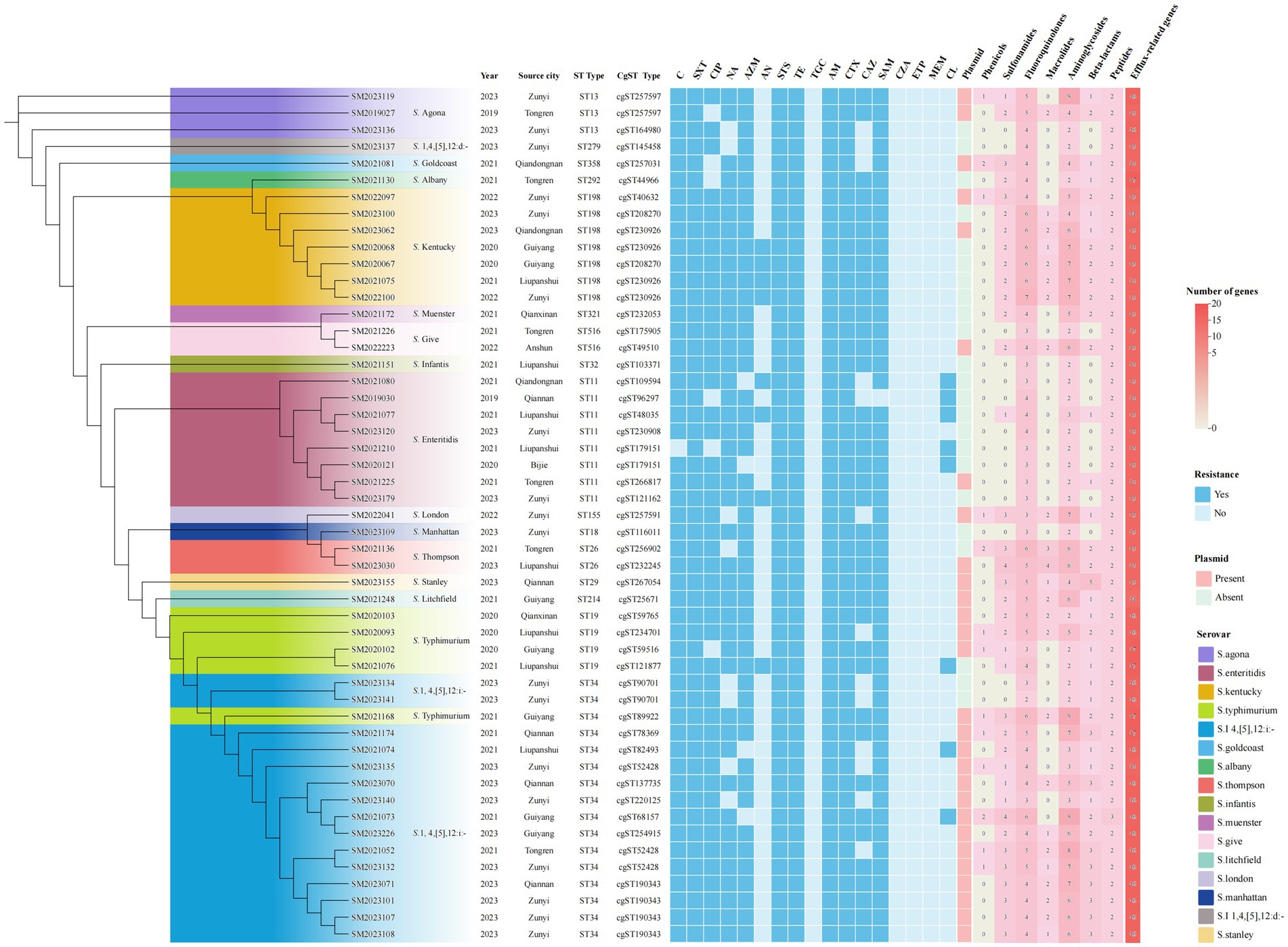
Figure 6. Phylogenetic analysis of 51 XDR Salmonella isolates using core genome MLST. The ML tree was constructed based on cgMLST profiles, with branch colors representing distinct serovars. Antimicrobial resistance phenotypes were depicted using square markers: filled blue squares indicated positive resistance phenotypes, while unfilled blue squares indicated susceptible isolates. The rightmost panel illustrated plasmid carriage and resistance gene distribution, where pink squares represented concurrent presence of both plasmids and resistance genes. Numeral within squares indicated the quantity of resistance genes corresponding to specific antibiotic classes.
4 Discussion
A tremendous increase in antimicrobial resistance among Salmonella isolates poses a significant global concern (Algammal et al., 2023; Chen et al., 2022; Cummins et al., 2020; Karampatakis, 2024; Liu B. et al., 2024; Sallam et al., 2024). In Guizhou province, surveillance data revealed a concerning escalation in XDR Salmonella prevalence, with detection rates climbing from 4.4% during 2013–2018 to 5.5% in the subsequent 2019–2023 period (Wei et al., 2023). Notably, our study revealed an accelerated upward trajectory, showing the detection rate of XDR Salmonella isolates nearly doubling from 3.8% in 2019 to 7.4% by 2023 within the same province. Due to their resistance to multiple antibiotic agents, the effective treatment of Salmonella infections was threatened, thus increasing the morbidity and mortality of patients. However, in 2022, the number of XDR isolates decreased, which may be attributed to environmental hygiene measures, less eating out, less travel, and less turnover during the pandemic of COVID-19. These changes highlighted the critical role of human mobility in the spread of resistant pathogens. In this study, we focused on XDR Salmonella isolates from humans because of the lack of data on this particular Salmonella phenotypes and resistance genes in Guizhou province and due to its severity in cases of outbreaks and surveillance. Limited data are available on genomic resistance characterization. Therefore, we investigated 51 XDR human Salmonella isolates from Guizhou province between 2019 and 2023 regarding genomic characterization, phylogenetic relationships, and resistance genes on chromosomes and plasmids. Understanding the underlying drug resistance mechanisms of these pathogens helps us finding solutions for the long-standing antibiotic resistance problem. This is the first study on genomic epidemiology of XDR human Salmonella isolates in Guizhou province, China.
In the present study, we noted that the prevalence of XDR Salmonella varied significantly across different regions, with the highest proportion of XDR isolates observed in Zunyi city, reaching up to 35.3%. These variations might be attributed to a combination of factors, including the distinctive geographical characteristics, the diverse habits of food consumption among local populations, as well as the climatic conditions. The climatic conditions in each region, including temperature, humidity, and seasonal changes, can greatly affect the survival and proliferation of XDR Salmonella. Zunyi city, located in the northern region of Guizhou province, is warmer and more humid conditions, which may contribute to a longer survival period for pathogens outside their host, potentially accelerating their transmission rates. Serological identification of 51 XDR Salmonella isolates revealed that S. 1,4,[5],12:i:-, S. Enteritidis, and S. Kentucky were the most frequent serovars, with ST34, ST11, and ST198 being the predominant sequence type, which was consistent with previous reports in Guangdong, Jiangsu, and other European countries, indicating a widespread clonal (Sun et al., 2024; Liu B. et al., 2024; European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC), 2019). These findings highlight the critical role of regional-specific environmental and behavioral factors in shaping the distribution and prevalence of XDR Salmonella.
The WGS analysis of 51 XDR Salmonella isolates revealed an extensive AMR landscape, with 105 ARGs conferring resistance to 15 antimicrobial classes. When examining genetic determinants contributing to resistance against FQs, we noted the presence of double mutations in the gyrA (D87 and S83) and one mutation in parC (S80I) in XDR isolates. These mutations were regarded as significant target-site alterations, which was consistent with findings from previous studies (Abd El-Aziz et al., 2021; Chen et al., 2024; Petrin et al., 2023). Furthermore, the PMQR genes determinants lead to decreased susceptibility to FQs and facilitate the selection of higher levels of FQ resistance (Chang et al., 2021; Vázquez et al., 2022). In the current study, eight PMQR genes were detected, with qnrS being the most prevalent in 47.1% of the isolates. Additionally, qnrS1 was identified among the examined isolates from various serovars, consistent with previous studies (Chen K. et al., 2020; Chen Z. et al. 2020). Meanwhile, it was important to note that qnr genes were found on multiple plasmids, which can disseminate across different regions and sources (She et al., 2023). In our study, 75.0% of the identified conjugative plasmid types were IncHI2/IncHI2A. Previous studies indicated that the IncHI2/IncHI2A plasmid was an essential lineage contributing to the spread of antibiotic resistance in Salmonella, suggesting that qnr genes could undergo horizontal gene transfer through conjugation between bacteria, thus promoting the spread of resistance genes (She et al., 2023).
In our study, the blaTEM-1 gene conferring ampicillin resistance was the most common β-lactam resistance gene, consistent with its global dominance in Salmonella serovars (Chen et al., 2024). Meanwhile, we identified four subtypes of blaCTX-M, a critical resistance gene family associated with third-generation cephalosporins resistance. Among these, blaCTX-M-55 gene was predominant, mirroring its high prevalence in Salmonella isolates from Australia and in zoonotic and human isolates in China (Ingle et al., 2021; Sun et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2023). The selective pressure from extensive clinical and veterinary use of third-generation cephalosporins has driven the global rise of CTX-M extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs), displaying traditional resistance determinants like TEM and SHV variants as the dominant ESBLs (Yu et al., 2024). This epidemiological shift was further exacerbated by the genetic mobility of blaCTX-M genes, which were frequently plasmids-mediated and capable of horizontal tranfer between bacterial isolates through conjugation (Wei et al., 2024; Yu et al., 2024). The increasing prevalence of blaCTX-M variants among Salmonella isolates poses a growing public health crisis, as these multidrug-resistant pathogens threatened the efficacy of frontline β-lactam therapies worldwide.
The production of AmpC β-lactamases has become a critical resistance mechanism in Gram-negative bacilli, conferring broad-spectrum resistance to β-lactam antibiotics. Of particular concern is the plasmid-mediated blaCMY-2 gene, which encoded an AmpC-type enzyme capable of hydrolyzing extended-spectrum cephalosporins. While blaCMY-2 has been extensively documented in food-producing animals and retail meat products across China, South Korea, and Spain (Na et al., 2020; Vázquez et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2024b), its detection in human clinical isolates remains uncommon. Recent evidence from China, however, has confirmed the emergence of blaCMY-2-harboring Salmonella in human infections (Zhang et al., 2024a), highlighting potential zoonotic transmission pathways. In this study, we identified one clinically derived S. Thompson isolate carrying blaCMY-2 on a IncC-type plasmid. Notably, this isolate concurrently harbored a distinct plasmid bearing macrolide resistance determinants (mphA, msrE, mphE, and mrx), creating a multidrug-resistant genetic configuration. The dual-plasmid system provided compelling evidence for horizontal gene transfer between environmental and clinical reservoirs. The colocalization of β-lactamase and macrolide resistance genes on mobile genetic elements raised critical concerns about coselection pressures that may perpetuate resistance traits, even under targeted antimicrobial stewardship. These findings highlighted the urgent priorities that enhanced surveillance of plasmid-mediated AmpC dissemination across the food-animal-human interface and implementation of stricter antimicrobial usage policies to disrupt resistance transmission networks.
Additionally, we identified one S. Typhimurium isolate carrying 18 ARGs, including blaNDM-1, oqxA/B, and mphA, on the IncHI2/IncHI2A plasmid for the first time. This isolate exhibited high resistance to third-generation cephalosporins (ceftazidime and cefotaxime), ciprofloxacin, azithromycin, and eleven other antimicrobials. The co-existence of ESBLs genes with other clinically significant ARGs, including qnr genes, was observed in recent studies (Li et al., 2022; Luo et al., 2020). The blaNDM-1 gene confers resistance to many β-lactam antimicrobials, including carbapenems (Pitout, 2012). The production of NDM by Salmonella spp. has been reported in the United States, China, and Singapore (Rahman et al., 2024; Song et al., 2023; Octavia et al., 2020). Infections caused by blaNDM-1 producers are difficult to treat, leading to increased morbidity, prolonged hospital stays, higher medical costs, and mortality due to ineffective standard treatments, which significantly affect treatment options and clinical outcomes (Octavia et al., 2020; Rahman et al., 2024; Song et al., 2023). The detection of such multidrug-resistant configurations in human pathogens emphasizes the need for One Health approaches to combat antimicrobial resistance.
The major determinants of AMR in the XDR isolates studied included genes associated with resistance to aminoglycosides, tetracyclines, and sulfonamides. Most of these genes have been documented in previous research. For example, the chromosomally encoded gene aac(6′)-Iaa was identified in S. 1,4,[5],12: i: - (Wei et al., 2024) and S. Typhimurium (Akinyemi et al., 2023) from human origin across multiple countries. Phenotypic resistance to tetracycline correlated with known genetic determinants, particularly the efflux pump gene tetA, which dominated observed resistance patterns (Zhao et al., 2022), a finding consistent with our data. While sulfonamide resistance was primarily associated with the genes sul1 and sul2 (Chen Z. et al., 2020), our study identified dfrA14 as the most prevalent sulfonamide resistance gene, contrasting with the expected predominance of sul1, sul2, and sul3. Notably, the macrolide resistance gene mphA was detected in 43.1% of the XDR Salmonella isolates. Its widespread presence raised clinical concerns, as mphA threatened the effectiveness of azithromycin for treating Salmonella infections (Wang et al., 2023). However, the mechanisms driving mphA dissemination remain unclear, highlighting the need for more in-depth comprehensive molecular epidemiological studies to elucidate transmission pathways. Both fosA3 and fosA7 fosfomycin resistance genes were identified, posing theoretical challenges for managing XDR Salmonella infections. Due to the absence of a fosfomycin-resistant phenotype in our isolates, we can not deterninate the clinical relevance of this fosfomycin resistance genes. These findings highlighted the importance of antimicrobial susceptibility testing when whole-genome sequencing might not provide a definitive assessment (Wang J. et al., 2024). Of particular concern was the detection of the plasmid-mediated mcr-1.1 colistin resistance gene in one S. 1,4,[5],12:i:- isolate. As colistin remains a last-resort antibiotic, this finding signals an alarming escalation in resistance to critically important antimicrobials (Liu J. H. et al., 2024).
The analysis of the four prevalent serovars harboring ARGs revealed that S. 1,4,[5],12:i:-isolates exhibited a broader range of resistance determinants compared to other serovars. In contrast, S. Enteritidis isolates contained fewer ARGs. Interestingly, when we analyzed the genetic factors contributing to FQs resistance, isolates from S. 1,4,[5],12:i:- and S. Typhimurium were primarily characterized by the presence of qnr genes. On the other hand, 87.5% of S. Kentucky isolates displayed double mutations in the gyrA gene (D87N and S83F) and a single mutation in the parC (S80I) gene. These mutations could be significant genetic factors contributing to FQs resistance, which was consistent to the dominant clone of S. Kentucky ST198 in Europe (European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC), 2019). Our findings revealed that the diversity of serovars was associated with different resistance genes and mechanisms. Notably, both tetB and tetR genes coexisted in S. 1,4,[5],12:i:-. Previous studies identified tetB in clinically significant clones of S. Typhimurium and its monophasic variant (Petrin et al., 2023). This suggested that there was genetic heterogeneity among the different serovars, likely a result of their adaptation and evolution in response to varying environmental and antimicrobial pressures. This heterogeneity was reflected in the distinct distribution and transmission patterns of drug resistance genes, which might be facilitated by horizontal gene transfer between isolates.
The dissemination of AMR was, in part, attribuable to the horizontal transfer of ARGs, frequently facilitated by plasmids (Castañeda-Barba et al., 2024). We conducted a further analysis of the chromosomal and plasmid-borne distribution of ARGs in 51 XDR Salmonella isolates from Guizhou province using WGS data. Our findings revealed that over half of the isolates harbored at least one plasmid, with IncHI2/IncHI2A plasmids being particularly prevalent, which indicated their widespread distribution among XDR human Salmonella isolates in this region. Notably, the carriage rate of IncHI2/IncHI2A plasmids in China significantly exceeded those reported in other countries (Sun et al., 2024). These plasmids were known to facilitate interbacterial ARG transfer through conjugation, accelerating the dissemination of resistance and posing a serious public health threat (Jiang et al., 2020). Several crucial ARGs identified on IncHI2/IncHI2A plasmids in Guizhou included tetA, PMQR genes, blaCTX-M, aph(3′)-Ia, mphA, sul1-3, dfrA14, blaTEM-1, mcr-1.1, and blaNDM-1. The accumulation of such ARGs on these plasmids enabled bacterial resistance to first-line antimicrobial, complicating clinial treatment (Wang and Dagan, 2024). Of particular concern was the detection of IncFIA(HI1)-HI1A-HI1B(R27) hybrid plasmid, which have been linked to the spread of high-risk ARGs like tet (X4) in Enterobacterales from both human and nonhuman sources (Yue et al., 2024; Zhai et al., 2024). These plasmids were classified as high-risk due to their association with clinically significant resistance mechanisms. These findings highlight the urgent need for sustained surveillence of plasmid-mediated ARGs to identify emerging resistance trends and inform targeted interventions.
Molecular typing for Salmonella isolates within the same serovars is critical for outbreak investigation and bacterial epidemiology. With the widespread application of WGS, WGS-based high-resolution subtyping methods have become popularized in tracing bacterial transmission and identifying outbreaks. Among these methods, cgMLST is the most widely used approach for the strain-level differentiation of Salmonella. This method offers high discriminatory power, making it invaluable in epidemiological and outbreak investigations (Zhao et al., 2022). CgMLST is analyzed variations in core genome loci (defined as genes present in 95–98% of the reference isolates used to establish the allele scheme) to construct phylogenetic relationships (Dangel et al., 2019). In this study, cgMLST analysis of 51 XDR Salmonella isolates revealed significant genetic diversity, with 39 distinct cgSTs identified. No evidence of localized outbreaks was observed in Guizhou. Four isolates of cgST190343 exhibited identical resistance profiles and carried IncHI2/IncHI2A plasmids with the same ARGs patterns. These isolates were originated from two distinct cities in 2023, indicating either the same source of infection or potential cross-regional transmission. The cgMLST results demonstrated robust discriminatory resolution, underscoring its utility in public health surveillance. By contributing genomic data from these XDR Salmonella isolates to global databases, we can enhance resources for pathogen tracking and strength international disease surveillance systems. Such efforts enable faster, more targeted public health interventions during outbreaks and improve preparedness for emerging antimicrobial resistance pathogens.
5 Conclusion
Our study presents the first data on the WGS-based characterization of XDR Salmonella isolates from humans between 2019 and 2023 in Guizhou province, China. The detection rate of XDR Salmonella isolates increased from 3.8% in 2019 to 7.4% in 2023. S. 1,4,[5],12:i:- isolates exhibited a broader range of resistance determinants than other serovars. Notably, one blaNDM-1 positive isolate was detected for the first time in Guizhou. Meanwhile, XDR Salmonella isolates carried multiple ARGs on plasmids, which could promote the acquisition and dissemination of ARGs. This study showed that implementing continuous dynamic surveillance will enhance our understanding of the epidemiology of XDR Salmonella in this region and help public health officials identify emerging trends and potential threats.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in this study were included in the article and its Supplementary material. The sequence data presented in this study were publicly available in figshare: https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.28521008. Further inquiries can contact the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of Guizhou Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
YW: Data curation, Formal analysis, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. JiW: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. LY: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. XW: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition. JuW: Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. SL: Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by Science and Technology Planning Support Project of Guizhou Province (Qian Ke He Support [2020]4Y143); Science and Technology Foundation Planning Project of Guizhou Province (gzwkj2025-136); Science and Technology Foundation Planning Project of Guizhou Province (Qian Ke He Basis [2017]1094); Infectious Disease Prevention and Control Talent Base Scientific Research Team Project of Guizhou Province (RCJD2104); Guizhou Key Laboratory of Microbiology and Infectious Disease Prevention & Control (ZDSYS[2023]004).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank nine Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Guizhou, including Anshun, Bijie, Guiyang, Liupanshui, Qiandongnan, Qiannan, Qianxinan, Tongren and Zunyi, for providing Salmonella isolates. At the same time, we would also like to thank the suppliers for their consistent support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1532036/full#supplementary-material
Footnotes
1. ^https://whonet.org/software.html
2. ^https://github.com/DerrickWood/kraken2
3. ^https://github.com/fenderglass/Flye
4. ^https://github.com/nanoporetech/medaka
5. ^http://www.denglab.info/SeqSero2
6. ^https://cge.food.dtu.dk/services/MLST/
8. ^https://github.com/smaegol/PlasFlow
9. ^https://cge.food.dtu.dk/services/PlasmidFinder/
10. ^https://bioinfo-mml.sjtu.edu.cn/oriTDB/index.php
11. ^https://bioinfo-mml.sjtu.edu.cn/SecReT4/
References
Abd El-Aziz, N. K., Tartor, Y. H., Gharieb, R. M. A., Erfan, A. M., Khalifa, E., Said, M. A., et al. (2021). Extensive drug-resistant Salmonella enterica isolated from poultry and humans: prevalence and molecular reterminants behind the co-resistance to ciprofloxacin and tigecycline. Front. Microbiol. 12:738784. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.738784
Akinyemi, K. O., Fakorede, C. O., Linde, J., Methner, U., Wareth, G., Tomaso, H., et al. (2023). Whole genome sequencing of Salmonella enterica serovars isolated from humans, animals, and the environment in Lagos, Nigeria. BMC Microbiol. 23:164. doi: 10.1186/s12866-023-02901-1
Algammal, A. M., El-Tarabili, R. M., Abd El-Ghany, W. A., Almanzalawi, E. A., Alqahtani, T. M., Ghabban, H., et al. (2023). Resistance profiles, virulence and antimicrobial resistance genes of XDR S. Enteritidis and S. Typhimurium. AMB Express 13:110. doi: 10.1186/s13568-023-01615-x
Castañeda-Barba, S., Top, E. M., and Stalder, T. (2024). Plasmids, a molecular cornerstone of antimicrobial resistance in the one health era. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 22, 18–32. doi: 10.1038/s41579-023-00926-x
Chang, M. X., Zhang, J. F., Sun, Y. H., Li, R. S., Lin, X. L., Yang, L., et al. (2021). Contribution of different mechanisms to ciprofloxacin resistance in Salmonella spp. Front. Microbiol. 12:663731. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.663731
Chen, Z., Kuang, D., Xu, X., González-Escalona, N., Erickson, D. L., Brown, E., et al. (2020). Genomic analyses of multidrug-resistant Salmonella Indiana, Typhimurium, and Enteritidis isolates using MinION and MiSeq sequencing technologies. PLoS One 15:e0235641. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0235641
Chen, Y., Liu, L., Guo, Y., Chu, J., Wang, B., Sui, Y., et al. (2024). Distribution and genetic characterization of fluoroquinolone resistance gene qnr among Salmonella strains from chicken in China. Microbiol. Spectr. 12:e0300023. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03000-23
Chen, C. M., Tang, H. L., Ke, S. C., Lin, Y. P., Lu, M. C., Lai, Y. C., et al. (2022). A nosocomial salmonellosis outbreak caused by Bla(OXA-48)-carrying, extensively drug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Goldcoast in a hospital respiratory care ward in Taiwan. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 29, 331–338. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2022.03.023
Chen, K., Yang, C., Dong, N., Xie, M., Ye, L., Chan, E. W. C., et al. (2020). Evolution of ciprofloxacin resistance-encoding genetic elements in Salmonella. mSystems 5:5. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.01234-20
CLSI (2023). Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. CLSI supplement M100. 33th Edn. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute.
Cummins, M. L., Sanderson-Smith, M., Newton, P., Carlile, N., Phalen, D. N., Maute, K., et al. (2020). Whole-genome sequence analysis of an extensively drug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Agona isolate from an Australian silver gull (chroicocephalus novaehollandiae) reveals the acquisition of multidrug resistance plasmids. mSphere 5:e00743-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00743-20
Dangel, A., Berger, A., Messelhäußer, U., Konrad, R., Hörmansdorfer, S., Ackermann, N., et al. (2019). Genetic diversity and delineation of Salmonella agona outbreak strains by next generation sequencing, Bavaria, Germany, 1993 to 2018. Euro Surveill. 24:1800303. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.Es.2019.24.18.1800303
European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) (2019). The European Union summary report on antimicrobial resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2017. EFSA J. 17:e05598. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2019.5598
European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) (2023). The European Union one health 2022 zoonoses report. EFSA J. 21:e8442. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2023.8442
Ford, L., Buuck, S., Eisenstein, T., Cote, A., Mccormic, Z. D., Kremer-Caldwell, S., et al. (2023). Salmonella outbreaks associated with not ready-to-eat breaded, stuffed chicken products - United States, 1998-2022. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 72, 484–487. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7218a2
GBD 2017 Non-Typhoidal Salmonella Invasive Disease Collaborators (2019). The global burden of non-typhoidal Salmonella invasive disease: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet Infect. Dis. 19, 1312–1324. doi: 10.1016/s1473-3099(19)30418-9
Grimont, P. A. D., and Weill, F. X. (2007). Antigenic formulae of the Salmonella Serovars. 9th Edn. Paris: WHO Collaborating Centre for Reference and Research on Salmonella.
Guibourdenche, M., Roggentin, P., Mikoleit, M., Fields, P. I., Bockemühl, J., Grimont, P. A. D., et al. (2010). Supplement 2003–2007 (no. 47) to the white-Kauffmann-Le minor scheme. Res. Microbiol. 161, 26–29. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2009.10.002
Hu, Y., Wang, J., Chen, S., Li, Y., Zhang, R., and Chen, S. (2022). Non-typhoidal Salmonella invasive infections in China. Lancet Infect. Dis. 22:939. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00347-4
Ingle, D. J., Ambrose, R. L., Baines, S. L., Duchene, S., Gonçalves Da Silva, A., Lee, D. Y. J., et al. (2021). Evolutionary dynamics of multidrug resistant Salmonella enterica serovar 4,[5],12:i:- in Australia. Nat. Commun. 12:4786. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25073-w
Jansson Mörk, M., Karamehmedovic, N., Hansen, A., Nederby Öhd, J., Lindblad, M., Östlund, E., et al. (2022). Outbreak of Salmonella Newport linked to imported frozen cooked crayfish in dill brine, Sweden, july to november 2019. Euro Surveill. 27:2100918. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.Es.2022.27.22.2100918
Jiang, Y., Wang, Y., Hua, X., Qu, Y., Peleg, A. Y., and Yu, Y. (2020). Pooled plasmid sequencing reveals the relationship between mobile genetic elements and antimicrobial resistance genes in clinically isolated Klebsiella pneumoniae. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 18, 539–548. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2020.12.002
Karampatakis, T. (2024). Molecular characterization of gram-negative bacteria: antimicrobial resistance, virulence and epidemiology. Antibiotics (Basel) 13:402. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13050402
Kerr, E. J., Stafford, R., Rathnayake, I. U., Graham, R. M. A., Fearnley, E., Gregory, J., et al. (2022). Multistate outbreak of Salmonella enterica serovar Heidelberg with unidentified source, Australia, 2018-2019. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 28, 238–241. doi: 10.3201/eid2801.211462
Lewis, G. L., Fenton, R. J., Moriyama, E. N., Loy, J. D., and Moxley, R. A. (2023). Association of ISVsa3 with multidrug resistance in Salmonella enterica isolates from cattle (bos taurus). Microorganisms 11:631. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11030631
Li, L., Wan, X., Olsen, R. H., Xiao, J., Wang, C., Xu, X., et al. (2022). Genomic characterization of mcr-1-carrying foodborne Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium and identification of a transferable plasmid carrying mcr-1, Bla (CTX-M-14), qnrS2, and oqxAB genes from ready-to-eat pork product in China. Front. Microbiol. 13:903268. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.903268
Li, X., Xie, Y., Liu, M., Tai, C., Sun, J., Deng, Z., et al. (2018). oriTfinder: a web-based tool for the identification of origin of transfers in DNA sequences of bacterial mobile genetic elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 46, W229–w234. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky352
Liu, J. H., Liu, Y. Y., Shen, Y. B., Yang, J., Walsh, T. R., Wang, Y., et al. (2024). Plasmid-mediated colistin-resistance genes: mcr. Trends Microbiol. 32, 365–378. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2023.10.006
Liu, B., Meng, C., Wang, Z., Li, Q., Xu, C., Kang, X., et al. (2024). Prevalence and transmission of extensively drug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky ST198 based on whole-genome sequence in an intensive laying hen farm in Jiangsu, China. Poult. Sci. 103:103608. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.103608
Luo, Q., Wan, F., Yu, X., Zheng, B., Chen, Y., Gong, C., et al. (2020). MDR Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium ST34 carrying mcr-1 isolated from cases of bloodstream and intestinal infection in children in China. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 75, 92–95. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkz415
Magiorakos, A. P., Srinivasan, A., Carey, R. B., Carmeli, Y., Falagas, M. E., Giske, C. G., et al. (2012). Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: an international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 18, 268–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03570.x
Na, S. H., Moon, D. C., Kang, H. Y., Song, H.-J., Kim, S.-J., Choi, J.-H., et al. (2020). Molecular characteristics of extended-spectrum β-lactamase/AmpC-producing Salmonella enterica serovar Virchow isolated from food-producing animals during 2010–2017 in South Korea. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 322:108572. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2020.108572
Octavia, S., Chew, K. L., Chew, K. L., Lin, R. T. P., and Teo, J. W. P. (2020). Multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar London carrying Bla(NDM-1) encoding plasmid from Singapore. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 26, 963–966. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.01.033
Petrin, S., Orsini, M., Massaro, A., Olsen, J. E., Barco, L., and Losasso, C. (2023). Phenotypic and genotypic antimicrobial resistance correlation and plasmid characterization in Salmonella spp. isolates from Italy reveal high heterogeneity among serovars 11, 11. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1221351
Pitout, J. D. (2012). Extraintestinal pathogenic escherichia coli: a combination of virulence with antibiotic resistance. Front. Microbiol. 3:9. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2012.00009
Rahman, M. K., Rodriguez-Mori, H., Loneragan, G. H., and Awosile, B. (2024). Beta-lactamase genes in bacteria from food animals, retail meat, and human surveillance programs in the United States from 2002 to 2021. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 106:102139. doi: 10.1016/j.cimid.2024.102139
Russo, I., Bencardino, D., Napoleoni, M., Andreoni, F., Schiavano, G. F., Baldelli, G., et al. (2022). Prevalence, antibiotic-resistance, and replicon-typing of Salmonella strains among serovars mainly isolated from food chain in Marche region, Italy. Antibiotics 11:725. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11060725
Sallam, K. I., Kasem, N. G., Abdelkhalek, A., and Elshebrawy, H. A. (2024). Extensively drug-, ciprofloxacin-, cefotaxime-, and azithromycin-resistant Salmonella enterica serovars isolated from camel meat in Egypt. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 411:110538. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2023.110538
She, Y., Jiang, Y., Luo, M., Duan, X., Xie, L., Yang, C., et al. (2023). Emergence of chromosomally located blaCTX-M-14b and qnrS1 in Salmonella enterica serotype Kentucky ST198 in China. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 62:106896. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106896
Song, H., Zou, S., Huang, Y., Jian, C., Liu, W., Tian, L., et al. (2023). Salmonella typhimurium with eight tandem copies of Bla(NDM-1) on a HI2 plasmid. Microorganisms 12:10020. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12010020
Sun, R. Y., Fang, L. X., Dai, J. J., Chen, K. C., Ke, B. X., Sun, J., et al. (2024). Antimicrobial resistance and population genomics of emerging multidrug-resistant Salmonella 4,[5],12:i:- in Guangdong, China. mSystems 9:e0116423. doi: 10.1128/msystems.01164-23
Vázquez, X., Fernández, J., Hernáez, S., Rodicio, R., and Rodicio, M. R. (2022). Plasmid- ediated quinolone resistance (PMQR) in two clinical strains of Salmonella enterica serovar Corvallis 10, 579. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10030579
Vázquez, X., García, V., Fernández, J., Bances, M., De Toro, M., Ladero, V., et al. (2021). Colistin resistance in monophasic isolates of Salmonella enterica ST34 collected from meat-derived products in Spain, with or without CMY-2 co-production. Front. Microbiol. 12:735364. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.735364
Wang, H., Cheng, H., Huang, B., Hu, X., Chen, Y., Zheng, L., et al. (2023). Characterization of resistance genes and plasmids from sick children caused by Salmonella enterica resistance to azithromycin in Shenzhen, China 13, 1116172. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1116172
Wang, Y., and Dagan, T. (2024). The evolution of antibiotic resistance islands occurs within the framework of plasmid lineages. Nat. Commun. 15:4555. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48352-8
Wang, M., Goh, Y. X., Tai, C., Wang, H., Deng, Z., and Ou, H. Y. (2022). VRprofile2: detection of antibiotic resistance-associated mobilome in bacterial pathogens. Nucleic Acids Res. 50, W768–w773. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac321
Wang, Z., Huang, C., Liu, Y., Chen, J., Yin, R., Jia, C., et al. (2024). Salmonellosis outbreak archive in China: data collection and assembly. Sci. Data 11:244. doi: 10.1038/s41597-024-03085-7
Wang, J., Li, Q., Jiang, Y., Wang, Z., and Jiao, X. (2024). fosA7: a silent fosfomycin resistance gene in Salmonella? Lancet Microbe 5:e211. doi: 10.1016/s2666-5247(23)00342-7
Wang, L. P., Zhou, S. X., Wang, X., Lu, Q. B., Shi, L. S., Ren, X., et al. (2021). Etiological, epidemiological, and clinical features of acute diarrhea in China. Nat. Commun. 12:2464. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22551-z
Wei, X., Long, L., You, L., Wang, M., Wang, D., Liu, C., et al. (2023). Serotype distribution, trend of multidrug resistance and prevalence of β-lactamase resistance genes in human Salmonella isolates from clinical specimens in Guizhou, China. PLoS One 18:e0282254. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0282254
Wei, J., Shen, S., Zhang, Q., Lu, J., Mao, S., Zou, C., et al. (2024). Emergence of a clinical Salmonella enterica serovar 1,4,[5], 12: i:-isolate, ST3606, in China with susceptibility decrease to ceftazidime-avibactam carrying a novel blaCTX-M-261 variant and a blaNDM-5. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 43, 829–840. doi: 10.1007/s10096-024-04765-3
Wu, J., Wen, Y., You, L., Wei, X., Wang, J., Zhu, G., et al. (2025). Genome analysis of colistin-resistant Salmonella isolates from human sources in Guizhou of southwestern China, 2019–2023. Front. Microbiol. 16:1498995. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1498995
Xie, J., Chen, Y., Cai, G., Cai, R., Hu, Z., and Wang, H. (2023). Tree visualization by one table (tvBOT): a web application for visualizing, modifying and annotating phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 51, W587–w592. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad359
Yu, K., Huang, Z., Xiao, Y., Gao, H., Bai, X., and Wang, D. (2024). Global spread characteristics of CTX-M-type extended-spectrum β-lactamases: a genomic epidemiology analysis. Drug Resist. Updat. 73:101036. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2023.101036
Yue, C., Bai, Y., Li, T., Deng, H., Lu, L., Lin, W., et al. (2024). Emergence of tet(X4)-positive enterobacterales in retail eggs and the widespread of IncFIA(HI1)-HI1A-HI1B(R27) plasmids carrying tet(X4). Int. J. Food Microbiol. 414:110574. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2024.110574
Zhai, W., Wang, Y., Sun, H., Fu, B., Zhang, Q., Wu, C., et al. (2024). Epidemiology and genetic characterization of tet(X4)-positive Klebsiella pneumoniae and Klebsiella quasipneumoniae isolated from raw meat in Chengdu City, China. Biosaf. Health 6, 116–124. doi: 10.1016/j.bsheal.2024.02.004
Zhang, Z., Kuang, D., Xu, X., Zhan, Z., Ren, H., and Shi, C. (2024a). Dissemination of IncC plasmids in Salmonella enterica serovar Thompson recovered from seafood and human diarrheic patients in China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 417:110708. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2024.110708
Zhang, Z., Li, B., Huang, H., Fang, Y., and Yang, W. (2024b). A food poisoning caused by Salmonella Enterica (S. Enteritidis) ST11 carrying multi-antimicrobial resistance genes in 2019, China. Infect. Drug Resist. 17, 1751–1762. doi: 10.2147/idr.S452295
Zhao, W., Li, X., Shi, X., Li, K., Shi, B., Sun, J., et al. (2022). Whole genome sequencing, antibiotic resistance, and epidemiology features of nontyphoidal Salmonella isolated from diarrheic children: evidence from North China. Front. Microbiol. 13:882647. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.882647
Zhou, L., Ye, Q., Zhou, Q., Wang, J., Li, G., Xiang, J., et al. (2024). Antimicrobial resistance and genomic investigation of Salmonella isolated from retail foods in Guizhou, China. Front. Microbiol. 15:1345045. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1345045
Keywords: Salmonella, extensively drug-resistant, plasmid, antimicrobial resistance genes, whole-genome sequencing
Citation: Wen Y, Wu J, You L, Wei X, Wang J and Li S (2025) Genomic analyses reveal presence of extensively drug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovars isolated from clinical samples in Guizhou province, China, 2019–2023. Front. Microbiol. 16:1532036. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1532036
Edited by:
João Perdigão, University of Lisbon, PortugalReviewed by:
Daniel F. M. Monte, North Carolina State University, United StatesHussein H. Abulreesh, Umm Al-Qura University, Saudi Arabia
Copyright © 2025 Wen, Wu, You, Wei, Wang and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaoyu Wei, d2VpeHl1c2VAZm94bWFpbC5jb20=
 Yongxian Wen
Yongxian Wen Jingtong Wu
Jingtong Wu Lv You2
Lv You2 Xiaoyu Wei
Xiaoyu Wei Shijun Li
Shijun Li